User login
2020 Update on Menopause
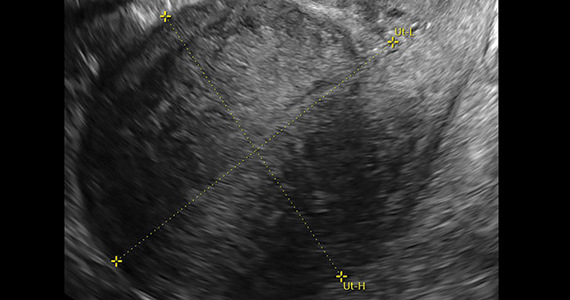
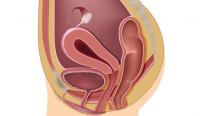
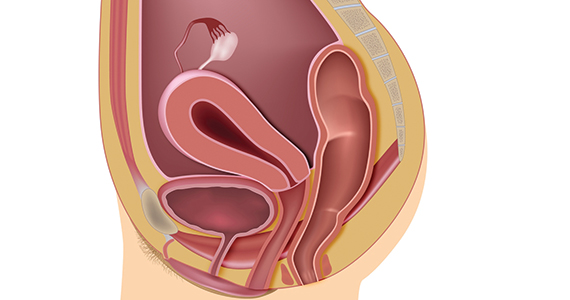
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
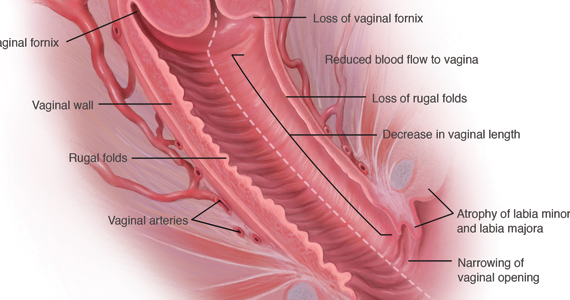
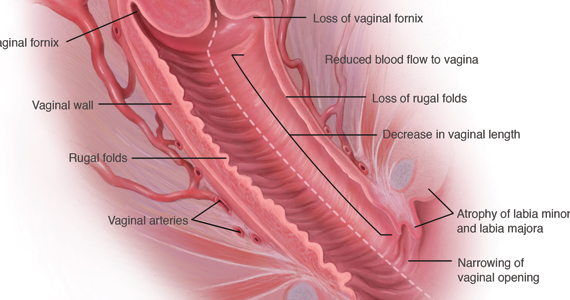
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2
Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2

Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2

Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
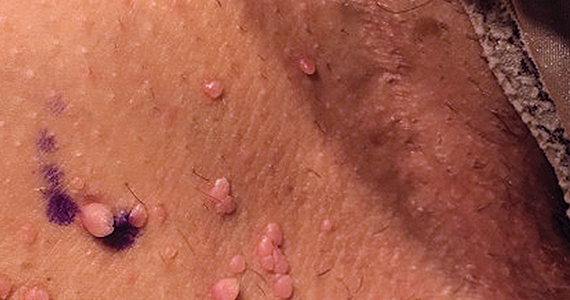
Can you identify these numerous papules in the groin area?
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2
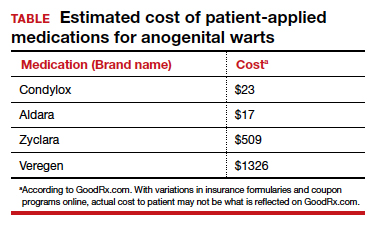
Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2

Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2

Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
CASE Skin tags on the groin
A 47-year-old woman with no personal history of skin cancer presents to a dermatologist for annual skin surveillance examination. She notes multiple “pink skin tags” on the groin, present for 4 months. She says they are asymptomatic and have not been treated previously. She states that she is in a long-term monogamous relationship. Physical examination reveals multiple smooth, flat-topped, pedunculated pink papules on the bilateral upper inner thighs. Shave biopsy of a lesion on the right upper medial thigh is performed to aid in diagnosis (FIGURE 1).
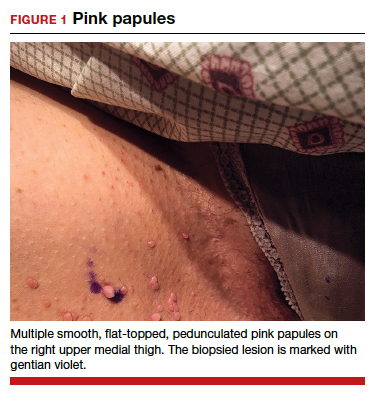
Breast cancer chemoprophylaxis in high-risk women: How persistent is the impact of an aromatase inhibitor after 5 years of use?
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
Can the office visit interval for routine pessary care be extended safely?
Propst K, Mellen C, O’Sullivan DM, et al. Timing of office-based pessary care: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 5. Doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003580.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vaginal pessaries are a common and effective approach for managing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) as well as stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Vaginal mucosal erosions, however, may complicate pessary use. The risk for erosions may be associated with the frequency of pessary change, which involves removing the pessary, washing it, and replacing it in the vagina. Existing data do not address the frequency of pessary change. Recently, however, investigators conducted a randomized noninferiority trial to evaluate the effect of pessary visit intervals on the development of vaginal epithelial abnormalities.
Details of the study
At a single US hospital, Propst and colleagues randomly assigned women who used pessaries for POP, SUI, or both to routine pessary care (offices visits every 12 weeks) or to extended interval pessary care (office visits every 24 weeks). The women used ring, incontinence dish, or Gelhorn pessaries, did not change their pessaries on their own, and had no vaginal mucosal abnormalities.
A total of 130 women were randomly assigned, 64 to the routine care group and 66 to the extended interval care group. The mean age was 79 years and 90% were white, 4.6% were black, and 4% were Hispanic. Approximately 74% of the women used vaginal estrogen.
The primary outcome was the rate of vaginal epithelial abnormalities, including epithelial breaks or erosions. The predetermined noninferiority margin was set at 7.5%.
Results. At the 48-week follow-up, the rate of epithelial erosion was 7.4% in the routine care group and 1.7% in the extended interval care group, thus meeting the prespecified criteria for noninferiority of extended interval pessary care.
Women in each care group reported a similar amount of bothersome vaginal discharge. This was reported on a 5-point scale, with higher numbers indicating greater degree of bother. The mean scores were 1.39 in the routine care group and 1.34 in the extended interval care group. No other pessary-related adverse events occurred in either care group.
Study strengths and limitations
This trial provides good evidence that the timing of office pessary care can be extended to 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. However, since nearly three-quarters of the study participants used vaginal estrogen, the results may not be applicable to pessary users who do not use vaginal estrogen.
Many women change their pessary at home as often as weekly or daily. For women who rely on office visits for pessary care, however, the trial by Propst and colleagues provides good quality evidence that pessaries can be changed as infrequently as every 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. An important limitation of these data is that since most study participants used vaginal estrogen, the findings may not apply to pessary use among women who do not use vaginal estrogen.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
Propst K, Mellen C, O’Sullivan DM, et al. Timing of office-based pessary care: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 5. Doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003580.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vaginal pessaries are a common and effective approach for managing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) as well as stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Vaginal mucosal erosions, however, may complicate pessary use. The risk for erosions may be associated with the frequency of pessary change, which involves removing the pessary, washing it, and replacing it in the vagina. Existing data do not address the frequency of pessary change. Recently, however, investigators conducted a randomized noninferiority trial to evaluate the effect of pessary visit intervals on the development of vaginal epithelial abnormalities.
Details of the study
At a single US hospital, Propst and colleagues randomly assigned women who used pessaries for POP, SUI, or both to routine pessary care (offices visits every 12 weeks) or to extended interval pessary care (office visits every 24 weeks). The women used ring, incontinence dish, or Gelhorn pessaries, did not change their pessaries on their own, and had no vaginal mucosal abnormalities.
A total of 130 women were randomly assigned, 64 to the routine care group and 66 to the extended interval care group. The mean age was 79 years and 90% were white, 4.6% were black, and 4% were Hispanic. Approximately 74% of the women used vaginal estrogen.
The primary outcome was the rate of vaginal epithelial abnormalities, including epithelial breaks or erosions. The predetermined noninferiority margin was set at 7.5%.
Results. At the 48-week follow-up, the rate of epithelial erosion was 7.4% in the routine care group and 1.7% in the extended interval care group, thus meeting the prespecified criteria for noninferiority of extended interval pessary care.
Women in each care group reported a similar amount of bothersome vaginal discharge. This was reported on a 5-point scale, with higher numbers indicating greater degree of bother. The mean scores were 1.39 in the routine care group and 1.34 in the extended interval care group. No other pessary-related adverse events occurred in either care group.
Study strengths and limitations
This trial provides good evidence that the timing of office pessary care can be extended to 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. However, since nearly three-quarters of the study participants used vaginal estrogen, the results may not be applicable to pessary users who do not use vaginal estrogen.
Many women change their pessary at home as often as weekly or daily. For women who rely on office visits for pessary care, however, the trial by Propst and colleagues provides good quality evidence that pessaries can be changed as infrequently as every 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. An important limitation of these data is that since most study participants used vaginal estrogen, the findings may not apply to pessary use among women who do not use vaginal estrogen.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
Propst K, Mellen C, O’Sullivan DM, et al. Timing of office-based pessary care: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 5. Doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003580.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vaginal pessaries are a common and effective approach for managing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) as well as stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Vaginal mucosal erosions, however, may complicate pessary use. The risk for erosions may be associated with the frequency of pessary change, which involves removing the pessary, washing it, and replacing it in the vagina. Existing data do not address the frequency of pessary change. Recently, however, investigators conducted a randomized noninferiority trial to evaluate the effect of pessary visit intervals on the development of vaginal epithelial abnormalities.
Details of the study
At a single US hospital, Propst and colleagues randomly assigned women who used pessaries for POP, SUI, or both to routine pessary care (offices visits every 12 weeks) or to extended interval pessary care (office visits every 24 weeks). The women used ring, incontinence dish, or Gelhorn pessaries, did not change their pessaries on their own, and had no vaginal mucosal abnormalities.
A total of 130 women were randomly assigned, 64 to the routine care group and 66 to the extended interval care group. The mean age was 79 years and 90% were white, 4.6% were black, and 4% were Hispanic. Approximately 74% of the women used vaginal estrogen.
The primary outcome was the rate of vaginal epithelial abnormalities, including epithelial breaks or erosions. The predetermined noninferiority margin was set at 7.5%.
Results. At the 48-week follow-up, the rate of epithelial erosion was 7.4% in the routine care group and 1.7% in the extended interval care group, thus meeting the prespecified criteria for noninferiority of extended interval pessary care.
Women in each care group reported a similar amount of bothersome vaginal discharge. This was reported on a 5-point scale, with higher numbers indicating greater degree of bother. The mean scores were 1.39 in the routine care group and 1.34 in the extended interval care group. No other pessary-related adverse events occurred in either care group.
Study strengths and limitations
This trial provides good evidence that the timing of office pessary care can be extended to 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. However, since nearly three-quarters of the study participants used vaginal estrogen, the results may not be applicable to pessary users who do not use vaginal estrogen.
Many women change their pessary at home as often as weekly or daily. For women who rely on office visits for pessary care, however, the trial by Propst and colleagues provides good quality evidence that pessaries can be changed as infrequently as every 24 weeks without compromising outcomes. An important limitation of these data is that since most study participants used vaginal estrogen, the findings may not apply to pessary use among women who do not use vaginal estrogen.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
Persistent vulvar itch: What is the diagnosis?
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores
Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores

Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores

Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
CASE Lingering vulvar pruritus developed during traveling
A 48-year-old premenopausal Hispanic woman with past medical history of breast cancer presents to a dermatologist with the chief complaint of persistent vulvar pruritus. The vulvar itching began while traveling and has continued for 6 months. Previous treatments have been trialed, including over-the-counter feminine hygiene products, wipes, and hydrocortisone ointment.
Physical examination reveals pink, symmetric, bilateral lichenified plaques on the labia majora, without evidence of atrophy or scarring ( FIGURE 1 ). Scant white vaginal discharge is also noted.
FIGURE 1 Bilateral labia majora show lichenification
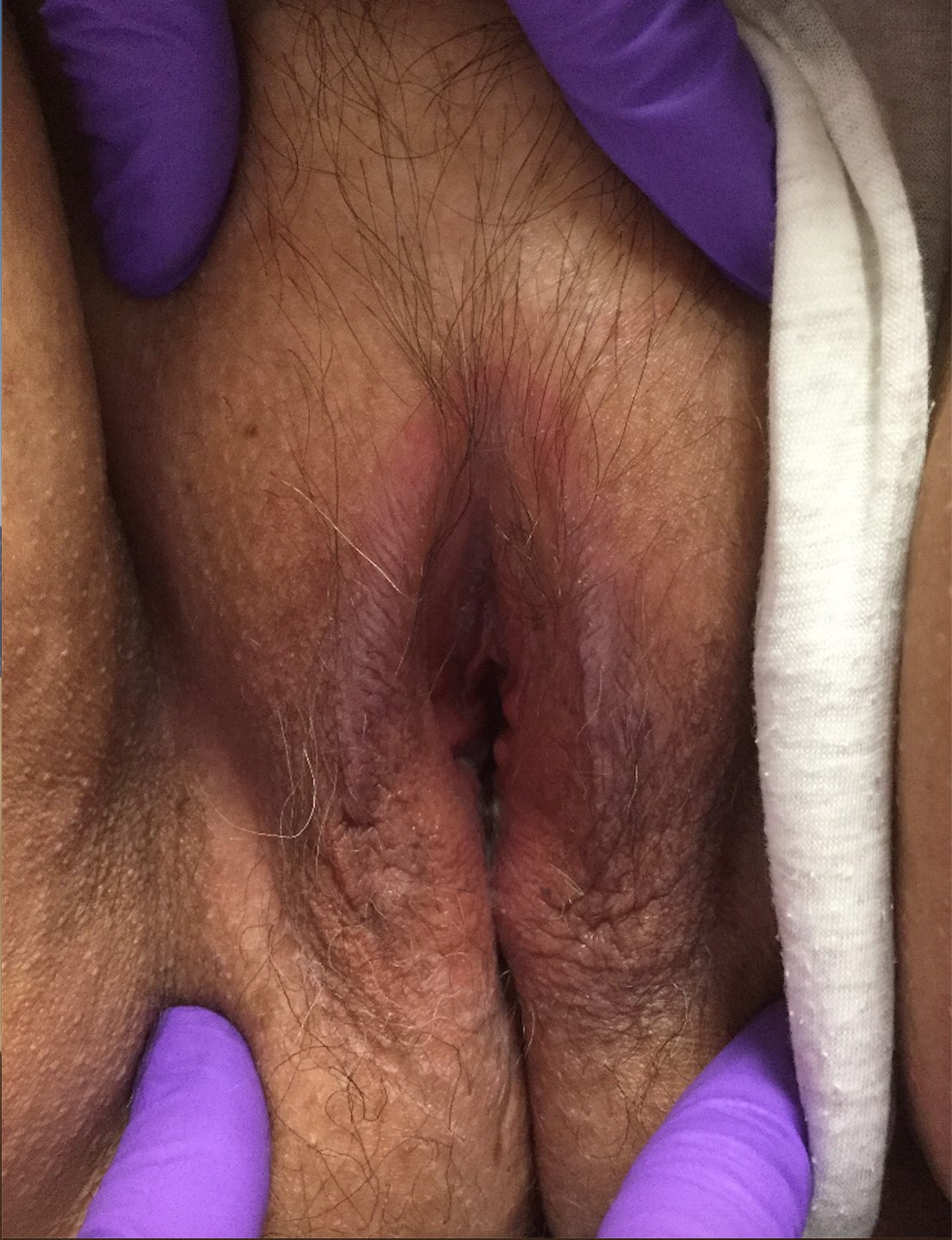
Figure caption: On bilateral labia majora, symmetric, pink plaques with accentuated skin markings (lichenification) noted on physical examination. Scant white vaginal discharge was noted on exam but is inconspicuous in photo.
Medical management of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-age women
Case 1 Multiparous woman presents with heavy regular menses
Over the past several years, a 34-year-old woman has noted increasing intensity and duration of menstrual flow, which now persists for 8 days and includes clots “the size of quarters” and soaks a pad within 1 hour. Sometimes she misses or leaves work on her heaviest days of flow. She reports that menstrual cramps prior to and during flow are increasingly bothersome and do not respond adequately to ibuprofen. She intermittently uses condoms for contraception. She does not wish to be pregnant currently; however, she recently entered into a new relationship and may wish to conceive in the future.
On bimanual examination, the uterus appears bulky. Her hemoglobin is 10.9 g/dL with low mean corpuscular volume and a serum ferritin level indicating iron depletion. Pelvic ultrasonography suggests uterine adenomyosis; no fibroids are imaged (FIGURE 1).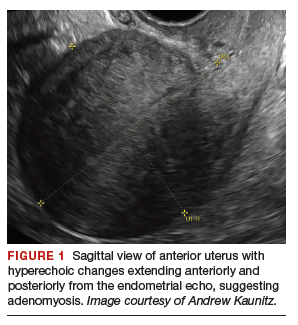
You advise the patient to take ferrous sulfate 325 mg every other day. After discussion with the patient regarding different treatment options, she chooses to proceed with placement of a 52-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD; Mirena or Liletta).
Case 2 Older adolescent presents with irregular bleeding
A 19-year-old patient reports approximately 6 bleeding episodes each year. She reports the duration of her bleeding as variable, and sometimes the bleeding is heavy with small clots passed. She has been previously diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives have been prescribed several times in the past, but she always has discontinued them due to nausea. The patient is in a same-sex relationship and does not anticipate being sexually active with a male. She reports having to shave her mustache and chin twice weekly for the past 1 to 2 years.
On physical examination, the patient is obese (body mass index [BMI], 32 kg/m2), facial acne and hirsutism are present, and hair extends from the mons toward the umbilicus. Bimanual examination reveals a normal size, mobile, nontender uterus without obvious adnexal pathology. Pelvic ultrasonography demonstrates a normal-appearing uterus with multiplanar endometrium (consistent with proliferative changes) (FIGURE 2). Ovarian imaging demonstrates ≥12 follicles per image (FIGURE 3).
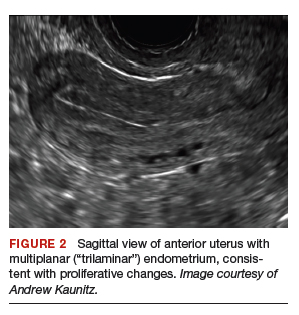

After reviewing various treatment options, you prescribe oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg (two 10-mg tablets) daily in a continuous fashion. You counsel her that she should not be surprised or concerned if frequent or even continuous bleeding occurs initially, and that she should continue this medication despite the occurrence of such.
About one-third of all women experience abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) sometime during their lifetime and AUB can impair quality of life.1 Surgical management, including hysterectomy and endometrial ablation, plays an important role in the management of AUB in patients who do not desire future pregnancies. However, many cases of AUB occur in women who may not have completed childbearing or in women who prefer to avoid surgery.2 AUB can be managed effectively medically in most cases.1 Accordingly, in this review, we focus on nonsurgical management of AUB.
Continue to: Because previously used terms, including...
Because previously used terms, including menorrhagia and meno-metrorrhagia, were inconsistently defined and confusing, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics introduced updated terminology in 2011 to better describe and characterize AUB in nonpregnant women. Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) refers to ovulatory (cyclic) bleeding that is more than 8 days’ duration, or sufficiently heavy to impair a woman’s quality of life. HMB is a pattern of AUB distinct from the irregular bleeding pattern typically caused by ovulatory dysfunction (AUB-O).1
Clinical evaluation
Obtain menstrual history. In addition to a medical, surgical, and gynecologic history, a thorough menstrual history should be obtained to further characterize the patient’s bleeding pattern. In contrast to the cyclical or ovulatory bleeding seen with HMB, bleeding associated with inconsistent ovulation (AUB-O) is unpredictable or irregular, and is commonly associated with PCOS. AUB-O is also encountered in recently menarchal girls (secondary to immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis) and in those who are perimenopausal. In addition, medications that can induce hyperprolactinemia (such as certain antipsychotics) can cause AUB-O.
Evaluate for all sources of bleeding. Be sure to evaluate for extrauterine causes of bleeding, including the cervix, vagina, vulva, or the urinary or gastrointestinal tracts for bleeding. Intermenstrual bleeding occurring between normal regular menses may be caused by an endometrial polyp, submucosal fibroid, endometritis, or an IUD. The patient report of postcoital bleeding suggests that cervical disease (cervicitis, polyp, or malignancy) may be present. Uterine leiomyoma or adenomyosis represent common causes of HMB. However, HMB also may be caused by a copper IUD, coagulation disorders (including von Willebrand disease), or use of anticoagulant medications. Hormonal contraceptives also can cause irregular bleeding.
Perform a pelvic examination and measure vital signs. The presence of fever suggests the possible presence of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), while orthostatic hypotension raises the possibility of hypovolemia. When vaginal speculum examination is performed, a cervical cause of abnormal bleeding may be noted. The presence of fresh or old blood or finding clots in the vaginal vault or at the cervical os are all consistent with AUB. A bimanual examination that reveals an enlarged or lobular uterus suggests leiomyoma or adenomyosis. Cervical or adnexal tenderness is often noted in women with PID, which itself may be associated with endometritis. The presence of hyperandrogenic signs on physical examination (eg, acne, hirsutism, or clitoromegaly) suggests PCOS. The finding of galactorrhea suggests that hyperprolactinemia may be present.
Laboratory assessment
Test for pregnancy, cervical disease, and sexually transmitted infection when appropriate. Pregnancy testing is appropriate for women with AUB aged 55 years or younger. If patients with AUB are not up to date with normal cervical cancer screening results, cervical cytology and/or human papillomavirus testing should be performed. Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Trichomonas vaginalis should be performed in patients:
- younger than 25 years
- when the history indicates new or multiple sexual partners, or
- when vaginal discharge, cervicitis, cervical motion, or adnexal tenderness is present.
Continue to: Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels...
Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels. In women presenting with HMB, iron depletion and iron deficiency anemia are common. The finding of leukocytosis raises the possibility of PID or postpartum endometritis. In women with presumptive AUB-O, checking the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, free T4, and prolactin should be performed.
Screen for a hemostasis disorder. Women with excessive menstrual bleeding should be clinically screened for an underlying disorder of hemostasis (TABLE 1).3 When a hemostasis disorder is suspected, initial laboratory evaluation includes a partial thromboplastin time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen. Women who have a positive clinical screen for a possible bleeding disorder or abnormal initial laboratory test results for disorders of hemostasis should undergo further laboratory evaluation, including von Willebrand factor antigen, ristocetin cofactor assay, and factor VIII. Consultation with a hematologist should be considered in these cases.

Perform endometrial biopsy when indicated
After excluding pregnancy, endometrial biopsy (through pipelle biospy or brush sampling; FIGURE 4) should be performed in women with AUB who are at increased risk for endometrial neoplasia. The prevalence of endometrial neoplasia is substantially higher among women ≥45 years of age4 and among patients with AUB who are also obese (BMI, ≥30 kg/m2).5 In addition, AUB patients with unopposed estrogen exposure (presumed anovulation/PCOS), as well as those with persistent AUB or failed medical management, should undergo endometrial biopsy.6
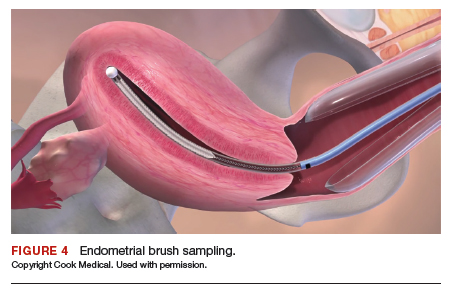
Utilize transvaginal ultrasonography
Transvaginal ultrasonography is often useful in the evaluation of patients with AUB, as it may identify uterine fibroids or adenomyosis, suggest intracavitary pathology (such as an endometrial polyp or submucosal fibroid), or raise the possibility of PCOS. In virginal patients or those in whom vaginal ultrasound is not appropriate, abdominal pelvic ultrasonography represents appropriate imaging. If unenhanced ultrasound suggests endometrial polyps or fibroids within the endometrial cavity, an office-based saline infusion sonogram (sonohysterogram) (FIGURE 5) or hysteroscopy should be performed. Targeted endometrial sampling and biopsy of intracavitary pathology can be performed at the time of hysteroscopy.
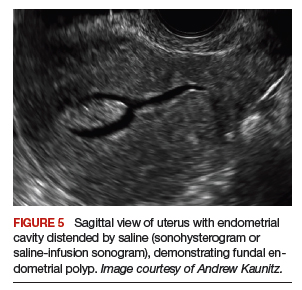
Treatment
When HMB impairs quality of life, is bothersome to the patient, or results in anemia, treatment is appropriate. Although bleeding episodes in women with AUB-O may be infrequent (as with Case 2), treatment prevents heavy or prolonged bleeding episodes as well as endometrial neoplasia that may otherwise occur in anovulatory women.
Many women with AUB can be managed medically. However, treatment choices will vary with respect to the patient’s desire for future fertility, medical comorbidities, personal preferences, and financial barriers. While many women may prefer outpatient medical management (TABLE 2),7-14 others might desire surgical therapy, including endometrial ablation or hysterectomy.

Oral contraceptives
Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives represent appropriate initial therapy for many women in the reproductive-age group with AUB, whether women have HMB or AUB-O. However, contraceptive doses of estrogen are not appropriate for some women with risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including those who smoke cigarettes and are age ≥35 years or those who have hypertension (TABLE 3).15,16
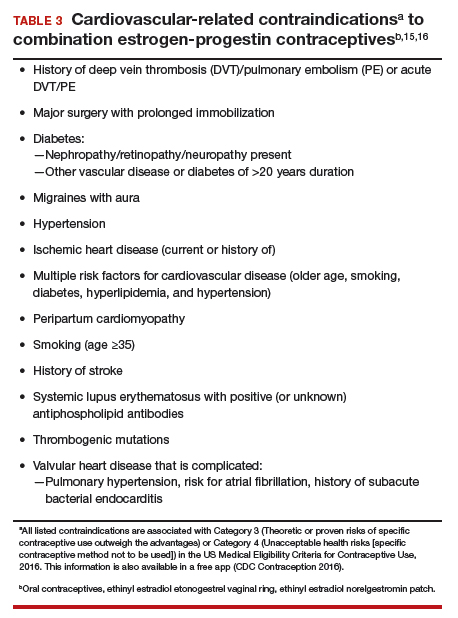
Continue to: Menopausal dosages of HT...
Menopausal dosages of HT
If use of contraceptive doses of estrogen is not appropriate, continuous off-label use of menopausal combination formulations (physiologic dosage) of hormonal therapy (HT; ie, lower doses of estrogen than contraceptives) may be effective in reducing or eliminating AUB. Options for menopausal combination formulations include generic ethinyl estradiol 5 µg/norethindrone acetate 1 mg or estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.7 High-dose oral progestin therapy (norethindrone acetate 5 mg tablet once daily or medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg tablets 1–3 times daily) also can be used when combination contraceptives are contraindicated and may be more effective than lower-dose combination formulations.
Package labeling, as well as some guidelines, indicate that oral progestins used to treat AUB should be taken cyclically.8 However, continuous daily use is easier for many patients and may be more effective in reducing bleeding. Accordingly, we counsel patients with AUB who are using progestins and who do not wish to conceive to take these medications continuously. High-dose oral progestin therapy may cause bloating, dysphoria, and increased appetite/weight gain. Women initiating hormonal management (including the progestin IUDs detailed below) for AUB should be counseled that irregular or even continuous light bleeding/spotting is common initially, but this bleeding pattern typically decreases with continued use.
IUDs
The LNG 52 mg IUD (Mirena or Liletta) effectively treats HMB, reducing bleeding in a manner comparable to that of endometrial ablation.9,10 The Mirena IUD is approved for treatment of HMB in women desiring intrauterine contraception. In contrast to oral medications, use of progestin IUDs does not involve daily administration and may represent an attractive option for women with HMB who would like to avoid surgery or preserve fertility. With ongoing use, continuous oral or intrauterine hormonal management may result in amenorrhea in some women with AUB.
When the LNG 52 mg IUD is used to treat HMB, the menstrual suppression impact may begin to attenuate after approximately 4 years of use; in this setting, replacing the IUD often restores effective menstrual suppression.11 The LNG 52 mg IUD effectively suppresses menses in women with coagulation disorders; if menstrual suppression with the progestin IUD is not adequate in this setting, it may be appropriate to add an oral combination estrogen-progestin contraceptive or high-dose oral progestin.11,12
NSAIDs and tranexamic acid
Off-label use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (naproxen 500–1,000 mg daily for 5 days beginning at the onset of menstrual flow or tranexamic acid two 650-mg tablets 3 times daily for up to 5 days during episodes of heavy flow) can suppress HMB and is useful for women who prefer to avoid or have contraindications to hormonal treatments.13,14 Unfortunately, these agents are not as effective as hormonal management in treating AUB.
Iron supplementation is often needed
Iron depletion commonly results from HMB, often resulting in iron deficiency anemia. When iron depletion (readily identified by checking a serum ferritin level) or iron deficiency anemia is identified, iron supplementation should be recommended. Every-other-day administration of iron supplements maximizes iron absorption while minimizing the adverse effects of unabsorbed iron, such as nausea. Sixty mg of elemental iron (ferrous sulfate 325 mg) administered every other day represents an inexpensive and effective treatment for iron deficiency/anemia.17 In patients who cannot tolerate oral iron supplementation or for those in whom oral therapy is not appropriate or effective, newer intravenous iron formulations are safe and effective.18
Continue to: Case 1 Follow-up...
Case 1 Follow-up
The patient noted marked improvement in her menstrual cramps following LNG-containing IUD placement. Although she also reported that she no longer experienced heavy menstrual flow or cramps, she was bothered by frequent, unpredictable light bleeding/spotting. You prescribed norethindrone acetate (NETA) 5-mg tablet orally once daily, to be used in addition to her IUD. After using the IUD with concomitant NETA for 2 months’ duration, she noted that her bleeding/spotting almost completely resolved; however, she did report feeling irritable with use of the progestin tablets. She subsequently stopped the NETA tablets and, after 6 months of additional follow-up, reported only minimal spotting and no cramps.
At this later follow-up visit, you noted that her hemoglobin level increased to 12.6 g/dL, and the ferritin level no longer indicated iron depletion. After the IUD had been in place for 4 years, she reported that she was beginning to experience frequent light bleeding again. A follow-up vaginal sonogram noted a well-positioned IUD, there was no suggestion of intracavitary pathology, and adenomyosis continued to be imaged. She underwent IUD removal and placement of a new LNG 52 mg IUD. This resulted in marked reduction in her bleeding.
Case 2 Follow-up
Two weeks after beginning continuous oral progestin therapy, the patient called reporting frequent irregular bleeding. She was reassured that this was not unexpected and encouraged to continue oral progestin therapy. During a 3-month follow-up visit, the patient noted little, if any, bleeding over the previous 2 months and was pleased with this result. She continued to note acne and hirsutism and asked about the possibility of adding spironolactone to her oral progestin regimen.
- Munro MG, Critchley HOD, Fraser IS; FIGO Menstrual Disorders Committee. The two FIGO systems for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding symptoms and classification of causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in the reproductive years: 2018 revisions. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2018;143:393-408.
- Kaunitz AM. Abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-age women. JAMA. 2019;321:2126-2127.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion no. 557: management of acute abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:891-896.
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Uterine Cancer. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/corp.html. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Wise MR, Gill P, Lensen S, et al. Body mass index trumps age in decision for endometrial biopsy: cohort study of symptomatic premenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:598.e1-598.e8.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Practice bulletin no. 128: diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:197-206.
- The North American Menopause Society. Menopause Practice–A Clinician’s Guide. 5th ed. NAMS: Mayfield Heights, OH; 2014.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Heavy menstrual bleeding: assessment and management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng88. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Kaunitz AM, Bissonnette F, Monteiro I, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or medroxyprogesterone for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:625-632.
- Kaunitz AM, Meredith S, Inki P, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and endometrial ablation in heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1104-1116.
- Kaunitz AM, Inki P. The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in heavy menstrual bleeding: a benefit-risk review. Drugs. 2012;72:193-215.
- James AH, Kouides PA, Abdul-Kadir R, et al. Von Willebrand disease and other bleeding disorders in women: consensus on diagnosis and management from an international expert panel. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:12.e1-8.
- Ylikorkala O, Pekonen F. Naproxen reduces idiopathic but not fibromyoma-induced menorrhagia. Obstet Gynecol. 1986;68:10-12.
- Lukes AS, Moore KA, Muse KN, et al. Tranexamic acid treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:865-875.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1–103.
- ACOG Practice Bulletin no. 206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Stoffel NU, Cercamondi CI, Brittenham G, et al. Iron absorption from oral iron supplements given on consecutive versus alternate days and as single morning doses versus twice-daily split dosing in iron-depleted women: two open-label, randomised controlled trials. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e524–e533.
- Auerbach M, Adamson JW. How we diagnose and treat iron deficiency anemia. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:31-38.
Case 1 Multiparous woman presents with heavy regular menses
Over the past several years, a 34-year-old woman has noted increasing intensity and duration of menstrual flow, which now persists for 8 days and includes clots “the size of quarters” and soaks a pad within 1 hour. Sometimes she misses or leaves work on her heaviest days of flow. She reports that menstrual cramps prior to and during flow are increasingly bothersome and do not respond adequately to ibuprofen. She intermittently uses condoms for contraception. She does not wish to be pregnant currently; however, she recently entered into a new relationship and may wish to conceive in the future.
On bimanual examination, the uterus appears bulky. Her hemoglobin is 10.9 g/dL with low mean corpuscular volume and a serum ferritin level indicating iron depletion. Pelvic ultrasonography suggests uterine adenomyosis; no fibroids are imaged (FIGURE 1).
You advise the patient to take ferrous sulfate 325 mg every other day. After discussion with the patient regarding different treatment options, she chooses to proceed with placement of a 52-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD; Mirena or Liletta).
Case 2 Older adolescent presents with irregular bleeding
A 19-year-old patient reports approximately 6 bleeding episodes each year. She reports the duration of her bleeding as variable, and sometimes the bleeding is heavy with small clots passed. She has been previously diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives have been prescribed several times in the past, but she always has discontinued them due to nausea. The patient is in a same-sex relationship and does not anticipate being sexually active with a male. She reports having to shave her mustache and chin twice weekly for the past 1 to 2 years.
On physical examination, the patient is obese (body mass index [BMI], 32 kg/m2), facial acne and hirsutism are present, and hair extends from the mons toward the umbilicus. Bimanual examination reveals a normal size, mobile, nontender uterus without obvious adnexal pathology. Pelvic ultrasonography demonstrates a normal-appearing uterus with multiplanar endometrium (consistent with proliferative changes) (FIGURE 2). Ovarian imaging demonstrates ≥12 follicles per image (FIGURE 3).


After reviewing various treatment options, you prescribe oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg (two 10-mg tablets) daily in a continuous fashion. You counsel her that she should not be surprised or concerned if frequent or even continuous bleeding occurs initially, and that she should continue this medication despite the occurrence of such.
About one-third of all women experience abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) sometime during their lifetime and AUB can impair quality of life.1 Surgical management, including hysterectomy and endometrial ablation, plays an important role in the management of AUB in patients who do not desire future pregnancies. However, many cases of AUB occur in women who may not have completed childbearing or in women who prefer to avoid surgery.2 AUB can be managed effectively medically in most cases.1 Accordingly, in this review, we focus on nonsurgical management of AUB.
Continue to: Because previously used terms, including...
Because previously used terms, including menorrhagia and meno-metrorrhagia, were inconsistently defined and confusing, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics introduced updated terminology in 2011 to better describe and characterize AUB in nonpregnant women. Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) refers to ovulatory (cyclic) bleeding that is more than 8 days’ duration, or sufficiently heavy to impair a woman’s quality of life. HMB is a pattern of AUB distinct from the irregular bleeding pattern typically caused by ovulatory dysfunction (AUB-O).1
Clinical evaluation
Obtain menstrual history. In addition to a medical, surgical, and gynecologic history, a thorough menstrual history should be obtained to further characterize the patient’s bleeding pattern. In contrast to the cyclical or ovulatory bleeding seen with HMB, bleeding associated with inconsistent ovulation (AUB-O) is unpredictable or irregular, and is commonly associated with PCOS. AUB-O is also encountered in recently menarchal girls (secondary to immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis) and in those who are perimenopausal. In addition, medications that can induce hyperprolactinemia (such as certain antipsychotics) can cause AUB-O.
Evaluate for all sources of bleeding. Be sure to evaluate for extrauterine causes of bleeding, including the cervix, vagina, vulva, or the urinary or gastrointestinal tracts for bleeding. Intermenstrual bleeding occurring between normal regular menses may be caused by an endometrial polyp, submucosal fibroid, endometritis, or an IUD. The patient report of postcoital bleeding suggests that cervical disease (cervicitis, polyp, or malignancy) may be present. Uterine leiomyoma or adenomyosis represent common causes of HMB. However, HMB also may be caused by a copper IUD, coagulation disorders (including von Willebrand disease), or use of anticoagulant medications. Hormonal contraceptives also can cause irregular bleeding.
Perform a pelvic examination and measure vital signs. The presence of fever suggests the possible presence of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), while orthostatic hypotension raises the possibility of hypovolemia. When vaginal speculum examination is performed, a cervical cause of abnormal bleeding may be noted. The presence of fresh or old blood or finding clots in the vaginal vault or at the cervical os are all consistent with AUB. A bimanual examination that reveals an enlarged or lobular uterus suggests leiomyoma or adenomyosis. Cervical or adnexal tenderness is often noted in women with PID, which itself may be associated with endometritis. The presence of hyperandrogenic signs on physical examination (eg, acne, hirsutism, or clitoromegaly) suggests PCOS. The finding of galactorrhea suggests that hyperprolactinemia may be present.
Laboratory assessment
Test for pregnancy, cervical disease, and sexually transmitted infection when appropriate. Pregnancy testing is appropriate for women with AUB aged 55 years or younger. If patients with AUB are not up to date with normal cervical cancer screening results, cervical cytology and/or human papillomavirus testing should be performed. Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Trichomonas vaginalis should be performed in patients:
- younger than 25 years
- when the history indicates new or multiple sexual partners, or
- when vaginal discharge, cervicitis, cervical motion, or adnexal tenderness is present.
Continue to: Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels...
Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels. In women presenting with HMB, iron depletion and iron deficiency anemia are common. The finding of leukocytosis raises the possibility of PID or postpartum endometritis. In women with presumptive AUB-O, checking the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, free T4, and prolactin should be performed.
Screen for a hemostasis disorder. Women with excessive menstrual bleeding should be clinically screened for an underlying disorder of hemostasis (TABLE 1).3 When a hemostasis disorder is suspected, initial laboratory evaluation includes a partial thromboplastin time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen. Women who have a positive clinical screen for a possible bleeding disorder or abnormal initial laboratory test results for disorders of hemostasis should undergo further laboratory evaluation, including von Willebrand factor antigen, ristocetin cofactor assay, and factor VIII. Consultation with a hematologist should be considered in these cases.

Perform endometrial biopsy when indicated
After excluding pregnancy, endometrial biopsy (through pipelle biospy or brush sampling; FIGURE 4) should be performed in women with AUB who are at increased risk for endometrial neoplasia. The prevalence of endometrial neoplasia is substantially higher among women ≥45 years of age4 and among patients with AUB who are also obese (BMI, ≥30 kg/m2).5 In addition, AUB patients with unopposed estrogen exposure (presumed anovulation/PCOS), as well as those with persistent AUB or failed medical management, should undergo endometrial biopsy.6

Utilize transvaginal ultrasonography
Transvaginal ultrasonography is often useful in the evaluation of patients with AUB, as it may identify uterine fibroids or adenomyosis, suggest intracavitary pathology (such as an endometrial polyp or submucosal fibroid), or raise the possibility of PCOS. In virginal patients or those in whom vaginal ultrasound is not appropriate, abdominal pelvic ultrasonography represents appropriate imaging. If unenhanced ultrasound suggests endometrial polyps or fibroids within the endometrial cavity, an office-based saline infusion sonogram (sonohysterogram) (FIGURE 5) or hysteroscopy should be performed. Targeted endometrial sampling and biopsy of intracavitary pathology can be performed at the time of hysteroscopy.

Treatment
When HMB impairs quality of life, is bothersome to the patient, or results in anemia, treatment is appropriate. Although bleeding episodes in women with AUB-O may be infrequent (as with Case 2), treatment prevents heavy or prolonged bleeding episodes as well as endometrial neoplasia that may otherwise occur in anovulatory women.
Many women with AUB can be managed medically. However, treatment choices will vary with respect to the patient’s desire for future fertility, medical comorbidities, personal preferences, and financial barriers. While many women may prefer outpatient medical management (TABLE 2),7-14 others might desire surgical therapy, including endometrial ablation or hysterectomy.

Oral contraceptives
Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives represent appropriate initial therapy for many women in the reproductive-age group with AUB, whether women have HMB or AUB-O. However, contraceptive doses of estrogen are not appropriate for some women with risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including those who smoke cigarettes and are age ≥35 years or those who have hypertension (TABLE 3).15,16

Continue to: Menopausal dosages of HT...
Menopausal dosages of HT
If use of contraceptive doses of estrogen is not appropriate, continuous off-label use of menopausal combination formulations (physiologic dosage) of hormonal therapy (HT; ie, lower doses of estrogen than contraceptives) may be effective in reducing or eliminating AUB. Options for menopausal combination formulations include generic ethinyl estradiol 5 µg/norethindrone acetate 1 mg or estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.7 High-dose oral progestin therapy (norethindrone acetate 5 mg tablet once daily or medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg tablets 1–3 times daily) also can be used when combination contraceptives are contraindicated and may be more effective than lower-dose combination formulations.
Package labeling, as well as some guidelines, indicate that oral progestins used to treat AUB should be taken cyclically.8 However, continuous daily use is easier for many patients and may be more effective in reducing bleeding. Accordingly, we counsel patients with AUB who are using progestins and who do not wish to conceive to take these medications continuously. High-dose oral progestin therapy may cause bloating, dysphoria, and increased appetite/weight gain. Women initiating hormonal management (including the progestin IUDs detailed below) for AUB should be counseled that irregular or even continuous light bleeding/spotting is common initially, but this bleeding pattern typically decreases with continued use.
IUDs
The LNG 52 mg IUD (Mirena or Liletta) effectively treats HMB, reducing bleeding in a manner comparable to that of endometrial ablation.9,10 The Mirena IUD is approved for treatment of HMB in women desiring intrauterine contraception. In contrast to oral medications, use of progestin IUDs does not involve daily administration and may represent an attractive option for women with HMB who would like to avoid surgery or preserve fertility. With ongoing use, continuous oral or intrauterine hormonal management may result in amenorrhea in some women with AUB.
When the LNG 52 mg IUD is used to treat HMB, the menstrual suppression impact may begin to attenuate after approximately 4 years of use; in this setting, replacing the IUD often restores effective menstrual suppression.11 The LNG 52 mg IUD effectively suppresses menses in women with coagulation disorders; if menstrual suppression with the progestin IUD is not adequate in this setting, it may be appropriate to add an oral combination estrogen-progestin contraceptive or high-dose oral progestin.11,12
NSAIDs and tranexamic acid
Off-label use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (naproxen 500–1,000 mg daily for 5 days beginning at the onset of menstrual flow or tranexamic acid two 650-mg tablets 3 times daily for up to 5 days during episodes of heavy flow) can suppress HMB and is useful for women who prefer to avoid or have contraindications to hormonal treatments.13,14 Unfortunately, these agents are not as effective as hormonal management in treating AUB.
Iron supplementation is often needed
Iron depletion commonly results from HMB, often resulting in iron deficiency anemia. When iron depletion (readily identified by checking a serum ferritin level) or iron deficiency anemia is identified, iron supplementation should be recommended. Every-other-day administration of iron supplements maximizes iron absorption while minimizing the adverse effects of unabsorbed iron, such as nausea. Sixty mg of elemental iron (ferrous sulfate 325 mg) administered every other day represents an inexpensive and effective treatment for iron deficiency/anemia.17 In patients who cannot tolerate oral iron supplementation or for those in whom oral therapy is not appropriate or effective, newer intravenous iron formulations are safe and effective.18
Continue to: Case 1 Follow-up...
Case 1 Follow-up
The patient noted marked improvement in her menstrual cramps following LNG-containing IUD placement. Although she also reported that she no longer experienced heavy menstrual flow or cramps, she was bothered by frequent, unpredictable light bleeding/spotting. You prescribed norethindrone acetate (NETA) 5-mg tablet orally once daily, to be used in addition to her IUD. After using the IUD with concomitant NETA for 2 months’ duration, she noted that her bleeding/spotting almost completely resolved; however, she did report feeling irritable with use of the progestin tablets. She subsequently stopped the NETA tablets and, after 6 months of additional follow-up, reported only minimal spotting and no cramps.
At this later follow-up visit, you noted that her hemoglobin level increased to 12.6 g/dL, and the ferritin level no longer indicated iron depletion. After the IUD had been in place for 4 years, she reported that she was beginning to experience frequent light bleeding again. A follow-up vaginal sonogram noted a well-positioned IUD, there was no suggestion of intracavitary pathology, and adenomyosis continued to be imaged. She underwent IUD removal and placement of a new LNG 52 mg IUD. This resulted in marked reduction in her bleeding.
Case 2 Follow-up
Two weeks after beginning continuous oral progestin therapy, the patient called reporting frequent irregular bleeding. She was reassured that this was not unexpected and encouraged to continue oral progestin therapy. During a 3-month follow-up visit, the patient noted little, if any, bleeding over the previous 2 months and was pleased with this result. She continued to note acne and hirsutism and asked about the possibility of adding spironolactone to her oral progestin regimen.
Case 1 Multiparous woman presents with heavy regular menses
Over the past several years, a 34-year-old woman has noted increasing intensity and duration of menstrual flow, which now persists for 8 days and includes clots “the size of quarters” and soaks a pad within 1 hour. Sometimes she misses or leaves work on her heaviest days of flow. She reports that menstrual cramps prior to and during flow are increasingly bothersome and do not respond adequately to ibuprofen. She intermittently uses condoms for contraception. She does not wish to be pregnant currently; however, she recently entered into a new relationship and may wish to conceive in the future.
On bimanual examination, the uterus appears bulky. Her hemoglobin is 10.9 g/dL with low mean corpuscular volume and a serum ferritin level indicating iron depletion. Pelvic ultrasonography suggests uterine adenomyosis; no fibroids are imaged (FIGURE 1).
You advise the patient to take ferrous sulfate 325 mg every other day. After discussion with the patient regarding different treatment options, she chooses to proceed with placement of a 52-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD; Mirena or Liletta).
Case 2 Older adolescent presents with irregular bleeding
A 19-year-old patient reports approximately 6 bleeding episodes each year. She reports the duration of her bleeding as variable, and sometimes the bleeding is heavy with small clots passed. She has been previously diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives have been prescribed several times in the past, but she always has discontinued them due to nausea. The patient is in a same-sex relationship and does not anticipate being sexually active with a male. She reports having to shave her mustache and chin twice weekly for the past 1 to 2 years.
On physical examination, the patient is obese (body mass index [BMI], 32 kg/m2), facial acne and hirsutism are present, and hair extends from the mons toward the umbilicus. Bimanual examination reveals a normal size, mobile, nontender uterus without obvious adnexal pathology. Pelvic ultrasonography demonstrates a normal-appearing uterus with multiplanar endometrium (consistent with proliferative changes) (FIGURE 2). Ovarian imaging demonstrates ≥12 follicles per image (FIGURE 3).


After reviewing various treatment options, you prescribe oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg (two 10-mg tablets) daily in a continuous fashion. You counsel her that she should not be surprised or concerned if frequent or even continuous bleeding occurs initially, and that she should continue this medication despite the occurrence of such.
About one-third of all women experience abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) sometime during their lifetime and AUB can impair quality of life.1 Surgical management, including hysterectomy and endometrial ablation, plays an important role in the management of AUB in patients who do not desire future pregnancies. However, many cases of AUB occur in women who may not have completed childbearing or in women who prefer to avoid surgery.2 AUB can be managed effectively medically in most cases.1 Accordingly, in this review, we focus on nonsurgical management of AUB.
Continue to: Because previously used terms, including...
Because previously used terms, including menorrhagia and meno-metrorrhagia, were inconsistently defined and confusing, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics introduced updated terminology in 2011 to better describe and characterize AUB in nonpregnant women. Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) refers to ovulatory (cyclic) bleeding that is more than 8 days’ duration, or sufficiently heavy to impair a woman’s quality of life. HMB is a pattern of AUB distinct from the irregular bleeding pattern typically caused by ovulatory dysfunction (AUB-O).1
Clinical evaluation
Obtain menstrual history. In addition to a medical, surgical, and gynecologic history, a thorough menstrual history should be obtained to further characterize the patient’s bleeding pattern. In contrast to the cyclical or ovulatory bleeding seen with HMB, bleeding associated with inconsistent ovulation (AUB-O) is unpredictable or irregular, and is commonly associated with PCOS. AUB-O is also encountered in recently menarchal girls (secondary to immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis) and in those who are perimenopausal. In addition, medications that can induce hyperprolactinemia (such as certain antipsychotics) can cause AUB-O.
Evaluate for all sources of bleeding. Be sure to evaluate for extrauterine causes of bleeding, including the cervix, vagina, vulva, or the urinary or gastrointestinal tracts for bleeding. Intermenstrual bleeding occurring between normal regular menses may be caused by an endometrial polyp, submucosal fibroid, endometritis, or an IUD. The patient report of postcoital bleeding suggests that cervical disease (cervicitis, polyp, or malignancy) may be present. Uterine leiomyoma or adenomyosis represent common causes of HMB. However, HMB also may be caused by a copper IUD, coagulation disorders (including von Willebrand disease), or use of anticoagulant medications. Hormonal contraceptives also can cause irregular bleeding.
Perform a pelvic examination and measure vital signs. The presence of fever suggests the possible presence of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), while orthostatic hypotension raises the possibility of hypovolemia. When vaginal speculum examination is performed, a cervical cause of abnormal bleeding may be noted. The presence of fresh or old blood or finding clots in the vaginal vault or at the cervical os are all consistent with AUB. A bimanual examination that reveals an enlarged or lobular uterus suggests leiomyoma or adenomyosis. Cervical or adnexal tenderness is often noted in women with PID, which itself may be associated with endometritis. The presence of hyperandrogenic signs on physical examination (eg, acne, hirsutism, or clitoromegaly) suggests PCOS. The finding of galactorrhea suggests that hyperprolactinemia may be present.
Laboratory assessment
Test for pregnancy, cervical disease, and sexually transmitted infection when appropriate. Pregnancy testing is appropriate for women with AUB aged 55 years or younger. If patients with AUB are not up to date with normal cervical cancer screening results, cervical cytology and/or human papillomavirus testing should be performed. Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Trichomonas vaginalis should be performed in patients:
- younger than 25 years
- when the history indicates new or multiple sexual partners, or
- when vaginal discharge, cervicitis, cervical motion, or adnexal tenderness is present.
Continue to: Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels...
Obtain a complete blood count and serum ferritin levels. In women presenting with HMB, iron depletion and iron deficiency anemia are common. The finding of leukocytosis raises the possibility of PID or postpartum endometritis. In women with presumptive AUB-O, checking the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, free T4, and prolactin should be performed.
Screen for a hemostasis disorder. Women with excessive menstrual bleeding should be clinically screened for an underlying disorder of hemostasis (TABLE 1).3 When a hemostasis disorder is suspected, initial laboratory evaluation includes a partial thromboplastin time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen. Women who have a positive clinical screen for a possible bleeding disorder or abnormal initial laboratory test results for disorders of hemostasis should undergo further laboratory evaluation, including von Willebrand factor antigen, ristocetin cofactor assay, and factor VIII. Consultation with a hematologist should be considered in these cases.

Perform endometrial biopsy when indicated
After excluding pregnancy, endometrial biopsy (through pipelle biospy or brush sampling; FIGURE 4) should be performed in women with AUB who are at increased risk for endometrial neoplasia. The prevalence of endometrial neoplasia is substantially higher among women ≥45 years of age4 and among patients with AUB who are also obese (BMI, ≥30 kg/m2).5 In addition, AUB patients with unopposed estrogen exposure (presumed anovulation/PCOS), as well as those with persistent AUB or failed medical management, should undergo endometrial biopsy.6

Utilize transvaginal ultrasonography
Transvaginal ultrasonography is often useful in the evaluation of patients with AUB, as it may identify uterine fibroids or adenomyosis, suggest intracavitary pathology (such as an endometrial polyp or submucosal fibroid), or raise the possibility of PCOS. In virginal patients or those in whom vaginal ultrasound is not appropriate, abdominal pelvic ultrasonography represents appropriate imaging. If unenhanced ultrasound suggests endometrial polyps or fibroids within the endometrial cavity, an office-based saline infusion sonogram (sonohysterogram) (FIGURE 5) or hysteroscopy should be performed. Targeted endometrial sampling and biopsy of intracavitary pathology can be performed at the time of hysteroscopy.

Treatment
When HMB impairs quality of life, is bothersome to the patient, or results in anemia, treatment is appropriate. Although bleeding episodes in women with AUB-O may be infrequent (as with Case 2), treatment prevents heavy or prolonged bleeding episodes as well as endometrial neoplasia that may otherwise occur in anovulatory women.
Many women with AUB can be managed medically. However, treatment choices will vary with respect to the patient’s desire for future fertility, medical comorbidities, personal preferences, and financial barriers. While many women may prefer outpatient medical management (TABLE 2),7-14 others might desire surgical therapy, including endometrial ablation or hysterectomy.

Oral contraceptives
Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives represent appropriate initial therapy for many women in the reproductive-age group with AUB, whether women have HMB or AUB-O. However, contraceptive doses of estrogen are not appropriate for some women with risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including those who smoke cigarettes and are age ≥35 years or those who have hypertension (TABLE 3).15,16

Continue to: Menopausal dosages of HT...
Menopausal dosages of HT
If use of contraceptive doses of estrogen is not appropriate, continuous off-label use of menopausal combination formulations (physiologic dosage) of hormonal therapy (HT; ie, lower doses of estrogen than contraceptives) may be effective in reducing or eliminating AUB. Options for menopausal combination formulations include generic ethinyl estradiol 5 µg/norethindrone acetate 1 mg or estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.7 High-dose oral progestin therapy (norethindrone acetate 5 mg tablet once daily or medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg tablets 1–3 times daily) also can be used when combination contraceptives are contraindicated and may be more effective than lower-dose combination formulations.
Package labeling, as well as some guidelines, indicate that oral progestins used to treat AUB should be taken cyclically.8 However, continuous daily use is easier for many patients and may be more effective in reducing bleeding. Accordingly, we counsel patients with AUB who are using progestins and who do not wish to conceive to take these medications continuously. High-dose oral progestin therapy may cause bloating, dysphoria, and increased appetite/weight gain. Women initiating hormonal management (including the progestin IUDs detailed below) for AUB should be counseled that irregular or even continuous light bleeding/spotting is common initially, but this bleeding pattern typically decreases with continued use.
IUDs
The LNG 52 mg IUD (Mirena or Liletta) effectively treats HMB, reducing bleeding in a manner comparable to that of endometrial ablation.9,10 The Mirena IUD is approved for treatment of HMB in women desiring intrauterine contraception. In contrast to oral medications, use of progestin IUDs does not involve daily administration and may represent an attractive option for women with HMB who would like to avoid surgery or preserve fertility. With ongoing use, continuous oral or intrauterine hormonal management may result in amenorrhea in some women with AUB.
When the LNG 52 mg IUD is used to treat HMB, the menstrual suppression impact may begin to attenuate after approximately 4 years of use; in this setting, replacing the IUD often restores effective menstrual suppression.11 The LNG 52 mg IUD effectively suppresses menses in women with coagulation disorders; if menstrual suppression with the progestin IUD is not adequate in this setting, it may be appropriate to add an oral combination estrogen-progestin contraceptive or high-dose oral progestin.11,12
NSAIDs and tranexamic acid
Off-label use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (naproxen 500–1,000 mg daily for 5 days beginning at the onset of menstrual flow or tranexamic acid two 650-mg tablets 3 times daily for up to 5 days during episodes of heavy flow) can suppress HMB and is useful for women who prefer to avoid or have contraindications to hormonal treatments.13,14 Unfortunately, these agents are not as effective as hormonal management in treating AUB.
Iron supplementation is often needed
Iron depletion commonly results from HMB, often resulting in iron deficiency anemia. When iron depletion (readily identified by checking a serum ferritin level) or iron deficiency anemia is identified, iron supplementation should be recommended. Every-other-day administration of iron supplements maximizes iron absorption while minimizing the adverse effects of unabsorbed iron, such as nausea. Sixty mg of elemental iron (ferrous sulfate 325 mg) administered every other day represents an inexpensive and effective treatment for iron deficiency/anemia.17 In patients who cannot tolerate oral iron supplementation or for those in whom oral therapy is not appropriate or effective, newer intravenous iron formulations are safe and effective.18
Continue to: Case 1 Follow-up...
Case 1 Follow-up
The patient noted marked improvement in her menstrual cramps following LNG-containing IUD placement. Although she also reported that she no longer experienced heavy menstrual flow or cramps, she was bothered by frequent, unpredictable light bleeding/spotting. You prescribed norethindrone acetate (NETA) 5-mg tablet orally once daily, to be used in addition to her IUD. After using the IUD with concomitant NETA for 2 months’ duration, she noted that her bleeding/spotting almost completely resolved; however, she did report feeling irritable with use of the progestin tablets. She subsequently stopped the NETA tablets and, after 6 months of additional follow-up, reported only minimal spotting and no cramps.
At this later follow-up visit, you noted that her hemoglobin level increased to 12.6 g/dL, and the ferritin level no longer indicated iron depletion. After the IUD had been in place for 4 years, she reported that she was beginning to experience frequent light bleeding again. A follow-up vaginal sonogram noted a well-positioned IUD, there was no suggestion of intracavitary pathology, and adenomyosis continued to be imaged. She underwent IUD removal and placement of a new LNG 52 mg IUD. This resulted in marked reduction in her bleeding.
Case 2 Follow-up
Two weeks after beginning continuous oral progestin therapy, the patient called reporting frequent irregular bleeding. She was reassured that this was not unexpected and encouraged to continue oral progestin therapy. During a 3-month follow-up visit, the patient noted little, if any, bleeding over the previous 2 months and was pleased with this result. She continued to note acne and hirsutism and asked about the possibility of adding spironolactone to her oral progestin regimen.
- Munro MG, Critchley HOD, Fraser IS; FIGO Menstrual Disorders Committee. The two FIGO systems for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding symptoms and classification of causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in the reproductive years: 2018 revisions. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2018;143:393-408.
- Kaunitz AM. Abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-age women. JAMA. 2019;321:2126-2127.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion no. 557: management of acute abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:891-896.
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Uterine Cancer. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/corp.html. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Wise MR, Gill P, Lensen S, et al. Body mass index trumps age in decision for endometrial biopsy: cohort study of symptomatic premenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:598.e1-598.e8.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Practice bulletin no. 128: diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:197-206.
- The North American Menopause Society. Menopause Practice–A Clinician’s Guide. 5th ed. NAMS: Mayfield Heights, OH; 2014.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Heavy menstrual bleeding: assessment and management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng88. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Kaunitz AM, Bissonnette F, Monteiro I, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or medroxyprogesterone for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:625-632.
- Kaunitz AM, Meredith S, Inki P, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and endometrial ablation in heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1104-1116.
- Kaunitz AM, Inki P. The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in heavy menstrual bleeding: a benefit-risk review. Drugs. 2012;72:193-215.
- James AH, Kouides PA, Abdul-Kadir R, et al. Von Willebrand disease and other bleeding disorders in women: consensus on diagnosis and management from an international expert panel. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:12.e1-8.
- Ylikorkala O, Pekonen F. Naproxen reduces idiopathic but not fibromyoma-induced menorrhagia. Obstet Gynecol. 1986;68:10-12.
- Lukes AS, Moore KA, Muse KN, et al. Tranexamic acid treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:865-875.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1–103.
- ACOG Practice Bulletin no. 206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Stoffel NU, Cercamondi CI, Brittenham G, et al. Iron absorption from oral iron supplements given on consecutive versus alternate days and as single morning doses versus twice-daily split dosing in iron-depleted women: two open-label, randomised controlled trials. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e524–e533.
- Auerbach M, Adamson JW. How we diagnose and treat iron deficiency anemia. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:31-38.
- Munro MG, Critchley HOD, Fraser IS; FIGO Menstrual Disorders Committee. The two FIGO systems for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding symptoms and classification of causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in the reproductive years: 2018 revisions. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2018;143:393-408.
- Kaunitz AM. Abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-age women. JAMA. 2019;321:2126-2127.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion no. 557: management of acute abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:891-896.
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Uterine Cancer. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/corp.html. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Wise MR, Gill P, Lensen S, et al. Body mass index trumps age in decision for endometrial biopsy: cohort study of symptomatic premenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:598.e1-598.e8.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Practice bulletin no. 128: diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:197-206.
- The North American Menopause Society. Menopause Practice–A Clinician’s Guide. 5th ed. NAMS: Mayfield Heights, OH; 2014.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Heavy menstrual bleeding: assessment and management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng88. Accessed October 10, 2019.
- Kaunitz AM, Bissonnette F, Monteiro I, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or medroxyprogesterone for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:625-632.
- Kaunitz AM, Meredith S, Inki P, et al. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and endometrial ablation in heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1104-1116.
- Kaunitz AM, Inki P. The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in heavy menstrual bleeding: a benefit-risk review. Drugs. 2012;72:193-215.
- James AH, Kouides PA, Abdul-Kadir R, et al. Von Willebrand disease and other bleeding disorders in women: consensus on diagnosis and management from an international expert panel. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:12.e1-8.
- Ylikorkala O, Pekonen F. Naproxen reduces idiopathic but not fibromyoma-induced menorrhagia. Obstet Gynecol. 1986;68:10-12.
- Lukes AS, Moore KA, Muse KN, et al. Tranexamic acid treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:865-875.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1–103.
- ACOG Practice Bulletin no. 206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Stoffel NU, Cercamondi CI, Brittenham G, et al. Iron absorption from oral iron supplements given on consecutive versus alternate days and as single morning doses versus twice-daily split dosing in iron-depleted women: two open-label, randomised controlled trials. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e524–e533.
- Auerbach M, Adamson JW. How we diagnose and treat iron deficiency anemia. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:31-38.
2019 Update on menopause
Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
2017 Update on menopause
Since publication of initial findings of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) in 2002, use of systemic menopausal hormone therapy (HT) has declined by some 80% among US women.1 Against this backdrop, this year’s Menopause Update highlights the “hot off the press” updated position statement on menopausal HT from The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), summarized by Dr. JoAnn V. Pinkerton. Although this guidance is chock full of practical, evidence-based guidance, the take-home message that Dr. Pinkerton and I would like to leave readers of OBG
Related Article:
Dr. Andrew M. Kaunitz on prescribing systemic HT to older women
Although menopausal vasomotor and related symptoms improve as women age, in untreated women, vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA, also known as genitourinary syndrome of menopause, or GSM) tends to progress, causing vaginal dryness and sexual dysfunction, among other symptoms. When symptomatic GSM represents the only indication for treatment, low-dose local vaginal estrogen, ospemifene, or dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) is safe and effective. However, as with systemic HT, specific treatments for GSM are substantially underutilized.2 The current package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen deters many appropriate candidates from using this safe, effective treatment. In this Update, Dr. JoAnn E. Manson reviews the rationale for updating this labeling as well as recent efforts to accomplish the task.
Read about updated NAMS guidelines on HT
Guidelines on HT have been updated by The North American Menopause Society
The North American Menopause Society Hormone Therapy (HT) Position Statement Advisory Panel, composed of more than 20 experts in menopausal women's HT, including clinicians, researchers, and epidemiologists, reviewed the 2012 HT Position Statement, evaluated prior and new literature and used levels of evidence to identify the quality of the evidence and strength of the recommendations and to find consensus for the guidelines. The following information comes from the NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement.3
What are the major findings?
HT is the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and GSM and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. Risks of HT may differ for women depending on type, dose, duration, route of administration, and timing of initiation and whether or not a progestogen is needed. Treatment should be individualized using the best available evidence to maximize benefits and minimize risks, with periodic reevaluation about benefits and risks of continuing or discontinuing HT.
For women who are younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindication, the clearest benefit of HT is for the treatment of VMS and prevention of bone loss in those at elevated risk.
The clinical guidelines were presented to NAMS audience at the 2016 annual clinical meeting, where NAMS recommended "determining the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT."4
When to initiate HT and duration of use
In its now-published 2017 guidelines on HT, NAMS affirms the safety and efficacy of HT for symptomatic menopausal women or those at high risk for bone loss who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause. NAMS encourages practitioners to employ shared decision making with their patients to find the appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT, making individualized decisions based on evidence-based information, the unique health risks of women, and with periodic reassessment.
In the clinical guidelines presented in the 2016 NAMS annual meeting,4 key recommendations taken from the 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement3 include the following: For women who are aged younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindications, the benefit/risk ratio appears favorable for treatment of bothersome VMS and in those at elevated risk for bone loss or fracture.
For women who initiate HT more than 10 years from menopause or after age 60, this benefit/risk ratio appears less favorable because of greater absolute risks of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia.
What about extended use of hormone therapy? There is no evidence to support routine discontinuation of HT after age 65. Decisions about longer durations of HT should be individualized and considered for indications such as persistent VMS or bone loss, with shared decision making, documentation, and periodic reevaluation. Longer duration is more favorable for estrogen therapy than for estrogen-progestin therapy, based on the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) randomized controlled trials.5
What about only vaginal symptoms? For bothersome GSM not relieved with over-the-counter therapies and without indications for use of systemic HT, low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or other therapies are recommended and can be continued as long as indicated since there is minimal systemic absorption of estrogen, with serum levels remaining within the normal postmenopausal range.6,7 For women with estrogen sensitive cancer, oncologists should be included in decision making, particularly for women on aromatase inhibitors.
Considerations for special populations Early menopause. For women with hypoestrogenism, primary ovarian insufficiency, or premature surgical menopause without contraindications, HT is recommended until at least the median age of menopause (52 years), as studies suggest that benefits outweigh the risks for effects on bone, heart, cognition, GSM, sexual function, and mood.8
Family history of breast cancer. Observational evidence suggests that use of HT does not further alter the risk for breast cancer in women with a family history of breast cancer. Family history is one risk, among others, that should be assessed when counseling women regarding HT.
Women who are BRCA-positive without breast cancer. For women who are BRCA-positive (higher genetic risk of breast cancer, primarily estrogen-receptor-negative), and have undergone surgical menopause (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), the benefits of estrogen to decrease health risks caused by premature loss of estrogen need to be considered on an individual basis.9 On the basis of limited observational studies, consider offering systemic HT until the median age of menopause (52 years) with longer use individualized.3
Related Article:
Is menopausal hormone therapy safe when your patient carries a BRCA mutation?
Survivors of endometrial and breast cancer with bothersome VMS. For women with prior estrogen-sensitive cancers, non-HTs should be considered first, particularly those agents studied through randomized controlled trials in this population and found to be effective. If systemic estrogen is considered for persistent symptoms after non-HT or complementary options have been unsuccessful, decisions should be made for compelling reasons and after detailed counseling, with shared decision making and in conjunction with their oncologist.3
Bothersome GSM. On the basis of limited observational data, there appears to be minimal to no demonstrated elevation in risk for recurrence of endometrial or breast cancer using low-dose vaginal estrogen,3,10 but decisions should be made in conjunction with an oncologist.
Related Article:
Focus on treating genital atrophy symptoms
The importance of relaying the new guidelines to patients
It is important for clinicians to talk to women about their menopausal symptoms and their options for relief of symptoms or prevention of bone loss. Discussion should take into account age and time from menopause, include evidence-based information11-13 about benefits and risks of different types of therapy, and employ shared decision making to choose the most appropriate therapy to maximize benefits and minimize risks for the individual woman.
Following the WHI initial release in 2002, both women and providers became fearful of HT and believed media hype and celebrities that compounded bioidentical HT was safer than FDA-approved HTs. However, compounded products lack safety and efficacy data, are not monitored or regulated by the FDA, and have unique risks associated with compounding, including concerns about sterility, impurities, and overdosing or underdosing, which could increase cancer risk.3
- Hormone therapy for symptomatic menopausal women is safe and effective for those under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Identify the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of hormone therapy for an individual woman based on evidence.
- We want to remove the fear of using hormone therapy for healthy symptomatic women who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Age at initiation of hormone therapy matters.
- NAMS endorses use of FDA-approved hormone therapy over compounded therapies.
Read about modifying low-dose vaginal estrogen’s black box warning
Physicians continue to underwhelmingly prescribe low-dose vaginal estrogen for GSM
Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, Bernick B, Mirkin S. The Women's EMPOWER survey: identifying women's perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14(3):413-424.
GSM is seriously underrecognized and undertreated.2,8,14 It has a major impact on women's lives--a silent epidemic affecting women's quality of life, sexual health, interpersonal relationships, and even physical health in terms of increased risk of urinary tract infections and urinary symptoms. Unfortunately, patients are reluctant to mention the problem to their clinicians, and they do not clearly recognize it as a medical condition that has available treatment options. Clinicians also rarely receive adequate training in the management of this condition and how to discuss it with their patients. Given busy schedules and time constraints, addressing this topic often falls through the cracks, representing a missed opportunity for helping our patients with safe and effective treatments. In a recent study by Kingsberg and colleagues, an astoundingly low percentageof women with GSM symptoms received treatment.
Details of the study
The study authors evaluated women's perceptions of GSM and available treatment options. US women aged 45 and older who reported GSM symptoms were surveyed. Of 1,858 women with a median age of 58 (range, 45-90), the study authors found that 50% had never used any treatment; 25% used over-the-counter medications; 18% were former users of GSM treatments; and 7% currently used prescribed GSM therapies.
When GSM was discussed, women were more likely than their clinicians to initiate the conversation. The main reason for women not mentioning their symptoms was the perception that GSM symptoms were a natural and inevitable part of aging. Hormonal products were perceived by women as having several downsides, including risk of systemic absorption, messiness of local creams, and the need to reuse an applicator. Overall, clinicians recommended vaginal estrogen therapy to only 23% and oral HTs to 18% of women.
The results of the study are consistent with results of earlier surveys of menopausal women. Although the survey included nearly 2,000 women, it has the potential for selection biases inherent to most Internet-based surveys. In addition, the respondents tended to be white and have higher socieconomic status, with limited representation from other groups.
Calls for the current boxed warning to be revised
GSM is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women; the condition has adverse effects on quality of life and sexual health.2,8,14 Safe and effective treatments are available but are underutilized.1,8,15,16 A current boxed warning appears on low-dose vaginal estrogen--class labeling that appears on all medications in the class of estrogen or HT, regardless of dose or route of administration. These warnings are based on findings from the WHI and other studies of systemic estrogen or estrogen plus progestin, which demonstrated a complex pattern of risks and benefits of HT (including increased risk of venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, stroke, and breast cancer [with estrogen plus progestin]).
These findings, however, do not appear to be relevant to low-dose vaginal estrogen, given minimal if any systemic absorption and much lower blood levels of hormones than found with systemic HT. Blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen remain in the normal postmenopausal range, compared to several-fold elevations in hormone levels with systemic HT.8,15,16 Additionally, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen, as well as short-term randomized clinical trials, show no evidence of an increased risk of venous thromboembolic events, heart disease, stroke, breast cancer, or dementia--the listed possible adverse effects in the boxed warning. The current warning is based on extrapolating findings from systemic HT, which is inappropriate and not evidence-based for low-dose vaginal estrogen.15
The inappropriate boxed warning contributes to the problem of undertreatment of GSM in women by discouraging clinicians from prescribing the medication and dissuading patients from taking it even after purchase. Testimonials from many clinicians caring for these women have underscored that women will fill their prescription, but after seeing the boxed warning will often become alarmed and decide not to take the medication. Clinicians reported that patients often say at their next appointment: "No, I never took it. I got very scared when I saw the boxed warning." As a result, clinicians often have to spend a great deal of time explaining the limitations of, and lack of evidence for, the boxed warning on low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Related Article:
2016 Update on menopause
Recommended label revisions
A modified label, without a boxed warning, would be safer for women because the key messages would not be obscured by the large amount of irrelevant information. Our Working Group recommended that the label explain that the listed risks were found in studies of systemic HT and their relevance to low-dose vaginal estrogen is unknown. The Group also recommended that warning text should be added in bold font to advise patients to seek medical attention if they have vaginal bleeding or spotting while taking the medication. In addition, patients who have a history of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer should discuss the use of the medication with their oncologist.
Status update on efforts to revise label. A citizen's petition was filed in the Spring of 2016, with signatures from more than 600 clinicians and patients and representatives of medical and professional organizations endorsing a more appropriate evidence-based label for low-dose vaginal estrogen. The FDA is continuing to review and deliberate on these issues but has not yet made a final decision.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Manson JM, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—Getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(9):803–806.
- Parish SJ, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society [published online ahead of print June 2017]. Menopause.
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy: 2016 NAMS position statement [abstract]. Menopause. 2016;23:1365.
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310(13):1353–1368.
- Lethaby A, Ayeleke RO, Roberts H. Local oestrogen for vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2016;8:CD001500.
- Management of symptomatic vulvovaginal atrophy: 2013 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2013;20(9):888–902.
- Faubion SS, Kuhle CL, Shuster LT, Rocca WA. Long-term health consequences of premature or early menopause and considerations for management. Climacteric. 2015;18(4):483–491.
- Chai X, Domchek S, Kauff N, Rebbeck T, Chen J. RE: Breast cancer risk after salpingo-oophorectomy in healthy BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: revisiting the evidence for risk reduction. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(9).
- Farrell R; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659 summary: The use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(3):618–619.
- Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(13):1221–1231.
- Marjoribanks J, Farquhar C, Roberts H, Lethaby A, Lee J. Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1:CD004143.
- Boardman HM, Hartley L, Eisinga A, et al. Hormone therapy for preventing cardiovascular disease in post-menopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD002229.
- Parish S, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- Manson JE, Goldstein SR, Kagan R, et al; Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause. Why the product labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen should be changed. Menopause. 2014;21(9):911–916.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(4):859-876.
Since publication of initial findings of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) in 2002, use of systemic menopausal hormone therapy (HT) has declined by some 80% among US women.1 Against this backdrop, this year’s Menopause Update highlights the “hot off the press” updated position statement on menopausal HT from The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), summarized by Dr. JoAnn V. Pinkerton. Although this guidance is chock full of practical, evidence-based guidance, the take-home message that Dr. Pinkerton and I would like to leave readers of OBG
Related Article:
Dr. Andrew M. Kaunitz on prescribing systemic HT to older women
Although menopausal vasomotor and related symptoms improve as women age, in untreated women, vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA, also known as genitourinary syndrome of menopause, or GSM) tends to progress, causing vaginal dryness and sexual dysfunction, among other symptoms. When symptomatic GSM represents the only indication for treatment, low-dose local vaginal estrogen, ospemifene, or dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) is safe and effective. However, as with systemic HT, specific treatments for GSM are substantially underutilized.2 The current package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen deters many appropriate candidates from using this safe, effective treatment. In this Update, Dr. JoAnn E. Manson reviews the rationale for updating this labeling as well as recent efforts to accomplish the task.
Read about updated NAMS guidelines on HT
Guidelines on HT have been updated by The North American Menopause Society
The North American Menopause Society Hormone Therapy (HT) Position Statement Advisory Panel, composed of more than 20 experts in menopausal women's HT, including clinicians, researchers, and epidemiologists, reviewed the 2012 HT Position Statement, evaluated prior and new literature and used levels of evidence to identify the quality of the evidence and strength of the recommendations and to find consensus for the guidelines. The following information comes from the NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement.3
What are the major findings?
HT is the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and GSM and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. Risks of HT may differ for women depending on type, dose, duration, route of administration, and timing of initiation and whether or not a progestogen is needed. Treatment should be individualized using the best available evidence to maximize benefits and minimize risks, with periodic reevaluation about benefits and risks of continuing or discontinuing HT.
For women who are younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindication, the clearest benefit of HT is for the treatment of VMS and prevention of bone loss in those at elevated risk.
The clinical guidelines were presented to NAMS audience at the 2016 annual clinical meeting, where NAMS recommended "determining the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT."4
When to initiate HT and duration of use
In its now-published 2017 guidelines on HT, NAMS affirms the safety and efficacy of HT for symptomatic menopausal women or those at high risk for bone loss who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause. NAMS encourages practitioners to employ shared decision making with their patients to find the appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT, making individualized decisions based on evidence-based information, the unique health risks of women, and with periodic reassessment.
In the clinical guidelines presented in the 2016 NAMS annual meeting,4 key recommendations taken from the 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement3 include the following: For women who are aged younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindications, the benefit/risk ratio appears favorable for treatment of bothersome VMS and in those at elevated risk for bone loss or fracture.
For women who initiate HT more than 10 years from menopause or after age 60, this benefit/risk ratio appears less favorable because of greater absolute risks of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia.
What about extended use of hormone therapy? There is no evidence to support routine discontinuation of HT after age 65. Decisions about longer durations of HT should be individualized and considered for indications such as persistent VMS or bone loss, with shared decision making, documentation, and periodic reevaluation. Longer duration is more favorable for estrogen therapy than for estrogen-progestin therapy, based on the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) randomized controlled trials.5
What about only vaginal symptoms? For bothersome GSM not relieved with over-the-counter therapies and without indications for use of systemic HT, low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or other therapies are recommended and can be continued as long as indicated since there is minimal systemic absorption of estrogen, with serum levels remaining within the normal postmenopausal range.6,7 For women with estrogen sensitive cancer, oncologists should be included in decision making, particularly for women on aromatase inhibitors.
Considerations for special populations Early menopause. For women with hypoestrogenism, primary ovarian insufficiency, or premature surgical menopause without contraindications, HT is recommended until at least the median age of menopause (52 years), as studies suggest that benefits outweigh the risks for effects on bone, heart, cognition, GSM, sexual function, and mood.8
Family history of breast cancer. Observational evidence suggests that use of HT does not further alter the risk for breast cancer in women with a family history of breast cancer. Family history is one risk, among others, that should be assessed when counseling women regarding HT.
Women who are BRCA-positive without breast cancer. For women who are BRCA-positive (higher genetic risk of breast cancer, primarily estrogen-receptor-negative), and have undergone surgical menopause (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), the benefits of estrogen to decrease health risks caused by premature loss of estrogen need to be considered on an individual basis.9 On the basis of limited observational studies, consider offering systemic HT until the median age of menopause (52 years) with longer use individualized.3
Related Article:
Is menopausal hormone therapy safe when your patient carries a BRCA mutation?
Survivors of endometrial and breast cancer with bothersome VMS. For women with prior estrogen-sensitive cancers, non-HTs should be considered first, particularly those agents studied through randomized controlled trials in this population and found to be effective. If systemic estrogen is considered for persistent symptoms after non-HT or complementary options have been unsuccessful, decisions should be made for compelling reasons and after detailed counseling, with shared decision making and in conjunction with their oncologist.3
Bothersome GSM. On the basis of limited observational data, there appears to be minimal to no demonstrated elevation in risk for recurrence of endometrial or breast cancer using low-dose vaginal estrogen,3,10 but decisions should be made in conjunction with an oncologist.
Related Article:
Focus on treating genital atrophy symptoms
The importance of relaying the new guidelines to patients
It is important for clinicians to talk to women about their menopausal symptoms and their options for relief of symptoms or prevention of bone loss. Discussion should take into account age and time from menopause, include evidence-based information11-13 about benefits and risks of different types of therapy, and employ shared decision making to choose the most appropriate therapy to maximize benefits and minimize risks for the individual woman.
Following the WHI initial release in 2002, both women and providers became fearful of HT and believed media hype and celebrities that compounded bioidentical HT was safer than FDA-approved HTs. However, compounded products lack safety and efficacy data, are not monitored or regulated by the FDA, and have unique risks associated with compounding, including concerns about sterility, impurities, and overdosing or underdosing, which could increase cancer risk.3
- Hormone therapy for symptomatic menopausal women is safe and effective for those under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Identify the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of hormone therapy for an individual woman based on evidence.
- We want to remove the fear of using hormone therapy for healthy symptomatic women who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Age at initiation of hormone therapy matters.
- NAMS endorses use of FDA-approved hormone therapy over compounded therapies.
Read about modifying low-dose vaginal estrogen’s black box warning
Physicians continue to underwhelmingly prescribe low-dose vaginal estrogen for GSM
Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, Bernick B, Mirkin S. The Women's EMPOWER survey: identifying women's perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14(3):413-424.
GSM is seriously underrecognized and undertreated.2,8,14 It has a major impact on women's lives--a silent epidemic affecting women's quality of life, sexual health, interpersonal relationships, and even physical health in terms of increased risk of urinary tract infections and urinary symptoms. Unfortunately, patients are reluctant to mention the problem to their clinicians, and they do not clearly recognize it as a medical condition that has available treatment options. Clinicians also rarely receive adequate training in the management of this condition and how to discuss it with their patients. Given busy schedules and time constraints, addressing this topic often falls through the cracks, representing a missed opportunity for helping our patients with safe and effective treatments. In a recent study by Kingsberg and colleagues, an astoundingly low percentageof women with GSM symptoms received treatment.
Details of the study
The study authors evaluated women's perceptions of GSM and available treatment options. US women aged 45 and older who reported GSM symptoms were surveyed. Of 1,858 women with a median age of 58 (range, 45-90), the study authors found that 50% had never used any treatment; 25% used over-the-counter medications; 18% were former users of GSM treatments; and 7% currently used prescribed GSM therapies.
When GSM was discussed, women were more likely than their clinicians to initiate the conversation. The main reason for women not mentioning their symptoms was the perception that GSM symptoms were a natural and inevitable part of aging. Hormonal products were perceived by women as having several downsides, including risk of systemic absorption, messiness of local creams, and the need to reuse an applicator. Overall, clinicians recommended vaginal estrogen therapy to only 23% and oral HTs to 18% of women.
The results of the study are consistent with results of earlier surveys of menopausal women. Although the survey included nearly 2,000 women, it has the potential for selection biases inherent to most Internet-based surveys. In addition, the respondents tended to be white and have higher socieconomic status, with limited representation from other groups.
Calls for the current boxed warning to be revised
GSM is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women; the condition has adverse effects on quality of life and sexual health.2,8,14 Safe and effective treatments are available but are underutilized.1,8,15,16 A current boxed warning appears on low-dose vaginal estrogen--class labeling that appears on all medications in the class of estrogen or HT, regardless of dose or route of administration. These warnings are based on findings from the WHI and other studies of systemic estrogen or estrogen plus progestin, which demonstrated a complex pattern of risks and benefits of HT (including increased risk of venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, stroke, and breast cancer [with estrogen plus progestin]).
These findings, however, do not appear to be relevant to low-dose vaginal estrogen, given minimal if any systemic absorption and much lower blood levels of hormones than found with systemic HT. Blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen remain in the normal postmenopausal range, compared to several-fold elevations in hormone levels with systemic HT.8,15,16 Additionally, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen, as well as short-term randomized clinical trials, show no evidence of an increased risk of venous thromboembolic events, heart disease, stroke, breast cancer, or dementia--the listed possible adverse effects in the boxed warning. The current warning is based on extrapolating findings from systemic HT, which is inappropriate and not evidence-based for low-dose vaginal estrogen.15
The inappropriate boxed warning contributes to the problem of undertreatment of GSM in women by discouraging clinicians from prescribing the medication and dissuading patients from taking it even after purchase. Testimonials from many clinicians caring for these women have underscored that women will fill their prescription, but after seeing the boxed warning will often become alarmed and decide not to take the medication. Clinicians reported that patients often say at their next appointment: "No, I never took it. I got very scared when I saw the boxed warning." As a result, clinicians often have to spend a great deal of time explaining the limitations of, and lack of evidence for, the boxed warning on low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Related Article:
2016 Update on menopause
Recommended label revisions
A modified label, without a boxed warning, would be safer for women because the key messages would not be obscured by the large amount of irrelevant information. Our Working Group recommended that the label explain that the listed risks were found in studies of systemic HT and their relevance to low-dose vaginal estrogen is unknown. The Group also recommended that warning text should be added in bold font to advise patients to seek medical attention if they have vaginal bleeding or spotting while taking the medication. In addition, patients who have a history of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer should discuss the use of the medication with their oncologist.
Status update on efforts to revise label. A citizen's petition was filed in the Spring of 2016, with signatures from more than 600 clinicians and patients and representatives of medical and professional organizations endorsing a more appropriate evidence-based label for low-dose vaginal estrogen. The FDA is continuing to review and deliberate on these issues but has not yet made a final decision.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Since publication of initial findings of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) in 2002, use of systemic menopausal hormone therapy (HT) has declined by some 80% among US women.1 Against this backdrop, this year’s Menopause Update highlights the “hot off the press” updated position statement on menopausal HT from The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), summarized by Dr. JoAnn V. Pinkerton. Although this guidance is chock full of practical, evidence-based guidance, the take-home message that Dr. Pinkerton and I would like to leave readers of OBG
Related Article:
Dr. Andrew M. Kaunitz on prescribing systemic HT to older women
Although menopausal vasomotor and related symptoms improve as women age, in untreated women, vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA, also known as genitourinary syndrome of menopause, or GSM) tends to progress, causing vaginal dryness and sexual dysfunction, among other symptoms. When symptomatic GSM represents the only indication for treatment, low-dose local vaginal estrogen, ospemifene, or dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) is safe and effective. However, as with systemic HT, specific treatments for GSM are substantially underutilized.2 The current package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen deters many appropriate candidates from using this safe, effective treatment. In this Update, Dr. JoAnn E. Manson reviews the rationale for updating this labeling as well as recent efforts to accomplish the task.
Read about updated NAMS guidelines on HT
Guidelines on HT have been updated by The North American Menopause Society
The North American Menopause Society Hormone Therapy (HT) Position Statement Advisory Panel, composed of more than 20 experts in menopausal women's HT, including clinicians, researchers, and epidemiologists, reviewed the 2012 HT Position Statement, evaluated prior and new literature and used levels of evidence to identify the quality of the evidence and strength of the recommendations and to find consensus for the guidelines. The following information comes from the NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement.3
What are the major findings?
HT is the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and GSM and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. Risks of HT may differ for women depending on type, dose, duration, route of administration, and timing of initiation and whether or not a progestogen is needed. Treatment should be individualized using the best available evidence to maximize benefits and minimize risks, with periodic reevaluation about benefits and risks of continuing or discontinuing HT.
For women who are younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindication, the clearest benefit of HT is for the treatment of VMS and prevention of bone loss in those at elevated risk.
The clinical guidelines were presented to NAMS audience at the 2016 annual clinical meeting, where NAMS recommended "determining the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT."4
When to initiate HT and duration of use
In its now-published 2017 guidelines on HT, NAMS affirms the safety and efficacy of HT for symptomatic menopausal women or those at high risk for bone loss who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause. NAMS encourages practitioners to employ shared decision making with their patients to find the appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of HT, making individualized decisions based on evidence-based information, the unique health risks of women, and with periodic reassessment.
In the clinical guidelines presented in the 2016 NAMS annual meeting,4 key recommendations taken from the 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement3 include the following: For women who are aged younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause and have no contraindications, the benefit/risk ratio appears favorable for treatment of bothersome VMS and in those at elevated risk for bone loss or fracture.
For women who initiate HT more than 10 years from menopause or after age 60, this benefit/risk ratio appears less favorable because of greater absolute risks of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia.
What about extended use of hormone therapy? There is no evidence to support routine discontinuation of HT after age 65. Decisions about longer durations of HT should be individualized and considered for indications such as persistent VMS or bone loss, with shared decision making, documentation, and periodic reevaluation. Longer duration is more favorable for estrogen therapy than for estrogen-progestin therapy, based on the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) randomized controlled trials.5
What about only vaginal symptoms? For bothersome GSM not relieved with over-the-counter therapies and without indications for use of systemic HT, low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or other therapies are recommended and can be continued as long as indicated since there is minimal systemic absorption of estrogen, with serum levels remaining within the normal postmenopausal range.6,7 For women with estrogen sensitive cancer, oncologists should be included in decision making, particularly for women on aromatase inhibitors.
Considerations for special populations Early menopause. For women with hypoestrogenism, primary ovarian insufficiency, or premature surgical menopause without contraindications, HT is recommended until at least the median age of menopause (52 years), as studies suggest that benefits outweigh the risks for effects on bone, heart, cognition, GSM, sexual function, and mood.8
Family history of breast cancer. Observational evidence suggests that use of HT does not further alter the risk for breast cancer in women with a family history of breast cancer. Family history is one risk, among others, that should be assessed when counseling women regarding HT.
Women who are BRCA-positive without breast cancer. For women who are BRCA-positive (higher genetic risk of breast cancer, primarily estrogen-receptor-negative), and have undergone surgical menopause (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), the benefits of estrogen to decrease health risks caused by premature loss of estrogen need to be considered on an individual basis.9 On the basis of limited observational studies, consider offering systemic HT until the median age of menopause (52 years) with longer use individualized.3
Related Article:
Is menopausal hormone therapy safe when your patient carries a BRCA mutation?
Survivors of endometrial and breast cancer with bothersome VMS. For women with prior estrogen-sensitive cancers, non-HTs should be considered first, particularly those agents studied through randomized controlled trials in this population and found to be effective. If systemic estrogen is considered for persistent symptoms after non-HT or complementary options have been unsuccessful, decisions should be made for compelling reasons and after detailed counseling, with shared decision making and in conjunction with their oncologist.3
Bothersome GSM. On the basis of limited observational data, there appears to be minimal to no demonstrated elevation in risk for recurrence of endometrial or breast cancer using low-dose vaginal estrogen,3,10 but decisions should be made in conjunction with an oncologist.
Related Article:
Focus on treating genital atrophy symptoms
The importance of relaying the new guidelines to patients
It is important for clinicians to talk to women about their menopausal symptoms and their options for relief of symptoms or prevention of bone loss. Discussion should take into account age and time from menopause, include evidence-based information11-13 about benefits and risks of different types of therapy, and employ shared decision making to choose the most appropriate therapy to maximize benefits and minimize risks for the individual woman.
Following the WHI initial release in 2002, both women and providers became fearful of HT and believed media hype and celebrities that compounded bioidentical HT was safer than FDA-approved HTs. However, compounded products lack safety and efficacy data, are not monitored or regulated by the FDA, and have unique risks associated with compounding, including concerns about sterility, impurities, and overdosing or underdosing, which could increase cancer risk.3
- Hormone therapy for symptomatic menopausal women is safe and effective for those under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Identify the most appropriate type, dose, formulation, and duration of hormone therapy for an individual woman based on evidence.
- We want to remove the fear of using hormone therapy for healthy symptomatic women who are under age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
- Age at initiation of hormone therapy matters.
- NAMS endorses use of FDA-approved hormone therapy over compounded therapies.
Read about modifying low-dose vaginal estrogen’s black box warning
Physicians continue to underwhelmingly prescribe low-dose vaginal estrogen for GSM
Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, Bernick B, Mirkin S. The Women's EMPOWER survey: identifying women's perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14(3):413-424.
GSM is seriously underrecognized and undertreated.2,8,14 It has a major impact on women's lives--a silent epidemic affecting women's quality of life, sexual health, interpersonal relationships, and even physical health in terms of increased risk of urinary tract infections and urinary symptoms. Unfortunately, patients are reluctant to mention the problem to their clinicians, and they do not clearly recognize it as a medical condition that has available treatment options. Clinicians also rarely receive adequate training in the management of this condition and how to discuss it with their patients. Given busy schedules and time constraints, addressing this topic often falls through the cracks, representing a missed opportunity for helping our patients with safe and effective treatments. In a recent study by Kingsberg and colleagues, an astoundingly low percentageof women with GSM symptoms received treatment.
Details of the study
The study authors evaluated women's perceptions of GSM and available treatment options. US women aged 45 and older who reported GSM symptoms were surveyed. Of 1,858 women with a median age of 58 (range, 45-90), the study authors found that 50% had never used any treatment; 25% used over-the-counter medications; 18% were former users of GSM treatments; and 7% currently used prescribed GSM therapies.
When GSM was discussed, women were more likely than their clinicians to initiate the conversation. The main reason for women not mentioning their symptoms was the perception that GSM symptoms were a natural and inevitable part of aging. Hormonal products were perceived by women as having several downsides, including risk of systemic absorption, messiness of local creams, and the need to reuse an applicator. Overall, clinicians recommended vaginal estrogen therapy to only 23% and oral HTs to 18% of women.
The results of the study are consistent with results of earlier surveys of menopausal women. Although the survey included nearly 2,000 women, it has the potential for selection biases inherent to most Internet-based surveys. In addition, the respondents tended to be white and have higher socieconomic status, with limited representation from other groups.
Calls for the current boxed warning to be revised
GSM is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women; the condition has adverse effects on quality of life and sexual health.2,8,14 Safe and effective treatments are available but are underutilized.1,8,15,16 A current boxed warning appears on low-dose vaginal estrogen--class labeling that appears on all medications in the class of estrogen or HT, regardless of dose or route of administration. These warnings are based on findings from the WHI and other studies of systemic estrogen or estrogen plus progestin, which demonstrated a complex pattern of risks and benefits of HT (including increased risk of venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, stroke, and breast cancer [with estrogen plus progestin]).
These findings, however, do not appear to be relevant to low-dose vaginal estrogen, given minimal if any systemic absorption and much lower blood levels of hormones than found with systemic HT. Blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen remain in the normal postmenopausal range, compared to several-fold elevations in hormone levels with systemic HT.8,15,16 Additionally, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen, as well as short-term randomized clinical trials, show no evidence of an increased risk of venous thromboembolic events, heart disease, stroke, breast cancer, or dementia--the listed possible adverse effects in the boxed warning. The current warning is based on extrapolating findings from systemic HT, which is inappropriate and not evidence-based for low-dose vaginal estrogen.15
The inappropriate boxed warning contributes to the problem of undertreatment of GSM in women by discouraging clinicians from prescribing the medication and dissuading patients from taking it even after purchase. Testimonials from many clinicians caring for these women have underscored that women will fill their prescription, but after seeing the boxed warning will often become alarmed and decide not to take the medication. Clinicians reported that patients often say at their next appointment: "No, I never took it. I got very scared when I saw the boxed warning." As a result, clinicians often have to spend a great deal of time explaining the limitations of, and lack of evidence for, the boxed warning on low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Related Article:
2016 Update on menopause
Recommended label revisions
A modified label, without a boxed warning, would be safer for women because the key messages would not be obscured by the large amount of irrelevant information. Our Working Group recommended that the label explain that the listed risks were found in studies of systemic HT and their relevance to low-dose vaginal estrogen is unknown. The Group also recommended that warning text should be added in bold font to advise patients to seek medical attention if they have vaginal bleeding or spotting while taking the medication. In addition, patients who have a history of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer should discuss the use of the medication with their oncologist.
Status update on efforts to revise label. A citizen's petition was filed in the Spring of 2016, with signatures from more than 600 clinicians and patients and representatives of medical and professional organizations endorsing a more appropriate evidence-based label for low-dose vaginal estrogen. The FDA is continuing to review and deliberate on these issues but has not yet made a final decision.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Manson JM, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—Getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(9):803–806.
- Parish SJ, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society [published online ahead of print June 2017]. Menopause.
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy: 2016 NAMS position statement [abstract]. Menopause. 2016;23:1365.
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310(13):1353–1368.
- Lethaby A, Ayeleke RO, Roberts H. Local oestrogen for vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2016;8:CD001500.
- Management of symptomatic vulvovaginal atrophy: 2013 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2013;20(9):888–902.
- Faubion SS, Kuhle CL, Shuster LT, Rocca WA. Long-term health consequences of premature or early menopause and considerations for management. Climacteric. 2015;18(4):483–491.
- Chai X, Domchek S, Kauff N, Rebbeck T, Chen J. RE: Breast cancer risk after salpingo-oophorectomy in healthy BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: revisiting the evidence for risk reduction. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(9).
- Farrell R; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659 summary: The use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(3):618–619.
- Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(13):1221–1231.
- Marjoribanks J, Farquhar C, Roberts H, Lethaby A, Lee J. Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1:CD004143.
- Boardman HM, Hartley L, Eisinga A, et al. Hormone therapy for preventing cardiovascular disease in post-menopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD002229.
- Parish S, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- Manson JE, Goldstein SR, Kagan R, et al; Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause. Why the product labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen should be changed. Menopause. 2014;21(9):911–916.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(4):859-876.
- Manson JM, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—Getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(9):803–806.
- Parish SJ, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society [published online ahead of print June 2017]. Menopause.
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy: 2016 NAMS position statement [abstract]. Menopause. 2016;23:1365.
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310(13):1353–1368.
- Lethaby A, Ayeleke RO, Roberts H. Local oestrogen for vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2016;8:CD001500.
- Management of symptomatic vulvovaginal atrophy: 2013 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2013;20(9):888–902.
- Faubion SS, Kuhle CL, Shuster LT, Rocca WA. Long-term health consequences of premature or early menopause and considerations for management. Climacteric. 2015;18(4):483–491.
- Chai X, Domchek S, Kauff N, Rebbeck T, Chen J. RE: Breast cancer risk after salpingo-oophorectomy in healthy BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: revisiting the evidence for risk reduction. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(9).
- Farrell R; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659 summary: The use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(3):618–619.
- Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(13):1221–1231.
- Marjoribanks J, Farquhar C, Roberts H, Lethaby A, Lee J. Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1:CD004143.
- Boardman HM, Hartley L, Eisinga A, et al. Hormone therapy for preventing cardiovascular disease in post-menopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD002229.
- Parish S, Nappi RE, Krychman ML, et al. Impact of vulvovaginal health on postmenopausal women: a review of surveys on symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy. Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:437–447.
- Manson JE, Goldstein SR, Kagan R, et al; Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause. Why the product labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen should be changed. Menopause. 2014;21(9):911–916.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(4):859-876.
Should risk-reducing gynecologic surgery for BRCA mutation carriers include hysterectomy?
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Although RRSO is routinely recommended to decrease the risk of ovarian as well as breast cancer in women who harbor BRCA mutations, whether or not surgery should include hysterectomy has not been clear. Shu and colleagues prospectively evaluated the risk of uterine cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers who underwent RRSO without hysterectomy at 1 of 9 centers in the United States or the United Kingdom, comparing it with rates expected from national surveillance data.
Details of the study
Among 1,083 women (median age, 45.6 years at the time of RRSO; median follow-up, 5.1 years), 8 incident uterine cancers were observed (4.3 were expected; observed to expected [O:E] ratio, 1.9; P = .09). In an analysis stratified by tumor subtype, no elevated risk for endometrioid endometrial cancer or sarcoma was noted. Five serous and/or serous-like endometrial cancers were observed after RRSO. Four were found in BRCA1 carriers and 1 in a BRCA2 carrier, with the O:E ratio of 22.2 (P<.001) for BRCA1 and 6.4 (P = .15) for BRCA2 carriers.
Details of the accompanying editorial
Commenting on the study, Leath and colleagues noted that while the number of cases was small, the study demonstrated a link between the presence of BRCA mutations (particularly BRCA1 mutations) and a "small but not null risk of endometrial cancer." Many of these uterine cancers have a serous histology, a concern due to the likelihood of worse outcomes compared with the more common endometrioid variant.
The authors suggest that clinicians make patients with BRCA mutations undergoing RRSO aware of the potential risks and benefits of concomitant hysterectomy and work to make an individualized decision based on the limitations of available data. They state, "Perhaps it is time to consider that the line for risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in patients with BRCA mutations not stop at the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Thus, concomitant hysterectomy with RRSO, when performed with a minimally invasive surgical approach, particularly for women with a BRCA1 mutation, should be able to be performed with minimum morbidity and allow for use of estrogen-only hormone therapy after surgery, if needed."
Although adding hysterectomy to RRSO increases the perioperative risks, these risks should be attenuated by the use of minimally invasive surgical approaches. Women diagnosed with serous endometrial cancer have worse outcomes than those with the more common endometrioid endometrial tumors, even when they are diagnosed with early stage disease. Future risk of any uterine malignancy is essentially eliminated when hysterectomy is performed.
Risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in BRCA carriers is optimally performed prior to age 40, meaning that unless hormone therapy is used, severe menopausal symptoms likely will occur, and women are at elevated risk for osteoporosis and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Given that hysterectomy allows estrogen (little or no impact on breast cancer risk) to be prescribed without progestin (small elevation in breast cancer risk), hysterectomy has particular advantages for younger mutation carriers undergoing risk-reducing gynecologic surgery.
I agree with the editorialists who provided an accompanying comment on the study that—provided a minimally invasive approach is used—we should encourage hysterectomy as part of risk-reducing surgery for women with BRCA mutations.
—ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Although RRSO is routinely recommended to decrease the risk of ovarian as well as breast cancer in women who harbor BRCA mutations, whether or not surgery should include hysterectomy has not been clear. Shu and colleagues prospectively evaluated the risk of uterine cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers who underwent RRSO without hysterectomy at 1 of 9 centers in the United States or the United Kingdom, comparing it with rates expected from national surveillance data.
Details of the study
Among 1,083 women (median age, 45.6 years at the time of RRSO; median follow-up, 5.1 years), 8 incident uterine cancers were observed (4.3 were expected; observed to expected [O:E] ratio, 1.9; P = .09). In an analysis stratified by tumor subtype, no elevated risk for endometrioid endometrial cancer or sarcoma was noted. Five serous and/or serous-like endometrial cancers were observed after RRSO. Four were found in BRCA1 carriers and 1 in a BRCA2 carrier, with the O:E ratio of 22.2 (P<.001) for BRCA1 and 6.4 (P = .15) for BRCA2 carriers.
Details of the accompanying editorial
Commenting on the study, Leath and colleagues noted that while the number of cases was small, the study demonstrated a link between the presence of BRCA mutations (particularly BRCA1 mutations) and a "small but not null risk of endometrial cancer." Many of these uterine cancers have a serous histology, a concern due to the likelihood of worse outcomes compared with the more common endometrioid variant.
The authors suggest that clinicians make patients with BRCA mutations undergoing RRSO aware of the potential risks and benefits of concomitant hysterectomy and work to make an individualized decision based on the limitations of available data. They state, "Perhaps it is time to consider that the line for risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in patients with BRCA mutations not stop at the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Thus, concomitant hysterectomy with RRSO, when performed with a minimally invasive surgical approach, particularly for women with a BRCA1 mutation, should be able to be performed with minimum morbidity and allow for use of estrogen-only hormone therapy after surgery, if needed."
Although adding hysterectomy to RRSO increases the perioperative risks, these risks should be attenuated by the use of minimally invasive surgical approaches. Women diagnosed with serous endometrial cancer have worse outcomes than those with the more common endometrioid endometrial tumors, even when they are diagnosed with early stage disease. Future risk of any uterine malignancy is essentially eliminated when hysterectomy is performed.
Risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in BRCA carriers is optimally performed prior to age 40, meaning that unless hormone therapy is used, severe menopausal symptoms likely will occur, and women are at elevated risk for osteoporosis and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Given that hysterectomy allows estrogen (little or no impact on breast cancer risk) to be prescribed without progestin (small elevation in breast cancer risk), hysterectomy has particular advantages for younger mutation carriers undergoing risk-reducing gynecologic surgery.
I agree with the editorialists who provided an accompanying comment on the study that—provided a minimally invasive approach is used—we should encourage hysterectomy as part of risk-reducing surgery for women with BRCA mutations.
—ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Although RRSO is routinely recommended to decrease the risk of ovarian as well as breast cancer in women who harbor BRCA mutations, whether or not surgery should include hysterectomy has not been clear. Shu and colleagues prospectively evaluated the risk of uterine cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers who underwent RRSO without hysterectomy at 1 of 9 centers in the United States or the United Kingdom, comparing it with rates expected from national surveillance data.
Details of the study
Among 1,083 women (median age, 45.6 years at the time of RRSO; median follow-up, 5.1 years), 8 incident uterine cancers were observed (4.3 were expected; observed to expected [O:E] ratio, 1.9; P = .09). In an analysis stratified by tumor subtype, no elevated risk for endometrioid endometrial cancer or sarcoma was noted. Five serous and/or serous-like endometrial cancers were observed after RRSO. Four were found in BRCA1 carriers and 1 in a BRCA2 carrier, with the O:E ratio of 22.2 (P<.001) for BRCA1 and 6.4 (P = .15) for BRCA2 carriers.
Details of the accompanying editorial
Commenting on the study, Leath and colleagues noted that while the number of cases was small, the study demonstrated a link between the presence of BRCA mutations (particularly BRCA1 mutations) and a "small but not null risk of endometrial cancer." Many of these uterine cancers have a serous histology, a concern due to the likelihood of worse outcomes compared with the more common endometrioid variant.
The authors suggest that clinicians make patients with BRCA mutations undergoing RRSO aware of the potential risks and benefits of concomitant hysterectomy and work to make an individualized decision based on the limitations of available data. They state, "Perhaps it is time to consider that the line for risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in patients with BRCA mutations not stop at the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Thus, concomitant hysterectomy with RRSO, when performed with a minimally invasive surgical approach, particularly for women with a BRCA1 mutation, should be able to be performed with minimum morbidity and allow for use of estrogen-only hormone therapy after surgery, if needed."
Although adding hysterectomy to RRSO increases the perioperative risks, these risks should be attenuated by the use of minimally invasive surgical approaches. Women diagnosed with serous endometrial cancer have worse outcomes than those with the more common endometrioid endometrial tumors, even when they are diagnosed with early stage disease. Future risk of any uterine malignancy is essentially eliminated when hysterectomy is performed.
Risk-reducing gynecologic surgery in BRCA carriers is optimally performed prior to age 40, meaning that unless hormone therapy is used, severe menopausal symptoms likely will occur, and women are at elevated risk for osteoporosis and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Given that hysterectomy allows estrogen (little or no impact on breast cancer risk) to be prescribed without progestin (small elevation in breast cancer risk), hysterectomy has particular advantages for younger mutation carriers undergoing risk-reducing gynecologic surgery.
I agree with the editorialists who provided an accompanying comment on the study that—provided a minimally invasive approach is used—we should encourage hysterectomy as part of risk-reducing surgery for women with BRCA mutations.
—ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.