User login
Iododerma Simulating Cryptococcal Infection
To the Editor:
A woman in her 40s presented with acute onset of rapidly spreading lesions on the face, trunk, and extremities. She reported high fever and endorsed malaise. She had a history of end-stage renal disease and was on renal dialysis. She recently underwent revision of an arteriovenous fistula.
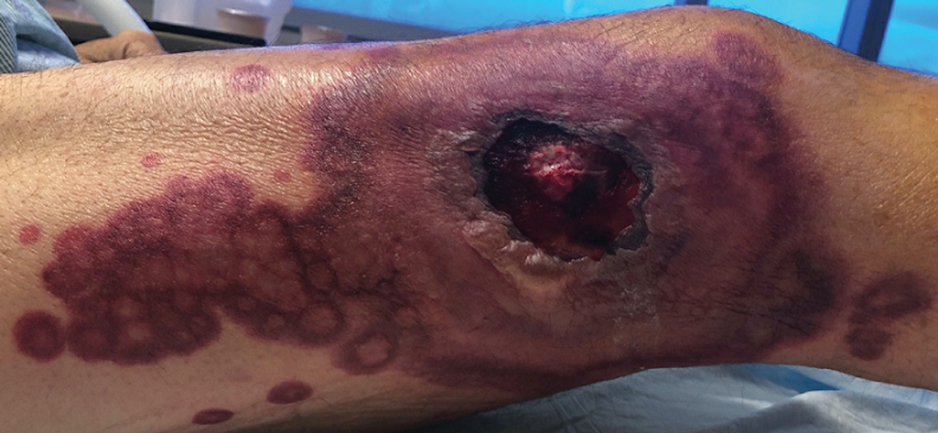
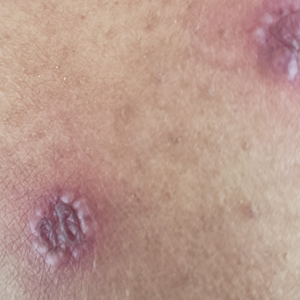
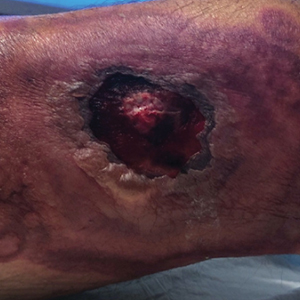
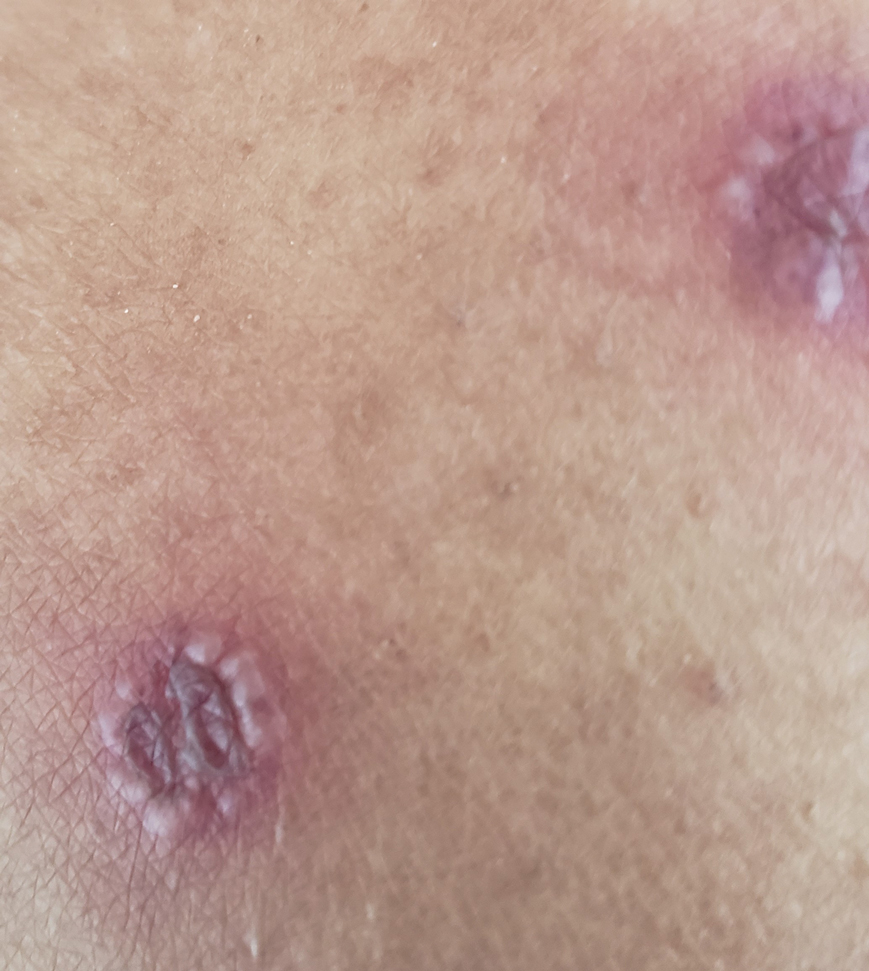
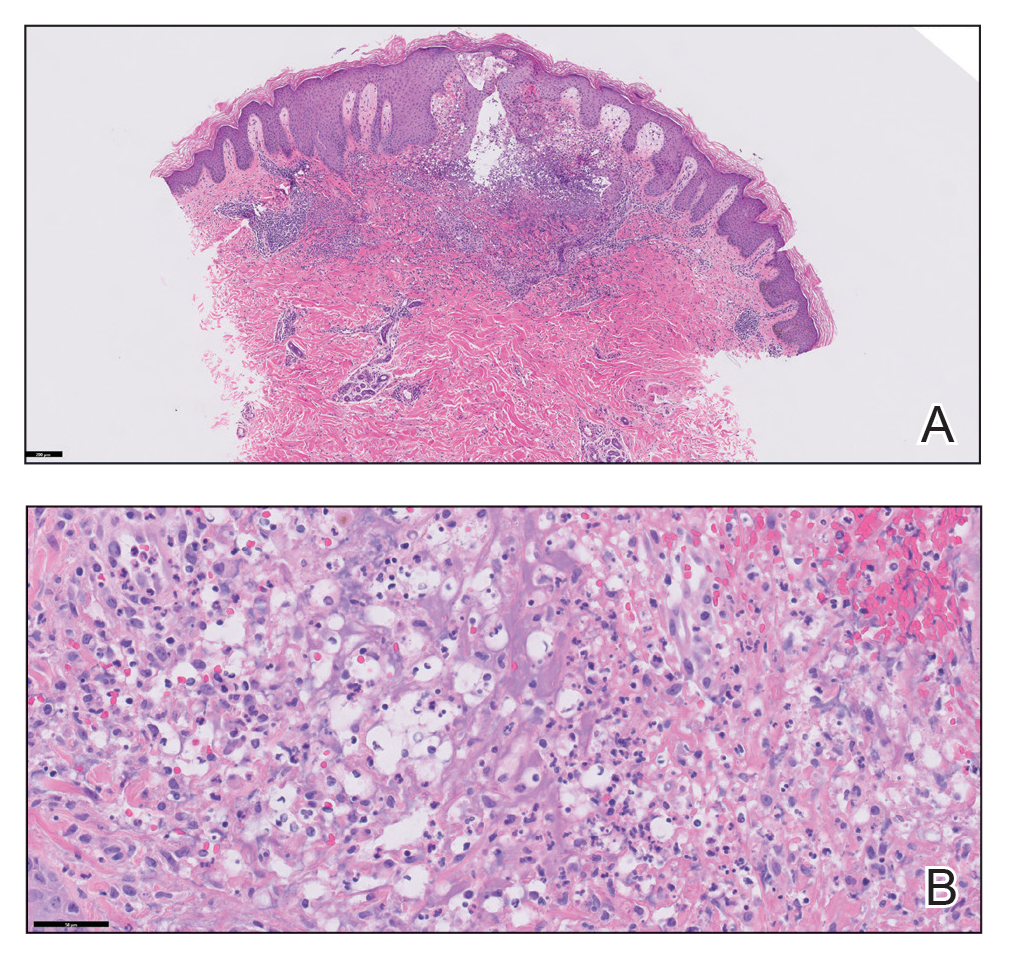
Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, firm papules and plaques with central hemorrhage and umbilication on the dorsal aspect of the nose, forehead, temples, and cheeks. There also were purpuric papules and plaques with a peripheral rim of vesiculation (Figure 1) on the medial and posterior thighs and buttocks. Histopathology of a biopsy specimen revealed an interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate in the superficial dermis and mid dermis with scattered, haloed, acellular structures simulating cryptococcal organisms (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), Grocott methenamine-silver, and mucicarmine staining was negative. Repeat biopsy showed similar findings. A (1-3)-β-
The findings compatible with a diagnosis of iododerma included umbilicated hemorrhagic papules and plaques, cryptococcal-like structures with negative staining on histopathology, and elevated iodine levels with a negative infectious workup. The patient was treated with topical corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up, the lesions had resolved.
Iododerma is a halogenoderma, a skin eruption that occurs after ingestion of or exposure to a halogen-containing substance (eg, iodine, bromine, fluorine) or medication (eg, lithium).1 Common sources of iodine include iodinated contrast media, potassium iodide ingestion, topical application of povidone–iodine, radioactive iodine administration, and the antiarrhythmic amiodarone. Excess exposure to iodine-containing compounds typically occurs in the setting of kidney disease or failure as well as due to reduced iodine clearance.1 Although the pathogenesis of iododerma is unknown, the most common hypothesis is that lesions are delayed hypersensitivity reactions secondary to formation of a protein-halogen complex.2
The presentation of iododerma is polymorphous and includes acneform, vegetative, or pustular eruptions; umbilicated papules and plaques can be present.2,3 Lesions can be either asymptomatic or painful and pruritic. Timing between iodine exposure and onset of lesions varies from hours to days to years.2,4
Systemic symptoms of iododerma can occur, including salivary gland swelling, hypotension and bradycardia, kidney injury, or thyroid and liver abnormalities. Histopathologic analysis demonstrates a dense neutrophilic dermatitis with negative staining for infectious causes.4,5 Cryptococcal-like structures have been described in iododerma3; neutrophilic dermatoses of various causes that mimic cryptococcal infection have been reported.6 Ultimately, iododerma remains a diagnosis of exclusion.
Withdrawal of an offending compound is remedial. Dialysis is beneficial in end-stage renal disease. Topical, intralesional, and systemic corticosteroids, as well as antibiotics, provide variable benefit.4,7 Lesions can take 4 to 6 weeks to clear after withdrawal of the offending agent. It is unclear whether recurrences happen; iodine-containing compounds need to be avoided after a patient has been affected.
Iododerma has a broad differential diagnosis due to the polymorphous presentation of the disorder, including acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (also known as Sweet syndrome), cutaneous cryptococcosis, and cutaneous histoplasmosis. Sweet syndrome presents as abrupt onset of edematous erythematous plaques with fever and leukocytosis. It is associated with infection, inflammatory disorders, medication, and malignancy.8 Histopathologic analysis reveals papillary dermal edema and a neutrophilic dermatosis. Cytoplasmic vacuolization resembling C neoformans has been reported.9 The diagnosis is less favored in the presence of renal disease, temporal association of the eruption with iodine exposure, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels, as in our patient.
Cutaneous cryptococcosis, an infection caused by C neoformans, typically occurs secondary to dissemination from the lungs; rarely, the disease is primary. Acneform plaques, vegetative plaques, and umbilicated lesions are seen.10 Histopathologic analysis shows characteristic yeast forms of cryptococcosis surrounded by gelatinous edema, which create a haloed effect, typically throughout the dermis. Capsules are positive for PAS or mucicarmine staining. Although C neoformans can closely mimic iododerma both clinically and histopathologically, negative infectious staining, localization of haloed structures to the upper dermis, a negative test for cryptococcal antigen, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels in this case all favored iododerma.
Cutaneous histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, most commonly as secondary dissemination from pulmonary infection but rarely from direct inoculation of the skin.11 Presentation includes erythematous to hemorrhagic, umbilicated papules and plaques. Histopathologic findings are round to oval, narrow-based, budding yeasts that stain positive for PAS or mucicarmine. Although histoplasmosis can clinically mimic iododerma, the disease is distinguished histologically by the presence of fungal microorganisms that lack the gelatinous edema and haloed effect of iododerma.
We presented a unique case of iododerma simulating cryptococcal infection both clinically and histopathologically. Prompt recognition of histologic mimickers of true infectious microorganisms is essential to prevent unnecessary delay of withdrawal of the offending substance and to initiate appropriate therapy.
- Alagheband M, Engineer L. Lithium and halogenoderma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:126-127. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.1.126
- Young AL, Grossman ME. Acute iododerma secondary to iodinated contrast media. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1377-1379. doi:10.1111/bjd.12852
- Runge M, Williams K, Scharnitz T, et al. Iodine toxicity after iodinated contrast: new observations in iododerma. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.006
- Chalela JG, Aguilar L. Iododerma from contrast material. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2477. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1512512
- Chang MW, Miner JE, Moiin A, et al. Iododerma after computed tomographic scan with intravenous radiopaque contrast media. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:1014-1016. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80291-5
- Ko JS, Fernandez AP, Anderson KA, et al. Morphologic mimickers of Cryptococcus occurring within inflammatory infiltrates in the setting of neutrophilic dermatitis: a series of three cases highlighting clinical dilemmas associated with a novel histopathologic pitfall. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:38-45. doi:10.1111/cup.12019
- Pranteda G, Grimaldi M, Salzetta M, et al. Vegetating iododerma and pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration. a simple co-occurrence? Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:480-481.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. M. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.064
- Wilson J, Gleghorn K, Kelly B. Cryptococcoid Sweet’s syndrome: two reports of Sweet’s syndrome mimicking cutaneous cryptococcosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:413-419. doi:10.1111/cup.12921
- Beatson M, Harwood M, Reese V, et al. Primary cutaneous cryptococcosis in an elderly pigeon breeder. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:433-435. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.03.006
- Raggio B. Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97:346-348. doi:10.1177/0145561318097010-1108
To the Editor:
A woman in her 40s presented with acute onset of rapidly spreading lesions on the face, trunk, and extremities. She reported high fever and endorsed malaise. She had a history of end-stage renal disease and was on renal dialysis. She recently underwent revision of an arteriovenous fistula.
Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, firm papules and plaques with central hemorrhage and umbilication on the dorsal aspect of the nose, forehead, temples, and cheeks. There also were purpuric papules and plaques with a peripheral rim of vesiculation (Figure 1) on the medial and posterior thighs and buttocks. Histopathology of a biopsy specimen revealed an interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate in the superficial dermis and mid dermis with scattered, haloed, acellular structures simulating cryptococcal organisms (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), Grocott methenamine-silver, and mucicarmine staining was negative. Repeat biopsy showed similar findings. A (1-3)-β-

The findings compatible with a diagnosis of iododerma included umbilicated hemorrhagic papules and plaques, cryptococcal-like structures with negative staining on histopathology, and elevated iodine levels with a negative infectious workup. The patient was treated with topical corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up, the lesions had resolved.

Iododerma is a halogenoderma, a skin eruption that occurs after ingestion of or exposure to a halogen-containing substance (eg, iodine, bromine, fluorine) or medication (eg, lithium).1 Common sources of iodine include iodinated contrast media, potassium iodide ingestion, topical application of povidone–iodine, radioactive iodine administration, and the antiarrhythmic amiodarone. Excess exposure to iodine-containing compounds typically occurs in the setting of kidney disease or failure as well as due to reduced iodine clearance.1 Although the pathogenesis of iododerma is unknown, the most common hypothesis is that lesions are delayed hypersensitivity reactions secondary to formation of a protein-halogen complex.2
The presentation of iododerma is polymorphous and includes acneform, vegetative, or pustular eruptions; umbilicated papules and plaques can be present.2,3 Lesions can be either asymptomatic or painful and pruritic. Timing between iodine exposure and onset of lesions varies from hours to days to years.2,4
Systemic symptoms of iododerma can occur, including salivary gland swelling, hypotension and bradycardia, kidney injury, or thyroid and liver abnormalities. Histopathologic analysis demonstrates a dense neutrophilic dermatitis with negative staining for infectious causes.4,5 Cryptococcal-like structures have been described in iododerma3; neutrophilic dermatoses of various causes that mimic cryptococcal infection have been reported.6 Ultimately, iododerma remains a diagnosis of exclusion.
Withdrawal of an offending compound is remedial. Dialysis is beneficial in end-stage renal disease. Topical, intralesional, and systemic corticosteroids, as well as antibiotics, provide variable benefit.4,7 Lesions can take 4 to 6 weeks to clear after withdrawal of the offending agent. It is unclear whether recurrences happen; iodine-containing compounds need to be avoided after a patient has been affected.
Iododerma has a broad differential diagnosis due to the polymorphous presentation of the disorder, including acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (also known as Sweet syndrome), cutaneous cryptococcosis, and cutaneous histoplasmosis. Sweet syndrome presents as abrupt onset of edematous erythematous plaques with fever and leukocytosis. It is associated with infection, inflammatory disorders, medication, and malignancy.8 Histopathologic analysis reveals papillary dermal edema and a neutrophilic dermatosis. Cytoplasmic vacuolization resembling C neoformans has been reported.9 The diagnosis is less favored in the presence of renal disease, temporal association of the eruption with iodine exposure, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels, as in our patient.
Cutaneous cryptococcosis, an infection caused by C neoformans, typically occurs secondary to dissemination from the lungs; rarely, the disease is primary. Acneform plaques, vegetative plaques, and umbilicated lesions are seen.10 Histopathologic analysis shows characteristic yeast forms of cryptococcosis surrounded by gelatinous edema, which create a haloed effect, typically throughout the dermis. Capsules are positive for PAS or mucicarmine staining. Although C neoformans can closely mimic iododerma both clinically and histopathologically, negative infectious staining, localization of haloed structures to the upper dermis, a negative test for cryptococcal antigen, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels in this case all favored iododerma.
Cutaneous histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, most commonly as secondary dissemination from pulmonary infection but rarely from direct inoculation of the skin.11 Presentation includes erythematous to hemorrhagic, umbilicated papules and plaques. Histopathologic findings are round to oval, narrow-based, budding yeasts that stain positive for PAS or mucicarmine. Although histoplasmosis can clinically mimic iododerma, the disease is distinguished histologically by the presence of fungal microorganisms that lack the gelatinous edema and haloed effect of iododerma.
We presented a unique case of iododerma simulating cryptococcal infection both clinically and histopathologically. Prompt recognition of histologic mimickers of true infectious microorganisms is essential to prevent unnecessary delay of withdrawal of the offending substance and to initiate appropriate therapy.
To the Editor:
A woman in her 40s presented with acute onset of rapidly spreading lesions on the face, trunk, and extremities. She reported high fever and endorsed malaise. She had a history of end-stage renal disease and was on renal dialysis. She recently underwent revision of an arteriovenous fistula.
Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, firm papules and plaques with central hemorrhage and umbilication on the dorsal aspect of the nose, forehead, temples, and cheeks. There also were purpuric papules and plaques with a peripheral rim of vesiculation (Figure 1) on the medial and posterior thighs and buttocks. Histopathology of a biopsy specimen revealed an interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate in the superficial dermis and mid dermis with scattered, haloed, acellular structures simulating cryptococcal organisms (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), Grocott methenamine-silver, and mucicarmine staining was negative. Repeat biopsy showed similar findings. A (1-3)-β-

The findings compatible with a diagnosis of iododerma included umbilicated hemorrhagic papules and plaques, cryptococcal-like structures with negative staining on histopathology, and elevated iodine levels with a negative infectious workup. The patient was treated with topical corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up, the lesions had resolved.

Iododerma is a halogenoderma, a skin eruption that occurs after ingestion of or exposure to a halogen-containing substance (eg, iodine, bromine, fluorine) or medication (eg, lithium).1 Common sources of iodine include iodinated contrast media, potassium iodide ingestion, topical application of povidone–iodine, radioactive iodine administration, and the antiarrhythmic amiodarone. Excess exposure to iodine-containing compounds typically occurs in the setting of kidney disease or failure as well as due to reduced iodine clearance.1 Although the pathogenesis of iododerma is unknown, the most common hypothesis is that lesions are delayed hypersensitivity reactions secondary to formation of a protein-halogen complex.2
The presentation of iododerma is polymorphous and includes acneform, vegetative, or pustular eruptions; umbilicated papules and plaques can be present.2,3 Lesions can be either asymptomatic or painful and pruritic. Timing between iodine exposure and onset of lesions varies from hours to days to years.2,4
Systemic symptoms of iododerma can occur, including salivary gland swelling, hypotension and bradycardia, kidney injury, or thyroid and liver abnormalities. Histopathologic analysis demonstrates a dense neutrophilic dermatitis with negative staining for infectious causes.4,5 Cryptococcal-like structures have been described in iododerma3; neutrophilic dermatoses of various causes that mimic cryptococcal infection have been reported.6 Ultimately, iododerma remains a diagnosis of exclusion.
Withdrawal of an offending compound is remedial. Dialysis is beneficial in end-stage renal disease. Topical, intralesional, and systemic corticosteroids, as well as antibiotics, provide variable benefit.4,7 Lesions can take 4 to 6 weeks to clear after withdrawal of the offending agent. It is unclear whether recurrences happen; iodine-containing compounds need to be avoided after a patient has been affected.
Iododerma has a broad differential diagnosis due to the polymorphous presentation of the disorder, including acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (also known as Sweet syndrome), cutaneous cryptococcosis, and cutaneous histoplasmosis. Sweet syndrome presents as abrupt onset of edematous erythematous plaques with fever and leukocytosis. It is associated with infection, inflammatory disorders, medication, and malignancy.8 Histopathologic analysis reveals papillary dermal edema and a neutrophilic dermatosis. Cytoplasmic vacuolization resembling C neoformans has been reported.9 The diagnosis is less favored in the presence of renal disease, temporal association of the eruption with iodine exposure, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels, as in our patient.
Cutaneous cryptococcosis, an infection caused by C neoformans, typically occurs secondary to dissemination from the lungs; rarely, the disease is primary. Acneform plaques, vegetative plaques, and umbilicated lesions are seen.10 Histopathologic analysis shows characteristic yeast forms of cryptococcosis surrounded by gelatinous edema, which create a haloed effect, typically throughout the dermis. Capsules are positive for PAS or mucicarmine staining. Although C neoformans can closely mimic iododerma both clinically and histopathologically, negative infectious staining, localization of haloed structures to the upper dermis, a negative test for cryptococcal antigen, and elevated blood and urine iodine levels in this case all favored iododerma.
Cutaneous histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, most commonly as secondary dissemination from pulmonary infection but rarely from direct inoculation of the skin.11 Presentation includes erythematous to hemorrhagic, umbilicated papules and plaques. Histopathologic findings are round to oval, narrow-based, budding yeasts that stain positive for PAS or mucicarmine. Although histoplasmosis can clinically mimic iododerma, the disease is distinguished histologically by the presence of fungal microorganisms that lack the gelatinous edema and haloed effect of iododerma.
We presented a unique case of iododerma simulating cryptococcal infection both clinically and histopathologically. Prompt recognition of histologic mimickers of true infectious microorganisms is essential to prevent unnecessary delay of withdrawal of the offending substance and to initiate appropriate therapy.
- Alagheband M, Engineer L. Lithium and halogenoderma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:126-127. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.1.126
- Young AL, Grossman ME. Acute iododerma secondary to iodinated contrast media. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1377-1379. doi:10.1111/bjd.12852
- Runge M, Williams K, Scharnitz T, et al. Iodine toxicity after iodinated contrast: new observations in iododerma. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.006
- Chalela JG, Aguilar L. Iododerma from contrast material. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2477. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1512512
- Chang MW, Miner JE, Moiin A, et al. Iododerma after computed tomographic scan with intravenous radiopaque contrast media. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:1014-1016. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80291-5
- Ko JS, Fernandez AP, Anderson KA, et al. Morphologic mimickers of Cryptococcus occurring within inflammatory infiltrates in the setting of neutrophilic dermatitis: a series of three cases highlighting clinical dilemmas associated with a novel histopathologic pitfall. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:38-45. doi:10.1111/cup.12019
- Pranteda G, Grimaldi M, Salzetta M, et al. Vegetating iododerma and pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration. a simple co-occurrence? Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:480-481.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. M. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.064
- Wilson J, Gleghorn K, Kelly B. Cryptococcoid Sweet’s syndrome: two reports of Sweet’s syndrome mimicking cutaneous cryptococcosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:413-419. doi:10.1111/cup.12921
- Beatson M, Harwood M, Reese V, et al. Primary cutaneous cryptococcosis in an elderly pigeon breeder. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:433-435. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.03.006
- Raggio B. Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97:346-348. doi:10.1177/0145561318097010-1108
- Alagheband M, Engineer L. Lithium and halogenoderma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:126-127. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.1.126
- Young AL, Grossman ME. Acute iododerma secondary to iodinated contrast media. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1377-1379. doi:10.1111/bjd.12852
- Runge M, Williams K, Scharnitz T, et al. Iodine toxicity after iodinated contrast: new observations in iododerma. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.006
- Chalela JG, Aguilar L. Iododerma from contrast material. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2477. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1512512
- Chang MW, Miner JE, Moiin A, et al. Iododerma after computed tomographic scan with intravenous radiopaque contrast media. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:1014-1016. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80291-5
- Ko JS, Fernandez AP, Anderson KA, et al. Morphologic mimickers of Cryptococcus occurring within inflammatory infiltrates in the setting of neutrophilic dermatitis: a series of three cases highlighting clinical dilemmas associated with a novel histopathologic pitfall. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:38-45. doi:10.1111/cup.12019
- Pranteda G, Grimaldi M, Salzetta M, et al. Vegetating iododerma and pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration. a simple co-occurrence? Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:480-481.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. M. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.064
- Wilson J, Gleghorn K, Kelly B. Cryptococcoid Sweet’s syndrome: two reports of Sweet’s syndrome mimicking cutaneous cryptococcosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:413-419. doi:10.1111/cup.12921
- Beatson M, Harwood M, Reese V, et al. Primary cutaneous cryptococcosis in an elderly pigeon breeder. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:433-435. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.03.006
- Raggio B. Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97:346-348. doi:10.1177/0145561318097010-1108
Practice Points
- Halogenodermas are rare cutaneous reactions to excess exposure to or ingestion of halogen-containing drugs or substances such as bromine, iodine (iododerma), fluorine, and rarely lithium.
- The clinical presentation of a halogenoderma varies; the most characteristic manifestation is a vegetative or exudative plaque with a peripheral rim of pustules.
- Histologically, lesions of a halogenoderma are characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia associated with numerous intraepidermal microabscesses overlying a dense mixed inflammatory infiltrate of neutrophils, plasma cells, eosinophils, histiocytes, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.
- Rarely, the dermal infiltrate of a halogenoderma contains abundant acellular bodies surrounded by capsulelike vacuolated spaces mimicking Cryptococcus neoformans.
Violaceous-Purpuric Targetoid Macules and Patches With Bullae and Ulceration
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
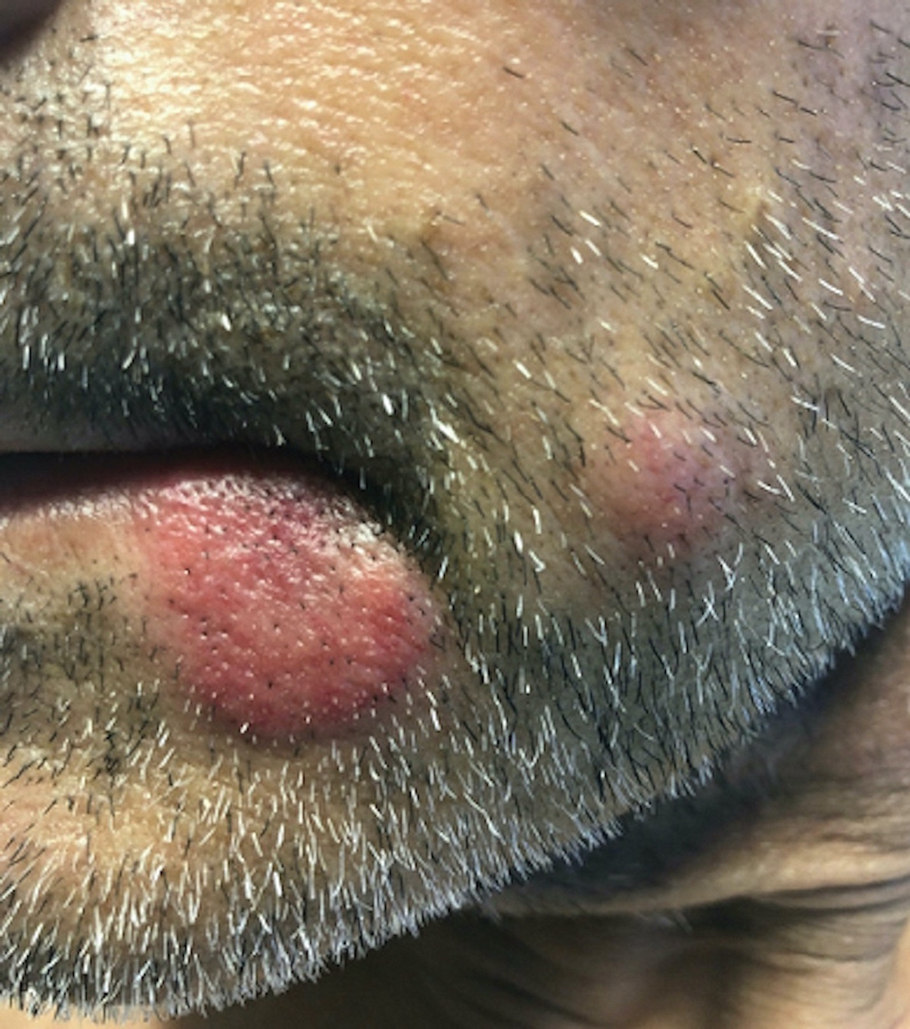
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.
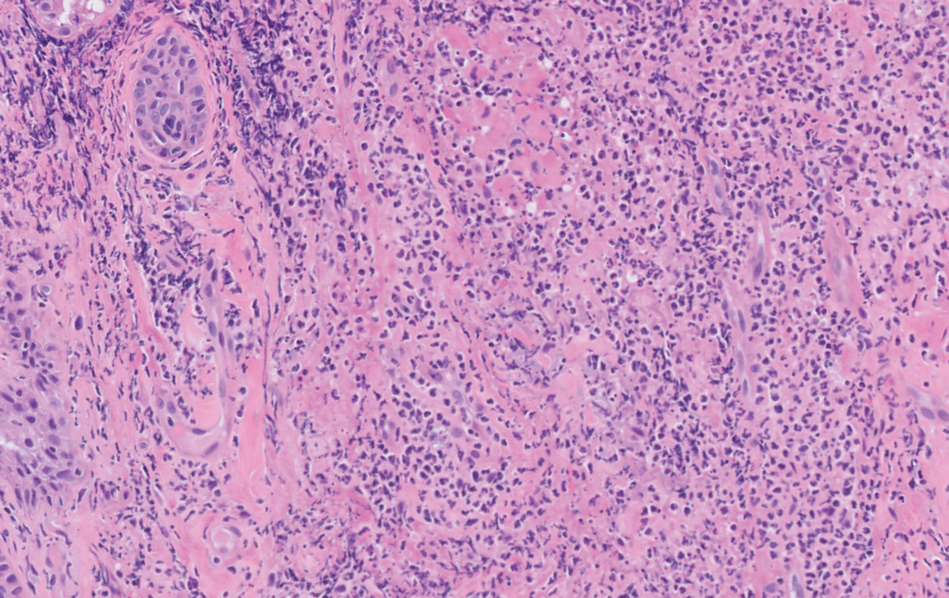
Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1
The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.

Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1

The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
The Diagnosis: Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
A skin biopsy of the right lower extremity demonstrated diffuse interstitial, perivascular, and periadnexal neutrophilic dermal infiltrate in the reticular dermis (Figure 1), consistent with a diagnosis of Sweet syndrome without evidence of leukemia cutis or infection. The firm erythematous papulonodules with follicular accentuation on the face (Figure 2) also were confirmed as Sweet syndrome on histopathology. Concern for leukemic transformation was confirmed with bone biopsy revealing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Our patient began a short course of prednisone, and the cutaneous lesions improved during hospitalization; however, he was lost to follow-up.

Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a rare inflammatory skin condition typically characterized by asymmetric, painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules involving the arms, face, and neck.1 It most commonly occurs in women and typically presents in patients aged 47 to 57 years. Although the pathogenesis of neutrophilic dermatoses is not completely understood, they are believed to be due to altered expression of inflammatory cytokines, irregular neutrophil function, and a genetic predisposition.2 There are 3 main categories of Sweet syndrome: classical (or idiopathic), drug induced, and malignancy associated.1 The lesions associated with Sweet syndrome vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters and may be annular or targetoid in the later stages. They also may form bullae and ulcerate. Fever, leukocytosis, and elevated acute-phase reactants also are common on presentation.1 Histopathologic analysis demonstrates an intense neutrophilic infiltrate within the reticular dermis with marked leukocytoclasia. Admixed within the neutrophil polymorphs are variable numbers of lymphocytes and histiocytes. Edema in the upper dermis also is characteristic.3 The exact pathogenesis of Sweet syndrome has yet to be elucidated but may involve a combination of cytokine dysregulation, hypersensitivity reactions, and genetics.4 Our case demonstrates 3 distinct morphologies of Sweet syndrome in a single patient, including classic edematous plaques, agminated targetoid plaques, and ulceration. Based on the clinical presentation, diagnostic workup for an undiagnosed malignancy was warranted, which confirmed AML. The malignancy-associated form of Sweet syndrome accounts for a substantial portion of cases, with approximately 21% of patients diagnosed with Sweet syndrome having an underlying malignancy, commonly a hematologic malignancy or myeloproliferative disorder with AML being the most common.1

The differential diagnosis for Sweet syndrome includes cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, which commonly presents with symmetric palpable purpura of the legs. Lesions may be round, port wine–colored plaques and even may form ulcers, vesicles, and targetoid lesions. However, skin biopsy shows polymorphonuclear infiltrate affecting postcapillary venules, fibrinoid deposits, and extravasation of red blood cells.5 Leukemia cutis describes any type of leukemia that manifests in the skin. It typically presents as violaceous or red-brown papules, nodules, and plaques most commonly on the legs. Histopathology varies by immunophenotype but generally demonstrates perivascular or periadnexal involvement or a diffuse, interstitial, or nodular infiltrate of the dermis or subcutis.6 Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis describes an aseptic neutrophilic infiltration around eccrine coils and glands. It may present as papules or plaques that usually are erythematous but also may be pigmented. Lesions can be asymptomatic or painful as in Sweet syndrome and are distributed proximally or on the distal extremities. Histopathologic examination demonstrates the degeneration of the eccrine gland and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates.7 Lastly, necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection of the deep soft tissue and fascia, classically caused by group A Streptococcus. The infected site may have erythema, tenderness, fluctuance, necrosis, and bullae.8 Although our patient had a fever, he did not display the tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and rapid deterioration that is common in necrotizing fasciitis.
Sweet syndrome may present with various morphologies within the same patient. Painful, erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, nodules, bullae, and ulcers may be seen. A workup for an underlying malignancy may be warranted based on clinical presentation. Most patients have a rapid and dramatic response to systemic corticosteroids.
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
- Cohen PR. Sweet’s syndrome—a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:34. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-34
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses: pathogenesis, Sweet syndrome, neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis, and Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/J .JAAD.2017.11.064
- Pulido-Pérez A, Bergon-Sendin M, Sacks CA. Images in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2020;16:382. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1911025
- Marzano AV, Hilbrands L, Le ST, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of Sweet’s syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00414
- Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6
- Hee Cho-Vega J, Jeffrey Medeiros L, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142. doi:10.1309/WYAC YWF6NGM3WBRT
- Bachmeyer C, Aractingi S. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:319-330. doi:10.1016/S0738-081X(99)00123-6
- Shimizu T, Tokuda Y. Necrotizing fasciitis. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1051-1057. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2964
A 64-year-old man with long-standing myelofibrosis presented with neutropenic fevers as well as progressive painful lesions of 3 days’ duration on the legs. A bone marrow biopsy during this hospitalization demonstrated a recent progression of the patient’s myelofibrosis to acute myeloid leukemia. Physical examination revealed round to oval, violaceous, targetoid plaques. Within a week, new erythematous and nodular lesions appeared on the right arm and left vermilion border. The lesions on the legs enlarged, formed bullae, and ulcerated.