User login
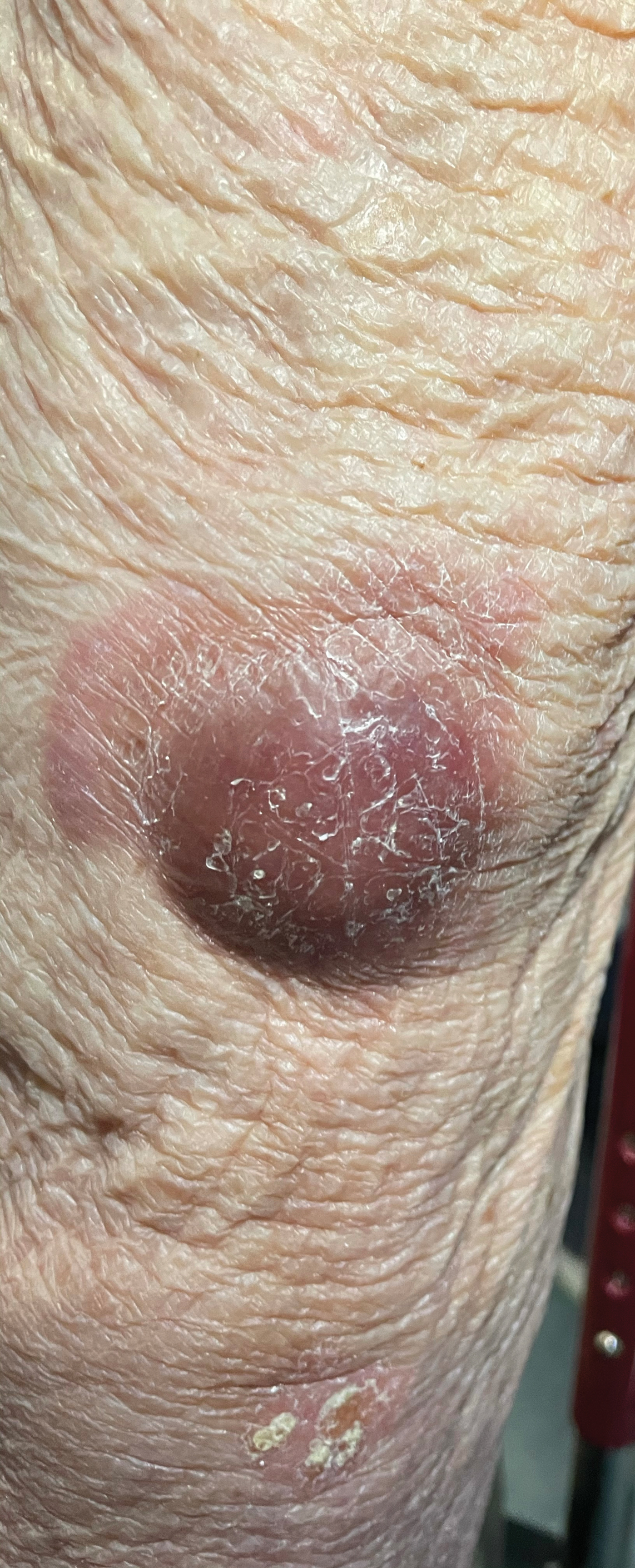
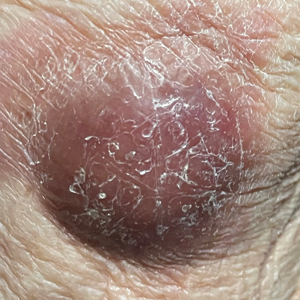
Subcutaneous Nodule on the Postauricular Neck
The Diagnosis: Pleomorphic Lipoma
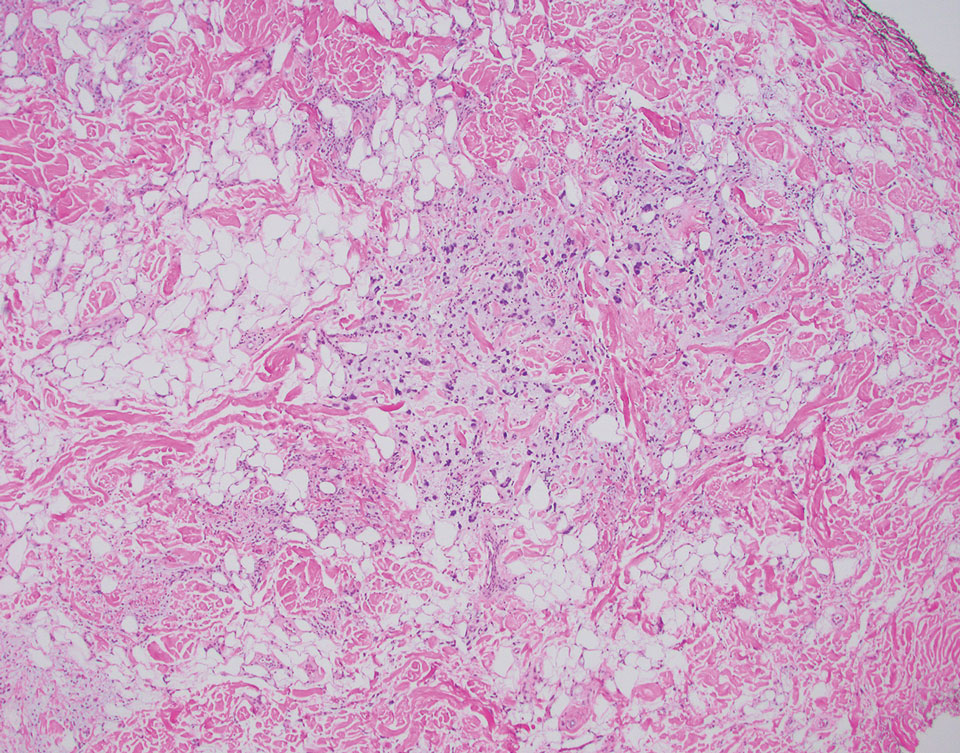
Pleomorphic lipoma is a rare, benign, adipocytic neoplasm that presents in the subcutaneous tissues of the upper shoulder, back, or neck. It predominantly affects men aged 50 to 70 years. Most lesions are situated in the subcutaneous tissues; few cases of intramuscular and retroperitoneal tumors have been reported.1 Clinically, pleomorphic lipomas present as painless, well-circumscribed lesions of the subcutaneous tissue that often resemble a lipoma or occasionally may be mistaken for liposarcoma. Histopathologic examination of ordinary lipomas reveals uniform mature adipocytes. However, pleomorphic lipomas consist of a mixture of multinucleated floretlike giant cells, variable-sized adipocytes, and fibrous tissue (ropy collagen bundles) with some myxoid and spindled areas.1,2 The most characteristic histologic feature of pleomorphic lipoma is multinucleated floretlike giant cells. The nuclei of these giant cells appear hyperchromatic, enlarged, and disposed to the periphery of the cell in a circular pattern. Additionally, tumors frequently contain excess mature dense collagen bundles that are strongly refractile in polarized light. Numerous mast cells are present. Atypical lipoblasts and capillary networks commonly are not visible in pleomorphic lipoma.3 The spindle cells express CD34 on immunohistochemistry. Loss of Rb-1 expression is typical.4
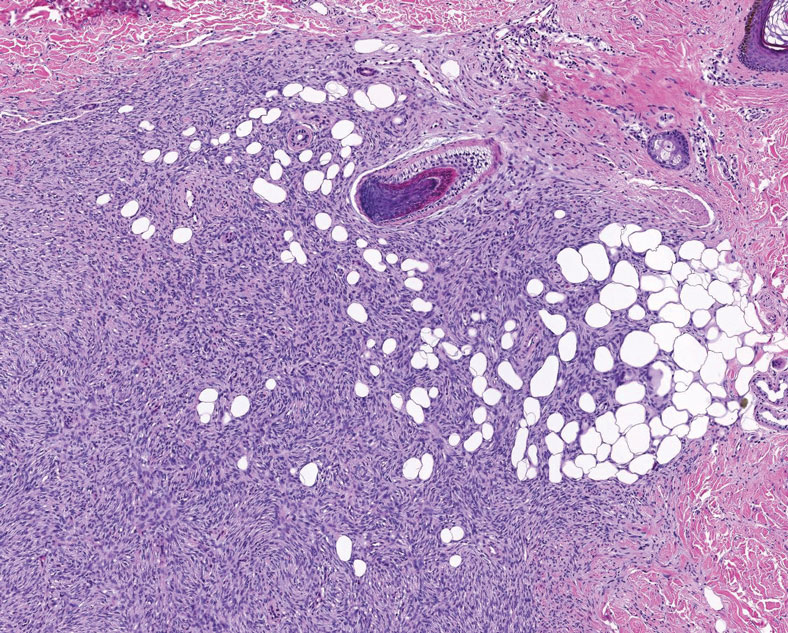
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a slow-growing soft tissue sarcoma that commonly begins as a pink or violet plaque on the trunk or upper limbs. Involvement of the head or neck accounts for only 10% to 15% of cases.5 This tumor has low metastatic potential but is highly infiltrative of surrounding tissues. It is associated with a translocation between chromosomes 22 and 17, leading to the fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor subunit β, PDGFB, and collagen type 1α1, COL1A1, genes.5 Clinically, patients often report that the lesion was present for several years prior to presentation with general stability in size and shape. Eventually, untreated lesions progress to become nodules or tumors and may even bleed or ulcerate. Histology reveals a storiform spindle cell proliferation throughout the dermis with infiltration into subcutaneous fat, commonly appearing in a honeycomblike pattern (Figure 1). Numerous histologic variants exist, including myxoid, sclerosing, pigmented (Bednar tumor), myoid, atrophic, or fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, as well as a giant cell fibroblastoma variant.6 These tumor subtypes can exist independently or in association with one another, creating hybrid lesions that can closely mimic other entities such as pleomorphic lipoma. The spindle cells stain positively for CD34. Treatment of these tumors involves complete surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery; however, recurrence is common for tumors involving the head or neck.5
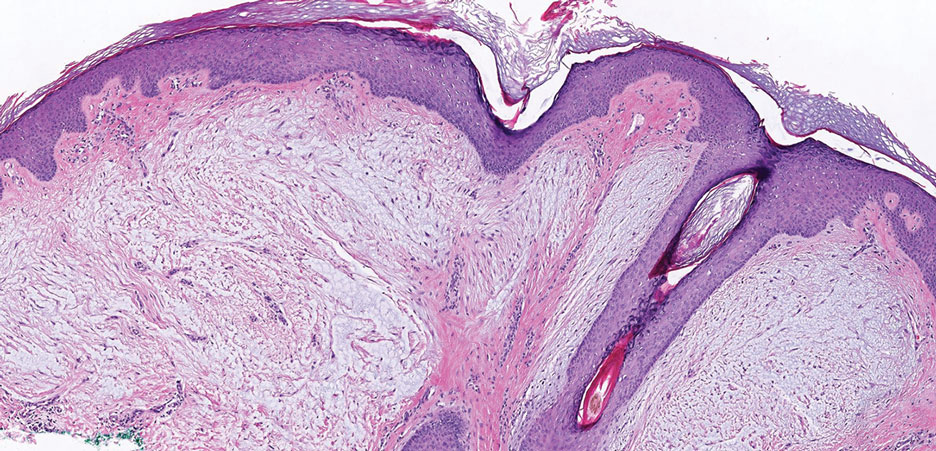
Superficial angiomyxoma is a slow-growing papule that most commonly appears on the trunk, head, or neck in middle-aged adults. Occasionally, patients with Carney complex also can develop lesions on the external ear or breast.7 Histologically, superficial angiomyxoma is a hypocellular tumor characterized by abundant myxoid stroma, thin blood vessels, and small spindled and stellate cells with minimal cytoplasm (Figure 2).8 Superficial angiomyxoma and pleomorphic lipoma present differently on histology; superficial angiomyxoma is not associated with nuclear atypia or pleomorphism, whereas pleomorphic lipoma characteristically contains multinucleated floretlike giant cells and pleomorphism. Frequently, there also is loss of normal PRKAR1A gene expression, which is responsible for protein kinase A regulatory subunit 1-alpha expression.8
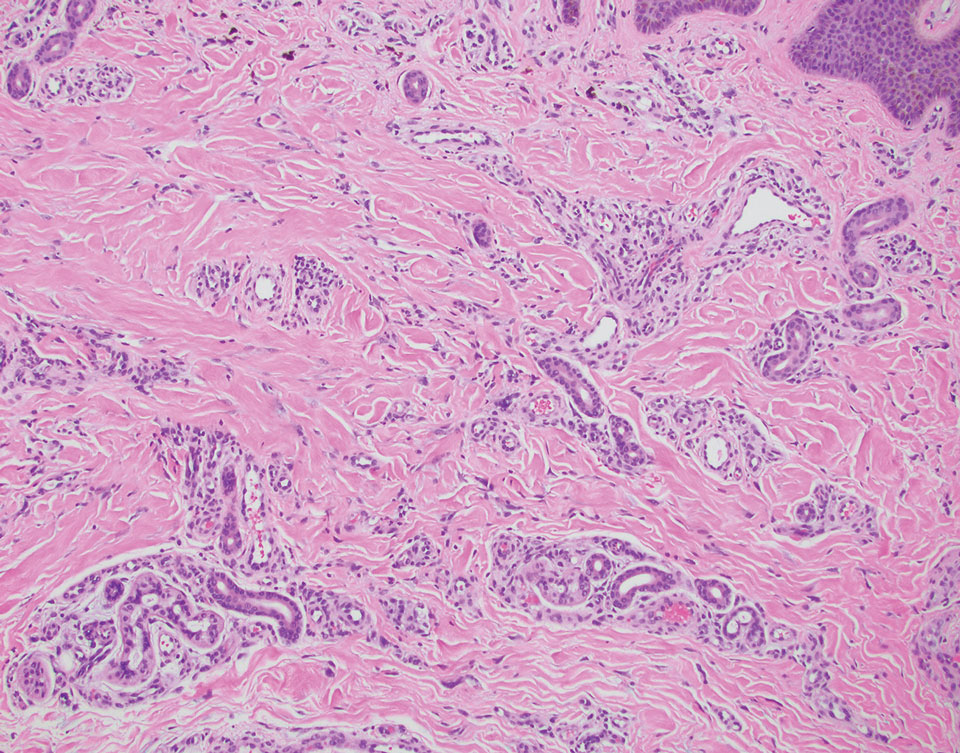
Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma is a rare benign proliferation that presents with numerous red-violet asymptomatic papules that commonly appear on the upper and lower extremities of women aged 40 to 70 years. Lesions feature both a fibrohistiocytic and vascular component.9 Histologic examination commonly shows multinucleated cells with angular outlining in the superficial dermis accompanied by fibrosis and ectatic small-caliber vessels (Figure 3). Although both pleomorphic lipoma and multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma have similar-appearing multinucleated giant cells, the latter has a proliferation of narrow vessels in thick collagen bundles and lacks an adipocytic component, which distinguishes it from the former.10 Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma also is characterized by a substantial number of factor XIIIa–positive fibrohistiocytic interstitial cells and vascular hyperplasia.9
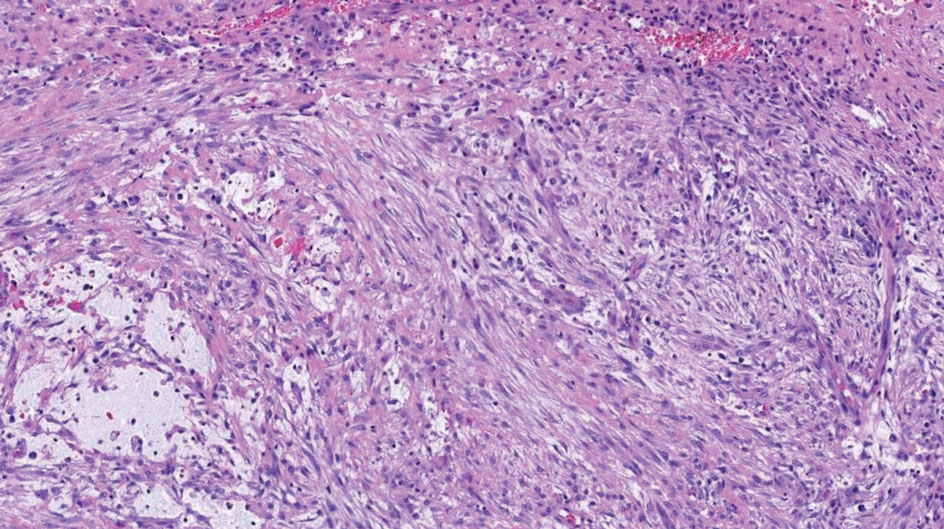
Nodular fasciitis is a benign lesion involving the rapid proliferation of myofibroblasts and fibroblasts in the subcutaneous tissue and most commonly is encountered on the extremities or head and neck regions. Many cases appear at sites of prior trauma, especially in patients aged 20 to 40 years. However, in infants and children the lesions typically are found in the head and neck regions.11 Clinically, lesions present as subcutaneous nodules. Histology reveals an infiltrative and poorly circumscribed proliferation of spindled myofibroblasts associated with myxoid stroma and dense collagen depositions. The spindled cells are loosely associated, rendering a tissue culture–like appearance (Figure 4). It also is common to see erythrocyte extravasation adjacent to myxoid stroma.11 Positive stains include vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and CD68, though immunohistochemistry often is not necessary for diagnosis.12 There often is abundant mitotic activity in nodular fasciitis, especially in early lesions, and the differential diagnosis includes sarcoma. Although nodular fasciitis is mitotically active, it does not show atypical mitotic figures. Nodular fasciitis commonly harbors a gene translocation of the MYH9 gene’s promoter region to the USP6 gene’s coding region.13
- Sakhadeo U, Mundhe R, DeSouza MA, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma: a gentle giant of pathology. J Cytol. 2015;32:201-203. doi:10.4103 /0970-9371.168904
- Shmookler BM, Enzinger FM. Pleomorphic lipoma: a benign tumor simulating liposarcoma. a clinicopathologic analysis of 48 cases. Cancer. 1981;47:126-133.
- Azzopardi JG, Iocco J, Salm R. Pleomorphic lipoma: a tumour simulating liposarcoma. Histopathology. 1983;7:511-523. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02264.x
- Jäger M, Winkelmann R, Eichler K, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:208-210. doi:10.1111/ddg.13422
- Allen A, Ahn C, Sangüeza OP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:483-488. doi:10.1016/j.det.2019.05.006
- Socoliuc C, Zurac S, Andrei R, et al. Multiple histological subtypes of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans occurring in the same tumor. Rom J Intern Med. 2015;53:79-88. doi:10.1515/rjim-2015-0011
- Abarzúa-Araya A, Lallas A, Piana S, et al. Superficial angiomyxoma of the skin. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:47-49. doi:10.5826 /dpc.0603a09
- Hornick J. Practical Soft Tissue Pathology A Diagnostic Approach. 2nd ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2017.
- Rato M, Monteiro AF, Parente J, et al. Case for diagnosis. multinucleated cell angiohistiocytoma. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:291-293. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.20186821
- Grgurich E, Quinn K, Oram C, et al. Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:59-61. doi:10.1111/cup.13361
- Zuber TJ, Finley JL. Nodular fasciitis. South Med J. 1994;87:842-844. doi:10.1097/00007611-199408000-00020
- Yver CM, Husson MA, Friedman O. Pathology clinic: nodular fasciitis involving the external ear [published online March 18, 2021]. Ear Nose Throat J. doi:10.1177/01455613211001958
- Erickson-Johnson M, Chou M, Evers B, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433. https://doi.org/10.1038 /labinvest.2011.118
The Diagnosis: Pleomorphic Lipoma
Pleomorphic lipoma is a rare, benign, adipocytic neoplasm that presents in the subcutaneous tissues of the upper shoulder, back, or neck. It predominantly affects men aged 50 to 70 years. Most lesions are situated in the subcutaneous tissues; few cases of intramuscular and retroperitoneal tumors have been reported.1 Clinically, pleomorphic lipomas present as painless, well-circumscribed lesions of the subcutaneous tissue that often resemble a lipoma or occasionally may be mistaken for liposarcoma. Histopathologic examination of ordinary lipomas reveals uniform mature adipocytes. However, pleomorphic lipomas consist of a mixture of multinucleated floretlike giant cells, variable-sized adipocytes, and fibrous tissue (ropy collagen bundles) with some myxoid and spindled areas.1,2 The most characteristic histologic feature of pleomorphic lipoma is multinucleated floretlike giant cells. The nuclei of these giant cells appear hyperchromatic, enlarged, and disposed to the periphery of the cell in a circular pattern. Additionally, tumors frequently contain excess mature dense collagen bundles that are strongly refractile in polarized light. Numerous mast cells are present. Atypical lipoblasts and capillary networks commonly are not visible in pleomorphic lipoma.3 The spindle cells express CD34 on immunohistochemistry. Loss of Rb-1 expression is typical.4
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a slow-growing soft tissue sarcoma that commonly begins as a pink or violet plaque on the trunk or upper limbs. Involvement of the head or neck accounts for only 10% to 15% of cases.5 This tumor has low metastatic potential but is highly infiltrative of surrounding tissues. It is associated with a translocation between chromosomes 22 and 17, leading to the fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor subunit β, PDGFB, and collagen type 1α1, COL1A1, genes.5 Clinically, patients often report that the lesion was present for several years prior to presentation with general stability in size and shape. Eventually, untreated lesions progress to become nodules or tumors and may even bleed or ulcerate. Histology reveals a storiform spindle cell proliferation throughout the dermis with infiltration into subcutaneous fat, commonly appearing in a honeycomblike pattern (Figure 1). Numerous histologic variants exist, including myxoid, sclerosing, pigmented (Bednar tumor), myoid, atrophic, or fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, as well as a giant cell fibroblastoma variant.6 These tumor subtypes can exist independently or in association with one another, creating hybrid lesions that can closely mimic other entities such as pleomorphic lipoma. The spindle cells stain positively for CD34. Treatment of these tumors involves complete surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery; however, recurrence is common for tumors involving the head or neck.5

Superficial angiomyxoma is a slow-growing papule that most commonly appears on the trunk, head, or neck in middle-aged adults. Occasionally, patients with Carney complex also can develop lesions on the external ear or breast.7 Histologically, superficial angiomyxoma is a hypocellular tumor characterized by abundant myxoid stroma, thin blood vessels, and small spindled and stellate cells with minimal cytoplasm (Figure 2).8 Superficial angiomyxoma and pleomorphic lipoma present differently on histology; superficial angiomyxoma is not associated with nuclear atypia or pleomorphism, whereas pleomorphic lipoma characteristically contains multinucleated floretlike giant cells and pleomorphism. Frequently, there also is loss of normal PRKAR1A gene expression, which is responsible for protein kinase A regulatory subunit 1-alpha expression.8

Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma is a rare benign proliferation that presents with numerous red-violet asymptomatic papules that commonly appear on the upper and lower extremities of women aged 40 to 70 years. Lesions feature both a fibrohistiocytic and vascular component.9 Histologic examination commonly shows multinucleated cells with angular outlining in the superficial dermis accompanied by fibrosis and ectatic small-caliber vessels (Figure 3). Although both pleomorphic lipoma and multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma have similar-appearing multinucleated giant cells, the latter has a proliferation of narrow vessels in thick collagen bundles and lacks an adipocytic component, which distinguishes it from the former.10 Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma also is characterized by a substantial number of factor XIIIa–positive fibrohistiocytic interstitial cells and vascular hyperplasia.9

Nodular fasciitis is a benign lesion involving the rapid proliferation of myofibroblasts and fibroblasts in the subcutaneous tissue and most commonly is encountered on the extremities or head and neck regions. Many cases appear at sites of prior trauma, especially in patients aged 20 to 40 years. However, in infants and children the lesions typically are found in the head and neck regions.11 Clinically, lesions present as subcutaneous nodules. Histology reveals an infiltrative and poorly circumscribed proliferation of spindled myofibroblasts associated with myxoid stroma and dense collagen depositions. The spindled cells are loosely associated, rendering a tissue culture–like appearance (Figure 4). It also is common to see erythrocyte extravasation adjacent to myxoid stroma.11 Positive stains include vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and CD68, though immunohistochemistry often is not necessary for diagnosis.12 There often is abundant mitotic activity in nodular fasciitis, especially in early lesions, and the differential diagnosis includes sarcoma. Although nodular fasciitis is mitotically active, it does not show atypical mitotic figures. Nodular fasciitis commonly harbors a gene translocation of the MYH9 gene’s promoter region to the USP6 gene’s coding region.13

The Diagnosis: Pleomorphic Lipoma
Pleomorphic lipoma is a rare, benign, adipocytic neoplasm that presents in the subcutaneous tissues of the upper shoulder, back, or neck. It predominantly affects men aged 50 to 70 years. Most lesions are situated in the subcutaneous tissues; few cases of intramuscular and retroperitoneal tumors have been reported.1 Clinically, pleomorphic lipomas present as painless, well-circumscribed lesions of the subcutaneous tissue that often resemble a lipoma or occasionally may be mistaken for liposarcoma. Histopathologic examination of ordinary lipomas reveals uniform mature adipocytes. However, pleomorphic lipomas consist of a mixture of multinucleated floretlike giant cells, variable-sized adipocytes, and fibrous tissue (ropy collagen bundles) with some myxoid and spindled areas.1,2 The most characteristic histologic feature of pleomorphic lipoma is multinucleated floretlike giant cells. The nuclei of these giant cells appear hyperchromatic, enlarged, and disposed to the periphery of the cell in a circular pattern. Additionally, tumors frequently contain excess mature dense collagen bundles that are strongly refractile in polarized light. Numerous mast cells are present. Atypical lipoblasts and capillary networks commonly are not visible in pleomorphic lipoma.3 The spindle cells express CD34 on immunohistochemistry. Loss of Rb-1 expression is typical.4
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a slow-growing soft tissue sarcoma that commonly begins as a pink or violet plaque on the trunk or upper limbs. Involvement of the head or neck accounts for only 10% to 15% of cases.5 This tumor has low metastatic potential but is highly infiltrative of surrounding tissues. It is associated with a translocation between chromosomes 22 and 17, leading to the fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor subunit β, PDGFB, and collagen type 1α1, COL1A1, genes.5 Clinically, patients often report that the lesion was present for several years prior to presentation with general stability in size and shape. Eventually, untreated lesions progress to become nodules or tumors and may even bleed or ulcerate. Histology reveals a storiform spindle cell proliferation throughout the dermis with infiltration into subcutaneous fat, commonly appearing in a honeycomblike pattern (Figure 1). Numerous histologic variants exist, including myxoid, sclerosing, pigmented (Bednar tumor), myoid, atrophic, or fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, as well as a giant cell fibroblastoma variant.6 These tumor subtypes can exist independently or in association with one another, creating hybrid lesions that can closely mimic other entities such as pleomorphic lipoma. The spindle cells stain positively for CD34. Treatment of these tumors involves complete surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery; however, recurrence is common for tumors involving the head or neck.5

Superficial angiomyxoma is a slow-growing papule that most commonly appears on the trunk, head, or neck in middle-aged adults. Occasionally, patients with Carney complex also can develop lesions on the external ear or breast.7 Histologically, superficial angiomyxoma is a hypocellular tumor characterized by abundant myxoid stroma, thin blood vessels, and small spindled and stellate cells with minimal cytoplasm (Figure 2).8 Superficial angiomyxoma and pleomorphic lipoma present differently on histology; superficial angiomyxoma is not associated with nuclear atypia or pleomorphism, whereas pleomorphic lipoma characteristically contains multinucleated floretlike giant cells and pleomorphism. Frequently, there also is loss of normal PRKAR1A gene expression, which is responsible for protein kinase A regulatory subunit 1-alpha expression.8

Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma is a rare benign proliferation that presents with numerous red-violet asymptomatic papules that commonly appear on the upper and lower extremities of women aged 40 to 70 years. Lesions feature both a fibrohistiocytic and vascular component.9 Histologic examination commonly shows multinucleated cells with angular outlining in the superficial dermis accompanied by fibrosis and ectatic small-caliber vessels (Figure 3). Although both pleomorphic lipoma and multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma have similar-appearing multinucleated giant cells, the latter has a proliferation of narrow vessels in thick collagen bundles and lacks an adipocytic component, which distinguishes it from the former.10 Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma also is characterized by a substantial number of factor XIIIa–positive fibrohistiocytic interstitial cells and vascular hyperplasia.9

Nodular fasciitis is a benign lesion involving the rapid proliferation of myofibroblasts and fibroblasts in the subcutaneous tissue and most commonly is encountered on the extremities or head and neck regions. Many cases appear at sites of prior trauma, especially in patients aged 20 to 40 years. However, in infants and children the lesions typically are found in the head and neck regions.11 Clinically, lesions present as subcutaneous nodules. Histology reveals an infiltrative and poorly circumscribed proliferation of spindled myofibroblasts associated with myxoid stroma and dense collagen depositions. The spindled cells are loosely associated, rendering a tissue culture–like appearance (Figure 4). It also is common to see erythrocyte extravasation adjacent to myxoid stroma.11 Positive stains include vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and CD68, though immunohistochemistry often is not necessary for diagnosis.12 There often is abundant mitotic activity in nodular fasciitis, especially in early lesions, and the differential diagnosis includes sarcoma. Although nodular fasciitis is mitotically active, it does not show atypical mitotic figures. Nodular fasciitis commonly harbors a gene translocation of the MYH9 gene’s promoter region to the USP6 gene’s coding region.13

- Sakhadeo U, Mundhe R, DeSouza MA, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma: a gentle giant of pathology. J Cytol. 2015;32:201-203. doi:10.4103 /0970-9371.168904
- Shmookler BM, Enzinger FM. Pleomorphic lipoma: a benign tumor simulating liposarcoma. a clinicopathologic analysis of 48 cases. Cancer. 1981;47:126-133.
- Azzopardi JG, Iocco J, Salm R. Pleomorphic lipoma: a tumour simulating liposarcoma. Histopathology. 1983;7:511-523. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02264.x
- Jäger M, Winkelmann R, Eichler K, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:208-210. doi:10.1111/ddg.13422
- Allen A, Ahn C, Sangüeza OP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:483-488. doi:10.1016/j.det.2019.05.006
- Socoliuc C, Zurac S, Andrei R, et al. Multiple histological subtypes of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans occurring in the same tumor. Rom J Intern Med. 2015;53:79-88. doi:10.1515/rjim-2015-0011
- Abarzúa-Araya A, Lallas A, Piana S, et al. Superficial angiomyxoma of the skin. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:47-49. doi:10.5826 /dpc.0603a09
- Hornick J. Practical Soft Tissue Pathology A Diagnostic Approach. 2nd ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2017.
- Rato M, Monteiro AF, Parente J, et al. Case for diagnosis. multinucleated cell angiohistiocytoma. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:291-293. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.20186821
- Grgurich E, Quinn K, Oram C, et al. Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:59-61. doi:10.1111/cup.13361
- Zuber TJ, Finley JL. Nodular fasciitis. South Med J. 1994;87:842-844. doi:10.1097/00007611-199408000-00020
- Yver CM, Husson MA, Friedman O. Pathology clinic: nodular fasciitis involving the external ear [published online March 18, 2021]. Ear Nose Throat J. doi:10.1177/01455613211001958
- Erickson-Johnson M, Chou M, Evers B, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433. https://doi.org/10.1038 /labinvest.2011.118
- Sakhadeo U, Mundhe R, DeSouza MA, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma: a gentle giant of pathology. J Cytol. 2015;32:201-203. doi:10.4103 /0970-9371.168904
- Shmookler BM, Enzinger FM. Pleomorphic lipoma: a benign tumor simulating liposarcoma. a clinicopathologic analysis of 48 cases. Cancer. 1981;47:126-133.
- Azzopardi JG, Iocco J, Salm R. Pleomorphic lipoma: a tumour simulating liposarcoma. Histopathology. 1983;7:511-523. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02264.x
- Jäger M, Winkelmann R, Eichler K, et al. Pleomorphic lipoma. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:208-210. doi:10.1111/ddg.13422
- Allen A, Ahn C, Sangüeza OP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:483-488. doi:10.1016/j.det.2019.05.006
- Socoliuc C, Zurac S, Andrei R, et al. Multiple histological subtypes of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans occurring in the same tumor. Rom J Intern Med. 2015;53:79-88. doi:10.1515/rjim-2015-0011
- Abarzúa-Araya A, Lallas A, Piana S, et al. Superficial angiomyxoma of the skin. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:47-49. doi:10.5826 /dpc.0603a09
- Hornick J. Practical Soft Tissue Pathology A Diagnostic Approach. 2nd ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2017.
- Rato M, Monteiro AF, Parente J, et al. Case for diagnosis. multinucleated cell angiohistiocytoma. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:291-293. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.20186821
- Grgurich E, Quinn K, Oram C, et al. Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:59-61. doi:10.1111/cup.13361
- Zuber TJ, Finley JL. Nodular fasciitis. South Med J. 1994;87:842-844. doi:10.1097/00007611-199408000-00020
- Yver CM, Husson MA, Friedman O. Pathology clinic: nodular fasciitis involving the external ear [published online March 18, 2021]. Ear Nose Throat J. doi:10.1177/01455613211001958
- Erickson-Johnson M, Chou M, Evers B, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433. https://doi.org/10.1038 /labinvest.2011.118
An otherwise healthy 56-year-old man with a family history of lymphoma presented with a raised lesion on the postauricular neck. He first noticed the nodule 3 months prior and was unsure if it was still getting larger. It was predominantly asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed a 1.5×1.5-cm, mobile, subcutaneous nodule. An incisional biopsy was performed and submitted for histologic evaluation.
Dome-Shaped Periorbital Papule
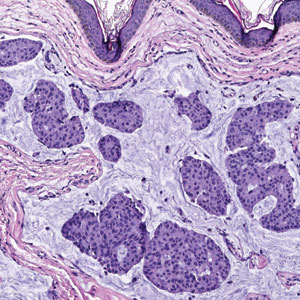
The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
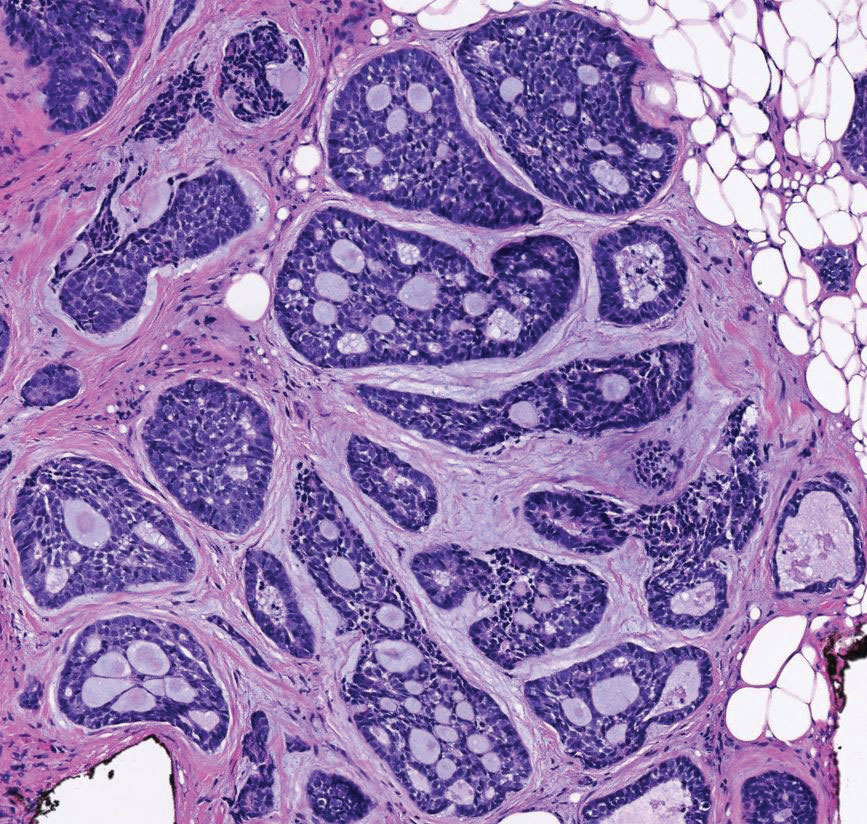
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
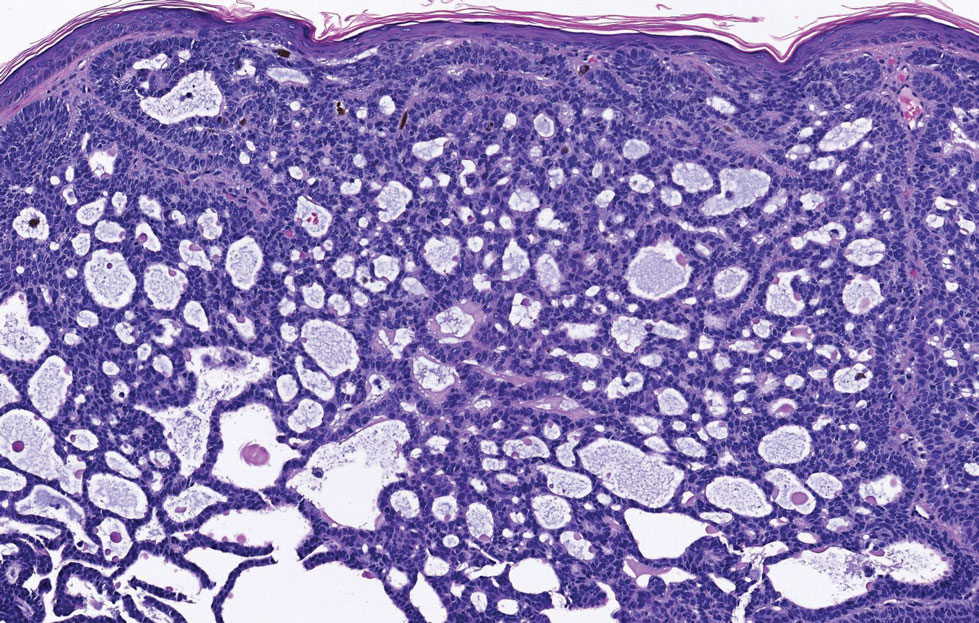
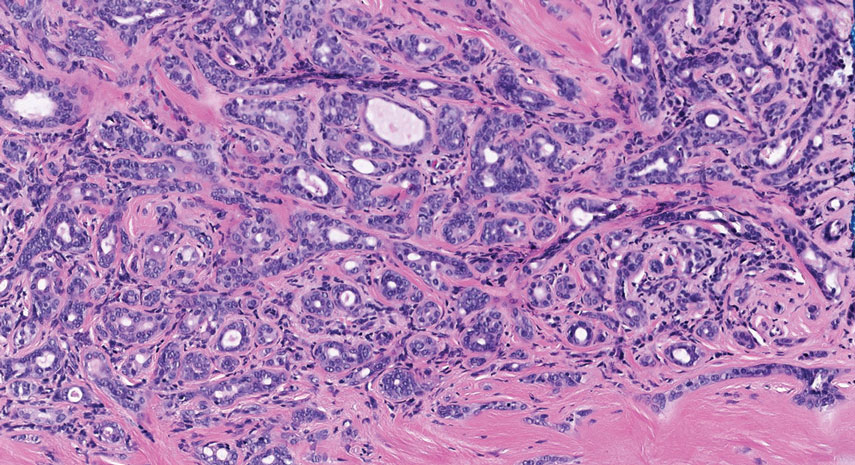
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7
Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2
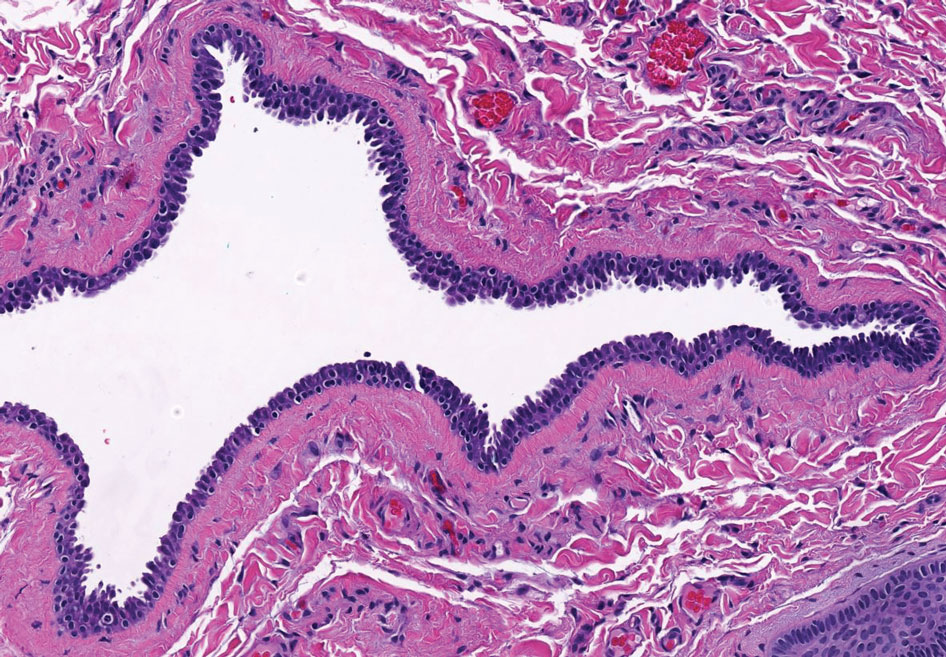
Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2
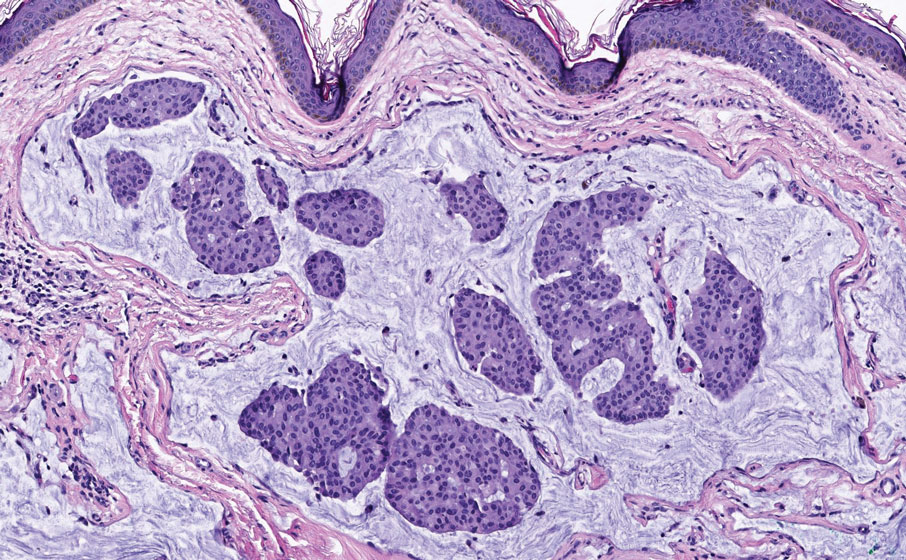
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.
- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7

Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2

Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2

Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.

The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7

Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2

Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2

Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.

- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
A 76-year-old woman presented with a slowly growing, asymptomatic, 5-mm, pink-brown, dome-shaped papule adjacent to the left lateral canthus of several years’ duration. Dermoscopic examination revealed fine linear peripheral blood vessels. The lesional cells were positive with cytokeratin 7, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, chromogranin, synaptophysin, and neuron-specific enolase. Cytokeratin 20 and p63 were negative, and the Ki-67 proliferative index was less than 5%.
Violaceous Nodules on the Lower Leg
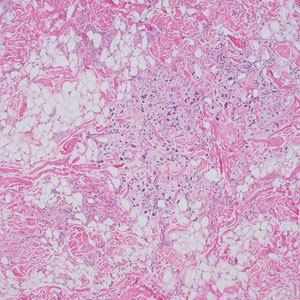
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
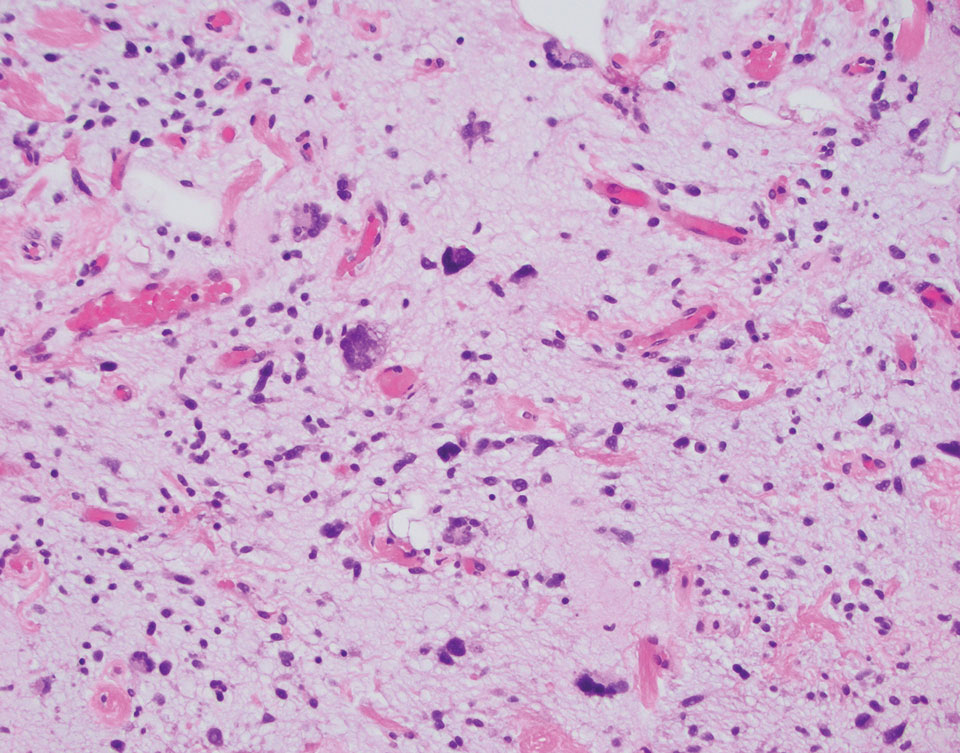
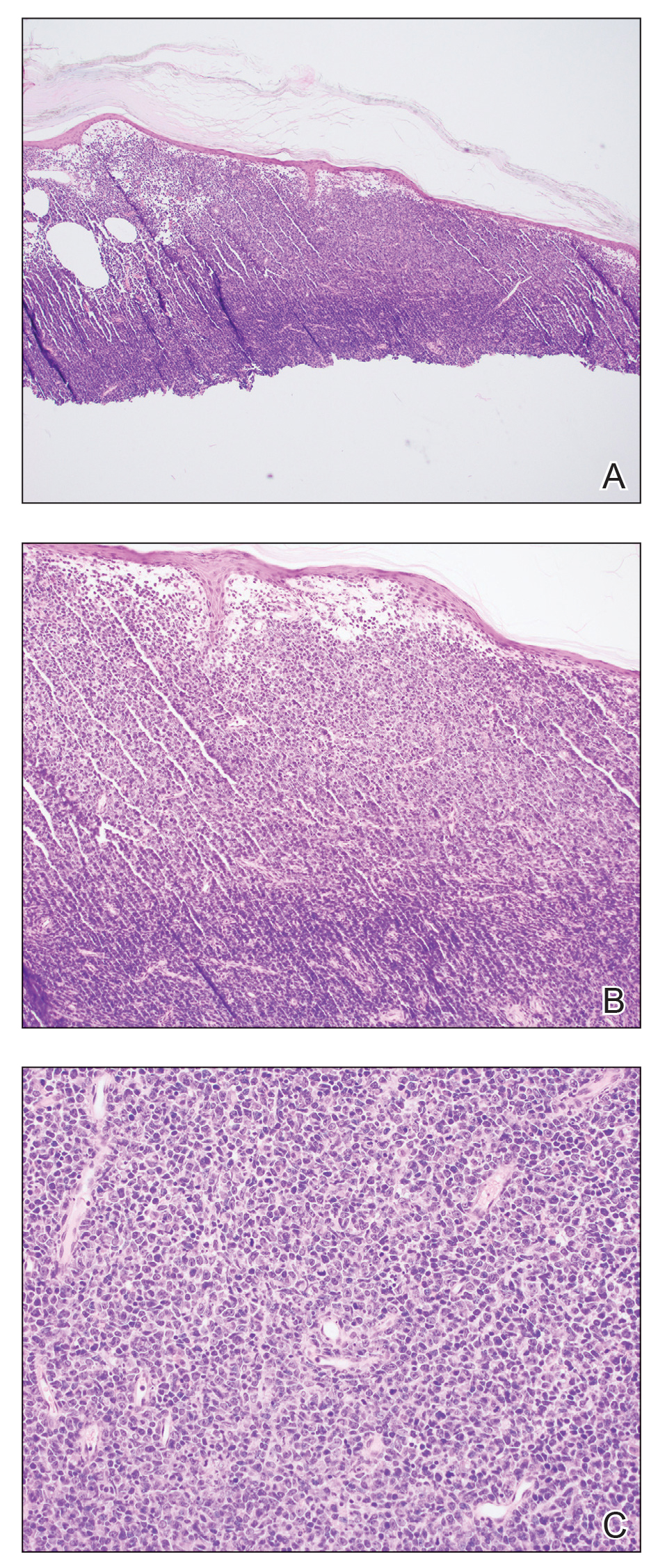
Shave biopsies of 3 lesions revealed a dense, diffuse, atypical lymphoid infiltrate occupying the entirety of the dermis and obscuring the dermoepidermal junction. The infiltrate consisted predominantly of largesized lymphoid cells with fine chromatin and conspicuous nucleoli (Figure). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD45 and CD20, indicating B-cell lineage. Bcl-2, multiple myeloma oncogene 1, and forkhead box protein P1 also were expressed in the vast majority of lesional cells, distinguishing the lesion from other forms of cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.1 These findings were consistent with large B-cell lymphoma with a high proliferation index, consistent with primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, which often presents on the lower leg.2 The patient had a negative systemic workup including bone marrow biopsy. He was started on the R-CEOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy regimen.
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, is an intermediately aggressive and rare form of B-cell lymphoma with a poor prognosis that primarily affects elderly female patients. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, accounts for only 1% to 3% of cutaneous lymphomas and approximately 10% to 20% of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.2 It typically presents as multiple red-brown or bluish nodules on the lower extremities or trunk. Presentation as a solitary nodule also is possible.1,2 Histologic analysis of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, reveals large cells with round nuclei (immunoblasts and centroblasts), and the immunohistochemical profile shows strong Bcl-2 expression often accompanied by the multiple myeloma oncogene 1 protein.3 The 5-year survival rate is approximately 50%, which is lower than other types of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas, and the progression of disease is characterized by frequent relapses and involvement of extracutaneous regions such as the lymph nodes, bone marrow, and central nervous system.1,2,4 Patients with multiple tumors on the leg have a particularly poor prognosis; in particular, having 1 or more lesions on the leg results in a 43% 3-year survival rate while having multiple lesions has a 36% 3-year survival rate compared with a 77% 3-year survival rate for patients with the non–leg subtype or a single lesion.3 Treatment with rituximab has been shown to be effective in at least short-term control of the disease, and the R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) regimen is the standard of treatment.3,4
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, can mimic multiple other cutaneous presentations of disease. Myeloid sarcoma (leukemia cutis) is a rare condition that presents as an extramedullary tumor often simultaneously with the onset or relapse of acute myeloid leukemia.5 Our patient had no history of leukemia, but myeloid sarcoma may predate acute myeloid leukemia in about a quarter of cases.5 It most commonly presents histologically as a diffuse dermal infiltrate that splays between collagen bundles and often is associated with an overlying Grenz zone. A nodular, or perivascular and periadnexal, pattern also may be seen. Upon closer inspection, the infiltrate is composed of immature myeloid cells (blasts) with background inflammation occasionally containing eosinophils. The immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the type of differentiation and degree of maturity of the cells. The histologic findings in our patient were inconsistent with myeloid sarcoma.
Erythema elevatum diutinum (EED) usually presents as dark red, brown, or violaceous papules or plaques and often is found on the extensor surfaces. It often is associated with hematologic abnormalities as well as recurrent bacterial or viral infections.6 Histologically, EED initially manifests as leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate typically featuring an abundance of neutrophils, making this condition unlikely in this case. As the lesion progresses, fibrosis and scarring ensue as inflammation wanes. The fibrosis often is described as having an onion skin–like pattern, which is characteristic of established EED lesions. Our patient had no history of vasculitis, and the histologic findings were inconsistent with EED.
Angiosarcoma can present as a central nodule surrounded by an erythematous plaque. Although potentially clinically similar to primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, angiosarcoma was unlikely in this case because of an absence of lymphedema and no history of radiation to the leg, both of which are key historical features of angiosarcoma.7 Additionally, the histology of cutaneous angiosarcoma is marked by vascular proliferation, which was not seen in the lesion biopsied in our patient. The histology of angiosarcoma is that of an atypical vascular proliferation, and a hallmark feature is infiltration between collagen, often referred to as giving the appearance of dissection between collagen bundles. The degree of atypia can vary widely, and epithelioid variants exist, producing a potential diagnostic pitfall. Lesional cells are positive for vascular markers, which can be used for confirmation of the endothelial lineage.
Sarcoidosis is notorious for its mimicry, which can be the case both clinically and histologically. Characteristic pathology of sarcoidosis is that of well-formed epithelioid granulomas with minimal associated inflammation and lack of caseating necrosis. Our patient had no known history of systemic sarcoidosis, and the pathologic features of noncaseating granulomas were not present. As a diagnosis of exclusion, correlation with special stains and culture studies is necessary to exclude an infectious process. The differential diagnosis for sarcoidal granulomatous dermatitis also includes foreign body reaction, inflammatory bowel disease, and granulomatous cheilitis, among others.
- Athalye L, Nami N, Shitabata P. A rare case of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type. Cutis. 2018;102:E31-E34.
- Sokol L, Naghashpour M, Glass LF. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: recent advances in diagnosis and management. Cancer Control. 2012;19:236-244. doi:10.1177/107327481201900308
- Grange F, Beylot-Barry M, Courville P, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type: clinicopathologic features and prognostic analysis in 60 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1144-1150. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1144
- Patsatsi A, Kyriakou A, Karavasilis V, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, with multiple local relapses: case presentation and brief review of literature. Hippokratia. 2013;17:174-176.
- Avni B, Koren-Michowitz M. Myeloid sarcoma: current approach and therapeutic options. Ther Adv Hematol. 2011;2:309-316.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Scholtz J, Mishra MM, Simman R. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the lower leg. Cutis. 2018;102:E8-E11.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Shave biopsies of 3 lesions revealed a dense, diffuse, atypical lymphoid infiltrate occupying the entirety of the dermis and obscuring the dermoepidermal junction. The infiltrate consisted predominantly of largesized lymphoid cells with fine chromatin and conspicuous nucleoli (Figure). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD45 and CD20, indicating B-cell lineage. Bcl-2, multiple myeloma oncogene 1, and forkhead box protein P1 also were expressed in the vast majority of lesional cells, distinguishing the lesion from other forms of cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.1 These findings were consistent with large B-cell lymphoma with a high proliferation index, consistent with primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, which often presents on the lower leg.2 The patient had a negative systemic workup including bone marrow biopsy. He was started on the R-CEOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy regimen.

Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, is an intermediately aggressive and rare form of B-cell lymphoma with a poor prognosis that primarily affects elderly female patients. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, accounts for only 1% to 3% of cutaneous lymphomas and approximately 10% to 20% of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.2 It typically presents as multiple red-brown or bluish nodules on the lower extremities or trunk. Presentation as a solitary nodule also is possible.1,2 Histologic analysis of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, reveals large cells with round nuclei (immunoblasts and centroblasts), and the immunohistochemical profile shows strong Bcl-2 expression often accompanied by the multiple myeloma oncogene 1 protein.3 The 5-year survival rate is approximately 50%, which is lower than other types of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas, and the progression of disease is characterized by frequent relapses and involvement of extracutaneous regions such as the lymph nodes, bone marrow, and central nervous system.1,2,4 Patients with multiple tumors on the leg have a particularly poor prognosis; in particular, having 1 or more lesions on the leg results in a 43% 3-year survival rate while having multiple lesions has a 36% 3-year survival rate compared with a 77% 3-year survival rate for patients with the non–leg subtype or a single lesion.3 Treatment with rituximab has been shown to be effective in at least short-term control of the disease, and the R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) regimen is the standard of treatment.3,4
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, can mimic multiple other cutaneous presentations of disease. Myeloid sarcoma (leukemia cutis) is a rare condition that presents as an extramedullary tumor often simultaneously with the onset or relapse of acute myeloid leukemia.5 Our patient had no history of leukemia, but myeloid sarcoma may predate acute myeloid leukemia in about a quarter of cases.5 It most commonly presents histologically as a diffuse dermal infiltrate that splays between collagen bundles and often is associated with an overlying Grenz zone. A nodular, or perivascular and periadnexal, pattern also may be seen. Upon closer inspection, the infiltrate is composed of immature myeloid cells (blasts) with background inflammation occasionally containing eosinophils. The immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the type of differentiation and degree of maturity of the cells. The histologic findings in our patient were inconsistent with myeloid sarcoma.
Erythema elevatum diutinum (EED) usually presents as dark red, brown, or violaceous papules or plaques and often is found on the extensor surfaces. It often is associated with hematologic abnormalities as well as recurrent bacterial or viral infections.6 Histologically, EED initially manifests as leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate typically featuring an abundance of neutrophils, making this condition unlikely in this case. As the lesion progresses, fibrosis and scarring ensue as inflammation wanes. The fibrosis often is described as having an onion skin–like pattern, which is characteristic of established EED lesions. Our patient had no history of vasculitis, and the histologic findings were inconsistent with EED.
Angiosarcoma can present as a central nodule surrounded by an erythematous plaque. Although potentially clinically similar to primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, angiosarcoma was unlikely in this case because of an absence of lymphedema and no history of radiation to the leg, both of which are key historical features of angiosarcoma.7 Additionally, the histology of cutaneous angiosarcoma is marked by vascular proliferation, which was not seen in the lesion biopsied in our patient. The histology of angiosarcoma is that of an atypical vascular proliferation, and a hallmark feature is infiltration between collagen, often referred to as giving the appearance of dissection between collagen bundles. The degree of atypia can vary widely, and epithelioid variants exist, producing a potential diagnostic pitfall. Lesional cells are positive for vascular markers, which can be used for confirmation of the endothelial lineage.
Sarcoidosis is notorious for its mimicry, which can be the case both clinically and histologically. Characteristic pathology of sarcoidosis is that of well-formed epithelioid granulomas with minimal associated inflammation and lack of caseating necrosis. Our patient had no known history of systemic sarcoidosis, and the pathologic features of noncaseating granulomas were not present. As a diagnosis of exclusion, correlation with special stains and culture studies is necessary to exclude an infectious process. The differential diagnosis for sarcoidal granulomatous dermatitis also includes foreign body reaction, inflammatory bowel disease, and granulomatous cheilitis, among others.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Shave biopsies of 3 lesions revealed a dense, diffuse, atypical lymphoid infiltrate occupying the entirety of the dermis and obscuring the dermoepidermal junction. The infiltrate consisted predominantly of largesized lymphoid cells with fine chromatin and conspicuous nucleoli (Figure). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD45 and CD20, indicating B-cell lineage. Bcl-2, multiple myeloma oncogene 1, and forkhead box protein P1 also were expressed in the vast majority of lesional cells, distinguishing the lesion from other forms of cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.1 These findings were consistent with large B-cell lymphoma with a high proliferation index, consistent with primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, which often presents on the lower leg.2 The patient had a negative systemic workup including bone marrow biopsy. He was started on the R-CEOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy regimen.

Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, is an intermediately aggressive and rare form of B-cell lymphoma with a poor prognosis that primarily affects elderly female patients. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, accounts for only 1% to 3% of cutaneous lymphomas and approximately 10% to 20% of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.2 It typically presents as multiple red-brown or bluish nodules on the lower extremities or trunk. Presentation as a solitary nodule also is possible.1,2 Histologic analysis of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, reveals large cells with round nuclei (immunoblasts and centroblasts), and the immunohistochemical profile shows strong Bcl-2 expression often accompanied by the multiple myeloma oncogene 1 protein.3 The 5-year survival rate is approximately 50%, which is lower than other types of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas, and the progression of disease is characterized by frequent relapses and involvement of extracutaneous regions such as the lymph nodes, bone marrow, and central nervous system.1,2,4 Patients with multiple tumors on the leg have a particularly poor prognosis; in particular, having 1 or more lesions on the leg results in a 43% 3-year survival rate while having multiple lesions has a 36% 3-year survival rate compared with a 77% 3-year survival rate for patients with the non–leg subtype or a single lesion.3 Treatment with rituximab has been shown to be effective in at least short-term control of the disease, and the R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) regimen is the standard of treatment.3,4
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, can mimic multiple other cutaneous presentations of disease. Myeloid sarcoma (leukemia cutis) is a rare condition that presents as an extramedullary tumor often simultaneously with the onset or relapse of acute myeloid leukemia.5 Our patient had no history of leukemia, but myeloid sarcoma may predate acute myeloid leukemia in about a quarter of cases.5 It most commonly presents histologically as a diffuse dermal infiltrate that splays between collagen bundles and often is associated with an overlying Grenz zone. A nodular, or perivascular and periadnexal, pattern also may be seen. Upon closer inspection, the infiltrate is composed of immature myeloid cells (blasts) with background inflammation occasionally containing eosinophils. The immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the type of differentiation and degree of maturity of the cells. The histologic findings in our patient were inconsistent with myeloid sarcoma.
Erythema elevatum diutinum (EED) usually presents as dark red, brown, or violaceous papules or plaques and often is found on the extensor surfaces. It often is associated with hematologic abnormalities as well as recurrent bacterial or viral infections.6 Histologically, EED initially manifests as leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate typically featuring an abundance of neutrophils, making this condition unlikely in this case. As the lesion progresses, fibrosis and scarring ensue as inflammation wanes. The fibrosis often is described as having an onion skin–like pattern, which is characteristic of established EED lesions. Our patient had no history of vasculitis, and the histologic findings were inconsistent with EED.
Angiosarcoma can present as a central nodule surrounded by an erythematous plaque. Although potentially clinically similar to primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, angiosarcoma was unlikely in this case because of an absence of lymphedema and no history of radiation to the leg, both of which are key historical features of angiosarcoma.7 Additionally, the histology of cutaneous angiosarcoma is marked by vascular proliferation, which was not seen in the lesion biopsied in our patient. The histology of angiosarcoma is that of an atypical vascular proliferation, and a hallmark feature is infiltration between collagen, often referred to as giving the appearance of dissection between collagen bundles. The degree of atypia can vary widely, and epithelioid variants exist, producing a potential diagnostic pitfall. Lesional cells are positive for vascular markers, which can be used for confirmation of the endothelial lineage.
Sarcoidosis is notorious for its mimicry, which can be the case both clinically and histologically. Characteristic pathology of sarcoidosis is that of well-formed epithelioid granulomas with minimal associated inflammation and lack of caseating necrosis. Our patient had no known history of systemic sarcoidosis, and the pathologic features of noncaseating granulomas were not present. As a diagnosis of exclusion, correlation with special stains and culture studies is necessary to exclude an infectious process. The differential diagnosis for sarcoidal granulomatous dermatitis also includes foreign body reaction, inflammatory bowel disease, and granulomatous cheilitis, among others.
- Athalye L, Nami N, Shitabata P. A rare case of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type. Cutis. 2018;102:E31-E34.
- Sokol L, Naghashpour M, Glass LF. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: recent advances in diagnosis and management. Cancer Control. 2012;19:236-244. doi:10.1177/107327481201900308
- Grange F, Beylot-Barry M, Courville P, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type: clinicopathologic features and prognostic analysis in 60 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1144-1150. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1144
- Patsatsi A, Kyriakou A, Karavasilis V, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, with multiple local relapses: case presentation and brief review of literature. Hippokratia. 2013;17:174-176.
- Avni B, Koren-Michowitz M. Myeloid sarcoma: current approach and therapeutic options. Ther Adv Hematol. 2011;2:309-316.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Scholtz J, Mishra MM, Simman R. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the lower leg. Cutis. 2018;102:E8-E11.
- Athalye L, Nami N, Shitabata P. A rare case of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type. Cutis. 2018;102:E31-E34.
- Sokol L, Naghashpour M, Glass LF. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: recent advances in diagnosis and management. Cancer Control. 2012;19:236-244. doi:10.1177/107327481201900308
- Grange F, Beylot-Barry M, Courville P, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type: clinicopathologic features and prognostic analysis in 60 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1144-1150. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1144
- Patsatsi A, Kyriakou A, Karavasilis V, et al. Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, with multiple local relapses: case presentation and brief review of literature. Hippokratia. 2013;17:174-176.
- Avni B, Koren-Michowitz M. Myeloid sarcoma: current approach and therapeutic options. Ther Adv Hematol. 2011;2:309-316.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Scholtz J, Mishra MM, Simman R. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the lower leg. Cutis. 2018;102:E8-E11.
A 79-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with 4 enlarging, asymptomatic, violaceous, desquamating nodules on the left pretibial region and calf of 3 months’ duration. He denied any constitutional symptoms such as night sweats or weight loss. His medical history included a malignant melanoma on the left ear that was excised 5 years prior. He also had a history of peripheral edema, hypertension, and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as a 50-pack-year history of smoking. Physical examination revealed 2 large nodules measuring 3.0×3.0 cm each and 2 smaller nodules measuring 1.0×1.0 cm each. There was no appreciable lymphadenopathy.