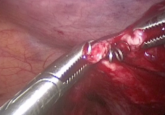
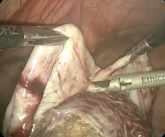
From Society of Gynecologic Surgeons
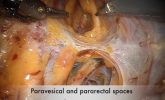
Cervical injection of methylene blue for identification of sentinel lymph nodes in cervical cancer
Brought to you by the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. A 34-year-old patient with stage 1B1 squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix underwent...