Pigmented purpuric dermatoses (PPDs) are a spectrum of chronic disorders that present as speckled brown to purpuric lesions and orange-brown discoloration of the skin.1 Eruptions generally occur in middle-aged to elderly patients and commonly follow a chronic waxing and waning course.2 Lesions usually are found in a localized distribution on the legs. Histologically, PPD presents with perivascular infiltrates of lymphocytes and macrophages centered around the superficial small blood vessels with narrowing of the lumina. Extravasation of red blood cells and hemosiderin deposition are commonly seen in the absence of vasculitis.
The etiology of PPD is unknown; however, important cofactors include venous hypertension, exercise and gravitational dependency, capillary fragility, focal infections, and chemical ingestions.1 Drugs are the most important provoking factors, including acetaminophen, aspirin, adalin, carbromal, chlordiazepoxide, glipizide, glybuzole, hydralazine, meprobamate, dipyridamole, reserpine, thiamine, and interferon-alfa, as well as medroxyprogesterone acetate injection. Other phenomena include contact allergy and alcohol ingestion.1
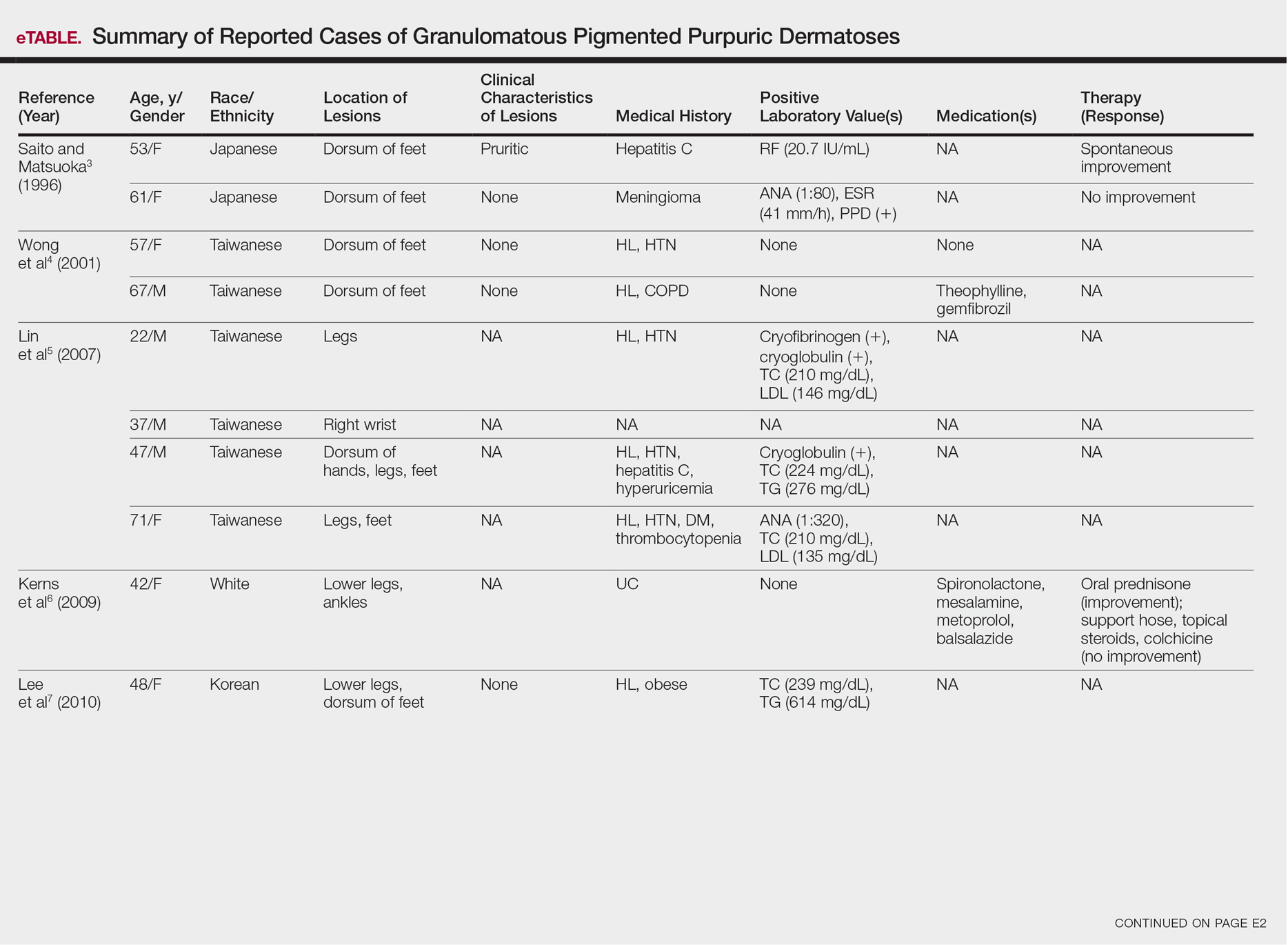
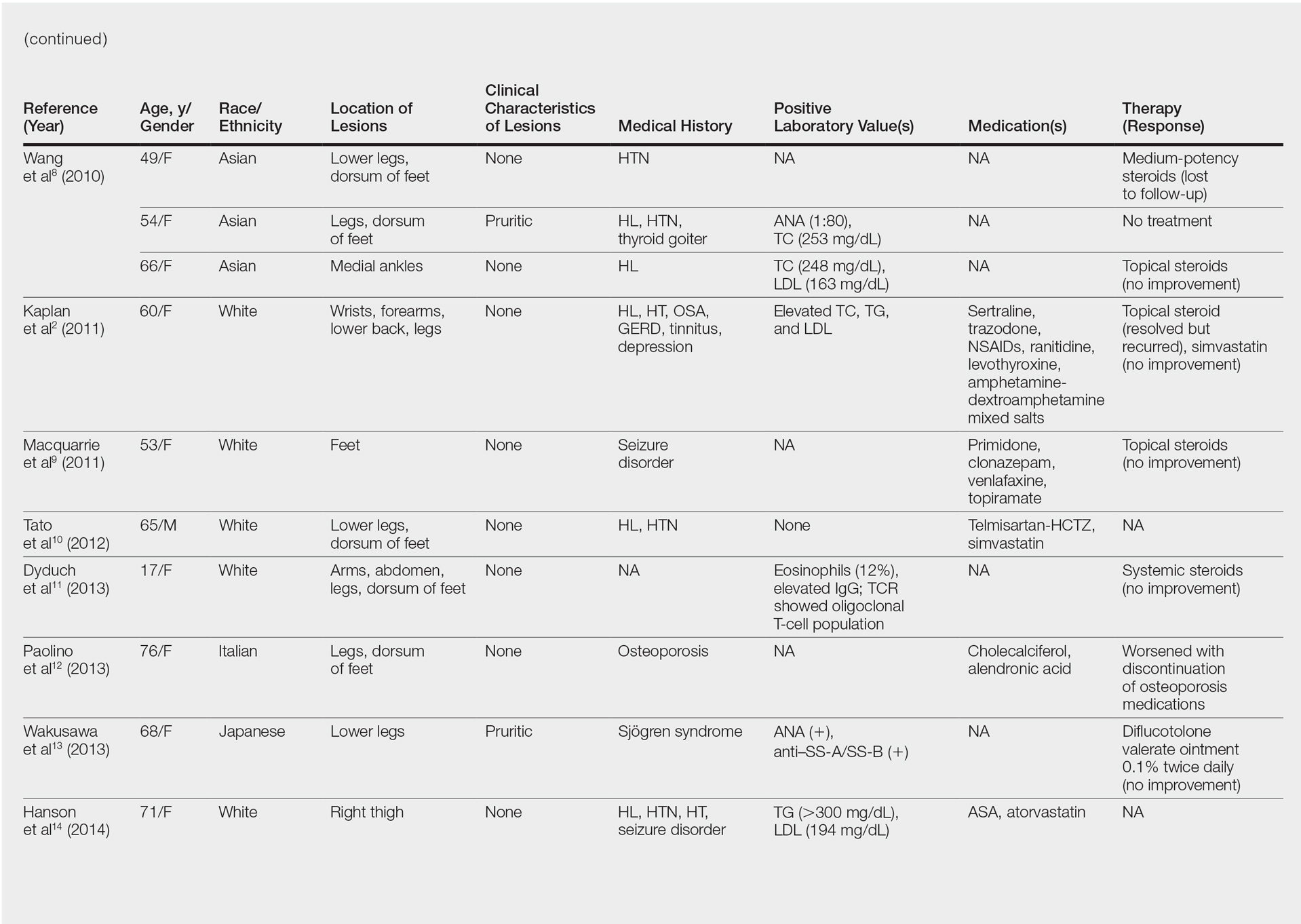
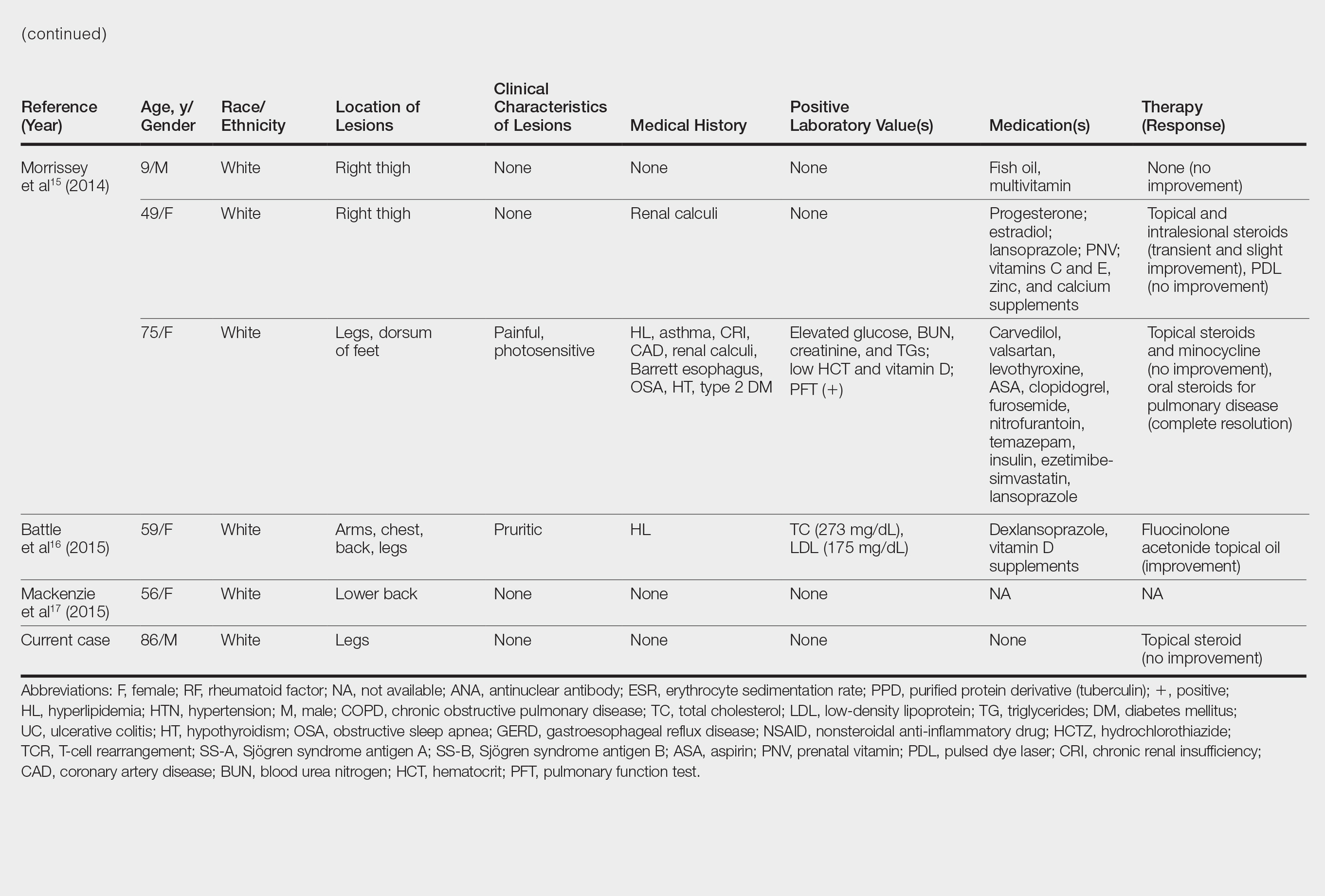
Although the diagnosis often is made clinically, many forms of PPD exist. The 4 main forms include Schaumberg disease, purpura annularis telangiectaticum of Majocchi, pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis of Gougerot and Blum, and eczematoidlike purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis. Less common variants include itching purpura of Lowenthal, lichen purpuricus, lichen aureus, granulomatous pigmented purpura, transitory pigmented purpuric dermatosis, and linear pigmented purpura.1Granulomatous PPD (GPPD) is a rare histologic variant of PPD. Clinically, it is indistinguishable from other forms of PPD but reveals itself histologically with granulomatous infiltrates superimposed on classic PPD. We report a case of GPPD and provide a thorough literature review focusing on epidemiology, clinical symptoms, and treatment.2-17 The eTable summarizes all reported cases of GPPD.
Case Report
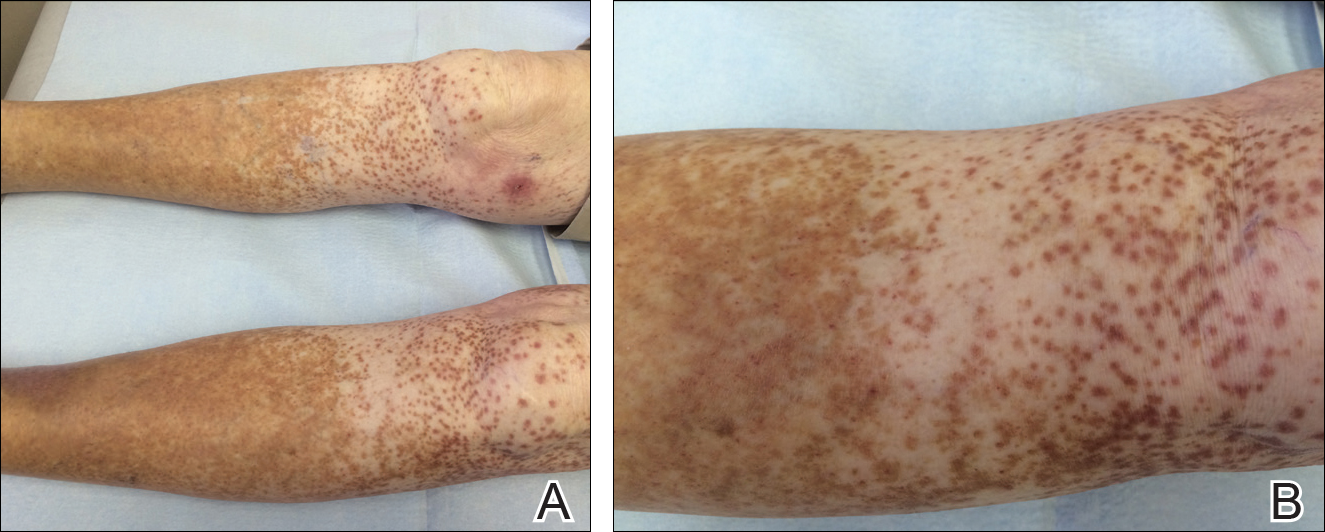
An 86-year-old white man with no remarkable medical history presented with an asymptomatic eruption over the bilateral shins extending up both thighs of 6 years’ duration (Figure 1). It began as a 15-cm patch on the right medial thigh that rapidly spread over 1 year to involve the majority of the legs. Physical examination revealed scattered 1- to 2-mm brown macules coalescing into patches on both legs. The patches increased in density distally and extended from the bilateral thighs to the ankles. Edema of the legs was absent, and lesions were nonblanchable and without scale or induration. The differential diagnoses included stasis dermatitis, vasculitis, and PPD. All laboratory values were within reference range, including complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, urine analysis, and lipid profile.
A punch biopsy from the distal right thigh revealed a superficial to mid dermal perivascular lymphocyte-predominant infiltrate with associated siderophages and a focal granulomatous infiltrate comprised of histiocytes (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff, acid-fast bacilli, and Fite stains were negative for microorganisms. No eosinophils or leukocytoclasia were seen. The patient applied betamethasone dipropionate cream 0.05% twice daily for several weeks without improvement. Because the lesions were asymptomatic, he discontinued the topical medication.
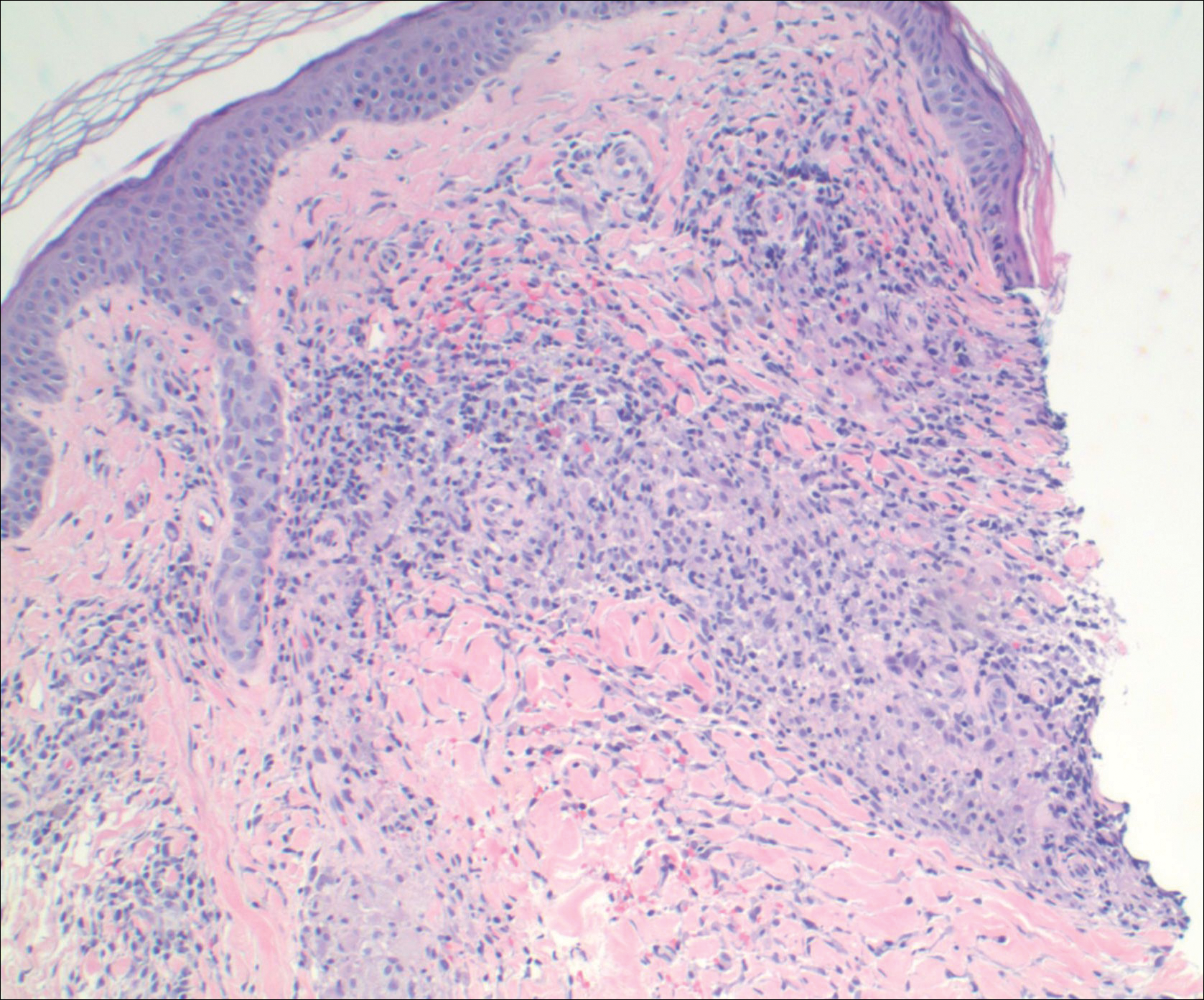
Figure 2. Granulomatous pigmented purpuric dermatosis histopathology revealed a superficial to mid dermal perivascular lymphocyte-predominant infiltrate with a focal granulomatous infiltrate comprised of histiocytes. Extravasated erythrocytes within granulomatous and lymphocytic inflammation was seen in the dermis (H&E, original magnification ×20).