To the Editor:
Long, dark, and thick eyelashes have been a focal point of society’s perception of beauty for thousands of years,1 and the use of makeup products such as mascaras, eyeliners, and eye shadows has further increased the perception of attractiveness of the eyes.2 Many eyelash enhancement methods have been developed or in some instances have been serendipitously discovered. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% originally was developed as an eye drop that was approved by the US Food and Drug Association (FDA) in 2001 for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. An unexpected side effect of this product was eyelash hypertrichosis.3,4 As a result, the FDA approved bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% as an eyelash solution with an eyelid applicator for treatment of eyelash hypotrichosis in 2008.5
Because all follicular development occurs during embryogenesis, the number of eyelash follicles does not increase over time.6 Bitmatoprost eyelash solution works by prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the eyelashes and stimulating the transition from the telogen (dormant) phase to the anagen phase. It also has been shown to increase the hair bulb diameter of follicles undergoing the anagen phase, resulting in thicker eyelashes.7 Although many patients have enjoyed this unexpected indication, prostaglandin (PG) analogues such as bimatoprost and latanoprost have a well-documented history of ocular side effects when applied directly to the eye. The most common adverse reactions include eye pruritus, conjunctival hyperemia, and eyelid pigmentation.3 The product safety information indicates that eyelid pigmentation typically is reversible.3,5 Iris pigmentation is perhaps the least desirable side effect of PG analogues and was first noted in latanoprost studies on primates.8 The underlying mechanism appears to be due to an increase in melanogenesis that results in an increase in melanin granules without concomitant proliferation of melanocytes, cellular atypia, or evidence of inflammatory reaction. Unfortunately, this pigmentation typically is permanent.3,5,9
Studies have shown that iris hyperpigmentation can occur when bimatoprost eye drops are applied to the eyes for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension, but reports associated with bimatoprost eyelash solution are rare.3,4,10 We report a case of iris hyperpigmentation following cosmetic use of bimatoprost eyelash solution.
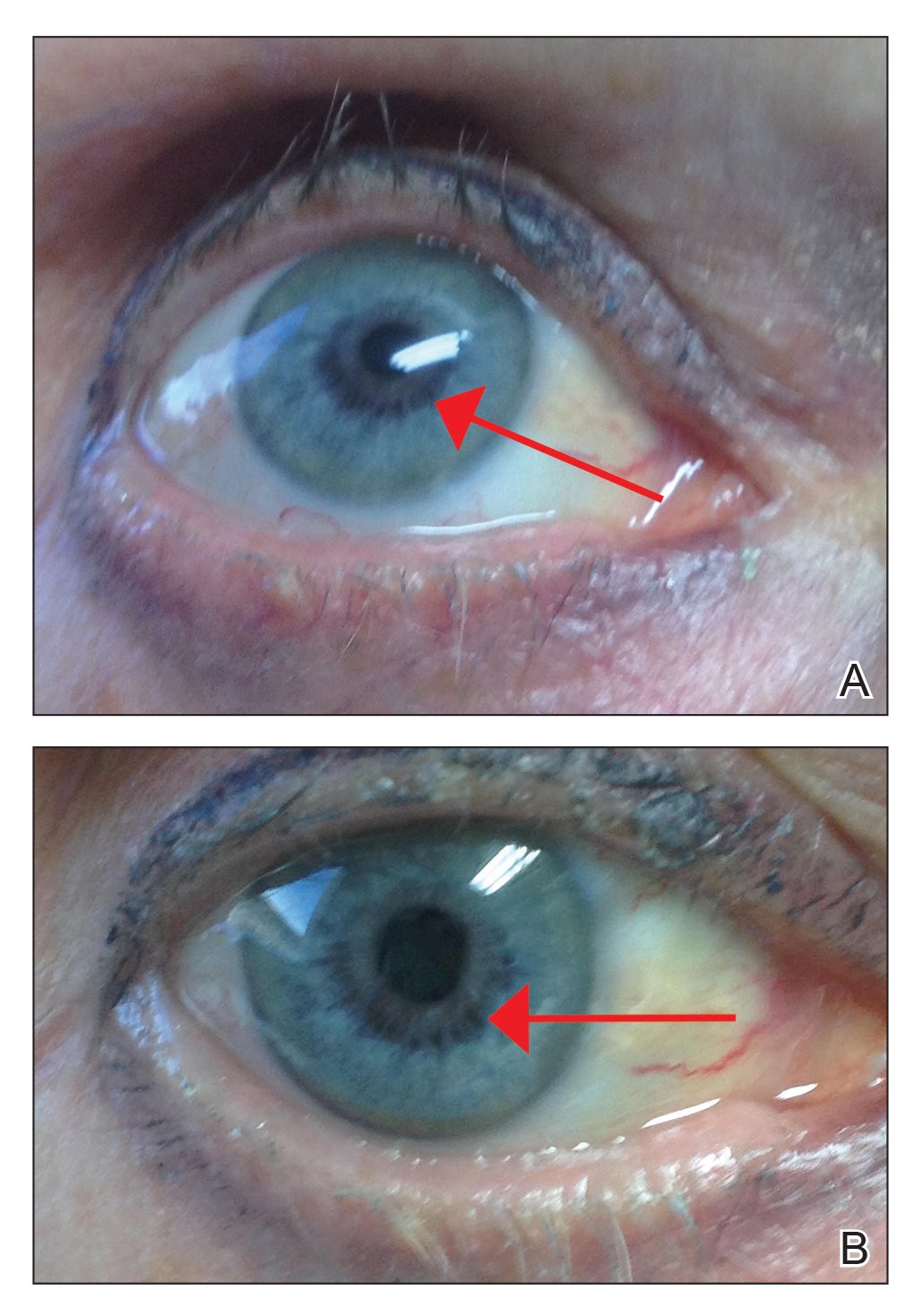
An otherwise healthy 63-year-old woman presented to our clinic for an annual skin examination. She noted that she had worsening dark pigmentation of the bilateral irises. The patient did not have any personal or family history of melanoma or ocular nevi, and there were no associated symptoms of eye tearing, pruritus, burning, or discharge. No prior surgical procedures had been performed on or around the eyes, and the patient never used contact lenses. She had been intermittently using bimatoprost eyelash solution prescribed by an outside physician for approximately 3 years to enhance her eyelashes. Although she never applied the product directly into her eyes, she noted that she often was unmethodical in application of the product and that runoff from the product may have occasionally leaked into the eyes. Physical examination revealed bilateral blue irises with ink spot–like, grayish black patches encircling the bilateral pupils (Figure).
The patient was advised to stop using the product, but no improvement of the iris hyperpigmentation was appreciated at 6-month follow-up. The patient declined referral to ophthalmology for evaluation to confirm a diagnosis and discuss treatment because the hyperpigmentation did not bother her.
There have been several studies of iris hyperpigmentation with use of PG analogues in the treatment of glaucoma. In a phase 3 clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of latanoprost for treatment of ocular hypertension, it was noted that 24 (12%) of 198 patients experienced iris hyperpigmentation and that patients with heterogeneous pigmentation (ie, hazel irises and mixed coloring) were at an increased risk.11 Other studies also have shown an increased risk of iris hyperpigmentation due to heterogeneous phenotype12 as well as older age.13