Dermpath Diagnosis
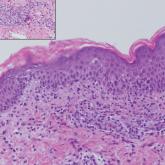
Erythematous Papules on the Scrotum, Trunk, and Extremities
A 54-year-old man presented with painful, nonpruritic, erythematous papules that began on the scrotum. The eruption progressed to involve the...
Dr. Wu is from the Department of Dermatology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China. Drs. Wu and Elston are from the Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, and Dr. Skipper is from the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, all at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Dirk M. Elston, MD, Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, 135 Rutledge Ave, MSC 578, Charleston, SC 29425 (elstond@musc.edu).

Sclerosing perineurioma, first described in 1997 by Fetsch and Miettinen,1 is a subtype of perineurioma with a strong predilection for the fingers and palms of young adults. Rare cases involving extra-acral sites including the forearm, elbow, axilla, back, neck, lower leg, thigh, knee, lips, nose, and mouth have been reported.2-4 Perineurioma is a relatively uncommon and benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor with exclusive perineurial differentiation.5 Perineurioma is divided into intraneural and extraneural types; the latter are further subclassified into soft tissue, sclerosing, reticular, and plexiform types. Other rare forms include the sclerosing, Pacinian corpuscle-like perineurioma, lipomatous perineurioma, perineurioma with xanthomatous areas, and perineurioma with granular cells.6,7
Clinically, sclerosing perineurioma usually presents as a solitary lesion; however, rare cases of multiple lesions have been reported.8 Our patient presented with a solitary papule on the nose. Histopathologically, sclerosing perineurioma demonstrates slender spindle cells in a whorled growth pattern (onion skin) embedded in a hyalinized, lamellar, and dense collagenous stroma with intervening cleftlike spaces. Immunohistochemically, the spindle cells of our case stained positive for epithelial membrane antigen (quiz images). Other positive immunostains for perineurioma include claudin-1 and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1). Perineurioma lacks expression of S-100 but can express CD34.2 As a benign tumor, the prognosis of sclerosing perineurioma is excellent. Complete local excision is considered curative.1
Angiofibroma, also known as fibrous papule, is a common and benign lesion located primarily on or in close proximity to the nose.9 Angiofibromas can be associated with genodermatoses such as tuberous sclerosis, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1, or Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. When angiofibromas involve the penis, they are called pearly penile papules. Ungual angiofibroma, also known as Koenen tumor, occurs underneath the nail.10-12 Both facial angiofibromas (>3) and ungual angiofibromas (>2) are independent major criteria for tuberous sclerosis.13 Clinically, angiofibroma presents as a small, dome-shaped, pink papule arising on the lower portion of the nose or nearby area of the central face. Histopathologically, angiofibromas classically demonstrate increased dilated vessels and fibrosis in the dermis. Stellate, plump, spindle-shaped, and multinucleated cells can be seen in the collagenous stroma. The collagen fibers around hair follicles are arranged concentrically, resulting in an onion skin-like appearance. The epidermal rete ridges can be effaced (Figure 1). Increased numbers of single-unit melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction can be seen in some cases. Immunohistochemically, a variable number of spindled and multinucleated cells in the dermis stain with factor XIIIa. There are at least 7 histologic variants of angiofibroma including hypercellular, pigmented, inflammatory, pleomorphic, clear cell, granular cell, and epithelioid.9,14
Desmoplastic nevus (DN) is a benign melanocytic neoplasm characterized by predominantly spindle-shaped nevus cells embedded within a fibrotic stroma. Although it can resemble a Spitz nevus, it is recognized as a distinct entity.15-17 Clinically, DN presents as a small and flesh-colored, erythematous or slightly pigmented papule or nodule that usually occurs on the arms and legs of young adults. Histopathologically, DN demonstrates a dermal-based proliferation of spindled melanocytes embedded in a dense collagenous stroma with sparse or absent melanin deposition. The collagen bundles often show artifactual clefts and onion skin-like accentuation around vessels. Melanocytes may be epithelioid (Figure 2).16 Immunohistochemically, DN expresses melanocytic markers such as S-100, Melan-A, and human melanoma black 45, but epithelial membrane antigen is negative. Human melanoma black 45 demonstrates maturation with stronger staining in superficial portions of the lesion and diminution of staining with increasing dermal depth.18 Many other melanocytic tumors share histologic similarities to DN including blue nevus and desmoplastic melanoma.17,19,20
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma, also referred to as solitary circumscribed neuroma, was first described by Reed et al21 in 1972. It is a benign and solitary, firm, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papule that occurs in middle-aged adults, predominately near mucocutaneous junctions of the face. Other locations include the oral mucosa, eyelid, nasal fossa, shoulder, arm, hand, foot, and glans penis.22,23 Histopathologically, palisaded encapsulated neuroma demonstrates a solitary, well-circumscribed, partially encapsulated, intradermal nodule composed of interweaving fascicles of spindle cells with prominent clefts (Figure 3). Rarely, palisaded encapsulated neuroma may have a plexiform or multinodular architecture.24 Immunohistochemically, tumor cells stain positively for S-100 protein, type IV collagen, and vimentin. The capsule, composed of perineural cells, stains positive for epithelial membrane antigen. A neurofilament stain will highlight axons within the tumor.24,25 Currently, palisaded encapsulated neuroma does not have a well-established link to known neurocutaneous or inherited syndromes. Excision is curative with a low risk of recurrence.26
Sclerotic fibromas (SFs) were first reported by Weary et al27 as multiple tumors involving the tongues of patients with Cowden syndrome. Sporadic or solitary SFs of the skin in patients without Cowden syndrome have been reported, and both multiple and solitary SFs present with similar pathologic changes.28-30 Clinically, the solitary variant manifests as a well-demarcated, flesh-colored to erythematous, waxy papule or nodule with no site or sex predilection.30,31 Histologically, SF demonstrates a well-demarcated, nonencapsulated dermal nodule composed of hypocellular and sclerotic collagen bundles with scattered spindled cells and prominent clefts resembling Vincent van Gogh's Starry Night or plywood (Figure 4). Immunohistochemically, the spindled cells strongly express CD34. Factor XIIIa and markers of melanocytic, neural, and muscular differentiation are negative. When rendering a diagnosis in a patient with multiple SFs, a comment regarding the possibility of Cowden syndrome should be mentioned.32

A 54-year-old man presented with painful, nonpruritic, erythematous papules that began on the scrotum. The eruption progressed to involve the...
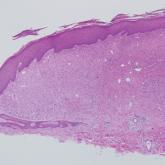
A 28-year-old man presented with a growing asymptomatic papule on the right leg.

A 37-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic, indurated, pigmented, subcutaneous nodule on the right shoulder of more than 3 years' duration...
