Photo Challenge
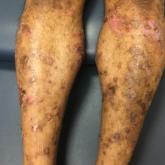
Bullae and Hyperpigmented Patches on the Legs
A 50-year-old man presented with a pruritic bullous dermatosis on the lower legs, arms, and back of 1 month’s duration. He had an 8-year history...
Dr. Spring is from the Department of Dermatology, Naval Medical Center, Camp Lejeune, North Carolina. Dr. Pybus is from the Department of Internal Medicine, Naval Medical Center San Diego, California. Dr. Crandall is from Arizona Dermatology, Phoenix.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the US Government.
Correspondence: Leah K. Spring, DO, 100 Brewster Ave, Camp Lejeune, NC 28547 (leah.k.spring@gmail.com).

A 42-year-old man presented with pruritic axillary plaques of 6 months’ duration that were exacerbated by heat and friction. He maintained a very active lifestyle and used an antiperspirant regularly. He denied any family history of similar lesions. Thick emollients provided no relief. Physical examination demonstrated numerous soft, hyperkeratotic, waxy, yellowish brown papules coalescing into plaques localized to the bilateral axillary vaults, affecting the right axilla more than the left. Although some papules were firmly adherent to the skin, others were friable and easily removed with a cotton-tipped applicator, revealing an underlying, faintly erythematous base.
Microscopic examination of a punch biopsy from the left axilla revealed verruciform epidermal hyperplasia with overlying parakeratosis and retention of keratohyalin granules in the stratum corneum (Figure). There was no evidence of acantholysis, dyskeratosis, epidermal neutrophils, or neutrophilic microabscesses.
The patient's history and characteristic histopathologic findings confirmed the diagnosis of granular parakeratosis (GP). He was instructed to discontinue his current antiperspirant and began treatment with topical fluocinolone oil 0.01% every morning and urea cream 20% every night. Complete resolution was achieved within 2 weeks, and he reported no recurrence at a 2-year follow-up visit.
Granular parakeratosis is a rare idiopathic skin condition characterized by hyperkeratotic papules and plaques, most often in intertriginous areas. Described by Northcutt et al1 as a contact reaction to antiperspirant in the axillae, GP also has been reported in the submammary and inguinal creases2 and rarely in nonintertriginous sites such as the abdomen.3 Although deodorants and antiperspirants in roll-on or stick form classically are implicated in GP, the condition also has been observed with exposure to laundry detergents containing benzalkonium chloride.4 Lesions with GP histology also have been incidentally observed in association with dermatophytosis,5 dermatomyositis,6 molluscum contagiosum,7 and carcinomas.8 Ding et al9 proposed that GP be reclassified as a reaction pattern observed in the skin as opposed to being a distinct disease entity.
Clinically, GP presents as pruritic intertriginous papules and coalescent plaques that most commonly are seen in the axillae but also may involve the groin or other sites.2,3 Both pruritus and disease burden can be aggravated by heat, sweating, or friction. There may be a history of a new irritant exposure prior to symptom onset, but GP has been observed in the absence of identifiable exposures and in the setting of long-term antiperspirant or deodorant use.3 Although a family history may be helpful, it can be difficult to distinguish GP from entities such as Hailey-Hailey disease or Darier disease based on history and examination alone; a biopsy often is necessary for definitive diagnosis.
Histologically, GP demonstrates acanthosis with parakeratosis and retention of keratohyalin granules in the stratum corneum.1 The stratum granulosum is preserved. On cursory examination, GP may resemble a psoriasiform dermatosis as can be seen in inverse psoriasis; however, neutrophilic microabscesses and infiltrates are not seen. Absence of acantholysis and dyskeratosis further differentiates GP from the clinically similar Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease. Spongiosis that is prominently found in allergic contact dermatitis also is absent.
Although a benign disorder, GP warrants treatment to achieve symptomatic relief. A mainstay of treatment is to eliminate exposure to suspected aggravating or inciting factors such as antiperspirants or deodorants. A variety of treatments including laser therapy, corticosteroids, isotretinoin, and vitamin D analogs such as calcipotriene and calcitriol have been reported to be effective treatments of GP in case studies and series.3,10 Large-scale clinical trials are not available because of the rarity of this condition. Our patient's clinical course suggests topical fluocinolone and urea in combination can be considered to achieve rapid resolution.

A 50-year-old man presented with a pruritic bullous dermatosis on the lower legs, arms, and back of 1 month’s duration. He had an 8-year history...
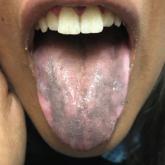
An otherwise healthy 17-year-old adolescent girl from Spain presented with hyperpigmentation on the tongue of several weeks’ duration. She denied...
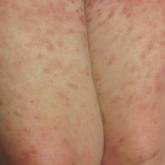
A woman in her seventies presented with a painful rash of 3 months’ duration, as well as fever, diaphoresis, and arthralgia of 3 weeks’ duration....
