Methods
Setting
The University of Michigan (UM) hospital is a 1000-bed tertiary care center in Ann Arbor, Michigan. The UM guidelines reflect evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of HIT.4 In 2016 the UM guidelines for laboratory testing included sending the PF4 antibody test first when there was clinical suspicion of HIT. The SRA was to be sent separately only when the PF4 returned positive (OD ≥ 0.400). Standard guidelines at UM also included switching patients with suspected HIT from heparin to a nonheparin anticoagulant and stopping all heparin products while awaiting the SRA results. The direct thrombin inhibitor argatroban is utilized at UM and monitored with anti-IIa levels. University of Michigan Hospital utilizes the Immucor PF4 IgG ELISA for detecting heparin-associated antibodies.9 In 2016, this PF4 test was performed in the UM onsite laboratory Monday through Friday. At UM the SRA is performed off site, with a turnaround time of 3 to 5 business days.
Baseline Data
We retrospectively reviewed PF4 and SRA testing as well as argatroban usage from December 2016 to May 2017. Despite the institutional guidelines, providers were sending PF4 and SRA simultaneously as soon as HIT was suspected; 62% of PF4 tests were ordered simultaneously with the SRA, but only 8% of these PF4 tests were positive with an OD ≥0.400. Of those patients with negative PF4 testing, argatroban was continued until the SRA returned negative, leading to many days of unnecessary argatroban usage. An informal survey of the anticoagulation pharmacists revealed that many recommended discontinuing argatroban when the PF4 test was negative, but providers routinely did not feel comfortable with this approach. This suggested many providers misunderstood the performance characteristics of the PF4 test.
Intervention
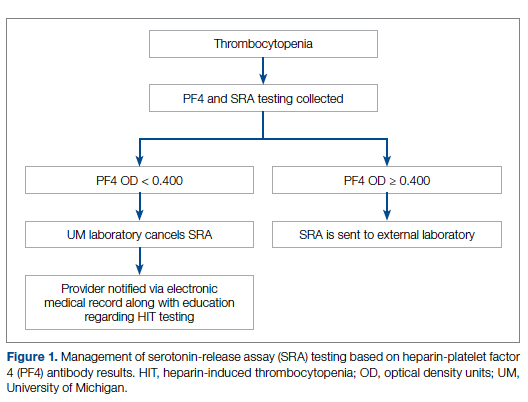
Our team consisted of hematology and internal medicine faculty, pharmacists, coagulation laboratory personnel, and quality improvement specialists. We designed and implemented an intervention in November 2017 focused on controlling the ordering of the SRA test. We chose to focus on this step due to the excellent sensitivity of the PF4 test with a cutoff of OD <0.400 and the significant expense of the SRA test. Under direction of the Coagulation Laboratory Director, a standard operating procedure was developed where the coagulation laboratory personnel did not send out the SRA until a positive PF4 test (OD ≥ 0.400) was reported. If the PF4 was negative, the SRA was canceled and the ordering provider received notification of the cancelled test via the electronic medical record, accompanied by education about HIT testing (Figure 1). In addition, the lab increased the availability of PF4 testing from 5 days to 7 days a week so there were no delays in tests ordered on Fridays or weekends.
Outcomes
Our primary goals were to decrease both SRA testing and argatroban use. Secondarily, we examined the cost-effectiveness of this intervention. We hypothesized that controlling the SRA testing at the laboratory level would decrease both SRA testing and argatroban use.
Data Collection
Pre- and postintervention data were collected retrospectively. Pre-intervention data were from January 2016 through November 2017, and postintervention data were from December 2017 through March 2020. The number of SRA tests performed were identified retrospectively via review of electronic ordering records. All patients who had a hospital admission after January 1, 2016, were included. These patients were filtered to include only those who had a result for an SRA test. In order to calculate cost-savings, we identified both the number of SRA tests ordered retrospectively as well as patients who had both an SRA resulted and had been administered argatroban. Cost-savings were calculated based on our institutional cost of $357 per SRA test.
At our institution, argatroban is supplied in 50-mL bags; therefore, we utilized the number of bags to identify argatroban usage. Savings were calculated using the average wholesale price (AWP) of $292.50 per 50-mL bag. The amounts billed or collected for the SRA testing or argatroban treatment were not collected. Costs were estimated using only direct costs to the institution. Safety data were not collected. As the intent of our project was a quality improvement activity, this project did not require institutional review board regulation per our institutional guidance.