User login
Challenges in managing chronic pelvic pain in women
Medical science’s broad knowledge of endometriosis notwithstanding, “many questions remain unanswered” about the management of a condition that is often refractory to established therapies, observed Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, at the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada. Dr. As-Sanie is Associate Professor and Director, Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery Fellowship, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. How, then, should clinicians approach the challenge of caring for women with this enigmatic disease in the larger context of chronic pelvic pain, in which, as Dr. As-Sanie said, “one size never fits all”?
Complex correlation between endometriosis and CPP
Despite high prevalence and negative impact on the health and quality of life of women who suffer from endometriosis, Dr. As-Sanie emphasized, it remains unclear why only some women with endometriosis develop chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and why there is little, if any, correlation between disease severity and the intensity of pain.
The clinical approach to endometriosis and CPP can be frustrating for several reasons: there is minimal relationship between extent or location of disease with pain symptoms; there is no consistent relationship among inflammatory markers, nerve-fiber density, and pain symptoms; and pain can recur after medical and surgical therapy—often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis. Furthermore, the differential diagnosis of CPP is broad, and also includes adenomyosis, adhesions, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids, pelvic congestion, ovarian remnant, and residual ovarian syndrome. Chronic overlapping pain conditions are prevalent, too, including interstitial cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and vulvodynia, to name a few.1
_
CPP is not just a pain disorder
Dr. As-Sanie said that understanding of CPP must extend to include fatigue, memory difficulties, poor sleep, and heightened sensitivity to multiple sensory stimuli (e.g., sound and light).2 So what, she asked, do we know about endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, and the brain? We know that CPP, with and without endometriosis, is associated with increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function.3-5 Central amplification of pain can lead to chronic pain independent of nociceptive signals, including multifocal, widespread pain; higher lifetime history of pain throughout the body; and pain triggered or exacerbated by stressors. And CPP brings with it other, potentially debilitating problems, including elevated distress, decreased activity, isolation, poor sleep, and maladaptive illness behaviors.
Finding, then addressing, the culprit
Identifying the underlying cause(s) of CPP in the individual woman should guide clinical care. This includes the decision to proceed with, or avoid, surgery. Remember: Patients with centralized pain respond differently to therapy; surgery is less likely to help relieve the pain.
Dr. As-Sanie offered several fundamental guidelines for managing CPP:
- Treat early, to prevent transition from acute to chronic pain; treatment delay increases connectivity between pain regulatory regions.
- Hysterectomy is not definitive therapy for all women with endometriosis or CPP.6
- Take a multisystem approach, comprising medical, behavioral, and interventional strategies.
- If an organ- or disease-based diagnostic and treatment approach does not work, reconsider the diagnosis; re-evaluate comorbid psychosocial variables; and consider treating centralized pain.
- Choice of treatment should include consideration of cost and adverse-effect profile.
- If one modality is ineffective, try another.
Continue to: What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
Available pharmacotherapeutic agents have modest benefit, possibly because the population of pain patients is heterogeneous, with various underlying mechanisms of pain. And, Dr. As-Sanie pointed out, clinical tools do not currently exist to pre-emptively select the right medicine for individual patients.
Evidence is strong, Dr. As-Sanie noted, for dual reuptake-inhibitor antidepressants, such as tricyclic compounds (amitriptyline, cyclobenzaprine) and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and for anticonvulsants with analgesic properties (pregabalin, gabapentin). Evidence is “modest,” Dr. As-Sanie said, for tramadol, gamma hydroxybutyrate, and low-dose naltrexone, and “weak” for cannabinoids, human growth hormone, 5-hydroxytryptamine, tropisetron, and S-adenosyl-L-methionine. There is no evidence for using opioids, corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, benzodiazepine and non–benzodiazepine hypnotics, or guaifenesin.7
When surgery or pharmacotherapy alone fail to yield the necessary outcome, consider adjunctive nonpharmacotherapy.8 For example, there is strong evidence for patient education, aerobic exercise, and cognitive behavior therapy; modest evidence for acupressure, acupuncture, strength training, hypnotherapy, biofeedback, trigger-point injection, and neuromodulation; but only weak evidence for chiropractic, manual and massage therapy, electrotherapy, and ultrasound. 7
_
With CPP, “one size never fits all”
Dr. As-Sanie concluded with a reminder that CPP can be the product of any of a range of underlying contributory causes. Pathology might stand foremost as you search for the source of pain and an effective treatment, but keep in mind that genetics, environment, co-existing pain conditions, the patient’s ability to cope, and her resilience and social support might play a role.
- Veasley C, Clare D, Clauw DJ, et al; Chronic Pain Research Alliance. Impact of chronic overlapping pain conditions on public health and the urgent need for safe and effective treatment. 2015 analysis and policy recommendations. May 2015. http://chronicpainresearch.org/public/CPRA_WhitePaper_2015-FINAL-Digital.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311:1547-1555.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Harte SE, et al. Increased pressure pain sensitivity in women with chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:1047-1055.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Napadow V, et al. Changes in regional gray matter volume in women with chronic pelvic pain: a voxel-based morphometry study. Pain. 2012;153(5):1006-1014.
- As-Sanie S, Kim J, Schmidt-Wilcke T, et al. Functional connectivity is associated with altered brain chemistry in women with endometriosis-associated chronic pelvic pain. J Pain. 2016;17:1-13.
- Brandsborg B. Pain following hysterectomy: epidemiological and clinical aspects. Dan Med J. 2012;59:B4374.
- Goldenberg DL, Burckhardt C, Crofford L. Management of fibromyalgia syndrome. JAMA. 2004;292:2388-2395.
- Till SR, Wahl HN, As-Sanie S. The role of nonpharmacologic therapies in management of chronic pelvic pain: what to do when surgery fails. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2017;29:231-239.
Medical science’s broad knowledge of endometriosis notwithstanding, “many questions remain unanswered” about the management of a condition that is often refractory to established therapies, observed Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, at the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada. Dr. As-Sanie is Associate Professor and Director, Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery Fellowship, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. How, then, should clinicians approach the challenge of caring for women with this enigmatic disease in the larger context of chronic pelvic pain, in which, as Dr. As-Sanie said, “one size never fits all”?
Complex correlation between endometriosis and CPP
Despite high prevalence and negative impact on the health and quality of life of women who suffer from endometriosis, Dr. As-Sanie emphasized, it remains unclear why only some women with endometriosis develop chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and why there is little, if any, correlation between disease severity and the intensity of pain.
The clinical approach to endometriosis and CPP can be frustrating for several reasons: there is minimal relationship between extent or location of disease with pain symptoms; there is no consistent relationship among inflammatory markers, nerve-fiber density, and pain symptoms; and pain can recur after medical and surgical therapy—often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis. Furthermore, the differential diagnosis of CPP is broad, and also includes adenomyosis, adhesions, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids, pelvic congestion, ovarian remnant, and residual ovarian syndrome. Chronic overlapping pain conditions are prevalent, too, including interstitial cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and vulvodynia, to name a few.1
_
CPP is not just a pain disorder
Dr. As-Sanie said that understanding of CPP must extend to include fatigue, memory difficulties, poor sleep, and heightened sensitivity to multiple sensory stimuli (e.g., sound and light).2 So what, she asked, do we know about endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, and the brain? We know that CPP, with and without endometriosis, is associated with increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function.3-5 Central amplification of pain can lead to chronic pain independent of nociceptive signals, including multifocal, widespread pain; higher lifetime history of pain throughout the body; and pain triggered or exacerbated by stressors. And CPP brings with it other, potentially debilitating problems, including elevated distress, decreased activity, isolation, poor sleep, and maladaptive illness behaviors.
Finding, then addressing, the culprit
Identifying the underlying cause(s) of CPP in the individual woman should guide clinical care. This includes the decision to proceed with, or avoid, surgery. Remember: Patients with centralized pain respond differently to therapy; surgery is less likely to help relieve the pain.
Dr. As-Sanie offered several fundamental guidelines for managing CPP:
- Treat early, to prevent transition from acute to chronic pain; treatment delay increases connectivity between pain regulatory regions.
- Hysterectomy is not definitive therapy for all women with endometriosis or CPP.6
- Take a multisystem approach, comprising medical, behavioral, and interventional strategies.
- If an organ- or disease-based diagnostic and treatment approach does not work, reconsider the diagnosis; re-evaluate comorbid psychosocial variables; and consider treating centralized pain.
- Choice of treatment should include consideration of cost and adverse-effect profile.
- If one modality is ineffective, try another.
Continue to: What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
Available pharmacotherapeutic agents have modest benefit, possibly because the population of pain patients is heterogeneous, with various underlying mechanisms of pain. And, Dr. As-Sanie pointed out, clinical tools do not currently exist to pre-emptively select the right medicine for individual patients.
Evidence is strong, Dr. As-Sanie noted, for dual reuptake-inhibitor antidepressants, such as tricyclic compounds (amitriptyline, cyclobenzaprine) and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and for anticonvulsants with analgesic properties (pregabalin, gabapentin). Evidence is “modest,” Dr. As-Sanie said, for tramadol, gamma hydroxybutyrate, and low-dose naltrexone, and “weak” for cannabinoids, human growth hormone, 5-hydroxytryptamine, tropisetron, and S-adenosyl-L-methionine. There is no evidence for using opioids, corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, benzodiazepine and non–benzodiazepine hypnotics, or guaifenesin.7
When surgery or pharmacotherapy alone fail to yield the necessary outcome, consider adjunctive nonpharmacotherapy.8 For example, there is strong evidence for patient education, aerobic exercise, and cognitive behavior therapy; modest evidence for acupressure, acupuncture, strength training, hypnotherapy, biofeedback, trigger-point injection, and neuromodulation; but only weak evidence for chiropractic, manual and massage therapy, electrotherapy, and ultrasound. 7
_
With CPP, “one size never fits all”
Dr. As-Sanie concluded with a reminder that CPP can be the product of any of a range of underlying contributory causes. Pathology might stand foremost as you search for the source of pain and an effective treatment, but keep in mind that genetics, environment, co-existing pain conditions, the patient’s ability to cope, and her resilience and social support might play a role.
Medical science’s broad knowledge of endometriosis notwithstanding, “many questions remain unanswered” about the management of a condition that is often refractory to established therapies, observed Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, at the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada. Dr. As-Sanie is Associate Professor and Director, Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery Fellowship, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. How, then, should clinicians approach the challenge of caring for women with this enigmatic disease in the larger context of chronic pelvic pain, in which, as Dr. As-Sanie said, “one size never fits all”?
Complex correlation between endometriosis and CPP
Despite high prevalence and negative impact on the health and quality of life of women who suffer from endometriosis, Dr. As-Sanie emphasized, it remains unclear why only some women with endometriosis develop chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and why there is little, if any, correlation between disease severity and the intensity of pain.
The clinical approach to endometriosis and CPP can be frustrating for several reasons: there is minimal relationship between extent or location of disease with pain symptoms; there is no consistent relationship among inflammatory markers, nerve-fiber density, and pain symptoms; and pain can recur after medical and surgical therapy—often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis. Furthermore, the differential diagnosis of CPP is broad, and also includes adenomyosis, adhesions, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids, pelvic congestion, ovarian remnant, and residual ovarian syndrome. Chronic overlapping pain conditions are prevalent, too, including interstitial cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and vulvodynia, to name a few.1
_
CPP is not just a pain disorder
Dr. As-Sanie said that understanding of CPP must extend to include fatigue, memory difficulties, poor sleep, and heightened sensitivity to multiple sensory stimuli (e.g., sound and light).2 So what, she asked, do we know about endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, and the brain? We know that CPP, with and without endometriosis, is associated with increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function.3-5 Central amplification of pain can lead to chronic pain independent of nociceptive signals, including multifocal, widespread pain; higher lifetime history of pain throughout the body; and pain triggered or exacerbated by stressors. And CPP brings with it other, potentially debilitating problems, including elevated distress, decreased activity, isolation, poor sleep, and maladaptive illness behaviors.
Finding, then addressing, the culprit
Identifying the underlying cause(s) of CPP in the individual woman should guide clinical care. This includes the decision to proceed with, or avoid, surgery. Remember: Patients with centralized pain respond differently to therapy; surgery is less likely to help relieve the pain.
Dr. As-Sanie offered several fundamental guidelines for managing CPP:
- Treat early, to prevent transition from acute to chronic pain; treatment delay increases connectivity between pain regulatory regions.
- Hysterectomy is not definitive therapy for all women with endometriosis or CPP.6
- Take a multisystem approach, comprising medical, behavioral, and interventional strategies.
- If an organ- or disease-based diagnostic and treatment approach does not work, reconsider the diagnosis; re-evaluate comorbid psychosocial variables; and consider treating centralized pain.
- Choice of treatment should include consideration of cost and adverse-effect profile.
- If one modality is ineffective, try another.
Continue to: What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
What are the levels of evidence for centralized pain treatment?
Available pharmacotherapeutic agents have modest benefit, possibly because the population of pain patients is heterogeneous, with various underlying mechanisms of pain. And, Dr. As-Sanie pointed out, clinical tools do not currently exist to pre-emptively select the right medicine for individual patients.
Evidence is strong, Dr. As-Sanie noted, for dual reuptake-inhibitor antidepressants, such as tricyclic compounds (amitriptyline, cyclobenzaprine) and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and for anticonvulsants with analgesic properties (pregabalin, gabapentin). Evidence is “modest,” Dr. As-Sanie said, for tramadol, gamma hydroxybutyrate, and low-dose naltrexone, and “weak” for cannabinoids, human growth hormone, 5-hydroxytryptamine, tropisetron, and S-adenosyl-L-methionine. There is no evidence for using opioids, corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, benzodiazepine and non–benzodiazepine hypnotics, or guaifenesin.7
When surgery or pharmacotherapy alone fail to yield the necessary outcome, consider adjunctive nonpharmacotherapy.8 For example, there is strong evidence for patient education, aerobic exercise, and cognitive behavior therapy; modest evidence for acupressure, acupuncture, strength training, hypnotherapy, biofeedback, trigger-point injection, and neuromodulation; but only weak evidence for chiropractic, manual and massage therapy, electrotherapy, and ultrasound. 7
_
With CPP, “one size never fits all”
Dr. As-Sanie concluded with a reminder that CPP can be the product of any of a range of underlying contributory causes. Pathology might stand foremost as you search for the source of pain and an effective treatment, but keep in mind that genetics, environment, co-existing pain conditions, the patient’s ability to cope, and her resilience and social support might play a role.
- Veasley C, Clare D, Clauw DJ, et al; Chronic Pain Research Alliance. Impact of chronic overlapping pain conditions on public health and the urgent need for safe and effective treatment. 2015 analysis and policy recommendations. May 2015. http://chronicpainresearch.org/public/CPRA_WhitePaper_2015-FINAL-Digital.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311:1547-1555.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Harte SE, et al. Increased pressure pain sensitivity in women with chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:1047-1055.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Napadow V, et al. Changes in regional gray matter volume in women with chronic pelvic pain: a voxel-based morphometry study. Pain. 2012;153(5):1006-1014.
- As-Sanie S, Kim J, Schmidt-Wilcke T, et al. Functional connectivity is associated with altered brain chemistry in women with endometriosis-associated chronic pelvic pain. J Pain. 2016;17:1-13.
- Brandsborg B. Pain following hysterectomy: epidemiological and clinical aspects. Dan Med J. 2012;59:B4374.
- Goldenberg DL, Burckhardt C, Crofford L. Management of fibromyalgia syndrome. JAMA. 2004;292:2388-2395.
- Till SR, Wahl HN, As-Sanie S. The role of nonpharmacologic therapies in management of chronic pelvic pain: what to do when surgery fails. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2017;29:231-239.
- Veasley C, Clare D, Clauw DJ, et al; Chronic Pain Research Alliance. Impact of chronic overlapping pain conditions on public health and the urgent need for safe and effective treatment. 2015 analysis and policy recommendations. May 2015. http://chronicpainresearch.org/public/CPRA_WhitePaper_2015-FINAL-Digital.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311:1547-1555.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Harte SE, et al. Increased pressure pain sensitivity in women with chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:1047-1055.
- As-Sanie S, Harris RE, Napadow V, et al. Changes in regional gray matter volume in women with chronic pelvic pain: a voxel-based morphometry study. Pain. 2012;153(5):1006-1014.
- As-Sanie S, Kim J, Schmidt-Wilcke T, et al. Functional connectivity is associated with altered brain chemistry in women with endometriosis-associated chronic pelvic pain. J Pain. 2016;17:1-13.
- Brandsborg B. Pain following hysterectomy: epidemiological and clinical aspects. Dan Med J. 2012;59:B4374.
- Goldenberg DL, Burckhardt C, Crofford L. Management of fibromyalgia syndrome. JAMA. 2004;292:2388-2395.
- Till SR, Wahl HN, As-Sanie S. The role of nonpharmacologic therapies in management of chronic pelvic pain: what to do when surgery fails. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2017;29:231-239.
Uterine tissue extraction: An update, with a look at tools and techniques
At the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada, Tommaso Falcone, MD, Chief of Staff, Chief Academic Officer, and Medical Director at Cleveland Clinic London, England, addressed the status of tissue morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy after several years’ controversy—noting that the specialty’s professional societies all support use of the technique, with precautions and in selected patients.
Morcellation history
Should electromechanical (‘power’) morcellation of tissue be a tool for performing minimally invasive hysterectomy and myomectomy? If so, what are the risks and benefits of using this tool, first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995?
The matter came under intense scrutiny and debate in 2014 as concerns rose about the potential of power morcellation to disseminate intraperitoneal malignancy in women with occult cancer (an estimated 1 in 370 women who undergo power morcellation during a minimally invasive hysterectomy have uterine cancer1). Early that year, the FDA moved to strongly discourage use of power morcellators for removing uterine fibroids.2
The aftermath, however, was that there were problems with the FDA’s [2014] statement, Dr. Falcone pointed out. In a study by Siedhoff and colleagues of a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 women with fibroids, for example, an abdominal approach resulted in more hysterectomy-related deaths and surgery-related complications than did a laparoscopic procedure with morcellation.3
Balancing risks and benefits of MIS
After continuing study of the risks presented by morcellation, the question today is: How do we balance preventing dissemination of cancer against diminishing the significant benefits of minimally invasive surgery, as surgical technique has been modified to avoid morcellation—including, Dr. Falcone said, by increased use of mini lap (i.e., extending the laparoscopy incision) tissue extraction, decreased use of supracervical hysterectomy, and a move to open approaches.
In fact, Dr. Falcone noted, power morcellation is banned in many institutions, having been replaced by scalpel, extraperitoneal, or in-bag morcellation. Last year, after further analysis, the FDA reiterated its recommendation against use of power morcellators to remove fibroids in most women.4
Continue to: Morcellation decisions
Morcellation decisions
Dr. Falcone pointed out that, at the Cleveland Clinic, morcellation is not performed in postmenopausal women, and for several other contraindications, including a history of >2 years of tamoxifen therapy; history of pelvic radiation; history of childhood retinoblastoma; personal history of hereditary leiomyomatosis or renal cell carcinoma; and the presence of a cancer-positive tissue specimen. Morcellation is not performed unless endometrial adenocarcinoma has been ruled out. The decision-making process when electing to use tissue extraction includes whether to use contained or noncontained morcellation; whether to favor knife excision over power morcellation; and, when using a mini lap approach, whether to proceed via the umbilicus or suprapubically.
Complications of morcellation include direct injury by the morcellator; dissemination, as noted, of tissue; ‘upstaging’ of uterine sarcoma, with a worsening prognosis; seeding of parasitic fibroids; and reoperation with laparotomy and extensive multi-organ resection to clear disease (3 patients in a published report).5
An important advancement in the use of morcellation in minimally invasive hysterectomy or myomectomy has been the development of contained systems for morcellating—generally a plastic specimen bag, sometimes pulled through the port and insufflated. Dr. Falcone’s presentation included video presentations of this important, and still evolving, technology. Whether these contained systems improve survival, and whether using them in a vaginal approach makes any difference, remain uncertain, however. Furthermore, some spillage from bags is inevitable—although how much spillage is clinically significant is open to question.
Takeaways
Dr. Falcone concluded with key points to guide the surgeon’s decision on whether to proceed with morcellation:
- There are no comparative data on which technique [of tissue removal] is best.
- Tissue spill will occur in uncontained morcellation—this is intrinsic to the device.
- Even with the current generation of tissue bags, leakage is common and puncture is possible.
If you choose to continue to use power morcellation, your decision is supported by the fact that all the professional societies still support it, Dr. Falcone noted. Furthermore, he pointed out that it is important to look to the standard of care in your community regarding risks and benefits before proceeding.
Last, the advantages and risks of morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy should be part of an in-depth discussion between patient and surgeon prior to the procedure. And you must, Dr. Falcone emphasized, obtain specific informed consent.
- Wright JD, Tergas AI, Burke WM, et al. Uterine pathology in women undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomy using morcellation. JAMA. Published online July 22, 2014. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170722215727/https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated June 6, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Siedhoff MT, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:591.e1–e8.
- FDA In Brief: FDA releases new findings on the risks of spreading hidden uterine cancer through the use of laparoscopic power morcellators. https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/fdainbrief/ucm589137.htm. Updated December 14, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Ramos A, Fader AN, Roche KL. Surgical cytoreduction for disseminated benign disease after open power uterine morcellation. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:99-102.
At the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada, Tommaso Falcone, MD, Chief of Staff, Chief Academic Officer, and Medical Director at Cleveland Clinic London, England, addressed the status of tissue morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy after several years’ controversy—noting that the specialty’s professional societies all support use of the technique, with precautions and in selected patients.
Morcellation history
Should electromechanical (‘power’) morcellation of tissue be a tool for performing minimally invasive hysterectomy and myomectomy? If so, what are the risks and benefits of using this tool, first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995?
The matter came under intense scrutiny and debate in 2014 as concerns rose about the potential of power morcellation to disseminate intraperitoneal malignancy in women with occult cancer (an estimated 1 in 370 women who undergo power morcellation during a minimally invasive hysterectomy have uterine cancer1). Early that year, the FDA moved to strongly discourage use of power morcellators for removing uterine fibroids.2
The aftermath, however, was that there were problems with the FDA’s [2014] statement, Dr. Falcone pointed out. In a study by Siedhoff and colleagues of a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 women with fibroids, for example, an abdominal approach resulted in more hysterectomy-related deaths and surgery-related complications than did a laparoscopic procedure with morcellation.3
Balancing risks and benefits of MIS
After continuing study of the risks presented by morcellation, the question today is: How do we balance preventing dissemination of cancer against diminishing the significant benefits of minimally invasive surgery, as surgical technique has been modified to avoid morcellation—including, Dr. Falcone said, by increased use of mini lap (i.e., extending the laparoscopy incision) tissue extraction, decreased use of supracervical hysterectomy, and a move to open approaches.
In fact, Dr. Falcone noted, power morcellation is banned in many institutions, having been replaced by scalpel, extraperitoneal, or in-bag morcellation. Last year, after further analysis, the FDA reiterated its recommendation against use of power morcellators to remove fibroids in most women.4
Continue to: Morcellation decisions
Morcellation decisions
Dr. Falcone pointed out that, at the Cleveland Clinic, morcellation is not performed in postmenopausal women, and for several other contraindications, including a history of >2 years of tamoxifen therapy; history of pelvic radiation; history of childhood retinoblastoma; personal history of hereditary leiomyomatosis or renal cell carcinoma; and the presence of a cancer-positive tissue specimen. Morcellation is not performed unless endometrial adenocarcinoma has been ruled out. The decision-making process when electing to use tissue extraction includes whether to use contained or noncontained morcellation; whether to favor knife excision over power morcellation; and, when using a mini lap approach, whether to proceed via the umbilicus or suprapubically.
Complications of morcellation include direct injury by the morcellator; dissemination, as noted, of tissue; ‘upstaging’ of uterine sarcoma, with a worsening prognosis; seeding of parasitic fibroids; and reoperation with laparotomy and extensive multi-organ resection to clear disease (3 patients in a published report).5
An important advancement in the use of morcellation in minimally invasive hysterectomy or myomectomy has been the development of contained systems for morcellating—generally a plastic specimen bag, sometimes pulled through the port and insufflated. Dr. Falcone’s presentation included video presentations of this important, and still evolving, technology. Whether these contained systems improve survival, and whether using them in a vaginal approach makes any difference, remain uncertain, however. Furthermore, some spillage from bags is inevitable—although how much spillage is clinically significant is open to question.
Takeaways
Dr. Falcone concluded with key points to guide the surgeon’s decision on whether to proceed with morcellation:
- There are no comparative data on which technique [of tissue removal] is best.
- Tissue spill will occur in uncontained morcellation—this is intrinsic to the device.
- Even with the current generation of tissue bags, leakage is common and puncture is possible.
If you choose to continue to use power morcellation, your decision is supported by the fact that all the professional societies still support it, Dr. Falcone noted. Furthermore, he pointed out that it is important to look to the standard of care in your community regarding risks and benefits before proceeding.
Last, the advantages and risks of morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy should be part of an in-depth discussion between patient and surgeon prior to the procedure. And you must, Dr. Falcone emphasized, obtain specific informed consent.
At the 2018 Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada, Tommaso Falcone, MD, Chief of Staff, Chief Academic Officer, and Medical Director at Cleveland Clinic London, England, addressed the status of tissue morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy after several years’ controversy—noting that the specialty’s professional societies all support use of the technique, with precautions and in selected patients.
Morcellation history
Should electromechanical (‘power’) morcellation of tissue be a tool for performing minimally invasive hysterectomy and myomectomy? If so, what are the risks and benefits of using this tool, first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995?
The matter came under intense scrutiny and debate in 2014 as concerns rose about the potential of power morcellation to disseminate intraperitoneal malignancy in women with occult cancer (an estimated 1 in 370 women who undergo power morcellation during a minimally invasive hysterectomy have uterine cancer1). Early that year, the FDA moved to strongly discourage use of power morcellators for removing uterine fibroids.2
The aftermath, however, was that there were problems with the FDA’s [2014] statement, Dr. Falcone pointed out. In a study by Siedhoff and colleagues of a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 women with fibroids, for example, an abdominal approach resulted in more hysterectomy-related deaths and surgery-related complications than did a laparoscopic procedure with morcellation.3
Balancing risks and benefits of MIS
After continuing study of the risks presented by morcellation, the question today is: How do we balance preventing dissemination of cancer against diminishing the significant benefits of minimally invasive surgery, as surgical technique has been modified to avoid morcellation—including, Dr. Falcone said, by increased use of mini lap (i.e., extending the laparoscopy incision) tissue extraction, decreased use of supracervical hysterectomy, and a move to open approaches.
In fact, Dr. Falcone noted, power morcellation is banned in many institutions, having been replaced by scalpel, extraperitoneal, or in-bag morcellation. Last year, after further analysis, the FDA reiterated its recommendation against use of power morcellators to remove fibroids in most women.4
Continue to: Morcellation decisions
Morcellation decisions
Dr. Falcone pointed out that, at the Cleveland Clinic, morcellation is not performed in postmenopausal women, and for several other contraindications, including a history of >2 years of tamoxifen therapy; history of pelvic radiation; history of childhood retinoblastoma; personal history of hereditary leiomyomatosis or renal cell carcinoma; and the presence of a cancer-positive tissue specimen. Morcellation is not performed unless endometrial adenocarcinoma has been ruled out. The decision-making process when electing to use tissue extraction includes whether to use contained or noncontained morcellation; whether to favor knife excision over power morcellation; and, when using a mini lap approach, whether to proceed via the umbilicus or suprapubically.
Complications of morcellation include direct injury by the morcellator; dissemination, as noted, of tissue; ‘upstaging’ of uterine sarcoma, with a worsening prognosis; seeding of parasitic fibroids; and reoperation with laparotomy and extensive multi-organ resection to clear disease (3 patients in a published report).5
An important advancement in the use of morcellation in minimally invasive hysterectomy or myomectomy has been the development of contained systems for morcellating—generally a plastic specimen bag, sometimes pulled through the port and insufflated. Dr. Falcone’s presentation included video presentations of this important, and still evolving, technology. Whether these contained systems improve survival, and whether using them in a vaginal approach makes any difference, remain uncertain, however. Furthermore, some spillage from bags is inevitable—although how much spillage is clinically significant is open to question.
Takeaways
Dr. Falcone concluded with key points to guide the surgeon’s decision on whether to proceed with morcellation:
- There are no comparative data on which technique [of tissue removal] is best.
- Tissue spill will occur in uncontained morcellation—this is intrinsic to the device.
- Even with the current generation of tissue bags, leakage is common and puncture is possible.
If you choose to continue to use power morcellation, your decision is supported by the fact that all the professional societies still support it, Dr. Falcone noted. Furthermore, he pointed out that it is important to look to the standard of care in your community regarding risks and benefits before proceeding.
Last, the advantages and risks of morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy should be part of an in-depth discussion between patient and surgeon prior to the procedure. And you must, Dr. Falcone emphasized, obtain specific informed consent.
- Wright JD, Tergas AI, Burke WM, et al. Uterine pathology in women undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomy using morcellation. JAMA. Published online July 22, 2014. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170722215727/https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated June 6, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Siedhoff MT, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:591.e1–e8.
- FDA In Brief: FDA releases new findings on the risks of spreading hidden uterine cancer through the use of laparoscopic power morcellators. https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/fdainbrief/ucm589137.htm. Updated December 14, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Ramos A, Fader AN, Roche KL. Surgical cytoreduction for disseminated benign disease after open power uterine morcellation. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:99-102.
- Wright JD, Tergas AI, Burke WM, et al. Uterine pathology in women undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomy using morcellation. JAMA. Published online July 22, 2014. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170722215727/https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated June 6, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Siedhoff MT, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:591.e1–e8.
- FDA In Brief: FDA releases new findings on the risks of spreading hidden uterine cancer through the use of laparoscopic power morcellators. https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/fdainbrief/ucm589137.htm. Updated December 14, 2017. Accessed December 10, 2018.
- Ramos A, Fader AN, Roche KL. Surgical cytoreduction for disseminated benign disease after open power uterine morcellation. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:99-102.
Does the preterm birth racial disparity persist among black and white IVF users?
Investigators from the National Institutes of Health and Shady Grove Fertility found that among women having a singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) that black women are at higher risk for lower gestational age and preterm delivery than white women.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Kate Devine, MD, coinvestigator of the retrospective cohort study said in an interview with OBG Management that “It’s been well documented that African Americans have a higher preterm birth rate in the United States compared to Caucasians and the overall population. While the exact mechanism of preterm birth is unknown and likely varied, and while the mechanism for the preterm birth rate being higher in African Americans is not well understood, it has been hypothesized that socioeconomic factors are responsible at least in part.”2 She added that the investigators used a population of women receiving IVF for the study because “access to reproductive care and IVF is in some way a leveling factor in terms of socioeconomics.”
Details of the study. The investigators reviewed all singleton IVF pregnancies ending in live birth among women self-identifying as white, black, Asian, or Hispanic from 2004 to 2016 at a private IVF practice (N=10,371). The primary outcome was gestational age at birth, calculated as the number of days from oocyte retrieval to birth, plus 14, among white, black, Asian, and Hispanic women receiving IVF.
Births among black women occurred more than 6 days earlier than births among white women. The researchers noted that some of the shorter gestations among the black women could be explained by the higher average body mass index of the group (P<.0001). Dr. Devine explained that another contributing factor was the higher incidence of fibroid uterus among the black women (P<.0001). But after adjusting for these and other demographic variables, the black women still delivered 5.5 days earlier than the white women, and they were more than 3 times as likely to have either very preterm or extremely preterm deliveries (TABLE).1
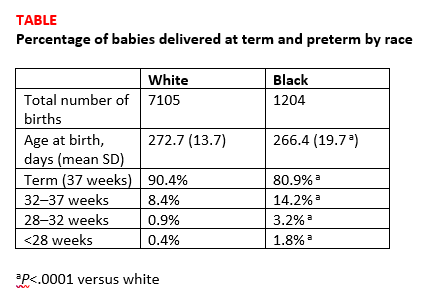
Research implications. Dr. Devine said that black pregnant patients “perhaps should be monitored more closely” for signs or symptoms suggestive of preterm labor and would like to see more research into understanding the mechanisms of preterm birth that are resulting in greater rates of preterm birth among black women. She mentioned that research into how fibroids impact obstetric outcomes is also important.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letters to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Bishop LA, Devine K, Sasson I, et al. Lower gestational age and increased risk of preterm birth associated with singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) among African American versus comparable Caucasian women. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e7.
Investigators from the National Institutes of Health and Shady Grove Fertility found that among women having a singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) that black women are at higher risk for lower gestational age and preterm delivery than white women.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Kate Devine, MD, coinvestigator of the retrospective cohort study said in an interview with OBG Management that “It’s been well documented that African Americans have a higher preterm birth rate in the United States compared to Caucasians and the overall population. While the exact mechanism of preterm birth is unknown and likely varied, and while the mechanism for the preterm birth rate being higher in African Americans is not well understood, it has been hypothesized that socioeconomic factors are responsible at least in part.”2 She added that the investigators used a population of women receiving IVF for the study because “access to reproductive care and IVF is in some way a leveling factor in terms of socioeconomics.”
Details of the study. The investigators reviewed all singleton IVF pregnancies ending in live birth among women self-identifying as white, black, Asian, or Hispanic from 2004 to 2016 at a private IVF practice (N=10,371). The primary outcome was gestational age at birth, calculated as the number of days from oocyte retrieval to birth, plus 14, among white, black, Asian, and Hispanic women receiving IVF.
Births among black women occurred more than 6 days earlier than births among white women. The researchers noted that some of the shorter gestations among the black women could be explained by the higher average body mass index of the group (P<.0001). Dr. Devine explained that another contributing factor was the higher incidence of fibroid uterus among the black women (P<.0001). But after adjusting for these and other demographic variables, the black women still delivered 5.5 days earlier than the white women, and they were more than 3 times as likely to have either very preterm or extremely preterm deliveries (TABLE).1

Research implications. Dr. Devine said that black pregnant patients “perhaps should be monitored more closely” for signs or symptoms suggestive of preterm labor and would like to see more research into understanding the mechanisms of preterm birth that are resulting in greater rates of preterm birth among black women. She mentioned that research into how fibroids impact obstetric outcomes is also important.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letters to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Investigators from the National Institutes of Health and Shady Grove Fertility found that among women having a singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) that black women are at higher risk for lower gestational age and preterm delivery than white women.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Kate Devine, MD, coinvestigator of the retrospective cohort study said in an interview with OBG Management that “It’s been well documented that African Americans have a higher preterm birth rate in the United States compared to Caucasians and the overall population. While the exact mechanism of preterm birth is unknown and likely varied, and while the mechanism for the preterm birth rate being higher in African Americans is not well understood, it has been hypothesized that socioeconomic factors are responsible at least in part.”2 She added that the investigators used a population of women receiving IVF for the study because “access to reproductive care and IVF is in some way a leveling factor in terms of socioeconomics.”
Details of the study. The investigators reviewed all singleton IVF pregnancies ending in live birth among women self-identifying as white, black, Asian, or Hispanic from 2004 to 2016 at a private IVF practice (N=10,371). The primary outcome was gestational age at birth, calculated as the number of days from oocyte retrieval to birth, plus 14, among white, black, Asian, and Hispanic women receiving IVF.
Births among black women occurred more than 6 days earlier than births among white women. The researchers noted that some of the shorter gestations among the black women could be explained by the higher average body mass index of the group (P<.0001). Dr. Devine explained that another contributing factor was the higher incidence of fibroid uterus among the black women (P<.0001). But after adjusting for these and other demographic variables, the black women still delivered 5.5 days earlier than the white women, and they were more than 3 times as likely to have either very preterm or extremely preterm deliveries (TABLE).1

Research implications. Dr. Devine said that black pregnant patients “perhaps should be monitored more closely” for signs or symptoms suggestive of preterm labor and would like to see more research into understanding the mechanisms of preterm birth that are resulting in greater rates of preterm birth among black women. She mentioned that research into how fibroids impact obstetric outcomes is also important.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letters to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Bishop LA, Devine K, Sasson I, et al. Lower gestational age and increased risk of preterm birth associated with singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) among African American versus comparable Caucasian women. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e7.
- Bishop LA, Devine K, Sasson I, et al. Lower gestational age and increased risk of preterm birth associated with singleton live birth resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF) among African American versus comparable Caucasian women. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e7.
Prior fertility treatment is associated with higher maternal morbidity during delivery
Investigators from the Stanford Hospital and Clinics in California found that while absolute risk is low, women who have received an infertility diagnosis or who have received fertility treatment are at higher risk of several markers of severe maternal morbidity than women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Gaya Murugappan, MD, lead investigator on the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “We know that in the last decade or so the rate of maternal morbidity has been rising gradually in the US, and we know that the utilization of fertility technology and the incidence of infertility are also rising.” The retrospective analysis set out to determine if a connection exists.
Methods. The investigators used a large insurance claims database to look at data from 2003 to 2016. They identified a group of infertile women who later conceived without fertility treatment (n=1822 deliveries) and a group of women who received fertility treatment (n=782 deliveries) and compared them with a control group of women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment (n=37,944 deliveries). Women who currently or previously had cancer were excluded from the study.
The primary outcome was the number of indicators of severe maternal morbidity that occurred during the 6 months prior to or following delivery.
Findings. Compared with the control group, the women diagnosed with infertility were almost 4 times as likely to experience severe anesthesia complications (0.38% vs 0.11%; odds ratio [OR], 3.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.69–8.70), about twice as likely to experience intraoperative heart failure (0.71% vs 0.31%; OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05–3.34), and more than 3 times as likely to receive a hysterectomy (1.04% vs 0.28%; OR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.02–5.40).
Similarly, compared with controls, women who had received fertility treatment had an OR of 2.66 for disseminated intravascular coagulation (2.81% vs 0.91%; 95% CI, 1.66–4.24), an OR of 5.17 for shock (0.90% vs 0.15%; 95% CI, 2.21–12.06), an OR of 1.61 for blood transfusions (3.71% vs 1.64%; 95% CI, 1.07–2.42), and an OR of 1.43 for cardiac monitoring (13.17% vs 8.14%; 95% CI, 1.14–1.79).
More research is needed. Dr. Murugappan noted, “I hope that these data help us identify high-risk populations of women so that we can minimize the occurrence of these potentially devastating health outcomes. Women need to be telling their ObGyns that they have a history of infertility and/or fertility treatment. Some women may not want to say that they conceived with donor egg, for example, but that could be a critical element of a patient’s history that an ObGyn should be aware of.”
More study is necessary, she added. For instance, “a study in the future looking at risk of maternal morbidity in patients who are infertile but then who go on to conceive spontaneously. Then we can tease out what is the effect of infertility versus the effect of fertility treatment.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Murugappan G, Li S, Lathi RB, Baker VL, Eisenberg ML. Increased risk of maternal morbidity in infertile women: analysis of US claims data. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e9.
Investigators from the Stanford Hospital and Clinics in California found that while absolute risk is low, women who have received an infertility diagnosis or who have received fertility treatment are at higher risk of several markers of severe maternal morbidity than women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Gaya Murugappan, MD, lead investigator on the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “We know that in the last decade or so the rate of maternal morbidity has been rising gradually in the US, and we know that the utilization of fertility technology and the incidence of infertility are also rising.” The retrospective analysis set out to determine if a connection exists.
Methods. The investigators used a large insurance claims database to look at data from 2003 to 2016. They identified a group of infertile women who later conceived without fertility treatment (n=1822 deliveries) and a group of women who received fertility treatment (n=782 deliveries) and compared them with a control group of women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment (n=37,944 deliveries). Women who currently or previously had cancer were excluded from the study.
The primary outcome was the number of indicators of severe maternal morbidity that occurred during the 6 months prior to or following delivery.
Findings. Compared with the control group, the women diagnosed with infertility were almost 4 times as likely to experience severe anesthesia complications (0.38% vs 0.11%; odds ratio [OR], 3.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.69–8.70), about twice as likely to experience intraoperative heart failure (0.71% vs 0.31%; OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05–3.34), and more than 3 times as likely to receive a hysterectomy (1.04% vs 0.28%; OR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.02–5.40).
Similarly, compared with controls, women who had received fertility treatment had an OR of 2.66 for disseminated intravascular coagulation (2.81% vs 0.91%; 95% CI, 1.66–4.24), an OR of 5.17 for shock (0.90% vs 0.15%; 95% CI, 2.21–12.06), an OR of 1.61 for blood transfusions (3.71% vs 1.64%; 95% CI, 1.07–2.42), and an OR of 1.43 for cardiac monitoring (13.17% vs 8.14%; 95% CI, 1.14–1.79).
More research is needed. Dr. Murugappan noted, “I hope that these data help us identify high-risk populations of women so that we can minimize the occurrence of these potentially devastating health outcomes. Women need to be telling their ObGyns that they have a history of infertility and/or fertility treatment. Some women may not want to say that they conceived with donor egg, for example, but that could be a critical element of a patient’s history that an ObGyn should be aware of.”
More study is necessary, she added. For instance, “a study in the future looking at risk of maternal morbidity in patients who are infertile but then who go on to conceive spontaneously. Then we can tease out what is the effect of infertility versus the effect of fertility treatment.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Investigators from the Stanford Hospital and Clinics in California found that while absolute risk is low, women who have received an infertility diagnosis or who have received fertility treatment are at higher risk of several markers of severe maternal morbidity than women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment.1 The study results were presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6 to 10, Denver, Colorado).
Gaya Murugappan, MD, lead investigator on the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “We know that in the last decade or so the rate of maternal morbidity has been rising gradually in the US, and we know that the utilization of fertility technology and the incidence of infertility are also rising.” The retrospective analysis set out to determine if a connection exists.
Methods. The investigators used a large insurance claims database to look at data from 2003 to 2016. They identified a group of infertile women who later conceived without fertility treatment (n=1822 deliveries) and a group of women who received fertility treatment (n=782 deliveries) and compared them with a control group of women who never received an infertility diagnosis or fertility treatment (n=37,944 deliveries). Women who currently or previously had cancer were excluded from the study.
The primary outcome was the number of indicators of severe maternal morbidity that occurred during the 6 months prior to or following delivery.
Findings. Compared with the control group, the women diagnosed with infertility were almost 4 times as likely to experience severe anesthesia complications (0.38% vs 0.11%; odds ratio [OR], 3.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.69–8.70), about twice as likely to experience intraoperative heart failure (0.71% vs 0.31%; OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05–3.34), and more than 3 times as likely to receive a hysterectomy (1.04% vs 0.28%; OR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.02–5.40).
Similarly, compared with controls, women who had received fertility treatment had an OR of 2.66 for disseminated intravascular coagulation (2.81% vs 0.91%; 95% CI, 1.66–4.24), an OR of 5.17 for shock (0.90% vs 0.15%; 95% CI, 2.21–12.06), an OR of 1.61 for blood transfusions (3.71% vs 1.64%; 95% CI, 1.07–2.42), and an OR of 1.43 for cardiac monitoring (13.17% vs 8.14%; 95% CI, 1.14–1.79).
More research is needed. Dr. Murugappan noted, “I hope that these data help us identify high-risk populations of women so that we can minimize the occurrence of these potentially devastating health outcomes. Women need to be telling their ObGyns that they have a history of infertility and/or fertility treatment. Some women may not want to say that they conceived with donor egg, for example, but that could be a critical element of a patient’s history that an ObGyn should be aware of.”
More study is necessary, she added. For instance, “a study in the future looking at risk of maternal morbidity in patients who are infertile but then who go on to conceive spontaneously. Then we can tease out what is the effect of infertility versus the effect of fertility treatment.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Murugappan G, Li S, Lathi RB, Baker VL, Eisenberg ML. Increased risk of maternal morbidity in infertile women: analysis of US claims data. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e9.
- Murugappan G, Li S, Lathi RB, Baker VL, Eisenberg ML. Increased risk of maternal morbidity in infertile women: analysis of US claims data. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e9.
Should return to fertility be a concern for nulliparous patients using an IUD?
Investigators from the University of Texas Southwestern are dispelling the myth that you shouldn’t recommend intrauterine devices (IUDs) for nulliparous women because the devices might make it more difficult for them to become pregnant after discontinuation. They found that nulliparous women can just as easily get pregnant after using a progestin intrauterine system (IUS) as parous women,1 according to results of a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6–10, Denver, Colorado).
Bruce R. Carr, MD, lead investigator of the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “There have been a number of studies—maybe 10 to 15 years ago—that looked at pregnancy rates when patients stopped using IUDs, but most of these studies were done in women who were multiparous. There is almost no data on patients who are nulliparous stopping an IUD and trying to get pregnant.”
Participants and methods. This prospective, multicenter, clinical trial, which is still ongoing, is evaluating the efficacy and safety for up to 10 years of the Liletta levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS in nulliparous and parous women ages 16 to 45 years. Every 3 months for up to 1 year, the investigators contacted the women who discontinued the IUS during the first 5 years of use and who were trying to become pregnant to determine pregnancy status.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was time to pregnancy among nulliparous vs parous women after discontinuation of a progestin IUS.
Findings. Overall, 132 (87%) of 152 women ages 16 to 35 years at the beginning of the study who attempted to become pregnant did so within 1 year of discontinuing the IUS, and there was no difference in pregnancy rates between nulliparous and parous women (87.5% vs 86.1%, respectively; P<.82) or between nulligravid and gravid women (88.2% vs 85.7%, respectively; P<.81). High percentages of women became pregnant by the end of 3 months (43.4%) and 6 months (69.7%), with a median time to conception of 91.5 days. The women used the IUS for a median of 34 months before discontinuation. Length of IUS use and age of the women at IUS discontinuation did not affect pregnancy rates at 12 months postdiscontinuation in either nulliparous or parous women (TABLE).1
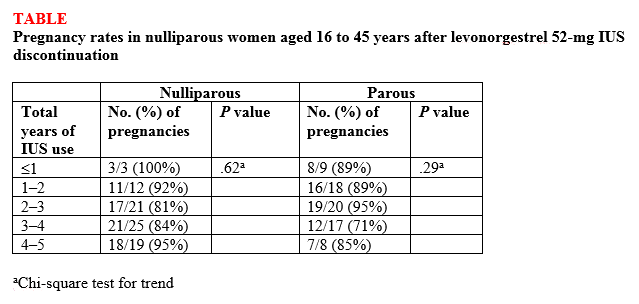
“The bottom line,” according to Dr. Carr, is that the “pregnancy rates were the same in women who had never been pregnant compared with women who had previously been pregnant.” He continued, “People worried that if a patient who had never been pregnant used an IUD that maybe she was going to have a harder time getting pregnant after discontinuing, and now we know that is not true. It [the study] reinforces the option of using progestin IUDs and not having to worry about future pregnancy.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
This article was updated October 15, 2018.
- Carr BR, Thomas MA, Gangestad A, Eisenberg DL, Olariu AI, Creinin MD. Return of fertility in nulliparous and parous women after levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system discontinuation [ASRM abstract O-104]. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e46.
Investigators from the University of Texas Southwestern are dispelling the myth that you shouldn’t recommend intrauterine devices (IUDs) for nulliparous women because the devices might make it more difficult for them to become pregnant after discontinuation. They found that nulliparous women can just as easily get pregnant after using a progestin intrauterine system (IUS) as parous women,1 according to results of a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6–10, Denver, Colorado).
Bruce R. Carr, MD, lead investigator of the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “There have been a number of studies—maybe 10 to 15 years ago—that looked at pregnancy rates when patients stopped using IUDs, but most of these studies were done in women who were multiparous. There is almost no data on patients who are nulliparous stopping an IUD and trying to get pregnant.”
Participants and methods. This prospective, multicenter, clinical trial, which is still ongoing, is evaluating the efficacy and safety for up to 10 years of the Liletta levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS in nulliparous and parous women ages 16 to 45 years. Every 3 months for up to 1 year, the investigators contacted the women who discontinued the IUS during the first 5 years of use and who were trying to become pregnant to determine pregnancy status.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was time to pregnancy among nulliparous vs parous women after discontinuation of a progestin IUS.
Findings. Overall, 132 (87%) of 152 women ages 16 to 35 years at the beginning of the study who attempted to become pregnant did so within 1 year of discontinuing the IUS, and there was no difference in pregnancy rates between nulliparous and parous women (87.5% vs 86.1%, respectively; P<.82) or between nulligravid and gravid women (88.2% vs 85.7%, respectively; P<.81). High percentages of women became pregnant by the end of 3 months (43.4%) and 6 months (69.7%), with a median time to conception of 91.5 days. The women used the IUS for a median of 34 months before discontinuation. Length of IUS use and age of the women at IUS discontinuation did not affect pregnancy rates at 12 months postdiscontinuation in either nulliparous or parous women (TABLE).1

“The bottom line,” according to Dr. Carr, is that the “pregnancy rates were the same in women who had never been pregnant compared with women who had previously been pregnant.” He continued, “People worried that if a patient who had never been pregnant used an IUD that maybe she was going to have a harder time getting pregnant after discontinuing, and now we know that is not true. It [the study] reinforces the option of using progestin IUDs and not having to worry about future pregnancy.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
This article was updated October 15, 2018.
Investigators from the University of Texas Southwestern are dispelling the myth that you shouldn’t recommend intrauterine devices (IUDs) for nulliparous women because the devices might make it more difficult for them to become pregnant after discontinuation. They found that nulliparous women can just as easily get pregnant after using a progestin intrauterine system (IUS) as parous women,1 according to results of a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) 2018 annual meeting (October 6–10, Denver, Colorado).
Bruce R. Carr, MD, lead investigator of the study, explained in an interview with OBG Management, “There have been a number of studies—maybe 10 to 15 years ago—that looked at pregnancy rates when patients stopped using IUDs, but most of these studies were done in women who were multiparous. There is almost no data on patients who are nulliparous stopping an IUD and trying to get pregnant.”
Participants and methods. This prospective, multicenter, clinical trial, which is still ongoing, is evaluating the efficacy and safety for up to 10 years of the Liletta levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS in nulliparous and parous women ages 16 to 45 years. Every 3 months for up to 1 year, the investigators contacted the women who discontinued the IUS during the first 5 years of use and who were trying to become pregnant to determine pregnancy status.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was time to pregnancy among nulliparous vs parous women after discontinuation of a progestin IUS.
Findings. Overall, 132 (87%) of 152 women ages 16 to 35 years at the beginning of the study who attempted to become pregnant did so within 1 year of discontinuing the IUS, and there was no difference in pregnancy rates between nulliparous and parous women (87.5% vs 86.1%, respectively; P<.82) or between nulligravid and gravid women (88.2% vs 85.7%, respectively; P<.81). High percentages of women became pregnant by the end of 3 months (43.4%) and 6 months (69.7%), with a median time to conception of 91.5 days. The women used the IUS for a median of 34 months before discontinuation. Length of IUS use and age of the women at IUS discontinuation did not affect pregnancy rates at 12 months postdiscontinuation in either nulliparous or parous women (TABLE).1

“The bottom line,” according to Dr. Carr, is that the “pregnancy rates were the same in women who had never been pregnant compared with women who had previously been pregnant.” He continued, “People worried that if a patient who had never been pregnant used an IUD that maybe she was going to have a harder time getting pregnant after discontinuing, and now we know that is not true. It [the study] reinforces the option of using progestin IUDs and not having to worry about future pregnancy.”
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
This article was updated October 15, 2018.
- Carr BR, Thomas MA, Gangestad A, Eisenberg DL, Olariu AI, Creinin MD. Return of fertility in nulliparous and parous women after levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system discontinuation [ASRM abstract O-104]. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e46.
- Carr BR, Thomas MA, Gangestad A, Eisenberg DL, Olariu AI, Creinin MD. Return of fertility in nulliparous and parous women after levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system discontinuation [ASRM abstract O-104]. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(45 suppl):e46.