User login
Meet the JCOM Author with Dr. Barkoudah: EHR Interventions to Improve Glucagon Prescription Rates for Individuals With T1DM
Glucagon Prescription Rates for Individuals With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Following Implementation of an Electronic Health Records Intervention
From Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN.
ABSTRACT
Objective: Severe hypoglycemia can alter consciousness and inhibit oral intake, requiring nonoral rescue glucagon administration to raise blood glucose to safe levels. Thus, current guidelines recommend glucagon kit prescriptions for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). At the diabetes outpatient clinic at a tertiary medical center, glucagon prescription rates for T1DM patients remained suboptimal.
Methods: A quality improvement team analyzed patient flow through the endocrinology clinic and identified the lack of a systematic approach to assessing patients for home glucagon prescriptions as a major barrier. The team implemented 2 successive interventions. First, intake staff indicated whether patients lacked an active glucagon prescription on patients’ face sheets. Second, clinical pharmacists reviewed patient prescriptions prior to scheduled visits and pended glucagon orders for patients without active prescriptions. Of note, when a pharmacy pends an order, the pharmacist enters an order into the electronic health record (EHR) but does not sign it. The order is saved for a provider to later access and sign. A statistical process control p-chart tracked monthly prescription rates.
Results: After 7 months, glucagon prescription rates increased from a baseline of 59% to 72% as the new steady state.
Conclusion: This project demonstrates that a series of interventions can improve glucagon prescription rates for patients at risk for hypoglycemia. The project’s success stemmed from combining an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary staff members’ involvement. Other endocrinology clinics may incorporate this approach to implement similar processes and improve glucagon prescription rates.
Keywords: diabetes, hypoglycemia, glucagon, quality improvement, prescription rates, medical student.
Hypoglycemia limits the management of blood glucose in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Severe hypoglycemia, characterized by altered mental status (AMS) or physical status requiring assistance for recovery, can lead to seizure, coma, or death.1 Hypoglycemia in diabetes often occurs iatrogenically, primarily from insulin therapy: 30% to 40% of patients with T1DM and 10% to 30% of patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus experience severe hypoglycemia in a given year.2 One study estimated that nearly 100,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia occur in the United States per year, with almost one-third resulting in hospitalization.3
Most patients self-treat mild hypoglycemia with oral intake of carbohydrates. However, since hypoglycemia-induced nausea and AMS can make oral intake more difficult or prevent it entirely, patients require a treatment that family, friends, or coworkers can administer. Rescue glucagon, prescribed as intramuscular injections or intranasal sprays, raises blood glucose to safe levels in 10 to 15 minutes.4 Therefore, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends glucagon for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with T1DM.5 Despite the ADA’s recommendation, current evidence suggests suboptimal glucagon prescription rates, particularly in patients with T1DM. One study reported that, although 85% of US adults with T1DM had formerly been prescribed glucagon, only 68% of these patients (57.8% overall) had a current prescription.4 Few quality improvement efforts have tackled increasing prescription rates. Prior successful studies have attempted to do so via pharmacist-led educational interventions for providers6 and via electronic health record (EHR) notifications for patient risk.7 The project described here aimed to expand upon prior studies with a quality improvement project to increase glucagon prescription rates among patients at risk for severe hypoglycemia.
This study was conducted at a tertiary medical center’s outpatient diabetes clinic; the clinic treats more than 9500 patients with DM annually, more than 2700 of whom have T1DM. In the clinic’s multidisciplinary care model, patients typically follow up every 3 to 6 months, alternating between appointments with fellowship-trained endocrinologists and advanced practice providers (APPs). In addition to having certified diabetes educators, the clinic employs 2 dedicated clinical pharmacists whose duties include assisting providers in prescription management, helping patients identify the most affordable way to obtain their medications, and educating patients regarding their medications.
Patient flow through the clinic involves close coordination with multiple health professionals. Medical assistants (MAs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs) perform patient intake, document vital signs, and ask screening questions, including dates of patients’ last hemoglobin A1c tests and diabetic eye examination. After intake, the provider (endocrinologist or APP) sees the patient. Once the appointment concludes, patients proceed to the in-house phlebotomy laboratory as indicated and check out with administrative staff to schedule future appointments.
From August 2021 through June 2022, teams of medical students at the tertiary center completed this project as part of a 4-week integrated science course on diabetes. Longitudinal supervision by an endocrinology faculty member ensured project continuity. The project employed the Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) method for reporting.8
Stakeholder analysis took place in August 2021. Surveyed clinic providers identified patients with T1DM as the most appropriate population and the outpatient setting as the most appropriate site for intervention. A fishbone diagram illustrated stakeholders to interview, impacts of the clinical flow, information technology to leverage, and potential holes contributing to glucagon prescription conversations falling through.
Interviews with T1DM patients, clinical pharmacists, APPs, MAs/LPNs, and endocrinologists identified barriers to glucagon prescription. The interviews and a process map analysis revealed several themes. While patients and providers understood the importance of glucagon prescription, barriers included glucagon cost, prescription fill burden, and, most pervasively, providers forgetting to ask patients whether they have a glucagon prescription and failing to consider glucagon prescriptions.For this study, each team of medical students worked on the project for 1 month. The revolving teams of medical students met approximately once per week for the duration of the project to review data and implementation phases. At the end of each month, the current team recorded the steps they had taken and information they had analyzed in a shared document, prepared short videos summarizing the work completed, and proposed next steps for the incoming team to support knowledge generation and continuity. Students from outgoing teams were available to contact if incoming teams had any questions.
Interventions
In the first implementation phase, which was carried out over 4 months (December 2021 to March 2022), the patient care manager trained MAs/LPNs to write a glucagon reminder on patients’ face sheets. At check-in, MAs/LPNs screened for a current glucagon prescription. If the patient lacked an up-to-date prescription, the MAs/LPNs hand-wrote a reminder on the patient’s face sheet, which was given to the provider immediately prior to seeing the patient. The clinical staff received an email explaining the intervention beforehand; the daily intake staff email included project reminders.
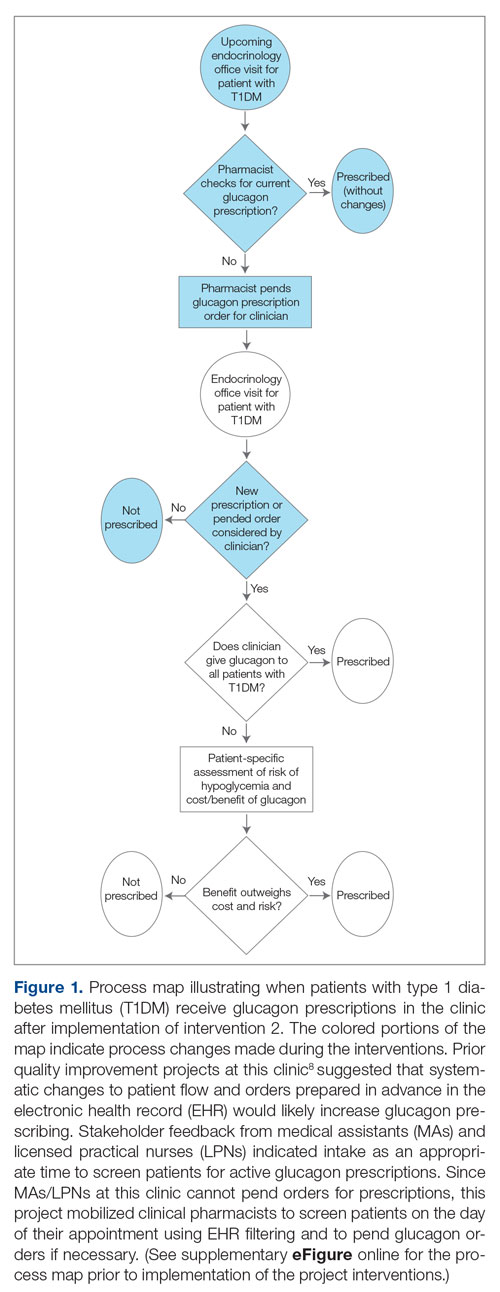
In the second implementation phase, which started in April 2022, had been carried out for 3 months at the time of this report, and is ongoing, clinical pharmacists have been pending glucagon prescriptions ahead of patients’ appointments. Each week, the pharmacists generate an EHR report that includes all patients with T1DM who have attended at least 1 appointment at the clinic within the past year (regardless of whether each patient possessed an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription) and the date of each patient’s next appointment. For patients who have an appointment in the upcoming week and lack an active glucagon prescription, the pharmacists run a benefits investigation to determine the insurance-preferred glucagon formulation and then pend the appropriate order in the EHR. During the patient’s next appointment, the EHR prompts the provider to review and sign the pharmacist’s pended order (Figure 1).
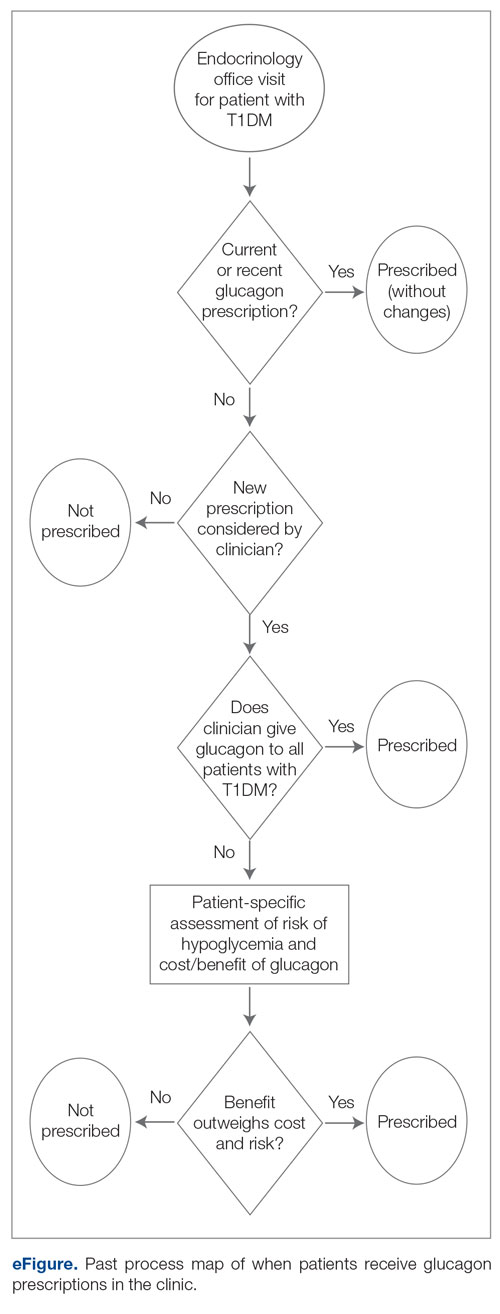
This project used a process measure in its analysis: the percentage of patients with T1DM with an active glucagon prescription at the time of their visit to the clinic. The patient population included all patients with a visit diagnosis of T1DM seen by an APP at the clinic during the time scope of the project. The project’s scope was limited to patients seen by APPs to help standardize appointment comparisons, with the intent to expand to the endocrinologist staff if the interventions proved successful with APPs. Patients seen by APPs were also under the care of endocrinologists and seen by them during this time period. The project excluded no patients.
Each individual patient appointment represented a data point: a time at which an APP could prescribe glucagon for a patient with T1DM. Thus, a single patient who had multiple appointments during the study period would generate multiple data points in this study.
For all T1DM patients at the clinic seen by an APP during the study period, the project aimed to increase the percentage with an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription from 58.8% to 70% over a 6-month period, a relatively modest goal appropriate for the time constraints and that would be similar to the changes seen in previous work in the same clinic.9
This project analyzed de-identified data using a statistical process control chart (specifically, a p-chart) and standard rules for assessing special-cause signals and thus statistical significance.
Results
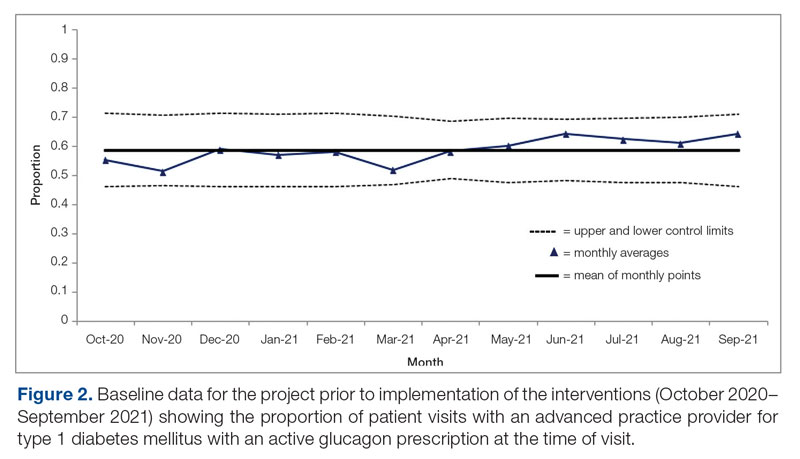
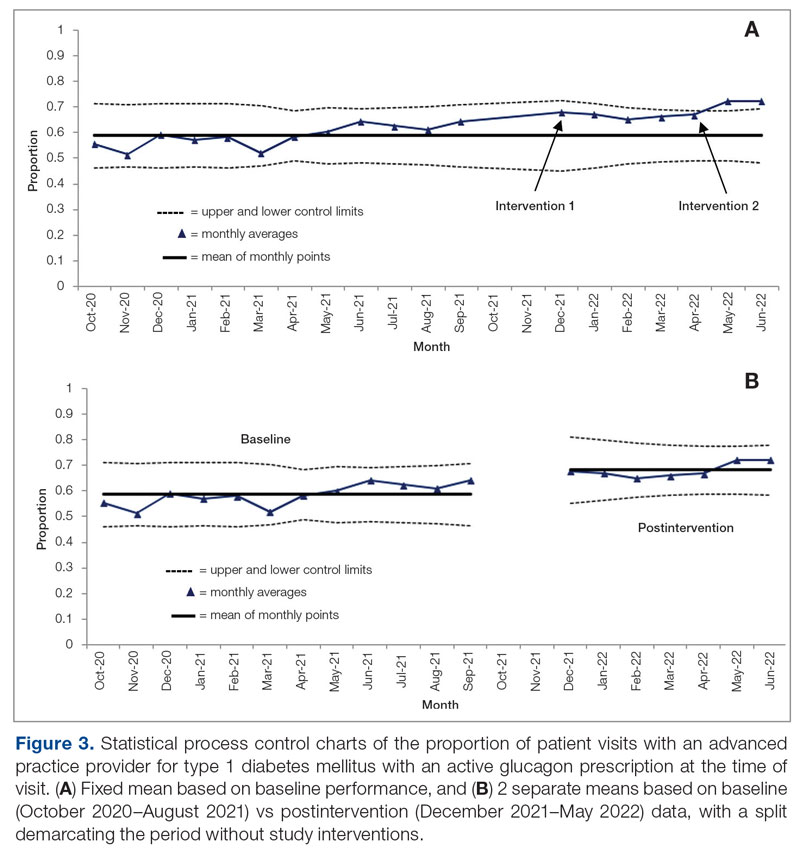
Baseline data were collected from October 2020 to September 2021. During this time, APPs saw 1959 T1DM patients, of whom 1152 (58.8%) had an active glucagon prescription at the time of visit and 41.2% lacked a glucagon prescription (Figure 2). During the 4 months of implementation phase 1, analysis of the statistical process control chart identified no special cause signal. Therefore, the project moved to a second intervention with implementation phase 2 in April 2022 (3 months of postintervention data are reported). During the entire intervention, 731 of 1080 (67.7%) patients had a glucagon prescription. The average for the last 2 months, with phase 2 fully implemented, was 72.3%, surpassing the 70% threshold identified as the study target (Figure 3).
Interviews with clinical pharmacists during implementation phase 2 revealed that generating the EHR report and reviewing patients with glucagon prescription indications resulted in variable daily workload increases ranging from approximately 15 to 45 minutes, depending on the number of patients requiring intervention that day. During the first month of implementation phase 2, the EHR report required repeated modification to fulfill the intervention needs. Staffing changes over the intervention period potentially impacted the pattern of glucagon prescribing. This project excluded the 2 months immediately prior to implementation phase 1, from October 2021 to November 2021, because the staff had begun having discussions about this initiative, which may have influenced glucagon prescription rates.
Discussion
This project evaluated 2 interventions over the course of 7 months to determine their efficacy in increasing the frequency of glucagon prescribing for individuals with T1DM in an endocrinology clinic. These interventions were associated with increased prescribing from a baseline of 58.8% to 72.3% over the last 2 months of the project. In the first intervention, performed over 4 months, MAs/LPNs wrote reminders on the appropriate patients’ face sheets, which were given to providers prior to appointments. This project adapted the approach from a successful previous quality improvement study on increasing microalbuminuria screening rates.9 However, glucagon prescription rates did not increase significantly, likely because, unlike with microalbuminuria screenings, MAs/LPNs could not pend glucagon prescriptions.
In the second intervention, performed over 3 months, clinical pharmacists pended glucagon prescriptions for identified eligible patients. Glucagon prescribing rates increased considerably, with rates of 72.3% and 72.4% over May and June 2021, respectively, indicating that the intervention successfully established a new higher steady state of proportion of patient visits with active glucagon prescriptions compared with the baseline rate of 58.8%. Given that the baseline data for this clinic were higher than the baseline glucagon prescription rates reported in other studies (49.3%),10 this intervention could have a major impact in clinics with a baseline more comparable to conditions in that study.
This project demonstrated how a combination of an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary involvement provides an actionable process to increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM. Compared to prior studies that implemented passive interventions, such as a note template that relies on provider adherence,7 this project emphasizes the benefit of implementing an active systems-level intervention with a pre-pended order.
Regarding prior studies, 1 large, 2-arm study of clinical pharmacists proactively pending orders for appropriate patients showed a 56% glucagon prescription rate in the intervention group, compared with 0.9% in the control group with no pharmacist intervention.11 Our project had a much higher baseline rate: 58.8% prior to intervention vs 0.9% in the nonintervention group for the previous study—likely due to its chosen location’s status as an endocrinology clinic rather than a general health care setting.
A different study that focused on patient education rather than glucagon prescription rates used similar EHR-generated reports to identify appropriate patients and assessed glucagon prescription needs during check-in. Following the educational interventions in that study, patients reporting self-comfort and education with glucagon administration significantly increased from 66.2% to 83.2%, and household member comfort and education with glucagon administration increased from 50.8% to 79.7%. This suggests the possibility of expanding the use of the EHR-generated report to assist not only with increasing glucagon prescription rates, but also with patient education on glucagon use rates and possibly fill rates.7 While novel glucagon products may change uptake rates, no new glucagon products arose or were prescribed at this clinic during the course of data collection.
Of note, our project increased the workload on clinical pharmacists. The pharmacists agreed to participate, despite the increased work, after a collaborative discussion about how to best address the need to increase glucagon prescriptions or patient safety; the pharmacy department had initially agreed to collaborate specifically to identify and attend to unmet needs such as this one. Although this project greatly benefited from the expertise and enthusiasm of the clinical pharmacists involved, this tradeoff requires further study to determine sustainability.
This project had several limitations. Because of the structure in which this intervention occurred (a year-long course with rotating groups of medical students), there was a necessary component of time constraint, and this project had just 2 implementation phases, for a total of 7 months of postintervention data. The clinic has permanently implemented these changes into its workflow, but subsequent assessments are needed to monitor the effects and assess sustainability.
The specific clinical site chosen for this study benefited from dedicated onsite clinical pharmacists, who are not available at all comparable clinical sites. Due to feasibility, this project only assessed whether the providers prescribed the glucagon, not whether the patients filled the prescriptions and used the glucagon when necessary. Although prescribing rates increased in our study, it cannot be assumed that fill rates increased identically.
Finally, interventions relying on EHR-generated reports carry inherent limitations, such as the risk of misidentification or omission of patients who had indications for a glucagon prescription. The project attempted to mitigate this limitation through random sampling of the EHR report to ensure accuracy. Additionally, EHR-generated reports encourage sustainability and expansion to all clinic patients, with far less required overhead work compared to manually derived data.
Future investigations may focus on expanding this intervention to all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, as well as to study further interventions into prescription fill rates and glucagon use rates.
Conclusion
This project indicates that a proactive, interdisciplinary quality improvement project can increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM in the outpatient setting. The most effective intervention mobilized clinical pharmacists to identify patients with indications for a glucagon prescription using an integrated EHR-generated report and subsequently pend a glucagon order for the endocrinology provider to sign during the visit. The strengths of the approach included using a multidisciplinary team, minimizing costs to patients by leveraging the pharmacists’ expertise to ensure insurance coverage of specific formulations, and utilizing automatic EHR reporting to streamline patient identification. Ideally, improvements in glucagon prescription rates should ultimately decrease hospitalizations and improve treatment of severe hypoglycemia for at-risk patients.
Corresponding author: Chase D. Hendrickson, MD, MPH; chase.d.hendrickson@vanderbilt.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Weinstock RS, Aleppo G, Bailey TS, et al. The Role of Blood Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management. American Diabetes Association; 2020.
2. Lamounier RN, Geloneze B, Leite SO, et al. Hypoglycemia incidence and awareness among insulin-treated patients with diabetes: the HAT study in Brazil. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10:83. doi:10.1186/s13098-018-0379-5
3. Li P, Geng Z, Ladage VP, et al. Early hypoglycaemia and adherence after basal insulin initiation in a nationally representative sample of Medicare beneficiaries with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(11):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/dom.13832
4. Haymond MW, Liu J, Bispham J, et al. Use of glucagon in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2019;37(2):162-166. doi:10.2337/cd18-0028
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S83-S96. doi:10.2337/dc22-S006
6. O’Reilly EA, Cross LV, Hayes JS, et al. Impact of pharmacist intervention on glucagon prescribing patterns in an outpatient internal medicine teaching clinic. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(2):384-390. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.04.0097.
7. Cobb EC, Watson NA, Wardian J, et al. Diabetes Center of Excellence Hypoglycemia Emergency Preparedness Project. Clin Diabetes. 2018;36(2):184-186. doi:10.2337/cd17-0040
8. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, et al. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
9. Kam S, Angaramo S, Antoun J, et al. Improving annual albuminuria testing for individuals with diabetes. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(1):e001591. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2021-001591
10. Mitchell BD, He X, Sturdy IM, et al. Glucagon prescription patterns in patients with either type 1 or 2 diabetes with newly prescribed insulin. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(2):123-135. doi:10.4158/EP15831.OR
11. Whitfield N, Gregory P, Liu B, et al. Impact of pharmacist outreach on glucagon prescribing. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2022;62(4):1384-1388.e.1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.01.017
From Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN.
ABSTRACT
Objective: Severe hypoglycemia can alter consciousness and inhibit oral intake, requiring nonoral rescue glucagon administration to raise blood glucose to safe levels. Thus, current guidelines recommend glucagon kit prescriptions for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). At the diabetes outpatient clinic at a tertiary medical center, glucagon prescription rates for T1DM patients remained suboptimal.
Methods: A quality improvement team analyzed patient flow through the endocrinology clinic and identified the lack of a systematic approach to assessing patients for home glucagon prescriptions as a major barrier. The team implemented 2 successive interventions. First, intake staff indicated whether patients lacked an active glucagon prescription on patients’ face sheets. Second, clinical pharmacists reviewed patient prescriptions prior to scheduled visits and pended glucagon orders for patients without active prescriptions. Of note, when a pharmacy pends an order, the pharmacist enters an order into the electronic health record (EHR) but does not sign it. The order is saved for a provider to later access and sign. A statistical process control p-chart tracked monthly prescription rates.
Results: After 7 months, glucagon prescription rates increased from a baseline of 59% to 72% as the new steady state.
Conclusion: This project demonstrates that a series of interventions can improve glucagon prescription rates for patients at risk for hypoglycemia. The project’s success stemmed from combining an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary staff members’ involvement. Other endocrinology clinics may incorporate this approach to implement similar processes and improve glucagon prescription rates.
Keywords: diabetes, hypoglycemia, glucagon, quality improvement, prescription rates, medical student.
Hypoglycemia limits the management of blood glucose in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Severe hypoglycemia, characterized by altered mental status (AMS) or physical status requiring assistance for recovery, can lead to seizure, coma, or death.1 Hypoglycemia in diabetes often occurs iatrogenically, primarily from insulin therapy: 30% to 40% of patients with T1DM and 10% to 30% of patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus experience severe hypoglycemia in a given year.2 One study estimated that nearly 100,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia occur in the United States per year, with almost one-third resulting in hospitalization.3
Most patients self-treat mild hypoglycemia with oral intake of carbohydrates. However, since hypoglycemia-induced nausea and AMS can make oral intake more difficult or prevent it entirely, patients require a treatment that family, friends, or coworkers can administer. Rescue glucagon, prescribed as intramuscular injections or intranasal sprays, raises blood glucose to safe levels in 10 to 15 minutes.4 Therefore, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends glucagon for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with T1DM.5 Despite the ADA’s recommendation, current evidence suggests suboptimal glucagon prescription rates, particularly in patients with T1DM. One study reported that, although 85% of US adults with T1DM had formerly been prescribed glucagon, only 68% of these patients (57.8% overall) had a current prescription.4 Few quality improvement efforts have tackled increasing prescription rates. Prior successful studies have attempted to do so via pharmacist-led educational interventions for providers6 and via electronic health record (EHR) notifications for patient risk.7 The project described here aimed to expand upon prior studies with a quality improvement project to increase glucagon prescription rates among patients at risk for severe hypoglycemia.
This study was conducted at a tertiary medical center’s outpatient diabetes clinic; the clinic treats more than 9500 patients with DM annually, more than 2700 of whom have T1DM. In the clinic’s multidisciplinary care model, patients typically follow up every 3 to 6 months, alternating between appointments with fellowship-trained endocrinologists and advanced practice providers (APPs). In addition to having certified diabetes educators, the clinic employs 2 dedicated clinical pharmacists whose duties include assisting providers in prescription management, helping patients identify the most affordable way to obtain their medications, and educating patients regarding their medications.
Patient flow through the clinic involves close coordination with multiple health professionals. Medical assistants (MAs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs) perform patient intake, document vital signs, and ask screening questions, including dates of patients’ last hemoglobin A1c tests and diabetic eye examination. After intake, the provider (endocrinologist or APP) sees the patient. Once the appointment concludes, patients proceed to the in-house phlebotomy laboratory as indicated and check out with administrative staff to schedule future appointments.
From August 2021 through June 2022, teams of medical students at the tertiary center completed this project as part of a 4-week integrated science course on diabetes. Longitudinal supervision by an endocrinology faculty member ensured project continuity. The project employed the Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) method for reporting.8
Stakeholder analysis took place in August 2021. Surveyed clinic providers identified patients with T1DM as the most appropriate population and the outpatient setting as the most appropriate site for intervention. A fishbone diagram illustrated stakeholders to interview, impacts of the clinical flow, information technology to leverage, and potential holes contributing to glucagon prescription conversations falling through.
Interviews with T1DM patients, clinical pharmacists, APPs, MAs/LPNs, and endocrinologists identified barriers to glucagon prescription. The interviews and a process map analysis revealed several themes. While patients and providers understood the importance of glucagon prescription, barriers included glucagon cost, prescription fill burden, and, most pervasively, providers forgetting to ask patients whether they have a glucagon prescription and failing to consider glucagon prescriptions.For this study, each team of medical students worked on the project for 1 month. The revolving teams of medical students met approximately once per week for the duration of the project to review data and implementation phases. At the end of each month, the current team recorded the steps they had taken and information they had analyzed in a shared document, prepared short videos summarizing the work completed, and proposed next steps for the incoming team to support knowledge generation and continuity. Students from outgoing teams were available to contact if incoming teams had any questions.
Interventions
In the first implementation phase, which was carried out over 4 months (December 2021 to March 2022), the patient care manager trained MAs/LPNs to write a glucagon reminder on patients’ face sheets. At check-in, MAs/LPNs screened for a current glucagon prescription. If the patient lacked an up-to-date prescription, the MAs/LPNs hand-wrote a reminder on the patient’s face sheet, which was given to the provider immediately prior to seeing the patient. The clinical staff received an email explaining the intervention beforehand; the daily intake staff email included project reminders.

In the second implementation phase, which started in April 2022, had been carried out for 3 months at the time of this report, and is ongoing, clinical pharmacists have been pending glucagon prescriptions ahead of patients’ appointments. Each week, the pharmacists generate an EHR report that includes all patients with T1DM who have attended at least 1 appointment at the clinic within the past year (regardless of whether each patient possessed an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription) and the date of each patient’s next appointment. For patients who have an appointment in the upcoming week and lack an active glucagon prescription, the pharmacists run a benefits investigation to determine the insurance-preferred glucagon formulation and then pend the appropriate order in the EHR. During the patient’s next appointment, the EHR prompts the provider to review and sign the pharmacist’s pended order (Figure 1).

This project used a process measure in its analysis: the percentage of patients with T1DM with an active glucagon prescription at the time of their visit to the clinic. The patient population included all patients with a visit diagnosis of T1DM seen by an APP at the clinic during the time scope of the project. The project’s scope was limited to patients seen by APPs to help standardize appointment comparisons, with the intent to expand to the endocrinologist staff if the interventions proved successful with APPs. Patients seen by APPs were also under the care of endocrinologists and seen by them during this time period. The project excluded no patients.
Each individual patient appointment represented a data point: a time at which an APP could prescribe glucagon for a patient with T1DM. Thus, a single patient who had multiple appointments during the study period would generate multiple data points in this study.
For all T1DM patients at the clinic seen by an APP during the study period, the project aimed to increase the percentage with an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription from 58.8% to 70% over a 6-month period, a relatively modest goal appropriate for the time constraints and that would be similar to the changes seen in previous work in the same clinic.9
This project analyzed de-identified data using a statistical process control chart (specifically, a p-chart) and standard rules for assessing special-cause signals and thus statistical significance.
Results
Baseline data were collected from October 2020 to September 2021. During this time, APPs saw 1959 T1DM patients, of whom 1152 (58.8%) had an active glucagon prescription at the time of visit and 41.2% lacked a glucagon prescription (Figure 2). During the 4 months of implementation phase 1, analysis of the statistical process control chart identified no special cause signal. Therefore, the project moved to a second intervention with implementation phase 2 in April 2022 (3 months of postintervention data are reported). During the entire intervention, 731 of 1080 (67.7%) patients had a glucagon prescription. The average for the last 2 months, with phase 2 fully implemented, was 72.3%, surpassing the 70% threshold identified as the study target (Figure 3).

Interviews with clinical pharmacists during implementation phase 2 revealed that generating the EHR report and reviewing patients with glucagon prescription indications resulted in variable daily workload increases ranging from approximately 15 to 45 minutes, depending on the number of patients requiring intervention that day. During the first month of implementation phase 2, the EHR report required repeated modification to fulfill the intervention needs. Staffing changes over the intervention period potentially impacted the pattern of glucagon prescribing. This project excluded the 2 months immediately prior to implementation phase 1, from October 2021 to November 2021, because the staff had begun having discussions about this initiative, which may have influenced glucagon prescription rates.

Discussion
This project evaluated 2 interventions over the course of 7 months to determine their efficacy in increasing the frequency of glucagon prescribing for individuals with T1DM in an endocrinology clinic. These interventions were associated with increased prescribing from a baseline of 58.8% to 72.3% over the last 2 months of the project. In the first intervention, performed over 4 months, MAs/LPNs wrote reminders on the appropriate patients’ face sheets, which were given to providers prior to appointments. This project adapted the approach from a successful previous quality improvement study on increasing microalbuminuria screening rates.9 However, glucagon prescription rates did not increase significantly, likely because, unlike with microalbuminuria screenings, MAs/LPNs could not pend glucagon prescriptions.
In the second intervention, performed over 3 months, clinical pharmacists pended glucagon prescriptions for identified eligible patients. Glucagon prescribing rates increased considerably, with rates of 72.3% and 72.4% over May and June 2021, respectively, indicating that the intervention successfully established a new higher steady state of proportion of patient visits with active glucagon prescriptions compared with the baseline rate of 58.8%. Given that the baseline data for this clinic were higher than the baseline glucagon prescription rates reported in other studies (49.3%),10 this intervention could have a major impact in clinics with a baseline more comparable to conditions in that study.
This project demonstrated how a combination of an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary involvement provides an actionable process to increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM. Compared to prior studies that implemented passive interventions, such as a note template that relies on provider adherence,7 this project emphasizes the benefit of implementing an active systems-level intervention with a pre-pended order.
Regarding prior studies, 1 large, 2-arm study of clinical pharmacists proactively pending orders for appropriate patients showed a 56% glucagon prescription rate in the intervention group, compared with 0.9% in the control group with no pharmacist intervention.11 Our project had a much higher baseline rate: 58.8% prior to intervention vs 0.9% in the nonintervention group for the previous study—likely due to its chosen location’s status as an endocrinology clinic rather than a general health care setting.
A different study that focused on patient education rather than glucagon prescription rates used similar EHR-generated reports to identify appropriate patients and assessed glucagon prescription needs during check-in. Following the educational interventions in that study, patients reporting self-comfort and education with glucagon administration significantly increased from 66.2% to 83.2%, and household member comfort and education with glucagon administration increased from 50.8% to 79.7%. This suggests the possibility of expanding the use of the EHR-generated report to assist not only with increasing glucagon prescription rates, but also with patient education on glucagon use rates and possibly fill rates.7 While novel glucagon products may change uptake rates, no new glucagon products arose or were prescribed at this clinic during the course of data collection.
Of note, our project increased the workload on clinical pharmacists. The pharmacists agreed to participate, despite the increased work, after a collaborative discussion about how to best address the need to increase glucagon prescriptions or patient safety; the pharmacy department had initially agreed to collaborate specifically to identify and attend to unmet needs such as this one. Although this project greatly benefited from the expertise and enthusiasm of the clinical pharmacists involved, this tradeoff requires further study to determine sustainability.
This project had several limitations. Because of the structure in which this intervention occurred (a year-long course with rotating groups of medical students), there was a necessary component of time constraint, and this project had just 2 implementation phases, for a total of 7 months of postintervention data. The clinic has permanently implemented these changes into its workflow, but subsequent assessments are needed to monitor the effects and assess sustainability.
The specific clinical site chosen for this study benefited from dedicated onsite clinical pharmacists, who are not available at all comparable clinical sites. Due to feasibility, this project only assessed whether the providers prescribed the glucagon, not whether the patients filled the prescriptions and used the glucagon when necessary. Although prescribing rates increased in our study, it cannot be assumed that fill rates increased identically.
Finally, interventions relying on EHR-generated reports carry inherent limitations, such as the risk of misidentification or omission of patients who had indications for a glucagon prescription. The project attempted to mitigate this limitation through random sampling of the EHR report to ensure accuracy. Additionally, EHR-generated reports encourage sustainability and expansion to all clinic patients, with far less required overhead work compared to manually derived data.
Future investigations may focus on expanding this intervention to all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, as well as to study further interventions into prescription fill rates and glucagon use rates.
Conclusion
This project indicates that a proactive, interdisciplinary quality improvement project can increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM in the outpatient setting. The most effective intervention mobilized clinical pharmacists to identify patients with indications for a glucagon prescription using an integrated EHR-generated report and subsequently pend a glucagon order for the endocrinology provider to sign during the visit. The strengths of the approach included using a multidisciplinary team, minimizing costs to patients by leveraging the pharmacists’ expertise to ensure insurance coverage of specific formulations, and utilizing automatic EHR reporting to streamline patient identification. Ideally, improvements in glucagon prescription rates should ultimately decrease hospitalizations and improve treatment of severe hypoglycemia for at-risk patients.
Corresponding author: Chase D. Hendrickson, MD, MPH; chase.d.hendrickson@vanderbilt.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
From Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN.
ABSTRACT
Objective: Severe hypoglycemia can alter consciousness and inhibit oral intake, requiring nonoral rescue glucagon administration to raise blood glucose to safe levels. Thus, current guidelines recommend glucagon kit prescriptions for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). At the diabetes outpatient clinic at a tertiary medical center, glucagon prescription rates for T1DM patients remained suboptimal.
Methods: A quality improvement team analyzed patient flow through the endocrinology clinic and identified the lack of a systematic approach to assessing patients for home glucagon prescriptions as a major barrier. The team implemented 2 successive interventions. First, intake staff indicated whether patients lacked an active glucagon prescription on patients’ face sheets. Second, clinical pharmacists reviewed patient prescriptions prior to scheduled visits and pended glucagon orders for patients without active prescriptions. Of note, when a pharmacy pends an order, the pharmacist enters an order into the electronic health record (EHR) but does not sign it. The order is saved for a provider to later access and sign. A statistical process control p-chart tracked monthly prescription rates.
Results: After 7 months, glucagon prescription rates increased from a baseline of 59% to 72% as the new steady state.
Conclusion: This project demonstrates that a series of interventions can improve glucagon prescription rates for patients at risk for hypoglycemia. The project’s success stemmed from combining an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary staff members’ involvement. Other endocrinology clinics may incorporate this approach to implement similar processes and improve glucagon prescription rates.
Keywords: diabetes, hypoglycemia, glucagon, quality improvement, prescription rates, medical student.
Hypoglycemia limits the management of blood glucose in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Severe hypoglycemia, characterized by altered mental status (AMS) or physical status requiring assistance for recovery, can lead to seizure, coma, or death.1 Hypoglycemia in diabetes often occurs iatrogenically, primarily from insulin therapy: 30% to 40% of patients with T1DM and 10% to 30% of patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus experience severe hypoglycemia in a given year.2 One study estimated that nearly 100,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia occur in the United States per year, with almost one-third resulting in hospitalization.3
Most patients self-treat mild hypoglycemia with oral intake of carbohydrates. However, since hypoglycemia-induced nausea and AMS can make oral intake more difficult or prevent it entirely, patients require a treatment that family, friends, or coworkers can administer. Rescue glucagon, prescribed as intramuscular injections or intranasal sprays, raises blood glucose to safe levels in 10 to 15 minutes.4 Therefore, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends glucagon for all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, especially patients with T1DM.5 Despite the ADA’s recommendation, current evidence suggests suboptimal glucagon prescription rates, particularly in patients with T1DM. One study reported that, although 85% of US adults with T1DM had formerly been prescribed glucagon, only 68% of these patients (57.8% overall) had a current prescription.4 Few quality improvement efforts have tackled increasing prescription rates. Prior successful studies have attempted to do so via pharmacist-led educational interventions for providers6 and via electronic health record (EHR) notifications for patient risk.7 The project described here aimed to expand upon prior studies with a quality improvement project to increase glucagon prescription rates among patients at risk for severe hypoglycemia.
This study was conducted at a tertiary medical center’s outpatient diabetes clinic; the clinic treats more than 9500 patients with DM annually, more than 2700 of whom have T1DM. In the clinic’s multidisciplinary care model, patients typically follow up every 3 to 6 months, alternating between appointments with fellowship-trained endocrinologists and advanced practice providers (APPs). In addition to having certified diabetes educators, the clinic employs 2 dedicated clinical pharmacists whose duties include assisting providers in prescription management, helping patients identify the most affordable way to obtain their medications, and educating patients regarding their medications.
Patient flow through the clinic involves close coordination with multiple health professionals. Medical assistants (MAs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs) perform patient intake, document vital signs, and ask screening questions, including dates of patients’ last hemoglobin A1c tests and diabetic eye examination. After intake, the provider (endocrinologist or APP) sees the patient. Once the appointment concludes, patients proceed to the in-house phlebotomy laboratory as indicated and check out with administrative staff to schedule future appointments.
From August 2021 through June 2022, teams of medical students at the tertiary center completed this project as part of a 4-week integrated science course on diabetes. Longitudinal supervision by an endocrinology faculty member ensured project continuity. The project employed the Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) method for reporting.8
Stakeholder analysis took place in August 2021. Surveyed clinic providers identified patients with T1DM as the most appropriate population and the outpatient setting as the most appropriate site for intervention. A fishbone diagram illustrated stakeholders to interview, impacts of the clinical flow, information technology to leverage, and potential holes contributing to glucagon prescription conversations falling through.
Interviews with T1DM patients, clinical pharmacists, APPs, MAs/LPNs, and endocrinologists identified barriers to glucagon prescription. The interviews and a process map analysis revealed several themes. While patients and providers understood the importance of glucagon prescription, barriers included glucagon cost, prescription fill burden, and, most pervasively, providers forgetting to ask patients whether they have a glucagon prescription and failing to consider glucagon prescriptions.For this study, each team of medical students worked on the project for 1 month. The revolving teams of medical students met approximately once per week for the duration of the project to review data and implementation phases. At the end of each month, the current team recorded the steps they had taken and information they had analyzed in a shared document, prepared short videos summarizing the work completed, and proposed next steps for the incoming team to support knowledge generation and continuity. Students from outgoing teams were available to contact if incoming teams had any questions.
Interventions
In the first implementation phase, which was carried out over 4 months (December 2021 to March 2022), the patient care manager trained MAs/LPNs to write a glucagon reminder on patients’ face sheets. At check-in, MAs/LPNs screened for a current glucagon prescription. If the patient lacked an up-to-date prescription, the MAs/LPNs hand-wrote a reminder on the patient’s face sheet, which was given to the provider immediately prior to seeing the patient. The clinical staff received an email explaining the intervention beforehand; the daily intake staff email included project reminders.

In the second implementation phase, which started in April 2022, had been carried out for 3 months at the time of this report, and is ongoing, clinical pharmacists have been pending glucagon prescriptions ahead of patients’ appointments. Each week, the pharmacists generate an EHR report that includes all patients with T1DM who have attended at least 1 appointment at the clinic within the past year (regardless of whether each patient possessed an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription) and the date of each patient’s next appointment. For patients who have an appointment in the upcoming week and lack an active glucagon prescription, the pharmacists run a benefits investigation to determine the insurance-preferred glucagon formulation and then pend the appropriate order in the EHR. During the patient’s next appointment, the EHR prompts the provider to review and sign the pharmacist’s pended order (Figure 1).

This project used a process measure in its analysis: the percentage of patients with T1DM with an active glucagon prescription at the time of their visit to the clinic. The patient population included all patients with a visit diagnosis of T1DM seen by an APP at the clinic during the time scope of the project. The project’s scope was limited to patients seen by APPs to help standardize appointment comparisons, with the intent to expand to the endocrinologist staff if the interventions proved successful with APPs. Patients seen by APPs were also under the care of endocrinologists and seen by them during this time period. The project excluded no patients.
Each individual patient appointment represented a data point: a time at which an APP could prescribe glucagon for a patient with T1DM. Thus, a single patient who had multiple appointments during the study period would generate multiple data points in this study.
For all T1DM patients at the clinic seen by an APP during the study period, the project aimed to increase the percentage with an active and up-to-date glucagon prescription from 58.8% to 70% over a 6-month period, a relatively modest goal appropriate for the time constraints and that would be similar to the changes seen in previous work in the same clinic.9
This project analyzed de-identified data using a statistical process control chart (specifically, a p-chart) and standard rules for assessing special-cause signals and thus statistical significance.
Results
Baseline data were collected from October 2020 to September 2021. During this time, APPs saw 1959 T1DM patients, of whom 1152 (58.8%) had an active glucagon prescription at the time of visit and 41.2% lacked a glucagon prescription (Figure 2). During the 4 months of implementation phase 1, analysis of the statistical process control chart identified no special cause signal. Therefore, the project moved to a second intervention with implementation phase 2 in April 2022 (3 months of postintervention data are reported). During the entire intervention, 731 of 1080 (67.7%) patients had a glucagon prescription. The average for the last 2 months, with phase 2 fully implemented, was 72.3%, surpassing the 70% threshold identified as the study target (Figure 3).

Interviews with clinical pharmacists during implementation phase 2 revealed that generating the EHR report and reviewing patients with glucagon prescription indications resulted in variable daily workload increases ranging from approximately 15 to 45 minutes, depending on the number of patients requiring intervention that day. During the first month of implementation phase 2, the EHR report required repeated modification to fulfill the intervention needs. Staffing changes over the intervention period potentially impacted the pattern of glucagon prescribing. This project excluded the 2 months immediately prior to implementation phase 1, from October 2021 to November 2021, because the staff had begun having discussions about this initiative, which may have influenced glucagon prescription rates.

Discussion
This project evaluated 2 interventions over the course of 7 months to determine their efficacy in increasing the frequency of glucagon prescribing for individuals with T1DM in an endocrinology clinic. These interventions were associated with increased prescribing from a baseline of 58.8% to 72.3% over the last 2 months of the project. In the first intervention, performed over 4 months, MAs/LPNs wrote reminders on the appropriate patients’ face sheets, which were given to providers prior to appointments. This project adapted the approach from a successful previous quality improvement study on increasing microalbuminuria screening rates.9 However, glucagon prescription rates did not increase significantly, likely because, unlike with microalbuminuria screenings, MAs/LPNs could not pend glucagon prescriptions.
In the second intervention, performed over 3 months, clinical pharmacists pended glucagon prescriptions for identified eligible patients. Glucagon prescribing rates increased considerably, with rates of 72.3% and 72.4% over May and June 2021, respectively, indicating that the intervention successfully established a new higher steady state of proportion of patient visits with active glucagon prescriptions compared with the baseline rate of 58.8%. Given that the baseline data for this clinic were higher than the baseline glucagon prescription rates reported in other studies (49.3%),10 this intervention could have a major impact in clinics with a baseline more comparable to conditions in that study.
This project demonstrated how a combination of an EHR-generated report and interdisciplinary involvement provides an actionable process to increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM. Compared to prior studies that implemented passive interventions, such as a note template that relies on provider adherence,7 this project emphasizes the benefit of implementing an active systems-level intervention with a pre-pended order.
Regarding prior studies, 1 large, 2-arm study of clinical pharmacists proactively pending orders for appropriate patients showed a 56% glucagon prescription rate in the intervention group, compared with 0.9% in the control group with no pharmacist intervention.11 Our project had a much higher baseline rate: 58.8% prior to intervention vs 0.9% in the nonintervention group for the previous study—likely due to its chosen location’s status as an endocrinology clinic rather than a general health care setting.
A different study that focused on patient education rather than glucagon prescription rates used similar EHR-generated reports to identify appropriate patients and assessed glucagon prescription needs during check-in. Following the educational interventions in that study, patients reporting self-comfort and education with glucagon administration significantly increased from 66.2% to 83.2%, and household member comfort and education with glucagon administration increased from 50.8% to 79.7%. This suggests the possibility of expanding the use of the EHR-generated report to assist not only with increasing glucagon prescription rates, but also with patient education on glucagon use rates and possibly fill rates.7 While novel glucagon products may change uptake rates, no new glucagon products arose or were prescribed at this clinic during the course of data collection.
Of note, our project increased the workload on clinical pharmacists. The pharmacists agreed to participate, despite the increased work, after a collaborative discussion about how to best address the need to increase glucagon prescriptions or patient safety; the pharmacy department had initially agreed to collaborate specifically to identify and attend to unmet needs such as this one. Although this project greatly benefited from the expertise and enthusiasm of the clinical pharmacists involved, this tradeoff requires further study to determine sustainability.
This project had several limitations. Because of the structure in which this intervention occurred (a year-long course with rotating groups of medical students), there was a necessary component of time constraint, and this project had just 2 implementation phases, for a total of 7 months of postintervention data. The clinic has permanently implemented these changes into its workflow, but subsequent assessments are needed to monitor the effects and assess sustainability.
The specific clinical site chosen for this study benefited from dedicated onsite clinical pharmacists, who are not available at all comparable clinical sites. Due to feasibility, this project only assessed whether the providers prescribed the glucagon, not whether the patients filled the prescriptions and used the glucagon when necessary. Although prescribing rates increased in our study, it cannot be assumed that fill rates increased identically.
Finally, interventions relying on EHR-generated reports carry inherent limitations, such as the risk of misidentification or omission of patients who had indications for a glucagon prescription. The project attempted to mitigate this limitation through random sampling of the EHR report to ensure accuracy. Additionally, EHR-generated reports encourage sustainability and expansion to all clinic patients, with far less required overhead work compared to manually derived data.
Future investigations may focus on expanding this intervention to all patients at risk for hypoglycemia, as well as to study further interventions into prescription fill rates and glucagon use rates.
Conclusion
This project indicates that a proactive, interdisciplinary quality improvement project can increase glucagon prescription rates for patients with T1DM in the outpatient setting. The most effective intervention mobilized clinical pharmacists to identify patients with indications for a glucagon prescription using an integrated EHR-generated report and subsequently pend a glucagon order for the endocrinology provider to sign during the visit. The strengths of the approach included using a multidisciplinary team, minimizing costs to patients by leveraging the pharmacists’ expertise to ensure insurance coverage of specific formulations, and utilizing automatic EHR reporting to streamline patient identification. Ideally, improvements in glucagon prescription rates should ultimately decrease hospitalizations and improve treatment of severe hypoglycemia for at-risk patients.
Corresponding author: Chase D. Hendrickson, MD, MPH; chase.d.hendrickson@vanderbilt.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Weinstock RS, Aleppo G, Bailey TS, et al. The Role of Blood Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management. American Diabetes Association; 2020.
2. Lamounier RN, Geloneze B, Leite SO, et al. Hypoglycemia incidence and awareness among insulin-treated patients with diabetes: the HAT study in Brazil. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10:83. doi:10.1186/s13098-018-0379-5
3. Li P, Geng Z, Ladage VP, et al. Early hypoglycaemia and adherence after basal insulin initiation in a nationally representative sample of Medicare beneficiaries with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(11):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/dom.13832
4. Haymond MW, Liu J, Bispham J, et al. Use of glucagon in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2019;37(2):162-166. doi:10.2337/cd18-0028
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S83-S96. doi:10.2337/dc22-S006
6. O’Reilly EA, Cross LV, Hayes JS, et al. Impact of pharmacist intervention on glucagon prescribing patterns in an outpatient internal medicine teaching clinic. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(2):384-390. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.04.0097.
7. Cobb EC, Watson NA, Wardian J, et al. Diabetes Center of Excellence Hypoglycemia Emergency Preparedness Project. Clin Diabetes. 2018;36(2):184-186. doi:10.2337/cd17-0040
8. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, et al. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
9. Kam S, Angaramo S, Antoun J, et al. Improving annual albuminuria testing for individuals with diabetes. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(1):e001591. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2021-001591
10. Mitchell BD, He X, Sturdy IM, et al. Glucagon prescription patterns in patients with either type 1 or 2 diabetes with newly prescribed insulin. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(2):123-135. doi:10.4158/EP15831.OR
11. Whitfield N, Gregory P, Liu B, et al. Impact of pharmacist outreach on glucagon prescribing. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2022;62(4):1384-1388.e.1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.01.017
1. Weinstock RS, Aleppo G, Bailey TS, et al. The Role of Blood Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management. American Diabetes Association; 2020.
2. Lamounier RN, Geloneze B, Leite SO, et al. Hypoglycemia incidence and awareness among insulin-treated patients with diabetes: the HAT study in Brazil. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10:83. doi:10.1186/s13098-018-0379-5
3. Li P, Geng Z, Ladage VP, et al. Early hypoglycaemia and adherence after basal insulin initiation in a nationally representative sample of Medicare beneficiaries with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(11):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/dom.13832
4. Haymond MW, Liu J, Bispham J, et al. Use of glucagon in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2019;37(2):162-166. doi:10.2337/cd18-0028
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S83-S96. doi:10.2337/dc22-S006
6. O’Reilly EA, Cross LV, Hayes JS, et al. Impact of pharmacist intervention on glucagon prescribing patterns in an outpatient internal medicine teaching clinic. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(2):384-390. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.04.0097.
7. Cobb EC, Watson NA, Wardian J, et al. Diabetes Center of Excellence Hypoglycemia Emergency Preparedness Project. Clin Diabetes. 2018;36(2):184-186. doi:10.2337/cd17-0040
8. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, et al. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
9. Kam S, Angaramo S, Antoun J, et al. Improving annual albuminuria testing for individuals with diabetes. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(1):e001591. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2021-001591
10. Mitchell BD, He X, Sturdy IM, et al. Glucagon prescription patterns in patients with either type 1 or 2 diabetes with newly prescribed insulin. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(2):123-135. doi:10.4158/EP15831.OR
11. Whitfield N, Gregory P, Liu B, et al. Impact of pharmacist outreach on glucagon prescribing. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2022;62(4):1384-1388.e.1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.01.017
Patient Safety in Transitions of Care: Addressing Discharge Communication Gaps and the Potential of the Teach-Back Method
Study 1 Overview (Trivedi et al)
Objective: This observational quality improvement study aimed to evaluate the discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals, specifically focusing on patient education and counseling in 6 key discharge communication domains.
Design: Observations were conducted over a 13-month period from September 2018 through October 2019, following the Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE) guidelines.
Setting and participants: The study involved a total of 33 English- and Spanish-speaking patients purposefully selected from the “discharge before noon” list at 2 urban tertiary-care teaching hospitals. A total of 155 observation hours were accumulated, with an average observation time of 4.7 hours per patient on the day of discharge.
Main outcome measures: The study assessed 6 discharge communication domains: (1) the name and function of medication changes, (2) the purpose of postdischarge appointments, (3) disease self-management, (4) red flags or warning signs for complications, (5) teach-back techniques to confirm patient understanding, and (6) staff solicitation of patient questions or concerns.
Main results: The study found several gaps in discharge communication practices. Among the 29 patients with medication changes, 28% were not informed about the name and basic function of the changes, while 59% did not receive counseling on the purpose for the medication change. In terms of postdischarge appointments, 48% of patients were not told the purpose of these appointments. Moreover, 54% of patients did not receive counseling on self-management of their primary discharge diagnosis or other diagnoses, and 73% were not informed about symptom expectations or the expected course of their illness after leaving the hospital. Most patients (82%) were not counseled on red-flag signs and symptoms that should prompt immediate return to care.
Teach-back techniques, which are critical for ensuring patient understanding, were used in only 3% of cases, and 85% of patients were not asked by health care providers if there might be barriers to following the care plan. Less than half (42%) of the patients were asked if they had any questions, with most questions being logistical and often deferred to another team member or met with uncertainty. Of note, among the 33 patients, only 2 patients received extensive information that covered 5 or 6 out of 6 discharge communication domains.
The study found variable roles in who communicated what aspects of discharge education, with most domains being communicated in an ad hoc manner and no clear pattern of responsibility. However, 2 exceptions were observed: nurses were more likely to provide information about new or changed medications and follow-up appointments, and the only example of teach-back was conducted by an attending physician.
Conclusion: The study highlights a significant need for improved discharge techniques to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital. Interventions should focus on increasing transparency in patient education and understanding, clarifying assumptions of roles among the interprofessional team, and implementing effective communication strategies and system redesigns that foster patient-centered discharge education. Also, the study revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, indicating systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further studies are needed to explore the development and assessment of such interventions to ensure optimal patient outcomes and equal care following hospital discharge.
Study 2 Overview (Marks et al)
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the impact of a nurse-led discharge medication education program, Teaching Important Medication Effects (TIME), on patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours post discharge. The specific objectives were to identify patients’ priority learning needs, evaluate the influence of TIME on patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge, and assess the effect of TIME on patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Design: The study employed a longitudinal pretest/post-test, 2-group design involving 107 randomly selected medical-surgical patients from an academic hospital. Participants were interviewed before and within 72 hours after discharge following administration of medication instructions. Bivariate analyses were performed to assess demographic and outcome variable differences between groups.
Setting and participants: Conducted on a 24-bed medical-surgical unit at a large Magnet® hospital over 18 months (2018-2019), the study included patients with at least 1 new medication, aged 18 years or older, able to read and speak English or Spanish, admitted from home with a minimum 1 overnight stay, and planning to return home post discharge. Excluded were cognitively impaired patients, those assigned to a resource pool nurse without TIME training, and those having a research team member assigned. Participants were randomly selected from a computerized list of patients scheduled for discharge.
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome measures included patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge and patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Main results: The usual care (n = 52) and TIME (n = 55) patients had similar baseline demographic characteristics. The study revealed that almost all patients in both usual care and TIME groups were aware of their new medication and its purpose at discharge. However, differences were observed in medication side effect responses, with 72.5% of the usual-care group knowing side effects compared to 94.3% of the TIME group (P = .003). Additionally, 81.5% of the usual-care group understood the medication purpose compared to 100% of the TIME group (P = .02). During the 48- to 72-hour postdischarge calls, consistent responses were found from both groups regarding knowledge of new medication, medication name, and medication purpose. Similar to discharge results, differences in medication side effect responses were observed, with 75.8% of the usual care group correctly identifying at least 1 medication side effect compared to 93.9% of the TIME group (P = .04). TIME was associated with higher satisfaction with medication education compared to usual care (97% vs. 46.9%, P < .001).
Conclusion: The nurse-led discharge medication education program TIME effectively enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge. The program also significantly improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These findings indicate that TIME is a valuable tool for augmenting patient education and medication adherence in a hospital setting. By incorporating the teach-back method, TIME offers a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge, leading to improved care transitions.
Commentary
Suboptimal communication between patients, caregivers, and providers upon hospital discharge is a major contributor to patients’ inadequate understanding of postdischarge care plans. This inadequate understanding leads to preventable harms, such as medication errors, adverse events, emergency room visits, and costly hospital readmissions.1 The issue is further exacerbated by a lack of clarity among health care team members’ respective roles in providing information that optimizes care transitions during the discharge communication process. Moreover, low health literacy, particularly prevalent among seniors, those from disadvantaged backgrouds, and those with lower education attainment or chronic illnesses, create additional barriers to effective discharge communication. A potential solution to this problem is the adoption of effective teaching strategies, specifically the teach-back method. This method employs techniques that ensure patients’ understanding and recall of new information regardless of health literacy, and places accountability on clinicians rather than patients. By closing communication gaps between clinicians and patients, the teach-back method can reduce hospital readmissions, hospital-acquired conditions, and mortality rates, while improving patient satisfaction with health care instructions and the overall hospital experience.2
Study 1, by Trivedi et al, and study 2, by Marks et al, aimed to identify and address problems related to poor communication between patients and health care team members at hospital discharge. Specifically, study 1 examined routine discharge communication practices to determine communication gaps, while study 2 evaluated a nurse-led teach-back intervention program designed to improve patients’ medication knowledge and satisfaction. These distinct objectives and designs reflected the unique ways each study approached the challenges associated with care transitions at the time of hospital discharge.
Study 1 used direct observation of patient-practitioner interactions to evaluate routine discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals. In the 33 patients observed, significant gaps in discharge communication practices were identified in the domains of medication changes, postdischarge appointments, disease self-management, and red flags or warning signs. Unsurprisingly, most of these domains were communicated in an ad hoc manner by members of the health care team without a clear pattern of responsibility in reference to patient discharge education, and teach-back was seldom used. These findings underscore the need for improved discharge techniques, effective communication strategies, and clarification of roles among the interprofessional team to enhance the safety, quality of care, and overall patient experience during hospital discharge.
Study 2 aimed to augment the hospital discharge communication process by implementing a nurse-led discharge medication education program (TIME), which targeted patients’ priority learning needs, new medication knowledge, and satisfaction with medication education. In the 107 patients assessed, this teach-back method enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge, as well as improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These results suggest that a teach-back method such as the TIME program could be a solution to care transition problems identified in the Trivedi et al study by providing a structured approach to patient education and enhancing communication practices during the hospital discharge process. Thus, by implementing the TIME program, hospitals may improve patient outcomes, safety, and overall quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Care transition at the time of hospital discharge is a particularly pivotal period in the care of vulnerable individuals. There is growing literature, including studies discussed in this review, to indicate that by focusing on improving patient-practitioner communication during the discharge process and using strategies such as the teach-back method, health care professionals can better prepare patients for self-management in the post-acute period and help them make informed decisions about their care. This emphasis on care-transition communication strategies may lead to a reduction in medication errors, adverse events, and hospital readmissions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and satisfaction. Barriers to system implementation of such strategies may include competing demands and responsibilities of busy practitioners as well as the inherent complexities associated with hospital discharge. Creative solutions, such as the utilization of telehealth and early transition-of-care visits, represent some potential approaches to counter these barriers.
While both studies illustrated barriers and facilitators of hospital discharge communication, each study had limitations that impacted their generalizability to real-world clinical practice. Limitations in study 1 included a small sample size, purposive sampling method, and a focus on planned discharges in a teaching hospital, which may introduce selection bias. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to unplanned discharges, patients who do not speak English or Spanish, or nonteaching hospitals. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which could have further impacted discharge education practices. The study also revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, which indicated systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further research is required to address this discrepancy. Limitations in study 2 included a relatively small and homogeneous sample, with most participants being younger, non-Hispanic White, English-speaking, and well-educated. This lack of diversity may limit the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, the study did not evaluate the patients’ knowledge of medication dosage and focused only on new medications. Future studies should examine the effect of teach-back on a broader range of self-management topics in preparation for discharge, while also including a more diverse population to account for factors related to social determinants of health. Taken together, further research is needed to address these limitations and ensure more generalizable results that can more broadly improve discharge education and care transitions that bridge acute and post-acute care.
Practice Points
- There is a significant need for improved discharge strategies to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
- Teach-back method may offer a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge and improve care transitions.
–Yuka Shichijo, MD, and Fred Ko, MD, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Hospital, New York, NY
1. Snow V, Beck D, Budnitz T, Miller DC, Potter J, Wears RL, Weiss KB, Williams MV; American College of Physicians; Society of General Internal Medicine; Society of Hospital Medicine; American Geriatrics Society; American College of Emergency Physicians; Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. Transitions of care consensus policy statement American College of Physicians-Society of General Internal Medicine-Society of Hospital Medicine-American Geriatrics Society-American College of Emergency Physicians-Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(8):971-976. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-0969-x
2. Yen PH, Leasure AR. Use and effectiveness of the teach-back method in patient education and health outcomes. Fed. Pract. 2019;36(6):284-289.
Study 1 Overview (Trivedi et al)
Objective: This observational quality improvement study aimed to evaluate the discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals, specifically focusing on patient education and counseling in 6 key discharge communication domains.
Design: Observations were conducted over a 13-month period from September 2018 through October 2019, following the Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE) guidelines.
Setting and participants: The study involved a total of 33 English- and Spanish-speaking patients purposefully selected from the “discharge before noon” list at 2 urban tertiary-care teaching hospitals. A total of 155 observation hours were accumulated, with an average observation time of 4.7 hours per patient on the day of discharge.
Main outcome measures: The study assessed 6 discharge communication domains: (1) the name and function of medication changes, (2) the purpose of postdischarge appointments, (3) disease self-management, (4) red flags or warning signs for complications, (5) teach-back techniques to confirm patient understanding, and (6) staff solicitation of patient questions or concerns.
Main results: The study found several gaps in discharge communication practices. Among the 29 patients with medication changes, 28% were not informed about the name and basic function of the changes, while 59% did not receive counseling on the purpose for the medication change. In terms of postdischarge appointments, 48% of patients were not told the purpose of these appointments. Moreover, 54% of patients did not receive counseling on self-management of their primary discharge diagnosis or other diagnoses, and 73% were not informed about symptom expectations or the expected course of their illness after leaving the hospital. Most patients (82%) were not counseled on red-flag signs and symptoms that should prompt immediate return to care.
Teach-back techniques, which are critical for ensuring patient understanding, were used in only 3% of cases, and 85% of patients were not asked by health care providers if there might be barriers to following the care plan. Less than half (42%) of the patients were asked if they had any questions, with most questions being logistical and often deferred to another team member or met with uncertainty. Of note, among the 33 patients, only 2 patients received extensive information that covered 5 or 6 out of 6 discharge communication domains.
The study found variable roles in who communicated what aspects of discharge education, with most domains being communicated in an ad hoc manner and no clear pattern of responsibility. However, 2 exceptions were observed: nurses were more likely to provide information about new or changed medications and follow-up appointments, and the only example of teach-back was conducted by an attending physician.
Conclusion: The study highlights a significant need for improved discharge techniques to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital. Interventions should focus on increasing transparency in patient education and understanding, clarifying assumptions of roles among the interprofessional team, and implementing effective communication strategies and system redesigns that foster patient-centered discharge education. Also, the study revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, indicating systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further studies are needed to explore the development and assessment of such interventions to ensure optimal patient outcomes and equal care following hospital discharge.
Study 2 Overview (Marks et al)
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the impact of a nurse-led discharge medication education program, Teaching Important Medication Effects (TIME), on patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours post discharge. The specific objectives were to identify patients’ priority learning needs, evaluate the influence of TIME on patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge, and assess the effect of TIME on patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Design: The study employed a longitudinal pretest/post-test, 2-group design involving 107 randomly selected medical-surgical patients from an academic hospital. Participants were interviewed before and within 72 hours after discharge following administration of medication instructions. Bivariate analyses were performed to assess demographic and outcome variable differences between groups.
Setting and participants: Conducted on a 24-bed medical-surgical unit at a large Magnet® hospital over 18 months (2018-2019), the study included patients with at least 1 new medication, aged 18 years or older, able to read and speak English or Spanish, admitted from home with a minimum 1 overnight stay, and planning to return home post discharge. Excluded were cognitively impaired patients, those assigned to a resource pool nurse without TIME training, and those having a research team member assigned. Participants were randomly selected from a computerized list of patients scheduled for discharge.
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome measures included patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge and patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Main results: The usual care (n = 52) and TIME (n = 55) patients had similar baseline demographic characteristics. The study revealed that almost all patients in both usual care and TIME groups were aware of their new medication and its purpose at discharge. However, differences were observed in medication side effect responses, with 72.5% of the usual-care group knowing side effects compared to 94.3% of the TIME group (P = .003). Additionally, 81.5% of the usual-care group understood the medication purpose compared to 100% of the TIME group (P = .02). During the 48- to 72-hour postdischarge calls, consistent responses were found from both groups regarding knowledge of new medication, medication name, and medication purpose. Similar to discharge results, differences in medication side effect responses were observed, with 75.8% of the usual care group correctly identifying at least 1 medication side effect compared to 93.9% of the TIME group (P = .04). TIME was associated with higher satisfaction with medication education compared to usual care (97% vs. 46.9%, P < .001).
Conclusion: The nurse-led discharge medication education program TIME effectively enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge. The program also significantly improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These findings indicate that TIME is a valuable tool for augmenting patient education and medication adherence in a hospital setting. By incorporating the teach-back method, TIME offers a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge, leading to improved care transitions.
Commentary
Suboptimal communication between patients, caregivers, and providers upon hospital discharge is a major contributor to patients’ inadequate understanding of postdischarge care plans. This inadequate understanding leads to preventable harms, such as medication errors, adverse events, emergency room visits, and costly hospital readmissions.1 The issue is further exacerbated by a lack of clarity among health care team members’ respective roles in providing information that optimizes care transitions during the discharge communication process. Moreover, low health literacy, particularly prevalent among seniors, those from disadvantaged backgrouds, and those with lower education attainment or chronic illnesses, create additional barriers to effective discharge communication. A potential solution to this problem is the adoption of effective teaching strategies, specifically the teach-back method. This method employs techniques that ensure patients’ understanding and recall of new information regardless of health literacy, and places accountability on clinicians rather than patients. By closing communication gaps between clinicians and patients, the teach-back method can reduce hospital readmissions, hospital-acquired conditions, and mortality rates, while improving patient satisfaction with health care instructions and the overall hospital experience.2
Study 1, by Trivedi et al, and study 2, by Marks et al, aimed to identify and address problems related to poor communication between patients and health care team members at hospital discharge. Specifically, study 1 examined routine discharge communication practices to determine communication gaps, while study 2 evaluated a nurse-led teach-back intervention program designed to improve patients’ medication knowledge and satisfaction. These distinct objectives and designs reflected the unique ways each study approached the challenges associated with care transitions at the time of hospital discharge.
Study 1 used direct observation of patient-practitioner interactions to evaluate routine discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals. In the 33 patients observed, significant gaps in discharge communication practices were identified in the domains of medication changes, postdischarge appointments, disease self-management, and red flags or warning signs. Unsurprisingly, most of these domains were communicated in an ad hoc manner by members of the health care team without a clear pattern of responsibility in reference to patient discharge education, and teach-back was seldom used. These findings underscore the need for improved discharge techniques, effective communication strategies, and clarification of roles among the interprofessional team to enhance the safety, quality of care, and overall patient experience during hospital discharge.
Study 2 aimed to augment the hospital discharge communication process by implementing a nurse-led discharge medication education program (TIME), which targeted patients’ priority learning needs, new medication knowledge, and satisfaction with medication education. In the 107 patients assessed, this teach-back method enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge, as well as improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These results suggest that a teach-back method such as the TIME program could be a solution to care transition problems identified in the Trivedi et al study by providing a structured approach to patient education and enhancing communication practices during the hospital discharge process. Thus, by implementing the TIME program, hospitals may improve patient outcomes, safety, and overall quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Care transition at the time of hospital discharge is a particularly pivotal period in the care of vulnerable individuals. There is growing literature, including studies discussed in this review, to indicate that by focusing on improving patient-practitioner communication during the discharge process and using strategies such as the teach-back method, health care professionals can better prepare patients for self-management in the post-acute period and help them make informed decisions about their care. This emphasis on care-transition communication strategies may lead to a reduction in medication errors, adverse events, and hospital readmissions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and satisfaction. Barriers to system implementation of such strategies may include competing demands and responsibilities of busy practitioners as well as the inherent complexities associated with hospital discharge. Creative solutions, such as the utilization of telehealth and early transition-of-care visits, represent some potential approaches to counter these barriers.
While both studies illustrated barriers and facilitators of hospital discharge communication, each study had limitations that impacted their generalizability to real-world clinical practice. Limitations in study 1 included a small sample size, purposive sampling method, and a focus on planned discharges in a teaching hospital, which may introduce selection bias. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to unplanned discharges, patients who do not speak English or Spanish, or nonteaching hospitals. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which could have further impacted discharge education practices. The study also revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, which indicated systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further research is required to address this discrepancy. Limitations in study 2 included a relatively small and homogeneous sample, with most participants being younger, non-Hispanic White, English-speaking, and well-educated. This lack of diversity may limit the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, the study did not evaluate the patients’ knowledge of medication dosage and focused only on new medications. Future studies should examine the effect of teach-back on a broader range of self-management topics in preparation for discharge, while also including a more diverse population to account for factors related to social determinants of health. Taken together, further research is needed to address these limitations and ensure more generalizable results that can more broadly improve discharge education and care transitions that bridge acute and post-acute care.
Practice Points
- There is a significant need for improved discharge strategies to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
- Teach-back method may offer a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge and improve care transitions.
–Yuka Shichijo, MD, and Fred Ko, MD, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Hospital, New York, NY
Study 1 Overview (Trivedi et al)
Objective: This observational quality improvement study aimed to evaluate the discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals, specifically focusing on patient education and counseling in 6 key discharge communication domains.
Design: Observations were conducted over a 13-month period from September 2018 through October 2019, following the Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE) guidelines.
Setting and participants: The study involved a total of 33 English- and Spanish-speaking patients purposefully selected from the “discharge before noon” list at 2 urban tertiary-care teaching hospitals. A total of 155 observation hours were accumulated, with an average observation time of 4.7 hours per patient on the day of discharge.
Main outcome measures: The study assessed 6 discharge communication domains: (1) the name and function of medication changes, (2) the purpose of postdischarge appointments, (3) disease self-management, (4) red flags or warning signs for complications, (5) teach-back techniques to confirm patient understanding, and (6) staff solicitation of patient questions or concerns.
Main results: The study found several gaps in discharge communication practices. Among the 29 patients with medication changes, 28% were not informed about the name and basic function of the changes, while 59% did not receive counseling on the purpose for the medication change. In terms of postdischarge appointments, 48% of patients were not told the purpose of these appointments. Moreover, 54% of patients did not receive counseling on self-management of their primary discharge diagnosis or other diagnoses, and 73% were not informed about symptom expectations or the expected course of their illness after leaving the hospital. Most patients (82%) were not counseled on red-flag signs and symptoms that should prompt immediate return to care.
Teach-back techniques, which are critical for ensuring patient understanding, were used in only 3% of cases, and 85% of patients were not asked by health care providers if there might be barriers to following the care plan. Less than half (42%) of the patients were asked if they had any questions, with most questions being logistical and often deferred to another team member or met with uncertainty. Of note, among the 33 patients, only 2 patients received extensive information that covered 5 or 6 out of 6 discharge communication domains.
The study found variable roles in who communicated what aspects of discharge education, with most domains being communicated in an ad hoc manner and no clear pattern of responsibility. However, 2 exceptions were observed: nurses were more likely to provide information about new or changed medications and follow-up appointments, and the only example of teach-back was conducted by an attending physician.
Conclusion: The study highlights a significant need for improved discharge techniques to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital. Interventions should focus on increasing transparency in patient education and understanding, clarifying assumptions of roles among the interprofessional team, and implementing effective communication strategies and system redesigns that foster patient-centered discharge education. Also, the study revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, indicating systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further studies are needed to explore the development and assessment of such interventions to ensure optimal patient outcomes and equal care following hospital discharge.
Study 2 Overview (Marks et al)
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the impact of a nurse-led discharge medication education program, Teaching Important Medication Effects (TIME), on patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours post discharge. The specific objectives were to identify patients’ priority learning needs, evaluate the influence of TIME on patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge, and assess the effect of TIME on patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Design: The study employed a longitudinal pretest/post-test, 2-group design involving 107 randomly selected medical-surgical patients from an academic hospital. Participants were interviewed before and within 72 hours after discharge following administration of medication instructions. Bivariate analyses were performed to assess demographic and outcome variable differences between groups.
Setting and participants: Conducted on a 24-bed medical-surgical unit at a large Magnet® hospital over 18 months (2018-2019), the study included patients with at least 1 new medication, aged 18 years or older, able to read and speak English or Spanish, admitted from home with a minimum 1 overnight stay, and planning to return home post discharge. Excluded were cognitively impaired patients, those assigned to a resource pool nurse without TIME training, and those having a research team member assigned. Participants were randomly selected from a computerized list of patients scheduled for discharge.
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome measures included patients’ new medication knowledge before and after discharge and patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education.
Main results: The usual care (n = 52) and TIME (n = 55) patients had similar baseline demographic characteristics. The study revealed that almost all patients in both usual care and TIME groups were aware of their new medication and its purpose at discharge. However, differences were observed in medication side effect responses, with 72.5% of the usual-care group knowing side effects compared to 94.3% of the TIME group (P = .003). Additionally, 81.5% of the usual-care group understood the medication purpose compared to 100% of the TIME group (P = .02). During the 48- to 72-hour postdischarge calls, consistent responses were found from both groups regarding knowledge of new medication, medication name, and medication purpose. Similar to discharge results, differences in medication side effect responses were observed, with 75.8% of the usual care group correctly identifying at least 1 medication side effect compared to 93.9% of the TIME group (P = .04). TIME was associated with higher satisfaction with medication education compared to usual care (97% vs. 46.9%, P < .001).
Conclusion: The nurse-led discharge medication education program TIME effectively enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge. The program also significantly improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These findings indicate that TIME is a valuable tool for augmenting patient education and medication adherence in a hospital setting. By incorporating the teach-back method, TIME offers a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge, leading to improved care transitions.
Commentary
Suboptimal communication between patients, caregivers, and providers upon hospital discharge is a major contributor to patients’ inadequate understanding of postdischarge care plans. This inadequate understanding leads to preventable harms, such as medication errors, adverse events, emergency room visits, and costly hospital readmissions.1 The issue is further exacerbated by a lack of clarity among health care team members’ respective roles in providing information that optimizes care transitions during the discharge communication process. Moreover, low health literacy, particularly prevalent among seniors, those from disadvantaged backgrouds, and those with lower education attainment or chronic illnesses, create additional barriers to effective discharge communication. A potential solution to this problem is the adoption of effective teaching strategies, specifically the teach-back method. This method employs techniques that ensure patients’ understanding and recall of new information regardless of health literacy, and places accountability on clinicians rather than patients. By closing communication gaps between clinicians and patients, the teach-back method can reduce hospital readmissions, hospital-acquired conditions, and mortality rates, while improving patient satisfaction with health care instructions and the overall hospital experience.2
Study 1, by Trivedi et al, and study 2, by Marks et al, aimed to identify and address problems related to poor communication between patients and health care team members at hospital discharge. Specifically, study 1 examined routine discharge communication practices to determine communication gaps, while study 2 evaluated a nurse-led teach-back intervention program designed to improve patients’ medication knowledge and satisfaction. These distinct objectives and designs reflected the unique ways each study approached the challenges associated with care transitions at the time of hospital discharge.
Study 1 used direct observation of patient-practitioner interactions to evaluate routine discharge communication practices in internal medicine services at 2 urban academic teaching hospitals. In the 33 patients observed, significant gaps in discharge communication practices were identified in the domains of medication changes, postdischarge appointments, disease self-management, and red flags or warning signs. Unsurprisingly, most of these domains were communicated in an ad hoc manner by members of the health care team without a clear pattern of responsibility in reference to patient discharge education, and teach-back was seldom used. These findings underscore the need for improved discharge techniques, effective communication strategies, and clarification of roles among the interprofessional team to enhance the safety, quality of care, and overall patient experience during hospital discharge.
Study 2 aimed to augment the hospital discharge communication process by implementing a nurse-led discharge medication education program (TIME), which targeted patients’ priority learning needs, new medication knowledge, and satisfaction with medication education. In the 107 patients assessed, this teach-back method enhanced patients’ new medication knowledge at discharge and 48 to 72 hours after discharge, as well as improved patients’ experience and satisfaction with medication education. These results suggest that a teach-back method such as the TIME program could be a solution to care transition problems identified in the Trivedi et al study by providing a structured approach to patient education and enhancing communication practices during the hospital discharge process. Thus, by implementing the TIME program, hospitals may improve patient outcomes, safety, and overall quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Care transition at the time of hospital discharge is a particularly pivotal period in the care of vulnerable individuals. There is growing literature, including studies discussed in this review, to indicate that by focusing on improving patient-practitioner communication during the discharge process and using strategies such as the teach-back method, health care professionals can better prepare patients for self-management in the post-acute period and help them make informed decisions about their care. This emphasis on care-transition communication strategies may lead to a reduction in medication errors, adverse events, and hospital readmissions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and satisfaction. Barriers to system implementation of such strategies may include competing demands and responsibilities of busy practitioners as well as the inherent complexities associated with hospital discharge. Creative solutions, such as the utilization of telehealth and early transition-of-care visits, represent some potential approaches to counter these barriers.
While both studies illustrated barriers and facilitators of hospital discharge communication, each study had limitations that impacted their generalizability to real-world clinical practice. Limitations in study 1 included a small sample size, purposive sampling method, and a focus on planned discharges in a teaching hospital, which may introduce selection bias. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to unplanned discharges, patients who do not speak English or Spanish, or nonteaching hospitals. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which could have further impacted discharge education practices. The study also revealed that some patients received more robust discharge education than others, which indicated systemic inequality in the patient experience. Further research is required to address this discrepancy. Limitations in study 2 included a relatively small and homogeneous sample, with most participants being younger, non-Hispanic White, English-speaking, and well-educated. This lack of diversity may limit the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, the study did not evaluate the patients’ knowledge of medication dosage and focused only on new medications. Future studies should examine the effect of teach-back on a broader range of self-management topics in preparation for discharge, while also including a more diverse population to account for factors related to social determinants of health. Taken together, further research is needed to address these limitations and ensure more generalizable results that can more broadly improve discharge education and care transitions that bridge acute and post-acute care.
Practice Points
- There is a significant need for improved discharge strategies to enhance patient safety and quality of care upon leaving the hospital.
- Teach-back method may offer a structured approach to educating patients about their medications at hospital discharge and improve care transitions.
–Yuka Shichijo, MD, and Fred Ko, MD, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Hospital, New York, NY
1. Snow V, Beck D, Budnitz T, Miller DC, Potter J, Wears RL, Weiss KB, Williams MV; American College of Physicians; Society of General Internal Medicine; Society of Hospital Medicine; American Geriatrics Society; American College of Emergency Physicians; Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. Transitions of care consensus policy statement American College of Physicians-Society of General Internal Medicine-Society of Hospital Medicine-American Geriatrics Society-American College of Emergency Physicians-Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(8):971-976. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-0969-x
2. Yen PH, Leasure AR. Use and effectiveness of the teach-back method in patient education and health outcomes. Fed. Pract. 2019;36(6):284-289.
1. Snow V, Beck D, Budnitz T, Miller DC, Potter J, Wears RL, Weiss KB, Williams MV; American College of Physicians; Society of General Internal Medicine; Society of Hospital Medicine; American Geriatrics Society; American College of Emergency Physicians; Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. Transitions of care consensus policy statement American College of Physicians-Society of General Internal Medicine-Society of Hospital Medicine-American Geriatrics Society-American College of Emergency Physicians-Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(8):971-976. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-0969-x
2. Yen PH, Leasure AR. Use and effectiveness of the teach-back method in patient education and health outcomes. Fed. Pract. 2019;36(6):284-289.
Meet the JCOM Author with Dr. Barkoudah: A Multidisciplinary Team–Based Clinical Care Pathway for Infective Endocarditis
Implementation of a Multidisciplinary Team–Based Clinical Care Pathway Is Associated With Increased Surgery Rates for Infective Endocarditis
From the University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO (Haley Crosby); Department of Clinical Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO (Dr. Pierce); and Department of Medicine, Divisions of Infectious Diseases and Pulmonary, Critical Care and Environmental Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, and Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Infectious Diseases, University of Maryland Baltimore Washington Medical Center, Glen Burnie, MD (Dr. Regunath).
ABSTRACT
Objective: Multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) improve outcomes for patients with infective endocarditis (IE), but methods of implementation vary. In our academic medical center, we developed an MDT approach guided by a clinical care pathway and assessed outcomes of patients with IE.
Methods: We compared outcomes of patients with IE and indications for surgery between December 2018 and June 2020 with our prior published data for the period January to December 2016. MDT interventions involved recurring conferences with infectious diseases physicians in team meetings and promoting a clinical care pathway to guide providers on steps in management. Primary outcomes were surgery and in-hospital death.
Results: Prior to the intervention, 6 of 21 (28.6%) patients with indications for surgery underwent surgery or were transferred to higher centers for surgery, and 6 (28.6%) patients died. Post intervention, 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients underwent or were transferred for surgery, and 5 (16.1%) died. After adjusting for age and gender, the odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) compared with the pre-intervention period. The odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21).
Conclusion: An MDT team approach using a clinical pathway was associated with an increased number of surgeries performed for IE and may lower rates of in-hospital mortality.
Keywords: infective endocarditis, clinical pathway, quality improvement, multidisciplinary team, valve surgery.
Infective endocarditis (IE) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.1 Rates of IE due to Staphylococcus aureus are increasing in the United States.2 Reported in-hospital mortality from IE ranges from 15% to 20%.3
Clinical pathways are defined as “structured, multidisciplinary plans of care used by health services to detail essential steps in the care of patients with a specific clinical problem.”12 In the modern era, these pathways are often developed and implemented via the electronic health record (EHR) system. Studies of clinical pathways generally demonstrate improvements in patient outcomes, quality of care, or resource utilization.13,14 Clinical pathways represent 1 possible approach to the implementation of a MDT in the care of patients with IE.15
In our earlier work, we used quality improvement principles in the design of an MDT approach to IE care at our institution.16 Despite having indications for surgery, 12 of 21 (57.1%) patients with IE did not undergo surgery, and we identified these missed opportunities for surgery as a leverage point for improvement of outcomes. With input from the various specialties and stakeholders, we developed a clinical pathway (algorithm) for the institutional management of IE that guides next steps in clinical care and their timelines, aiming to reduce by 50% (from 57.1% to 28.6%) the number of patients with IE who do not undergo surgery despite guideline indications for early surgical intervention. In this report, we describe the implementation of this clinical pathway as our MDT approach to the care of patients with IE at our institution.
Methods
The University of Missouri, Columbia, is a tertiary care academic health system with 5 hospitals and more than 60 clinic locations across central Missouri. In the spring of 2018, an MDT was developed, with support from administrative leaders, to improve the care of patients with IE at our institution. The work group prioritized one leverage point to improve IE outcomes, which was improving the number of surgeries performed on those IE patients who had guideline indications for surgery. A clinical pathway was developed around this leverage point (Figure 1). The pathway leveraged the 6 T’s (Table 1) to guide providers through the evaluation and management of IE.17 The pathway focused on improving adherence to standards of care and reduction in practice variation by defining indications for referrals and diagnostic interventions, helping to reduce delays in consultation and diagnosis. The pathway also clearly outlined the surgical indications and timing for patients with IE and provided the basis for decisions to proceed with surgery.
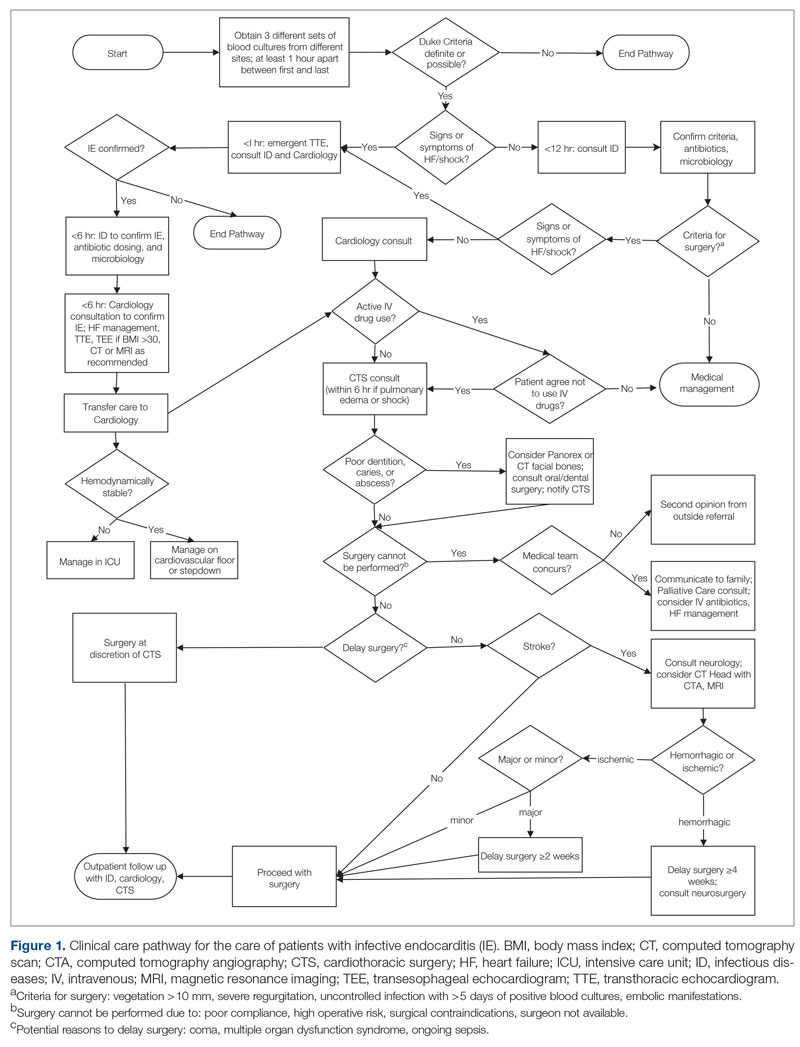
Starting in late 2018, in collaboration with cardiology and CTS teams, ID specialists socialized the clinical pathway to inpatient services that cared for patients with IE. Infectious diseases physicians also provided recurring conferences on the effectiveness of MDTs in IE management and participated in heart-valve team case discussions. Finally, in May 2019, an electronic version of the pathway was embedded in the EHR system using a Cerner PowerChart feature known as Care Pathways. The feature presents the user with algorithm questions in the EHR and provides recommendations, relevant orders, timelines, and other decision support in the clinical pathway. The feature is available to all providers in the health system.
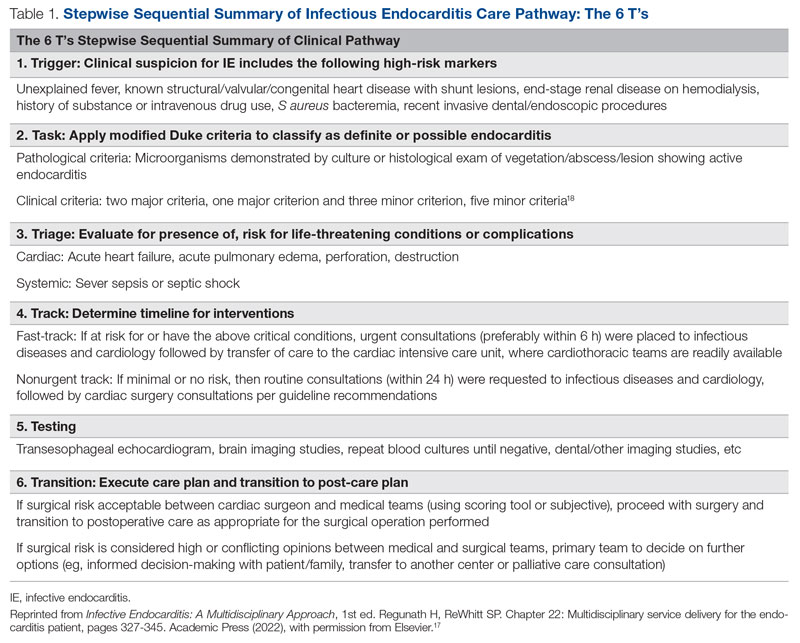
To evaluate the effectiveness of our intervention, we recorded outcomes for patients with IE with surgical indications between December 2018 and June 2020 and compared them with our prior published data from January to December 2016. Cases of IE for the current study period were identified via retrospective chart review. Records from December 2018 to June 2020 were searched using International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) discharge codes for IE (I33, I33.0, I33.9, I38, I39, M32.11). To select those patients with definitive IE and indications for surgery, the following criteria were applied: age ≥ 18 years; fulfilled modified Duke criteria for definite IE18; and met ≥ 1 American Heart Association (AHA)/Infection Diseases Society of America criteria for recommendation for surgery. Indications for surgery were ≥ 1 of the following: left-sided endocarditis caused by S aureus, fungal, or highly resistant organism; new heart block; annular or aortic abscess; persistent bacteremia or fever despite 5 days of appropriate antimicrobials; vegetation size ≥ 10 mm and evidence of embolic phenomena; recurrence of prosthetic valve infection; recurrent emboli and persistent vegetation despite antimicrobials; and increase in vegetation size despite antimicrobials.16
Age was treated as a categorical variable, using the age groups 18 to 44 years, 45 to 64 years, and 65 years and older. Gender was self-reported. Primary outcomes were surgery or transfer to a higher center for surgery and in-hospital death. Secondary outcomes included consults to teams involved in multidisciplinary care of patients with IE, including ID, cardiology, and CTS. Bivariate analyses were performed using Pearson χ2 tests. Odds ratios for surgery and death were calculated using a multivariate logistic regression model including age and gender covariates. Statistical significance was defined at α = 0.05, and statistical analysis was performed using Stata/IC v16.1 (StataCorp LLC). Our university institutional review board (IRB) reviewed the project (#2010858-QI) and determined that the project was quality-improvement activity, not human subject research, and therefore did not require additional IRB review.
Results
We identified 21 patients in the pre-intervention period and 31 patients in the postintervention period with definitive IE who had guideline indications for surgery. The postintervention cohort was older and had more male patients; this difference was not statistically significant. No differences were noted between the groups for race, gender, or intravenous (IV) drug use (Table 2). Chi-square tests of independence were performed to assess the relationship between age and our primary outcomes. There was a significant relationship between age and the likelihood of receiving or being transferred for surgery (59.3% vs 50% vs 7.7% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 [2, N = 52] = 9.67; P = .008), but not between age and mortality (14.8% vs 25.0% vs 30.8% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 = 1.48 [2, N = 52; P = .478]. The electronic version of the clinical pathway was activated and used in only 3 of the 31 patients in the postintervention period. Consultations to ID, cardiology, and CTS teams were compared between the study periods (Table 2). Although more consultations were seen in the postintervention period, differences were not statistically significant.
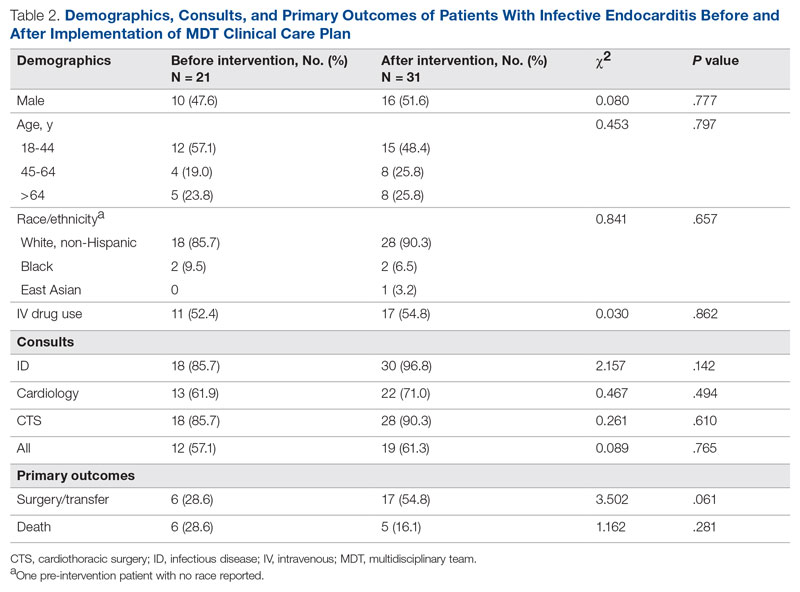
The unadjusted primary outcomes are shown in Table 2. More surgeries were performed per guideline indications, and fewer deaths were noted in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period, but the differences were not statistically significant (Table 2).
Because the postintervention period had more male patients and older patients, we evaluated the outcomes using a logistic regression model controlling for both age and gender. The odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) as compared with the pre-intervention period, and the odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period compared with the pre-intervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21) (Figure 2).
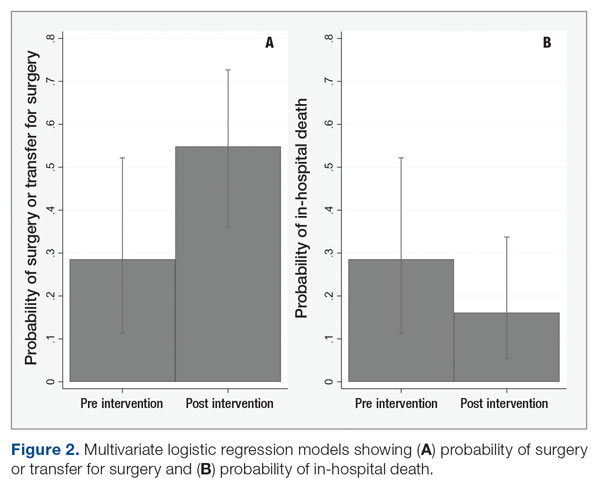
Discussion
In our study, patients with IE with guideline indications for surgery had significantly higher rates of surgery in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period. The implementation of an MDT, recurring educational sessions, and efforts to implement and familiarize team members with the clinical pathway approach are the most likely reasons for this change. The increased rates of surgery in the postintervention period were the likely proximate cause of the 60% reduction in in-hospital mortality. This improvement in mortality, while not statistically significant, is very likely to be clinically significant and helps reinforce the value of the MDT intervention used.
Our findings are consistent with existing and mounting literature on the use of MDTs to improve outcomes for patients with IE, including 2 studies that noted an increased rate of surgery for patients with indications.8,19 Several other studies in both Europe and North America have found significant decreases in mortality,6-11,20,21 rates of complications,9 time to diagnosis and treatment,11 and length of stay9,20 for patients with IE managed with an MDT strategy. Although current AHA guidelines for care of patients with IE do suggest an MDT approach, the strategy for this approach is not well established.22 Only 1 study that has implemented a new MDT protocol for care of IE has been conducted in the United States.8
While effective MDTs certainly improve outcomes in patients with IE, there are reported differences in implementation of such an approach. With the MDT model as the core, various implementations included regular case conferences,10,11,19,21,23 formation of a consulting team,6,8 or establishment of a new protocol or algorithm for care.8,9,20 Our approach used a clinical pathway as a basis for improved communication among consulting services, education of learning providers via regular case conferences, and implementation of an electronic clinical care pathway to guide them step by step. Our pathway followed the institutionally standardized algorithm (Figure 1), using what we called the 6 T’s approach (Table 1), that guides providers to evaluate critical cases in a fast track.17
To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first report of an MDT that used an electronic clinical care pathway embedded within the EHR. The electronic version of our clinical pathway went live for only the second half of the postintervention study period, which is the most likely reason for its limited utilization. It is also possible that educational efforts in the first half of the intervention period were sufficient to familiarize providers with the care pathway such that the electronic version was seldom needed. We are exploring other possible ways of improving electronic pathway utilization, such as improving the feature usability and further systemwide educational efforts.
Our study has other limitations. Quasi-experimental before-and-after comparisons are subject to confounding from concurrent interventions. We had a substantial change in cardiothoracic faculty soon after the commencement of our efforts to form the MDT, and thus cannot rule out differences related to their comfort level in considering or offering surgery. We also cannot rule out a Hawthorne effect, where knowledge of the ongoing quality-improvement project changed provider behavior, making surgery more likely. We did not evaluate rates of right- versus left-sided endocarditis, which have been linked to mortality.24 Our study also was performed across a single academic institution, which may limit its generalizability. Finally, our study may not have been adequately powered to detect differences in mortality due to implementation of the MDT approach.
Conclusion
Our work suggests that an MDT for IE can be successfully designed and implemented with a clinical pathway using quality-improvement tools in centers where subspecialty services are available. Our approach was associated with a higher rate of surgery among patients with guideline indications for surgery and may reduce in-hospital mortality. An electronic clinical care pathway embedded in the EHR is feasible and may have a role in MDT implementation.
These data were also accepted as a poster at IDWeek 2022, Washington, DC. The poster abstract is published in an online supplement of Open Forum Infectious Diseases as an abstract publication.
Corresponding author: Haley Crosby; hwc2pd@health.missouri.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132(15):1435-1486. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000296
2. Federspiel JJ, Stearns SC, Peppercorn AF, et al. Increasing US rates of endocarditis with Staphylococcus aureus: 1999-2008. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(4):363-365. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.1027
3. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(23):e521-e643. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000031
4. Chambers J, Sandoe J, Ray S, et al. The infective endocarditis team: recommendations from an international working group. Heart. 2014;100(7):524-527. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304354
5. Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-3128. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv319
6. Chirillo F, Scotton P, Rocco F, et al. Impact of a multidisciplinary management strategy on the outcome of patients with native valve infective endocarditis. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1171-1176. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.060
7. Botelho-Nevers E, Thuny F, Casalta JP, et al. Dramatic reduction in infective endocarditis-related mortality with a management-based approach. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(14):1290-1298. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.192
8. El-Dalati S, Cronin D, Riddell IV J, et al. The clinical impact of implementation of a multidisciplinary endocarditis team. Ann Thorac Surg. 2022;113(1):118-124.
9. Carrasco-Chinchilla F, Sánchez-Espín G, Ruiz-Morales J, et al. Influence of a multidisciplinary alert strategy on mortality due to left-sided infective endocarditis. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014;67(5):380-386. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2013.09.010
10. Issa N, Dijos M, Greib C, et al. Impact of an endocarditis team in the management of 357 infective endocarditis [abstract]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(suppl 1):S201. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofw172.825
11. Kaura A, Byrne J, Fife A, et al. Inception of the ‘endocarditis team’ is associated with improved survival in patients with infective endocarditis who are managed medically: findings from a before-and-after study. Open Heart. 2017;4(2):e000699. doi:10.1136/openhrt-2017-000699
12. Rotter T, Kinsman L, James E, et al. Clinical pathways: effects on professional practice, patient outcomes, length of stay and hospital costs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(3):Cd006632. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006632.pub2
13. Neame MT, Chacko J, Surace AE, et al. A systematic review of the effects of implementing clinical pathways supported by health information technologies. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(4):356-363. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy176
14. Trimarchi L, Caruso R, Magon G, et al. Clinical pathways and patient-related outcomes in hospital-based settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Biomed. 2021;92(1):e2021093. doi:10.23750/abm.v92i1.10639
15. Gibbons EF, Huang G, Aldea G, et al. A multidisciplinary pathway for the diagnosis and treatment of infectious endocarditis. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2020;19(4):187-194. doi:10.1097/hpc.0000000000000224
16. Regunath H, Vasudevan A, Vyas K, et al. A quality improvement initiative: developing a multi-disciplinary team for infective endocarditis. Mo Med. 2019;116(4):291-296.
17. Regunath H, Whitt SP. Multidisciplinary service delivery for the endocarditis patient. In: Infective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 1st ed. Kilic A, ed. Academic Press; 2022.
18. Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med. 1994;96(3):200-209. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(94)90143-0
19. Tan C, Hansen MS, Cohen G, et al. Case conferences for infective endocarditis: a quality improvement initiative. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205528. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0205528
20. Ruch Y, Mazzucotelli JP, Lefebvre F, et al. Impact of setting up an “endocarditis team” on the management of infective endocarditis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(9):ofz308. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz308
21. Camou F, Dijos M, Barandon L, et al. Management of infective endocarditis and multidisciplinary approach. Med Mal Infect. 2019;49(1):17-22. doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2018.06.007
22. Pettersson GB, Hussain ST. Current AATS guidelines on surgical treatment of infective endocarditis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;8(6):630-644. doi:10.21037/acs.2019.10.05
23. Mestres CA, Paré JC, Miró JM. Organization and functioning of a multidisciplinary team for the diagnosis and treatment of infective endocarditis: a 30-year perspective (1985-2014). Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2015;68(5):363-368. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2014.10.006
24. Stavi V, Brandstaetter E, Sagy I, et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics and prognosis in patients with right- and left-sided infective endocarditis. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2019;10(1):e00003. doi:10.5041/rmmj.10338
From the University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO (Haley Crosby); Department of Clinical Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO (Dr. Pierce); and Department of Medicine, Divisions of Infectious Diseases and Pulmonary, Critical Care and Environmental Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, and Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Infectious Diseases, University of Maryland Baltimore Washington Medical Center, Glen Burnie, MD (Dr. Regunath).
ABSTRACT
Objective: Multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) improve outcomes for patients with infective endocarditis (IE), but methods of implementation vary. In our academic medical center, we developed an MDT approach guided by a clinical care pathway and assessed outcomes of patients with IE.
Methods: We compared outcomes of patients with IE and indications for surgery between December 2018 and June 2020 with our prior published data for the period January to December 2016. MDT interventions involved recurring conferences with infectious diseases physicians in team meetings and promoting a clinical care pathway to guide providers on steps in management. Primary outcomes were surgery and in-hospital death.
Results: Prior to the intervention, 6 of 21 (28.6%) patients with indications for surgery underwent surgery or were transferred to higher centers for surgery, and 6 (28.6%) patients died. Post intervention, 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients underwent or were transferred for surgery, and 5 (16.1%) died. After adjusting for age and gender, the odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) compared with the pre-intervention period. The odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21).
Conclusion: An MDT team approach using a clinical pathway was associated with an increased number of surgeries performed for IE and may lower rates of in-hospital mortality.
Keywords: infective endocarditis, clinical pathway, quality improvement, multidisciplinary team, valve surgery.
Infective endocarditis (IE) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.1 Rates of IE due to Staphylococcus aureus are increasing in the United States.2 Reported in-hospital mortality from IE ranges from 15% to 20%.3
Clinical pathways are defined as “structured, multidisciplinary plans of care used by health services to detail essential steps in the care of patients with a specific clinical problem.”12 In the modern era, these pathways are often developed and implemented via the electronic health record (EHR) system. Studies of clinical pathways generally demonstrate improvements in patient outcomes, quality of care, or resource utilization.13,14 Clinical pathways represent 1 possible approach to the implementation of a MDT in the care of patients with IE.15
In our earlier work, we used quality improvement principles in the design of an MDT approach to IE care at our institution.16 Despite having indications for surgery, 12 of 21 (57.1%) patients with IE did not undergo surgery, and we identified these missed opportunities for surgery as a leverage point for improvement of outcomes. With input from the various specialties and stakeholders, we developed a clinical pathway (algorithm) for the institutional management of IE that guides next steps in clinical care and their timelines, aiming to reduce by 50% (from 57.1% to 28.6%) the number of patients with IE who do not undergo surgery despite guideline indications for early surgical intervention. In this report, we describe the implementation of this clinical pathway as our MDT approach to the care of patients with IE at our institution.
Methods
The University of Missouri, Columbia, is a tertiary care academic health system with 5 hospitals and more than 60 clinic locations across central Missouri. In the spring of 2018, an MDT was developed, with support from administrative leaders, to improve the care of patients with IE at our institution. The work group prioritized one leverage point to improve IE outcomes, which was improving the number of surgeries performed on those IE patients who had guideline indications for surgery. A clinical pathway was developed around this leverage point (Figure 1). The pathway leveraged the 6 T’s (Table 1) to guide providers through the evaluation and management of IE.17 The pathway focused on improving adherence to standards of care and reduction in practice variation by defining indications for referrals and diagnostic interventions, helping to reduce delays in consultation and diagnosis. The pathway also clearly outlined the surgical indications and timing for patients with IE and provided the basis for decisions to proceed with surgery.

Starting in late 2018, in collaboration with cardiology and CTS teams, ID specialists socialized the clinical pathway to inpatient services that cared for patients with IE. Infectious diseases physicians also provided recurring conferences on the effectiveness of MDTs in IE management and participated in heart-valve team case discussions. Finally, in May 2019, an electronic version of the pathway was embedded in the EHR system using a Cerner PowerChart feature known as Care Pathways. The feature presents the user with algorithm questions in the EHR and provides recommendations, relevant orders, timelines, and other decision support in the clinical pathway. The feature is available to all providers in the health system.

To evaluate the effectiveness of our intervention, we recorded outcomes for patients with IE with surgical indications between December 2018 and June 2020 and compared them with our prior published data from January to December 2016. Cases of IE for the current study period were identified via retrospective chart review. Records from December 2018 to June 2020 were searched using International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) discharge codes for IE (I33, I33.0, I33.9, I38, I39, M32.11). To select those patients with definitive IE and indications for surgery, the following criteria were applied: age ≥ 18 years; fulfilled modified Duke criteria for definite IE18; and met ≥ 1 American Heart Association (AHA)/Infection Diseases Society of America criteria for recommendation for surgery. Indications for surgery were ≥ 1 of the following: left-sided endocarditis caused by S aureus, fungal, or highly resistant organism; new heart block; annular or aortic abscess; persistent bacteremia or fever despite 5 days of appropriate antimicrobials; vegetation size ≥ 10 mm and evidence of embolic phenomena; recurrence of prosthetic valve infection; recurrent emboli and persistent vegetation despite antimicrobials; and increase in vegetation size despite antimicrobials.16
Age was treated as a categorical variable, using the age groups 18 to 44 years, 45 to 64 years, and 65 years and older. Gender was self-reported. Primary outcomes were surgery or transfer to a higher center for surgery and in-hospital death. Secondary outcomes included consults to teams involved in multidisciplinary care of patients with IE, including ID, cardiology, and CTS. Bivariate analyses were performed using Pearson χ2 tests. Odds ratios for surgery and death were calculated using a multivariate logistic regression model including age and gender covariates. Statistical significance was defined at α = 0.05, and statistical analysis was performed using Stata/IC v16.1 (StataCorp LLC). Our university institutional review board (IRB) reviewed the project (#2010858-QI) and determined that the project was quality-improvement activity, not human subject research, and therefore did not require additional IRB review.
Results
We identified 21 patients in the pre-intervention period and 31 patients in the postintervention period with definitive IE who had guideline indications for surgery. The postintervention cohort was older and had more male patients; this difference was not statistically significant. No differences were noted between the groups for race, gender, or intravenous (IV) drug use (Table 2). Chi-square tests of independence were performed to assess the relationship between age and our primary outcomes. There was a significant relationship between age and the likelihood of receiving or being transferred for surgery (59.3% vs 50% vs 7.7% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 [2, N = 52] = 9.67; P = .008), but not between age and mortality (14.8% vs 25.0% vs 30.8% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 = 1.48 [2, N = 52; P = .478]. The electronic version of the clinical pathway was activated and used in only 3 of the 31 patients in the postintervention period. Consultations to ID, cardiology, and CTS teams were compared between the study periods (Table 2). Although more consultations were seen in the postintervention period, differences were not statistically significant.

The unadjusted primary outcomes are shown in Table 2. More surgeries were performed per guideline indications, and fewer deaths were noted in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period, but the differences were not statistically significant (Table 2).
Because the postintervention period had more male patients and older patients, we evaluated the outcomes using a logistic regression model controlling for both age and gender. The odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) as compared with the pre-intervention period, and the odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period compared with the pre-intervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21) (Figure 2).

Discussion
In our study, patients with IE with guideline indications for surgery had significantly higher rates of surgery in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period. The implementation of an MDT, recurring educational sessions, and efforts to implement and familiarize team members with the clinical pathway approach are the most likely reasons for this change. The increased rates of surgery in the postintervention period were the likely proximate cause of the 60% reduction in in-hospital mortality. This improvement in mortality, while not statistically significant, is very likely to be clinically significant and helps reinforce the value of the MDT intervention used.
Our findings are consistent with existing and mounting literature on the use of MDTs to improve outcomes for patients with IE, including 2 studies that noted an increased rate of surgery for patients with indications.8,19 Several other studies in both Europe and North America have found significant decreases in mortality,6-11,20,21 rates of complications,9 time to diagnosis and treatment,11 and length of stay9,20 for patients with IE managed with an MDT strategy. Although current AHA guidelines for care of patients with IE do suggest an MDT approach, the strategy for this approach is not well established.22 Only 1 study that has implemented a new MDT protocol for care of IE has been conducted in the United States.8
While effective MDTs certainly improve outcomes in patients with IE, there are reported differences in implementation of such an approach. With the MDT model as the core, various implementations included regular case conferences,10,11,19,21,23 formation of a consulting team,6,8 or establishment of a new protocol or algorithm for care.8,9,20 Our approach used a clinical pathway as a basis for improved communication among consulting services, education of learning providers via regular case conferences, and implementation of an electronic clinical care pathway to guide them step by step. Our pathway followed the institutionally standardized algorithm (Figure 1), using what we called the 6 T’s approach (Table 1), that guides providers to evaluate critical cases in a fast track.17
To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first report of an MDT that used an electronic clinical care pathway embedded within the EHR. The electronic version of our clinical pathway went live for only the second half of the postintervention study period, which is the most likely reason for its limited utilization. It is also possible that educational efforts in the first half of the intervention period were sufficient to familiarize providers with the care pathway such that the electronic version was seldom needed. We are exploring other possible ways of improving electronic pathway utilization, such as improving the feature usability and further systemwide educational efforts.
Our study has other limitations. Quasi-experimental before-and-after comparisons are subject to confounding from concurrent interventions. We had a substantial change in cardiothoracic faculty soon after the commencement of our efforts to form the MDT, and thus cannot rule out differences related to their comfort level in considering or offering surgery. We also cannot rule out a Hawthorne effect, where knowledge of the ongoing quality-improvement project changed provider behavior, making surgery more likely. We did not evaluate rates of right- versus left-sided endocarditis, which have been linked to mortality.24 Our study also was performed across a single academic institution, which may limit its generalizability. Finally, our study may not have been adequately powered to detect differences in mortality due to implementation of the MDT approach.
Conclusion
Our work suggests that an MDT for IE can be successfully designed and implemented with a clinical pathway using quality-improvement tools in centers where subspecialty services are available. Our approach was associated with a higher rate of surgery among patients with guideline indications for surgery and may reduce in-hospital mortality. An electronic clinical care pathway embedded in the EHR is feasible and may have a role in MDT implementation.
These data were also accepted as a poster at IDWeek 2022, Washington, DC. The poster abstract is published in an online supplement of Open Forum Infectious Diseases as an abstract publication.
Corresponding author: Haley Crosby; hwc2pd@health.missouri.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
From the University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO (Haley Crosby); Department of Clinical Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO (Dr. Pierce); and Department of Medicine, Divisions of Infectious Diseases and Pulmonary, Critical Care and Environmental Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, and Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Infectious Diseases, University of Maryland Baltimore Washington Medical Center, Glen Burnie, MD (Dr. Regunath).
ABSTRACT
Objective: Multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) improve outcomes for patients with infective endocarditis (IE), but methods of implementation vary. In our academic medical center, we developed an MDT approach guided by a clinical care pathway and assessed outcomes of patients with IE.
Methods: We compared outcomes of patients with IE and indications for surgery between December 2018 and June 2020 with our prior published data for the period January to December 2016. MDT interventions involved recurring conferences with infectious diseases physicians in team meetings and promoting a clinical care pathway to guide providers on steps in management. Primary outcomes were surgery and in-hospital death.
Results: Prior to the intervention, 6 of 21 (28.6%) patients with indications for surgery underwent surgery or were transferred to higher centers for surgery, and 6 (28.6%) patients died. Post intervention, 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients underwent or were transferred for surgery, and 5 (16.1%) died. After adjusting for age and gender, the odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) compared with the pre-intervention period. The odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21).
Conclusion: An MDT team approach using a clinical pathway was associated with an increased number of surgeries performed for IE and may lower rates of in-hospital mortality.
Keywords: infective endocarditis, clinical pathway, quality improvement, multidisciplinary team, valve surgery.
Infective endocarditis (IE) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.1 Rates of IE due to Staphylococcus aureus are increasing in the United States.2 Reported in-hospital mortality from IE ranges from 15% to 20%.3
Clinical pathways are defined as “structured, multidisciplinary plans of care used by health services to detail essential steps in the care of patients with a specific clinical problem.”12 In the modern era, these pathways are often developed and implemented via the electronic health record (EHR) system. Studies of clinical pathways generally demonstrate improvements in patient outcomes, quality of care, or resource utilization.13,14 Clinical pathways represent 1 possible approach to the implementation of a MDT in the care of patients with IE.15
In our earlier work, we used quality improvement principles in the design of an MDT approach to IE care at our institution.16 Despite having indications for surgery, 12 of 21 (57.1%) patients with IE did not undergo surgery, and we identified these missed opportunities for surgery as a leverage point for improvement of outcomes. With input from the various specialties and stakeholders, we developed a clinical pathway (algorithm) for the institutional management of IE that guides next steps in clinical care and their timelines, aiming to reduce by 50% (from 57.1% to 28.6%) the number of patients with IE who do not undergo surgery despite guideline indications for early surgical intervention. In this report, we describe the implementation of this clinical pathway as our MDT approach to the care of patients with IE at our institution.
Methods
The University of Missouri, Columbia, is a tertiary care academic health system with 5 hospitals and more than 60 clinic locations across central Missouri. In the spring of 2018, an MDT was developed, with support from administrative leaders, to improve the care of patients with IE at our institution. The work group prioritized one leverage point to improve IE outcomes, which was improving the number of surgeries performed on those IE patients who had guideline indications for surgery. A clinical pathway was developed around this leverage point (Figure 1). The pathway leveraged the 6 T’s (Table 1) to guide providers through the evaluation and management of IE.17 The pathway focused on improving adherence to standards of care and reduction in practice variation by defining indications for referrals and diagnostic interventions, helping to reduce delays in consultation and diagnosis. The pathway also clearly outlined the surgical indications and timing for patients with IE and provided the basis for decisions to proceed with surgery.

Starting in late 2018, in collaboration with cardiology and CTS teams, ID specialists socialized the clinical pathway to inpatient services that cared for patients with IE. Infectious diseases physicians also provided recurring conferences on the effectiveness of MDTs in IE management and participated in heart-valve team case discussions. Finally, in May 2019, an electronic version of the pathway was embedded in the EHR system using a Cerner PowerChart feature known as Care Pathways. The feature presents the user with algorithm questions in the EHR and provides recommendations, relevant orders, timelines, and other decision support in the clinical pathway. The feature is available to all providers in the health system.

To evaluate the effectiveness of our intervention, we recorded outcomes for patients with IE with surgical indications between December 2018 and June 2020 and compared them with our prior published data from January to December 2016. Cases of IE for the current study period were identified via retrospective chart review. Records from December 2018 to June 2020 were searched using International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) discharge codes for IE (I33, I33.0, I33.9, I38, I39, M32.11). To select those patients with definitive IE and indications for surgery, the following criteria were applied: age ≥ 18 years; fulfilled modified Duke criteria for definite IE18; and met ≥ 1 American Heart Association (AHA)/Infection Diseases Society of America criteria for recommendation for surgery. Indications for surgery were ≥ 1 of the following: left-sided endocarditis caused by S aureus, fungal, or highly resistant organism; new heart block; annular or aortic abscess; persistent bacteremia or fever despite 5 days of appropriate antimicrobials; vegetation size ≥ 10 mm and evidence of embolic phenomena; recurrence of prosthetic valve infection; recurrent emboli and persistent vegetation despite antimicrobials; and increase in vegetation size despite antimicrobials.16
Age was treated as a categorical variable, using the age groups 18 to 44 years, 45 to 64 years, and 65 years and older. Gender was self-reported. Primary outcomes were surgery or transfer to a higher center for surgery and in-hospital death. Secondary outcomes included consults to teams involved in multidisciplinary care of patients with IE, including ID, cardiology, and CTS. Bivariate analyses were performed using Pearson χ2 tests. Odds ratios for surgery and death were calculated using a multivariate logistic regression model including age and gender covariates. Statistical significance was defined at α = 0.05, and statistical analysis was performed using Stata/IC v16.1 (StataCorp LLC). Our university institutional review board (IRB) reviewed the project (#2010858-QI) and determined that the project was quality-improvement activity, not human subject research, and therefore did not require additional IRB review.
Results
We identified 21 patients in the pre-intervention period and 31 patients in the postintervention period with definitive IE who had guideline indications for surgery. The postintervention cohort was older and had more male patients; this difference was not statistically significant. No differences were noted between the groups for race, gender, or intravenous (IV) drug use (Table 2). Chi-square tests of independence were performed to assess the relationship between age and our primary outcomes. There was a significant relationship between age and the likelihood of receiving or being transferred for surgery (59.3% vs 50% vs 7.7% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 [2, N = 52] = 9.67; P = .008), but not between age and mortality (14.8% vs 25.0% vs 30.8% for 18-44 y, 45-64 y, and ≥ 65 y, respectively; χ2 = 1.48 [2, N = 52; P = .478]. The electronic version of the clinical pathway was activated and used in only 3 of the 31 patients in the postintervention period. Consultations to ID, cardiology, and CTS teams were compared between the study periods (Table 2). Although more consultations were seen in the postintervention period, differences were not statistically significant.

The unadjusted primary outcomes are shown in Table 2. More surgeries were performed per guideline indications, and fewer deaths were noted in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period, but the differences were not statistically significant (Table 2).
Because the postintervention period had more male patients and older patients, we evaluated the outcomes using a logistic regression model controlling for both age and gender. The odds of surgery or transfer for surgery for patients in the postintervention period were 4.88 (95% CI, 1.20-19.79; P = .027) as compared with the pre-intervention period, and the odds ratio for death among patients in the postintervention period compared with the pre-intervention period was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.09-1.69; P = .21) (Figure 2).

Discussion
In our study, patients with IE with guideline indications for surgery had significantly higher rates of surgery in the postintervention period than in the pre-intervention period. The implementation of an MDT, recurring educational sessions, and efforts to implement and familiarize team members with the clinical pathway approach are the most likely reasons for this change. The increased rates of surgery in the postintervention period were the likely proximate cause of the 60% reduction in in-hospital mortality. This improvement in mortality, while not statistically significant, is very likely to be clinically significant and helps reinforce the value of the MDT intervention used.
Our findings are consistent with existing and mounting literature on the use of MDTs to improve outcomes for patients with IE, including 2 studies that noted an increased rate of surgery for patients with indications.8,19 Several other studies in both Europe and North America have found significant decreases in mortality,6-11,20,21 rates of complications,9 time to diagnosis and treatment,11 and length of stay9,20 for patients with IE managed with an MDT strategy. Although current AHA guidelines for care of patients with IE do suggest an MDT approach, the strategy for this approach is not well established.22 Only 1 study that has implemented a new MDT protocol for care of IE has been conducted in the United States.8
While effective MDTs certainly improve outcomes in patients with IE, there are reported differences in implementation of such an approach. With the MDT model as the core, various implementations included regular case conferences,10,11,19,21,23 formation of a consulting team,6,8 or establishment of a new protocol or algorithm for care.8,9,20 Our approach used a clinical pathway as a basis for improved communication among consulting services, education of learning providers via regular case conferences, and implementation of an electronic clinical care pathway to guide them step by step. Our pathway followed the institutionally standardized algorithm (Figure 1), using what we called the 6 T’s approach (Table 1), that guides providers to evaluate critical cases in a fast track.17
To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first report of an MDT that used an electronic clinical care pathway embedded within the EHR. The electronic version of our clinical pathway went live for only the second half of the postintervention study period, which is the most likely reason for its limited utilization. It is also possible that educational efforts in the first half of the intervention period were sufficient to familiarize providers with the care pathway such that the electronic version was seldom needed. We are exploring other possible ways of improving electronic pathway utilization, such as improving the feature usability and further systemwide educational efforts.
Our study has other limitations. Quasi-experimental before-and-after comparisons are subject to confounding from concurrent interventions. We had a substantial change in cardiothoracic faculty soon after the commencement of our efforts to form the MDT, and thus cannot rule out differences related to their comfort level in considering or offering surgery. We also cannot rule out a Hawthorne effect, where knowledge of the ongoing quality-improvement project changed provider behavior, making surgery more likely. We did not evaluate rates of right- versus left-sided endocarditis, which have been linked to mortality.24 Our study also was performed across a single academic institution, which may limit its generalizability. Finally, our study may not have been adequately powered to detect differences in mortality due to implementation of the MDT approach.
Conclusion
Our work suggests that an MDT for IE can be successfully designed and implemented with a clinical pathway using quality-improvement tools in centers where subspecialty services are available. Our approach was associated with a higher rate of surgery among patients with guideline indications for surgery and may reduce in-hospital mortality. An electronic clinical care pathway embedded in the EHR is feasible and may have a role in MDT implementation.
These data were also accepted as a poster at IDWeek 2022, Washington, DC. The poster abstract is published in an online supplement of Open Forum Infectious Diseases as an abstract publication.
Corresponding author: Haley Crosby; hwc2pd@health.missouri.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132(15):1435-1486. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000296
2. Federspiel JJ, Stearns SC, Peppercorn AF, et al. Increasing US rates of endocarditis with Staphylococcus aureus: 1999-2008. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(4):363-365. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.1027
3. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(23):e521-e643. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000031
4. Chambers J, Sandoe J, Ray S, et al. The infective endocarditis team: recommendations from an international working group. Heart. 2014;100(7):524-527. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304354
5. Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-3128. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv319
6. Chirillo F, Scotton P, Rocco F, et al. Impact of a multidisciplinary management strategy on the outcome of patients with native valve infective endocarditis. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1171-1176. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.060
7. Botelho-Nevers E, Thuny F, Casalta JP, et al. Dramatic reduction in infective endocarditis-related mortality with a management-based approach. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(14):1290-1298. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.192
8. El-Dalati S, Cronin D, Riddell IV J, et al. The clinical impact of implementation of a multidisciplinary endocarditis team. Ann Thorac Surg. 2022;113(1):118-124.
9. Carrasco-Chinchilla F, Sánchez-Espín G, Ruiz-Morales J, et al. Influence of a multidisciplinary alert strategy on mortality due to left-sided infective endocarditis. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014;67(5):380-386. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2013.09.010
10. Issa N, Dijos M, Greib C, et al. Impact of an endocarditis team in the management of 357 infective endocarditis [abstract]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(suppl 1):S201. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofw172.825
11. Kaura A, Byrne J, Fife A, et al. Inception of the ‘endocarditis team’ is associated with improved survival in patients with infective endocarditis who are managed medically: findings from a before-and-after study. Open Heart. 2017;4(2):e000699. doi:10.1136/openhrt-2017-000699
12. Rotter T, Kinsman L, James E, et al. Clinical pathways: effects on professional practice, patient outcomes, length of stay and hospital costs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(3):Cd006632. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006632.pub2
13. Neame MT, Chacko J, Surace AE, et al. A systematic review of the effects of implementing clinical pathways supported by health information technologies. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(4):356-363. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy176
14. Trimarchi L, Caruso R, Magon G, et al. Clinical pathways and patient-related outcomes in hospital-based settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Biomed. 2021;92(1):e2021093. doi:10.23750/abm.v92i1.10639
15. Gibbons EF, Huang G, Aldea G, et al. A multidisciplinary pathway for the diagnosis and treatment of infectious endocarditis. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2020;19(4):187-194. doi:10.1097/hpc.0000000000000224
16. Regunath H, Vasudevan A, Vyas K, et al. A quality improvement initiative: developing a multi-disciplinary team for infective endocarditis. Mo Med. 2019;116(4):291-296.
17. Regunath H, Whitt SP. Multidisciplinary service delivery for the endocarditis patient. In: Infective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 1st ed. Kilic A, ed. Academic Press; 2022.
18. Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med. 1994;96(3):200-209. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(94)90143-0
19. Tan C, Hansen MS, Cohen G, et al. Case conferences for infective endocarditis: a quality improvement initiative. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205528. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0205528
20. Ruch Y, Mazzucotelli JP, Lefebvre F, et al. Impact of setting up an “endocarditis team” on the management of infective endocarditis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(9):ofz308. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz308
21. Camou F, Dijos M, Barandon L, et al. Management of infective endocarditis and multidisciplinary approach. Med Mal Infect. 2019;49(1):17-22. doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2018.06.007
22. Pettersson GB, Hussain ST. Current AATS guidelines on surgical treatment of infective endocarditis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;8(6):630-644. doi:10.21037/acs.2019.10.05
23. Mestres CA, Paré JC, Miró JM. Organization and functioning of a multidisciplinary team for the diagnosis and treatment of infective endocarditis: a 30-year perspective (1985-2014). Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2015;68(5):363-368. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2014.10.006
24. Stavi V, Brandstaetter E, Sagy I, et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics and prognosis in patients with right- and left-sided infective endocarditis. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2019;10(1):e00003. doi:10.5041/rmmj.10338
1. Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132(15):1435-1486. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000296
2. Federspiel JJ, Stearns SC, Peppercorn AF, et al. Increasing US rates of endocarditis with Staphylococcus aureus: 1999-2008. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(4):363-365. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.1027
3. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(23):e521-e643. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000031
4. Chambers J, Sandoe J, Ray S, et al. The infective endocarditis team: recommendations from an international working group. Heart. 2014;100(7):524-527. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304354
5. Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-3128. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv319
6. Chirillo F, Scotton P, Rocco F, et al. Impact of a multidisciplinary management strategy on the outcome of patients with native valve infective endocarditis. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1171-1176. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.060
7. Botelho-Nevers E, Thuny F, Casalta JP, et al. Dramatic reduction in infective endocarditis-related mortality with a management-based approach. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(14):1290-1298. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.192
8. El-Dalati S, Cronin D, Riddell IV J, et al. The clinical impact of implementation of a multidisciplinary endocarditis team. Ann Thorac Surg. 2022;113(1):118-124.
9. Carrasco-Chinchilla F, Sánchez-Espín G, Ruiz-Morales J, et al. Influence of a multidisciplinary alert strategy on mortality due to left-sided infective endocarditis. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014;67(5):380-386. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2013.09.010
10. Issa N, Dijos M, Greib C, et al. Impact of an endocarditis team in the management of 357 infective endocarditis [abstract]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(suppl 1):S201. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofw172.825
11. Kaura A, Byrne J, Fife A, et al. Inception of the ‘endocarditis team’ is associated with improved survival in patients with infective endocarditis who are managed medically: findings from a before-and-after study. Open Heart. 2017;4(2):e000699. doi:10.1136/openhrt-2017-000699
12. Rotter T, Kinsman L, James E, et al. Clinical pathways: effects on professional practice, patient outcomes, length of stay and hospital costs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(3):Cd006632. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006632.pub2
13. Neame MT, Chacko J, Surace AE, et al. A systematic review of the effects of implementing clinical pathways supported by health information technologies. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(4):356-363. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy176
14. Trimarchi L, Caruso R, Magon G, et al. Clinical pathways and patient-related outcomes in hospital-based settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Biomed. 2021;92(1):e2021093. doi:10.23750/abm.v92i1.10639
15. Gibbons EF, Huang G, Aldea G, et al. A multidisciplinary pathway for the diagnosis and treatment of infectious endocarditis. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2020;19(4):187-194. doi:10.1097/hpc.0000000000000224
16. Regunath H, Vasudevan A, Vyas K, et al. A quality improvement initiative: developing a multi-disciplinary team for infective endocarditis. Mo Med. 2019;116(4):291-296.
17. Regunath H, Whitt SP. Multidisciplinary service delivery for the endocarditis patient. In: Infective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 1st ed. Kilic A, ed. Academic Press; 2022.
18. Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med. 1994;96(3):200-209. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(94)90143-0
19. Tan C, Hansen MS, Cohen G, et al. Case conferences for infective endocarditis: a quality improvement initiative. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205528. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0205528
20. Ruch Y, Mazzucotelli JP, Lefebvre F, et al. Impact of setting up an “endocarditis team” on the management of infective endocarditis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(9):ofz308. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz308
21. Camou F, Dijos M, Barandon L, et al. Management of infective endocarditis and multidisciplinary approach. Med Mal Infect. 2019;49(1):17-22. doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2018.06.007
22. Pettersson GB, Hussain ST. Current AATS guidelines on surgical treatment of infective endocarditis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;8(6):630-644. doi:10.21037/acs.2019.10.05
23. Mestres CA, Paré JC, Miró JM. Organization and functioning of a multidisciplinary team for the diagnosis and treatment of infective endocarditis: a 30-year perspective (1985-2014). Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2015;68(5):363-368. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2014.10.006
24. Stavi V, Brandstaetter E, Sagy I, et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics and prognosis in patients with right- and left-sided infective endocarditis. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2019;10(1):e00003. doi:10.5041/rmmj.10338
The Shifting Landscape of Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Best Practice Implementation and Clinical Inertia
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.
Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; ebarkoudah@bwh.harvard.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.

Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; ebarkoudah@bwh.harvard.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.

Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; ebarkoudah@bwh.harvard.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
The Role of Revascularization and Viability Testing in Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease and Severely Reduced Ejection Fraction
Study 1 Overview (STICHES Investigators)
Objective: To assess the survival benefit of coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) added to guideline-directed medical therapy, compared to optimal medical therapy (OMT) alone, in patients with coronary artery disease, heart failure, and severe left ventricular dysfunction. Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study with extended follow-up (median duration of 9.8 years).
Setting and participants: A total of 1212 patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or less and coronary artery disease were randomized to medical therapy plus CABG or OMT alone at 127 clinical sites in 26 countries.
Main outcome measures: The primary endpoint was death from any cause. Main secondary endpoints were death from cardiovascular causes and a composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes.
Main results: There were 359 primary outcome all-cause deaths (58.9%) in the CABG group and 398 (66.1%) in the medical therapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97; P = .02). Death from cardiovascular causes was reported in 247 patients (40.5%) in the CABG group and 297 patients (49.3%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.66-0.93; P < .01). The composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes occurred in 467 patients (76.6%) in the CABG group and 467 patients (87.0%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.64-0.82; P < .01).
Conclusion: Over a median follow-up of 9.8 years in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with severely reduced ejection fraction, the rates of death from any cause, death from cardiovascular causes, and the composite of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes were significantly lower in patients undergoing CABG than in patients receiving medical therapy alone.
Study 2 Overview (REVIVED BCIS Trial Group)
Objective: To assess whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can improve survival and left ventricular function in patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction as compared to OMT alone.
Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study.
Setting and participants: A total of 700 patients with LVEF <35% with severe coronary artery disease amendable to PCI and demonstrable myocardial viability were randomly assigned to either PCI plus optimal medical therapy (PCI group) or OMT alone (OMT group).
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure. The main secondary outcomes were LVEF at 6 and 12 months and quality of life (QOL) scores.
Main results: Over a median follow-up of 41 months, the primary outcome was reported in 129 patients (37.2%) in the PCI group and in 134 patients (38.0%) in the OMT group (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.78-1.27; P = .96). The LVEF was similar in the 2 groups at 6 months (mean difference, –1.6 percentage points; 95% CI, –3.7 to 0.5) and at 12 months (mean difference, 0.9 percentage points; 95% CI, –1.7 to 3.4). QOL scores at 6 and 12 months favored the PCI group, but the difference had diminished at 24 months.
Conclusion: In patients with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy, revascularization by PCI in addition to OMT did not result in a lower incidence of death from any cause or hospitalization from heart failure.
Commentary
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and an important cause of mortality.1 Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction are often considered for revascularization in addition to OMT and device therapies. Although there have been multiple retrospective studies and registries suggesting that cardiac outcomes and LVEF improve with revascularization, the number of large-scale prospective studies that assessed this clinical question and randomized patients to revascularization plus OMT compared to OMT alone has been limited.
In the Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) study,2,3 eligible patients had coronary artery disease amendable to CABG and a LVEF of 35% or less. Patients (N = 1212) were randomly assigned to CABG plus OMT or OMT alone between July 2002 and May 2007. The original study, with a median follow-up of 5 years, did not show survival benefit, but the investigators reported that the primary outcome of death from any cause was significantly lower in the CABG group compared to OMT alone when follow-up of the same study population was extended to 9.8 years (58.9% vs 66.1%, P = .02). The findings from this study led to a class I guideline recommendation of CABG over medical therapy in patients with multivessel disease and low ejection fraction.4
Since the STICH trial was designed, there have been significant improvements in devices and techniques used for PCI, and the procedure is now widely performed in patients with multivessel disease.5 The advantages of PCI over CABG include shorter recovery times and lower risk of immediate complications. In this context, the recently reported Revascularization for Ischemic Ventricular Dysfunction (REVIVED) study assessed clinical outcomes in patients with severe coronary artery disease and reduced ejection fraction by randomizing patients to either PCI with OMT or OMT alone.6 At a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the investigators found no difference in the primary outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure (37.2% vs 38.0%; 95% CI, 0.78-1.28; P = .96). Moreover, the degree of LVEF improvement, assessed by follow-up echocardiogram read by the core lab, showed no difference in the degree of LVEF improvement between groups at 6 and 12 months. Finally, although results of the QOL assessment using the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated, patient-reported, heart-failure-specific QOL scale, favored the PCI group at 6 and 12 months of follow-up, the difference had diminished at 24 months.
The main strength of the REVIVED study was that it targeted a patient population with severe coronary artery disease, including left main disease and severely reduced ejection fraction, that historically have been excluded from large-scale randomized controlled studies evaluating PCI with OMT compared to OMT alone.7 However, there are several points to consider when interpreting the results of this study. First, further details of the PCI procedures are necessary. The REVIVED study recommended revascularization of all territories with viable myocardium; the anatomical revascularization index utilizing the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society (BCIS) Jeopardy Score was 71%. It is important to note that this jeopardy score was operator-reported and the core-lab adjudicated anatomical revascularization rate may be lower. Although viability testing primarily utilizing cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed in most patients, correlation between the revascularization territory and the viable segments has yet to be reported. Moreover, procedural details such as use of intravascular ultrasound and physiological testing, known to improve clinical outcome, need to be reported.8,9
Second, there is a high prevalence of ischemic cardiomyopathy, and it is important to note that the patients included in this study were highly selected from daily clinical practice, as evidenced by the prolonged enrollment period (8 years). Individuals were largely stable patients with less complex coronary anatomy as evidenced by the median interval from angiography to randomization of 80 days. Taking into consideration the degree of left ventricular dysfunction for patients included in the trial, only 14% of the patients had left main disease and half of the patients only had 2-vessel disease. The severity of the left main disease also needs to be clarified as it is likely that patients the operator determined to be critical were not enrolled in the study. Furthermore, the standard of care based on the STICH trial is to refer patients with severe multivessel coronary artery disease to CABG, making it more likely that patients with more severe and complex disease were not included in this trial. It is also important to note that this study enrolled patients with stable ischemic heart disease, and the data do not apply to patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome.
Third, although the primary outcome was similar between the groups, the secondary outcome of unplanned revascularization was lower in the PCI group. In addition, the rate of acute myocardial infarction (MI) was similar between the 2 groups, but the rate of spontaneous MI was lower in the PCI group compared to the OMT group (5.2% vs 9.3%) as 40% of MI cases in the PCI group were periprocedural MIs. The correlation between periprocedural MI and long-term outcomes has been modest compared to spontaneous MI. Moreover, with the longer follow-up, the number of spontaneous MI cases is expected to rise while the number of periprocedural MI cases is not. Extending the follow-up period is also important, as the STICH extension trial showed a statistically significant difference at 10-year follow up despite negative results at the time of the original publication.
Fourth, the REVIVED trial randomized a significantly lower number of patients compared to the STICH trial, and the authors reported fewer primary-outcome events than the estimated number needed to achieve the power to assess the primary hypothesis. In addition, significant improvements in medical treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction since the STICH trial make comparison of PCI vs CABG in this patient population unfeasible.
Finally, although severe angina was not an exclusion criterion, two-thirds of the patients enrolled had no angina, and only 2% of the patients had baseline severe angina. This is important to consider when interpreting the results of the patient-reported health status as previous studies have shown that patients with worse angina at baseline derive the largest improvement in their QOL,10,11 and symptom improvement is the main indication for PCI in patients with stable ischemic heart disease.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
In patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction and multivessel stable ischemic heart disease who are well compensated and have little or no angina at baseline, OMT alone as an initial strategy may be considered against the addition of PCI after careful risk and benefit discussion. Further details about revascularization and extended follow-up data from the REVIVED trial are necessary.
Practice Points
- Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction have been an understudied population in previous studies.
- Further studies are necessary to understand the benefits of revascularization and the role of viability testing in this population.
– Taishi Hirai MD, and Ziad Sayed Ahmad, MD
University of Missouri, Columbia, MO
1. Nowbar AN, Gitto M, Howard JP, et al. Mortality from ischemic heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(6):e005375. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES
2. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Deja MA, et al; for the STICH Investigators. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(17):1607-1616. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100356
3. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Jones RH, et al. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1511-1520. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1602001
4. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(2):e21-e129. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006
5. Kirtane AJ, Doshi D, Leon MB, et al. Treatment of higher-risk patients with an indication for revascularization: evolution within the field of contemporary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2016;134(5):422-431. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
6. Perera D, Clayton T, O’Kane PD, et al. Percutaneous revascularization for ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(15):1351-1360. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2206606
7. Maron DJ, Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, et al. Initial invasive or conservative strategy for stable coronary disease. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1725-1735. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
8. De Bruyne B, Pijls NH, Kalesan B, et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided PCI versus medical therapy in stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(11):991-1001. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1205361
9. Zhang J, Gao X, Kan J, et al. Intravascular ultrasound versus angiography-guided drug-eluting stent implantation: The ULTIMATE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(24):3126-3137. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.013
10. Spertus JA, Jones PG, Maron DJ, et al. Health-status outcomes with invasive or conservative care in coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(15):1408-1419. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1916370
11. Hirai T, Grantham JA, Sapontis J, et al. Quality of life changes after chronic total occlusion angioplasty in patients with baseline refractory angina. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:e007558. doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.007558
Study 1 Overview (STICHES Investigators)
Objective: To assess the survival benefit of coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) added to guideline-directed medical therapy, compared to optimal medical therapy (OMT) alone, in patients with coronary artery disease, heart failure, and severe left ventricular dysfunction. Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study with extended follow-up (median duration of 9.8 years).
Setting and participants: A total of 1212 patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or less and coronary artery disease were randomized to medical therapy plus CABG or OMT alone at 127 clinical sites in 26 countries.
Main outcome measures: The primary endpoint was death from any cause. Main secondary endpoints were death from cardiovascular causes and a composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes.
Main results: There were 359 primary outcome all-cause deaths (58.9%) in the CABG group and 398 (66.1%) in the medical therapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97; P = .02). Death from cardiovascular causes was reported in 247 patients (40.5%) in the CABG group and 297 patients (49.3%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.66-0.93; P < .01). The composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes occurred in 467 patients (76.6%) in the CABG group and 467 patients (87.0%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.64-0.82; P < .01).
Conclusion: Over a median follow-up of 9.8 years in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with severely reduced ejection fraction, the rates of death from any cause, death from cardiovascular causes, and the composite of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes were significantly lower in patients undergoing CABG than in patients receiving medical therapy alone.
Study 2 Overview (REVIVED BCIS Trial Group)
Objective: To assess whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can improve survival and left ventricular function in patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction as compared to OMT alone.
Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study.
Setting and participants: A total of 700 patients with LVEF <35% with severe coronary artery disease amendable to PCI and demonstrable myocardial viability were randomly assigned to either PCI plus optimal medical therapy (PCI group) or OMT alone (OMT group).
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure. The main secondary outcomes were LVEF at 6 and 12 months and quality of life (QOL) scores.
Main results: Over a median follow-up of 41 months, the primary outcome was reported in 129 patients (37.2%) in the PCI group and in 134 patients (38.0%) in the OMT group (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.78-1.27; P = .96). The LVEF was similar in the 2 groups at 6 months (mean difference, –1.6 percentage points; 95% CI, –3.7 to 0.5) and at 12 months (mean difference, 0.9 percentage points; 95% CI, –1.7 to 3.4). QOL scores at 6 and 12 months favored the PCI group, but the difference had diminished at 24 months.
Conclusion: In patients with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy, revascularization by PCI in addition to OMT did not result in a lower incidence of death from any cause or hospitalization from heart failure.
Commentary
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and an important cause of mortality.1 Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction are often considered for revascularization in addition to OMT and device therapies. Although there have been multiple retrospective studies and registries suggesting that cardiac outcomes and LVEF improve with revascularization, the number of large-scale prospective studies that assessed this clinical question and randomized patients to revascularization plus OMT compared to OMT alone has been limited.
In the Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) study,2,3 eligible patients had coronary artery disease amendable to CABG and a LVEF of 35% or less. Patients (N = 1212) were randomly assigned to CABG plus OMT or OMT alone between July 2002 and May 2007. The original study, with a median follow-up of 5 years, did not show survival benefit, but the investigators reported that the primary outcome of death from any cause was significantly lower in the CABG group compared to OMT alone when follow-up of the same study population was extended to 9.8 years (58.9% vs 66.1%, P = .02). The findings from this study led to a class I guideline recommendation of CABG over medical therapy in patients with multivessel disease and low ejection fraction.4
Since the STICH trial was designed, there have been significant improvements in devices and techniques used for PCI, and the procedure is now widely performed in patients with multivessel disease.5 The advantages of PCI over CABG include shorter recovery times and lower risk of immediate complications. In this context, the recently reported Revascularization for Ischemic Ventricular Dysfunction (REVIVED) study assessed clinical outcomes in patients with severe coronary artery disease and reduced ejection fraction by randomizing patients to either PCI with OMT or OMT alone.6 At a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the investigators found no difference in the primary outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure (37.2% vs 38.0%; 95% CI, 0.78-1.28; P = .96). Moreover, the degree of LVEF improvement, assessed by follow-up echocardiogram read by the core lab, showed no difference in the degree of LVEF improvement between groups at 6 and 12 months. Finally, although results of the QOL assessment using the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated, patient-reported, heart-failure-specific QOL scale, favored the PCI group at 6 and 12 months of follow-up, the difference had diminished at 24 months.
The main strength of the REVIVED study was that it targeted a patient population with severe coronary artery disease, including left main disease and severely reduced ejection fraction, that historically have been excluded from large-scale randomized controlled studies evaluating PCI with OMT compared to OMT alone.7 However, there are several points to consider when interpreting the results of this study. First, further details of the PCI procedures are necessary. The REVIVED study recommended revascularization of all territories with viable myocardium; the anatomical revascularization index utilizing the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society (BCIS) Jeopardy Score was 71%. It is important to note that this jeopardy score was operator-reported and the core-lab adjudicated anatomical revascularization rate may be lower. Although viability testing primarily utilizing cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed in most patients, correlation between the revascularization territory and the viable segments has yet to be reported. Moreover, procedural details such as use of intravascular ultrasound and physiological testing, known to improve clinical outcome, need to be reported.8,9
Second, there is a high prevalence of ischemic cardiomyopathy, and it is important to note that the patients included in this study were highly selected from daily clinical practice, as evidenced by the prolonged enrollment period (8 years). Individuals were largely stable patients with less complex coronary anatomy as evidenced by the median interval from angiography to randomization of 80 days. Taking into consideration the degree of left ventricular dysfunction for patients included in the trial, only 14% of the patients had left main disease and half of the patients only had 2-vessel disease. The severity of the left main disease also needs to be clarified as it is likely that patients the operator determined to be critical were not enrolled in the study. Furthermore, the standard of care based on the STICH trial is to refer patients with severe multivessel coronary artery disease to CABG, making it more likely that patients with more severe and complex disease were not included in this trial. It is also important to note that this study enrolled patients with stable ischemic heart disease, and the data do not apply to patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome.
Third, although the primary outcome was similar between the groups, the secondary outcome of unplanned revascularization was lower in the PCI group. In addition, the rate of acute myocardial infarction (MI) was similar between the 2 groups, but the rate of spontaneous MI was lower in the PCI group compared to the OMT group (5.2% vs 9.3%) as 40% of MI cases in the PCI group were periprocedural MIs. The correlation between periprocedural MI and long-term outcomes has been modest compared to spontaneous MI. Moreover, with the longer follow-up, the number of spontaneous MI cases is expected to rise while the number of periprocedural MI cases is not. Extending the follow-up period is also important, as the STICH extension trial showed a statistically significant difference at 10-year follow up despite negative results at the time of the original publication.
Fourth, the REVIVED trial randomized a significantly lower number of patients compared to the STICH trial, and the authors reported fewer primary-outcome events than the estimated number needed to achieve the power to assess the primary hypothesis. In addition, significant improvements in medical treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction since the STICH trial make comparison of PCI vs CABG in this patient population unfeasible.
Finally, although severe angina was not an exclusion criterion, two-thirds of the patients enrolled had no angina, and only 2% of the patients had baseline severe angina. This is important to consider when interpreting the results of the patient-reported health status as previous studies have shown that patients with worse angina at baseline derive the largest improvement in their QOL,10,11 and symptom improvement is the main indication for PCI in patients with stable ischemic heart disease.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
In patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction and multivessel stable ischemic heart disease who are well compensated and have little or no angina at baseline, OMT alone as an initial strategy may be considered against the addition of PCI after careful risk and benefit discussion. Further details about revascularization and extended follow-up data from the REVIVED trial are necessary.
Practice Points
- Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction have been an understudied population in previous studies.
- Further studies are necessary to understand the benefits of revascularization and the role of viability testing in this population.
– Taishi Hirai MD, and Ziad Sayed Ahmad, MD
University of Missouri, Columbia, MO
Study 1 Overview (STICHES Investigators)
Objective: To assess the survival benefit of coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) added to guideline-directed medical therapy, compared to optimal medical therapy (OMT) alone, in patients with coronary artery disease, heart failure, and severe left ventricular dysfunction. Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study with extended follow-up (median duration of 9.8 years).
Setting and participants: A total of 1212 patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or less and coronary artery disease were randomized to medical therapy plus CABG or OMT alone at 127 clinical sites in 26 countries.
Main outcome measures: The primary endpoint was death from any cause. Main secondary endpoints were death from cardiovascular causes and a composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes.
Main results: There were 359 primary outcome all-cause deaths (58.9%) in the CABG group and 398 (66.1%) in the medical therapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97; P = .02). Death from cardiovascular causes was reported in 247 patients (40.5%) in the CABG group and 297 patients (49.3%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.66-0.93; P < .01). The composite outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes occurred in 467 patients (76.6%) in the CABG group and 467 patients (87.0%) in the medical therapy group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.64-0.82; P < .01).
Conclusion: Over a median follow-up of 9.8 years in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with severely reduced ejection fraction, the rates of death from any cause, death from cardiovascular causes, and the composite of death from any cause or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes were significantly lower in patients undergoing CABG than in patients receiving medical therapy alone.
Study 2 Overview (REVIVED BCIS Trial Group)
Objective: To assess whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can improve survival and left ventricular function in patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction as compared to OMT alone.
Design: Multicenter, randomized, prospective study.
Setting and participants: A total of 700 patients with LVEF <35% with severe coronary artery disease amendable to PCI and demonstrable myocardial viability were randomly assigned to either PCI plus optimal medical therapy (PCI group) or OMT alone (OMT group).
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure. The main secondary outcomes were LVEF at 6 and 12 months and quality of life (QOL) scores.
Main results: Over a median follow-up of 41 months, the primary outcome was reported in 129 patients (37.2%) in the PCI group and in 134 patients (38.0%) in the OMT group (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.78-1.27; P = .96). The LVEF was similar in the 2 groups at 6 months (mean difference, –1.6 percentage points; 95% CI, –3.7 to 0.5) and at 12 months (mean difference, 0.9 percentage points; 95% CI, –1.7 to 3.4). QOL scores at 6 and 12 months favored the PCI group, but the difference had diminished at 24 months.
Conclusion: In patients with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy, revascularization by PCI in addition to OMT did not result in a lower incidence of death from any cause or hospitalization from heart failure.
Commentary
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and an important cause of mortality.1 Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction are often considered for revascularization in addition to OMT and device therapies. Although there have been multiple retrospective studies and registries suggesting that cardiac outcomes and LVEF improve with revascularization, the number of large-scale prospective studies that assessed this clinical question and randomized patients to revascularization plus OMT compared to OMT alone has been limited.
In the Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) study,2,3 eligible patients had coronary artery disease amendable to CABG and a LVEF of 35% or less. Patients (N = 1212) were randomly assigned to CABG plus OMT or OMT alone between July 2002 and May 2007. The original study, with a median follow-up of 5 years, did not show survival benefit, but the investigators reported that the primary outcome of death from any cause was significantly lower in the CABG group compared to OMT alone when follow-up of the same study population was extended to 9.8 years (58.9% vs 66.1%, P = .02). The findings from this study led to a class I guideline recommendation of CABG over medical therapy in patients with multivessel disease and low ejection fraction.4
Since the STICH trial was designed, there have been significant improvements in devices and techniques used for PCI, and the procedure is now widely performed in patients with multivessel disease.5 The advantages of PCI over CABG include shorter recovery times and lower risk of immediate complications. In this context, the recently reported Revascularization for Ischemic Ventricular Dysfunction (REVIVED) study assessed clinical outcomes in patients with severe coronary artery disease and reduced ejection fraction by randomizing patients to either PCI with OMT or OMT alone.6 At a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the investigators found no difference in the primary outcome of death from any cause or hospitalization for heart failure (37.2% vs 38.0%; 95% CI, 0.78-1.28; P = .96). Moreover, the degree of LVEF improvement, assessed by follow-up echocardiogram read by the core lab, showed no difference in the degree of LVEF improvement between groups at 6 and 12 months. Finally, although results of the QOL assessment using the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated, patient-reported, heart-failure-specific QOL scale, favored the PCI group at 6 and 12 months of follow-up, the difference had diminished at 24 months.
The main strength of the REVIVED study was that it targeted a patient population with severe coronary artery disease, including left main disease and severely reduced ejection fraction, that historically have been excluded from large-scale randomized controlled studies evaluating PCI with OMT compared to OMT alone.7 However, there are several points to consider when interpreting the results of this study. First, further details of the PCI procedures are necessary. The REVIVED study recommended revascularization of all territories with viable myocardium; the anatomical revascularization index utilizing the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society (BCIS) Jeopardy Score was 71%. It is important to note that this jeopardy score was operator-reported and the core-lab adjudicated anatomical revascularization rate may be lower. Although viability testing primarily utilizing cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed in most patients, correlation between the revascularization territory and the viable segments has yet to be reported. Moreover, procedural details such as use of intravascular ultrasound and physiological testing, known to improve clinical outcome, need to be reported.8,9
Second, there is a high prevalence of ischemic cardiomyopathy, and it is important to note that the patients included in this study were highly selected from daily clinical practice, as evidenced by the prolonged enrollment period (8 years). Individuals were largely stable patients with less complex coronary anatomy as evidenced by the median interval from angiography to randomization of 80 days. Taking into consideration the degree of left ventricular dysfunction for patients included in the trial, only 14% of the patients had left main disease and half of the patients only had 2-vessel disease. The severity of the left main disease also needs to be clarified as it is likely that patients the operator determined to be critical were not enrolled in the study. Furthermore, the standard of care based on the STICH trial is to refer patients with severe multivessel coronary artery disease to CABG, making it more likely that patients with more severe and complex disease were not included in this trial. It is also important to note that this study enrolled patients with stable ischemic heart disease, and the data do not apply to patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome.
Third, although the primary outcome was similar between the groups, the secondary outcome of unplanned revascularization was lower in the PCI group. In addition, the rate of acute myocardial infarction (MI) was similar between the 2 groups, but the rate of spontaneous MI was lower in the PCI group compared to the OMT group (5.2% vs 9.3%) as 40% of MI cases in the PCI group were periprocedural MIs. The correlation between periprocedural MI and long-term outcomes has been modest compared to spontaneous MI. Moreover, with the longer follow-up, the number of spontaneous MI cases is expected to rise while the number of periprocedural MI cases is not. Extending the follow-up period is also important, as the STICH extension trial showed a statistically significant difference at 10-year follow up despite negative results at the time of the original publication.
Fourth, the REVIVED trial randomized a significantly lower number of patients compared to the STICH trial, and the authors reported fewer primary-outcome events than the estimated number needed to achieve the power to assess the primary hypothesis. In addition, significant improvements in medical treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction since the STICH trial make comparison of PCI vs CABG in this patient population unfeasible.
Finally, although severe angina was not an exclusion criterion, two-thirds of the patients enrolled had no angina, and only 2% of the patients had baseline severe angina. This is important to consider when interpreting the results of the patient-reported health status as previous studies have shown that patients with worse angina at baseline derive the largest improvement in their QOL,10,11 and symptom improvement is the main indication for PCI in patients with stable ischemic heart disease.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
In patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction and multivessel stable ischemic heart disease who are well compensated and have little or no angina at baseline, OMT alone as an initial strategy may be considered against the addition of PCI after careful risk and benefit discussion. Further details about revascularization and extended follow-up data from the REVIVED trial are necessary.
Practice Points
- Patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with reduced ejection fraction have been an understudied population in previous studies.
- Further studies are necessary to understand the benefits of revascularization and the role of viability testing in this population.
– Taishi Hirai MD, and Ziad Sayed Ahmad, MD
University of Missouri, Columbia, MO
1. Nowbar AN, Gitto M, Howard JP, et al. Mortality from ischemic heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(6):e005375. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES
2. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Deja MA, et al; for the STICH Investigators. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(17):1607-1616. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100356
3. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Jones RH, et al. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1511-1520. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1602001
4. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(2):e21-e129. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006
5. Kirtane AJ, Doshi D, Leon MB, et al. Treatment of higher-risk patients with an indication for revascularization: evolution within the field of contemporary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2016;134(5):422-431. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
6. Perera D, Clayton T, O’Kane PD, et al. Percutaneous revascularization for ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(15):1351-1360. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2206606
7. Maron DJ, Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, et al. Initial invasive or conservative strategy for stable coronary disease. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1725-1735. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
8. De Bruyne B, Pijls NH, Kalesan B, et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided PCI versus medical therapy in stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(11):991-1001. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1205361
9. Zhang J, Gao X, Kan J, et al. Intravascular ultrasound versus angiography-guided drug-eluting stent implantation: The ULTIMATE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(24):3126-3137. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.013
10. Spertus JA, Jones PG, Maron DJ, et al. Health-status outcomes with invasive or conservative care in coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(15):1408-1419. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1916370
11. Hirai T, Grantham JA, Sapontis J, et al. Quality of life changes after chronic total occlusion angioplasty in patients with baseline refractory angina. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:e007558. doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.007558
1. Nowbar AN, Gitto M, Howard JP, et al. Mortality from ischemic heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(6):e005375. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES
2. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Deja MA, et al; for the STICH Investigators. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(17):1607-1616. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100356
3. Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Jones RH, et al. Coronary-artery bypass surgery in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1511-1520. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1602001
4. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(2):e21-e129. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006
5. Kirtane AJ, Doshi D, Leon MB, et al. Treatment of higher-risk patients with an indication for revascularization: evolution within the field of contemporary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2016;134(5):422-431. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
6. Perera D, Clayton T, O’Kane PD, et al. Percutaneous revascularization for ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(15):1351-1360. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2206606
7. Maron DJ, Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, et al. Initial invasive or conservative strategy for stable coronary disease. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1725-1735. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA
8. De Bruyne B, Pijls NH, Kalesan B, et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided PCI versus medical therapy in stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(11):991-1001. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1205361
9. Zhang J, Gao X, Kan J, et al. Intravascular ultrasound versus angiography-guided drug-eluting stent implantation: The ULTIMATE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(24):3126-3137. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.013
10. Spertus JA, Jones PG, Maron DJ, et al. Health-status outcomes with invasive or conservative care in coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(15):1408-1419. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1916370
11. Hirai T, Grantham JA, Sapontis J, et al. Quality of life changes after chronic total occlusion angioplasty in patients with baseline refractory angina. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:e007558. doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.007558
Anesthetic Choices and Postoperative Delirium Incidence: Propofol vs Sevoflurane
Study 1 Overview (Chang et al)
Objective: To assess the incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) following propofol- vs sevoflurane-based anesthesia in geriatric spine surgery patients.
Design: Retrospective, single-blinded observational study of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia cohorts.
Setting and participants: Patients eligible for this study were aged 65 years or older admitted to the SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center (Seoul, South Korea). All patients underwent general anesthesia either via intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane for spine surgery between January 2015 and December 2019. Patients were retrospectively identified via electronic medical records. Patient exclusion criteria included preoperative delirium, history of dementia, psychiatric disease, alcoholism, hepatic or renal dysfunction, postoperative mechanical ventilation dependence, other surgery within the recent 6 months, maintenance of intraoperative anesthesia with combined anesthetics, or incomplete medical record.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was the incidence of POD after administration of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia during hospitalization. Patients were screened for POD regularly by attending nurses using the Nursing Delirium Screening Scale (disorientation, inappropriate behavior, inappropriate communication, hallucination, and psychomotor retardation) during the entirety of the patient’s hospital stay; if 1 or more screening criteria were met, a psychiatrist was consulted for the proper diagnosis and management of delirium. A psychiatric diagnosis was required for a case to be counted toward the incidence of POD in this study. Secondary outcomes included postoperative 30-day complications (angina, myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack/stroke, pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute kidney injury, or infection) and length of postoperative hospital stay.
Main results: POD occurred in 29 patients (10.3%) out of the total cohort of 281. POD was more common in the sevoflurane group than in the propofol group (15.7% vs 5.0%; P = .003). Using multivariable logistic regression, inhalational sevoflurane was associated with an increased risk of POD as compared to propofol-based anesthesia (odds ratio [OR], 4.120; 95% CI, 1.549-10.954; P = .005). There was no association between choice of anesthetic and postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. Both older age (OR, 1.242; 95% CI, 1.130-1.366; P < .001) and higher pain score at postoperative day 1 (OR, 1.338; 95% CI, 1.056-1.696; P = .016) were associated with increased risk of POD.
Conclusion: Propofol-based anesthesia was associated with a lower incidence of and risk for POD than sevoflurane-based anesthesia in older patients undergoing spine surgery.
Study 2 Overview (Mei et al)
Objective: To determine the incidence and duration of POD in older patients after total knee/hip replacement (TKR/THR) under intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane general anesthesia.
Design: Randomized clinical trial of propofol and sevoflurane groups.
Setting and participants: This study was conducted at the Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital and involved 209 participants enrolled between June 2016 and November 2019. All participants were 60 years of age or older, scheduled for TKR/THR surgery under general anesthesia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class I to III, and assessed to be of normal cognitive function preoperatively via a Mini-Mental State Examination. Participant exclusion criteria included preexisting delirium as assessed by the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM), prior diagnosed neurological diseases (eg, Parkinson’s disease), prior diagnosed mental disorders (eg, schizophrenia), or impaired vision or hearing that would influence cognitive assessments. All participants were randomly assigned to either sevoflurane or propofol anesthesia for their surgery via a computer-generated list. Of these, 103 received inhalational sevoflurane and 106 received intravenous propofol. All participants received standardized postoperative care.
Main outcome measures: All participants were interviewed by investigators, who were blinded to the anesthesia regimen, twice daily on postoperative days 1, 2, and 3 using CAM and a CAM-based scoring system (CAM-S) to assess delirium severity. The CAM encapsulated 4 criteria: acute onset and fluctuating course, agitation, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. To diagnose delirium, both the first and second criteria must be met, in addition to either the third or fourth criterion. The averages of the scores across the 3 postoperative days indicated delirium severity, while the incidence and duration of delirium was assessed by the presence of delirium as determined by CAM on any postoperative day.
Main results: All eligible participants (N = 209; mean [SD] age 71.2 [6.7] years; 29.2% male) were included in the final analysis. The incidence of POD was not statistically different between the propofol and sevoflurane groups (33.0% vs 23.3%; P = .119, Chi-square test). It was estimated that 316 participants in each arm of the study were needed to detect statistical differences. The number of days of POD per person were higher with propofol anesthesia as compared to sevoflurane (0.5 [0.8] vs 0.3 [0.5]; P = .049, Student’s t-test).
Conclusion: This underpowered study showed a 9.7% difference in the incidence of POD between older adults who received propofol (33.0%) and sevoflurane (23.3%) after THR/TKR. Further studies with a larger sample size are needed to compare general anesthetics and their role in POD.
Commentary
Delirium is characterized by an acute state of confusion with fluctuating mental status, inattention, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. It is often caused by medications and/or their related adverse effects, infections, electrolyte imbalances, and other clinical etiologies. Delirium often manifests in post-surgical settings, disproportionately affecting older patients and leading to increased risk of morbidity, mortality, hospital length of stay, and health care costs.1 Intraoperative risk factors for POD are determined by the degree of operative stress (eg, lower-risk surgeries put the patient at reduced risk for POD as compared to higher-risk surgeries) and are additive to preexisting patient-specific risk factors, such as older age and functional impairment.1 Because operative stress is associated with risk for POD, limiting operative stress in controlled ways, such as through the choice of anesthetic agent administered, may be a pragmatic way to manage operative risks and optimize outcomes, especially when serving a surgically vulnerable population.
In Study 1, Chang et al sought to assess whether 2 commonly utilized general anesthetics, propofol and sevoflurane, in older patients undergoing spine surgery differentially affected the incidence of POD. In this retrospective, single-blinded observational study of 281 geriatric patients, the researchers found that sevoflurane was associated with a higher risk of POD as compared to propofol. However, these anesthetics were not associated with surgical outcomes such as postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. While these findings added new knowledge to this field of research, several limitations should be kept in mind when interpreting this study’s results. For instance, the sample size was relatively small, with all cases selected from a single center utilizing a retrospective analysis. In addition, although a standardized nursing screening tool was used as a method for delirium detection, hypoactive delirium or less symptomatic delirium may have been missed, which in turn would lead to an underestimation of POD incidence. The latter is a common limitation in delirium research.
In Study 2, Mei et al similarly explored the effects of general anesthetics on POD in older surgical patients. Specifically, using a randomized clinical trial design, the investigators compared propofol with sevoflurane in older patients who underwent TKR/THR, and their roles in POD severity and duration. Although the incidence of POD was higher in those who received propofol compared to sevoflurane, this trial was underpowered and the results did not reach statistical significance. In addition, while the duration of POD was slightly longer in the propofol group compared to the sevoflurane group (0.5 vs 0.3 days), it was unclear if this finding was clinically significant. Similar to many research studies in POD, limitations of Study 2 included a small sample size of 209 patients, with all participants enrolled from a single center. On the other hand, this study illustrated the feasibility of a method that allowed reproducible prospective assessment of POD time course using CAM and CAM-S.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
The delineation of risk factors that contribute to delirium after surgery in older patients is key to mitigating risks for POD and improving clinical outcomes. An important step towards a better understanding of these modifiable risk factors is to clearly quantify intraoperative risk of POD attributable to specific anesthetics. While preclinical studies have shown differential neurotoxicity effects of propofol and sevoflurane, their impact on clinically important neurologic outcomes such as delirium and cognitive decline remains poorly understood. Although Studies 1 and 2 both provided head-to-head comparisons of propofol and sevoflurane as risk factors for POD in high-operative-stress surgeries in older patients, the results were inconsistent. That being said, this small incremental increase in knowledge was not unexpected in the course of discovery around a clinically complex research question. Importantly, these studies provided evidence regarding the methodological approaches that could be taken to further this line of research.
The mediating factors of the differences on neurologic outcomes between anesthetic agents are likely pharmacological, biological, and methodological. Pharmacologically, the differences between target receptors, such as GABAA (propofol, etomidate) or NMDA (ketamine), could be a defining feature in the difference in incidence of POD. Additionally, secondary actions of anesthetic agents on glycine, nicotinic, and acetylcholine receptors could play a role as well. Biologically, genes such as CYP2E1, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, GSTP1, UGT1A9, SULT1A1, and NQO1 have all been identified as genetic factors in the metabolism of anesthetics, and variations in such genes could result in different responses to anesthetics.2 Methodologically, routes of anesthetic administration (eg, inhalation vs intravenous), preexisting anatomical structures, or confounding medical conditions (eg, lower respiratory volume due to older age) may influence POD incidence, duration, or severity. Moreover, methodological differences between Studies 1 and 2, such as surgeries performed (spinal vs TKR/THR), patient populations (South Korean vs Chinese), and the diagnosis and monitoring of delirium (retrospective screening and diagnosis vs prospective CAM/CAM-S) may impact delirium outcomes. Thus, these factors should be considered in the design of future clinical trials undertaken to investigate the effects of anesthetics on POD.
Given the high prevalence of delirium and its associated adverse outcomes in the immediate postoperative period in older patients, further research is warranted to determine how anesthetics affect POD in order to optimize perioperative care and mitigate risks in this vulnerable population. Moreover, parallel investigations into how anesthetics differentially impact the development of transient or longer-term cognitive impairment after a surgical procedure (ie, postoperative cognitive dysfunction) in older adults are urgently needed in order to improve their cognitive health.
Practice Points
- Intravenous propofol and inhalational sevoflurane may be differentially associated with incidence, duration, and severity of POD in geriatric surgical patients.
- Further larger-scale studies are warranted to clarify the role of anesthetic choice in POD in order to optimize surgical outcomes in older patients.
–Jared Doan, BS, and Fred Ko, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
1. Dasgupta M, Dumbrell AC. Preoperative risk assessment for delirium after noncardiac surgery: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(10):1578-1589. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00893.x
2. Mikstacki A, Skrzypczak-Zielinska M, Tamowicz B, et al. The impact of genetic factors on response to anaesthetics. Adv Med Sci. 2013;58(1):9-14. doi:10.2478/v10039-012-0065-z
Study 1 Overview (Chang et al)
Objective: To assess the incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) following propofol- vs sevoflurane-based anesthesia in geriatric spine surgery patients.
Design: Retrospective, single-blinded observational study of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia cohorts.
Setting and participants: Patients eligible for this study were aged 65 years or older admitted to the SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center (Seoul, South Korea). All patients underwent general anesthesia either via intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane for spine surgery between January 2015 and December 2019. Patients were retrospectively identified via electronic medical records. Patient exclusion criteria included preoperative delirium, history of dementia, psychiatric disease, alcoholism, hepatic or renal dysfunction, postoperative mechanical ventilation dependence, other surgery within the recent 6 months, maintenance of intraoperative anesthesia with combined anesthetics, or incomplete medical record.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was the incidence of POD after administration of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia during hospitalization. Patients were screened for POD regularly by attending nurses using the Nursing Delirium Screening Scale (disorientation, inappropriate behavior, inappropriate communication, hallucination, and psychomotor retardation) during the entirety of the patient’s hospital stay; if 1 or more screening criteria were met, a psychiatrist was consulted for the proper diagnosis and management of delirium. A psychiatric diagnosis was required for a case to be counted toward the incidence of POD in this study. Secondary outcomes included postoperative 30-day complications (angina, myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack/stroke, pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute kidney injury, or infection) and length of postoperative hospital stay.
Main results: POD occurred in 29 patients (10.3%) out of the total cohort of 281. POD was more common in the sevoflurane group than in the propofol group (15.7% vs 5.0%; P = .003). Using multivariable logistic regression, inhalational sevoflurane was associated with an increased risk of POD as compared to propofol-based anesthesia (odds ratio [OR], 4.120; 95% CI, 1.549-10.954; P = .005). There was no association between choice of anesthetic and postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. Both older age (OR, 1.242; 95% CI, 1.130-1.366; P < .001) and higher pain score at postoperative day 1 (OR, 1.338; 95% CI, 1.056-1.696; P = .016) were associated with increased risk of POD.
Conclusion: Propofol-based anesthesia was associated with a lower incidence of and risk for POD than sevoflurane-based anesthesia in older patients undergoing spine surgery.
Study 2 Overview (Mei et al)
Objective: To determine the incidence and duration of POD in older patients after total knee/hip replacement (TKR/THR) under intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane general anesthesia.
Design: Randomized clinical trial of propofol and sevoflurane groups.
Setting and participants: This study was conducted at the Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital and involved 209 participants enrolled between June 2016 and November 2019. All participants were 60 years of age or older, scheduled for TKR/THR surgery under general anesthesia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class I to III, and assessed to be of normal cognitive function preoperatively via a Mini-Mental State Examination. Participant exclusion criteria included preexisting delirium as assessed by the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM), prior diagnosed neurological diseases (eg, Parkinson’s disease), prior diagnosed mental disorders (eg, schizophrenia), or impaired vision or hearing that would influence cognitive assessments. All participants were randomly assigned to either sevoflurane or propofol anesthesia for their surgery via a computer-generated list. Of these, 103 received inhalational sevoflurane and 106 received intravenous propofol. All participants received standardized postoperative care.
Main outcome measures: All participants were interviewed by investigators, who were blinded to the anesthesia regimen, twice daily on postoperative days 1, 2, and 3 using CAM and a CAM-based scoring system (CAM-S) to assess delirium severity. The CAM encapsulated 4 criteria: acute onset and fluctuating course, agitation, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. To diagnose delirium, both the first and second criteria must be met, in addition to either the third or fourth criterion. The averages of the scores across the 3 postoperative days indicated delirium severity, while the incidence and duration of delirium was assessed by the presence of delirium as determined by CAM on any postoperative day.
Main results: All eligible participants (N = 209; mean [SD] age 71.2 [6.7] years; 29.2% male) were included in the final analysis. The incidence of POD was not statistically different between the propofol and sevoflurane groups (33.0% vs 23.3%; P = .119, Chi-square test). It was estimated that 316 participants in each arm of the study were needed to detect statistical differences. The number of days of POD per person were higher with propofol anesthesia as compared to sevoflurane (0.5 [0.8] vs 0.3 [0.5]; P = .049, Student’s t-test).
Conclusion: This underpowered study showed a 9.7% difference in the incidence of POD between older adults who received propofol (33.0%) and sevoflurane (23.3%) after THR/TKR. Further studies with a larger sample size are needed to compare general anesthetics and their role in POD.
Commentary
Delirium is characterized by an acute state of confusion with fluctuating mental status, inattention, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. It is often caused by medications and/or their related adverse effects, infections, electrolyte imbalances, and other clinical etiologies. Delirium often manifests in post-surgical settings, disproportionately affecting older patients and leading to increased risk of morbidity, mortality, hospital length of stay, and health care costs.1 Intraoperative risk factors for POD are determined by the degree of operative stress (eg, lower-risk surgeries put the patient at reduced risk for POD as compared to higher-risk surgeries) and are additive to preexisting patient-specific risk factors, such as older age and functional impairment.1 Because operative stress is associated with risk for POD, limiting operative stress in controlled ways, such as through the choice of anesthetic agent administered, may be a pragmatic way to manage operative risks and optimize outcomes, especially when serving a surgically vulnerable population.
In Study 1, Chang et al sought to assess whether 2 commonly utilized general anesthetics, propofol and sevoflurane, in older patients undergoing spine surgery differentially affected the incidence of POD. In this retrospective, single-blinded observational study of 281 geriatric patients, the researchers found that sevoflurane was associated with a higher risk of POD as compared to propofol. However, these anesthetics were not associated with surgical outcomes such as postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. While these findings added new knowledge to this field of research, several limitations should be kept in mind when interpreting this study’s results. For instance, the sample size was relatively small, with all cases selected from a single center utilizing a retrospective analysis. In addition, although a standardized nursing screening tool was used as a method for delirium detection, hypoactive delirium or less symptomatic delirium may have been missed, which in turn would lead to an underestimation of POD incidence. The latter is a common limitation in delirium research.
In Study 2, Mei et al similarly explored the effects of general anesthetics on POD in older surgical patients. Specifically, using a randomized clinical trial design, the investigators compared propofol with sevoflurane in older patients who underwent TKR/THR, and their roles in POD severity and duration. Although the incidence of POD was higher in those who received propofol compared to sevoflurane, this trial was underpowered and the results did not reach statistical significance. In addition, while the duration of POD was slightly longer in the propofol group compared to the sevoflurane group (0.5 vs 0.3 days), it was unclear if this finding was clinically significant. Similar to many research studies in POD, limitations of Study 2 included a small sample size of 209 patients, with all participants enrolled from a single center. On the other hand, this study illustrated the feasibility of a method that allowed reproducible prospective assessment of POD time course using CAM and CAM-S.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
The delineation of risk factors that contribute to delirium after surgery in older patients is key to mitigating risks for POD and improving clinical outcomes. An important step towards a better understanding of these modifiable risk factors is to clearly quantify intraoperative risk of POD attributable to specific anesthetics. While preclinical studies have shown differential neurotoxicity effects of propofol and sevoflurane, their impact on clinically important neurologic outcomes such as delirium and cognitive decline remains poorly understood. Although Studies 1 and 2 both provided head-to-head comparisons of propofol and sevoflurane as risk factors for POD in high-operative-stress surgeries in older patients, the results were inconsistent. That being said, this small incremental increase in knowledge was not unexpected in the course of discovery around a clinically complex research question. Importantly, these studies provided evidence regarding the methodological approaches that could be taken to further this line of research.
The mediating factors of the differences on neurologic outcomes between anesthetic agents are likely pharmacological, biological, and methodological. Pharmacologically, the differences between target receptors, such as GABAA (propofol, etomidate) or NMDA (ketamine), could be a defining feature in the difference in incidence of POD. Additionally, secondary actions of anesthetic agents on glycine, nicotinic, and acetylcholine receptors could play a role as well. Biologically, genes such as CYP2E1, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, GSTP1, UGT1A9, SULT1A1, and NQO1 have all been identified as genetic factors in the metabolism of anesthetics, and variations in such genes could result in different responses to anesthetics.2 Methodologically, routes of anesthetic administration (eg, inhalation vs intravenous), preexisting anatomical structures, or confounding medical conditions (eg, lower respiratory volume due to older age) may influence POD incidence, duration, or severity. Moreover, methodological differences between Studies 1 and 2, such as surgeries performed (spinal vs TKR/THR), patient populations (South Korean vs Chinese), and the diagnosis and monitoring of delirium (retrospective screening and diagnosis vs prospective CAM/CAM-S) may impact delirium outcomes. Thus, these factors should be considered in the design of future clinical trials undertaken to investigate the effects of anesthetics on POD.
Given the high prevalence of delirium and its associated adverse outcomes in the immediate postoperative period in older patients, further research is warranted to determine how anesthetics affect POD in order to optimize perioperative care and mitigate risks in this vulnerable population. Moreover, parallel investigations into how anesthetics differentially impact the development of transient or longer-term cognitive impairment after a surgical procedure (ie, postoperative cognitive dysfunction) in older adults are urgently needed in order to improve their cognitive health.
Practice Points
- Intravenous propofol and inhalational sevoflurane may be differentially associated with incidence, duration, and severity of POD in geriatric surgical patients.
- Further larger-scale studies are warranted to clarify the role of anesthetic choice in POD in order to optimize surgical outcomes in older patients.
–Jared Doan, BS, and Fred Ko, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Study 1 Overview (Chang et al)
Objective: To assess the incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) following propofol- vs sevoflurane-based anesthesia in geriatric spine surgery patients.
Design: Retrospective, single-blinded observational study of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia cohorts.
Setting and participants: Patients eligible for this study were aged 65 years or older admitted to the SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center (Seoul, South Korea). All patients underwent general anesthesia either via intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane for spine surgery between January 2015 and December 2019. Patients were retrospectively identified via electronic medical records. Patient exclusion criteria included preoperative delirium, history of dementia, psychiatric disease, alcoholism, hepatic or renal dysfunction, postoperative mechanical ventilation dependence, other surgery within the recent 6 months, maintenance of intraoperative anesthesia with combined anesthetics, or incomplete medical record.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was the incidence of POD after administration of propofol- and sevoflurane-based anesthesia during hospitalization. Patients were screened for POD regularly by attending nurses using the Nursing Delirium Screening Scale (disorientation, inappropriate behavior, inappropriate communication, hallucination, and psychomotor retardation) during the entirety of the patient’s hospital stay; if 1 or more screening criteria were met, a psychiatrist was consulted for the proper diagnosis and management of delirium. A psychiatric diagnosis was required for a case to be counted toward the incidence of POD in this study. Secondary outcomes included postoperative 30-day complications (angina, myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack/stroke, pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute kidney injury, or infection) and length of postoperative hospital stay.
Main results: POD occurred in 29 patients (10.3%) out of the total cohort of 281. POD was more common in the sevoflurane group than in the propofol group (15.7% vs 5.0%; P = .003). Using multivariable logistic regression, inhalational sevoflurane was associated with an increased risk of POD as compared to propofol-based anesthesia (odds ratio [OR], 4.120; 95% CI, 1.549-10.954; P = .005). There was no association between choice of anesthetic and postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. Both older age (OR, 1.242; 95% CI, 1.130-1.366; P < .001) and higher pain score at postoperative day 1 (OR, 1.338; 95% CI, 1.056-1.696; P = .016) were associated with increased risk of POD.
Conclusion: Propofol-based anesthesia was associated with a lower incidence of and risk for POD than sevoflurane-based anesthesia in older patients undergoing spine surgery.
Study 2 Overview (Mei et al)
Objective: To determine the incidence and duration of POD in older patients after total knee/hip replacement (TKR/THR) under intravenous propofol or inhalational sevoflurane general anesthesia.
Design: Randomized clinical trial of propofol and sevoflurane groups.
Setting and participants: This study was conducted at the Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital and involved 209 participants enrolled between June 2016 and November 2019. All participants were 60 years of age or older, scheduled for TKR/THR surgery under general anesthesia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class I to III, and assessed to be of normal cognitive function preoperatively via a Mini-Mental State Examination. Participant exclusion criteria included preexisting delirium as assessed by the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM), prior diagnosed neurological diseases (eg, Parkinson’s disease), prior diagnosed mental disorders (eg, schizophrenia), or impaired vision or hearing that would influence cognitive assessments. All participants were randomly assigned to either sevoflurane or propofol anesthesia for their surgery via a computer-generated list. Of these, 103 received inhalational sevoflurane and 106 received intravenous propofol. All participants received standardized postoperative care.
Main outcome measures: All participants were interviewed by investigators, who were blinded to the anesthesia regimen, twice daily on postoperative days 1, 2, and 3 using CAM and a CAM-based scoring system (CAM-S) to assess delirium severity. The CAM encapsulated 4 criteria: acute onset and fluctuating course, agitation, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. To diagnose delirium, both the first and second criteria must be met, in addition to either the third or fourth criterion. The averages of the scores across the 3 postoperative days indicated delirium severity, while the incidence and duration of delirium was assessed by the presence of delirium as determined by CAM on any postoperative day.
Main results: All eligible participants (N = 209; mean [SD] age 71.2 [6.7] years; 29.2% male) were included in the final analysis. The incidence of POD was not statistically different between the propofol and sevoflurane groups (33.0% vs 23.3%; P = .119, Chi-square test). It was estimated that 316 participants in each arm of the study were needed to detect statistical differences. The number of days of POD per person were higher with propofol anesthesia as compared to sevoflurane (0.5 [0.8] vs 0.3 [0.5]; P = .049, Student’s t-test).
Conclusion: This underpowered study showed a 9.7% difference in the incidence of POD between older adults who received propofol (33.0%) and sevoflurane (23.3%) after THR/TKR. Further studies with a larger sample size are needed to compare general anesthetics and their role in POD.
Commentary
Delirium is characterized by an acute state of confusion with fluctuating mental status, inattention, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. It is often caused by medications and/or their related adverse effects, infections, electrolyte imbalances, and other clinical etiologies. Delirium often manifests in post-surgical settings, disproportionately affecting older patients and leading to increased risk of morbidity, mortality, hospital length of stay, and health care costs.1 Intraoperative risk factors for POD are determined by the degree of operative stress (eg, lower-risk surgeries put the patient at reduced risk for POD as compared to higher-risk surgeries) and are additive to preexisting patient-specific risk factors, such as older age and functional impairment.1 Because operative stress is associated with risk for POD, limiting operative stress in controlled ways, such as through the choice of anesthetic agent administered, may be a pragmatic way to manage operative risks and optimize outcomes, especially when serving a surgically vulnerable population.
In Study 1, Chang et al sought to assess whether 2 commonly utilized general anesthetics, propofol and sevoflurane, in older patients undergoing spine surgery differentially affected the incidence of POD. In this retrospective, single-blinded observational study of 281 geriatric patients, the researchers found that sevoflurane was associated with a higher risk of POD as compared to propofol. However, these anesthetics were not associated with surgical outcomes such as postoperative 30-day complications or the length of postoperative hospital stay. While these findings added new knowledge to this field of research, several limitations should be kept in mind when interpreting this study’s results. For instance, the sample size was relatively small, with all cases selected from a single center utilizing a retrospective analysis. In addition, although a standardized nursing screening tool was used as a method for delirium detection, hypoactive delirium or less symptomatic delirium may have been missed, which in turn would lead to an underestimation of POD incidence. The latter is a common limitation in delirium research.
In Study 2, Mei et al similarly explored the effects of general anesthetics on POD in older surgical patients. Specifically, using a randomized clinical trial design, the investigators compared propofol with sevoflurane in older patients who underwent TKR/THR, and their roles in POD severity and duration. Although the incidence of POD was higher in those who received propofol compared to sevoflurane, this trial was underpowered and the results did not reach statistical significance. In addition, while the duration of POD was slightly longer in the propofol group compared to the sevoflurane group (0.5 vs 0.3 days), it was unclear if this finding was clinically significant. Similar to many research studies in POD, limitations of Study 2 included a small sample size of 209 patients, with all participants enrolled from a single center. On the other hand, this study illustrated the feasibility of a method that allowed reproducible prospective assessment of POD time course using CAM and CAM-S.
Applications for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
The delineation of risk factors that contribute to delirium after surgery in older patients is key to mitigating risks for POD and improving clinical outcomes. An important step towards a better understanding of these modifiable risk factors is to clearly quantify intraoperative risk of POD attributable to specific anesthetics. While preclinical studies have shown differential neurotoxicity effects of propofol and sevoflurane, their impact on clinically important neurologic outcomes such as delirium and cognitive decline remains poorly understood. Although Studies 1 and 2 both provided head-to-head comparisons of propofol and sevoflurane as risk factors for POD in high-operative-stress surgeries in older patients, the results were inconsistent. That being said, this small incremental increase in knowledge was not unexpected in the course of discovery around a clinically complex research question. Importantly, these studies provided evidence regarding the methodological approaches that could be taken to further this line of research.
The mediating factors of the differences on neurologic outcomes between anesthetic agents are likely pharmacological, biological, and methodological. Pharmacologically, the differences between target receptors, such as GABAA (propofol, etomidate) or NMDA (ketamine), could be a defining feature in the difference in incidence of POD. Additionally, secondary actions of anesthetic agents on glycine, nicotinic, and acetylcholine receptors could play a role as well. Biologically, genes such as CYP2E1, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, GSTP1, UGT1A9, SULT1A1, and NQO1 have all been identified as genetic factors in the metabolism of anesthetics, and variations in such genes could result in different responses to anesthetics.2 Methodologically, routes of anesthetic administration (eg, inhalation vs intravenous), preexisting anatomical structures, or confounding medical conditions (eg, lower respiratory volume due to older age) may influence POD incidence, duration, or severity. Moreover, methodological differences between Studies 1 and 2, such as surgeries performed (spinal vs TKR/THR), patient populations (South Korean vs Chinese), and the diagnosis and monitoring of delirium (retrospective screening and diagnosis vs prospective CAM/CAM-S) may impact delirium outcomes. Thus, these factors should be considered in the design of future clinical trials undertaken to investigate the effects of anesthetics on POD.
Given the high prevalence of delirium and its associated adverse outcomes in the immediate postoperative period in older patients, further research is warranted to determine how anesthetics affect POD in order to optimize perioperative care and mitigate risks in this vulnerable population. Moreover, parallel investigations into how anesthetics differentially impact the development of transient or longer-term cognitive impairment after a surgical procedure (ie, postoperative cognitive dysfunction) in older adults are urgently needed in order to improve their cognitive health.
Practice Points
- Intravenous propofol and inhalational sevoflurane may be differentially associated with incidence, duration, and severity of POD in geriatric surgical patients.
- Further larger-scale studies are warranted to clarify the role of anesthetic choice in POD in order to optimize surgical outcomes in older patients.
–Jared Doan, BS, and Fred Ko, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
1. Dasgupta M, Dumbrell AC. Preoperative risk assessment for delirium after noncardiac surgery: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(10):1578-1589. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00893.x
2. Mikstacki A, Skrzypczak-Zielinska M, Tamowicz B, et al. The impact of genetic factors on response to anaesthetics. Adv Med Sci. 2013;58(1):9-14. doi:10.2478/v10039-012-0065-z
1. Dasgupta M, Dumbrell AC. Preoperative risk assessment for delirium after noncardiac surgery: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(10):1578-1589. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00893.x
2. Mikstacki A, Skrzypczak-Zielinska M, Tamowicz B, et al. The impact of genetic factors on response to anaesthetics. Adv Med Sci. 2013;58(1):9-14. doi:10.2478/v10039-012-0065-z
Diabetes Population Health Innovations in the Age of COVID-19: Insights From the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative
From the T1D Exchange, Boston, MA (Ann Mungmode, Nicole Rioles, Jesse Cases, Dr. Ebekozien); The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust, New York, NY (Laurel Koester); and the University of Mississippi School of Population Health, Jackson, MS (Dr. Ebekozien).
Abstract
There have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, but these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus as the field focuses on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes. This article reviews select population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative, a learning health network that focuses on improving care and outcomes for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Such innovations include expanded telemedicine access, collection of real-world data, machine learning and artificial intelligence, and new diabetes medications and devices. In addition, multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and advocacy efforts for specific populations have been successful. Looking to the future, work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities and to look for additional innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes, learning health network, continuous glucose monitoring, health equity
One in 10 people in the United States has diabetes.1 Diabetes is the nation’s second leading cause of death, costing the US health system more than $300 billion annually.2 The COVID-19 pandemic presented additional health burdens for people living with diabetes. For example, preexisting diabetes was identified as a risk factor for COVID-19–associated morbidity and mortality.3,4 Over the past 2 years, there have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management, including stem cell therapy and new medication options. Additionally, improved technology solutions have aided in diabetes management through continuous glucose monitors (CGM), smart insulin pens, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems, and continuous subcutaneous insulin injections.5,6 Unfortunately, these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus, as the field is rightfully focused on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes.
Learning health networks like the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI) have implemented some of these innovative solutions to improve care for people with diabetes.7 T1DX-QI has more than 50 data-sharing endocrinology centers that care for over 75,000 people with diabetes across the United States (Figure 1). Centers participating in the T1DX-QI use quality improvement (QI) and implementation science methods to quickly translate research into evidence-based clinical practice. T1DX-QI leads diabetes population health and health system research and supports widespread transferability across health care organizations through regular collaborative calls, conferences, and case study documentation.8
In this review, we summarize impactful population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of T1DX-QI (see Figure 2 for relevant definitions). This review is limited in scope and is not meant to be an exhaustive list of innovations. The review also reflects significant changes from the perspective of academic diabetes centers, which may not apply to rural or primary care diabetes practices.
Methods
The first (A.M.), second (H.H.), and senior (O.E.) authors conducted a scoping review of published literature using terms related to diabetes, population health, and innovation on PubMed Central and Google Scholar for the period March 2020 to June 2022. To complement the review, A.M. and O.E. also reviewed abstracts from presentations at major international diabetes conferences, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), the T1DX-QI Learning Session Conference, and the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) 2020 to 2022 conferences.9-14 The authors also searched FDA.gov and ClinicalTrials.gov for relevant insights. A.M. and O.E. sorted the reviewed literature into major themes (Figure 3) from the population health improvement perspective of the T1DX-QI.
Population Health Innovations in Diabetes Management
Expansion of Telemedicine Access
Telemedicine is cost-effective for patients with diabetes,15 including those with complex cases.16 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine and virtual care were rare in diabetes management. However, the pandemic offered a new opportunity to expand the practice of telemedicine in diabetes management. A study from the T1DX-QI showed that telemedicine visits grew from comprising <1% of visits pre-pandemic (December 2019) to 95.2% during the pandemic (August 2020).17 Additional studies, like those conducted by Phillip et al,18 confirmed the noninferiority of telemedicine practice for patients with diabetes.Telemedicine was also found to be an effective strategy to educate patients on the use of diabetes technologies.19
Real-World Data and Disease Surveillance
As the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated outcomes for people with type 1 diabetes (T1D), a need arose to understand the immediate effects of the pandemic on people with T1D through real-world data and disease surveillance. In April 2020, the T1DX-QI initiated a multicenter surveillance study to collect data and analyze the impact of COVID-19 on people with T1D. The existing health collaborative served as a springboard for robust surveillance study, documenting numerous works on the effects of COVID-19.3,4,20-28 Other investigators also embraced the power of real-world surveillance and real-world data.29,30
Big Data, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence
The past 2 years have seen a shift toward embracing the incredible opportunity to tap the large volume of data generated from routine care for practical insights.31 In particular, researchers have demonstrated the widespread application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve diabetes management.32 The T1DX-QI also harnessed the growing power of big data by expanding the functionality of innovative benchmarking software. The T1DX QI Portal uses electronic medical record data of diabetes patients for clinic-to-clinic benchmarking and data analysis, using business intelligence solutions.33
Health Equity
While inequities across various health outcomes have been well documented for years,34 the COVID-19 pandemic further exaggerated racial/ethnic health inequities in T1D.23,35 In response, several organizations have outlined specific strategies to address these health inequities. Emboldened by the pandemic, the T1DX-QI announced a multipronged approach to address health inequities among patients with T1D through the Health Equity Advancement Lab (HEAL).36 One of HEAL’s main components is using real-world data to champion population-level insights and demonstrate progress in QI efforts.
Multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and these studies are expanding our understanding of the chasm.37 There have also been innovative solutions to addressing these inequities, with multiple studies published over the past 2 years.38 A source of inequity among patients with T1D is the lack of representation of racial/ethnic minorities with T1D in clinical trials.39 The T1DX-QI suggests that the equity-adapted framework for QI can be applied by research leaders to support trial diversity and representation, ensuring future device innovations are meaningful for all people with T1D.40
Diabetes Devices
Glucose monitoring and insulin therapy are vital tools to support individuals living with T1D, and devices such as CGM and insulin pumps have become the standard of care for diabetes management (Table).41 Innovations in diabetes technology and device access are imperative for a chronic disease with no cure.
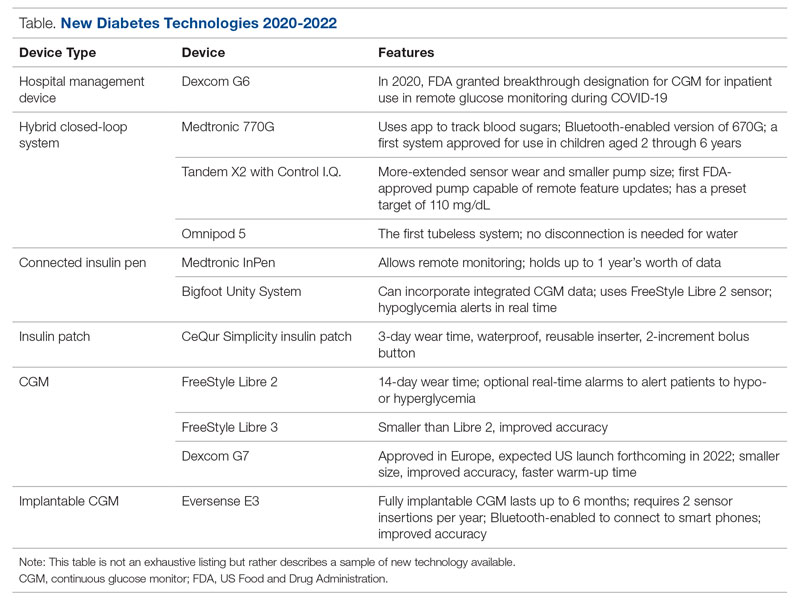
The COVID-19 pandemic created an opportunity to increase access to diabetes devices in inpatient settings. In 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration expanded the use of CGM to support remote monitoring of patients in inpatient hospital settings, simultaneously supporting the glucose monitoring needs of patients with T1D and reducing COVID-19 transmission through reduced patient-clinician contact.42 This effort has been expanded and will continue in 2022 and beyond,43 and aligns with the growing consensus that supports patients wearing both CGMs and insulin pumps in ambulatory settings to improve patient health outcomes.44
Since 2020, innovations in diabetes technology have improved and increased the variety of options available to people with T1D and made them easier to use (Table). New, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems have progressed to offer Bluetooth features, including automatic software upgrades, tubeless systems, and the ability to allow parents to use their smartphones to bolus for children.45-47 The next big step in insulin delivery innovation is the release of functioning, fully closed loop systems, of which several are currently in clinical trials.48 These systems support reduced hypoglycemia and improved time in range.49
Additional innovations in insulin delivery have improved the user experience and expanded therapeutic options, including a variety of smart insulin pens complete with dosing logs50,51 and even a patch to deliver insulin without the burden of injections.52 As barriers to diabetes technology persist,53 innovations in alternate insulin delivery provide people with T1D more options to align with their personal access and technology preferences.
Innovations in CGM address cited barriers to their use, including size or overall wear.53-55 CGMs released in the past few years are smaller in physical size, have longer durations of time between changings, are more accurate, and do not require calibrations for accuracy.
New Diabetes Medications
Many new medications and therapeutic advances have become available in the past 2 years.56 Additionally, more medications are being tested as adjunct therapies to support glycemic management in patients with T1D, including metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 and 2 inhibitors, pramlintide, glucagon-like polypeptide-1 analogs, and glucagon receptor agonists.57 Other recent advances include stem cell replacement therapy for patients with T1D.58 The ultra-long-acting biosimilar insulins are one medical innovation that has been stalled, rather than propelled, during the COVID-19 pandemic.59
Diabetes Policy Advocacy
People with T1D require insulin to survive. The cost of insulin has increased in recent years, with some studies citing a 64% to 100% increase in the past decade.60,61 In fact, 1 in 4 insulin users report that cost has impacted their insulin use, including rationing their insulin.62 Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic stressed US families financially, increasing the urgency for insulin cost caps.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic halted national conversations on drug financing,63 advocacy efforts have succeeded for specific populations. The new Medicare Part D Senior Savings Model will cap the cost of insulin at $35 for a 30-day supply,64 and 20 states passed legislation capping insulin pricing.62 Efforts to codify national cost caps are under debate, including the passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act, which passed the House in March 2022 and is currently under review in the Senate.65
Perspective: The Role of Private Philanthropy in Supporting Population Health Innovations
Funders and industry partners play a crucial role in leading and supporting innovations that improve the lives of people with T1D and reduce society’s costs of living with the disease. Data infrastructure is critical to supporting population health. While building the data infrastructure to support population health is both time- and resource-intensive, private foundations such as Helmsley are uniquely positioned—and have a responsibility—to take large, informed risks to help reach all communities with T1D.
The T1DX-QI is the largest source of population health data on T1D in the United States and is becoming the premiere data authority on its incidence, prevalence, and outcomes. The T1DX-QI enables a robust understanding of T1D-related health trends at the population level, as well as trends among clinics and providers. Pilot centers in the T1DX-QI have reported reductions in patients’ A1c and acute diabetes-related events, as well as improvements in device usage and depression screening. The ability to capture changes speaks to the promise and power of these data to demonstrate the clinical impact of QI interventions and to support the spread of best practices and learnings across health systems.
Additional philanthropic efforts have supported innovation in the last 2 years. For example, the JDRF, a nonprofit philanthropic equity firm, has supported efforts in developing artificial pancreas systems and cell therapies currently in clinical trials like teplizumab, a drug that has demonstrated delayed onset of T1D through JDRF’s T1D Fund.66 Industry partners also have an opportunity for significant influence in this area, as they continue to fund meaningful projects to advance care for people with T1D.67
Conclusion
We are optimistic that the innovations summarized here describe a shift in the tide of equitable T1D outcomes; however, future work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities. We also see further opportunities for innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Corresponding author: Ann Mungmode, MPH, T1D Exchange, 11 Avenue de Lafayette, Boston, MA 02111; Email: amungmode@t1dexchange.org
Disclosures: Dr. Ebekozien serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for the Medtronic Advisory Board and received research grants from Medtronic Diabetes, Eli Lilly, and Dexcom.
Funding: The T1DX-QI is funded by The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes fast facts. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/quick-facts.html
3. O’Malley G, Ebekozien O, Desimone M, et al. COVID-19 hospitalization in adults with type 1 diabetes: results from the T1D Exchange Multicenter Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(2):e936-e942. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa825
4. Ebekozien OA, Noor N, Gallagher MP, Alonso GT. Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: preliminary findings from a multicenter surveillance study in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(8):e83-e85. doi:10.2337/dc20-1088
5. Zimmerman C, Albanese-O’Neill A, Haller MJ. Advances in type 1 diabetes technology over the last decade. Eur Endocrinol. 2019;15(2):70-76. doi:10.17925/ee.2019.15.2.70
6. Wake DJ, Gibb FW, Kar P, et al. Endocrinology in the time of COVID-19: remodelling diabetes services and emerging innovation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183(2):G67-G77. doi:10.1530/eje-20-0377
7. Alonso GT, Corathers S, Shah A, et al. Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI). Clin Diabetes. 2020;38(2):141-151. doi:10.2337/cd19-0032
8. Ginnard OZB, Alonso GT, Corathers SD, et al. Quality improvement in diabetes care: a review of initiatives and outcomes in the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):256-263. doi:10.2337/cd21-0029
9. ATTD 2021 invited speaker abstracts. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S2):A1-A206. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.2525.abstracts
10. Rompicherla SN, Edelen N, Gallagher R, et al. Children and adolescent patients with pre-existing type 1 diabetes and additional comorbidities have an increased risk of hospitalization from COVID-19; data from the T1D Exchange COVID Registry. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22(S30):3-32. doi:10.1111/pedi.13268
11. Abstracts for the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative (T1DX-QI) Learning Session 2021. November 8-9, 2021. J Diabetes. 2021;13(S1):3-17. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13227
12. The Official Journal of ATTD Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes conference 27-30 April 2022. Barcelona and online. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):A1-A237. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2525.abstracts
13. Ebekozien ON, Kamboj N, Odugbesan MK, et al. Inequities in glycemic outcomes for patients with type 1 diabetes: six-year (2016-2021) longitudinal follow-up by race and ethnicity of 36,390 patients in the T1DX-QI Collaborative. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-167-OR
14. Narayan KA, Noor M, Rompicherla N, et al. No BMI increase during the COVID-pandemic in children and adults with T1D in three continents: joint analysis of ADDN, T1DX, and DPV registries. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-269-OR
15. Lee JY, Lee SWH. Telemedicine cost-effectiveness for diabetes management: a systematic review. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018;20(7):492-500. doi:10.1089/dia.2018.0098
16. McDonnell ME. Telemedicine in complex diabetes management. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(7):42. doi:10.1007/s11892-018-1015-3
17. Lee JM, Carlson E, Albanese-O’Neill A, et al. Adoption of telemedicine for type 1 diabetes care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(9):642-651. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0080
18. Phillip M, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, et al. The digital/virtual diabetes clinic: the future is now–recommendations from an international panel on diabetes digital technologies introduction. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(2):146-154. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0375
19. Garg SK, Rodriguez E. COVID‐19 pandemic and diabetes care. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S2-S20. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2501
20. Beliard K, Ebekozien O, Demeterco-Berggren C, et al. Increased DKA at presentation among newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients with or without COVID-19: data from a multi-site surveillance registry. J Diabetes. 2021;13(3):270-272. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13141
21. Ebekozien O, Agarwal S, Noor N, et al. Inequities in diabetic ketoacidosis among patients with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from 52 US clinical centers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(4):1755-1762. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa920
22. Alonso GT, Ebekozien O, Gallagher MP, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis drives COVID-19 related hospitalizations in children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2021;13(8):681-687. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13184
23. Noor N, Ebekozien O, Levin L, et al. Diabetes technology use for management of type 1 diabetes is associated with fewer adverse COVID-19 outcomes: findings from the T1D Exchange COVID-19 Surveillance Registry. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(8):e160-e162. doi:10.2337/dc21-0074
24. Demeterco-Berggren C, Ebekozien O, Rompicherla S, et al. Age and hospitalization risk in people with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from the T1D Exchange Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;107(2):410-418. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab668
25. DeSalvo DJ, Noor N, Xie C, et al. Patient demographics and clinical outcomes among type 1 diabetes patients using continuous glucose monitors: data from T1D Exchange real-world observational study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021 Oct 9. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1177/19322968211049783
26. Gallagher MP, Rompicherla S, Ebekozien O, et al. Differences in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with type 1 diabetes: first vs later surges. J Clin Outcomes Manage. 2022;29(1):27-31. doi:10.12788/jcom.0084
27. Wolf RM, Noor N, Izquierdo R, et al. Increase in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in youth during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States: a multi-center analysis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022;23(4):433-438. doi:10.1111/pedi.13328
28. Lavik AR, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Trends in type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 surges at 7 US centers: highest burden on non-Hispanic Black patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(7):1948-1955. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgac158
29. van der Linden J, Welsh JB, Hirsch IB, Garg SK. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and its impact on time in range. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S1):S1-S7. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0649
30. Nwosu BU, Al-Halbouni L, Parajuli S, et al. COVID-19 pandemic and pediatric type 1 diabetes: no significant change in glycemic control during the pandemic lockdown of 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:703905. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.703905
31. Ellahham S. Artificial intelligence: the future for diabetes care. Am J Med. 2020;133(8):895-900. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.03.033
32. Nomura A, Noguchi M, Kometani M, et al. Artificial intelligence in current diabetes management and prediction. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(12):61. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01423-2
33. Mungmode A, Noor N, Weinstock RS, et al. Making diabetes electronic medical record data actionable: promoting benchmarking and population health using the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Portal. Clin Diabetes. Forthcoming 2022.
34. Lavizzo-Mourey RJ, Besser RE, Williams DR. Understanding and mitigating health inequities—past, current, and future directions. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1681-1684. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008628
35. Majidi S, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Inequities in health outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: data from the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):278-283. doi:10.2337/cd21-0028
36. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Odugbesan O, et al. Addressing type 1 diabetes health inequities in the United States: approaches from the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative. J Diabetes. 2022;14(1):79-82. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13235
37. Odugbesan O, Addala A, Nelson G, et al. Implicit racial-ethnic and insurance-mediated bias to recommending diabetes technology: insights from T1D Exchange multicenter pediatric and adult diabetes provider cohort. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022 Jun 13. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1089/dia.2022.0042
38. Schmitt J, Fogle K, Scott ML, Iyer P. Improving equitable access to continuous glucose monitors for Alabama’s children with type 1 diabetes: a quality improvement project. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(7):481-491. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0511
39. Akturk HK, Agarwal S, Hoffecker L, Shah VN. Inequity in racial-ethnic representation in randomized controlled trials of diabetes technologies in type 1 diabetes: critical need for new standards. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(6):e121-e123. doi:10.2337/dc20-3063
40. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Buckingham D, et al. Achieving equity in diabetes research: borrowing from the field of quality improvement using a practical framework and improvement tools. Diabetes Spectr. 2022;35(3):304-312. doi:10.2237/dsi22-0002
41. Zhang J, Xu J, Lim J, et al. Wearable glucose monitoring and implantable drug delivery systems for diabetes management. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(17):e2100194. doi:10.1002/adhm.202100194
42. FDA expands remote patient monitoring in hospitals for people with diabetes during COVID-19; manufacturers donate CGM supplies. News release. April 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/2020/fda-remote-patient-monitoring-cgm
43. Campbell P. FDA grants Dexcom CGM breakthrough designation for in-hospital use. March 2, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.endocrinologynetwork.com/view/fda-grants-dexcom-cgm-breakthrough-designation-for-in-hospital-use
44. Yeh T, Yeung M, Mendelsohn Curanaj FA. Managing patients with insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors in the hospital: to wear or not to wear. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(2):7. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01375-7
45. Medtronic announces FDA approval for MiniMed 770G insulin pump system. News release. September 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3TyEna4
46. Tandem Diabetes Care announces commercial launch of the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology in the United States. News release. January 15, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://investor.tandemdiabetes.com/news-releases/news-release-details/tandem-diabetes-care-announces-commercial-launch-tslim-x2-0
47. Garza M, Gutow H, Mahoney K. Omnipod 5 cleared by the FDA. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribe.org/omnipod-5-approved-fda
48. Boughton CK. Fully closed-loop insulin delivery—are we nearly there yet? Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(11):e689-e690. doi:10.1016/s2589-7500(21)00218-1
49. Noor N, Kamboj MK, Triolo T, et al. Hybrid closed-loop systems and glycemic outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: real-world evidence from a U.S.-based multicenter collaborative. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(8):e118-e119. doi:10.2337/dc22-0329
50. Medtronic launches InPen with real-time Guardian Connect CGM data--the first integrated smart insulin pen for people with diabetes on MDI. News release. November 12, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3CTSWPL
51. Bigfoot Biomedical receives FDA clearance for Bigfoot Unity Diabetes Management System, featuring first-of-its-kind smart pen caps for insulin pens used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. News release. May 10, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3BeyoAh
52. Vieira G. All about the CeQur Simplicity insulin patch. Updated May 24, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://beyondtype1.org/cequr-simplicity-insulin-patch/.
53. Messer LH, Tanenbaum ML, Cook PF, et al. Cost, hassle, and on-body experience: barriers to diabetes device use in adolescents and potential intervention targets. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(10):760-767. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0509
54. Hilliard ME, Levy W, Anderson BJ, et al. Benefits and barriers of continuous glucose monitoring in young children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(9):493-498. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0142
55. Dexcom G7 Release Delayed Until Late 2022. News release. August 8, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://diatribe.org/dexcom-g7-release-delayed-until-late-2022
56. Drucker DJ. Transforming type 1 diabetes: the next wave of innovation. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1059-1065. doi:10.1007/s00125-021-05396-5
57. Garg SK, Rodriguez E, Shah VN, Hirsch IB. New medications for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S190-S208. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2513
58. Melton D. The promise of stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1030-1036. doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05367-2
59. Danne T, Heinemann L, Bolinder J. New insulins, biosimilars, and insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S35-S57. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2503
60. Kenney J. Insulin copay caps–a path to affordability. July 6, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribechange.org/news/insulin-copay-caps-path-affordability
61. Glied SA, Zhu B. Not so sweet: insulin affordability over time. September 25, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2020/sep/not-so-sweet-insulin-affordability-over-time
62. American Diabetes Association. Insulin and drug affordability. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/advocacy/insulin-and-drug-affordability
63. Sullivan P. Chances for drug pricing, surprise billing action fade until November. March 24, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://thehill.com/policy/healthcare/489334-chances-for-drug-pricing-surprise-billing-action-fade-until-november/
64. Brown TD. How Medicare’s new Senior Savings Model makes insulin more affordable. June 4, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/blog/how-medicares-new-senior-savings-model-makes-insulin-more-affordable
65. American Diabetes Association. ADA applauds the U.S. House of Representatives passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act. News release. April 1, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/official-statement/2022/ada-applauds-us-house-of-representatives-passage-of-the-affordable-insulin-now-act
66. JDRF. Driving T1D cures during challenging times. 2022.
67. Medtronic announces ongoing initiatives to address health equity for people of color living with diabetes. News release. April 7, 2021. Access August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3KGTOZU
From the T1D Exchange, Boston, MA (Ann Mungmode, Nicole Rioles, Jesse Cases, Dr. Ebekozien); The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust, New York, NY (Laurel Koester); and the University of Mississippi School of Population Health, Jackson, MS (Dr. Ebekozien).
Abstract
There have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, but these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus as the field focuses on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes. This article reviews select population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative, a learning health network that focuses on improving care and outcomes for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Such innovations include expanded telemedicine access, collection of real-world data, machine learning and artificial intelligence, and new diabetes medications and devices. In addition, multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and advocacy efforts for specific populations have been successful. Looking to the future, work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities and to look for additional innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes, learning health network, continuous glucose monitoring, health equity
One in 10 people in the United States has diabetes.1 Diabetes is the nation’s second leading cause of death, costing the US health system more than $300 billion annually.2 The COVID-19 pandemic presented additional health burdens for people living with diabetes. For example, preexisting diabetes was identified as a risk factor for COVID-19–associated morbidity and mortality.3,4 Over the past 2 years, there have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management, including stem cell therapy and new medication options. Additionally, improved technology solutions have aided in diabetes management through continuous glucose monitors (CGM), smart insulin pens, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems, and continuous subcutaneous insulin injections.5,6 Unfortunately, these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus, as the field is rightfully focused on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes.

Learning health networks like the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI) have implemented some of these innovative solutions to improve care for people with diabetes.7 T1DX-QI has more than 50 data-sharing endocrinology centers that care for over 75,000 people with diabetes across the United States (Figure 1). Centers participating in the T1DX-QI use quality improvement (QI) and implementation science methods to quickly translate research into evidence-based clinical practice. T1DX-QI leads diabetes population health and health system research and supports widespread transferability across health care organizations through regular collaborative calls, conferences, and case study documentation.8
In this review, we summarize impactful population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of T1DX-QI (see Figure 2 for relevant definitions). This review is limited in scope and is not meant to be an exhaustive list of innovations. The review also reflects significant changes from the perspective of academic diabetes centers, which may not apply to rural or primary care diabetes practices.
Methods
The first (A.M.), second (H.H.), and senior (O.E.) authors conducted a scoping review of published literature using terms related to diabetes, population health, and innovation on PubMed Central and Google Scholar for the period March 2020 to June 2022. To complement the review, A.M. and O.E. also reviewed abstracts from presentations at major international diabetes conferences, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), the T1DX-QI Learning Session Conference, and the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) 2020 to 2022 conferences.9-14 The authors also searched FDA.gov and ClinicalTrials.gov for relevant insights. A.M. and O.E. sorted the reviewed literature into major themes (Figure 3) from the population health improvement perspective of the T1DX-QI.

Population Health Innovations in Diabetes Management
Expansion of Telemedicine Access
Telemedicine is cost-effective for patients with diabetes,15 including those with complex cases.16 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine and virtual care were rare in diabetes management. However, the pandemic offered a new opportunity to expand the practice of telemedicine in diabetes management. A study from the T1DX-QI showed that telemedicine visits grew from comprising <1% of visits pre-pandemic (December 2019) to 95.2% during the pandemic (August 2020).17 Additional studies, like those conducted by Phillip et al,18 confirmed the noninferiority of telemedicine practice for patients with diabetes.Telemedicine was also found to be an effective strategy to educate patients on the use of diabetes technologies.19
Real-World Data and Disease Surveillance
As the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated outcomes for people with type 1 diabetes (T1D), a need arose to understand the immediate effects of the pandemic on people with T1D through real-world data and disease surveillance. In April 2020, the T1DX-QI initiated a multicenter surveillance study to collect data and analyze the impact of COVID-19 on people with T1D. The existing health collaborative served as a springboard for robust surveillance study, documenting numerous works on the effects of COVID-19.3,4,20-28 Other investigators also embraced the power of real-world surveillance and real-world data.29,30
Big Data, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence
The past 2 years have seen a shift toward embracing the incredible opportunity to tap the large volume of data generated from routine care for practical insights.31 In particular, researchers have demonstrated the widespread application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve diabetes management.32 The T1DX-QI also harnessed the growing power of big data by expanding the functionality of innovative benchmarking software. The T1DX QI Portal uses electronic medical record data of diabetes patients for clinic-to-clinic benchmarking and data analysis, using business intelligence solutions.33
Health Equity
While inequities across various health outcomes have been well documented for years,34 the COVID-19 pandemic further exaggerated racial/ethnic health inequities in T1D.23,35 In response, several organizations have outlined specific strategies to address these health inequities. Emboldened by the pandemic, the T1DX-QI announced a multipronged approach to address health inequities among patients with T1D through the Health Equity Advancement Lab (HEAL).36 One of HEAL’s main components is using real-world data to champion population-level insights and demonstrate progress in QI efforts.
Multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and these studies are expanding our understanding of the chasm.37 There have also been innovative solutions to addressing these inequities, with multiple studies published over the past 2 years.38 A source of inequity among patients with T1D is the lack of representation of racial/ethnic minorities with T1D in clinical trials.39 The T1DX-QI suggests that the equity-adapted framework for QI can be applied by research leaders to support trial diversity and representation, ensuring future device innovations are meaningful for all people with T1D.40
Diabetes Devices
Glucose monitoring and insulin therapy are vital tools to support individuals living with T1D, and devices such as CGM and insulin pumps have become the standard of care for diabetes management (Table).41 Innovations in diabetes technology and device access are imperative for a chronic disease with no cure.

The COVID-19 pandemic created an opportunity to increase access to diabetes devices in inpatient settings. In 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration expanded the use of CGM to support remote monitoring of patients in inpatient hospital settings, simultaneously supporting the glucose monitoring needs of patients with T1D and reducing COVID-19 transmission through reduced patient-clinician contact.42 This effort has been expanded and will continue in 2022 and beyond,43 and aligns with the growing consensus that supports patients wearing both CGMs and insulin pumps in ambulatory settings to improve patient health outcomes.44
Since 2020, innovations in diabetes technology have improved and increased the variety of options available to people with T1D and made them easier to use (Table). New, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems have progressed to offer Bluetooth features, including automatic software upgrades, tubeless systems, and the ability to allow parents to use their smartphones to bolus for children.45-47 The next big step in insulin delivery innovation is the release of functioning, fully closed loop systems, of which several are currently in clinical trials.48 These systems support reduced hypoglycemia and improved time in range.49
Additional innovations in insulin delivery have improved the user experience and expanded therapeutic options, including a variety of smart insulin pens complete with dosing logs50,51 and even a patch to deliver insulin without the burden of injections.52 As barriers to diabetes technology persist,53 innovations in alternate insulin delivery provide people with T1D more options to align with their personal access and technology preferences.
Innovations in CGM address cited barriers to their use, including size or overall wear.53-55 CGMs released in the past few years are smaller in physical size, have longer durations of time between changings, are more accurate, and do not require calibrations for accuracy.
New Diabetes Medications
Many new medications and therapeutic advances have become available in the past 2 years.56 Additionally, more medications are being tested as adjunct therapies to support glycemic management in patients with T1D, including metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 and 2 inhibitors, pramlintide, glucagon-like polypeptide-1 analogs, and glucagon receptor agonists.57 Other recent advances include stem cell replacement therapy for patients with T1D.58 The ultra-long-acting biosimilar insulins are one medical innovation that has been stalled, rather than propelled, during the COVID-19 pandemic.59
Diabetes Policy Advocacy
People with T1D require insulin to survive. The cost of insulin has increased in recent years, with some studies citing a 64% to 100% increase in the past decade.60,61 In fact, 1 in 4 insulin users report that cost has impacted their insulin use, including rationing their insulin.62 Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic stressed US families financially, increasing the urgency for insulin cost caps.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic halted national conversations on drug financing,63 advocacy efforts have succeeded for specific populations. The new Medicare Part D Senior Savings Model will cap the cost of insulin at $35 for a 30-day supply,64 and 20 states passed legislation capping insulin pricing.62 Efforts to codify national cost caps are under debate, including the passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act, which passed the House in March 2022 and is currently under review in the Senate.65
Perspective: The Role of Private Philanthropy in Supporting Population Health Innovations
Funders and industry partners play a crucial role in leading and supporting innovations that improve the lives of people with T1D and reduce society’s costs of living with the disease. Data infrastructure is critical to supporting population health. While building the data infrastructure to support population health is both time- and resource-intensive, private foundations such as Helmsley are uniquely positioned—and have a responsibility—to take large, informed risks to help reach all communities with T1D.
The T1DX-QI is the largest source of population health data on T1D in the United States and is becoming the premiere data authority on its incidence, prevalence, and outcomes. The T1DX-QI enables a robust understanding of T1D-related health trends at the population level, as well as trends among clinics and providers. Pilot centers in the T1DX-QI have reported reductions in patients’ A1c and acute diabetes-related events, as well as improvements in device usage and depression screening. The ability to capture changes speaks to the promise and power of these data to demonstrate the clinical impact of QI interventions and to support the spread of best practices and learnings across health systems.
Additional philanthropic efforts have supported innovation in the last 2 years. For example, the JDRF, a nonprofit philanthropic equity firm, has supported efforts in developing artificial pancreas systems and cell therapies currently in clinical trials like teplizumab, a drug that has demonstrated delayed onset of T1D through JDRF’s T1D Fund.66 Industry partners also have an opportunity for significant influence in this area, as they continue to fund meaningful projects to advance care for people with T1D.67
Conclusion
We are optimistic that the innovations summarized here describe a shift in the tide of equitable T1D outcomes; however, future work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities. We also see further opportunities for innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Corresponding author: Ann Mungmode, MPH, T1D Exchange, 11 Avenue de Lafayette, Boston, MA 02111; Email: amungmode@t1dexchange.org
Disclosures: Dr. Ebekozien serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for the Medtronic Advisory Board and received research grants from Medtronic Diabetes, Eli Lilly, and Dexcom.
Funding: The T1DX-QI is funded by The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust.
From the T1D Exchange, Boston, MA (Ann Mungmode, Nicole Rioles, Jesse Cases, Dr. Ebekozien); The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust, New York, NY (Laurel Koester); and the University of Mississippi School of Population Health, Jackson, MS (Dr. Ebekozien).
Abstract
There have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, but these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus as the field focuses on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes. This article reviews select population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative, a learning health network that focuses on improving care and outcomes for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Such innovations include expanded telemedicine access, collection of real-world data, machine learning and artificial intelligence, and new diabetes medications and devices. In addition, multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and advocacy efforts for specific populations have been successful. Looking to the future, work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities and to look for additional innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes, learning health network, continuous glucose monitoring, health equity
One in 10 people in the United States has diabetes.1 Diabetes is the nation’s second leading cause of death, costing the US health system more than $300 billion annually.2 The COVID-19 pandemic presented additional health burdens for people living with diabetes. For example, preexisting diabetes was identified as a risk factor for COVID-19–associated morbidity and mortality.3,4 Over the past 2 years, there have been remarkable innovations in diabetes management, including stem cell therapy and new medication options. Additionally, improved technology solutions have aided in diabetes management through continuous glucose monitors (CGM), smart insulin pens, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems, and continuous subcutaneous insulin injections.5,6 Unfortunately, these groundbreaking innovations are drawing limited focus, as the field is rightfully focused on the adverse impact of the pandemic on patients with diabetes.

Learning health networks like the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI) have implemented some of these innovative solutions to improve care for people with diabetes.7 T1DX-QI has more than 50 data-sharing endocrinology centers that care for over 75,000 people with diabetes across the United States (Figure 1). Centers participating in the T1DX-QI use quality improvement (QI) and implementation science methods to quickly translate research into evidence-based clinical practice. T1DX-QI leads diabetes population health and health system research and supports widespread transferability across health care organizations through regular collaborative calls, conferences, and case study documentation.8
In this review, we summarize impactful population health innovations in diabetes management that have become available over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of T1DX-QI (see Figure 2 for relevant definitions). This review is limited in scope and is not meant to be an exhaustive list of innovations. The review also reflects significant changes from the perspective of academic diabetes centers, which may not apply to rural or primary care diabetes practices.
Methods
The first (A.M.), second (H.H.), and senior (O.E.) authors conducted a scoping review of published literature using terms related to diabetes, population health, and innovation on PubMed Central and Google Scholar for the period March 2020 to June 2022. To complement the review, A.M. and O.E. also reviewed abstracts from presentations at major international diabetes conferences, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), the T1DX-QI Learning Session Conference, and the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) 2020 to 2022 conferences.9-14 The authors also searched FDA.gov and ClinicalTrials.gov for relevant insights. A.M. and O.E. sorted the reviewed literature into major themes (Figure 3) from the population health improvement perspective of the T1DX-QI.

Population Health Innovations in Diabetes Management
Expansion of Telemedicine Access
Telemedicine is cost-effective for patients with diabetes,15 including those with complex cases.16 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine and virtual care were rare in diabetes management. However, the pandemic offered a new opportunity to expand the practice of telemedicine in diabetes management. A study from the T1DX-QI showed that telemedicine visits grew from comprising <1% of visits pre-pandemic (December 2019) to 95.2% during the pandemic (August 2020).17 Additional studies, like those conducted by Phillip et al,18 confirmed the noninferiority of telemedicine practice for patients with diabetes.Telemedicine was also found to be an effective strategy to educate patients on the use of diabetes technologies.19
Real-World Data and Disease Surveillance
As the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated outcomes for people with type 1 diabetes (T1D), a need arose to understand the immediate effects of the pandemic on people with T1D through real-world data and disease surveillance. In April 2020, the T1DX-QI initiated a multicenter surveillance study to collect data and analyze the impact of COVID-19 on people with T1D. The existing health collaborative served as a springboard for robust surveillance study, documenting numerous works on the effects of COVID-19.3,4,20-28 Other investigators also embraced the power of real-world surveillance and real-world data.29,30
Big Data, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence
The past 2 years have seen a shift toward embracing the incredible opportunity to tap the large volume of data generated from routine care for practical insights.31 In particular, researchers have demonstrated the widespread application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve diabetes management.32 The T1DX-QI also harnessed the growing power of big data by expanding the functionality of innovative benchmarking software. The T1DX QI Portal uses electronic medical record data of diabetes patients for clinic-to-clinic benchmarking and data analysis, using business intelligence solutions.33
Health Equity
While inequities across various health outcomes have been well documented for years,34 the COVID-19 pandemic further exaggerated racial/ethnic health inequities in T1D.23,35 In response, several organizations have outlined specific strategies to address these health inequities. Emboldened by the pandemic, the T1DX-QI announced a multipronged approach to address health inequities among patients with T1D through the Health Equity Advancement Lab (HEAL).36 One of HEAL’s main components is using real-world data to champion population-level insights and demonstrate progress in QI efforts.
Multiple innovative studies have been undertaken to explore contributors to health inequities in diabetes, and these studies are expanding our understanding of the chasm.37 There have also been innovative solutions to addressing these inequities, with multiple studies published over the past 2 years.38 A source of inequity among patients with T1D is the lack of representation of racial/ethnic minorities with T1D in clinical trials.39 The T1DX-QI suggests that the equity-adapted framework for QI can be applied by research leaders to support trial diversity and representation, ensuring future device innovations are meaningful for all people with T1D.40
Diabetes Devices
Glucose monitoring and insulin therapy are vital tools to support individuals living with T1D, and devices such as CGM and insulin pumps have become the standard of care for diabetes management (Table).41 Innovations in diabetes technology and device access are imperative for a chronic disease with no cure.

The COVID-19 pandemic created an opportunity to increase access to diabetes devices in inpatient settings. In 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration expanded the use of CGM to support remote monitoring of patients in inpatient hospital settings, simultaneously supporting the glucose monitoring needs of patients with T1D and reducing COVID-19 transmission through reduced patient-clinician contact.42 This effort has been expanded and will continue in 2022 and beyond,43 and aligns with the growing consensus that supports patients wearing both CGMs and insulin pumps in ambulatory settings to improve patient health outcomes.44
Since 2020, innovations in diabetes technology have improved and increased the variety of options available to people with T1D and made them easier to use (Table). New, advanced hybrid closed-loop systems have progressed to offer Bluetooth features, including automatic software upgrades, tubeless systems, and the ability to allow parents to use their smartphones to bolus for children.45-47 The next big step in insulin delivery innovation is the release of functioning, fully closed loop systems, of which several are currently in clinical trials.48 These systems support reduced hypoglycemia and improved time in range.49
Additional innovations in insulin delivery have improved the user experience and expanded therapeutic options, including a variety of smart insulin pens complete with dosing logs50,51 and even a patch to deliver insulin without the burden of injections.52 As barriers to diabetes technology persist,53 innovations in alternate insulin delivery provide people with T1D more options to align with their personal access and technology preferences.
Innovations in CGM address cited barriers to their use, including size or overall wear.53-55 CGMs released in the past few years are smaller in physical size, have longer durations of time between changings, are more accurate, and do not require calibrations for accuracy.
New Diabetes Medications
Many new medications and therapeutic advances have become available in the past 2 years.56 Additionally, more medications are being tested as adjunct therapies to support glycemic management in patients with T1D, including metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 and 2 inhibitors, pramlintide, glucagon-like polypeptide-1 analogs, and glucagon receptor agonists.57 Other recent advances include stem cell replacement therapy for patients with T1D.58 The ultra-long-acting biosimilar insulins are one medical innovation that has been stalled, rather than propelled, during the COVID-19 pandemic.59
Diabetes Policy Advocacy
People with T1D require insulin to survive. The cost of insulin has increased in recent years, with some studies citing a 64% to 100% increase in the past decade.60,61 In fact, 1 in 4 insulin users report that cost has impacted their insulin use, including rationing their insulin.62 Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic stressed US families financially, increasing the urgency for insulin cost caps.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic halted national conversations on drug financing,63 advocacy efforts have succeeded for specific populations. The new Medicare Part D Senior Savings Model will cap the cost of insulin at $35 for a 30-day supply,64 and 20 states passed legislation capping insulin pricing.62 Efforts to codify national cost caps are under debate, including the passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act, which passed the House in March 2022 and is currently under review in the Senate.65
Perspective: The Role of Private Philanthropy in Supporting Population Health Innovations
Funders and industry partners play a crucial role in leading and supporting innovations that improve the lives of people with T1D and reduce society’s costs of living with the disease. Data infrastructure is critical to supporting population health. While building the data infrastructure to support population health is both time- and resource-intensive, private foundations such as Helmsley are uniquely positioned—and have a responsibility—to take large, informed risks to help reach all communities with T1D.
The T1DX-QI is the largest source of population health data on T1D in the United States and is becoming the premiere data authority on its incidence, prevalence, and outcomes. The T1DX-QI enables a robust understanding of T1D-related health trends at the population level, as well as trends among clinics and providers. Pilot centers in the T1DX-QI have reported reductions in patients’ A1c and acute diabetes-related events, as well as improvements in device usage and depression screening. The ability to capture changes speaks to the promise and power of these data to demonstrate the clinical impact of QI interventions and to support the spread of best practices and learnings across health systems.
Additional philanthropic efforts have supported innovation in the last 2 years. For example, the JDRF, a nonprofit philanthropic equity firm, has supported efforts in developing artificial pancreas systems and cell therapies currently in clinical trials like teplizumab, a drug that has demonstrated delayed onset of T1D through JDRF’s T1D Fund.66 Industry partners also have an opportunity for significant influence in this area, as they continue to fund meaningful projects to advance care for people with T1D.67
Conclusion
We are optimistic that the innovations summarized here describe a shift in the tide of equitable T1D outcomes; however, future work is required to explore additional health equity successes that do not further exacerbate inequities. We also see further opportunities for innovative ways to engage people with T1D in their health care through conversations on social determinants of health and societal structures.
Corresponding author: Ann Mungmode, MPH, T1D Exchange, 11 Avenue de Lafayette, Boston, MA 02111; Email: amungmode@t1dexchange.org
Disclosures: Dr. Ebekozien serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for the Medtronic Advisory Board and received research grants from Medtronic Diabetes, Eli Lilly, and Dexcom.
Funding: The T1DX-QI is funded by The Leona M. and Harry B. Hemsley Charitable Trust.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes fast facts. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/quick-facts.html
3. O’Malley G, Ebekozien O, Desimone M, et al. COVID-19 hospitalization in adults with type 1 diabetes: results from the T1D Exchange Multicenter Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(2):e936-e942. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa825
4. Ebekozien OA, Noor N, Gallagher MP, Alonso GT. Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: preliminary findings from a multicenter surveillance study in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(8):e83-e85. doi:10.2337/dc20-1088
5. Zimmerman C, Albanese-O’Neill A, Haller MJ. Advances in type 1 diabetes technology over the last decade. Eur Endocrinol. 2019;15(2):70-76. doi:10.17925/ee.2019.15.2.70
6. Wake DJ, Gibb FW, Kar P, et al. Endocrinology in the time of COVID-19: remodelling diabetes services and emerging innovation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183(2):G67-G77. doi:10.1530/eje-20-0377
7. Alonso GT, Corathers S, Shah A, et al. Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI). Clin Diabetes. 2020;38(2):141-151. doi:10.2337/cd19-0032
8. Ginnard OZB, Alonso GT, Corathers SD, et al. Quality improvement in diabetes care: a review of initiatives and outcomes in the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):256-263. doi:10.2337/cd21-0029
9. ATTD 2021 invited speaker abstracts. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S2):A1-A206. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.2525.abstracts
10. Rompicherla SN, Edelen N, Gallagher R, et al. Children and adolescent patients with pre-existing type 1 diabetes and additional comorbidities have an increased risk of hospitalization from COVID-19; data from the T1D Exchange COVID Registry. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22(S30):3-32. doi:10.1111/pedi.13268
11. Abstracts for the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative (T1DX-QI) Learning Session 2021. November 8-9, 2021. J Diabetes. 2021;13(S1):3-17. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13227
12. The Official Journal of ATTD Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes conference 27-30 April 2022. Barcelona and online. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):A1-A237. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2525.abstracts
13. Ebekozien ON, Kamboj N, Odugbesan MK, et al. Inequities in glycemic outcomes for patients with type 1 diabetes: six-year (2016-2021) longitudinal follow-up by race and ethnicity of 36,390 patients in the T1DX-QI Collaborative. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-167-OR
14. Narayan KA, Noor M, Rompicherla N, et al. No BMI increase during the COVID-pandemic in children and adults with T1D in three continents: joint analysis of ADDN, T1DX, and DPV registries. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-269-OR
15. Lee JY, Lee SWH. Telemedicine cost-effectiveness for diabetes management: a systematic review. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018;20(7):492-500. doi:10.1089/dia.2018.0098
16. McDonnell ME. Telemedicine in complex diabetes management. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(7):42. doi:10.1007/s11892-018-1015-3
17. Lee JM, Carlson E, Albanese-O’Neill A, et al. Adoption of telemedicine for type 1 diabetes care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(9):642-651. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0080
18. Phillip M, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, et al. The digital/virtual diabetes clinic: the future is now–recommendations from an international panel on diabetes digital technologies introduction. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(2):146-154. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0375
19. Garg SK, Rodriguez E. COVID‐19 pandemic and diabetes care. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S2-S20. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2501
20. Beliard K, Ebekozien O, Demeterco-Berggren C, et al. Increased DKA at presentation among newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients with or without COVID-19: data from a multi-site surveillance registry. J Diabetes. 2021;13(3):270-272. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13141
21. Ebekozien O, Agarwal S, Noor N, et al. Inequities in diabetic ketoacidosis among patients with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from 52 US clinical centers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(4):1755-1762. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa920
22. Alonso GT, Ebekozien O, Gallagher MP, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis drives COVID-19 related hospitalizations in children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2021;13(8):681-687. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13184
23. Noor N, Ebekozien O, Levin L, et al. Diabetes technology use for management of type 1 diabetes is associated with fewer adverse COVID-19 outcomes: findings from the T1D Exchange COVID-19 Surveillance Registry. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(8):e160-e162. doi:10.2337/dc21-0074
24. Demeterco-Berggren C, Ebekozien O, Rompicherla S, et al. Age and hospitalization risk in people with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from the T1D Exchange Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;107(2):410-418. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab668
25. DeSalvo DJ, Noor N, Xie C, et al. Patient demographics and clinical outcomes among type 1 diabetes patients using continuous glucose monitors: data from T1D Exchange real-world observational study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021 Oct 9. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1177/19322968211049783
26. Gallagher MP, Rompicherla S, Ebekozien O, et al. Differences in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with type 1 diabetes: first vs later surges. J Clin Outcomes Manage. 2022;29(1):27-31. doi:10.12788/jcom.0084
27. Wolf RM, Noor N, Izquierdo R, et al. Increase in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in youth during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States: a multi-center analysis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022;23(4):433-438. doi:10.1111/pedi.13328
28. Lavik AR, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Trends in type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 surges at 7 US centers: highest burden on non-Hispanic Black patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(7):1948-1955. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgac158
29. van der Linden J, Welsh JB, Hirsch IB, Garg SK. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and its impact on time in range. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S1):S1-S7. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0649
30. Nwosu BU, Al-Halbouni L, Parajuli S, et al. COVID-19 pandemic and pediatric type 1 diabetes: no significant change in glycemic control during the pandemic lockdown of 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:703905. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.703905
31. Ellahham S. Artificial intelligence: the future for diabetes care. Am J Med. 2020;133(8):895-900. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.03.033
32. Nomura A, Noguchi M, Kometani M, et al. Artificial intelligence in current diabetes management and prediction. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(12):61. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01423-2
33. Mungmode A, Noor N, Weinstock RS, et al. Making diabetes electronic medical record data actionable: promoting benchmarking and population health using the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Portal. Clin Diabetes. Forthcoming 2022.
34. Lavizzo-Mourey RJ, Besser RE, Williams DR. Understanding and mitigating health inequities—past, current, and future directions. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1681-1684. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008628
35. Majidi S, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Inequities in health outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: data from the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):278-283. doi:10.2337/cd21-0028
36. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Odugbesan O, et al. Addressing type 1 diabetes health inequities in the United States: approaches from the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative. J Diabetes. 2022;14(1):79-82. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13235
37. Odugbesan O, Addala A, Nelson G, et al. Implicit racial-ethnic and insurance-mediated bias to recommending diabetes technology: insights from T1D Exchange multicenter pediatric and adult diabetes provider cohort. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022 Jun 13. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1089/dia.2022.0042
38. Schmitt J, Fogle K, Scott ML, Iyer P. Improving equitable access to continuous glucose monitors for Alabama’s children with type 1 diabetes: a quality improvement project. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(7):481-491. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0511
39. Akturk HK, Agarwal S, Hoffecker L, Shah VN. Inequity in racial-ethnic representation in randomized controlled trials of diabetes technologies in type 1 diabetes: critical need for new standards. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(6):e121-e123. doi:10.2337/dc20-3063
40. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Buckingham D, et al. Achieving equity in diabetes research: borrowing from the field of quality improvement using a practical framework and improvement tools. Diabetes Spectr. 2022;35(3):304-312. doi:10.2237/dsi22-0002
41. Zhang J, Xu J, Lim J, et al. Wearable glucose monitoring and implantable drug delivery systems for diabetes management. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(17):e2100194. doi:10.1002/adhm.202100194
42. FDA expands remote patient monitoring in hospitals for people with diabetes during COVID-19; manufacturers donate CGM supplies. News release. April 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/2020/fda-remote-patient-monitoring-cgm
43. Campbell P. FDA grants Dexcom CGM breakthrough designation for in-hospital use. March 2, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.endocrinologynetwork.com/view/fda-grants-dexcom-cgm-breakthrough-designation-for-in-hospital-use
44. Yeh T, Yeung M, Mendelsohn Curanaj FA. Managing patients with insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors in the hospital: to wear or not to wear. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(2):7. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01375-7
45. Medtronic announces FDA approval for MiniMed 770G insulin pump system. News release. September 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3TyEna4
46. Tandem Diabetes Care announces commercial launch of the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology in the United States. News release. January 15, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://investor.tandemdiabetes.com/news-releases/news-release-details/tandem-diabetes-care-announces-commercial-launch-tslim-x2-0
47. Garza M, Gutow H, Mahoney K. Omnipod 5 cleared by the FDA. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribe.org/omnipod-5-approved-fda
48. Boughton CK. Fully closed-loop insulin delivery—are we nearly there yet? Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(11):e689-e690. doi:10.1016/s2589-7500(21)00218-1
49. Noor N, Kamboj MK, Triolo T, et al. Hybrid closed-loop systems and glycemic outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: real-world evidence from a U.S.-based multicenter collaborative. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(8):e118-e119. doi:10.2337/dc22-0329
50. Medtronic launches InPen with real-time Guardian Connect CGM data--the first integrated smart insulin pen for people with diabetes on MDI. News release. November 12, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3CTSWPL
51. Bigfoot Biomedical receives FDA clearance for Bigfoot Unity Diabetes Management System, featuring first-of-its-kind smart pen caps for insulin pens used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. News release. May 10, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3BeyoAh
52. Vieira G. All about the CeQur Simplicity insulin patch. Updated May 24, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://beyondtype1.org/cequr-simplicity-insulin-patch/.
53. Messer LH, Tanenbaum ML, Cook PF, et al. Cost, hassle, and on-body experience: barriers to diabetes device use in adolescents and potential intervention targets. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(10):760-767. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0509
54. Hilliard ME, Levy W, Anderson BJ, et al. Benefits and barriers of continuous glucose monitoring in young children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(9):493-498. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0142
55. Dexcom G7 Release Delayed Until Late 2022. News release. August 8, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://diatribe.org/dexcom-g7-release-delayed-until-late-2022
56. Drucker DJ. Transforming type 1 diabetes: the next wave of innovation. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1059-1065. doi:10.1007/s00125-021-05396-5
57. Garg SK, Rodriguez E, Shah VN, Hirsch IB. New medications for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S190-S208. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2513
58. Melton D. The promise of stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1030-1036. doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05367-2
59. Danne T, Heinemann L, Bolinder J. New insulins, biosimilars, and insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S35-S57. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2503
60. Kenney J. Insulin copay caps–a path to affordability. July 6, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribechange.org/news/insulin-copay-caps-path-affordability
61. Glied SA, Zhu B. Not so sweet: insulin affordability over time. September 25, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2020/sep/not-so-sweet-insulin-affordability-over-time
62. American Diabetes Association. Insulin and drug affordability. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/advocacy/insulin-and-drug-affordability
63. Sullivan P. Chances for drug pricing, surprise billing action fade until November. March 24, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://thehill.com/policy/healthcare/489334-chances-for-drug-pricing-surprise-billing-action-fade-until-november/
64. Brown TD. How Medicare’s new Senior Savings Model makes insulin more affordable. June 4, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/blog/how-medicares-new-senior-savings-model-makes-insulin-more-affordable
65. American Diabetes Association. ADA applauds the U.S. House of Representatives passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act. News release. April 1, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/official-statement/2022/ada-applauds-us-house-of-representatives-passage-of-the-affordable-insulin-now-act
66. JDRF. Driving T1D cures during challenging times. 2022.
67. Medtronic announces ongoing initiatives to address health equity for people of color living with diabetes. News release. April 7, 2021. Access August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3KGTOZU
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes fast facts. Accessed August 30, 2022. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/quick-facts.html
3. O’Malley G, Ebekozien O, Desimone M, et al. COVID-19 hospitalization in adults with type 1 diabetes: results from the T1D Exchange Multicenter Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(2):e936-e942. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa825
4. Ebekozien OA, Noor N, Gallagher MP, Alonso GT. Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: preliminary findings from a multicenter surveillance study in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(8):e83-e85. doi:10.2337/dc20-1088
5. Zimmerman C, Albanese-O’Neill A, Haller MJ. Advances in type 1 diabetes technology over the last decade. Eur Endocrinol. 2019;15(2):70-76. doi:10.17925/ee.2019.15.2.70
6. Wake DJ, Gibb FW, Kar P, et al. Endocrinology in the time of COVID-19: remodelling diabetes services and emerging innovation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183(2):G67-G77. doi:10.1530/eje-20-0377
7. Alonso GT, Corathers S, Shah A, et al. Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI). Clin Diabetes. 2020;38(2):141-151. doi:10.2337/cd19-0032
8. Ginnard OZB, Alonso GT, Corathers SD, et al. Quality improvement in diabetes care: a review of initiatives and outcomes in the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):256-263. doi:10.2337/cd21-0029
9. ATTD 2021 invited speaker abstracts. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S2):A1-A206. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.2525.abstracts
10. Rompicherla SN, Edelen N, Gallagher R, et al. Children and adolescent patients with pre-existing type 1 diabetes and additional comorbidities have an increased risk of hospitalization from COVID-19; data from the T1D Exchange COVID Registry. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22(S30):3-32. doi:10.1111/pedi.13268
11. Abstracts for the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative (T1DX-QI) Learning Session 2021. November 8-9, 2021. J Diabetes. 2021;13(S1):3-17. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13227
12. The Official Journal of ATTD Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes conference 27-30 April 2022. Barcelona and online. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):A1-A237. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2525.abstracts
13. Ebekozien ON, Kamboj N, Odugbesan MK, et al. Inequities in glycemic outcomes for patients with type 1 diabetes: six-year (2016-2021) longitudinal follow-up by race and ethnicity of 36,390 patients in the T1DX-QI Collaborative. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-167-OR
14. Narayan KA, Noor M, Rompicherla N, et al. No BMI increase during the COVID-pandemic in children and adults with T1D in three continents: joint analysis of ADDN, T1DX, and DPV registries. Diabetes. 2022;71(suppl 1). doi:10.2337/db22-269-OR
15. Lee JY, Lee SWH. Telemedicine cost-effectiveness for diabetes management: a systematic review. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018;20(7):492-500. doi:10.1089/dia.2018.0098
16. McDonnell ME. Telemedicine in complex diabetes management. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(7):42. doi:10.1007/s11892-018-1015-3
17. Lee JM, Carlson E, Albanese-O’Neill A, et al. Adoption of telemedicine for type 1 diabetes care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(9):642-651. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0080
18. Phillip M, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, et al. The digital/virtual diabetes clinic: the future is now–recommendations from an international panel on diabetes digital technologies introduction. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(2):146-154. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0375
19. Garg SK, Rodriguez E. COVID‐19 pandemic and diabetes care. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S2-S20. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2501
20. Beliard K, Ebekozien O, Demeterco-Berggren C, et al. Increased DKA at presentation among newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients with or without COVID-19: data from a multi-site surveillance registry. J Diabetes. 2021;13(3):270-272. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13141
21. Ebekozien O, Agarwal S, Noor N, et al. Inequities in diabetic ketoacidosis among patients with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from 52 US clinical centers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;106(4):1755-1762. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa920
22. Alonso GT, Ebekozien O, Gallagher MP, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis drives COVID-19 related hospitalizations in children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2021;13(8):681-687. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13184
23. Noor N, Ebekozien O, Levin L, et al. Diabetes technology use for management of type 1 diabetes is associated with fewer adverse COVID-19 outcomes: findings from the T1D Exchange COVID-19 Surveillance Registry. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(8):e160-e162. doi:10.2337/dc21-0074
24. Demeterco-Berggren C, Ebekozien O, Rompicherla S, et al. Age and hospitalization risk in people with type 1 diabetes and COVID-19: data from the T1D Exchange Surveillance Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;107(2):410-418. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab668
25. DeSalvo DJ, Noor N, Xie C, et al. Patient demographics and clinical outcomes among type 1 diabetes patients using continuous glucose monitors: data from T1D Exchange real-world observational study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021 Oct 9. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1177/19322968211049783
26. Gallagher MP, Rompicherla S, Ebekozien O, et al. Differences in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with type 1 diabetes: first vs later surges. J Clin Outcomes Manage. 2022;29(1):27-31. doi:10.12788/jcom.0084
27. Wolf RM, Noor N, Izquierdo R, et al. Increase in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in youth during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States: a multi-center analysis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022;23(4):433-438. doi:10.1111/pedi.13328
28. Lavik AR, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Trends in type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 surges at 7 US centers: highest burden on non-Hispanic Black patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(7):1948-1955. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgac158
29. van der Linden J, Welsh JB, Hirsch IB, Garg SK. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and its impact on time in range. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S1):S1-S7. doi:10.1089/dia.2020.0649
30. Nwosu BU, Al-Halbouni L, Parajuli S, et al. COVID-19 pandemic and pediatric type 1 diabetes: no significant change in glycemic control during the pandemic lockdown of 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:703905. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.703905
31. Ellahham S. Artificial intelligence: the future for diabetes care. Am J Med. 2020;133(8):895-900. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.03.033
32. Nomura A, Noguchi M, Kometani M, et al. Artificial intelligence in current diabetes management and prediction. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(12):61. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01423-2
33. Mungmode A, Noor N, Weinstock RS, et al. Making diabetes electronic medical record data actionable: promoting benchmarking and population health using the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Portal. Clin Diabetes. Forthcoming 2022.
34. Lavizzo-Mourey RJ, Besser RE, Williams DR. Understanding and mitigating health inequities—past, current, and future directions. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1681-1684. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008628
35. Majidi S, Ebekozien O, Noor N, et al. Inequities in health outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: data from the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(3):278-283. doi:10.2337/cd21-0028
36. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Odugbesan O, et al. Addressing type 1 diabetes health inequities in the United States: approaches from the T1D Exchange QI Collaborative. J Diabetes. 2022;14(1):79-82. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13235
37. Odugbesan O, Addala A, Nelson G, et al. Implicit racial-ethnic and insurance-mediated bias to recommending diabetes technology: insights from T1D Exchange multicenter pediatric and adult diabetes provider cohort. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022 Jun 13. [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1089/dia.2022.0042
38. Schmitt J, Fogle K, Scott ML, Iyer P. Improving equitable access to continuous glucose monitors for Alabama’s children with type 1 diabetes: a quality improvement project. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(7):481-491. doi:10.1089/dia.2021.0511
39. Akturk HK, Agarwal S, Hoffecker L, Shah VN. Inequity in racial-ethnic representation in randomized controlled trials of diabetes technologies in type 1 diabetes: critical need for new standards. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(6):e121-e123. doi:10.2337/dc20-3063
40. Ebekozien O, Mungmode A, Buckingham D, et al. Achieving equity in diabetes research: borrowing from the field of quality improvement using a practical framework and improvement tools. Diabetes Spectr. 2022;35(3):304-312. doi:10.2237/dsi22-0002
41. Zhang J, Xu J, Lim J, et al. Wearable glucose monitoring and implantable drug delivery systems for diabetes management. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(17):e2100194. doi:10.1002/adhm.202100194
42. FDA expands remote patient monitoring in hospitals for people with diabetes during COVID-19; manufacturers donate CGM supplies. News release. April 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/2020/fda-remote-patient-monitoring-cgm
43. Campbell P. FDA grants Dexcom CGM breakthrough designation for in-hospital use. March 2, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.endocrinologynetwork.com/view/fda-grants-dexcom-cgm-breakthrough-designation-for-in-hospital-use
44. Yeh T, Yeung M, Mendelsohn Curanaj FA. Managing patients with insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors in the hospital: to wear or not to wear. Curr Diab Rep. 2021;21(2):7. doi:10.1007/s11892-021-01375-7
45. Medtronic announces FDA approval for MiniMed 770G insulin pump system. News release. September 21, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3TyEna4
46. Tandem Diabetes Care announces commercial launch of the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology in the United States. News release. January 15, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://investor.tandemdiabetes.com/news-releases/news-release-details/tandem-diabetes-care-announces-commercial-launch-tslim-x2-0
47. Garza M, Gutow H, Mahoney K. Omnipod 5 cleared by the FDA. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribe.org/omnipod-5-approved-fda
48. Boughton CK. Fully closed-loop insulin delivery—are we nearly there yet? Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(11):e689-e690. doi:10.1016/s2589-7500(21)00218-1
49. Noor N, Kamboj MK, Triolo T, et al. Hybrid closed-loop systems and glycemic outcomes in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: real-world evidence from a U.S.-based multicenter collaborative. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(8):e118-e119. doi:10.2337/dc22-0329
50. Medtronic launches InPen with real-time Guardian Connect CGM data--the first integrated smart insulin pen for people with diabetes on MDI. News release. November 12, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3CTSWPL
51. Bigfoot Biomedical receives FDA clearance for Bigfoot Unity Diabetes Management System, featuring first-of-its-kind smart pen caps for insulin pens used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. News release. May 10, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3BeyoAh
52. Vieira G. All about the CeQur Simplicity insulin patch. Updated May 24, 2022. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://beyondtype1.org/cequr-simplicity-insulin-patch/.
53. Messer LH, Tanenbaum ML, Cook PF, et al. Cost, hassle, and on-body experience: barriers to diabetes device use in adolescents and potential intervention targets. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(10):760-767. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0509
54. Hilliard ME, Levy W, Anderson BJ, et al. Benefits and barriers of continuous glucose monitoring in young children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(9):493-498. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0142
55. Dexcom G7 Release Delayed Until Late 2022. News release. August 8, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://diatribe.org/dexcom-g7-release-delayed-until-late-2022
56. Drucker DJ. Transforming type 1 diabetes: the next wave of innovation. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1059-1065. doi:10.1007/s00125-021-05396-5
57. Garg SK, Rodriguez E, Shah VN, Hirsch IB. New medications for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S190-S208. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2513
58. Melton D. The promise of stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy. Diabetologia. 2021;64(5):1030-1036. doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05367-2
59. Danne T, Heinemann L, Bolinder J. New insulins, biosimilars, and insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(S1):S35-S57. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.2503
60. Kenney J. Insulin copay caps–a path to affordability. July 6, 2021. Accessed August 30, 2022.https://diatribechange.org/news/insulin-copay-caps-path-affordability
61. Glied SA, Zhu B. Not so sweet: insulin affordability over time. September 25, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2020/sep/not-so-sweet-insulin-affordability-over-time
62. American Diabetes Association. Insulin and drug affordability. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/advocacy/insulin-and-drug-affordability
63. Sullivan P. Chances for drug pricing, surprise billing action fade until November. March 24, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://thehill.com/policy/healthcare/489334-chances-for-drug-pricing-surprise-billing-action-fade-until-november/
64. Brown TD. How Medicare’s new Senior Savings Model makes insulin more affordable. June 4, 2020. Accessed August 30, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/blog/how-medicares-new-senior-savings-model-makes-insulin-more-affordable
65. American Diabetes Association. ADA applauds the U.S. House of Representatives passage of the Affordable Insulin Now Act. News release. April 1, 2022. https://www.diabetes.org/newsroom/official-statement/2022/ada-applauds-us-house-of-representatives-passage-of-the-affordable-insulin-now-act
66. JDRF. Driving T1D cures during challenging times. 2022.
67. Medtronic announces ongoing initiatives to address health equity for people of color living with diabetes. News release. April 7, 2021. Access August 30, 2022. https://bit.ly/3KGTOZU