User login
European committee recommends approval of baricitinib for severe alopecia areata
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
Facial Follicular Spicules: A Rare Cutaneous Presentation of Trichodysplasia Spinulosa
To the Editor:
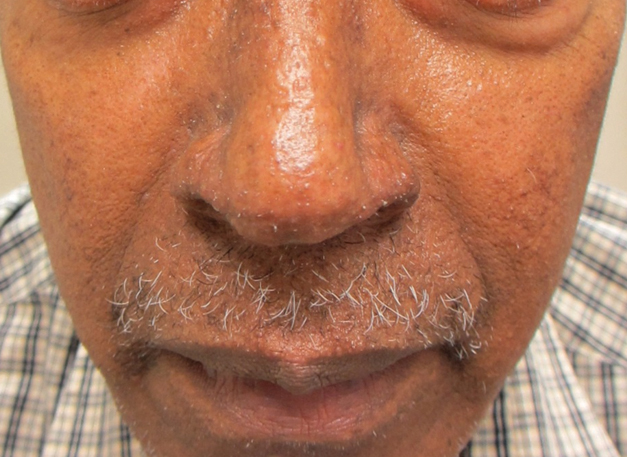
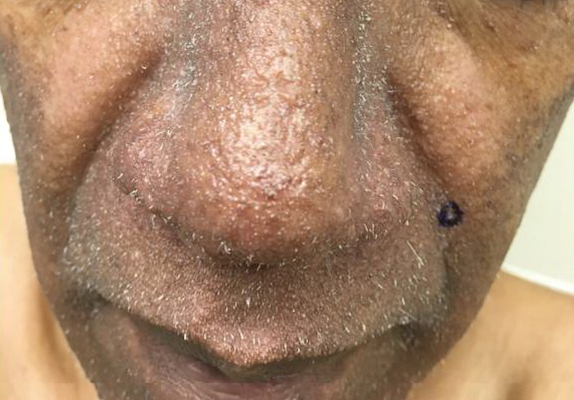
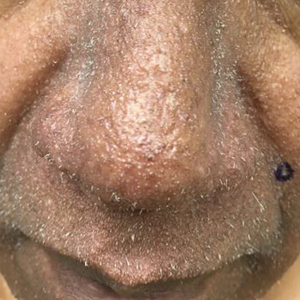
A 57-year-old man with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and congestive heart failure presented with a disfiguring eruption comprised of asymptomatic papules on the face that appeared 12 months post–heart transplantation. Immunosuppressive medications included mycophenolic acid and tacrolimus ointment (FK506). The pinpoint papules spread from the central face to the ears, arms, and legs. Physical examination revealed multiple 0.5- to 1-mm flesh-colored papules over the glabella, nose, nasolabial folds, philtrum, chin, ears, arms, and legs sparing the trunk. The initial appearance of the facial rash resembled the surface of a nutmeg grater with central white spiny excrescences overlying fine papules (spinulosism)(Figure 1). In addition, eyebrow alopecia was present.
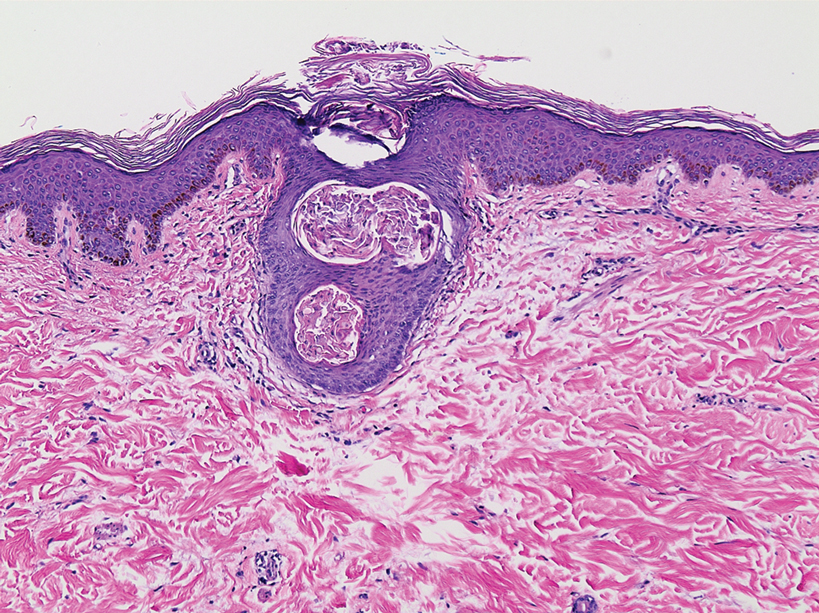
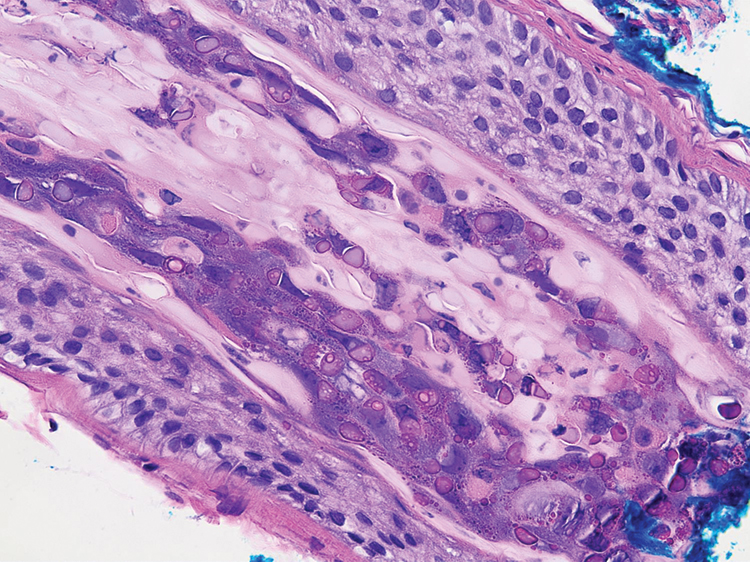
A 3-mm punch biopsy of a papule with a central spine was performed on the left thigh. Microscopic examination revealed marked dilatation of anagen hair follicles with a proliferation of haphazard inner root sheath cells replacing the follicular lumen. Hair shafts were absent, and plugged infundibula were observed (Figure 2). The inner root sheath keratinocytes were enlarged and dystrophic with deeply eosinophilic trichohyalin granules (Figure 3). The epidermis, outer root sheath epithelium, and eccrine structures were unremarkable.
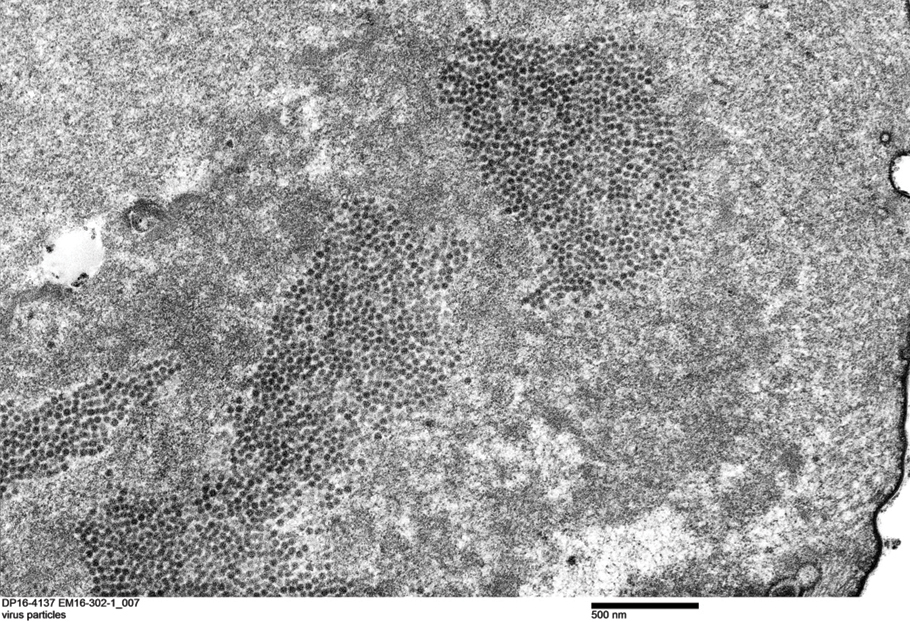
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirmed the presence of intranuclear viral inclusions within affected inner root sheath keratinocytes composed of nonenveloped icosahedral viral particles measuring 33 to 38 nm in diameter (Figure 4). These findings morphologically were consistent with a polyomavirus. No intracytoplasmic or extracellular viral particles were identified. The clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and electron microscopy features strongly supported the diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) despite insufficient material being retrieved for polymerase chain reaction identification.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first described by Haycox et al1 in 1999. The authors suggested a viral etiology. Eleven years later, TS-associated polyomavirus (TSPyV) was identified by van der Meijden et al.2 Follicular keratinocytes are the specific target for TSPyV.3 Evidence has been presented suggesting that TS is caused by a primary infection or reactivation of TSPyV in the setting of immunosuppression.4,5
Patients with TS present with papular eruptions that appear on the central face with spiny excrescences and various degrees of alopecia involving the eyebrows or eyelashes. Histopathologic features include distended hair follicles with expansion of inner root sheath cells, eosinophilic trichohyalin granules, and the absence of hair shafts. The viral protein can be verified through immunohistochemistry TSPyV VP1 staining that demonstrates co-localization with trichohyalin. Viral particles also can be visualized as 35- to 38-nm intranuclear particles with an organized crystalloid morphology on TEM.6,7 The negative polymerase chain reaction in our patient could be the result of suboptimal template DNA concentration extracted from the limited amount of tissue remaining in the block after hematoxylin and eosin staining.
The clinical differential diagnosis of central facial spinulosism includes the follicular spicules of multiple myeloma (FSMM). In fact, FSMM and TS can only be differentiated after obtaining a blood profile and bone marrow biopsy that excludes the diagnosis of FSMM. A history of immunosuppression typically suggests TS. Histopathology often is equivocal in FSMM8; however, TEM reveals viral particles (TSPyV) in TS. Transmission electron microscopy in FSMM demonstrates fibrillary structures arranged in a paracrystalline configuration with unknown significance instead of viral particles. Despite the absence of viral particles on TEM, a low mean copy number of Merkel cell polyomavirus was isolated from a patient with FSMM who responded dramatically to treatment with topical cidofovir gel 1%.8 In addition to treating the underlying multiple myeloma in FSMM, topical cidofovir gel 1% also may have a role in treatment of these patients, suggesting a possible viral rather than simply paraneoplastic etiology of FSMM. Therefore, polyomavirus infection should be considered in the initial workup of any patient with fine facial follicular spicules.
The most effective management of TS in transplant recipients is to reduce immunosuppression to the lowest level possible without jeopardizing the transplanted organ.9 In our case, reduction of immunosuppressive drugs was not possible. In fact, immunosuppression in our patient was increased following evidence of early rejection of the heart transplant. Although manual extraction of the keratin spicules resulted in considerable improvement in a similar facial eruption in a patient with pediatric pre–B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia developing TS,10 it is impossible to apply this approach to patients such as ours who have thousands of tiny lesions. Fortunately, custom-compounded cidofovir gel 1% applied twice daily to the patient’s face and ears for 4 weeks led to near-complete clearance at follow-up (Figure 5). Due to the high cost of the medication (approaching $700 for one tube), our patient applied this medication to the face only several times weekly with excellent improvement. Thus, it appears that it is possible to suppress this virus with topical medication alone.
Polyomavirus infection should be considered in patients presenting with fine follicular spiny papules, especially those who are immunosuppressed. The possibility of coexisting multiple myeloma should be excluded.
Acknowledgment—We sincerely thank Glenn A. Hoskins (Jackson, Mississippi), the electron microscopy technologist, for the detection of viral particles and the electron microscope photographs.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- van der Meijden E, Janssens RWA, Lauber C, et al. Discovery of a new human polyomavirus associated with trichodysplasia spinulosa in an immunocompromized patient. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:E1001024.
- Rouanet J, Aubin F, Gaboriaud P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a polyomavirus infection specifically targeting follicular keratinocytes in immunocompromised patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:629-632.
- van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- van der Meijden E, Horváth B, Nijland M, et al. Primary polyomavirus infection, not reactivation, as the cause of trichodysplasia spinulosa in immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1080-1084.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:726-733.
- Kazem S, van der Meijden E, Feltkamp MC. The trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus: virological background and clinical implications. APMIS. 2013;121:770-782.
- van Boheemen S, Jones T, Muhlemann B, et al. Cidofovir gel as treatment of follicular spicules in multiple myeloma. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:82-84.
- DeCrescenzo AJ, Philips RC, Wilkerson MG. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a rare complication of immunosuppression. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:307-309.
- Barton M, Lockhart S, Sidbury R, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa in a 7-year-old boy managed using physical extraction of keratin spicules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:E74-E76.
To the Editor:
A 57-year-old man with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and congestive heart failure presented with a disfiguring eruption comprised of asymptomatic papules on the face that appeared 12 months post–heart transplantation. Immunosuppressive medications included mycophenolic acid and tacrolimus ointment (FK506). The pinpoint papules spread from the central face to the ears, arms, and legs. Physical examination revealed multiple 0.5- to 1-mm flesh-colored papules over the glabella, nose, nasolabial folds, philtrum, chin, ears, arms, and legs sparing the trunk. The initial appearance of the facial rash resembled the surface of a nutmeg grater with central white spiny excrescences overlying fine papules (spinulosism)(Figure 1). In addition, eyebrow alopecia was present.
A 3-mm punch biopsy of a papule with a central spine was performed on the left thigh. Microscopic examination revealed marked dilatation of anagen hair follicles with a proliferation of haphazard inner root sheath cells replacing the follicular lumen. Hair shafts were absent, and plugged infundibula were observed (Figure 2). The inner root sheath keratinocytes were enlarged and dystrophic with deeply eosinophilic trichohyalin granules (Figure 3). The epidermis, outer root sheath epithelium, and eccrine structures were unremarkable.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirmed the presence of intranuclear viral inclusions within affected inner root sheath keratinocytes composed of nonenveloped icosahedral viral particles measuring 33 to 38 nm in diameter (Figure 4). These findings morphologically were consistent with a polyomavirus. No intracytoplasmic or extracellular viral particles were identified. The clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and electron microscopy features strongly supported the diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) despite insufficient material being retrieved for polymerase chain reaction identification.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first described by Haycox et al1 in 1999. The authors suggested a viral etiology. Eleven years later, TS-associated polyomavirus (TSPyV) was identified by van der Meijden et al.2 Follicular keratinocytes are the specific target for TSPyV.3 Evidence has been presented suggesting that TS is caused by a primary infection or reactivation of TSPyV in the setting of immunosuppression.4,5
Patients with TS present with papular eruptions that appear on the central face with spiny excrescences and various degrees of alopecia involving the eyebrows or eyelashes. Histopathologic features include distended hair follicles with expansion of inner root sheath cells, eosinophilic trichohyalin granules, and the absence of hair shafts. The viral protein can be verified through immunohistochemistry TSPyV VP1 staining that demonstrates co-localization with trichohyalin. Viral particles also can be visualized as 35- to 38-nm intranuclear particles with an organized crystalloid morphology on TEM.6,7 The negative polymerase chain reaction in our patient could be the result of suboptimal template DNA concentration extracted from the limited amount of tissue remaining in the block after hematoxylin and eosin staining.
The clinical differential diagnosis of central facial spinulosism includes the follicular spicules of multiple myeloma (FSMM). In fact, FSMM and TS can only be differentiated after obtaining a blood profile and bone marrow biopsy that excludes the diagnosis of FSMM. A history of immunosuppression typically suggests TS. Histopathology often is equivocal in FSMM8; however, TEM reveals viral particles (TSPyV) in TS. Transmission electron microscopy in FSMM demonstrates fibrillary structures arranged in a paracrystalline configuration with unknown significance instead of viral particles. Despite the absence of viral particles on TEM, a low mean copy number of Merkel cell polyomavirus was isolated from a patient with FSMM who responded dramatically to treatment with topical cidofovir gel 1%.8 In addition to treating the underlying multiple myeloma in FSMM, topical cidofovir gel 1% also may have a role in treatment of these patients, suggesting a possible viral rather than simply paraneoplastic etiology of FSMM. Therefore, polyomavirus infection should be considered in the initial workup of any patient with fine facial follicular spicules.
The most effective management of TS in transplant recipients is to reduce immunosuppression to the lowest level possible without jeopardizing the transplanted organ.9 In our case, reduction of immunosuppressive drugs was not possible. In fact, immunosuppression in our patient was increased following evidence of early rejection of the heart transplant. Although manual extraction of the keratin spicules resulted in considerable improvement in a similar facial eruption in a patient with pediatric pre–B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia developing TS,10 it is impossible to apply this approach to patients such as ours who have thousands of tiny lesions. Fortunately, custom-compounded cidofovir gel 1% applied twice daily to the patient’s face and ears for 4 weeks led to near-complete clearance at follow-up (Figure 5). Due to the high cost of the medication (approaching $700 for one tube), our patient applied this medication to the face only several times weekly with excellent improvement. Thus, it appears that it is possible to suppress this virus with topical medication alone.
Polyomavirus infection should be considered in patients presenting with fine follicular spiny papules, especially those who are immunosuppressed. The possibility of coexisting multiple myeloma should be excluded.
Acknowledgment—We sincerely thank Glenn A. Hoskins (Jackson, Mississippi), the electron microscopy technologist, for the detection of viral particles and the electron microscope photographs.
To the Editor:
A 57-year-old man with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and congestive heart failure presented with a disfiguring eruption comprised of asymptomatic papules on the face that appeared 12 months post–heart transplantation. Immunosuppressive medications included mycophenolic acid and tacrolimus ointment (FK506). The pinpoint papules spread from the central face to the ears, arms, and legs. Physical examination revealed multiple 0.5- to 1-mm flesh-colored papules over the glabella, nose, nasolabial folds, philtrum, chin, ears, arms, and legs sparing the trunk. The initial appearance of the facial rash resembled the surface of a nutmeg grater with central white spiny excrescences overlying fine papules (spinulosism)(Figure 1). In addition, eyebrow alopecia was present.
A 3-mm punch biopsy of a papule with a central spine was performed on the left thigh. Microscopic examination revealed marked dilatation of anagen hair follicles with a proliferation of haphazard inner root sheath cells replacing the follicular lumen. Hair shafts were absent, and plugged infundibula were observed (Figure 2). The inner root sheath keratinocytes were enlarged and dystrophic with deeply eosinophilic trichohyalin granules (Figure 3). The epidermis, outer root sheath epithelium, and eccrine structures were unremarkable.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirmed the presence of intranuclear viral inclusions within affected inner root sheath keratinocytes composed of nonenveloped icosahedral viral particles measuring 33 to 38 nm in diameter (Figure 4). These findings morphologically were consistent with a polyomavirus. No intracytoplasmic or extracellular viral particles were identified. The clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and electron microscopy features strongly supported the diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) despite insufficient material being retrieved for polymerase chain reaction identification.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first described by Haycox et al1 in 1999. The authors suggested a viral etiology. Eleven years later, TS-associated polyomavirus (TSPyV) was identified by van der Meijden et al.2 Follicular keratinocytes are the specific target for TSPyV.3 Evidence has been presented suggesting that TS is caused by a primary infection or reactivation of TSPyV in the setting of immunosuppression.4,5
Patients with TS present with papular eruptions that appear on the central face with spiny excrescences and various degrees of alopecia involving the eyebrows or eyelashes. Histopathologic features include distended hair follicles with expansion of inner root sheath cells, eosinophilic trichohyalin granules, and the absence of hair shafts. The viral protein can be verified through immunohistochemistry TSPyV VP1 staining that demonstrates co-localization with trichohyalin. Viral particles also can be visualized as 35- to 38-nm intranuclear particles with an organized crystalloid morphology on TEM.6,7 The negative polymerase chain reaction in our patient could be the result of suboptimal template DNA concentration extracted from the limited amount of tissue remaining in the block after hematoxylin and eosin staining.
The clinical differential diagnosis of central facial spinulosism includes the follicular spicules of multiple myeloma (FSMM). In fact, FSMM and TS can only be differentiated after obtaining a blood profile and bone marrow biopsy that excludes the diagnosis of FSMM. A history of immunosuppression typically suggests TS. Histopathology often is equivocal in FSMM8; however, TEM reveals viral particles (TSPyV) in TS. Transmission electron microscopy in FSMM demonstrates fibrillary structures arranged in a paracrystalline configuration with unknown significance instead of viral particles. Despite the absence of viral particles on TEM, a low mean copy number of Merkel cell polyomavirus was isolated from a patient with FSMM who responded dramatically to treatment with topical cidofovir gel 1%.8 In addition to treating the underlying multiple myeloma in FSMM, topical cidofovir gel 1% also may have a role in treatment of these patients, suggesting a possible viral rather than simply paraneoplastic etiology of FSMM. Therefore, polyomavirus infection should be considered in the initial workup of any patient with fine facial follicular spicules.
The most effective management of TS in transplant recipients is to reduce immunosuppression to the lowest level possible without jeopardizing the transplanted organ.9 In our case, reduction of immunosuppressive drugs was not possible. In fact, immunosuppression in our patient was increased following evidence of early rejection of the heart transplant. Although manual extraction of the keratin spicules resulted in considerable improvement in a similar facial eruption in a patient with pediatric pre–B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia developing TS,10 it is impossible to apply this approach to patients such as ours who have thousands of tiny lesions. Fortunately, custom-compounded cidofovir gel 1% applied twice daily to the patient’s face and ears for 4 weeks led to near-complete clearance at follow-up (Figure 5). Due to the high cost of the medication (approaching $700 for one tube), our patient applied this medication to the face only several times weekly with excellent improvement. Thus, it appears that it is possible to suppress this virus with topical medication alone.
Polyomavirus infection should be considered in patients presenting with fine follicular spiny papules, especially those who are immunosuppressed. The possibility of coexisting multiple myeloma should be excluded.
Acknowledgment—We sincerely thank Glenn A. Hoskins (Jackson, Mississippi), the electron microscopy technologist, for the detection of viral particles and the electron microscope photographs.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- van der Meijden E, Janssens RWA, Lauber C, et al. Discovery of a new human polyomavirus associated with trichodysplasia spinulosa in an immunocompromized patient. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:E1001024.
- Rouanet J, Aubin F, Gaboriaud P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a polyomavirus infection specifically targeting follicular keratinocytes in immunocompromised patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:629-632.
- van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- van der Meijden E, Horváth B, Nijland M, et al. Primary polyomavirus infection, not reactivation, as the cause of trichodysplasia spinulosa in immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1080-1084.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:726-733.
- Kazem S, van der Meijden E, Feltkamp MC. The trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus: virological background and clinical implications. APMIS. 2013;121:770-782.
- van Boheemen S, Jones T, Muhlemann B, et al. Cidofovir gel as treatment of follicular spicules in multiple myeloma. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:82-84.
- DeCrescenzo AJ, Philips RC, Wilkerson MG. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a rare complication of immunosuppression. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:307-309.
- Barton M, Lockhart S, Sidbury R, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa in a 7-year-old boy managed using physical extraction of keratin spicules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:E74-E76.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- van der Meijden E, Janssens RWA, Lauber C, et al. Discovery of a new human polyomavirus associated with trichodysplasia spinulosa in an immunocompromized patient. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:E1001024.
- Rouanet J, Aubin F, Gaboriaud P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a polyomavirus infection specifically targeting follicular keratinocytes in immunocompromised patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:629-632.
- van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- van der Meijden E, Horváth B, Nijland M, et al. Primary polyomavirus infection, not reactivation, as the cause of trichodysplasia spinulosa in immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1080-1084.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:726-733.
- Kazem S, van der Meijden E, Feltkamp MC. The trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus: virological background and clinical implications. APMIS. 2013;121:770-782.
- van Boheemen S, Jones T, Muhlemann B, et al. Cidofovir gel as treatment of follicular spicules in multiple myeloma. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:82-84.
- DeCrescenzo AJ, Philips RC, Wilkerson MG. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a rare complication of immunosuppression. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:307-309.
- Barton M, Lockhart S, Sidbury R, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa in a 7-year-old boy managed using physical extraction of keratin spicules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:E74-E76.
Practice Points
- Trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) is a rare skin disease caused by primary TS-associated polyomavirus (TSPyV) infecting follicular keratinocytes in immunocompromised patients.
- Trichodysplasia spinulosa typically presents with papular eruptions that appear on the central face with spiny excrescences and various degrees of alopecia involving the eyebrows or eyelashes.
- The viral protein can be verified through immunohistochemistry TSPyV major capsid protein VP1 staining or can be visualized on transmission electron microscopy.
- Follicular spicules of multiple myeloma should be ruled out before initiating treatment with cidofovir gel 1% for TS.
Hair loss: Consider a patient’s supplement use
BOSTON – .
This is an important question because patients consider supplements as “natural and healthy,” not as drugs or chemicals, Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Some of these products contain botanicals, which are not always safe, added Dr. Bergfeld, professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic. “They have many activities, and they are being touted as having some activity in helping the hair or enhancing hair growth,” including having 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors as an ingredient. “Saw palmetto is probably the most common one, but there are a host of natural ingredients that are being put into these supplements, including those that promote androgen induction, as well as antioxidants and anti-inflammatories.”
In the opinion of Dr. Bergfeld, a nutrition-focused physical assessment should include an examination of the scalp and all hairy areas. “It’s also important to see the symmetry and shape of hair growth or hair loss areas, the distribution, hair color, the thickness and texture of the hair fibers,” she added.
Besides asking about what supplements patients are taking, other questions to ask during the visit include: Are you noticing more hair on your brush, pillow, and shoulders, or in the shower? Do you think your hair is thinning? What are your medical problems? Have you experienced rapid weight loss? Have you started any new medications? What medication(s) are you on? What foods do you eat? Do you have a family history of hair loss?
Possible causes of hair loss or changes include environmental factors, stress, hormonal changes, medications, and nutrition.
Common ingredients contained in healthy hair supplements include biotin, folic acid, L-cysteine, L-methionine, MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), vitamin B complex, and vitamins A, C, D, and E. “Vitamin D and A are associated on the hair follicle receptor sites, and they balance each other, so if one is down the other is usually down,” said Dr. Bergfeld, who directs Cleveland Clinic’s hair disorders clinic and its dermatopathology program. Other important ingredients include iron, zinc, manganese, amino acids including L-Lysine, and fatty acids.
Iron deficiency is a known cause of hair loss. “The absorption of iron relies on vitamin C and sometimes lysine,” she said. Red meat has a high iron content and since many patients are restricting red meat intake, “they do need to think about that.” Zinc deficiency is less common in Western countries, she continued, “but when you find it, it’s revolutionary because if they’re shedding hair and their hair character is changing, often some supplementation will do the trick. But remember: Zinc is not only an anti-inflammatory, it’s also an antiandrogen. It has 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor capabilities.”.
Dr. Bergfeld noted that biotin, also known as vitamin B7 and found in many foods, is used in many vitamin supplements marketed for hair loss. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) is 30 mcg/day in adults but the amount in hair supplements can be up to 650% of RDA. “Biotin at high levels is believed to be safe, but can interfere with troponin and other lab testing,” she cautioned. “This can lead to dangerous false laboratory results.”
To date, insufficient data exist to recommend supplementation with zinc, riboflavin, folic acid, or vitamin B12 for hair loss, “but they may help in cases of deficiency,” said Dr. Bergfeld, a past president of the American Hair Research Society. The use of vitamin E and biotin supplementation is not supported in the literature for treating androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium. Excessive vitamin A (not beta carotene) and selenium can contribute to hair loss and studies have shown a relationship between androgenetic alopecia and low vitamin D levels. “Vitamin D should be supplemented if serum levels are low, but more studies are needed to determine the effect of iron and zinc supplementation” in patients with androgenetic alopecia, she said.
While there are not enough data to support a recommendation for supplementation of folic or B12 for alopecia, she said, “vitamin B12 deficiency may occur in androgenetic alopecia patients, associated with pernicious anemia.”
She added that the use biotin supplementation for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia is not supported by available data, and “it is also unclear if selenium plays a role in this disease.”
Dr. Bergfeld reported having no disclosures related to her presentation.
BOSTON – .
This is an important question because patients consider supplements as “natural and healthy,” not as drugs or chemicals, Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Some of these products contain botanicals, which are not always safe, added Dr. Bergfeld, professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic. “They have many activities, and they are being touted as having some activity in helping the hair or enhancing hair growth,” including having 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors as an ingredient. “Saw palmetto is probably the most common one, but there are a host of natural ingredients that are being put into these supplements, including those that promote androgen induction, as well as antioxidants and anti-inflammatories.”
In the opinion of Dr. Bergfeld, a nutrition-focused physical assessment should include an examination of the scalp and all hairy areas. “It’s also important to see the symmetry and shape of hair growth or hair loss areas, the distribution, hair color, the thickness and texture of the hair fibers,” she added.
Besides asking about what supplements patients are taking, other questions to ask during the visit include: Are you noticing more hair on your brush, pillow, and shoulders, or in the shower? Do you think your hair is thinning? What are your medical problems? Have you experienced rapid weight loss? Have you started any new medications? What medication(s) are you on? What foods do you eat? Do you have a family history of hair loss?
Possible causes of hair loss or changes include environmental factors, stress, hormonal changes, medications, and nutrition.
Common ingredients contained in healthy hair supplements include biotin, folic acid, L-cysteine, L-methionine, MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), vitamin B complex, and vitamins A, C, D, and E. “Vitamin D and A are associated on the hair follicle receptor sites, and they balance each other, so if one is down the other is usually down,” said Dr. Bergfeld, who directs Cleveland Clinic’s hair disorders clinic and its dermatopathology program. Other important ingredients include iron, zinc, manganese, amino acids including L-Lysine, and fatty acids.
Iron deficiency is a known cause of hair loss. “The absorption of iron relies on vitamin C and sometimes lysine,” she said. Red meat has a high iron content and since many patients are restricting red meat intake, “they do need to think about that.” Zinc deficiency is less common in Western countries, she continued, “but when you find it, it’s revolutionary because if they’re shedding hair and their hair character is changing, often some supplementation will do the trick. But remember: Zinc is not only an anti-inflammatory, it’s also an antiandrogen. It has 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor capabilities.”.
Dr. Bergfeld noted that biotin, also known as vitamin B7 and found in many foods, is used in many vitamin supplements marketed for hair loss. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) is 30 mcg/day in adults but the amount in hair supplements can be up to 650% of RDA. “Biotin at high levels is believed to be safe, but can interfere with troponin and other lab testing,” she cautioned. “This can lead to dangerous false laboratory results.”
To date, insufficient data exist to recommend supplementation with zinc, riboflavin, folic acid, or vitamin B12 for hair loss, “but they may help in cases of deficiency,” said Dr. Bergfeld, a past president of the American Hair Research Society. The use of vitamin E and biotin supplementation is not supported in the literature for treating androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium. Excessive vitamin A (not beta carotene) and selenium can contribute to hair loss and studies have shown a relationship between androgenetic alopecia and low vitamin D levels. “Vitamin D should be supplemented if serum levels are low, but more studies are needed to determine the effect of iron and zinc supplementation” in patients with androgenetic alopecia, she said.
While there are not enough data to support a recommendation for supplementation of folic or B12 for alopecia, she said, “vitamin B12 deficiency may occur in androgenetic alopecia patients, associated with pernicious anemia.”
She added that the use biotin supplementation for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia is not supported by available data, and “it is also unclear if selenium plays a role in this disease.”
Dr. Bergfeld reported having no disclosures related to her presentation.
BOSTON – .
This is an important question because patients consider supplements as “natural and healthy,” not as drugs or chemicals, Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Some of these products contain botanicals, which are not always safe, added Dr. Bergfeld, professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic. “They have many activities, and they are being touted as having some activity in helping the hair or enhancing hair growth,” including having 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors as an ingredient. “Saw palmetto is probably the most common one, but there are a host of natural ingredients that are being put into these supplements, including those that promote androgen induction, as well as antioxidants and anti-inflammatories.”
In the opinion of Dr. Bergfeld, a nutrition-focused physical assessment should include an examination of the scalp and all hairy areas. “It’s also important to see the symmetry and shape of hair growth or hair loss areas, the distribution, hair color, the thickness and texture of the hair fibers,” she added.
Besides asking about what supplements patients are taking, other questions to ask during the visit include: Are you noticing more hair on your brush, pillow, and shoulders, or in the shower? Do you think your hair is thinning? What are your medical problems? Have you experienced rapid weight loss? Have you started any new medications? What medication(s) are you on? What foods do you eat? Do you have a family history of hair loss?
Possible causes of hair loss or changes include environmental factors, stress, hormonal changes, medications, and nutrition.
Common ingredients contained in healthy hair supplements include biotin, folic acid, L-cysteine, L-methionine, MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), vitamin B complex, and vitamins A, C, D, and E. “Vitamin D and A are associated on the hair follicle receptor sites, and they balance each other, so if one is down the other is usually down,” said Dr. Bergfeld, who directs Cleveland Clinic’s hair disorders clinic and its dermatopathology program. Other important ingredients include iron, zinc, manganese, amino acids including L-Lysine, and fatty acids.
Iron deficiency is a known cause of hair loss. “The absorption of iron relies on vitamin C and sometimes lysine,” she said. Red meat has a high iron content and since many patients are restricting red meat intake, “they do need to think about that.” Zinc deficiency is less common in Western countries, she continued, “but when you find it, it’s revolutionary because if they’re shedding hair and their hair character is changing, often some supplementation will do the trick. But remember: Zinc is not only an anti-inflammatory, it’s also an antiandrogen. It has 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor capabilities.”.
Dr. Bergfeld noted that biotin, also known as vitamin B7 and found in many foods, is used in many vitamin supplements marketed for hair loss. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) is 30 mcg/day in adults but the amount in hair supplements can be up to 650% of RDA. “Biotin at high levels is believed to be safe, but can interfere with troponin and other lab testing,” she cautioned. “This can lead to dangerous false laboratory results.”
To date, insufficient data exist to recommend supplementation with zinc, riboflavin, folic acid, or vitamin B12 for hair loss, “but they may help in cases of deficiency,” said Dr. Bergfeld, a past president of the American Hair Research Society. The use of vitamin E and biotin supplementation is not supported in the literature for treating androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium. Excessive vitamin A (not beta carotene) and selenium can contribute to hair loss and studies have shown a relationship between androgenetic alopecia and low vitamin D levels. “Vitamin D should be supplemented if serum levels are low, but more studies are needed to determine the effect of iron and zinc supplementation” in patients with androgenetic alopecia, she said.
While there are not enough data to support a recommendation for supplementation of folic or B12 for alopecia, she said, “vitamin B12 deficiency may occur in androgenetic alopecia patients, associated with pernicious anemia.”
She added that the use biotin supplementation for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia is not supported by available data, and “it is also unclear if selenium plays a role in this disease.”
Dr. Bergfeld reported having no disclosures related to her presentation.
AT AAD 22
Trichotillomania: What you should know about this common hair-pulling disorder
Trichotillomania is a chronic psychiatric disorder that causes people to repeatedly pull out their own hair. Not only does it result in alopecia with no other underlying causes but it can have significant psychosocial ramifications and rare, but serious, complications. Though the reported prevalence rates are up to approximately 2%, it’s probable that you’ll come upon a patient suffering with this disorder at your practice, if you haven’t already.
To find out more about the best methods for diagnosing and treating this disorder, we spoke with Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH, a leading trichotillomania researcher and part of the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago.
Defining trichotillomania
What were the earliest descriptions of trichotillomania in medical literature?
The first real discussion of it probably goes back to Hippocrates, but from a modern medical perspective, discussion began in the 19th century with reports from the French dermatologist François Hallopeau.
They didn’t really call them disorders then – it was long before the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) – but they described this in young men who kept pulling their hair for unclear reasons. These early case reports don’t provide a lot of psychological perspective, but they seem consistent with what we see now.
What are the diagnostic criteria for trichotillomania?
The current DSM-5 criteria are recurrent pulling out of hair, an inability to stop it, the pulling resulting in some noticeable thinning or hair loss, and that it causes some level of distress or some type of impairment in functioning.
At what age do most people experience an onset of symptoms?
Generally speaking, it’s in early adolescence, post puberty, around 12-15 years of age. Having said that, we do see children as young as 1-2 years who are pulling their hair, and we occasionally see somebody far older who is doing it for the first time, a sort of geriatric onset.
Overlap and differences with other disorders
You’ve written that although trichotillomania is grouped with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in the DSM-5, the thinking around that has recently shifted. Why is that?
At first, it was noticed that many of these people pulled their hair repetitively in an almost ritualized manner, perhaps every night before bed. That looked like a compulsion of OCD.
When DSM-5 came out in 2013, they grouped it with OCD. Yet people shifted to thinking that it’s kind of a cousin of OCD because it has this compulsive quality but doesn’t really have obsessive thinking that drives it. Many people just pull their hair. They’re not even always aware of it: sometimes yes, sometimes no.
We know that it has some links to OCD. You’ll see more OCD in folks with trichotillomania, but it clearly is not just the same as OCD. One of the biggest pieces of evidence for that is that our first-line treatment for OCD – a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant – does not really help hair pulling.
Having said that, if people are looking for help with trichotillomania, they often are best served by therapists and doctors who have a familiarity with OCD and have kept it on their radar over the past couple of decades.
How does trichotillomania overlap with skin picking disorder, which is another condition that you’ve closely researched?
It does have some overlap with skin picking in the sense that it often seems familial. For example, the mother may pull her hair and child picks their skin.
It also has a fair amount of comorbidity with skin picking. Many people who pull will pick a little bit or did at some point. Many people who pick pulled their hair at some point. It seems closely related to nail biting as well.
Studies have also shown that one of the things that runs in the histories of most families of people with trichotillomania might be substance abuse – alcohol or drug addiction.
All of this has led people to believe that there might be subtypes of trichotillomania: one that’s more like an OCD and one that’s more like an addiction. That’s similar to the debate with other mental health conditions, that there are probably multiple types of depression, multiple types of schizophrenia.
Is there a component of this that could be defined as self-harm?
That’s been its own debate. It doesn’t seem to have the same developmental trajectory that we see with self-harm, or even some of the personality features.
However, there may be a small segment of folks with trichotillomania that might more appropriately fit that category. For example, those with family histories of trauma, higher rates of posttraumatic stress disorder, or borderline personality. But it wouldn’t be the majority.
The problem is, if you look at some of the pediatrician data, they often group picking, pulling, and cutting. I think that’s far too all-inclusive.
A gap in clinician education
Are adolescent patients likely to self-report this behavior, or is it something that physicians need to suss out for themselves?
Clearly, if child psychologists, psychiatrists, or pediatricians see young people with patches of alopecia – eyebrows or eyelashes missing, head hair with spots – in addition to a dermatologic assessment, they should simply ask, “Do you pull your hair?”
But it’s interesting that with the internet, young people are much more likely to disclose and actually come forward and tell their parents that they think they have trichotillomania.
I also hear from a lot of the adolescents that they have to educate their doctors about trichotillomania because so often physicians don’t know much about it and will assume that it’s self-injury or just a symptom of anxiety. It’s a little bit of a flip from what we might have seen 20 years ago.
I’ve seen several patients who’ve said, basically, “I’m tired of no professionals seeming to know about this. I shouldn’t have to be educating my doctors about this.” I tell them that I completely agree. It’s a shame because if a doctor doesn’t know about it, then how can they get the appropriate care?
What are the complications that accompany trichotillomania?
A small percentage, maybe about 10%, will ingest their hair, much like people who bite and swallow their fingernails. The concern there is that because hair is nondigestible, it could create an intestinal plug that could rupture and be potentially life-threatening. That makes it all the more important to ask those who pull their hair what they do with the hair once they pull it.
However, with most people, the real problem is with self-esteem. Young people may not want to socialize, go on dates, or do other things they would normally do because of it. In adults, you may find that they’re far more educated than their job allows but don’t want to go to an interview because they don’t want to have somebody sit there and look at them and notice that perhaps they don’t have any eyebrows, or that they’re wearing a wig. Those psychosocial implications are huge for so many people.
Treatment options
In a 2021 study, you showed that nearly one-quarter of people with trichotillomania do naturally recover from it. What characteristics do they seem to have?
It’s interesting because we see natural recovery across many mental health problems: alcohol addition, gambling, OCD. The question then becomes why is that some people can seemingly just stop doing a behavior? Can we learn from those people?
We did see that those who naturally recovered were less likely to have some other mental health comorbidities. It seems like when you have other things such as skin picking or OCD plus trichotillomania, that it probably speaks to something that perhaps synergistically is keeping it going. But this is just a first study; learning how to harness and understand it is the next step.
What’s the goal of treating trichotillomania?
The desired goal is zero pulling. The realistic goal is more likely significantly reduced pulling that then leads to greater function in life, greater quality-of-life.
One doesn’t have to go from 100 to 0 in order to do that. I always tell people that maybe every now and then, every few months, when something is going on in life, you might find yourself pulling a hair or two. That’s okay. If you’re not pulling every day and it’s significantly reduced, we’ll call that a success. I think that setting reasonable goals at this point is really important.
And what would the treatment pathway look like for most patients?
The standard approach is probably some type of habit-reversal therapy, of which there have been many variants over the years. It involves doing something different with your hand, identifying the triggers that may set you off, and then doing something in response to those triggers that is not pulling and might neutralize whatever that anxious or stressed feeling is. That could be different with each person.
At this point, there is no drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for trichotillomania. Our best approaches have included N-acetylcysteine, a glutamate modulator, which we’ve done research in.
That’s kind of a go-to option for people because its side-effect profile is generally innocuous. The data show that it could be beneficial in many people with very few, if any, side effects. That would be one “medication,” although it’s actually an over-the-counter vitamin. But we’re constantly looking for better and better treatments.
Do you have any final advice for clinicians or researchers?
Given how common it is, I don’t think clinicians should just see it as an innocuous little habit that people should be able to stop on their own. Clinicians should educate themselves about trichotillomania and know where the person should get the appropriate care.
From the research perspective, given the fact that we see this in animals of multiple species – that they overgroom – this seems to be deeply ingrained in us as animals. So when it comes to the underlying neuroscience, people should pay more attention because it probably has a lot to do with our understanding of habit and compulsive behaviors. It arguably can cut across a lot of different behaviors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trichotillomania is a chronic psychiatric disorder that causes people to repeatedly pull out their own hair. Not only does it result in alopecia with no other underlying causes but it can have significant psychosocial ramifications and rare, but serious, complications. Though the reported prevalence rates are up to approximately 2%, it’s probable that you’ll come upon a patient suffering with this disorder at your practice, if you haven’t already.
To find out more about the best methods for diagnosing and treating this disorder, we spoke with Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH, a leading trichotillomania researcher and part of the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago.
Defining trichotillomania
What were the earliest descriptions of trichotillomania in medical literature?
The first real discussion of it probably goes back to Hippocrates, but from a modern medical perspective, discussion began in the 19th century with reports from the French dermatologist François Hallopeau.
They didn’t really call them disorders then – it was long before the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) – but they described this in young men who kept pulling their hair for unclear reasons. These early case reports don’t provide a lot of psychological perspective, but they seem consistent with what we see now.
What are the diagnostic criteria for trichotillomania?
The current DSM-5 criteria are recurrent pulling out of hair, an inability to stop it, the pulling resulting in some noticeable thinning or hair loss, and that it causes some level of distress or some type of impairment in functioning.
At what age do most people experience an onset of symptoms?
Generally speaking, it’s in early adolescence, post puberty, around 12-15 years of age. Having said that, we do see children as young as 1-2 years who are pulling their hair, and we occasionally see somebody far older who is doing it for the first time, a sort of geriatric onset.
Overlap and differences with other disorders
You’ve written that although trichotillomania is grouped with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in the DSM-5, the thinking around that has recently shifted. Why is that?
At first, it was noticed that many of these people pulled their hair repetitively in an almost ritualized manner, perhaps every night before bed. That looked like a compulsion of OCD.
When DSM-5 came out in 2013, they grouped it with OCD. Yet people shifted to thinking that it’s kind of a cousin of OCD because it has this compulsive quality but doesn’t really have obsessive thinking that drives it. Many people just pull their hair. They’re not even always aware of it: sometimes yes, sometimes no.
We know that it has some links to OCD. You’ll see more OCD in folks with trichotillomania, but it clearly is not just the same as OCD. One of the biggest pieces of evidence for that is that our first-line treatment for OCD – a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant – does not really help hair pulling.
Having said that, if people are looking for help with trichotillomania, they often are best served by therapists and doctors who have a familiarity with OCD and have kept it on their radar over the past couple of decades.
How does trichotillomania overlap with skin picking disorder, which is another condition that you’ve closely researched?
It does have some overlap with skin picking in the sense that it often seems familial. For example, the mother may pull her hair and child picks their skin.
It also has a fair amount of comorbidity with skin picking. Many people who pull will pick a little bit or did at some point. Many people who pick pulled their hair at some point. It seems closely related to nail biting as well.
Studies have also shown that one of the things that runs in the histories of most families of people with trichotillomania might be substance abuse – alcohol or drug addiction.
All of this has led people to believe that there might be subtypes of trichotillomania: one that’s more like an OCD and one that’s more like an addiction. That’s similar to the debate with other mental health conditions, that there are probably multiple types of depression, multiple types of schizophrenia.
Is there a component of this that could be defined as self-harm?
That’s been its own debate. It doesn’t seem to have the same developmental trajectory that we see with self-harm, or even some of the personality features.
However, there may be a small segment of folks with trichotillomania that might more appropriately fit that category. For example, those with family histories of trauma, higher rates of posttraumatic stress disorder, or borderline personality. But it wouldn’t be the majority.
The problem is, if you look at some of the pediatrician data, they often group picking, pulling, and cutting. I think that’s far too all-inclusive.
A gap in clinician education
Are adolescent patients likely to self-report this behavior, or is it something that physicians need to suss out for themselves?
Clearly, if child psychologists, psychiatrists, or pediatricians see young people with patches of alopecia – eyebrows or eyelashes missing, head hair with spots – in addition to a dermatologic assessment, they should simply ask, “Do you pull your hair?”
But it’s interesting that with the internet, young people are much more likely to disclose and actually come forward and tell their parents that they think they have trichotillomania.
I also hear from a lot of the adolescents that they have to educate their doctors about trichotillomania because so often physicians don’t know much about it and will assume that it’s self-injury or just a symptom of anxiety. It’s a little bit of a flip from what we might have seen 20 years ago.
I’ve seen several patients who’ve said, basically, “I’m tired of no professionals seeming to know about this. I shouldn’t have to be educating my doctors about this.” I tell them that I completely agree. It’s a shame because if a doctor doesn’t know about it, then how can they get the appropriate care?
What are the complications that accompany trichotillomania?
A small percentage, maybe about 10%, will ingest their hair, much like people who bite and swallow their fingernails. The concern there is that because hair is nondigestible, it could create an intestinal plug that could rupture and be potentially life-threatening. That makes it all the more important to ask those who pull their hair what they do with the hair once they pull it.
However, with most people, the real problem is with self-esteem. Young people may not want to socialize, go on dates, or do other things they would normally do because of it. In adults, you may find that they’re far more educated than their job allows but don’t want to go to an interview because they don’t want to have somebody sit there and look at them and notice that perhaps they don’t have any eyebrows, or that they’re wearing a wig. Those psychosocial implications are huge for so many people.
Treatment options
In a 2021 study, you showed that nearly one-quarter of people with trichotillomania do naturally recover from it. What characteristics do they seem to have?
It’s interesting because we see natural recovery across many mental health problems: alcohol addition, gambling, OCD. The question then becomes why is that some people can seemingly just stop doing a behavior? Can we learn from those people?
We did see that those who naturally recovered were less likely to have some other mental health comorbidities. It seems like when you have other things such as skin picking or OCD plus trichotillomania, that it probably speaks to something that perhaps synergistically is keeping it going. But this is just a first study; learning how to harness and understand it is the next step.
What’s the goal of treating trichotillomania?
The desired goal is zero pulling. The realistic goal is more likely significantly reduced pulling that then leads to greater function in life, greater quality-of-life.
One doesn’t have to go from 100 to 0 in order to do that. I always tell people that maybe every now and then, every few months, when something is going on in life, you might find yourself pulling a hair or two. That’s okay. If you’re not pulling every day and it’s significantly reduced, we’ll call that a success. I think that setting reasonable goals at this point is really important.
And what would the treatment pathway look like for most patients?
The standard approach is probably some type of habit-reversal therapy, of which there have been many variants over the years. It involves doing something different with your hand, identifying the triggers that may set you off, and then doing something in response to those triggers that is not pulling and might neutralize whatever that anxious or stressed feeling is. That could be different with each person.
At this point, there is no drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for trichotillomania. Our best approaches have included N-acetylcysteine, a glutamate modulator, which we’ve done research in.
That’s kind of a go-to option for people because its side-effect profile is generally innocuous. The data show that it could be beneficial in many people with very few, if any, side effects. That would be one “medication,” although it’s actually an over-the-counter vitamin. But we’re constantly looking for better and better treatments.
Do you have any final advice for clinicians or researchers?
Given how common it is, I don’t think clinicians should just see it as an innocuous little habit that people should be able to stop on their own. Clinicians should educate themselves about trichotillomania and know where the person should get the appropriate care.
From the research perspective, given the fact that we see this in animals of multiple species – that they overgroom – this seems to be deeply ingrained in us as animals. So when it comes to the underlying neuroscience, people should pay more attention because it probably has a lot to do with our understanding of habit and compulsive behaviors. It arguably can cut across a lot of different behaviors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trichotillomania is a chronic psychiatric disorder that causes people to repeatedly pull out their own hair. Not only does it result in alopecia with no other underlying causes but it can have significant psychosocial ramifications and rare, but serious, complications. Though the reported prevalence rates are up to approximately 2%, it’s probable that you’ll come upon a patient suffering with this disorder at your practice, if you haven’t already.
To find out more about the best methods for diagnosing and treating this disorder, we spoke with Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH, a leading trichotillomania researcher and part of the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago.
Defining trichotillomania
What were the earliest descriptions of trichotillomania in medical literature?
The first real discussion of it probably goes back to Hippocrates, but from a modern medical perspective, discussion began in the 19th century with reports from the French dermatologist François Hallopeau.
They didn’t really call them disorders then – it was long before the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) – but they described this in young men who kept pulling their hair for unclear reasons. These early case reports don’t provide a lot of psychological perspective, but they seem consistent with what we see now.
What are the diagnostic criteria for trichotillomania?
The current DSM-5 criteria are recurrent pulling out of hair, an inability to stop it, the pulling resulting in some noticeable thinning or hair loss, and that it causes some level of distress or some type of impairment in functioning.
At what age do most people experience an onset of symptoms?
Generally speaking, it’s in early adolescence, post puberty, around 12-15 years of age. Having said that, we do see children as young as 1-2 years who are pulling their hair, and we occasionally see somebody far older who is doing it for the first time, a sort of geriatric onset.
Overlap and differences with other disorders
You’ve written that although trichotillomania is grouped with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in the DSM-5, the thinking around that has recently shifted. Why is that?
At first, it was noticed that many of these people pulled their hair repetitively in an almost ritualized manner, perhaps every night before bed. That looked like a compulsion of OCD.
When DSM-5 came out in 2013, they grouped it with OCD. Yet people shifted to thinking that it’s kind of a cousin of OCD because it has this compulsive quality but doesn’t really have obsessive thinking that drives it. Many people just pull their hair. They’re not even always aware of it: sometimes yes, sometimes no.
We know that it has some links to OCD. You’ll see more OCD in folks with trichotillomania, but it clearly is not just the same as OCD. One of the biggest pieces of evidence for that is that our first-line treatment for OCD – a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant – does not really help hair pulling.
Having said that, if people are looking for help with trichotillomania, they often are best served by therapists and doctors who have a familiarity with OCD and have kept it on their radar over the past couple of decades.
How does trichotillomania overlap with skin picking disorder, which is another condition that you’ve closely researched?
It does have some overlap with skin picking in the sense that it often seems familial. For example, the mother may pull her hair and child picks their skin.
It also has a fair amount of comorbidity with skin picking. Many people who pull will pick a little bit or did at some point. Many people who pick pulled their hair at some point. It seems closely related to nail biting as well.
Studies have also shown that one of the things that runs in the histories of most families of people with trichotillomania might be substance abuse – alcohol or drug addiction.
All of this has led people to believe that there might be subtypes of trichotillomania: one that’s more like an OCD and one that’s more like an addiction. That’s similar to the debate with other mental health conditions, that there are probably multiple types of depression, multiple types of schizophrenia.
Is there a component of this that could be defined as self-harm?
That’s been its own debate. It doesn’t seem to have the same developmental trajectory that we see with self-harm, or even some of the personality features.
However, there may be a small segment of folks with trichotillomania that might more appropriately fit that category. For example, those with family histories of trauma, higher rates of posttraumatic stress disorder, or borderline personality. But it wouldn’t be the majority.
The problem is, if you look at some of the pediatrician data, they often group picking, pulling, and cutting. I think that’s far too all-inclusive.
A gap in clinician education
Are adolescent patients likely to self-report this behavior, or is it something that physicians need to suss out for themselves?
Clearly, if child psychologists, psychiatrists, or pediatricians see young people with patches of alopecia – eyebrows or eyelashes missing, head hair with spots – in addition to a dermatologic assessment, they should simply ask, “Do you pull your hair?”
But it’s interesting that with the internet, young people are much more likely to disclose and actually come forward and tell their parents that they think they have trichotillomania.
I also hear from a lot of the adolescents that they have to educate their doctors about trichotillomania because so often physicians don’t know much about it and will assume that it’s self-injury or just a symptom of anxiety. It’s a little bit of a flip from what we might have seen 20 years ago.
I’ve seen several patients who’ve said, basically, “I’m tired of no professionals seeming to know about this. I shouldn’t have to be educating my doctors about this.” I tell them that I completely agree. It’s a shame because if a doctor doesn’t know about it, then how can they get the appropriate care?
What are the complications that accompany trichotillomania?
A small percentage, maybe about 10%, will ingest their hair, much like people who bite and swallow their fingernails. The concern there is that because hair is nondigestible, it could create an intestinal plug that could rupture and be potentially life-threatening. That makes it all the more important to ask those who pull their hair what they do with the hair once they pull it.
However, with most people, the real problem is with self-esteem. Young people may not want to socialize, go on dates, or do other things they would normally do because of it. In adults, you may find that they’re far more educated than their job allows but don’t want to go to an interview because they don’t want to have somebody sit there and look at them and notice that perhaps they don’t have any eyebrows, or that they’re wearing a wig. Those psychosocial implications are huge for so many people.
Treatment options
In a 2021 study, you showed that nearly one-quarter of people with trichotillomania do naturally recover from it. What characteristics do they seem to have?
It’s interesting because we see natural recovery across many mental health problems: alcohol addition, gambling, OCD. The question then becomes why is that some people can seemingly just stop doing a behavior? Can we learn from those people?
We did see that those who naturally recovered were less likely to have some other mental health comorbidities. It seems like when you have other things such as skin picking or OCD plus trichotillomania, that it probably speaks to something that perhaps synergistically is keeping it going. But this is just a first study; learning how to harness and understand it is the next step.
What’s the goal of treating trichotillomania?
The desired goal is zero pulling. The realistic goal is more likely significantly reduced pulling that then leads to greater function in life, greater quality-of-life.
One doesn’t have to go from 100 to 0 in order to do that. I always tell people that maybe every now and then, every few months, when something is going on in life, you might find yourself pulling a hair or two. That’s okay. If you’re not pulling every day and it’s significantly reduced, we’ll call that a success. I think that setting reasonable goals at this point is really important.
And what would the treatment pathway look like for most patients?
The standard approach is probably some type of habit-reversal therapy, of which there have been many variants over the years. It involves doing something different with your hand, identifying the triggers that may set you off, and then doing something in response to those triggers that is not pulling and might neutralize whatever that anxious or stressed feeling is. That could be different with each person.
At this point, there is no drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for trichotillomania. Our best approaches have included N-acetylcysteine, a glutamate modulator, which we’ve done research in.
That’s kind of a go-to option for people because its side-effect profile is generally innocuous. The data show that it could be beneficial in many people with very few, if any, side effects. That would be one “medication,” although it’s actually an over-the-counter vitamin. But we’re constantly looking for better and better treatments.
Do you have any final advice for clinicians or researchers?
Given how common it is, I don’t think clinicians should just see it as an innocuous little habit that people should be able to stop on their own. Clinicians should educate themselves about trichotillomania and know where the person should get the appropriate care.
From the research perspective, given the fact that we see this in animals of multiple species – that they overgroom – this seems to be deeply ingrained in us as animals. So when it comes to the underlying neuroscience, people should pay more attention because it probably has a lot to do with our understanding of habit and compulsive behaviors. It arguably can cut across a lot of different behaviors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oscars fight highlights for many the toll alopecia may carry
The Academy Awards ceremony on March 27 is a buzzing topic of conversation.
Troy Kotsur became the first deaf man to win an Oscar – and the highly coveted best supporting actor award, at that.
But it was what happened afterward that arguably stole the show.
Viewers and audience members alike watched in awe as actor Will Smith marched on stage and struck award presenter and comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, for her shaved head.
and can lead to feelings of depression or mental illness.
About 700,000 people in the United States have alopecia areata, according to a 2020 study. Of them, slightly more than half are women, and more than 77% are White.
Shortly after the awards show, the Los Angeles Police Department released a statement saying it was aware of the incident and Mr. Rock had not pressed charges against Mr. Smith.
The incident set social media ablaze, and strong sentiments were heard from those who have been personally affected by alopecia.
Illness is never funny
Mr. Rock’s comment can be triggering to the millions who have been affected by hair loss, said Carolyn Goh, MD, a dermatologist at UCLA Health.
“As someone with alopecia myself, I consider it a microaggression,” Dr. Goh said. “I’ve experienced many similar comments. These build up over time and wear us down.”
One U.K.-based Instagram user, Kitty Dry, said the expression on Ms. Pinkett Smith’s face represented the hurt felt by so many with this condition.
“I want to preface this post by saying that in no way do I condone any sort of violence, but thank you Will Smith,” said Ms. Dry, 23, who was diagnosed with alopecia universalis after losing all her hair in 12 weeks.
“That slap was for anyone with alopecia who has ever been at the butt of an unwanted joke, comment or stare,” Ms. Dry said.
Others posted comments raising awareness of the tragic passing of Rio Allred, a 12-year-old girl with alopecia who recently died by suicide.
Rio Allred is said to have endured serious bullying at school, with classmates pulling off her wig and smacking her head, according to the Canadian Alopecia Areata Foundation.
It’s common for those who have hair loss conditions to feel helpless, and sometimes confused, said Amy McMichael, MD, a professor and chair of the dermatology department at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. That’s why it’s critical for those people to see a board-certified dermatologist, so they know they are not alone.
“As dermatologists, we can not only diagnose the type of alopecia, but we can also render treatment,” Dr. McMichael said.
Alopecia awareness
Dermatologists can also help connect patients to organizations that address the physical and emotional struggles of those who have hair loss, such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, Dr. McMichael said.
She hopes the event shows people the “many faces of hair loss” and shows that these conditions can happen to people of all ages, ethnicities, and genders.
The National Alopecia Areata Foundation calls what happened at the Oscars a “teachable” moment.
“We encourage both our community and the broader public to learn more about alopecia areata so we can end the stigma around this disease,” the organization said in a statement.
Dr. Goh said that anyone with hair loss should feel free to explore potential medical causes and, if needed, seek out mental health treatment, too.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Academy Awards ceremony on March 27 is a buzzing topic of conversation.
Troy Kotsur became the first deaf man to win an Oscar – and the highly coveted best supporting actor award, at that.
But it was what happened afterward that arguably stole the show.
Viewers and audience members alike watched in awe as actor Will Smith marched on stage and struck award presenter and comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, for her shaved head.
and can lead to feelings of depression or mental illness.
About 700,000 people in the United States have alopecia areata, according to a 2020 study. Of them, slightly more than half are women, and more than 77% are White.
Shortly after the awards show, the Los Angeles Police Department released a statement saying it was aware of the incident and Mr. Rock had not pressed charges against Mr. Smith.
The incident set social media ablaze, and strong sentiments were heard from those who have been personally affected by alopecia.
Illness is never funny
Mr. Rock’s comment can be triggering to the millions who have been affected by hair loss, said Carolyn Goh, MD, a dermatologist at UCLA Health.
“As someone with alopecia myself, I consider it a microaggression,” Dr. Goh said. “I’ve experienced many similar comments. These build up over time and wear us down.”
One U.K.-based Instagram user, Kitty Dry, said the expression on Ms. Pinkett Smith’s face represented the hurt felt by so many with this condition.
“I want to preface this post by saying that in no way do I condone any sort of violence, but thank you Will Smith,” said Ms. Dry, 23, who was diagnosed with alopecia universalis after losing all her hair in 12 weeks.
“That slap was for anyone with alopecia who has ever been at the butt of an unwanted joke, comment or stare,” Ms. Dry said.
Others posted comments raising awareness of the tragic passing of Rio Allred, a 12-year-old girl with alopecia who recently died by suicide.
Rio Allred is said to have endured serious bullying at school, with classmates pulling off her wig and smacking her head, according to the Canadian Alopecia Areata Foundation.
It’s common for those who have hair loss conditions to feel helpless, and sometimes confused, said Amy McMichael, MD, a professor and chair of the dermatology department at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. That’s why it’s critical for those people to see a board-certified dermatologist, so they know they are not alone.
“As dermatologists, we can not only diagnose the type of alopecia, but we can also render treatment,” Dr. McMichael said.
Alopecia awareness
Dermatologists can also help connect patients to organizations that address the physical and emotional struggles of those who have hair loss, such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, Dr. McMichael said.
She hopes the event shows people the “many faces of hair loss” and shows that these conditions can happen to people of all ages, ethnicities, and genders.
The National Alopecia Areata Foundation calls what happened at the Oscars a “teachable” moment.
“We encourage both our community and the broader public to learn more about alopecia areata so we can end the stigma around this disease,” the organization said in a statement.
Dr. Goh said that anyone with hair loss should feel free to explore potential medical causes and, if needed, seek out mental health treatment, too.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Academy Awards ceremony on March 27 is a buzzing topic of conversation.
Troy Kotsur became the first deaf man to win an Oscar – and the highly coveted best supporting actor award, at that.
But it was what happened afterward that arguably stole the show.
Viewers and audience members alike watched in awe as actor Will Smith marched on stage and struck award presenter and comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, for her shaved head.
and can lead to feelings of depression or mental illness.
About 700,000 people in the United States have alopecia areata, according to a 2020 study. Of them, slightly more than half are women, and more than 77% are White.
Shortly after the awards show, the Los Angeles Police Department released a statement saying it was aware of the incident and Mr. Rock had not pressed charges against Mr. Smith.
The incident set social media ablaze, and strong sentiments were heard from those who have been personally affected by alopecia.
Illness is never funny
Mr. Rock’s comment can be triggering to the millions who have been affected by hair loss, said Carolyn Goh, MD, a dermatologist at UCLA Health.
“As someone with alopecia myself, I consider it a microaggression,” Dr. Goh said. “I’ve experienced many similar comments. These build up over time and wear us down.”
One U.K.-based Instagram user, Kitty Dry, said the expression on Ms. Pinkett Smith’s face represented the hurt felt by so many with this condition.
“I want to preface this post by saying that in no way do I condone any sort of violence, but thank you Will Smith,” said Ms. Dry, 23, who was diagnosed with alopecia universalis after losing all her hair in 12 weeks.
“That slap was for anyone with alopecia who has ever been at the butt of an unwanted joke, comment or stare,” Ms. Dry said.
Others posted comments raising awareness of the tragic passing of Rio Allred, a 12-year-old girl with alopecia who recently died by suicide.
Rio Allred is said to have endured serious bullying at school, with classmates pulling off her wig and smacking her head, according to the Canadian Alopecia Areata Foundation.
It’s common for those who have hair loss conditions to feel helpless, and sometimes confused, said Amy McMichael, MD, a professor and chair of the dermatology department at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. That’s why it’s critical for those people to see a board-certified dermatologist, so they know they are not alone.
“As dermatologists, we can not only diagnose the type of alopecia, but we can also render treatment,” Dr. McMichael said.
Alopecia awareness
Dermatologists can also help connect patients to organizations that address the physical and emotional struggles of those who have hair loss, such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, Dr. McMichael said.
She hopes the event shows people the “many faces of hair loss” and shows that these conditions can happen to people of all ages, ethnicities, and genders.
The National Alopecia Areata Foundation calls what happened at the Oscars a “teachable” moment.
“We encourage both our community and the broader public to learn more about alopecia areata so we can end the stigma around this disease,” the organization said in a statement.
Dr. Goh said that anyone with hair loss should feel free to explore potential medical causes and, if needed, seek out mental health treatment, too.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Clinical clarity grows about toenail disorder, experts report
BOSTON – The main commonly leading to the wrong therapy and no resolution to the problem, according to an expert update at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Misinterpretation of the yellow discoloration, a common feature of retronychia, means “many patients are maintained on antifungal therapy for years and years with no change in their condition,” reported Phoebe Rich, MD, director of the Nail Disorders Clinic, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Infection is not commonly involved in retronychia, but importantly, antifungals and antibiotics “have no role in treating the underlying disorder,” Dr. Rich said.
The term retronychia and its description is only about 20 years old, according to Dr. Rich, who cited work by David A. de Berker, MBBS, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at University Hospitals in Bristol, England. His publication on this disorder appeared in 1999, with a more detailed description published about 10 years later.
Recently, the body of literature on this disorder has been growing, contributing to an increasing consensus about etiology, diagnosis, and treatments to consider in the context of causes and severity, Dr. Rich said.
Some but not all patients have abnormal formation of the nail bed, increasing susceptibility to retronychia, but trauma or microtrauma typically serve as a trigger in most cases. Dancing, high heels, steel-toed shoes, and other sources of trauma to the toes are implicated.
Whether or not patients have an inherent susceptibility, injury separates the existing nail from the matrix and nail bed so that newly forming nail begins to grow under the nail rather continuing to push out the old nail.
Susceptibility is increased substantially in individuals with a shortened nail bed, according to Dr. Rich. In severe cases, when there is simply inadequate nail bed for the nail growth to attach, recurrence is common or even inevitable. Even when the nail is removed and regrowth appears normal at the end of a year, those patients with very short nail beds cannot count on a cure.
“Due to the slow growth of nails, it might take 2 or 3 years for the problem to recur,” Dr. Rich cautioned. For this reason, cure rates reported for the various interventions at 1 year might not predict longer-term benefit.
Retronychia is usually a clinical diagnosis based on the presence of the increased bulk of the toenail when overlapping nails cannot be seen. This is not necessarily a single overgrowth. In some cases, multiple layers of nails are stacked one on top of the other. Xanthonychia (yellow nail) is usually present.
“The layering might not be visible without removing the nail,” said Dr. Rich, explaining one reason that the diagnosis is sometimes missed. Ultrasound is a noninvasive means to confirm the problem, although Rich warned that imaging is not necessarily reimbursed.
“There is no diagnosis by histopathology, so it cannot be confirmed with biopsy,” Dr. Rich said.
Treatments range from conservative strategies, particularly topical or intralesional steroids in mild cases, to more invasive procedures such as clipping of the nail plate or surgical avulsion. All can be effective when used appropriately, according to Dr. Rich.
“The more invasive procedures are the more effective, but the caveat is they are also associated with more complications,” said Dr. Rich, citing, for example, the risk of nail dystrophies. Because of the increasing number of studies, the relative benefits and risks of retronychia treatment have now been summarized in a recent review. Dr. Rich suggested the review is one of the most recent and detailed evaluations of the topic that “I encourage everyone to read.”
Despite progress in describing retronychia, Dr. Rich said that there might be more to learn about risk. In particular, she cited the work of Dana W. Stern, MD, a specialist in nail disorders who is in private practice in New York. Dr. Stern is pursuing a hypothesis that at least some cases are caused by potentially targetable biomechanical issues.
“I have observed that many of the younger patients in my practice with retronychia seem to have atypical foot anatomy,” Dr. Stern said in an interview. “I am collecting cases and hoping to explore this issue in more depth.”
She said that foot anatomy in relationship to retronychia has not been adequately evaluated.
“In my review of the literature, I could not find a single study that showed imagery of the feet,” she said. She is considering a collaboration with others, including Rich, to explore this as a factor in retronychia.
Asked about risk of misdiagnosis, Dr. Stern reiterated some of the points made by Dr. Rich. In particular, she agreed that discolored nails alone should not be a reason to initiate antimycotic therapy without considering the possibility of retronychia.
“So many providers are not familiar with the diagnosis, and only 50% of yellow thickened nails are in fact onychomycosis,” she said. “We end up seeing a plethora of patients [with retronychia] who are unfortunately misdiagnosed for years.”
Dr. Rich reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Stern reported a financial relationship with Rare Beauty Brands. Neither Dr. Rich nor Dr. Stern said they had any disclosures related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – The main commonly leading to the wrong therapy and no resolution to the problem, according to an expert update at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Misinterpretation of the yellow discoloration, a common feature of retronychia, means “many patients are maintained on antifungal therapy for years and years with no change in their condition,” reported Phoebe Rich, MD, director of the Nail Disorders Clinic, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Infection is not commonly involved in retronychia, but importantly, antifungals and antibiotics “have no role in treating the underlying disorder,” Dr. Rich said.
The term retronychia and its description is only about 20 years old, according to Dr. Rich, who cited work by David A. de Berker, MBBS, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at University Hospitals in Bristol, England. His publication on this disorder appeared in 1999, with a more detailed description published about 10 years later.
Recently, the body of literature on this disorder has been growing, contributing to an increasing consensus about etiology, diagnosis, and treatments to consider in the context of causes and severity, Dr. Rich said.
Some but not all patients have abnormal formation of the nail bed, increasing susceptibility to retronychia, but trauma or microtrauma typically serve as a trigger in most cases. Dancing, high heels, steel-toed shoes, and other sources of trauma to the toes are implicated.
Whether or not patients have an inherent susceptibility, injury separates the existing nail from the matrix and nail bed so that newly forming nail begins to grow under the nail rather continuing to push out the old nail.
Susceptibility is increased substantially in individuals with a shortened nail bed, according to Dr. Rich. In severe cases, when there is simply inadequate nail bed for the nail growth to attach, recurrence is common or even inevitable. Even when the nail is removed and regrowth appears normal at the end of a year, those patients with very short nail beds cannot count on a cure.
“Due to the slow growth of nails, it might take 2 or 3 years for the problem to recur,” Dr. Rich cautioned. For this reason, cure rates reported for the various interventions at 1 year might not predict longer-term benefit.
Retronychia is usually a clinical diagnosis based on the presence of the increased bulk of the toenail when overlapping nails cannot be seen. This is not necessarily a single overgrowth. In some cases, multiple layers of nails are stacked one on top of the other. Xanthonychia (yellow nail) is usually present.
“The layering might not be visible without removing the nail,” said Dr. Rich, explaining one reason that the diagnosis is sometimes missed. Ultrasound is a noninvasive means to confirm the problem, although Rich warned that imaging is not necessarily reimbursed.
“There is no diagnosis by histopathology, so it cannot be confirmed with biopsy,” Dr. Rich said.
Treatments range from conservative strategies, particularly topical or intralesional steroids in mild cases, to more invasive procedures such as clipping of the nail plate or surgical avulsion. All can be effective when used appropriately, according to Dr. Rich.
“The more invasive procedures are the more effective, but the caveat is they are also associated with more complications,” said Dr. Rich, citing, for example, the risk of nail dystrophies. Because of the increasing number of studies, the relative benefits and risks of retronychia treatment have now been summarized in a recent review. Dr. Rich suggested the review is one of the most recent and detailed evaluations of the topic that “I encourage everyone to read.”
Despite progress in describing retronychia, Dr. Rich said that there might be more to learn about risk. In particular, she cited the work of Dana W. Stern, MD, a specialist in nail disorders who is in private practice in New York. Dr. Stern is pursuing a hypothesis that at least some cases are caused by potentially targetable biomechanical issues.
“I have observed that many of the younger patients in my practice with retronychia seem to have atypical foot anatomy,” Dr. Stern said in an interview. “I am collecting cases and hoping to explore this issue in more depth.”
She said that foot anatomy in relationship to retronychia has not been adequately evaluated.
“In my review of the literature, I could not find a single study that showed imagery of the feet,” she said. She is considering a collaboration with others, including Rich, to explore this as a factor in retronychia.
Asked about risk of misdiagnosis, Dr. Stern reiterated some of the points made by Dr. Rich. In particular, she agreed that discolored nails alone should not be a reason to initiate antimycotic therapy without considering the possibility of retronychia.
“So many providers are not familiar with the diagnosis, and only 50% of yellow thickened nails are in fact onychomycosis,” she said. “We end up seeing a plethora of patients [with retronychia] who are unfortunately misdiagnosed for years.”
Dr. Rich reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Stern reported a financial relationship with Rare Beauty Brands. Neither Dr. Rich nor Dr. Stern said they had any disclosures related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – The main commonly leading to the wrong therapy and no resolution to the problem, according to an expert update at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Misinterpretation of the yellow discoloration, a common feature of retronychia, means “many patients are maintained on antifungal therapy for years and years with no change in their condition,” reported Phoebe Rich, MD, director of the Nail Disorders Clinic, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Infection is not commonly involved in retronychia, but importantly, antifungals and antibiotics “have no role in treating the underlying disorder,” Dr. Rich said.
The term retronychia and its description is only about 20 years old, according to Dr. Rich, who cited work by David A. de Berker, MBBS, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at University Hospitals in Bristol, England. His publication on this disorder appeared in 1999, with a more detailed description published about 10 years later.
Recently, the body of literature on this disorder has been growing, contributing to an increasing consensus about etiology, diagnosis, and treatments to consider in the context of causes and severity, Dr. Rich said.
Some but not all patients have abnormal formation of the nail bed, increasing susceptibility to retronychia, but trauma or microtrauma typically serve as a trigger in most cases. Dancing, high heels, steel-toed shoes, and other sources of trauma to the toes are implicated.
Whether or not patients have an inherent susceptibility, injury separates the existing nail from the matrix and nail bed so that newly forming nail begins to grow under the nail rather continuing to push out the old nail.
Susceptibility is increased substantially in individuals with a shortened nail bed, according to Dr. Rich. In severe cases, when there is simply inadequate nail bed for the nail growth to attach, recurrence is common or even inevitable. Even when the nail is removed and regrowth appears normal at the end of a year, those patients with very short nail beds cannot count on a cure.
“Due to the slow growth of nails, it might take 2 or 3 years for the problem to recur,” Dr. Rich cautioned. For this reason, cure rates reported for the various interventions at 1 year might not predict longer-term benefit.
Retronychia is usually a clinical diagnosis based on the presence of the increased bulk of the toenail when overlapping nails cannot be seen. This is not necessarily a single overgrowth. In some cases, multiple layers of nails are stacked one on top of the other. Xanthonychia (yellow nail) is usually present.
“The layering might not be visible without removing the nail,” said Dr. Rich, explaining one reason that the diagnosis is sometimes missed. Ultrasound is a noninvasive means to confirm the problem, although Rich warned that imaging is not necessarily reimbursed.
“There is no diagnosis by histopathology, so it cannot be confirmed with biopsy,” Dr. Rich said.
Treatments range from conservative strategies, particularly topical or intralesional steroids in mild cases, to more invasive procedures such as clipping of the nail plate or surgical avulsion. All can be effective when used appropriately, according to Dr. Rich.
“The more invasive procedures are the more effective, but the caveat is they are also associated with more complications,” said Dr. Rich, citing, for example, the risk of nail dystrophies. Because of the increasing number of studies, the relative benefits and risks of retronychia treatment have now been summarized in a recent review. Dr. Rich suggested the review is one of the most recent and detailed evaluations of the topic that “I encourage everyone to read.”
Despite progress in describing retronychia, Dr. Rich said that there might be more to learn about risk. In particular, she cited the work of Dana W. Stern, MD, a specialist in nail disorders who is in private practice in New York. Dr. Stern is pursuing a hypothesis that at least some cases are caused by potentially targetable biomechanical issues.
“I have observed that many of the younger patients in my practice with retronychia seem to have atypical foot anatomy,” Dr. Stern said in an interview. “I am collecting cases and hoping to explore this issue in more depth.”
She said that foot anatomy in relationship to retronychia has not been adequately evaluated.
“In my review of the literature, I could not find a single study that showed imagery of the feet,” she said. She is considering a collaboration with others, including Rich, to explore this as a factor in retronychia.
Asked about risk of misdiagnosis, Dr. Stern reiterated some of the points made by Dr. Rich. In particular, she agreed that discolored nails alone should not be a reason to initiate antimycotic therapy without considering the possibility of retronychia.
“So many providers are not familiar with the diagnosis, and only 50% of yellow thickened nails are in fact onychomycosis,” she said. “We end up seeing a plethora of patients [with retronychia] who are unfortunately misdiagnosed for years.”
Dr. Rich reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Stern reported a financial relationship with Rare Beauty Brands. Neither Dr. Rich nor Dr. Stern said they had any disclosures related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2022
New trial data show hair growth in more alopecia areata patients
BOSTON – according to updated results from two phase 3 trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The results indicate improved response rates and hair growth among trial participants, said Brett King, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He is the lead author of the analyses and presented the research.
Dr. King presented 36-week results from the clinical trials at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The same results were also published March 26, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Every bit of data we’ve had is hugely important,” Dr. King said in an interview. “Every time we add 16 weeks of data across hundreds of patients, we are making a huge step forward toward the goal of [Food and Drug Administration approval for a medication for alopecia areata.”
All patients enrolled in the two trials, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, had severe alopecia areata, defined as a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of at least 50, meaning 50% or less scalp coverage. The score ranges from 0 (no hair loss) to 100 (complete hair loss). The primary endpoint was a SALT score of 20 or less (80% scalp hair coverage).
The researchers pooled data from both clinical trials, with a combined enrollment of 1,200, for the 52-week results presented at the meeting. The placebo group stopped at 36 weeks, and these patients were randomly reassigned to either the 4-mg or 2-mg once-daily baricitinib treatment groups.
At baseline, patients enrolled in the trial had a mean SALT score of 85.5. After 52 weeks, 39.0% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. Of this group, nearly three out of four (74.1%) had at least 90% scalp coverage, or a SALT score of 10 or less.
In patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib, 22.6% had a SALT score of 20 or less 20 (at least 80% scalp hair coverage) at 52 weeks, and two-thirds of that group (67.5%) had at least 90% scalp hair coverage at 52 weeks.
Comparatively, at 36 weeks, 35.2% of participants in BRAVE-AA1 and 32.5% of participants in BRAVE-AA2 receiving 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. In the group taking the lower dose, 21.7% and 17.3% of patients in the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, respectively, had achieved at least 80% scalp coverage at 36 weeks. (These percentages differ slightly from the NEJM article because of a different analysis of missing data, Dr. King said. For comparison of both 36- and 52-week results, the percentages from the EADV are used above.)
The results indicate that 5% more patients reached the primary endpoint in the additional 16 weeks of the trial, Dr. King said.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where immune cells attack hair follicles, causing the hair to fall out, and is associated with emotional and psychological distress. Any hair follicle can be attacked, but they are rarely destroyed, so hair can regrow.
"Many underestimate the impact of this autoimmune hair loss condition," Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, told this news organization. He was not involved with the trial. "The burden of the disease, which certainly is an emotional but also a physical one, definitely needs to be addressed with indicated FDA-approved drugs," he noted, which is the goal of these trials.
The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials focused on scalp hair regrowth.
Eyebrow and eyelash growth, secondary outcomes, also improved between 36 and 52 weeks in both groups, calculated using the proportion of participants who had achieved full regrowth or regrowth with minimal gaps. At 36 weeks, about 31%-35% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib regrew eyebrow and eyelash hair. By 52 weeks, more than two out of five patients regrew eyebrow (44.1%) and eyelash (45.3%) hair.
“It’s a fantastic achievement and a major step forward in alopecia areata, especially for patients with the most severe and refractory cases,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPH, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Mostaghimi is on the advisory board for Eli Lilly, which manufactures baricitinib, and Brigham and Women’s was one of the clinical sites of the trial.
While dermatologists have been aware of how JAK inhibitors can affect hair regrowth in alopecia patients, they have been using these drugs off label, Dr. Friedman said. Therefore, these drugs are expensive and more difficult to access. These trials provide "data that proves the efficacy and safety of [baricitinib] under the umbrella of the FDA portal," he added, which will hopefully lead to an approved indication for alopecia areata, so it can be more accessible to patients.
Adverse events at 52 weeks were consistent with data from 36 weeks, which found that none of these adverse events occurred in more than 10% of participants. The most common adverse events were headache, acne, and increases in muscle-related blood markers. The most common infections reported were pneumonia, herpes zoster, and urinary tract infection.
In February 2022, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib for the treatment of severe alopecia areata. Lilly expects a regulatory decision by the end of 2022, they said in a press release.
Lilly provided funding for the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials. Dr. King reported financial relationships with Aclaris, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceutics, Dermavant, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, and Viela Bio. Dr. Mostaghimi has reported serving on an advisory board for Lilly. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 3/28/2022 to include Dr. Friedman's comments, and on 3/31/2022 to correct the statement regarding adverse events reported in the study
BOSTON – according to updated results from two phase 3 trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The results indicate improved response rates and hair growth among trial participants, said Brett King, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He is the lead author of the analyses and presented the research.
Dr. King presented 36-week results from the clinical trials at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The same results were also published March 26, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Every bit of data we’ve had is hugely important,” Dr. King said in an interview. “Every time we add 16 weeks of data across hundreds of patients, we are making a huge step forward toward the goal of [Food and Drug Administration approval for a medication for alopecia areata.”
All patients enrolled in the two trials, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, had severe alopecia areata, defined as a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of at least 50, meaning 50% or less scalp coverage. The score ranges from 0 (no hair loss) to 100 (complete hair loss). The primary endpoint was a SALT score of 20 or less (80% scalp hair coverage).
The researchers pooled data from both clinical trials, with a combined enrollment of 1,200, for the 52-week results presented at the meeting. The placebo group stopped at 36 weeks, and these patients were randomly reassigned to either the 4-mg or 2-mg once-daily baricitinib treatment groups.
At baseline, patients enrolled in the trial had a mean SALT score of 85.5. After 52 weeks, 39.0% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. Of this group, nearly three out of four (74.1%) had at least 90% scalp coverage, or a SALT score of 10 or less.
In patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib, 22.6% had a SALT score of 20 or less 20 (at least 80% scalp hair coverage) at 52 weeks, and two-thirds of that group (67.5%) had at least 90% scalp hair coverage at 52 weeks.
Comparatively, at 36 weeks, 35.2% of participants in BRAVE-AA1 and 32.5% of participants in BRAVE-AA2 receiving 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. In the group taking the lower dose, 21.7% and 17.3% of patients in the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, respectively, had achieved at least 80% scalp coverage at 36 weeks. (These percentages differ slightly from the NEJM article because of a different analysis of missing data, Dr. King said. For comparison of both 36- and 52-week results, the percentages from the EADV are used above.)
The results indicate that 5% more patients reached the primary endpoint in the additional 16 weeks of the trial, Dr. King said.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where immune cells attack hair follicles, causing the hair to fall out, and is associated with emotional and psychological distress. Any hair follicle can be attacked, but they are rarely destroyed, so hair can regrow.
"Many underestimate the impact of this autoimmune hair loss condition," Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, told this news organization. He was not involved with the trial. "The burden of the disease, which certainly is an emotional but also a physical one, definitely needs to be addressed with indicated FDA-approved drugs," he noted, which is the goal of these trials.
The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials focused on scalp hair regrowth.
Eyebrow and eyelash growth, secondary outcomes, also improved between 36 and 52 weeks in both groups, calculated using the proportion of participants who had achieved full regrowth or regrowth with minimal gaps. At 36 weeks, about 31%-35% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib regrew eyebrow and eyelash hair. By 52 weeks, more than two out of five patients regrew eyebrow (44.1%) and eyelash (45.3%) hair.
“It’s a fantastic achievement and a major step forward in alopecia areata, especially for patients with the most severe and refractory cases,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPH, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Mostaghimi is on the advisory board for Eli Lilly, which manufactures baricitinib, and Brigham and Women’s was one of the clinical sites of the trial.
While dermatologists have been aware of how JAK inhibitors can affect hair regrowth in alopecia patients, they have been using these drugs off label, Dr. Friedman said. Therefore, these drugs are expensive and more difficult to access. These trials provide "data that proves the efficacy and safety of [baricitinib] under the umbrella of the FDA portal," he added, which will hopefully lead to an approved indication for alopecia areata, so it can be more accessible to patients.
Adverse events at 52 weeks were consistent with data from 36 weeks, which found that none of these adverse events occurred in more than 10% of participants. The most common adverse events were headache, acne, and increases in muscle-related blood markers. The most common infections reported were pneumonia, herpes zoster, and urinary tract infection.
In February 2022, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib for the treatment of severe alopecia areata. Lilly expects a regulatory decision by the end of 2022, they said in a press release.
Lilly provided funding for the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials. Dr. King reported financial relationships with Aclaris, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceutics, Dermavant, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, and Viela Bio. Dr. Mostaghimi has reported serving on an advisory board for Lilly. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 3/28/2022 to include Dr. Friedman's comments, and on 3/31/2022 to correct the statement regarding adverse events reported in the study
BOSTON – according to updated results from two phase 3 trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The results indicate improved response rates and hair growth among trial participants, said Brett King, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He is the lead author of the analyses and presented the research.
Dr. King presented 36-week results from the clinical trials at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The same results were also published March 26, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Every bit of data we’ve had is hugely important,” Dr. King said in an interview. “Every time we add 16 weeks of data across hundreds of patients, we are making a huge step forward toward the goal of [Food and Drug Administration approval for a medication for alopecia areata.”
All patients enrolled in the two trials, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, had severe alopecia areata, defined as a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of at least 50, meaning 50% or less scalp coverage. The score ranges from 0 (no hair loss) to 100 (complete hair loss). The primary endpoint was a SALT score of 20 or less (80% scalp hair coverage).
The researchers pooled data from both clinical trials, with a combined enrollment of 1,200, for the 52-week results presented at the meeting. The placebo group stopped at 36 weeks, and these patients were randomly reassigned to either the 4-mg or 2-mg once-daily baricitinib treatment groups.
At baseline, patients enrolled in the trial had a mean SALT score of 85.5. After 52 weeks, 39.0% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. Of this group, nearly three out of four (74.1%) had at least 90% scalp coverage, or a SALT score of 10 or less.
In patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib, 22.6% had a SALT score of 20 or less 20 (at least 80% scalp hair coverage) at 52 weeks, and two-thirds of that group (67.5%) had at least 90% scalp hair coverage at 52 weeks.
Comparatively, at 36 weeks, 35.2% of participants in BRAVE-AA1 and 32.5% of participants in BRAVE-AA2 receiving 4 mg of baricitinib had at least 80% scalp coverage. In the group taking the lower dose, 21.7% and 17.3% of patients in the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, respectively, had achieved at least 80% scalp coverage at 36 weeks. (These percentages differ slightly from the NEJM article because of a different analysis of missing data, Dr. King said. For comparison of both 36- and 52-week results, the percentages from the EADV are used above.)
The results indicate that 5% more patients reached the primary endpoint in the additional 16 weeks of the trial, Dr. King said.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where immune cells attack hair follicles, causing the hair to fall out, and is associated with emotional and psychological distress. Any hair follicle can be attacked, but they are rarely destroyed, so hair can regrow.
"Many underestimate the impact of this autoimmune hair loss condition," Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, told this news organization. He was not involved with the trial. "The burden of the disease, which certainly is an emotional but also a physical one, definitely needs to be addressed with indicated FDA-approved drugs," he noted, which is the goal of these trials.
The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials focused on scalp hair regrowth.
Eyebrow and eyelash growth, secondary outcomes, also improved between 36 and 52 weeks in both groups, calculated using the proportion of participants who had achieved full regrowth or regrowth with minimal gaps. At 36 weeks, about 31%-35% of patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib regrew eyebrow and eyelash hair. By 52 weeks, more than two out of five patients regrew eyebrow (44.1%) and eyelash (45.3%) hair.
“It’s a fantastic achievement and a major step forward in alopecia areata, especially for patients with the most severe and refractory cases,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPH, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Mostaghimi is on the advisory board for Eli Lilly, which manufactures baricitinib, and Brigham and Women’s was one of the clinical sites of the trial.
While dermatologists have been aware of how JAK inhibitors can affect hair regrowth in alopecia patients, they have been using these drugs off label, Dr. Friedman said. Therefore, these drugs are expensive and more difficult to access. These trials provide "data that proves the efficacy and safety of [baricitinib] under the umbrella of the FDA portal," he added, which will hopefully lead to an approved indication for alopecia areata, so it can be more accessible to patients.
Adverse events at 52 weeks were consistent with data from 36 weeks, which found that none of these adverse events occurred in more than 10% of participants. The most common adverse events were headache, acne, and increases in muscle-related blood markers. The most common infections reported were pneumonia, herpes zoster, and urinary tract infection.
In February 2022, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib for the treatment of severe alopecia areata. Lilly expects a regulatory decision by the end of 2022, they said in a press release.
Lilly provided funding for the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials. Dr. King reported financial relationships with Aclaris, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceutics, Dermavant, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, and Viela Bio. Dr. Mostaghimi has reported serving on an advisory board for Lilly. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 3/28/2022 to include Dr. Friedman's comments, and on 3/31/2022 to correct the statement regarding adverse events reported in the study
AT AAD 2022
Platelet-rich plasma for hair regrowth requires art and science
or administer the highly technique-dependent treatment, which creates plenty of room for suboptimal results, according to several experts at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“The process is the product,” emphasized Terrence Keaney, MD, clinical associate professor at George Washington University, Washington, as well as cofounder of SkinDC, a private practice in Arlington, Va. He characterized PRP as a “growth factor cytokine cocktail,” for which relative benefits are fully dependent on the ingredients.
In other words, the efficacy of PRP is mostly dependent on the multiple steps in which blood drawn from a patient is separated into its components, processed to create a platelet-rich product, and then administered to the patient by injection or in conjunction with microneedles. While the goal is a platelet concentration two- to fivefold greater than that found in whole blood, this is not as straightforward as it sounds.
Many PRP device kits available
“There are a ton of [centrifuge] devices on the market and a lot of differences in the methodology in optimizing the platelet concentration,” Dr. Keaney explained. In addition, there are numerous proprietary collection tubes using different types of anticoagulants and different separator gels that also play a role in the goal of optimizing a platelet-rich and readily activated product.
“Recognize that each step in the preparation of PRP introduces a source of variation that affects the composition and efficacy of the final product,” said Steven Krueger, MD, who is completing his residency in dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, but who has become an expert in the field. He contributed a chapter on this topic in the recently published book, Aesthetic Clinician’s Guide to Platelet Rich Plasma.
The importance of technique is reflected in inconsistent results from published controlled trials. Unfortunately, the authors of many studies have failed to provide details of their protocol. Ultimately, Dr. Krueger said this lack of clarity among available protocols has created a serious obstacle for establishing which steps are important and how to move the field forward.
Dr. Keaney agreed. Because of the frequent lack of details about how PRP was processed in available studies, the effort to draw conclusions about the experiences at different centers is like “comparing apples to oranges.”
“What is the ideal dose and concentrate? We don’t know,” Dr. Keaney said.
The first centrifuge device to receive regulatory approval was developed for orthopedic indications more than 20 years ago. There are now at least 20 centrifuge devices with 510K Food and Drug Administration clearance for separating blood components to produce PRP. The 510K designation means that they are “substantially equivalent” to an already approved device, but Dr. Krueger cautioned that their use in preparing PRP for treatment of hair loss remains off label.
Substandard devices are marketed
In the rapidly expanding world of PRP, there is also a growing array of PRP kits. Some of these kits have been cleared by the FDA but others have not. Dr. Krueger warned that collection tubes are being marketed that are substandard imitations of better-established products. He specifically cautioned against do-it-yourself PRP kits, which are likely to be less effective for isolating platelets and can also be contaminated with pyogenes that cause infection.
“Please use an FDA-cleared kit,” he said, warning that the risk of failing to do so is not just associated with lack of efficacy but also a significant risk of serious adverse events.
Of the centrifuge devices, both Dr. Krueger and Dr. Keaney generally recommend single-spin over double-spin devices, particularly at centers with a limited volume of PRP-based hair loss interventions. These are generally simpler.
Once the PRP has been properly prepared, the efficacy of PRP upon application can also be influenced by strategies for activation. Although the exact mechanism of PRP in stimulating hair growth is incompletely defined, the role of platelets in releasing growth factors is believed to be critical. There are a number of methods to stimulate platelets upon administration, such as exposure to endogenous collagen or thrombin or exogenous chemicals, such as calcium chloride, but again, techniques differ and the optimal approach is unknown.
One concern is the recent and largely unregulated growth of regenerative cell and tissue products for treating a large array of clinical disorders or cosmetic issues, according to Dr. Keaney. He warned of a “wild, wild west mentality” that has attracted providers with inadequate training and experience. In turn, this is now attracting the attention of the FDA as well as those involved in enforcing FDA directives.
“There is definitely more scrutiny of regenerative products,” he said, noting that he is careful about how he markets PRP. While it is reasonable to offer this off-label treatment as an in-office procedure, he noted that it is illegal to advertise off-label products. He reported that he has become more prudent when including this option among hair regrowth services provided in his practice.
Omer E. Ibrahim, MD, a dermatologist affiliated with Chicago Cosmetic Surgery and Dermatology, agreed. While he also feels there is good evidence to support PRP as a hair loss treatment option, particularly for androgenic alopecia, he also expressed caution about promoting this approach in exclusion of other options.
“Patients ask me for a PRP consultation, but there is no such thing as a PRP consultation in my practice,” Dr. Ibrahim said. He incorporates PRP into other strategies. “I stress that it is one part of a multipronged approach,” he added.
Dr. Ibrahim has reported financial relationships with Alastin Skincare, Allergan, Eclipse Medical, Galderma USA, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Keaney has reported financial relationships with Allergan, DermTech, Evolus, Galderma USA, Merz Aesthetics, Revance Therapeutics, and Syneron Candela. Dr. Krueger has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
or administer the highly technique-dependent treatment, which creates plenty of room for suboptimal results, according to several experts at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“The process is the product,” emphasized Terrence Keaney, MD, clinical associate professor at George Washington University, Washington, as well as cofounder of SkinDC, a private practice in Arlington, Va. He characterized PRP as a “growth factor cytokine cocktail,” for which relative benefits are fully dependent on the ingredients.
In other words, the efficacy of PRP is mostly dependent on the multiple steps in which blood drawn from a patient is separated into its components, processed to create a platelet-rich product, and then administered to the patient by injection or in conjunction with microneedles. While the goal is a platelet concentration two- to fivefold greater than that found in whole blood, this is not as straightforward as it sounds.
Many PRP device kits available
“There are a ton of [centrifuge] devices on the market and a lot of differences in the methodology in optimizing the platelet concentration,” Dr. Keaney explained. In addition, there are numerous proprietary collection tubes using different types of anticoagulants and different separator gels that also play a role in the goal of optimizing a platelet-rich and readily activated product.
“Recognize that each step in the preparation of PRP introduces a source of variation that affects the composition and efficacy of the final product,” said Steven Krueger, MD, who is completing his residency in dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, but who has become an expert in the field. He contributed a chapter on this topic in the recently published book, Aesthetic Clinician’s Guide to Platelet Rich Plasma.
The importance of technique is reflected in inconsistent results from published controlled trials. Unfortunately, the authors of many studies have failed to provide details of their protocol. Ultimately, Dr. Krueger said this lack of clarity among available protocols has created a serious obstacle for establishing which steps are important and how to move the field forward.
Dr. Keaney agreed. Because of the frequent lack of details about how PRP was processed in available studies, the effort to draw conclusions about the experiences at different centers is like “comparing apples to oranges.”
“What is the ideal dose and concentrate? We don’t know,” Dr. Keaney said.
The first centrifuge device to receive regulatory approval was developed for orthopedic indications more than 20 years ago. There are now at least 20 centrifuge devices with 510K Food and Drug Administration clearance for separating blood components to produce PRP. The 510K designation means that they are “substantially equivalent” to an already approved device, but Dr. Krueger cautioned that their use in preparing PRP for treatment of hair loss remains off label.
Substandard devices are marketed
In the rapidly expanding world of PRP, there is also a growing array of PRP kits. Some of these kits have been cleared by the FDA but others have not. Dr. Krueger warned that collection tubes are being marketed that are substandard imitations of better-established products. He specifically cautioned against do-it-yourself PRP kits, which are likely to be less effective for isolating platelets and can also be contaminated with pyogenes that cause infection.
“Please use an FDA-cleared kit,” he said, warning that the risk of failing to do so is not just associated with lack of efficacy but also a significant risk of serious adverse events.
Of the centrifuge devices, both Dr. Krueger and Dr. Keaney generally recommend single-spin over double-spin devices, particularly at centers with a limited volume of PRP-based hair loss interventions. These are generally simpler.
Once the PRP has been properly prepared, the efficacy of PRP upon application can also be influenced by strategies for activation. Although the exact mechanism of PRP in stimulating hair growth is incompletely defined, the role of platelets in releasing growth factors is believed to be critical. There are a number of methods to stimulate platelets upon administration, such as exposure to endogenous collagen or thrombin or exogenous chemicals, such as calcium chloride, but again, techniques differ and the optimal approach is unknown.
One concern is the recent and largely unregulated growth of regenerative cell and tissue products for treating a large array of clinical disorders or cosmetic issues, according to Dr. Keaney. He warned of a “wild, wild west mentality” that has attracted providers with inadequate training and experience. In turn, this is now attracting the attention of the FDA as well as those involved in enforcing FDA directives.
“There is definitely more scrutiny of regenerative products,” he said, noting that he is careful about how he markets PRP. While it is reasonable to offer this off-label treatment as an in-office procedure, he noted that it is illegal to advertise off-label products. He reported that he has become more prudent when including this option among hair regrowth services provided in his practice.
Omer E. Ibrahim, MD, a dermatologist affiliated with Chicago Cosmetic Surgery and Dermatology, agreed. While he also feels there is good evidence to support PRP as a hair loss treatment option, particularly for androgenic alopecia, he also expressed caution about promoting this approach in exclusion of other options.
“Patients ask me for a PRP consultation, but there is no such thing as a PRP consultation in my practice,” Dr. Ibrahim said. He incorporates PRP into other strategies. “I stress that it is one part of a multipronged approach,” he added.
Dr. Ibrahim has reported financial relationships with Alastin Skincare, Allergan, Eclipse Medical, Galderma USA, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Keaney has reported financial relationships with Allergan, DermTech, Evolus, Galderma USA, Merz Aesthetics, Revance Therapeutics, and Syneron Candela. Dr. Krueger has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
or administer the highly technique-dependent treatment, which creates plenty of room for suboptimal results, according to several experts at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“The process is the product,” emphasized Terrence Keaney, MD, clinical associate professor at George Washington University, Washington, as well as cofounder of SkinDC, a private practice in Arlington, Va. He characterized PRP as a “growth factor cytokine cocktail,” for which relative benefits are fully dependent on the ingredients.
In other words, the efficacy of PRP is mostly dependent on the multiple steps in which blood drawn from a patient is separated into its components, processed to create a platelet-rich product, and then administered to the patient by injection or in conjunction with microneedles. While the goal is a platelet concentration two- to fivefold greater than that found in whole blood, this is not as straightforward as it sounds.
Many PRP device kits available
“There are a ton of [centrifuge] devices on the market and a lot of differences in the methodology in optimizing the platelet concentration,” Dr. Keaney explained. In addition, there are numerous proprietary collection tubes using different types of anticoagulants and different separator gels that also play a role in the goal of optimizing a platelet-rich and readily activated product.
“Recognize that each step in the preparation of PRP introduces a source of variation that affects the composition and efficacy of the final product,” said Steven Krueger, MD, who is completing his residency in dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, but who has become an expert in the field. He contributed a chapter on this topic in the recently published book, Aesthetic Clinician’s Guide to Platelet Rich Plasma.
The importance of technique is reflected in inconsistent results from published controlled trials. Unfortunately, the authors of many studies have failed to provide details of their protocol. Ultimately, Dr. Krueger said this lack of clarity among available protocols has created a serious obstacle for establishing which steps are important and how to move the field forward.
Dr. Keaney agreed. Because of the frequent lack of details about how PRP was processed in available studies, the effort to draw conclusions about the experiences at different centers is like “comparing apples to oranges.”
“What is the ideal dose and concentrate? We don’t know,” Dr. Keaney said.
The first centrifuge device to receive regulatory approval was developed for orthopedic indications more than 20 years ago. There are now at least 20 centrifuge devices with 510K Food and Drug Administration clearance for separating blood components to produce PRP. The 510K designation means that they are “substantially equivalent” to an already approved device, but Dr. Krueger cautioned that their use in preparing PRP for treatment of hair loss remains off label.
Substandard devices are marketed
In the rapidly expanding world of PRP, there is also a growing array of PRP kits. Some of these kits have been cleared by the FDA but others have not. Dr. Krueger warned that collection tubes are being marketed that are substandard imitations of better-established products. He specifically cautioned against do-it-yourself PRP kits, which are likely to be less effective for isolating platelets and can also be contaminated with pyogenes that cause infection.
“Please use an FDA-cleared kit,” he said, warning that the risk of failing to do so is not just associated with lack of efficacy but also a significant risk of serious adverse events.
Of the centrifuge devices, both Dr. Krueger and Dr. Keaney generally recommend single-spin over double-spin devices, particularly at centers with a limited volume of PRP-based hair loss interventions. These are generally simpler.
Once the PRP has been properly prepared, the efficacy of PRP upon application can also be influenced by strategies for activation. Although the exact mechanism of PRP in stimulating hair growth is incompletely defined, the role of platelets in releasing growth factors is believed to be critical. There are a number of methods to stimulate platelets upon administration, such as exposure to endogenous collagen or thrombin or exogenous chemicals, such as calcium chloride, but again, techniques differ and the optimal approach is unknown.
One concern is the recent and largely unregulated growth of regenerative cell and tissue products for treating a large array of clinical disorders or cosmetic issues, according to Dr. Keaney. He warned of a “wild, wild west mentality” that has attracted providers with inadequate training and experience. In turn, this is now attracting the attention of the FDA as well as those involved in enforcing FDA directives.
“There is definitely more scrutiny of regenerative products,” he said, noting that he is careful about how he markets PRP. While it is reasonable to offer this off-label treatment as an in-office procedure, he noted that it is illegal to advertise off-label products. He reported that he has become more prudent when including this option among hair regrowth services provided in his practice.
Omer E. Ibrahim, MD, a dermatologist affiliated with Chicago Cosmetic Surgery and Dermatology, agreed. While he also feels there is good evidence to support PRP as a hair loss treatment option, particularly for androgenic alopecia, he also expressed caution about promoting this approach in exclusion of other options.
“Patients ask me for a PRP consultation, but there is no such thing as a PRP consultation in my practice,” Dr. Ibrahim said. He incorporates PRP into other strategies. “I stress that it is one part of a multipronged approach,” he added.
Dr. Ibrahim has reported financial relationships with Alastin Skincare, Allergan, Eclipse Medical, Galderma USA, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Keaney has reported financial relationships with Allergan, DermTech, Evolus, Galderma USA, Merz Aesthetics, Revance Therapeutics, and Syneron Candela. Dr. Krueger has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2022
COVID-19–alopecia areata link? Review doesn’t find much evidence
A new
If there is a connection, it’s likely not a strong one, said study author Rachel E. Christensen, a graduate student at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, in an interview. “Based on the reported number of cases following COVID-19, alopecia areata appears to be low on the list of common skin manifestations of COVID-19,” she said. Of 402 articles screened from three databases in the review, only 11 were identified as related to alopecia areata (AA) and COVID-19, and only 9 of those met the study inclusion criteria. “This number alone highlights the very low number of published articles investigating this connection.”
The review was published in JAAD International.
While COVID-19 has been linked to a variety of skin conditions, a 2021 South Korean study of 7,958 cases and 218,779 controls found no connection between infection and AA even after covariates such as age, gender, and income level were taken into account. In a letter to the editor published in 2020, dermatologists in Turkey reported that the percentage of patients with AA at the dermatology outpatient clinic jumped from 0.97% in May 2019 to 1.48% in May 2020. The number of patients in each group wasn’t reported.
Systematic review
The investigators launched the systematic review to gain a wider perspective, although there are still limitations. On the one hand, Ms. Christensen said, “we do know that COVID-19, like other viruses, has been linked to various dermatological disorders.”
However, “it is difficult to tease apart whether any worsening of alopecia areata we see following COVID-19 is due to the virus itself or the increased psychological burden related to the infection or to the pandemic in general,” she said. Indeed, the authors of the report in Turkey attributed the rise in cases to stress.
For the review, the researchers analyzed studies from Italy (four), Turkey (two), Brazil (one), the United States (one), and Poland (one).
Six of the studies reported cases of new-onset AA following COVID-19 infection (seven cases; average age, 37 years; females, three). Another study was a retrospective review of 32 patients with preexisting AA who developed COVID-19; none experienced significant worsening of AA within 6 months.
The review also included a study based on a survey of 389 patients with AA. The investigators found that, at a median 2.14 months after infection, 44% of those who had COVID-19 vs. 12% of those who were COVID negative had a relapse. Finally, a case report noted a patient with preexisting AA whose condition worsened following COVID infection.
The findings suggest that AA “could be a dermatological manifestation of COVID-19, with cases most often appearing 1-2 months following infection,” the authors wrote. “However, the heterogeneity of study designs and high proportion of case reports make it challenging to draw any conclusion.”
In an interview, dermatologist Brett King, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the review findings suggest that “there is little concern of alopecia areata following COVID infection.
Does new-onset AA happen, and are there exacerbations of preexisting disease related to COVID infection? Probably yes, but rarely.”
However, he noted that another form of alopecia, telogen effluvium (TE), is more common after COVID-19 infection. According to Dr. King, who was not involved with the systematic review, TE is typically time-limited, compared with AA’s more common chronic waxing-and-waning course.
“Distinguishing TE and AA is usually straightforward because AA typically presents with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss,” such as circular patches, “while TE manifests as diffuse hair loss,” he explained. “Rarely, however, AA does manifest diffuse hair loss without patches, similar to TE. In those cases, it may be difficult to distinguish them. A biopsy may be helpful if there is a question of the diagnosis.”
No study funding is reported. The review authors and Dr. King report no relevant disclosures.
A new
If there is a connection, it’s likely not a strong one, said study author Rachel E. Christensen, a graduate student at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, in an interview. “Based on the reported number of cases following COVID-19, alopecia areata appears to be low on the list of common skin manifestations of COVID-19,” she said. Of 402 articles screened from three databases in the review, only 11 were identified as related to alopecia areata (AA) and COVID-19, and only 9 of those met the study inclusion criteria. “This number alone highlights the very low number of published articles investigating this connection.”
The review was published in JAAD International.
While COVID-19 has been linked to a variety of skin conditions, a 2021 South Korean study of 7,958 cases and 218,779 controls found no connection between infection and AA even after covariates such as age, gender, and income level were taken into account. In a letter to the editor published in 2020, dermatologists in Turkey reported that the percentage of patients with AA at the dermatology outpatient clinic jumped from 0.97% in May 2019 to 1.48% in May 2020. The number of patients in each group wasn’t reported.
Systematic review
The investigators launched the systematic review to gain a wider perspective, although there are still limitations. On the one hand, Ms. Christensen said, “we do know that COVID-19, like other viruses, has been linked to various dermatological disorders.”
However, “it is difficult to tease apart whether any worsening of alopecia areata we see following COVID-19 is due to the virus itself or the increased psychological burden related to the infection or to the pandemic in general,” she said. Indeed, the authors of the report in Turkey attributed the rise in cases to stress.
For the review, the researchers analyzed studies from Italy (four), Turkey (two), Brazil (one), the United States (one), and Poland (one).
Six of the studies reported cases of new-onset AA following COVID-19 infection (seven cases; average age, 37 years; females, three). Another study was a retrospective review of 32 patients with preexisting AA who developed COVID-19; none experienced significant worsening of AA within 6 months.
The review also included a study based on a survey of 389 patients with AA. The investigators found that, at a median 2.14 months after infection, 44% of those who had COVID-19 vs. 12% of those who were COVID negative had a relapse. Finally, a case report noted a patient with preexisting AA whose condition worsened following COVID infection.
The findings suggest that AA “could be a dermatological manifestation of COVID-19, with cases most often appearing 1-2 months following infection,” the authors wrote. “However, the heterogeneity of study designs and high proportion of case reports make it challenging to draw any conclusion.”
In an interview, dermatologist Brett King, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the review findings suggest that “there is little concern of alopecia areata following COVID infection.
Does new-onset AA happen, and are there exacerbations of preexisting disease related to COVID infection? Probably yes, but rarely.”
However, he noted that another form of alopecia, telogen effluvium (TE), is more common after COVID-19 infection. According to Dr. King, who was not involved with the systematic review, TE is typically time-limited, compared with AA’s more common chronic waxing-and-waning course.
“Distinguishing TE and AA is usually straightforward because AA typically presents with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss,” such as circular patches, “while TE manifests as diffuse hair loss,” he explained. “Rarely, however, AA does manifest diffuse hair loss without patches, similar to TE. In those cases, it may be difficult to distinguish them. A biopsy may be helpful if there is a question of the diagnosis.”
No study funding is reported. The review authors and Dr. King report no relevant disclosures.
A new
If there is a connection, it’s likely not a strong one, said study author Rachel E. Christensen, a graduate student at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, in an interview. “Based on the reported number of cases following COVID-19, alopecia areata appears to be low on the list of common skin manifestations of COVID-19,” she said. Of 402 articles screened from three databases in the review, only 11 were identified as related to alopecia areata (AA) and COVID-19, and only 9 of those met the study inclusion criteria. “This number alone highlights the very low number of published articles investigating this connection.”
The review was published in JAAD International.
While COVID-19 has been linked to a variety of skin conditions, a 2021 South Korean study of 7,958 cases and 218,779 controls found no connection between infection and AA even after covariates such as age, gender, and income level were taken into account. In a letter to the editor published in 2020, dermatologists in Turkey reported that the percentage of patients with AA at the dermatology outpatient clinic jumped from 0.97% in May 2019 to 1.48% in May 2020. The number of patients in each group wasn’t reported.
Systematic review
The investigators launched the systematic review to gain a wider perspective, although there are still limitations. On the one hand, Ms. Christensen said, “we do know that COVID-19, like other viruses, has been linked to various dermatological disorders.”
However, “it is difficult to tease apart whether any worsening of alopecia areata we see following COVID-19 is due to the virus itself or the increased psychological burden related to the infection or to the pandemic in general,” she said. Indeed, the authors of the report in Turkey attributed the rise in cases to stress.
For the review, the researchers analyzed studies from Italy (four), Turkey (two), Brazil (one), the United States (one), and Poland (one).
Six of the studies reported cases of new-onset AA following COVID-19 infection (seven cases; average age, 37 years; females, three). Another study was a retrospective review of 32 patients with preexisting AA who developed COVID-19; none experienced significant worsening of AA within 6 months.
The review also included a study based on a survey of 389 patients with AA. The investigators found that, at a median 2.14 months after infection, 44% of those who had COVID-19 vs. 12% of those who were COVID negative had a relapse. Finally, a case report noted a patient with preexisting AA whose condition worsened following COVID infection.
The findings suggest that AA “could be a dermatological manifestation of COVID-19, with cases most often appearing 1-2 months following infection,” the authors wrote. “However, the heterogeneity of study designs and high proportion of case reports make it challenging to draw any conclusion.”
In an interview, dermatologist Brett King, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the review findings suggest that “there is little concern of alopecia areata following COVID infection.
Does new-onset AA happen, and are there exacerbations of preexisting disease related to COVID infection? Probably yes, but rarely.”
However, he noted that another form of alopecia, telogen effluvium (TE), is more common after COVID-19 infection. According to Dr. King, who was not involved with the systematic review, TE is typically time-limited, compared with AA’s more common chronic waxing-and-waning course.
“Distinguishing TE and AA is usually straightforward because AA typically presents with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss,” such as circular patches, “while TE manifests as diffuse hair loss,” he explained. “Rarely, however, AA does manifest diffuse hair loss without patches, similar to TE. In those cases, it may be difficult to distinguish them. A biopsy may be helpful if there is a question of the diagnosis.”
No study funding is reported. The review authors and Dr. King report no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAAD INTERNATIONAL
Oral tofacitinib produces hair regrowth in children with alopecia areata
and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The 11 pediatric patients, ages 8-18 years, all with a diagnosis of AA, were treated with tofacitinib. Eight patients, or nearly 73%, experienced hair regrowth, while the other three (27.3%) did not, as the investigators reported in the retrospective chart review.
“A success rate of 73% is very good,” said lead author Cory A. Dunnick, MD, professor of dermatology and director of clinical trials at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. No serious adverse events occurred, and adverse events of any kind were limited, the researchers found.
“It is important to get information into the literature about potential treatments for severe alopecia areata because there is no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved therapy at the present time,” Dr. Dunnick told this news organization. Patients’ insurance plans often deny non–FDA-approved therapies unless there are data to support their use.
The researchers found no correlation between the dose, duration of treatment, or the presence of comorbidities and clinical response.
Oral tofacitinib has been shown to be effective and well tolerated for AA in adults, the researchers said. They referred to recent studies that have used JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib, “in an effort to inhibit T-cell activation and halt disease progression in adult and pediatric patients” with AA.
Study details
Of the 11 patients evaluated, 6 had alopecia universalis, 1 had alopecia totalis, and 4 had patchy AA. Concomitant medical conditions known to be associated with AA affected four patients. These included atopic dermatitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, and asthma. One patient reported having two brothers with AA.
The median disease duration was 6 years. “In my experience, JAK inhibitors are less effective for patients with longstanding – more than 10 years – alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis,” Dr. Dunnick said.
Previously, patients had been given methotrexate, oral prednisone, intralesional triamcinolone, topical corticosteroids, and topical diphenylcyclopropenone. During treatment with tofacitinib, 5 of the 11 patients also received topical steroid treatment.
The study was a retrospective chart review, so dosing was not standardized, the researchers said. Most took 5-10 mg twice daily. Median treatment time was 32 months, with a range of 5-39 months.
Patients with a complete or near complete clinical response were categorized as responders; subjectively, these were the patients who had persistent hair regrowth over more than 50% of affected areas. Five patients had complete regrowth of hair on the scalp, eyebrows, and body during treatment. Others had incomplete responses. For instance, one patient had improved growth of eyelashes and eyebrows but not on the scalp. Once the medication was increased to 15 mg daily, the patient had complete regrowth of body hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows but slow regrowth on the scalp after 1 year of treatment.
“Patients are very happy with regrowth of their hair,” Dr. Dunnick said, noting that severe AA affects self-esteem and quality of life.
Other research
In a retrospective study that looked at the effects of oral tofacitinib given to 14 preadolescent patients with AA, 9 experienced “clinically significant improvement” in their Severity of Alopecia Tool score. Three had complete remission, and seven (63.6%) had more than a 50% improvement in the score.
Mechanisms, concerns
The researchers of the current study explained that interferon signaling activity through the JAK pathways is a key mediator of the inflammation and cytotoxic T-cell response in AA. That modulation of the signaling may decrease disease progression, as the results of the current chart review suggest.
A main concern, the researchers wrote, is the potential for significant adverse events. Although this chart review did not find any, the researchers did see some transient lab abnormalities. One study found lab abnormalities in such measures as triglycerides and cholesterol.
Asked to comment on the study results, Brett King, MD, PHD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said that the study “is an important addition to a series of articles dating back to 2017 showing efficacy of tofacitinib in the pediatric age group.” The results are similar to those of previous studies, “showing that severe AA can be treated effectively with tofacitinib. Cumulatively, there is significant data to support treatment of this age group with JAK inhibitors,” he said.
At the 2021 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting, Dr. King presented the results of two phase 3 studies, which found that treatment with the oral JAK inhibitor baricitinib resulted in substantial hair growth in adults with AA. He and colleagues have also reported positive results of tofacitinib in treating AA in four children ages 8-10, with alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, and in adolescents with AA.
Currently, three large, randomized, phase 3 clinical trials of other JAK inhibitors for AA are underway – ritlecitinib, baricitinib, and ruxolitinib – and the ritlecitinib trial includes adolescents (ages 12 years and older). “It is the results of these trials that we eagerly await, because FDA approval will bring greater access to these treatments,” Dr. King said.
Dr. Dunnick has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. King has served on advisory boards and/or is a consultant and/or a clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Pfizer, and others. He is on speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Incyte, Pfizer, and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The 11 pediatric patients, ages 8-18 years, all with a diagnosis of AA, were treated with tofacitinib. Eight patients, or nearly 73%, experienced hair regrowth, while the other three (27.3%) did not, as the investigators reported in the retrospective chart review.
“A success rate of 73% is very good,” said lead author Cory A. Dunnick, MD, professor of dermatology and director of clinical trials at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. No serious adverse events occurred, and adverse events of any kind were limited, the researchers found.
“It is important to get information into the literature about potential treatments for severe alopecia areata because there is no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved therapy at the present time,” Dr. Dunnick told this news organization. Patients’ insurance plans often deny non–FDA-approved therapies unless there are data to support their use.
The researchers found no correlation between the dose, duration of treatment, or the presence of comorbidities and clinical response.
Oral tofacitinib has been shown to be effective and well tolerated for AA in adults, the researchers said. They referred to recent studies that have used JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib, “in an effort to inhibit T-cell activation and halt disease progression in adult and pediatric patients” with AA.
Study details
Of the 11 patients evaluated, 6 had alopecia universalis, 1 had alopecia totalis, and 4 had patchy AA. Concomitant medical conditions known to be associated with AA affected four patients. These included atopic dermatitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, and asthma. One patient reported having two brothers with AA.
The median disease duration was 6 years. “In my experience, JAK inhibitors are less effective for patients with longstanding – more than 10 years – alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis,” Dr. Dunnick said.
Previously, patients had been given methotrexate, oral prednisone, intralesional triamcinolone, topical corticosteroids, and topical diphenylcyclopropenone. During treatment with tofacitinib, 5 of the 11 patients also received topical steroid treatment.
The study was a retrospective chart review, so dosing was not standardized, the researchers said. Most took 5-10 mg twice daily. Median treatment time was 32 months, with a range of 5-39 months.
Patients with a complete or near complete clinical response were categorized as responders; subjectively, these were the patients who had persistent hair regrowth over more than 50% of affected areas. Five patients had complete regrowth of hair on the scalp, eyebrows, and body during treatment. Others had incomplete responses. For instance, one patient had improved growth of eyelashes and eyebrows but not on the scalp. Once the medication was increased to 15 mg daily, the patient had complete regrowth of body hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows but slow regrowth on the scalp after 1 year of treatment.
“Patients are very happy with regrowth of their hair,” Dr. Dunnick said, noting that severe AA affects self-esteem and quality of life.
Other research
In a retrospective study that looked at the effects of oral tofacitinib given to 14 preadolescent patients with AA, 9 experienced “clinically significant improvement” in their Severity of Alopecia Tool score. Three had complete remission, and seven (63.6%) had more than a 50% improvement in the score.
Mechanisms, concerns
The researchers of the current study explained that interferon signaling activity through the JAK pathways is a key mediator of the inflammation and cytotoxic T-cell response in AA. That modulation of the signaling may decrease disease progression, as the results of the current chart review suggest.
A main concern, the researchers wrote, is the potential for significant adverse events. Although this chart review did not find any, the researchers did see some transient lab abnormalities. One study found lab abnormalities in such measures as triglycerides and cholesterol.
Asked to comment on the study results, Brett King, MD, PHD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said that the study “is an important addition to a series of articles dating back to 2017 showing efficacy of tofacitinib in the pediatric age group.” The results are similar to those of previous studies, “showing that severe AA can be treated effectively with tofacitinib. Cumulatively, there is significant data to support treatment of this age group with JAK inhibitors,” he said.
At the 2021 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting, Dr. King presented the results of two phase 3 studies, which found that treatment with the oral JAK inhibitor baricitinib resulted in substantial hair growth in adults with AA. He and colleagues have also reported positive results of tofacitinib in treating AA in four children ages 8-10, with alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, and in adolescents with AA.
Currently, three large, randomized, phase 3 clinical trials of other JAK inhibitors for AA are underway – ritlecitinib, baricitinib, and ruxolitinib – and the ritlecitinib trial includes adolescents (ages 12 years and older). “It is the results of these trials that we eagerly await, because FDA approval will bring greater access to these treatments,” Dr. King said.
Dr. Dunnick has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. King has served on advisory boards and/or is a consultant and/or a clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Pfizer, and others. He is on speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Incyte, Pfizer, and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The 11 pediatric patients, ages 8-18 years, all with a diagnosis of AA, were treated with tofacitinib. Eight patients, or nearly 73%, experienced hair regrowth, while the other three (27.3%) did not, as the investigators reported in the retrospective chart review.
“A success rate of 73% is very good,” said lead author Cory A. Dunnick, MD, professor of dermatology and director of clinical trials at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. No serious adverse events occurred, and adverse events of any kind were limited, the researchers found.
“It is important to get information into the literature about potential treatments for severe alopecia areata because there is no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved therapy at the present time,” Dr. Dunnick told this news organization. Patients’ insurance plans often deny non–FDA-approved therapies unless there are data to support their use.
The researchers found no correlation between the dose, duration of treatment, or the presence of comorbidities and clinical response.
Oral tofacitinib has been shown to be effective and well tolerated for AA in adults, the researchers said. They referred to recent studies that have used JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib, “in an effort to inhibit T-cell activation and halt disease progression in adult and pediatric patients” with AA.
Study details
Of the 11 patients evaluated, 6 had alopecia universalis, 1 had alopecia totalis, and 4 had patchy AA. Concomitant medical conditions known to be associated with AA affected four patients. These included atopic dermatitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, and asthma. One patient reported having two brothers with AA.
The median disease duration was 6 years. “In my experience, JAK inhibitors are less effective for patients with longstanding – more than 10 years – alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis,” Dr. Dunnick said.
Previously, patients had been given methotrexate, oral prednisone, intralesional triamcinolone, topical corticosteroids, and topical diphenylcyclopropenone. During treatment with tofacitinib, 5 of the 11 patients also received topical steroid treatment.
The study was a retrospective chart review, so dosing was not standardized, the researchers said. Most took 5-10 mg twice daily. Median treatment time was 32 months, with a range of 5-39 months.
Patients with a complete or near complete clinical response were categorized as responders; subjectively, these were the patients who had persistent hair regrowth over more than 50% of affected areas. Five patients had complete regrowth of hair on the scalp, eyebrows, and body during treatment. Others had incomplete responses. For instance, one patient had improved growth of eyelashes and eyebrows but not on the scalp. Once the medication was increased to 15 mg daily, the patient had complete regrowth of body hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows but slow regrowth on the scalp after 1 year of treatment.
“Patients are very happy with regrowth of their hair,” Dr. Dunnick said, noting that severe AA affects self-esteem and quality of life.
Other research
In a retrospective study that looked at the effects of oral tofacitinib given to 14 preadolescent patients with AA, 9 experienced “clinically significant improvement” in their Severity of Alopecia Tool score. Three had complete remission, and seven (63.6%) had more than a 50% improvement in the score.
Mechanisms, concerns
The researchers of the current study explained that interferon signaling activity through the JAK pathways is a key mediator of the inflammation and cytotoxic T-cell response in AA. That modulation of the signaling may decrease disease progression, as the results of the current chart review suggest.
A main concern, the researchers wrote, is the potential for significant adverse events. Although this chart review did not find any, the researchers did see some transient lab abnormalities. One study found lab abnormalities in such measures as triglycerides and cholesterol.
Asked to comment on the study results, Brett King, MD, PHD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said that the study “is an important addition to a series of articles dating back to 2017 showing efficacy of tofacitinib in the pediatric age group.” The results are similar to those of previous studies, “showing that severe AA can be treated effectively with tofacitinib. Cumulatively, there is significant data to support treatment of this age group with JAK inhibitors,” he said.
At the 2021 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting, Dr. King presented the results of two phase 3 studies, which found that treatment with the oral JAK inhibitor baricitinib resulted in substantial hair growth in adults with AA. He and colleagues have also reported positive results of tofacitinib in treating AA in four children ages 8-10, with alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, and in adolescents with AA.
Currently, three large, randomized, phase 3 clinical trials of other JAK inhibitors for AA are underway – ritlecitinib, baricitinib, and ruxolitinib – and the ritlecitinib trial includes adolescents (ages 12 years and older). “It is the results of these trials that we eagerly await, because FDA approval will bring greater access to these treatments,” Dr. King said.
Dr. Dunnick has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. King has served on advisory boards and/or is a consultant and/or a clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Pfizer, and others. He is on speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Incyte, Pfizer, and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY