User login
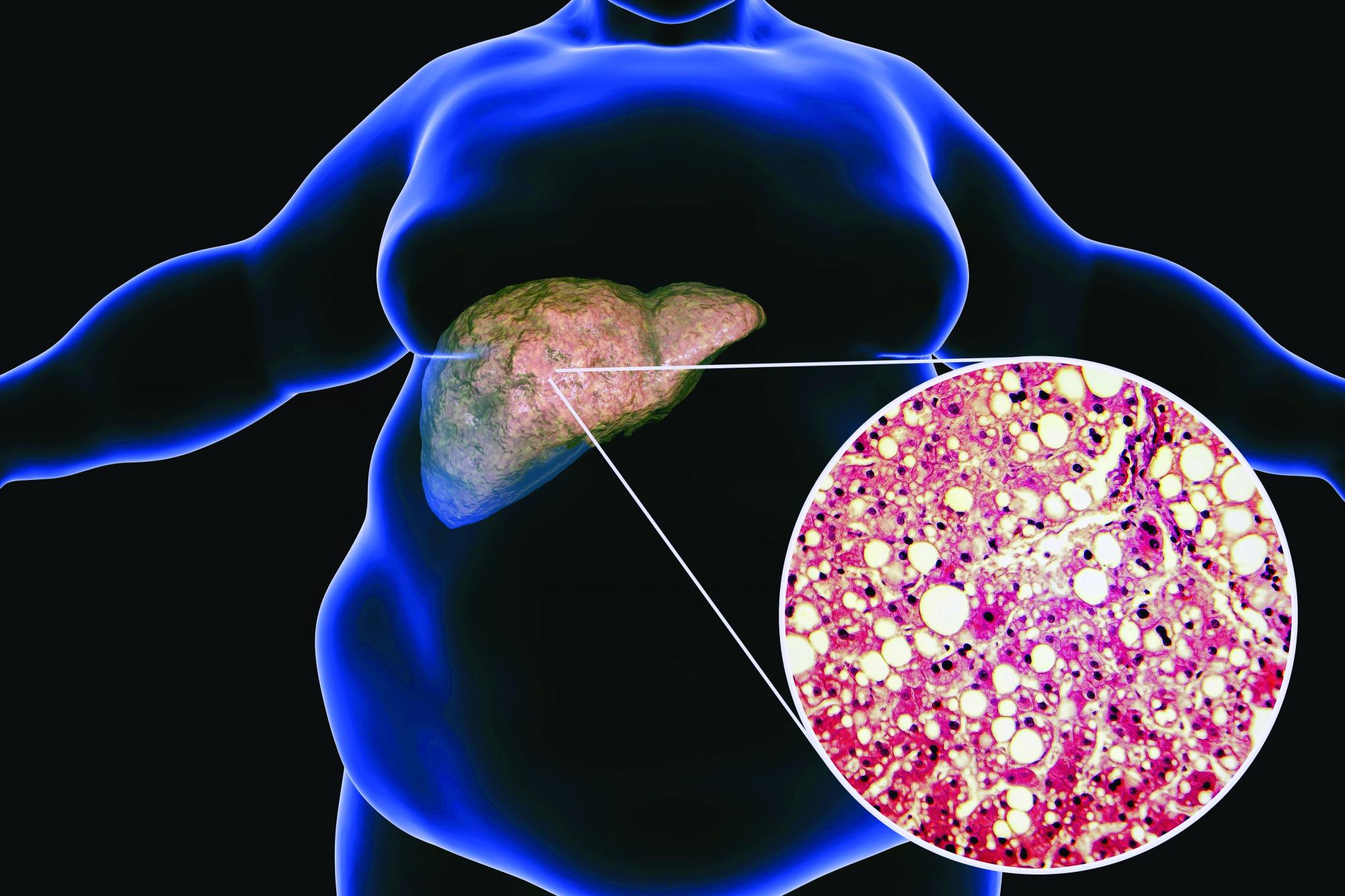
Low-carb, high-fat diet improves A1c, reduces liver fat
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022
Acute hepatitis cases in children show declining trend; adenovirus, COVID-19 remain key leads
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022
Pemvidutide promising for fatty liver disease
LONDON – Weight loss, lipid reductions, and “robust improvements” in lipid species associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease were achieved in patients who were treated with pemvidutide in a first-in-human, phase 1 clinical trial reported at the annual International Liver Congress, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The presenting study investigator, Stephen A. Harrison, MD, said that pemvidutide, which is also being developed for the treatment of obesity, appeared to be well tolerated. There were no serious or severe adverse events, and no patient had to discontinue treatment because of side effects.
Overall, “pemvidutide represents a promising new agent,” said Dr. Harrison, medical director of Pinnacle Research in San Antonio, Texas.
Dual incretin effect
Pemvidutide is a “balanced” dual agonist of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucagon, Dr. Harrison explained in his oral abstract.
“With glucagon, we are working to drive energy expenditure up, and with GLP-1, we’re decreasing food intake,” Dr. Harrison said.
What might set pemvidutide apart from other incretins lies within its structure, Dr. Harrison suggested. The structure has two main regions – one with greater GLP-1 specificity and the other with greater glucagon specificity, and these two areas are linked by a propriety technology called a EuPort™ domain. This is an area which allows the drug to bind to albumin, which increases its serum half-life and enables weekly dosing while slowing its entry into the bloodstream.
“Ultimately, we think that this has impacts, hypothetically, on tolerability and potentially mitigating the need for dose escalation,” said Dr. Harrison.
Weight loss results
The phase 1 study Dr. Harrison presented had a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design with single and multiple ascending doses (SAD/MAD) of pemvidutide being tested. He presented data on the MAD phase only, noting that the SAD phase had been used to determine what doses to use in the latter.
Seventy individuals with a body mass index of between 25 and 40 kg/m2 were recruited and 34 of these were enrolled in the MAD phase of the study. Three doses of pemvidutide were used, given subcutaneously once a week for 12 weeks: Seven participants received 1.2 mg, 9 were given 1.8 mg, 11 had 2.4 mg, and 7 subjects were treated with placebo. Dr. Harrison noted that there were no caloric restrictions in the trial and no lifestyle modifications or interventions.
The average age of study participants ranged from 27 to 35 years and the mean BMI was 30-31 kg/m2 across each group, with their lipid parameters in the upper range of normal.
Clear weight loss reductions were seen across all the pemvidutide groups versus placebo, with the greatest percentage changes in weight loss seen with the two higher doses used. At week 12, there was a 4.9%, 10.3% and 9.0% weight loss in the 1.2-mg, 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg pemvidutide groups compared to 1.6% in placebo-treated individuals.
All patients in the 1.8-mg group achieved a 5% or greater weight loss, Dr. Harrison observed, but there “was a plateauing” effect with the 2.4-mg dose with 89% of patients achieving this target. In comparison, a third of patients on the lowest dose and 20% of those on placebo achieved this target.
The trajectory of weight loss seen in the trial suggests that “the rate of weight loss would continue beyond 12 weeks if we were to continue the therapy” Dr. Harrison said.
Lipid changes and liver fat reductions
Levels of serum lipids from baseline to week 12 fell to a greater extent with pemvidutide treatment than with placebo, in the range of –27% for total cholesterol in the two highest dose groups, –25% for LDL-cholesterol for those groups, –37% for triglycerides for the 1.2- and 1.8-mg groups, and reductions in apolipoprotein B were seen.
“We saw an initial decline in HDL [high-density lipoprotein],” Dr. Harrison said, noting that “this is consistent with prior studies looking at rapid weight loss, and over time, this mitigates as you continue to treat at least based on other mechanisms of action or other drugs with similar mechanisms.”
Pemvidutide treatment was also associated with increased lipid oxidation and decreased lipid synthesis, and “there was a robust decrease in lipids implicated in NASH inflammation,” Dr. Harrison pointed out.
Importantly, in five of eight participants who had high levels of liver fat at baseline – defined as a 5% or greater magnetic resonance imaging–derived proton-density-fat-fraction (MRI-PDFF) – showed a decrease to undetectable limits (1.5% or less). This was a greater than 90% reduction in liver fat, Dr. Harrison said. All five patients were in the 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg groups.
As for side effects, these were “predominantly upper GI, with nausea and vomiting.” These were mild in most cases, but he pointed out that five patients treated with the 1.8-mg dose experienced moderate nausea and three experienced moderate vomiting. Mild diarrhea and constipation were also seen in two of patients given this dose but was not reported in any of the other groups.
During the discussion following the presentation, it was pointed out that there was no clear dose-dependent effect considering the 1.8-mg dose seemed to have a stronger effect in some areas than the 2.4-mg dose. That’s a fair point, Dr. Harrison responded, reiterating it was a small study with a short treatment duration, but that there did look like a plateauing effect, “at least in patients with a mean BMI of between 30 and 31.”
Dr. Harrison was asked about potential effects on insulin levels and if that was a worry because, if glucagon is stimulated, it could increase insulin. That in turn might encourage insulin resistance and promote worse outcomes.
“If you look outside of just this program, glucagon agonism has been dosed in a lot of patients over time, and we haven’t seen that,” Dr. Harrison replied. Pemvidutide is an agonist rather than antagonist, so perhaps the [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis]–inducing effects seen before with glucagon antagonism won’t occur, he suggested.
Dr. Harrison disclosed ties to Altimmune (the study sponsor), Akero, Axcella, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cirius, CiVi Biopharma, Conatus, Corcept, CymaBay, Enyo, Galectin, Genentech, Genfit, Gilead, Hepion, Hightide, HistoIndex, Intercept, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Bio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, NorthSea, Pfizer, Sagimet, Viking, and 89Bio.
LONDON – Weight loss, lipid reductions, and “robust improvements” in lipid species associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease were achieved in patients who were treated with pemvidutide in a first-in-human, phase 1 clinical trial reported at the annual International Liver Congress, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The presenting study investigator, Stephen A. Harrison, MD, said that pemvidutide, which is also being developed for the treatment of obesity, appeared to be well tolerated. There were no serious or severe adverse events, and no patient had to discontinue treatment because of side effects.
Overall, “pemvidutide represents a promising new agent,” said Dr. Harrison, medical director of Pinnacle Research in San Antonio, Texas.
Dual incretin effect
Pemvidutide is a “balanced” dual agonist of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucagon, Dr. Harrison explained in his oral abstract.
“With glucagon, we are working to drive energy expenditure up, and with GLP-1, we’re decreasing food intake,” Dr. Harrison said.
What might set pemvidutide apart from other incretins lies within its structure, Dr. Harrison suggested. The structure has two main regions – one with greater GLP-1 specificity and the other with greater glucagon specificity, and these two areas are linked by a propriety technology called a EuPort™ domain. This is an area which allows the drug to bind to albumin, which increases its serum half-life and enables weekly dosing while slowing its entry into the bloodstream.
“Ultimately, we think that this has impacts, hypothetically, on tolerability and potentially mitigating the need for dose escalation,” said Dr. Harrison.
Weight loss results
The phase 1 study Dr. Harrison presented had a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design with single and multiple ascending doses (SAD/MAD) of pemvidutide being tested. He presented data on the MAD phase only, noting that the SAD phase had been used to determine what doses to use in the latter.
Seventy individuals with a body mass index of between 25 and 40 kg/m2 were recruited and 34 of these were enrolled in the MAD phase of the study. Three doses of pemvidutide were used, given subcutaneously once a week for 12 weeks: Seven participants received 1.2 mg, 9 were given 1.8 mg, 11 had 2.4 mg, and 7 subjects were treated with placebo. Dr. Harrison noted that there were no caloric restrictions in the trial and no lifestyle modifications or interventions.
The average age of study participants ranged from 27 to 35 years and the mean BMI was 30-31 kg/m2 across each group, with their lipid parameters in the upper range of normal.
Clear weight loss reductions were seen across all the pemvidutide groups versus placebo, with the greatest percentage changes in weight loss seen with the two higher doses used. At week 12, there was a 4.9%, 10.3% and 9.0% weight loss in the 1.2-mg, 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg pemvidutide groups compared to 1.6% in placebo-treated individuals.
All patients in the 1.8-mg group achieved a 5% or greater weight loss, Dr. Harrison observed, but there “was a plateauing” effect with the 2.4-mg dose with 89% of patients achieving this target. In comparison, a third of patients on the lowest dose and 20% of those on placebo achieved this target.
The trajectory of weight loss seen in the trial suggests that “the rate of weight loss would continue beyond 12 weeks if we were to continue the therapy” Dr. Harrison said.
Lipid changes and liver fat reductions
Levels of serum lipids from baseline to week 12 fell to a greater extent with pemvidutide treatment than with placebo, in the range of –27% for total cholesterol in the two highest dose groups, –25% for LDL-cholesterol for those groups, –37% for triglycerides for the 1.2- and 1.8-mg groups, and reductions in apolipoprotein B were seen.
“We saw an initial decline in HDL [high-density lipoprotein],” Dr. Harrison said, noting that “this is consistent with prior studies looking at rapid weight loss, and over time, this mitigates as you continue to treat at least based on other mechanisms of action or other drugs with similar mechanisms.”
Pemvidutide treatment was also associated with increased lipid oxidation and decreased lipid synthesis, and “there was a robust decrease in lipids implicated in NASH inflammation,” Dr. Harrison pointed out.
Importantly, in five of eight participants who had high levels of liver fat at baseline – defined as a 5% or greater magnetic resonance imaging–derived proton-density-fat-fraction (MRI-PDFF) – showed a decrease to undetectable limits (1.5% or less). This was a greater than 90% reduction in liver fat, Dr. Harrison said. All five patients were in the 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg groups.
As for side effects, these were “predominantly upper GI, with nausea and vomiting.” These were mild in most cases, but he pointed out that five patients treated with the 1.8-mg dose experienced moderate nausea and three experienced moderate vomiting. Mild diarrhea and constipation were also seen in two of patients given this dose but was not reported in any of the other groups.
During the discussion following the presentation, it was pointed out that there was no clear dose-dependent effect considering the 1.8-mg dose seemed to have a stronger effect in some areas than the 2.4-mg dose. That’s a fair point, Dr. Harrison responded, reiterating it was a small study with a short treatment duration, but that there did look like a plateauing effect, “at least in patients with a mean BMI of between 30 and 31.”
Dr. Harrison was asked about potential effects on insulin levels and if that was a worry because, if glucagon is stimulated, it could increase insulin. That in turn might encourage insulin resistance and promote worse outcomes.
“If you look outside of just this program, glucagon agonism has been dosed in a lot of patients over time, and we haven’t seen that,” Dr. Harrison replied. Pemvidutide is an agonist rather than antagonist, so perhaps the [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis]–inducing effects seen before with glucagon antagonism won’t occur, he suggested.
Dr. Harrison disclosed ties to Altimmune (the study sponsor), Akero, Axcella, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cirius, CiVi Biopharma, Conatus, Corcept, CymaBay, Enyo, Galectin, Genentech, Genfit, Gilead, Hepion, Hightide, HistoIndex, Intercept, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Bio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, NorthSea, Pfizer, Sagimet, Viking, and 89Bio.
LONDON – Weight loss, lipid reductions, and “robust improvements” in lipid species associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease were achieved in patients who were treated with pemvidutide in a first-in-human, phase 1 clinical trial reported at the annual International Liver Congress, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The presenting study investigator, Stephen A. Harrison, MD, said that pemvidutide, which is also being developed for the treatment of obesity, appeared to be well tolerated. There were no serious or severe adverse events, and no patient had to discontinue treatment because of side effects.
Overall, “pemvidutide represents a promising new agent,” said Dr. Harrison, medical director of Pinnacle Research in San Antonio, Texas.
Dual incretin effect
Pemvidutide is a “balanced” dual agonist of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucagon, Dr. Harrison explained in his oral abstract.
“With glucagon, we are working to drive energy expenditure up, and with GLP-1, we’re decreasing food intake,” Dr. Harrison said.
What might set pemvidutide apart from other incretins lies within its structure, Dr. Harrison suggested. The structure has two main regions – one with greater GLP-1 specificity and the other with greater glucagon specificity, and these two areas are linked by a propriety technology called a EuPort™ domain. This is an area which allows the drug to bind to albumin, which increases its serum half-life and enables weekly dosing while slowing its entry into the bloodstream.
“Ultimately, we think that this has impacts, hypothetically, on tolerability and potentially mitigating the need for dose escalation,” said Dr. Harrison.
Weight loss results
The phase 1 study Dr. Harrison presented had a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design with single and multiple ascending doses (SAD/MAD) of pemvidutide being tested. He presented data on the MAD phase only, noting that the SAD phase had been used to determine what doses to use in the latter.
Seventy individuals with a body mass index of between 25 and 40 kg/m2 were recruited and 34 of these were enrolled in the MAD phase of the study. Three doses of pemvidutide were used, given subcutaneously once a week for 12 weeks: Seven participants received 1.2 mg, 9 were given 1.8 mg, 11 had 2.4 mg, and 7 subjects were treated with placebo. Dr. Harrison noted that there were no caloric restrictions in the trial and no lifestyle modifications or interventions.
The average age of study participants ranged from 27 to 35 years and the mean BMI was 30-31 kg/m2 across each group, with their lipid parameters in the upper range of normal.
Clear weight loss reductions were seen across all the pemvidutide groups versus placebo, with the greatest percentage changes in weight loss seen with the two higher doses used. At week 12, there was a 4.9%, 10.3% and 9.0% weight loss in the 1.2-mg, 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg pemvidutide groups compared to 1.6% in placebo-treated individuals.
All patients in the 1.8-mg group achieved a 5% or greater weight loss, Dr. Harrison observed, but there “was a plateauing” effect with the 2.4-mg dose with 89% of patients achieving this target. In comparison, a third of patients on the lowest dose and 20% of those on placebo achieved this target.
The trajectory of weight loss seen in the trial suggests that “the rate of weight loss would continue beyond 12 weeks if we were to continue the therapy” Dr. Harrison said.
Lipid changes and liver fat reductions
Levels of serum lipids from baseline to week 12 fell to a greater extent with pemvidutide treatment than with placebo, in the range of –27% for total cholesterol in the two highest dose groups, –25% for LDL-cholesterol for those groups, –37% for triglycerides for the 1.2- and 1.8-mg groups, and reductions in apolipoprotein B were seen.
“We saw an initial decline in HDL [high-density lipoprotein],” Dr. Harrison said, noting that “this is consistent with prior studies looking at rapid weight loss, and over time, this mitigates as you continue to treat at least based on other mechanisms of action or other drugs with similar mechanisms.”
Pemvidutide treatment was also associated with increased lipid oxidation and decreased lipid synthesis, and “there was a robust decrease in lipids implicated in NASH inflammation,” Dr. Harrison pointed out.
Importantly, in five of eight participants who had high levels of liver fat at baseline – defined as a 5% or greater magnetic resonance imaging–derived proton-density-fat-fraction (MRI-PDFF) – showed a decrease to undetectable limits (1.5% or less). This was a greater than 90% reduction in liver fat, Dr. Harrison said. All five patients were in the 1.8-mg and 2.4-mg groups.
As for side effects, these were “predominantly upper GI, with nausea and vomiting.” These were mild in most cases, but he pointed out that five patients treated with the 1.8-mg dose experienced moderate nausea and three experienced moderate vomiting. Mild diarrhea and constipation were also seen in two of patients given this dose but was not reported in any of the other groups.
During the discussion following the presentation, it was pointed out that there was no clear dose-dependent effect considering the 1.8-mg dose seemed to have a stronger effect in some areas than the 2.4-mg dose. That’s a fair point, Dr. Harrison responded, reiterating it was a small study with a short treatment duration, but that there did look like a plateauing effect, “at least in patients with a mean BMI of between 30 and 31.”
Dr. Harrison was asked about potential effects on insulin levels and if that was a worry because, if glucagon is stimulated, it could increase insulin. That in turn might encourage insulin resistance and promote worse outcomes.
“If you look outside of just this program, glucagon agonism has been dosed in a lot of patients over time, and we haven’t seen that,” Dr. Harrison replied. Pemvidutide is an agonist rather than antagonist, so perhaps the [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis]–inducing effects seen before with glucagon antagonism won’t occur, he suggested.
Dr. Harrison disclosed ties to Altimmune (the study sponsor), Akero, Axcella, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cirius, CiVi Biopharma, Conatus, Corcept, CymaBay, Enyo, Galectin, Genentech, Genfit, Gilead, Hepion, Hightide, HistoIndex, Intercept, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Bio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, NorthSea, Pfizer, Sagimet, Viking, and 89Bio.
AT ILC 2022
Fatty liver disease drives rise in liver cancer deaths
LONDON – Around the world, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has driven an increase in deaths from liver cancer over the past decade, overtaking alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, according to an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
A global rise in liver cancer deaths and chronic liver disease reflects changes in underlying health patterns, said Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor and chair, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., who presented the analysis at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“NAFLD and NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] are rapidly becoming the main causes of cirrhosis and liver cancer in the world,” Dr. Younossi told this news organization. “We have known about the increasing prevalence for some time, but now the outcomes in terms of mortality are catching up,” he said.
“The bottom line of this study is that the burden of this disease [NAFLD] is going up, and it will be the most important disease of the next decade or so,” he said, adding that “the largest annual percentage increase in rates of mortality from liver cancer or chronic liver disease cirrhosis is related to NAFLD.”
Specifically, during the decade of 2009-2019, the annual percent change (APC) of +1.33% in the global liver cancer death rate was driven by the fact that the APC for NAFLD was +2.47%. By comparison, the APC for alcoholic liver disease was +1.91%; for hepatitis B, the APC was +0.21%; and for hepatitis C, the APC was +1.12%.
Aleksander Krag, MD, PhD, professor and senior consultant of hepatology and director of Odense Liver Research Centre at SDU and Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who chaired the session in which this presentation was a part, acknowledged the importance of recognizing the contribution of NAFLD to liver cancer mortality.
“Liver diseases are on the rise. They are the fastest rising cause of death in the United Kingdom, faster than heart disease and other cancers. NAFLD in particular is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer, and the leading cause in France and the United States,” he remarked.
Dr. Krag also highlighted the costs of disease management.
“Managing fatty liver disease in Europe is estimated at €35 billion in direct health care, so we need to do something now,” he stressed.
“The global burden of NAFLD is so high that we need both prevention and treatment tools,” Dr. Krag said. “Change to lifestyle is a ‘no-brainer’ and costs governments very little. For the sake of our young people, we need to take this very seriously. At a political level, we can easily implement this, for example, by banning junk food advertisements, but also educating young people and their families. Good drugs will also help.”
NAFLD: The liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes
About 25%-30% of the global population have NAFLD, and 3%-5% have NASH. Dr. Younossi highlighted that the U.S. transplant database shows that NAFLD was the second indication for all liver transplants in the country. NAFLD also was a leading cause of liver transplants for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
There are around two billion cases of chronic liver disease globally, he said. He noted that over time, there has been an increase in all kinds of liver diseases, as reflected in the annual percent change.
“The global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes is driving the rise in NAFLD, but even among lean people, the prevalence of NAFLD is around 9%,” Dr. Younossi said. “Alongside the eye and kidney complications of diabetes, this is the liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes.”
To assess global liver disease and death, Dr. Younossi and his colleagues turned to the Global Burden of Disease Study, which gathered data from around 7,000 investigators located across 22 different regions of the world, comprising 156 countries.
They calculated the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) in relation to liver cancer and chronic liver disease, including the APC. They linked the data to changes in four liver diseases: NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B infection, and hepatitis C infection.
The cases of NAFLD reported in the study had been diagnosed by ultrasound or other imaging. Importantly, the prevalence of NAFLD was adjusted for alcohol use in the various national populations, explained Dr. Younossi.
In 2019, they reported that globally, the overall prevalence of liver disease reached 1.69 billion (liver cancer, 0.04%; chronic liver disease, 99.96%), with an incidence of 2.59 million (liver cancer, 20.7%; chronic liver disease, 79.3%), mortality of 1.95 million (liver cancer, 24.8%; chronic liver disease, 75.3%), and DALYs of 58.7 million (liver cancer, 21.3%; chronic liver disease, 78.7%).
Between 2009 and 2019, deaths from liver cancer rose by 27.2%, and deaths from chronic liver disease rose by 10.6%. DALYs from liver cancer rose by 21.9%, and DALYs from chronic liver disease were up by 5.1%.
In contrast to the increase in liver cancer deaths, deaths from chronic liver disease decreased (APC, –0.18%). The decrease was driven by a decrease in hepatitis B (APC, –1.83%). APCs for hepatitis C (+0.37%), alcoholic liver disease (+0.45%), and NAFLD (+1.33%) increased.
“The burden of hepatitis B–related mortality has decreased because we have been so good at vaccinating people,” Dr. Younossi remarked.
NAFLD ‘exploding’ in Middle East, North Africa, and East Asia
The increase in NAFLD has been seen in all regions of the world, but a breakdown by region shows that NAFLD is primarily “exploding” with highest prevalence and mortality in the Middle East (mostly Egypt, Iran, and Turkey), North Africa, and East Asia, said Dr. Younossi. In addition, there are large increases in the West and South America.
“We knew that the prevalence was high in the Middle East, but we now know that mortality is also high, so we are connecting these data,” said Dr. Younossi.
Awareness lacking
Dr. Younossi pressed the fact that awareness among the general population, primary care providers, and policymakers is very low. “From my perspective, raising awareness of NAFLD is the number one priority, and that is the value of this study.”
He added that more people will become aware as testing becomes more manageable.
“There are some noninvasive tests being developed, so in the future, we won’t have to do liver biopsies to diagnose these patients,” he said. “Currently, there are some excellent treatments being developed.”
“The WHO [World Health Organization] does not mention NAFLD as an important noncommunicable disease, and this too has to change,” Dr. Younossi added.
Dr. Younossi has received research funds and/or has consulted for Abbott, Allergan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Krag has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Around the world, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has driven an increase in deaths from liver cancer over the past decade, overtaking alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, according to an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
A global rise in liver cancer deaths and chronic liver disease reflects changes in underlying health patterns, said Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor and chair, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., who presented the analysis at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“NAFLD and NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] are rapidly becoming the main causes of cirrhosis and liver cancer in the world,” Dr. Younossi told this news organization. “We have known about the increasing prevalence for some time, but now the outcomes in terms of mortality are catching up,” he said.
“The bottom line of this study is that the burden of this disease [NAFLD] is going up, and it will be the most important disease of the next decade or so,” he said, adding that “the largest annual percentage increase in rates of mortality from liver cancer or chronic liver disease cirrhosis is related to NAFLD.”
Specifically, during the decade of 2009-2019, the annual percent change (APC) of +1.33% in the global liver cancer death rate was driven by the fact that the APC for NAFLD was +2.47%. By comparison, the APC for alcoholic liver disease was +1.91%; for hepatitis B, the APC was +0.21%; and for hepatitis C, the APC was +1.12%.
Aleksander Krag, MD, PhD, professor and senior consultant of hepatology and director of Odense Liver Research Centre at SDU and Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who chaired the session in which this presentation was a part, acknowledged the importance of recognizing the contribution of NAFLD to liver cancer mortality.
“Liver diseases are on the rise. They are the fastest rising cause of death in the United Kingdom, faster than heart disease and other cancers. NAFLD in particular is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer, and the leading cause in France and the United States,” he remarked.
Dr. Krag also highlighted the costs of disease management.
“Managing fatty liver disease in Europe is estimated at €35 billion in direct health care, so we need to do something now,” he stressed.
“The global burden of NAFLD is so high that we need both prevention and treatment tools,” Dr. Krag said. “Change to lifestyle is a ‘no-brainer’ and costs governments very little. For the sake of our young people, we need to take this very seriously. At a political level, we can easily implement this, for example, by banning junk food advertisements, but also educating young people and their families. Good drugs will also help.”
NAFLD: The liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes
About 25%-30% of the global population have NAFLD, and 3%-5% have NASH. Dr. Younossi highlighted that the U.S. transplant database shows that NAFLD was the second indication for all liver transplants in the country. NAFLD also was a leading cause of liver transplants for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
There are around two billion cases of chronic liver disease globally, he said. He noted that over time, there has been an increase in all kinds of liver diseases, as reflected in the annual percent change.
“The global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes is driving the rise in NAFLD, but even among lean people, the prevalence of NAFLD is around 9%,” Dr. Younossi said. “Alongside the eye and kidney complications of diabetes, this is the liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes.”
To assess global liver disease and death, Dr. Younossi and his colleagues turned to the Global Burden of Disease Study, which gathered data from around 7,000 investigators located across 22 different regions of the world, comprising 156 countries.
They calculated the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) in relation to liver cancer and chronic liver disease, including the APC. They linked the data to changes in four liver diseases: NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B infection, and hepatitis C infection.
The cases of NAFLD reported in the study had been diagnosed by ultrasound or other imaging. Importantly, the prevalence of NAFLD was adjusted for alcohol use in the various national populations, explained Dr. Younossi.
In 2019, they reported that globally, the overall prevalence of liver disease reached 1.69 billion (liver cancer, 0.04%; chronic liver disease, 99.96%), with an incidence of 2.59 million (liver cancer, 20.7%; chronic liver disease, 79.3%), mortality of 1.95 million (liver cancer, 24.8%; chronic liver disease, 75.3%), and DALYs of 58.7 million (liver cancer, 21.3%; chronic liver disease, 78.7%).
Between 2009 and 2019, deaths from liver cancer rose by 27.2%, and deaths from chronic liver disease rose by 10.6%. DALYs from liver cancer rose by 21.9%, and DALYs from chronic liver disease were up by 5.1%.
In contrast to the increase in liver cancer deaths, deaths from chronic liver disease decreased (APC, –0.18%). The decrease was driven by a decrease in hepatitis B (APC, –1.83%). APCs for hepatitis C (+0.37%), alcoholic liver disease (+0.45%), and NAFLD (+1.33%) increased.
“The burden of hepatitis B–related mortality has decreased because we have been so good at vaccinating people,” Dr. Younossi remarked.
NAFLD ‘exploding’ in Middle East, North Africa, and East Asia
The increase in NAFLD has been seen in all regions of the world, but a breakdown by region shows that NAFLD is primarily “exploding” with highest prevalence and mortality in the Middle East (mostly Egypt, Iran, and Turkey), North Africa, and East Asia, said Dr. Younossi. In addition, there are large increases in the West and South America.
“We knew that the prevalence was high in the Middle East, but we now know that mortality is also high, so we are connecting these data,” said Dr. Younossi.
Awareness lacking
Dr. Younossi pressed the fact that awareness among the general population, primary care providers, and policymakers is very low. “From my perspective, raising awareness of NAFLD is the number one priority, and that is the value of this study.”
He added that more people will become aware as testing becomes more manageable.
“There are some noninvasive tests being developed, so in the future, we won’t have to do liver biopsies to diagnose these patients,” he said. “Currently, there are some excellent treatments being developed.”
“The WHO [World Health Organization] does not mention NAFLD as an important noncommunicable disease, and this too has to change,” Dr. Younossi added.
Dr. Younossi has received research funds and/or has consulted for Abbott, Allergan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Krag has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Around the world, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has driven an increase in deaths from liver cancer over the past decade, overtaking alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, according to an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
A global rise in liver cancer deaths and chronic liver disease reflects changes in underlying health patterns, said Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor and chair, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., who presented the analysis at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“NAFLD and NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] are rapidly becoming the main causes of cirrhosis and liver cancer in the world,” Dr. Younossi told this news organization. “We have known about the increasing prevalence for some time, but now the outcomes in terms of mortality are catching up,” he said.
“The bottom line of this study is that the burden of this disease [NAFLD] is going up, and it will be the most important disease of the next decade or so,” he said, adding that “the largest annual percentage increase in rates of mortality from liver cancer or chronic liver disease cirrhosis is related to NAFLD.”
Specifically, during the decade of 2009-2019, the annual percent change (APC) of +1.33% in the global liver cancer death rate was driven by the fact that the APC for NAFLD was +2.47%. By comparison, the APC for alcoholic liver disease was +1.91%; for hepatitis B, the APC was +0.21%; and for hepatitis C, the APC was +1.12%.
Aleksander Krag, MD, PhD, professor and senior consultant of hepatology and director of Odense Liver Research Centre at SDU and Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who chaired the session in which this presentation was a part, acknowledged the importance of recognizing the contribution of NAFLD to liver cancer mortality.
“Liver diseases are on the rise. They are the fastest rising cause of death in the United Kingdom, faster than heart disease and other cancers. NAFLD in particular is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer, and the leading cause in France and the United States,” he remarked.
Dr. Krag also highlighted the costs of disease management.
“Managing fatty liver disease in Europe is estimated at €35 billion in direct health care, so we need to do something now,” he stressed.
“The global burden of NAFLD is so high that we need both prevention and treatment tools,” Dr. Krag said. “Change to lifestyle is a ‘no-brainer’ and costs governments very little. For the sake of our young people, we need to take this very seriously. At a political level, we can easily implement this, for example, by banning junk food advertisements, but also educating young people and their families. Good drugs will also help.”
NAFLD: The liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes
About 25%-30% of the global population have NAFLD, and 3%-5% have NASH. Dr. Younossi highlighted that the U.S. transplant database shows that NAFLD was the second indication for all liver transplants in the country. NAFLD also was a leading cause of liver transplants for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
There are around two billion cases of chronic liver disease globally, he said. He noted that over time, there has been an increase in all kinds of liver diseases, as reflected in the annual percent change.
“The global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes is driving the rise in NAFLD, but even among lean people, the prevalence of NAFLD is around 9%,” Dr. Younossi said. “Alongside the eye and kidney complications of diabetes, this is the liver manifestation of type 2 diabetes.”
To assess global liver disease and death, Dr. Younossi and his colleagues turned to the Global Burden of Disease Study, which gathered data from around 7,000 investigators located across 22 different regions of the world, comprising 156 countries.
They calculated the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) in relation to liver cancer and chronic liver disease, including the APC. They linked the data to changes in four liver diseases: NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B infection, and hepatitis C infection.
The cases of NAFLD reported in the study had been diagnosed by ultrasound or other imaging. Importantly, the prevalence of NAFLD was adjusted for alcohol use in the various national populations, explained Dr. Younossi.
In 2019, they reported that globally, the overall prevalence of liver disease reached 1.69 billion (liver cancer, 0.04%; chronic liver disease, 99.96%), with an incidence of 2.59 million (liver cancer, 20.7%; chronic liver disease, 79.3%), mortality of 1.95 million (liver cancer, 24.8%; chronic liver disease, 75.3%), and DALYs of 58.7 million (liver cancer, 21.3%; chronic liver disease, 78.7%).
Between 2009 and 2019, deaths from liver cancer rose by 27.2%, and deaths from chronic liver disease rose by 10.6%. DALYs from liver cancer rose by 21.9%, and DALYs from chronic liver disease were up by 5.1%.
In contrast to the increase in liver cancer deaths, deaths from chronic liver disease decreased (APC, –0.18%). The decrease was driven by a decrease in hepatitis B (APC, –1.83%). APCs for hepatitis C (+0.37%), alcoholic liver disease (+0.45%), and NAFLD (+1.33%) increased.
“The burden of hepatitis B–related mortality has decreased because we have been so good at vaccinating people,” Dr. Younossi remarked.
NAFLD ‘exploding’ in Middle East, North Africa, and East Asia
The increase in NAFLD has been seen in all regions of the world, but a breakdown by region shows that NAFLD is primarily “exploding” with highest prevalence and mortality in the Middle East (mostly Egypt, Iran, and Turkey), North Africa, and East Asia, said Dr. Younossi. In addition, there are large increases in the West and South America.
“We knew that the prevalence was high in the Middle East, but we now know that mortality is also high, so we are connecting these data,” said Dr. Younossi.
Awareness lacking
Dr. Younossi pressed the fact that awareness among the general population, primary care providers, and policymakers is very low. “From my perspective, raising awareness of NAFLD is the number one priority, and that is the value of this study.”
He added that more people will become aware as testing becomes more manageable.
“There are some noninvasive tests being developed, so in the future, we won’t have to do liver biopsies to diagnose these patients,” he said. “Currently, there are some excellent treatments being developed.”
“The WHO [World Health Organization] does not mention NAFLD as an important noncommunicable disease, and this too has to change,” Dr. Younossi added.
Dr. Younossi has received research funds and/or has consulted for Abbott, Allergan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Krag has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022
Novel liver-targeting drug offers hope for AAT deficiency
LONDON – The novel liver-targeting agent fazirsiran has fared well in a small, but significant, study looking at its ability to improve liver histology in adults with alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency.
Not only were serum and liver levels of the aberrant Z-AAT protein decreased, but also reductions in key liver enzymes were observed.
AAT is “a greatly understudied disease,” said study investigator Pavel Strnad, MD, who presented the results of the phase 2 AROAAT-2002 study at a meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“We have a great candidate drug, but we will only be able to bring this drug into the clinic when we understand the disease much better, and for this I would like to ask all of you for your support,” he said to delegates at the meeting.
There is currently no pharmacological treatment for AAT, observed Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, who chaired the late-breaker session during which the study findings were presented.
“It is a rare disease, but it really does affect the patients who have it. So it would be great to have a therapeutic solution for these patients,” said Dr. Tsochatzis in an interview.
Dr. Tsochatzis, who is professor of hepatology and Consultant Hepatologist at the UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital in London, noted that AAT was associated with liver impairment, fibrosis and cirrhosis, and ultimately end-stage liver disease in which the only option for some patients would be a liver transplant.
“It depends on the stage; many patients are not at the stage that they require a liver transplant,” he said. “For those with significant liver disease, not yet at the cirrhosis stage, you might be able to intervene early and prevent them from progressing to needing a liver transplant.”
Dr. Tsochatzis speculated: “If this becomes an approved treatment, it is a breakthrough for patients.”
New hope for AAT deficiency
There is still a long way to go before fazirsiran is anywhere near ready for clinical use, but the early data presented by Dr. Strnad offer a glimpse that a treatment could be on the horizon.
Naturally occurring AAT is produced in the liver and is thought to play a role in protecting against lung damage via its antiprotease activity. However, mutations in the SERPINA1 gene coding for the AAT protein leads to loss-of-function pulmonary disease and gain-of-function liver disease.
“The PI ZZ [proteinase inhibitor ZZ] genotype occurs in about one in 2,500 to 3,500 Caucasians, so actually is pretty common, and a third of them may actually have a clinically significant liver fibrosis,” said Dr. Strnad.
As levels of Z-AAT accumulate in the liver this “presumably causes the liver toxicity,” he observed. So, the thinking is that stopping the production of this mutant protein might help to reduce liver damage and allow the liver to regenerate and repair itself.
Study details
To test out this theory, a phase 2, open-label study was performed in 16 patients with confirmed AAT deficiency, all of whom had the PI ZZ genotype.
Eight patients were treated with fazirsiran, also known as ARO-AAT, for 24 weeks (cohorts 1 and 1b), while the other eight were treated for 48 weeks (cohort 2); cohort 1 (n = 4) and cohort 2 (n = 8) received 200 mg, while cohort 1b (n = 4), which was added during the trial to evaluate dose response, received 100 mg. In all cases, fazirsiran was given as a subcutaneous injection on day 1, day 4, and then every 12 weeks. All patients had biopsies at baseline, then at either 24 weeks (cohorts 1/1b) or 48 weeks (cohort 2).
“We saw a dramatic reduction in Z-AAT both in serum and in liver biopsies,” Dr. Strnad reported. Indeed, reductions in Z-AAT were around 80%-88%, he said, with a median reduction of 83% at week 24 or 48 according to the published paper.
To illustrate the clear results, Dr. Strand showed a sample biopsy slide where globules of Z-AAT present at the initial assessment were “virtually gone after 48 weeks of treatment.”
“The change in the serum and hepatic Z-AAT levels translated into improvement in liver function tests,” said Dr. Strnad.
Alanine aminotransferase levels were normalized in all patients and there was “marked improvement” in gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) with the 200-mg dose of fazirsiran. Substantial changes in liver stiffness were recorded with the higher dose, –18% at 24 weeks and –15% at 48 weeks. There were also reductions in serum Pro-C3 of –36% and –17% at 52 weeks.
“Histological changes showed an improvement in liver inflammation and hepatocyte cell death in most of the patients,” Dr. Strnad said. He also noted that there were multiple cases where there was no change and a few where there was a deterioration.
Liver fibrosis was improved in seven of 12 patients given the highest dose of fazirsiran; however, there was no change in three patients and a worsening of 1 point or more in two patients. None of the three patients with evaluable biopsies who received 100 mg showed regression of fibrosis.
Stopping or rolling back fibrosis will be the final goal of proving clinical benefit in liver disease associated with AAT, Dr. Strnad and coinvestigators observe in their published paper, and while the changes seen so far with fazirsiran may not be uniform, they appear to be in the right direction.
Safety findings
”We didn’t see any drug discontinuation, dose interruption, or premature study withdrawals,” said Dr. Strnad.
“We had four different SAE [serious adverse events] which were kind of all over the place and did not seem to be related to treatment.” Those SAEs included viral myocarditis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection, diverticulitis, dyspnea in a subject with a history of lung disease, and vestibular neuronitis after COVID-19 vaccination.
No significant safety signals were seen regarding lung function. Time will of course tell, he said in response to a question, but “our hope, our hypothesis, is that this will not change lung function dramatically.
“I would not expect any major things over a few years. Of course, whether this can lead to something over 20 years it is difficult to say.”
The current experience with fazirsiran looks good so far, but placebo-controlled, larger and longer studies are needed.
The study was funded by Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Strnad was an investigator in the study and acknowledged receipt of research funding via his institution from the company. Dr. Strnad also acknowledged paid and unpaid relationships with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Alpha1 Deutschland, Alpha1 Global, CSL Behring, Grifols Biologicals, Ono Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda California. Dr. Tsochatzis, chaired the late-breaker session at ILC 2022 during which the study findings were presented, was not connected to the study, and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
LONDON – The novel liver-targeting agent fazirsiran has fared well in a small, but significant, study looking at its ability to improve liver histology in adults with alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency.
Not only were serum and liver levels of the aberrant Z-AAT protein decreased, but also reductions in key liver enzymes were observed.
AAT is “a greatly understudied disease,” said study investigator Pavel Strnad, MD, who presented the results of the phase 2 AROAAT-2002 study at a meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“We have a great candidate drug, but we will only be able to bring this drug into the clinic when we understand the disease much better, and for this I would like to ask all of you for your support,” he said to delegates at the meeting.
There is currently no pharmacological treatment for AAT, observed Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, who chaired the late-breaker session during which the study findings were presented.
“It is a rare disease, but it really does affect the patients who have it. So it would be great to have a therapeutic solution for these patients,” said Dr. Tsochatzis in an interview.
Dr. Tsochatzis, who is professor of hepatology and Consultant Hepatologist at the UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital in London, noted that AAT was associated with liver impairment, fibrosis and cirrhosis, and ultimately end-stage liver disease in which the only option for some patients would be a liver transplant.
“It depends on the stage; many patients are not at the stage that they require a liver transplant,” he said. “For those with significant liver disease, not yet at the cirrhosis stage, you might be able to intervene early and prevent them from progressing to needing a liver transplant.”
Dr. Tsochatzis speculated: “If this becomes an approved treatment, it is a breakthrough for patients.”
New hope for AAT deficiency
There is still a long way to go before fazirsiran is anywhere near ready for clinical use, but the early data presented by Dr. Strnad offer a glimpse that a treatment could be on the horizon.
Naturally occurring AAT is produced in the liver and is thought to play a role in protecting against lung damage via its antiprotease activity. However, mutations in the SERPINA1 gene coding for the AAT protein leads to loss-of-function pulmonary disease and gain-of-function liver disease.
“The PI ZZ [proteinase inhibitor ZZ] genotype occurs in about one in 2,500 to 3,500 Caucasians, so actually is pretty common, and a third of them may actually have a clinically significant liver fibrosis,” said Dr. Strnad.
As levels of Z-AAT accumulate in the liver this “presumably causes the liver toxicity,” he observed. So, the thinking is that stopping the production of this mutant protein might help to reduce liver damage and allow the liver to regenerate and repair itself.
Study details
To test out this theory, a phase 2, open-label study was performed in 16 patients with confirmed AAT deficiency, all of whom had the PI ZZ genotype.
Eight patients were treated with fazirsiran, also known as ARO-AAT, for 24 weeks (cohorts 1 and 1b), while the other eight were treated for 48 weeks (cohort 2); cohort 1 (n = 4) and cohort 2 (n = 8) received 200 mg, while cohort 1b (n = 4), which was added during the trial to evaluate dose response, received 100 mg. In all cases, fazirsiran was given as a subcutaneous injection on day 1, day 4, and then every 12 weeks. All patients had biopsies at baseline, then at either 24 weeks (cohorts 1/1b) or 48 weeks (cohort 2).
“We saw a dramatic reduction in Z-AAT both in serum and in liver biopsies,” Dr. Strnad reported. Indeed, reductions in Z-AAT were around 80%-88%, he said, with a median reduction of 83% at week 24 or 48 according to the published paper.
To illustrate the clear results, Dr. Strand showed a sample biopsy slide where globules of Z-AAT present at the initial assessment were “virtually gone after 48 weeks of treatment.”
“The change in the serum and hepatic Z-AAT levels translated into improvement in liver function tests,” said Dr. Strnad.
Alanine aminotransferase levels were normalized in all patients and there was “marked improvement” in gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) with the 200-mg dose of fazirsiran. Substantial changes in liver stiffness were recorded with the higher dose, –18% at 24 weeks and –15% at 48 weeks. There were also reductions in serum Pro-C3 of –36% and –17% at 52 weeks.
“Histological changes showed an improvement in liver inflammation and hepatocyte cell death in most of the patients,” Dr. Strnad said. He also noted that there were multiple cases where there was no change and a few where there was a deterioration.
Liver fibrosis was improved in seven of 12 patients given the highest dose of fazirsiran; however, there was no change in three patients and a worsening of 1 point or more in two patients. None of the three patients with evaluable biopsies who received 100 mg showed regression of fibrosis.
Stopping or rolling back fibrosis will be the final goal of proving clinical benefit in liver disease associated with AAT, Dr. Strnad and coinvestigators observe in their published paper, and while the changes seen so far with fazirsiran may not be uniform, they appear to be in the right direction.
Safety findings
”We didn’t see any drug discontinuation, dose interruption, or premature study withdrawals,” said Dr. Strnad.
“We had four different SAE [serious adverse events] which were kind of all over the place and did not seem to be related to treatment.” Those SAEs included viral myocarditis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection, diverticulitis, dyspnea in a subject with a history of lung disease, and vestibular neuronitis after COVID-19 vaccination.
No significant safety signals were seen regarding lung function. Time will of course tell, he said in response to a question, but “our hope, our hypothesis, is that this will not change lung function dramatically.
“I would not expect any major things over a few years. Of course, whether this can lead to something over 20 years it is difficult to say.”
The current experience with fazirsiran looks good so far, but placebo-controlled, larger and longer studies are needed.
The study was funded by Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Strnad was an investigator in the study and acknowledged receipt of research funding via his institution from the company. Dr. Strnad also acknowledged paid and unpaid relationships with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Alpha1 Deutschland, Alpha1 Global, CSL Behring, Grifols Biologicals, Ono Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda California. Dr. Tsochatzis, chaired the late-breaker session at ILC 2022 during which the study findings were presented, was not connected to the study, and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
LONDON – The novel liver-targeting agent fazirsiran has fared well in a small, but significant, study looking at its ability to improve liver histology in adults with alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency.
Not only were serum and liver levels of the aberrant Z-AAT protein decreased, but also reductions in key liver enzymes were observed.
AAT is “a greatly understudied disease,” said study investigator Pavel Strnad, MD, who presented the results of the phase 2 AROAAT-2002 study at a meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“We have a great candidate drug, but we will only be able to bring this drug into the clinic when we understand the disease much better, and for this I would like to ask all of you for your support,” he said to delegates at the meeting.
There is currently no pharmacological treatment for AAT, observed Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, who chaired the late-breaker session during which the study findings were presented.
“It is a rare disease, but it really does affect the patients who have it. So it would be great to have a therapeutic solution for these patients,” said Dr. Tsochatzis in an interview.
Dr. Tsochatzis, who is professor of hepatology and Consultant Hepatologist at the UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital in London, noted that AAT was associated with liver impairment, fibrosis and cirrhosis, and ultimately end-stage liver disease in which the only option for some patients would be a liver transplant.
“It depends on the stage; many patients are not at the stage that they require a liver transplant,” he said. “For those with significant liver disease, not yet at the cirrhosis stage, you might be able to intervene early and prevent them from progressing to needing a liver transplant.”
Dr. Tsochatzis speculated: “If this becomes an approved treatment, it is a breakthrough for patients.”
New hope for AAT deficiency
There is still a long way to go before fazirsiran is anywhere near ready for clinical use, but the early data presented by Dr. Strnad offer a glimpse that a treatment could be on the horizon.
Naturally occurring AAT is produced in the liver and is thought to play a role in protecting against lung damage via its antiprotease activity. However, mutations in the SERPINA1 gene coding for the AAT protein leads to loss-of-function pulmonary disease and gain-of-function liver disease.
“The PI ZZ [proteinase inhibitor ZZ] genotype occurs in about one in 2,500 to 3,500 Caucasians, so actually is pretty common, and a third of them may actually have a clinically significant liver fibrosis,” said Dr. Strnad.
As levels of Z-AAT accumulate in the liver this “presumably causes the liver toxicity,” he observed. So, the thinking is that stopping the production of this mutant protein might help to reduce liver damage and allow the liver to regenerate and repair itself.
Study details
To test out this theory, a phase 2, open-label study was performed in 16 patients with confirmed AAT deficiency, all of whom had the PI ZZ genotype.
Eight patients were treated with fazirsiran, also known as ARO-AAT, for 24 weeks (cohorts 1 and 1b), while the other eight were treated for 48 weeks (cohort 2); cohort 1 (n = 4) and cohort 2 (n = 8) received 200 mg, while cohort 1b (n = 4), which was added during the trial to evaluate dose response, received 100 mg. In all cases, fazirsiran was given as a subcutaneous injection on day 1, day 4, and then every 12 weeks. All patients had biopsies at baseline, then at either 24 weeks (cohorts 1/1b) or 48 weeks (cohort 2).
“We saw a dramatic reduction in Z-AAT both in serum and in liver biopsies,” Dr. Strnad reported. Indeed, reductions in Z-AAT were around 80%-88%, he said, with a median reduction of 83% at week 24 or 48 according to the published paper.
To illustrate the clear results, Dr. Strand showed a sample biopsy slide where globules of Z-AAT present at the initial assessment were “virtually gone after 48 weeks of treatment.”
“The change in the serum and hepatic Z-AAT levels translated into improvement in liver function tests,” said Dr. Strnad.
Alanine aminotransferase levels were normalized in all patients and there was “marked improvement” in gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) with the 200-mg dose of fazirsiran. Substantial changes in liver stiffness were recorded with the higher dose, –18% at 24 weeks and –15% at 48 weeks. There were also reductions in serum Pro-C3 of –36% and –17% at 52 weeks.
“Histological changes showed an improvement in liver inflammation and hepatocyte cell death in most of the patients,” Dr. Strnad said. He also noted that there were multiple cases where there was no change and a few where there was a deterioration.
Liver fibrosis was improved in seven of 12 patients given the highest dose of fazirsiran; however, there was no change in three patients and a worsening of 1 point or more in two patients. None of the three patients with evaluable biopsies who received 100 mg showed regression of fibrosis.
Stopping or rolling back fibrosis will be the final goal of proving clinical benefit in liver disease associated with AAT, Dr. Strnad and coinvestigators observe in their published paper, and while the changes seen so far with fazirsiran may not be uniform, they appear to be in the right direction.
Safety findings
”We didn’t see any drug discontinuation, dose interruption, or premature study withdrawals,” said Dr. Strnad.
“We had four different SAE [serious adverse events] which were kind of all over the place and did not seem to be related to treatment.” Those SAEs included viral myocarditis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection, diverticulitis, dyspnea in a subject with a history of lung disease, and vestibular neuronitis after COVID-19 vaccination.
No significant safety signals were seen regarding lung function. Time will of course tell, he said in response to a question, but “our hope, our hypothesis, is that this will not change lung function dramatically.
“I would not expect any major things over a few years. Of course, whether this can lead to something over 20 years it is difficult to say.”
The current experience with fazirsiran looks good so far, but placebo-controlled, larger and longer studies are needed.
The study was funded by Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Strnad was an investigator in the study and acknowledged receipt of research funding via his institution from the company. Dr. Strnad also acknowledged paid and unpaid relationships with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Alpha1 Deutschland, Alpha1 Global, CSL Behring, Grifols Biologicals, Ono Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda California. Dr. Tsochatzis, chaired the late-breaker session at ILC 2022 during which the study findings were presented, was not connected to the study, and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
AT ILC 2022
Are pain meds the only option for chronic pain in cirrhosis?
Pain is common in patients with cirrhosis, and its management presents significant challenges to health care providers, such as worries about GI bleeding, renal injury, falls, and hepatic encephalopathy.
To address those issues, researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, authored a review, published in Hepatology, that describes the pain syndromes experienced by patients, as well as pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical treatment options.
“I think it’s a very pragmatic approach to a very common problem. Health care providers are concerned about prescribing analgesia for people with cirrhosis for a number of different reasons. One of them is acetaminophen can be toxic to the liver, but generally only in pretty large doses. It’s actually a pretty good option in a dose of less than about 2 g/day because it doesn’t have some of the side effects that other painkillers such as the NSAIDs have. It doesn’t irritate the stomach, and it doesn’t affect kidney function,” said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the review. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases at the University of Miami.
He appreciated the discussion of both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions, including diet and psychological interventions. “And I think it provides a useful overview of the pharmacological agents we can use in patients with cirrhosis, so I think it’s a very useful contribution to the literature,” said Dr. Martin.
An estimated 40%-79% of cirrhosis patients experience chronic pain, and it can be a key factor in worsening functional status and quality of life. The authors noted that, although recent practice guidance had recommended involving palliative care providers, psychiatry, and physical therapy in for patients with decompensated cirrhosis, this is not always feasible. The authors also pointed out that there are different pain phenotypes in cirrhosis, and these require different management strategies.
They described three mechanistic categories of chronic pain: Nociceptive pain involves tissue damage and inflammation; neuropathic pain results from nerve damage; and nociplastic pain describes situations in which there is no evidence of tissue or nerve damage, but clinical or psychophysical signs suggest changes to nociception.
The different pain types are best assessed using different tools: The 2016 Fibromyalgia Survey Criteria is useful for nociplastic pain, the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire and painDETECT can be useful for neuropathic pain, and a physical examination can pinpoint nociceptive pain.
When managing chronic pain, the initial patient workup should include a complete evaluation of the location, quality, and severity of pain, along with any functional interference or associated symptoms like fatigue, mood disturbance, or sensory sensitivity. One option is to use a body map to assess how widespread the pain is. Multisite pain is often a signal that it could be nociplastic. Any comorbid psychiatric disorders should be identified and treated.
The first treatment option for any pain should be self-directed, nonpharmacologic interventions. This is because most analgesics are only modestly effective in the treatment of chronic pain, leading to improvement in only about one in three cases, the authors noted. Opioids have poor efficacy against chronic pain, particularly nociplastic pain, which may even be worsened by opioid use.
Although there is evidence that patients are motivated to seek out nonpharmacologic pain treatment, they have reported frustration by a dearth of simple, evidence-based therapies. The authors noted that digital self-management tools for pain have been developed, including their own PainGuide, which focuses on exercise and behavioral interventions for chronic pain. Other nonpharmacologic approaches include diet modification and sleep hygiene. Patients should be allowed to choose the approach that interests them most, with the physician emphasizing the importance of self-directed management.
Pharmacologic therapy may be added to these approaches, but they have limited utility and are associated with adverse effects. For nociceptive pain, topical NSAIDs like diclofenac gel can be used, as can acetaminophen (500 mg every 6 hours, maximum dose of 2 g/day). Opioids can be employed for short-term treatment of acute pain (for example: hydromorphone 1 mg every 6 hours as needed, oxycodone 2.5 mg by mouth every 6-8 hours as needed, or fentanyl patch in select patients). Tricyclic antidepressants may be used for multiple symptoms or neuropathic pain, but with caution. Neuropathic pain, as well as associated depression or fatigue, can be treated with low-dose serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, though there is a small risk of hepatotoxicity. Neuropathic pain, sleep difficulties, or anxiety can be treated with gabapentin at low starting doses (for example, 300 mg/day) or pregabalin (for example, 50 mg twice a day). Lidocaine patches are an option for peripheral neuropathic pain or postherpetic neuralgia, and topical capsaicin may be used for peripheral neuropathic pain.
“Since all pain types can co-occur, interventions to address nociplastic pain may be broadly therapeutic,” the authors concluded. “The treatment of nociplastic pain emphasizes nonpharmacologic management, including self-management techniques addressing mood, cognitions, behaviors, sleep, and environment. Future research should continue to explore methods of pain phenotyping, as well as self-management therapies, including implementation tools.”
The authors and Dr. Martin reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Pain is common in patients with cirrhosis, and its management presents significant challenges to health care providers, such as worries about GI bleeding, renal injury, falls, and hepatic encephalopathy.
To address those issues, researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, authored a review, published in Hepatology, that describes the pain syndromes experienced by patients, as well as pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical treatment options.
“I think it’s a very pragmatic approach to a very common problem. Health care providers are concerned about prescribing analgesia for people with cirrhosis for a number of different reasons. One of them is acetaminophen can be toxic to the liver, but generally only in pretty large doses. It’s actually a pretty good option in a dose of less than about 2 g/day because it doesn’t have some of the side effects that other painkillers such as the NSAIDs have. It doesn’t irritate the stomach, and it doesn’t affect kidney function,” said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the review. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases at the University of Miami.
He appreciated the discussion of both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions, including diet and psychological interventions. “And I think it provides a useful overview of the pharmacological agents we can use in patients with cirrhosis, so I think it’s a very useful contribution to the literature,” said Dr. Martin.
An estimated 40%-79% of cirrhosis patients experience chronic pain, and it can be a key factor in worsening functional status and quality of life. The authors noted that, although recent practice guidance had recommended involving palliative care providers, psychiatry, and physical therapy in for patients with decompensated cirrhosis, this is not always feasible. The authors also pointed out that there are different pain phenotypes in cirrhosis, and these require different management strategies.
They described three mechanistic categories of chronic pain: Nociceptive pain involves tissue damage and inflammation; neuropathic pain results from nerve damage; and nociplastic pain describes situations in which there is no evidence of tissue or nerve damage, but clinical or psychophysical signs suggest changes to nociception.
The different pain types are best assessed using different tools: The 2016 Fibromyalgia Survey Criteria is useful for nociplastic pain, the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire and painDETECT can be useful for neuropathic pain, and a physical examination can pinpoint nociceptive pain.
When managing chronic pain, the initial patient workup should include a complete evaluation of the location, quality, and severity of pain, along with any functional interference or associated symptoms like fatigue, mood disturbance, or sensory sensitivity. One option is to use a body map to assess how widespread the pain is. Multisite pain is often a signal that it could be nociplastic. Any comorbid psychiatric disorders should be identified and treated.
The first treatment option for any pain should be self-directed, nonpharmacologic interventions. This is because most analgesics are only modestly effective in the treatment of chronic pain, leading to improvement in only about one in three cases, the authors noted. Opioids have poor efficacy against chronic pain, particularly nociplastic pain, which may even be worsened by opioid use.
Although there is evidence that patients are motivated to seek out nonpharmacologic pain treatment, they have reported frustration by a dearth of simple, evidence-based therapies. The authors noted that digital self-management tools for pain have been developed, including their own PainGuide, which focuses on exercise and behavioral interventions for chronic pain. Other nonpharmacologic approaches include diet modification and sleep hygiene. Patients should be allowed to choose the approach that interests them most, with the physician emphasizing the importance of self-directed management.
Pharmacologic therapy may be added to these approaches, but they have limited utility and are associated with adverse effects. For nociceptive pain, topical NSAIDs like diclofenac gel can be used, as can acetaminophen (500 mg every 6 hours, maximum dose of 2 g/day). Opioids can be employed for short-term treatment of acute pain (for example: hydromorphone 1 mg every 6 hours as needed, oxycodone 2.5 mg by mouth every 6-8 hours as needed, or fentanyl patch in select patients). Tricyclic antidepressants may be used for multiple symptoms or neuropathic pain, but with caution. Neuropathic pain, as well as associated depression or fatigue, can be treated with low-dose serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, though there is a small risk of hepatotoxicity. Neuropathic pain, sleep difficulties, or anxiety can be treated with gabapentin at low starting doses (for example, 300 mg/day) or pregabalin (for example, 50 mg twice a day). Lidocaine patches are an option for peripheral neuropathic pain or postherpetic neuralgia, and topical capsaicin may be used for peripheral neuropathic pain.
“Since all pain types can co-occur, interventions to address nociplastic pain may be broadly therapeutic,” the authors concluded. “The treatment of nociplastic pain emphasizes nonpharmacologic management, including self-management techniques addressing mood, cognitions, behaviors, sleep, and environment. Future research should continue to explore methods of pain phenotyping, as well as self-management therapies, including implementation tools.”
The authors and Dr. Martin reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Pain is common in patients with cirrhosis, and its management presents significant challenges to health care providers, such as worries about GI bleeding, renal injury, falls, and hepatic encephalopathy.
To address those issues, researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, authored a review, published in Hepatology, that describes the pain syndromes experienced by patients, as well as pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical treatment options.
“I think it’s a very pragmatic approach to a very common problem. Health care providers are concerned about prescribing analgesia for people with cirrhosis for a number of different reasons. One of them is acetaminophen can be toxic to the liver, but generally only in pretty large doses. It’s actually a pretty good option in a dose of less than about 2 g/day because it doesn’t have some of the side effects that other painkillers such as the NSAIDs have. It doesn’t irritate the stomach, and it doesn’t affect kidney function,” said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the review. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases at the University of Miami.
He appreciated the discussion of both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions, including diet and psychological interventions. “And I think it provides a useful overview of the pharmacological agents we can use in patients with cirrhosis, so I think it’s a very useful contribution to the literature,” said Dr. Martin.
An estimated 40%-79% of cirrhosis patients experience chronic pain, and it can be a key factor in worsening functional status and quality of life. The authors noted that, although recent practice guidance had recommended involving palliative care providers, psychiatry, and physical therapy in for patients with decompensated cirrhosis, this is not always feasible. The authors also pointed out that there are different pain phenotypes in cirrhosis, and these require different management strategies.
They described three mechanistic categories of chronic pain: Nociceptive pain involves tissue damage and inflammation; neuropathic pain results from nerve damage; and nociplastic pain describes situations in which there is no evidence of tissue or nerve damage, but clinical or psychophysical signs suggest changes to nociception.
The different pain types are best assessed using different tools: The 2016 Fibromyalgia Survey Criteria is useful for nociplastic pain, the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire and painDETECT can be useful for neuropathic pain, and a physical examination can pinpoint nociceptive pain.
When managing chronic pain, the initial patient workup should include a complete evaluation of the location, quality, and severity of pain, along with any functional interference or associated symptoms like fatigue, mood disturbance, or sensory sensitivity. One option is to use a body map to assess how widespread the pain is. Multisite pain is often a signal that it could be nociplastic. Any comorbid psychiatric disorders should be identified and treated.
The first treatment option for any pain should be self-directed, nonpharmacologic interventions. This is because most analgesics are only modestly effective in the treatment of chronic pain, leading to improvement in only about one in three cases, the authors noted. Opioids have poor efficacy against chronic pain, particularly nociplastic pain, which may even be worsened by opioid use.
Although there is evidence that patients are motivated to seek out nonpharmacologic pain treatment, they have reported frustration by a dearth of simple, evidence-based therapies. The authors noted that digital self-management tools for pain have been developed, including their own PainGuide, which focuses on exercise and behavioral interventions for chronic pain. Other nonpharmacologic approaches include diet modification and sleep hygiene. Patients should be allowed to choose the approach that interests them most, with the physician emphasizing the importance of self-directed management.
Pharmacologic therapy may be added to these approaches, but they have limited utility and are associated with adverse effects. For nociceptive pain, topical NSAIDs like diclofenac gel can be used, as can acetaminophen (500 mg every 6 hours, maximum dose of 2 g/day). Opioids can be employed for short-term treatment of acute pain (for example: hydromorphone 1 mg every 6 hours as needed, oxycodone 2.5 mg by mouth every 6-8 hours as needed, or fentanyl patch in select patients). Tricyclic antidepressants may be used for multiple symptoms or neuropathic pain, but with caution. Neuropathic pain, as well as associated depression or fatigue, can be treated with low-dose serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, though there is a small risk of hepatotoxicity. Neuropathic pain, sleep difficulties, or anxiety can be treated with gabapentin at low starting doses (for example, 300 mg/day) or pregabalin (for example, 50 mg twice a day). Lidocaine patches are an option for peripheral neuropathic pain or postherpetic neuralgia, and topical capsaicin may be used for peripheral neuropathic pain.
“Since all pain types can co-occur, interventions to address nociplastic pain may be broadly therapeutic,” the authors concluded. “The treatment of nociplastic pain emphasizes nonpharmacologic management, including self-management techniques addressing mood, cognitions, behaviors, sleep, and environment. Future research should continue to explore methods of pain phenotyping, as well as self-management therapies, including implementation tools.”
The authors and Dr. Martin reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM HEPATOLOGY
Liver-related telehealth faces tech barriers
Telemedicine for patients with liver disease has made progress in recent years, but some key hurdles remain. Strategies that rely on patient ownership of mobile devices or reliable internet access will likely miss patients who have the greatest need for remote access.
This is one of the conclusions from a county-by-county study of access to liver specialty care and mortality, using data drawn from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiological Research (WONDER). The study was led by Jacqueline B. Henson, MD, of the Division of Gastroenterology, department of medicine, Duke University, Durham, N.C., and published in Hepatology.
Low-access areas
“Ultimately, no single telehealth strategy will be successful in all areas, and these will need to be tailored at the local and state level,” the authors wrote. “They will also depend on the persistence of policy changes enacted during the pandemic which made use and reimbursement for telehealth less restrictive.”
The researchers found that 69.5% of American counties had no gastrointestinal physicians. Moreover, 41.1% of counties were more than 100 miles away from a liver transplant (LT) center; 33.7% had no GI physicians and were more than 100 miles from a LT center. These categories represented populations of 48.8 million, 53.7 million, and 17.8 million. These counties had higher poverty rates, more unemployment, and lower educational attainment than did those that had GI physicians or were closer to LT centers. Distance from LT centers was associated with higher liver-related mortality (r = 0.24; P < .001) and density of GI providers (r = –0.12; P < .001).
Reduced access to specialty care for liver disease was also associated with decreased access to technology, including cell phones, smart phones, and internet service. Among counties in the highest death quartile and lowest access to care, 35.5% of households had no computer, 43.1% had no home internet, and only 19.2% of these had internet at broadband speeds.
“Use of platforms with lower internet speed requirements and that are compatible with mobile devices may help extend access, as could partnerships with local primary care and GI clinics,” they concluded. Further work should be done at the local and state levels to better understand the optimal strategies to reach their populations of need.
Missing ‘baseline ingredients’
Commenting on the study, Nancy Reau, MD, professor of medicine and chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said that “anyone who takes care of vulnerable populations, whether elderly individuals or those who may be socioeconomically disadvantaged, realizes that we have to improve access to medical resources, and telehealth is certainly an attractive way of doing that.”
She added that a key message from the study is that attempts to improve access to disadvantaged populations, no matter how well-intentioned, are likely to provide the most benefit to those who have more resources than others. For example, not everyone has access to a smart phone or tablet: “Even if you have a tablet [or cell phone], you might have to go to the public library to get high speed internet, or you may not even have a public library. So, when something sounds like a great idea, such as expanding the academic footprint or access to integrative medicine through something like a virtual option, a lot of the individuals that you are targeting may not be able to engage,” said Dr. Reau.
For those working to expand access, it’s critical to get the perspective of underserved communities and remember that every patient is unique. Physicians may treat patients who are poor, or from disadvantaged areas, who nevertheless have successful telehealth visits. But that doesn’t mean everyone’s experience will be similar. “You can’t use those who have been successful in accessing telemedicine as an example for everyone else. Just because one person can do it doesn’t mean that everyone else can. Involving a practitioner or an advocate from the area that you’re trying to reach is imperative,” she explained.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a big push for telehealth, and it may be tempting to believe that the transition to telehealth has been smooth. This study “demonstrates in a very granular way that a large number of Americans have no access to high-speed internet, or if they do, many don’t have access to the tools that would let them engage this way. You can’t make assumptions and use them to build a product,” continued Dr. Reau.
Innovative options are needed, such as working with primary care providers in rural or disadvantaged areas to setup pop-up hot spots where e-consultations could be performed. Working directly with broadband internet providers to set up access in specific locations for telehealth, or using products like Amazon Echo Show as a portal for telehealth, can also be tried. “Think about being innovative and recognize that these areas probably don’t have the baseline ingredients we thought they had,” suggested Dr. Reau.
The authors reported having no financial support. Dr. Reau has no relevant financial disclosures.
Telemedicine for patients with liver disease has made progress in recent years, but some key hurdles remain. Strategies that rely on patient ownership of mobile devices or reliable internet access will likely miss patients who have the greatest need for remote access.
This is one of the conclusions from a county-by-county study of access to liver specialty care and mortality, using data drawn from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiological Research (WONDER). The study was led by Jacqueline B. Henson, MD, of the Division of Gastroenterology, department of medicine, Duke University, Durham, N.C., and published in Hepatology.
Low-access areas
“Ultimately, no single telehealth strategy will be successful in all areas, and these will need to be tailored at the local and state level,” the authors wrote. “They will also depend on the persistence of policy changes enacted during the pandemic which made use and reimbursement for telehealth less restrictive.”
The researchers found that 69.5% of American counties had no gastrointestinal physicians. Moreover, 41.1% of counties were more than 100 miles away from a liver transplant (LT) center; 33.7% had no GI physicians and were more than 100 miles from a LT center. These categories represented populations of 48.8 million, 53.7 million, and 17.8 million. These counties had higher poverty rates, more unemployment, and lower educational attainment than did those that had GI physicians or were closer to LT centers. Distance from LT centers was associated with higher liver-related mortality (r = 0.24; P < .001) and density of GI providers (r = –0.12; P < .001).
Reduced access to specialty care for liver disease was also associated with decreased access to technology, including cell phones, smart phones, and internet service. Among counties in the highest death quartile and lowest access to care, 35.5% of households had no computer, 43.1% had no home internet, and only 19.2% of these had internet at broadband speeds.
“Use of platforms with lower internet speed requirements and that are compatible with mobile devices may help extend access, as could partnerships with local primary care and GI clinics,” they concluded. Further work should be done at the local and state levels to better understand the optimal strategies to reach their populations of need.
Missing ‘baseline ingredients’
Commenting on the study, Nancy Reau, MD, professor of medicine and chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said that “anyone who takes care of vulnerable populations, whether elderly individuals or those who may be socioeconomically disadvantaged, realizes that we have to improve access to medical resources, and telehealth is certainly an attractive way of doing that.”
She added that a key message from the study is that attempts to improve access to disadvantaged populations, no matter how well-intentioned, are likely to provide the most benefit to those who have more resources than others. For example, not everyone has access to a smart phone or tablet: “Even if you have a tablet [or cell phone], you might have to go to the public library to get high speed internet, or you may not even have a public library. So, when something sounds like a great idea, such as expanding the academic footprint or access to integrative medicine through something like a virtual option, a lot of the individuals that you are targeting may not be able to engage,” said Dr. Reau.
For those working to expand access, it’s critical to get the perspective of underserved communities and remember that every patient is unique. Physicians may treat patients who are poor, or from disadvantaged areas, who nevertheless have successful telehealth visits. But that doesn’t mean everyone’s experience will be similar. “You can’t use those who have been successful in accessing telemedicine as an example for everyone else. Just because one person can do it doesn’t mean that everyone else can. Involving a practitioner or an advocate from the area that you’re trying to reach is imperative,” she explained.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a big push for telehealth, and it may be tempting to believe that the transition to telehealth has been smooth. This study “demonstrates in a very granular way that a large number of Americans have no access to high-speed internet, or if they do, many don’t have access to the tools that would let them engage this way. You can’t make assumptions and use them to build a product,” continued Dr. Reau.
Innovative options are needed, such as working with primary care providers in rural or disadvantaged areas to setup pop-up hot spots where e-consultations could be performed. Working directly with broadband internet providers to set up access in specific locations for telehealth, or using products like Amazon Echo Show as a portal for telehealth, can also be tried. “Think about being innovative and recognize that these areas probably don’t have the baseline ingredients we thought they had,” suggested Dr. Reau.
The authors reported having no financial support. Dr. Reau has no relevant financial disclosures.
Telemedicine for patients with liver disease has made progress in recent years, but some key hurdles remain. Strategies that rely on patient ownership of mobile devices or reliable internet access will likely miss patients who have the greatest need for remote access.
This is one of the conclusions from a county-by-county study of access to liver specialty care and mortality, using data drawn from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiological Research (WONDER). The study was led by Jacqueline B. Henson, MD, of the Division of Gastroenterology, department of medicine, Duke University, Durham, N.C., and published in Hepatology.
Low-access areas
“Ultimately, no single telehealth strategy will be successful in all areas, and these will need to be tailored at the local and state level,” the authors wrote. “They will also depend on the persistence of policy changes enacted during the pandemic which made use and reimbursement for telehealth less restrictive.”
The researchers found that 69.5% of American counties had no gastrointestinal physicians. Moreover, 41.1% of counties were more than 100 miles away from a liver transplant (LT) center; 33.7% had no GI physicians and were more than 100 miles from a LT center. These categories represented populations of 48.8 million, 53.7 million, and 17.8 million. These counties had higher poverty rates, more unemployment, and lower educational attainment than did those that had GI physicians or were closer to LT centers. Distance from LT centers was associated with higher liver-related mortality (r = 0.24; P < .001) and density of GI providers (r = –0.12; P < .001).
Reduced access to specialty care for liver disease was also associated with decreased access to technology, including cell phones, smart phones, and internet service. Among counties in the highest death quartile and lowest access to care, 35.5% of households had no computer, 43.1% had no home internet, and only 19.2% of these had internet at broadband speeds.
“Use of platforms with lower internet speed requirements and that are compatible with mobile devices may help extend access, as could partnerships with local primary care and GI clinics,” they concluded. Further work should be done at the local and state levels to better understand the optimal strategies to reach their populations of need.
Missing ‘baseline ingredients’
Commenting on the study, Nancy Reau, MD, professor of medicine and chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said that “anyone who takes care of vulnerable populations, whether elderly individuals or those who may be socioeconomically disadvantaged, realizes that we have to improve access to medical resources, and telehealth is certainly an attractive way of doing that.”
She added that a key message from the study is that attempts to improve access to disadvantaged populations, no matter how well-intentioned, are likely to provide the most benefit to those who have more resources than others. For example, not everyone has access to a smart phone or tablet: “Even if you have a tablet [or cell phone], you might have to go to the public library to get high speed internet, or you may not even have a public library. So, when something sounds like a great idea, such as expanding the academic footprint or access to integrative medicine through something like a virtual option, a lot of the individuals that you are targeting may not be able to engage,” said Dr. Reau.
For those working to expand access, it’s critical to get the perspective of underserved communities and remember that every patient is unique. Physicians may treat patients who are poor, or from disadvantaged areas, who nevertheless have successful telehealth visits. But that doesn’t mean everyone’s experience will be similar. “You can’t use those who have been successful in accessing telemedicine as an example for everyone else. Just because one person can do it doesn’t mean that everyone else can. Involving a practitioner or an advocate from the area that you’re trying to reach is imperative,” she explained.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a big push for telehealth, and it may be tempting to believe that the transition to telehealth has been smooth. This study “demonstrates in a very granular way that a large number of Americans have no access to high-speed internet, or if they do, many don’t have access to the tools that would let them engage this way. You can’t make assumptions and use them to build a product,” continued Dr. Reau.
Innovative options are needed, such as working with primary care providers in rural or disadvantaged areas to setup pop-up hot spots where e-consultations could be performed. Working directly with broadband internet providers to set up access in specific locations for telehealth, or using products like Amazon Echo Show as a portal for telehealth, can also be tried. “Think about being innovative and recognize that these areas probably don’t have the baseline ingredients we thought they had,” suggested Dr. Reau.
The authors reported having no financial support. Dr. Reau has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM HEPATOLOGY
PI-based DAAs appear safe in decompensated patients
SAN DIEGO – An analysis of a large, international cohort suggests that treatment with protease-inhibitor (PI)–based direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) may be safe for patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) with cirrhosis and early-stage liver decompensation.
The study relied on data from the REAL-C registry, including 935 patients treated with oral DAAs at 27 centers in the U.S., Europe, and Asia Pacific countries. The researchers compared efficacy and tolerability outcomes from PI-based and non PI-based DAA regimens in patients deemed to have decompensated HCV cirrhosis.
The findings were encouraging. “It is something important because currently we are short of treatments for decompensated HCV patients. If the tolerability is similar, we perhaps should not withhold [PI] treatment for these patients that sometimes need them the most,” said Yu Jun Wong, MD, who presented the study at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). Dr. Wong is a second-year consultant at Changchi General Hospital in Singapore.
“I think it was a very interesting study and something that needed to be done. It was encouraging that patients who did have some level of decompensated cirrhosis did not worsen compared to those who were on a non PI-based therapy,” said Meena Bansal, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
However, the study was limited by some uncertainty around the definition of decompensation among the study participants. During the Q&A session, audience members questioned whether patients categorized as decompensated were truly decompensated at the time of treatment initiation. Dr. Bansal noted, for example, that a patient might experience a variceal bleed in the context of heavy alcohol consumption, and therefore be considered decompensated, but might stop drinking afterward with a reduction in portal hypertension and recovery of liver function. “So it would be important to know if they were still decompensated at the time they initiated therapy. If that was the case, then these results are more promising,” said Dr. Bansal.
Despite these limitations, the study is good news. “If you do not have access to non-PI based therapy, you might feel a little bit more secure starting a PI-based therapy, particularly the second generation PI-based therapies, if they’re at least on the earlier side of that decompensation scale. But it’s still unclear in true decompensated Child’s B or C whether or not PI-based therapy would have the same results,” said Dr. Bansal.
Dr. Wong acknowledged the limitation that the study doesn’t apply to more severely decompensated patients. “Whether it remains safe in patients with higher Child-Pugh scores is hard to extrapolate at this point of time. We still need to look further into the data,” said Dr. Wong.
Still, the results offer hope to physicians and patients who might find themselves in difficult circumstances. “If you’re resource limited, and you don’t even have access to transplant, these findings suggest that early decompensated patients may benefit from PI-based therapy. If I say to the patient, there’s a chance this could make you worse, but there’s a chance this could make you better, [this is an option] as long as the patient is aware of the possible outcomes,” said Dr. Bansal.
The study included patients with a history of ascites, variceal bleeding, jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy 6 months before treatment with DAA, or baseline measures of Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score ≥7 or Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score >10. The analysis included data between 2014 and 2021.
The mean age was 64, and 59.6% of participants were male. Overall, 70.8% had genotype 1, and 32% were treatment experienced. In total, 45.2% were treated with PI-based DAAs.
The PI cohort was older (64.6 versus 62.7; P = .01), and more likely to have genotype 1 (87.2% versus 56.3%; P < .001) and chronic renal disease (64.0% vs. 53.9%; P = .001).
The two groups had similar rates of sustained virologic response at 12 and 24 weeks, as well as similar rates of significant improvement or significant worsening, suggesting similar tolerability. There was a lower frequency of liver decompensation in the PI group at 12 weeks (4.4% vs. 7.9%; P = .04) and a trend at 24 weeks (8.8% versus 12.6%; P = .08).
Another limitation of the study is the potential for bias due to its retrospective nature.
Dr. Wong has been an invited speaker for AbbVie and Gilead. Dr. Bansal has no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – An analysis of a large, international cohort suggests that treatment with protease-inhibitor (PI)–based direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) may be safe for patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) with cirrhosis and early-stage liver decompensation.
The study relied on data from the REAL-C registry, including 935 patients treated with oral DAAs at 27 centers in the U.S., Europe, and Asia Pacific countries. The researchers compared efficacy and tolerability outcomes from PI-based and non PI-based DAA regimens in patients deemed to have decompensated HCV cirrhosis.
The findings were encouraging. “It is something important because currently we are short of treatments for decompensated HCV patients. If the tolerability is similar, we perhaps should not withhold [PI] treatment for these patients that sometimes need them the most,” said Yu Jun Wong, MD, who presented the study at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). Dr. Wong is a second-year consultant at Changchi General Hospital in Singapore.
“I think it was a very interesting study and something that needed to be done. It was encouraging that patients who did have some level of decompensated cirrhosis did not worsen compared to those who were on a non PI-based therapy,” said Meena Bansal, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
However, the study was limited by some uncertainty around the definition of decompensation among the study participants. During the Q&A session, audience members questioned whether patients categorized as decompensated were truly decompensated at the time of treatment initiation. Dr. Bansal noted, for example, that a patient might experience a variceal bleed in the context of heavy alcohol consumption, and therefore be considered decompensated, but might stop drinking afterward with a reduction in portal hypertension and recovery of liver function. “So it would be important to know if they were still decompensated at the time they initiated therapy. If that was the case, then these results are more promising,” said Dr. Bansal.
Despite these limitations, the study is good news. “If you do not have access to non-PI based therapy, you might feel a little bit more secure starting a PI-based therapy, particularly the second generation PI-based therapies, if they’re at least on the earlier side of that decompensation scale. But it’s still unclear in true decompensated Child’s B or C whether or not PI-based therapy would have the same results,” said Dr. Bansal.
Dr. Wong acknowledged the limitation that the study doesn’t apply to more severely decompensated patients. “Whether it remains safe in patients with higher Child-Pugh scores is hard to extrapolate at this point of time. We still need to look further into the data,” said Dr. Wong.
Still, the results offer hope to physicians and patients who might find themselves in difficult circumstances. “If you’re resource limited, and you don’t even have access to transplant, these findings suggest that early decompensated patients may benefit from PI-based therapy. If I say to the patient, there’s a chance this could make you worse, but there’s a chance this could make you better, [this is an option] as long as the patient is aware of the possible outcomes,” said Dr. Bansal.
The study included patients with a history of ascites, variceal bleeding, jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy 6 months before treatment with DAA, or baseline measures of Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score ≥7 or Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score >10. The analysis included data between 2014 and 2021.
The mean age was 64, and 59.6% of participants were male. Overall, 70.8% had genotype 1, and 32% were treatment experienced. In total, 45.2% were treated with PI-based DAAs.
The PI cohort was older (64.6 versus 62.7; P = .01), and more likely to have genotype 1 (87.2% versus 56.3%; P < .001) and chronic renal disease (64.0% vs. 53.9%; P = .001).
The two groups had similar rates of sustained virologic response at 12 and 24 weeks, as well as similar rates of significant improvement or significant worsening, suggesting similar tolerability. There was a lower frequency of liver decompensation in the PI group at 12 weeks (4.4% vs. 7.9%; P = .04) and a trend at 24 weeks (8.8% versus 12.6%; P = .08).
Another limitation of the study is the potential for bias due to its retrospective nature.
Dr. Wong has been an invited speaker for AbbVie and Gilead. Dr. Bansal has no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – An analysis of a large, international cohort suggests that treatment with protease-inhibitor (PI)–based direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) may be safe for patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) with cirrhosis and early-stage liver decompensation.
The study relied on data from the REAL-C registry, including 935 patients treated with oral DAAs at 27 centers in the U.S., Europe, and Asia Pacific countries. The researchers compared efficacy and tolerability outcomes from PI-based and non PI-based DAA regimens in patients deemed to have decompensated HCV cirrhosis.
The findings were encouraging. “It is something important because currently we are short of treatments for decompensated HCV patients. If the tolerability is similar, we perhaps should not withhold [PI] treatment for these patients that sometimes need them the most,” said Yu Jun Wong, MD, who presented the study at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). Dr. Wong is a second-year consultant at Changchi General Hospital in Singapore.
“I think it was a very interesting study and something that needed to be done. It was encouraging that patients who did have some level of decompensated cirrhosis did not worsen compared to those who were on a non PI-based therapy,” said Meena Bansal, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
However, the study was limited by some uncertainty around the definition of decompensation among the study participants. During the Q&A session, audience members questioned whether patients categorized as decompensated were truly decompensated at the time of treatment initiation. Dr. Bansal noted, for example, that a patient might experience a variceal bleed in the context of heavy alcohol consumption, and therefore be considered decompensated, but might stop drinking afterward with a reduction in portal hypertension and recovery of liver function. “So it would be important to know if they were still decompensated at the time they initiated therapy. If that was the case, then these results are more promising,” said Dr. Bansal.
Despite these limitations, the study is good news. “If you do not have access to non-PI based therapy, you might feel a little bit more secure starting a PI-based therapy, particularly the second generation PI-based therapies, if they’re at least on the earlier side of that decompensation scale. But it’s still unclear in true decompensated Child’s B or C whether or not PI-based therapy would have the same results,” said Dr. Bansal.
Dr. Wong acknowledged the limitation that the study doesn’t apply to more severely decompensated patients. “Whether it remains safe in patients with higher Child-Pugh scores is hard to extrapolate at this point of time. We still need to look further into the data,” said Dr. Wong.
Still, the results offer hope to physicians and patients who might find themselves in difficult circumstances. “If you’re resource limited, and you don’t even have access to transplant, these findings suggest that early decompensated patients may benefit from PI-based therapy. If I say to the patient, there’s a chance this could make you worse, but there’s a chance this could make you better, [this is an option] as long as the patient is aware of the possible outcomes,” said Dr. Bansal.
The study included patients with a history of ascites, variceal bleeding, jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy 6 months before treatment with DAA, or baseline measures of Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score ≥7 or Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score >10. The analysis included data between 2014 and 2021.
The mean age was 64, and 59.6% of participants were male. Overall, 70.8% had genotype 1, and 32% were treatment experienced. In total, 45.2% were treated with PI-based DAAs.
The PI cohort was older (64.6 versus 62.7; P = .01), and more likely to have genotype 1 (87.2% versus 56.3%; P < .001) and chronic renal disease (64.0% vs. 53.9%; P = .001).
The two groups had similar rates of sustained virologic response at 12 and 24 weeks, as well as similar rates of significant improvement or significant worsening, suggesting similar tolerability. There was a lower frequency of liver decompensation in the PI group at 12 weeks (4.4% vs. 7.9%; P = .04) and a trend at 24 weeks (8.8% versus 12.6%; P = .08).
Another limitation of the study is the potential for bias due to its retrospective nature.
Dr. Wong has been an invited speaker for AbbVie and Gilead. Dr. Bansal has no relevant financial disclosures.
AT DDW 2022
Treatment for alcohol abuse reduces hepatitis readmission
SAN DIEGO – Treating people with alcoholic hepatitis for alcohol abuse may reduce their risk of hospital readmission, researchers reported.
In a retrospective analysis of nationwide data, 7.83% of those patients who received psychotherapy, counseling, or drug treatment for alcohol abuse were readmitted within 30 days, versus 11.67% of those who did not receive these kinds of treatment.
The finding lends support to the argument that hospitals should invest more in the treatments, despite the complexities involved.
“It takes a multidisciplinary approach, starting from the physician or the health care provider along with the pharmacists, the behavioral health specialists, or a psychiatrist or psychologist, along with case management as well,” said Harleen Chela, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She presented the findings at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The researchers started with the premise that patients with alcoholic hepatitis can prevent the condition from worsening by abstaining from alcohol. To see whether interventions aimed at encouraging that abstention could prevent readmissions, Dr. Chela and colleagues analyzed data on readmissions for the first 11 months of the year 2018.
They included patients who were at least 18 years of age and who had a nonelective admission with a principal diagnosis of alcohol abuse.
Using procedure codes, they compared those patients given psychotherapy (including cognitive behavioral therapy), formal inpatient counseling, and drug treatment for alcohol abuse to those who didn’t. Then they counted how many patients were readmitted within 30 days.
They found records of 45,617 patients admitted for alcoholic hepatitis of whom 1,552 received treatment for alcohol abuse and 44,065 did not.
They did not find any significant difference between the two groups in demographics, income, or insurance status.
Adjusting for such factors, the researchers found that people who received alcohol abuse treatment were 64% as likely to be readmitted as were those who did not (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.91; P = 0.01).
If alcohol abuse treatment is so effective, why isn’t it routine? “It’s not always feasible to implement this, on the inpatient side, because it takes more than a day or two just to get some of these things put in place,” Dr. Chela told this news organization.
They did find that people were more likely to get treatment for alcohol abuse if they were admitted to a hospital in a big city rather than a small town and if their hospital was owned by private investors rather than by a not-for-profit organization or the government.
“Larger hospitals and private sector institutions have more access to resources and money to have those kinds of systems in place for the patients,” said Dr. Chela.
She became interested in the issue at her hospital when she noticed that patients with alcoholic hepatitis were not getting behavioral counseling. “The inpatient load in the behavioral health side is so much that they don’t have time for these kinds of consults,” she said. “That’s one of the challenges: A shortage of behavioral specialists like psychiatrists.”
And hospitals tend to focus on treating conditions that threaten their patients’ lives in the short term. “Someone who has a heart attack or a gastrointestinal bleed – there’s more focus on resources for those kinds of patients,” she said.
Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond provides alcohol abuse treatment to patients with alcoholic hepatitis partly using telehealth, said Richard Sterling, MD, MSc, chief of hepatology, who was not involved in the study. “For people who live too far away, don’t have transportation, or have other health disparities, we now have technology and mechanisms to keep them engaged in care,” he told this news organization. “We’re doing a lot of Zoom visits.”
Dr. Chela and colleagues also found that those who got alcohol abuse treatment were less likely to be discharged to a skilled nursing facility or to home health. The data couldn’t give the researchers a definitive reason for this, but Dr. Chela speculated that the patients who received treatment for alcohol abuse stayed longer in the hospital and may have been in better shape when they were discharged.
The U.S. health care system doesn’t necessarily provide incentives to keep patients healthy, Dr. Sterling said. “Hospital systems make money off of filling beds, and providing a lot of inpatient care and hospital days,” he said. “That may be not necessarily congruent with a health system that is supposed to provide health for these covered lives.”
Neither Dr. Chela nor Dr. Sterling reported any relevant financial relationships.
SAN DIEGO – Treating people with alcoholic hepatitis for alcohol abuse may reduce their risk of hospital readmission, researchers reported.
In a retrospective analysis of nationwide data, 7.83% of those patients who received psychotherapy, counseling, or drug treatment for alcohol abuse were readmitted within 30 days, versus 11.67% of those who did not receive these kinds of treatment.
The finding lends support to the argument that hospitals should invest more in the treatments, despite the complexities involved.
“It takes a multidisciplinary approach, starting from the physician or the health care provider along with the pharmacists, the behavioral health specialists, or a psychiatrist or psychologist, along with case management as well,” said Harleen Chela, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She presented the findings at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The researchers started with the premise that patients with alcoholic hepatitis can prevent the condition from worsening by abstaining from alcohol. To see whether interventions aimed at encouraging that abstention could prevent readmissions, Dr. Chela and colleagues analyzed data on readmissions for the first 11 months of the year 2018.
They included patients who were at least 18 years of age and who had a nonelective admission with a principal diagnosis of alcohol abuse.
Using procedure codes, they compared those patients given psychotherapy (including cognitive behavioral therapy), formal inpatient counseling, and drug treatment for alcohol abuse to those who didn’t. Then they counted how many patients were readmitted within 30 days.
They found records of 45,617 patients admitted for alcoholic hepatitis of whom 1,552 received treatment for alcohol abuse and 44,065 did not.
They did not find any significant difference between the two groups in demographics, income, or insurance status.
Adjusting for such factors, the researchers found that people who received alcohol abuse treatment were 64% as likely to be readmitted as were those who did not (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.91; P = 0.01).
If alcohol abuse treatment is so effective, why isn’t it routine? “It’s not always feasible to implement this, on the inpatient side, because it takes more than a day or two just to get some of these things put in place,” Dr. Chela told this news organization.
They did find that people were more likely to get treatment for alcohol abuse if they were admitted to a hospital in a big city rather than a small town and if their hospital was owned by private investors rather than by a not-for-profit organization or the government.
“Larger hospitals and private sector institutions have more access to resources and money to have those kinds of systems in place for the patients,” said Dr. Chela.
She became interested in the issue at her hospital when she noticed that patients with alcoholic hepatitis were not getting behavioral counseling. “The inpatient load in the behavioral health side is so much that they don’t have time for these kinds of consults,” she said. “That’s one of the challenges: A shortage of behavioral specialists like psychiatrists.”
And hospitals tend to focus on treating conditions that threaten their patients’ lives in the short term. “Someone who has a heart attack or a gastrointestinal bleed – there’s more focus on resources for those kinds of patients,” she said.
Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond provides alcohol abuse treatment to patients with alcoholic hepatitis partly using telehealth, said Richard Sterling, MD, MSc, chief of hepatology, who was not involved in the study. “For people who live too far away, don’t have transportation, or have other health disparities, we now have technology and mechanisms to keep them engaged in care,” he told this news organization. “We’re doing a lot of Zoom visits.”
Dr. Chela and colleagues also found that those who got alcohol abuse treatment were less likely to be discharged to a skilled nursing facility or to home health. The data couldn’t give the researchers a definitive reason for this, but Dr. Chela speculated that the patients who received treatment for alcohol abuse stayed longer in the hospital and may have been in better shape when they were discharged.
The U.S. health care system doesn’t necessarily provide incentives to keep patients healthy, Dr. Sterling said. “Hospital systems make money off of filling beds, and providing a lot of inpatient care and hospital days,” he said. “That may be not necessarily congruent with a health system that is supposed to provide health for these covered lives.”
Neither Dr. Chela nor Dr. Sterling reported any relevant financial relationships.
SAN DIEGO – Treating people with alcoholic hepatitis for alcohol abuse may reduce their risk of hospital readmission, researchers reported.
In a retrospective analysis of nationwide data, 7.83% of those patients who received psychotherapy, counseling, or drug treatment for alcohol abuse were readmitted within 30 days, versus 11.67% of those who did not receive these kinds of treatment.
The finding lends support to the argument that hospitals should invest more in the treatments, despite the complexities involved.
“It takes a multidisciplinary approach, starting from the physician or the health care provider along with the pharmacists, the behavioral health specialists, or a psychiatrist or psychologist, along with case management as well,” said Harleen Chela, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She presented the findings at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The researchers started with the premise that patients with alcoholic hepatitis can prevent the condition from worsening by abstaining from alcohol. To see whether interventions aimed at encouraging that abstention could prevent readmissions, Dr. Chela and colleagues analyzed data on readmissions for the first 11 months of the year 2018.
They included patients who were at least 18 years of age and who had a nonelective admission with a principal diagnosis of alcohol abuse.
Using procedure codes, they compared those patients given psychotherapy (including cognitive behavioral therapy), formal inpatient counseling, and drug treatment for alcohol abuse to those who didn’t. Then they counted how many patients were readmitted within 30 days.
They found records of 45,617 patients admitted for alcoholic hepatitis of whom 1,552 received treatment for alcohol abuse and 44,065 did not.
They did not find any significant difference between the two groups in demographics, income, or insurance status.
Adjusting for such factors, the researchers found that people who received alcohol abuse treatment were 64% as likely to be readmitted as were those who did not (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.91; P = 0.01).
If alcohol abuse treatment is so effective, why isn’t it routine? “It’s not always feasible to implement this, on the inpatient side, because it takes more than a day or two just to get some of these things put in place,” Dr. Chela told this news organization.
They did find that people were more likely to get treatment for alcohol abuse if they were admitted to a hospital in a big city rather than a small town and if their hospital was owned by private investors rather than by a not-for-profit organization or the government.
“Larger hospitals and private sector institutions have more access to resources and money to have those kinds of systems in place for the patients,” said Dr. Chela.
She became interested in the issue at her hospital when she noticed that patients with alcoholic hepatitis were not getting behavioral counseling. “The inpatient load in the behavioral health side is so much that they don’t have time for these kinds of consults,” she said. “That’s one of the challenges: A shortage of behavioral specialists like psychiatrists.”
And hospitals tend to focus on treating conditions that threaten their patients’ lives in the short term. “Someone who has a heart attack or a gastrointestinal bleed – there’s more focus on resources for those kinds of patients,” she said.
Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond provides alcohol abuse treatment to patients with alcoholic hepatitis partly using telehealth, said Richard Sterling, MD, MSc, chief of hepatology, who was not involved in the study. “For people who live too far away, don’t have transportation, or have other health disparities, we now have technology and mechanisms to keep them engaged in care,” he told this news organization. “We’re doing a lot of Zoom visits.”
Dr. Chela and colleagues also found that those who got alcohol abuse treatment were less likely to be discharged to a skilled nursing facility or to home health. The data couldn’t give the researchers a definitive reason for this, but Dr. Chela speculated that the patients who received treatment for alcohol abuse stayed longer in the hospital and may have been in better shape when they were discharged.
The U.S. health care system doesn’t necessarily provide incentives to keep patients healthy, Dr. Sterling said. “Hospital systems make money off of filling beds, and providing a lot of inpatient care and hospital days,” he said. “That may be not necessarily congruent with a health system that is supposed to provide health for these covered lives.”
Neither Dr. Chela nor Dr. Sterling reported any relevant financial relationships.
AT DDW 2022
Creatinine variability linked to liver transplant outcomes
Patients with greater changes in serum creatinine are more likely to have worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes. Moreover, underserved patients may be most frequently affected, according to a retrospective analysis of UNOS (United Network for Organ Sharing) data.
These results should drive further development of serum creatinine coefficient of variation (sCr CoV) as an independent predictor of renal-related mortality risk, according to lead author Giuseppe Cullaro, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
“Intra-individual clinical and laboratory parameter dynamics often provide additional prognostic information – added information that goes beyond what can be found with cross-sectional data,” the researchers wrote in Hepatology. “This finding has been seen in several scenarios in the general population – intra-individual variability in blood pressure, weight, hemoglobin, and kidney function, have all been associated with worse clinical outcomes. However, in cirrhosis patients, and more specifically in patients awaiting a liver transplant, kidney function dynamics as a predictor of clinical outcomes has yet to be investigated.”
To gauge the predictive power of shifting kidney values, Dr. Cullaro and colleagues analyzed UNOS/OPTN (Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network) registry data from 2011 through 2019. Exclusion criteria included patients who were aged younger than 18 years, were listed as status 1, received a living donor liver transplantation, were on hemodialysis, or had fewer than three updates. The final dataset included 25,204 patients.
After the researchers sorted patients into low, intermediate, and high sCr CoV tertiles, they used logistic regression to determine relationships between higher sCr and a variety of covariates, such as age, sex, diagnosis, presence of acute kidney injury, or chronic kidney disease. A competing risk regression was then done to look for associations between wait list mortality and the covariables, with liver transplant used as the competing risk.
The median sCr CoV was 17.4% (interquartile range [IQR], 10.8%-29.5%). Patients in the bottom sCr CoV tertile had a median value of 8.8% (IQR, 6.6%-10.8%), compared with 17.4% (IQR, 14.8%-20.4%) in the intermediate variability group and 36.8% (IQR, 29.5%-48.8%) in the high variability group. High variability was associated with female sex, Hispanic ethnicity, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy as well as higher body mass index, MELDNa score, and serum creatinine.
Of note, each decreasing serum creatinine variability tertile was associated with a significantly lower rate of wait list mortality (34.7% vs. 19.6% vs. 11.7%; P < .001). The creatinine variability profiles were similarly associated with the likelihood of receiving a liver transplant (52.3% vs. 48.9% vs. 43.7%; P < .001) and posttransplant mortality (7.5% vs. 5.5% vs. 3.9%; P < .001).
A multivariate model showed that each 10% increase in sCr CoV predicted an 8% increased risk of a combined outcome comprising post–liver transplant death or post–liver transplant kidney transplant (KALT), independently of other variables (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.11).
“These data highlight that all fluctuations in sCr are associated with worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes,” the investigators concluded. “Moreover, the groups that are most underserved by sCr, specifically women, were most likely to have greater sCr CoVs. We believe our work lays the foundation for implementing the sCr CoV as an independent metric of renal-related mortality risk and may be most beneficial for those groups most underserved by sCr values alone.”
According to Brian P. Lee, MD, a hepatologist with Keck Medicine of USC and assistant professor of clinical medicine with the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles, “this is a great study ... in an area of high need” that used “high quality data.”
Current liver allocation strategies depend on a snapshot of kidney function, but these new findings suggest that a more dynamic approach may be needed. “As a practicing liver specialist I see that creatinine numbers can fluctuate a lot. ... So which number do you use when you’re trying to calculate what a patient’s risk of death is on the wait list? This study gets toward that answer. If there is a lot of variability, these might be higher risk patients; these might be patients that we should put higher on the transplant waiting list,” said Dr. Lee.
He suggested that clinicians should account for creatinine fluctuations when considering mortality risk; however, the evidence is “not quite there yet ... in terms of changing transplant policy and allocation.” He pointed out three unanswered questions: Why are creatinine values fluctuating? How should fluctuations be scored for risk modeling? And, what impact would those risk scores have on transplant waitlist prioritization?
“I think that that’s the work that you would need to do before you could really change national transplant policy,” Dr. Lee concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the UCSF Liver Center. Dr. Cullaro and another author have disclosed relationships with Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals and Axcella Health, respectively. Dr. Lee reported no conflicts of interest.
Patients with greater changes in serum creatinine are more likely to have worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes. Moreover, underserved patients may be most frequently affected, according to a retrospective analysis of UNOS (United Network for Organ Sharing) data.
These results should drive further development of serum creatinine coefficient of variation (sCr CoV) as an independent predictor of renal-related mortality risk, according to lead author Giuseppe Cullaro, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
“Intra-individual clinical and laboratory parameter dynamics often provide additional prognostic information – added information that goes beyond what can be found with cross-sectional data,” the researchers wrote in Hepatology. “This finding has been seen in several scenarios in the general population – intra-individual variability in blood pressure, weight, hemoglobin, and kidney function, have all been associated with worse clinical outcomes. However, in cirrhosis patients, and more specifically in patients awaiting a liver transplant, kidney function dynamics as a predictor of clinical outcomes has yet to be investigated.”
To gauge the predictive power of shifting kidney values, Dr. Cullaro and colleagues analyzed UNOS/OPTN (Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network) registry data from 2011 through 2019. Exclusion criteria included patients who were aged younger than 18 years, were listed as status 1, received a living donor liver transplantation, were on hemodialysis, or had fewer than three updates. The final dataset included 25,204 patients.
After the researchers sorted patients into low, intermediate, and high sCr CoV tertiles, they used logistic regression to determine relationships between higher sCr and a variety of covariates, such as age, sex, diagnosis, presence of acute kidney injury, or chronic kidney disease. A competing risk regression was then done to look for associations between wait list mortality and the covariables, with liver transplant used as the competing risk.
The median sCr CoV was 17.4% (interquartile range [IQR], 10.8%-29.5%). Patients in the bottom sCr CoV tertile had a median value of 8.8% (IQR, 6.6%-10.8%), compared with 17.4% (IQR, 14.8%-20.4%) in the intermediate variability group and 36.8% (IQR, 29.5%-48.8%) in the high variability group. High variability was associated with female sex, Hispanic ethnicity, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy as well as higher body mass index, MELDNa score, and serum creatinine.
Of note, each decreasing serum creatinine variability tertile was associated with a significantly lower rate of wait list mortality (34.7% vs. 19.6% vs. 11.7%; P < .001). The creatinine variability profiles were similarly associated with the likelihood of receiving a liver transplant (52.3% vs. 48.9% vs. 43.7%; P < .001) and posttransplant mortality (7.5% vs. 5.5% vs. 3.9%; P < .001).
A multivariate model showed that each 10% increase in sCr CoV predicted an 8% increased risk of a combined outcome comprising post–liver transplant death or post–liver transplant kidney transplant (KALT), independently of other variables (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.11).
“These data highlight that all fluctuations in sCr are associated with worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes,” the investigators concluded. “Moreover, the groups that are most underserved by sCr, specifically women, were most likely to have greater sCr CoVs. We believe our work lays the foundation for implementing the sCr CoV as an independent metric of renal-related mortality risk and may be most beneficial for those groups most underserved by sCr values alone.”
According to Brian P. Lee, MD, a hepatologist with Keck Medicine of USC and assistant professor of clinical medicine with the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles, “this is a great study ... in an area of high need” that used “high quality data.”
Current liver allocation strategies depend on a snapshot of kidney function, but these new findings suggest that a more dynamic approach may be needed. “As a practicing liver specialist I see that creatinine numbers can fluctuate a lot. ... So which number do you use when you’re trying to calculate what a patient’s risk of death is on the wait list? This study gets toward that answer. If there is a lot of variability, these might be higher risk patients; these might be patients that we should put higher on the transplant waiting list,” said Dr. Lee.
He suggested that clinicians should account for creatinine fluctuations when considering mortality risk; however, the evidence is “not quite there yet ... in terms of changing transplant policy and allocation.” He pointed out three unanswered questions: Why are creatinine values fluctuating? How should fluctuations be scored for risk modeling? And, what impact would those risk scores have on transplant waitlist prioritization?
“I think that that’s the work that you would need to do before you could really change national transplant policy,” Dr. Lee concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the UCSF Liver Center. Dr. Cullaro and another author have disclosed relationships with Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals and Axcella Health, respectively. Dr. Lee reported no conflicts of interest.
Patients with greater changes in serum creatinine are more likely to have worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes. Moreover, underserved patients may be most frequently affected, according to a retrospective analysis of UNOS (United Network for Organ Sharing) data.
These results should drive further development of serum creatinine coefficient of variation (sCr CoV) as an independent predictor of renal-related mortality risk, according to lead author Giuseppe Cullaro, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
“Intra-individual clinical and laboratory parameter dynamics often provide additional prognostic information – added information that goes beyond what can be found with cross-sectional data,” the researchers wrote in Hepatology. “This finding has been seen in several scenarios in the general population – intra-individual variability in blood pressure, weight, hemoglobin, and kidney function, have all been associated with worse clinical outcomes. However, in cirrhosis patients, and more specifically in patients awaiting a liver transplant, kidney function dynamics as a predictor of clinical outcomes has yet to be investigated.”
To gauge the predictive power of shifting kidney values, Dr. Cullaro and colleagues analyzed UNOS/OPTN (Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network) registry data from 2011 through 2019. Exclusion criteria included patients who were aged younger than 18 years, were listed as status 1, received a living donor liver transplantation, were on hemodialysis, or had fewer than three updates. The final dataset included 25,204 patients.
After the researchers sorted patients into low, intermediate, and high sCr CoV tertiles, they used logistic regression to determine relationships between higher sCr and a variety of covariates, such as age, sex, diagnosis, presence of acute kidney injury, or chronic kidney disease. A competing risk regression was then done to look for associations between wait list mortality and the covariables, with liver transplant used as the competing risk.
The median sCr CoV was 17.4% (interquartile range [IQR], 10.8%-29.5%). Patients in the bottom sCr CoV tertile had a median value of 8.8% (IQR, 6.6%-10.8%), compared with 17.4% (IQR, 14.8%-20.4%) in the intermediate variability group and 36.8% (IQR, 29.5%-48.8%) in the high variability group. High variability was associated with female sex, Hispanic ethnicity, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy as well as higher body mass index, MELDNa score, and serum creatinine.
Of note, each decreasing serum creatinine variability tertile was associated with a significantly lower rate of wait list mortality (34.7% vs. 19.6% vs. 11.7%; P < .001). The creatinine variability profiles were similarly associated with the likelihood of receiving a liver transplant (52.3% vs. 48.9% vs. 43.7%; P < .001) and posttransplant mortality (7.5% vs. 5.5% vs. 3.9%; P < .001).
A multivariate model showed that each 10% increase in sCr CoV predicted an 8% increased risk of a combined outcome comprising post–liver transplant death or post–liver transplant kidney transplant (KALT), independently of other variables (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.11).
“These data highlight that all fluctuations in sCr are associated with worse pre- and post–liver transplant outcomes,” the investigators concluded. “Moreover, the groups that are most underserved by sCr, specifically women, were most likely to have greater sCr CoVs. We believe our work lays the foundation for implementing the sCr CoV as an independent metric of renal-related mortality risk and may be most beneficial for those groups most underserved by sCr values alone.”
According to Brian P. Lee, MD, a hepatologist with Keck Medicine of USC and assistant professor of clinical medicine with the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles, “this is a great study ... in an area of high need” that used “high quality data.”
Current liver allocation strategies depend on a snapshot of kidney function, but these new findings suggest that a more dynamic approach may be needed. “As a practicing liver specialist I see that creatinine numbers can fluctuate a lot. ... So which number do you use when you’re trying to calculate what a patient’s risk of death is on the wait list? This study gets toward that answer. If there is a lot of variability, these might be higher risk patients; these might be patients that we should put higher on the transplant waiting list,” said Dr. Lee.
He suggested that clinicians should account for creatinine fluctuations when considering mortality risk; however, the evidence is “not quite there yet ... in terms of changing transplant policy and allocation.” He pointed out three unanswered questions: Why are creatinine values fluctuating? How should fluctuations be scored for risk modeling? And, what impact would those risk scores have on transplant waitlist prioritization?
“I think that that’s the work that you would need to do before you could really change national transplant policy,” Dr. Lee concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the UCSF Liver Center. Dr. Cullaro and another author have disclosed relationships with Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals and Axcella Health, respectively. Dr. Lee reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM HEPATOLOGY