User login
For MD-IQ on Family Practice News, but a regular topic for Rheumatology News
Experts review the year in rheumatology ... and what lies ahead
MAUI, HAWAII – Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, program director for the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium, likes to close out the meeting each year in high style by assembling selected conference faculty to offer their personal picks for the top developments in the field during the past year and make predictions about the year to come.
Here’s how they called it:
The top events in rheumatology during the last year
The rise of oral small molecules: The Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors and other oral small molecules that have begun reaching the marketplace, with many more in development, will bring a paradigm shift in the treatment not only of rheumatic diseases, but in inflammatory bowel disease and skin diseases as well, predicted Alvin F. Wells, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who is also director of the Rheumatology and Immunotherapy Center in Franklin, Wisc.
“The challenge is whether Medicare will cover the pills the way they cover the infusions and the other things we do,” according to Dr. Wells.
A bevy of new drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: “I think the most important advance in the past year was the approval of a profusion of drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. It’s really opened up the landscape for us in terms of treatment options. The downside is it’s going to take us a while to sort through which drugs fit where,” noted Eric J. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief of clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The drug I was most impressed with was tofacitinib [Xeljanz, an oral JAK inhibitor], not just by its effectiveness but by its potential to change the game, and particularly the data in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor inadequate responders. That was pretty solid data. It really opens the way to oral small molecules for joint diseases,” he added.
Interleukin-18 binding protein for monogenic inflammasome diseases: The biggest recent breakthrough in pediatric rheumatology was the Food and Drug Administration’s April 2017 designation of Breakthrough Therapy status for the recombinant human IL-18 binding protein known as tadekinig alfa for monogenic IL-18-associated autoinflammatory conditions, as well as the biologic’s Orphan Drug Designation for treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, according to Anne M. Stevens, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chief of pediatric rheumatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Novel treatment concept emerges in severe SLE: The study that knocked the socks off of Martin J. Bergman, MD, in 2017 was the Dutch SymBiose study, presented at both the European League Against Rheumatism and American College of Rheumatology annual meetings. It included just 14 patients with severe refractory SLE – including 10 with lupus nephritis – and tested a treatment strategy of rituximab (Rituxan) followed a few weeks later by a course of belimumab (Benlysta).
“The results were very dramatic, to say the least,” said Dr. Bergman of Drexel University in Philadelphia. Indeed, this one-two therapeutic punch resulted in sharply reduced levels of pathogenic autoantibodies and immune complex-mediated neutrophil extracellular traps while also knocking down very high baseline Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) scores to near zero, even while enabling patients to discontinue systemic corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept). Several much larger clinical trials of this regimen and other similar ones are ongoing in an effort to duplicate the results.
Dr. Kavanaugh said the SymBiose study was one of his own top picks for study of the year as well.
Mainstream use of dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: “This is a total game changer. It’s really changed a lot of people’s lives,” commented George M. Martin, MD, a dermatologist in private practice on Maui.
“Interestingly, historically drugs that started out in your realm later made their way to dermatology, but now we’re seeing the IL-23 inhibitors starting with us and then making their way into rheumatology and gastroenterology. The IL-23 inhibitors are very powerful drugs; when we’re seeing half of our psoriasis patients achieve PASI 100 responses, it’s very exciting. And these are durable responses,” he noted.
The opioid crisis: What’s the most important recent event in rheumatology?
“That’s easy: The biggest thing in all of medicine is the opioid crisis. Whether you recognize it or not, it’s gigantic. It’s $500 billion of the U.S. economy, every year. Forty percent of rheumatoid arthritis patients and 30% with ankylosing spondylitis are on opioids, and what goes along with that is a lot of ugly stuff,” said John J. Cush, MD, professor of medicine and rheumatology at Baylor University in Dallas.
Moreover, the FDA is now so leery of opioids that the agency has set the bar unrealistically high for approval of newer agents offering reduced abuse potential.
“I’ve been involved with or watched at least six FDA advisory panels looking at new, lower abuse-potential opioids in the last couple years. Only one agent got through,” according to Dr. Cush.
Dr. Troum commented, “I really think this whole opioid epidemic started with the campaign to make pain the fifth vital sign back in the 1990s. Some of the pharmaceutical companies took that concept and really ran with it.”
Rapamycin for inclusion body myositis: Dr. Kavanaugh’s pick for study of the year was what he described as “a brilliant presentation” of a French multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trial of rapamycin for patients with inclusion body myositis at the 2017 ACR annual meeting.
“The French group considers IBM [inclusion body myositis] to be essentially Alzheimer’s disease of the muscle, marked by amyloid deposition. They chose to study rapamycin, which not only has immunosuppressive properties because it binds to mTOR [the mammalian target of rapamycin], but it also has the ability to inhibit amyloid protein deposition,” he explained.
The investigators reported improved 6-minute-walk distance and pulmonary function in the rapamycin group, whereas placebo-treated controls rapidly deteriorated.
“This is an approved drug for other indications, and we scratch our heads with IBM. It’s super nice to have something like that,” Dr. Kavanaugh observed.
A look at what’s in store
More tele-rheumatology: “I think the biggest thing is going to be more tele-rheumatology, more tele-ultrasound. Kaiser Permanente said 49% of their visits last year were virtual visits; that number is just going to grow,” predicted Dr. Wells.
Especially in medically underserved areas of the country, including large rural expanses, demand for remote tele-rheumatologic consults with high-quality imaging is going to increase, he added.
Here come cannabinoids for pain control: Dr. Troum predicted that in the depths of the national opioid epidemic, in a climate that discourages legitimate prescribing of traditional pain medications, rheumatologists can anticipate growing patient demand for cannabidiol and other cannabinoids for pain relief.
“I have patients coming in their 60s, 70s, and 80s – these are not young people – who are whispering to me, ‘Can I use this for my chronic pain?’ I think there’s going to be a big push for ways other than opioids to treat our patients’ pain,” according to Dr. Troum.
Tipping point nears for JAK inhibitors: In 2018, it will become clear just how seriously the Food and Drug Administration views the signal of possible increased venous thromboembolic risk associated with the oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. The agency is expected to rule on Eli Lilly and Incyte’s resubmitted application for marketing approval for the JAK inhibitor baricitinib, which was tripped up earlier based in part upon VTE concerns.
“I think the big story in 2018 will be how the JAK story shakes out – whether this VTE thing has legs,” Dr. Ruderman predicted. “A sea change could be coming in our field, and it’s not coming next year or the year after, but 10 years from now: Are we going to move past the era of methotrexate and use generic small molecules instead? We’re going to find out within the next year whether that’s going to happen.”
Phase 3 results coming on tocilizumab for systemic sclerosis: “I think we’re going to see some really exciting systemic sclerosis data coming out this year,” Dr. Stevens said. Based upon the positive phase 2 results presented for tocilizumab (Actemra) last year, she’s optimistic that the ongoing phase 3 randomized trial will demonstrate a significant advantage over placebo in lung function. Also, ongoing separate clinical trials are evaluating an antifibrotic drug and rapamycin for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Bergman, too, has high hopes for these studies: “I think we may finally be getting to a place where we can see effective drugs in systemic sclerosis.”
Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JPMorgan Chase form a nonprofit to improve employee health care: In a recent press conference, the three CEOs weren’t specific about their plans, but Dr. Martin predicted the companies are likely to self-insure, bypassing Cigna and the other major health insurance companies and then contracting with physicians. He forecast that “probably within the next 5 years, what they do is going to affect everybody in this room.”
Rheumatologists will need to master a new mindset: Many rheumatologists have gotten comfortable with an all-tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment menu for their patients with moderate or severe rheumatoid arthritis. That’s got to change, according to Dr. Cush.
“We now have two IL-6 inhibitors, two IL-17 inhibitors, and we’ll soon have two JAK inhibitors. That’s going to be a direct threat to the not right- or left-brain, but the TNF-brain rheumatologist who now writes prescriptions for three TNF inhibitors in a row before questioning the efficacy. The idea is you will now be using drugs with other mechanisms of action first-line, or at the very least, second-line, and that’s going to be a paradigm shift for a lot of people,” he explained.
None of the speakers reported having financial conflicts regarding their comments.
MAUI, HAWAII – Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, program director for the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium, likes to close out the meeting each year in high style by assembling selected conference faculty to offer their personal picks for the top developments in the field during the past year and make predictions about the year to come.
Here’s how they called it:
The top events in rheumatology during the last year
The rise of oral small molecules: The Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors and other oral small molecules that have begun reaching the marketplace, with many more in development, will bring a paradigm shift in the treatment not only of rheumatic diseases, but in inflammatory bowel disease and skin diseases as well, predicted Alvin F. Wells, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who is also director of the Rheumatology and Immunotherapy Center in Franklin, Wisc.
“The challenge is whether Medicare will cover the pills the way they cover the infusions and the other things we do,” according to Dr. Wells.
A bevy of new drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: “I think the most important advance in the past year was the approval of a profusion of drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. It’s really opened up the landscape for us in terms of treatment options. The downside is it’s going to take us a while to sort through which drugs fit where,” noted Eric J. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief of clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The drug I was most impressed with was tofacitinib [Xeljanz, an oral JAK inhibitor], not just by its effectiveness but by its potential to change the game, and particularly the data in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor inadequate responders. That was pretty solid data. It really opens the way to oral small molecules for joint diseases,” he added.
Interleukin-18 binding protein for monogenic inflammasome diseases: The biggest recent breakthrough in pediatric rheumatology was the Food and Drug Administration’s April 2017 designation of Breakthrough Therapy status for the recombinant human IL-18 binding protein known as tadekinig alfa for monogenic IL-18-associated autoinflammatory conditions, as well as the biologic’s Orphan Drug Designation for treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, according to Anne M. Stevens, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chief of pediatric rheumatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Novel treatment concept emerges in severe SLE: The study that knocked the socks off of Martin J. Bergman, MD, in 2017 was the Dutch SymBiose study, presented at both the European League Against Rheumatism and American College of Rheumatology annual meetings. It included just 14 patients with severe refractory SLE – including 10 with lupus nephritis – and tested a treatment strategy of rituximab (Rituxan) followed a few weeks later by a course of belimumab (Benlysta).
“The results were very dramatic, to say the least,” said Dr. Bergman of Drexel University in Philadelphia. Indeed, this one-two therapeutic punch resulted in sharply reduced levels of pathogenic autoantibodies and immune complex-mediated neutrophil extracellular traps while also knocking down very high baseline Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) scores to near zero, even while enabling patients to discontinue systemic corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept). Several much larger clinical trials of this regimen and other similar ones are ongoing in an effort to duplicate the results.
Dr. Kavanaugh said the SymBiose study was one of his own top picks for study of the year as well.
Mainstream use of dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: “This is a total game changer. It’s really changed a lot of people’s lives,” commented George M. Martin, MD, a dermatologist in private practice on Maui.
“Interestingly, historically drugs that started out in your realm later made their way to dermatology, but now we’re seeing the IL-23 inhibitors starting with us and then making their way into rheumatology and gastroenterology. The IL-23 inhibitors are very powerful drugs; when we’re seeing half of our psoriasis patients achieve PASI 100 responses, it’s very exciting. And these are durable responses,” he noted.
The opioid crisis: What’s the most important recent event in rheumatology?
“That’s easy: The biggest thing in all of medicine is the opioid crisis. Whether you recognize it or not, it’s gigantic. It’s $500 billion of the U.S. economy, every year. Forty percent of rheumatoid arthritis patients and 30% with ankylosing spondylitis are on opioids, and what goes along with that is a lot of ugly stuff,” said John J. Cush, MD, professor of medicine and rheumatology at Baylor University in Dallas.
Moreover, the FDA is now so leery of opioids that the agency has set the bar unrealistically high for approval of newer agents offering reduced abuse potential.
“I’ve been involved with or watched at least six FDA advisory panels looking at new, lower abuse-potential opioids in the last couple years. Only one agent got through,” according to Dr. Cush.
Dr. Troum commented, “I really think this whole opioid epidemic started with the campaign to make pain the fifth vital sign back in the 1990s. Some of the pharmaceutical companies took that concept and really ran with it.”
Rapamycin for inclusion body myositis: Dr. Kavanaugh’s pick for study of the year was what he described as “a brilliant presentation” of a French multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trial of rapamycin for patients with inclusion body myositis at the 2017 ACR annual meeting.
“The French group considers IBM [inclusion body myositis] to be essentially Alzheimer’s disease of the muscle, marked by amyloid deposition. They chose to study rapamycin, which not only has immunosuppressive properties because it binds to mTOR [the mammalian target of rapamycin], but it also has the ability to inhibit amyloid protein deposition,” he explained.
The investigators reported improved 6-minute-walk distance and pulmonary function in the rapamycin group, whereas placebo-treated controls rapidly deteriorated.
“This is an approved drug for other indications, and we scratch our heads with IBM. It’s super nice to have something like that,” Dr. Kavanaugh observed.
A look at what’s in store
More tele-rheumatology: “I think the biggest thing is going to be more tele-rheumatology, more tele-ultrasound. Kaiser Permanente said 49% of their visits last year were virtual visits; that number is just going to grow,” predicted Dr. Wells.
Especially in medically underserved areas of the country, including large rural expanses, demand for remote tele-rheumatologic consults with high-quality imaging is going to increase, he added.
Here come cannabinoids for pain control: Dr. Troum predicted that in the depths of the national opioid epidemic, in a climate that discourages legitimate prescribing of traditional pain medications, rheumatologists can anticipate growing patient demand for cannabidiol and other cannabinoids for pain relief.
“I have patients coming in their 60s, 70s, and 80s – these are not young people – who are whispering to me, ‘Can I use this for my chronic pain?’ I think there’s going to be a big push for ways other than opioids to treat our patients’ pain,” according to Dr. Troum.
Tipping point nears for JAK inhibitors: In 2018, it will become clear just how seriously the Food and Drug Administration views the signal of possible increased venous thromboembolic risk associated with the oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. The agency is expected to rule on Eli Lilly and Incyte’s resubmitted application for marketing approval for the JAK inhibitor baricitinib, which was tripped up earlier based in part upon VTE concerns.
“I think the big story in 2018 will be how the JAK story shakes out – whether this VTE thing has legs,” Dr. Ruderman predicted. “A sea change could be coming in our field, and it’s not coming next year or the year after, but 10 years from now: Are we going to move past the era of methotrexate and use generic small molecules instead? We’re going to find out within the next year whether that’s going to happen.”
Phase 3 results coming on tocilizumab for systemic sclerosis: “I think we’re going to see some really exciting systemic sclerosis data coming out this year,” Dr. Stevens said. Based upon the positive phase 2 results presented for tocilizumab (Actemra) last year, she’s optimistic that the ongoing phase 3 randomized trial will demonstrate a significant advantage over placebo in lung function. Also, ongoing separate clinical trials are evaluating an antifibrotic drug and rapamycin for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Bergman, too, has high hopes for these studies: “I think we may finally be getting to a place where we can see effective drugs in systemic sclerosis.”
Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JPMorgan Chase form a nonprofit to improve employee health care: In a recent press conference, the three CEOs weren’t specific about their plans, but Dr. Martin predicted the companies are likely to self-insure, bypassing Cigna and the other major health insurance companies and then contracting with physicians. He forecast that “probably within the next 5 years, what they do is going to affect everybody in this room.”
Rheumatologists will need to master a new mindset: Many rheumatologists have gotten comfortable with an all-tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment menu for their patients with moderate or severe rheumatoid arthritis. That’s got to change, according to Dr. Cush.
“We now have two IL-6 inhibitors, two IL-17 inhibitors, and we’ll soon have two JAK inhibitors. That’s going to be a direct threat to the not right- or left-brain, but the TNF-brain rheumatologist who now writes prescriptions for three TNF inhibitors in a row before questioning the efficacy. The idea is you will now be using drugs with other mechanisms of action first-line, or at the very least, second-line, and that’s going to be a paradigm shift for a lot of people,” he explained.
None of the speakers reported having financial conflicts regarding their comments.
MAUI, HAWAII – Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, program director for the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium, likes to close out the meeting each year in high style by assembling selected conference faculty to offer their personal picks for the top developments in the field during the past year and make predictions about the year to come.
Here’s how they called it:
The top events in rheumatology during the last year
The rise of oral small molecules: The Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors and other oral small molecules that have begun reaching the marketplace, with many more in development, will bring a paradigm shift in the treatment not only of rheumatic diseases, but in inflammatory bowel disease and skin diseases as well, predicted Alvin F. Wells, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who is also director of the Rheumatology and Immunotherapy Center in Franklin, Wisc.
“The challenge is whether Medicare will cover the pills the way they cover the infusions and the other things we do,” according to Dr. Wells.
A bevy of new drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: “I think the most important advance in the past year was the approval of a profusion of drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. It’s really opened up the landscape for us in terms of treatment options. The downside is it’s going to take us a while to sort through which drugs fit where,” noted Eric J. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief of clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The drug I was most impressed with was tofacitinib [Xeljanz, an oral JAK inhibitor], not just by its effectiveness but by its potential to change the game, and particularly the data in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor inadequate responders. That was pretty solid data. It really opens the way to oral small molecules for joint diseases,” he added.
Interleukin-18 binding protein for monogenic inflammasome diseases: The biggest recent breakthrough in pediatric rheumatology was the Food and Drug Administration’s April 2017 designation of Breakthrough Therapy status for the recombinant human IL-18 binding protein known as tadekinig alfa for monogenic IL-18-associated autoinflammatory conditions, as well as the biologic’s Orphan Drug Designation for treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, according to Anne M. Stevens, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chief of pediatric rheumatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Novel treatment concept emerges in severe SLE: The study that knocked the socks off of Martin J. Bergman, MD, in 2017 was the Dutch SymBiose study, presented at both the European League Against Rheumatism and American College of Rheumatology annual meetings. It included just 14 patients with severe refractory SLE – including 10 with lupus nephritis – and tested a treatment strategy of rituximab (Rituxan) followed a few weeks later by a course of belimumab (Benlysta).
“The results were very dramatic, to say the least,” said Dr. Bergman of Drexel University in Philadelphia. Indeed, this one-two therapeutic punch resulted in sharply reduced levels of pathogenic autoantibodies and immune complex-mediated neutrophil extracellular traps while also knocking down very high baseline Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) scores to near zero, even while enabling patients to discontinue systemic corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept). Several much larger clinical trials of this regimen and other similar ones are ongoing in an effort to duplicate the results.
Dr. Kavanaugh said the SymBiose study was one of his own top picks for study of the year as well.
Mainstream use of dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: “This is a total game changer. It’s really changed a lot of people’s lives,” commented George M. Martin, MD, a dermatologist in private practice on Maui.
“Interestingly, historically drugs that started out in your realm later made their way to dermatology, but now we’re seeing the IL-23 inhibitors starting with us and then making their way into rheumatology and gastroenterology. The IL-23 inhibitors are very powerful drugs; when we’re seeing half of our psoriasis patients achieve PASI 100 responses, it’s very exciting. And these are durable responses,” he noted.
The opioid crisis: What’s the most important recent event in rheumatology?
“That’s easy: The biggest thing in all of medicine is the opioid crisis. Whether you recognize it or not, it’s gigantic. It’s $500 billion of the U.S. economy, every year. Forty percent of rheumatoid arthritis patients and 30% with ankylosing spondylitis are on opioids, and what goes along with that is a lot of ugly stuff,” said John J. Cush, MD, professor of medicine and rheumatology at Baylor University in Dallas.
Moreover, the FDA is now so leery of opioids that the agency has set the bar unrealistically high for approval of newer agents offering reduced abuse potential.
“I’ve been involved with or watched at least six FDA advisory panels looking at new, lower abuse-potential opioids in the last couple years. Only one agent got through,” according to Dr. Cush.
Dr. Troum commented, “I really think this whole opioid epidemic started with the campaign to make pain the fifth vital sign back in the 1990s. Some of the pharmaceutical companies took that concept and really ran with it.”
Rapamycin for inclusion body myositis: Dr. Kavanaugh’s pick for study of the year was what he described as “a brilliant presentation” of a French multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trial of rapamycin for patients with inclusion body myositis at the 2017 ACR annual meeting.
“The French group considers IBM [inclusion body myositis] to be essentially Alzheimer’s disease of the muscle, marked by amyloid deposition. They chose to study rapamycin, which not only has immunosuppressive properties because it binds to mTOR [the mammalian target of rapamycin], but it also has the ability to inhibit amyloid protein deposition,” he explained.
The investigators reported improved 6-minute-walk distance and pulmonary function in the rapamycin group, whereas placebo-treated controls rapidly deteriorated.
“This is an approved drug for other indications, and we scratch our heads with IBM. It’s super nice to have something like that,” Dr. Kavanaugh observed.
A look at what’s in store
More tele-rheumatology: “I think the biggest thing is going to be more tele-rheumatology, more tele-ultrasound. Kaiser Permanente said 49% of their visits last year were virtual visits; that number is just going to grow,” predicted Dr. Wells.
Especially in medically underserved areas of the country, including large rural expanses, demand for remote tele-rheumatologic consults with high-quality imaging is going to increase, he added.
Here come cannabinoids for pain control: Dr. Troum predicted that in the depths of the national opioid epidemic, in a climate that discourages legitimate prescribing of traditional pain medications, rheumatologists can anticipate growing patient demand for cannabidiol and other cannabinoids for pain relief.
“I have patients coming in their 60s, 70s, and 80s – these are not young people – who are whispering to me, ‘Can I use this for my chronic pain?’ I think there’s going to be a big push for ways other than opioids to treat our patients’ pain,” according to Dr. Troum.
Tipping point nears for JAK inhibitors: In 2018, it will become clear just how seriously the Food and Drug Administration views the signal of possible increased venous thromboembolic risk associated with the oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. The agency is expected to rule on Eli Lilly and Incyte’s resubmitted application for marketing approval for the JAK inhibitor baricitinib, which was tripped up earlier based in part upon VTE concerns.
“I think the big story in 2018 will be how the JAK story shakes out – whether this VTE thing has legs,” Dr. Ruderman predicted. “A sea change could be coming in our field, and it’s not coming next year or the year after, but 10 years from now: Are we going to move past the era of methotrexate and use generic small molecules instead? We’re going to find out within the next year whether that’s going to happen.”
Phase 3 results coming on tocilizumab for systemic sclerosis: “I think we’re going to see some really exciting systemic sclerosis data coming out this year,” Dr. Stevens said. Based upon the positive phase 2 results presented for tocilizumab (Actemra) last year, she’s optimistic that the ongoing phase 3 randomized trial will demonstrate a significant advantage over placebo in lung function. Also, ongoing separate clinical trials are evaluating an antifibrotic drug and rapamycin for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Bergman, too, has high hopes for these studies: “I think we may finally be getting to a place where we can see effective drugs in systemic sclerosis.”
Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JPMorgan Chase form a nonprofit to improve employee health care: In a recent press conference, the three CEOs weren’t specific about their plans, but Dr. Martin predicted the companies are likely to self-insure, bypassing Cigna and the other major health insurance companies and then contracting with physicians. He forecast that “probably within the next 5 years, what they do is going to affect everybody in this room.”
Rheumatologists will need to master a new mindset: Many rheumatologists have gotten comfortable with an all-tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment menu for their patients with moderate or severe rheumatoid arthritis. That’s got to change, according to Dr. Cush.
“We now have two IL-6 inhibitors, two IL-17 inhibitors, and we’ll soon have two JAK inhibitors. That’s going to be a direct threat to the not right- or left-brain, but the TNF-brain rheumatologist who now writes prescriptions for three TNF inhibitors in a row before questioning the efficacy. The idea is you will now be using drugs with other mechanisms of action first-line, or at the very least, second-line, and that’s going to be a paradigm shift for a lot of people,” he explained.
None of the speakers reported having financial conflicts regarding their comments.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM RWCS 2018
Turmeric-, frankincense-derived supplement shows OA benefit
A combination of curcumin extracted from the turmeric rhizome and boswellic acid extracted from Indian frankincense root beat placebo for reducing pain-related symptoms from knee osteoarthritis in a 12-week clinical trial from Armenia with 201 patients 40-70 years old.
The combination (Curamin) also beat a standalone curcumin preparation (CuraMed), according to a report in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
It appears that combining the two “increases the efficacy of treatment of OA presumably due to synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acid”; it’s also possible that boswellic acid increases curcumin bioavailability, said investigators led by Armine Haroyan, PhD, head of rheumatology at Erebuni Medical Center in Yerevan, Armenia.
The subjects were randomized evenly to the combination, curcumin alone, or placebo, all in 500-mg capsules taken three times daily. They had been diagnosed with degenerative hypertrophic OA of knee bone joints.
At the end of 12 weeks, patients on the combination outperformed those on placebo in physical performance tests and joint pain scores; curcumin outperformed placebo in only a few of the physical tests.
For instance, patients on the combination were a mean of 2.03 seconds quicker than baseline in a stair-climbing exercise by the end of the study, versus 0.22 seconds in the placebo group and 1.66 seconds in the curcumin group. Combination patients had a mean 7.38-point improvement on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, versus 2.26 points in the placebo arm and 6.34 points in the curcumin group. The differences versus placebo were statistically significant for the combination, but not for stand-alone curcumin.
The treatments were well tolerated, with only a few patients in each arm reporting nausea, gastroesophageal reflux, and similar problems.
The work was funded in part by EuroPharma USA, maker of the supplements. The authors said they had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Haroyan A et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 9;18:7. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2062-z
A combination of curcumin extracted from the turmeric rhizome and boswellic acid extracted from Indian frankincense root beat placebo for reducing pain-related symptoms from knee osteoarthritis in a 12-week clinical trial from Armenia with 201 patients 40-70 years old.
The combination (Curamin) also beat a standalone curcumin preparation (CuraMed), according to a report in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
It appears that combining the two “increases the efficacy of treatment of OA presumably due to synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acid”; it’s also possible that boswellic acid increases curcumin bioavailability, said investigators led by Armine Haroyan, PhD, head of rheumatology at Erebuni Medical Center in Yerevan, Armenia.
The subjects were randomized evenly to the combination, curcumin alone, or placebo, all in 500-mg capsules taken three times daily. They had been diagnosed with degenerative hypertrophic OA of knee bone joints.
At the end of 12 weeks, patients on the combination outperformed those on placebo in physical performance tests and joint pain scores; curcumin outperformed placebo in only a few of the physical tests.
For instance, patients on the combination were a mean of 2.03 seconds quicker than baseline in a stair-climbing exercise by the end of the study, versus 0.22 seconds in the placebo group and 1.66 seconds in the curcumin group. Combination patients had a mean 7.38-point improvement on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, versus 2.26 points in the placebo arm and 6.34 points in the curcumin group. The differences versus placebo were statistically significant for the combination, but not for stand-alone curcumin.
The treatments were well tolerated, with only a few patients in each arm reporting nausea, gastroesophageal reflux, and similar problems.
The work was funded in part by EuroPharma USA, maker of the supplements. The authors said they had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Haroyan A et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 9;18:7. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2062-z
A combination of curcumin extracted from the turmeric rhizome and boswellic acid extracted from Indian frankincense root beat placebo for reducing pain-related symptoms from knee osteoarthritis in a 12-week clinical trial from Armenia with 201 patients 40-70 years old.
The combination (Curamin) also beat a standalone curcumin preparation (CuraMed), according to a report in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
It appears that combining the two “increases the efficacy of treatment of OA presumably due to synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acid”; it’s also possible that boswellic acid increases curcumin bioavailability, said investigators led by Armine Haroyan, PhD, head of rheumatology at Erebuni Medical Center in Yerevan, Armenia.
The subjects were randomized evenly to the combination, curcumin alone, or placebo, all in 500-mg capsules taken three times daily. They had been diagnosed with degenerative hypertrophic OA of knee bone joints.
At the end of 12 weeks, patients on the combination outperformed those on placebo in physical performance tests and joint pain scores; curcumin outperformed placebo in only a few of the physical tests.
For instance, patients on the combination were a mean of 2.03 seconds quicker than baseline in a stair-climbing exercise by the end of the study, versus 0.22 seconds in the placebo group and 1.66 seconds in the curcumin group. Combination patients had a mean 7.38-point improvement on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, versus 2.26 points in the placebo arm and 6.34 points in the curcumin group. The differences versus placebo were statistically significant for the combination, but not for stand-alone curcumin.
The treatments were well tolerated, with only a few patients in each arm reporting nausea, gastroesophageal reflux, and similar problems.
The work was funded in part by EuroPharma USA, maker of the supplements. The authors said they had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Haroyan A et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 9;18:7. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2062-z
FROM BMC COMPLEMENTARY AND ALTERNATIVE MEDICINE
Arthritis treatment costs per person held steady from 2008 to 2014
but the rise in proportion of the arthritis patients in the U.S. population led to billions more dollars being spent on this population, reported Amit D. Raval, PhD, and Ami Vyas, PhD, of the University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
Aggregate expenditures for patients with arthritis rose from $584.8 billion in 2008 to $645 billion in 2014, accounting for about 4% of the U.S. gross domestic product in these years, the investigators reported in the Journal of Rheumatology. “The increase in aggregate unadjusted total direct health care expenditures was mainly driven through an increase in weighted population of individuals with arthritis,” which rose from 56.1 million adults with arthritis in 2008 to 65.1 million in 2014. Nonetheless, there was a “slowdown in the intensity of adjusted incremental expenditures and [out of pocket expenditures] specifically from 2013, which led to a huge decline in the aggregate direct healthcare expenditures in 2014.”
During this time period, there was an increase in the percentage of Hispanics, poor, obese, and individuals with activity limitations and mental health disorders among both those with and without arthritis. This is consistent with the study findings that incremental health care expenditures in persons with arthritis were largely driven by difference in age, health status, and chronic conditions, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease, among those with and without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas said.
Annual total health care expenditures in persons with arthritis fell from $10,424 in 2008 to $9,910 in 2014. The average annual total out-of-pocket expenditures in 2008 was $1,493, which was 14% of total health care expenditures that year; in 2014, this fell to $1,099. There were similar trends in persons without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas reported.
The top three expenditure categories in 2008 were outpatient (32.6%), inpatient (29.0%), and prescription drug costs (24.7%); in 2014, these changed to outpatient (33.8%), prescription drug (26.8%), and inpatient costs (26.4%). There are a number of ways to explain these trends, the researchers said. It is likely that outpatient services, such as outpatient orthopedic surgeries, are becoming “a common management option for arthritis.” Also, outpatient medication services now may include administration of injectables such as biologics. There also were “relatively stable” inpatient expenditures from 2008 to 2013 and a decline in 2014. “Our findings are consistent with studies assessing the effect of the Affordable Care Act, such as introduction of the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program,” said Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas.
SOURCE: Amit R et al. J Rheumatol. 2018 Jan 15. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170368.
but the rise in proportion of the arthritis patients in the U.S. population led to billions more dollars being spent on this population, reported Amit D. Raval, PhD, and Ami Vyas, PhD, of the University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
Aggregate expenditures for patients with arthritis rose from $584.8 billion in 2008 to $645 billion in 2014, accounting for about 4% of the U.S. gross domestic product in these years, the investigators reported in the Journal of Rheumatology. “The increase in aggregate unadjusted total direct health care expenditures was mainly driven through an increase in weighted population of individuals with arthritis,” which rose from 56.1 million adults with arthritis in 2008 to 65.1 million in 2014. Nonetheless, there was a “slowdown in the intensity of adjusted incremental expenditures and [out of pocket expenditures] specifically from 2013, which led to a huge decline in the aggregate direct healthcare expenditures in 2014.”
During this time period, there was an increase in the percentage of Hispanics, poor, obese, and individuals with activity limitations and mental health disorders among both those with and without arthritis. This is consistent with the study findings that incremental health care expenditures in persons with arthritis were largely driven by difference in age, health status, and chronic conditions, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease, among those with and without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas said.
Annual total health care expenditures in persons with arthritis fell from $10,424 in 2008 to $9,910 in 2014. The average annual total out-of-pocket expenditures in 2008 was $1,493, which was 14% of total health care expenditures that year; in 2014, this fell to $1,099. There were similar trends in persons without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas reported.
The top three expenditure categories in 2008 were outpatient (32.6%), inpatient (29.0%), and prescription drug costs (24.7%); in 2014, these changed to outpatient (33.8%), prescription drug (26.8%), and inpatient costs (26.4%). There are a number of ways to explain these trends, the researchers said. It is likely that outpatient services, such as outpatient orthopedic surgeries, are becoming “a common management option for arthritis.” Also, outpatient medication services now may include administration of injectables such as biologics. There also were “relatively stable” inpatient expenditures from 2008 to 2013 and a decline in 2014. “Our findings are consistent with studies assessing the effect of the Affordable Care Act, such as introduction of the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program,” said Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas.
SOURCE: Amit R et al. J Rheumatol. 2018 Jan 15. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170368.
but the rise in proportion of the arthritis patients in the U.S. population led to billions more dollars being spent on this population, reported Amit D. Raval, PhD, and Ami Vyas, PhD, of the University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
Aggregate expenditures for patients with arthritis rose from $584.8 billion in 2008 to $645 billion in 2014, accounting for about 4% of the U.S. gross domestic product in these years, the investigators reported in the Journal of Rheumatology. “The increase in aggregate unadjusted total direct health care expenditures was mainly driven through an increase in weighted population of individuals with arthritis,” which rose from 56.1 million adults with arthritis in 2008 to 65.1 million in 2014. Nonetheless, there was a “slowdown in the intensity of adjusted incremental expenditures and [out of pocket expenditures] specifically from 2013, which led to a huge decline in the aggregate direct healthcare expenditures in 2014.”
During this time period, there was an increase in the percentage of Hispanics, poor, obese, and individuals with activity limitations and mental health disorders among both those with and without arthritis. This is consistent with the study findings that incremental health care expenditures in persons with arthritis were largely driven by difference in age, health status, and chronic conditions, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease, among those with and without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas said.
Annual total health care expenditures in persons with arthritis fell from $10,424 in 2008 to $9,910 in 2014. The average annual total out-of-pocket expenditures in 2008 was $1,493, which was 14% of total health care expenditures that year; in 2014, this fell to $1,099. There were similar trends in persons without arthritis, Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas reported.
The top three expenditure categories in 2008 were outpatient (32.6%), inpatient (29.0%), and prescription drug costs (24.7%); in 2014, these changed to outpatient (33.8%), prescription drug (26.8%), and inpatient costs (26.4%). There are a number of ways to explain these trends, the researchers said. It is likely that outpatient services, such as outpatient orthopedic surgeries, are becoming “a common management option for arthritis.” Also, outpatient medication services now may include administration of injectables such as biologics. There also were “relatively stable” inpatient expenditures from 2008 to 2013 and a decline in 2014. “Our findings are consistent with studies assessing the effect of the Affordable Care Act, such as introduction of the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program,” said Dr. Raval and Dr. Vyas.
SOURCE: Amit R et al. J Rheumatol. 2018 Jan 15. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170368.
FROM JOURNAL OF RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: The annual direct health care expenditures per person with arthritis remained relatively stable over the years 2008 to 2014.
Major finding: Aggregate expenditures for patients with arthritis rose from $584.8 billion in 2008 to $645 billion in 2014.
Study details: Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) data from approximately 5,000-6,000 persons aged 18 years and older with arthritis each year during 2008-2014 and approximately 17,000-20,000 persons without arthritis each year during that period.
Disclosures: No information on relevant financial disclosures was evident.
Source: Amit R et al. J Rheumatol. 2018 Jan 15. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170368.
Sprifermin shows cartilage-building potential in knee OA patients
in the initial 2-year results of the ongoing FORWARD trial.
“Sprifermin appears to be the first investigational medicinal product to show dose-dependent prevention of cartilage loss and an increase in cartilage thickness, not only in the total tibiofemoral joint [TFJ] but also in both the medial and lateral compartments, including the central medial femorotibial region,” said Marc H. Hochberg, MD, primary investigator in the trial and division head of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. “The recommendation is that these findings should be further evaluated in phase 3 clinical trials.”
He and his colleagues randomized 549 osteoarthritis (OA) patients to double-blind treatment with one of four different dosing regimens of sprifermin or placebo. These patients were aged 40-85 with symptomatic radiographic primary femorotibial knee OA measuring grade 2 or 3 on the Kellgren-Lawrence scale and a medial minimum joint space width (mJSW) 2.5 mm or greater.
At 2 years, researchers observed a significant dose-dependent relationship between the amount of sprifermin given and the increase in total TFJ cartilage thickness. Patients who received three 100-mcg intra-articular injections of sprifermin every 6 months (group 1) showed a gain in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.03 mm as seen on MRI, while those who received three 100-mcg injections of sprifermin every 12 months (group 2) had a gain of 0.02 mm, Dr. Hochberg said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. By contrast, those who received placebo had a loss in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.02 mm (P less than .001). The other two groups received 30 mcg of sprifermin in three weekly injections every 6 months (group 3) or every 12 months (group 4), and these had TFJ cartilage thickness losses of about 0.01 mm or less.
Similar dose-dependent relationships were observed for some of the secondary endpoints, which included changes in cartilage thickness seen in the medial and lateral compartments, changes in cartilage thickness in the compartments’ subregions, and changes in mJSW. Significant differences in cartilage thickness were observed between sprifermin treatment groups and placebo in the medial (group 1, gain of 0.02 mm vs. loss of 0.03 mm; P less than .001) and lateral (groups 1 and 2, gain of 0.04 mm vs. loss of 0.01 mm; P less than .001) TFJ compartments, and in central medial and lateral TFJ subregions.
Changes in mJSW as seen on x-ray between those in group 1 and those on placebo were significant for the lateral compartment, with an increase in mJSW at the higher doses and a decline in the placebo group, but not for the medial compartment.
There were no significant differences in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores among the treatment groups. Dr. Hochberg noted that patients were permitted to take pain medications during the study, which could have affected this result.
The most frequently reported adverse events were musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders, specifically arthralgias and back pain, Dr. Hochberg said. The incidence of acute inflammatory reactions was higher with sprifermin, compared with placebo, but the increase was only significant after the first injection cycle, he said.
Merck KGaA and the EMD Serono Research Institute funded the study. Dr. Hochberg reported receiving consulting fees from numerous companies that market or are developing OA drugs, including EMD Serono.
in the initial 2-year results of the ongoing FORWARD trial.
“Sprifermin appears to be the first investigational medicinal product to show dose-dependent prevention of cartilage loss and an increase in cartilage thickness, not only in the total tibiofemoral joint [TFJ] but also in both the medial and lateral compartments, including the central medial femorotibial region,” said Marc H. Hochberg, MD, primary investigator in the trial and division head of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. “The recommendation is that these findings should be further evaluated in phase 3 clinical trials.”
He and his colleagues randomized 549 osteoarthritis (OA) patients to double-blind treatment with one of four different dosing regimens of sprifermin or placebo. These patients were aged 40-85 with symptomatic radiographic primary femorotibial knee OA measuring grade 2 or 3 on the Kellgren-Lawrence scale and a medial minimum joint space width (mJSW) 2.5 mm or greater.
At 2 years, researchers observed a significant dose-dependent relationship between the amount of sprifermin given and the increase in total TFJ cartilage thickness. Patients who received three 100-mcg intra-articular injections of sprifermin every 6 months (group 1) showed a gain in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.03 mm as seen on MRI, while those who received three 100-mcg injections of sprifermin every 12 months (group 2) had a gain of 0.02 mm, Dr. Hochberg said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. By contrast, those who received placebo had a loss in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.02 mm (P less than .001). The other two groups received 30 mcg of sprifermin in three weekly injections every 6 months (group 3) or every 12 months (group 4), and these had TFJ cartilage thickness losses of about 0.01 mm or less.
Similar dose-dependent relationships were observed for some of the secondary endpoints, which included changes in cartilage thickness seen in the medial and lateral compartments, changes in cartilage thickness in the compartments’ subregions, and changes in mJSW. Significant differences in cartilage thickness were observed between sprifermin treatment groups and placebo in the medial (group 1, gain of 0.02 mm vs. loss of 0.03 mm; P less than .001) and lateral (groups 1 and 2, gain of 0.04 mm vs. loss of 0.01 mm; P less than .001) TFJ compartments, and in central medial and lateral TFJ subregions.
Changes in mJSW as seen on x-ray between those in group 1 and those on placebo were significant for the lateral compartment, with an increase in mJSW at the higher doses and a decline in the placebo group, but not for the medial compartment.
There were no significant differences in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores among the treatment groups. Dr. Hochberg noted that patients were permitted to take pain medications during the study, which could have affected this result.
The most frequently reported adverse events were musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders, specifically arthralgias and back pain, Dr. Hochberg said. The incidence of acute inflammatory reactions was higher with sprifermin, compared with placebo, but the increase was only significant after the first injection cycle, he said.
Merck KGaA and the EMD Serono Research Institute funded the study. Dr. Hochberg reported receiving consulting fees from numerous companies that market or are developing OA drugs, including EMD Serono.
in the initial 2-year results of the ongoing FORWARD trial.
“Sprifermin appears to be the first investigational medicinal product to show dose-dependent prevention of cartilage loss and an increase in cartilage thickness, not only in the total tibiofemoral joint [TFJ] but also in both the medial and lateral compartments, including the central medial femorotibial region,” said Marc H. Hochberg, MD, primary investigator in the trial and division head of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. “The recommendation is that these findings should be further evaluated in phase 3 clinical trials.”
He and his colleagues randomized 549 osteoarthritis (OA) patients to double-blind treatment with one of four different dosing regimens of sprifermin or placebo. These patients were aged 40-85 with symptomatic radiographic primary femorotibial knee OA measuring grade 2 or 3 on the Kellgren-Lawrence scale and a medial minimum joint space width (mJSW) 2.5 mm or greater.
At 2 years, researchers observed a significant dose-dependent relationship between the amount of sprifermin given and the increase in total TFJ cartilage thickness. Patients who received three 100-mcg intra-articular injections of sprifermin every 6 months (group 1) showed a gain in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.03 mm as seen on MRI, while those who received three 100-mcg injections of sprifermin every 12 months (group 2) had a gain of 0.02 mm, Dr. Hochberg said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. By contrast, those who received placebo had a loss in TFJ cartilage thickness of 0.02 mm (P less than .001). The other two groups received 30 mcg of sprifermin in three weekly injections every 6 months (group 3) or every 12 months (group 4), and these had TFJ cartilage thickness losses of about 0.01 mm or less.
Similar dose-dependent relationships were observed for some of the secondary endpoints, which included changes in cartilage thickness seen in the medial and lateral compartments, changes in cartilage thickness in the compartments’ subregions, and changes in mJSW. Significant differences in cartilage thickness were observed between sprifermin treatment groups and placebo in the medial (group 1, gain of 0.02 mm vs. loss of 0.03 mm; P less than .001) and lateral (groups 1 and 2, gain of 0.04 mm vs. loss of 0.01 mm; P less than .001) TFJ compartments, and in central medial and lateral TFJ subregions.
Changes in mJSW as seen on x-ray between those in group 1 and those on placebo were significant for the lateral compartment, with an increase in mJSW at the higher doses and a decline in the placebo group, but not for the medial compartment.
There were no significant differences in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores among the treatment groups. Dr. Hochberg noted that patients were permitted to take pain medications during the study, which could have affected this result.
The most frequently reported adverse events were musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders, specifically arthralgias and back pain, Dr. Hochberg said. The incidence of acute inflammatory reactions was higher with sprifermin, compared with placebo, but the increase was only significant after the first injection cycle, he said.
Merck KGaA and the EMD Serono Research Institute funded the study. Dr. Hochberg reported receiving consulting fees from numerous companies that market or are developing OA drugs, including EMD Serono.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2017
Key clinical point: Sprifermin may help build knee joint cartilage in patients with OA.
Major finding: Patients taking sprifermin 100 mcg three times a week every 6 months or every 12 months had gains in tibiofemoral joint cartilage thickness of 0.03 mm and 0.02 mm, respectively, over a 2-year period.
Study details: A study of 549 patients with symptomatic knee OA randomized to receive either 30 mcg or 100 mcg of sprifermin three times a week every 6 or every 12 months, or placebo.
Disclosures: Merck KGaA and the EMD Serono Research Institute funded the study. The presenter reported receiving consulting fees from numerous companies that market or are developing OA drugs, including EMD Serono.
Source: Hochberg M et al. ACR 2017 abstract 1L.
Evidence builds for long-term ineffectiveness of steroid shots for knee OA
SAN DIEGO – Real-world, nontrial research confirms the findings of a high-profile study released earlier in 2017: Corticosteroid shots are ineffective in the long term for knee osteoarthritis. In fact, researchers found a greater likelihood of a worsening condition in knees treated with the injections.
“Our findings are consistent with the latest randomized, controlled trial,” said study coauthor Jie Wei, MD, of Central South University in Changsha, China. She spoke in a plenary presentation about the study findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The use of corticosteroids for knee OA is a controversial topic. As Dr. Wei noted, there has been wide disagreement among medical societies about whether the treatment is useful in the long term for patients with pain flare-ups.
For the randomized, controlled study released in 2017, researchers tracked 140 patients aged 45 and older with inflammation of the synovial membrane. They were randomly assigned to injections of intra-articular triamcinolone or a placebo.
After 2 years of injections every 12 weeks, there was no difference in reported pain between the intervention and control groups. Also, those who received injections lost more cartilage (JAMA. 2017 May 16;317[19]:1967-75).
Researchers launched the new study to seek insight through a real-life cohort. They examined findings from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a longitudinal study of 4,796 patients aged 45-79 at four U.S. clinics with knee OA or high risk of knee OA. Patients underwent annual examinations at baseline and annually for 4 years.
In an adjusted marginal structural analysis, knee replacement or worsening of Kellgren Lawrence grade at the tibial femoral joint was more likely in 149 injection knees than 2,191 noninjection knees (odds ratio, 5.74; 95% confidence interval, 2.01-16.42).
Knee replacement or joint space width worsening at the tibial femoral joint was also more likely in 120 injection knees than 2,112 noninjection knees (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 0.91-2.93).
In another analysis, researchers tracked 134 injection knees (58 whose OA progressed) and 498 noninjection knees (132 whose OA progressed) for up to 8 years. After adjustment, the injection knees were more likely to have progressed (hazard ratio, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.21-2.12,).
“Several explanations may account for our study findings,” Dr. Wei said. One possibility, she said, is that corticosteroids may hurt chondrocytes by, among other things, inducing apoptosis and synovial membrane inflammation.
It’s also possible, she said, that patients may feel pain relief after injections and subsequently boost the risk of OA progression by increasing their physical activity.
“We need to know what types of physical activities may increase the OA progression,” she said. “Did patients who received steroid injection indeed increase this type of physical activity compared to subjects without steroid injection?”
Dr. Wei noted the study’s limitations, including the fact that patients who received injections had more pain at baseline, potentially indicating they had worse structural lesions that are more susceptible to progression.
The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. The National Natural Science Foundation of China funded the study. The Osteoarthritis Initiative is a partnership between the National Institutes of Health and Merck, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, and Pfizer.
SAN DIEGO – Real-world, nontrial research confirms the findings of a high-profile study released earlier in 2017: Corticosteroid shots are ineffective in the long term for knee osteoarthritis. In fact, researchers found a greater likelihood of a worsening condition in knees treated with the injections.
“Our findings are consistent with the latest randomized, controlled trial,” said study coauthor Jie Wei, MD, of Central South University in Changsha, China. She spoke in a plenary presentation about the study findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The use of corticosteroids for knee OA is a controversial topic. As Dr. Wei noted, there has been wide disagreement among medical societies about whether the treatment is useful in the long term for patients with pain flare-ups.
For the randomized, controlled study released in 2017, researchers tracked 140 patients aged 45 and older with inflammation of the synovial membrane. They were randomly assigned to injections of intra-articular triamcinolone or a placebo.
After 2 years of injections every 12 weeks, there was no difference in reported pain between the intervention and control groups. Also, those who received injections lost more cartilage (JAMA. 2017 May 16;317[19]:1967-75).
Researchers launched the new study to seek insight through a real-life cohort. They examined findings from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a longitudinal study of 4,796 patients aged 45-79 at four U.S. clinics with knee OA or high risk of knee OA. Patients underwent annual examinations at baseline and annually for 4 years.
In an adjusted marginal structural analysis, knee replacement or worsening of Kellgren Lawrence grade at the tibial femoral joint was more likely in 149 injection knees than 2,191 noninjection knees (odds ratio, 5.74; 95% confidence interval, 2.01-16.42).
Knee replacement or joint space width worsening at the tibial femoral joint was also more likely in 120 injection knees than 2,112 noninjection knees (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 0.91-2.93).
In another analysis, researchers tracked 134 injection knees (58 whose OA progressed) and 498 noninjection knees (132 whose OA progressed) for up to 8 years. After adjustment, the injection knees were more likely to have progressed (hazard ratio, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.21-2.12,).
“Several explanations may account for our study findings,” Dr. Wei said. One possibility, she said, is that corticosteroids may hurt chondrocytes by, among other things, inducing apoptosis and synovial membrane inflammation.
It’s also possible, she said, that patients may feel pain relief after injections and subsequently boost the risk of OA progression by increasing their physical activity.
“We need to know what types of physical activities may increase the OA progression,” she said. “Did patients who received steroid injection indeed increase this type of physical activity compared to subjects without steroid injection?”
Dr. Wei noted the study’s limitations, including the fact that patients who received injections had more pain at baseline, potentially indicating they had worse structural lesions that are more susceptible to progression.
The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. The National Natural Science Foundation of China funded the study. The Osteoarthritis Initiative is a partnership between the National Institutes of Health and Merck, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, and Pfizer.
SAN DIEGO – Real-world, nontrial research confirms the findings of a high-profile study released earlier in 2017: Corticosteroid shots are ineffective in the long term for knee osteoarthritis. In fact, researchers found a greater likelihood of a worsening condition in knees treated with the injections.
“Our findings are consistent with the latest randomized, controlled trial,” said study coauthor Jie Wei, MD, of Central South University in Changsha, China. She spoke in a plenary presentation about the study findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The use of corticosteroids for knee OA is a controversial topic. As Dr. Wei noted, there has been wide disagreement among medical societies about whether the treatment is useful in the long term for patients with pain flare-ups.
For the randomized, controlled study released in 2017, researchers tracked 140 patients aged 45 and older with inflammation of the synovial membrane. They were randomly assigned to injections of intra-articular triamcinolone or a placebo.
After 2 years of injections every 12 weeks, there was no difference in reported pain between the intervention and control groups. Also, those who received injections lost more cartilage (JAMA. 2017 May 16;317[19]:1967-75).
Researchers launched the new study to seek insight through a real-life cohort. They examined findings from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a longitudinal study of 4,796 patients aged 45-79 at four U.S. clinics with knee OA or high risk of knee OA. Patients underwent annual examinations at baseline and annually for 4 years.
In an adjusted marginal structural analysis, knee replacement or worsening of Kellgren Lawrence grade at the tibial femoral joint was more likely in 149 injection knees than 2,191 noninjection knees (odds ratio, 5.74; 95% confidence interval, 2.01-16.42).
Knee replacement or joint space width worsening at the tibial femoral joint was also more likely in 120 injection knees than 2,112 noninjection knees (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 0.91-2.93).
In another analysis, researchers tracked 134 injection knees (58 whose OA progressed) and 498 noninjection knees (132 whose OA progressed) for up to 8 years. After adjustment, the injection knees were more likely to have progressed (hazard ratio, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.21-2.12,).
“Several explanations may account for our study findings,” Dr. Wei said. One possibility, she said, is that corticosteroids may hurt chondrocytes by, among other things, inducing apoptosis and synovial membrane inflammation.
It’s also possible, she said, that patients may feel pain relief after injections and subsequently boost the risk of OA progression by increasing their physical activity.
“We need to know what types of physical activities may increase the OA progression,” she said. “Did patients who received steroid injection indeed increase this type of physical activity compared to subjects without steroid injection?”
Dr. Wei noted the study’s limitations, including the fact that patients who received injections had more pain at baseline, potentially indicating they had worse structural lesions that are more susceptible to progression.
The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. The National Natural Science Foundation of China funded the study. The Osteoarthritis Initiative is a partnership between the National Institutes of Health and Merck, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, and Pfizer.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In adjusted analysis of 134 injection knees and 498 noninjection knees tracked for up to 8 years, OA in injection knees was more likely to have progressed (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.21-2.12).
Study details: Cohort analysis of data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, which tracked patients with (or at high risk of) knee OA at four U.S. clinics.
Disclosures: The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. The National Natural Science Foundation of China funded the study. The Osteoarthritis Initiative is a partnership between the National Institutes of Health and Merck, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, and Pfizer.
Source: Lei G et al. ACR 2017 Abstract 1788.
FDA recommends voluntary recall of Limbrel
The Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 4 that it recommends the voluntary recall of Limbrel, a medical food product in capsule form that is currently marketed to “manage the metabolic processes associated with osteoarthritis.”
The FDA’s ongoing investigation at this point considers the product to be an unapproved new drug rather than a medical food product. However, the agency does not have mandatory recall authority. It has recommended the recall to the product’s manufacturer, Primus Pharmaceuticals, on the basis of the risk of liver injury and hypersensitivity pneumonitis associated with continued use of the product.
The agency had received 194 adverse event reports as of Nov. 21, of which it found a likely association of the events with Limbrel in at least 30 cases, and continues to evaluate reports, which consumers can submit through MedWatch. The FDA is currently testing samples of the product and has advised consumers to cease taking it, though the manufacturer has declined thus far to recall it.
The safety alert advises that “health care providers who are aware that their patients are taking Limbrel should advise them to immediately stop taking the product.”
The Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 4 that it recommends the voluntary recall of Limbrel, a medical food product in capsule form that is currently marketed to “manage the metabolic processes associated with osteoarthritis.”
The FDA’s ongoing investigation at this point considers the product to be an unapproved new drug rather than a medical food product. However, the agency does not have mandatory recall authority. It has recommended the recall to the product’s manufacturer, Primus Pharmaceuticals, on the basis of the risk of liver injury and hypersensitivity pneumonitis associated with continued use of the product.
The agency had received 194 adverse event reports as of Nov. 21, of which it found a likely association of the events with Limbrel in at least 30 cases, and continues to evaluate reports, which consumers can submit through MedWatch. The FDA is currently testing samples of the product and has advised consumers to cease taking it, though the manufacturer has declined thus far to recall it.
The safety alert advises that “health care providers who are aware that their patients are taking Limbrel should advise them to immediately stop taking the product.”
The Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 4 that it recommends the voluntary recall of Limbrel, a medical food product in capsule form that is currently marketed to “manage the metabolic processes associated with osteoarthritis.”
The FDA’s ongoing investigation at this point considers the product to be an unapproved new drug rather than a medical food product. However, the agency does not have mandatory recall authority. It has recommended the recall to the product’s manufacturer, Primus Pharmaceuticals, on the basis of the risk of liver injury and hypersensitivity pneumonitis associated with continued use of the product.
The agency had received 194 adverse event reports as of Nov. 21, of which it found a likely association of the events with Limbrel in at least 30 cases, and continues to evaluate reports, which consumers can submit through MedWatch. The FDA is currently testing samples of the product and has advised consumers to cease taking it, though the manufacturer has declined thus far to recall it.
The safety alert advises that “health care providers who are aware that their patients are taking Limbrel should advise them to immediately stop taking the product.”
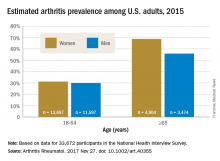
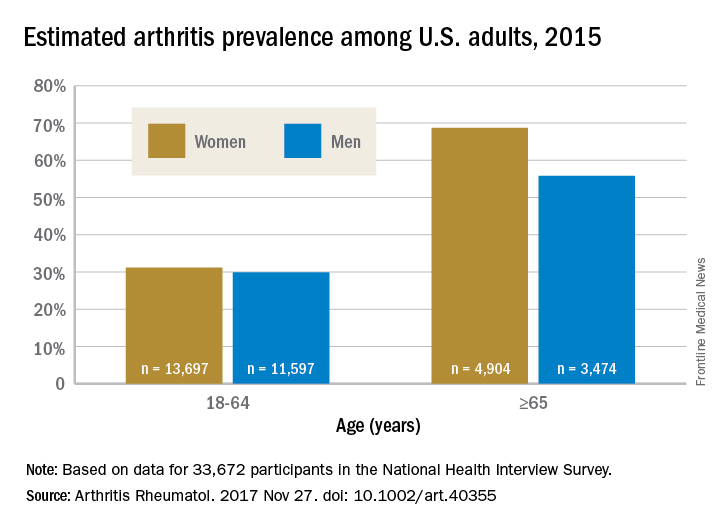
Arthritis prevalence higher than previously thought, especially in adults under 65
The prevalence of arthritis in the United States is much higher than current estimates indicate, especially among adults under 65 years of age, a study showed.
The higher prevalence can be largely attributed to “the previous underestimate of arthritis in adults between 18-64 years of age,” according to S. Reza Jafarzadeh, PhD, and David T. Felson , MD, both of Boston University. Using a new surveillance model, they estimated that 91.2 million adults in the United States (36.8%) had arthritis in 2015, compared with a previously reported national estimate of 54.4 million adults (22.7%). Of these, 61.1 million were between 18 and 64 years of age (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40355).
Arthritis prevalence was 29.9% in men aged 18-64 years (95% probability interval, 23.4-42.3), 31.2% in women aged 18-64 years (95% PI, 25.8-44.1), 55.8% in men aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 49.9-70.4), and 68.7% in women aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 62.1-79.9), the authors reported.
Among respondents aged 18-64 years, 19.3% of men and 16.7% of women reported that they had chronic joint symptoms but no physician-diagnosed arthritis. Among those 65 years of age or older, 15.7% of men and 13.5% of women responded that they had chronic joint symptoms without physician-diagnosed arthritis.
Current methodology for estimating arthritis prevalence is based on a single survey question asking whether a health care provider has ever told the patient that he or she has arthritis, a method that has previously been shown to have a sensitivity of 68.8% in adults 65 years of age and older and 52.5% for those aged 45-64 years, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson reported. “Such a low sensitivity, especially in a younger population, where almost half of true arthritis cases are missed, results in substantial misclassification and underestimation of prevalence and would have a detrimental effect for planning and needs assessment,” the authors wrote.
The two additional questions on joint pain, aching, and stiffness that the investigators included in the study captured “a substantial (i.e., 65%-80%) fraction of the population with arthritis, who are between 18-64 years of age, but are misclassified as healthy by the doctor-diagnosed arthritis criterion due to low sensitivity,” they said.
The study authors also speculated that younger patients might be more likely to ignore symptoms or visit a doctor less often.
“Further studies are needed to evaluate potential changes in the specific causes of arthritis, especially among adults below the age of 65,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. The investigators did not disclose any other conflicts of interest.
By including two additional survey criteria in their study of arthritis prevalence, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson introduced a method that “may be considerably more accurate than prior estimates that use the single NHIS [National Health Interview Survey] item on doctor-diagnosed arthritis,” said Jeffrey N. Katz, MD, in an editorial accompanying the study.
The study raises important questions about how “arthritis” is defined, as well as how prevalence estimates could affect policy agendas, and could potentially have “far-reaching consequences” related to investment in research, prevention, and treatment, he added.
Dr. Katz is with the Orthopedic and Arthritis Center for Outcomes Research at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40357). No conflicts of interest were disclosed.
By including two additional survey criteria in their study of arthritis prevalence, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson introduced a method that “may be considerably more accurate than prior estimates that use the single NHIS [National Health Interview Survey] item on doctor-diagnosed arthritis,” said Jeffrey N. Katz, MD, in an editorial accompanying the study.
The study raises important questions about how “arthritis” is defined, as well as how prevalence estimates could affect policy agendas, and could potentially have “far-reaching consequences” related to investment in research, prevention, and treatment, he added.
Dr. Katz is with the Orthopedic and Arthritis Center for Outcomes Research at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40357). No conflicts of interest were disclosed.
By including two additional survey criteria in their study of arthritis prevalence, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson introduced a method that “may be considerably more accurate than prior estimates that use the single NHIS [National Health Interview Survey] item on doctor-diagnosed arthritis,” said Jeffrey N. Katz, MD, in an editorial accompanying the study.
The study raises important questions about how “arthritis” is defined, as well as how prevalence estimates could affect policy agendas, and could potentially have “far-reaching consequences” related to investment in research, prevention, and treatment, he added.
Dr. Katz is with the Orthopedic and Arthritis Center for Outcomes Research at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40357). No conflicts of interest were disclosed.
The prevalence of arthritis in the United States is much higher than current estimates indicate, especially among adults under 65 years of age, a study showed.
The higher prevalence can be largely attributed to “the previous underestimate of arthritis in adults between 18-64 years of age,” according to S. Reza Jafarzadeh, PhD, and David T. Felson , MD, both of Boston University. Using a new surveillance model, they estimated that 91.2 million adults in the United States (36.8%) had arthritis in 2015, compared with a previously reported national estimate of 54.4 million adults (22.7%). Of these, 61.1 million were between 18 and 64 years of age (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40355).
Arthritis prevalence was 29.9% in men aged 18-64 years (95% probability interval, 23.4-42.3), 31.2% in women aged 18-64 years (95% PI, 25.8-44.1), 55.8% in men aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 49.9-70.4), and 68.7% in women aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 62.1-79.9), the authors reported.
Among respondents aged 18-64 years, 19.3% of men and 16.7% of women reported that they had chronic joint symptoms but no physician-diagnosed arthritis. Among those 65 years of age or older, 15.7% of men and 13.5% of women responded that they had chronic joint symptoms without physician-diagnosed arthritis.
Current methodology for estimating arthritis prevalence is based on a single survey question asking whether a health care provider has ever told the patient that he or she has arthritis, a method that has previously been shown to have a sensitivity of 68.8% in adults 65 years of age and older and 52.5% for those aged 45-64 years, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson reported. “Such a low sensitivity, especially in a younger population, where almost half of true arthritis cases are missed, results in substantial misclassification and underestimation of prevalence and would have a detrimental effect for planning and needs assessment,” the authors wrote.
The two additional questions on joint pain, aching, and stiffness that the investigators included in the study captured “a substantial (i.e., 65%-80%) fraction of the population with arthritis, who are between 18-64 years of age, but are misclassified as healthy by the doctor-diagnosed arthritis criterion due to low sensitivity,” they said.
The study authors also speculated that younger patients might be more likely to ignore symptoms or visit a doctor less often.
“Further studies are needed to evaluate potential changes in the specific causes of arthritis, especially among adults below the age of 65,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. The investigators did not disclose any other conflicts of interest.
The prevalence of arthritis in the United States is much higher than current estimates indicate, especially among adults under 65 years of age, a study showed.
The higher prevalence can be largely attributed to “the previous underestimate of arthritis in adults between 18-64 years of age,” according to S. Reza Jafarzadeh, PhD, and David T. Felson , MD, both of Boston University. Using a new surveillance model, they estimated that 91.2 million adults in the United States (36.8%) had arthritis in 2015, compared with a previously reported national estimate of 54.4 million adults (22.7%). Of these, 61.1 million were between 18 and 64 years of age (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/art.40355).
Arthritis prevalence was 29.9% in men aged 18-64 years (95% probability interval, 23.4-42.3), 31.2% in women aged 18-64 years (95% PI, 25.8-44.1), 55.8% in men aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 49.9-70.4), and 68.7% in women aged 65 years and older (95% PI, 62.1-79.9), the authors reported.
Among respondents aged 18-64 years, 19.3% of men and 16.7% of women reported that they had chronic joint symptoms but no physician-diagnosed arthritis. Among those 65 years of age or older, 15.7% of men and 13.5% of women responded that they had chronic joint symptoms without physician-diagnosed arthritis.
Current methodology for estimating arthritis prevalence is based on a single survey question asking whether a health care provider has ever told the patient that he or she has arthritis, a method that has previously been shown to have a sensitivity of 68.8% in adults 65 years of age and older and 52.5% for those aged 45-64 years, Dr. Jafarzadeh and Dr. Felson reported. “Such a low sensitivity, especially in a younger population, where almost half of true arthritis cases are missed, results in substantial misclassification and underestimation of prevalence and would have a detrimental effect for planning and needs assessment,” the authors wrote.
The two additional questions on joint pain, aching, and stiffness that the investigators included in the study captured “a substantial (i.e., 65%-80%) fraction of the population with arthritis, who are between 18-64 years of age, but are misclassified as healthy by the doctor-diagnosed arthritis criterion due to low sensitivity,” they said.
The study authors also speculated that younger patients might be more likely to ignore symptoms or visit a doctor less often.
“Further studies are needed to evaluate potential changes in the specific causes of arthritis, especially among adults below the age of 65,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. The investigators did not disclose any other conflicts of interest.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: An estimated 91.2 million adults in the United States (36.8%) had arthritis in 2015, compared with a previously reported national estimate of 54.4 million adults (22.7%).
Data source: Data from 33,672 respondents to the 2015 National Health Interview Survey.
Disclosures: The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. The investigators did not disclose any other conflicts of interest.
Injectable agent found to improve knee function in OA patients
SAN DIEGO – Among patients with mild to moderate patellofemoral osteoarthritis, intra-articular administration of the novel agent TPX-100 was safe and associated with functional benefits up to 1 year, a proof-of-concept study showed.
“We don’t yet have a disease-modifying drug for osteoarthritis [OA]; that’s sort of the holy grail for researchers,” lead study author Dawn McGuire, MD, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. “All of the patient-reported outcome and patient function indices that we studied moved in the same direction, showing a benefit of TPX-100. I think this is very promising.”
The study consisted of two parts. In Part A, four dose cohorts ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection were enrolled. There were no dose-limiting toxicities or safety concerns at any dose, and the 200-mg dose was selected dose for Part B of the study.
The median age of the 118 patients was 60 years and their median body mass index was 29.2 kg/m2. No drug-related serious adverse events and no dose-limiting toxicities occurred across doses ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection. The incidence of common adverse events such as knee pain was similar between placebo- and TPX-100-treated knees.
Quantitative MRI showed no measurable between-knee differences in cartilage thickness or volume at 6 or 12 months. However, statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences in knee function were observed in favor of TPX-100-treated knees, compared with controls, including KOOS activities of daily living (P = .008 at 6 and 12 months), KOOS knee-related quality of life (P = .21 at 6 months and P = .03 at 12 months), and a significant reduction in pain going up or down stairs (P = .004 at 12 months). Subjects’ use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications declined by 63% during the study.
“In this study, we see some terrific, long-term results in knee-related core activities, which certainly were disease modifying from the patients’ perspective,” said Dr. McGuire, who noted that a phase 3 study is being planned. “In addition, patient’s pain going up and down stairs improved significantly, with a marked reduction in analgesic use. Any of us who are experienced in these tough areas of medicine know that early results can look extremely promising, but we have to do larger confirmatory studies.”
SAN DIEGO – Among patients with mild to moderate patellofemoral osteoarthritis, intra-articular administration of the novel agent TPX-100 was safe and associated with functional benefits up to 1 year, a proof-of-concept study showed.
“We don’t yet have a disease-modifying drug for osteoarthritis [OA]; that’s sort of the holy grail for researchers,” lead study author Dawn McGuire, MD, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. “All of the patient-reported outcome and patient function indices that we studied moved in the same direction, showing a benefit of TPX-100. I think this is very promising.”
The study consisted of two parts. In Part A, four dose cohorts ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection were enrolled. There were no dose-limiting toxicities or safety concerns at any dose, and the 200-mg dose was selected dose for Part B of the study.
The median age of the 118 patients was 60 years and their median body mass index was 29.2 kg/m2. No drug-related serious adverse events and no dose-limiting toxicities occurred across doses ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection. The incidence of common adverse events such as knee pain was similar between placebo- and TPX-100-treated knees.
Quantitative MRI showed no measurable between-knee differences in cartilage thickness or volume at 6 or 12 months. However, statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences in knee function were observed in favor of TPX-100-treated knees, compared with controls, including KOOS activities of daily living (P = .008 at 6 and 12 months), KOOS knee-related quality of life (P = .21 at 6 months and P = .03 at 12 months), and a significant reduction in pain going up or down stairs (P = .004 at 12 months). Subjects’ use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications declined by 63% during the study.
“In this study, we see some terrific, long-term results in knee-related core activities, which certainly were disease modifying from the patients’ perspective,” said Dr. McGuire, who noted that a phase 3 study is being planned. “In addition, patient’s pain going up and down stairs improved significantly, with a marked reduction in analgesic use. Any of us who are experienced in these tough areas of medicine know that early results can look extremely promising, but we have to do larger confirmatory studies.”
SAN DIEGO – Among patients with mild to moderate patellofemoral osteoarthritis, intra-articular administration of the novel agent TPX-100 was safe and associated with functional benefits up to 1 year, a proof-of-concept study showed.
“We don’t yet have a disease-modifying drug for osteoarthritis [OA]; that’s sort of the holy grail for researchers,” lead study author Dawn McGuire, MD, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. “All of the patient-reported outcome and patient function indices that we studied moved in the same direction, showing a benefit of TPX-100. I think this is very promising.”
The study consisted of two parts. In Part A, four dose cohorts ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection were enrolled. There were no dose-limiting toxicities or safety concerns at any dose, and the 200-mg dose was selected dose for Part B of the study.
The median age of the 118 patients was 60 years and their median body mass index was 29.2 kg/m2. No drug-related serious adverse events and no dose-limiting toxicities occurred across doses ranging from 20 mg to 200 mg per injection. The incidence of common adverse events such as knee pain was similar between placebo- and TPX-100-treated knees.
Quantitative MRI showed no measurable between-knee differences in cartilage thickness or volume at 6 or 12 months. However, statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences in knee function were observed in favor of TPX-100-treated knees, compared with controls, including KOOS activities of daily living (P = .008 at 6 and 12 months), KOOS knee-related quality of life (P = .21 at 6 months and P = .03 at 12 months), and a significant reduction in pain going up or down stairs (P = .004 at 12 months). Subjects’ use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications declined by 63% during the study.
“In this study, we see some terrific, long-term results in knee-related core activities, which certainly were disease modifying from the patients’ perspective,” said Dr. McGuire, who noted that a phase 3 study is being planned. “In addition, patient’s pain going up and down stairs improved significantly, with a marked reduction in analgesic use. Any of us who are experienced in these tough areas of medicine know that early results can look extremely promising, but we have to do larger confirmatory studies.”
AT ACR 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Statistically significant differences in knee function were observed in favor of TPX-100-treated knees, compared with controls, using Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score activities of daily living (P = .008 at 6 and 12 months) and a significant reduction in pain going up or down stairs (P = .004 at 12 months).
Study details: A randomized, proof-of-concept study involving 118 patients with patellofemoral knee OA.
Disclosures: OrthoTrophix sponsored the study. Dr. McGuire is chief medical officer and a cofounder of the company.
FDA approves first extended-release steroid injection for OA knee pain
Flexion Therapeutics announced Oct. 6 the approval of Zilretta (triamcinolone acetonide extended-release injectable suspension) as the first and only extended-release, intra-articular injection for osteoarthritis knee pain.
Zilretta uses a proprietary microsphere-based formulation of triamcinolone acetonide to provide pain relief over 12 weeks by prolonging the release of triamcinolone acetonide inside the synovial fluid. The approval is based on data from a phase 3 clinical trial. The randomized, double-blind study enrolled 484 patients at 37 centers worldwide. The label also includes the results from a double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial, which examined blood glucose concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes to show how Zilretta can avoid blood glucose spikes observed with corticosteroid use.
Zilretta is expected to be available in the United States by the end of October.
Flexion Therapeutics announced Oct. 6 the approval of Zilretta (triamcinolone acetonide extended-release injectable suspension) as the first and only extended-release, intra-articular injection for osteoarthritis knee pain.
Zilretta uses a proprietary microsphere-based formulation of triamcinolone acetonide to provide pain relief over 12 weeks by prolonging the release of triamcinolone acetonide inside the synovial fluid. The approval is based on data from a phase 3 clinical trial. The randomized, double-blind study enrolled 484 patients at 37 centers worldwide. The label also includes the results from a double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial, which examined blood glucose concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes to show how Zilretta can avoid blood glucose spikes observed with corticosteroid use.
Zilretta is expected to be available in the United States by the end of October.
Flexion Therapeutics announced Oct. 6 the approval of Zilretta (triamcinolone acetonide extended-release injectable suspension) as the first and only extended-release, intra-articular injection for osteoarthritis knee pain.
Zilretta uses a proprietary microsphere-based formulation of triamcinolone acetonide to provide pain relief over 12 weeks by prolonging the release of triamcinolone acetonide inside the synovial fluid. The approval is based on data from a phase 3 clinical trial. The randomized, double-blind study enrolled 484 patients at 37 centers worldwide. The label also includes the results from a double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial, which examined blood glucose concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes to show how Zilretta can avoid blood glucose spikes observed with corticosteroid use.
Zilretta is expected to be available in the United States by the end of October.
Dr. Clyde Yancy: CANTOS wows, opens new therapeutic avenues
BARCELONA – For Clyde Yancy, MD, presentation of the bombshell CANTOS trial results at the annual congress of the European Congress of Cardiology made for “a really good day.”
Those results showed that inhibiting the interleukin-1 beta innate immunity pathway with canakinumab reduced recurrent cardiovascular events and lung cancer. But further, they introduced a new way of identifying and treating patients for secondary prevention.
“Here is an alternative way to get to cardiovascular events; here is bringing inflammation right to the front page of what we do as cardiologists to prevent events; here is a brand-new agent that is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin that may be modifying this risk, and … a remarkable advantage that really needs to be replicated,” said Dr. Yancy, chief of medicine-cardiology at Northwestern University in Chicago, in a video interview.
“This is a really good day” because we’ve got new things to think about, new ways to approach our patients, and [we may soon be] entering the realm where we’ll want personalized therapy based on the unique phenotype a patient represents, and think about the pathways to disease through these brand new schemes” that are helping us understand the burden of disease, he declared.
BARCELONA – For Clyde Yancy, MD, presentation of the bombshell CANTOS trial results at the annual congress of the European Congress of Cardiology made for “a really good day.”
Those results showed that inhibiting the interleukin-1 beta innate immunity pathway with canakinumab reduced recurrent cardiovascular events and lung cancer. But further, they introduced a new way of identifying and treating patients for secondary prevention.
“Here is an alternative way to get to cardiovascular events; here is bringing inflammation right to the front page of what we do as cardiologists to prevent events; here is a brand-new agent that is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin that may be modifying this risk, and … a remarkable advantage that really needs to be replicated,” said Dr. Yancy, chief of medicine-cardiology at Northwestern University in Chicago, in a video interview.
“This is a really good day” because we’ve got new things to think about, new ways to approach our patients, and [we may soon be] entering the realm where we’ll want personalized therapy based on the unique phenotype a patient represents, and think about the pathways to disease through these brand new schemes” that are helping us understand the burden of disease, he declared.
BARCELONA – For Clyde Yancy, MD, presentation of the bombshell CANTOS trial results at the annual congress of the European Congress of Cardiology made for “a really good day.”
Those results showed that inhibiting the interleukin-1 beta innate immunity pathway with canakinumab reduced recurrent cardiovascular events and lung cancer. But further, they introduced a new way of identifying and treating patients for secondary prevention.
“Here is an alternative way to get to cardiovascular events; here is bringing inflammation right to the front page of what we do as cardiologists to prevent events; here is a brand-new agent that is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin that may be modifying this risk, and … a remarkable advantage that really needs to be replicated,” said Dr. Yancy, chief of medicine-cardiology at Northwestern University in Chicago, in a video interview.
“This is a really good day” because we’ve got new things to think about, new ways to approach our patients, and [we may soon be] entering the realm where we’ll want personalized therapy based on the unique phenotype a patient represents, and think about the pathways to disease through these brand new schemes” that are helping us understand the burden of disease, he declared.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2017