User login
Difficulty fitting family into career: Female oncologists
In a survey of just over 1,000 female oncologists, 95% said their career plans were at least somewhat associated with the timing of when to start a family.
The most striking finding was that one third of respondents had miscarried and another one third reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
One third reported experiencing discrimination during pregnancy, and another third said they experienced discrimination for taking maternity leave, and having more than one child increased the likelihood of this.
The most common negative factor associated with family planning was long work hours and heavy workload (66.6%),
These findings suggest there are systemic changes needed not only in the healthcare setting but in society as a whole around women in the workplace and their choices of childbearing, say the authors.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open and led by Anna Lee MD, MPH, from the department of radiation oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
In an invited commentary, Mona Saleh, MD, and Stephanie Blank, MD, from the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggest that cultural changes are needed that go beyond women in medicine.
“These cultural values are so deeply pervasive (one could also say invasive) that they affect even these most educated and wealthy professional women, such as those who participated in this survey,” the editorialists write.
“[The researchers] advocate for early education on assisted reproductive technology (ART) risks, benefits, and success rates, but this is not getting at the underlying issue: Pregnancy discrimination and unfair distribution of childbearing responsibilities are a reflection of a larger problematic culture rather than an issue specific to women in medicine,” they add.
Survey details
The survey comprised a novel 39-item questionnaire distributed to 1,004 U.S. female oncologists from May 7 to June 30, 2020, via email and social media channels.
Most respondents (84.4%) were married, and 71% were currently working full-time.
About one-third (35%) worked in radiation oncology, another third (34.3%) in medical oncology, 18.4% in surgical oncology, and 9.1% in pediatric oncology.
A total of 768 respondents (76.5%) had children, and of these, 415 (41.3%) first gave birth during postgraduate training and 275 (27.4%) gave birth in years 1-5 as an attending physician.
Of all respondents who had been pregnant, approximately two-thirds (65.7%) had some type of pregnancy complication. About one-third of respondents (31.7%) reported having experienced a miscarriage after a confirmed pregnancy; of those, 61.6% reported one miscarriage, while the remainder had two or more miscarriages (38.4%).
Approximately one-third (31.4%) of respondents reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
The questionnaire also asked about assisted reproductive technology, and 164 participants (16.3%) reported the use of fertility medications, and 53 (5.3%) reported cryopreservation of eggs. Nearly 13% reported the use of intrauterine insemination and 13.2% reported the use of in vivo fertilization. Among those who experienced fertility concerns, 36.6% (232 of 634) reported facing financial burdens because of fertility or pregnancy that was in some way associated with their career choice.
When asked on the survey if fertility preservation should be discussed with women during medical school and/or residency, 65.7% of respondents stated that it should.
However, the editorialists suggest that “encouraging formal and directed education regarding the infertility risks specifically toward female physicians (which Lee et al. recommend) could be perceived as a blanket recommendation that it is best for women in medicine to delay childbearing and pursue ART.”
“Medical schools and residency and fellowship training programs should instead focus their energy on creating a framework and culture that normalizes conception during these points in training while also subsidizing and supporting trainees and physicians who prefer to use ART and delay fertility until after training,” they suggest.
The editorialists also emphasized that women may choose to become pregnant at any point during the years that it takes to go from being a medical student to resident/fellow to attending physician, and they should be supported by their workplace on their decisions.
The study was funded by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center.
Dr. Lee and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blank reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca, Aravive, Akesobio, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Seattle Genetics outside the submitted work. Dr. Saleh reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a survey of just over 1,000 female oncologists, 95% said their career plans were at least somewhat associated with the timing of when to start a family.
The most striking finding was that one third of respondents had miscarried and another one third reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
One third reported experiencing discrimination during pregnancy, and another third said they experienced discrimination for taking maternity leave, and having more than one child increased the likelihood of this.
The most common negative factor associated with family planning was long work hours and heavy workload (66.6%),
These findings suggest there are systemic changes needed not only in the healthcare setting but in society as a whole around women in the workplace and their choices of childbearing, say the authors.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open and led by Anna Lee MD, MPH, from the department of radiation oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
In an invited commentary, Mona Saleh, MD, and Stephanie Blank, MD, from the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggest that cultural changes are needed that go beyond women in medicine.
“These cultural values are so deeply pervasive (one could also say invasive) that they affect even these most educated and wealthy professional women, such as those who participated in this survey,” the editorialists write.
“[The researchers] advocate for early education on assisted reproductive technology (ART) risks, benefits, and success rates, but this is not getting at the underlying issue: Pregnancy discrimination and unfair distribution of childbearing responsibilities are a reflection of a larger problematic culture rather than an issue specific to women in medicine,” they add.
Survey details
The survey comprised a novel 39-item questionnaire distributed to 1,004 U.S. female oncologists from May 7 to June 30, 2020, via email and social media channels.
Most respondents (84.4%) were married, and 71% were currently working full-time.
About one-third (35%) worked in radiation oncology, another third (34.3%) in medical oncology, 18.4% in surgical oncology, and 9.1% in pediatric oncology.
A total of 768 respondents (76.5%) had children, and of these, 415 (41.3%) first gave birth during postgraduate training and 275 (27.4%) gave birth in years 1-5 as an attending physician.
Of all respondents who had been pregnant, approximately two-thirds (65.7%) had some type of pregnancy complication. About one-third of respondents (31.7%) reported having experienced a miscarriage after a confirmed pregnancy; of those, 61.6% reported one miscarriage, while the remainder had two or more miscarriages (38.4%).
Approximately one-third (31.4%) of respondents reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
The questionnaire also asked about assisted reproductive technology, and 164 participants (16.3%) reported the use of fertility medications, and 53 (5.3%) reported cryopreservation of eggs. Nearly 13% reported the use of intrauterine insemination and 13.2% reported the use of in vivo fertilization. Among those who experienced fertility concerns, 36.6% (232 of 634) reported facing financial burdens because of fertility or pregnancy that was in some way associated with their career choice.
When asked on the survey if fertility preservation should be discussed with women during medical school and/or residency, 65.7% of respondents stated that it should.
However, the editorialists suggest that “encouraging formal and directed education regarding the infertility risks specifically toward female physicians (which Lee et al. recommend) could be perceived as a blanket recommendation that it is best for women in medicine to delay childbearing and pursue ART.”
“Medical schools and residency and fellowship training programs should instead focus their energy on creating a framework and culture that normalizes conception during these points in training while also subsidizing and supporting trainees and physicians who prefer to use ART and delay fertility until after training,” they suggest.
The editorialists also emphasized that women may choose to become pregnant at any point during the years that it takes to go from being a medical student to resident/fellow to attending physician, and they should be supported by their workplace on their decisions.
The study was funded by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center.
Dr. Lee and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blank reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca, Aravive, Akesobio, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Seattle Genetics outside the submitted work. Dr. Saleh reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a survey of just over 1,000 female oncologists, 95% said their career plans were at least somewhat associated with the timing of when to start a family.
The most striking finding was that one third of respondents had miscarried and another one third reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
One third reported experiencing discrimination during pregnancy, and another third said they experienced discrimination for taking maternity leave, and having more than one child increased the likelihood of this.
The most common negative factor associated with family planning was long work hours and heavy workload (66.6%),
These findings suggest there are systemic changes needed not only in the healthcare setting but in society as a whole around women in the workplace and their choices of childbearing, say the authors.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open and led by Anna Lee MD, MPH, from the department of radiation oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
In an invited commentary, Mona Saleh, MD, and Stephanie Blank, MD, from the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggest that cultural changes are needed that go beyond women in medicine.
“These cultural values are so deeply pervasive (one could also say invasive) that they affect even these most educated and wealthy professional women, such as those who participated in this survey,” the editorialists write.
“[The researchers] advocate for early education on assisted reproductive technology (ART) risks, benefits, and success rates, but this is not getting at the underlying issue: Pregnancy discrimination and unfair distribution of childbearing responsibilities are a reflection of a larger problematic culture rather than an issue specific to women in medicine,” they add.
Survey details
The survey comprised a novel 39-item questionnaire distributed to 1,004 U.S. female oncologists from May 7 to June 30, 2020, via email and social media channels.
Most respondents (84.4%) were married, and 71% were currently working full-time.
About one-third (35%) worked in radiation oncology, another third (34.3%) in medical oncology, 18.4% in surgical oncology, and 9.1% in pediatric oncology.
A total of 768 respondents (76.5%) had children, and of these, 415 (41.3%) first gave birth during postgraduate training and 275 (27.4%) gave birth in years 1-5 as an attending physician.
Of all respondents who had been pregnant, approximately two-thirds (65.7%) had some type of pregnancy complication. About one-third of respondents (31.7%) reported having experienced a miscarriage after a confirmed pregnancy; of those, 61.6% reported one miscarriage, while the remainder had two or more miscarriages (38.4%).
Approximately one-third (31.4%) of respondents reported difficulty with infertility that required fertility counseling and/or treatment.
The questionnaire also asked about assisted reproductive technology, and 164 participants (16.3%) reported the use of fertility medications, and 53 (5.3%) reported cryopreservation of eggs. Nearly 13% reported the use of intrauterine insemination and 13.2% reported the use of in vivo fertilization. Among those who experienced fertility concerns, 36.6% (232 of 634) reported facing financial burdens because of fertility or pregnancy that was in some way associated with their career choice.
When asked on the survey if fertility preservation should be discussed with women during medical school and/or residency, 65.7% of respondents stated that it should.
However, the editorialists suggest that “encouraging formal and directed education regarding the infertility risks specifically toward female physicians (which Lee et al. recommend) could be perceived as a blanket recommendation that it is best for women in medicine to delay childbearing and pursue ART.”
“Medical schools and residency and fellowship training programs should instead focus their energy on creating a framework and culture that normalizes conception during these points in training while also subsidizing and supporting trainees and physicians who prefer to use ART and delay fertility until after training,” they suggest.
The editorialists also emphasized that women may choose to become pregnant at any point during the years that it takes to go from being a medical student to resident/fellow to attending physician, and they should be supported by their workplace on their decisions.
The study was funded by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center.
Dr. Lee and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blank reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca, Aravive, Akesobio, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Seattle Genetics outside the submitted work. Dr. Saleh reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Women with cycle disorders across their life span may be at increased risk of cardiovascular disease
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Endometrial receptivity testing before IVF seen as unnecessary
Endometrial receptivity testing (ERT) did not increase the chances of achieving live birth in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization.
The study was promoted by widespread use of the tests in reproductive medicine and earlier conflicting studies regarding its effectiveness. The procedure, in which doctors extract cells from a woman’s endometrial lining in an effort to determine the best day to perform in vitro fertilization, requires a biopsy, can take a month to generate results, and costs up to $1,000.
But the new study, published online December 6 in the Journal of the American Medical Association, found that embryo transfer based on the timing of ERT was no better than that based on the standard protocol.
“Endometrial receptivity testing ended up not being beneficial in the population of interest, a good-prognosis IVF patient population,” said Nicole Doyle, MD, PhD, of Shady Grove Fertility, in Arlington, Va., who led the study. “For this particular patient population I would not recommend ERT based on the results of the trial.”
“Unfortunately, as is our history in reproductive medicine, we may embrace technology prematurely given patient desperation and physician eagerness to improve pregnancy outcomes,” said Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Orlando, who was not involved in the new research.
The double-blind, randomized clinical trial enrolled 726 women treated at Dr. Doyle’s clinic between May 2018 and September 2020.
All the women underwent ERT. Of those who received adjusted progesterone exposure after the test, live birth occurred in 58.5% of transfers (223 of 381). Among those in a control group who did not have their progesterone adjusted after ERT and underwent IVF on a standardized schedule, 61.9% of transfers (239 of 386) resulted in live birth, according to the researchers.
The differences in rates of clinical (77.2% vs. 79.5% [95% confidence interval, −10.4% to 2.4%]) and biochemical pregnancy (68.8% vs. 72.8% [95% CI, −8.2% to 3.5%]) were not statistically significant between the two groups, Dr. Doyle and her colleagues reported.
Women who experienced recurrent implantation failure (RIF), defined as more than two failed embryo transfers, were excluded from the study. “We can’t assess the benefit of an endometrial receptivity testing in this particular patient population,” Dr. Doyle said.
However, she noted that the number of women who undergo RIF is “a very small fraction of all IVF patients, less than 5%.” Of those, half are expected to have embryos that are not suitable for implantation, Dr. Doyle said.
As a result, she said, “it’s really only about 2.5% of IVF patients for which we don’t yet have an answer regarding the utility of ERT.”
Dr. Trolice, also a professor at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, expressed certainty that the “one-size-fits-all approach” for ERT has been disproven by the study’s failure to find a benefit from the procedure in women with a “good prognosis.” But, he added, whether ERT is of value in a subset of patients, such as those with recurrent implantation failure, remains “a question of vital importance.”
Dr. Doyle and Dr. Trolice reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endometrial receptivity testing (ERT) did not increase the chances of achieving live birth in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization.
The study was promoted by widespread use of the tests in reproductive medicine and earlier conflicting studies regarding its effectiveness. The procedure, in which doctors extract cells from a woman’s endometrial lining in an effort to determine the best day to perform in vitro fertilization, requires a biopsy, can take a month to generate results, and costs up to $1,000.
But the new study, published online December 6 in the Journal of the American Medical Association, found that embryo transfer based on the timing of ERT was no better than that based on the standard protocol.
“Endometrial receptivity testing ended up not being beneficial in the population of interest, a good-prognosis IVF patient population,” said Nicole Doyle, MD, PhD, of Shady Grove Fertility, in Arlington, Va., who led the study. “For this particular patient population I would not recommend ERT based on the results of the trial.”
“Unfortunately, as is our history in reproductive medicine, we may embrace technology prematurely given patient desperation and physician eagerness to improve pregnancy outcomes,” said Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Orlando, who was not involved in the new research.
The double-blind, randomized clinical trial enrolled 726 women treated at Dr. Doyle’s clinic between May 2018 and September 2020.
All the women underwent ERT. Of those who received adjusted progesterone exposure after the test, live birth occurred in 58.5% of transfers (223 of 381). Among those in a control group who did not have their progesterone adjusted after ERT and underwent IVF on a standardized schedule, 61.9% of transfers (239 of 386) resulted in live birth, according to the researchers.
The differences in rates of clinical (77.2% vs. 79.5% [95% confidence interval, −10.4% to 2.4%]) and biochemical pregnancy (68.8% vs. 72.8% [95% CI, −8.2% to 3.5%]) were not statistically significant between the two groups, Dr. Doyle and her colleagues reported.
Women who experienced recurrent implantation failure (RIF), defined as more than two failed embryo transfers, were excluded from the study. “We can’t assess the benefit of an endometrial receptivity testing in this particular patient population,” Dr. Doyle said.
However, she noted that the number of women who undergo RIF is “a very small fraction of all IVF patients, less than 5%.” Of those, half are expected to have embryos that are not suitable for implantation, Dr. Doyle said.
As a result, she said, “it’s really only about 2.5% of IVF patients for which we don’t yet have an answer regarding the utility of ERT.”
Dr. Trolice, also a professor at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, expressed certainty that the “one-size-fits-all approach” for ERT has been disproven by the study’s failure to find a benefit from the procedure in women with a “good prognosis.” But, he added, whether ERT is of value in a subset of patients, such as those with recurrent implantation failure, remains “a question of vital importance.”
Dr. Doyle and Dr. Trolice reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endometrial receptivity testing (ERT) did not increase the chances of achieving live birth in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization.
The study was promoted by widespread use of the tests in reproductive medicine and earlier conflicting studies regarding its effectiveness. The procedure, in which doctors extract cells from a woman’s endometrial lining in an effort to determine the best day to perform in vitro fertilization, requires a biopsy, can take a month to generate results, and costs up to $1,000.
But the new study, published online December 6 in the Journal of the American Medical Association, found that embryo transfer based on the timing of ERT was no better than that based on the standard protocol.
“Endometrial receptivity testing ended up not being beneficial in the population of interest, a good-prognosis IVF patient population,” said Nicole Doyle, MD, PhD, of Shady Grove Fertility, in Arlington, Va., who led the study. “For this particular patient population I would not recommend ERT based on the results of the trial.”
“Unfortunately, as is our history in reproductive medicine, we may embrace technology prematurely given patient desperation and physician eagerness to improve pregnancy outcomes,” said Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Orlando, who was not involved in the new research.
The double-blind, randomized clinical trial enrolled 726 women treated at Dr. Doyle’s clinic between May 2018 and September 2020.
All the women underwent ERT. Of those who received adjusted progesterone exposure after the test, live birth occurred in 58.5% of transfers (223 of 381). Among those in a control group who did not have their progesterone adjusted after ERT and underwent IVF on a standardized schedule, 61.9% of transfers (239 of 386) resulted in live birth, according to the researchers.
The differences in rates of clinical (77.2% vs. 79.5% [95% confidence interval, −10.4% to 2.4%]) and biochemical pregnancy (68.8% vs. 72.8% [95% CI, −8.2% to 3.5%]) were not statistically significant between the two groups, Dr. Doyle and her colleagues reported.
Women who experienced recurrent implantation failure (RIF), defined as more than two failed embryo transfers, were excluded from the study. “We can’t assess the benefit of an endometrial receptivity testing in this particular patient population,” Dr. Doyle said.
However, she noted that the number of women who undergo RIF is “a very small fraction of all IVF patients, less than 5%.” Of those, half are expected to have embryos that are not suitable for implantation, Dr. Doyle said.
As a result, she said, “it’s really only about 2.5% of IVF patients for which we don’t yet have an answer regarding the utility of ERT.”
Dr. Trolice, also a professor at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, expressed certainty that the “one-size-fits-all approach” for ERT has been disproven by the study’s failure to find a benefit from the procedure in women with a “good prognosis.” But, he added, whether ERT is of value in a subset of patients, such as those with recurrent implantation failure, remains “a question of vital importance.”
Dr. Doyle and Dr. Trolice reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Immune dysregulation may drive long-term postpartum depression
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF REPRODUCTIVE IMMUNOLOGY
Getting testosterone online is easy. Solid advice, not so much
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
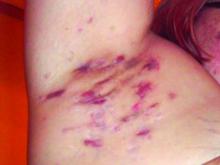
Consider quality of life, comorbidities in hidradenitis suppurativa
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Top 10 unproven infertility tests and treatments
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
Giving birth may permanently alter a mother’s bones
Female primates who had been pregnant showed lower levels of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorous in their bones, revealing for the first time new ways that females are changed by pregnancy and breastfeeding, according to a study published by PLOS One.
“Our findings provide additional evidence of the profound impact that reproduction has on the female organism, further demonstrating that the skeleton is not a static organ but a dynamic one that changes with life events,” said lead author and New York University doctoral student Paola Cerrito in a news release.
The study evaluated the bones of rhesus macaques, also known as rhesus monkeys, which share 93% of genes with humans, according to the National Primate Research Centers. They have been used in research that paved the way for many medical breakthroughs such as treatments for HIV/AIDS; they’re also used in Alzheimer’s research.
Menopause has long been known to impact bone health, which is tied to calcium and phosphorous levels. This latest research does not address how bone health is affected by pregnancy and lactation but further points to the everchanging state of bones based on life events.
“Our research shows that even before the cessation of fertility, the skeleton responds dynamically to changes in reproductive status,” Ms. Cerrito said. “Moreover, these findings reaffirm the significant impact giving birth has on a female organism – quite simply, evidence of reproduction is ‘written in the bones’ for life.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Female primates who had been pregnant showed lower levels of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorous in their bones, revealing for the first time new ways that females are changed by pregnancy and breastfeeding, according to a study published by PLOS One.
“Our findings provide additional evidence of the profound impact that reproduction has on the female organism, further demonstrating that the skeleton is not a static organ but a dynamic one that changes with life events,” said lead author and New York University doctoral student Paola Cerrito in a news release.
The study evaluated the bones of rhesus macaques, also known as rhesus monkeys, which share 93% of genes with humans, according to the National Primate Research Centers. They have been used in research that paved the way for many medical breakthroughs such as treatments for HIV/AIDS; they’re also used in Alzheimer’s research.
Menopause has long been known to impact bone health, which is tied to calcium and phosphorous levels. This latest research does not address how bone health is affected by pregnancy and lactation but further points to the everchanging state of bones based on life events.
“Our research shows that even before the cessation of fertility, the skeleton responds dynamically to changes in reproductive status,” Ms. Cerrito said. “Moreover, these findings reaffirm the significant impact giving birth has on a female organism – quite simply, evidence of reproduction is ‘written in the bones’ for life.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Female primates who had been pregnant showed lower levels of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorous in their bones, revealing for the first time new ways that females are changed by pregnancy and breastfeeding, according to a study published by PLOS One.
“Our findings provide additional evidence of the profound impact that reproduction has on the female organism, further demonstrating that the skeleton is not a static organ but a dynamic one that changes with life events,” said lead author and New York University doctoral student Paola Cerrito in a news release.
The study evaluated the bones of rhesus macaques, also known as rhesus monkeys, which share 93% of genes with humans, according to the National Primate Research Centers. They have been used in research that paved the way for many medical breakthroughs such as treatments for HIV/AIDS; they’re also used in Alzheimer’s research.
Menopause has long been known to impact bone health, which is tied to calcium and phosphorous levels. This latest research does not address how bone health is affected by pregnancy and lactation but further points to the everchanging state of bones based on life events.
“Our research shows that even before the cessation of fertility, the skeleton responds dynamically to changes in reproductive status,” Ms. Cerrito said. “Moreover, these findings reaffirm the significant impact giving birth has on a female organism – quite simply, evidence of reproduction is ‘written in the bones’ for life.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM PLOS ONE
Link between PCOS and increased risk of pancreatic cancer?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Testosterone ranges for young men could help classify deficiency
Normative ranges of testosterone in young men have been identified on the basis of a nationally representative data in a new study, and these data are expected to provide guidance when evaluating younger individuals presenting with signs and symptoms of potential testosterone deficiency, according to the investigators.
It has long been known that the ranges of normal testosterone differ by age, but the authors of this study contend that this is the first large-scale, population-based analysis conducted in the United States of testosterone levels among in men aged 20-44 years.
“These findings will provide valuable information that clinicians can use in the evaluation and management of young men presenting with concerns about testosterone deficiency,” reported a team of investigators led by Alex Zhu, MD, a urology resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in the Journal of Urology.
Outside experts, however, disagree, one saying that the conclusions are “far off and irrational.”
A normative range of testosterone is particularly important for the evaluation of hypogonadism because values vary markedly between individuals and within individuals on repeat measurements over a 24-hour period. At least partially because of this variability, many guidelines, including those issued in by the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association, recommend testosterone assays only in symptomatic individuals in order to reduce risk of detecting low relative levels that are not clinically relevant.
NHANES data provide norms
The data for this study were drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), which sample representative United States residents. The analytic cohort included 1,486 men stratified in 5-year age intervals (20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, and 40-44).
Because of the known diurnal variation in endocrine levels, only morning total testosterone levels were considered, for consistency. Individuals at risk of disturbed testosterone levels, such as those on hormonal therapy or with a history of testicular cancer, were excluded. Unlike previous analyses that have limited measurements to nonobese individuals without major comorbidities, no such restrictions were imposed in this analysis, which included a sample balanced by race.
After dividing the testosterone levels collected in the NHANES data by tertiles, the cutoff for reduced testosterone were defined as the lowest tertile for each of the five age groups studied.
Consistent with previous reports that testosterone levels decline with age, the cutoff for low testosterone declined for each increase in 5-year age interval after the age of 29 years.
Specifically, these cutoffs were, in order of advancing age, 409 ng/dL (middle tertile range, 409-558), 413 ng/dL (range, 413-575), 359 ng/dL (range, 359-498), 352 ng/dL (range, 352-478), and 350 ng/dL (range, 350-473).
As in the AUA guidelines, which define a total testosterone level below 300 ng/dL “as a reasonable cutoff in support of the diagnosis of low testosterone,” these cutoffs were established without correlation with symptoms. In younger men, like older men, testosterone levels must be within a clinical context.
“Per the AUA guidelines, clinician should consider measuring testosterone levels in patients with certain medical conditions or signs or symptoms of testosterone deficiency, such as depression, reduced motivation, infertility, reduced sex drive, and changes in erectile function,” Dr. Zhu said in an interview, adding that it is appropriate to follow the AUA guidelines “regardless of age.”
Hormone levels and symptoms not correlated
These recommendations are based on the fact that the correlation between symptomatic hypogonadism and testosterone levels is poor, meaning that other factors should be considered when considering whether symptoms relate to deficiency. However, Dr. Zhu contended that objective evidence of a low level of testosterone is useful in considering the role of hormone deficiency.
“Even if one were to choose a different cutoff, our age-specific normative testosterone ranges still provide young men and their physicians a framework for counseling,” according to Dr. Zhu. Because of the risk of nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue and diminished physical performance, he called for “a high index of suspicion for testosterone deficiency even when evaluating younger men.”
Considering the diurnal fluctuations, the single measurement employed to calculate normative ranges is a limitation of this study, the authors acknowledged. They cited data suggested that up to 35% of men classified as hypogonadal on the basis of a single testosterone assay will not meet the same criterion even if evaluated in the subsequent 24 hours. It is for this reason that guidelines typically recommend measuring testosterone at least twice or with more than one type of assay.
Up until now, decisions about testosterone deficiency have been with a one-size-fits-all approach, but it has long been known that patient age is a variable in determining average levels of this hormone, Dr. Zhu reported. For this reason, he predicted that these data will have clinical utility.
“We believe that our new cutoffs play an important role in evaluating younger men presenting with symptoms [of testosterone deficiency],” Dr. Zhu said. “However, clinicians should still remember that these symptoms have causes other than low testosterone, so we cannot only focus only on testing testosterone.”
However, given the lack of correlation between symptoms and testosterone levels, this area remains controversial.
Value of tertile cutoffs questioned
Two independent experts challenged the methodology and conclusions of this study.
Victor Adlin, MD, an associate professor emeritus at Temple University, Philadelphia, questioned tertile levels as an approach to defining normal.
“The authors propose unusually high cut-points for a definition of low testosterone in young men,” said Dr. Adlin, whose published a comment on age-related low testosterone in response to 2020 guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians. He is concerned that these data could lead to overtreatment.
The authors “imply that [these data] would justify treatment with testosterone in many young men with symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and lack of vigor, whose relation to low testosterone is controversial,” he said in an interview. “Trials in older men have failed to show a clear response of such symptoms to testosterone therapy.”
The first author of the 2018 Endocrine Society guidelines, Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, director of a research program in aging and metabolism at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, was even more skeptical.
“The whole premise of generating cutoffs for a disease or condition based on the middle tertile is just so far off and irrational,” he said. A coauthor of a 2017 study designed to define harmonized testosterone reference ranges by decade of age (that he described as providing “a much larger sample size and a wider age range” than this current study), Dr. Bhasin did not see any value in the NHANES-based analysis.
Rather, he called for an effort “to dispel this ill-conceived idea that could mislead young men to think they need testosterone treatment when they are healthy.”
Dr. Zhu and Dr. Adlin reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhasin reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron, and Takeda.
Normative ranges of testosterone in young men have been identified on the basis of a nationally representative data in a new study, and these data are expected to provide guidance when evaluating younger individuals presenting with signs and symptoms of potential testosterone deficiency, according to the investigators.
It has long been known that the ranges of normal testosterone differ by age, but the authors of this study contend that this is the first large-scale, population-based analysis conducted in the United States of testosterone levels among in men aged 20-44 years.
“These findings will provide valuable information that clinicians can use in the evaluation and management of young men presenting with concerns about testosterone deficiency,” reported a team of investigators led by Alex Zhu, MD, a urology resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in the Journal of Urology.
Outside experts, however, disagree, one saying that the conclusions are “far off and irrational.”
A normative range of testosterone is particularly important for the evaluation of hypogonadism because values vary markedly between individuals and within individuals on repeat measurements over a 24-hour period. At least partially because of this variability, many guidelines, including those issued in by the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association, recommend testosterone assays only in symptomatic individuals in order to reduce risk of detecting low relative levels that are not clinically relevant.
NHANES data provide norms
The data for this study were drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), which sample representative United States residents. The analytic cohort included 1,486 men stratified in 5-year age intervals (20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, and 40-44).
Because of the known diurnal variation in endocrine levels, only morning total testosterone levels were considered, for consistency. Individuals at risk of disturbed testosterone levels, such as those on hormonal therapy or with a history of testicular cancer, were excluded. Unlike previous analyses that have limited measurements to nonobese individuals without major comorbidities, no such restrictions were imposed in this analysis, which included a sample balanced by race.
After dividing the testosterone levels collected in the NHANES data by tertiles, the cutoff for reduced testosterone were defined as the lowest tertile for each of the five age groups studied.
Consistent with previous reports that testosterone levels decline with age, the cutoff for low testosterone declined for each increase in 5-year age interval after the age of 29 years.
Specifically, these cutoffs were, in order of advancing age, 409 ng/dL (middle tertile range, 409-558), 413 ng/dL (range, 413-575), 359 ng/dL (range, 359-498), 352 ng/dL (range, 352-478), and 350 ng/dL (range, 350-473).
As in the AUA guidelines, which define a total testosterone level below 300 ng/dL “as a reasonable cutoff in support of the diagnosis of low testosterone,” these cutoffs were established without correlation with symptoms. In younger men, like older men, testosterone levels must be within a clinical context.
“Per the AUA guidelines, clinician should consider measuring testosterone levels in patients with certain medical conditions or signs or symptoms of testosterone deficiency, such as depression, reduced motivation, infertility, reduced sex drive, and changes in erectile function,” Dr. Zhu said in an interview, adding that it is appropriate to follow the AUA guidelines “regardless of age.”
Hormone levels and symptoms not correlated
These recommendations are based on the fact that the correlation between symptomatic hypogonadism and testosterone levels is poor, meaning that other factors should be considered when considering whether symptoms relate to deficiency. However, Dr. Zhu contended that objective evidence of a low level of testosterone is useful in considering the role of hormone deficiency.
“Even if one were to choose a different cutoff, our age-specific normative testosterone ranges still provide young men and their physicians a framework for counseling,” according to Dr. Zhu. Because of the risk of nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue and diminished physical performance, he called for “a high index of suspicion for testosterone deficiency even when evaluating younger men.”
Considering the diurnal fluctuations, the single measurement employed to calculate normative ranges is a limitation of this study, the authors acknowledged. They cited data suggested that up to 35% of men classified as hypogonadal on the basis of a single testosterone assay will not meet the same criterion even if evaluated in the subsequent 24 hours. It is for this reason that guidelines typically recommend measuring testosterone at least twice or with more than one type of assay.
Up until now, decisions about testosterone deficiency have been with a one-size-fits-all approach, but it has long been known that patient age is a variable in determining average levels of this hormone, Dr. Zhu reported. For this reason, he predicted that these data will have clinical utility.
“We believe that our new cutoffs play an important role in evaluating younger men presenting with symptoms [of testosterone deficiency],” Dr. Zhu said. “However, clinicians should still remember that these symptoms have causes other than low testosterone, so we cannot only focus only on testing testosterone.”
However, given the lack of correlation between symptoms and testosterone levels, this area remains controversial.
Value of tertile cutoffs questioned
Two independent experts challenged the methodology and conclusions of this study.
Victor Adlin, MD, an associate professor emeritus at Temple University, Philadelphia, questioned tertile levels as an approach to defining normal.
“The authors propose unusually high cut-points for a definition of low testosterone in young men,” said Dr. Adlin, whose published a comment on age-related low testosterone in response to 2020 guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians. He is concerned that these data could lead to overtreatment.
The authors “imply that [these data] would justify treatment with testosterone in many young men with symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and lack of vigor, whose relation to low testosterone is controversial,” he said in an interview. “Trials in older men have failed to show a clear response of such symptoms to testosterone therapy.”
The first author of the 2018 Endocrine Society guidelines, Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, director of a research program in aging and metabolism at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, was even more skeptical.
“The whole premise of generating cutoffs for a disease or condition based on the middle tertile is just so far off and irrational,” he said. A coauthor of a 2017 study designed to define harmonized testosterone reference ranges by decade of age (that he described as providing “a much larger sample size and a wider age range” than this current study), Dr. Bhasin did not see any value in the NHANES-based analysis.
Rather, he called for an effort “to dispel this ill-conceived idea that could mislead young men to think they need testosterone treatment when they are healthy.”
Dr. Zhu and Dr. Adlin reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhasin reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron, and Takeda.
Normative ranges of testosterone in young men have been identified on the basis of a nationally representative data in a new study, and these data are expected to provide guidance when evaluating younger individuals presenting with signs and symptoms of potential testosterone deficiency, according to the investigators.
It has long been known that the ranges of normal testosterone differ by age, but the authors of this study contend that this is the first large-scale, population-based analysis conducted in the United States of testosterone levels among in men aged 20-44 years.
“These findings will provide valuable information that clinicians can use in the evaluation and management of young men presenting with concerns about testosterone deficiency,” reported a team of investigators led by Alex Zhu, MD, a urology resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in the Journal of Urology.
Outside experts, however, disagree, one saying that the conclusions are “far off and irrational.”
A normative range of testosterone is particularly important for the evaluation of hypogonadism because values vary markedly between individuals and within individuals on repeat measurements over a 24-hour period. At least partially because of this variability, many guidelines, including those issued in by the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association, recommend testosterone assays only in symptomatic individuals in order to reduce risk of detecting low relative levels that are not clinically relevant.
NHANES data provide norms
The data for this study were drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), which sample representative United States residents. The analytic cohort included 1,486 men stratified in 5-year age intervals (20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, and 40-44).
Because of the known diurnal variation in endocrine levels, only morning total testosterone levels were considered, for consistency. Individuals at risk of disturbed testosterone levels, such as those on hormonal therapy or with a history of testicular cancer, were excluded. Unlike previous analyses that have limited measurements to nonobese individuals without major comorbidities, no such restrictions were imposed in this analysis, which included a sample balanced by race.
After dividing the testosterone levels collected in the NHANES data by tertiles, the cutoff for reduced testosterone were defined as the lowest tertile for each of the five age groups studied.
Consistent with previous reports that testosterone levels decline with age, the cutoff for low testosterone declined for each increase in 5-year age interval after the age of 29 years.
Specifically, these cutoffs were, in order of advancing age, 409 ng/dL (middle tertile range, 409-558), 413 ng/dL (range, 413-575), 359 ng/dL (range, 359-498), 352 ng/dL (range, 352-478), and 350 ng/dL (range, 350-473).
As in the AUA guidelines, which define a total testosterone level below 300 ng/dL “as a reasonable cutoff in support of the diagnosis of low testosterone,” these cutoffs were established without correlation with symptoms. In younger men, like older men, testosterone levels must be within a clinical context.
“Per the AUA guidelines, clinician should consider measuring testosterone levels in patients with certain medical conditions or signs or symptoms of testosterone deficiency, such as depression, reduced motivation, infertility, reduced sex drive, and changes in erectile function,” Dr. Zhu said in an interview, adding that it is appropriate to follow the AUA guidelines “regardless of age.”
Hormone levels and symptoms not correlated
These recommendations are based on the fact that the correlation between symptomatic hypogonadism and testosterone levels is poor, meaning that other factors should be considered when considering whether symptoms relate to deficiency. However, Dr. Zhu contended that objective evidence of a low level of testosterone is useful in considering the role of hormone deficiency.
“Even if one were to choose a different cutoff, our age-specific normative testosterone ranges still provide young men and their physicians a framework for counseling,” according to Dr. Zhu. Because of the risk of nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue and diminished physical performance, he called for “a high index of suspicion for testosterone deficiency even when evaluating younger men.”
Considering the diurnal fluctuations, the single measurement employed to calculate normative ranges is a limitation of this study, the authors acknowledged. They cited data suggested that up to 35% of men classified as hypogonadal on the basis of a single testosterone assay will not meet the same criterion even if evaluated in the subsequent 24 hours. It is for this reason that guidelines typically recommend measuring testosterone at least twice or with more than one type of assay.
Up until now, decisions about testosterone deficiency have been with a one-size-fits-all approach, but it has long been known that patient age is a variable in determining average levels of this hormone, Dr. Zhu reported. For this reason, he predicted that these data will have clinical utility.
“We believe that our new cutoffs play an important role in evaluating younger men presenting with symptoms [of testosterone deficiency],” Dr. Zhu said. “However, clinicians should still remember that these symptoms have causes other than low testosterone, so we cannot only focus only on testing testosterone.”
However, given the lack of correlation between symptoms and testosterone levels, this area remains controversial.
Value of tertile cutoffs questioned
Two independent experts challenged the methodology and conclusions of this study.
Victor Adlin, MD, an associate professor emeritus at Temple University, Philadelphia, questioned tertile levels as an approach to defining normal.
“The authors propose unusually high cut-points for a definition of low testosterone in young men,” said Dr. Adlin, whose published a comment on age-related low testosterone in response to 2020 guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians. He is concerned that these data could lead to overtreatment.
The authors “imply that [these data] would justify treatment with testosterone in many young men with symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and lack of vigor, whose relation to low testosterone is controversial,” he said in an interview. “Trials in older men have failed to show a clear response of such symptoms to testosterone therapy.”
The first author of the 2018 Endocrine Society guidelines, Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, director of a research program in aging and metabolism at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, was even more skeptical.
“The whole premise of generating cutoffs for a disease or condition based on the middle tertile is just so far off and irrational,” he said. A coauthor of a 2017 study designed to define harmonized testosterone reference ranges by decade of age (that he described as providing “a much larger sample size and a wider age range” than this current study), Dr. Bhasin did not see any value in the NHANES-based analysis.
Rather, he called for an effort “to dispel this ill-conceived idea that could mislead young men to think they need testosterone treatment when they are healthy.”
Dr. Zhu and Dr. Adlin reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhasin reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron, and Takeda.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY