User login
Dysphagia in a patient with schizophrenia: Is the antipsychotic the culprit?
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
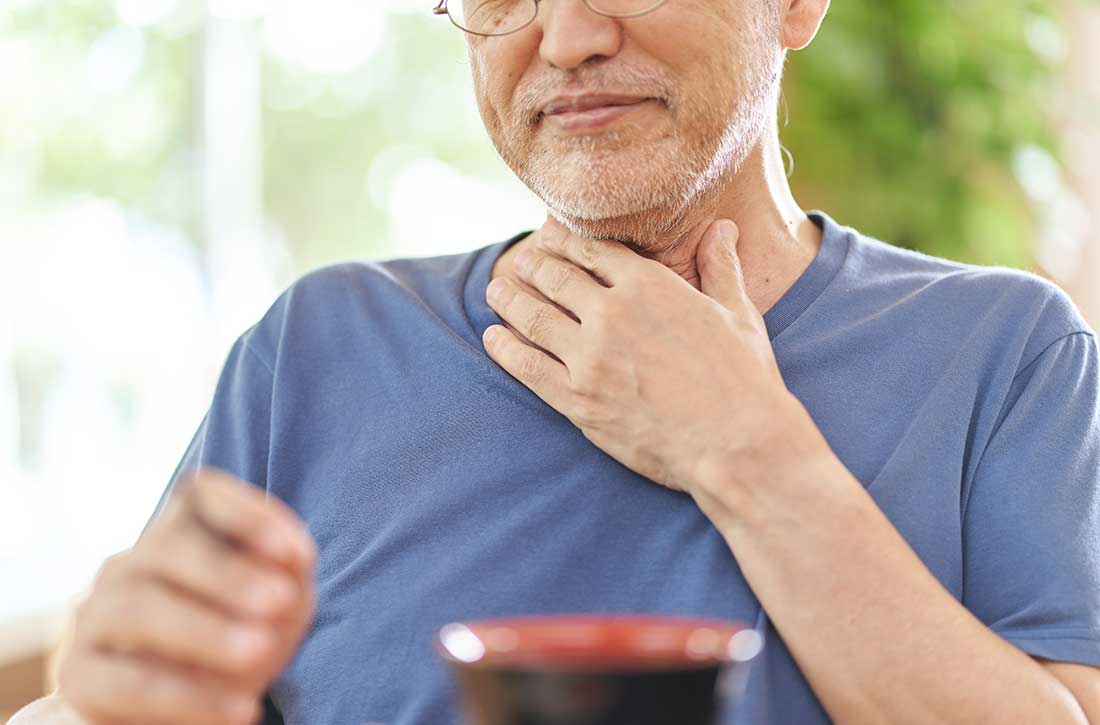
Mr. N, age 58, has a history of schizophrenia, tobacco use disorder, and alcohol use disorder. For many years, Mr. N has been receiving IM olanzapine 2.5 mg/d to treat his schizophrenia. He lives in a psychiatric hospital but was sent to our hospital after being found to have severe oropharyngeal dysphasia on a modified barium swallow study. There was concern for aspiration due to a history of choking episodes, which had been occurring for almost 1 month. During the modified barium swallow study, Mr. N was noted to have aspiration with deep laryngeal penetration during the pharyngeal stages of swallowing to all consistencies; this did not improve with the chin-tuck maneuver. In addition, during a CT scan of the cervical spine, an osteophyte was noted at the C5-C6 level, with possible impingement of the cervical esophagus and decreased upper esophageal sphincter opening.
Due to these findings, Mr. N was sent to our emergency department (ED) for further evaluation. In the ED, his vital signs were stable. He endorsed having a cough after eating, a sensation of having food stuck in his throat, and some hoarseness. His physical examination was notable for poor dentition. Results of a standard laboratory workup were all within normal limits. X-ray was notable for hazy opacities in the right upper to mid lung zones. Mr. N was admitted to the medical unit for further evaluation and management.
Narrowing the diagnosis
Because Mr. N was aspirating both liquids and solids, it was imperative that we identify the cause as soon as possible. The consultations that followed slowly guided the treatment team toward a diagnosis of antipsychotic-induced dysphagia. Otolaryngology identified insensate larynx during a flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy exam, which was highly suggestive of a neurological dysfunction such as dystonia. Furthermore, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy found no structural abnormalities to explain Mr. N’s dysphagia, which ruled out impingement of the cervical esophagus by the osteophyte. An MRI of the brain ruled out structural abnormalities or evidence of stroke. Finally, a speech and language pathologist confirmed decreased laryngeal closure and airway protection with a repeat modified barium swallow, which led to aspiration during swallowing. Psychiatry recommended starting diphenhydramine to treat Mr. N’s extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). A 6-day trial was initiated, with a single 50 mg IV dose on the first day followed by 25 mL oral twice daily for the remaining 5 days. In addition, olanzapine was discontinued.
Switching to a different diet and antipsychotic
Two days after starting diphenhydramine, Mr. N was switched to a puree diet. His ability to swallow improved, and he no longer coughed. However, on repeat modified barium swallow, aspiration was still noted for all types of liquids and solids. No structural improvements were seen.
Mr. N was discharged back to his psychiatric hospital, and his antipsychotic was changed from olanzapine to oral aripiprazole 2 mg/d. The aripiprazole dose was kept low to prevent the recurrence of dystonia and because at the time, his schizophrenia was asymptomatic. Mr. N was also prescribed oral diphenhydramine 25 mL twice daily.
At a 2-week follow-up appointment, Mr. N continued to show clinical improvement on the puree diet with thin liquids and continued the prescribed medication regimen.
Dysphagia as a manifestation of EPS
All antipsychotics, and particularly first-generation agents, are associated with EPS.1 These symptoms may be the result of antagonistic binding of dopaminergic D2 receptors within mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways of the brain, as well as parts of basal ganglia such as the caudate nucleus.2
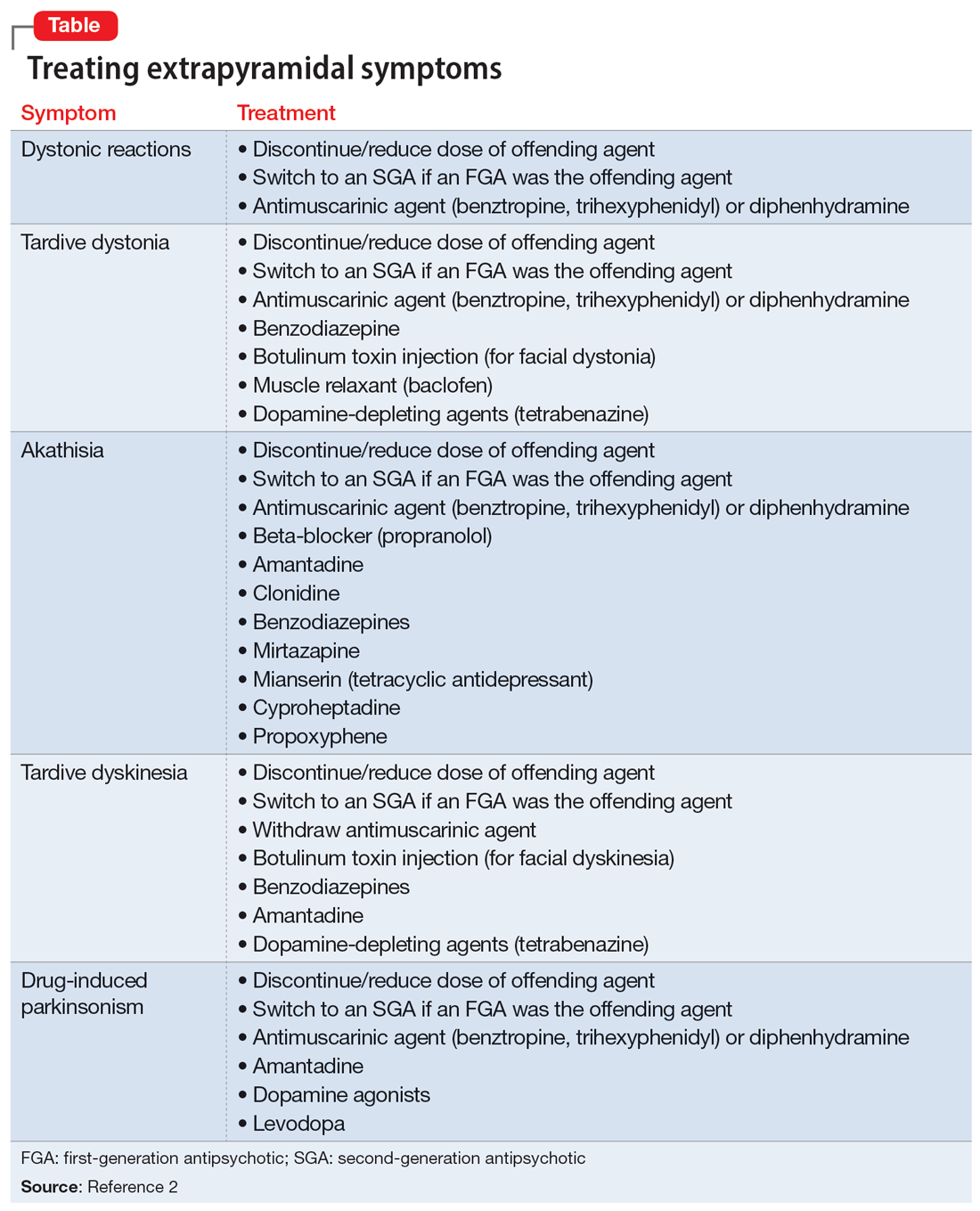
In addition to the examples listed in the Table,2 EPS can present as dysphagia, esophageal dysmotility, or aspiration, none of which may be recognized as EPS. Research has found haloperidol, loxapine, trifluoperazine, olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine, clozapine, and aripiprazole are associated with dysphagia.3-6 Strategies to treat antipsychotic-induced dysphagia include discontinuing the antipsychotic, lowering the dose, and changing to another medication.7
1. Crouse EL, Alastanos JN, Bozymski KM, et al. Dysphagia with second-generation antipsychotics: a case report and review of the literature. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(2):56-64. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.03.056
2. D’Souza RS, Hooten WM. Extrapyramidal symptoms. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed April 28, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534115/
3. Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Schnabel M, et al. Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia: case report and literature review. Dysphagia. 2007;22(1):63-67. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9032-9
4. Kalf JG, de Swart BJ, Bloem BR, et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006
5. Lin TW, Lee BS, Liao YC, et al. High dosage of aripiprazole-induced dysphagia. Int J Eat Disord. 2012;45(2):305-306. doi:10.1002/eat.20934
6. Stewart JT. Dysphagia associated with risperidone therapy. Dysphagia. 2003;18(4):274-275. doi:10.1007/s00455-003-0006-x
7. Lee JC, Takeshita J. Antipsychotic-induced dysphagia: a case report. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2015;17(5):10.4088/PCC.15I01792. doi:10.4088/PCC.15I01792
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Mr. N, age 58, has a history of schizophrenia, tobacco use disorder, and alcohol use disorder. For many years, Mr. N has been receiving IM olanzapine 2.5 mg/d to treat his schizophrenia. He lives in a psychiatric hospital but was sent to our hospital after being found to have severe oropharyngeal dysphasia on a modified barium swallow study. There was concern for aspiration due to a history of choking episodes, which had been occurring for almost 1 month. During the modified barium swallow study, Mr. N was noted to have aspiration with deep laryngeal penetration during the pharyngeal stages of swallowing to all consistencies; this did not improve with the chin-tuck maneuver. In addition, during a CT scan of the cervical spine, an osteophyte was noted at the C5-C6 level, with possible impingement of the cervical esophagus and decreased upper esophageal sphincter opening.
Due to these findings, Mr. N was sent to our emergency department (ED) for further evaluation. In the ED, his vital signs were stable. He endorsed having a cough after eating, a sensation of having food stuck in his throat, and some hoarseness. His physical examination was notable for poor dentition. Results of a standard laboratory workup were all within normal limits. X-ray was notable for hazy opacities in the right upper to mid lung zones. Mr. N was admitted to the medical unit for further evaluation and management.
Narrowing the diagnosis
Because Mr. N was aspirating both liquids and solids, it was imperative that we identify the cause as soon as possible. The consultations that followed slowly guided the treatment team toward a diagnosis of antipsychotic-induced dysphagia. Otolaryngology identified insensate larynx during a flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy exam, which was highly suggestive of a neurological dysfunction such as dystonia. Furthermore, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy found no structural abnormalities to explain Mr. N’s dysphagia, which ruled out impingement of the cervical esophagus by the osteophyte. An MRI of the brain ruled out structural abnormalities or evidence of stroke. Finally, a speech and language pathologist confirmed decreased laryngeal closure and airway protection with a repeat modified barium swallow, which led to aspiration during swallowing. Psychiatry recommended starting diphenhydramine to treat Mr. N’s extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). A 6-day trial was initiated, with a single 50 mg IV dose on the first day followed by 25 mL oral twice daily for the remaining 5 days. In addition, olanzapine was discontinued.
Switching to a different diet and antipsychotic
Two days after starting diphenhydramine, Mr. N was switched to a puree diet. His ability to swallow improved, and he no longer coughed. However, on repeat modified barium swallow, aspiration was still noted for all types of liquids and solids. No structural improvements were seen.
Mr. N was discharged back to his psychiatric hospital, and his antipsychotic was changed from olanzapine to oral aripiprazole 2 mg/d. The aripiprazole dose was kept low to prevent the recurrence of dystonia and because at the time, his schizophrenia was asymptomatic. Mr. N was also prescribed oral diphenhydramine 25 mL twice daily.
At a 2-week follow-up appointment, Mr. N continued to show clinical improvement on the puree diet with thin liquids and continued the prescribed medication regimen.
Dysphagia as a manifestation of EPS
All antipsychotics, and particularly first-generation agents, are associated with EPS.1 These symptoms may be the result of antagonistic binding of dopaminergic D2 receptors within mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways of the brain, as well as parts of basal ganglia such as the caudate nucleus.2
In addition to the examples listed in the Table,2 EPS can present as dysphagia, esophageal dysmotility, or aspiration, none of which may be recognized as EPS. Research has found haloperidol, loxapine, trifluoperazine, olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine, clozapine, and aripiprazole are associated with dysphagia.3-6 Strategies to treat antipsychotic-induced dysphagia include discontinuing the antipsychotic, lowering the dose, and changing to another medication.7

Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Mr. N, age 58, has a history of schizophrenia, tobacco use disorder, and alcohol use disorder. For many years, Mr. N has been receiving IM olanzapine 2.5 mg/d to treat his schizophrenia. He lives in a psychiatric hospital but was sent to our hospital after being found to have severe oropharyngeal dysphasia on a modified barium swallow study. There was concern for aspiration due to a history of choking episodes, which had been occurring for almost 1 month. During the modified barium swallow study, Mr. N was noted to have aspiration with deep laryngeal penetration during the pharyngeal stages of swallowing to all consistencies; this did not improve with the chin-tuck maneuver. In addition, during a CT scan of the cervical spine, an osteophyte was noted at the C5-C6 level, with possible impingement of the cervical esophagus and decreased upper esophageal sphincter opening.
Due to these findings, Mr. N was sent to our emergency department (ED) for further evaluation. In the ED, his vital signs were stable. He endorsed having a cough after eating, a sensation of having food stuck in his throat, and some hoarseness. His physical examination was notable for poor dentition. Results of a standard laboratory workup were all within normal limits. X-ray was notable for hazy opacities in the right upper to mid lung zones. Mr. N was admitted to the medical unit for further evaluation and management.
Narrowing the diagnosis
Because Mr. N was aspirating both liquids and solids, it was imperative that we identify the cause as soon as possible. The consultations that followed slowly guided the treatment team toward a diagnosis of antipsychotic-induced dysphagia. Otolaryngology identified insensate larynx during a flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy exam, which was highly suggestive of a neurological dysfunction such as dystonia. Furthermore, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy found no structural abnormalities to explain Mr. N’s dysphagia, which ruled out impingement of the cervical esophagus by the osteophyte. An MRI of the brain ruled out structural abnormalities or evidence of stroke. Finally, a speech and language pathologist confirmed decreased laryngeal closure and airway protection with a repeat modified barium swallow, which led to aspiration during swallowing. Psychiatry recommended starting diphenhydramine to treat Mr. N’s extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). A 6-day trial was initiated, with a single 50 mg IV dose on the first day followed by 25 mL oral twice daily for the remaining 5 days. In addition, olanzapine was discontinued.
Switching to a different diet and antipsychotic
Two days after starting diphenhydramine, Mr. N was switched to a puree diet. His ability to swallow improved, and he no longer coughed. However, on repeat modified barium swallow, aspiration was still noted for all types of liquids and solids. No structural improvements were seen.
Mr. N was discharged back to his psychiatric hospital, and his antipsychotic was changed from olanzapine to oral aripiprazole 2 mg/d. The aripiprazole dose was kept low to prevent the recurrence of dystonia and because at the time, his schizophrenia was asymptomatic. Mr. N was also prescribed oral diphenhydramine 25 mL twice daily.
At a 2-week follow-up appointment, Mr. N continued to show clinical improvement on the puree diet with thin liquids and continued the prescribed medication regimen.
Dysphagia as a manifestation of EPS
All antipsychotics, and particularly first-generation agents, are associated with EPS.1 These symptoms may be the result of antagonistic binding of dopaminergic D2 receptors within mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways of the brain, as well as parts of basal ganglia such as the caudate nucleus.2
In addition to the examples listed in the Table,2 EPS can present as dysphagia, esophageal dysmotility, or aspiration, none of which may be recognized as EPS. Research has found haloperidol, loxapine, trifluoperazine, olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine, clozapine, and aripiprazole are associated with dysphagia.3-6 Strategies to treat antipsychotic-induced dysphagia include discontinuing the antipsychotic, lowering the dose, and changing to another medication.7

1. Crouse EL, Alastanos JN, Bozymski KM, et al. Dysphagia with second-generation antipsychotics: a case report and review of the literature. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(2):56-64. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.03.056
2. D’Souza RS, Hooten WM. Extrapyramidal symptoms. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed April 28, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534115/
3. Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Schnabel M, et al. Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia: case report and literature review. Dysphagia. 2007;22(1):63-67. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9032-9
4. Kalf JG, de Swart BJ, Bloem BR, et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006
5. Lin TW, Lee BS, Liao YC, et al. High dosage of aripiprazole-induced dysphagia. Int J Eat Disord. 2012;45(2):305-306. doi:10.1002/eat.20934
6. Stewart JT. Dysphagia associated with risperidone therapy. Dysphagia. 2003;18(4):274-275. doi:10.1007/s00455-003-0006-x
7. Lee JC, Takeshita J. Antipsychotic-induced dysphagia: a case report. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2015;17(5):10.4088/PCC.15I01792. doi:10.4088/PCC.15I01792
1. Crouse EL, Alastanos JN, Bozymski KM, et al. Dysphagia with second-generation antipsychotics: a case report and review of the literature. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(2):56-64. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.03.056
2. D’Souza RS, Hooten WM. Extrapyramidal symptoms. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed April 28, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534115/
3. Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Schnabel M, et al. Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia: case report and literature review. Dysphagia. 2007;22(1):63-67. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9032-9
4. Kalf JG, de Swart BJ, Bloem BR, et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006
5. Lin TW, Lee BS, Liao YC, et al. High dosage of aripiprazole-induced dysphagia. Int J Eat Disord. 2012;45(2):305-306. doi:10.1002/eat.20934
6. Stewart JT. Dysphagia associated with risperidone therapy. Dysphagia. 2003;18(4):274-275. doi:10.1007/s00455-003-0006-x
7. Lee JC, Takeshita J. Antipsychotic-induced dysphagia: a case report. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2015;17(5):10.4088/PCC.15I01792. doi:10.4088/PCC.15I01792
Quick medication, better communication linked to less violence at inpatient psych unit
SAN FRANCISCO – Physically violent events at an inpatient psychiatric unit in Pennsylvania dropped by 59.8% in the months after it implemented a plan to administer antipsychotic medications to patients more quickly – both in the emergency department and in the unit – and improve handoffs between providers and nurses, researchers reported.
“We were able to significantly reduce violence,” said Michael Chen, MD, Lehigh Valley Health Network psychiatry resident and lead author of an abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “Furthermore, the interventions were effective in reducing episodes of violence rather than redirecting it. And the overall feeling of safety on the inpatient psychiatric unit improved.”
Violence is common in psychiatric units, although it’s not clear how often it occurs. “The data has shown that patients with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia or a mood disorder with psychotic features such as bipolar disorder tend to account for most of the episodes of violence on the unit,” Dr. Chen said in an interview. “This inevitably results in a higher risk for violence on inpatient psychiatric units as a large portion of patients admitted to inpatient psychiatric units have these diagnoses.”
Enlisting the pharmacy department
For the new study, investigators tracked episodes of violence – including verbal attacks – at an Allentown, Penn.–area inpatient psychiatric unit from December 2021 to September 2022. According to Dr. Chen, unit leaders implemented the new plan in May 2022 in the wake of higher levels of violence during the COVID-19 pandemic and the concurrent staff shortages.
Clinic leaders sought to identify potentially aggressive patients in the emergency department and treat them with antipsychotics prior to admission to the psychiatric unit, ensure that the pharmacy provides access to as-needed or standing medications, and develop “standardized huddles to ensure proper handoffs between providers and nurses.”
Medical staff relied on the Dynamic Appraisal of Situational Aggression scale, risk factors, and clinical judgment to determine which patients had the potential to be violent, Dr. Chen said.
As for treatment, first-line antipsychotics are typically given orally, but they can be injected if patients must be treated over their objections, he said. “We would only consider starting standing medications against objections in patients who are involuntarily committed.”
During the 5 months before the intervention was implemented versus the following 5 months, the average monthly number of physically violent events in the psychiatric unit fell from 12.4 to 4.8 (–61.1%, P = .04), and verbal threats dipped from 7.2 to 4 (–44.4%, P = .15). The total average number of violent events per month, including violence against property, fell from an average of 25.4 to 10.2 (–59.8%, P = .03).
The total patient population didn’t vary significantly over time, Dr. Chen said. “Thus, the decrease in violence was not correlated with a decrease in patient load.”
While “there were concerns that there would just be higher episodes of violence in the ED while psychiatry patients awaited placement,” Dr. Chen said, the numbers actually showed reductions in violence in that setting. The average number of physically violent events per month in the ED fell from 49.6 to 39.4 (–20.6%, P = .03). Verbal threats dropped from 38 to 34.6 (–8.9%, P = .5) and overall violent events dipped from 87.6 to 74 (–15.6%, P = .08).
Why did the interventions seem to work? “Standing doses as well as as-needed medications started for psychiatric patients in the emergency department have been crucial to prevent delay of care,” Dr. Chen said. Enlisting the pharmacy department “helped ensure all patients had appropriate as-needed medications to prevent them from decompensating on the units,” he added, and “involvement of nursing and ancillary staff in high-risk rounds allowed the treatment team to rapidly anticipate and address concerns.”
The study authors also reported that nursing staff felt safer. Scores on a perception-of-safety scale – with 1 most unsafe and 7 most safe – improved from 3.3 to 4.2 (+27%, P < .01).
Dr. Chen said there was a “minimal” increase in cost to implement the intervention, although coordination is necessary. “The emergency department and psychiatry department have to work together to initiate treatment in the ED while awaiting beds,” he said. “The treatment team needs to communicate concerns during rounds. The pharmacist and psychiatrist need to work together to ensure that proper as-needed medications are available.”
‘Good clinical practice’
In an interview, psychiatrist Mark J. Russ, MD, of NewYork-Presbyterian/Westchester Behavioral Health and Weill Cornell Medical College, said violent incidents in inpatient psychiatric units are influenced by many factors, such as history of violence, substance use, history of trauma, psychosis/paranoia, and medical problems.
The units themselves can contribute to the risk of violence through power struggles and lack of attention paid to respect and dignity, he said. “Attention to these issues is important in reducing violence,” he noted. “Generalized training for staff in de-escalation techniques and trauma-informed care is imperative. There may be value in developing specialized psychiatric ICUs where staff are meticulously trained in these and other approaches.”
The new study, Dr. Russ said, suggests that “early identification of patients at risk of engaging in violent behavior on the inpatient unit, pharmacologic treatment, and good communication helps reduce violence.” The findings, he added, suggest that “interventions known to constitute good clinical practice are indeed helpful.”
However, he cautioned that “treating all at-risk patients with antipsychotics, regardless of their psychiatric diagnosis, might well be considered chemical restraint, depending on [the] circumstances.”
There was no study funding. The study authors and Dr. Russ have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Physically violent events at an inpatient psychiatric unit in Pennsylvania dropped by 59.8% in the months after it implemented a plan to administer antipsychotic medications to patients more quickly – both in the emergency department and in the unit – and improve handoffs between providers and nurses, researchers reported.
“We were able to significantly reduce violence,” said Michael Chen, MD, Lehigh Valley Health Network psychiatry resident and lead author of an abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “Furthermore, the interventions were effective in reducing episodes of violence rather than redirecting it. And the overall feeling of safety on the inpatient psychiatric unit improved.”
Violence is common in psychiatric units, although it’s not clear how often it occurs. “The data has shown that patients with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia or a mood disorder with psychotic features such as bipolar disorder tend to account for most of the episodes of violence on the unit,” Dr. Chen said in an interview. “This inevitably results in a higher risk for violence on inpatient psychiatric units as a large portion of patients admitted to inpatient psychiatric units have these diagnoses.”
Enlisting the pharmacy department
For the new study, investigators tracked episodes of violence – including verbal attacks – at an Allentown, Penn.–area inpatient psychiatric unit from December 2021 to September 2022. According to Dr. Chen, unit leaders implemented the new plan in May 2022 in the wake of higher levels of violence during the COVID-19 pandemic and the concurrent staff shortages.
Clinic leaders sought to identify potentially aggressive patients in the emergency department and treat them with antipsychotics prior to admission to the psychiatric unit, ensure that the pharmacy provides access to as-needed or standing medications, and develop “standardized huddles to ensure proper handoffs between providers and nurses.”
Medical staff relied on the Dynamic Appraisal of Situational Aggression scale, risk factors, and clinical judgment to determine which patients had the potential to be violent, Dr. Chen said.
As for treatment, first-line antipsychotics are typically given orally, but they can be injected if patients must be treated over their objections, he said. “We would only consider starting standing medications against objections in patients who are involuntarily committed.”
During the 5 months before the intervention was implemented versus the following 5 months, the average monthly number of physically violent events in the psychiatric unit fell from 12.4 to 4.8 (–61.1%, P = .04), and verbal threats dipped from 7.2 to 4 (–44.4%, P = .15). The total average number of violent events per month, including violence against property, fell from an average of 25.4 to 10.2 (–59.8%, P = .03).
The total patient population didn’t vary significantly over time, Dr. Chen said. “Thus, the decrease in violence was not correlated with a decrease in patient load.”
While “there were concerns that there would just be higher episodes of violence in the ED while psychiatry patients awaited placement,” Dr. Chen said, the numbers actually showed reductions in violence in that setting. The average number of physically violent events per month in the ED fell from 49.6 to 39.4 (–20.6%, P = .03). Verbal threats dropped from 38 to 34.6 (–8.9%, P = .5) and overall violent events dipped from 87.6 to 74 (–15.6%, P = .08).
Why did the interventions seem to work? “Standing doses as well as as-needed medications started for psychiatric patients in the emergency department have been crucial to prevent delay of care,” Dr. Chen said. Enlisting the pharmacy department “helped ensure all patients had appropriate as-needed medications to prevent them from decompensating on the units,” he added, and “involvement of nursing and ancillary staff in high-risk rounds allowed the treatment team to rapidly anticipate and address concerns.”
The study authors also reported that nursing staff felt safer. Scores on a perception-of-safety scale – with 1 most unsafe and 7 most safe – improved from 3.3 to 4.2 (+27%, P < .01).
Dr. Chen said there was a “minimal” increase in cost to implement the intervention, although coordination is necessary. “The emergency department and psychiatry department have to work together to initiate treatment in the ED while awaiting beds,” he said. “The treatment team needs to communicate concerns during rounds. The pharmacist and psychiatrist need to work together to ensure that proper as-needed medications are available.”
‘Good clinical practice’
In an interview, psychiatrist Mark J. Russ, MD, of NewYork-Presbyterian/Westchester Behavioral Health and Weill Cornell Medical College, said violent incidents in inpatient psychiatric units are influenced by many factors, such as history of violence, substance use, history of trauma, psychosis/paranoia, and medical problems.
The units themselves can contribute to the risk of violence through power struggles and lack of attention paid to respect and dignity, he said. “Attention to these issues is important in reducing violence,” he noted. “Generalized training for staff in de-escalation techniques and trauma-informed care is imperative. There may be value in developing specialized psychiatric ICUs where staff are meticulously trained in these and other approaches.”
The new study, Dr. Russ said, suggests that “early identification of patients at risk of engaging in violent behavior on the inpatient unit, pharmacologic treatment, and good communication helps reduce violence.” The findings, he added, suggest that “interventions known to constitute good clinical practice are indeed helpful.”
However, he cautioned that “treating all at-risk patients with antipsychotics, regardless of their psychiatric diagnosis, might well be considered chemical restraint, depending on [the] circumstances.”
There was no study funding. The study authors and Dr. Russ have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Physically violent events at an inpatient psychiatric unit in Pennsylvania dropped by 59.8% in the months after it implemented a plan to administer antipsychotic medications to patients more quickly – both in the emergency department and in the unit – and improve handoffs between providers and nurses, researchers reported.
“We were able to significantly reduce violence,” said Michael Chen, MD, Lehigh Valley Health Network psychiatry resident and lead author of an abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “Furthermore, the interventions were effective in reducing episodes of violence rather than redirecting it. And the overall feeling of safety on the inpatient psychiatric unit improved.”
Violence is common in psychiatric units, although it’s not clear how often it occurs. “The data has shown that patients with a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia or a mood disorder with psychotic features such as bipolar disorder tend to account for most of the episodes of violence on the unit,” Dr. Chen said in an interview. “This inevitably results in a higher risk for violence on inpatient psychiatric units as a large portion of patients admitted to inpatient psychiatric units have these diagnoses.”
Enlisting the pharmacy department
For the new study, investigators tracked episodes of violence – including verbal attacks – at an Allentown, Penn.–area inpatient psychiatric unit from December 2021 to September 2022. According to Dr. Chen, unit leaders implemented the new plan in May 2022 in the wake of higher levels of violence during the COVID-19 pandemic and the concurrent staff shortages.
Clinic leaders sought to identify potentially aggressive patients in the emergency department and treat them with antipsychotics prior to admission to the psychiatric unit, ensure that the pharmacy provides access to as-needed or standing medications, and develop “standardized huddles to ensure proper handoffs between providers and nurses.”
Medical staff relied on the Dynamic Appraisal of Situational Aggression scale, risk factors, and clinical judgment to determine which patients had the potential to be violent, Dr. Chen said.
As for treatment, first-line antipsychotics are typically given orally, but they can be injected if patients must be treated over their objections, he said. “We would only consider starting standing medications against objections in patients who are involuntarily committed.”
During the 5 months before the intervention was implemented versus the following 5 months, the average monthly number of physically violent events in the psychiatric unit fell from 12.4 to 4.8 (–61.1%, P = .04), and verbal threats dipped from 7.2 to 4 (–44.4%, P = .15). The total average number of violent events per month, including violence against property, fell from an average of 25.4 to 10.2 (–59.8%, P = .03).
The total patient population didn’t vary significantly over time, Dr. Chen said. “Thus, the decrease in violence was not correlated with a decrease in patient load.”
While “there were concerns that there would just be higher episodes of violence in the ED while psychiatry patients awaited placement,” Dr. Chen said, the numbers actually showed reductions in violence in that setting. The average number of physically violent events per month in the ED fell from 49.6 to 39.4 (–20.6%, P = .03). Verbal threats dropped from 38 to 34.6 (–8.9%, P = .5) and overall violent events dipped from 87.6 to 74 (–15.6%, P = .08).
Why did the interventions seem to work? “Standing doses as well as as-needed medications started for psychiatric patients in the emergency department have been crucial to prevent delay of care,” Dr. Chen said. Enlisting the pharmacy department “helped ensure all patients had appropriate as-needed medications to prevent them from decompensating on the units,” he added, and “involvement of nursing and ancillary staff in high-risk rounds allowed the treatment team to rapidly anticipate and address concerns.”
The study authors also reported that nursing staff felt safer. Scores on a perception-of-safety scale – with 1 most unsafe and 7 most safe – improved from 3.3 to 4.2 (+27%, P < .01).
Dr. Chen said there was a “minimal” increase in cost to implement the intervention, although coordination is necessary. “The emergency department and psychiatry department have to work together to initiate treatment in the ED while awaiting beds,” he said. “The treatment team needs to communicate concerns during rounds. The pharmacist and psychiatrist need to work together to ensure that proper as-needed medications are available.”
‘Good clinical practice’
In an interview, psychiatrist Mark J. Russ, MD, of NewYork-Presbyterian/Westchester Behavioral Health and Weill Cornell Medical College, said violent incidents in inpatient psychiatric units are influenced by many factors, such as history of violence, substance use, history of trauma, psychosis/paranoia, and medical problems.
The units themselves can contribute to the risk of violence through power struggles and lack of attention paid to respect and dignity, he said. “Attention to these issues is important in reducing violence,” he noted. “Generalized training for staff in de-escalation techniques and trauma-informed care is imperative. There may be value in developing specialized psychiatric ICUs where staff are meticulously trained in these and other approaches.”
The new study, Dr. Russ said, suggests that “early identification of patients at risk of engaging in violent behavior on the inpatient unit, pharmacologic treatment, and good communication helps reduce violence.” The findings, he added, suggest that “interventions known to constitute good clinical practice are indeed helpful.”
However, he cautioned that “treating all at-risk patients with antipsychotics, regardless of their psychiatric diagnosis, might well be considered chemical restraint, depending on [the] circumstances.”
There was no study funding. The study authors and Dr. Russ have no disclosures.
AT APA 2023
Black patients most likely to be restrained in EDs, Latino patients least likely
SAN FRANCISCO – .
In contrast, Hispanic/Latino patients were less likely to be restrained than both Black and White patients, researchers reported in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. The study authors also found that clinicians rarely turned to restraints, using them in just 2,712 of 882,390 ED visits (0.3%) over a 7-year period.
The study doesn’t examine why the disparities exist. But lead author Erika Chang-Sing, a medical student at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview that it’s clear that racial bias is the cause of the differences in restraint rates among White, Black, and Hispanics/Latino patients. “We think that there are multiple contributing factors to the higher rates of restraint for Black patients brought to the hospital by police, and all of them are rooted in systemic racism,” she said, adding that “the lower odds of restraint in the Hispanic or Latino group are also rooted in systemic racism and inequity.”
According to Ms. Chang-Sing, researchers launched the study to gain insight into the use of the restraints in the Southeast and to see what’s happening in light of the recent publicizing of killings of Black people by police. Being taken to the hospital by police “might contribute both to the individual patient’s behavior and the health care provider’s assessment of risk in determining whether or not to apply restraints,” she said.
Other research has linked ethnicity to higher rates of restraint use. For example, a 2021 study of 32,054 cases of patients under mandatory psychiatric hold in 11 Massachusetts emergency rooms found that Black (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22) and Hispanic (aOR, 1.45) patients were more likely to be restrained than White patients.
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked 885,102 emergency room visits at three North Carolina emergency departments from 2015 to 2022, including 9,130 who were brought in by police and 2,712 who were physically restrained because of the perceived risk of violence. “Providers use restraints, or straps, to secure the patient’s wrists and ankles to the bed,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Among all patients, 52.5% were Black, but 66% of those who were restrained were Black. The numbers for White patients were 35.7% and 23.9%, respectively, and 5.7% and 3.2% for Hispanics/Latino patients. Black patients were less likely than White patients to get a psychiatric primary emergency department diagnosis (aOR, 0.67), but those in that category were more likely than their White counterparts to be restrained (aOR, 1.36).
The higher risk of restraint use in Black patients overall disappeared when researchers adjusted their statistics to account for the effects of sex, age, and type of insurance (aOR, 0.86). Ms. Chang-Sing said the study team is reanalyzing the data since they think insurance may not be a confounder.
Why might Hispanic/Latino ethnicity be protective against restraint use? “This may be due to language barriers, fear of law enforcement, and avoidance of the hospital in the first place,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Emergency physician Wendy Macias-Konstantopoulos, MD, MPH, MBA, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, coauthored the 2021 study on police restraints. In an interview, she said the new findings add to previous research by providing data about the role played by the police who bring patients to the ED. She added that there is no evidence that certain populations simply need more restraints.
What can be done to reduce disparities in restraint use? Mental health teams can make a difference by responding to mental health emergencies, Ms. Chang-Sing said. “These providers can be instrumental in communicating to patients that the intention is to care for them, not to punish them.”
Another strategy is to increase the number of clinics and crisis response centers, she said. Hospital-based crisis response teams can also be helpful, she said. “Because these teams are focused only on behavioral emergencies, they can be more thoughtful in avoiding the use of restraints.”
No study funding was reported. The study authors and Dr. Macias-Konstantopoulos have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – .
In contrast, Hispanic/Latino patients were less likely to be restrained than both Black and White patients, researchers reported in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. The study authors also found that clinicians rarely turned to restraints, using them in just 2,712 of 882,390 ED visits (0.3%) over a 7-year period.
The study doesn’t examine why the disparities exist. But lead author Erika Chang-Sing, a medical student at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview that it’s clear that racial bias is the cause of the differences in restraint rates among White, Black, and Hispanics/Latino patients. “We think that there are multiple contributing factors to the higher rates of restraint for Black patients brought to the hospital by police, and all of them are rooted in systemic racism,” she said, adding that “the lower odds of restraint in the Hispanic or Latino group are also rooted in systemic racism and inequity.”
According to Ms. Chang-Sing, researchers launched the study to gain insight into the use of the restraints in the Southeast and to see what’s happening in light of the recent publicizing of killings of Black people by police. Being taken to the hospital by police “might contribute both to the individual patient’s behavior and the health care provider’s assessment of risk in determining whether or not to apply restraints,” she said.
Other research has linked ethnicity to higher rates of restraint use. For example, a 2021 study of 32,054 cases of patients under mandatory psychiatric hold in 11 Massachusetts emergency rooms found that Black (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22) and Hispanic (aOR, 1.45) patients were more likely to be restrained than White patients.
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked 885,102 emergency room visits at three North Carolina emergency departments from 2015 to 2022, including 9,130 who were brought in by police and 2,712 who were physically restrained because of the perceived risk of violence. “Providers use restraints, or straps, to secure the patient’s wrists and ankles to the bed,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Among all patients, 52.5% were Black, but 66% of those who were restrained were Black. The numbers for White patients were 35.7% and 23.9%, respectively, and 5.7% and 3.2% for Hispanics/Latino patients. Black patients were less likely than White patients to get a psychiatric primary emergency department diagnosis (aOR, 0.67), but those in that category were more likely than their White counterparts to be restrained (aOR, 1.36).
The higher risk of restraint use in Black patients overall disappeared when researchers adjusted their statistics to account for the effects of sex, age, and type of insurance (aOR, 0.86). Ms. Chang-Sing said the study team is reanalyzing the data since they think insurance may not be a confounder.
Why might Hispanic/Latino ethnicity be protective against restraint use? “This may be due to language barriers, fear of law enforcement, and avoidance of the hospital in the first place,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Emergency physician Wendy Macias-Konstantopoulos, MD, MPH, MBA, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, coauthored the 2021 study on police restraints. In an interview, she said the new findings add to previous research by providing data about the role played by the police who bring patients to the ED. She added that there is no evidence that certain populations simply need more restraints.
What can be done to reduce disparities in restraint use? Mental health teams can make a difference by responding to mental health emergencies, Ms. Chang-Sing said. “These providers can be instrumental in communicating to patients that the intention is to care for them, not to punish them.”
Another strategy is to increase the number of clinics and crisis response centers, she said. Hospital-based crisis response teams can also be helpful, she said. “Because these teams are focused only on behavioral emergencies, they can be more thoughtful in avoiding the use of restraints.”
No study funding was reported. The study authors and Dr. Macias-Konstantopoulos have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – .
In contrast, Hispanic/Latino patients were less likely to be restrained than both Black and White patients, researchers reported in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. The study authors also found that clinicians rarely turned to restraints, using them in just 2,712 of 882,390 ED visits (0.3%) over a 7-year period.
The study doesn’t examine why the disparities exist. But lead author Erika Chang-Sing, a medical student at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview that it’s clear that racial bias is the cause of the differences in restraint rates among White, Black, and Hispanics/Latino patients. “We think that there are multiple contributing factors to the higher rates of restraint for Black patients brought to the hospital by police, and all of them are rooted in systemic racism,” she said, adding that “the lower odds of restraint in the Hispanic or Latino group are also rooted in systemic racism and inequity.”
According to Ms. Chang-Sing, researchers launched the study to gain insight into the use of the restraints in the Southeast and to see what’s happening in light of the recent publicizing of killings of Black people by police. Being taken to the hospital by police “might contribute both to the individual patient’s behavior and the health care provider’s assessment of risk in determining whether or not to apply restraints,” she said.
Other research has linked ethnicity to higher rates of restraint use. For example, a 2021 study of 32,054 cases of patients under mandatory psychiatric hold in 11 Massachusetts emergency rooms found that Black (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22) and Hispanic (aOR, 1.45) patients were more likely to be restrained than White patients.
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked 885,102 emergency room visits at three North Carolina emergency departments from 2015 to 2022, including 9,130 who were brought in by police and 2,712 who were physically restrained because of the perceived risk of violence. “Providers use restraints, or straps, to secure the patient’s wrists and ankles to the bed,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Among all patients, 52.5% were Black, but 66% of those who were restrained were Black. The numbers for White patients were 35.7% and 23.9%, respectively, and 5.7% and 3.2% for Hispanics/Latino patients. Black patients were less likely than White patients to get a psychiatric primary emergency department diagnosis (aOR, 0.67), but those in that category were more likely than their White counterparts to be restrained (aOR, 1.36).
The higher risk of restraint use in Black patients overall disappeared when researchers adjusted their statistics to account for the effects of sex, age, and type of insurance (aOR, 0.86). Ms. Chang-Sing said the study team is reanalyzing the data since they think insurance may not be a confounder.
Why might Hispanic/Latino ethnicity be protective against restraint use? “This may be due to language barriers, fear of law enforcement, and avoidance of the hospital in the first place,” Ms. Chang-Sing said.
Emergency physician Wendy Macias-Konstantopoulos, MD, MPH, MBA, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, coauthored the 2021 study on police restraints. In an interview, she said the new findings add to previous research by providing data about the role played by the police who bring patients to the ED. She added that there is no evidence that certain populations simply need more restraints.
What can be done to reduce disparities in restraint use? Mental health teams can make a difference by responding to mental health emergencies, Ms. Chang-Sing said. “These providers can be instrumental in communicating to patients that the intention is to care for them, not to punish them.”
Another strategy is to increase the number of clinics and crisis response centers, she said. Hospital-based crisis response teams can also be helpful, she said. “Because these teams are focused only on behavioral emergencies, they can be more thoughtful in avoiding the use of restraints.”
No study funding was reported. The study authors and Dr. Macias-Konstantopoulos have no disclosures.
AT APA 2023
Choosing our terms: The diagnostic words we use can be harmful
We are living in an era of increasing sensitivity to our diversity and the ways we interact, but also an era of growing resistance to change and accommodation. As clinicians, we hope to be among the sensitive and the progressive, open to improving our views and interactions. And as part of our respect for those we treat, we seek to speak clearly with them about our assessment of what is disrupting their lives and about their options.
Using the right words is crucial in that work. Well-chosen words can be heard and understood. Poorly chosen words can be confusing or off-putting; they may miscommunicate or be offensive. Careful choice of words is also important among colleagues, who may not always mean the same things when using the same words.
In psychiatry, consumer knowledge and access are growing. There are effective standard treatments and promising new ones. But our terminology is often antique and obscure. This is so despite a recognition that some terms we use may communicate poorly and some are deprecating.
A notable example is “schizophrenia.” Originally referring to cognitive phenomena that were not adequately coherent with reality or one another, it has gone through periods of describing most psychosis to particular subsets of psychoses. Debates persist on specific criteria for key symptoms and typical course. Even two clinicians trained in the same site may not agree on the defining criteria, and the public, mostly informed by books, movies, and newspapers, is even more confused, often believing schizophrenia is multiple-personality disorder. In addition, the press and public often associate schizophrenia with violent behavior and uniformly bad outcomes, and for those reasons, a diagnosis is not only frightening but also stigmatizing.1
Many papers have presented the case for retiring “schizophrenia.”2 And practical efforts to rename schizophrenia have been made. These efforts have occurred in countries in which English is not the primary language.3 In Japan, schizophrenia was replaced by “integration disorder.” In Hong Kong, “disorder of thought and perception” was implemented. Korea chose “attunement disorder.” A recent large survey of stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers, and consumers in the United States, explored alternatives in English.4 Terms receiving approval included: “psychosis spectrum syndrome,” “altered perception syndrome,” and “neuro-emotional integration disorder.”
Despite these recommendations, the standard manuals of diagnosis, the ICD and DSM, have maintained the century-old term “schizophrenia” in their most recent editions, released in 2022. Aside from the inertia commonly associated with long-standing practices, it has been noted that many of the alternatives suggested or, in some places, implemented, are complex, somewhat vague, or too inclusive to distinguish different clinical presentations requiring different treatment approaches. They might not be compelling for use or optimal to guide caregiving.
Perhaps more concerning than “schizophrenia” are terms used to describe personality disorders.5 “Personality disorder” itself is problematic, implying a core and possibly unalterable fault in an individual. And among the personality disorders, words for the related group of disorders called “Cluster B” in the DSM raise issues. This includes the terms narcissistic, antisocial, histrionic, and borderline in DSM-5-TR. The first three terms are clearly pejorative. The last is unclear: What is the border between? Originally, it was bordering on psychosis, but as explained in DSM and ICD, borderline disorder is much more closely related to other personality disorders.
Notably, the “Cluster B” disorders run together in families, but men are more likely to be called antisocial and women borderline, even though the overlap in signs and symptoms is profound, suggesting marginally different manifestations of the same condition. The ICD has made changes to address the problems associated with some of these terms. ICD proposes personality “difficulty” to replace personality “disorder”; a modest change but less offensive. And it proposes seeing all, or at least most, personality disorders as being related to one another. Most share features of disturbances in sense-of-self and relationships with others. As descriptors, ICD kept “borderline pattern,” but replaced “antisocial” with “dissocial,” in an effort to be accurate but less demeaning. Other descriptors it proposes are negative affectivity, detachment, disinhibition, and anankastia, the last referring to compulsions.
These are notable advances. Can the field find even better terms to communicate hard to hear information, with words that are less problematic? In search of options, we surveyed clinicians at academic centers about the terms they preferred to avoid and the ones they prefer to use in talking with patients.6 Their practices may be informative.
Briefly summarized, these clinicians preferred not to use “schizophrenia” and very few used “antisocial,” “histrionic,” or “narcissistic.” Most avoided using “borderline” as well. Instead, they recommended discussing specific symptoms and manifestations of illness or dysfunctional behavior and relationships with their patients. They employed terms including “psychosis,” “hallucination,” “delusion,” “thinking disorder,” and “mood disorder.” They explained these terms, as needed, and found that patients understood them.
For Cluster B personality disorders, they spoke of personality traits and styles and specifically about “conduct,” “rule breaking,” “coping,” “self-focus,” “emotionality,” and “reactivity.” Those choices are not perfect, of course. Medical terms are often not standard words used in a conversational way. But the words chosen by these clinicians are generally straightforward and may communicate in a clear and acceptable fashion. It is also notable that the terms match how the clinicians assess and treat their patients, as observed in a separate study of their practices.7 That is, the clinicians advised that they look for and suggest treatments for the specific symptoms they see that most disrupt an individual’s life, such as delusions or mood instability. They are not much guided by diagnoses, like schizophrenia or borderline disorder. That makes the chosen terms not only less confusing or off-putting but also more practical.
Changing terminology in any field is difficult. We are trained to use standard terms. Clearly, however, many clinicians avoid some terms and use alternatives in their work. Asked why, they responded that they did so precisely to communicate more effectively and more respectfully. That is key to their treatment goals. Perhaps others will consider these choices useful in their work. And perhaps both the DSM and the ICD will not only continue to consider but will decide to implement alternatives for problematic terms in the years ahead, as they discuss their next revisions.
Dr. Cohen is director of the Program for Neuropsychiatric Research at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and Robertson-Steele Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
References
1. Lasalvia A et al. Renaming schizophrenia? A survey among psychiatrists, mental health service users and family members in Italy. Schizophr Res. 2021;228:502-9.
2. Gülöksüz S et al. Renaming schizophrenia: 5 x 5. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019;28(3):254-7.
3. Sartorius N et al. Name change for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(2):255-8.
4. Mesholam-Gately RI et al. Are we ready for a name change for schizophrenia? A survey of multiple stakeholders. Schizophr Res. 2021;238:152-60.
5. Mulder R. The evolving nosology of personality disorder and its clinical utility. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):361-2.
6. Cohen BM et al. Diagnostic terms psychiatrists prefer to use for common psychotic and personality disorders. J Psychiatr Res. 2022 Sep 5;155:226-31.
7. Cohen BM, et al. Use of DSM-5 diagnoses vs. other clinical information by US academic-affiliated psychiatrists in assessing and treating psychotic disorders. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):447-8.
We are living in an era of increasing sensitivity to our diversity and the ways we interact, but also an era of growing resistance to change and accommodation. As clinicians, we hope to be among the sensitive and the progressive, open to improving our views and interactions. And as part of our respect for those we treat, we seek to speak clearly with them about our assessment of what is disrupting their lives and about their options.
Using the right words is crucial in that work. Well-chosen words can be heard and understood. Poorly chosen words can be confusing or off-putting; they may miscommunicate or be offensive. Careful choice of words is also important among colleagues, who may not always mean the same things when using the same words.
In psychiatry, consumer knowledge and access are growing. There are effective standard treatments and promising new ones. But our terminology is often antique and obscure. This is so despite a recognition that some terms we use may communicate poorly and some are deprecating.
A notable example is “schizophrenia.” Originally referring to cognitive phenomena that were not adequately coherent with reality or one another, it has gone through periods of describing most psychosis to particular subsets of psychoses. Debates persist on specific criteria for key symptoms and typical course. Even two clinicians trained in the same site may not agree on the defining criteria, and the public, mostly informed by books, movies, and newspapers, is even more confused, often believing schizophrenia is multiple-personality disorder. In addition, the press and public often associate schizophrenia with violent behavior and uniformly bad outcomes, and for those reasons, a diagnosis is not only frightening but also stigmatizing.1
Many papers have presented the case for retiring “schizophrenia.”2 And practical efforts to rename schizophrenia have been made. These efforts have occurred in countries in which English is not the primary language.3 In Japan, schizophrenia was replaced by “integration disorder.” In Hong Kong, “disorder of thought and perception” was implemented. Korea chose “attunement disorder.” A recent large survey of stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers, and consumers in the United States, explored alternatives in English.4 Terms receiving approval included: “psychosis spectrum syndrome,” “altered perception syndrome,” and “neuro-emotional integration disorder.”
Despite these recommendations, the standard manuals of diagnosis, the ICD and DSM, have maintained the century-old term “schizophrenia” in their most recent editions, released in 2022. Aside from the inertia commonly associated with long-standing practices, it has been noted that many of the alternatives suggested or, in some places, implemented, are complex, somewhat vague, or too inclusive to distinguish different clinical presentations requiring different treatment approaches. They might not be compelling for use or optimal to guide caregiving.
Perhaps more concerning than “schizophrenia” are terms used to describe personality disorders.5 “Personality disorder” itself is problematic, implying a core and possibly unalterable fault in an individual. And among the personality disorders, words for the related group of disorders called “Cluster B” in the DSM raise issues. This includes the terms narcissistic, antisocial, histrionic, and borderline in DSM-5-TR. The first three terms are clearly pejorative. The last is unclear: What is the border between? Originally, it was bordering on psychosis, but as explained in DSM and ICD, borderline disorder is much more closely related to other personality disorders.
Notably, the “Cluster B” disorders run together in families, but men are more likely to be called antisocial and women borderline, even though the overlap in signs and symptoms is profound, suggesting marginally different manifestations of the same condition. The ICD has made changes to address the problems associated with some of these terms. ICD proposes personality “difficulty” to replace personality “disorder”; a modest change but less offensive. And it proposes seeing all, or at least most, personality disorders as being related to one another. Most share features of disturbances in sense-of-self and relationships with others. As descriptors, ICD kept “borderline pattern,” but replaced “antisocial” with “dissocial,” in an effort to be accurate but less demeaning. Other descriptors it proposes are negative affectivity, detachment, disinhibition, and anankastia, the last referring to compulsions.
These are notable advances. Can the field find even better terms to communicate hard to hear information, with words that are less problematic? In search of options, we surveyed clinicians at academic centers about the terms they preferred to avoid and the ones they prefer to use in talking with patients.6 Their practices may be informative.
Briefly summarized, these clinicians preferred not to use “schizophrenia” and very few used “antisocial,” “histrionic,” or “narcissistic.” Most avoided using “borderline” as well. Instead, they recommended discussing specific symptoms and manifestations of illness or dysfunctional behavior and relationships with their patients. They employed terms including “psychosis,” “hallucination,” “delusion,” “thinking disorder,” and “mood disorder.” They explained these terms, as needed, and found that patients understood them.
For Cluster B personality disorders, they spoke of personality traits and styles and specifically about “conduct,” “rule breaking,” “coping,” “self-focus,” “emotionality,” and “reactivity.” Those choices are not perfect, of course. Medical terms are often not standard words used in a conversational way. But the words chosen by these clinicians are generally straightforward and may communicate in a clear and acceptable fashion. It is also notable that the terms match how the clinicians assess and treat their patients, as observed in a separate study of their practices.7 That is, the clinicians advised that they look for and suggest treatments for the specific symptoms they see that most disrupt an individual’s life, such as delusions or mood instability. They are not much guided by diagnoses, like schizophrenia or borderline disorder. That makes the chosen terms not only less confusing or off-putting but also more practical.
Changing terminology in any field is difficult. We are trained to use standard terms. Clearly, however, many clinicians avoid some terms and use alternatives in their work. Asked why, they responded that they did so precisely to communicate more effectively and more respectfully. That is key to their treatment goals. Perhaps others will consider these choices useful in their work. And perhaps both the DSM and the ICD will not only continue to consider but will decide to implement alternatives for problematic terms in the years ahead, as they discuss their next revisions.
Dr. Cohen is director of the Program for Neuropsychiatric Research at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and Robertson-Steele Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
References
1. Lasalvia A et al. Renaming schizophrenia? A survey among psychiatrists, mental health service users and family members in Italy. Schizophr Res. 2021;228:502-9.
2. Gülöksüz S et al. Renaming schizophrenia: 5 x 5. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019;28(3):254-7.
3. Sartorius N et al. Name change for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(2):255-8.
4. Mesholam-Gately RI et al. Are we ready for a name change for schizophrenia? A survey of multiple stakeholders. Schizophr Res. 2021;238:152-60.
5. Mulder R. The evolving nosology of personality disorder and its clinical utility. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):361-2.
6. Cohen BM et al. Diagnostic terms psychiatrists prefer to use for common psychotic and personality disorders. J Psychiatr Res. 2022 Sep 5;155:226-31.
7. Cohen BM, et al. Use of DSM-5 diagnoses vs. other clinical information by US academic-affiliated psychiatrists in assessing and treating psychotic disorders. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):447-8.
We are living in an era of increasing sensitivity to our diversity and the ways we interact, but also an era of growing resistance to change and accommodation. As clinicians, we hope to be among the sensitive and the progressive, open to improving our views and interactions. And as part of our respect for those we treat, we seek to speak clearly with them about our assessment of what is disrupting their lives and about their options.
Using the right words is crucial in that work. Well-chosen words can be heard and understood. Poorly chosen words can be confusing or off-putting; they may miscommunicate or be offensive. Careful choice of words is also important among colleagues, who may not always mean the same things when using the same words.
In psychiatry, consumer knowledge and access are growing. There are effective standard treatments and promising new ones. But our terminology is often antique and obscure. This is so despite a recognition that some terms we use may communicate poorly and some are deprecating.
A notable example is “schizophrenia.” Originally referring to cognitive phenomena that were not adequately coherent with reality or one another, it has gone through periods of describing most psychosis to particular subsets of psychoses. Debates persist on specific criteria for key symptoms and typical course. Even two clinicians trained in the same site may not agree on the defining criteria, and the public, mostly informed by books, movies, and newspapers, is even more confused, often believing schizophrenia is multiple-personality disorder. In addition, the press and public often associate schizophrenia with violent behavior and uniformly bad outcomes, and for those reasons, a diagnosis is not only frightening but also stigmatizing.1
Many papers have presented the case for retiring “schizophrenia.”2 And practical efforts to rename schizophrenia have been made. These efforts have occurred in countries in which English is not the primary language.3 In Japan, schizophrenia was replaced by “integration disorder.” In Hong Kong, “disorder of thought and perception” was implemented. Korea chose “attunement disorder.” A recent large survey of stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers, and consumers in the United States, explored alternatives in English.4 Terms receiving approval included: “psychosis spectrum syndrome,” “altered perception syndrome,” and “neuro-emotional integration disorder.”
Despite these recommendations, the standard manuals of diagnosis, the ICD and DSM, have maintained the century-old term “schizophrenia” in their most recent editions, released in 2022. Aside from the inertia commonly associated with long-standing practices, it has been noted that many of the alternatives suggested or, in some places, implemented, are complex, somewhat vague, or too inclusive to distinguish different clinical presentations requiring different treatment approaches. They might not be compelling for use or optimal to guide caregiving.
Perhaps more concerning than “schizophrenia” are terms used to describe personality disorders.5 “Personality disorder” itself is problematic, implying a core and possibly unalterable fault in an individual. And among the personality disorders, words for the related group of disorders called “Cluster B” in the DSM raise issues. This includes the terms narcissistic, antisocial, histrionic, and borderline in DSM-5-TR. The first three terms are clearly pejorative. The last is unclear: What is the border between? Originally, it was bordering on psychosis, but as explained in DSM and ICD, borderline disorder is much more closely related to other personality disorders.
Notably, the “Cluster B” disorders run together in families, but men are more likely to be called antisocial and women borderline, even though the overlap in signs and symptoms is profound, suggesting marginally different manifestations of the same condition. The ICD has made changes to address the problems associated with some of these terms. ICD proposes personality “difficulty” to replace personality “disorder”; a modest change but less offensive. And it proposes seeing all, or at least most, personality disorders as being related to one another. Most share features of disturbances in sense-of-self and relationships with others. As descriptors, ICD kept “borderline pattern,” but replaced “antisocial” with “dissocial,” in an effort to be accurate but less demeaning. Other descriptors it proposes are negative affectivity, detachment, disinhibition, and anankastia, the last referring to compulsions.
These are notable advances. Can the field find even better terms to communicate hard to hear information, with words that are less problematic? In search of options, we surveyed clinicians at academic centers about the terms they preferred to avoid and the ones they prefer to use in talking with patients.6 Their practices may be informative.
Briefly summarized, these clinicians preferred not to use “schizophrenia” and very few used “antisocial,” “histrionic,” or “narcissistic.” Most avoided using “borderline” as well. Instead, they recommended discussing specific symptoms and manifestations of illness or dysfunctional behavior and relationships with their patients. They employed terms including “psychosis,” “hallucination,” “delusion,” “thinking disorder,” and “mood disorder.” They explained these terms, as needed, and found that patients understood them.
For Cluster B personality disorders, they spoke of personality traits and styles and specifically about “conduct,” “rule breaking,” “coping,” “self-focus,” “emotionality,” and “reactivity.” Those choices are not perfect, of course. Medical terms are often not standard words used in a conversational way. But the words chosen by these clinicians are generally straightforward and may communicate in a clear and acceptable fashion. It is also notable that the terms match how the clinicians assess and treat their patients, as observed in a separate study of their practices.7 That is, the clinicians advised that they look for and suggest treatments for the specific symptoms they see that most disrupt an individual’s life, such as delusions or mood instability. They are not much guided by diagnoses, like schizophrenia or borderline disorder. That makes the chosen terms not only less confusing or off-putting but also more practical.
Changing terminology in any field is difficult. We are trained to use standard terms. Clearly, however, many clinicians avoid some terms and use alternatives in their work. Asked why, they responded that they did so precisely to communicate more effectively and more respectfully. That is key to their treatment goals. Perhaps others will consider these choices useful in their work. And perhaps both the DSM and the ICD will not only continue to consider but will decide to implement alternatives for problematic terms in the years ahead, as they discuss their next revisions.
Dr. Cohen is director of the Program for Neuropsychiatric Research at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and Robertson-Steele Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
References
1. Lasalvia A et al. Renaming schizophrenia? A survey among psychiatrists, mental health service users and family members in Italy. Schizophr Res. 2021;228:502-9.
2. Gülöksüz S et al. Renaming schizophrenia: 5 x 5. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019;28(3):254-7.
3. Sartorius N et al. Name change for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(2):255-8.
4. Mesholam-Gately RI et al. Are we ready for a name change for schizophrenia? A survey of multiple stakeholders. Schizophr Res. 2021;238:152-60.
5. Mulder R. The evolving nosology of personality disorder and its clinical utility. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):361-2.
6. Cohen BM et al. Diagnostic terms psychiatrists prefer to use for common psychotic and personality disorders. J Psychiatr Res. 2022 Sep 5;155:226-31.
7. Cohen BM, et al. Use of DSM-5 diagnoses vs. other clinical information by US academic-affiliated psychiatrists in assessing and treating psychotic disorders. World Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;20(3):447-8.
Young men at highest schizophrenia risk from cannabis abuse
A new study confirms the robust link between cannabis use and schizophrenia among men and women but suggests that young men may be especially susceptible to schizophrenia from cannabis abuse.
Of note,
“The entanglement of substance use disorders and mental illnesses is a major public health issue, requiring urgent action and support for people who need it,” study coauthor Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a news release.
“As access to potent cannabis products continues to expand, it is crucial that we also expand prevention, screening, and treatment for people who may experience mental illnesses associated with cannabis use,” Dr. Volkow added.
The study was published online in Psychological Medicine.
A modifiable risk factor
The researchers analyzed Danish registry data spanning 5 decades and representing more than 6.9 million people in Denmark to estimate the population-level percentage of schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD.
A total of 60,563 participants were diagnosed with CUD. Three-quarters of cases were in men; there were 45,327 incident cases of schizophrenia during the study period.
The overall adjusted hazard ratio for CUD on schizophrenia was slightly higher among males than females (aHR, 2.42 vs. 2.02); however, among those aged 16 to 20 years, the adjusted incidence risk ratio for males was more than twice that for females (aIRR, 3.84 vs. 1.81).
The researchers estimate that, in 2021, about 15% of schizophrenia cases among males aged 16-49 could have been avoided by preventing CUD, compared with 4% among females in this age range.
For young men aged 21-30, the proportion of preventable schizophrenia cases related to CUD may be as high as 30%, the authors reported.
“Alongside the increasing evidence that CUD is a modifiable risk factor for schizophrenia, our findings underscore the importance of evidence-based strategies to regulate cannabis use and to effectively prevent, screen for, and treat CUD as well as schizophrenia,” the researchers wrote.
Legalization sends the wrong message
In a press statement, lead investigator Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, with the University of Copenhagen, noted that “increases in the legalization of cannabis over the past few decades have made it one of the most frequently used psychoactive substances in the world, while also decreasing the public’s perception of its harm. This study adds to our growing understanding that cannabis use is not harmless, and that risks are not fixed at one point in time.”
In a prior study, Dr. Hjorthøj and colleagues found that the proportion of new schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD has consistently increased over the past 20 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” Dr. Hjorthøj said at the time this research was published.
“It is of course nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” Dr. Hjorthøj added.
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study confirms the robust link between cannabis use and schizophrenia among men and women but suggests that young men may be especially susceptible to schizophrenia from cannabis abuse.
Of note,
“The entanglement of substance use disorders and mental illnesses is a major public health issue, requiring urgent action and support for people who need it,” study coauthor Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a news release.
“As access to potent cannabis products continues to expand, it is crucial that we also expand prevention, screening, and treatment for people who may experience mental illnesses associated with cannabis use,” Dr. Volkow added.
The study was published online in Psychological Medicine.
A modifiable risk factor
The researchers analyzed Danish registry data spanning 5 decades and representing more than 6.9 million people in Denmark to estimate the population-level percentage of schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD.
A total of 60,563 participants were diagnosed with CUD. Three-quarters of cases were in men; there were 45,327 incident cases of schizophrenia during the study period.
The overall adjusted hazard ratio for CUD on schizophrenia was slightly higher among males than females (aHR, 2.42 vs. 2.02); however, among those aged 16 to 20 years, the adjusted incidence risk ratio for males was more than twice that for females (aIRR, 3.84 vs. 1.81).
The researchers estimate that, in 2021, about 15% of schizophrenia cases among males aged 16-49 could have been avoided by preventing CUD, compared with 4% among females in this age range.
For young men aged 21-30, the proportion of preventable schizophrenia cases related to CUD may be as high as 30%, the authors reported.
“Alongside the increasing evidence that CUD is a modifiable risk factor for schizophrenia, our findings underscore the importance of evidence-based strategies to regulate cannabis use and to effectively prevent, screen for, and treat CUD as well as schizophrenia,” the researchers wrote.
Legalization sends the wrong message
In a press statement, lead investigator Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, with the University of Copenhagen, noted that “increases in the legalization of cannabis over the past few decades have made it one of the most frequently used psychoactive substances in the world, while also decreasing the public’s perception of its harm. This study adds to our growing understanding that cannabis use is not harmless, and that risks are not fixed at one point in time.”
In a prior study, Dr. Hjorthøj and colleagues found that the proportion of new schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD has consistently increased over the past 20 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” Dr. Hjorthøj said at the time this research was published.
“It is of course nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” Dr. Hjorthøj added.
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study confirms the robust link between cannabis use and schizophrenia among men and women but suggests that young men may be especially susceptible to schizophrenia from cannabis abuse.
Of note,
“The entanglement of substance use disorders and mental illnesses is a major public health issue, requiring urgent action and support for people who need it,” study coauthor Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a news release.
“As access to potent cannabis products continues to expand, it is crucial that we also expand prevention, screening, and treatment for people who may experience mental illnesses associated with cannabis use,” Dr. Volkow added.
The study was published online in Psychological Medicine.
A modifiable risk factor
The researchers analyzed Danish registry data spanning 5 decades and representing more than 6.9 million people in Denmark to estimate the population-level percentage of schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD.
A total of 60,563 participants were diagnosed with CUD. Three-quarters of cases were in men; there were 45,327 incident cases of schizophrenia during the study period.
The overall adjusted hazard ratio for CUD on schizophrenia was slightly higher among males than females (aHR, 2.42 vs. 2.02); however, among those aged 16 to 20 years, the adjusted incidence risk ratio for males was more than twice that for females (aIRR, 3.84 vs. 1.81).
The researchers estimate that, in 2021, about 15% of schizophrenia cases among males aged 16-49 could have been avoided by preventing CUD, compared with 4% among females in this age range.
For young men aged 21-30, the proportion of preventable schizophrenia cases related to CUD may be as high as 30%, the authors reported.
“Alongside the increasing evidence that CUD is a modifiable risk factor for schizophrenia, our findings underscore the importance of evidence-based strategies to regulate cannabis use and to effectively prevent, screen for, and treat CUD as well as schizophrenia,” the researchers wrote.
Legalization sends the wrong message
In a press statement, lead investigator Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, with the University of Copenhagen, noted that “increases in the legalization of cannabis over the past few decades have made it one of the most frequently used psychoactive substances in the world, while also decreasing the public’s perception of its harm. This study adds to our growing understanding that cannabis use is not harmless, and that risks are not fixed at one point in time.”
In a prior study, Dr. Hjorthøj and colleagues found that the proportion of new schizophrenia cases attributable to CUD has consistently increased over the past 20 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” Dr. Hjorthøj said at the time this research was published.
“It is of course nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” Dr. Hjorthøj added.
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHOLOGICAL MEDICINE
Widespread prescribing of stimulants with other CNS-active meds
Investigators analyzed prescription drug claims for over 9.1 million U.S. adults over a 1-year period and found that 276,223 (3%) had used a schedule II stimulant, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, during that time. Of these 276,223 patients, 45% combined these agents with one or more additional CNS-active drugs and almost 25% were simultaneously using two or more additional CNS-active drugs.
Close to half of the stimulant users were taking an antidepressant, while close to one-third filled prescriptions for anxiolytic/sedative/hypnotic meditations, and one-fifth received opioid prescriptions.
The widespread, often off-label use of these stimulants in combination therapy with antidepressants, anxiolytics, opioids, and other psychoactive drugs, “reveals new patterns of utilization beyond the approved use of stimulants as monotherapy for ADHD, but because there are so few studies of these kinds of combination therapy, both the advantages and additional risks [of this type of prescribing] remain unknown,” study investigator Thomas J. Moore, AB, faculty associate in epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in BMJ Open.
‘Dangerous’ substances
Amphetamines and methylphenidate are CNS stimulants that have been in use for almost a century. Like opioids and barbiturates, they’re considered “dangerous” and classified as schedule II Controlled Substances because of their high potential for abuse.
Over many years, these stimulants have been used for multiple purposes, including nasal congestion, narcolepsy, appetite suppression, binge eating, depression, senile behavior, lethargy, and ADHD, the researchers note.
Observational studies suggest medical use of these agents has been increasing in the United States. The investigators conducted previous research that revealed a 79% increase from 2013 to 2018 in the number of adults who self-report their use. The current study, said Mr. Moore, explores how these stimulants are being used.
For the study, data was extracted from the MarketScan 2019 and 2020 Commercial Claims and Encounters Databases, focusing on 9.1 million adults aged 19-64 years who were continuously enrolled in an included commercial benefit plan from Oct. 1, 2019 to Dec. 31, 2020.
The primary outcome consisted of an outpatient prescription claim, service date, and days’ supply for the CNS-active drugs.
The researchers defined “combination-2” therapy as 60 or more days of combination treatment with a schedule II stimulant and at least one additional CNS-active drug. “Combination-3” therapy was defined as the addition of at least two additional CNS-active drugs.
The researchers used service date and days’ supply to examine the number of stimulant and other CNS-active drugs for each of the days of 2020.
CNS-active drug classes included antidepressants, anxiolytics/sedatives/hypnotics, antipsychotics, opioids, anticonvulsants, and other CNS-active drugs.
Prescribing cascade
Of the total number of adults enrolled, 3% (n = 276,223) were taking schedule II stimulants during 2020, with a median of 8 (interquartile range, 4-11) prescriptions. These drugs provided 227 (IQR, 110-322) treatment days of exposure.
Among those taking stimulants 45.5% combined the use of at least one additional CNS-active drug for a median of 213 (IQR, 126-301) treatment days; and 24.3% used at least two additional CNS-active drugs for a median of 182 (IQR, 108-276) days.
“Clinicians should beware of the prescribing cascade. Sometimes it begins with an antidepressant that causes too much sedation, so a stimulant gets added, which leads to insomnia, so alprazolam gets added to the mix,” Mr. Moore said.
He cautioned that this “leaves a patient with multiple drugs, all with discontinuation effects of different kinds and clashing effects.”
These new findings, the investigators note, “add new public health concerns to those raised by our previous study. ... this more-detailed profile reveals several new patterns.”
Most patients become “long-term users” once treatment has started, with 75% continuing for a 1-year period.
“This underscores the possible risks of nonmedical use and dependence that have warranted the classification of these drugs as having high potential for psychological or physical dependence and their prominent appearance in toxicology drug rankings of fatal overdose cases,” they write.
They note that the data “do not indicate which intervention may have come first – a stimulant added to compensate for excess sedation from the benzodiazepine, or the alprazolam added to calm excessive CNS stimulation and/or insomnia from the stimulants or other drugs.”
Several limitations cited by the authors include the fact that, although the population encompassed 9.1 million people, it “may not represent all commercially insured adults,” and it doesn’t include people who aren’t covered by commercial insurance.
Moreover, the MarketScan dataset included up to four diagnosis codes for each outpatient and emergency department encounter; therefore, it was not possible to directly link the diagnoses to specific prescription drug claims, and thus the diagnoses were not evaluated.
“Since many providers will not accept a drug claim for a schedule II stimulant without an on-label diagnosis of ADHD,” the authors suspect that “large numbers of this diagnosis were present.”
Complex prescribing regimens
Mark Olfson, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry, medicine, and law and professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said the report “highlights the pharmacological complexity of adults who are treated with stimulants.”
Dr. Olfson, who is a research psychiatrist at the New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, and was not involved with the study, observed there is “evidence to support stimulants as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant unipolar depression in older adults.”
However, he added, “this indication is unlikely to fully explain the high proportion of nonelderly, stimulant-treated adults who also receive antidepressants.”
These new findings “call for research to increase our understanding of the clinical contexts that motivate these complex prescribing regimens as well as their effectiveness and safety,” said Dr. Olfson.
The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Mr. Moore declares no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor G. Caleb Alexander, MD, is past chair and a current member of the Food and Drug Administration’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Advisory Committee; is a cofounding principal and equity holder in Monument Analytics, a health care consultancy whose clients include the life sciences industry as well as plaintiffs in opioid litigation, for whom he has served as a paid expert witness; and is a past member of OptumRx’s National P&T Committee. Dr. Olfson declares no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed prescription drug claims for over 9.1 million U.S. adults over a 1-year period and found that 276,223 (3%) had used a schedule II stimulant, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, during that time. Of these 276,223 patients, 45% combined these agents with one or more additional CNS-active drugs and almost 25% were simultaneously using two or more additional CNS-active drugs.
Close to half of the stimulant users were taking an antidepressant, while close to one-third filled prescriptions for anxiolytic/sedative/hypnotic meditations, and one-fifth received opioid prescriptions.
The widespread, often off-label use of these stimulants in combination therapy with antidepressants, anxiolytics, opioids, and other psychoactive drugs, “reveals new patterns of utilization beyond the approved use of stimulants as monotherapy for ADHD, but because there are so few studies of these kinds of combination therapy, both the advantages and additional risks [of this type of prescribing] remain unknown,” study investigator Thomas J. Moore, AB, faculty associate in epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in BMJ Open.
‘Dangerous’ substances
Amphetamines and methylphenidate are CNS stimulants that have been in use for almost a century. Like opioids and barbiturates, they’re considered “dangerous” and classified as schedule II Controlled Substances because of their high potential for abuse.
Over many years, these stimulants have been used for multiple purposes, including nasal congestion, narcolepsy, appetite suppression, binge eating, depression, senile behavior, lethargy, and ADHD, the researchers note.
Observational studies suggest medical use of these agents has been increasing in the United States. The investigators conducted previous research that revealed a 79% increase from 2013 to 2018 in the number of adults who self-report their use. The current study, said Mr. Moore, explores how these stimulants are being used.
For the study, data was extracted from the MarketScan 2019 and 2020 Commercial Claims and Encounters Databases, focusing on 9.1 million adults aged 19-64 years who were continuously enrolled in an included commercial benefit plan from Oct. 1, 2019 to Dec. 31, 2020.
The primary outcome consisted of an outpatient prescription claim, service date, and days’ supply for the CNS-active drugs.
The researchers defined “combination-2” therapy as 60 or more days of combination treatment with a schedule II stimulant and at least one additional CNS-active drug. “Combination-3” therapy was defined as the addition of at least two additional CNS-active drugs.
The researchers used service date and days’ supply to examine the number of stimulant and other CNS-active drugs for each of the days of 2020.
CNS-active drug classes included antidepressants, anxiolytics/sedatives/hypnotics, antipsychotics, opioids, anticonvulsants, and other CNS-active drugs.
Prescribing cascade
Of the total number of adults enrolled, 3% (n = 276,223) were taking schedule II stimulants during 2020, with a median of 8 (interquartile range, 4-11) prescriptions. These drugs provided 227 (IQR, 110-322) treatment days of exposure.
Among those taking stimulants 45.5% combined the use of at least one additional CNS-active drug for a median of 213 (IQR, 126-301) treatment days; and 24.3% used at least two additional CNS-active drugs for a median of 182 (IQR, 108-276) days.
“Clinicians should beware of the prescribing cascade. Sometimes it begins with an antidepressant that causes too much sedation, so a stimulant gets added, which leads to insomnia, so alprazolam gets added to the mix,” Mr. Moore said.
He cautioned that this “leaves a patient with multiple drugs, all with discontinuation effects of different kinds and clashing effects.”
These new findings, the investigators note, “add new public health concerns to those raised by our previous study. ... this more-detailed profile reveals several new patterns.”
Most patients become “long-term users” once treatment has started, with 75% continuing for a 1-year period.
“This underscores the possible risks of nonmedical use and dependence that have warranted the classification of these drugs as having high potential for psychological or physical dependence and their prominent appearance in toxicology drug rankings of fatal overdose cases,” they write.
They note that the data “do not indicate which intervention may have come first – a stimulant added to compensate for excess sedation from the benzodiazepine, or the alprazolam added to calm excessive CNS stimulation and/or insomnia from the stimulants or other drugs.”
Several limitations cited by the authors include the fact that, although the population encompassed 9.1 million people, it “may not represent all commercially insured adults,” and it doesn’t include people who aren’t covered by commercial insurance.
Moreover, the MarketScan dataset included up to four diagnosis codes for each outpatient and emergency department encounter; therefore, it was not possible to directly link the diagnoses to specific prescription drug claims, and thus the diagnoses were not evaluated.
“Since many providers will not accept a drug claim for a schedule II stimulant without an on-label diagnosis of ADHD,” the authors suspect that “large numbers of this diagnosis were present.”
Complex prescribing regimens
Mark Olfson, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry, medicine, and law and professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said the report “highlights the pharmacological complexity of adults who are treated with stimulants.”
Dr. Olfson, who is a research psychiatrist at the New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, and was not involved with the study, observed there is “evidence to support stimulants as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant unipolar depression in older adults.”
However, he added, “this indication is unlikely to fully explain the high proportion of nonelderly, stimulant-treated adults who also receive antidepressants.”
These new findings “call for research to increase our understanding of the clinical contexts that motivate these complex prescribing regimens as well as their effectiveness and safety,” said Dr. Olfson.
The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Mr. Moore declares no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor G. Caleb Alexander, MD, is past chair and a current member of the Food and Drug Administration’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Advisory Committee; is a cofounding principal and equity holder in Monument Analytics, a health care consultancy whose clients include the life sciences industry as well as plaintiffs in opioid litigation, for whom he has served as a paid expert witness; and is a past member of OptumRx’s National P&T Committee. Dr. Olfson declares no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed prescription drug claims for over 9.1 million U.S. adults over a 1-year period and found that 276,223 (3%) had used a schedule II stimulant, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, during that time. Of these 276,223 patients, 45% combined these agents with one or more additional CNS-active drugs and almost 25% were simultaneously using two or more additional CNS-active drugs.
Close to half of the stimulant users were taking an antidepressant, while close to one-third filled prescriptions for anxiolytic/sedative/hypnotic meditations, and one-fifth received opioid prescriptions.
The widespread, often off-label use of these stimulants in combination therapy with antidepressants, anxiolytics, opioids, and other psychoactive drugs, “reveals new patterns of utilization beyond the approved use of stimulants as monotherapy for ADHD, but because there are so few studies of these kinds of combination therapy, both the advantages and additional risks [of this type of prescribing] remain unknown,” study investigator Thomas J. Moore, AB, faculty associate in epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in BMJ Open.
‘Dangerous’ substances
Amphetamines and methylphenidate are CNS stimulants that have been in use for almost a century. Like opioids and barbiturates, they’re considered “dangerous” and classified as schedule II Controlled Substances because of their high potential for abuse.
Over many years, these stimulants have been used for multiple purposes, including nasal congestion, narcolepsy, appetite suppression, binge eating, depression, senile behavior, lethargy, and ADHD, the researchers note.
Observational studies suggest medical use of these agents has been increasing in the United States. The investigators conducted previous research that revealed a 79% increase from 2013 to 2018 in the number of adults who self-report their use. The current study, said Mr. Moore, explores how these stimulants are being used.
For the study, data was extracted from the MarketScan 2019 and 2020 Commercial Claims and Encounters Databases, focusing on 9.1 million adults aged 19-64 years who were continuously enrolled in an included commercial benefit plan from Oct. 1, 2019 to Dec. 31, 2020.
The primary outcome consisted of an outpatient prescription claim, service date, and days’ supply for the CNS-active drugs.
The researchers defined “combination-2” therapy as 60 or more days of combination treatment with a schedule II stimulant and at least one additional CNS-active drug. “Combination-3” therapy was defined as the addition of at least two additional CNS-active drugs.
The researchers used service date and days’ supply to examine the number of stimulant and other CNS-active drugs for each of the days of 2020.
CNS-active drug classes included antidepressants, anxiolytics/sedatives/hypnotics, antipsychotics, opioids, anticonvulsants, and other CNS-active drugs.
Prescribing cascade
Of the total number of adults enrolled, 3% (n = 276,223) were taking schedule II stimulants during 2020, with a median of 8 (interquartile range, 4-11) prescriptions. These drugs provided 227 (IQR, 110-322) treatment days of exposure.
Among those taking stimulants 45.5% combined the use of at least one additional CNS-active drug for a median of 213 (IQR, 126-301) treatment days; and 24.3% used at least two additional CNS-active drugs for a median of 182 (IQR, 108-276) days.
“Clinicians should beware of the prescribing cascade. Sometimes it begins with an antidepressant that causes too much sedation, so a stimulant gets added, which leads to insomnia, so alprazolam gets added to the mix,” Mr. Moore said.
He cautioned that this “leaves a patient with multiple drugs, all with discontinuation effects of different kinds and clashing effects.”
These new findings, the investigators note, “add new public health concerns to those raised by our previous study. ... this more-detailed profile reveals several new patterns.”
Most patients become “long-term users” once treatment has started, with 75% continuing for a 1-year period.
“This underscores the possible risks of nonmedical use and dependence that have warranted the classification of these drugs as having high potential for psychological or physical dependence and their prominent appearance in toxicology drug rankings of fatal overdose cases,” they write.
They note that the data “do not indicate which intervention may have come first – a stimulant added to compensate for excess sedation from the benzodiazepine, or the alprazolam added to calm excessive CNS stimulation and/or insomnia from the stimulants or other drugs.”
Several limitations cited by the authors include the fact that, although the population encompassed 9.1 million people, it “may not represent all commercially insured adults,” and it doesn’t include people who aren’t covered by commercial insurance.
Moreover, the MarketScan dataset included up to four diagnosis codes for each outpatient and emergency department encounter; therefore, it was not possible to directly link the diagnoses to specific prescription drug claims, and thus the diagnoses were not evaluated.
“Since many providers will not accept a drug claim for a schedule II stimulant without an on-label diagnosis of ADHD,” the authors suspect that “large numbers of this diagnosis were present.”
Complex prescribing regimens
Mark Olfson, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry, medicine, and law and professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said the report “highlights the pharmacological complexity of adults who are treated with stimulants.”
Dr. Olfson, who is a research psychiatrist at the New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, and was not involved with the study, observed there is “evidence to support stimulants as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant unipolar depression in older adults.”
However, he added, “this indication is unlikely to fully explain the high proportion of nonelderly, stimulant-treated adults who also receive antidepressants.”
These new findings “call for research to increase our understanding of the clinical contexts that motivate these complex prescribing regimens as well as their effectiveness and safety,” said Dr. Olfson.
The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Mr. Moore declares no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor G. Caleb Alexander, MD, is past chair and a current member of the Food and Drug Administration’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Advisory Committee; is a cofounding principal and equity holder in Monument Analytics, a health care consultancy whose clients include the life sciences industry as well as plaintiffs in opioid litigation, for whom he has served as a paid expert witness; and is a past member of OptumRx’s National P&T Committee. Dr. Olfson declares no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMJ OPEN
New tool accurately predicts suicide risk in serious mental illness
The 17-question Oxford Mental Illness and Suicide Tool (OxMIS) assessment is designed to predict 12-month suicide risk in people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and bipolar disorder based on risk factors such as familial traits, antisocial traits, and information about self-harm.
“We have demonstrated the clinical utility of OxMIS in two separate studies and countries. As with any clinical risk prediction tool, it will not improve outcomes unless coupled with effective interventions,” lead investigator Amir Sariaslan, PhD, a senior research fellow in psychiatric epidemiology at the University of Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
Twice validated
Dr. Sariaslan and his team originally developed and validated the OxMIS in a cohort of 75,000 people with SMI in Sweden. Recognizing the lack of externally validated prognostic models in the mental health field, the team wanted to validate the instrument in a new, population-based sample in Finland.
The investigators accessed information about patient diagnosis and treatment from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care, which contains de-identified information for all individuals between ages 15 and 65 years diagnosed with an SMI between Jan. 1, 1996, and Dec. 31, 2017.
They included 137,000 patients with somatic symptom disorder or bipolar disorder for a total of more than 5 million episodes of inpatient or outpatient treatment. Investigators linked the cohort to the Causes of Death Register to identify those who had died by suicide within 12 months of an index treatment episode, which investigators randomly selected for each person.
The investigators found that 1,475 individuals in the sample died by suicide within 1 year of their index episode (1.1%).
Each patient was assigned a clinical suicide risk score based on their clinical information, familial traits, prescription information, and comorbid conditions. Using OxMIS, the investigators found that the instrument accurately predicted suicide with an area under the curve of 0.70.
In other words, in 70% of the instances where the investigators randomly selected two people from the sample, one of whom died by suicide and the other of whom did not, the individual who died by suicide had a higher OxMIS risk score.
The investigators note the model overestimated the risk for patients who were at extremely high risk for suicide (those with a predicted suicide risk of > 5%). “In our complementary sensitivity analysis, we observed improved calibration in these patients when we assigned them a suicide risk prediction of no more than 5%,” they write.
Dr. Sariaslan said that the findings highlight the importance of safety planning interventions. “It is also essential to remember that OxMIS is not intended to replace clinical decision-making, but rather to support it,” he said.
As to whether the tool could be used in other populations, such as in the United States, Dr. Sariaslan said, “there is no good evidence that the contribution of risk factors to suicide in this population is different in the U.S. than in northern Europe, so there is no a priori reason to have to do multiple external validations before it can be used for research or clinical purposes.”
One size does not fit all
Commenting on the study, Ronald Kessler, PhD, McNeil Family Professor, department of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that he’d be “surprised” if OxMIS was adopted in the United States because there is already an existing tool that is “slightly more accurate,” which he helped develop.
“In addition, when we start thinking about uses for such scales, it becomes clear that different scales should be used for different segments of the population, depending on intervention options,” Dr. Kessler said.
“So, for example, a different scale would probably be optimal in deciding how to manage psychiatric inpatients in the transition back to the community after hospital discharge than [it would be], say, in deciding how to respond to suicidality among patients presenting at an emergency department. No one scale will fit for all the scenarios in which prediction is desired,” he added.
The study was funded by the Academy of Finland. Dr. Kessler receives funding from the National Institute of Mental Health, Department of Defense, and Veterans Administration to develop suicide prediction models. Dr. Sariaslan has no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 17-question Oxford Mental Illness and Suicide Tool (OxMIS) assessment is designed to predict 12-month suicide risk in people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and bipolar disorder based on risk factors such as familial traits, antisocial traits, and information about self-harm.
“We have demonstrated the clinical utility of OxMIS in two separate studies and countries. As with any clinical risk prediction tool, it will not improve outcomes unless coupled with effective interventions,” lead investigator Amir Sariaslan, PhD, a senior research fellow in psychiatric epidemiology at the University of Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
Twice validated
Dr. Sariaslan and his team originally developed and validated the OxMIS in a cohort of 75,000 people with SMI in Sweden. Recognizing the lack of externally validated prognostic models in the mental health field, the team wanted to validate the instrument in a new, population-based sample in Finland.
The investigators accessed information about patient diagnosis and treatment from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care, which contains de-identified information for all individuals between ages 15 and 65 years diagnosed with an SMI between Jan. 1, 1996, and Dec. 31, 2017.
They included 137,000 patients with somatic symptom disorder or bipolar disorder for a total of more than 5 million episodes of inpatient or outpatient treatment. Investigators linked the cohort to the Causes of Death Register to identify those who had died by suicide within 12 months of an index treatment episode, which investigators randomly selected for each person.
The investigators found that 1,475 individuals in the sample died by suicide within 1 year of their index episode (1.1%).
Each patient was assigned a clinical suicide risk score based on their clinical information, familial traits, prescription information, and comorbid conditions. Using OxMIS, the investigators found that the instrument accurately predicted suicide with an area under the curve of 0.70.
In other words, in 70% of the instances where the investigators randomly selected two people from the sample, one of whom died by suicide and the other of whom did not, the individual who died by suicide had a higher OxMIS risk score.
The investigators note the model overestimated the risk for patients who were at extremely high risk for suicide (those with a predicted suicide risk of > 5%). “In our complementary sensitivity analysis, we observed improved calibration in these patients when we assigned them a suicide risk prediction of no more than 5%,” they write.
Dr. Sariaslan said that the findings highlight the importance of safety planning interventions. “It is also essential to remember that OxMIS is not intended to replace clinical decision-making, but rather to support it,” he said.
As to whether the tool could be used in other populations, such as in the United States, Dr. Sariaslan said, “there is no good evidence that the contribution of risk factors to suicide in this population is different in the U.S. than in northern Europe, so there is no a priori reason to have to do multiple external validations before it can be used for research or clinical purposes.”
One size does not fit all
Commenting on the study, Ronald Kessler, PhD, McNeil Family Professor, department of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that he’d be “surprised” if OxMIS was adopted in the United States because there is already an existing tool that is “slightly more accurate,” which he helped develop.
“In addition, when we start thinking about uses for such scales, it becomes clear that different scales should be used for different segments of the population, depending on intervention options,” Dr. Kessler said.
“So, for example, a different scale would probably be optimal in deciding how to manage psychiatric inpatients in the transition back to the community after hospital discharge than [it would be], say, in deciding how to respond to suicidality among patients presenting at an emergency department. No one scale will fit for all the scenarios in which prediction is desired,” he added.
The study was funded by the Academy of Finland. Dr. Kessler receives funding from the National Institute of Mental Health, Department of Defense, and Veterans Administration to develop suicide prediction models. Dr. Sariaslan has no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 17-question Oxford Mental Illness and Suicide Tool (OxMIS) assessment is designed to predict 12-month suicide risk in people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and bipolar disorder based on risk factors such as familial traits, antisocial traits, and information about self-harm.
“We have demonstrated the clinical utility of OxMIS in two separate studies and countries. As with any clinical risk prediction tool, it will not improve outcomes unless coupled with effective interventions,” lead investigator Amir Sariaslan, PhD, a senior research fellow in psychiatric epidemiology at the University of Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
Twice validated
Dr. Sariaslan and his team originally developed and validated the OxMIS in a cohort of 75,000 people with SMI in Sweden. Recognizing the lack of externally validated prognostic models in the mental health field, the team wanted to validate the instrument in a new, population-based sample in Finland.
The investigators accessed information about patient diagnosis and treatment from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care, which contains de-identified information for all individuals between ages 15 and 65 years diagnosed with an SMI between Jan. 1, 1996, and Dec. 31, 2017.
They included 137,000 patients with somatic symptom disorder or bipolar disorder for a total of more than 5 million episodes of inpatient or outpatient treatment. Investigators linked the cohort to the Causes of Death Register to identify those who had died by suicide within 12 months of an index treatment episode, which investigators randomly selected for each person.
The investigators found that 1,475 individuals in the sample died by suicide within 1 year of their index episode (1.1%).
Each patient was assigned a clinical suicide risk score based on their clinical information, familial traits, prescription information, and comorbid conditions. Using OxMIS, the investigators found that the instrument accurately predicted suicide with an area under the curve of 0.70.
In other words, in 70% of the instances where the investigators randomly selected two people from the sample, one of whom died by suicide and the other of whom did not, the individual who died by suicide had a higher OxMIS risk score.
The investigators note the model overestimated the risk for patients who were at extremely high risk for suicide (those with a predicted suicide risk of > 5%). “In our complementary sensitivity analysis, we observed improved calibration in these patients when we assigned them a suicide risk prediction of no more than 5%,” they write.
Dr. Sariaslan said that the findings highlight the importance of safety planning interventions. “It is also essential to remember that OxMIS is not intended to replace clinical decision-making, but rather to support it,” he said.
As to whether the tool could be used in other populations, such as in the United States, Dr. Sariaslan said, “there is no good evidence that the contribution of risk factors to suicide in this population is different in the U.S. than in northern Europe, so there is no a priori reason to have to do multiple external validations before it can be used for research or clinical purposes.”
One size does not fit all
Commenting on the study, Ronald Kessler, PhD, McNeil Family Professor, department of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that he’d be “surprised” if OxMIS was adopted in the United States because there is already an existing tool that is “slightly more accurate,” which he helped develop.
“In addition, when we start thinking about uses for such scales, it becomes clear that different scales should be used for different segments of the population, depending on intervention options,” Dr. Kessler said.
“So, for example, a different scale would probably be optimal in deciding how to manage psychiatric inpatients in the transition back to the community after hospital discharge than [it would be], say, in deciding how to respond to suicidality among patients presenting at an emergency department. No one scale will fit for all the scenarios in which prediction is desired,” he added.
The study was funded by the Academy of Finland. Dr. Kessler receives funding from the National Institute of Mental Health, Department of Defense, and Veterans Administration to develop suicide prediction models. Dr. Sariaslan has no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM TRANSLATIONAL PSYCHIATRY
Erratic sleep, lack of activity tied to worsening schizophrenia symptoms
The findings also showed that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSDs) who lived in residential facilities experienced rigid routines, which correlated with a higher degree of negative symptoms.
The rigid routines were problematic for the patients living in residential settings, lead investigator Fabio Ferrarelli, MD, PhD, told this news organization. Dr. Ferrarelli is an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Engaging in different activities at different times in activities associated with motivation and social interaction – this helps to ameliorate difficult-to-treat negative symptoms,” he said.
The findings were published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
Need to increase activity levels
While there is no shortage of research on sleep disturbances among people with schizophrenia, research focusing specifically on rest-activity rhythm disturbances and their relationships to symptoms of schizophrenia has been limited by small sample sizes or the lack of a control group, the investigators note.
To address this research gap, the investigators recruited 230 patients with SSD from participating residential facilities and communities throughout Italy. The participants included 108 healthy control participants, 54 community-dwelling patients with SSD who were receiving outpatient services, and 68 patients with SSD who were living in residential facilities.
All participants wore an actigraph for 7 consecutive days so that investigators could monitor sleep-wake patterns.
Compared with healthy control participants, both SSD groups had more total sleep time and spent more time resting or being passive (P < .001). In contrast, healthy control participants were much more active.
Part of the explanation for this may be that most of the control participants had jobs or attended school. In addition, the investigators note that many medications used to treat SSD can be highly sedating, causing some patients to sleep up to 15 hours per day.
Among residential participants with SSD, there was a higher level of inter-daily stability and higher daily rest-activity-rest fragmentation than occurred among healthy control participants or community-dwelling patients with SSD (P < .001). There was also a higher level of negative symptoms among residential participants with SSD than among the community-dwelling group with SSD.
When the findings were taken together, Dr. Ferrarelli and his team interpreted them to mean that inter-daily stability could reflect premature aging or neurodegenerative processes in patients with more severe forms of schizophrenia.
Another explanation could be that the rigid routine of the residential facility was making negative symptoms worse, Dr. Ferrarelli said. It is important to add variety into the mix – getting people to engage in different activities at different times of day would likely help residential SSD patients overcome negative symptoms of the disorder.
Although participants were recruited in Italy, Dr. Ferrarelli said he believes the findings are generalizable.
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting on the findings, Matcheri Keshavan, MD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School in Boston, said the results are consistent with “well-known clinical observations that SSD patients tend to spend more time in bed and have more dysregulated sleep.
“Negative symptoms are also common, especially in residential patients. However, it is difficult to determine causality, as we do not know whether excessive sleepiness and decreased physical activity cause negative symptoms, or vice versa, or whether this is a bidirectional relationship,” Dr. Keshavan said.
He emphasized that physical exercise is known to increase sleep quality for people with mental illness and may also improve negative symptoms. “A useful approach in clinical practice is to increase activity levels, especially physical activities like walking and gardening.”
Dr. Keshavan said he would like to see future research that focuses on whether an intervention such as aerobic exercise would improve sleep quality as well as negative symptoms.
He also said that future research should ideally examine the characteristics of sleep alterations in schizophrenia.
“For example, while sleep duration is increased in schizophrenia, studies suggest that time spent in deep sleep is reduced; sleep spindles, which are important for consolidating memory during sleep, are also reduced. Correcting these deficits may improve negative symptoms and cognitive deficits,” he added.
The study was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health and the National Institute of Mental Health. There were no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings also showed that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSDs) who lived in residential facilities experienced rigid routines, which correlated with a higher degree of negative symptoms.
The rigid routines were problematic for the patients living in residential settings, lead investigator Fabio Ferrarelli, MD, PhD, told this news organization. Dr. Ferrarelli is an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Engaging in different activities at different times in activities associated with motivation and social interaction – this helps to ameliorate difficult-to-treat negative symptoms,” he said.
The findings were published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
Need to increase activity levels
While there is no shortage of research on sleep disturbances among people with schizophrenia, research focusing specifically on rest-activity rhythm disturbances and their relationships to symptoms of schizophrenia has been limited by small sample sizes or the lack of a control group, the investigators note.
To address this research gap, the investigators recruited 230 patients with SSD from participating residential facilities and communities throughout Italy. The participants included 108 healthy control participants, 54 community-dwelling patients with SSD who were receiving outpatient services, and 68 patients with SSD who were living in residential facilities.
All participants wore an actigraph for 7 consecutive days so that investigators could monitor sleep-wake patterns.
Compared with healthy control participants, both SSD groups had more total sleep time and spent more time resting or being passive (P < .001). In contrast, healthy control participants were much more active.
Part of the explanation for this may be that most of the control participants had jobs or attended school. In addition, the investigators note that many medications used to treat SSD can be highly sedating, causing some patients to sleep up to 15 hours per day.
Among residential participants with SSD, there was a higher level of inter-daily stability and higher daily rest-activity-rest fragmentation than occurred among healthy control participants or community-dwelling patients with SSD (P < .001). There was also a higher level of negative symptoms among residential participants with SSD than among the community-dwelling group with SSD.
When the findings were taken together, Dr. Ferrarelli and his team interpreted them to mean that inter-daily stability could reflect premature aging or neurodegenerative processes in patients with more severe forms of schizophrenia.
Another explanation could be that the rigid routine of the residential facility was making negative symptoms worse, Dr. Ferrarelli said. It is important to add variety into the mix – getting people to engage in different activities at different times of day would likely help residential SSD patients overcome negative symptoms of the disorder.
Although participants were recruited in Italy, Dr. Ferrarelli said he believes the findings are generalizable.
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting on the findings, Matcheri Keshavan, MD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School in Boston, said the results are consistent with “well-known clinical observations that SSD patients tend to spend more time in bed and have more dysregulated sleep.
“Negative symptoms are also common, especially in residential patients. However, it is difficult to determine causality, as we do not know whether excessive sleepiness and decreased physical activity cause negative symptoms, or vice versa, or whether this is a bidirectional relationship,” Dr. Keshavan said.
He emphasized that physical exercise is known to increase sleep quality for people with mental illness and may also improve negative symptoms. “A useful approach in clinical practice is to increase activity levels, especially physical activities like walking and gardening.”
Dr. Keshavan said he would like to see future research that focuses on whether an intervention such as aerobic exercise would improve sleep quality as well as negative symptoms.
He also said that future research should ideally examine the characteristics of sleep alterations in schizophrenia.
“For example, while sleep duration is increased in schizophrenia, studies suggest that time spent in deep sleep is reduced; sleep spindles, which are important for consolidating memory during sleep, are also reduced. Correcting these deficits may improve negative symptoms and cognitive deficits,” he added.
The study was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health and the National Institute of Mental Health. There were no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings also showed that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSDs) who lived in residential facilities experienced rigid routines, which correlated with a higher degree of negative symptoms.
The rigid routines were problematic for the patients living in residential settings, lead investigator Fabio Ferrarelli, MD, PhD, told this news organization. Dr. Ferrarelli is an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Engaging in different activities at different times in activities associated with motivation and social interaction – this helps to ameliorate difficult-to-treat negative symptoms,” he said.
The findings were published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
Need to increase activity levels
While there is no shortage of research on sleep disturbances among people with schizophrenia, research focusing specifically on rest-activity rhythm disturbances and their relationships to symptoms of schizophrenia has been limited by small sample sizes or the lack of a control group, the investigators note.
To address this research gap, the investigators recruited 230 patients with SSD from participating residential facilities and communities throughout Italy. The participants included 108 healthy control participants, 54 community-dwelling patients with SSD who were receiving outpatient services, and 68 patients with SSD who were living in residential facilities.
All participants wore an actigraph for 7 consecutive days so that investigators could monitor sleep-wake patterns.
Compared with healthy control participants, both SSD groups had more total sleep time and spent more time resting or being passive (P < .001). In contrast, healthy control participants were much more active.
Part of the explanation for this may be that most of the control participants had jobs or attended school. In addition, the investigators note that many medications used to treat SSD can be highly sedating, causing some patients to sleep up to 15 hours per day.
Among residential participants with SSD, there was a higher level of inter-daily stability and higher daily rest-activity-rest fragmentation than occurred among healthy control participants or community-dwelling patients with SSD (P < .001). There was also a higher level of negative symptoms among residential participants with SSD than among the community-dwelling group with SSD.
When the findings were taken together, Dr. Ferrarelli and his team interpreted them to mean that inter-daily stability could reflect premature aging or neurodegenerative processes in patients with more severe forms of schizophrenia.
Another explanation could be that the rigid routine of the residential facility was making negative symptoms worse, Dr. Ferrarelli said. It is important to add variety into the mix – getting people to engage in different activities at different times of day would likely help residential SSD patients overcome negative symptoms of the disorder.
Although participants were recruited in Italy, Dr. Ferrarelli said he believes the findings are generalizable.
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting on the findings, Matcheri Keshavan, MD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School in Boston, said the results are consistent with “well-known clinical observations that SSD patients tend to spend more time in bed and have more dysregulated sleep.
“Negative symptoms are also common, especially in residential patients. However, it is difficult to determine causality, as we do not know whether excessive sleepiness and decreased physical activity cause negative symptoms, or vice versa, or whether this is a bidirectional relationship,” Dr. Keshavan said.
He emphasized that physical exercise is known to increase sleep quality for people with mental illness and may also improve negative symptoms. “A useful approach in clinical practice is to increase activity levels, especially physical activities like walking and gardening.”
Dr. Keshavan said he would like to see future research that focuses on whether an intervention such as aerobic exercise would improve sleep quality as well as negative symptoms.
He also said that future research should ideally examine the characteristics of sleep alterations in schizophrenia.
“For example, while sleep duration is increased in schizophrenia, studies suggest that time spent in deep sleep is reduced; sleep spindles, which are important for consolidating memory during sleep, are also reduced. Correcting these deficits may improve negative symptoms and cognitive deficits,” he added.
The study was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health and the National Institute of Mental Health. There were no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MOLECULAR PSYCHIATRY
Clozapine may curb schizophrenia’s ‘most dreaded outcome’
Investigators reviewed over 53,000 autopsy records, including over 600 from individuals whose autopsies revealed the presence of the antipsychotics clozapine or olanzapine, and found that those who took clozapine were significantly less likely to have died by suicide, compared with their counterparts who were taking olanzapine.
“Clozapine is an important and effective antisuicide medicine and should be strongly considered for treatment-resistant psychotic disorders, especially when the patient may be at risk for suicide,” study investigator Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Underutilized medication
Clozapine is the only medication indicated for treatment-resistant schizophrenia and is considered “the most efficacious antipsychotic,” the investigators note. Unfortunately, it has “long been underutilized” for several reasons, including prescriber hesitancy and concerns about side effects.
The authors note that its mechanism of action and the basis for superior efficacy are “still poorly understood” but “may extend beyond neurotransmitter receptor binding.”
Importantly, it may have a beneficial impact on domains other than positive symptoms of schizophrenia, including suicidality. Several studies have shown that it’s beneficial in this regard, but it is “unclear whether the unique antisuicidal properties of clozapine are related to better symptom control ... or to the closer monitoring and follow-up mandated for clozapine use,” they note.
A previous trial, the International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT), demonstrated that clozapine is associated with a greater reduction in suicidality, and the findings “led to an FDA indication for clozapine in reducing the risk of recurrent suicidal behavior.”
However, the authors note, “in the severely ill populations in these studies, it is difficult to be certain about patients’ adherence to prescribed clozapine.”
“Other studies, such as InterSePT, have shown some evidence of clozapine working to reduce suicide-related outcomes, such as attempts or suicidal ideation, but few have been sufficiently powered to measure an effect on actual suicide deaths,” said Dr. Nestadt.
“As a suicidologist, I feel it is very important that we understand what treatments and interventions can actually prevent suicide deaths, as most suicides are not associated with past attempts or ideation, with suicide decedents usually looking very different from characteristic nonfatal attempters, from a clinical or epidemiological standpoint,” he added.
“If we could show that clozapine actually decreases the likelihood of suicide deaths in our patients, it gives us more reason to choose it over less effective neuroleptics in our clinics – especially for patients at high risk of suicide,” he said.
For the study, the researchers reviewed 19-year state-wide autopsy records of Maryland’s Office of the Chief Medical Examiner, which “performs uniquely comprehensive death investigations.” Data included in these investigations are full toxicologic panels with postmortem blood levels of antipsychotics.
The researchers compared decedents who tested positive for clozapine and decedents who tested positive for olanzapine. They evaluated demographics, clinical features, and manner-of-death outcomes.
‘Untapped resource’
Of 53,133 decedents, olanzapine or clozapine was detected in the blood of 621 persons (n = 571 and n = 50, respectively).
There were no significant differences in age, sex, race, or urban residence between the decedents who were treated with olanzapine and those who received clozapine.
The odds of a death by suicide in those treated with clozapine were less than half of the odds among decedents who had been treated with olanzapine (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84; P = .011).
In sensitivity analyses, the investigators reanalyzed the data to compare clozapine with other antipsychotics, including chlorpromazine, thioridazine, quetiapine, and olanzapine, and the results were similar. The odds of suicide (compared with accident) in those taking clozapine were much lower than in those taking any other tested antipsychotics individually or in combination (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.73; P = .002).
Dr. Nestadt outlined several hypotheses regarding the mechanism of clozapine’s antisuicidal properties.
“Most theories stem from the differences in its receptor affinity, compared [with] the other neuroleptics,” he said. “In addition to the more typical dopaminergic blockade seen in neuroleptics, clozapine enhances serotonin release and greatly increases peripheral norepinephrine.”
This has been shown to “grant clozapine a greater antidepressant effect than other neuroleptics while also potentially decreasing aggression and impulsivity, which are both strongly associated with suicide risk,” he said.
Clozapine may also “work to reduce the inflammation-triggered activation of the kynurenine pathway, which otherwise contributes to serotonin depletion,” he added.
He noted that some studies have shown that as many as 1 in 10 patients with schizophrenia die by suicide, “so addressing this risk is paramount,” and that clozapine can play an important role in this.
The authors note that the findings “also highlight the utility of state-wide autopsy records, an untapped resource for investigating the potential protective effect of psychiatric medications on suicide at a population level.
“Importantly, we can be certain that this was not an issue of nonadherence to treatment in either group, which is a common issue in the use of these drugs because, instead of prescription records or self-report, we used actual measurements of drug presence in decedents’ blood at death,” said Dr. Nestadt.
‘Strongly suggestive’ data
Commenting on the study, Maria Oquendo, MD, PhD, Ruth Meltzer Professor and chair of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said most work on antisuicidal psychopharmacologic approaches “focuses on suicidal ideation or suicide attempts, due to the rarity of suicide death, even in high-risk populations.”
“Showing that clozapine may decrease risk for the most dreaded outcome of schizophrenia – suicide – is critically important,” said Dr. Oquendo, past president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Nevertheless, some questions remain, said Dr. Oquendo, who was not involved with the study. “Comparison of suicides to only accidental deaths has limitations. Many individuals who die due to accidents, like many suicides, are not similar to the general population,” she added.
However, she acknowledged, the data are strongly suggestive that clozapine protects against suicide.
“While not definitive, ideally these findings will stimulate changes in prescribing practices which may be lifesaving both literally – in terms of preventing suicides – and figuratively, given the drug’s effect on symptoms that impact quality of life and functioning,” said Dr. Oquendo.
The study received no funding or support. Dr. Nestadt is supported by the American Foundation for Suicide prevention and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Oquendo receives royalties from the Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene for the commercial use of the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale. She serves as an advisor to Alkermes, Mind Medicine, Sage Therapeutics, St. George’s University, and Fundacion Jimenez Diaz. Her family owns stock in Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators reviewed over 53,000 autopsy records, including over 600 from individuals whose autopsies revealed the presence of the antipsychotics clozapine or olanzapine, and found that those who took clozapine were significantly less likely to have died by suicide, compared with their counterparts who were taking olanzapine.
“Clozapine is an important and effective antisuicide medicine and should be strongly considered for treatment-resistant psychotic disorders, especially when the patient may be at risk for suicide,” study investigator Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Underutilized medication
Clozapine is the only medication indicated for treatment-resistant schizophrenia and is considered “the most efficacious antipsychotic,” the investigators note. Unfortunately, it has “long been underutilized” for several reasons, including prescriber hesitancy and concerns about side effects.
The authors note that its mechanism of action and the basis for superior efficacy are “still poorly understood” but “may extend beyond neurotransmitter receptor binding.”
Importantly, it may have a beneficial impact on domains other than positive symptoms of schizophrenia, including suicidality. Several studies have shown that it’s beneficial in this regard, but it is “unclear whether the unique antisuicidal properties of clozapine are related to better symptom control ... or to the closer monitoring and follow-up mandated for clozapine use,” they note.
A previous trial, the International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT), demonstrated that clozapine is associated with a greater reduction in suicidality, and the findings “led to an FDA indication for clozapine in reducing the risk of recurrent suicidal behavior.”
However, the authors note, “in the severely ill populations in these studies, it is difficult to be certain about patients’ adherence to prescribed clozapine.”
“Other studies, such as InterSePT, have shown some evidence of clozapine working to reduce suicide-related outcomes, such as attempts or suicidal ideation, but few have been sufficiently powered to measure an effect on actual suicide deaths,” said Dr. Nestadt.
“As a suicidologist, I feel it is very important that we understand what treatments and interventions can actually prevent suicide deaths, as most suicides are not associated with past attempts or ideation, with suicide decedents usually looking very different from characteristic nonfatal attempters, from a clinical or epidemiological standpoint,” he added.
“If we could show that clozapine actually decreases the likelihood of suicide deaths in our patients, it gives us more reason to choose it over less effective neuroleptics in our clinics – especially for patients at high risk of suicide,” he said.
For the study, the researchers reviewed 19-year state-wide autopsy records of Maryland’s Office of the Chief Medical Examiner, which “performs uniquely comprehensive death investigations.” Data included in these investigations are full toxicologic panels with postmortem blood levels of antipsychotics.
The researchers compared decedents who tested positive for clozapine and decedents who tested positive for olanzapine. They evaluated demographics, clinical features, and manner-of-death outcomes.
‘Untapped resource’
Of 53,133 decedents, olanzapine or clozapine was detected in the blood of 621 persons (n = 571 and n = 50, respectively).
There were no significant differences in age, sex, race, or urban residence between the decedents who were treated with olanzapine and those who received clozapine.
The odds of a death by suicide in those treated with clozapine were less than half of the odds among decedents who had been treated with olanzapine (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84; P = .011).
In sensitivity analyses, the investigators reanalyzed the data to compare clozapine with other antipsychotics, including chlorpromazine, thioridazine, quetiapine, and olanzapine, and the results were similar. The odds of suicide (compared with accident) in those taking clozapine were much lower than in those taking any other tested antipsychotics individually or in combination (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.73; P = .002).
Dr. Nestadt outlined several hypotheses regarding the mechanism of clozapine’s antisuicidal properties.
“Most theories stem from the differences in its receptor affinity, compared [with] the other neuroleptics,” he said. “In addition to the more typical dopaminergic blockade seen in neuroleptics, clozapine enhances serotonin release and greatly increases peripheral norepinephrine.”
This has been shown to “grant clozapine a greater antidepressant effect than other neuroleptics while also potentially decreasing aggression and impulsivity, which are both strongly associated with suicide risk,” he said.
Clozapine may also “work to reduce the inflammation-triggered activation of the kynurenine pathway, which otherwise contributes to serotonin depletion,” he added.
He noted that some studies have shown that as many as 1 in 10 patients with schizophrenia die by suicide, “so addressing this risk is paramount,” and that clozapine can play an important role in this.
The authors note that the findings “also highlight the utility of state-wide autopsy records, an untapped resource for investigating the potential protective effect of psychiatric medications on suicide at a population level.
“Importantly, we can be certain that this was not an issue of nonadherence to treatment in either group, which is a common issue in the use of these drugs because, instead of prescription records or self-report, we used actual measurements of drug presence in decedents’ blood at death,” said Dr. Nestadt.
‘Strongly suggestive’ data
Commenting on the study, Maria Oquendo, MD, PhD, Ruth Meltzer Professor and chair of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said most work on antisuicidal psychopharmacologic approaches “focuses on suicidal ideation or suicide attempts, due to the rarity of suicide death, even in high-risk populations.”
“Showing that clozapine may decrease risk for the most dreaded outcome of schizophrenia – suicide – is critically important,” said Dr. Oquendo, past president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Nevertheless, some questions remain, said Dr. Oquendo, who was not involved with the study. “Comparison of suicides to only accidental deaths has limitations. Many individuals who die due to accidents, like many suicides, are not similar to the general population,” she added.
However, she acknowledged, the data are strongly suggestive that clozapine protects against suicide.
“While not definitive, ideally these findings will stimulate changes in prescribing practices which may be lifesaving both literally – in terms of preventing suicides – and figuratively, given the drug’s effect on symptoms that impact quality of life and functioning,” said Dr. Oquendo.
The study received no funding or support. Dr. Nestadt is supported by the American Foundation for Suicide prevention and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Oquendo receives royalties from the Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene for the commercial use of the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale. She serves as an advisor to Alkermes, Mind Medicine, Sage Therapeutics, St. George’s University, and Fundacion Jimenez Diaz. Her family owns stock in Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators reviewed over 53,000 autopsy records, including over 600 from individuals whose autopsies revealed the presence of the antipsychotics clozapine or olanzapine, and found that those who took clozapine were significantly less likely to have died by suicide, compared with their counterparts who were taking olanzapine.
“Clozapine is an important and effective antisuicide medicine and should be strongly considered for treatment-resistant psychotic disorders, especially when the patient may be at risk for suicide,” study investigator Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Underutilized medication
Clozapine is the only medication indicated for treatment-resistant schizophrenia and is considered “the most efficacious antipsychotic,” the investigators note. Unfortunately, it has “long been underutilized” for several reasons, including prescriber hesitancy and concerns about side effects.
The authors note that its mechanism of action and the basis for superior efficacy are “still poorly understood” but “may extend beyond neurotransmitter receptor binding.”
Importantly, it may have a beneficial impact on domains other than positive symptoms of schizophrenia, including suicidality. Several studies have shown that it’s beneficial in this regard, but it is “unclear whether the unique antisuicidal properties of clozapine are related to better symptom control ... or to the closer monitoring and follow-up mandated for clozapine use,” they note.
A previous trial, the International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT), demonstrated that clozapine is associated with a greater reduction in suicidality, and the findings “led to an FDA indication for clozapine in reducing the risk of recurrent suicidal behavior.”
However, the authors note, “in the severely ill populations in these studies, it is difficult to be certain about patients’ adherence to prescribed clozapine.”
“Other studies, such as InterSePT, have shown some evidence of clozapine working to reduce suicide-related outcomes, such as attempts or suicidal ideation, but few have been sufficiently powered to measure an effect on actual suicide deaths,” said Dr. Nestadt.
“As a suicidologist, I feel it is very important that we understand what treatments and interventions can actually prevent suicide deaths, as most suicides are not associated with past attempts or ideation, with suicide decedents usually looking very different from characteristic nonfatal attempters, from a clinical or epidemiological standpoint,” he added.
“If we could show that clozapine actually decreases the likelihood of suicide deaths in our patients, it gives us more reason to choose it over less effective neuroleptics in our clinics – especially for patients at high risk of suicide,” he said.
For the study, the researchers reviewed 19-year state-wide autopsy records of Maryland’s Office of the Chief Medical Examiner, which “performs uniquely comprehensive death investigations.” Data included in these investigations are full toxicologic panels with postmortem blood levels of antipsychotics.
The researchers compared decedents who tested positive for clozapine and decedents who tested positive for olanzapine. They evaluated demographics, clinical features, and manner-of-death outcomes.
‘Untapped resource’
Of 53,133 decedents, olanzapine or clozapine was detected in the blood of 621 persons (n = 571 and n = 50, respectively).
There were no significant differences in age, sex, race, or urban residence between the decedents who were treated with olanzapine and those who received clozapine.
The odds of a death by suicide in those treated with clozapine were less than half of the odds among decedents who had been treated with olanzapine (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84; P = .011).
In sensitivity analyses, the investigators reanalyzed the data to compare clozapine with other antipsychotics, including chlorpromazine, thioridazine, quetiapine, and olanzapine, and the results were similar. The odds of suicide (compared with accident) in those taking clozapine were much lower than in those taking any other tested antipsychotics individually or in combination (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.73; P = .002).
Dr. Nestadt outlined several hypotheses regarding the mechanism of clozapine’s antisuicidal properties.
“Most theories stem from the differences in its receptor affinity, compared [with] the other neuroleptics,” he said. “In addition to the more typical dopaminergic blockade seen in neuroleptics, clozapine enhances serotonin release and greatly increases peripheral norepinephrine.”
This has been shown to “grant clozapine a greater antidepressant effect than other neuroleptics while also potentially decreasing aggression and impulsivity, which are both strongly associated with suicide risk,” he said.
Clozapine may also “work to reduce the inflammation-triggered activation of the kynurenine pathway, which otherwise contributes to serotonin depletion,” he added.
He noted that some studies have shown that as many as 1 in 10 patients with schizophrenia die by suicide, “so addressing this risk is paramount,” and that clozapine can play an important role in this.
The authors note that the findings “also highlight the utility of state-wide autopsy records, an untapped resource for investigating the potential protective effect of psychiatric medications on suicide at a population level.
“Importantly, we can be certain that this was not an issue of nonadherence to treatment in either group, which is a common issue in the use of these drugs because, instead of prescription records or self-report, we used actual measurements of drug presence in decedents’ blood at death,” said Dr. Nestadt.
‘Strongly suggestive’ data
Commenting on the study, Maria Oquendo, MD, PhD, Ruth Meltzer Professor and chair of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said most work on antisuicidal psychopharmacologic approaches “focuses on suicidal ideation or suicide attempts, due to the rarity of suicide death, even in high-risk populations.”
“Showing that clozapine may decrease risk for the most dreaded outcome of schizophrenia – suicide – is critically important,” said Dr. Oquendo, past president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Nevertheless, some questions remain, said Dr. Oquendo, who was not involved with the study. “Comparison of suicides to only accidental deaths has limitations. Many individuals who die due to accidents, like many suicides, are not similar to the general population,” she added.
However, she acknowledged, the data are strongly suggestive that clozapine protects against suicide.
“While not definitive, ideally these findings will stimulate changes in prescribing practices which may be lifesaving both literally – in terms of preventing suicides – and figuratively, given the drug’s effect on symptoms that impact quality of life and functioning,” said Dr. Oquendo.
The study received no funding or support. Dr. Nestadt is supported by the American Foundation for Suicide prevention and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Oquendo receives royalties from the Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene for the commercial use of the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale. She serves as an advisor to Alkermes, Mind Medicine, Sage Therapeutics, St. George’s University, and Fundacion Jimenez Diaz. Her family owns stock in Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
New schizophrenia genes identified
The genes were identified through a meta-analysis comparing gene sequences of 35,828 people with schizophrenia to 107,877 people without the condition.
The study builds on a report published last year that identified 10 genes with rare variants that are directly tied to schizophrenia risk. But that study, like most prior genetic analyses on psychiatric illnesses, was done on the DNA from people of European ancestry.
About 40% of the genetic samples included in this new work came from people of non-European ancestry, which researchers say makes it the most ethnically diverse schizophrenia genetics study to date.
Based on the findings, researchers concluded that the schizophrenia risk conferred by the rare genetic variants found on the new genes they discovered and on those previously identified is conserved across ethnicities.
The new genes, SRRM2 and AKAP11, contain rare protein-truncating variants (PTVs) that investigators say could be the cause of schizophrenia in some patients. The results could have significant implications for drug development.
“It’s not curing the illness, but it is taking us a step closer so that we’re able to say that this may be the cause of the illness in a particular patient,” senior investigator Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, genetics and genomic sciences, neuroscience, and neurosurgery, at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in Nature Genetics.
Schizophrenia’s genetic architecture
Prior studies suggest the genetic architecture of schizophrenia may be influenced by common single-nucleotide polymorphisms, copy number variants and rare PTVs.
Investigators note that rare PTVs are important because they can link disease risk directly to individual genes. But identifying the PTVs and the genes that harbor them requires large patient cohorts, far bigger than any single institution can provide.
Dr. Charney and other researchers are part of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, a collaboration of researchers from hundreds of institutions around the world established in 2007 to create large cohorts for genetic studies of psychiatric disease.
For this study, investigators sequenced a new cohort of 11,580 schizophrenia cases and 10,555 controls of diverse ancestries. The analysis showed that the findings previously established in predominantly European cohorts extended to non-European populations.
They then conducted a meta-analysis of the new cohort combined with datasets from earlier studies, creating a pooled sample of 35,828 cases and 107,877 controls.
This meta-analysis revealed two new genes linked to schizophrenia, SRRM2 and AKAP11. The third gene flagged in the study, PCLO, was previously implicated in schizophrenia but is now identified as having a shared risk for schizophrenia and autism.
The rare PVTs on the 12 genes identified so far through this type of study are probably only involved in a small fraction of schizophrenia cases, Dr. Charney acknowledged. However, the discovery could lead to new treatments that could benefit all patients with the disease, he added.
“There are multiple pathways to psychosis and there’s also multiple pathways to treat psychosis,” Dr. Charney said. “There’s reason to believe if you can find a mechanism by which a human being could develop a psychosis, then reversing that mechanism could help a lot of people who have psychosis for another reason.”
Importance of diverse cohorts
Commenting on the findings, Jennifer Gladys Mulle, MHS, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School at Rutgers University, Piscataway, N.J., noted that while genetic discoveries have led to new therapies in other medical conditions, that has not been the case with schizophrenia.
“In other disorders, having genetic findings have really opened a window into the molecular mechanisms, which has allowed us to develop pharmaceuticals and understand the disease process better,” said Dr. Mulle, who was not part of this study. “But because we haven’t had that in schizophrenia, it’s really held us back. Having genetic variants associated with schizophrenia may really help us understand the mechanism.”
The inclusion of diverse populations is also a key contribution of this study, Dr. Mulle added.
“So far a lot of the work we’ve done in genetics has been on people of European ancestry,” Dr. Mulle said. “The fact that they have found results that are generalizable across multiple ethnicities really suggests that if we develop pharmaceutical agents based on these findings, it will help many people.”
More attention has been paid recently to a growing problem in the study of genetics of psychiatric disorders: More than 95% of participants in genome-wide association studies that seek to identify gene variants linked to disease are of European ancestry.
Dr. Charney and his colleagues had that in mind when they designed the study.
“We can’t get to a place where genetics is clinically useful if we don’t know the extent to which a particular observation that’s found in one population is also true for other populations,” Dr. Charney said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Charney and Dr. Mulle report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The genes were identified through a meta-analysis comparing gene sequences of 35,828 people with schizophrenia to 107,877 people without the condition.
The study builds on a report published last year that identified 10 genes with rare variants that are directly tied to schizophrenia risk. But that study, like most prior genetic analyses on psychiatric illnesses, was done on the DNA from people of European ancestry.
About 40% of the genetic samples included in this new work came from people of non-European ancestry, which researchers say makes it the most ethnically diverse schizophrenia genetics study to date.
Based on the findings, researchers concluded that the schizophrenia risk conferred by the rare genetic variants found on the new genes they discovered and on those previously identified is conserved across ethnicities.
The new genes, SRRM2 and AKAP11, contain rare protein-truncating variants (PTVs) that investigators say could be the cause of schizophrenia in some patients. The results could have significant implications for drug development.
“It’s not curing the illness, but it is taking us a step closer so that we’re able to say that this may be the cause of the illness in a particular patient,” senior investigator Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, genetics and genomic sciences, neuroscience, and neurosurgery, at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in Nature Genetics.
Schizophrenia’s genetic architecture
Prior studies suggest the genetic architecture of schizophrenia may be influenced by common single-nucleotide polymorphisms, copy number variants and rare PTVs.
Investigators note that rare PTVs are important because they can link disease risk directly to individual genes. But identifying the PTVs and the genes that harbor them requires large patient cohorts, far bigger than any single institution can provide.
Dr. Charney and other researchers are part of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, a collaboration of researchers from hundreds of institutions around the world established in 2007 to create large cohorts for genetic studies of psychiatric disease.
For this study, investigators sequenced a new cohort of 11,580 schizophrenia cases and 10,555 controls of diverse ancestries. The analysis showed that the findings previously established in predominantly European cohorts extended to non-European populations.
They then conducted a meta-analysis of the new cohort combined with datasets from earlier studies, creating a pooled sample of 35,828 cases and 107,877 controls.
This meta-analysis revealed two new genes linked to schizophrenia, SRRM2 and AKAP11. The third gene flagged in the study, PCLO, was previously implicated in schizophrenia but is now identified as having a shared risk for schizophrenia and autism.
The rare PVTs on the 12 genes identified so far through this type of study are probably only involved in a small fraction of schizophrenia cases, Dr. Charney acknowledged. However, the discovery could lead to new treatments that could benefit all patients with the disease, he added.
“There are multiple pathways to psychosis and there’s also multiple pathways to treat psychosis,” Dr. Charney said. “There’s reason to believe if you can find a mechanism by which a human being could develop a psychosis, then reversing that mechanism could help a lot of people who have psychosis for another reason.”
Importance of diverse cohorts
Commenting on the findings, Jennifer Gladys Mulle, MHS, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School at Rutgers University, Piscataway, N.J., noted that while genetic discoveries have led to new therapies in other medical conditions, that has not been the case with schizophrenia.
“In other disorders, having genetic findings have really opened a window into the molecular mechanisms, which has allowed us to develop pharmaceuticals and understand the disease process better,” said Dr. Mulle, who was not part of this study. “But because we haven’t had that in schizophrenia, it’s really held us back. Having genetic variants associated with schizophrenia may really help us understand the mechanism.”
The inclusion of diverse populations is also a key contribution of this study, Dr. Mulle added.
“So far a lot of the work we’ve done in genetics has been on people of European ancestry,” Dr. Mulle said. “The fact that they have found results that are generalizable across multiple ethnicities really suggests that if we develop pharmaceutical agents based on these findings, it will help many people.”
More attention has been paid recently to a growing problem in the study of genetics of psychiatric disorders: More than 95% of participants in genome-wide association studies that seek to identify gene variants linked to disease are of European ancestry.
Dr. Charney and his colleagues had that in mind when they designed the study.
“We can’t get to a place where genetics is clinically useful if we don’t know the extent to which a particular observation that’s found in one population is also true for other populations,” Dr. Charney said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Charney and Dr. Mulle report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The genes were identified through a meta-analysis comparing gene sequences of 35,828 people with schizophrenia to 107,877 people without the condition.
The study builds on a report published last year that identified 10 genes with rare variants that are directly tied to schizophrenia risk. But that study, like most prior genetic analyses on psychiatric illnesses, was done on the DNA from people of European ancestry.
About 40% of the genetic samples included in this new work came from people of non-European ancestry, which researchers say makes it the most ethnically diverse schizophrenia genetics study to date.
Based on the findings, researchers concluded that the schizophrenia risk conferred by the rare genetic variants found on the new genes they discovered and on those previously identified is conserved across ethnicities.
The new genes, SRRM2 and AKAP11, contain rare protein-truncating variants (PTVs) that investigators say could be the cause of schizophrenia in some patients. The results could have significant implications for drug development.
“It’s not curing the illness, but it is taking us a step closer so that we’re able to say that this may be the cause of the illness in a particular patient,” senior investigator Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, genetics and genomic sciences, neuroscience, and neurosurgery, at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in Nature Genetics.
Schizophrenia’s genetic architecture
Prior studies suggest the genetic architecture of schizophrenia may be influenced by common single-nucleotide polymorphisms, copy number variants and rare PTVs.
Investigators note that rare PTVs are important because they can link disease risk directly to individual genes. But identifying the PTVs and the genes that harbor them requires large patient cohorts, far bigger than any single institution can provide.
Dr. Charney and other researchers are part of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, a collaboration of researchers from hundreds of institutions around the world established in 2007 to create large cohorts for genetic studies of psychiatric disease.
For this study, investigators sequenced a new cohort of 11,580 schizophrenia cases and 10,555 controls of diverse ancestries. The analysis showed that the findings previously established in predominantly European cohorts extended to non-European populations.
They then conducted a meta-analysis of the new cohort combined with datasets from earlier studies, creating a pooled sample of 35,828 cases and 107,877 controls.
This meta-analysis revealed two new genes linked to schizophrenia, SRRM2 and AKAP11. The third gene flagged in the study, PCLO, was previously implicated in schizophrenia but is now identified as having a shared risk for schizophrenia and autism.
The rare PVTs on the 12 genes identified so far through this type of study are probably only involved in a small fraction of schizophrenia cases, Dr. Charney acknowledged. However, the discovery could lead to new treatments that could benefit all patients with the disease, he added.
“There are multiple pathways to psychosis and there’s also multiple pathways to treat psychosis,” Dr. Charney said. “There’s reason to believe if you can find a mechanism by which a human being could develop a psychosis, then reversing that mechanism could help a lot of people who have psychosis for another reason.”
Importance of diverse cohorts
Commenting on the findings, Jennifer Gladys Mulle, MHS, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School at Rutgers University, Piscataway, N.J., noted that while genetic discoveries have led to new therapies in other medical conditions, that has not been the case with schizophrenia.
“In other disorders, having genetic findings have really opened a window into the molecular mechanisms, which has allowed us to develop pharmaceuticals and understand the disease process better,” said Dr. Mulle, who was not part of this study. “But because we haven’t had that in schizophrenia, it’s really held us back. Having genetic variants associated with schizophrenia may really help us understand the mechanism.”
The inclusion of diverse populations is also a key contribution of this study, Dr. Mulle added.
“So far a lot of the work we’ve done in genetics has been on people of European ancestry,” Dr. Mulle said. “The fact that they have found results that are generalizable across multiple ethnicities really suggests that if we develop pharmaceutical agents based on these findings, it will help many people.”
More attention has been paid recently to a growing problem in the study of genetics of psychiatric disorders: More than 95% of participants in genome-wide association studies that seek to identify gene variants linked to disease are of European ancestry.
Dr. Charney and his colleagues had that in mind when they designed the study.
“We can’t get to a place where genetics is clinically useful if we don’t know the extent to which a particular observation that’s found in one population is also true for other populations,” Dr. Charney said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Charney and Dr. Mulle report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE GENETICS












