User login
Brain volume patterns vary across psychiatric disorders
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
Infested with worms, but are they really there?
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
Verbal working memory deterioration predicts relapse in remitted psychosis
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH
Schizophrenia up to three times more common than previously thought
, according to the first study to estimate the national prevalence of schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
This finding is “especially important,” given that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders experience “high levels of disability that present significant challenges in all aspects of their life,” principal investigator Heather Ringeisen, PhD, with RTI International, a nonprofit research institute based on Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in a statement.
The results “highlight the need to improve systems of care and access to treatment for people with schizophrenia and other mental health disorders,” added co–principal investigator Mark J. Edlund, MD, PhD, also with RTI.
The study also found that prevalence rates of many other nonpsychotic disorders were generally within an expected range in light of findings from prior research – with three exceptions.
Rates of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were higher than reported in past nationally representative samples.
The new data come from the Mental and Substance Use Disorder Prevalence Study (MDPS), a pilot program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
A nationally representative sample of 5,679 adults aged 18-65 residing in U.S. households, prisons, homeless shelters, and state psychiatric hospitals were interviewed, virtually or in person, between October 2020 and October 2022.
The research team used a population-based version of the Structured Clinical Interview of the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5; SCID-5) for mental health and substance use disorder diagnostic assessment.
Among the key findings in the report:
- Nearly 2% of adults (about 3.7 million) had a lifetime history of schizophrenia spectrum disorders, which include schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophreniform disorder.
- Roughly 2.5 million adults (1.2%) met diagnostic criteria for a schizophrenia spectrum disorder in the past year.
- The two most common mental disorders among adults were MDD (15.5%, or about 31.4 million) and GAD (10.0%, or about 20.2 million).
- Approximately 8.2 million adults (4.1%) had past-year posttraumatic stress disorder, about 5.0 million (2.5%) had OCD, and roughly 3.1 million (1.5%) had bipolar I disorder.
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD) was the most common substance use disorder among adults aged 18-65; roughly 13.4 million adults (6.7%) met criteria for AUD in the past year.
- About 7.7 million adults (3.8%) had cannabis use disorder, about 3.2 million (1.6%) had stimulant use disorder, and about 1 million (0.5%) had opioid use disorder.
Multiple comorbidities
The data also show that one in four adults had at least one mental health disorder in the past year, most commonly MDD and GAD.
About 11% of adults met the criteria for at least one substance use disorder, with AUD and cannabis use disorder the most common.
In addition, an estimated 11 million adults aged 18-65 had both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder in the past year.
Encouragingly, the findings suggest that more individuals are seeking and accessing treatment compared with previous studies, the authors noted; 61% of adults with a mental health disorder reported having at least one visit with a treatment provider in the past year.
However, considerable treatment gaps still exist for the most common mental health disorders, they reported. Within the past year, more than 40% of adults with MDD and more than 30% of those with GAD did not receive any treatment services.
The full report is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the first study to estimate the national prevalence of schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
This finding is “especially important,” given that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders experience “high levels of disability that present significant challenges in all aspects of their life,” principal investigator Heather Ringeisen, PhD, with RTI International, a nonprofit research institute based on Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in a statement.
The results “highlight the need to improve systems of care and access to treatment for people with schizophrenia and other mental health disorders,” added co–principal investigator Mark J. Edlund, MD, PhD, also with RTI.
The study also found that prevalence rates of many other nonpsychotic disorders were generally within an expected range in light of findings from prior research – with three exceptions.
Rates of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were higher than reported in past nationally representative samples.
The new data come from the Mental and Substance Use Disorder Prevalence Study (MDPS), a pilot program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
A nationally representative sample of 5,679 adults aged 18-65 residing in U.S. households, prisons, homeless shelters, and state psychiatric hospitals were interviewed, virtually or in person, between October 2020 and October 2022.
The research team used a population-based version of the Structured Clinical Interview of the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5; SCID-5) for mental health and substance use disorder diagnostic assessment.
Among the key findings in the report:
- Nearly 2% of adults (about 3.7 million) had a lifetime history of schizophrenia spectrum disorders, which include schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophreniform disorder.
- Roughly 2.5 million adults (1.2%) met diagnostic criteria for a schizophrenia spectrum disorder in the past year.
- The two most common mental disorders among adults were MDD (15.5%, or about 31.4 million) and GAD (10.0%, or about 20.2 million).
- Approximately 8.2 million adults (4.1%) had past-year posttraumatic stress disorder, about 5.0 million (2.5%) had OCD, and roughly 3.1 million (1.5%) had bipolar I disorder.
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD) was the most common substance use disorder among adults aged 18-65; roughly 13.4 million adults (6.7%) met criteria for AUD in the past year.
- About 7.7 million adults (3.8%) had cannabis use disorder, about 3.2 million (1.6%) had stimulant use disorder, and about 1 million (0.5%) had opioid use disorder.
Multiple comorbidities
The data also show that one in four adults had at least one mental health disorder in the past year, most commonly MDD and GAD.
About 11% of adults met the criteria for at least one substance use disorder, with AUD and cannabis use disorder the most common.
In addition, an estimated 11 million adults aged 18-65 had both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder in the past year.
Encouragingly, the findings suggest that more individuals are seeking and accessing treatment compared with previous studies, the authors noted; 61% of adults with a mental health disorder reported having at least one visit with a treatment provider in the past year.
However, considerable treatment gaps still exist for the most common mental health disorders, they reported. Within the past year, more than 40% of adults with MDD and more than 30% of those with GAD did not receive any treatment services.
The full report is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the first study to estimate the national prevalence of schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
This finding is “especially important,” given that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders experience “high levels of disability that present significant challenges in all aspects of their life,” principal investigator Heather Ringeisen, PhD, with RTI International, a nonprofit research institute based on Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in a statement.
The results “highlight the need to improve systems of care and access to treatment for people with schizophrenia and other mental health disorders,” added co–principal investigator Mark J. Edlund, MD, PhD, also with RTI.
The study also found that prevalence rates of many other nonpsychotic disorders were generally within an expected range in light of findings from prior research – with three exceptions.
Rates of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were higher than reported in past nationally representative samples.
The new data come from the Mental and Substance Use Disorder Prevalence Study (MDPS), a pilot program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
A nationally representative sample of 5,679 adults aged 18-65 residing in U.S. households, prisons, homeless shelters, and state psychiatric hospitals were interviewed, virtually or in person, between October 2020 and October 2022.
The research team used a population-based version of the Structured Clinical Interview of the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5; SCID-5) for mental health and substance use disorder diagnostic assessment.
Among the key findings in the report:
- Nearly 2% of adults (about 3.7 million) had a lifetime history of schizophrenia spectrum disorders, which include schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophreniform disorder.
- Roughly 2.5 million adults (1.2%) met diagnostic criteria for a schizophrenia spectrum disorder in the past year.
- The two most common mental disorders among adults were MDD (15.5%, or about 31.4 million) and GAD (10.0%, or about 20.2 million).
- Approximately 8.2 million adults (4.1%) had past-year posttraumatic stress disorder, about 5.0 million (2.5%) had OCD, and roughly 3.1 million (1.5%) had bipolar I disorder.
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD) was the most common substance use disorder among adults aged 18-65; roughly 13.4 million adults (6.7%) met criteria for AUD in the past year.
- About 7.7 million adults (3.8%) had cannabis use disorder, about 3.2 million (1.6%) had stimulant use disorder, and about 1 million (0.5%) had opioid use disorder.
Multiple comorbidities
The data also show that one in four adults had at least one mental health disorder in the past year, most commonly MDD and GAD.
About 11% of adults met the criteria for at least one substance use disorder, with AUD and cannabis use disorder the most common.
In addition, an estimated 11 million adults aged 18-65 had both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder in the past year.
Encouragingly, the findings suggest that more individuals are seeking and accessing treatment compared with previous studies, the authors noted; 61% of adults with a mental health disorder reported having at least one visit with a treatment provider in the past year.
However, considerable treatment gaps still exist for the most common mental health disorders, they reported. Within the past year, more than 40% of adults with MDD and more than 30% of those with GAD did not receive any treatment services.
The full report is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy programs: How they can be improved
A Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) is a drug safety program the FDA can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks (Box1). The FDA may require medication guides, patient package inserts, communication plans for health care professionals, and/or certain packaging and safe disposal technologies for medications that pose a serious risk of abuse or overdose. The FDA may also require elements to assure safe use and/or an implementation system be included in the REMS. Pharmaceutical manufacturers then develop a proposed REMS for FDA review.2 If the FDA approves the proposed REMS, the manufacturer is responsible for implementing the REMS requirements.
Box
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding psychiatry, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illness. Some of the most common myths include:
The FDA provides this description of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS):
“A [REMS] is a drug safety program that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks. REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication. While all medications have labeling that informs health care stakeholders about medication risks, only a few medications require a REMS. REMS are not designed to mitigate all the adverse events of a medication, these are communicated to health care providers in the medication’s prescribing information. Rather, REMS focus on preventing, monitoring and/or managing a specific serious risk by informing, educating and/or reinforcing actions to reduce the frequency and/or severity of the event.”1
The REMS program for clozapine3 has been the subject of much discussion in the psychiatric community. The adverse impact of the 2015 update to the clozapine REMS program was emphasized at meetings of both the American Psychiatric Association and the College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists. A white paper published by the National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors shortly after the 2015 update concluded, “clozapine is underused due to a variety of barriers related to the drug and its properties, the health care system, regulatory requirements, and reimbursement issues.”4 After an update to the clozapine REMS program in 2021, the FDA temporarily suspended enforcement of certain requirements due to concerns from health care professionals about patient access to the medication because of problems with implementing the clozapine REMS program.5,6 In November 2022, the FDA issued a second announcement of enforcement discretion related to additional requirements of the REMS program.5 The FDA had previously announced a decision to not take action regarding adherence to REMS requirements for certain laboratory tests in March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic.7
REMS programs for other psychiatric medications may also present challenges. The REMS programs for esketamine8 and olanzapine for extended-release (ER) injectable suspension9 include certain risks that require postadministration monitoring. Some facilities have had to dedicate additional space and clinician time to ensure REMS requirements are met.
To further understand health care professionals’ perspectives regarding the value and burden of these REMS programs, a collaborative effort of the University of Maryland (College Park and Baltimore campuses) Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation with the FDA was undertaken. The REMS for clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine were examined to develop recommendations for improving patient access while ensuring safe medication use and limiting the impact on health care professionals.
Assessing the REMS programs
Focus groups were held with health care professionals nominated by professional organizations to gather their perspectives on the REMS requirements. There was 1 focus group for each of the 3 medications. A facilitator’s guide was developed that contained the details of how to conduct the focus group along with the medication-specific questions. The questions were based on the REMS requirements as of May 2021 and assessed the impact of the REMS on patient safety, patient access, and health care professional workload; effects from the COVID-19 pandemic; and suggestions to improve the REMS programs. The University of Maryland Institutional Review Board reviewed the materials and processes and made the determination of exempt.
Health care professionals were eligible to participate in a focus group if they had ≥1 year of experience working with patients who use the specific medication and ≥6 months of experience within the past year working with the REMS program for that medication. Participants were excluded if they were employed by a pharmaceutical manufacturer or the FDA. The focus groups were conducted virtually using an online conferencing service during summer 2021 and were scheduled for 90 minutes. Prior to the focus group, participants received information from the “Goals” and “Summary” tabs of the FDA REMS website10 for the specific medication along with patient/caregiver guides, which were available for clozapine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension. For each focus group, there was a target sample size of 6 to 9 participants. However, there were only 4 participants in the olanzapine for ER injectable suspension focus group, which we believed was due to lower national utilization of this medication. Individuals were only able to participate in 1 focus group, so the unique participant count for all 3 focus groups totaled 17 (Table 1).
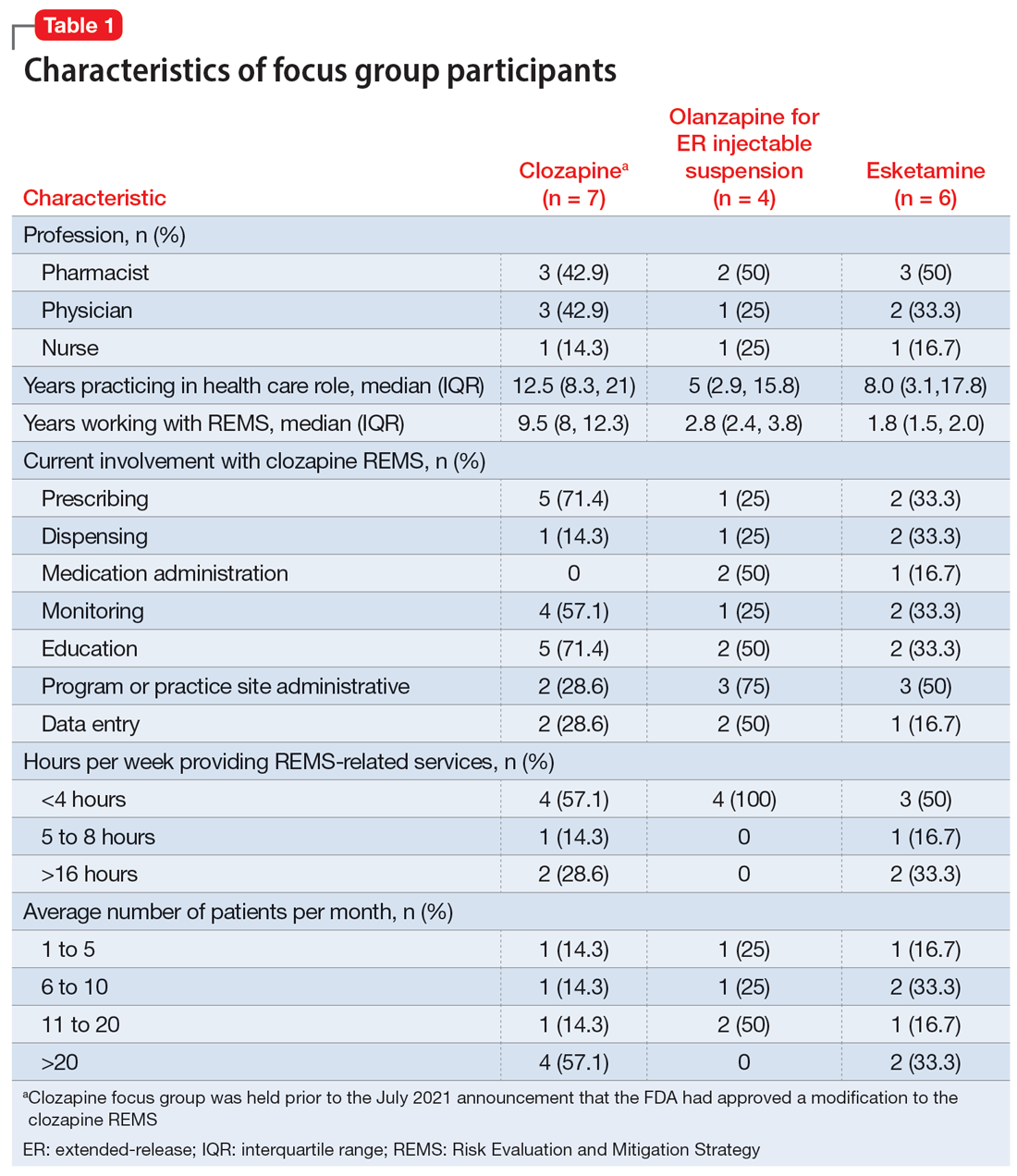
Themes extracted from qualitative analysis of the focus group responses were the value of the REMS programs; registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites; monitoring requirements; care transitions; and COVID considerations (Table 2). While the REMS programs were perceived to increase practitioner and patient awareness of potential harms, discussions centered on the relative cost-to-benefit of the required reporting and other REMS requirements. There were challenges with the registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites that also affected patient care during transitions to different health care settings or clinicians. Patient access was affected by disparities in care related to monitoring requirements and clinician availability.
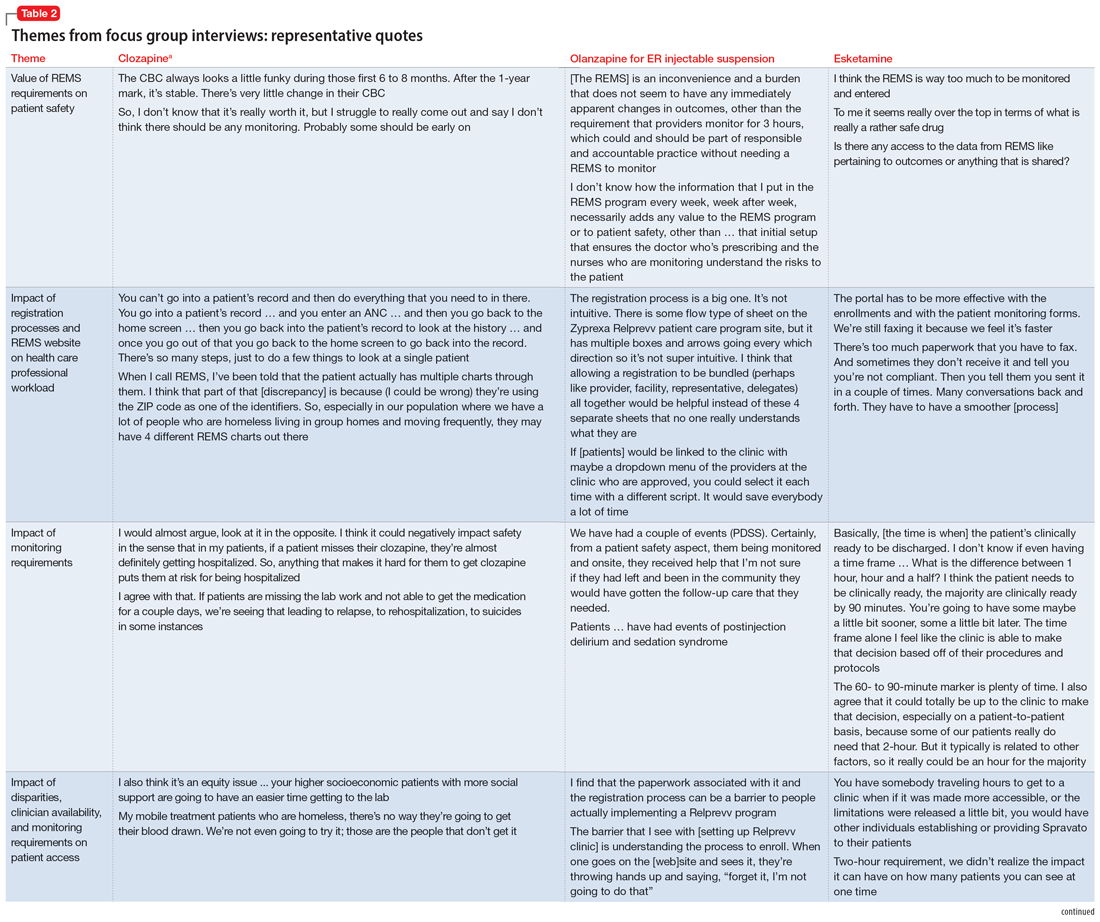

Continue to: COVID impacted all REMS...
COVID impacted all REMS programs. Physical distancing was an issue for medications that required extensive postadministration monitoring (ie, esketamine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension). Access to laboratory services was an issue for clozapine.
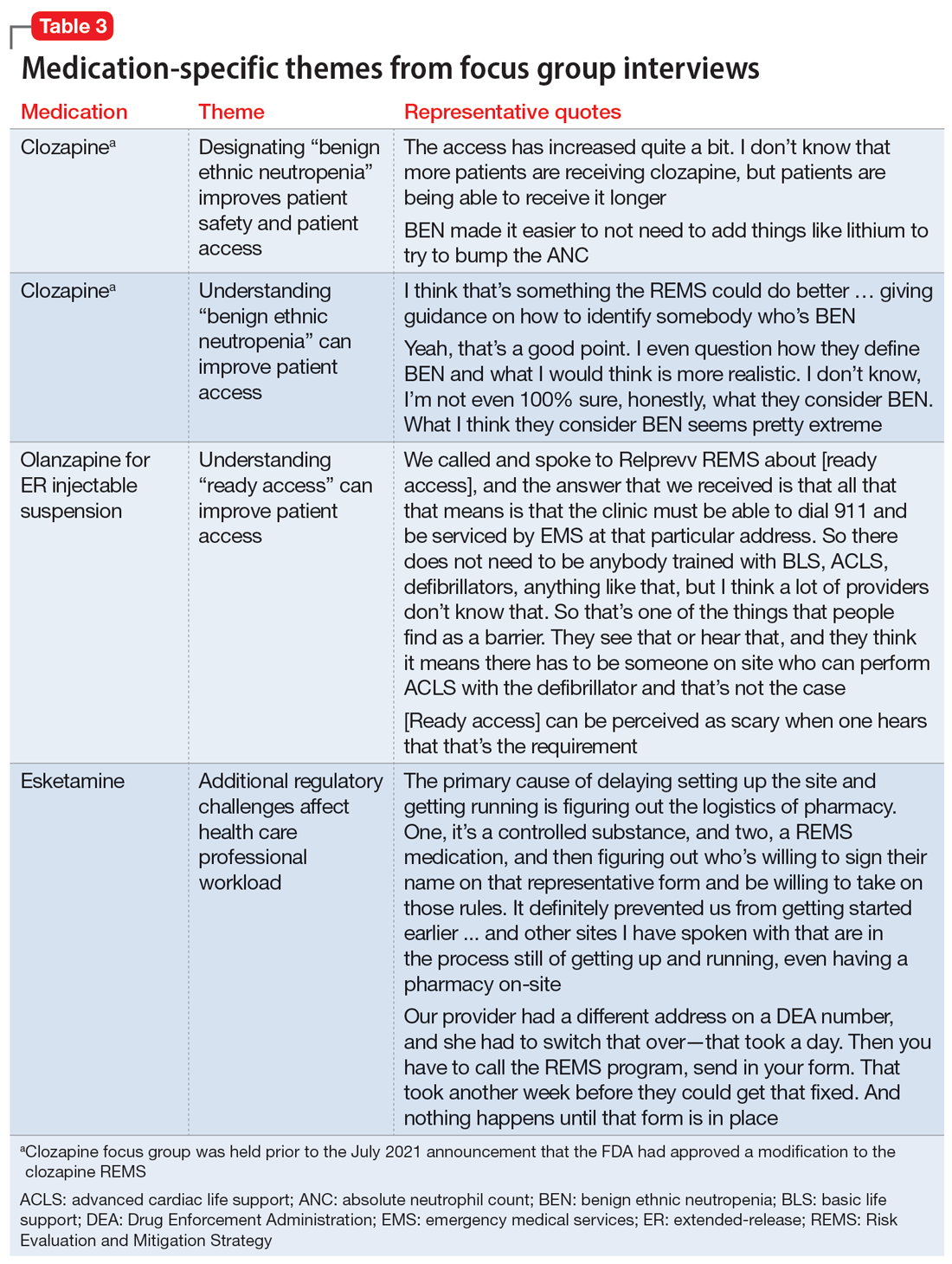
Medication-specific themes are listed in Table 3 and relate to terms and descriptions in the REMS or additional regulatory requirements from the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). Suggestions for improvement to the REMS are presented in Table 4.
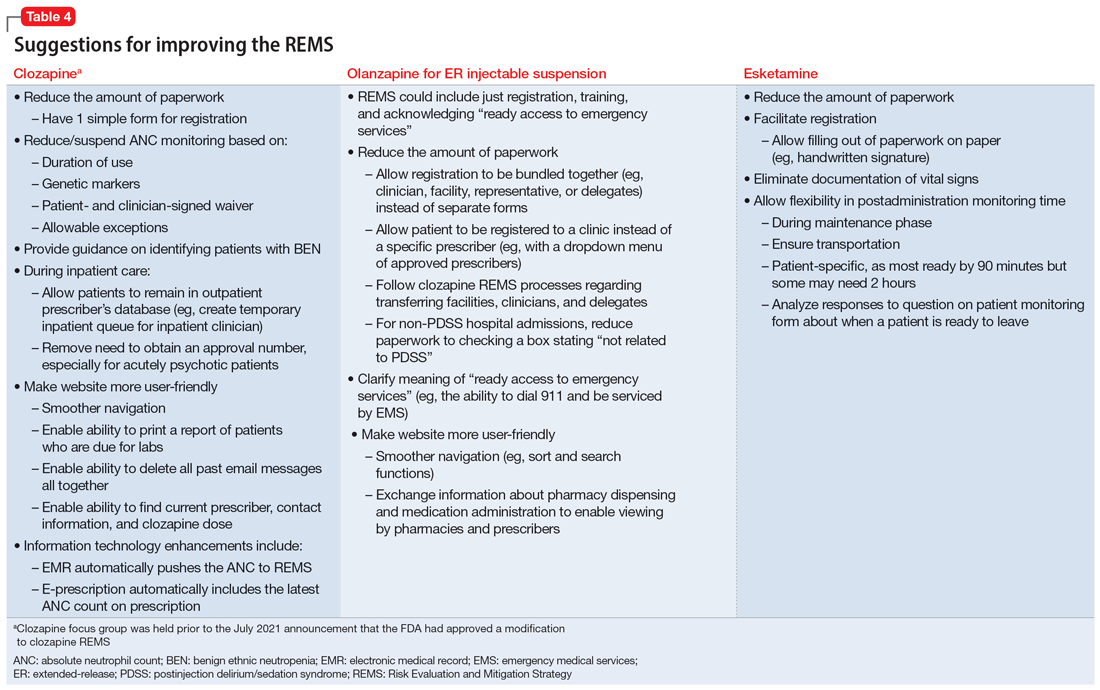
Recommendations for improving REMS
A group consisting of health care professionals, policy experts, and mental health advocates reviewed the information provided by the focus groups and developed the following recommendations.
Overarching recommendations
Each REMS should include a section providing justification for its existence, including a risk analysis of the data regarding the risk the REMS is designed to mitigate. This analysis should be repeated on a regular basis as scientific evidence regarding the risk and its epidemiology evolves. This additional section should also explain how the program requirements of the REMS as implemented (or planned) will achieve the aims of the REMS and weigh the potential benefits of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer vs the potential risks of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer.
Each REMS should have specific quantifiable outcomes. For example, it should specify a reduction in occurrence of the rate of the concerned risk by a specified amount.
Continue to: Ensure adequate...
Ensure adequate stakeholder input during the REMS development and real-world testing in multiple environments before implementing the REMS to identify unanticipated consequences that might impact patient access, patient safety, and health care professional burden. Implementation testing should explore issues such as purchasing and procurement, billing and reimbursement, and relevant factors such as other federal regulations or requirements (eg, the DEA or Medicare).
Ensure harmonization of the REMS forms and processes (eg, initiation and monitoring) for different medications where possible. A prescriber, pharmacist, or system should not face additional barriers to participate in a REMS based on REMS-specific intricacies (ie, prescription systems, data submission systems, or ordering systems). This streamlining will likely decrease clinical inertia to initiate care with the REMS medication, decrease health care professional burden, and improve compliance with REMS requirements.
REMS should anticipate the need for care transitions and employ provisions to ensure seamless care. Considerations should be given to transitions that occur due to:
- Different care settings (eg, inpatient, outpatient, or long-term care)
- Different geographies (eg, patient moves)
- Changes in clinicians, including leaves or absences
- Changes in facilities (eg, pharmacies).
REMS should mirror normal health care professional workflow, including how monitoring data are collected and how and with which frequency pharmacies fill prescriptions.Enhanced information technology to support REMS programs is needed. For example, REMS should be integrated with major electronic patient health record and pharmacy systems to reduce the effort required for clinicians to supply data and automate REMS processes.
For medications that are subject to other agencies and their regulations (eg, the CDC, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or the DEA), REMS should be required to meet all standards of all agencies with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
Continue to: REMS should have a...
REMS should have a standard disclaimer that allows the health care professional to waive certain provisions of the REMS in cases when the specific provisions of the REMS pose a greater risk to the patient than the risk posed by waiving the requirement.
Assure the actions implemented by the industry to meet the requirements for each REMS program are based on peer-reviewed evidence and provide a reasonable expectation to achieve the anticipated benefit.
Ensure that manufacturers make all accumulated REMS data available in a deidentified manner for use by qualified scientific researchers. Additionally, each REMS should have a plan for data access upon initiation and termination of the REMS.
Each REMS should collect data on the performance of the centers and/or personnel who operate the REMS and submit this data for review by qualified outside reviewers. Parameters to assess could include:
- timeliness of response
- timeliness of problem resolution
- data availability and its helpfulness to patient care
- adequacy of resources.
Recommendations for clozapine REMS
These comments relate to the clozapine REMS program prior to the July 2021 announcement that FDA had approved a modification.
Provide a clear definition for “benign ethnic neutropenia.”
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for monitoring. During COVID, the FDA allowed clinicians to “use their best medical judgment in weighing the benefits and risks of continuing treatment in the absence of laboratory testing.”7 This guidance, which allowed flexibility to absolute neutrophil count (ANC) monitoring, was perceived as positive and safe. Before the changes in the REMS requirements, patients with benign ethnic neutropenia were restricted from accessing their medication or encountered harm from additional pharmacotherapy to mitigate ANC levels.
Continue to: Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Provide clear explicit instructions on what is required to have “ready access to emergency services.”
Ensure the REMS include patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring (eg, sedation or blood pressure). Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of olanzapine for ER injectable suspension by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness are included in the REMS. How was the 3-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure the REMS requirements allow for seamless care during transitions, particularly when clinicians are on vacation.
Continue to: Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring. Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of esketamine by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness of requirements are included in the REMS. How was the 2-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure that the REMS meet all standards of the DEA, with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
A summary of the findings
Overall, the REMS programs for these 3 medications were positively perceived for raising awareness of safe medication use for clinicians and patients. Monitoring patients for safety concerns is important and REMS requirements provide accountability.
Continue to: The use of a single shared...
The use of a single shared REMS system for documenting requirements for clozapine (compared to separate systems for each manufacturer) was a positive move forward in implementation. The focus group welcomed the increased awareness of benign ethnic neutropenia as a result of this condition being incorporated in the revised monitoring requirements of the clozapine REMS.
Focus group participants raised the issue of the real-world efficiency of the REMS programs (reduced access and increased clinician workload) vs the benefits (patient safety). They noted that excessive workload could lead to clinicians becoming unwilling to use a medication that requires a REMS. Clinician workload may be further compromised when REMS logistics disrupt the normal workflow and transitions of care between clinicians or settings. This latter aspect is of particular concern for clozapine.
The complexities of the registration and reporting system for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension and the lack of clarity about monitoring were noted to have discouraged the opening of treatment sites. This scarcity of sites may make clinicians hesitant to use this medication, and instead opt for alternative treatments in patients who may be appropriate candidates.
There has also been limited growth of esketamine treatment sites, especially in comparison to ketamine treatment sites.11-14 Esketamine is FDA-approved for treatment-resistant depression in adults and for depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder with acute suicidal ideation or behavior. Ketamine is not FDA-approved for treating depression but is being used off-label to treat this disorder.15 The FDA determined that ketamine does not require a REMS to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks for its approved indications as an anesthetic agent, anesthesia-inducing agent, or supplement to anesthesia. Since ketamine has no REMS requirements, there may be a lower burden for its use. Thus, clinicians are treating patients for depression with this medication without needing to comply with a REMS.16
Technology plays a role in workload burden, and integrating health care processes within current workflow systems, such as using electronic patient health records and pharmacy systems, is recommended. The FDA has been exploring technologies to facilitate the completion of REMS requirements, including mandatory education within the prescribers’ and pharmacists’ workflow.17 This is a complex task that requires multiple stakeholders with differing perspectives and incentives to align.
Continue to: The data collected for the REMS...
The data collected for the REMS program belongs to the medication’s manufacturer. Current regulations do not require manufacturers to make this data available to qualified scientific researchers. A regulatory mandate to establish data sharing methods would improve transparency and enhance efforts to better understand the outcomes of the REMS programs.
A few caveats
Both the overarching and medication-specific recommendations were based on a small number of participants’ discussions related to clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine. These recommendations do not include other medications with REMS that are used to treat psychiatric disorders, such as loxapine, buprenorphine ER, and buprenorphine transmucosal products. Larger-scale qualitative and quantitative research is needed to better understand health care professionals’ perspectives. Lastly, some of the recommendations outlined in this article are beyond the current purview or authority of the FDA and may require legislative or regulatory action to implement.
Bottom Line
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) programs are designed to help reduce the occurrence and/or severity of serious risks or to inform decision-making. However, REMS requirements may adversely impact patient access to certain REMS medications and clinician burden. Health care professionals can provide informed recommendations for improving the REMS programs for clozapine, olanzapine for extended-release injectable suspension, and esketamine.
Related Resources
- FDA. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about REMS. www.fda.gov/drugs/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems/frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-rems
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine extended-release • Sublocade
Buprenorphine transmucosal • Subutex, Suboxone
Clozapine • Clozaril
Esketamine • Spravato
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Loxapine • Adasuve
Olanzapine extended-release injectable suspension • Zyprexa Relprevv
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Format and Content of a REMS Document. Guidance for Industry. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/77846/download
3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Clozapine. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=RemsDetails.page&REMS=351
4. The National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors. Clozapine underutilization: addressing the barriers. Accessed September 30, 2019. https://nasmhpd.org/sites/default/files/Assessment%201_Clozapine%20Underutilization.pdf
5. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA is temporarily exercising enforcement discretion with respect to certain clozapine REMS program requirements to ensure continuity of care for patients taking clozapine. Updated November 22, 2022. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-temporarily-exercising-enforcement-discretion-respect-certain-clozapine-rems-program
6. Tanzi M. REMS issues affect clozapine, isotretinoin. Pharmacy Today. 2022;28(3):49.
7. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA provides update on patient access to certain REMS drugs during COVID-19 public health emergency. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-provides-update-patient-access-certain-rems-drugs-during-covid-19
8. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Spravato (esketamine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=386
9. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Zyprexa Relprevv (olanzapine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=74
10. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm
11. Parikh SV, Lopez D, Vande Voort JL, et al. Developing an IV ketamine clinic for treatment-resistant depression: a primer. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2021;51(3):109-124.
12. Dodge D. The ketamine cure. The New York Times. November 4, 2021. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/04/well/ketamine-therapy-depression.html
13. Burton KW. Time for a national ketamine registry, experts say. Medscape. February 15, 2023. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/988310
14. Wilkinson ST, Howard DH, Busch SH. Psychiatric practice patterns and barriers to the adoption of esketamine. JAMA. 2019;322(11):1039-1040. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.10728
15. Wilkinson ST, Toprak M, Turner MS, et al. A survey of the clinical, off-label use of ketamine as a treatment for psychiatric disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(7):695-696. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17020239
16. Pai SM, Gries JM; ACCP Public Policy Committee. Off-label use of ketamine: a challenging drug treatment delivery model with an inherently unfavorable risk-benefit profile. J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;62(1):10-13. doi:10.1002/jcph.1983
17. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) Integration. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://confluence.hl7.org/display/COD/Risk+Evaluation+and+Mitigation+Strategies+%28REMS%29+Integration
A Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) is a drug safety program the FDA can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks (Box1). The FDA may require medication guides, patient package inserts, communication plans for health care professionals, and/or certain packaging and safe disposal technologies for medications that pose a serious risk of abuse or overdose. The FDA may also require elements to assure safe use and/or an implementation system be included in the REMS. Pharmaceutical manufacturers then develop a proposed REMS for FDA review.2 If the FDA approves the proposed REMS, the manufacturer is responsible for implementing the REMS requirements.
Box
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding psychiatry, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illness. Some of the most common myths include:
The FDA provides this description of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS):
“A [REMS] is a drug safety program that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks. REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication. While all medications have labeling that informs health care stakeholders about medication risks, only a few medications require a REMS. REMS are not designed to mitigate all the adverse events of a medication, these are communicated to health care providers in the medication’s prescribing information. Rather, REMS focus on preventing, monitoring and/or managing a specific serious risk by informing, educating and/or reinforcing actions to reduce the frequency and/or severity of the event.”1
The REMS program for clozapine3 has been the subject of much discussion in the psychiatric community. The adverse impact of the 2015 update to the clozapine REMS program was emphasized at meetings of both the American Psychiatric Association and the College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists. A white paper published by the National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors shortly after the 2015 update concluded, “clozapine is underused due to a variety of barriers related to the drug and its properties, the health care system, regulatory requirements, and reimbursement issues.”4 After an update to the clozapine REMS program in 2021, the FDA temporarily suspended enforcement of certain requirements due to concerns from health care professionals about patient access to the medication because of problems with implementing the clozapine REMS program.5,6 In November 2022, the FDA issued a second announcement of enforcement discretion related to additional requirements of the REMS program.5 The FDA had previously announced a decision to not take action regarding adherence to REMS requirements for certain laboratory tests in March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic.7
REMS programs for other psychiatric medications may also present challenges. The REMS programs for esketamine8 and olanzapine for extended-release (ER) injectable suspension9 include certain risks that require postadministration monitoring. Some facilities have had to dedicate additional space and clinician time to ensure REMS requirements are met.
To further understand health care professionals’ perspectives regarding the value and burden of these REMS programs, a collaborative effort of the University of Maryland (College Park and Baltimore campuses) Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation with the FDA was undertaken. The REMS for clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine were examined to develop recommendations for improving patient access while ensuring safe medication use and limiting the impact on health care professionals.
Assessing the REMS programs
Focus groups were held with health care professionals nominated by professional organizations to gather their perspectives on the REMS requirements. There was 1 focus group for each of the 3 medications. A facilitator’s guide was developed that contained the details of how to conduct the focus group along with the medication-specific questions. The questions were based on the REMS requirements as of May 2021 and assessed the impact of the REMS on patient safety, patient access, and health care professional workload; effects from the COVID-19 pandemic; and suggestions to improve the REMS programs. The University of Maryland Institutional Review Board reviewed the materials and processes and made the determination of exempt.
Health care professionals were eligible to participate in a focus group if they had ≥1 year of experience working with patients who use the specific medication and ≥6 months of experience within the past year working with the REMS program for that medication. Participants were excluded if they were employed by a pharmaceutical manufacturer or the FDA. The focus groups were conducted virtually using an online conferencing service during summer 2021 and were scheduled for 90 minutes. Prior to the focus group, participants received information from the “Goals” and “Summary” tabs of the FDA REMS website10 for the specific medication along with patient/caregiver guides, which were available for clozapine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension. For each focus group, there was a target sample size of 6 to 9 participants. However, there were only 4 participants in the olanzapine for ER injectable suspension focus group, which we believed was due to lower national utilization of this medication. Individuals were only able to participate in 1 focus group, so the unique participant count for all 3 focus groups totaled 17 (Table 1).

Themes extracted from qualitative analysis of the focus group responses were the value of the REMS programs; registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites; monitoring requirements; care transitions; and COVID considerations (Table 2). While the REMS programs were perceived to increase practitioner and patient awareness of potential harms, discussions centered on the relative cost-to-benefit of the required reporting and other REMS requirements. There were challenges with the registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites that also affected patient care during transitions to different health care settings or clinicians. Patient access was affected by disparities in care related to monitoring requirements and clinician availability.


Continue to: COVID impacted all REMS...
COVID impacted all REMS programs. Physical distancing was an issue for medications that required extensive postadministration monitoring (ie, esketamine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension). Access to laboratory services was an issue for clozapine.

Medication-specific themes are listed in Table 3 and relate to terms and descriptions in the REMS or additional regulatory requirements from the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). Suggestions for improvement to the REMS are presented in Table 4.

Recommendations for improving REMS
A group consisting of health care professionals, policy experts, and mental health advocates reviewed the information provided by the focus groups and developed the following recommendations.
Overarching recommendations
Each REMS should include a section providing justification for its existence, including a risk analysis of the data regarding the risk the REMS is designed to mitigate. This analysis should be repeated on a regular basis as scientific evidence regarding the risk and its epidemiology evolves. This additional section should also explain how the program requirements of the REMS as implemented (or planned) will achieve the aims of the REMS and weigh the potential benefits of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer vs the potential risks of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer.
Each REMS should have specific quantifiable outcomes. For example, it should specify a reduction in occurrence of the rate of the concerned risk by a specified amount.
Continue to: Ensure adequate...
Ensure adequate stakeholder input during the REMS development and real-world testing in multiple environments before implementing the REMS to identify unanticipated consequences that might impact patient access, patient safety, and health care professional burden. Implementation testing should explore issues such as purchasing and procurement, billing and reimbursement, and relevant factors such as other federal regulations or requirements (eg, the DEA or Medicare).
Ensure harmonization of the REMS forms and processes (eg, initiation and monitoring) for different medications where possible. A prescriber, pharmacist, or system should not face additional barriers to participate in a REMS based on REMS-specific intricacies (ie, prescription systems, data submission systems, or ordering systems). This streamlining will likely decrease clinical inertia to initiate care with the REMS medication, decrease health care professional burden, and improve compliance with REMS requirements.
REMS should anticipate the need for care transitions and employ provisions to ensure seamless care. Considerations should be given to transitions that occur due to:
- Different care settings (eg, inpatient, outpatient, or long-term care)
- Different geographies (eg, patient moves)
- Changes in clinicians, including leaves or absences
- Changes in facilities (eg, pharmacies).
REMS should mirror normal health care professional workflow, including how monitoring data are collected and how and with which frequency pharmacies fill prescriptions.Enhanced information technology to support REMS programs is needed. For example, REMS should be integrated with major electronic patient health record and pharmacy systems to reduce the effort required for clinicians to supply data and automate REMS processes.
For medications that are subject to other agencies and their regulations (eg, the CDC, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or the DEA), REMS should be required to meet all standards of all agencies with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
Continue to: REMS should have a...
REMS should have a standard disclaimer that allows the health care professional to waive certain provisions of the REMS in cases when the specific provisions of the REMS pose a greater risk to the patient than the risk posed by waiving the requirement.
Assure the actions implemented by the industry to meet the requirements for each REMS program are based on peer-reviewed evidence and provide a reasonable expectation to achieve the anticipated benefit.
Ensure that manufacturers make all accumulated REMS data available in a deidentified manner for use by qualified scientific researchers. Additionally, each REMS should have a plan for data access upon initiation and termination of the REMS.
Each REMS should collect data on the performance of the centers and/or personnel who operate the REMS and submit this data for review by qualified outside reviewers. Parameters to assess could include:
- timeliness of response
- timeliness of problem resolution
- data availability and its helpfulness to patient care
- adequacy of resources.
Recommendations for clozapine REMS
These comments relate to the clozapine REMS program prior to the July 2021 announcement that FDA had approved a modification.
Provide a clear definition for “benign ethnic neutropenia.”
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for monitoring. During COVID, the FDA allowed clinicians to “use their best medical judgment in weighing the benefits and risks of continuing treatment in the absence of laboratory testing.”7 This guidance, which allowed flexibility to absolute neutrophil count (ANC) monitoring, was perceived as positive and safe. Before the changes in the REMS requirements, patients with benign ethnic neutropenia were restricted from accessing their medication or encountered harm from additional pharmacotherapy to mitigate ANC levels.
Continue to: Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Provide clear explicit instructions on what is required to have “ready access to emergency services.”
Ensure the REMS include patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring (eg, sedation or blood pressure). Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of olanzapine for ER injectable suspension by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness are included in the REMS. How was the 3-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure the REMS requirements allow for seamless care during transitions, particularly when clinicians are on vacation.
Continue to: Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring. Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of esketamine by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness of requirements are included in the REMS. How was the 2-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure that the REMS meet all standards of the DEA, with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
A summary of the findings
Overall, the REMS programs for these 3 medications were positively perceived for raising awareness of safe medication use for clinicians and patients. Monitoring patients for safety concerns is important and REMS requirements provide accountability.
Continue to: The use of a single shared...
The use of a single shared REMS system for documenting requirements for clozapine (compared to separate systems for each manufacturer) was a positive move forward in implementation. The focus group welcomed the increased awareness of benign ethnic neutropenia as a result of this condition being incorporated in the revised monitoring requirements of the clozapine REMS.
Focus group participants raised the issue of the real-world efficiency of the REMS programs (reduced access and increased clinician workload) vs the benefits (patient safety). They noted that excessive workload could lead to clinicians becoming unwilling to use a medication that requires a REMS. Clinician workload may be further compromised when REMS logistics disrupt the normal workflow and transitions of care between clinicians or settings. This latter aspect is of particular concern for clozapine.
The complexities of the registration and reporting system for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension and the lack of clarity about monitoring were noted to have discouraged the opening of treatment sites. This scarcity of sites may make clinicians hesitant to use this medication, and instead opt for alternative treatments in patients who may be appropriate candidates.
There has also been limited growth of esketamine treatment sites, especially in comparison to ketamine treatment sites.11-14 Esketamine is FDA-approved for treatment-resistant depression in adults and for depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder with acute suicidal ideation or behavior. Ketamine is not FDA-approved for treating depression but is being used off-label to treat this disorder.15 The FDA determined that ketamine does not require a REMS to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks for its approved indications as an anesthetic agent, anesthesia-inducing agent, or supplement to anesthesia. Since ketamine has no REMS requirements, there may be a lower burden for its use. Thus, clinicians are treating patients for depression with this medication without needing to comply with a REMS.16
Technology plays a role in workload burden, and integrating health care processes within current workflow systems, such as using electronic patient health records and pharmacy systems, is recommended. The FDA has been exploring technologies to facilitate the completion of REMS requirements, including mandatory education within the prescribers’ and pharmacists’ workflow.17 This is a complex task that requires multiple stakeholders with differing perspectives and incentives to align.
Continue to: The data collected for the REMS...
The data collected for the REMS program belongs to the medication’s manufacturer. Current regulations do not require manufacturers to make this data available to qualified scientific researchers. A regulatory mandate to establish data sharing methods would improve transparency and enhance efforts to better understand the outcomes of the REMS programs.
A few caveats
Both the overarching and medication-specific recommendations were based on a small number of participants’ discussions related to clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine. These recommendations do not include other medications with REMS that are used to treat psychiatric disorders, such as loxapine, buprenorphine ER, and buprenorphine transmucosal products. Larger-scale qualitative and quantitative research is needed to better understand health care professionals’ perspectives. Lastly, some of the recommendations outlined in this article are beyond the current purview or authority of the FDA and may require legislative or regulatory action to implement.
Bottom Line
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) programs are designed to help reduce the occurrence and/or severity of serious risks or to inform decision-making. However, REMS requirements may adversely impact patient access to certain REMS medications and clinician burden. Health care professionals can provide informed recommendations for improving the REMS programs for clozapine, olanzapine for extended-release injectable suspension, and esketamine.
Related Resources
- FDA. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about REMS. www.fda.gov/drugs/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems/frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-rems
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine extended-release • Sublocade
Buprenorphine transmucosal • Subutex, Suboxone
Clozapine • Clozaril
Esketamine • Spravato
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Loxapine • Adasuve
Olanzapine extended-release injectable suspension • Zyprexa Relprevv
A Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) is a drug safety program the FDA can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks (Box1). The FDA may require medication guides, patient package inserts, communication plans for health care professionals, and/or certain packaging and safe disposal technologies for medications that pose a serious risk of abuse or overdose. The FDA may also require elements to assure safe use and/or an implementation system be included in the REMS. Pharmaceutical manufacturers then develop a proposed REMS for FDA review.2 If the FDA approves the proposed REMS, the manufacturer is responsible for implementing the REMS requirements.
Box
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding psychiatry, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illness. Some of the most common myths include:
The FDA provides this description of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS):
“A [REMS] is a drug safety program that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can require for certain medications with serious safety concerns to help ensure the benefits of the medication outweigh its risks. REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication. While all medications have labeling that informs health care stakeholders about medication risks, only a few medications require a REMS. REMS are not designed to mitigate all the adverse events of a medication, these are communicated to health care providers in the medication’s prescribing information. Rather, REMS focus on preventing, monitoring and/or managing a specific serious risk by informing, educating and/or reinforcing actions to reduce the frequency and/or severity of the event.”1
The REMS program for clozapine3 has been the subject of much discussion in the psychiatric community. The adverse impact of the 2015 update to the clozapine REMS program was emphasized at meetings of both the American Psychiatric Association and the College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists. A white paper published by the National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors shortly after the 2015 update concluded, “clozapine is underused due to a variety of barriers related to the drug and its properties, the health care system, regulatory requirements, and reimbursement issues.”4 After an update to the clozapine REMS program in 2021, the FDA temporarily suspended enforcement of certain requirements due to concerns from health care professionals about patient access to the medication because of problems with implementing the clozapine REMS program.5,6 In November 2022, the FDA issued a second announcement of enforcement discretion related to additional requirements of the REMS program.5 The FDA had previously announced a decision to not take action regarding adherence to REMS requirements for certain laboratory tests in March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic.7
REMS programs for other psychiatric medications may also present challenges. The REMS programs for esketamine8 and olanzapine for extended-release (ER) injectable suspension9 include certain risks that require postadministration monitoring. Some facilities have had to dedicate additional space and clinician time to ensure REMS requirements are met.
To further understand health care professionals’ perspectives regarding the value and burden of these REMS programs, a collaborative effort of the University of Maryland (College Park and Baltimore campuses) Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation with the FDA was undertaken. The REMS for clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine were examined to develop recommendations for improving patient access while ensuring safe medication use and limiting the impact on health care professionals.
Assessing the REMS programs
Focus groups were held with health care professionals nominated by professional organizations to gather their perspectives on the REMS requirements. There was 1 focus group for each of the 3 medications. A facilitator’s guide was developed that contained the details of how to conduct the focus group along with the medication-specific questions. The questions were based on the REMS requirements as of May 2021 and assessed the impact of the REMS on patient safety, patient access, and health care professional workload; effects from the COVID-19 pandemic; and suggestions to improve the REMS programs. The University of Maryland Institutional Review Board reviewed the materials and processes and made the determination of exempt.
Health care professionals were eligible to participate in a focus group if they had ≥1 year of experience working with patients who use the specific medication and ≥6 months of experience within the past year working with the REMS program for that medication. Participants were excluded if they were employed by a pharmaceutical manufacturer or the FDA. The focus groups were conducted virtually using an online conferencing service during summer 2021 and were scheduled for 90 minutes. Prior to the focus group, participants received information from the “Goals” and “Summary” tabs of the FDA REMS website10 for the specific medication along with patient/caregiver guides, which were available for clozapine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension. For each focus group, there was a target sample size of 6 to 9 participants. However, there were only 4 participants in the olanzapine for ER injectable suspension focus group, which we believed was due to lower national utilization of this medication. Individuals were only able to participate in 1 focus group, so the unique participant count for all 3 focus groups totaled 17 (Table 1).

Themes extracted from qualitative analysis of the focus group responses were the value of the REMS programs; registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites; monitoring requirements; care transitions; and COVID considerations (Table 2). While the REMS programs were perceived to increase practitioner and patient awareness of potential harms, discussions centered on the relative cost-to-benefit of the required reporting and other REMS requirements. There were challenges with the registration/enrollment processes and REMS websites that also affected patient care during transitions to different health care settings or clinicians. Patient access was affected by disparities in care related to monitoring requirements and clinician availability.


Continue to: COVID impacted all REMS...
COVID impacted all REMS programs. Physical distancing was an issue for medications that required extensive postadministration monitoring (ie, esketamine and olanzapine for ER injectable suspension). Access to laboratory services was an issue for clozapine.

Medication-specific themes are listed in Table 3 and relate to terms and descriptions in the REMS or additional regulatory requirements from the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). Suggestions for improvement to the REMS are presented in Table 4.

Recommendations for improving REMS
A group consisting of health care professionals, policy experts, and mental health advocates reviewed the information provided by the focus groups and developed the following recommendations.
Overarching recommendations
Each REMS should include a section providing justification for its existence, including a risk analysis of the data regarding the risk the REMS is designed to mitigate. This analysis should be repeated on a regular basis as scientific evidence regarding the risk and its epidemiology evolves. This additional section should also explain how the program requirements of the REMS as implemented (or planned) will achieve the aims of the REMS and weigh the potential benefits of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer vs the potential risks of the REMS requirements as implemented (or planned) by the manufacturer.
Each REMS should have specific quantifiable outcomes. For example, it should specify a reduction in occurrence of the rate of the concerned risk by a specified amount.
Continue to: Ensure adequate...
Ensure adequate stakeholder input during the REMS development and real-world testing in multiple environments before implementing the REMS to identify unanticipated consequences that might impact patient access, patient safety, and health care professional burden. Implementation testing should explore issues such as purchasing and procurement, billing and reimbursement, and relevant factors such as other federal regulations or requirements (eg, the DEA or Medicare).
Ensure harmonization of the REMS forms and processes (eg, initiation and monitoring) for different medications where possible. A prescriber, pharmacist, or system should not face additional barriers to participate in a REMS based on REMS-specific intricacies (ie, prescription systems, data submission systems, or ordering systems). This streamlining will likely decrease clinical inertia to initiate care with the REMS medication, decrease health care professional burden, and improve compliance with REMS requirements.
REMS should anticipate the need for care transitions and employ provisions to ensure seamless care. Considerations should be given to transitions that occur due to:
- Different care settings (eg, inpatient, outpatient, or long-term care)
- Different geographies (eg, patient moves)
- Changes in clinicians, including leaves or absences
- Changes in facilities (eg, pharmacies).
REMS should mirror normal health care professional workflow, including how monitoring data are collected and how and with which frequency pharmacies fill prescriptions.Enhanced information technology to support REMS programs is needed. For example, REMS should be integrated with major electronic patient health record and pharmacy systems to reduce the effort required for clinicians to supply data and automate REMS processes.
For medications that are subject to other agencies and their regulations (eg, the CDC, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or the DEA), REMS should be required to meet all standards of all agencies with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
Continue to: REMS should have a...
REMS should have a standard disclaimer that allows the health care professional to waive certain provisions of the REMS in cases when the specific provisions of the REMS pose a greater risk to the patient than the risk posed by waiving the requirement.
Assure the actions implemented by the industry to meet the requirements for each REMS program are based on peer-reviewed evidence and provide a reasonable expectation to achieve the anticipated benefit.
Ensure that manufacturers make all accumulated REMS data available in a deidentified manner for use by qualified scientific researchers. Additionally, each REMS should have a plan for data access upon initiation and termination of the REMS.
Each REMS should collect data on the performance of the centers and/or personnel who operate the REMS and submit this data for review by qualified outside reviewers. Parameters to assess could include:
- timeliness of response
- timeliness of problem resolution
- data availability and its helpfulness to patient care
- adequacy of resources.
Recommendations for clozapine REMS
These comments relate to the clozapine REMS program prior to the July 2021 announcement that FDA had approved a modification.
Provide a clear definition for “benign ethnic neutropenia.”
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for monitoring. During COVID, the FDA allowed clinicians to “use their best medical judgment in weighing the benefits and risks of continuing treatment in the absence of laboratory testing.”7 This guidance, which allowed flexibility to absolute neutrophil count (ANC) monitoring, was perceived as positive and safe. Before the changes in the REMS requirements, patients with benign ethnic neutropenia were restricted from accessing their medication or encountered harm from additional pharmacotherapy to mitigate ANC levels.
Continue to: Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Recommendations for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension REMS
Provide clear explicit instructions on what is required to have “ready access to emergency services.”
Ensure the REMS include patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring (eg, sedation or blood pressure). Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of olanzapine for ER injectable suspension by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness are included in the REMS. How was the 3-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure the REMS requirements allow for seamless care during transitions, particularly when clinicians are on vacation.
Continue to: Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Recommendations for esketamine REMS
Ensure the REMS includes patient-specific adjustments to allow flexibility for postadministration monitoring. Specific patient groups may have differential access to certain types of facilities, transportation, or other resources. For example, consider the administration of esketamine by a mobile treatment team with an adequate protocol (eg, via videoconferencing or phone calls).
Ensure actions with peer-reviewed evidence demonstrating efficacy/effectiveness of requirements are included in the REMS. How was the 2-hour cut-point determined? Has it been reevaluated?
Ensure that the REMS meet all standards of the DEA, with a single system that accommodates normal health care professional workflow.
A summary of the findings
Overall, the REMS programs for these 3 medications were positively perceived for raising awareness of safe medication use for clinicians and patients. Monitoring patients for safety concerns is important and REMS requirements provide accountability.
Continue to: The use of a single shared...
The use of a single shared REMS system for documenting requirements for clozapine (compared to separate systems for each manufacturer) was a positive move forward in implementation. The focus group welcomed the increased awareness of benign ethnic neutropenia as a result of this condition being incorporated in the revised monitoring requirements of the clozapine REMS.
Focus group participants raised the issue of the real-world efficiency of the REMS programs (reduced access and increased clinician workload) vs the benefits (patient safety). They noted that excessive workload could lead to clinicians becoming unwilling to use a medication that requires a REMS. Clinician workload may be further compromised when REMS logistics disrupt the normal workflow and transitions of care between clinicians or settings. This latter aspect is of particular concern for clozapine.
The complexities of the registration and reporting system for olanzapine for ER injectable suspension and the lack of clarity about monitoring were noted to have discouraged the opening of treatment sites. This scarcity of sites may make clinicians hesitant to use this medication, and instead opt for alternative treatments in patients who may be appropriate candidates.
There has also been limited growth of esketamine treatment sites, especially in comparison to ketamine treatment sites.11-14 Esketamine is FDA-approved for treatment-resistant depression in adults and for depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder with acute suicidal ideation or behavior. Ketamine is not FDA-approved for treating depression but is being used off-label to treat this disorder.15 The FDA determined that ketamine does not require a REMS to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks for its approved indications as an anesthetic agent, anesthesia-inducing agent, or supplement to anesthesia. Since ketamine has no REMS requirements, there may be a lower burden for its use. Thus, clinicians are treating patients for depression with this medication without needing to comply with a REMS.16
Technology plays a role in workload burden, and integrating health care processes within current workflow systems, such as using electronic patient health records and pharmacy systems, is recommended. The FDA has been exploring technologies to facilitate the completion of REMS requirements, including mandatory education within the prescribers’ and pharmacists’ workflow.17 This is a complex task that requires multiple stakeholders with differing perspectives and incentives to align.
Continue to: The data collected for the REMS...
The data collected for the REMS program belongs to the medication’s manufacturer. Current regulations do not require manufacturers to make this data available to qualified scientific researchers. A regulatory mandate to establish data sharing methods would improve transparency and enhance efforts to better understand the outcomes of the REMS programs.
A few caveats
Both the overarching and medication-specific recommendations were based on a small number of participants’ discussions related to clozapine, olanzapine for ER injectable suspension, and esketamine. These recommendations do not include other medications with REMS that are used to treat psychiatric disorders, such as loxapine, buprenorphine ER, and buprenorphine transmucosal products. Larger-scale qualitative and quantitative research is needed to better understand health care professionals’ perspectives. Lastly, some of the recommendations outlined in this article are beyond the current purview or authority of the FDA and may require legislative or regulatory action to implement.
Bottom Line
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) programs are designed to help reduce the occurrence and/or severity of serious risks or to inform decision-making. However, REMS requirements may adversely impact patient access to certain REMS medications and clinician burden. Health care professionals can provide informed recommendations for improving the REMS programs for clozapine, olanzapine for extended-release injectable suspension, and esketamine.
Related Resources
- FDA. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about REMS. www.fda.gov/drugs/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems/frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-rems
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine extended-release • Sublocade
Buprenorphine transmucosal • Subutex, Suboxone
Clozapine • Clozaril
Esketamine • Spravato
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Loxapine • Adasuve
Olanzapine extended-release injectable suspension • Zyprexa Relprevv
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Format and Content of a REMS Document. Guidance for Industry. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/77846/download
3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Clozapine. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=RemsDetails.page&REMS=351
4. The National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors. Clozapine underutilization: addressing the barriers. Accessed September 30, 2019. https://nasmhpd.org/sites/default/files/Assessment%201_Clozapine%20Underutilization.pdf
5. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA is temporarily exercising enforcement discretion with respect to certain clozapine REMS program requirements to ensure continuity of care for patients taking clozapine. Updated November 22, 2022. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-temporarily-exercising-enforcement-discretion-respect-certain-clozapine-rems-program
6. Tanzi M. REMS issues affect clozapine, isotretinoin. Pharmacy Today. 2022;28(3):49.
7. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA provides update on patient access to certain REMS drugs during COVID-19 public health emergency. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-provides-update-patient-access-certain-rems-drugs-during-covid-19
8. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Spravato (esketamine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=386
9. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Zyprexa Relprevv (olanzapine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=74
10. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm
11. Parikh SV, Lopez D, Vande Voort JL, et al. Developing an IV ketamine clinic for treatment-resistant depression: a primer. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2021;51(3):109-124.
12. Dodge D. The ketamine cure. The New York Times. November 4, 2021. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/04/well/ketamine-therapy-depression.html
13. Burton KW. Time for a national ketamine registry, experts say. Medscape. February 15, 2023. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/988310
14. Wilkinson ST, Howard DH, Busch SH. Psychiatric practice patterns and barriers to the adoption of esketamine. JAMA. 2019;322(11):1039-1040. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.10728
15. Wilkinson ST, Toprak M, Turner MS, et al. A survey of the clinical, off-label use of ketamine as a treatment for psychiatric disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(7):695-696. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17020239
16. Pai SM, Gries JM; ACCP Public Policy Committee. Off-label use of ketamine: a challenging drug treatment delivery model with an inherently unfavorable risk-benefit profile. J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;62(1):10-13. doi:10.1002/jcph.1983
17. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) Integration. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://confluence.hl7.org/display/COD/Risk+Evaluation+and+Mitigation+Strategies+%28REMS%29+Integration
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategies-rems
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Format and Content of a REMS Document. Guidance for Industry. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/77846/download
3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Clozapine. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=RemsDetails.page&REMS=351
4. The National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors. Clozapine underutilization: addressing the barriers. Accessed September 30, 2019. https://nasmhpd.org/sites/default/files/Assessment%201_Clozapine%20Underutilization.pdf
5. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA is temporarily exercising enforcement discretion with respect to certain clozapine REMS program requirements to ensure continuity of care for patients taking clozapine. Updated November 22, 2022. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-temporarily-exercising-enforcement-discretion-respect-certain-clozapine-rems-program
6. Tanzi M. REMS issues affect clozapine, isotretinoin. Pharmacy Today. 2022;28(3):49.
7. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA provides update on patient access to certain REMS drugs during COVID-19 public health emergency. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-provides-update-patient-access-certain-rems-drugs-during-covid-19
8. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Spravato (esketamine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=386
9. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Zyprexa Relprevv (olanzapine). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm?event=IndvRemsDetails.page&REMS=74
10. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS). Accessed January 18, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/rems/index.cfm
11. Parikh SV, Lopez D, Vande Voort JL, et al. Developing an IV ketamine clinic for treatment-resistant depression: a primer. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2021;51(3):109-124.
12. Dodge D. The ketamine cure. The New York Times. November 4, 2021. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/04/well/ketamine-therapy-depression.html
13. Burton KW. Time for a national ketamine registry, experts say. Medscape. February 15, 2023. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/988310
14. Wilkinson ST, Howard DH, Busch SH. Psychiatric practice patterns and barriers to the adoption of esketamine. JAMA. 2019;322(11):1039-1040. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.10728
15. Wilkinson ST, Toprak M, Turner MS, et al. A survey of the clinical, off-label use of ketamine as a treatment for psychiatric disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(7):695-696. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17020239
16. Pai SM, Gries JM; ACCP Public Policy Committee. Off-label use of ketamine: a challenging drug treatment delivery model with an inherently unfavorable risk-benefit profile. J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;62(1):10-13. doi:10.1002/jcph.1983
17. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) Integration. Accessed June 1, 2023. https://confluence.hl7.org/display/COD/Risk+Evaluation+and+Mitigation+Strategies+%28REMS%29+Integration
Tips for addressing uptick in mental health visits: Primary care providers collaborate, innovate
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Ketamine may be a viable alternative to ECT for severe depression
“The take-home message right now is that if somebody is being referred for ECT, the treating clinician should think of offering ketamine first,” study investigator Amit Anand, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘Preferred treatment’
More than one-third of cases of depression are treatment resistant, said Dr. Anand, who is also director of Psychiatry Translational Clinical Trials at Mass General Brigham. He noted that ECT has been the “gold standard for treating severe depression for over 80 years.”
He added that although ECT is very effective and is fast acting, “it requires anesthesia, can be socially stigmatizing, and is associated with memory problems following the treatment.”
An anesthetic agent, ketamine has been shown to have rapid antidepressant effects and does not cause memory loss or carry the stigma associated with ECT, he added. For these reasons, the investigators examined whether it may be a viable alternative to ECT.
To date, no large, head-to-head trials have compared ECT to intravenous ketamine. A recent meta-analysis showed that ECT was superior to ketamine for major depression, but the total number of patients included in the analysis was small, Dr. Anand said.
In addition, most of the participants in that trial were drawn from a single center. Approximately 95 patients were enrolled in each arm of the trial, which included some participants with features of psychosis. “ECT is very effective for depression associated with psychotic features, which may be one reason ECT had a better response in that trial,” said Dr. Anand.
The investigators compared ECT to ketamine in a larger sample that excluded patients with psychosis. They randomly assigned 403 patients at five clinical sites in a 1:1 ratio to receive either ketamine or ECT (n = 200 and 203, respectively; 53% and 49.3% women, respectively; aged 45.6 ± 14.8 and 47.1 ± 14.1 years, respectively).
Patients were required to have had an unsatisfactory response to two or more adequate trials of antidepressant treatment.
Prior to initiation of the assigned treatment, 38 patients withdrew, leaving 195 in the ketamine group and 170 in the ECT group.
Treatment was administered over a 3-week period, during which patients received either ECT three times per week or ketamine (0.5 mg/kg of body weight) twice per week.
The primary outcome was treatment response, defined as a decrease of 50% or more from baseline in the16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16). Secondary outcomes included scores on memory tests and patient-reported quality of life.
Patients who had a response were followed for 6 months after the initial treatment phase.
More research needed
Following the 3-week treatment period, a total of 55.4% patients who received ketamine and 41.2% of patients who underwent ECT responded to treatment, which translates into a difference of 14.2 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 3.9-24.2; P < .001) – a finding that fell within the noninferiority threshold set by the investigators.
ECT was associated with decreased memory recall after the 3 weeks of treatment, with a mean (standard deviation) decrease in the T-score for delayed recall on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test–Revised of –0.9 (1.1) in the ketamine group vs. –9.7 (1.2) in the ECT group (difference, –1.8 points [–2.8 to –0.8]).
Remission, determined on the basis of QIDS-SR-16 score, occurred in 32% of the ketamine group and in 20% in the ECT group. Similar findings were seen on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
Both groups showed significant improvements in quality of life, with changes of 12.3 and 12.9 points, respectively, on the 16-item Quality of Life Scale.
“ECT was associated with musculoskeletal adverse events, whereas ketamine was associated with dissociation,” the investigators note.
During the 6-month follow-up period, there were differences in relapse rates between the groups (defined as QIDS-SRS-16 score > 11). At 1 month, the rates were 19.0% for those receiving ketamine and 35.4% for those receiving ECT. At 3 months, the rates were 25.0% and 50.9%, respectively; at 6 months, the rates were 34.5% and 56.3%, respectively.
ECT has been shown to be effective for older adults, patients with MDD and psychosis, and in inpatient and research settings. Future studies are needed to determine the comparative effectiveness of ketamine in these populations, the authors note.
Not life-changing
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, NYU Langone Health, New York, called it an “extraordinarily important and clinically relevant study, large, well-designed, and well-conducted.”
Dr. Iosifescu, director of the clinical research division, Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, N.Y., who was not involved with the study, noted that the study wasn’t powered to determine whether one treatment was superior to the other, but rather it assessed noninferiority.
“The main point of this study is that the two treatments are largely equivalent, although numerically, ketamine was slightly associated with more beneficial outcomes and fewer cognitive side effects,” he said.
The findings suggest “that people who have no contraindications and are candidates for both ketamine and ECT – which is the vast majority of people with treatment-resistant depression – should consider getting ketamine first because it is somewhat easier in terms of side effects and logistics and consider ECT afterwards if the ketamine doesn’t work.”
In an accompanying editorial, Robert Freedman, MD, clinical professor, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that although “3 weeks of lightened mood is undoubtedly a gift ... the results of this current trial suggests that the 3-week treatment was not life-changing,” since effects had largely worn off by 6 months in both groups.
Longer-term treatment with ketamine “increases the likelihood of both drug dependence and cognitive adverse effects, including dissociation, paranoia, and other psychotic symptoms,” Dr. Freedman said.
He recommends that informed consent documents be used to caution patients and clinicians considering ketamine “that temporary relief may come with longer-term costs.”
The study was supported by a grant from PCORI to Dr. Anand. Dr. Freedman has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. In the past 2 years, Dr. Iosifescu has been a consultant for Axsome, Allergan, Biogen, Clexio, Jazz, Neumora, Relmada, and Sage. He has also received a research grant from Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The take-home message right now is that if somebody is being referred for ECT, the treating clinician should think of offering ketamine first,” study investigator Amit Anand, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘Preferred treatment’
More than one-third of cases of depression are treatment resistant, said Dr. Anand, who is also director of Psychiatry Translational Clinical Trials at Mass General Brigham. He noted that ECT has been the “gold standard for treating severe depression for over 80 years.”
He added that although ECT is very effective and is fast acting, “it requires anesthesia, can be socially stigmatizing, and is associated with memory problems following the treatment.”
An anesthetic agent, ketamine has been shown to have rapid antidepressant effects and does not cause memory loss or carry the stigma associated with ECT, he added. For these reasons, the investigators examined whether it may be a viable alternative to ECT.
To date, no large, head-to-head trials have compared ECT to intravenous ketamine. A recent meta-analysis showed that ECT was superior to ketamine for major depression, but the total number of patients included in the analysis was small, Dr. Anand said.
In addition, most of the participants in that trial were drawn from a single center. Approximately 95 patients were enrolled in each arm of the trial, which included some participants with features of psychosis. “ECT is very effective for depression associated with psychotic features, which may be one reason ECT had a better response in that trial,” said Dr. Anand.
The investigators compared ECT to ketamine in a larger sample that excluded patients with psychosis. They randomly assigned 403 patients at five clinical sites in a 1:1 ratio to receive either ketamine or ECT (n = 200 and 203, respectively; 53% and 49.3% women, respectively; aged 45.6 ± 14.8 and 47.1 ± 14.1 years, respectively).
Patients were required to have had an unsatisfactory response to two or more adequate trials of antidepressant treatment.
Prior to initiation of the assigned treatment, 38 patients withdrew, leaving 195 in the ketamine group and 170 in the ECT group.
Treatment was administered over a 3-week period, during which patients received either ECT three times per week or ketamine (0.5 mg/kg of body weight) twice per week.
The primary outcome was treatment response, defined as a decrease of 50% or more from baseline in the16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16). Secondary outcomes included scores on memory tests and patient-reported quality of life.
Patients who had a response were followed for 6 months after the initial treatment phase.
More research needed
Following the 3-week treatment period, a total of 55.4% patients who received ketamine and 41.2% of patients who underwent ECT responded to treatment, which translates into a difference of 14.2 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 3.9-24.2; P < .001) – a finding that fell within the noninferiority threshold set by the investigators.
ECT was associated with decreased memory recall after the 3 weeks of treatment, with a mean (standard deviation) decrease in the T-score for delayed recall on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test–Revised of –0.9 (1.1) in the ketamine group vs. –9.7 (1.2) in the ECT group (difference, –1.8 points [–2.8 to –0.8]).
Remission, determined on the basis of QIDS-SR-16 score, occurred in 32% of the ketamine group and in 20% in the ECT group. Similar findings were seen on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
Both groups showed significant improvements in quality of life, with changes of 12.3 and 12.9 points, respectively, on the 16-item Quality of Life Scale.
“ECT was associated with musculoskeletal adverse events, whereas ketamine was associated with dissociation,” the investigators note.
During the 6-month follow-up period, there were differences in relapse rates between the groups (defined as QIDS-SRS-16 score > 11). At 1 month, the rates were 19.0% for those receiving ketamine and 35.4% for those receiving ECT. At 3 months, the rates were 25.0% and 50.9%, respectively; at 6 months, the rates were 34.5% and 56.3%, respectively.
ECT has been shown to be effective for older adults, patients with MDD and psychosis, and in inpatient and research settings. Future studies are needed to determine the comparative effectiveness of ketamine in these populations, the authors note.
Not life-changing
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, NYU Langone Health, New York, called it an “extraordinarily important and clinically relevant study, large, well-designed, and well-conducted.”
Dr. Iosifescu, director of the clinical research division, Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, N.Y., who was not involved with the study, noted that the study wasn’t powered to determine whether one treatment was superior to the other, but rather it assessed noninferiority.
“The main point of this study is that the two treatments are largely equivalent, although numerically, ketamine was slightly associated with more beneficial outcomes and fewer cognitive side effects,” he said.
The findings suggest “that people who have no contraindications and are candidates for both ketamine and ECT – which is the vast majority of people with treatment-resistant depression – should consider getting ketamine first because it is somewhat easier in terms of side effects and logistics and consider ECT afterwards if the ketamine doesn’t work.”
In an accompanying editorial, Robert Freedman, MD, clinical professor, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that although “3 weeks of lightened mood is undoubtedly a gift ... the results of this current trial suggests that the 3-week treatment was not life-changing,” since effects had largely worn off by 6 months in both groups.
Longer-term treatment with ketamine “increases the likelihood of both drug dependence and cognitive adverse effects, including dissociation, paranoia, and other psychotic symptoms,” Dr. Freedman said.
He recommends that informed consent documents be used to caution patients and clinicians considering ketamine “that temporary relief may come with longer-term costs.”
The study was supported by a grant from PCORI to Dr. Anand. Dr. Freedman has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. In the past 2 years, Dr. Iosifescu has been a consultant for Axsome, Allergan, Biogen, Clexio, Jazz, Neumora, Relmada, and Sage. He has also received a research grant from Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The take-home message right now is that if somebody is being referred for ECT, the treating clinician should think of offering ketamine first,” study investigator Amit Anand, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘Preferred treatment’
More than one-third of cases of depression are treatment resistant, said Dr. Anand, who is also director of Psychiatry Translational Clinical Trials at Mass General Brigham. He noted that ECT has been the “gold standard for treating severe depression for over 80 years.”
He added that although ECT is very effective and is fast acting, “it requires anesthesia, can be socially stigmatizing, and is associated with memory problems following the treatment.”
An anesthetic agent, ketamine has been shown to have rapid antidepressant effects and does not cause memory loss or carry the stigma associated with ECT, he added. For these reasons, the investigators examined whether it may be a viable alternative to ECT.
To date, no large, head-to-head trials have compared ECT to intravenous ketamine. A recent meta-analysis showed that ECT was superior to ketamine for major depression, but the total number of patients included in the analysis was small, Dr. Anand said.
In addition, most of the participants in that trial were drawn from a single center. Approximately 95 patients were enrolled in each arm of the trial, which included some participants with features of psychosis. “ECT is very effective for depression associated with psychotic features, which may be one reason ECT had a better response in that trial,” said Dr. Anand.
The investigators compared ECT to ketamine in a larger sample that excluded patients with psychosis. They randomly assigned 403 patients at five clinical sites in a 1:1 ratio to receive either ketamine or ECT (n = 200 and 203, respectively; 53% and 49.3% women, respectively; aged 45.6 ± 14.8 and 47.1 ± 14.1 years, respectively).
Patients were required to have had an unsatisfactory response to two or more adequate trials of antidepressant treatment.
Prior to initiation of the assigned treatment, 38 patients withdrew, leaving 195 in the ketamine group and 170 in the ECT group.
Treatment was administered over a 3-week period, during which patients received either ECT three times per week or ketamine (0.5 mg/kg of body weight) twice per week.
The primary outcome was treatment response, defined as a decrease of 50% or more from baseline in the16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16). Secondary outcomes included scores on memory tests and patient-reported quality of life.
Patients who had a response were followed for 6 months after the initial treatment phase.
More research needed
Following the 3-week treatment period, a total of 55.4% patients who received ketamine and 41.2% of patients who underwent ECT responded to treatment, which translates into a difference of 14.2 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 3.9-24.2; P < .001) – a finding that fell within the noninferiority threshold set by the investigators.
ECT was associated with decreased memory recall after the 3 weeks of treatment, with a mean (standard deviation) decrease in the T-score for delayed recall on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test–Revised of –0.9 (1.1) in the ketamine group vs. –9.7 (1.2) in the ECT group (difference, –1.8 points [–2.8 to –0.8]).
Remission, determined on the basis of QIDS-SR-16 score, occurred in 32% of the ketamine group and in 20% in the ECT group. Similar findings were seen on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
Both groups showed significant improvements in quality of life, with changes of 12.3 and 12.9 points, respectively, on the 16-item Quality of Life Scale.
“ECT was associated with musculoskeletal adverse events, whereas ketamine was associated with dissociation,” the investigators note.
During the 6-month follow-up period, there were differences in relapse rates between the groups (defined as QIDS-SRS-16 score > 11). At 1 month, the rates were 19.0% for those receiving ketamine and 35.4% for those receiving ECT. At 3 months, the rates were 25.0% and 50.9%, respectively; at 6 months, the rates were 34.5% and 56.3%, respectively.
ECT has been shown to be effective for older adults, patients with MDD and psychosis, and in inpatient and research settings. Future studies are needed to determine the comparative effectiveness of ketamine in these populations, the authors note.
Not life-changing
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, NYU Langone Health, New York, called it an “extraordinarily important and clinically relevant study, large, well-designed, and well-conducted.”
Dr. Iosifescu, director of the clinical research division, Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, N.Y., who was not involved with the study, noted that the study wasn’t powered to determine whether one treatment was superior to the other, but rather it assessed noninferiority.
“The main point of this study is that the two treatments are largely equivalent, although numerically, ketamine was slightly associated with more beneficial outcomes and fewer cognitive side effects,” he said.
The findings suggest “that people who have no contraindications and are candidates for both ketamine and ECT – which is the vast majority of people with treatment-resistant depression – should consider getting ketamine first because it is somewhat easier in terms of side effects and logistics and consider ECT afterwards if the ketamine doesn’t work.”
In an accompanying editorial, Robert Freedman, MD, clinical professor, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that although “3 weeks of lightened mood is undoubtedly a gift ... the results of this current trial suggests that the 3-week treatment was not life-changing,” since effects had largely worn off by 6 months in both groups.
Longer-term treatment with ketamine “increases the likelihood of both drug dependence and cognitive adverse effects, including dissociation, paranoia, and other psychotic symptoms,” Dr. Freedman said.
He recommends that informed consent documents be used to caution patients and clinicians considering ketamine “that temporary relief may come with longer-term costs.”
The study was supported by a grant from PCORI to Dr. Anand. Dr. Freedman has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. In the past 2 years, Dr. Iosifescu has been a consultant for Axsome, Allergan, Biogen, Clexio, Jazz, Neumora, Relmada, and Sage. He has also received a research grant from Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Music therapy helps motivate patients with schizophrenia
SAN FRANCISCO –
Although the study had conflicting results regarding the effects of music therapy on positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thoughts, it consistently shows that music therapy improves negative symptoms, poster presenter Amy Agrawal, MD, VA Boston Healthcare System and instructor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Current antipsychotic drugs aren’t very effective in addressing negative symptoms of schizophrenia, and many patients are noncompliant with these drug regimens because of side effects.
“We need to target the negative symptoms of schizophrenia better,” said Dr. Agrawal. “The antipsychotic medications we have are not enough, so why don’t we start incorporating music therapy groups into the inpatient psychiatry setting as a standard of care?”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Agrawal has long been interested in music. As a child, she was a member of a state choir, but she hadn’t sung for years. After receiving several medals for her clarinet playing during her youth, she stopped playing while in medical school.
Instant boost
During the pandemic, though, she turned back to music and started singing regularly. “I noticed an instant boost in my mood and wondered why I stopped making music for so long, as it made me feel so much happier and calmer.”
She also noticed how music affected her sister, who has paranoid schizophrenia. She described an incident in which her sibling became so loud and paranoid at a restaurant that Dr. Agrawal thought they would be asked to leave.
Then her sister started singing a song she’d sung during a beauty contest years before. “With the music, she calmed right down; she was smiling; she was happy,” said Dr. Agrawal.
That incident made Dr. Agrawal feel, “I had my sister back.” She decided to bring music therapy to her inpatient psychiatry unit and soon noted the benefits for individual patients.
For this new study, Dr. Agrawal and her mentor carried out a literature search. “I was surprised at how many articles popped up, because the field of psychiatry can be very heavily medication based, but people are now getting very interested in this topic,” said Dr. Agrawal.
The review included seven articles, most of which were published within the past 3 years. Some articles specified that the therapy was conducted on an inpatient psychiatric unit, but others didn’t indicate the setting. Studies also didn’t specify whether the therapy was delivered by a trained music therapist.
There was an overall lack of clear measures, graphs, or statistics quantifying the benefits of music therapy on schizophrenia, noted Dr. Agrawal. “But from general statements in the articles, music therapy helped treat sleep disturbances and improved negative symptoms.”
Gets patients socializing
The music, she said, led patients to start socializing, talking about their emotions, and opening up to their clinicians about their mental health symptoms. “Some patients just did not engage at all, and then when the music came on, they would actively participate with the clinician.”
Dancing to music also tended to motivate patients to participate in their treatment, she added. Different forms of movement, such as rhythmic movements and creative exercises, can be added during music therapy.
In addition to improving negative schizophrenia symptoms, music therapy helps with sleep disturbances, depression, and regulating emotional behavior, the research shows. “When patients were agitated or upset, certain music would help them regulate their own affect,” said Dr. Agrawal.
However, it’s not clear from these studies what type of music – classical, rock, country, etc. – was most effective for people.
One article discussed the positive impact of music on patients with schizophrenia while at work. “They seem to have improved work performance,” Dr. Agrawal said.
The length of exposure to music therapy did not seem to make a difference in terms of whether the therapy had a positive effect, she added.
Key research wave
A “key next wave” of research should be to determine whether music therapy decreases the hospital readmission rate, said Dr. Agrawal.
There are several barriers to implementing music therapy programs in hospitals, including cost, the availability of trained therapists, and time constraints, she said.
“Regardless of the barriers, hospital administrators and psychiatrists need to know about this research so they will invest more efforts in recruiting music therapists and incorporating music group therapy into standard clinical practice for psychiatric patients so there are better clinical outcomes.”
Commenting on the research, Michelle B. Riba, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said the study adds to the literature “and helps us think about adjunctive treatments in a very difficult population.”
She added, “It’s good to see physicians get interested in this topic.”
Difficult topic to study
Although she found the review “very limited,” she recognizes the difficulty of studying music therapy on in-patient psychiatry units.
“Patients are there for short stays, most are getting other treatments, and it’s hard to segment people into negative vs. positive. Also, the ages and genders are different, and their previous treatments are different.”
While it’s sometimes difficult to conduct major research on a topic, “that doesn’t mean we can’t help people,” said Dr. Riba.
She noted that music therapy is beneficial not only for patients with schizophrenia but also is “soothing and relaxing” for those with other conditions. She runs a psychiatric oncology program at her institution’s cancer center, which offers music therapy along with art therapy.
Kevin M. Malone, MD, of University College Dublin, also has firsthand experience with music therapy. “We had a terrific music therapist as part of our clinical psychosis team,” he said in an interview.
The music therapist is no longer there, but, he said, “as far as I’m concerned, every clinical psychosis team should have a music therapist as an essential team member.”
Dr. Agrawal, Dr. Riba, and Dr. Malone had no reported disclosures.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO –
Although the study had conflicting results regarding the effects of music therapy on positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thoughts, it consistently shows that music therapy improves negative symptoms, poster presenter Amy Agrawal, MD, VA Boston Healthcare System and instructor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Current antipsychotic drugs aren’t very effective in addressing negative symptoms of schizophrenia, and many patients are noncompliant with these drug regimens because of side effects.
“We need to target the negative symptoms of schizophrenia better,” said Dr. Agrawal. “The antipsychotic medications we have are not enough, so why don’t we start incorporating music therapy groups into the inpatient psychiatry setting as a standard of care?”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Agrawal has long been interested in music. As a child, she was a member of a state choir, but she hadn’t sung for years. After receiving several medals for her clarinet playing during her youth, she stopped playing while in medical school.
Instant boost
During the pandemic, though, she turned back to music and started singing regularly. “I noticed an instant boost in my mood and wondered why I stopped making music for so long, as it made me feel so much happier and calmer.”
She also noticed how music affected her sister, who has paranoid schizophrenia. She described an incident in which her sibling became so loud and paranoid at a restaurant that Dr. Agrawal thought they would be asked to leave.
Then her sister started singing a song she’d sung during a beauty contest years before. “With the music, she calmed right down; she was smiling; she was happy,” said Dr. Agrawal.
That incident made Dr. Agrawal feel, “I had my sister back.” She decided to bring music therapy to her inpatient psychiatry unit and soon noted the benefits for individual patients.
For this new study, Dr. Agrawal and her mentor carried out a literature search. “I was surprised at how many articles popped up, because the field of psychiatry can be very heavily medication based, but people are now getting very interested in this topic,” said Dr. Agrawal.
The review included seven articles, most of which were published within the past 3 years. Some articles specified that the therapy was conducted on an inpatient psychiatric unit, but others didn’t indicate the setting. Studies also didn’t specify whether the therapy was delivered by a trained music therapist.
There was an overall lack of clear measures, graphs, or statistics quantifying the benefits of music therapy on schizophrenia, noted Dr. Agrawal. “But from general statements in the articles, music therapy helped treat sleep disturbances and improved negative symptoms.”
Gets patients socializing
The music, she said, led patients to start socializing, talking about their emotions, and opening up to their clinicians about their mental health symptoms. “Some patients just did not engage at all, and then when the music came on, they would actively participate with the clinician.”
Dancing to music also tended to motivate patients to participate in their treatment, she added. Different forms of movement, such as rhythmic movements and creative exercises, can be added during music therapy.
In addition to improving negative schizophrenia symptoms, music therapy helps with sleep disturbances, depression, and regulating emotional behavior, the research shows. “When patients were agitated or upset, certain music would help them regulate their own affect,” said Dr. Agrawal.
However, it’s not clear from these studies what type of music – classical, rock, country, etc. – was most effective for people.
One article discussed the positive impact of music on patients with schizophrenia while at work. “They seem to have improved work performance,” Dr. Agrawal said.
The length of exposure to music therapy did not seem to make a difference in terms of whether the therapy had a positive effect, she added.
Key research wave
A “key next wave” of research should be to determine whether music therapy decreases the hospital readmission rate, said Dr. Agrawal.
There are several barriers to implementing music therapy programs in hospitals, including cost, the availability of trained therapists, and time constraints, she said.
“Regardless of the barriers, hospital administrators and psychiatrists need to know about this research so they will invest more efforts in recruiting music therapists and incorporating music group therapy into standard clinical practice for psychiatric patients so there are better clinical outcomes.”
Commenting on the research, Michelle B. Riba, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said the study adds to the literature “and helps us think about adjunctive treatments in a very difficult population.”
She added, “It’s good to see physicians get interested in this topic.”
Difficult topic to study
Although she found the review “very limited,” she recognizes the difficulty of studying music therapy on in-patient psychiatry units.
“Patients are there for short stays, most are getting other treatments, and it’s hard to segment people into negative vs. positive. Also, the ages and genders are different, and their previous treatments are different.”
While it’s sometimes difficult to conduct major research on a topic, “that doesn’t mean we can’t help people,” said Dr. Riba.
She noted that music therapy is beneficial not only for patients with schizophrenia but also is “soothing and relaxing” for those with other conditions. She runs a psychiatric oncology program at her institution’s cancer center, which offers music therapy along with art therapy.
Kevin M. Malone, MD, of University College Dublin, also has firsthand experience with music therapy. “We had a terrific music therapist as part of our clinical psychosis team,” he said in an interview.
The music therapist is no longer there, but, he said, “as far as I’m concerned, every clinical psychosis team should have a music therapist as an essential team member.”
Dr. Agrawal, Dr. Riba, and Dr. Malone had no reported disclosures.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO –
Although the study had conflicting results regarding the effects of music therapy on positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thoughts, it consistently shows that music therapy improves negative symptoms, poster presenter Amy Agrawal, MD, VA Boston Healthcare System and instructor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Current antipsychotic drugs aren’t very effective in addressing negative symptoms of schizophrenia, and many patients are noncompliant with these drug regimens because of side effects.
“We need to target the negative symptoms of schizophrenia better,” said Dr. Agrawal. “The antipsychotic medications we have are not enough, so why don’t we start incorporating music therapy groups into the inpatient psychiatry setting as a standard of care?”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Agrawal has long been interested in music. As a child, she was a member of a state choir, but she hadn’t sung for years. After receiving several medals for her clarinet playing during her youth, she stopped playing while in medical school.
Instant boost
During the pandemic, though, she turned back to music and started singing regularly. “I noticed an instant boost in my mood and wondered why I stopped making music for so long, as it made me feel so much happier and calmer.”
She also noticed how music affected her sister, who has paranoid schizophrenia. She described an incident in which her sibling became so loud and paranoid at a restaurant that Dr. Agrawal thought they would be asked to leave.
Then her sister started singing a song she’d sung during a beauty contest years before. “With the music, she calmed right down; she was smiling; she was happy,” said Dr. Agrawal.
That incident made Dr. Agrawal feel, “I had my sister back.” She decided to bring music therapy to her inpatient psychiatry unit and soon noted the benefits for individual patients.
For this new study, Dr. Agrawal and her mentor carried out a literature search. “I was surprised at how many articles popped up, because the field of psychiatry can be very heavily medication based, but people are now getting very interested in this topic,” said Dr. Agrawal.
The review included seven articles, most of which were published within the past 3 years. Some articles specified that the therapy was conducted on an inpatient psychiatric unit, but others didn’t indicate the setting. Studies also didn’t specify whether the therapy was delivered by a trained music therapist.
There was an overall lack of clear measures, graphs, or statistics quantifying the benefits of music therapy on schizophrenia, noted Dr. Agrawal. “But from general statements in the articles, music therapy helped treat sleep disturbances and improved negative symptoms.”
Gets patients socializing
The music, she said, led patients to start socializing, talking about their emotions, and opening up to their clinicians about their mental health symptoms. “Some patients just did not engage at all, and then when the music came on, they would actively participate with the clinician.”
Dancing to music also tended to motivate patients to participate in their treatment, she added. Different forms of movement, such as rhythmic movements and creative exercises, can be added during music therapy.
In addition to improving negative schizophrenia symptoms, music therapy helps with sleep disturbances, depression, and regulating emotional behavior, the research shows. “When patients were agitated or upset, certain music would help them regulate their own affect,” said Dr. Agrawal.
However, it’s not clear from these studies what type of music – classical, rock, country, etc. – was most effective for people.
One article discussed the positive impact of music on patients with schizophrenia while at work. “They seem to have improved work performance,” Dr. Agrawal said.
The length of exposure to music therapy did not seem to make a difference in terms of whether the therapy had a positive effect, she added.
Key research wave
A “key next wave” of research should be to determine whether music therapy decreases the hospital readmission rate, said Dr. Agrawal.
There are several barriers to implementing music therapy programs in hospitals, including cost, the availability of trained therapists, and time constraints, she said.
“Regardless of the barriers, hospital administrators and psychiatrists need to know about this research so they will invest more efforts in recruiting music therapists and incorporating music group therapy into standard clinical practice for psychiatric patients so there are better clinical outcomes.”
Commenting on the research, Michelle B. Riba, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said the study adds to the literature “and helps us think about adjunctive treatments in a very difficult population.”
She added, “It’s good to see physicians get interested in this topic.”
Difficult topic to study
Although she found the review “very limited,” she recognizes the difficulty of studying music therapy on in-patient psychiatry units.
“Patients are there for short stays, most are getting other treatments, and it’s hard to segment people into negative vs. positive. Also, the ages and genders are different, and their previous treatments are different.”
While it’s sometimes difficult to conduct major research on a topic, “that doesn’t mean we can’t help people,” said Dr. Riba.
She noted that music therapy is beneficial not only for patients with schizophrenia but also is “soothing and relaxing” for those with other conditions. She runs a psychiatric oncology program at her institution’s cancer center, which offers music therapy along with art therapy.
Kevin M. Malone, MD, of University College Dublin, also has firsthand experience with music therapy. “We had a terrific music therapist as part of our clinical psychosis team,” he said in an interview.
The music therapist is no longer there, but, he said, “as far as I’m concerned, every clinical psychosis team should have a music therapist as an essential team member.”
Dr. Agrawal, Dr. Riba, and Dr. Malone had no reported disclosures.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
AT APA 2023
Psychiatrists: Don’t fear clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia
SAN FRANCISCO – A trio of psychiatrists urged colleagues at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association to embrace the venerable antipsychotic clozapine in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. They cautioned that clinicians may overestimate the true risk of the adverse effect of neutropenia in minority populations.
“Although clozapine is known to be a life-improving and even potentially lifesaving treatment, it remains underutilized in the U.S.,” said Claire C. Holderness, MD, a psychiatrist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “It’s been estimated that between 35% and 40% of all patients with schizophrenia should be considered for a clozapine trial. However, only 4%-5% of patients with schizophrenia in the U.S. have ever received clozapine. This is in sharp contrast to other industrialized countries where approximately 20% or more of patients with schizophrenia are treated with clozapine.”
According to Dr. Holderness, research has shown that clozapine is even less likely to be prescribed to racial and ethnic minorities. A 2022 systematic review, for example, found that Black patients in the United States had between one-third and two-thirds the odds of being treated with the drug, compared with White patients after adjustment for potential confounders such as demographics. Hispanic/Latino patients were also less likely than Whites to be prescribed the drug.
As Dr. Holderness put it, the drug “been shown to be more effective in treatment-resistant schizophrenia than any other antipsychotic medication. Clozapine is also the most cost-effective treatment for treatment-resistant schizophrenia.” So why does this disparity exist despite clozapine’s benefits?
A 2018 systematic review of barriers to the drug’s usage identified several factors: “mandatory blood testing, fear of serious side-effects and lack of adherence by the patients, difficulty in identifying suitable patients, service fragmentation, and inadequate training in or exposure to using clozapine.” A 2016 British study, meanwhile, looked at the reasons that 45% of 316 patients stopped clozapine before 2 years. More than half of these patients stopped because of adverse effects.
Risk of neutropenia
At the APA presentation, psychiatrist Laura Clarke, MD, also of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, noted that there’s concern about one adverse effect in particular: neutropenia, or an abnormally low white blood cell count. Clozapine, she said, has a boxed warning about severe neutropenia that can lead to death.
However, she cautioned that white blood cell counts can be misleading. Some people in non-White ethnic groups have a condition known as benign ethnic neutropenia: their white blood cell counts are abnormal by the standards of people of European heritage, but they’re otherwise healthy. “These individuals do not show an increased risk of infections, and their response to infection is similar to those without them,” she said.
As many as 25%-50% of people of African ancestry may have benign ethnic neutropenia, making their blood levels appear abnormally low. Others with higher levels of the condition include certain Middle Eastern ethnicities and other ethnic groups with darker skin.
In these patents, “clinicians may avoid prescribing clozapine out of the mistaken concern that it can worsen neutropenia,” Dr. Clarke said. In fact, benign ethnic neutropenia “does not increase the risk of clozapine-induced severe neutropenia.”
Dr. Clarke highlighted drug use guidelines from the Clozapine Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, a Food and Drug Administration–mandated safety program designed to prevent severe neutropenia in patients taking clozapine. The guidelines note that the recommended absolute neutrophil count monitoring algorithm differs when patients are diagnosed with benign ethnic neutropenia.
T. Scott Stroup, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist at Columbia University, New York, urged his colleagues to consider clozapine early on in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. “Don’t go through three, four, or five antipsychotics. Even after trying two, I’d encourage people to [try clozapine].”
However, he acknowledged that “not everyone believes that. Many of my colleagues think that, before you try clozapine, you should have a trial of long-acting injectable medications to rule out pseudo–treatment resistance. I don’t totally agree with that, but I’ve more or less lost that battle,” he added.
In the big picture, Dr. Stroup said, clozapine “is good when other things aren’t working efficacy wise.”
Dr. Holderness and Dr. Clarke have no disclosures. Dr. Stroup discloses grants from the National Institutes of Health and royalties from APA Publishing and UpToDate.
SAN FRANCISCO – A trio of psychiatrists urged colleagues at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association to embrace the venerable antipsychotic clozapine in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. They cautioned that clinicians may overestimate the true risk of the adverse effect of neutropenia in minority populations.
“Although clozapine is known to be a life-improving and even potentially lifesaving treatment, it remains underutilized in the U.S.,” said Claire C. Holderness, MD, a psychiatrist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “It’s been estimated that between 35% and 40% of all patients with schizophrenia should be considered for a clozapine trial. However, only 4%-5% of patients with schizophrenia in the U.S. have ever received clozapine. This is in sharp contrast to other industrialized countries where approximately 20% or more of patients with schizophrenia are treated with clozapine.”
According to Dr. Holderness, research has shown that clozapine is even less likely to be prescribed to racial and ethnic minorities. A 2022 systematic review, for example, found that Black patients in the United States had between one-third and two-thirds the odds of being treated with the drug, compared with White patients after adjustment for potential confounders such as demographics. Hispanic/Latino patients were also less likely than Whites to be prescribed the drug.
As Dr. Holderness put it, the drug “been shown to be more effective in treatment-resistant schizophrenia than any other antipsychotic medication. Clozapine is also the most cost-effective treatment for treatment-resistant schizophrenia.” So why does this disparity exist despite clozapine’s benefits?
A 2018 systematic review of barriers to the drug’s usage identified several factors: “mandatory blood testing, fear of serious side-effects and lack of adherence by the patients, difficulty in identifying suitable patients, service fragmentation, and inadequate training in or exposure to using clozapine.” A 2016 British study, meanwhile, looked at the reasons that 45% of 316 patients stopped clozapine before 2 years. More than half of these patients stopped because of adverse effects.
Risk of neutropenia
At the APA presentation, psychiatrist Laura Clarke, MD, also of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, noted that there’s concern about one adverse effect in particular: neutropenia, or an abnormally low white blood cell count. Clozapine, she said, has a boxed warning about severe neutropenia that can lead to death.
However, she cautioned that white blood cell counts can be misleading. Some people in non-White ethnic groups have a condition known as benign ethnic neutropenia: their white blood cell counts are abnormal by the standards of people of European heritage, but they’re otherwise healthy. “These individuals do not show an increased risk of infections, and their response to infection is similar to those without them,” she said.
As many as 25%-50% of people of African ancestry may have benign ethnic neutropenia, making their blood levels appear abnormally low. Others with higher levels of the condition include certain Middle Eastern ethnicities and other ethnic groups with darker skin.
In these patents, “clinicians may avoid prescribing clozapine out of the mistaken concern that it can worsen neutropenia,” Dr. Clarke said. In fact, benign ethnic neutropenia “does not increase the risk of clozapine-induced severe neutropenia.”
Dr. Clarke highlighted drug use guidelines from the Clozapine Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, a Food and Drug Administration–mandated safety program designed to prevent severe neutropenia in patients taking clozapine. The guidelines note that the recommended absolute neutrophil count monitoring algorithm differs when patients are diagnosed with benign ethnic neutropenia.
T. Scott Stroup, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist at Columbia University, New York, urged his colleagues to consider clozapine early on in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. “Don’t go through three, four, or five antipsychotics. Even after trying two, I’d encourage people to [try clozapine].”
However, he acknowledged that “not everyone believes that. Many of my colleagues think that, before you try clozapine, you should have a trial of long-acting injectable medications to rule out pseudo–treatment resistance. I don’t totally agree with that, but I’ve more or less lost that battle,” he added.
In the big picture, Dr. Stroup said, clozapine “is good when other things aren’t working efficacy wise.”
Dr. Holderness and Dr. Clarke have no disclosures. Dr. Stroup discloses grants from the National Institutes of Health and royalties from APA Publishing and UpToDate.
SAN FRANCISCO – A trio of psychiatrists urged colleagues at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association to embrace the venerable antipsychotic clozapine in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. They cautioned that clinicians may overestimate the true risk of the adverse effect of neutropenia in minority populations.
“Although clozapine is known to be a life-improving and even potentially lifesaving treatment, it remains underutilized in the U.S.,” said Claire C. Holderness, MD, a psychiatrist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “It’s been estimated that between 35% and 40% of all patients with schizophrenia should be considered for a clozapine trial. However, only 4%-5% of patients with schizophrenia in the U.S. have ever received clozapine. This is in sharp contrast to other industrialized countries where approximately 20% or more of patients with schizophrenia are treated with clozapine.”
According to Dr. Holderness, research has shown that clozapine is even less likely to be prescribed to racial and ethnic minorities. A 2022 systematic review, for example, found that Black patients in the United States had between one-third and two-thirds the odds of being treated with the drug, compared with White patients after adjustment for potential confounders such as demographics. Hispanic/Latino patients were also less likely than Whites to be prescribed the drug.
As Dr. Holderness put it, the drug “been shown to be more effective in treatment-resistant schizophrenia than any other antipsychotic medication. Clozapine is also the most cost-effective treatment for treatment-resistant schizophrenia.” So why does this disparity exist despite clozapine’s benefits?
A 2018 systematic review of barriers to the drug’s usage identified several factors: “mandatory blood testing, fear of serious side-effects and lack of adherence by the patients, difficulty in identifying suitable patients, service fragmentation, and inadequate training in or exposure to using clozapine.” A 2016 British study, meanwhile, looked at the reasons that 45% of 316 patients stopped clozapine before 2 years. More than half of these patients stopped because of adverse effects.
Risk of neutropenia
At the APA presentation, psychiatrist Laura Clarke, MD, also of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, noted that there’s concern about one adverse effect in particular: neutropenia, or an abnormally low white blood cell count. Clozapine, she said, has a boxed warning about severe neutropenia that can lead to death.
However, she cautioned that white blood cell counts can be misleading. Some people in non-White ethnic groups have a condition known as benign ethnic neutropenia: their white blood cell counts are abnormal by the standards of people of European heritage, but they’re otherwise healthy. “These individuals do not show an increased risk of infections, and their response to infection is similar to those without them,” she said.
As many as 25%-50% of people of African ancestry may have benign ethnic neutropenia, making their blood levels appear abnormally low. Others with higher levels of the condition include certain Middle Eastern ethnicities and other ethnic groups with darker skin.
In these patents, “clinicians may avoid prescribing clozapine out of the mistaken concern that it can worsen neutropenia,” Dr. Clarke said. In fact, benign ethnic neutropenia “does not increase the risk of clozapine-induced severe neutropenia.”
Dr. Clarke highlighted drug use guidelines from the Clozapine Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, a Food and Drug Administration–mandated safety program designed to prevent severe neutropenia in patients taking clozapine. The guidelines note that the recommended absolute neutrophil count monitoring algorithm differs when patients are diagnosed with benign ethnic neutropenia.
T. Scott Stroup, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist at Columbia University, New York, urged his colleagues to consider clozapine early on in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. “Don’t go through three, four, or five antipsychotics. Even after trying two, I’d encourage people to [try clozapine].”
However, he acknowledged that “not everyone believes that. Many of my colleagues think that, before you try clozapine, you should have a trial of long-acting injectable medications to rule out pseudo–treatment resistance. I don’t totally agree with that, but I’ve more or less lost that battle,” he added.
In the big picture, Dr. Stroup said, clozapine “is good when other things aren’t working efficacy wise.”
Dr. Holderness and Dr. Clarke have no disclosures. Dr. Stroup discloses grants from the National Institutes of Health and royalties from APA Publishing and UpToDate.
AT APA 2023
When a patient wants to stop taking their antipsychotic: Be ‘A SPORT’
For patients with schizophrenia, adherence to antipsychotic treatment reduces the rate of relapse of psychosis, lowers the rate of rehospitalization, and reduces the severity of illness.1 Despite this, patients may want to discontinue their medications for multiple reasons, including limited insight, adverse effects, or a negative attitude toward medication.1 Understanding a patient’s reason for wanting to discontinue their antipsychotic is critical to providing patient-centered care, building the therapeutic alliance, and offering potential solutions.
Clinicians can recall the mnemonic “A SPORT” (Table) to help ensure they have a thorough discussion with patients about the risks of discontinuation and potential solutions.

Points to cover
First, explore and acknowledge if a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, which may be causing them to have a negative attitude toward medications. If a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, offer interventions to mitigate those effects, such as adding an anticholinergic agent to address extrapyramidal symptoms. Decreasing the antipsychotic dosage might reduce the adverse effects burden while still optimizing the benefits from the antipsychotic. Additionally, switching to an alternate medication with a more favorable adverse effect profile may be an option. Whether the patient is experiencing intolerable adverse effects or just has a negative view of their prescribed antipsychotic, it is important to discuss switching medications.
Identifying patient attitudes and their general perspective toward their medication and illness is key. Similarly, a patient’s impaired insight into their mental illness has been associated with treatment discontinuation.2 A strong therapeutic alliance with your patient is of the utmost importance in these situations.
Long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) are useful clinical tools for patients who struggle to adhere to oral medications. Educating patients and caregivers about other formulations—namely LAIs—can help clarify any misconceptions they may have. One study found that patients who were prescribed oral antipsychotics thought LAIs would be painful, have worse adverse effects, and would not be beneficial in preventing relapse.3 In addition to LAIs, other formulations of antipsychotic medications, such as patches, sublingual tablets, or liquids, may be an option.
For patients to be able to provide informed consent regarding the decision to discontinue their antipsychotic, it is important to educate them about the risks of not taking an antipsychotic, such as an increased risk of relapse, hospitalization, and poor outcomes. Explain that patients with first-episode psychosis who achieve remission of symptoms while taking an antipsychotic can remain in remission with continued treatment, but there is a 5-fold increased risk of relapse when discontinuing an antipsychotic during first-episode psychosis.4
Lastly, despite discussing the risks and benefits, if a patient is determined to discontinue their antipsychotic, we recommend a slow taper of medication rather than abrupt discontinuation. Research has shown that more than one-half of patients who abruptly discontinue an antipsychotic experience withdrawal symptoms, including (but not limited to) nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and headaches, as well as anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia.5 These symptoms may occur within 4 weeks after discontinuation.5 While there are no clear guidelines on deprescribing antipsychotics, it is best to individualize the taper based on patient response. Family and caregiver involvement, close follow-up, and symptom monitoring should be integrated into the tapering process.6
1. Velligan DI, Sajatovic M, Hatch A, et al. Why do psychiatric patients stop antipsychotic medication? A systematic review of reasons for nonadherence to medication in patients with serious mental illness. Patient Prefer Adherenc. 2017;11:449-468. doi:10.2147/PPA.S124658
2. Kim J, Ozzoude M, Nakajima S, et al. Insight and medication adherence in schizophrenia: an analysis of the CATIE trial. Neuropharmacology. 2020;168:107634. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.011
3. Sugawara N, Kudo S, Ishioka M, et al. Attitudes toward long-acting injectable antipsychotics among patients with schizophrenia in Japan. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:205-211. doi:10.2147/NDT.S188337
4. Winton-Brown TT, Elanjithara T, Power P, et al. Five-fold increased risk of relapse following breaks in antipsychotic treatment of first episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2017;179:50-56. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.09.029
5. Brandt L, Bschor T, Henssler J, et al. Antipsychotic withdrawal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:569912. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.569912
6. Gupta S, Cahill JD, Miller R. Deprescribing antipsychotics: a guide for clinicians. BJPsych Advances. 2018;24(5):295-302. doi:10.1192/bja.2018.2
For patients with schizophrenia, adherence to antipsychotic treatment reduces the rate of relapse of psychosis, lowers the rate of rehospitalization, and reduces the severity of illness.1 Despite this, patients may want to discontinue their medications for multiple reasons, including limited insight, adverse effects, or a negative attitude toward medication.1 Understanding a patient’s reason for wanting to discontinue their antipsychotic is critical to providing patient-centered care, building the therapeutic alliance, and offering potential solutions.
Clinicians can recall the mnemonic “A SPORT” (Table) to help ensure they have a thorough discussion with patients about the risks of discontinuation and potential solutions.

Points to cover
First, explore and acknowledge if a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, which may be causing them to have a negative attitude toward medications. If a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, offer interventions to mitigate those effects, such as adding an anticholinergic agent to address extrapyramidal symptoms. Decreasing the antipsychotic dosage might reduce the adverse effects burden while still optimizing the benefits from the antipsychotic. Additionally, switching to an alternate medication with a more favorable adverse effect profile may be an option. Whether the patient is experiencing intolerable adverse effects or just has a negative view of their prescribed antipsychotic, it is important to discuss switching medications.
Identifying patient attitudes and their general perspective toward their medication and illness is key. Similarly, a patient’s impaired insight into their mental illness has been associated with treatment discontinuation.2 A strong therapeutic alliance with your patient is of the utmost importance in these situations.
Long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) are useful clinical tools for patients who struggle to adhere to oral medications. Educating patients and caregivers about other formulations—namely LAIs—can help clarify any misconceptions they may have. One study found that patients who were prescribed oral antipsychotics thought LAIs would be painful, have worse adverse effects, and would not be beneficial in preventing relapse.3 In addition to LAIs, other formulations of antipsychotic medications, such as patches, sublingual tablets, or liquids, may be an option.
For patients to be able to provide informed consent regarding the decision to discontinue their antipsychotic, it is important to educate them about the risks of not taking an antipsychotic, such as an increased risk of relapse, hospitalization, and poor outcomes. Explain that patients with first-episode psychosis who achieve remission of symptoms while taking an antipsychotic can remain in remission with continued treatment, but there is a 5-fold increased risk of relapse when discontinuing an antipsychotic during first-episode psychosis.4
Lastly, despite discussing the risks and benefits, if a patient is determined to discontinue their antipsychotic, we recommend a slow taper of medication rather than abrupt discontinuation. Research has shown that more than one-half of patients who abruptly discontinue an antipsychotic experience withdrawal symptoms, including (but not limited to) nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and headaches, as well as anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia.5 These symptoms may occur within 4 weeks after discontinuation.5 While there are no clear guidelines on deprescribing antipsychotics, it is best to individualize the taper based on patient response. Family and caregiver involvement, close follow-up, and symptom monitoring should be integrated into the tapering process.6
For patients with schizophrenia, adherence to antipsychotic treatment reduces the rate of relapse of psychosis, lowers the rate of rehospitalization, and reduces the severity of illness.1 Despite this, patients may want to discontinue their medications for multiple reasons, including limited insight, adverse effects, or a negative attitude toward medication.1 Understanding a patient’s reason for wanting to discontinue their antipsychotic is critical to providing patient-centered care, building the therapeutic alliance, and offering potential solutions.
Clinicians can recall the mnemonic “A SPORT” (Table) to help ensure they have a thorough discussion with patients about the risks of discontinuation and potential solutions.

Points to cover
First, explore and acknowledge if a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, which may be causing them to have a negative attitude toward medications. If a patient is experiencing adverse effects from their antipsychotic, offer interventions to mitigate those effects, such as adding an anticholinergic agent to address extrapyramidal symptoms. Decreasing the antipsychotic dosage might reduce the adverse effects burden while still optimizing the benefits from the antipsychotic. Additionally, switching to an alternate medication with a more favorable adverse effect profile may be an option. Whether the patient is experiencing intolerable adverse effects or just has a negative view of their prescribed antipsychotic, it is important to discuss switching medications.
Identifying patient attitudes and their general perspective toward their medication and illness is key. Similarly, a patient’s impaired insight into their mental illness has been associated with treatment discontinuation.2 A strong therapeutic alliance with your patient is of the utmost importance in these situations.
Long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) are useful clinical tools for patients who struggle to adhere to oral medications. Educating patients and caregivers about other formulations—namely LAIs—can help clarify any misconceptions they may have. One study found that patients who were prescribed oral antipsychotics thought LAIs would be painful, have worse adverse effects, and would not be beneficial in preventing relapse.3 In addition to LAIs, other formulations of antipsychotic medications, such as patches, sublingual tablets, or liquids, may be an option.
For patients to be able to provide informed consent regarding the decision to discontinue their antipsychotic, it is important to educate them about the risks of not taking an antipsychotic, such as an increased risk of relapse, hospitalization, and poor outcomes. Explain that patients with first-episode psychosis who achieve remission of symptoms while taking an antipsychotic can remain in remission with continued treatment, but there is a 5-fold increased risk of relapse when discontinuing an antipsychotic during first-episode psychosis.4
Lastly, despite discussing the risks and benefits, if a patient is determined to discontinue their antipsychotic, we recommend a slow taper of medication rather than abrupt discontinuation. Research has shown that more than one-half of patients who abruptly discontinue an antipsychotic experience withdrawal symptoms, including (but not limited to) nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and headaches, as well as anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia.5 These symptoms may occur within 4 weeks after discontinuation.5 While there are no clear guidelines on deprescribing antipsychotics, it is best to individualize the taper based on patient response. Family and caregiver involvement, close follow-up, and symptom monitoring should be integrated into the tapering process.6
1. Velligan DI, Sajatovic M, Hatch A, et al. Why do psychiatric patients stop antipsychotic medication? A systematic review of reasons for nonadherence to medication in patients with serious mental illness. Patient Prefer Adherenc. 2017;11:449-468. doi:10.2147/PPA.S124658
2. Kim J, Ozzoude M, Nakajima S, et al. Insight and medication adherence in schizophrenia: an analysis of the CATIE trial. Neuropharmacology. 2020;168:107634. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.011
3. Sugawara N, Kudo S, Ishioka M, et al. Attitudes toward long-acting injectable antipsychotics among patients with schizophrenia in Japan. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:205-211. doi:10.2147/NDT.S188337
4. Winton-Brown TT, Elanjithara T, Power P, et al. Five-fold increased risk of relapse following breaks in antipsychotic treatment of first episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2017;179:50-56. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.09.029
5. Brandt L, Bschor T, Henssler J, et al. Antipsychotic withdrawal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:569912. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.569912
6. Gupta S, Cahill JD, Miller R. Deprescribing antipsychotics: a guide for clinicians. BJPsych Advances. 2018;24(5):295-302. doi:10.1192/bja.2018.2
1. Velligan DI, Sajatovic M, Hatch A, et al. Why do psychiatric patients stop antipsychotic medication? A systematic review of reasons for nonadherence to medication in patients with serious mental illness. Patient Prefer Adherenc. 2017;11:449-468. doi:10.2147/PPA.S124658
2. Kim J, Ozzoude M, Nakajima S, et al. Insight and medication adherence in schizophrenia: an analysis of the CATIE trial. Neuropharmacology. 2020;168:107634. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.011
3. Sugawara N, Kudo S, Ishioka M, et al. Attitudes toward long-acting injectable antipsychotics among patients with schizophrenia in Japan. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:205-211. doi:10.2147/NDT.S188337
4. Winton-Brown TT, Elanjithara T, Power P, et al. Five-fold increased risk of relapse following breaks in antipsychotic treatment of first episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2017;179:50-56. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.09.029
5. Brandt L, Bschor T, Henssler J, et al. Antipsychotic withdrawal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:569912. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.569912
6. Gupta S, Cahill JD, Miller R. Deprescribing antipsychotics: a guide for clinicians. BJPsych Advances. 2018;24(5):295-302. doi:10.1192/bja.2018.2