User login
E-Consults in Dermatology: A Retrospective Analysis
Dermatologic conditions affect approximately one-third of individuals in the United States.1,2 Nearly 1 in 4 physician office visits in the United States are for skin conditions, and less than one-third of these visits are with dermatologists. Although many of these patients may prefer to see a dermatologist for their concerns, they may not be able to access specialist care.3 The limited supply and urban-focused distribution of dermatologists along with reduced acceptance of state-funded insurance plans and long appointment wait times all pose considerable challenges to individuals seeking dermatologic care.2 Electronic consultations (e-consults) have emerged as a promising solution to overcoming these barriers while providing high-quality dermatologic care to a large diverse patient population.2,4 Although e-consults can be of service to all dermatology patients, this modality may be especially beneficial to underserved populations, such as the uninsured and Medicaid patients—groups that historically have experienced limited access to dermatology care due to the low reimbursement rates and high administrative burdens accompanying care delivery.4 This limited access leads to inequity in care, as timely access to dermatology is associated with improved diagnostic accuracy and disease outcomes.3 E-consult implementation can facilitate timely access for these underserved populations and bypass additional barriers to care such as lack of transportation or time off work. Prior e-consult studies have demonstrated relatively high numbers of Medicaid patients utilizing e-consult services.3,5
Although in-person visits remain the gold standard for diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic conditions, e-consults placed by primary care providers (PCPs) can improve access and help triage patients who require in-person dermatology visits.6 In this study, we conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the e-consults requested of the dermatology department at a large tertiary care medical center in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Methods
The electronic health record (EHR) of Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) was screened for eligible patients from January 1, 2020, to May 31, 2021. Patients—both adult (aged ≥18 years) and pediatric (aged <18 years)—were included if they underwent a dermatology e-consult within this time frame. Provider notes in the medical records were reviewed to determine the nature of the lesion, how long the dermatologist took to complete the e-consult, whether an in-person appointment was recommended, and whether the patient was seen by dermatology within 90 days of the e-consult. Institutional review board approval was obtained.
For each e-consult, the PCP obtained clinical photographs of the lesion in question either through the EHR mobile application or by having patients upload their own photographs directly to their medical records. The referring PCP then completed a brief template regarding the patient’s clinical question and medical history and then sent the completed information to the consulting dermatologist’s EHR inbox. From there, the dermatologist could view the clinical question, documented photographs, and patient medical record to create a brief consult note with recommendations. The note was then sent back via EHR to the PCP to follow up with the patient. Patients were not charged for the e-consult.
Results
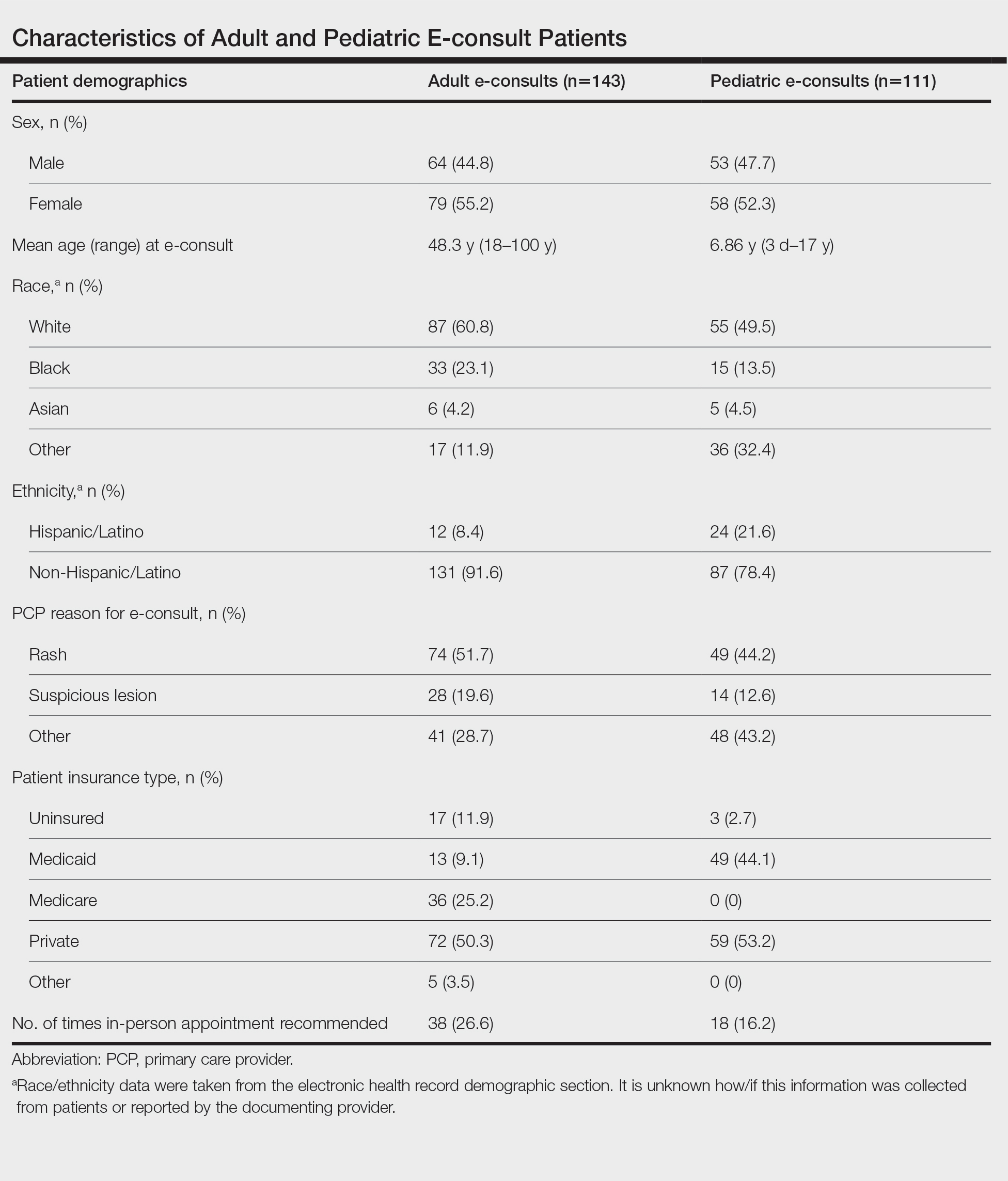
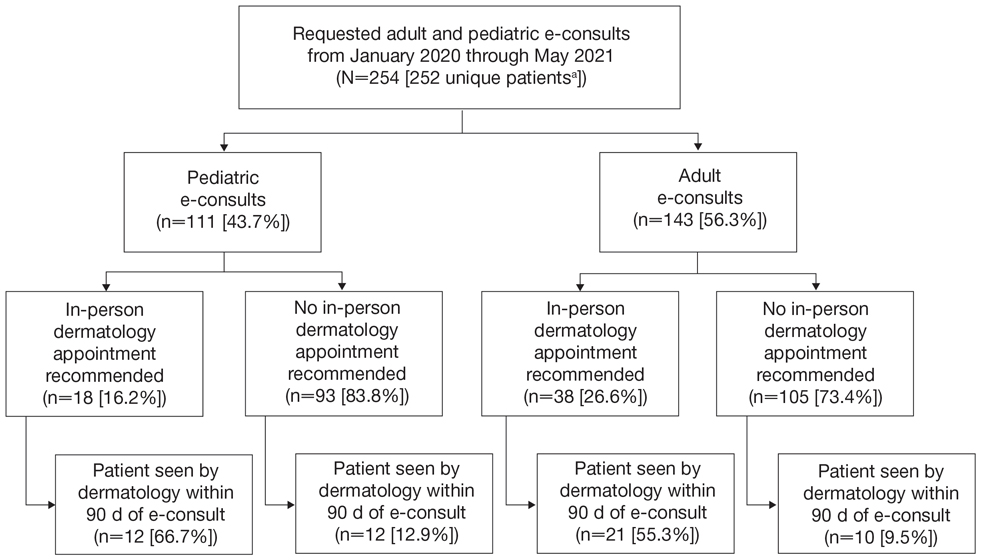
Two hundred fifty-four dermatology e-consults were requested by providers at the study center (eTable), which included 252 unique patients (2 patients had 2 separate e-consults regarding different clinical questions). The median time for completion of the e-consult—from submission of the PCP’s e-consult request to dermatologist completion—was 0.37 days. Fifty-six patients (22.0%) were recommended for an in-person appointment (Figure), 33 (58.9%) of whom ultimately scheduled the in-person appointment, and the median length of time between the completion of the e-consult and the in-person appointment was 16.5 days. The remaining 198 patients (78.0%) were not triaged to receive an in-person appointment following the e-consult,but 2 patients (8.7%) were ultimately seen in-person anyway via other referral pathways, with a median length of 33 days between e-consult completion and the in-person appointment. One hundred seventy-six patients (69.8%) avoided an in-person dermatology visit, although 38 (21.6%) of those patients were fewer than 90 days out from their e-consults at the time of data collection. The 254 e-consults included patients from 50 different zip codes, 49 (98.0%) of which were in North Carolina.
Comment
An e-consult is an asynchronous telehealth modality through which PCPs can request specialty evaluation to provide diagnostic and therapeutic guidance, facilitate PCP-specialist coordination of care, and increase access to specialty care with reduced wait times.7,8 Increased care access is especially important, as specialty referral can decrease overall health care expenditure; however, the demand for specialists often exceeds the availability.8 Our e-consult program drastically reduced the time from patients’ initial presentation at their PCP’s office to dermatologist recommendations for treatment or need for in-person dermatology follow-up.
In our analysis, patients were of different racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic backgrounds and lived across a variety of zip codes, predominantly in central and western North Carolina. Almost three-quarters of the patients resided in zip codes where the average income was less than the North Carolina median household income ($66,196).9 Additionally, 82 patients (32.3%) were uninsured or on Medicaid (eTable). These economically disadvantaged patient populations historically have had limited access to dermatologic care.4 One study showed that privately insured individuals were accepted as new patients by dermatologists 91% of the time compared to a 29.8% acceptance rate for publicly insured individuals.10 Uninsured and Medicaid patients also have to wait 34% longer for an appointment compared to individuals with Medicare or private insurance.2 Considering these patients may already be at an economic disadvantage when it comes to seeing and paying for dermatologic services, e-consults may reduce patient travel and appointment expenses while increasing access to specialty care. Based on a 2020 study, each e-consult generates an estimated savings of $80 out-of-pocket per patient per avoided in-person visit.11
In our study, the most common condition for an e-consult in both adult and pediatric patients was rash, which is consistent with prior e-consult studies.5,11 We found that most e-consult patients were not recommended for an in-person dermatology visit, and for those who were recommended to have an in-person visit, the wait time was reduced (Figure). These results corroborate that e-consults may be used as an important triage tool for determining whether a specialist appointment is indicated as well as a public health tool, as timely evaluation is associated with better dermatologic health care outcomes.3 However, the number of patients who did not present for an in-person appointment in our study may be overestimated, as 38 patients’ (21.6%) e-consults were conducted fewer than 90 days before our data collection. Although none of these patients had been seen in person, it is possible they requested an in-person visit after their medical records were reviewed for this study. Additionally, it is possible patients sought care from outside providers not documented in the EHR.
With regard to the payment model for the e-consult program, Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist initially piloted the e-consult system through a partnership with the American Academy of Medical Colleges’ Project CORE: Coordinating Optimal Referral Experiences (https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/health-care/project-core). Grant funding through Project CORE allowed both the referring PCP and the specialist completing the e-consult to each receive approximately 0.5 relative value units in payment for each consult completed. Based on early adoption successes, the institution has created additional internal funding to support the continued expansion of the e-consult system and is incentivized to continue funding, as proper utilization of e-consults improves patient access to timely specialist care, avoids no-shows or last-minute cancellations for specialist appointments, and decreases back-door access to specialist care through the emergency department and urgent care facilities.5 Although 0.5 relative value units is not equivalent compensation to an in-person office visit, our study showed that e-consults can be completed much more quickly and efficiently and do not utilize nursing staff or other office resources.
Conclusion
E-consults are an effective telehealth modality that can increase patients’ access to dermatologic specialty care.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank the Wake Forest University School of Medicine Department of Medical Education and Department of Dermatology (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their contributions to this research study as well as the Wake Forest Clinical and Translational Science Institute (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their help extracting EHR data.
- Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, et al. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1527-1534.
- Naka F, Lu J, Porto A, et al. Impact of dermatology econsults on access to care and skin cancer screening in underserved populations: a model for teledermatology services in community health centers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:293-302.
- Mulcahy A, Mehrotra A, Edison K, et al. Variation in dermatologist visits by sociodemographic characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:918-924.
- Yang X, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL. Cost analysis of a store-and-forward teledermatology consult system in Philadelphia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:758-764.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an econsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1633-1638.
- Lee KJ, Finnane A, Soyer HP. Recent trends in teledermatology and teledermoscopy. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2018;8:214-223.
- Parikh PJ, Mowrey C, Gallimore J, et al. Evaluating e-consultation implementations based on use and time-line across various specialties. Int J Med Inform. 2017;108:42-48.
- Wasfy JH, Rao SK, Kalwani N, et al. Longer-term impact of cardiology e-consults. Am Heart J. 2016;173:86-93.
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: North Carolina; United States. Accessed February 26, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/NC,US/PST045222
- Alghothani L, Jacks SK, Vander Horst A, et al. Disparities in access to dermatologic care according to insurance type. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:956-957.
- Seiger K, Hawryluk EB, Kroshinsky D, et al. Pediatric dermatology econsults: reduced wait times and dermatology office visits. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:804-810.
Dermatologic conditions affect approximately one-third of individuals in the United States.1,2 Nearly 1 in 4 physician office visits in the United States are for skin conditions, and less than one-third of these visits are with dermatologists. Although many of these patients may prefer to see a dermatologist for their concerns, they may not be able to access specialist care.3 The limited supply and urban-focused distribution of dermatologists along with reduced acceptance of state-funded insurance plans and long appointment wait times all pose considerable challenges to individuals seeking dermatologic care.2 Electronic consultations (e-consults) have emerged as a promising solution to overcoming these barriers while providing high-quality dermatologic care to a large diverse patient population.2,4 Although e-consults can be of service to all dermatology patients, this modality may be especially beneficial to underserved populations, such as the uninsured and Medicaid patients—groups that historically have experienced limited access to dermatology care due to the low reimbursement rates and high administrative burdens accompanying care delivery.4 This limited access leads to inequity in care, as timely access to dermatology is associated with improved diagnostic accuracy and disease outcomes.3 E-consult implementation can facilitate timely access for these underserved populations and bypass additional barriers to care such as lack of transportation or time off work. Prior e-consult studies have demonstrated relatively high numbers of Medicaid patients utilizing e-consult services.3,5
Although in-person visits remain the gold standard for diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic conditions, e-consults placed by primary care providers (PCPs) can improve access and help triage patients who require in-person dermatology visits.6 In this study, we conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the e-consults requested of the dermatology department at a large tertiary care medical center in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Methods
The electronic health record (EHR) of Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) was screened for eligible patients from January 1, 2020, to May 31, 2021. Patients—both adult (aged ≥18 years) and pediatric (aged <18 years)—were included if they underwent a dermatology e-consult within this time frame. Provider notes in the medical records were reviewed to determine the nature of the lesion, how long the dermatologist took to complete the e-consult, whether an in-person appointment was recommended, and whether the patient was seen by dermatology within 90 days of the e-consult. Institutional review board approval was obtained.
For each e-consult, the PCP obtained clinical photographs of the lesion in question either through the EHR mobile application or by having patients upload their own photographs directly to their medical records. The referring PCP then completed a brief template regarding the patient’s clinical question and medical history and then sent the completed information to the consulting dermatologist’s EHR inbox. From there, the dermatologist could view the clinical question, documented photographs, and patient medical record to create a brief consult note with recommendations. The note was then sent back via EHR to the PCP to follow up with the patient. Patients were not charged for the e-consult.

Results
Two hundred fifty-four dermatology e-consults were requested by providers at the study center (eTable), which included 252 unique patients (2 patients had 2 separate e-consults regarding different clinical questions). The median time for completion of the e-consult—from submission of the PCP’s e-consult request to dermatologist completion—was 0.37 days. Fifty-six patients (22.0%) were recommended for an in-person appointment (Figure), 33 (58.9%) of whom ultimately scheduled the in-person appointment, and the median length of time between the completion of the e-consult and the in-person appointment was 16.5 days. The remaining 198 patients (78.0%) were not triaged to receive an in-person appointment following the e-consult,but 2 patients (8.7%) were ultimately seen in-person anyway via other referral pathways, with a median length of 33 days between e-consult completion and the in-person appointment. One hundred seventy-six patients (69.8%) avoided an in-person dermatology visit, although 38 (21.6%) of those patients were fewer than 90 days out from their e-consults at the time of data collection. The 254 e-consults included patients from 50 different zip codes, 49 (98.0%) of which were in North Carolina.

Comment
An e-consult is an asynchronous telehealth modality through which PCPs can request specialty evaluation to provide diagnostic and therapeutic guidance, facilitate PCP-specialist coordination of care, and increase access to specialty care with reduced wait times.7,8 Increased care access is especially important, as specialty referral can decrease overall health care expenditure; however, the demand for specialists often exceeds the availability.8 Our e-consult program drastically reduced the time from patients’ initial presentation at their PCP’s office to dermatologist recommendations for treatment or need for in-person dermatology follow-up.
In our analysis, patients were of different racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic backgrounds and lived across a variety of zip codes, predominantly in central and western North Carolina. Almost three-quarters of the patients resided in zip codes where the average income was less than the North Carolina median household income ($66,196).9 Additionally, 82 patients (32.3%) were uninsured or on Medicaid (eTable). These economically disadvantaged patient populations historically have had limited access to dermatologic care.4 One study showed that privately insured individuals were accepted as new patients by dermatologists 91% of the time compared to a 29.8% acceptance rate for publicly insured individuals.10 Uninsured and Medicaid patients also have to wait 34% longer for an appointment compared to individuals with Medicare or private insurance.2 Considering these patients may already be at an economic disadvantage when it comes to seeing and paying for dermatologic services, e-consults may reduce patient travel and appointment expenses while increasing access to specialty care. Based on a 2020 study, each e-consult generates an estimated savings of $80 out-of-pocket per patient per avoided in-person visit.11
In our study, the most common condition for an e-consult in both adult and pediatric patients was rash, which is consistent with prior e-consult studies.5,11 We found that most e-consult patients were not recommended for an in-person dermatology visit, and for those who were recommended to have an in-person visit, the wait time was reduced (Figure). These results corroborate that e-consults may be used as an important triage tool for determining whether a specialist appointment is indicated as well as a public health tool, as timely evaluation is associated with better dermatologic health care outcomes.3 However, the number of patients who did not present for an in-person appointment in our study may be overestimated, as 38 patients’ (21.6%) e-consults were conducted fewer than 90 days before our data collection. Although none of these patients had been seen in person, it is possible they requested an in-person visit after their medical records were reviewed for this study. Additionally, it is possible patients sought care from outside providers not documented in the EHR.
With regard to the payment model for the e-consult program, Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist initially piloted the e-consult system through a partnership with the American Academy of Medical Colleges’ Project CORE: Coordinating Optimal Referral Experiences (https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/health-care/project-core). Grant funding through Project CORE allowed both the referring PCP and the specialist completing the e-consult to each receive approximately 0.5 relative value units in payment for each consult completed. Based on early adoption successes, the institution has created additional internal funding to support the continued expansion of the e-consult system and is incentivized to continue funding, as proper utilization of e-consults improves patient access to timely specialist care, avoids no-shows or last-minute cancellations for specialist appointments, and decreases back-door access to specialist care through the emergency department and urgent care facilities.5 Although 0.5 relative value units is not equivalent compensation to an in-person office visit, our study showed that e-consults can be completed much more quickly and efficiently and do not utilize nursing staff or other office resources.
Conclusion
E-consults are an effective telehealth modality that can increase patients’ access to dermatologic specialty care.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank the Wake Forest University School of Medicine Department of Medical Education and Department of Dermatology (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their contributions to this research study as well as the Wake Forest Clinical and Translational Science Institute (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their help extracting EHR data.
Dermatologic conditions affect approximately one-third of individuals in the United States.1,2 Nearly 1 in 4 physician office visits in the United States are for skin conditions, and less than one-third of these visits are with dermatologists. Although many of these patients may prefer to see a dermatologist for their concerns, they may not be able to access specialist care.3 The limited supply and urban-focused distribution of dermatologists along with reduced acceptance of state-funded insurance plans and long appointment wait times all pose considerable challenges to individuals seeking dermatologic care.2 Electronic consultations (e-consults) have emerged as a promising solution to overcoming these barriers while providing high-quality dermatologic care to a large diverse patient population.2,4 Although e-consults can be of service to all dermatology patients, this modality may be especially beneficial to underserved populations, such as the uninsured and Medicaid patients—groups that historically have experienced limited access to dermatology care due to the low reimbursement rates and high administrative burdens accompanying care delivery.4 This limited access leads to inequity in care, as timely access to dermatology is associated with improved diagnostic accuracy and disease outcomes.3 E-consult implementation can facilitate timely access for these underserved populations and bypass additional barriers to care such as lack of transportation or time off work. Prior e-consult studies have demonstrated relatively high numbers of Medicaid patients utilizing e-consult services.3,5
Although in-person visits remain the gold standard for diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic conditions, e-consults placed by primary care providers (PCPs) can improve access and help triage patients who require in-person dermatology visits.6 In this study, we conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the e-consults requested of the dermatology department at a large tertiary care medical center in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Methods
The electronic health record (EHR) of Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) was screened for eligible patients from January 1, 2020, to May 31, 2021. Patients—both adult (aged ≥18 years) and pediatric (aged <18 years)—were included if they underwent a dermatology e-consult within this time frame. Provider notes in the medical records were reviewed to determine the nature of the lesion, how long the dermatologist took to complete the e-consult, whether an in-person appointment was recommended, and whether the patient was seen by dermatology within 90 days of the e-consult. Institutional review board approval was obtained.
For each e-consult, the PCP obtained clinical photographs of the lesion in question either through the EHR mobile application or by having patients upload their own photographs directly to their medical records. The referring PCP then completed a brief template regarding the patient’s clinical question and medical history and then sent the completed information to the consulting dermatologist’s EHR inbox. From there, the dermatologist could view the clinical question, documented photographs, and patient medical record to create a brief consult note with recommendations. The note was then sent back via EHR to the PCP to follow up with the patient. Patients were not charged for the e-consult.

Results
Two hundred fifty-four dermatology e-consults were requested by providers at the study center (eTable), which included 252 unique patients (2 patients had 2 separate e-consults regarding different clinical questions). The median time for completion of the e-consult—from submission of the PCP’s e-consult request to dermatologist completion—was 0.37 days. Fifty-six patients (22.0%) were recommended for an in-person appointment (Figure), 33 (58.9%) of whom ultimately scheduled the in-person appointment, and the median length of time between the completion of the e-consult and the in-person appointment was 16.5 days. The remaining 198 patients (78.0%) were not triaged to receive an in-person appointment following the e-consult,but 2 patients (8.7%) were ultimately seen in-person anyway via other referral pathways, with a median length of 33 days between e-consult completion and the in-person appointment. One hundred seventy-six patients (69.8%) avoided an in-person dermatology visit, although 38 (21.6%) of those patients were fewer than 90 days out from their e-consults at the time of data collection. The 254 e-consults included patients from 50 different zip codes, 49 (98.0%) of which were in North Carolina.

Comment
An e-consult is an asynchronous telehealth modality through which PCPs can request specialty evaluation to provide diagnostic and therapeutic guidance, facilitate PCP-specialist coordination of care, and increase access to specialty care with reduced wait times.7,8 Increased care access is especially important, as specialty referral can decrease overall health care expenditure; however, the demand for specialists often exceeds the availability.8 Our e-consult program drastically reduced the time from patients’ initial presentation at their PCP’s office to dermatologist recommendations for treatment or need for in-person dermatology follow-up.
In our analysis, patients were of different racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic backgrounds and lived across a variety of zip codes, predominantly in central and western North Carolina. Almost three-quarters of the patients resided in zip codes where the average income was less than the North Carolina median household income ($66,196).9 Additionally, 82 patients (32.3%) were uninsured or on Medicaid (eTable). These economically disadvantaged patient populations historically have had limited access to dermatologic care.4 One study showed that privately insured individuals were accepted as new patients by dermatologists 91% of the time compared to a 29.8% acceptance rate for publicly insured individuals.10 Uninsured and Medicaid patients also have to wait 34% longer for an appointment compared to individuals with Medicare or private insurance.2 Considering these patients may already be at an economic disadvantage when it comes to seeing and paying for dermatologic services, e-consults may reduce patient travel and appointment expenses while increasing access to specialty care. Based on a 2020 study, each e-consult generates an estimated savings of $80 out-of-pocket per patient per avoided in-person visit.11
In our study, the most common condition for an e-consult in both adult and pediatric patients was rash, which is consistent with prior e-consult studies.5,11 We found that most e-consult patients were not recommended for an in-person dermatology visit, and for those who were recommended to have an in-person visit, the wait time was reduced (Figure). These results corroborate that e-consults may be used as an important triage tool for determining whether a specialist appointment is indicated as well as a public health tool, as timely evaluation is associated with better dermatologic health care outcomes.3 However, the number of patients who did not present for an in-person appointment in our study may be overestimated, as 38 patients’ (21.6%) e-consults were conducted fewer than 90 days before our data collection. Although none of these patients had been seen in person, it is possible they requested an in-person visit after their medical records were reviewed for this study. Additionally, it is possible patients sought care from outside providers not documented in the EHR.
With regard to the payment model for the e-consult program, Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist initially piloted the e-consult system through a partnership with the American Academy of Medical Colleges’ Project CORE: Coordinating Optimal Referral Experiences (https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/health-care/project-core). Grant funding through Project CORE allowed both the referring PCP and the specialist completing the e-consult to each receive approximately 0.5 relative value units in payment for each consult completed. Based on early adoption successes, the institution has created additional internal funding to support the continued expansion of the e-consult system and is incentivized to continue funding, as proper utilization of e-consults improves patient access to timely specialist care, avoids no-shows or last-minute cancellations for specialist appointments, and decreases back-door access to specialist care through the emergency department and urgent care facilities.5 Although 0.5 relative value units is not equivalent compensation to an in-person office visit, our study showed that e-consults can be completed much more quickly and efficiently and do not utilize nursing staff or other office resources.
Conclusion
E-consults are an effective telehealth modality that can increase patients’ access to dermatologic specialty care.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank the Wake Forest University School of Medicine Department of Medical Education and Department of Dermatology (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their contributions to this research study as well as the Wake Forest Clinical and Translational Science Institute (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) for their help extracting EHR data.
- Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, et al. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1527-1534.
- Naka F, Lu J, Porto A, et al. Impact of dermatology econsults on access to care and skin cancer screening in underserved populations: a model for teledermatology services in community health centers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:293-302.
- Mulcahy A, Mehrotra A, Edison K, et al. Variation in dermatologist visits by sociodemographic characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:918-924.
- Yang X, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL. Cost analysis of a store-and-forward teledermatology consult system in Philadelphia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:758-764.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an econsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1633-1638.
- Lee KJ, Finnane A, Soyer HP. Recent trends in teledermatology and teledermoscopy. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2018;8:214-223.
- Parikh PJ, Mowrey C, Gallimore J, et al. Evaluating e-consultation implementations based on use and time-line across various specialties. Int J Med Inform. 2017;108:42-48.
- Wasfy JH, Rao SK, Kalwani N, et al. Longer-term impact of cardiology e-consults. Am Heart J. 2016;173:86-93.
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: North Carolina; United States. Accessed February 26, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/NC,US/PST045222
- Alghothani L, Jacks SK, Vander Horst A, et al. Disparities in access to dermatologic care according to insurance type. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:956-957.
- Seiger K, Hawryluk EB, Kroshinsky D, et al. Pediatric dermatology econsults: reduced wait times and dermatology office visits. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:804-810.
- Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, et al. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1527-1534.
- Naka F, Lu J, Porto A, et al. Impact of dermatology econsults on access to care and skin cancer screening in underserved populations: a model for teledermatology services in community health centers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:293-302.
- Mulcahy A, Mehrotra A, Edison K, et al. Variation in dermatologist visits by sociodemographic characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:918-924.
- Yang X, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL. Cost analysis of a store-and-forward teledermatology consult system in Philadelphia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:758-764.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an econsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1633-1638.
- Lee KJ, Finnane A, Soyer HP. Recent trends in teledermatology and teledermoscopy. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2018;8:214-223.
- Parikh PJ, Mowrey C, Gallimore J, et al. Evaluating e-consultation implementations based on use and time-line across various specialties. Int J Med Inform. 2017;108:42-48.
- Wasfy JH, Rao SK, Kalwani N, et al. Longer-term impact of cardiology e-consults. Am Heart J. 2016;173:86-93.
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: North Carolina; United States. Accessed February 26, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/NC,US/PST045222
- Alghothani L, Jacks SK, Vander Horst A, et al. Disparities in access to dermatologic care according to insurance type. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:956-957.
- Seiger K, Hawryluk EB, Kroshinsky D, et al. Pediatric dermatology econsults: reduced wait times and dermatology office visits. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:804-810.
Practice Points
- Most electronic consult patients may be able to avoid in-person dermatology appointments.
- E-consults can increase patient access to dermatologic specialty care.
Factors Influencing Patient Preferences for Phototherapy: A Survey Study
Phototherapy—particularly UVB phototherapy, which utilizes UVB rays of specific wavelengths within the UV spectrum—is indicated for a wide variety of dermatoses. In-office and at-home UVB treatments commonly are used, as are salon tanning and sunbathing. When selecting a form of phototherapy, patients are likely to consider safety, cost, effectiveness, insurance issues, and convenience. Research on patient preferences; the reasons for these preferences; and which options patients perceive to be the safest, most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient is lacking. We aimed to assess the forms of phototherapy that patients would most consider using; the factors influencing patient preferences; and the forms patients perceived as the safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient.
Methods
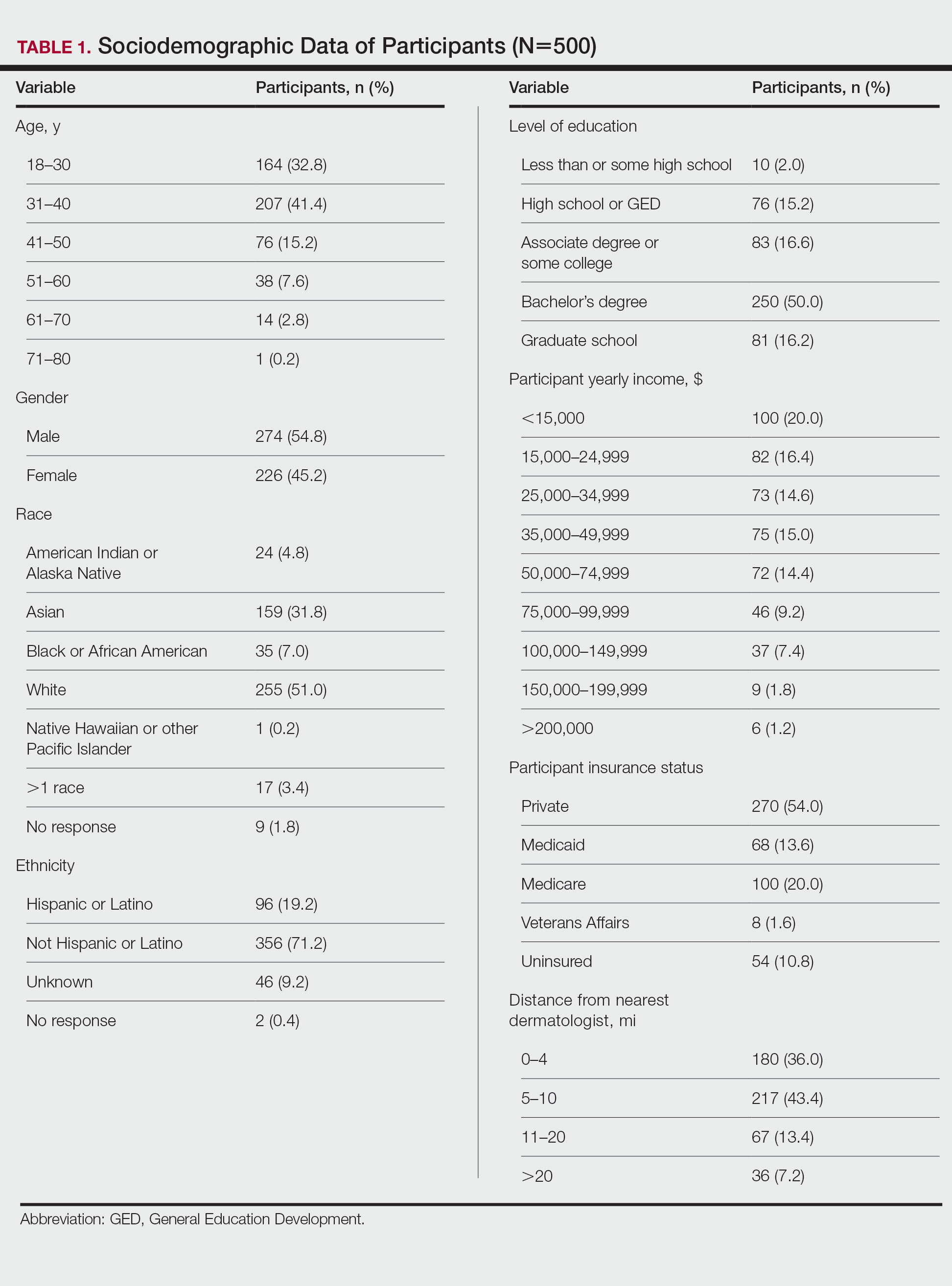
Study Participants—We recruited 500 Amazon Mechanical Turk users who were 18 years or older to complete our REDCap-generated survey. The study was approved by the Wake Forest University institutional review board (Winston-Salem, North Carolina).
Evaluation—Participants were asked, “If you were diagnosed with a skin disease that benefited from UV therapy, which of the following forms of UV therapy would you consider choosing?” Participants were instructed to choose all of the forms they would consider using. Available options included in-office UV, at-home UV, home tanning, salon tanning, sunbathing, and other. Participants were asked to select which factors—from safety, cost, effectiveness, issues with insurance, convenience, and other—influenced their decision-making; which form of phototherapy they would most consider along with the factors that influenced their preference for this specific form of phototherapy; and which options they considered to be safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient. Participants were asked to provide basic sociodemographic information, level of education, income, insurance status (private, Medicare, Medicaid, Veterans Affairs, and uninsured), and distance from the nearest dermatologist.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive and inferential statistics (χ2 test) were used to analyze the data with a significance set at P<.05.
Results
Five hundred participants completed the survey (Table 1).
Factors Influencing Patient Preferences—When asked to select all forms of phototherapy they would consider, 186 (37.2%) participants selected in-office UVB, 263 (52.6%) selected at-home UV, 141 (28.2%) selected home tanning, 117 (23.4%) selected salon tanning, 191 (38.2%) selected sunbathing, and 3 (0.6%) selected other. Participants who selected in-office UVB as an option were more likely to also select salon tanning (P<.012). No other relationship was found between the UVB options and the tanning options. When asked which factors influenced their phototherapy preferences, 295 (59%) selected convenience, 266 (53.2%) selected effectiveness, 220 (44%) selected safety, 218 (43.6%) selected cost, 72 (14.4%) selected issues with insurance, and 4 (0.8%) selected other. Forms of Phototherapy Patients Consider Using—When asked which form of phototherapy they would most consider using, 179 (35.8%) participants selected at-home UVB, 108 (21.6%) selected sunbathing, 92 (18.4%) selected in-office UVB, 62 (12.4%) selected home-tanning, 57 (11.4%) selected salon tanning, 1 (0.2%) selected other, and 1 participant provided no response (P<.001).
Reasons for Using Phototherapy—Of the 179 who selected at-home UVB, 125 (70%) cited convenience as a reason. Of the 108 who selected salon tanning as their top choice, 62 (57%) cited cost as a reason. Convenience (P<.001), cost (P<.001), and safety (P=.023) were related to top preference. Issues with insurance did not have a statistically significant relationship with the top preference. However, participant insurance type was related to top phototherapy preference (P=.021), with privately insured patients more likely to select in-office UVB, whereas those with Medicaid and Medicare were more likely to select home or salon tanning. Efficacy was not related to top preference. Furthermore, age, gender, education, income, and distance from nearest dermatologist were not related to top preference.
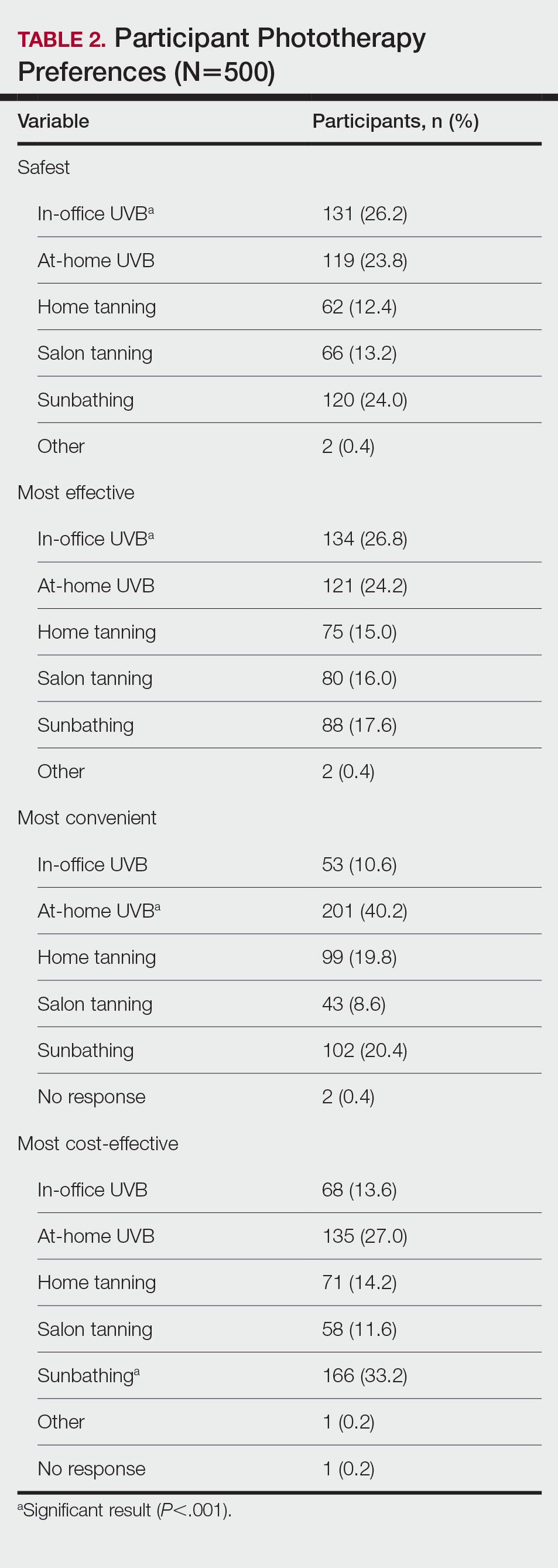
In-office UVB was perceived to be safest (P<.001) and most efficacious (P<.001). Meanwhile, at-home UVB was selected as most convenient (P<.001). Lastly, sunbathing was determined to be most cost-effective (P<.001)(Table 2). Cost-effectiveness had a relationship (P<.001) with the participant’s insurance, as those with private insurance were more likely to select at-home UVB, whereas those with Medicare or Medicaid were more likely to select the tanning options. Additionally, of the54 uninsured participants in the survey, 29 selected sunbathing as the most cost-effective option.
Comment
Phototherapy Treatment—UVB phototherapy at a wavelength of 290 to 320 nm (311–313 nm for narrowband UVB) is used to treat various dermatoses, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. UVB alters skin cytokines, induces apoptosis, promotes immunosuppression, causes DNA damage, and decreases the proliferation of dendritic cells and other cells of the innate immune system.1 In-office and at-home UV therapies make use of UVB wavelengths for treatment, while tanning and sunbathing contain not only UVB but also potentially harmful UVA rays. The wavelengths for indoor tanning devices include UVB at 280 to 315 nm and UVA at 315 to 400 nm, which are similar to those of the sun but with a different ratio of UVB to UVA and more intense total UV.2 When in-office and at-home UVB options are not available, various forms of tanning such as salon tanning and sunbathing may be alternatives that are widely used.3 One of the main reasons patients consider alternative phototherapy options is cost, as 1 in-office UVB treatment may cost $140, but a month of unlimited tanning may cost $30 or perhaps nothing if a patient has a gym membership with access to a tanning bed. Lack of insurance benefits covering phototherapy can exacerbate cost burden.4 However, tanning beds are associated with an increased risk for melanoma and nonmelanoma cancers.5,6 Additionally, all forms of phototherapy are associated with photoaging, but it is more intense with tanning and heliotherapy because of the presence of UVA, which penetrates deeper into the dermis.7 Meanwhile, for those who choose UVB therapy, deciding between an in-office and at-home UVB treatment could be a matter of convenience, as patients must consider long trips to the physician’s office; insurance status, as some insurances may not cover at-home UVB; or efficacy, which might be influenced by the presence of a physician or other medical staff. In many cases, patients may not be informed that at-home UVB is an option.
Patient Preferences—At-home UVB therapy was the most popular option in our study population, with most participants (52.6%) considering using it, and 35.9% choosing it as their top choice over all other phototherapy options. Safety, cost, and convenience were all found to be related to the option participants would most consider using. Prior analysis between at-home UVB and in-office UVB for the treatment of psoriasis determined that at-home UVB is as safe and cost-effective as in-office UVB without the inconvenience of the patient having to take time out of the week to visit the physician’s office,8,9 making at-home UVB an option dermatologists may strongly consider for patients who value safety, cost, and convenience. Oddly, efficacy was not related to the top preference, despite being the second highest–cited factor (53.2%) for which forms of phototherapy participants would consider using. For insurance coverage, those with Medicaid and Medicare selected the cheaper tanning options with higher-than-expected frequencies. Although problems with insurance were not related to the top preference, insurance status was related, suggesting that preferences are tied to cost. Of note, while the number of dermatologists that accept Medicare has increased in the last few years, there still remains an uneven distribution of phototherapy clinics. As of 2015, there were 19 million individuals who qualified for Medicare without a clinic within driving distance.10 This problem likely also exists for many Medicaid patients who may not qualify for at-home UVB. In this scenario, tanning or heliotherapy may be effective alternatives.
In-Office vs At-Home Options—Although in-office UVB was the option considered safest (26.2%) and most efficacious (26.8%), it was followed closely by at-home UVB in both categories (safest, 23.8%; most efficacious, 24.2%). Meanwhile, at-home UVB (40.2%) was chosen as the most convenient. Some patients consider tanning options over in-office UVB because of the inconvenience of traveling to an appointment.11 Therefore, at-home tanning may be a convenient alternative for these patients.
Considerations—Although our study was limited to an adult population, issues with convenience exist for the pediatric population as well, as children may need to miss multiple days of school each week to be treated in the office. For these pediatric patients, an at-home unit is preferable; however; issues with insurance coverage remain a challenge.12 Increasing insurance coverage of at-home units for the pediatric population therefore would be most prudent. However, when other options have been exhausted, including in-office UVB, tanning and sunbathing may be viable alternatives because of cost and convenience. In our study, sunbathing (33.2%) was considered the most cost-effective, likely because it does not require expensive equipment or a visit to a salon or physician’s office. Sunbathing has been effective in treating some dermatologic conditions, such as atopic dermatitis.13 However, it may only be effective during certain months and at different latitudes—conditions that make UVB sun rays more accessible—particularly when treating psoriasis.14 Furthermore, sunbathing may not be as cost-effective in patients with average-severity psoriasis compared with conventional psoriasis therapy because of the costs of travel to areas with sufficient UVB rays for treatment.15 Additionally, insurance status was related to which option was selected as the most cost-effective, as 29 (53.7%) of 54 uninsured participants chose sunbathing as the most cost-effective option, while only 92 (34.2%) of 269 privately insured patients selected sunbathing. Therefore, insurance status may be a factor for dermatologists to consider if a patient prefers a treatment that is cost-effective. Overall, dermatologists could perhaps consider guiding patients and optimizing their treatment plans based on the factors most important to the patients while understanding that costs and insurance status may ultimately determine the treatment option.
Limitations—Survey participants were recruited on Amazon Mechanical Turk, which could create sampling bias. Furthermore, these participants were representative of the general public and not exclusively patients on phototherapy, therefore representing the opinions of the general public and not those who may require phototherapy. Furthermore, given the nature of the survey, the study was limited to the adult population.
- Totonchy MB, Chiu MW. UV-based therapy. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:399-413, ix-x.
- Nilsen LT, Hannevik M, Veierød MB. Ultraviolet exposure from indoor tanning devices: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:730-740.
- Su J, Pearce DJ, Feldman SR. The role of commercial tanning beds and ultraviolet A light in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2005;16:324-326.
- Anderson KL, Huang KE, Huang WW, et al. Dermatology residents are prescribing tanning bed treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt19h4k7sx.
- Wehner MR, Shive ML, Chren MM, et al. Indoor tanning and non-melanoma skin cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5909.
- Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P, et al. Cutaneous melanomaattributable to sunbed use: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:E4757.
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407.
- Koek MB, Buskens E, van Weelden H, et al. Home versus outpatient ultraviolet B phototherapy for mild to severe psoriasis: pragmatic multicentre randomized controlled non-inferiority trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2009;338:b1542.
- Koek MB, Sigurdsson V, van Weelden H, et al. Cost effectiveness of home ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis: economic evaluation of a randomized controlled trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2010;340:c1490.
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679.
- Felton S, Adinoff B, Jeon-Slaughter H, et al. The significant health threat from tanning bed use as a self-treatment for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1015-1017.
- Juarez MC, Grossberg AL. Phototherapy in the pediatric population. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:91-108.
- Autio P, Komulainen P, Larni HM. Heliotherapy in atopic dermatitis: a prospective study on climatotherapy using the SCORAD index. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:436-440.
- Krzys´cin JW, Jarosławski J, Rajewska-Wie˛ch B, et al. Effectiveness of heliotherapy for psoriasis clearance in low and mid-latitudinal regions: a theoretical approach. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2012;115:35-41.
- Snellman E, Maljanen T, Aromaa A, et al. Effect of heliotherapy on the cost of psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:288-292.
Phototherapy—particularly UVB phototherapy, which utilizes UVB rays of specific wavelengths within the UV spectrum—is indicated for a wide variety of dermatoses. In-office and at-home UVB treatments commonly are used, as are salon tanning and sunbathing. When selecting a form of phototherapy, patients are likely to consider safety, cost, effectiveness, insurance issues, and convenience. Research on patient preferences; the reasons for these preferences; and which options patients perceive to be the safest, most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient is lacking. We aimed to assess the forms of phototherapy that patients would most consider using; the factors influencing patient preferences; and the forms patients perceived as the safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient.
Methods
Study Participants—We recruited 500 Amazon Mechanical Turk users who were 18 years or older to complete our REDCap-generated survey. The study was approved by the Wake Forest University institutional review board (Winston-Salem, North Carolina).
Evaluation—Participants were asked, “If you were diagnosed with a skin disease that benefited from UV therapy, which of the following forms of UV therapy would you consider choosing?” Participants were instructed to choose all of the forms they would consider using. Available options included in-office UV, at-home UV, home tanning, salon tanning, sunbathing, and other. Participants were asked to select which factors—from safety, cost, effectiveness, issues with insurance, convenience, and other—influenced their decision-making; which form of phototherapy they would most consider along with the factors that influenced their preference for this specific form of phototherapy; and which options they considered to be safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient. Participants were asked to provide basic sociodemographic information, level of education, income, insurance status (private, Medicare, Medicaid, Veterans Affairs, and uninsured), and distance from the nearest dermatologist.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive and inferential statistics (χ2 test) were used to analyze the data with a significance set at P<.05.
Results
Five hundred participants completed the survey (Table 1).

Factors Influencing Patient Preferences—When asked to select all forms of phototherapy they would consider, 186 (37.2%) participants selected in-office UVB, 263 (52.6%) selected at-home UV, 141 (28.2%) selected home tanning, 117 (23.4%) selected salon tanning, 191 (38.2%) selected sunbathing, and 3 (0.6%) selected other. Participants who selected in-office UVB as an option were more likely to also select salon tanning (P<.012). No other relationship was found between the UVB options and the tanning options. When asked which factors influenced their phototherapy preferences, 295 (59%) selected convenience, 266 (53.2%) selected effectiveness, 220 (44%) selected safety, 218 (43.6%) selected cost, 72 (14.4%) selected issues with insurance, and 4 (0.8%) selected other. Forms of Phototherapy Patients Consider Using—When asked which form of phototherapy they would most consider using, 179 (35.8%) participants selected at-home UVB, 108 (21.6%) selected sunbathing, 92 (18.4%) selected in-office UVB, 62 (12.4%) selected home-tanning, 57 (11.4%) selected salon tanning, 1 (0.2%) selected other, and 1 participant provided no response (P<.001).
Reasons for Using Phototherapy—Of the 179 who selected at-home UVB, 125 (70%) cited convenience as a reason. Of the 108 who selected salon tanning as their top choice, 62 (57%) cited cost as a reason. Convenience (P<.001), cost (P<.001), and safety (P=.023) were related to top preference. Issues with insurance did not have a statistically significant relationship with the top preference. However, participant insurance type was related to top phototherapy preference (P=.021), with privately insured patients more likely to select in-office UVB, whereas those with Medicaid and Medicare were more likely to select home or salon tanning. Efficacy was not related to top preference. Furthermore, age, gender, education, income, and distance from nearest dermatologist were not related to top preference.
In-office UVB was perceived to be safest (P<.001) and most efficacious (P<.001). Meanwhile, at-home UVB was selected as most convenient (P<.001). Lastly, sunbathing was determined to be most cost-effective (P<.001)(Table 2). Cost-effectiveness had a relationship (P<.001) with the participant’s insurance, as those with private insurance were more likely to select at-home UVB, whereas those with Medicare or Medicaid were more likely to select the tanning options. Additionally, of the54 uninsured participants in the survey, 29 selected sunbathing as the most cost-effective option.

Comment
Phototherapy Treatment—UVB phototherapy at a wavelength of 290 to 320 nm (311–313 nm for narrowband UVB) is used to treat various dermatoses, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. UVB alters skin cytokines, induces apoptosis, promotes immunosuppression, causes DNA damage, and decreases the proliferation of dendritic cells and other cells of the innate immune system.1 In-office and at-home UV therapies make use of UVB wavelengths for treatment, while tanning and sunbathing contain not only UVB but also potentially harmful UVA rays. The wavelengths for indoor tanning devices include UVB at 280 to 315 nm and UVA at 315 to 400 nm, which are similar to those of the sun but with a different ratio of UVB to UVA and more intense total UV.2 When in-office and at-home UVB options are not available, various forms of tanning such as salon tanning and sunbathing may be alternatives that are widely used.3 One of the main reasons patients consider alternative phototherapy options is cost, as 1 in-office UVB treatment may cost $140, but a month of unlimited tanning may cost $30 or perhaps nothing if a patient has a gym membership with access to a tanning bed. Lack of insurance benefits covering phototherapy can exacerbate cost burden.4 However, tanning beds are associated with an increased risk for melanoma and nonmelanoma cancers.5,6 Additionally, all forms of phototherapy are associated with photoaging, but it is more intense with tanning and heliotherapy because of the presence of UVA, which penetrates deeper into the dermis.7 Meanwhile, for those who choose UVB therapy, deciding between an in-office and at-home UVB treatment could be a matter of convenience, as patients must consider long trips to the physician’s office; insurance status, as some insurances may not cover at-home UVB; or efficacy, which might be influenced by the presence of a physician or other medical staff. In many cases, patients may not be informed that at-home UVB is an option.
Patient Preferences—At-home UVB therapy was the most popular option in our study population, with most participants (52.6%) considering using it, and 35.9% choosing it as their top choice over all other phototherapy options. Safety, cost, and convenience were all found to be related to the option participants would most consider using. Prior analysis between at-home UVB and in-office UVB for the treatment of psoriasis determined that at-home UVB is as safe and cost-effective as in-office UVB without the inconvenience of the patient having to take time out of the week to visit the physician’s office,8,9 making at-home UVB an option dermatologists may strongly consider for patients who value safety, cost, and convenience. Oddly, efficacy was not related to the top preference, despite being the second highest–cited factor (53.2%) for which forms of phototherapy participants would consider using. For insurance coverage, those with Medicaid and Medicare selected the cheaper tanning options with higher-than-expected frequencies. Although problems with insurance were not related to the top preference, insurance status was related, suggesting that preferences are tied to cost. Of note, while the number of dermatologists that accept Medicare has increased in the last few years, there still remains an uneven distribution of phototherapy clinics. As of 2015, there were 19 million individuals who qualified for Medicare without a clinic within driving distance.10 This problem likely also exists for many Medicaid patients who may not qualify for at-home UVB. In this scenario, tanning or heliotherapy may be effective alternatives.
In-Office vs At-Home Options—Although in-office UVB was the option considered safest (26.2%) and most efficacious (26.8%), it was followed closely by at-home UVB in both categories (safest, 23.8%; most efficacious, 24.2%). Meanwhile, at-home UVB (40.2%) was chosen as the most convenient. Some patients consider tanning options over in-office UVB because of the inconvenience of traveling to an appointment.11 Therefore, at-home tanning may be a convenient alternative for these patients.
Considerations—Although our study was limited to an adult population, issues with convenience exist for the pediatric population as well, as children may need to miss multiple days of school each week to be treated in the office. For these pediatric patients, an at-home unit is preferable; however; issues with insurance coverage remain a challenge.12 Increasing insurance coverage of at-home units for the pediatric population therefore would be most prudent. However, when other options have been exhausted, including in-office UVB, tanning and sunbathing may be viable alternatives because of cost and convenience. In our study, sunbathing (33.2%) was considered the most cost-effective, likely because it does not require expensive equipment or a visit to a salon or physician’s office. Sunbathing has been effective in treating some dermatologic conditions, such as atopic dermatitis.13 However, it may only be effective during certain months and at different latitudes—conditions that make UVB sun rays more accessible—particularly when treating psoriasis.14 Furthermore, sunbathing may not be as cost-effective in patients with average-severity psoriasis compared with conventional psoriasis therapy because of the costs of travel to areas with sufficient UVB rays for treatment.15 Additionally, insurance status was related to which option was selected as the most cost-effective, as 29 (53.7%) of 54 uninsured participants chose sunbathing as the most cost-effective option, while only 92 (34.2%) of 269 privately insured patients selected sunbathing. Therefore, insurance status may be a factor for dermatologists to consider if a patient prefers a treatment that is cost-effective. Overall, dermatologists could perhaps consider guiding patients and optimizing their treatment plans based on the factors most important to the patients while understanding that costs and insurance status may ultimately determine the treatment option.
Limitations—Survey participants were recruited on Amazon Mechanical Turk, which could create sampling bias. Furthermore, these participants were representative of the general public and not exclusively patients on phototherapy, therefore representing the opinions of the general public and not those who may require phototherapy. Furthermore, given the nature of the survey, the study was limited to the adult population.
Phototherapy—particularly UVB phototherapy, which utilizes UVB rays of specific wavelengths within the UV spectrum—is indicated for a wide variety of dermatoses. In-office and at-home UVB treatments commonly are used, as are salon tanning and sunbathing. When selecting a form of phototherapy, patients are likely to consider safety, cost, effectiveness, insurance issues, and convenience. Research on patient preferences; the reasons for these preferences; and which options patients perceive to be the safest, most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient is lacking. We aimed to assess the forms of phototherapy that patients would most consider using; the factors influencing patient preferences; and the forms patients perceived as the safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient.
Methods
Study Participants—We recruited 500 Amazon Mechanical Turk users who were 18 years or older to complete our REDCap-generated survey. The study was approved by the Wake Forest University institutional review board (Winston-Salem, North Carolina).
Evaluation—Participants were asked, “If you were diagnosed with a skin disease that benefited from UV therapy, which of the following forms of UV therapy would you consider choosing?” Participants were instructed to choose all of the forms they would consider using. Available options included in-office UV, at-home UV, home tanning, salon tanning, sunbathing, and other. Participants were asked to select which factors—from safety, cost, effectiveness, issues with insurance, convenience, and other—influenced their decision-making; which form of phototherapy they would most consider along with the factors that influenced their preference for this specific form of phototherapy; and which options they considered to be safest and most cost-effective, efficacious, and convenient. Participants were asked to provide basic sociodemographic information, level of education, income, insurance status (private, Medicare, Medicaid, Veterans Affairs, and uninsured), and distance from the nearest dermatologist.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive and inferential statistics (χ2 test) were used to analyze the data with a significance set at P<.05.
Results
Five hundred participants completed the survey (Table 1).

Factors Influencing Patient Preferences—When asked to select all forms of phototherapy they would consider, 186 (37.2%) participants selected in-office UVB, 263 (52.6%) selected at-home UV, 141 (28.2%) selected home tanning, 117 (23.4%) selected salon tanning, 191 (38.2%) selected sunbathing, and 3 (0.6%) selected other. Participants who selected in-office UVB as an option were more likely to also select salon tanning (P<.012). No other relationship was found between the UVB options and the tanning options. When asked which factors influenced their phototherapy preferences, 295 (59%) selected convenience, 266 (53.2%) selected effectiveness, 220 (44%) selected safety, 218 (43.6%) selected cost, 72 (14.4%) selected issues with insurance, and 4 (0.8%) selected other. Forms of Phototherapy Patients Consider Using—When asked which form of phototherapy they would most consider using, 179 (35.8%) participants selected at-home UVB, 108 (21.6%) selected sunbathing, 92 (18.4%) selected in-office UVB, 62 (12.4%) selected home-tanning, 57 (11.4%) selected salon tanning, 1 (0.2%) selected other, and 1 participant provided no response (P<.001).
Reasons for Using Phototherapy—Of the 179 who selected at-home UVB, 125 (70%) cited convenience as a reason. Of the 108 who selected salon tanning as their top choice, 62 (57%) cited cost as a reason. Convenience (P<.001), cost (P<.001), and safety (P=.023) were related to top preference. Issues with insurance did not have a statistically significant relationship with the top preference. However, participant insurance type was related to top phototherapy preference (P=.021), with privately insured patients more likely to select in-office UVB, whereas those with Medicaid and Medicare were more likely to select home or salon tanning. Efficacy was not related to top preference. Furthermore, age, gender, education, income, and distance from nearest dermatologist were not related to top preference.
In-office UVB was perceived to be safest (P<.001) and most efficacious (P<.001). Meanwhile, at-home UVB was selected as most convenient (P<.001). Lastly, sunbathing was determined to be most cost-effective (P<.001)(Table 2). Cost-effectiveness had a relationship (P<.001) with the participant’s insurance, as those with private insurance were more likely to select at-home UVB, whereas those with Medicare or Medicaid were more likely to select the tanning options. Additionally, of the54 uninsured participants in the survey, 29 selected sunbathing as the most cost-effective option.

Comment
Phototherapy Treatment—UVB phototherapy at a wavelength of 290 to 320 nm (311–313 nm for narrowband UVB) is used to treat various dermatoses, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. UVB alters skin cytokines, induces apoptosis, promotes immunosuppression, causes DNA damage, and decreases the proliferation of dendritic cells and other cells of the innate immune system.1 In-office and at-home UV therapies make use of UVB wavelengths for treatment, while tanning and sunbathing contain not only UVB but also potentially harmful UVA rays. The wavelengths for indoor tanning devices include UVB at 280 to 315 nm and UVA at 315 to 400 nm, which are similar to those of the sun but with a different ratio of UVB to UVA and more intense total UV.2 When in-office and at-home UVB options are not available, various forms of tanning such as salon tanning and sunbathing may be alternatives that are widely used.3 One of the main reasons patients consider alternative phototherapy options is cost, as 1 in-office UVB treatment may cost $140, but a month of unlimited tanning may cost $30 or perhaps nothing if a patient has a gym membership with access to a tanning bed. Lack of insurance benefits covering phototherapy can exacerbate cost burden.4 However, tanning beds are associated with an increased risk for melanoma and nonmelanoma cancers.5,6 Additionally, all forms of phototherapy are associated with photoaging, but it is more intense with tanning and heliotherapy because of the presence of UVA, which penetrates deeper into the dermis.7 Meanwhile, for those who choose UVB therapy, deciding between an in-office and at-home UVB treatment could be a matter of convenience, as patients must consider long trips to the physician’s office; insurance status, as some insurances may not cover at-home UVB; or efficacy, which might be influenced by the presence of a physician or other medical staff. In many cases, patients may not be informed that at-home UVB is an option.
Patient Preferences—At-home UVB therapy was the most popular option in our study population, with most participants (52.6%) considering using it, and 35.9% choosing it as their top choice over all other phototherapy options. Safety, cost, and convenience were all found to be related to the option participants would most consider using. Prior analysis between at-home UVB and in-office UVB for the treatment of psoriasis determined that at-home UVB is as safe and cost-effective as in-office UVB without the inconvenience of the patient having to take time out of the week to visit the physician’s office,8,9 making at-home UVB an option dermatologists may strongly consider for patients who value safety, cost, and convenience. Oddly, efficacy was not related to the top preference, despite being the second highest–cited factor (53.2%) for which forms of phototherapy participants would consider using. For insurance coverage, those with Medicaid and Medicare selected the cheaper tanning options with higher-than-expected frequencies. Although problems with insurance were not related to the top preference, insurance status was related, suggesting that preferences are tied to cost. Of note, while the number of dermatologists that accept Medicare has increased in the last few years, there still remains an uneven distribution of phototherapy clinics. As of 2015, there were 19 million individuals who qualified for Medicare without a clinic within driving distance.10 This problem likely also exists for many Medicaid patients who may not qualify for at-home UVB. In this scenario, tanning or heliotherapy may be effective alternatives.
In-Office vs At-Home Options—Although in-office UVB was the option considered safest (26.2%) and most efficacious (26.8%), it was followed closely by at-home UVB in both categories (safest, 23.8%; most efficacious, 24.2%). Meanwhile, at-home UVB (40.2%) was chosen as the most convenient. Some patients consider tanning options over in-office UVB because of the inconvenience of traveling to an appointment.11 Therefore, at-home tanning may be a convenient alternative for these patients.
Considerations—Although our study was limited to an adult population, issues with convenience exist for the pediatric population as well, as children may need to miss multiple days of school each week to be treated in the office. For these pediatric patients, an at-home unit is preferable; however; issues with insurance coverage remain a challenge.12 Increasing insurance coverage of at-home units for the pediatric population therefore would be most prudent. However, when other options have been exhausted, including in-office UVB, tanning and sunbathing may be viable alternatives because of cost and convenience. In our study, sunbathing (33.2%) was considered the most cost-effective, likely because it does not require expensive equipment or a visit to a salon or physician’s office. Sunbathing has been effective in treating some dermatologic conditions, such as atopic dermatitis.13 However, it may only be effective during certain months and at different latitudes—conditions that make UVB sun rays more accessible—particularly when treating psoriasis.14 Furthermore, sunbathing may not be as cost-effective in patients with average-severity psoriasis compared with conventional psoriasis therapy because of the costs of travel to areas with sufficient UVB rays for treatment.15 Additionally, insurance status was related to which option was selected as the most cost-effective, as 29 (53.7%) of 54 uninsured participants chose sunbathing as the most cost-effective option, while only 92 (34.2%) of 269 privately insured patients selected sunbathing. Therefore, insurance status may be a factor for dermatologists to consider if a patient prefers a treatment that is cost-effective. Overall, dermatologists could perhaps consider guiding patients and optimizing their treatment plans based on the factors most important to the patients while understanding that costs and insurance status may ultimately determine the treatment option.
Limitations—Survey participants were recruited on Amazon Mechanical Turk, which could create sampling bias. Furthermore, these participants were representative of the general public and not exclusively patients on phototherapy, therefore representing the opinions of the general public and not those who may require phototherapy. Furthermore, given the nature of the survey, the study was limited to the adult population.
- Totonchy MB, Chiu MW. UV-based therapy. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:399-413, ix-x.
- Nilsen LT, Hannevik M, Veierød MB. Ultraviolet exposure from indoor tanning devices: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:730-740.
- Su J, Pearce DJ, Feldman SR. The role of commercial tanning beds and ultraviolet A light in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2005;16:324-326.
- Anderson KL, Huang KE, Huang WW, et al. Dermatology residents are prescribing tanning bed treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt19h4k7sx.
- Wehner MR, Shive ML, Chren MM, et al. Indoor tanning and non-melanoma skin cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5909.
- Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P, et al. Cutaneous melanomaattributable to sunbed use: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:E4757.
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407.
- Koek MB, Buskens E, van Weelden H, et al. Home versus outpatient ultraviolet B phototherapy for mild to severe psoriasis: pragmatic multicentre randomized controlled non-inferiority trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2009;338:b1542.
- Koek MB, Sigurdsson V, van Weelden H, et al. Cost effectiveness of home ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis: economic evaluation of a randomized controlled trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2010;340:c1490.
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679.
- Felton S, Adinoff B, Jeon-Slaughter H, et al. The significant health threat from tanning bed use as a self-treatment for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1015-1017.
- Juarez MC, Grossberg AL. Phototherapy in the pediatric population. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:91-108.
- Autio P, Komulainen P, Larni HM. Heliotherapy in atopic dermatitis: a prospective study on climatotherapy using the SCORAD index. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:436-440.
- Krzys´cin JW, Jarosławski J, Rajewska-Wie˛ch B, et al. Effectiveness of heliotherapy for psoriasis clearance in low and mid-latitudinal regions: a theoretical approach. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2012;115:35-41.
- Snellman E, Maljanen T, Aromaa A, et al. Effect of heliotherapy on the cost of psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:288-292.
- Totonchy MB, Chiu MW. UV-based therapy. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:399-413, ix-x.
- Nilsen LT, Hannevik M, Veierød MB. Ultraviolet exposure from indoor tanning devices: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:730-740.
- Su J, Pearce DJ, Feldman SR. The role of commercial tanning beds and ultraviolet A light in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2005;16:324-326.
- Anderson KL, Huang KE, Huang WW, et al. Dermatology residents are prescribing tanning bed treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt19h4k7sx.
- Wehner MR, Shive ML, Chren MM, et al. Indoor tanning and non-melanoma skin cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5909.
- Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P, et al. Cutaneous melanomaattributable to sunbed use: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:E4757.
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407.
- Koek MB, Buskens E, van Weelden H, et al. Home versus outpatient ultraviolet B phototherapy for mild to severe psoriasis: pragmatic multicentre randomized controlled non-inferiority trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2009;338:b1542.
- Koek MB, Sigurdsson V, van Weelden H, et al. Cost effectiveness of home ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis: economic evaluation of a randomized controlled trial (PLUTO study). BMJ. 2010;340:c1490.
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679.
- Felton S, Adinoff B, Jeon-Slaughter H, et al. The significant health threat from tanning bed use as a self-treatment for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1015-1017.
- Juarez MC, Grossberg AL. Phototherapy in the pediatric population. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:91-108.
- Autio P, Komulainen P, Larni HM. Heliotherapy in atopic dermatitis: a prospective study on climatotherapy using the SCORAD index. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:436-440.
- Krzys´cin JW, Jarosławski J, Rajewska-Wie˛ch B, et al. Effectiveness of heliotherapy for psoriasis clearance in low and mid-latitudinal regions: a theoretical approach. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2012;115:35-41.
- Snellman E, Maljanen T, Aromaa A, et al. Effect of heliotherapy on the cost of psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:288-292.
Practice Points
- Patients have different priorities when selecting phototherapy, including safety, costs, effectiveness, insurance issues, and convenience.
- By offering and educating patients on all forms of phototherapy, dermatologists may help guide patients to their optimal treatment plan according to patient priorities.