User login
A New Treatment Target for PTSD?
Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums than unaffected adults, suggesting that this part of the brain may be a potential therapeutic target.
According to recent research on more than 4000 adults, cerebellum volume was significantly smaller (by about 2%) in those with PTSD than in trauma-exposed and trauma-naive controls without PTSD.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing functions,” lead author Ashley Huggins, PhD, said in a news release.
“If we know what areas are implicated, then we can start to focus interventions like brain stimulation on the cerebellum and potentially improve treatment outcomes,” said Dr. Huggins, who worked on the study while a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Rajendra A. Morey, MD, at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and is now at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
While the cerebellum is known for its role in coordinating movement and balance, it also plays a key role in emotions and memory, which are affected by PTSD.
Smaller cerebellar volume has been observed in some adult and pediatric populations with PTSD.
However, those studies have been limited by either small sample sizes, the failure to consider key neuroanatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum, or a focus on certain populations such as veterans of sexual assault victims with PTSD.
To overcome these limitations, the researchers conducted a mega-analysis of total and subregional cerebellar volumes in a large, multicohort dataset from the Enhancing NeuroImaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA)-Psychiatric Genomics Consortium PTSD workgroup that was published online on January 10, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry.
They employed a novel, standardized ENIGMA cerebellum parcellation protocol to quantify cerebellar lobule volumes using structural MRI data from 1642 adults with PTSD and 2573 healthy controls without PTSD (88% trauma-exposed and 12% trauma-naive).
After adjustment for age, gender, and total intracranial volume, PTSD was associated with significant gray and white matter reductions of the cerebellum.
People with PTSD demonstrated smaller total cerebellum volume as well as reduced volume in subregions primarily within the posterior cerebellum, vermis, and flocculonodular cerebellum than controls.
In general, PTSD severity was more robustly associated with cerebellar volume differences than PTSD diagnosis.
Focusing purely on a “yes-or-no” categorical diagnosis didn’t always provide the clearest picture. “When we looked at PTSD severity, people who had more severe forms of the disorder had an even smaller cerebellar volume,” Dr. Huggins explained in the news release.
Novel Treatment Target
These findings add to “an emerging literature that underscores the relevance of cerebellar structure in the pathophysiology of PTSD,” the researchers noted.
They caution that despite the significant findings suggesting associations between PTSD and smaller cerebellar volumes, effect sizes were small. “As such, it is unlikely that structural cerebellar volumes alone will provide a clinically useful biomarker (eg, for individual-level prediction).”
Nonetheless, the study highlights the cerebellum as a “novel treatment target that may be leveraged to improve treatment outcomes for PTSD,” they wrote.
They noted that prior work has shown that the cerebellum is sensitive to external modulation. For example, noninvasive brain stimulation of the cerebellum has been shown to modulate cognitive, emotional, and social processes commonly disrupted in PTSD.
Commenting on this research, Cyrus A. Raji, MD, PhD, associate professor of radiology and neurology at Washington University in St. Louis, noted that this “large neuroimaging study links PTSD to cerebellar volume loss.”
“However, PTSD and traumatic brain injury frequently co-occur, and PTSD also frequently arises after TBI. Additionally, TBI is strongly linked to cerebellar volume loss,” Dr. Raji pointed out.
“Future studies need to better delineate volume loss from these conditions, especially when they are comorbid, though the expectation is these effects would be additive with TBI being the initial and most severe driving force,” Dr. Raji added.
The research had no commercial funding. Author disclosures are listed with the original article. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution Medicine LLC.
A version of this article appears on Medscape.com.
Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums than unaffected adults, suggesting that this part of the brain may be a potential therapeutic target.
According to recent research on more than 4000 adults, cerebellum volume was significantly smaller (by about 2%) in those with PTSD than in trauma-exposed and trauma-naive controls without PTSD.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing functions,” lead author Ashley Huggins, PhD, said in a news release.
“If we know what areas are implicated, then we can start to focus interventions like brain stimulation on the cerebellum and potentially improve treatment outcomes,” said Dr. Huggins, who worked on the study while a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Rajendra A. Morey, MD, at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and is now at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
While the cerebellum is known for its role in coordinating movement and balance, it also plays a key role in emotions and memory, which are affected by PTSD.
Smaller cerebellar volume has been observed in some adult and pediatric populations with PTSD.
However, those studies have been limited by either small sample sizes, the failure to consider key neuroanatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum, or a focus on certain populations such as veterans of sexual assault victims with PTSD.
To overcome these limitations, the researchers conducted a mega-analysis of total and subregional cerebellar volumes in a large, multicohort dataset from the Enhancing NeuroImaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA)-Psychiatric Genomics Consortium PTSD workgroup that was published online on January 10, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry.
They employed a novel, standardized ENIGMA cerebellum parcellation protocol to quantify cerebellar lobule volumes using structural MRI data from 1642 adults with PTSD and 2573 healthy controls without PTSD (88% trauma-exposed and 12% trauma-naive).
After adjustment for age, gender, and total intracranial volume, PTSD was associated with significant gray and white matter reductions of the cerebellum.
People with PTSD demonstrated smaller total cerebellum volume as well as reduced volume in subregions primarily within the posterior cerebellum, vermis, and flocculonodular cerebellum than controls.
In general, PTSD severity was more robustly associated with cerebellar volume differences than PTSD diagnosis.
Focusing purely on a “yes-or-no” categorical diagnosis didn’t always provide the clearest picture. “When we looked at PTSD severity, people who had more severe forms of the disorder had an even smaller cerebellar volume,” Dr. Huggins explained in the news release.
Novel Treatment Target
These findings add to “an emerging literature that underscores the relevance of cerebellar structure in the pathophysiology of PTSD,” the researchers noted.
They caution that despite the significant findings suggesting associations between PTSD and smaller cerebellar volumes, effect sizes were small. “As such, it is unlikely that structural cerebellar volumes alone will provide a clinically useful biomarker (eg, for individual-level prediction).”
Nonetheless, the study highlights the cerebellum as a “novel treatment target that may be leveraged to improve treatment outcomes for PTSD,” they wrote.
They noted that prior work has shown that the cerebellum is sensitive to external modulation. For example, noninvasive brain stimulation of the cerebellum has been shown to modulate cognitive, emotional, and social processes commonly disrupted in PTSD.
Commenting on this research, Cyrus A. Raji, MD, PhD, associate professor of radiology and neurology at Washington University in St. Louis, noted that this “large neuroimaging study links PTSD to cerebellar volume loss.”
“However, PTSD and traumatic brain injury frequently co-occur, and PTSD also frequently arises after TBI. Additionally, TBI is strongly linked to cerebellar volume loss,” Dr. Raji pointed out.
“Future studies need to better delineate volume loss from these conditions, especially when they are comorbid, though the expectation is these effects would be additive with TBI being the initial and most severe driving force,” Dr. Raji added.
The research had no commercial funding. Author disclosures are listed with the original article. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution Medicine LLC.
A version of this article appears on Medscape.com.
Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums than unaffected adults, suggesting that this part of the brain may be a potential therapeutic target.
According to recent research on more than 4000 adults, cerebellum volume was significantly smaller (by about 2%) in those with PTSD than in trauma-exposed and trauma-naive controls without PTSD.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing functions,” lead author Ashley Huggins, PhD, said in a news release.
“If we know what areas are implicated, then we can start to focus interventions like brain stimulation on the cerebellum and potentially improve treatment outcomes,” said Dr. Huggins, who worked on the study while a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Rajendra A. Morey, MD, at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and is now at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
While the cerebellum is known for its role in coordinating movement and balance, it also plays a key role in emotions and memory, which are affected by PTSD.
Smaller cerebellar volume has been observed in some adult and pediatric populations with PTSD.
However, those studies have been limited by either small sample sizes, the failure to consider key neuroanatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum, or a focus on certain populations such as veterans of sexual assault victims with PTSD.
To overcome these limitations, the researchers conducted a mega-analysis of total and subregional cerebellar volumes in a large, multicohort dataset from the Enhancing NeuroImaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA)-Psychiatric Genomics Consortium PTSD workgroup that was published online on January 10, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry.
They employed a novel, standardized ENIGMA cerebellum parcellation protocol to quantify cerebellar lobule volumes using structural MRI data from 1642 adults with PTSD and 2573 healthy controls without PTSD (88% trauma-exposed and 12% trauma-naive).
After adjustment for age, gender, and total intracranial volume, PTSD was associated with significant gray and white matter reductions of the cerebellum.
People with PTSD demonstrated smaller total cerebellum volume as well as reduced volume in subregions primarily within the posterior cerebellum, vermis, and flocculonodular cerebellum than controls.
In general, PTSD severity was more robustly associated with cerebellar volume differences than PTSD diagnosis.
Focusing purely on a “yes-or-no” categorical diagnosis didn’t always provide the clearest picture. “When we looked at PTSD severity, people who had more severe forms of the disorder had an even smaller cerebellar volume,” Dr. Huggins explained in the news release.
Novel Treatment Target
These findings add to “an emerging literature that underscores the relevance of cerebellar structure in the pathophysiology of PTSD,” the researchers noted.
They caution that despite the significant findings suggesting associations between PTSD and smaller cerebellar volumes, effect sizes were small. “As such, it is unlikely that structural cerebellar volumes alone will provide a clinically useful biomarker (eg, for individual-level prediction).”
Nonetheless, the study highlights the cerebellum as a “novel treatment target that may be leveraged to improve treatment outcomes for PTSD,” they wrote.
They noted that prior work has shown that the cerebellum is sensitive to external modulation. For example, noninvasive brain stimulation of the cerebellum has been shown to modulate cognitive, emotional, and social processes commonly disrupted in PTSD.
Commenting on this research, Cyrus A. Raji, MD, PhD, associate professor of radiology and neurology at Washington University in St. Louis, noted that this “large neuroimaging study links PTSD to cerebellar volume loss.”
“However, PTSD and traumatic brain injury frequently co-occur, and PTSD also frequently arises after TBI. Additionally, TBI is strongly linked to cerebellar volume loss,” Dr. Raji pointed out.
“Future studies need to better delineate volume loss from these conditions, especially when they are comorbid, though the expectation is these effects would be additive with TBI being the initial and most severe driving force,” Dr. Raji added.
The research had no commercial funding. Author disclosures are listed with the original article. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution Medicine LLC.
A version of this article appears on Medscape.com.
Shelf Life for Opioid Overdose Drug Naloxone Extended
At the request of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Emergent BioSolutions has extended the shelf life of the rapid opioid overdose reversal agent, naloxone (4 mg) nasal spray (Narcan), from 3 to 4 years.
Naloxone is “an important tool” in addressing opioid overdoses, and this extension supports the FDA’s “efforts to ensure more OTC naloxone products remain available to the public,” Marta Sokolowska, PhD, with the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
Naloxone nasal spray was first approved by the FDA in 2015 as a prescription drug. Last spring, the agency approved the drug for over-the-counter use.
“The shelf life of products that were produced and distributed prior to this announcement is not affected and remains unchanged. Prescribers, patients, and caregivers are advised to continue to abide by the expiration date printed on each product’s packaging and within the product’s labeling,” the FDA advised.
“FDA’s request for this shelf-life extension is a testament to the agency’s continuing progress toward implementing the FDA Overdose Prevention Framework, which provides our vision to undertake impactful, creative actions to encourage harm reduction and innovation in reducing controlled substance-related overdoses and deaths,” the agency said.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 1999 to 2021, nearly 645,000 people died from an overdose involving any opioid, including prescription and illicit opioids.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
At the request of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Emergent BioSolutions has extended the shelf life of the rapid opioid overdose reversal agent, naloxone (4 mg) nasal spray (Narcan), from 3 to 4 years.
Naloxone is “an important tool” in addressing opioid overdoses, and this extension supports the FDA’s “efforts to ensure more OTC naloxone products remain available to the public,” Marta Sokolowska, PhD, with the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
Naloxone nasal spray was first approved by the FDA in 2015 as a prescription drug. Last spring, the agency approved the drug for over-the-counter use.
“The shelf life of products that were produced and distributed prior to this announcement is not affected and remains unchanged. Prescribers, patients, and caregivers are advised to continue to abide by the expiration date printed on each product’s packaging and within the product’s labeling,” the FDA advised.
“FDA’s request for this shelf-life extension is a testament to the agency’s continuing progress toward implementing the FDA Overdose Prevention Framework, which provides our vision to undertake impactful, creative actions to encourage harm reduction and innovation in reducing controlled substance-related overdoses and deaths,” the agency said.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 1999 to 2021, nearly 645,000 people died from an overdose involving any opioid, including prescription and illicit opioids.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
At the request of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Emergent BioSolutions has extended the shelf life of the rapid opioid overdose reversal agent, naloxone (4 mg) nasal spray (Narcan), from 3 to 4 years.
Naloxone is “an important tool” in addressing opioid overdoses, and this extension supports the FDA’s “efforts to ensure more OTC naloxone products remain available to the public,” Marta Sokolowska, PhD, with the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
Naloxone nasal spray was first approved by the FDA in 2015 as a prescription drug. Last spring, the agency approved the drug for over-the-counter use.
“The shelf life of products that were produced and distributed prior to this announcement is not affected and remains unchanged. Prescribers, patients, and caregivers are advised to continue to abide by the expiration date printed on each product’s packaging and within the product’s labeling,” the FDA advised.
“FDA’s request for this shelf-life extension is a testament to the agency’s continuing progress toward implementing the FDA Overdose Prevention Framework, which provides our vision to undertake impactful, creative actions to encourage harm reduction and innovation in reducing controlled substance-related overdoses and deaths,” the agency said.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 1999 to 2021, nearly 645,000 people died from an overdose involving any opioid, including prescription and illicit opioids.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Positive Phase 3 Results for Novel Antipsychotic in Schizophrenia
in the phase 3 EMERGENT-2 trial, a new study shows.
Xanomeline-trospium treatment was not associated with weight gain compared with placebo, and the incidences of extrapyramidal motor symptoms or akathisia were low and similar between treatment groups.
The EMERGENT-2 results “support the potential for KarXT to represent a new class of effective and well-tolerated antipsychotic medicines based on activating muscarinic receptors, not the D2 dopamine receptor-blocking mechanism of all current antipsychotic medications,” write the authors, led by Inder Kaul, MD, with Karuna Therapeutics, Boston, Massachusetts.
The US Food and Drug Administration has accepted the company’s new drug application for KarXT for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. The Prescription Drug User Fee Act action date is September 26, 2024.
Results of the EMERGENT-2 trial were published online on December 14, 2023, in The Lancet.
Beyond the Dopamine System
Evidence suggests the muscarinic cholinergic system is involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Xanomeline is an oral muscarinic cholinergic receptor agonist that does not have direct effects on the dopamine receptor. Combining it with trospium chloride, an oral pan-muscarinic receptor antagonist, is thought to reduce side effects associated with xanomeline’s activation of peripheral muscarinic receptors in peripheral tissues.
EMERGENT-2 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 252 adults with schizophrenia who recently experienced a worsening of psychotic symptoms warranting hospitalization.
Patients were treated for 5 weeks, with xanomeline-trospium titrated from 50 mg/20 mg twice daily to 125 mg/30 mg twice daily. Efficacy and safety analyses were conducted in those who had received at least one dose of the study drug.
The primary endpoint was change in baseline to week 5 in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score (range, 30-210, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms).
At the end of the treatment period, xanomeline-trospium was associated with a significant 9.6-point reduction in PANSS total scores relative to placebo. PANSS total scores fell by 21.2 points with xanomeline-trospium vs 11.6 points with placebo (P < .0001; Cohen d effect size, 0.61).
All secondary endpoints were also met, with active treatment demonstrating statistically significant reductions compared with placebo at week 5 (P < .05).
These secondary endpoints included change in PANSS positive subscale, PANSS negative subscale, PANSS Marder negative factor, Clinical Global Impression-Severity score, and percentage of participants achieving at least a 30% reduction from baseline to week 5 in PANSS total score.
Rates of discontinuation related to side effects were similar with active treatment and placebo (7% and 6%, respectively). The most common side effects with xanomeline-trospium were constipation (21%), dyspepsia (19%), nausea (19%), vomiting (14%), headache (14%), hypertension (10%), dizziness (9%), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (6%).
Xanomeline-trospium demonstrated a “distinctive safety and tolerability profile and was not associated with many of the adverse events typically associated with current antipsychotic treatments, including extrapyramidal motor symptoms, weight gain, changes in lipid and glucose parameters, and somnolence,” the authors report.
Potential ‘Game-Changer’
Xanomeline-trospium is a potential “game-changer” for patients with schizophrenia, Ann Shinn, MD, MPH, director of clinical research, Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder Research Program, McLean Hospital, and assistant professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
There was a “clear separation between the people who were randomized to KarXT vs placebo. It’s not just a statistically significant but also a clinically significant difference in the reduction in symptoms of psychosis,” said Dr. Shinn, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“What’s really exciting” is that the drug did not cause weight gain or extrapyramidal symptoms compared with placebo. “Both from an efficacy and side-effect perspective, I think more patients with schizophrenia are going to be willing to take medication,” Dr. Shinn noted.
Also commenting on this research for this news organization, René Kahn, MD, PhD, professor and chair of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, noted that current antipsychotic medications for schizophrenia work “directly on the dopamine system — either as dopamine antagonists or partial agonist.”
Xanomeline-trospium provides a “new mechanism of action, a new system that’s being targeted in the treatment of schizophrenia, and the effect size was rather large, so the drug didn’t just squeak by,” Dr. Kahn said.
Nonetheless, “we’ll have to wait and see whether it’s as effective or more effective than drugs currently on the market. The proof of the pudding will come when it’s marketed and used on thousands and thousands of patients,” Dr. Kahn added.
The coauthors of an accompanying commentary say the EMERGENT-2 findings “strongly support the possibility that agonism of muscarinic receptors provides the first viable antipsychotic alternative to blocking the dopamine D2 receptor for more than 70 years, and as such encourage further research.”
However, as a regulatory trial, EMERGENT-2 does not provide comparative data on the benefits and harms of KarXT with existing alternatives.
This represents a “missed opportunity to provide patients and clinicians with the information that is clinically needed — what is the treatment of choice for a patient?” writes Andrea Cipriani, MD, PhD, with the Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, and co-authors.
The study was funded by Karuna Therapeutics. Several authors disclosed relationships with the company. Dr. Kahn disclosed various relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Dr. Cipriani received research, educational, and consultancy fees from the Italian Network for Paediatric Trials, the CARIPLO Foundation, Lundbeck, and Angelini Pharma and was chief investigator of one trial about seltorexant in adolescent depression, sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Shinn had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in the phase 3 EMERGENT-2 trial, a new study shows.
Xanomeline-trospium treatment was not associated with weight gain compared with placebo, and the incidences of extrapyramidal motor symptoms or akathisia were low and similar between treatment groups.
The EMERGENT-2 results “support the potential for KarXT to represent a new class of effective and well-tolerated antipsychotic medicines based on activating muscarinic receptors, not the D2 dopamine receptor-blocking mechanism of all current antipsychotic medications,” write the authors, led by Inder Kaul, MD, with Karuna Therapeutics, Boston, Massachusetts.
The US Food and Drug Administration has accepted the company’s new drug application for KarXT for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. The Prescription Drug User Fee Act action date is September 26, 2024.
Results of the EMERGENT-2 trial were published online on December 14, 2023, in The Lancet.
Beyond the Dopamine System
Evidence suggests the muscarinic cholinergic system is involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Xanomeline is an oral muscarinic cholinergic receptor agonist that does not have direct effects on the dopamine receptor. Combining it with trospium chloride, an oral pan-muscarinic receptor antagonist, is thought to reduce side effects associated with xanomeline’s activation of peripheral muscarinic receptors in peripheral tissues.
EMERGENT-2 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 252 adults with schizophrenia who recently experienced a worsening of psychotic symptoms warranting hospitalization.
Patients were treated for 5 weeks, with xanomeline-trospium titrated from 50 mg/20 mg twice daily to 125 mg/30 mg twice daily. Efficacy and safety analyses were conducted in those who had received at least one dose of the study drug.
The primary endpoint was change in baseline to week 5 in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score (range, 30-210, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms).
At the end of the treatment period, xanomeline-trospium was associated with a significant 9.6-point reduction in PANSS total scores relative to placebo. PANSS total scores fell by 21.2 points with xanomeline-trospium vs 11.6 points with placebo (P < .0001; Cohen d effect size, 0.61).
All secondary endpoints were also met, with active treatment demonstrating statistically significant reductions compared with placebo at week 5 (P < .05).
These secondary endpoints included change in PANSS positive subscale, PANSS negative subscale, PANSS Marder negative factor, Clinical Global Impression-Severity score, and percentage of participants achieving at least a 30% reduction from baseline to week 5 in PANSS total score.
Rates of discontinuation related to side effects were similar with active treatment and placebo (7% and 6%, respectively). The most common side effects with xanomeline-trospium were constipation (21%), dyspepsia (19%), nausea (19%), vomiting (14%), headache (14%), hypertension (10%), dizziness (9%), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (6%).
Xanomeline-trospium demonstrated a “distinctive safety and tolerability profile and was not associated with many of the adverse events typically associated with current antipsychotic treatments, including extrapyramidal motor symptoms, weight gain, changes in lipid and glucose parameters, and somnolence,” the authors report.
Potential ‘Game-Changer’
Xanomeline-trospium is a potential “game-changer” for patients with schizophrenia, Ann Shinn, MD, MPH, director of clinical research, Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder Research Program, McLean Hospital, and assistant professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
There was a “clear separation between the people who were randomized to KarXT vs placebo. It’s not just a statistically significant but also a clinically significant difference in the reduction in symptoms of psychosis,” said Dr. Shinn, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“What’s really exciting” is that the drug did not cause weight gain or extrapyramidal symptoms compared with placebo. “Both from an efficacy and side-effect perspective, I think more patients with schizophrenia are going to be willing to take medication,” Dr. Shinn noted.
Also commenting on this research for this news organization, René Kahn, MD, PhD, professor and chair of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, noted that current antipsychotic medications for schizophrenia work “directly on the dopamine system — either as dopamine antagonists or partial agonist.”
Xanomeline-trospium provides a “new mechanism of action, a new system that’s being targeted in the treatment of schizophrenia, and the effect size was rather large, so the drug didn’t just squeak by,” Dr. Kahn said.
Nonetheless, “we’ll have to wait and see whether it’s as effective or more effective than drugs currently on the market. The proof of the pudding will come when it’s marketed and used on thousands and thousands of patients,” Dr. Kahn added.
The coauthors of an accompanying commentary say the EMERGENT-2 findings “strongly support the possibility that agonism of muscarinic receptors provides the first viable antipsychotic alternative to blocking the dopamine D2 receptor for more than 70 years, and as such encourage further research.”
However, as a regulatory trial, EMERGENT-2 does not provide comparative data on the benefits and harms of KarXT with existing alternatives.
This represents a “missed opportunity to provide patients and clinicians with the information that is clinically needed — what is the treatment of choice for a patient?” writes Andrea Cipriani, MD, PhD, with the Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, and co-authors.
The study was funded by Karuna Therapeutics. Several authors disclosed relationships with the company. Dr. Kahn disclosed various relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Dr. Cipriani received research, educational, and consultancy fees from the Italian Network for Paediatric Trials, the CARIPLO Foundation, Lundbeck, and Angelini Pharma and was chief investigator of one trial about seltorexant in adolescent depression, sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Shinn had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in the phase 3 EMERGENT-2 trial, a new study shows.
Xanomeline-trospium treatment was not associated with weight gain compared with placebo, and the incidences of extrapyramidal motor symptoms or akathisia were low and similar between treatment groups.
The EMERGENT-2 results “support the potential for KarXT to represent a new class of effective and well-tolerated antipsychotic medicines based on activating muscarinic receptors, not the D2 dopamine receptor-blocking mechanism of all current antipsychotic medications,” write the authors, led by Inder Kaul, MD, with Karuna Therapeutics, Boston, Massachusetts.
The US Food and Drug Administration has accepted the company’s new drug application for KarXT for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. The Prescription Drug User Fee Act action date is September 26, 2024.
Results of the EMERGENT-2 trial were published online on December 14, 2023, in The Lancet.
Beyond the Dopamine System
Evidence suggests the muscarinic cholinergic system is involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Xanomeline is an oral muscarinic cholinergic receptor agonist that does not have direct effects on the dopamine receptor. Combining it with trospium chloride, an oral pan-muscarinic receptor antagonist, is thought to reduce side effects associated with xanomeline’s activation of peripheral muscarinic receptors in peripheral tissues.
EMERGENT-2 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 252 adults with schizophrenia who recently experienced a worsening of psychotic symptoms warranting hospitalization.
Patients were treated for 5 weeks, with xanomeline-trospium titrated from 50 mg/20 mg twice daily to 125 mg/30 mg twice daily. Efficacy and safety analyses were conducted in those who had received at least one dose of the study drug.
The primary endpoint was change in baseline to week 5 in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score (range, 30-210, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms).
At the end of the treatment period, xanomeline-trospium was associated with a significant 9.6-point reduction in PANSS total scores relative to placebo. PANSS total scores fell by 21.2 points with xanomeline-trospium vs 11.6 points with placebo (P < .0001; Cohen d effect size, 0.61).
All secondary endpoints were also met, with active treatment demonstrating statistically significant reductions compared with placebo at week 5 (P < .05).
These secondary endpoints included change in PANSS positive subscale, PANSS negative subscale, PANSS Marder negative factor, Clinical Global Impression-Severity score, and percentage of participants achieving at least a 30% reduction from baseline to week 5 in PANSS total score.
Rates of discontinuation related to side effects were similar with active treatment and placebo (7% and 6%, respectively). The most common side effects with xanomeline-trospium were constipation (21%), dyspepsia (19%), nausea (19%), vomiting (14%), headache (14%), hypertension (10%), dizziness (9%), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (6%).
Xanomeline-trospium demonstrated a “distinctive safety and tolerability profile and was not associated with many of the adverse events typically associated with current antipsychotic treatments, including extrapyramidal motor symptoms, weight gain, changes in lipid and glucose parameters, and somnolence,” the authors report.
Potential ‘Game-Changer’
Xanomeline-trospium is a potential “game-changer” for patients with schizophrenia, Ann Shinn, MD, MPH, director of clinical research, Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder Research Program, McLean Hospital, and assistant professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
There was a “clear separation between the people who were randomized to KarXT vs placebo. It’s not just a statistically significant but also a clinically significant difference in the reduction in symptoms of psychosis,” said Dr. Shinn, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“What’s really exciting” is that the drug did not cause weight gain or extrapyramidal symptoms compared with placebo. “Both from an efficacy and side-effect perspective, I think more patients with schizophrenia are going to be willing to take medication,” Dr. Shinn noted.
Also commenting on this research for this news organization, René Kahn, MD, PhD, professor and chair of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, noted that current antipsychotic medications for schizophrenia work “directly on the dopamine system — either as dopamine antagonists or partial agonist.”
Xanomeline-trospium provides a “new mechanism of action, a new system that’s being targeted in the treatment of schizophrenia, and the effect size was rather large, so the drug didn’t just squeak by,” Dr. Kahn said.
Nonetheless, “we’ll have to wait and see whether it’s as effective or more effective than drugs currently on the market. The proof of the pudding will come when it’s marketed and used on thousands and thousands of patients,” Dr. Kahn added.
The coauthors of an accompanying commentary say the EMERGENT-2 findings “strongly support the possibility that agonism of muscarinic receptors provides the first viable antipsychotic alternative to blocking the dopamine D2 receptor for more than 70 years, and as such encourage further research.”
However, as a regulatory trial, EMERGENT-2 does not provide comparative data on the benefits and harms of KarXT with existing alternatives.
This represents a “missed opportunity to provide patients and clinicians with the information that is clinically needed — what is the treatment of choice for a patient?” writes Andrea Cipriani, MD, PhD, with the Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, and co-authors.
The study was funded by Karuna Therapeutics. Several authors disclosed relationships with the company. Dr. Kahn disclosed various relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Dr. Cipriani received research, educational, and consultancy fees from the Italian Network for Paediatric Trials, the CARIPLO Foundation, Lundbeck, and Angelini Pharma and was chief investigator of one trial about seltorexant in adolescent depression, sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Shinn had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Deaths on Decline, But New Cancer Cases to Hit Record High This Year
Overall cancer mortality in the United States has continued to decline, with more than 4 million cancer deaths averted since 1991, according to the 2024 American Cancer Society (ACS) annual report on cancer trends.
The “good news is that we are continuing to see a decline in cancer mortality,” which follows the steady decline we’ve observed in cancer mortality over the past three decades, Rebecca Siegel, MPH, with ACS, and lead author of the new report, told this news organization.
However, these gains are “threatened by increasing incidence for many common cancers, including 6 of the top 10 most commonly diagnosed cancers,” Ms. Siegel said.
Overall, new cancer diagnoses are projected to top 2 million in 2024. That’s an average of 5480 new diagnoses each day or one person diagnosed every 15 seconds.
“In the US, the way our healthcare system is designed, we like to treat more than we like to prevent disease, and I would personally like to see a shift towards more emphasis on cancer prevention,” she added.
The full report was published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
Cancer Hitting at Younger Ages
Although advancing age remains the strongest determinate of cancer risk, the new data showed that cancer incidence is steadily increasing in younger populations.
What’s most alarming is the increase in cancer diagnoses in adults under 50 years.
Between 2015 and 2019, incidence rates increased by 0.6%-1% annually for breast, pancreas, and uterine corpus cancers, by 1%-2% annually for cervical cancer in women between 30 and 44 years, and by 2%-3% annually for prostate, kidney, melanoma, and human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers, as well as liver cancer in women.
The continuing rise in colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence in younger adults, in particular, is “very concerning,” Ms. Siegel said, and has shifted mortality patterns among adults younger than 50 years.
In this group, CRC is now the leading cause of cancer death in men and the second-leading cause in women behind breast cancer — up from the fourth leading cause of cancer death in both younger men and women 2 decades ago.
The obesity epidemic is likely a contributing factor in rising CRC rates, “but it’s not the whole story,” Ms. Siegel told this news organization. “A lot of work is going on to try to uncover what exactly is causing an increased risk of colorectal cancer.”
The proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 50-64 years has also increased — from 25% in 1995 to 30% in 2019-2020 — while the proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 65 years and older fell from 61% to 58% in that time frame. Among this older population, the authors observed steep declines in the incidence of prostate cancer and smoking-related cancers.
“Every generation born after the 1950s has had higher cancer risk than the previous generation. That tells us is that there is some exposure that is yet unknown that is causing this increased risk,” Ms. Siegel noted.
To halt and reverse this trend, it will be important to increase screening uptake as well as awareness of noninvasive stool tests and follow-up care in younger adults, Ahmedin Jemal, PhD, with ACS, commented in a press release.
Other key findings in the report include the sharp decline in cervical cancer incidence rates in women in their 20s — the first cohort to receive the HPV vaccine — but increases of nearly 2% in women 30-44 years, highlighting the need for more screening in young women as well as broader uptake of the vaccine, the authors said.
After decades of increases, cancer incidence in children has leveled off, although rates continue to increase among adolescents aged 15-19 years. The largest increase was a 4% per year rise in thyroid cancer, much of which is likely due to overdiagnosis.
On the survival front, uterine cancer is the only cancer for which survival decreased over the past few decades.
Progress against cancer has been hampered by persistent and widespread cancer disparities. Mortality rates are twofold higher among Black patients with prostate, stomach, and endometrial cancers than among White patients, and twofold higher among Native Americans with liver, stomach, and kidney cancers.
Black women are more often diagnosed at more advanced stages (44% vs 23%) and have worse 5‐year survival rates (63% vs 84%) than White women.
“This report underscores the need for public policy interventions to help reduce these cancer disparities and save more lives,” Lisa Lacasse, with the ACS Cancer Action Network, said in the release. “We urge lawmakers at all levels of government to advance policies that ensure more people have health insurance coverage as well as improved access to and affordability of care, such as increased funding for cancer research and screening programs.”
The authors of a linked editorial noted that while the report shows continued progress in oncology overall, certain ethnic, racial, age, and geographic populations face a disproportionate burden of cancer incidence and mortality.
“Like others, we find these health disparities wholly unacceptable and agree with the National Cancer Plan and Biden Moonshot Initiative that bold and new collaborations and thinking will be needed to produce different outcomes,” the editorialists said.
Overall, the editorialists noted, “every 15 seconds presents a real reminder of the urgency to end cancer as we know it for everyone.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall cancer mortality in the United States has continued to decline, with more than 4 million cancer deaths averted since 1991, according to the 2024 American Cancer Society (ACS) annual report on cancer trends.
The “good news is that we are continuing to see a decline in cancer mortality,” which follows the steady decline we’ve observed in cancer mortality over the past three decades, Rebecca Siegel, MPH, with ACS, and lead author of the new report, told this news organization.
However, these gains are “threatened by increasing incidence for many common cancers, including 6 of the top 10 most commonly diagnosed cancers,” Ms. Siegel said.
Overall, new cancer diagnoses are projected to top 2 million in 2024. That’s an average of 5480 new diagnoses each day or one person diagnosed every 15 seconds.
“In the US, the way our healthcare system is designed, we like to treat more than we like to prevent disease, and I would personally like to see a shift towards more emphasis on cancer prevention,” she added.
The full report was published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
Cancer Hitting at Younger Ages
Although advancing age remains the strongest determinate of cancer risk, the new data showed that cancer incidence is steadily increasing in younger populations.
What’s most alarming is the increase in cancer diagnoses in adults under 50 years.
Between 2015 and 2019, incidence rates increased by 0.6%-1% annually for breast, pancreas, and uterine corpus cancers, by 1%-2% annually for cervical cancer in women between 30 and 44 years, and by 2%-3% annually for prostate, kidney, melanoma, and human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers, as well as liver cancer in women.
The continuing rise in colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence in younger adults, in particular, is “very concerning,” Ms. Siegel said, and has shifted mortality patterns among adults younger than 50 years.
In this group, CRC is now the leading cause of cancer death in men and the second-leading cause in women behind breast cancer — up from the fourth leading cause of cancer death in both younger men and women 2 decades ago.
The obesity epidemic is likely a contributing factor in rising CRC rates, “but it’s not the whole story,” Ms. Siegel told this news organization. “A lot of work is going on to try to uncover what exactly is causing an increased risk of colorectal cancer.”
The proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 50-64 years has also increased — from 25% in 1995 to 30% in 2019-2020 — while the proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 65 years and older fell from 61% to 58% in that time frame. Among this older population, the authors observed steep declines in the incidence of prostate cancer and smoking-related cancers.
“Every generation born after the 1950s has had higher cancer risk than the previous generation. That tells us is that there is some exposure that is yet unknown that is causing this increased risk,” Ms. Siegel noted.
To halt and reverse this trend, it will be important to increase screening uptake as well as awareness of noninvasive stool tests and follow-up care in younger adults, Ahmedin Jemal, PhD, with ACS, commented in a press release.
Other key findings in the report include the sharp decline in cervical cancer incidence rates in women in their 20s — the first cohort to receive the HPV vaccine — but increases of nearly 2% in women 30-44 years, highlighting the need for more screening in young women as well as broader uptake of the vaccine, the authors said.
After decades of increases, cancer incidence in children has leveled off, although rates continue to increase among adolescents aged 15-19 years. The largest increase was a 4% per year rise in thyroid cancer, much of which is likely due to overdiagnosis.
On the survival front, uterine cancer is the only cancer for which survival decreased over the past few decades.
Progress against cancer has been hampered by persistent and widespread cancer disparities. Mortality rates are twofold higher among Black patients with prostate, stomach, and endometrial cancers than among White patients, and twofold higher among Native Americans with liver, stomach, and kidney cancers.
Black women are more often diagnosed at more advanced stages (44% vs 23%) and have worse 5‐year survival rates (63% vs 84%) than White women.
“This report underscores the need for public policy interventions to help reduce these cancer disparities and save more lives,” Lisa Lacasse, with the ACS Cancer Action Network, said in the release. “We urge lawmakers at all levels of government to advance policies that ensure more people have health insurance coverage as well as improved access to and affordability of care, such as increased funding for cancer research and screening programs.”
The authors of a linked editorial noted that while the report shows continued progress in oncology overall, certain ethnic, racial, age, and geographic populations face a disproportionate burden of cancer incidence and mortality.
“Like others, we find these health disparities wholly unacceptable and agree with the National Cancer Plan and Biden Moonshot Initiative that bold and new collaborations and thinking will be needed to produce different outcomes,” the editorialists said.
Overall, the editorialists noted, “every 15 seconds presents a real reminder of the urgency to end cancer as we know it for everyone.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall cancer mortality in the United States has continued to decline, with more than 4 million cancer deaths averted since 1991, according to the 2024 American Cancer Society (ACS) annual report on cancer trends.
The “good news is that we are continuing to see a decline in cancer mortality,” which follows the steady decline we’ve observed in cancer mortality over the past three decades, Rebecca Siegel, MPH, with ACS, and lead author of the new report, told this news organization.
However, these gains are “threatened by increasing incidence for many common cancers, including 6 of the top 10 most commonly diagnosed cancers,” Ms. Siegel said.
Overall, new cancer diagnoses are projected to top 2 million in 2024. That’s an average of 5480 new diagnoses each day or one person diagnosed every 15 seconds.
“In the US, the way our healthcare system is designed, we like to treat more than we like to prevent disease, and I would personally like to see a shift towards more emphasis on cancer prevention,” she added.
The full report was published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
Cancer Hitting at Younger Ages
Although advancing age remains the strongest determinate of cancer risk, the new data showed that cancer incidence is steadily increasing in younger populations.
What’s most alarming is the increase in cancer diagnoses in adults under 50 years.
Between 2015 and 2019, incidence rates increased by 0.6%-1% annually for breast, pancreas, and uterine corpus cancers, by 1%-2% annually for cervical cancer in women between 30 and 44 years, and by 2%-3% annually for prostate, kidney, melanoma, and human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers, as well as liver cancer in women.
The continuing rise in colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence in younger adults, in particular, is “very concerning,” Ms. Siegel said, and has shifted mortality patterns among adults younger than 50 years.
In this group, CRC is now the leading cause of cancer death in men and the second-leading cause in women behind breast cancer — up from the fourth leading cause of cancer death in both younger men and women 2 decades ago.
The obesity epidemic is likely a contributing factor in rising CRC rates, “but it’s not the whole story,” Ms. Siegel told this news organization. “A lot of work is going on to try to uncover what exactly is causing an increased risk of colorectal cancer.”
The proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 50-64 years has also increased — from 25% in 1995 to 30% in 2019-2020 — while the proportion of new cancers diagnosed in adults aged 65 years and older fell from 61% to 58% in that time frame. Among this older population, the authors observed steep declines in the incidence of prostate cancer and smoking-related cancers.
“Every generation born after the 1950s has had higher cancer risk than the previous generation. That tells us is that there is some exposure that is yet unknown that is causing this increased risk,” Ms. Siegel noted.
To halt and reverse this trend, it will be important to increase screening uptake as well as awareness of noninvasive stool tests and follow-up care in younger adults, Ahmedin Jemal, PhD, with ACS, commented in a press release.
Other key findings in the report include the sharp decline in cervical cancer incidence rates in women in their 20s — the first cohort to receive the HPV vaccine — but increases of nearly 2% in women 30-44 years, highlighting the need for more screening in young women as well as broader uptake of the vaccine, the authors said.
After decades of increases, cancer incidence in children has leveled off, although rates continue to increase among adolescents aged 15-19 years. The largest increase was a 4% per year rise in thyroid cancer, much of which is likely due to overdiagnosis.
On the survival front, uterine cancer is the only cancer for which survival decreased over the past few decades.
Progress against cancer has been hampered by persistent and widespread cancer disparities. Mortality rates are twofold higher among Black patients with prostate, stomach, and endometrial cancers than among White patients, and twofold higher among Native Americans with liver, stomach, and kidney cancers.
Black women are more often diagnosed at more advanced stages (44% vs 23%) and have worse 5‐year survival rates (63% vs 84%) than White women.
“This report underscores the need for public policy interventions to help reduce these cancer disparities and save more lives,” Lisa Lacasse, with the ACS Cancer Action Network, said in the release. “We urge lawmakers at all levels of government to advance policies that ensure more people have health insurance coverage as well as improved access to and affordability of care, such as increased funding for cancer research and screening programs.”
The authors of a linked editorial noted that while the report shows continued progress in oncology overall, certain ethnic, racial, age, and geographic populations face a disproportionate burden of cancer incidence and mortality.
“Like others, we find these health disparities wholly unacceptable and agree with the National Cancer Plan and Biden Moonshot Initiative that bold and new collaborations and thinking will be needed to produce different outcomes,” the editorialists said.
Overall, the editorialists noted, “every 15 seconds presents a real reminder of the urgency to end cancer as we know it for everyone.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
No Compelling Evidence of Pancreatic Cancer Risk With GLP-1s
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data provide no support for an increased risk for pancreatic cancer with use of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) for up to 7 years, although longer-term data are needed, researchers said.
METHODOLOGY:
- Some studies have raised concern about a possible increased risk for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients taking a GLP-1 RA.
- Investigators behind this population-based cohort study assessed the association of GLP-1 RA treatment with pancreatic cancer incidence over a median of 7 years in 543,595 adults (mean age, 59.9 years; 51% women) with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment with basal insulin was used as an active comparator.
- The analyses accounted for major confounding factors and time-related biases and adjusted for treatment with other glucose-lowering medications and a history of pancreatitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 33,377 patients (6.1%) used GLP-1 RAs and 106,849 (19.7%) used basal insulin, with 1665 of all patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
- There was no evidence that GLP-1 RA use increased pancreatic cancer risk compared with basal insulin.
- The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for pancreatic cancer associated with incremental use of one defined daily dose per day of GLP-1 RA compared with basal insulin in years 5-7 was 0.50 (95% CI, 0.15-1.71).
- New-user and prevalent new-user analyses showed HRs from year 5 onward following initiation of a GLP-1 RA vs basal insulin was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.19-1.41) and 0.75 (95% CI, 0.37-1.53), respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
Using several analytical approaches, these findings do not suggest an increase in pancreatic cancer incidence over 7 years following the start of GLP-1 RA treatment, according to the investigation. “However, monitoring for pancreatic cancer risk beyond 7 years following initiation of treatment is still required,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rachel Dankner, MD, MPH, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Israel, was published online on January 4, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on the exact type of GLP-1 RA were not available. The analyses accounted for history of pancreatitis but not alcohol use or exposure to pesticides/chemicals. Because of the risk for bias due to reverse causation, an emphasis was placed on drug effects several years after their initiation. However, this reduced the number of pancreatic cancer cases available and led to estimated HRs with wider CIs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Multivitamins and Cognition: New Data From COSMOS
New data from the Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) suggest that a daily multivitamin may help protect the aging brain. However, at least one expert has concerns about the study’s methodology and, as a result, the interpretation of its findings.
The meta-analysis of three separate cognition studies provides “strong and consistent evidence that taking a daily multivitamin, containing more than 20 essential micronutrients, can help prevent memory loss and slow down cognitive aging,” study investigator Chirag Vyas, MBBS, MPH, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“We are not now recommending multivitamin use, but the evidence is compelling that supports the promise of multivitamins to help prevent cognitive decline,” Dr. Vyas said.
The new data, from the cognitive substudies of COSMOS, were published online in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Clinically Meaningful Benefit?
To recap, COSMOS was a 2 x 2 factorial trial of coca extract (500 mg/d flavanols) and/or a daily commercial multivitamin-mineral (MVM) supplement for cardiovascular disease and cancer prevention among more than 21,000 US adults aged 60 years or older.
Neither the cocoa extract nor the MVM supplement had a significant impact on cancer or cardiovascular disease events.
COMOS-Mind was a substudy of 2262 participants aged 65 or older without dementia who completed telephone-based cognitive assessments at baseline and annually for 3 years.
As previously reported by this news organization in COSMOS-Mind, there was no cognitive benefit of daily cocoa extract, but daily MVM supplementation was associated with improved global cognition, episodic memory, and executive function. However, the difference in global cognitive function between MVM and placebo was small, with a mean 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at 3 years.
COSMOS-Web was a substudy of 3562 original participants who were evaluated annually for 3 years using an internet-based battery of neuropsychological tests.
In this analysis, those taking the MVM supplement performed better on a test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words); they were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. However, they did not improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition.
The new data are from COSMOS-Clinic, an analysis of 573 participants who completed in-person cognitive assessments.
COSMOS-Clinic showed a modest benefit of MVM, compared with placebo, on global cognition over 2 years (mean difference, 0.06 SD units [SU]), with a significantly more favorable change in episodic memory (mean difference, 0.12 SU) but not in executive function/attention (mean difference, 0.04 SU), the researchers reported.
They also conducted a meta-analysis based on the three separate cognitive substudies, with 5200 nonoverlapping COSMOS participants.
The results showed “clear evidence” of MVM benefits on global cognition (mean difference, 0.07 SU; P = .0009) and episodic memory (mean difference, 0.06 SU; P =.0007), they reported, with the magnitude of effect on global cognition equivalent to reducing cognitive aging by 2 years.
In a statement, JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who led the overall COSMOS trial, said that “the finding that a daily multivitamin improved memory and slowed cognitive aging in three separate placebo-controlled studies in COSMOS is exciting and further supports the promise of multivitamins as a safe, accessible, and affordable approach to protecting cognitive health in older adults.”
Not a Meta-analysis?
In an interview with this news organization, Christopher Labos, MD CM, MSc, a cardiologist and epidemiologist based in Montreal, Canada, who wasn’t involved in COSMOS, cautioned that the evidence to date on multivitamins for memory and brain health are “not all that impressive.”
Dr. Labos is a columnist for this news organization and previously has written about the COSMOS trial.
He said it is important to note that this “meta-analysis of COSMOS data, strictly speaking, is not a meta-analysis” because the patients were all from the original COSMOS study without including any additional patients, “so you don’t have any more data than what you started with.
“The fact that the results are consistent with the original trial is not surprising. In fact, it would be concerning if they were not consistent because they’re the same population. They were just assessed differently — by phone, online, or in person,” Dr. Labos explained.
“It is hard to tell what the benefit with multivitamins actually means in terms of hard clinical endpoints that matter to patients. Scoring a little bit better on a standardized test — I guess that’s a good thing, but does that mean you’re less likely to get dementia? I’m not sure we’re there yet,” he told this news organization.
The bottom line, said Dr. Labos, is that “at this point, the evidence does not support recommending multivitamins purely for brain health. There is also a cost and potential downside associated with their use.”
Also weighing in on the new analyses from COSMOS, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, said while there are now “positive, large-scale, long-term studies that show that multivitamin-mineral supplementation for older adults may slow cognitive aging, the Alzheimer’s Association is not ready to recommend widespread use of a multivitamin supplement to reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
“Independent confirmatory studies are needed in larger, more diverse, and representative study populations. COSMOS-Clinic, for example, had less than 2% non-White in the multivitamin group and 5% non-White in the placebo group. It is critical that future treatments and preventions are effective in all populations,” Dr. Sexton told this news organization.
She noted that multivitamin supplements are “generally easy to find and relatively affordable. With confirmation, these promising findings have the potential to significantly impact public health — improving brain health, lowering healthcare costs, reducing caregiver burden — especially among older adults.”
The Alzheimer’s Association, Dr. Sexton said, “envisions a future where there are multiple treatments available that address the disease in multiple ways — like heart disease and cancer — and that can be combined into powerful combination therapies, in conjunction with brain-healthy guidelines for lifestyle, like diet and physical activity.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to evaluate whether lifestyle interventions that target multiple risk factors can protect cognition in older adults at increased risk for cognitive decline.
COSMOS-Clinic and the cognition studies in the meta-analysis were supported by investigator-initiated grants from Mars Edge, a segment of Mars Inc., and the National Institutes of Health. Multivitamin and placebo tablets and packaging were donated by Pfizer, Inc Consumer Healthcare (now Haleon). Disclosures for the COSMOS investigators are available with the original article. Dr. Labos and Dr. Sexton have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) suggest that a daily multivitamin may help protect the aging brain. However, at least one expert has concerns about the study’s methodology and, as a result, the interpretation of its findings.
The meta-analysis of three separate cognition studies provides “strong and consistent evidence that taking a daily multivitamin, containing more than 20 essential micronutrients, can help prevent memory loss and slow down cognitive aging,” study investigator Chirag Vyas, MBBS, MPH, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“We are not now recommending multivitamin use, but the evidence is compelling that supports the promise of multivitamins to help prevent cognitive decline,” Dr. Vyas said.
The new data, from the cognitive substudies of COSMOS, were published online in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Clinically Meaningful Benefit?
To recap, COSMOS was a 2 x 2 factorial trial of coca extract (500 mg/d flavanols) and/or a daily commercial multivitamin-mineral (MVM) supplement for cardiovascular disease and cancer prevention among more than 21,000 US adults aged 60 years or older.
Neither the cocoa extract nor the MVM supplement had a significant impact on cancer or cardiovascular disease events.
COMOS-Mind was a substudy of 2262 participants aged 65 or older without dementia who completed telephone-based cognitive assessments at baseline and annually for 3 years.
As previously reported by this news organization in COSMOS-Mind, there was no cognitive benefit of daily cocoa extract, but daily MVM supplementation was associated with improved global cognition, episodic memory, and executive function. However, the difference in global cognitive function between MVM and placebo was small, with a mean 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at 3 years.
COSMOS-Web was a substudy of 3562 original participants who were evaluated annually for 3 years using an internet-based battery of neuropsychological tests.
In this analysis, those taking the MVM supplement performed better on a test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words); they were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. However, they did not improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition.
The new data are from COSMOS-Clinic, an analysis of 573 participants who completed in-person cognitive assessments.
COSMOS-Clinic showed a modest benefit of MVM, compared with placebo, on global cognition over 2 years (mean difference, 0.06 SD units [SU]), with a significantly more favorable change in episodic memory (mean difference, 0.12 SU) but not in executive function/attention (mean difference, 0.04 SU), the researchers reported.
They also conducted a meta-analysis based on the three separate cognitive substudies, with 5200 nonoverlapping COSMOS participants.
The results showed “clear evidence” of MVM benefits on global cognition (mean difference, 0.07 SU; P = .0009) and episodic memory (mean difference, 0.06 SU; P =.0007), they reported, with the magnitude of effect on global cognition equivalent to reducing cognitive aging by 2 years.
In a statement, JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who led the overall COSMOS trial, said that “the finding that a daily multivitamin improved memory and slowed cognitive aging in three separate placebo-controlled studies in COSMOS is exciting and further supports the promise of multivitamins as a safe, accessible, and affordable approach to protecting cognitive health in older adults.”
Not a Meta-analysis?
In an interview with this news organization, Christopher Labos, MD CM, MSc, a cardiologist and epidemiologist based in Montreal, Canada, who wasn’t involved in COSMOS, cautioned that the evidence to date on multivitamins for memory and brain health are “not all that impressive.”
Dr. Labos is a columnist for this news organization and previously has written about the COSMOS trial.
He said it is important to note that this “meta-analysis of COSMOS data, strictly speaking, is not a meta-analysis” because the patients were all from the original COSMOS study without including any additional patients, “so you don’t have any more data than what you started with.
“The fact that the results are consistent with the original trial is not surprising. In fact, it would be concerning if they were not consistent because they’re the same population. They were just assessed differently — by phone, online, or in person,” Dr. Labos explained.
“It is hard to tell what the benefit with multivitamins actually means in terms of hard clinical endpoints that matter to patients. Scoring a little bit better on a standardized test — I guess that’s a good thing, but does that mean you’re less likely to get dementia? I’m not sure we’re there yet,” he told this news organization.
The bottom line, said Dr. Labos, is that “at this point, the evidence does not support recommending multivitamins purely for brain health. There is also a cost and potential downside associated with their use.”
Also weighing in on the new analyses from COSMOS, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, said while there are now “positive, large-scale, long-term studies that show that multivitamin-mineral supplementation for older adults may slow cognitive aging, the Alzheimer’s Association is not ready to recommend widespread use of a multivitamin supplement to reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
“Independent confirmatory studies are needed in larger, more diverse, and representative study populations. COSMOS-Clinic, for example, had less than 2% non-White in the multivitamin group and 5% non-White in the placebo group. It is critical that future treatments and preventions are effective in all populations,” Dr. Sexton told this news organization.
She noted that multivitamin supplements are “generally easy to find and relatively affordable. With confirmation, these promising findings have the potential to significantly impact public health — improving brain health, lowering healthcare costs, reducing caregiver burden — especially among older adults.”
The Alzheimer’s Association, Dr. Sexton said, “envisions a future where there are multiple treatments available that address the disease in multiple ways — like heart disease and cancer — and that can be combined into powerful combination therapies, in conjunction with brain-healthy guidelines for lifestyle, like diet and physical activity.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to evaluate whether lifestyle interventions that target multiple risk factors can protect cognition in older adults at increased risk for cognitive decline.
COSMOS-Clinic and the cognition studies in the meta-analysis were supported by investigator-initiated grants from Mars Edge, a segment of Mars Inc., and the National Institutes of Health. Multivitamin and placebo tablets and packaging were donated by Pfizer, Inc Consumer Healthcare (now Haleon). Disclosures for the COSMOS investigators are available with the original article. Dr. Labos and Dr. Sexton have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) suggest that a daily multivitamin may help protect the aging brain. However, at least one expert has concerns about the study’s methodology and, as a result, the interpretation of its findings.
The meta-analysis of three separate cognition studies provides “strong and consistent evidence that taking a daily multivitamin, containing more than 20 essential micronutrients, can help prevent memory loss and slow down cognitive aging,” study investigator Chirag Vyas, MBBS, MPH, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“We are not now recommending multivitamin use, but the evidence is compelling that supports the promise of multivitamins to help prevent cognitive decline,” Dr. Vyas said.
The new data, from the cognitive substudies of COSMOS, were published online in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Clinically Meaningful Benefit?
To recap, COSMOS was a 2 x 2 factorial trial of coca extract (500 mg/d flavanols) and/or a daily commercial multivitamin-mineral (MVM) supplement for cardiovascular disease and cancer prevention among more than 21,000 US adults aged 60 years or older.
Neither the cocoa extract nor the MVM supplement had a significant impact on cancer or cardiovascular disease events.
COMOS-Mind was a substudy of 2262 participants aged 65 or older without dementia who completed telephone-based cognitive assessments at baseline and annually for 3 years.
As previously reported by this news organization in COSMOS-Mind, there was no cognitive benefit of daily cocoa extract, but daily MVM supplementation was associated with improved global cognition, episodic memory, and executive function. However, the difference in global cognitive function between MVM and placebo was small, with a mean 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at 3 years.
COSMOS-Web was a substudy of 3562 original participants who were evaluated annually for 3 years using an internet-based battery of neuropsychological tests.
In this analysis, those taking the MVM supplement performed better on a test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words); they were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. However, they did not improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition.
The new data are from COSMOS-Clinic, an analysis of 573 participants who completed in-person cognitive assessments.
COSMOS-Clinic showed a modest benefit of MVM, compared with placebo, on global cognition over 2 years (mean difference, 0.06 SD units [SU]), with a significantly more favorable change in episodic memory (mean difference, 0.12 SU) but not in executive function/attention (mean difference, 0.04 SU), the researchers reported.
They also conducted a meta-analysis based on the three separate cognitive substudies, with 5200 nonoverlapping COSMOS participants.
The results showed “clear evidence” of MVM benefits on global cognition (mean difference, 0.07 SU; P = .0009) and episodic memory (mean difference, 0.06 SU; P =.0007), they reported, with the magnitude of effect on global cognition equivalent to reducing cognitive aging by 2 years.
In a statement, JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who led the overall COSMOS trial, said that “the finding that a daily multivitamin improved memory and slowed cognitive aging in three separate placebo-controlled studies in COSMOS is exciting and further supports the promise of multivitamins as a safe, accessible, and affordable approach to protecting cognitive health in older adults.”
Not a Meta-analysis?
In an interview with this news organization, Christopher Labos, MD CM, MSc, a cardiologist and epidemiologist based in Montreal, Canada, who wasn’t involved in COSMOS, cautioned that the evidence to date on multivitamins for memory and brain health are “not all that impressive.”
Dr. Labos is a columnist for this news organization and previously has written about the COSMOS trial.
He said it is important to note that this “meta-analysis of COSMOS data, strictly speaking, is not a meta-analysis” because the patients were all from the original COSMOS study without including any additional patients, “so you don’t have any more data than what you started with.
“The fact that the results are consistent with the original trial is not surprising. In fact, it would be concerning if they were not consistent because they’re the same population. They were just assessed differently — by phone, online, or in person,” Dr. Labos explained.
“It is hard to tell what the benefit with multivitamins actually means in terms of hard clinical endpoints that matter to patients. Scoring a little bit better on a standardized test — I guess that’s a good thing, but does that mean you’re less likely to get dementia? I’m not sure we’re there yet,” he told this news organization.
The bottom line, said Dr. Labos, is that “at this point, the evidence does not support recommending multivitamins purely for brain health. There is also a cost and potential downside associated with their use.”
Also weighing in on the new analyses from COSMOS, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, said while there are now “positive, large-scale, long-term studies that show that multivitamin-mineral supplementation for older adults may slow cognitive aging, the Alzheimer’s Association is not ready to recommend widespread use of a multivitamin supplement to reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
“Independent confirmatory studies are needed in larger, more diverse, and representative study populations. COSMOS-Clinic, for example, had less than 2% non-White in the multivitamin group and 5% non-White in the placebo group. It is critical that future treatments and preventions are effective in all populations,” Dr. Sexton told this news organization.
She noted that multivitamin supplements are “generally easy to find and relatively affordable. With confirmation, these promising findings have the potential to significantly impact public health — improving brain health, lowering healthcare costs, reducing caregiver burden — especially among older adults.”
The Alzheimer’s Association, Dr. Sexton said, “envisions a future where there are multiple treatments available that address the disease in multiple ways — like heart disease and cancer — and that can be combined into powerful combination therapies, in conjunction with brain-healthy guidelines for lifestyle, like diet and physical activity.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to evaluate whether lifestyle interventions that target multiple risk factors can protect cognition in older adults at increased risk for cognitive decline.
COSMOS-Clinic and the cognition studies in the meta-analysis were supported by investigator-initiated grants from Mars Edge, a segment of Mars Inc., and the National Institutes of Health. Multivitamin and placebo tablets and packaging were donated by Pfizer, Inc Consumer Healthcare (now Haleon). Disclosures for the COSMOS investigators are available with the original article. Dr. Labos and Dr. Sexton have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NUTRITION
Standard Therapy Beats Out Primary Surgery in Rectal Cancer
TOPLINE:
demonstrating better disease-free survival and lower recurrence rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- The standard treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer is chemoradiation followed by surgery, which is known to reduce the likelihood of local recurrence; however, it is also linked to adverse effects including and bowel/sexual dysfunction.
- A previous trial found that preoperative MRI could delineate tumor involvement of the mesorectal fascia (MRF).
- This Chinese, noninferiority trial tested whether patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with MRI-predicted negative MRF can skip preoperative chemoradiation.
- The study included 275 patients with T3-4aN0 or T1-4aN1-2 rectal adenocarcinoma, an inferior tumor edge 6-12 cm from the anal verge, and gross primary or nodal disease > 1 mm from the MRF — all based on preoperative MRI.
- Patients in the intervention group, 140, were assigned to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (50.4 Gy in 28 fractions with followed by capecitabine/ started 4 weeks after surgery) and the remaining 135 to upfront surgery followed by adjuvant chemo/chemoradiation when there was tumor within 1 mm of circumferential margins.
TAKEAWAY:
- After a median follow-up of 34.6 months, there were six (4.4%) local recurrences in the intervention group and none in the control group.
- In the intention-to-treat population, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.8% in the intervention group vs 85.4% in the control group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.76).
- In the per protocol dataset, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.1% in the primary surgery group vs 86.6% in the preoperative chemoradiation group — a difference of −5.4% (HR, 2.02), prompting the researchers to stop the trial early.
IN PRACTICE:
“This trial was shut down earlier due to an excessive number of [disease-free survival] and local recurrence events observed in the interventional group of primary surgery. Based on our findings, in [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients with high risk though negative MRF, primary surgery would potentially compromise their [disease-free survival] rates. Therefore, primary surgery is an inferior strategy, compared to preoperative [chemoradiation] followed by surgery, and cannot be recommended for [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients in clinical practice,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Jun Li, MD, Department of Colorectal Surgery and Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China, was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample size will result in compromises in stratified randomization and lower the power for survival analysis. A relatively high proportion of patients (n = 32) crossed over from the neoadjuvant (chemoradiation) group to the primary surgery group. Follow-up time was relatively short, with only 43% of patients completing 3 years of follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
demonstrating better disease-free survival and lower recurrence rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- The standard treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer is chemoradiation followed by surgery, which is known to reduce the likelihood of local recurrence; however, it is also linked to adverse effects including and bowel/sexual dysfunction.
- A previous trial found that preoperative MRI could delineate tumor involvement of the mesorectal fascia (MRF).
- This Chinese, noninferiority trial tested whether patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with MRI-predicted negative MRF can skip preoperative chemoradiation.
- The study included 275 patients with T3-4aN0 or T1-4aN1-2 rectal adenocarcinoma, an inferior tumor edge 6-12 cm from the anal verge, and gross primary or nodal disease > 1 mm from the MRF — all based on preoperative MRI.
- Patients in the intervention group, 140, were assigned to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (50.4 Gy in 28 fractions with followed by capecitabine/ started 4 weeks after surgery) and the remaining 135 to upfront surgery followed by adjuvant chemo/chemoradiation when there was tumor within 1 mm of circumferential margins.
TAKEAWAY:
- After a median follow-up of 34.6 months, there were six (4.4%) local recurrences in the intervention group and none in the control group.
- In the intention-to-treat population, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.8% in the intervention group vs 85.4% in the control group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.76).
- In the per protocol dataset, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.1% in the primary surgery group vs 86.6% in the preoperative chemoradiation group — a difference of −5.4% (HR, 2.02), prompting the researchers to stop the trial early.
IN PRACTICE:
“This trial was shut down earlier due to an excessive number of [disease-free survival] and local recurrence events observed in the interventional group of primary surgery. Based on our findings, in [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients with high risk though negative MRF, primary surgery would potentially compromise their [disease-free survival] rates. Therefore, primary surgery is an inferior strategy, compared to preoperative [chemoradiation] followed by surgery, and cannot be recommended for [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients in clinical practice,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Jun Li, MD, Department of Colorectal Surgery and Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China, was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample size will result in compromises in stratified randomization and lower the power for survival analysis. A relatively high proportion of patients (n = 32) crossed over from the neoadjuvant (chemoradiation) group to the primary surgery group. Follow-up time was relatively short, with only 43% of patients completing 3 years of follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
demonstrating better disease-free survival and lower recurrence rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- The standard treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer is chemoradiation followed by surgery, which is known to reduce the likelihood of local recurrence; however, it is also linked to adverse effects including and bowel/sexual dysfunction.
- A previous trial found that preoperative MRI could delineate tumor involvement of the mesorectal fascia (MRF).
- This Chinese, noninferiority trial tested whether patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with MRI-predicted negative MRF can skip preoperative chemoradiation.
- The study included 275 patients with T3-4aN0 or T1-4aN1-2 rectal adenocarcinoma, an inferior tumor edge 6-12 cm from the anal verge, and gross primary or nodal disease > 1 mm from the MRF — all based on preoperative MRI.
- Patients in the intervention group, 140, were assigned to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (50.4 Gy in 28 fractions with followed by capecitabine/ started 4 weeks after surgery) and the remaining 135 to upfront surgery followed by adjuvant chemo/chemoradiation when there was tumor within 1 mm of circumferential margins.
TAKEAWAY:
- After a median follow-up of 34.6 months, there were six (4.4%) local recurrences in the intervention group and none in the control group.
- In the intention-to-treat population, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.8% in the intervention group vs 85.4% in the control group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.76).
- In the per protocol dataset, the 3-year disease-free survival rate was 81.1% in the primary surgery group vs 86.6% in the preoperative chemoradiation group — a difference of −5.4% (HR, 2.02), prompting the researchers to stop the trial early.
IN PRACTICE:
“This trial was shut down earlier due to an excessive number of [disease-free survival] and local recurrence events observed in the interventional group of primary surgery. Based on our findings, in [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients with high risk though negative MRF, primary surgery would potentially compromise their [disease-free survival] rates. Therefore, primary surgery is an inferior strategy, compared to preoperative [chemoradiation] followed by surgery, and cannot be recommended for [locally advanced rectal cancer] patients in clinical practice,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Jun Li, MD, Department of Colorectal Surgery and Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China, was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample size will result in compromises in stratified randomization and lower the power for survival analysis. A relatively high proportion of patients (n = 32) crossed over from the neoadjuvant (chemoradiation) group to the primary surgery group. Follow-up time was relatively short, with only 43% of patients completing 3 years of follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Smoking and Drinking Up the Risk for Diverticulitis
TOPLINE:
New data link smoking and heavy drinking with an increased risk for diverticulitis, with the greatest risk seen in adults who smoke and consume two or more drinks daily.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers studied 84,232 women in the Nurses’ Health Study II who were 39-52 years old and without known diverticulitis at baseline in 2003.
- In 2015 and 2017, participants were asked via questionnaire whether they had been diagnosed with diverticulitis requiring antibiotic therapy or hospitalization. Diverticulitis was defined as a computed tomography scan or pathology report of diverticulitis or a provider diagnosis with a clinical presentation consistent with diverticulitis.
- Smoking was assessed every 2 years and alcohol consumption every 4 years using standard questionnaires.
- Consistent with prior studies on risk factors for diverticulitis, multivariable models adjusted for age, menopausal hormone status and hormone use, body mass index, physical activity, aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, intake of fiber and red/processed meat, and other factors were used.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 1 million person-years of follow-up, 3018 incident cases of diverticulitis were identified.
- Both current and past smoking were associated with increased risk for diverticulitis (hazard ratio [HR], 1.2) compared with never smoking, although no dose-response relationship was evident. In an analysis restricted to participants who had surgery for diverticulitis, the magnitude of the association was strengthened (HR, 1.48 for current smokers and 1.46 for past smokers vs never smokers).
- Consumption of ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol (2+ drinks/day) was associated with an increased risk for incident diverticulitis (HR, 1.26) compared with not drinking.
- A joint analysis of smoking and alcohol found that individuals who ever smoked and consumed ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol were at the highest risk for diverticulitis (multivariate HR, 1.53) compared with individuals who never smoked and reported no alcohol use.
IN PRACTICE:
“As there are currently no medical means to prevent diverticulitis other than dietary and lifestyle interventions, counseling patients about the avoidance of smoking and alcohol may help lower the risk for developing diverticulitis,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Sara Gunby, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Diverticulitis diagnoses were self-reported, although a review of a subset of medical records confirmed the diagnosis in more than 90% of cases establishing the validity of self-report in this population. The study was limited to female nurses, so it is possible the findings may not be generalizable to men or other populations. Residual confounding may have impacted the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data link smoking and heavy drinking with an increased risk for diverticulitis, with the greatest risk seen in adults who smoke and consume two or more drinks daily.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers studied 84,232 women in the Nurses’ Health Study II who were 39-52 years old and without known diverticulitis at baseline in 2003.
- In 2015 and 2017, participants were asked via questionnaire whether they had been diagnosed with diverticulitis requiring antibiotic therapy or hospitalization. Diverticulitis was defined as a computed tomography scan or pathology report of diverticulitis or a provider diagnosis with a clinical presentation consistent with diverticulitis.
- Smoking was assessed every 2 years and alcohol consumption every 4 years using standard questionnaires.
- Consistent with prior studies on risk factors for diverticulitis, multivariable models adjusted for age, menopausal hormone status and hormone use, body mass index, physical activity, aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, intake of fiber and red/processed meat, and other factors were used.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 1 million person-years of follow-up, 3018 incident cases of diverticulitis were identified.
- Both current and past smoking were associated with increased risk for diverticulitis (hazard ratio [HR], 1.2) compared with never smoking, although no dose-response relationship was evident. In an analysis restricted to participants who had surgery for diverticulitis, the magnitude of the association was strengthened (HR, 1.48 for current smokers and 1.46 for past smokers vs never smokers).
- Consumption of ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol (2+ drinks/day) was associated with an increased risk for incident diverticulitis (HR, 1.26) compared with not drinking.
- A joint analysis of smoking and alcohol found that individuals who ever smoked and consumed ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol were at the highest risk for diverticulitis (multivariate HR, 1.53) compared with individuals who never smoked and reported no alcohol use.
IN PRACTICE:
“As there are currently no medical means to prevent diverticulitis other than dietary and lifestyle interventions, counseling patients about the avoidance of smoking and alcohol may help lower the risk for developing diverticulitis,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Sara Gunby, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Diverticulitis diagnoses were self-reported, although a review of a subset of medical records confirmed the diagnosis in more than 90% of cases establishing the validity of self-report in this population. The study was limited to female nurses, so it is possible the findings may not be generalizable to men or other populations. Residual confounding may have impacted the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New data link smoking and heavy drinking with an increased risk for diverticulitis, with the greatest risk seen in adults who smoke and consume two or more drinks daily.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers studied 84,232 women in the Nurses’ Health Study II who were 39-52 years old and without known diverticulitis at baseline in 2003.
- In 2015 and 2017, participants were asked via questionnaire whether they had been diagnosed with diverticulitis requiring antibiotic therapy or hospitalization. Diverticulitis was defined as a computed tomography scan or pathology report of diverticulitis or a provider diagnosis with a clinical presentation consistent with diverticulitis.
- Smoking was assessed every 2 years and alcohol consumption every 4 years using standard questionnaires.
- Consistent with prior studies on risk factors for diverticulitis, multivariable models adjusted for age, menopausal hormone status and hormone use, body mass index, physical activity, aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, intake of fiber and red/processed meat, and other factors were used.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 1 million person-years of follow-up, 3018 incident cases of diverticulitis were identified.
- Both current and past smoking were associated with increased risk for diverticulitis (hazard ratio [HR], 1.2) compared with never smoking, although no dose-response relationship was evident. In an analysis restricted to participants who had surgery for diverticulitis, the magnitude of the association was strengthened (HR, 1.48 for current smokers and 1.46 for past smokers vs never smokers).
- Consumption of ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol (2+ drinks/day) was associated with an increased risk for incident diverticulitis (HR, 1.26) compared with not drinking.
- A joint analysis of smoking and alcohol found that individuals who ever smoked and consumed ≥ 30 g/d of alcohol were at the highest risk for diverticulitis (multivariate HR, 1.53) compared with individuals who never smoked and reported no alcohol use.
IN PRACTICE:
“As there are currently no medical means to prevent diverticulitis other than dietary and lifestyle interventions, counseling patients about the avoidance of smoking and alcohol may help lower the risk for developing diverticulitis,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Sara Gunby, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Diverticulitis diagnoses were self-reported, although a review of a subset of medical records confirmed the diagnosis in more than 90% of cases establishing the validity of self-report in this population. The study was limited to female nurses, so it is possible the findings may not be generalizable to men or other populations. Residual confounding may have impacted the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Psilocybin-Assisted Group Therapy Promising for Depression in Cancer Patients
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Continued Caution Needed Combining Nitrates With ED Drugs
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.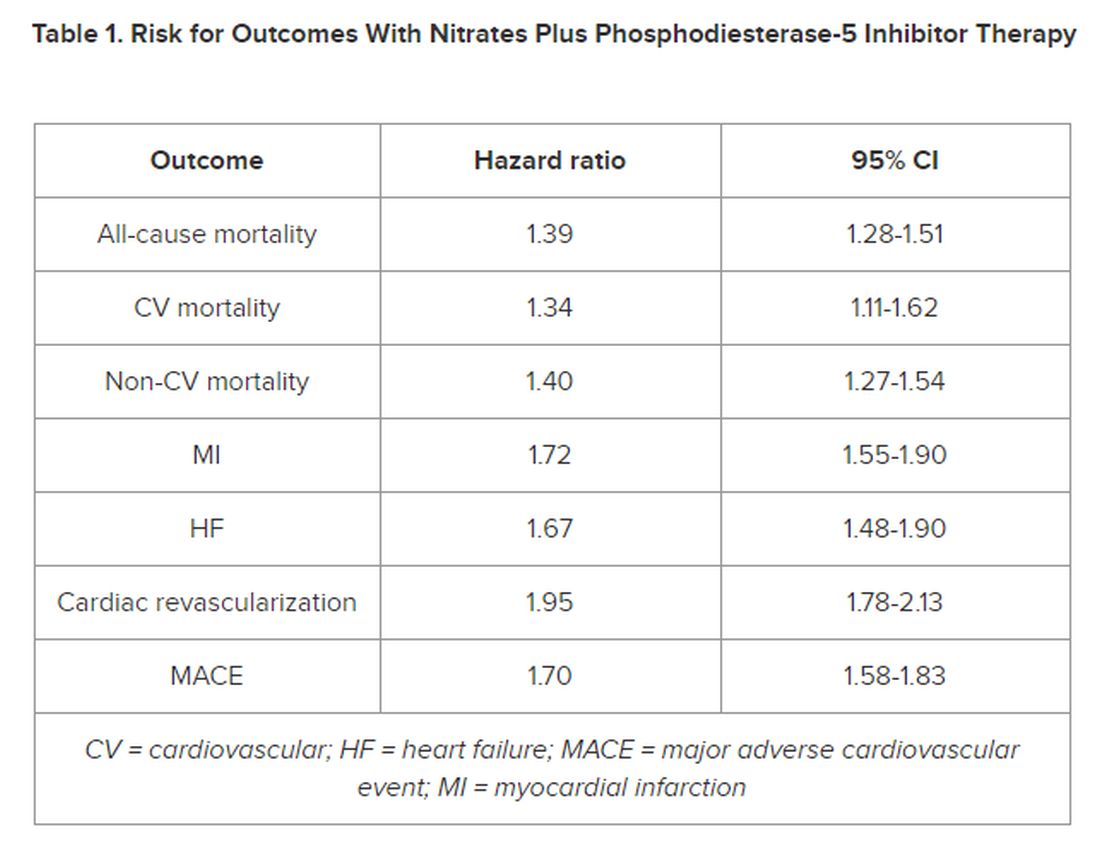
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.