User login
Doc faces U.S. federal charges for hacking, ransomware
According to a statement from the U.S. Department of Justice, 55-year-old Moises Luis Zagala Gonzalez, MD, is charged with creating and distributing ransomware with a “doomsday” clock and sharing in profits from ransomware attacks.
Dr. Zagala, also known as “Nosophoros,” “Aesculapius,” and “Nebuchadnezzar,” is a citizen of France and Venezuela who currently lives in Ciudad Bolivar, Venezuela.
Breon Peace, U.S. attorney for the Eastern District of New York, and Michael J. Driscoll, assistant director in charge of the Federal Bureau of Investigaton’s New York Field Office, announced the charges.
“As alleged, the multitasking doctor treated patients, created and named his cyber tool after death, profited from a global ransomware ecosystem in which he sold the tools for conducting ransomware attacks, trained the attackers about how to extort victims, and then boasted about successful attacks, including by malicious actors associated with the government of Iran,” Mr. Peace said in the news release from the DOJ.
“We allege Zagala not only created and sold ransomware products to hackers, but also trained them in their use. Our actions today will prevent Zagala from further victimizing users,” Mr. Driscoll said. “However, many other malicious criminals are searching for businesses and organizations that haven’t taken steps to protect their systems – which is an incredibly vital step in stopping the next ransomware attack.”
Ransomware tools are malicious software that cybercriminals use to extort money from companies, nonprofits, and other institutions by encrypting their files and then demanding a ransom for the decryption keys.
One of Dr. Zagala’s early ransomware tools, called “Jigsaw v. 2,” had what Dr. Zagala described as a doomsday counter that kept track of how many times the user tried to remove the ransomware. “If the user kills the ransomware too many times, then it’s clear he won’t pay so better erase the whole hard drive,” Dr. Zagala wrote.
According to the DOJ, beginning in late 2019, Dr. Zagala began advertising a new tool as a “private ransomware builder,” which he called Thanos. The name appears to be in reference to a fictional villain responsible for destroying half of all life in the universe and to “Thanatos” from Greek mythology, who is associated with death.
Dr. Zagala’s Thanos software allows users to create their own unique ransomware software for personal use or to rent to other cybercriminals.
Dr. Zagala allegedly not only sold or rented out his ransomware tools to cybercriminals, but he also taught users how to deploy the tools, steal passwords from victim computers, and set up a Bitcoin address for ransom payments.
Dr. Zagala’s customers were happy with his products, the DOJ release noted. In a message posted in July 2020, one user said the ransomware was “very powerful” and claimed that he had used it to infect a network of roughly 3,000 computers.
In December 2020, another user wrote a post in Russian: “We have been working with this product for over a month now, we have a good profit! Best support I’ve met.”
Earlier in May, law enforcement agents interviewed a relative of Dr. Zagala who lives in Florida and whose PayPal account was used by Dr. Zagala to receive illicit proceeds.
According to the DOJ, the relative confirmed that Dr. Zagala lives in Venezuela and had taught himself computer programming. The relative also showed agents contact information for Dr. Zagala that matched the registered email for malicious infrastructure associated with the Thanos ransomware.
Dr. Zagala, who remains in Venezuela, faces up to 10 years in prison for attempted computer intrusions and conspiracy charges if brought to justice in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
According to a statement from the U.S. Department of Justice, 55-year-old Moises Luis Zagala Gonzalez, MD, is charged with creating and distributing ransomware with a “doomsday” clock and sharing in profits from ransomware attacks.
Dr. Zagala, also known as “Nosophoros,” “Aesculapius,” and “Nebuchadnezzar,” is a citizen of France and Venezuela who currently lives in Ciudad Bolivar, Venezuela.
Breon Peace, U.S. attorney for the Eastern District of New York, and Michael J. Driscoll, assistant director in charge of the Federal Bureau of Investigaton’s New York Field Office, announced the charges.
“As alleged, the multitasking doctor treated patients, created and named his cyber tool after death, profited from a global ransomware ecosystem in which he sold the tools for conducting ransomware attacks, trained the attackers about how to extort victims, and then boasted about successful attacks, including by malicious actors associated with the government of Iran,” Mr. Peace said in the news release from the DOJ.
“We allege Zagala not only created and sold ransomware products to hackers, but also trained them in their use. Our actions today will prevent Zagala from further victimizing users,” Mr. Driscoll said. “However, many other malicious criminals are searching for businesses and organizations that haven’t taken steps to protect their systems – which is an incredibly vital step in stopping the next ransomware attack.”
Ransomware tools are malicious software that cybercriminals use to extort money from companies, nonprofits, and other institutions by encrypting their files and then demanding a ransom for the decryption keys.
One of Dr. Zagala’s early ransomware tools, called “Jigsaw v. 2,” had what Dr. Zagala described as a doomsday counter that kept track of how many times the user tried to remove the ransomware. “If the user kills the ransomware too many times, then it’s clear he won’t pay so better erase the whole hard drive,” Dr. Zagala wrote.
According to the DOJ, beginning in late 2019, Dr. Zagala began advertising a new tool as a “private ransomware builder,” which he called Thanos. The name appears to be in reference to a fictional villain responsible for destroying half of all life in the universe and to “Thanatos” from Greek mythology, who is associated with death.
Dr. Zagala’s Thanos software allows users to create their own unique ransomware software for personal use or to rent to other cybercriminals.
Dr. Zagala allegedly not only sold or rented out his ransomware tools to cybercriminals, but he also taught users how to deploy the tools, steal passwords from victim computers, and set up a Bitcoin address for ransom payments.
Dr. Zagala’s customers were happy with his products, the DOJ release noted. In a message posted in July 2020, one user said the ransomware was “very powerful” and claimed that he had used it to infect a network of roughly 3,000 computers.
In December 2020, another user wrote a post in Russian: “We have been working with this product for over a month now, we have a good profit! Best support I’ve met.”
Earlier in May, law enforcement agents interviewed a relative of Dr. Zagala who lives in Florida and whose PayPal account was used by Dr. Zagala to receive illicit proceeds.
According to the DOJ, the relative confirmed that Dr. Zagala lives in Venezuela and had taught himself computer programming. The relative also showed agents contact information for Dr. Zagala that matched the registered email for malicious infrastructure associated with the Thanos ransomware.
Dr. Zagala, who remains in Venezuela, faces up to 10 years in prison for attempted computer intrusions and conspiracy charges if brought to justice in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
According to a statement from the U.S. Department of Justice, 55-year-old Moises Luis Zagala Gonzalez, MD, is charged with creating and distributing ransomware with a “doomsday” clock and sharing in profits from ransomware attacks.
Dr. Zagala, also known as “Nosophoros,” “Aesculapius,” and “Nebuchadnezzar,” is a citizen of France and Venezuela who currently lives in Ciudad Bolivar, Venezuela.
Breon Peace, U.S. attorney for the Eastern District of New York, and Michael J. Driscoll, assistant director in charge of the Federal Bureau of Investigaton’s New York Field Office, announced the charges.
“As alleged, the multitasking doctor treated patients, created and named his cyber tool after death, profited from a global ransomware ecosystem in which he sold the tools for conducting ransomware attacks, trained the attackers about how to extort victims, and then boasted about successful attacks, including by malicious actors associated with the government of Iran,” Mr. Peace said in the news release from the DOJ.
“We allege Zagala not only created and sold ransomware products to hackers, but also trained them in their use. Our actions today will prevent Zagala from further victimizing users,” Mr. Driscoll said. “However, many other malicious criminals are searching for businesses and organizations that haven’t taken steps to protect their systems – which is an incredibly vital step in stopping the next ransomware attack.”
Ransomware tools are malicious software that cybercriminals use to extort money from companies, nonprofits, and other institutions by encrypting their files and then demanding a ransom for the decryption keys.
One of Dr. Zagala’s early ransomware tools, called “Jigsaw v. 2,” had what Dr. Zagala described as a doomsday counter that kept track of how many times the user tried to remove the ransomware. “If the user kills the ransomware too many times, then it’s clear he won’t pay so better erase the whole hard drive,” Dr. Zagala wrote.
According to the DOJ, beginning in late 2019, Dr. Zagala began advertising a new tool as a “private ransomware builder,” which he called Thanos. The name appears to be in reference to a fictional villain responsible for destroying half of all life in the universe and to “Thanatos” from Greek mythology, who is associated with death.
Dr. Zagala’s Thanos software allows users to create their own unique ransomware software for personal use or to rent to other cybercriminals.
Dr. Zagala allegedly not only sold or rented out his ransomware tools to cybercriminals, but he also taught users how to deploy the tools, steal passwords from victim computers, and set up a Bitcoin address for ransom payments.
Dr. Zagala’s customers were happy with his products, the DOJ release noted. In a message posted in July 2020, one user said the ransomware was “very powerful” and claimed that he had used it to infect a network of roughly 3,000 computers.
In December 2020, another user wrote a post in Russian: “We have been working with this product for over a month now, we have a good profit! Best support I’ve met.”
Earlier in May, law enforcement agents interviewed a relative of Dr. Zagala who lives in Florida and whose PayPal account was used by Dr. Zagala to receive illicit proceeds.
According to the DOJ, the relative confirmed that Dr. Zagala lives in Venezuela and had taught himself computer programming. The relative also showed agents contact information for Dr. Zagala that matched the registered email for malicious infrastructure associated with the Thanos ransomware.
Dr. Zagala, who remains in Venezuela, faces up to 10 years in prison for attempted computer intrusions and conspiracy charges if brought to justice in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does suicide risk show up in the blood?
Investigators found patients with MDD who died by suicide had a gene expression signature in blood distinct from patients with MDD who died by other means.
The signature included genes involved in stress response changes, including polyamine metabolism, circadian rhythm, immune dysregulation, and telomere maintenance.
“These blood biomarkers are an important step toward developing blood tests to identify patients with imminent risk of ending their lives,” study investigator Adolfo Sequeira, PhD, associate researcher in the department of psychiatry and human behavior, University of California, Irvine, said in a news release.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze blood and brain samples in a well-defined population of MDDs demonstrating significant differences in gene expression associated with completed suicide,” Dr. Sequeira added.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
A pressing challenge
Suicide rates in the United States have jumped by more than 35% over the past 2 decades, with more than 48,000 deaths by suicide occurring just last year. MDD is the most common diagnosis among completed suicides, and identifying individuals at the highest risk for suicide remains a “pressing challenge,” the researchers noted.
They looked for changes in gene expression associated with suicide in archived postmortem blood and brain samples from adults with MDD who died by suicide (MDD-S) or by other means (MDD-NS), as well as a group of controls with no psychiatric illness.
In total, there were blood and brain samples for 45 adults, including 53 blood samples and 69 dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) tissue samples.
In blood, investigators identified 14 genes that significantly differentiated MDD-S from MDD-NS. The top six genes differentially expressed in blood were PER3, MTPAP, SLC25A26, CD19, SOX9, and GAR1.
In addition, four genes showed significant changes in brain and blood between the MDD-S and MDD-NS groups. SOX9 was decreased and PER3 was increased in MDD-S in both blood and brain samples, while CD19 and TERF1 were increased in blood but decreased in DLPFC.
SOX9, an astrocytic marker in the brain and B-cell marker in blood, has been shown to be decreased in MDD-S compared with controls in the prefrontal cortex.
In the current study, researchers found that SOX9 expression was significantly reduced both in blood and brain in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS, “suggesting similar immune/astrocytic dysregulations in suicide that could be further investigated.”
Potential signatures, potential targets
PER3 is a circadian rhythm gene implicated in sleep disorders associated with shifts in circadian rhythms and is thought to increase susceptibility to MDD.
Mutations in PER3 have been shown previously to alter multiple systems, including response to antidepressants; and increased blood expression of PER1 has been linked to suicidality in women, the researchers noted.
There also were significantly higher levels of two inflammatory markers (CD19 and CD6 genes) in blood of MDD-S patients compared to MDD-NS patients.
Another “significant” finding was the involvement of several mitochondrial genes in suicide, the researchers said.
Two nuclear genes coding for mitochondria-located proteins MTPAP (a mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase) and the mitochondrial polyamine transporter SLC25A26 were increased in blood in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS and controls, suggesting that “mitochondrial alterations could be used as potential signatures to differentiate MDD-S from MDD-NS patients and also from controls.”
The researchers added that the genes found to be dysregulated in suicide represent potential targets for future drug therapies to prevent suicide and could also be used to develop a molecular test to identify individuals at high risk for suicide.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the American Society for Suicide Prevention, and the Pritzker Family Philanthropic Fund. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found patients with MDD who died by suicide had a gene expression signature in blood distinct from patients with MDD who died by other means.
The signature included genes involved in stress response changes, including polyamine metabolism, circadian rhythm, immune dysregulation, and telomere maintenance.
“These blood biomarkers are an important step toward developing blood tests to identify patients with imminent risk of ending their lives,” study investigator Adolfo Sequeira, PhD, associate researcher in the department of psychiatry and human behavior, University of California, Irvine, said in a news release.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze blood and brain samples in a well-defined population of MDDs demonstrating significant differences in gene expression associated with completed suicide,” Dr. Sequeira added.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
A pressing challenge
Suicide rates in the United States have jumped by more than 35% over the past 2 decades, with more than 48,000 deaths by suicide occurring just last year. MDD is the most common diagnosis among completed suicides, and identifying individuals at the highest risk for suicide remains a “pressing challenge,” the researchers noted.
They looked for changes in gene expression associated with suicide in archived postmortem blood and brain samples from adults with MDD who died by suicide (MDD-S) or by other means (MDD-NS), as well as a group of controls with no psychiatric illness.
In total, there were blood and brain samples for 45 adults, including 53 blood samples and 69 dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) tissue samples.
In blood, investigators identified 14 genes that significantly differentiated MDD-S from MDD-NS. The top six genes differentially expressed in blood were PER3, MTPAP, SLC25A26, CD19, SOX9, and GAR1.
In addition, four genes showed significant changes in brain and blood between the MDD-S and MDD-NS groups. SOX9 was decreased and PER3 was increased in MDD-S in both blood and brain samples, while CD19 and TERF1 were increased in blood but decreased in DLPFC.
SOX9, an astrocytic marker in the brain and B-cell marker in blood, has been shown to be decreased in MDD-S compared with controls in the prefrontal cortex.
In the current study, researchers found that SOX9 expression was significantly reduced both in blood and brain in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS, “suggesting similar immune/astrocytic dysregulations in suicide that could be further investigated.”
Potential signatures, potential targets
PER3 is a circadian rhythm gene implicated in sleep disorders associated with shifts in circadian rhythms and is thought to increase susceptibility to MDD.
Mutations in PER3 have been shown previously to alter multiple systems, including response to antidepressants; and increased blood expression of PER1 has been linked to suicidality in women, the researchers noted.
There also were significantly higher levels of two inflammatory markers (CD19 and CD6 genes) in blood of MDD-S patients compared to MDD-NS patients.
Another “significant” finding was the involvement of several mitochondrial genes in suicide, the researchers said.
Two nuclear genes coding for mitochondria-located proteins MTPAP (a mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase) and the mitochondrial polyamine transporter SLC25A26 were increased in blood in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS and controls, suggesting that “mitochondrial alterations could be used as potential signatures to differentiate MDD-S from MDD-NS patients and also from controls.”
The researchers added that the genes found to be dysregulated in suicide represent potential targets for future drug therapies to prevent suicide and could also be used to develop a molecular test to identify individuals at high risk for suicide.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the American Society for Suicide Prevention, and the Pritzker Family Philanthropic Fund. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found patients with MDD who died by suicide had a gene expression signature in blood distinct from patients with MDD who died by other means.
The signature included genes involved in stress response changes, including polyamine metabolism, circadian rhythm, immune dysregulation, and telomere maintenance.
“These blood biomarkers are an important step toward developing blood tests to identify patients with imminent risk of ending their lives,” study investigator Adolfo Sequeira, PhD, associate researcher in the department of psychiatry and human behavior, University of California, Irvine, said in a news release.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze blood and brain samples in a well-defined population of MDDs demonstrating significant differences in gene expression associated with completed suicide,” Dr. Sequeira added.
The findings were published online in Translational Psychiatry.
A pressing challenge
Suicide rates in the United States have jumped by more than 35% over the past 2 decades, with more than 48,000 deaths by suicide occurring just last year. MDD is the most common diagnosis among completed suicides, and identifying individuals at the highest risk for suicide remains a “pressing challenge,” the researchers noted.
They looked for changes in gene expression associated with suicide in archived postmortem blood and brain samples from adults with MDD who died by suicide (MDD-S) or by other means (MDD-NS), as well as a group of controls with no psychiatric illness.
In total, there were blood and brain samples for 45 adults, including 53 blood samples and 69 dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) tissue samples.
In blood, investigators identified 14 genes that significantly differentiated MDD-S from MDD-NS. The top six genes differentially expressed in blood were PER3, MTPAP, SLC25A26, CD19, SOX9, and GAR1.
In addition, four genes showed significant changes in brain and blood between the MDD-S and MDD-NS groups. SOX9 was decreased and PER3 was increased in MDD-S in both blood and brain samples, while CD19 and TERF1 were increased in blood but decreased in DLPFC.
SOX9, an astrocytic marker in the brain and B-cell marker in blood, has been shown to be decreased in MDD-S compared with controls in the prefrontal cortex.
In the current study, researchers found that SOX9 expression was significantly reduced both in blood and brain in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS, “suggesting similar immune/astrocytic dysregulations in suicide that could be further investigated.”
Potential signatures, potential targets
PER3 is a circadian rhythm gene implicated in sleep disorders associated with shifts in circadian rhythms and is thought to increase susceptibility to MDD.
Mutations in PER3 have been shown previously to alter multiple systems, including response to antidepressants; and increased blood expression of PER1 has been linked to suicidality in women, the researchers noted.
There also were significantly higher levels of two inflammatory markers (CD19 and CD6 genes) in blood of MDD-S patients compared to MDD-NS patients.
Another “significant” finding was the involvement of several mitochondrial genes in suicide, the researchers said.
Two nuclear genes coding for mitochondria-located proteins MTPAP (a mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase) and the mitochondrial polyamine transporter SLC25A26 were increased in blood in MDD-S compared with MDD-NS and controls, suggesting that “mitochondrial alterations could be used as potential signatures to differentiate MDD-S from MDD-NS patients and also from controls.”
The researchers added that the genes found to be dysregulated in suicide represent potential targets for future drug therapies to prevent suicide and could also be used to develop a molecular test to identify individuals at high risk for suicide.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the American Society for Suicide Prevention, and the Pritzker Family Philanthropic Fund. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM TRANSLATIONAL PSYCHIATRY
Neuropsychiatric risks of COVID-19: New data
The neuropsychiatric ramifications of severe COVID-19 infection appear to be no different than for other severe acute respiratory infections (SARI).
This suggests that disease severity, rather than pathogen, is the most relevant factor in new-onset neuropsychiatric illness, the investigators note.
The risk of new-onset neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection are “substantial, but similar to those after other severe respiratory infections,” study investigator Peter Watkinson, MD, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, and John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Significant mental health burden
Research has shown a significant burden of neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection. However, it’s unclear how this risk compares to SARI.
To investigate, Dr. Watkinson and colleagues evaluated electronic health record data on more than 8.3 million adults, including 16,679 (0.02%) who survived a hospital admission for SARI and 32,525 (0.03%) who survived a hospital stay for COVID-19.
Compared with the remaining population, risks of new anxiety disorder, dementia, psychotic disorder, depression, and bipolar disorder diagnoses were significantly and similarly increased in adults surviving hospitalization for either COVID-19 or SARI.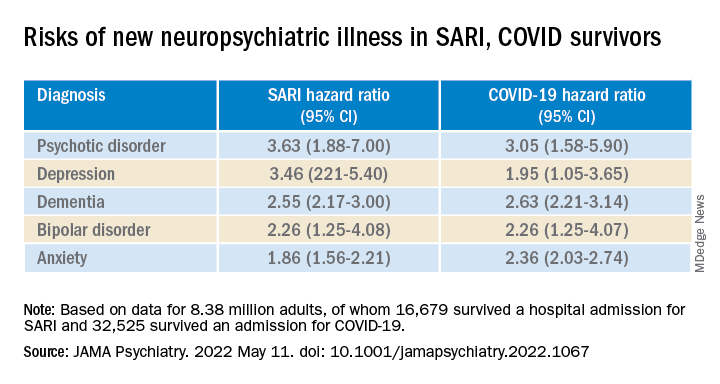
Compared with the wider population, survivors of severe SARI or COVID-19 were also at increased risk of starting treatment with antidepressants, hypnotics/anxiolytics, or antipsychotics.
When comparing survivors of SARI hospitalization to survivors of COVID-19 hospitalization, no significant differences were observed in the postdischarge rates of new-onset anxiety disorder, dementia, depression, or bipolar affective disorder.
The SARI and COVID groups also did not differ in terms of their postdischarge risks of antidepressant or hypnotic/anxiolytic use, but the COVID survivors had a 20% lower risk of starting an antipsychotic.
“In this cohort study, SARI were found to be associated with significant postacute neuropsychiatric morbidity, for which COVID-19 is not distinctly different,” Dr. Watkinson and colleagues write.
“These results may help refine our understanding of the post–severe COVID-19 phenotype and may inform post-discharge support for patients requiring hospital-based and intensive care for SARI regardless of causative pathogen,” they write.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Kevin McConway, PhD, emeritus professor of applied statistics at the Open University in Milton Keynes, England, described the study as “impressive.” However, he pointed out that the study’s observational design is a limitation.
“One can never be absolutely certain about the interpretation of findings of an observational study. What the research can’t tell us is what caused the increased psychiatric risks for people hospitalized with COVID-19 or some other serious respiratory disease,” Dr. McConway said.
“It can’t tell us what might happen in the future, when, we all hope, many fewer are being hospitalized with COVID-19 than was the case in those first two waves, and the current backlog of provision of some health services has decreased,” he added.
“So we can’t just say that, in general, serious COVID-19 has much the same neuropsychiatric consequences as other very serious respiratory illness. Maybe it does, maybe it doesn’t,” Dr. McConway cautioned.
Max Taquet, PhD, with the University of Oxford, noted that the study is limited to hospitalized adult patients, leaving open the question of risk in nonhospitalized individuals – which is the overwhelming majority of patients with COVID-19 – or in children.
Whether the neuropsychiatric risks have remained the same since the emergence of the Omicron variant also remains “an open question since all patients in this study were diagnosed before July 2021,” Dr. Taquet said in statement.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust, the John Fell Oxford University Press Research Fund, the Oxford Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund and Cancer Research UK, through the Cancer Research UK Oxford Centre. Dr. Watkinson disclosed grants from the National Institute for Health Research and Sensyne Health outside the submitted work; and serving as chief medical officer for Sensyne Health prior to this work, as well as holding shares in the company. Dr. McConway is a trustee of the UK Science Media Centre and a member of its advisory committee. His comments were provided in his capacity as an independent professional statistician. Dr. Taquet has worked on similar studies trying to identify, quantify, and specify the neurological and psychiatric consequences of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The neuropsychiatric ramifications of severe COVID-19 infection appear to be no different than for other severe acute respiratory infections (SARI).
This suggests that disease severity, rather than pathogen, is the most relevant factor in new-onset neuropsychiatric illness, the investigators note.
The risk of new-onset neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection are “substantial, but similar to those after other severe respiratory infections,” study investigator Peter Watkinson, MD, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, and John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Significant mental health burden
Research has shown a significant burden of neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection. However, it’s unclear how this risk compares to SARI.
To investigate, Dr. Watkinson and colleagues evaluated electronic health record data on more than 8.3 million adults, including 16,679 (0.02%) who survived a hospital admission for SARI and 32,525 (0.03%) who survived a hospital stay for COVID-19.
Compared with the remaining population, risks of new anxiety disorder, dementia, psychotic disorder, depression, and bipolar disorder diagnoses were significantly and similarly increased in adults surviving hospitalization for either COVID-19 or SARI.
Compared with the wider population, survivors of severe SARI or COVID-19 were also at increased risk of starting treatment with antidepressants, hypnotics/anxiolytics, or antipsychotics.
When comparing survivors of SARI hospitalization to survivors of COVID-19 hospitalization, no significant differences were observed in the postdischarge rates of new-onset anxiety disorder, dementia, depression, or bipolar affective disorder.
The SARI and COVID groups also did not differ in terms of their postdischarge risks of antidepressant or hypnotic/anxiolytic use, but the COVID survivors had a 20% lower risk of starting an antipsychotic.
“In this cohort study, SARI were found to be associated with significant postacute neuropsychiatric morbidity, for which COVID-19 is not distinctly different,” Dr. Watkinson and colleagues write.
“These results may help refine our understanding of the post–severe COVID-19 phenotype and may inform post-discharge support for patients requiring hospital-based and intensive care for SARI regardless of causative pathogen,” they write.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Kevin McConway, PhD, emeritus professor of applied statistics at the Open University in Milton Keynes, England, described the study as “impressive.” However, he pointed out that the study’s observational design is a limitation.
“One can never be absolutely certain about the interpretation of findings of an observational study. What the research can’t tell us is what caused the increased psychiatric risks for people hospitalized with COVID-19 or some other serious respiratory disease,” Dr. McConway said.
“It can’t tell us what might happen in the future, when, we all hope, many fewer are being hospitalized with COVID-19 than was the case in those first two waves, and the current backlog of provision of some health services has decreased,” he added.
“So we can’t just say that, in general, serious COVID-19 has much the same neuropsychiatric consequences as other very serious respiratory illness. Maybe it does, maybe it doesn’t,” Dr. McConway cautioned.
Max Taquet, PhD, with the University of Oxford, noted that the study is limited to hospitalized adult patients, leaving open the question of risk in nonhospitalized individuals – which is the overwhelming majority of patients with COVID-19 – or in children.
Whether the neuropsychiatric risks have remained the same since the emergence of the Omicron variant also remains “an open question since all patients in this study were diagnosed before July 2021,” Dr. Taquet said in statement.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust, the John Fell Oxford University Press Research Fund, the Oxford Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund and Cancer Research UK, through the Cancer Research UK Oxford Centre. Dr. Watkinson disclosed grants from the National Institute for Health Research and Sensyne Health outside the submitted work; and serving as chief medical officer for Sensyne Health prior to this work, as well as holding shares in the company. Dr. McConway is a trustee of the UK Science Media Centre and a member of its advisory committee. His comments were provided in his capacity as an independent professional statistician. Dr. Taquet has worked on similar studies trying to identify, quantify, and specify the neurological and psychiatric consequences of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The neuropsychiatric ramifications of severe COVID-19 infection appear to be no different than for other severe acute respiratory infections (SARI).
This suggests that disease severity, rather than pathogen, is the most relevant factor in new-onset neuropsychiatric illness, the investigators note.
The risk of new-onset neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection are “substantial, but similar to those after other severe respiratory infections,” study investigator Peter Watkinson, MD, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, and John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Significant mental health burden
Research has shown a significant burden of neuropsychological illness after severe COVID-19 infection. However, it’s unclear how this risk compares to SARI.
To investigate, Dr. Watkinson and colleagues evaluated electronic health record data on more than 8.3 million adults, including 16,679 (0.02%) who survived a hospital admission for SARI and 32,525 (0.03%) who survived a hospital stay for COVID-19.
Compared with the remaining population, risks of new anxiety disorder, dementia, psychotic disorder, depression, and bipolar disorder diagnoses were significantly and similarly increased in adults surviving hospitalization for either COVID-19 or SARI.
Compared with the wider population, survivors of severe SARI or COVID-19 were also at increased risk of starting treatment with antidepressants, hypnotics/anxiolytics, or antipsychotics.
When comparing survivors of SARI hospitalization to survivors of COVID-19 hospitalization, no significant differences were observed in the postdischarge rates of new-onset anxiety disorder, dementia, depression, or bipolar affective disorder.
The SARI and COVID groups also did not differ in terms of their postdischarge risks of antidepressant or hypnotic/anxiolytic use, but the COVID survivors had a 20% lower risk of starting an antipsychotic.
“In this cohort study, SARI were found to be associated with significant postacute neuropsychiatric morbidity, for which COVID-19 is not distinctly different,” Dr. Watkinson and colleagues write.
“These results may help refine our understanding of the post–severe COVID-19 phenotype and may inform post-discharge support for patients requiring hospital-based and intensive care for SARI regardless of causative pathogen,” they write.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Kevin McConway, PhD, emeritus professor of applied statistics at the Open University in Milton Keynes, England, described the study as “impressive.” However, he pointed out that the study’s observational design is a limitation.
“One can never be absolutely certain about the interpretation of findings of an observational study. What the research can’t tell us is what caused the increased psychiatric risks for people hospitalized with COVID-19 or some other serious respiratory disease,” Dr. McConway said.
“It can’t tell us what might happen in the future, when, we all hope, many fewer are being hospitalized with COVID-19 than was the case in those first two waves, and the current backlog of provision of some health services has decreased,” he added.
“So we can’t just say that, in general, serious COVID-19 has much the same neuropsychiatric consequences as other very serious respiratory illness. Maybe it does, maybe it doesn’t,” Dr. McConway cautioned.
Max Taquet, PhD, with the University of Oxford, noted that the study is limited to hospitalized adult patients, leaving open the question of risk in nonhospitalized individuals – which is the overwhelming majority of patients with COVID-19 – or in children.
Whether the neuropsychiatric risks have remained the same since the emergence of the Omicron variant also remains “an open question since all patients in this study were diagnosed before July 2021,” Dr. Taquet said in statement.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust, the John Fell Oxford University Press Research Fund, the Oxford Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund and Cancer Research UK, through the Cancer Research UK Oxford Centre. Dr. Watkinson disclosed grants from the National Institute for Health Research and Sensyne Health outside the submitted work; and serving as chief medical officer for Sensyne Health prior to this work, as well as holding shares in the company. Dr. McConway is a trustee of the UK Science Media Centre and a member of its advisory committee. His comments were provided in his capacity as an independent professional statistician. Dr. Taquet has worked on similar studies trying to identify, quantify, and specify the neurological and psychiatric consequences of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves oral form of ALS drug edaravone
Edaravone is a pyrazolone free-radical scavenger thought to lessen the effects of oxidative stress, which is a probable factor in ALS onset and progression. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an intravenous (IV) infusion to treat ALS.
Radicava ORS is self-administered and can be taken at home. After fasting overnight, Radicava ORS should be taken in the morning orally or through a feeding tube. The oral version has the same dosing regimen as the original IV version, with an initial treatment cycle of daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period and subsequent treatment cycles consisting of daily dosing for 10 out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods.
Compared with the IV formation of Radicava, Radicava ORS has been shown to generate comparable levels of active drug in the bloodstream, the FDA said.
The FDA determined that IV Radicava was effective based on a 6-month clinical trial in Japan involving 137 individuals who were randomly chosen to receive either the drug or a placebo. At 24 weeks, individuals receiving Radicava showed less decline on a clinical assessment of daily functioning, compared with those receiving placebo.
The most common side effects of Radicava are bruising, problems walking, and headache. Fatigue is also a possible side effect from Radicava ORS. Both formulations can have serious side effects associated with allergic reactions, including hives, rash, and shortness of breath.
Full prescribing information, including additional information on risks associated with Radicava ORS, is available online.
The FDA granted Radicava ORS orphan drug status, priority review, and Fast Track designations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Edaravone is a pyrazolone free-radical scavenger thought to lessen the effects of oxidative stress, which is a probable factor in ALS onset and progression. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an intravenous (IV) infusion to treat ALS.
Radicava ORS is self-administered and can be taken at home. After fasting overnight, Radicava ORS should be taken in the morning orally or through a feeding tube. The oral version has the same dosing regimen as the original IV version, with an initial treatment cycle of daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period and subsequent treatment cycles consisting of daily dosing for 10 out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods.
Compared with the IV formation of Radicava, Radicava ORS has been shown to generate comparable levels of active drug in the bloodstream, the FDA said.
The FDA determined that IV Radicava was effective based on a 6-month clinical trial in Japan involving 137 individuals who were randomly chosen to receive either the drug or a placebo. At 24 weeks, individuals receiving Radicava showed less decline on a clinical assessment of daily functioning, compared with those receiving placebo.
The most common side effects of Radicava are bruising, problems walking, and headache. Fatigue is also a possible side effect from Radicava ORS. Both formulations can have serious side effects associated with allergic reactions, including hives, rash, and shortness of breath.
Full prescribing information, including additional information on risks associated with Radicava ORS, is available online.
The FDA granted Radicava ORS orphan drug status, priority review, and Fast Track designations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Edaravone is a pyrazolone free-radical scavenger thought to lessen the effects of oxidative stress, which is a probable factor in ALS onset and progression. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an intravenous (IV) infusion to treat ALS.
Radicava ORS is self-administered and can be taken at home. After fasting overnight, Radicava ORS should be taken in the morning orally or through a feeding tube. The oral version has the same dosing regimen as the original IV version, with an initial treatment cycle of daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period and subsequent treatment cycles consisting of daily dosing for 10 out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods.
Compared with the IV formation of Radicava, Radicava ORS has been shown to generate comparable levels of active drug in the bloodstream, the FDA said.
The FDA determined that IV Radicava was effective based on a 6-month clinical trial in Japan involving 137 individuals who were randomly chosen to receive either the drug or a placebo. At 24 weeks, individuals receiving Radicava showed less decline on a clinical assessment of daily functioning, compared with those receiving placebo.
The most common side effects of Radicava are bruising, problems walking, and headache. Fatigue is also a possible side effect from Radicava ORS. Both formulations can have serious side effects associated with allergic reactions, including hives, rash, and shortness of breath.
Full prescribing information, including additional information on risks associated with Radicava ORS, is available online.
The FDA granted Radicava ORS orphan drug status, priority review, and Fast Track designations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mixing BP meds with NSAID may be ‘triple whammy’ for kidneys
The study also looked at risk factors associated with the effect of triple therapy with these agents, which has been called “triple whammy” AKI.
“It’s not that everyone who happens to take this combination of drugs is going to have problems,” Anita Layton, PhD, University of Waterloo, Ontario, said in a statement. “But the research shows it’s enough of a problem that you should exercise caution.”
The study was published online in Mathematical Biosciences.
In an earlier study, triple therapy with a diuretic, RAS inhibitor, and NSAID was associated with a 31% increased risk for AKI, relative to diuretic and RAS inhibitor therapy only.
However, the factors that predispose some patients to develop “triple whammy” AKI are unclear.
To better understand the mechanism by which triple therapy increases risk for AKI, Dr. Layton and colleagues used computational models to gauge interactions between concurrent use of a diuretic, a RAS inhibitor, and an NSAID.
They identified dehydration and high sensitivity to drug treatment as key contributing factors to the development of triple whammy AKI.
Their model simulations suggested that low water intake, the myogenic response (that is, the reflex response of arteries and arterioles to changes in blood pressure to maintain consistent blood flow), and drug sensitivity “may predispose patients with hypertension to develop triple whammy-induced AKI,” they wrote.
“We hypothesize that individuals with an impaired myogenic response may be particularly susceptible to triple whammy AKI. Additionally, increased drug sensitivity or low water intake can predispose patients to triple whammy AKI,” they added.
In the absence of additional risk factors, there was no indication of an elevated risk for AKI when an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and NSAID are combined, the study team said.
In contrast, when an ACE inhibitor, diuretic, and NSAID are combined, critical blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) regulatory mechanisms are simultaneously interrupted, they reported.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, model simulations indicate that triple treatment reduces GFR more than single or double treatments in all individuals. However, under triple treatment, urine volume and GFR have not been predicted to fall sufficiently far to indicate AKI,” they wrote. “This result is consistent with the fact that only a fraction of individuals develop AKI following triple treatment.”
They expect, therefore, that hypertensive patients who are otherwise healthy will be able to withstand triple treatment, in the absence of these aggravating factors, the researchers concluded.
Nonetheless, it’s wise to “always be careful when mixing medications,” Dr. Layton told this news organization.
She noted that “triple whammy AKI is known among kidney researchers and nephrologists. To what extent nonspecialists are aware, it isn’t clear.
“More importantly,” Dr. Layton said, “NSAIDs can be obtained over the counter, and triple whammy AKI isn’t common knowledge outside of the medical community.”
This research was supported by the Canada 150 Research Chair program and by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study also looked at risk factors associated with the effect of triple therapy with these agents, which has been called “triple whammy” AKI.
“It’s not that everyone who happens to take this combination of drugs is going to have problems,” Anita Layton, PhD, University of Waterloo, Ontario, said in a statement. “But the research shows it’s enough of a problem that you should exercise caution.”
The study was published online in Mathematical Biosciences.
In an earlier study, triple therapy with a diuretic, RAS inhibitor, and NSAID was associated with a 31% increased risk for AKI, relative to diuretic and RAS inhibitor therapy only.
However, the factors that predispose some patients to develop “triple whammy” AKI are unclear.
To better understand the mechanism by which triple therapy increases risk for AKI, Dr. Layton and colleagues used computational models to gauge interactions between concurrent use of a diuretic, a RAS inhibitor, and an NSAID.
They identified dehydration and high sensitivity to drug treatment as key contributing factors to the development of triple whammy AKI.
Their model simulations suggested that low water intake, the myogenic response (that is, the reflex response of arteries and arterioles to changes in blood pressure to maintain consistent blood flow), and drug sensitivity “may predispose patients with hypertension to develop triple whammy-induced AKI,” they wrote.
“We hypothesize that individuals with an impaired myogenic response may be particularly susceptible to triple whammy AKI. Additionally, increased drug sensitivity or low water intake can predispose patients to triple whammy AKI,” they added.
In the absence of additional risk factors, there was no indication of an elevated risk for AKI when an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and NSAID are combined, the study team said.
In contrast, when an ACE inhibitor, diuretic, and NSAID are combined, critical blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) regulatory mechanisms are simultaneously interrupted, they reported.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, model simulations indicate that triple treatment reduces GFR more than single or double treatments in all individuals. However, under triple treatment, urine volume and GFR have not been predicted to fall sufficiently far to indicate AKI,” they wrote. “This result is consistent with the fact that only a fraction of individuals develop AKI following triple treatment.”
They expect, therefore, that hypertensive patients who are otherwise healthy will be able to withstand triple treatment, in the absence of these aggravating factors, the researchers concluded.
Nonetheless, it’s wise to “always be careful when mixing medications,” Dr. Layton told this news organization.
She noted that “triple whammy AKI is known among kidney researchers and nephrologists. To what extent nonspecialists are aware, it isn’t clear.
“More importantly,” Dr. Layton said, “NSAIDs can be obtained over the counter, and triple whammy AKI isn’t common knowledge outside of the medical community.”
This research was supported by the Canada 150 Research Chair program and by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study also looked at risk factors associated with the effect of triple therapy with these agents, which has been called “triple whammy” AKI.
“It’s not that everyone who happens to take this combination of drugs is going to have problems,” Anita Layton, PhD, University of Waterloo, Ontario, said in a statement. “But the research shows it’s enough of a problem that you should exercise caution.”
The study was published online in Mathematical Biosciences.
In an earlier study, triple therapy with a diuretic, RAS inhibitor, and NSAID was associated with a 31% increased risk for AKI, relative to diuretic and RAS inhibitor therapy only.
However, the factors that predispose some patients to develop “triple whammy” AKI are unclear.
To better understand the mechanism by which triple therapy increases risk for AKI, Dr. Layton and colleagues used computational models to gauge interactions between concurrent use of a diuretic, a RAS inhibitor, and an NSAID.
They identified dehydration and high sensitivity to drug treatment as key contributing factors to the development of triple whammy AKI.
Their model simulations suggested that low water intake, the myogenic response (that is, the reflex response of arteries and arterioles to changes in blood pressure to maintain consistent blood flow), and drug sensitivity “may predispose patients with hypertension to develop triple whammy-induced AKI,” they wrote.
“We hypothesize that individuals with an impaired myogenic response may be particularly susceptible to triple whammy AKI. Additionally, increased drug sensitivity or low water intake can predispose patients to triple whammy AKI,” they added.
In the absence of additional risk factors, there was no indication of an elevated risk for AKI when an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and NSAID are combined, the study team said.
In contrast, when an ACE inhibitor, diuretic, and NSAID are combined, critical blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) regulatory mechanisms are simultaneously interrupted, they reported.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, model simulations indicate that triple treatment reduces GFR more than single or double treatments in all individuals. However, under triple treatment, urine volume and GFR have not been predicted to fall sufficiently far to indicate AKI,” they wrote. “This result is consistent with the fact that only a fraction of individuals develop AKI following triple treatment.”
They expect, therefore, that hypertensive patients who are otherwise healthy will be able to withstand triple treatment, in the absence of these aggravating factors, the researchers concluded.
Nonetheless, it’s wise to “always be careful when mixing medications,” Dr. Layton told this news organization.
She noted that “triple whammy AKI is known among kidney researchers and nephrologists. To what extent nonspecialists are aware, it isn’t clear.
“More importantly,” Dr. Layton said, “NSAIDs can be obtained over the counter, and triple whammy AKI isn’t common knowledge outside of the medical community.”
This research was supported by the Canada 150 Research Chair program and by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MATHEMATICAL BIOSCIENCES
DOJ complaint flags HCV drug denials for people with addiction
A complaint filed with the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) alleges that Alabama’s Medicaid program is illegally denying curative drug treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection to people with substance use disorder.
The complaint was filed May 9 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School, in partnership with AIDS Alabama.
It alleges that Alabama Medicaid has a policy of denying HCV treatment to people who have used illegal drugs or alcohol in the past 6 months.
CHLPI and AIDS Alabama argue that these restrictions violate the Americans With Disabilities Act, which protects people who are disabled because of substance use disorder.
“Forced sobriety policies don’t just unfairly prevent people with substance use disorder from accessing life-saving treatment; they also severely hamper public health efforts to stop the spread of the disease,” Kevin Costello, CHLPI’s litigation director, said in a statement.
“These policies are rooted in stigma, not science, and they violate antidiscrimination provisions of the Americans With Disabilities Act,” Mr. Costello said.
Filing an administrative complaint against Alabama is “an important milestone in fighting sobriety restrictions,” he added.
Morally wrong
Kathie Hiers, CEO of AIDS Alabama, noted that Alabama’s health outcomes are among the worst in the nation.
“Policies that prevent adequate medical care from being provided must end. HCV now has a cure, and withholding that cure from Alabamians based on a moral judgment is wrong and certainly doesn’t follow the science,” Ms. Hiers added.
Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy can cure up to 99% of people living with HCV.
The complaint against Alabama Medicaid builds on CHLPI’s successful policy advocacy and litigation campaigns to expand access to DAA therapy in state Medicaid programs across the country.
Since 2017, 19 states have removed treatment restrictions that were based on drug or alcohol use. In other states, however, “severe, illegal sobriety restrictions remain,” according to CHLPI.
Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, South Carolina, and South Dakota still require Medicaid enrollees with HCV to prove they have not used drugs or alcohol for 6 months before they can receive treatment. Iowa, North Dakota, and West Virginia have a 3-month abstinence requirement.
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend DAA therapy for all patients with chronic HCV infection, regardless of drug or alcohol use.
CHLPI intends to expand this “enforcement campaign” to all states where sobriety restrictions persist.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A complaint filed with the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) alleges that Alabama’s Medicaid program is illegally denying curative drug treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection to people with substance use disorder.
The complaint was filed May 9 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School, in partnership with AIDS Alabama.
It alleges that Alabama Medicaid has a policy of denying HCV treatment to people who have used illegal drugs or alcohol in the past 6 months.
CHLPI and AIDS Alabama argue that these restrictions violate the Americans With Disabilities Act, which protects people who are disabled because of substance use disorder.
“Forced sobriety policies don’t just unfairly prevent people with substance use disorder from accessing life-saving treatment; they also severely hamper public health efforts to stop the spread of the disease,” Kevin Costello, CHLPI’s litigation director, said in a statement.
“These policies are rooted in stigma, not science, and they violate antidiscrimination provisions of the Americans With Disabilities Act,” Mr. Costello said.
Filing an administrative complaint against Alabama is “an important milestone in fighting sobriety restrictions,” he added.
Morally wrong
Kathie Hiers, CEO of AIDS Alabama, noted that Alabama’s health outcomes are among the worst in the nation.
“Policies that prevent adequate medical care from being provided must end. HCV now has a cure, and withholding that cure from Alabamians based on a moral judgment is wrong and certainly doesn’t follow the science,” Ms. Hiers added.
Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy can cure up to 99% of people living with HCV.
The complaint against Alabama Medicaid builds on CHLPI’s successful policy advocacy and litigation campaigns to expand access to DAA therapy in state Medicaid programs across the country.
Since 2017, 19 states have removed treatment restrictions that were based on drug or alcohol use. In other states, however, “severe, illegal sobriety restrictions remain,” according to CHLPI.
Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, South Carolina, and South Dakota still require Medicaid enrollees with HCV to prove they have not used drugs or alcohol for 6 months before they can receive treatment. Iowa, North Dakota, and West Virginia have a 3-month abstinence requirement.
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend DAA therapy for all patients with chronic HCV infection, regardless of drug or alcohol use.
CHLPI intends to expand this “enforcement campaign” to all states where sobriety restrictions persist.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A complaint filed with the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) alleges that Alabama’s Medicaid program is illegally denying curative drug treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection to people with substance use disorder.
The complaint was filed May 9 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School, in partnership with AIDS Alabama.
It alleges that Alabama Medicaid has a policy of denying HCV treatment to people who have used illegal drugs or alcohol in the past 6 months.
CHLPI and AIDS Alabama argue that these restrictions violate the Americans With Disabilities Act, which protects people who are disabled because of substance use disorder.
“Forced sobriety policies don’t just unfairly prevent people with substance use disorder from accessing life-saving treatment; they also severely hamper public health efforts to stop the spread of the disease,” Kevin Costello, CHLPI’s litigation director, said in a statement.
“These policies are rooted in stigma, not science, and they violate antidiscrimination provisions of the Americans With Disabilities Act,” Mr. Costello said.
Filing an administrative complaint against Alabama is “an important milestone in fighting sobriety restrictions,” he added.
Morally wrong
Kathie Hiers, CEO of AIDS Alabama, noted that Alabama’s health outcomes are among the worst in the nation.
“Policies that prevent adequate medical care from being provided must end. HCV now has a cure, and withholding that cure from Alabamians based on a moral judgment is wrong and certainly doesn’t follow the science,” Ms. Hiers added.
Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy can cure up to 99% of people living with HCV.
The complaint against Alabama Medicaid builds on CHLPI’s successful policy advocacy and litigation campaigns to expand access to DAA therapy in state Medicaid programs across the country.
Since 2017, 19 states have removed treatment restrictions that were based on drug or alcohol use. In other states, however, “severe, illegal sobriety restrictions remain,” according to CHLPI.
Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, South Carolina, and South Dakota still require Medicaid enrollees with HCV to prove they have not used drugs or alcohol for 6 months before they can receive treatment. Iowa, North Dakota, and West Virginia have a 3-month abstinence requirement.
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend DAA therapy for all patients with chronic HCV infection, regardless of drug or alcohol use.
CHLPI intends to expand this “enforcement campaign” to all states where sobriety restrictions persist.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can fecal transplants help reverse aging?
Transplanting fecal microbiota from young mice into older mice can reverse signs of aging in the gut, brain, and eyes, a team of scientists from the United Kingdom has found. Conversely, transplanting microbiota from old mice to young mice has the opposite effect.
This research provides “tantalizing evidence for the direct involvement of gut microbes in aging and the functional decline of brain function and vision and offers a potential solution in the form of gut microbe replacement therapy,” Simon Carding, PhD, who heads the gut microbes and health research program at the Quadram Institute in Norwich, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Microbiome.
The fountain of youth?
Age-related changes in diversity, composition, and function of the gut microbiota are associated with low-grade systemic inflammation, declining tissue function, and increased susceptibility to age-related chronic diseases.
Dr. Carding and colleagues at the Quadram Institute and the University of East Anglia used fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) to exchange the intestinal microbiota of young mice and aged mice.
Young mice who received aged microbiota showed increased intestinal barrier permeability (leaky gut) coupled with upregulated inflammation in the brain and retina, as well as loss of a key functional protein in the eye, they report.
Conversely, these detrimental effects were reversed when microbiota from young mice was transferred to aged mice. FMT with young microbiota also led to enrichment of beneficial taxa in aged mice.
“Our data support the suggestion that altered gut microbiota in old age contributes to intestinal and systemic inflammation, and so may contribute to driving inflammatory pathologies of aged organs,” the study team wrote.
“Targeting the gut-brain axis in aging, by modification of microbial composition to modulate immune and metabolic pathways, may therefore be a potential avenue for therapeutic approaches to age-associated inflammatory and functional decline,” they suggested.
In ongoing studies, the study team are working to understand how long the beneficial effects of young donor microbiota last, which will establish whether FMT can promote long-term health benefits in aged individuals and ameliorate age-associated neurodegeneration and retinal functional deterioration.
“Our results provide more evidence of the important links between microbes in the gut and healthy aging of tissues and organs around the body,” lead author Aimée Parker, PhD, from the Quadram Institute, said in the release.
“We hope that our findings will contribute ultimately to understanding how we can manipulate our diet and our gut bacteria to maximize good health in later life,” she added.
Support for this research was provided by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. The authors report no relevant financial relationships .
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplanting fecal microbiota from young mice into older mice can reverse signs of aging in the gut, brain, and eyes, a team of scientists from the United Kingdom has found. Conversely, transplanting microbiota from old mice to young mice has the opposite effect.
This research provides “tantalizing evidence for the direct involvement of gut microbes in aging and the functional decline of brain function and vision and offers a potential solution in the form of gut microbe replacement therapy,” Simon Carding, PhD, who heads the gut microbes and health research program at the Quadram Institute in Norwich, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Microbiome.
The fountain of youth?
Age-related changes in diversity, composition, and function of the gut microbiota are associated with low-grade systemic inflammation, declining tissue function, and increased susceptibility to age-related chronic diseases.
Dr. Carding and colleagues at the Quadram Institute and the University of East Anglia used fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) to exchange the intestinal microbiota of young mice and aged mice.
Young mice who received aged microbiota showed increased intestinal barrier permeability (leaky gut) coupled with upregulated inflammation in the brain and retina, as well as loss of a key functional protein in the eye, they report.
Conversely, these detrimental effects were reversed when microbiota from young mice was transferred to aged mice. FMT with young microbiota also led to enrichment of beneficial taxa in aged mice.
“Our data support the suggestion that altered gut microbiota in old age contributes to intestinal and systemic inflammation, and so may contribute to driving inflammatory pathologies of aged organs,” the study team wrote.
“Targeting the gut-brain axis in aging, by modification of microbial composition to modulate immune and metabolic pathways, may therefore be a potential avenue for therapeutic approaches to age-associated inflammatory and functional decline,” they suggested.
In ongoing studies, the study team are working to understand how long the beneficial effects of young donor microbiota last, which will establish whether FMT can promote long-term health benefits in aged individuals and ameliorate age-associated neurodegeneration and retinal functional deterioration.
“Our results provide more evidence of the important links between microbes in the gut and healthy aging of tissues and organs around the body,” lead author Aimée Parker, PhD, from the Quadram Institute, said in the release.
“We hope that our findings will contribute ultimately to understanding how we can manipulate our diet and our gut bacteria to maximize good health in later life,” she added.
Support for this research was provided by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. The authors report no relevant financial relationships .
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplanting fecal microbiota from young mice into older mice can reverse signs of aging in the gut, brain, and eyes, a team of scientists from the United Kingdom has found. Conversely, transplanting microbiota from old mice to young mice has the opposite effect.
This research provides “tantalizing evidence for the direct involvement of gut microbes in aging and the functional decline of brain function and vision and offers a potential solution in the form of gut microbe replacement therapy,” Simon Carding, PhD, who heads the gut microbes and health research program at the Quadram Institute in Norwich, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Microbiome.
The fountain of youth?
Age-related changes in diversity, composition, and function of the gut microbiota are associated with low-grade systemic inflammation, declining tissue function, and increased susceptibility to age-related chronic diseases.
Dr. Carding and colleagues at the Quadram Institute and the University of East Anglia used fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) to exchange the intestinal microbiota of young mice and aged mice.
Young mice who received aged microbiota showed increased intestinal barrier permeability (leaky gut) coupled with upregulated inflammation in the brain and retina, as well as loss of a key functional protein in the eye, they report.
Conversely, these detrimental effects were reversed when microbiota from young mice was transferred to aged mice. FMT with young microbiota also led to enrichment of beneficial taxa in aged mice.
“Our data support the suggestion that altered gut microbiota in old age contributes to intestinal and systemic inflammation, and so may contribute to driving inflammatory pathologies of aged organs,” the study team wrote.
“Targeting the gut-brain axis in aging, by modification of microbial composition to modulate immune and metabolic pathways, may therefore be a potential avenue for therapeutic approaches to age-associated inflammatory and functional decline,” they suggested.
In ongoing studies, the study team are working to understand how long the beneficial effects of young donor microbiota last, which will establish whether FMT can promote long-term health benefits in aged individuals and ameliorate age-associated neurodegeneration and retinal functional deterioration.
“Our results provide more evidence of the important links between microbes in the gut and healthy aging of tissues and organs around the body,” lead author Aimée Parker, PhD, from the Quadram Institute, said in the release.
“We hope that our findings will contribute ultimately to understanding how we can manipulate our diet and our gut bacteria to maximize good health in later life,” she added.
Support for this research was provided by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. The authors report no relevant financial relationships .
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do psychotropic meds raise or lower COVID risk in psych patients?
Investigators found that second-generation antipsychotics were associated with a 48% lower risk of COVID-19, while valproic acid was associated with a 39% increased risk of the disease.
“Exposures to several psychotropic medications were associated with risk of COVID-19 infection among inpatients with serious mental illness; decreased risk was observed with the use of second generation antipsychotics, with paliperidone use associated with the largest effect size. Valproic acid use was associated with an increased risk of infection,” the investigators, led by Katlyn Nemani, MD, at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Vulnerable population
Patients with serious mental illness are particularly vulnerable to COVID-19. Several psychotropic medications have been identified as potential therapeutic agents to prevent or treat COVID-19, but they have not been systematically studied in this patient population.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,958 adults who were continuously hospitalized with serious mental illness from March 8 to July 1, 2020. The mean age was 51.4 years, and 1,442 (74%) were men.
A total of 969 patients (49.5%) had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 while hospitalized, and 38 (3.9%) died – a mortality rate four times higher than estimates from the general population in New York during the same time frame, the researchers note.
“This finding is consistent with prior studies that have found increased rates of infection in congregate settings and increased mortality after infection among patients with serious mental illness,” the investigators write.
The use of second-generation antipsychotic medications, as a class, was associated with a lower likelihood of COVID-19 (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.86), while the use of mood stabilizers was associated with increased likelihood of infection (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.03-1.47).
In a multivariable model of individual medications, use of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone was associated with a lower odds of infection (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.41-0.84), and use of valproic acid was associated with increased odds of infection (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.10-1.76).
Valproic acid downregulates angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelial cells, which may impair immune function and contribute to poor outcomes for patients with COVID-19, the researchers say.
The use of clozapine was associated with reduced odds of COVID-related death (unadjusted OR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.10-0.62; fully adjusted OR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.17-1.12).
“Although there have been concerns about clozapine use during the pandemic as a risk factor for pneumonia and potential toxic effects during acute infection, clozapine use was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 infection or death in the present study. In fact, unadjusted estimates suggested a significant protective association,” the investigators write.
However, they note, data on clozapine and COVID-19 have been mixed.
Two prior studies of health record data showed an increased risk of COVID-19 associated with clozapine treatment, while a study that was limited to inpatients found a lower risk of infection and a lower risk of symptomatic disease in association with clozapine use.
The researchers also found a lower mortality risk in patients taking antidepressants; there were no COVID-related deaths among patients taking escitalopram, venlafaxine, bupropion, or fluvoxamine.
Although the association was not statistically significant, this observation is in line with larger studies that showed reduced risk of adverse outcomes associated with antidepressant use, the researchers note.
A matter of debate
In an accompanying commentary, Benedetta Vai, PhD, and Mario Gennaro Mazza, MD, with IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, point out that the link between psychopharmacologic compounds, in particular antipsychotics, and severe COVID-19 outcomes remains “a matter of debate, with inconsistent findings between studies.”
They note further research is needed to determine whether the protective role of second-generation antipsychotics on risk of COVID-19 is mediated by an immune effect or by the direct antiviral properties of these molecules.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Nemani, Dr. Vai, and Dr. Mazza have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that second-generation antipsychotics were associated with a 48% lower risk of COVID-19, while valproic acid was associated with a 39% increased risk of the disease.
“Exposures to several psychotropic medications were associated with risk of COVID-19 infection among inpatients with serious mental illness; decreased risk was observed with the use of second generation antipsychotics, with paliperidone use associated with the largest effect size. Valproic acid use was associated with an increased risk of infection,” the investigators, led by Katlyn Nemani, MD, at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Vulnerable population
Patients with serious mental illness are particularly vulnerable to COVID-19. Several psychotropic medications have been identified as potential therapeutic agents to prevent or treat COVID-19, but they have not been systematically studied in this patient population.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,958 adults who were continuously hospitalized with serious mental illness from March 8 to July 1, 2020. The mean age was 51.4 years, and 1,442 (74%) were men.
A total of 969 patients (49.5%) had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 while hospitalized, and 38 (3.9%) died – a mortality rate four times higher than estimates from the general population in New York during the same time frame, the researchers note.
“This finding is consistent with prior studies that have found increased rates of infection in congregate settings and increased mortality after infection among patients with serious mental illness,” the investigators write.
The use of second-generation antipsychotic medications, as a class, was associated with a lower likelihood of COVID-19 (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.86), while the use of mood stabilizers was associated with increased likelihood of infection (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.03-1.47).
In a multivariable model of individual medications, use of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone was associated with a lower odds of infection (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.41-0.84), and use of valproic acid was associated with increased odds of infection (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.10-1.76).
Valproic acid downregulates angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelial cells, which may impair immune function and contribute to poor outcomes for patients with COVID-19, the researchers say.
The use of clozapine was associated with reduced odds of COVID-related death (unadjusted OR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.10-0.62; fully adjusted OR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.17-1.12).
“Although there have been concerns about clozapine use during the pandemic as a risk factor for pneumonia and potential toxic effects during acute infection, clozapine use was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 infection or death in the present study. In fact, unadjusted estimates suggested a significant protective association,” the investigators write.
However, they note, data on clozapine and COVID-19 have been mixed.
Two prior studies of health record data showed an increased risk of COVID-19 associated with clozapine treatment, while a study that was limited to inpatients found a lower risk of infection and a lower risk of symptomatic disease in association with clozapine use.
The researchers also found a lower mortality risk in patients taking antidepressants; there were no COVID-related deaths among patients taking escitalopram, venlafaxine, bupropion, or fluvoxamine.
Although the association was not statistically significant, this observation is in line with larger studies that showed reduced risk of adverse outcomes associated with antidepressant use, the researchers note.
A matter of debate
In an accompanying commentary, Benedetta Vai, PhD, and Mario Gennaro Mazza, MD, with IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, point out that the link between psychopharmacologic compounds, in particular antipsychotics, and severe COVID-19 outcomes remains “a matter of debate, with inconsistent findings between studies.”
They note further research is needed to determine whether the protective role of second-generation antipsychotics on risk of COVID-19 is mediated by an immune effect or by the direct antiviral properties of these molecules.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Nemani, Dr. Vai, and Dr. Mazza have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that second-generation antipsychotics were associated with a 48% lower risk of COVID-19, while valproic acid was associated with a 39% increased risk of the disease.
“Exposures to several psychotropic medications were associated with risk of COVID-19 infection among inpatients with serious mental illness; decreased risk was observed with the use of second generation antipsychotics, with paliperidone use associated with the largest effect size. Valproic acid use was associated with an increased risk of infection,” the investigators, led by Katlyn Nemani, MD, at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Vulnerable population
Patients with serious mental illness are particularly vulnerable to COVID-19. Several psychotropic medications have been identified as potential therapeutic agents to prevent or treat COVID-19, but they have not been systematically studied in this patient population.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,958 adults who were continuously hospitalized with serious mental illness from March 8 to July 1, 2020. The mean age was 51.4 years, and 1,442 (74%) were men.
A total of 969 patients (49.5%) had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 while hospitalized, and 38 (3.9%) died – a mortality rate four times higher than estimates from the general population in New York during the same time frame, the researchers note.
“This finding is consistent with prior studies that have found increased rates of infection in congregate settings and increased mortality after infection among patients with serious mental illness,” the investigators write.
The use of second-generation antipsychotic medications, as a class, was associated with a lower likelihood of COVID-19 (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.86), while the use of mood stabilizers was associated with increased likelihood of infection (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.03-1.47).
In a multivariable model of individual medications, use of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone was associated with a lower odds of infection (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.41-0.84), and use of valproic acid was associated with increased odds of infection (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.10-1.76).
Valproic acid downregulates angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelial cells, which may impair immune function and contribute to poor outcomes for patients with COVID-19, the researchers say.
The use of clozapine was associated with reduced odds of COVID-related death (unadjusted OR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.10-0.62; fully adjusted OR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.17-1.12).
“Although there have been concerns about clozapine use during the pandemic as a risk factor for pneumonia and potential toxic effects during acute infection, clozapine use was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 infection or death in the present study. In fact, unadjusted estimates suggested a significant protective association,” the investigators write.
However, they note, data on clozapine and COVID-19 have been mixed.
Two prior studies of health record data showed an increased risk of COVID-19 associated with clozapine treatment, while a study that was limited to inpatients found a lower risk of infection and a lower risk of symptomatic disease in association with clozapine use.
The researchers also found a lower mortality risk in patients taking antidepressants; there were no COVID-related deaths among patients taking escitalopram, venlafaxine, bupropion, or fluvoxamine.
Although the association was not statistically significant, this observation is in line with larger studies that showed reduced risk of adverse outcomes associated with antidepressant use, the researchers note.
A matter of debate
In an accompanying commentary, Benedetta Vai, PhD, and Mario Gennaro Mazza, MD, with IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, point out that the link between psychopharmacologic compounds, in particular antipsychotics, and severe COVID-19 outcomes remains “a matter of debate, with inconsistent findings between studies.”
They note further research is needed to determine whether the protective role of second-generation antipsychotics on risk of COVID-19 is mediated by an immune effect or by the direct antiviral properties of these molecules.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Nemani, Dr. Vai, and Dr. Mazza have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Cold forceps on par with cold snare polypectomy for tiny polyps
For nonpedunculated polyps measuring 3 mm or less, cold forceps polypectomy is noninferior to cold snare polypectomy and takes significantly less time, according to the results of the TINYPOLYP trial.
“In our trial, which is the largest to date evaluating complete resection of polyps ≤ 3 mm using cold forceps versus cold snare, we demonstrate that it is acceptable to remove ≤ 3 mm polyps with either cold snare or cold forceps,” lead author Mike Wei, MD, a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Stanford University, California, told this news organization.
“Cold forceps can oftentimes be the more efficient way to remove polyps compared to cold snare, and, as such, it was important to provide validation for this practice,” Dr. Wei said.
The study was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Evaluating two techniques
Both the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommend that diminutive (< 5 mm) and small (6-9 mm) polyps be removed by cold snare polypectomy (CSP).
But whether CSP has a significant advantage over cold forceps polypectomy (CFP) for polyps ≤ 3 mm was unclear.
The TINYPOLYP trial enrolled 179 adults aged 18 years and older who underwent colonoscopy for any indication; colonoscopy was performed by four board-certified endoscopists who each had at least 4 years of experience after completing their fellowship.
A total of 279 nonpedunculated polyps ≤ 3 mm were identified; 138 were removed by CSP, and 141 were removed by CFP. Patient and procedure characteristics were similar in the two groups.
The polyps were similar in size in the CSP and CFP groups (2.5 and 2.6 mm, respectively), as was the distribution of polyps (33.3% and 26.2% in the ascending colon; 26.8% and 24.8% in the transverse colon). A higher proportion of tubular adenomas were removed by CSP than by CFP (79.7% vs. 66.0%).
CSP took significantly longer to perform than CFP (42.3 sec vs. 23.2 sec, P < .001). But with CFP, it was significantly more likely that polyps would need to be removed in more than one piece, compared with CSP (15.6% vs. 3.6%, P < .001).
Hemostatic clip was deployed for one polyp in the CFP group (0.7%); none were used in the CSP group, which was a nonsignificant difference.
There was also no significant difference in positive margins on biopsy (two cases in each group; 1.7%) or in the rate of complete resection (98.3% in both groups), demonstrating noninferiority of CFP, compared with CSP, the study team says.
There were no 30-day complications in either group, including perforation, postpolypectomy bleeding, and postpolypectomy syndrome, and no patient required management of postpolypectomy bleeding. No patient died within 30 days of colonoscopy.
On the basis of their results, Dr. Wei and colleagues say, “When an endoscopist encounters a diminutive polyp ≤ 3 mm, either a cold forceps or cold snare can be utilized during the procedure.”
Guidance for endoscopists
Reached for comment, Emre Gorgun, MD, in the department of colorectal surgery at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said this is an “interesting” study that attempts to pinpoint the “best endoscopic management of tiny polyps.”
“From previously published, well-designed studies, we know that the cold snare technique works very well for polyps up to 10 mm. There have been more recent studies showing that the cold snare technique can be used even in larger polyps, 10-15 mm,” Dr. Gorgun said in an interview.
On the other hand, for polyps < 5 mm, “cold snare technique may take longer and may not provide any added benefits,” he noted. “It may be associated with higher cost due to utilizing more tools, as well as more procedure time and provider services.”
Dr. Gorgun said that the results of the TINYPOLYP study “can help endoscopists in decisionmaking when they come across polyps smaller than 5 mm.”
The study demonstrates that these tiny polyps can “certainly be destroyed/removed by the cold forceps approach,” he added.
The trial had no specific funding. Dr. Wei reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gorgun is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, and Dilumen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For nonpedunculated polyps measuring 3 mm or less, cold forceps polypectomy is noninferior to cold snare polypectomy and takes significantly less time, according to the results of the TINYPOLYP trial.
“In our trial, which is the largest to date evaluating complete resection of polyps ≤ 3 mm using cold forceps versus cold snare, we demonstrate that it is acceptable to remove ≤ 3 mm polyps with either cold snare or cold forceps,” lead author Mike Wei, MD, a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Stanford University, California, told this news organization.
“Cold forceps can oftentimes be the more efficient way to remove polyps compared to cold snare, and, as such, it was important to provide validation for this practice,” Dr. Wei said.
The study was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Evaluating two techniques
Both the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommend that diminutive (< 5 mm) and small (6-9 mm) polyps be removed by cold snare polypectomy (CSP).
But whether CSP has a significant advantage over cold forceps polypectomy (CFP) for polyps ≤ 3 mm was unclear.
The TINYPOLYP trial enrolled 179 adults aged 18 years and older who underwent colonoscopy for any indication; colonoscopy was performed by four board-certified endoscopists who each had at least 4 years of experience after completing their fellowship.
A total of 279 nonpedunculated polyps ≤ 3 mm were identified; 138 were removed by CSP, and 141 were removed by CFP. Patient and procedure characteristics were similar in the two groups.
The polyps were similar in size in the CSP and CFP groups (2.5 and 2.6 mm, respectively), as was the distribution of polyps (33.3% and 26.2% in the ascending colon; 26.8% and 24.8% in the transverse colon). A higher proportion of tubular adenomas were removed by CSP than by CFP (79.7% vs. 66.0%).
CSP took significantly longer to perform than CFP (42.3 sec vs. 23.2 sec, P < .001). But with CFP, it was significantly more likely that polyps would need to be removed in more than one piece, compared with CSP (15.6% vs. 3.6%, P < .001).
Hemostatic clip was deployed for one polyp in the CFP group (0.7%); none were used in the CSP group, which was a nonsignificant difference.
There was also no significant difference in positive margins on biopsy (two cases in each group; 1.7%) or in the rate of complete resection (98.3% in both groups), demonstrating noninferiority of CFP, compared with CSP, the study team says.
There were no 30-day complications in either group, including perforation, postpolypectomy bleeding, and postpolypectomy syndrome, and no patient required management of postpolypectomy bleeding. No patient died within 30 days of colonoscopy.
On the basis of their results, Dr. Wei and colleagues say, “When an endoscopist encounters a diminutive polyp ≤ 3 mm, either a cold forceps or cold snare can be utilized during the procedure.”
Guidance for endoscopists
Reached for comment, Emre Gorgun, MD, in the department of colorectal surgery at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said this is an “interesting” study that attempts to pinpoint the “best endoscopic management of tiny polyps.”
“From previously published, well-designed studies, we know that the cold snare technique works very well for polyps up to 10 mm. There have been more recent studies showing that the cold snare technique can be used even in larger polyps, 10-15 mm,” Dr. Gorgun said in an interview.
On the other hand, for polyps < 5 mm, “cold snare technique may take longer and may not provide any added benefits,” he noted. “It may be associated with higher cost due to utilizing more tools, as well as more procedure time and provider services.”
Dr. Gorgun said that the results of the TINYPOLYP study “can help endoscopists in decisionmaking when they come across polyps smaller than 5 mm.”
The study demonstrates that these tiny polyps can “certainly be destroyed/removed by the cold forceps approach,” he added.
The trial had no specific funding. Dr. Wei reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gorgun is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, and Dilumen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For nonpedunculated polyps measuring 3 mm or less, cold forceps polypectomy is noninferior to cold snare polypectomy and takes significantly less time, according to the results of the TINYPOLYP trial.
“In our trial, which is the largest to date evaluating complete resection of polyps ≤ 3 mm using cold forceps versus cold snare, we demonstrate that it is acceptable to remove ≤ 3 mm polyps with either cold snare or cold forceps,” lead author Mike Wei, MD, a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Stanford University, California, told this news organization.
“Cold forceps can oftentimes be the more efficient way to remove polyps compared to cold snare, and, as such, it was important to provide validation for this practice,” Dr. Wei said.
The study was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Evaluating two techniques
Both the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommend that diminutive (< 5 mm) and small (6-9 mm) polyps be removed by cold snare polypectomy (CSP).
But whether CSP has a significant advantage over cold forceps polypectomy (CFP) for polyps ≤ 3 mm was unclear.
The TINYPOLYP trial enrolled 179 adults aged 18 years and older who underwent colonoscopy for any indication; colonoscopy was performed by four board-certified endoscopists who each had at least 4 years of experience after completing their fellowship.
A total of 279 nonpedunculated polyps ≤ 3 mm were identified; 138 were removed by CSP, and 141 were removed by CFP. Patient and procedure characteristics were similar in the two groups.
The polyps were similar in size in the CSP and CFP groups (2.5 and 2.6 mm, respectively), as was the distribution of polyps (33.3% and 26.2% in the ascending colon; 26.8% and 24.8% in the transverse colon). A higher proportion of tubular adenomas were removed by CSP than by CFP (79.7% vs. 66.0%).
CSP took significantly longer to perform than CFP (42.3 sec vs. 23.2 sec, P < .001). But with CFP, it was significantly more likely that polyps would need to be removed in more than one piece, compared with CSP (15.6% vs. 3.6%, P < .001).
Hemostatic clip was deployed for one polyp in the CFP group (0.7%); none were used in the CSP group, which was a nonsignificant difference.
There was also no significant difference in positive margins on biopsy (two cases in each group; 1.7%) or in the rate of complete resection (98.3% in both groups), demonstrating noninferiority of CFP, compared with CSP, the study team says.
There were no 30-day complications in either group, including perforation, postpolypectomy bleeding, and postpolypectomy syndrome, and no patient required management of postpolypectomy bleeding. No patient died within 30 days of colonoscopy.
On the basis of their results, Dr. Wei and colleagues say, “When an endoscopist encounters a diminutive polyp ≤ 3 mm, either a cold forceps or cold snare can be utilized during the procedure.”
Guidance for endoscopists
Reached for comment, Emre Gorgun, MD, in the department of colorectal surgery at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said this is an “interesting” study that attempts to pinpoint the “best endoscopic management of tiny polyps.”
“From previously published, well-designed studies, we know that the cold snare technique works very well for polyps up to 10 mm. There have been more recent studies showing that the cold snare technique can be used even in larger polyps, 10-15 mm,” Dr. Gorgun said in an interview.
On the other hand, for polyps < 5 mm, “cold snare technique may take longer and may not provide any added benefits,” he noted. “It may be associated with higher cost due to utilizing more tools, as well as more procedure time and provider services.”
Dr. Gorgun said that the results of the TINYPOLYP study “can help endoscopists in decisionmaking when they come across polyps smaller than 5 mm.”
The study demonstrates that these tiny polyps can “certainly be destroyed/removed by the cold forceps approach,” he added.
The trial had no specific funding. Dr. Wei reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gorgun is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, and Dilumen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
How social determinants of health impact disparities in IBD care, outcomes
The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is on the rise among racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States, and social determinants of health (SDOH) contribute to disparities in IBD care and outcome, say the authors of a new paper on the topic.
It’s an “overdue priority to acknowledge the weight and influence of the SDOH on health disparities in IBD care,” write Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, PhD, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and co-authors.
“Only after this acknowledgement can we begin to develop alternative systems that work to rectify the deleterious effects of our current policies in a more longitudinal and effective manner,” they say.
Their paper was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Upstream factors propagate downstream outcomes
The authors found multiple examples in the literature of how upstream SDOH (for example, racism, poverty, neighborhood violence, and under-insurance) lead to midstream SDOH (for example, lack of social support, lack of access to specialized IBD care, poor housing conditions, and food insecurity) that result in poor downstream outcomes in IBD (for example, delayed diagnosis, increased disease activity, IBD flares, and suboptimal medical management).
The IBD literature shows that Black/African American adults with IBD often have worse outcomes across the IBD care continuum than White peers, with higher hospitalization rates, longer stays, increased hospitalization costs, higher readmission rates, and more complications after IBD surgery.
Unequal access to specialized IBD care is a factor, with Black/African American patients less likely to undergo annual visits to a gastroenterologist or IBD specialist, twice as likely than White patients to visit the emergency department over a 12-month period, and less likely to receive treatment with infliximab.
As has been shown for other chronic digestive diseases and cancers, disparities in outcomes related to IBD exist across race, ethnicity, differential insurance status and coverage, and socioeconomic status, the authors note.
Yet, they point out that, interestingly, a 2021 study of patients with Medicaid insurance from four states revealed no disparities in the use of IBD-specific medications between Black/African American and White patients, suggesting that when access to care is equal, disparities diminish.
Target multiple stakeholders to achieve IBD health equity
Achieving health equity in IBD will require strategies targeting medical trainees, providers, practices, and health systems, as well as community and industry leaders and policymakers, Dr. Anyane-Yeboa and colleagues say.
At the medical trainee level, racism and bias should be addressed early in medical student, resident, and fellow training and education. Curricula should move away from race-based training, where race is considered an independent risk factor for disease and often used to guide differential diagnoses and treatment, they suggest.
At the provider level, they say self-reflection around one’s own beliefs, biases, perceptions, and interactions with diverse and vulnerable patient groups is “paramount.” Individual self-reflection should be coupled with mandatory and effective implicit bias and anti-racism training.
At the practice or hospital system level, screening for SDOH at the point of care, addressing barriers to needed treatment, and connecting patients to appropriate resources are all important, they write.
The researchers also call for policy-level changes to increase funding for health equity research, which is historically undervalued and underfunded.
“Focusing on SDOH as the root cause of health inequity in IBD is essential to improve outcomes for marginalized patients,” they write.
Given that research describing specific interventions to address SDOH in IBD is currently nonexistent, “our paper serves as a call to action for more work to be done in this area,” they say.
“As medical providers and health care organizations, we all have a responsibility to address the SDOH when caring for our patients in order to provide each patient with IBD the opportunity to achieve the best health possible,” they conclude.
This research had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is on the rise among racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States, and social determinants of health (SDOH) contribute to disparities in IBD care and outcome, say the authors of a new paper on the topic.
It’s an “overdue priority to acknowledge the weight and influence of the SDOH on health disparities in IBD care,” write Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, PhD, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and co-authors.
“Only after this acknowledgement can we begin to develop alternative systems that work to rectify the deleterious effects of our current policies in a more longitudinal and effective manner,” they say.
Their paper was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Upstream factors propagate downstream outcomes
The authors found multiple examples in the literature of how upstream SDOH (for example, racism, poverty, neighborhood violence, and under-insurance) lead to midstream SDOH (for example, lack of social support, lack of access to specialized IBD care, poor housing conditions, and food insecurity) that result in poor downstream outcomes in IBD (for example, delayed diagnosis, increased disease activity, IBD flares, and suboptimal medical management).
The IBD literature shows that Black/African American adults with IBD often have worse outcomes across the IBD care continuum than White peers, with higher hospitalization rates, longer stays, increased hospitalization costs, higher readmission rates, and more complications after IBD surgery.
Unequal access to specialized IBD care is a factor, with Black/African American patients less likely to undergo annual visits to a gastroenterologist or IBD specialist, twice as likely than White patients to visit the emergency department over a 12-month period, and less likely to receive treatment with infliximab.
As has been shown for other chronic digestive diseases and cancers, disparities in outcomes related to IBD exist across race, ethnicity, differential insurance status and coverage, and socioeconomic status, the authors note.
Yet, they point out that, interestingly, a 2021 study of patients with Medicaid insurance from four states revealed no disparities in the use of IBD-specific medications between Black/African American and White patients, suggesting that when access to care is equal, disparities diminish.
Target multiple stakeholders to achieve IBD health equity
Achieving health equity in IBD will require strategies targeting medical trainees, providers, practices, and health systems, as well as community and industry leaders and policymakers, Dr. Anyane-Yeboa and colleagues say.
At the medical trainee level, racism and bias should be addressed early in medical student, resident, and fellow training and education. Curricula should move away from race-based training, where race is considered an independent risk factor for disease and often used to guide differential diagnoses and treatment, they suggest.
At the provider level, they say self-reflection around one’s own beliefs, biases, perceptions, and interactions with diverse and vulnerable patient groups is “paramount.” Individual self-reflection should be coupled with mandatory and effective implicit bias and anti-racism training.
At the practice or hospital system level, screening for SDOH at the point of care, addressing barriers to needed treatment, and connecting patients to appropriate resources are all important, they write.
The researchers also call for policy-level changes to increase funding for health equity research, which is historically undervalued and underfunded.
“Focusing on SDOH as the root cause of health inequity in IBD is essential to improve outcomes for marginalized patients,” they write.
Given that research describing specific interventions to address SDOH in IBD is currently nonexistent, “our paper serves as a call to action for more work to be done in this area,” they say.
“As medical providers and health care organizations, we all have a responsibility to address the SDOH when caring for our patients in order to provide each patient with IBD the opportunity to achieve the best health possible,” they conclude.
This research had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is on the rise among racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States, and social determinants of health (SDOH) contribute to disparities in IBD care and outcome, say the authors of a new paper on the topic.
It’s an “overdue priority to acknowledge the weight and influence of the SDOH on health disparities in IBD care,” write Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, PhD, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and co-authors.
“Only after this acknowledgement can we begin to develop alternative systems that work to rectify the deleterious effects of our current policies in a more longitudinal and effective manner,” they say.
Their paper was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Upstream factors propagate downstream outcomes
The authors found multiple examples in the literature of how upstream SDOH (for example, racism, poverty, neighborhood violence, and under-insurance) lead to midstream SDOH (for example, lack of social support, lack of access to specialized IBD care, poor housing conditions, and food insecurity) that result in poor downstream outcomes in IBD (for example, delayed diagnosis, increased disease activity, IBD flares, and suboptimal medical management).
The IBD literature shows that Black/African American adults with IBD often have worse outcomes across the IBD care continuum than White peers, with higher hospitalization rates, longer stays, increased hospitalization costs, higher readmission rates, and more complications after IBD surgery.
Unequal access to specialized IBD care is a factor, with Black/African American patients less likely to undergo annual visits to a gastroenterologist or IBD specialist, twice as likely than White patients to visit the emergency department over a 12-month period, and less likely to receive treatment with infliximab.
As has been shown for other chronic digestive diseases and cancers, disparities in outcomes related to IBD exist across race, ethnicity, differential insurance status and coverage, and socioeconomic status, the authors note.
Yet, they point out that, interestingly, a 2021 study of patients with Medicaid insurance from four states revealed no disparities in the use of IBD-specific medications between Black/African American and White patients, suggesting that when access to care is equal, disparities diminish.
Target multiple stakeholders to achieve IBD health equity
Achieving health equity in IBD will require strategies targeting medical trainees, providers, practices, and health systems, as well as community and industry leaders and policymakers, Dr. Anyane-Yeboa and colleagues say.
At the medical trainee level, racism and bias should be addressed early in medical student, resident, and fellow training and education. Curricula should move away from race-based training, where race is considered an independent risk factor for disease and often used to guide differential diagnoses and treatment, they suggest.
At the provider level, they say self-reflection around one’s own beliefs, biases, perceptions, and interactions with diverse and vulnerable patient groups is “paramount.” Individual self-reflection should be coupled with mandatory and effective implicit bias and anti-racism training.
At the practice or hospital system level, screening for SDOH at the point of care, addressing barriers to needed treatment, and connecting patients to appropriate resources are all important, they write.
The researchers also call for policy-level changes to increase funding for health equity research, which is historically undervalued and underfunded.
“Focusing on SDOH as the root cause of health inequity in IBD is essential to improve outcomes for marginalized patients,” they write.
Given that research describing specific interventions to address SDOH in IBD is currently nonexistent, “our paper serves as a call to action for more work to be done in this area,” they say.
“As medical providers and health care organizations, we all have a responsibility to address the SDOH when caring for our patients in order to provide each patient with IBD the opportunity to achieve the best health possible,” they conclude.
This research had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY




