User login
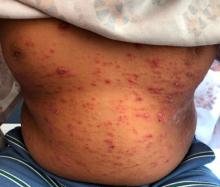
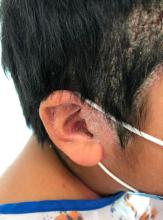
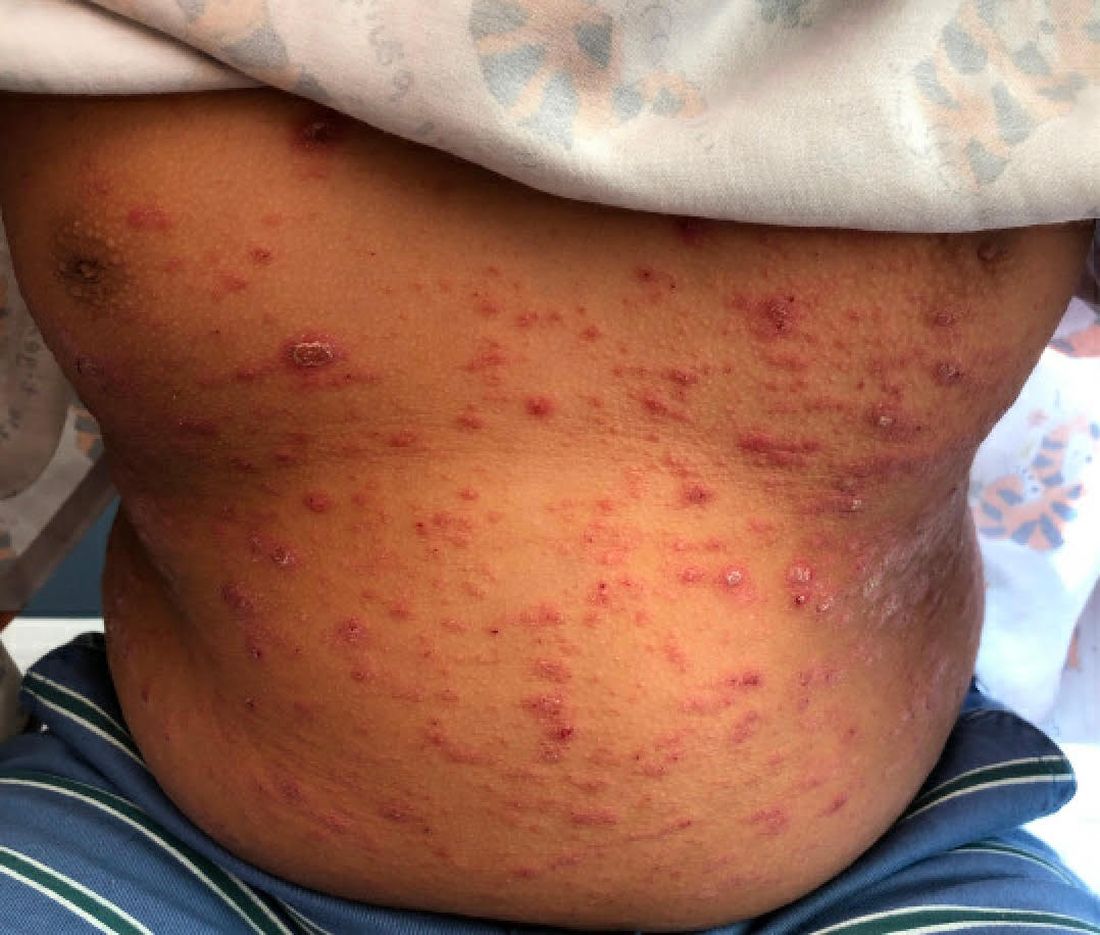
A 9-year-old male presents with multiple thick scaly plaques on scalp, ears, and trunk
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated disease that is characterized by well-demarcated thick scaly plaques on face, scalp, and intertriginous skin. Psoriasis is more common in adults than children, but the incidence of psoriasis in children has increased over time.1 Clinical presentation of psoriasis includes erythematous hyperkeratotic plaques, usually sharply demarcated. Pediatric patients may have multiple small papules and plaques less than 1 cm in size – “drop-size” – known as guttate lesions. Scalp and facial involvement are common in children. Chronic, inflamed plaques with coarse scale can involve ears, elbows, knees, and umbilicus, and nail changes can include pits, ridges, hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis or “oil spots.” While the diagnosis is clinical, biopsy can sometimes be useful to distinguish psoriasis from other papulosquamous conditions. Psoriasis in children is associated with obesity, higher rates of cardiovascular disease over a lifetime, as well as arthritis and mental health disorders.2
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for psoriasis can include papulosquamous diseases such as nummular eczema, pityriasis rosea, and pityriasis rubra pilaris. Tinea corporis may also be considered.
Nummular eczema, also known as “discoid eczema” is characterized by multiple pruritic, coin-shaped, eczematous lesions that may be actively oozing. The term “nummular” is derived from the Latin for “coin,” as lesions are distinct and annular. It is commonly associated with atopic dermatitis, and may be seen with contact dermatitis as well. Oozing, lichenification, hyperpigmentation and limited extent of skin coverage can help distinguish nummular dermatitis from psoriasis.
Pityriasis rosea is a common self-limited disease that is characterized by the appearance of acute, oval, papulosquamous patches on the trunk and proximal areas of the extremities. It usually begins with a characteristic “herald” patch, a single round or oval, sharply demarcated, pink lesion on the chest, neck, or back. Pityriasis rosea and guttate psoriasis may show similar clinical findings but the latter lacks a herald patch and is often preceded by streptococcal throat infection.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rarer inflammatory disease characterized by follicular, hyperkeratotic papules, thick orange waxy palms (palmoplantar keratoderma), and erythroderma. It can also cause hair loss, nail changes, and itching. The rash shows areas with no involvement, “islands of sparing,” which is a signature characteristic of pityriasis rubra pilaris. Skin biopsies are an important diagnostic tool for pityriasis rubra pilaris. In the case of circumscribed pityriasis rubra pilaris, it may look similar to psoriasis, but it can be differentiated in that it is often accompanied by characteristic follicular papules and involvement of the palms, which are more waxy and orange in color.
When evaluating annular scaly patches, it is always important to consider tinea corporis. Tinea corporis will commonly have an annular border of scale with relative clearing in the center of lesions. In addition, when topical corticosteroids are used for prolonged periods, skin fungal infections can develop into “tinea incognito,” with paradoxical worsening since the immune response is suppressed and the fungal infection worsens.
Our patient had been previously treated with topical corticosteroids (medium to high strength) and topical calcineurin inhibitors without significant improvement. Other topical therapies for psoriasis include vitamin analogues, tazarotene, and newer therapies such as topical roflumilast (a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis in children over 12 years of age).3,4 In addition, as the indications for biological agents have been expanded, there are various options for treating psoriasis in children and adolescents when more active treatment is needed. Systemic therapies for more severe disease include traditional systemic immunosuppressives (for example, methotrexate, cyclosporine) and biologic agents. The four biologic agents currently approved for children are etanercept, ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Our patient was treated with ustekinumab, which is an injectable biologic agent that blocks interleukin-12/23, with good response to date.
Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Dr. Choi is a visiting research physician in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice-chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Tollefson MM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62(6):979-87.
2. Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(1):161-201.
3. Mark G et al. JAMA. 2022;328(11):1073-84.
4. Eichenfield LF et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35(2):170-81.
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated disease that is characterized by well-demarcated thick scaly plaques on face, scalp, and intertriginous skin. Psoriasis is more common in adults than children, but the incidence of psoriasis in children has increased over time.1 Clinical presentation of psoriasis includes erythematous hyperkeratotic plaques, usually sharply demarcated. Pediatric patients may have multiple small papules and plaques less than 1 cm in size – “drop-size” – known as guttate lesions. Scalp and facial involvement are common in children. Chronic, inflamed plaques with coarse scale can involve ears, elbows, knees, and umbilicus, and nail changes can include pits, ridges, hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis or “oil spots.” While the diagnosis is clinical, biopsy can sometimes be useful to distinguish psoriasis from other papulosquamous conditions. Psoriasis in children is associated with obesity, higher rates of cardiovascular disease over a lifetime, as well as arthritis and mental health disorders.2
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for psoriasis can include papulosquamous diseases such as nummular eczema, pityriasis rosea, and pityriasis rubra pilaris. Tinea corporis may also be considered.
Nummular eczema, also known as “discoid eczema” is characterized by multiple pruritic, coin-shaped, eczematous lesions that may be actively oozing. The term “nummular” is derived from the Latin for “coin,” as lesions are distinct and annular. It is commonly associated with atopic dermatitis, and may be seen with contact dermatitis as well. Oozing, lichenification, hyperpigmentation and limited extent of skin coverage can help distinguish nummular dermatitis from psoriasis.
Pityriasis rosea is a common self-limited disease that is characterized by the appearance of acute, oval, papulosquamous patches on the trunk and proximal areas of the extremities. It usually begins with a characteristic “herald” patch, a single round or oval, sharply demarcated, pink lesion on the chest, neck, or back. Pityriasis rosea and guttate psoriasis may show similar clinical findings but the latter lacks a herald patch and is often preceded by streptococcal throat infection.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rarer inflammatory disease characterized by follicular, hyperkeratotic papules, thick orange waxy palms (palmoplantar keratoderma), and erythroderma. It can also cause hair loss, nail changes, and itching. The rash shows areas with no involvement, “islands of sparing,” which is a signature characteristic of pityriasis rubra pilaris. Skin biopsies are an important diagnostic tool for pityriasis rubra pilaris. In the case of circumscribed pityriasis rubra pilaris, it may look similar to psoriasis, but it can be differentiated in that it is often accompanied by characteristic follicular papules and involvement of the palms, which are more waxy and orange in color.
When evaluating annular scaly patches, it is always important to consider tinea corporis. Tinea corporis will commonly have an annular border of scale with relative clearing in the center of lesions. In addition, when topical corticosteroids are used for prolonged periods, skin fungal infections can develop into “tinea incognito,” with paradoxical worsening since the immune response is suppressed and the fungal infection worsens.
Our patient had been previously treated with topical corticosteroids (medium to high strength) and topical calcineurin inhibitors without significant improvement. Other topical therapies for psoriasis include vitamin analogues, tazarotene, and newer therapies such as topical roflumilast (a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis in children over 12 years of age).3,4 In addition, as the indications for biological agents have been expanded, there are various options for treating psoriasis in children and adolescents when more active treatment is needed. Systemic therapies for more severe disease include traditional systemic immunosuppressives (for example, methotrexate, cyclosporine) and biologic agents. The four biologic agents currently approved for children are etanercept, ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Our patient was treated with ustekinumab, which is an injectable biologic agent that blocks interleukin-12/23, with good response to date.
Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Dr. Choi is a visiting research physician in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice-chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Tollefson MM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62(6):979-87.
2. Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(1):161-201.
3. Mark G et al. JAMA. 2022;328(11):1073-84.
4. Eichenfield LF et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35(2):170-81.
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated disease that is characterized by well-demarcated thick scaly plaques on face, scalp, and intertriginous skin. Psoriasis is more common in adults than children, but the incidence of psoriasis in children has increased over time.1 Clinical presentation of psoriasis includes erythematous hyperkeratotic plaques, usually sharply demarcated. Pediatric patients may have multiple small papules and plaques less than 1 cm in size – “drop-size” – known as guttate lesions. Scalp and facial involvement are common in children. Chronic, inflamed plaques with coarse scale can involve ears, elbows, knees, and umbilicus, and nail changes can include pits, ridges, hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis or “oil spots.” While the diagnosis is clinical, biopsy can sometimes be useful to distinguish psoriasis from other papulosquamous conditions. Psoriasis in children is associated with obesity, higher rates of cardiovascular disease over a lifetime, as well as arthritis and mental health disorders.2
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for psoriasis can include papulosquamous diseases such as nummular eczema, pityriasis rosea, and pityriasis rubra pilaris. Tinea corporis may also be considered.
Nummular eczema, also known as “discoid eczema” is characterized by multiple pruritic, coin-shaped, eczematous lesions that may be actively oozing. The term “nummular” is derived from the Latin for “coin,” as lesions are distinct and annular. It is commonly associated with atopic dermatitis, and may be seen with contact dermatitis as well. Oozing, lichenification, hyperpigmentation and limited extent of skin coverage can help distinguish nummular dermatitis from psoriasis.
Pityriasis rosea is a common self-limited disease that is characterized by the appearance of acute, oval, papulosquamous patches on the trunk and proximal areas of the extremities. It usually begins with a characteristic “herald” patch, a single round or oval, sharply demarcated, pink lesion on the chest, neck, or back. Pityriasis rosea and guttate psoriasis may show similar clinical findings but the latter lacks a herald patch and is often preceded by streptococcal throat infection.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rarer inflammatory disease characterized by follicular, hyperkeratotic papules, thick orange waxy palms (palmoplantar keratoderma), and erythroderma. It can also cause hair loss, nail changes, and itching. The rash shows areas with no involvement, “islands of sparing,” which is a signature characteristic of pityriasis rubra pilaris. Skin biopsies are an important diagnostic tool for pityriasis rubra pilaris. In the case of circumscribed pityriasis rubra pilaris, it may look similar to psoriasis, but it can be differentiated in that it is often accompanied by characteristic follicular papules and involvement of the palms, which are more waxy and orange in color.
When evaluating annular scaly patches, it is always important to consider tinea corporis. Tinea corporis will commonly have an annular border of scale with relative clearing in the center of lesions. In addition, when topical corticosteroids are used for prolonged periods, skin fungal infections can develop into “tinea incognito,” with paradoxical worsening since the immune response is suppressed and the fungal infection worsens.
Our patient had been previously treated with topical corticosteroids (medium to high strength) and topical calcineurin inhibitors without significant improvement. Other topical therapies for psoriasis include vitamin analogues, tazarotene, and newer therapies such as topical roflumilast (a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis in children over 12 years of age).3,4 In addition, as the indications for biological agents have been expanded, there are various options for treating psoriasis in children and adolescents when more active treatment is needed. Systemic therapies for more severe disease include traditional systemic immunosuppressives (for example, methotrexate, cyclosporine) and biologic agents. The four biologic agents currently approved for children are etanercept, ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Our patient was treated with ustekinumab, which is an injectable biologic agent that blocks interleukin-12/23, with good response to date.
Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Dr. Choi is a visiting research physician in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice-chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Tollefson MM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62(6):979-87.
2. Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(1):161-201.
3. Mark G et al. JAMA. 2022;328(11):1073-84.
4. Eichenfield LF et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35(2):170-81.
A 9-year-old male is seen in the clinic with a 1-year history of multiple thick scaly plaques on scalp, ears, and trunk. He has been treated with hydrocortisone 1% ointment with no change in the lesions. He had upper respiratory tract symptoms 3 weeks prior to the visit.
Examination reveals erythematous, well-demarcated plaques of the anterior scalp with thick overlying micaceous scale with some extension onto the forehead and temples. Additionally, erythematous scaly patches on the ear, axilla, and umbilicus were noted. There was no palmar or plantar involvement. He denied joint swelling, stiffness, or pain in the morning.
Past, Present, and Future of Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis Management
Atopic dermatitis (AD), or eczema, is a common inflammatory skin disease notorious for its chronic, relapsing, and often frustrating disease course. Although as many as 25% of children in the United States are affected by this condition and its impact on the quality of life of affected patients and families is profound,1-3 therapeutic advances in the pediatric population have been fairly limited until recently.
Over the last 10 years, there has been robust investigation into pediatric AD therapeutics, with many topical and systemic medications either recently approved or under clinical investigation. These developments are changing the landscape of the management of pediatric AD and raise a set of fascinating questions about how early and aggressive intervention might change the course of this disease. We discuss current limitations in the field that may be addressed with additional research.
New Topical Medications
In the last several years, there has been a rapid increase in efforts to develop new topical agents to manage AD. Until the beginning of the 21st century, the dermatologist’s arsenal was limited to topical corticosteroids (TCs). In the early 2000s, attention shifted to topical calcineurin inhibitors as nonsteroidal alternatives when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved topical tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for AD. In 2016, crisaborole (a phosphodiesterase-4 [PDE4] inhibitor) was approved by the FDA for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 2 years and older, marking a new age of development for topical AD therapies. In 2021, the FDA approved ruxolitinib (a topical Janus kinase [JAK] 1/2 inhibitor) for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 12 years and older.
Roflumilast (ARQ-151) and difamilast (OPA-15406)(members of the PDE4 inhibitor class) are undergoing investigation for pediatric AD. A phase 3 clinical trial for roflumilast for AD is underway (ClinicalTrial.gov Identifier: NCT04845620); it is already approved for psoriasis in patients 12 years and older. A phase 3 trial of difamilast (NCT03911401) was recently completed, with results supporting the drug’s safety and efficacy in AD management.4 Efforts to synthesize new better-targeted PDE4 inhibitors are ongoing.5
Tapinarof (a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor-modulating agent) is approved for psoriasis in adults, and a phase 3 trial for management of pediatric AD is underway (NCT05032859) after phase 2 trials revealed promising results.6
Lastly, the microbiome is a target for AD topical therapies. A recently completed phase 1 trial of bacteriotherapy with Staphylococcus hominis A9 transplant lotion showed promising results (NCT03151148).7 Although this bacteriotherapy technique is early in development and has been studied only in adult patients, results are exciting because they represent a gateway to a largely unexplored realm of potential future therapies.
Standard of Care—How will these new topical therapies impact our standard of care for pediatric AD patients? Topical corticosteroids are still a pillar of topical AD therapy, but the potential for nonsteroidal topical agents as alternatives and used in combination therapeutic regimens has expanded exponentially. It is uncertain how we might individualize regimens tailored to patient-specific factors because the standard approach has been to test drugs as monotherapy, with vehicle comparisons or with reference medications in Europe.
Newer topical nonsteroidal agents may offer several opportunities. First, they may help avoid local and systemic adverse effects that often limit the use of current standard therapy.8 This capability may prove essential in bridging TC treatments and serving as long-term maintenance therapies to decrease the frequency of eczema flares. Second, they can alleviate the need for different medication strengths for different body regions, thereby allowing for simplification of regimens and potentially increased adherence and decreased disease burden—a boon to affected patients and caregivers.
Although the efficacy and long-term safety profile of these new drugs require further study, it does not seem unreasonable to look forward to achieving levels of optimization and individualization with topical regimens for AD in the near future that makes flares in patients with mild to moderate AD a phenomenon of the past.
Advances in Systemic Therapy
Systemic therapeutics in pediatric AD also recently entered an exciting era of development. Traditional systemic agents, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil, have existed for decades but have not been widely utilized for moderate to severe AD in the United States, especially in the pediatric population, likely because these drugs lacked FDA approval and they can cause a range of adverse effects, including notable immunosuppression.9
Introduction and approval of dupilumab in 2017 by the FDA was revolutionary in this field. As a monoclonal antibody targeted against IL-4 and IL-13, dupilumab has consistently demonstrated strong long-term efficacy for pediatric AD and has an acceptable safety profile in children and adolescents.10-14 Expansion of the label to include children as young as 6 months with moderate to severe AD seems an important milestone in pediatric AD care.
Since the approval of dupilumab for adolescents and children aged 6 to 12 years, global experience has supported expanded use of systemic agents for patients who have an inadequate response to TCs and previously approved nonsteroidal topical agents. How expansive the use of systemics will be in younger children depends on how their long-term use impacts the disease course, whether therapy is disease modifying, and whether early use can curb the development of comorbidities.
Investigations into targeted systemic therapeutics for eczematous dermatitis are not limited to dupilumab. In a study of adolescents as young as 12 years, tralokinumab (an IL-13 pathway inhibitor) demonstrated an Eczema Area Severity Index-75 of 27.8% to 28.6% and a mean decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index of 27.5 to 29.1, with minimal adverse effects.15 Lebrikizumab, another biologic IL-13 inhibitor with strong published safety and efficacy data in adults, has completed short- and longer-term studies in adolescents (NCT04178967 and NCT04146363).16 The drug received FDA Fast Track designation for moderate to severe AD in patients 12 years and older after showing positive data.17
This push to targeted therapy stretches beyond monoclonal antibodies. In the last few years, oral JAK inhibitors have emerged as a new class of systemic therapy for eczematous dermatitis. Upadacitinib, a JAK1 selective inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in 2022 for patients 12 years and older with AD and has data that supports its efficacy in adolescents and adults.18 Other JAK inhibitors including the selective JAK1 inhibitor abrocitinib and the combined JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib are being studied for pediatric AD (NCT04564755, NCT03422822, and NCT03952559), with most evidence to date supporting their safety and efficacy, at least over the short-term.19
The study of these and other advanced systemic therapies for eczematous dermatitis is transforming the toolbox for pediatric AD care. Although long-term data are lacking for some of these medications, it is possible that newer agents may decrease reliance on older immunosuppressants, such as systemic corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate. Unanswered questions include: How and which systemic medications may alter the course of the disease? What is the disease modification for AD? What is the impact on comorbidities over time?
What’s Missing?
The field of pediatric AD has experienced exciting new developments with the emergence of targeted therapeutics, but those new agents require more long-term study, though we already have longer-term data on crisaborole and dupilumab.10-14,20 Studies of the long-term use of these new treatments on comorbidities of pediatric AD—mental health outcomes, cardiovascular disease, effects on the family, and other allergic conditions—are needed.21 Furthermore, clinical guidelines that address indications, timing of use, tapering, and discontinuation of new treatments depend on long-term experience and data collection.
Therefore, it is prudent that investigators, companies, payers, patients, and families support phase 4, long-term extension, and registry studies, which will expand our knowledge of AD medications and their impact on the disease over time.
Final Thoughts
Medications to treat AD are reaching a new level of advancement—from topical agents that target novel pathways to revolutionary biologics and systemic medications. Although there are knowledge gaps on these new therapeutics, the standard of care is already rapidly changing as the expectations of clinicians, patients, and families advance with each addition to the provider’s toolbox.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Kiebert G, Sorensen SV, Revicki D, et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a decrement in health-related quality of life. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:151-158. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01436.x
- Al Shobaili HA. The impact of childhood atopic dermatitis on the patients’ family. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:618-623. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01215.x
- Saeki H, Baba N, Ito K, et al. Difamilast, a selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, ointment in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase III randomized double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial [published online November 1, 2021]. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:40-49. doi:10.1111/bjd.20655
- Chu Z, Xu Q, Zhu Q, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzoxaborole derivatives as potent PDE4 inhibitors for topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;213:113171. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113171
- Paller AS, Stein Gold L, Soung J, et al. Efficacy and patient-reported outcomes from a phase 2b, randomized clinical trial of tapinarof cream for the treatment of adolescents and adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:632-638. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.135
- Nakatsuji T, Hata TR, Tong Y, et al. Development of a human skin commensal microbe for bacteriotherapy of atopic dermatitis and use in a phase 1 randomized clinical trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:700-709. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01256-2
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.023
- Sidbury R, Davis DM, Cohen DE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 3. management and treatment with phototherapy and systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:327-349. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.030
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC-H, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with uncontrolled moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:44-56. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3336
- Blauvelt A, Guttman-Yassky E, Paller AS, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopicdermatitis: results through week 52 from a phase III open-label extension trial (LIBERTY AD PED-OLE). Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:365-383. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00683-2
- Cork MJ, D, Eichenfield LF, et al. Dupilumab provides favourable long-term safety and efficacy in children aged ≥ 6 to < 12 years with uncontrolled severe atopic dermatitis: results from an open-label phase IIa study and subsequent phase III open-label extension study. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:857-870. doi:10.1111/bjd.19460
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab demonstrates rapid and consistent improvement in extent and signs of atopic dermatitis across all anatomical regions in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1643-1656. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00568-y
- Paller A, Blauvelt A, Soong W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tralokinumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: results of the phase 3 ECZTRA 6 trial. SKIN. 2022;6:S29. doi:10.25251/skin.6.supp.s29
- Guttman-Yassky E, Blauvelt A, Eichenfield LF, et al. Efficacy and safety of lebrikizumab, a high-affinity interleukin 13 inhibitor, in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 2b randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:411-420. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0079
- Lebrikizumab dosed every four weeks maintained durable skin clearance in Lilly’s phase 3 monotherapy atopic dermatitis trials [news release]. Eli Lilly and Company; September 8, 2022. Accessed October 19, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lebrikizumab-dosed-every-four-weeks-maintained-durable-skin
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00588-2
- Chovatiya R, Paller AS. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:927-940. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2021.08.009
- Geng B, Hebert AA, Takiya L, et al. Efficacy and safety trends with continuous, long-term crisaborole use in patients aged ≥ 2 years with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1667-1678. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00584-y
- Appiah MM, Haft MA, Kleinman E, et al. Atopic dermatitis: review of comorbidities and therapeutics. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022;129:142-149. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2022.05.015
Atopic dermatitis (AD), or eczema, is a common inflammatory skin disease notorious for its chronic, relapsing, and often frustrating disease course. Although as many as 25% of children in the United States are affected by this condition and its impact on the quality of life of affected patients and families is profound,1-3 therapeutic advances in the pediatric population have been fairly limited until recently.
Over the last 10 years, there has been robust investigation into pediatric AD therapeutics, with many topical and systemic medications either recently approved or under clinical investigation. These developments are changing the landscape of the management of pediatric AD and raise a set of fascinating questions about how early and aggressive intervention might change the course of this disease. We discuss current limitations in the field that may be addressed with additional research.
New Topical Medications
In the last several years, there has been a rapid increase in efforts to develop new topical agents to manage AD. Until the beginning of the 21st century, the dermatologist’s arsenal was limited to topical corticosteroids (TCs). In the early 2000s, attention shifted to topical calcineurin inhibitors as nonsteroidal alternatives when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved topical tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for AD. In 2016, crisaborole (a phosphodiesterase-4 [PDE4] inhibitor) was approved by the FDA for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 2 years and older, marking a new age of development for topical AD therapies. In 2021, the FDA approved ruxolitinib (a topical Janus kinase [JAK] 1/2 inhibitor) for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 12 years and older.
Roflumilast (ARQ-151) and difamilast (OPA-15406)(members of the PDE4 inhibitor class) are undergoing investigation for pediatric AD. A phase 3 clinical trial for roflumilast for AD is underway (ClinicalTrial.gov Identifier: NCT04845620); it is already approved for psoriasis in patients 12 years and older. A phase 3 trial of difamilast (NCT03911401) was recently completed, with results supporting the drug’s safety and efficacy in AD management.4 Efforts to synthesize new better-targeted PDE4 inhibitors are ongoing.5
Tapinarof (a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor-modulating agent) is approved for psoriasis in adults, and a phase 3 trial for management of pediatric AD is underway (NCT05032859) after phase 2 trials revealed promising results.6
Lastly, the microbiome is a target for AD topical therapies. A recently completed phase 1 trial of bacteriotherapy with Staphylococcus hominis A9 transplant lotion showed promising results (NCT03151148).7 Although this bacteriotherapy technique is early in development and has been studied only in adult patients, results are exciting because they represent a gateway to a largely unexplored realm of potential future therapies.
Standard of Care—How will these new topical therapies impact our standard of care for pediatric AD patients? Topical corticosteroids are still a pillar of topical AD therapy, but the potential for nonsteroidal topical agents as alternatives and used in combination therapeutic regimens has expanded exponentially. It is uncertain how we might individualize regimens tailored to patient-specific factors because the standard approach has been to test drugs as monotherapy, with vehicle comparisons or with reference medications in Europe.
Newer topical nonsteroidal agents may offer several opportunities. First, they may help avoid local and systemic adverse effects that often limit the use of current standard therapy.8 This capability may prove essential in bridging TC treatments and serving as long-term maintenance therapies to decrease the frequency of eczema flares. Second, they can alleviate the need for different medication strengths for different body regions, thereby allowing for simplification of regimens and potentially increased adherence and decreased disease burden—a boon to affected patients and caregivers.
Although the efficacy and long-term safety profile of these new drugs require further study, it does not seem unreasonable to look forward to achieving levels of optimization and individualization with topical regimens for AD in the near future that makes flares in patients with mild to moderate AD a phenomenon of the past.
Advances in Systemic Therapy
Systemic therapeutics in pediatric AD also recently entered an exciting era of development. Traditional systemic agents, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil, have existed for decades but have not been widely utilized for moderate to severe AD in the United States, especially in the pediatric population, likely because these drugs lacked FDA approval and they can cause a range of adverse effects, including notable immunosuppression.9
Introduction and approval of dupilumab in 2017 by the FDA was revolutionary in this field. As a monoclonal antibody targeted against IL-4 and IL-13, dupilumab has consistently demonstrated strong long-term efficacy for pediatric AD and has an acceptable safety profile in children and adolescents.10-14 Expansion of the label to include children as young as 6 months with moderate to severe AD seems an important milestone in pediatric AD care.
Since the approval of dupilumab for adolescents and children aged 6 to 12 years, global experience has supported expanded use of systemic agents for patients who have an inadequate response to TCs and previously approved nonsteroidal topical agents. How expansive the use of systemics will be in younger children depends on how their long-term use impacts the disease course, whether therapy is disease modifying, and whether early use can curb the development of comorbidities.
Investigations into targeted systemic therapeutics for eczematous dermatitis are not limited to dupilumab. In a study of adolescents as young as 12 years, tralokinumab (an IL-13 pathway inhibitor) demonstrated an Eczema Area Severity Index-75 of 27.8% to 28.6% and a mean decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index of 27.5 to 29.1, with minimal adverse effects.15 Lebrikizumab, another biologic IL-13 inhibitor with strong published safety and efficacy data in adults, has completed short- and longer-term studies in adolescents (NCT04178967 and NCT04146363).16 The drug received FDA Fast Track designation for moderate to severe AD in patients 12 years and older after showing positive data.17
This push to targeted therapy stretches beyond monoclonal antibodies. In the last few years, oral JAK inhibitors have emerged as a new class of systemic therapy for eczematous dermatitis. Upadacitinib, a JAK1 selective inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in 2022 for patients 12 years and older with AD and has data that supports its efficacy in adolescents and adults.18 Other JAK inhibitors including the selective JAK1 inhibitor abrocitinib and the combined JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib are being studied for pediatric AD (NCT04564755, NCT03422822, and NCT03952559), with most evidence to date supporting their safety and efficacy, at least over the short-term.19
The study of these and other advanced systemic therapies for eczematous dermatitis is transforming the toolbox for pediatric AD care. Although long-term data are lacking for some of these medications, it is possible that newer agents may decrease reliance on older immunosuppressants, such as systemic corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate. Unanswered questions include: How and which systemic medications may alter the course of the disease? What is the disease modification for AD? What is the impact on comorbidities over time?
What’s Missing?
The field of pediatric AD has experienced exciting new developments with the emergence of targeted therapeutics, but those new agents require more long-term study, though we already have longer-term data on crisaborole and dupilumab.10-14,20 Studies of the long-term use of these new treatments on comorbidities of pediatric AD—mental health outcomes, cardiovascular disease, effects on the family, and other allergic conditions—are needed.21 Furthermore, clinical guidelines that address indications, timing of use, tapering, and discontinuation of new treatments depend on long-term experience and data collection.
Therefore, it is prudent that investigators, companies, payers, patients, and families support phase 4, long-term extension, and registry studies, which will expand our knowledge of AD medications and their impact on the disease over time.
Final Thoughts
Medications to treat AD are reaching a new level of advancement—from topical agents that target novel pathways to revolutionary biologics and systemic medications. Although there are knowledge gaps on these new therapeutics, the standard of care is already rapidly changing as the expectations of clinicians, patients, and families advance with each addition to the provider’s toolbox.
Atopic dermatitis (AD), or eczema, is a common inflammatory skin disease notorious for its chronic, relapsing, and often frustrating disease course. Although as many as 25% of children in the United States are affected by this condition and its impact on the quality of life of affected patients and families is profound,1-3 therapeutic advances in the pediatric population have been fairly limited until recently.
Over the last 10 years, there has been robust investigation into pediatric AD therapeutics, with many topical and systemic medications either recently approved or under clinical investigation. These developments are changing the landscape of the management of pediatric AD and raise a set of fascinating questions about how early and aggressive intervention might change the course of this disease. We discuss current limitations in the field that may be addressed with additional research.
New Topical Medications
In the last several years, there has been a rapid increase in efforts to develop new topical agents to manage AD. Until the beginning of the 21st century, the dermatologist’s arsenal was limited to topical corticosteroids (TCs). In the early 2000s, attention shifted to topical calcineurin inhibitors as nonsteroidal alternatives when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved topical tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for AD. In 2016, crisaborole (a phosphodiesterase-4 [PDE4] inhibitor) was approved by the FDA for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 2 years and older, marking a new age of development for topical AD therapies. In 2021, the FDA approved ruxolitinib (a topical Janus kinase [JAK] 1/2 inhibitor) for use in mild to moderate AD in patients 12 years and older.
Roflumilast (ARQ-151) and difamilast (OPA-15406)(members of the PDE4 inhibitor class) are undergoing investigation for pediatric AD. A phase 3 clinical trial for roflumilast for AD is underway (ClinicalTrial.gov Identifier: NCT04845620); it is already approved for psoriasis in patients 12 years and older. A phase 3 trial of difamilast (NCT03911401) was recently completed, with results supporting the drug’s safety and efficacy in AD management.4 Efforts to synthesize new better-targeted PDE4 inhibitors are ongoing.5
Tapinarof (a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor-modulating agent) is approved for psoriasis in adults, and a phase 3 trial for management of pediatric AD is underway (NCT05032859) after phase 2 trials revealed promising results.6
Lastly, the microbiome is a target for AD topical therapies. A recently completed phase 1 trial of bacteriotherapy with Staphylococcus hominis A9 transplant lotion showed promising results (NCT03151148).7 Although this bacteriotherapy technique is early in development and has been studied only in adult patients, results are exciting because they represent a gateway to a largely unexplored realm of potential future therapies.
Standard of Care—How will these new topical therapies impact our standard of care for pediatric AD patients? Topical corticosteroids are still a pillar of topical AD therapy, but the potential for nonsteroidal topical agents as alternatives and used in combination therapeutic regimens has expanded exponentially. It is uncertain how we might individualize regimens tailored to patient-specific factors because the standard approach has been to test drugs as monotherapy, with vehicle comparisons or with reference medications in Europe.
Newer topical nonsteroidal agents may offer several opportunities. First, they may help avoid local and systemic adverse effects that often limit the use of current standard therapy.8 This capability may prove essential in bridging TC treatments and serving as long-term maintenance therapies to decrease the frequency of eczema flares. Second, they can alleviate the need for different medication strengths for different body regions, thereby allowing for simplification of regimens and potentially increased adherence and decreased disease burden—a boon to affected patients and caregivers.
Although the efficacy and long-term safety profile of these new drugs require further study, it does not seem unreasonable to look forward to achieving levels of optimization and individualization with topical regimens for AD in the near future that makes flares in patients with mild to moderate AD a phenomenon of the past.
Advances in Systemic Therapy
Systemic therapeutics in pediatric AD also recently entered an exciting era of development. Traditional systemic agents, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil, have existed for decades but have not been widely utilized for moderate to severe AD in the United States, especially in the pediatric population, likely because these drugs lacked FDA approval and they can cause a range of adverse effects, including notable immunosuppression.9
Introduction and approval of dupilumab in 2017 by the FDA was revolutionary in this field. As a monoclonal antibody targeted against IL-4 and IL-13, dupilumab has consistently demonstrated strong long-term efficacy for pediatric AD and has an acceptable safety profile in children and adolescents.10-14 Expansion of the label to include children as young as 6 months with moderate to severe AD seems an important milestone in pediatric AD care.
Since the approval of dupilumab for adolescents and children aged 6 to 12 years, global experience has supported expanded use of systemic agents for patients who have an inadequate response to TCs and previously approved nonsteroidal topical agents. How expansive the use of systemics will be in younger children depends on how their long-term use impacts the disease course, whether therapy is disease modifying, and whether early use can curb the development of comorbidities.
Investigations into targeted systemic therapeutics for eczematous dermatitis are not limited to dupilumab. In a study of adolescents as young as 12 years, tralokinumab (an IL-13 pathway inhibitor) demonstrated an Eczema Area Severity Index-75 of 27.8% to 28.6% and a mean decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index of 27.5 to 29.1, with minimal adverse effects.15 Lebrikizumab, another biologic IL-13 inhibitor with strong published safety and efficacy data in adults, has completed short- and longer-term studies in adolescents (NCT04178967 and NCT04146363).16 The drug received FDA Fast Track designation for moderate to severe AD in patients 12 years and older after showing positive data.17
This push to targeted therapy stretches beyond monoclonal antibodies. In the last few years, oral JAK inhibitors have emerged as a new class of systemic therapy for eczematous dermatitis. Upadacitinib, a JAK1 selective inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in 2022 for patients 12 years and older with AD and has data that supports its efficacy in adolescents and adults.18 Other JAK inhibitors including the selective JAK1 inhibitor abrocitinib and the combined JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib are being studied for pediatric AD (NCT04564755, NCT03422822, and NCT03952559), with most evidence to date supporting their safety and efficacy, at least over the short-term.19
The study of these and other advanced systemic therapies for eczematous dermatitis is transforming the toolbox for pediatric AD care. Although long-term data are lacking for some of these medications, it is possible that newer agents may decrease reliance on older immunosuppressants, such as systemic corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate. Unanswered questions include: How and which systemic medications may alter the course of the disease? What is the disease modification for AD? What is the impact on comorbidities over time?
What’s Missing?
The field of pediatric AD has experienced exciting new developments with the emergence of targeted therapeutics, but those new agents require more long-term study, though we already have longer-term data on crisaborole and dupilumab.10-14,20 Studies of the long-term use of these new treatments on comorbidities of pediatric AD—mental health outcomes, cardiovascular disease, effects on the family, and other allergic conditions—are needed.21 Furthermore, clinical guidelines that address indications, timing of use, tapering, and discontinuation of new treatments depend on long-term experience and data collection.
Therefore, it is prudent that investigators, companies, payers, patients, and families support phase 4, long-term extension, and registry studies, which will expand our knowledge of AD medications and their impact on the disease over time.
Final Thoughts
Medications to treat AD are reaching a new level of advancement—from topical agents that target novel pathways to revolutionary biologics and systemic medications. Although there are knowledge gaps on these new therapeutics, the standard of care is already rapidly changing as the expectations of clinicians, patients, and families advance with each addition to the provider’s toolbox.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Kiebert G, Sorensen SV, Revicki D, et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a decrement in health-related quality of life. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:151-158. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01436.x
- Al Shobaili HA. The impact of childhood atopic dermatitis on the patients’ family. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:618-623. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01215.x
- Saeki H, Baba N, Ito K, et al. Difamilast, a selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, ointment in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase III randomized double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial [published online November 1, 2021]. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:40-49. doi:10.1111/bjd.20655
- Chu Z, Xu Q, Zhu Q, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzoxaborole derivatives as potent PDE4 inhibitors for topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;213:113171. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113171
- Paller AS, Stein Gold L, Soung J, et al. Efficacy and patient-reported outcomes from a phase 2b, randomized clinical trial of tapinarof cream for the treatment of adolescents and adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:632-638. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.135
- Nakatsuji T, Hata TR, Tong Y, et al. Development of a human skin commensal microbe for bacteriotherapy of atopic dermatitis and use in a phase 1 randomized clinical trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:700-709. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01256-2
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.023
- Sidbury R, Davis DM, Cohen DE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 3. management and treatment with phototherapy and systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:327-349. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.030
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC-H, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with uncontrolled moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:44-56. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3336
- Blauvelt A, Guttman-Yassky E, Paller AS, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopicdermatitis: results through week 52 from a phase III open-label extension trial (LIBERTY AD PED-OLE). Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:365-383. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00683-2
- Cork MJ, D, Eichenfield LF, et al. Dupilumab provides favourable long-term safety and efficacy in children aged ≥ 6 to < 12 years with uncontrolled severe atopic dermatitis: results from an open-label phase IIa study and subsequent phase III open-label extension study. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:857-870. doi:10.1111/bjd.19460
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab demonstrates rapid and consistent improvement in extent and signs of atopic dermatitis across all anatomical regions in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1643-1656. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00568-y
- Paller A, Blauvelt A, Soong W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tralokinumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: results of the phase 3 ECZTRA 6 trial. SKIN. 2022;6:S29. doi:10.25251/skin.6.supp.s29
- Guttman-Yassky E, Blauvelt A, Eichenfield LF, et al. Efficacy and safety of lebrikizumab, a high-affinity interleukin 13 inhibitor, in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 2b randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:411-420. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0079
- Lebrikizumab dosed every four weeks maintained durable skin clearance in Lilly’s phase 3 monotherapy atopic dermatitis trials [news release]. Eli Lilly and Company; September 8, 2022. Accessed October 19, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lebrikizumab-dosed-every-four-weeks-maintained-durable-skin
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00588-2
- Chovatiya R, Paller AS. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:927-940. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2021.08.009
- Geng B, Hebert AA, Takiya L, et al. Efficacy and safety trends with continuous, long-term crisaborole use in patients aged ≥ 2 years with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1667-1678. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00584-y
- Appiah MM, Haft MA, Kleinman E, et al. Atopic dermatitis: review of comorbidities and therapeutics. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022;129:142-149. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2022.05.015
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Kiebert G, Sorensen SV, Revicki D, et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a decrement in health-related quality of life. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:151-158. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01436.x
- Al Shobaili HA. The impact of childhood atopic dermatitis on the patients’ family. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:618-623. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01215.x
- Saeki H, Baba N, Ito K, et al. Difamilast, a selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, ointment in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase III randomized double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial [published online November 1, 2021]. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:40-49. doi:10.1111/bjd.20655
- Chu Z, Xu Q, Zhu Q, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzoxaborole derivatives as potent PDE4 inhibitors for topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;213:113171. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113171
- Paller AS, Stein Gold L, Soung J, et al. Efficacy and patient-reported outcomes from a phase 2b, randomized clinical trial of tapinarof cream for the treatment of adolescents and adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:632-638. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.135
- Nakatsuji T, Hata TR, Tong Y, et al. Development of a human skin commensal microbe for bacteriotherapy of atopic dermatitis and use in a phase 1 randomized clinical trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:700-709. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01256-2
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.023
- Sidbury R, Davis DM, Cohen DE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: part 3. management and treatment with phototherapy and systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:327-349. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.030
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC-H, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with uncontrolled moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:44-56. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3336
- Blauvelt A, Guttman-Yassky E, Paller AS, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopicdermatitis: results through week 52 from a phase III open-label extension trial (LIBERTY AD PED-OLE). Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:365-383. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00683-2
- Cork MJ, D, Eichenfield LF, et al. Dupilumab provides favourable long-term safety and efficacy in children aged ≥ 6 to < 12 years with uncontrolled severe atopic dermatitis: results from an open-label phase IIa study and subsequent phase III open-label extension study. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:857-870. doi:10.1111/bjd.19460
- Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab demonstrates rapid and consistent improvement in extent and signs of atopic dermatitis across all anatomical regions in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1643-1656. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00568-y
- Paller A, Blauvelt A, Soong W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tralokinumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: results of the phase 3 ECZTRA 6 trial. SKIN. 2022;6:S29. doi:10.25251/skin.6.supp.s29
- Guttman-Yassky E, Blauvelt A, Eichenfield LF, et al. Efficacy and safety of lebrikizumab, a high-affinity interleukin 13 inhibitor, in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 2b randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:411-420. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0079
- Lebrikizumab dosed every four weeks maintained durable skin clearance in Lilly’s phase 3 monotherapy atopic dermatitis trials [news release]. Eli Lilly and Company; September 8, 2022. Accessed October 19, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lebrikizumab-dosed-every-four-weeks-maintained-durable-skin
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00588-2
- Chovatiya R, Paller AS. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:927-940. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2021.08.009
- Geng B, Hebert AA, Takiya L, et al. Efficacy and safety trends with continuous, long-term crisaborole use in patients aged ≥ 2 years with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11:1667-1678. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00584-y
- Appiah MM, Haft MA, Kleinman E, et al. Atopic dermatitis: review of comorbidities and therapeutics. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022;129:142-149. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2022.05.015
PRACTICE POINTS
- Pediatric atopic dermatitis (AD) therapeutics have rapidly evolved over the last decade and dermatologists should be aware of new tools in their treatment arsenal.
- New topical nonsteroidal agents serve as useful alternatives to topical corticosteroids through mitigating adverse effects from current standard therapy and potentially simplifying topical regimens.
- Monoclonal antibodies and Janus kinase inhibitors are part of an important set of new systemic therapeutics for pediatric AD.
- Long-term data on these new therapeutics is required to better understand their impact on pediatric AD comorbidities and impact on the longitudinal disease course.