User login
Accuracy Comparisons between Manual and Automated Respiratory Rate for Detecting Clinical Deterioration in Ward Patients
Respiratory rate is the most accurate vital sign for predicting adverse outcomes in ward patients.1,2 Though other vital signs are typically collected by using machines, respiratory rate is collected manually by caregivers counting the breathing rate. However, studies have shown significant discrepancies between a patient’s respiratory rate documented in the medical record, which is often 18 or 20, and the value measured by counting the rate over a full minute.3 Thus, despite the high accuracy of respiratory rate, it is possible that these values do not represent true patient physiology. It is unknown whether a valid automated measurement of respiratory rate would be more predictive than a manually collected respiratory rate for identifying patients who develop deterioration. The aim of this study was to compare the distribution and predictive accuracy of manually and automatically recorded respiratory rates.
METHODS
In this prospective cohort study, adult patients admitted to one oncology ward at the University of Chicago from April 2015 to May 2016 were approached for consent (Institutional Review Board #14-0682). Enrolled patients were fit with a cableless, FDA-approved respiratory pod device (Philips IntelliVue clResp Pod; Philips Healthcare, Andover, MA) that automatically recorded respiratory rate and heart rate every 15 minutes while they remained on the ward. Pod data were paired with vital sign data documented in the electronic health record (EHR) by taking the automated value closest, but prior to, the manual value up to a maximum of 4 hours. Automated and manual respiratory rate were compared by using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for whether an intensive care unit (ICU) transfer occurred within 24 hours of each paired observation without accounting for patient-level clustering.
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
In this prospective cohort study, we found that manual respiratory rates were different than those collected from an automated system and, yet, were significantly more accurate for predicting ICU transfer. These results suggest that the predictive accuracy of respiratory rates documented in the EHR is due to more than just physiology. Our findings have important implications for the risk stratification of ward patients.
Though previous literature has suggested that respiratory rate is the most accurate predictor of deterioration, this may not be true.1 Respiratory rates manually recorded by clinical staff may contain information beyond pure physiology, such as a proxy of clinician concern, which may inflate the predictive value. Nursing staff may record standard respiratory rate values for patients that appear to be well (eg, 18) but count actual rates for those patients they suspect have a more severe disease, which is one possible explanation for our findings. In addition, automated assessments are likely to be more sensitive to intermittent fluctuations in respiratory rate associated with patient movement or emotion. This might explain the improved accuracy at higher rates for manually recorded vital signs.
Although limited by its small sample size, our results have important implications for patient monitoring and early warning scores designed to identify high-risk ward patients given that both simple scores and statistically derived models include respiratory rates as a predictor.4 As hospitals move to use newer technologies to automate vital sign monitoring and decrease nursing workload, our findings suggest that accuracy for identifying high-risk patients may be lost. Additional methods for capturing subjective assessments from clinical providers may be necessary and could be incorporated into risk scores.5 For example, the 7-point subjective Patient Acuity Rating has been shown to augment the Modified Early Warning Score for predicting ICU transfer, rapid response activation, or cardiac arrest within 24 hours.6
Manually recorded respiratory rate may include information beyond pure physiology, which inflates its predictive value. This has important implications for the use of automated monitoring technology in hospitals and the integration of these measurements into early warning scores.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pamela McCall, BSN, OCN for her assistance with study implementation, Kevin Ig-Izevbekhai and Shivraj Grewal for assistance with data collection, UCM Clinical Engineering for technical support, and Timothy Holper, MS, Julie Johnson, MPH, RN, and Thomas Sutton for assistance with data abstraction.
Disclosure
Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080) and has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Dr. Churpek and Dr. Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), research support from the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX) and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and research support from EarlySense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. This study was supported by a grant from Philips Healthcare in Andover, MA. The sponsor had no role in data collection, interpretation of results, or drafting of the manuscript.
1. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Huber MT, Park SY, Hall JB, Edelson DP. Predicting cardiac arrest on the wards: a nested case-control study. Chest. 2012;141(5):1170-1176. PubMed
2. Fieselmann JF, Hendryx MS, Helms CM, Wakefield DS. Respiratory rate predicts cardiopulmonary arrest for internal medicine inpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8(7):354-360. PubMed
3. Semler MW, Stover DG, Copland AP, et al. Flash mob research: a single-day, multicenter, resident-directed study of respiratory rate. Chest. 2013;143(6):1740-1744. PubMed
4. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Edelson DP. Risk stratification of hospitalized patients on the wards. Chest. 2013;143(6):1758-1765. PubMed
5. Edelson DP, Retzer E, Weidman EK, et al. Patient acuity rating: quantifying clinical judgment regarding inpatient stability. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(8):475-479. PubMed
6. Patel AR, Zadravecz FJ, Young RS, Williams MV, Churpek MM, Edelson DP. The value of clinical judgment in the detection of clinical deterioration. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(3):456-458. PubMed
Respiratory rate is the most accurate vital sign for predicting adverse outcomes in ward patients.1,2 Though other vital signs are typically collected by using machines, respiratory rate is collected manually by caregivers counting the breathing rate. However, studies have shown significant discrepancies between a patient’s respiratory rate documented in the medical record, which is often 18 or 20, and the value measured by counting the rate over a full minute.3 Thus, despite the high accuracy of respiratory rate, it is possible that these values do not represent true patient physiology. It is unknown whether a valid automated measurement of respiratory rate would be more predictive than a manually collected respiratory rate for identifying patients who develop deterioration. The aim of this study was to compare the distribution and predictive accuracy of manually and automatically recorded respiratory rates.
METHODS
In this prospective cohort study, adult patients admitted to one oncology ward at the University of Chicago from April 2015 to May 2016 were approached for consent (Institutional Review Board #14-0682). Enrolled patients were fit with a cableless, FDA-approved respiratory pod device (Philips IntelliVue clResp Pod; Philips Healthcare, Andover, MA) that automatically recorded respiratory rate and heart rate every 15 minutes while they remained on the ward. Pod data were paired with vital sign data documented in the electronic health record (EHR) by taking the automated value closest, but prior to, the manual value up to a maximum of 4 hours. Automated and manual respiratory rate were compared by using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for whether an intensive care unit (ICU) transfer occurred within 24 hours of each paired observation without accounting for patient-level clustering.
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
In this prospective cohort study, we found that manual respiratory rates were different than those collected from an automated system and, yet, were significantly more accurate for predicting ICU transfer. These results suggest that the predictive accuracy of respiratory rates documented in the EHR is due to more than just physiology. Our findings have important implications for the risk stratification of ward patients.
Though previous literature has suggested that respiratory rate is the most accurate predictor of deterioration, this may not be true.1 Respiratory rates manually recorded by clinical staff may contain information beyond pure physiology, such as a proxy of clinician concern, which may inflate the predictive value. Nursing staff may record standard respiratory rate values for patients that appear to be well (eg, 18) but count actual rates for those patients they suspect have a more severe disease, which is one possible explanation for our findings. In addition, automated assessments are likely to be more sensitive to intermittent fluctuations in respiratory rate associated with patient movement or emotion. This might explain the improved accuracy at higher rates for manually recorded vital signs.
Although limited by its small sample size, our results have important implications for patient monitoring and early warning scores designed to identify high-risk ward patients given that both simple scores and statistically derived models include respiratory rates as a predictor.4 As hospitals move to use newer technologies to automate vital sign monitoring and decrease nursing workload, our findings suggest that accuracy for identifying high-risk patients may be lost. Additional methods for capturing subjective assessments from clinical providers may be necessary and could be incorporated into risk scores.5 For example, the 7-point subjective Patient Acuity Rating has been shown to augment the Modified Early Warning Score for predicting ICU transfer, rapid response activation, or cardiac arrest within 24 hours.6
Manually recorded respiratory rate may include information beyond pure physiology, which inflates its predictive value. This has important implications for the use of automated monitoring technology in hospitals and the integration of these measurements into early warning scores.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pamela McCall, BSN, OCN for her assistance with study implementation, Kevin Ig-Izevbekhai and Shivraj Grewal for assistance with data collection, UCM Clinical Engineering for technical support, and Timothy Holper, MS, Julie Johnson, MPH, RN, and Thomas Sutton for assistance with data abstraction.
Disclosure
Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080) and has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Dr. Churpek and Dr. Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), research support from the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX) and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and research support from EarlySense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. This study was supported by a grant from Philips Healthcare in Andover, MA. The sponsor had no role in data collection, interpretation of results, or drafting of the manuscript.
Respiratory rate is the most accurate vital sign for predicting adverse outcomes in ward patients.1,2 Though other vital signs are typically collected by using machines, respiratory rate is collected manually by caregivers counting the breathing rate. However, studies have shown significant discrepancies between a patient’s respiratory rate documented in the medical record, which is often 18 or 20, and the value measured by counting the rate over a full minute.3 Thus, despite the high accuracy of respiratory rate, it is possible that these values do not represent true patient physiology. It is unknown whether a valid automated measurement of respiratory rate would be more predictive than a manually collected respiratory rate for identifying patients who develop deterioration. The aim of this study was to compare the distribution and predictive accuracy of manually and automatically recorded respiratory rates.
METHODS
In this prospective cohort study, adult patients admitted to one oncology ward at the University of Chicago from April 2015 to May 2016 were approached for consent (Institutional Review Board #14-0682). Enrolled patients were fit with a cableless, FDA-approved respiratory pod device (Philips IntelliVue clResp Pod; Philips Healthcare, Andover, MA) that automatically recorded respiratory rate and heart rate every 15 minutes while they remained on the ward. Pod data were paired with vital sign data documented in the electronic health record (EHR) by taking the automated value closest, but prior to, the manual value up to a maximum of 4 hours. Automated and manual respiratory rate were compared by using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for whether an intensive care unit (ICU) transfer occurred within 24 hours of each paired observation without accounting for patient-level clustering.
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
In this prospective cohort study, we found that manual respiratory rates were different than those collected from an automated system and, yet, were significantly more accurate for predicting ICU transfer. These results suggest that the predictive accuracy of respiratory rates documented in the EHR is due to more than just physiology. Our findings have important implications for the risk stratification of ward patients.
Though previous literature has suggested that respiratory rate is the most accurate predictor of deterioration, this may not be true.1 Respiratory rates manually recorded by clinical staff may contain information beyond pure physiology, such as a proxy of clinician concern, which may inflate the predictive value. Nursing staff may record standard respiratory rate values for patients that appear to be well (eg, 18) but count actual rates for those patients they suspect have a more severe disease, which is one possible explanation for our findings. In addition, automated assessments are likely to be more sensitive to intermittent fluctuations in respiratory rate associated with patient movement or emotion. This might explain the improved accuracy at higher rates for manually recorded vital signs.
Although limited by its small sample size, our results have important implications for patient monitoring and early warning scores designed to identify high-risk ward patients given that both simple scores and statistically derived models include respiratory rates as a predictor.4 As hospitals move to use newer technologies to automate vital sign monitoring and decrease nursing workload, our findings suggest that accuracy for identifying high-risk patients may be lost. Additional methods for capturing subjective assessments from clinical providers may be necessary and could be incorporated into risk scores.5 For example, the 7-point subjective Patient Acuity Rating has been shown to augment the Modified Early Warning Score for predicting ICU transfer, rapid response activation, or cardiac arrest within 24 hours.6
Manually recorded respiratory rate may include information beyond pure physiology, which inflates its predictive value. This has important implications for the use of automated monitoring technology in hospitals and the integration of these measurements into early warning scores.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pamela McCall, BSN, OCN for her assistance with study implementation, Kevin Ig-Izevbekhai and Shivraj Grewal for assistance with data collection, UCM Clinical Engineering for technical support, and Timothy Holper, MS, Julie Johnson, MPH, RN, and Thomas Sutton for assistance with data abstraction.
Disclosure
Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080) and has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Dr. Churpek and Dr. Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), research support from the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX) and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and research support from EarlySense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. This study was supported by a grant from Philips Healthcare in Andover, MA. The sponsor had no role in data collection, interpretation of results, or drafting of the manuscript.
1. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Huber MT, Park SY, Hall JB, Edelson DP. Predicting cardiac arrest on the wards: a nested case-control study. Chest. 2012;141(5):1170-1176. PubMed
2. Fieselmann JF, Hendryx MS, Helms CM, Wakefield DS. Respiratory rate predicts cardiopulmonary arrest for internal medicine inpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8(7):354-360. PubMed
3. Semler MW, Stover DG, Copland AP, et al. Flash mob research: a single-day, multicenter, resident-directed study of respiratory rate. Chest. 2013;143(6):1740-1744. PubMed
4. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Edelson DP. Risk stratification of hospitalized patients on the wards. Chest. 2013;143(6):1758-1765. PubMed
5. Edelson DP, Retzer E, Weidman EK, et al. Patient acuity rating: quantifying clinical judgment regarding inpatient stability. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(8):475-479. PubMed
6. Patel AR, Zadravecz FJ, Young RS, Williams MV, Churpek MM, Edelson DP. The value of clinical judgment in the detection of clinical deterioration. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(3):456-458. PubMed
1. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Huber MT, Park SY, Hall JB, Edelson DP. Predicting cardiac arrest on the wards: a nested case-control study. Chest. 2012;141(5):1170-1176. PubMed
2. Fieselmann JF, Hendryx MS, Helms CM, Wakefield DS. Respiratory rate predicts cardiopulmonary arrest for internal medicine inpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8(7):354-360. PubMed
3. Semler MW, Stover DG, Copland AP, et al. Flash mob research: a single-day, multicenter, resident-directed study of respiratory rate. Chest. 2013;143(6):1740-1744. PubMed
4. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Edelson DP. Risk stratification of hospitalized patients on the wards. Chest. 2013;143(6):1758-1765. PubMed
5. Edelson DP, Retzer E, Weidman EK, et al. Patient acuity rating: quantifying clinical judgment regarding inpatient stability. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(8):475-479. PubMed
6. Patel AR, Zadravecz FJ, Young RS, Williams MV, Churpek MM, Edelson DP. The value of clinical judgment in the detection of clinical deterioration. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(3):456-458. PubMed
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine
Electronic Assessment of Mental Status
Altered mental status (AMS) is a complex spectrum of cognitive deficits that includes orientation, memory, language, visuospatial ability, and perception.[1] The clinical definitions of both delirium and dementia include AMS as a hallmark clinical prerequisite. Regardless of etiology, this broader AMS definition is particularly salient in the hospital setting, where AMS is present in up to 60% of inpatients and is associated with longer hospital stay as well as increased morbidity and mortality.[2, 3] Not surprisingly, due to the complexity of identifying and assessing changes in mental status, clinically relevant AMS is often undetected among inpatients.[2] However, when detected, the most common causes of AMS (infection, polypharmacy, and pain) are treatable, suggesting that early AMS identification could alert clinicians to early signs of clinical decompensation, potentially improving clinical outcomes.[4]
Because rapid and systemic clinical detection of AMS is limited by the complexity of mental status, a number of assessments have been created, each with their own advantages, limitations, and target populations. These assessments are often limited by time‐intensive administration, subjectivity of mental status assessment, and lack of sensitivity in general medicine patients. Time‐intensive measures, such as the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ) have utility in the research setting, whereas current common clinical risk stratification tools (eg, National Early Warning Score) utilize simpler measures such as the Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive (AVPU) and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) as measures of mental status.[2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
To address the need for a brief, clinically feasible, accurate tool in clinical detection of AMS, our group developed a mobile application for working memory testing, the Functional Assessment of Mentation (FAMTM). In this study, we aimed to identify baseline scoring distributions of the FAMTM in a nonhospitalized subgroup, as well as assess the correlation of the FAMTM to discharge disposition and compare it to the SPMSQ in inpatients.
METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a prospective observational study. Data were collected from both hospitalized and nonhospitalized adult participants as 2 distinct subgroups. Nonhospitalized adult subjects were recruited from a university medical campus (June 2013July 2013; IRB‐12‐0175). Hospitalized participants were recruited from the general medicine service as part of an ongoing study measuring quality of care and resource allocation at the same academic medical center (June 2014August 2014; IRB‐9967).[10]
FAMTM Application
The FAMTM application is a bedside tool for working memory assessment developed for the iPhone mobile operating system (Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA) and presented on an iPad mini (Apple). The application interface displays 4 colored rectangles individually labeled with a number (see Supporting Figure 1 in the online version of this article). The testing portion of the application presents a sequence of numbered rectangles, illuminated 1 at a time in random order. Subjects are prompted first to watch and remember the sequence and then repeat the sequence by touching the screen within each numbered rectangle. Successful reproduction of the sequence is followed by a distinct and longer sequence, whereas unsuccessful attempts are followed by a shorter sequence. The final FAMTM score corresponds to the longest sequence of rectangles successfully repeated by the subject.
Data Collection
In the nonhospitalized subject population, research assistants collected demographic data immediately prior to FAMTM administration. Among hospitalized subjects, GCS information was collected by nursing staff as part of standard clinical care. One research assistant administered the SPMSQ while a second assistant, blinded to the SPMSQ and GCS scores, administered the FAMTM. Clinical data were obtained from medical records (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI). Discharge disposition was dichotomized as discharged home or not.
Statistical Analyses
Demographic characteristics of the 2 subject populations were compared using Student t tests (continuous variables) and 2 tests (categorical variables). Score distribution and discharge disposition comparison was conducted with the Mann‐Whitney U test and area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) analysis, using the trapezoidal rule.[11] Multivariable linear regression was used to investigate the impact of age, race, education, discharge disposition, and hospitalization status on patient scores and times. Correlations between the FAMTM and SPMSQ scores and between the GCS and SPMSQ scores were calculated using the Spearman rank test. Significance was set at a 2‐sided P value of <0.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata version 13.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
A total of 931 subjects were enrolled in the study. In the nonhospitalized subgroup, 651 consented to study participation and 612 were included in final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they started but did not complete the application (n = 36) or were under the age of 18 years (n = 3). Of the 363 hospitalized subjects approached for enrollment, 319 were included in the final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they refused to participate (n = 23), were under the age of 18 (n = 2), had technical failures (n = 5), or had physical or visual limitations that precluded them from participation (n = 14). Within the hospitalized subgroup, 268 subjects were discharged home (85%). The table displays demographics and score distributions by subgroup.1
| Nonhospitalized Subjects, n = 612 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Home, n = 268 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Elsewhere, n = 48 | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Age, y | 52 18 | 52 19 | 62 17 | <0.001 |
| Female sex | 343 (56%) | 158 (59%) | 26 (54%) | 0.63 |
| Education | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school graduate | 31 (5%) | 32 (12%) | 7 (15%) | |
| High school graduate | 312 (51%) | 153 (57%) | 26 (54%) | |
| College graduate | 263 (43%) | 43 (16%) | 8 (17%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 40 (15%) | 7 (15%) | |
| Race | <0.001 | |||
| Black | 196 (32%) | 185 (69%) | 34 (71%) | |
| White | 324 (53%) | 75 (28%) | 13 (27%) | |
| Other | 86 (14%) | 4 (1%) | 4 (1%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 4 (1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| FAMTM score, median (IQR) | 5 (47) | 5 (36) | 3 (15) | <0.001 |
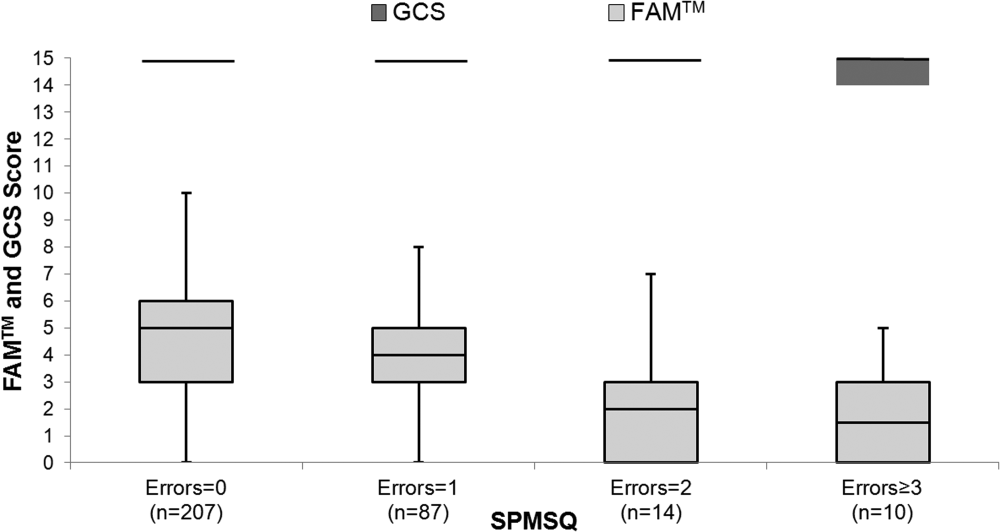
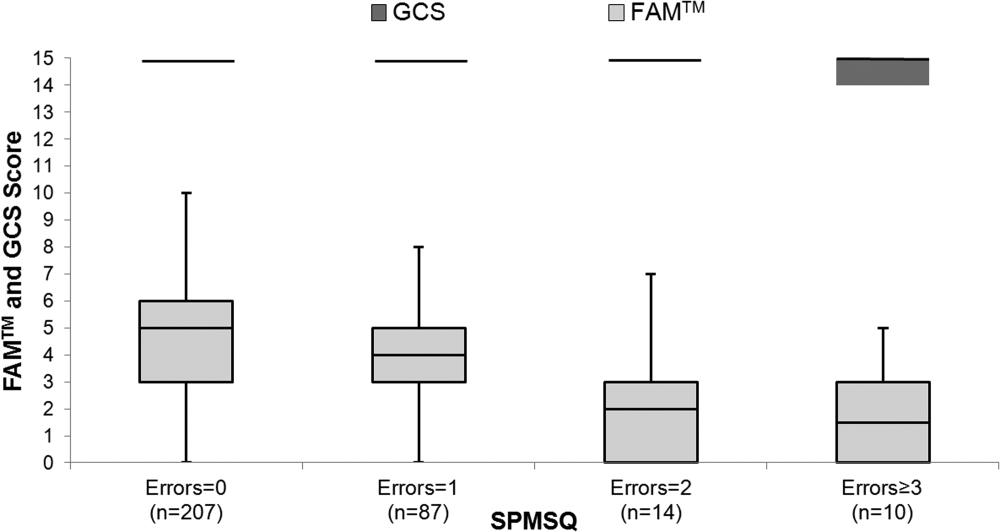
The median FAMTM score for the combined study population was 5 (interquartile range [IQR] 36), and median time to completion was 55 seconds (IQR 4567 seconds). A graded reduction was found in the FAMTM score for all stepwise comparisons between nonhospitalized subjects, hospitalized subjects discharged home, and hospitalized subjects not discharged home (median 5 [IQR 47] vs 5 [IQR 36] vs 3 [IQR 15]; P < 0.001 for all pairwise comparisons). The AUC for the FAMTM predicting discharge disposition (home vs not) was 0.66 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.58‐0.74]. After adjusting for confounders, higher FAMTM scores were independently associated with not being hospitalized, being discharged home, higher levels of education, younger age, and white race (see Supporting Table 1 in the online version of this article). Additionally, in the hospitalized subgroup, decreasing FAMTM score was significantly correlated with increasing errors on the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.27, P < 0.001), whereas the GCS score was not correlated with the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.05, P = 0.40) (Figure 1).
DISCUSSION
We demonstrated the utility of a rapid and accurate mobile application for assessment of mental status. The FAMTM was able to be quickly administered with a median time to completion of approximately 1 minute. The ability to detect mild alterations in mental status was shown through concurrent validity by FAMTM correlation with the SPMSQ and predictive validity with the association between the FAMTM and discharge disposition. Our study highlights the potential for the FAMTM to be used as a sensitive marker of AMS.
The novel design of the FAMTM presents unique advantages compared to current mental status testing. First, the FAMTM could allow patients with hearing impairment or language barriers to complete a mental status assessment. Additionally, the approximately 1‐minute median time to completion is much faster than other established mental status assessments including the SPMSQ (510 minutes). Compared to the SPMSQ taking 5 minutes, in a 400‐bed hospital, taken once per nursing shift, the FAMTM would save approximately 20,000 hours and 10 nursing full‐time equivalents per year.[5] Finally, many current mental status tests such as the Confusion Assessment Model utilize subjective mental status assessments.[2] However, the FAMTM is designed to be conducted through self‐assessment and, thus, could theoretically be free of observer bias. This potential for self‐administration expands beyond other proposed alternative testing mechanisms of the AMS such as ultrabrief assessments that include items such as asking subjects the months of the year backwards, and what is the day of the week?, and assessing arousal.[12, 13, 14]
In research settings and commonly in hospitals, the GCS and AVPU are used clinically for mental status assessment of hospitalized patients.[6, 15] However, similar to previous literature, our study found that the vast majority of hospitalized patients were defined as neurologically intact by the GCS, which is the more accurate predictor of the 2.[7] One major strength of the FAMTM was that it identified an extensive gradation of scores for patients previously labeled as merely alert, providing greater resolution than the GCS in quantifying mental status.
One of the key benefits of the FAMTM is that it can be measured longitudinally over the course of a patient's hospital stay. Therefore, once a baseline FAMTM score is established, variation from the patient's personal baseline could indicate mental status deterioration, which would not be affected by the patient's demographics, health status, or underlying neurocognitive deficits.
There were important limitations to this study. First, limited generalizability of these data may exist due to the single‐center setting and patient population. However, this initial study provides pilot data for further expansion into the potential broad applicability of the FAMTM to other patient populations and settings. Additionally, the cost of large‐scale implementation of the FAMTM is unknown and was beyond the scope of this pilot study. However, to reduce costs, the FAMTM technology could be integrated into existing hospital technology infrastructure. Finally, the scope of this study prevented a complete assessment of all validity measures or comparison to other mental status assessments such as the digit span or serial sevens tests. However, predictive and concurrent validity were assessed with comparison by discharge disposition, SPMSQ, and GCS scores.
In conclusion, this pilot study identifies the FAMTM application as a potentially clinically useful, novel, rapid, and feasible assessment tool of mental status in a general medicine inpatient setting.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Frank Zadravecz, MPH, for his support with this project.
Disclosures: This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIA 2T35AG029795‐07) and in part by career development awards granted to Dr. Churpek, Dr. Edelson, and Dr. Press by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080, K23 HL097157, and K23 HL118151, respectively). Dr. Churpek has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
- , . Altered mental status in older patients in the emergency department. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013;29(1):101–136.
- , , , , , . Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113(12):941–948.
- , , , , . Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , . Early recognition of delirium: review of the literature. J Clin Nurs. 2001;10(6):721–729.
- . A short portable mental status questionnaire for the assessment of organic brain deficit in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975;23(10):433–441.
- , , , , . The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit admission, and death. Resuscitation. 2013;84(4):465–470.
- , , , et al. Comparison of mental‐status scales for predicting mortality on the general wards. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):658–663.
- , . Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness: a practical scale. Lancet. 1974;304(7872):81–84.
- , , , . Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire as a Screening Test for Dementia and Delirium Among the Elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987;35(5):412–416.
- , , , et al. Effects of physician experience on costs and outcomes on an academic general medicine service: results of a trial of hospitalists. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(11):866–874.
- , , . Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , , , et al. Preliminary development of an ultrabrief two‐item bedside test for delirium. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):645–650.
- , , , , , . The association between an ultrabrief cognitive screening in older adults and hospital outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):651–657.
- , , , et al. Selecting optimal screening items for delirium: an application of item response theory. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:8.
- , , . Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
Altered mental status (AMS) is a complex spectrum of cognitive deficits that includes orientation, memory, language, visuospatial ability, and perception.[1] The clinical definitions of both delirium and dementia include AMS as a hallmark clinical prerequisite. Regardless of etiology, this broader AMS definition is particularly salient in the hospital setting, where AMS is present in up to 60% of inpatients and is associated with longer hospital stay as well as increased morbidity and mortality.[2, 3] Not surprisingly, due to the complexity of identifying and assessing changes in mental status, clinically relevant AMS is often undetected among inpatients.[2] However, when detected, the most common causes of AMS (infection, polypharmacy, and pain) are treatable, suggesting that early AMS identification could alert clinicians to early signs of clinical decompensation, potentially improving clinical outcomes.[4]
Because rapid and systemic clinical detection of AMS is limited by the complexity of mental status, a number of assessments have been created, each with their own advantages, limitations, and target populations. These assessments are often limited by time‐intensive administration, subjectivity of mental status assessment, and lack of sensitivity in general medicine patients. Time‐intensive measures, such as the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ) have utility in the research setting, whereas current common clinical risk stratification tools (eg, National Early Warning Score) utilize simpler measures such as the Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive (AVPU) and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) as measures of mental status.[2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
To address the need for a brief, clinically feasible, accurate tool in clinical detection of AMS, our group developed a mobile application for working memory testing, the Functional Assessment of Mentation (FAMTM). In this study, we aimed to identify baseline scoring distributions of the FAMTM in a nonhospitalized subgroup, as well as assess the correlation of the FAMTM to discharge disposition and compare it to the SPMSQ in inpatients.
METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a prospective observational study. Data were collected from both hospitalized and nonhospitalized adult participants as 2 distinct subgroups. Nonhospitalized adult subjects were recruited from a university medical campus (June 2013July 2013; IRB‐12‐0175). Hospitalized participants were recruited from the general medicine service as part of an ongoing study measuring quality of care and resource allocation at the same academic medical center (June 2014August 2014; IRB‐9967).[10]
FAMTM Application
The FAMTM application is a bedside tool for working memory assessment developed for the iPhone mobile operating system (Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA) and presented on an iPad mini (Apple). The application interface displays 4 colored rectangles individually labeled with a number (see Supporting Figure 1 in the online version of this article). The testing portion of the application presents a sequence of numbered rectangles, illuminated 1 at a time in random order. Subjects are prompted first to watch and remember the sequence and then repeat the sequence by touching the screen within each numbered rectangle. Successful reproduction of the sequence is followed by a distinct and longer sequence, whereas unsuccessful attempts are followed by a shorter sequence. The final FAMTM score corresponds to the longest sequence of rectangles successfully repeated by the subject.

Data Collection
In the nonhospitalized subject population, research assistants collected demographic data immediately prior to FAMTM administration. Among hospitalized subjects, GCS information was collected by nursing staff as part of standard clinical care. One research assistant administered the SPMSQ while a second assistant, blinded to the SPMSQ and GCS scores, administered the FAMTM. Clinical data were obtained from medical records (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI). Discharge disposition was dichotomized as discharged home or not.
Statistical Analyses
Demographic characteristics of the 2 subject populations were compared using Student t tests (continuous variables) and 2 tests (categorical variables). Score distribution and discharge disposition comparison was conducted with the Mann‐Whitney U test and area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) analysis, using the trapezoidal rule.[11] Multivariable linear regression was used to investigate the impact of age, race, education, discharge disposition, and hospitalization status on patient scores and times. Correlations between the FAMTM and SPMSQ scores and between the GCS and SPMSQ scores were calculated using the Spearman rank test. Significance was set at a 2‐sided P value of <0.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata version 13.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
A total of 931 subjects were enrolled in the study. In the nonhospitalized subgroup, 651 consented to study participation and 612 were included in final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they started but did not complete the application (n = 36) or were under the age of 18 years (n = 3). Of the 363 hospitalized subjects approached for enrollment, 319 were included in the final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they refused to participate (n = 23), were under the age of 18 (n = 2), had technical failures (n = 5), or had physical or visual limitations that precluded them from participation (n = 14). Within the hospitalized subgroup, 268 subjects were discharged home (85%). The table displays demographics and score distributions by subgroup.1
| Nonhospitalized Subjects, n = 612 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Home, n = 268 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Elsewhere, n = 48 | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Age, y | 52 18 | 52 19 | 62 17 | <0.001 |
| Female sex | 343 (56%) | 158 (59%) | 26 (54%) | 0.63 |
| Education | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school graduate | 31 (5%) | 32 (12%) | 7 (15%) | |
| High school graduate | 312 (51%) | 153 (57%) | 26 (54%) | |
| College graduate | 263 (43%) | 43 (16%) | 8 (17%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 40 (15%) | 7 (15%) | |
| Race | <0.001 | |||
| Black | 196 (32%) | 185 (69%) | 34 (71%) | |
| White | 324 (53%) | 75 (28%) | 13 (27%) | |
| Other | 86 (14%) | 4 (1%) | 4 (1%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 4 (1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| FAMTM score, median (IQR) | 5 (47) | 5 (36) | 3 (15) | <0.001 |
The median FAMTM score for the combined study population was 5 (interquartile range [IQR] 36), and median time to completion was 55 seconds (IQR 4567 seconds). A graded reduction was found in the FAMTM score for all stepwise comparisons between nonhospitalized subjects, hospitalized subjects discharged home, and hospitalized subjects not discharged home (median 5 [IQR 47] vs 5 [IQR 36] vs 3 [IQR 15]; P < 0.001 for all pairwise comparisons). The AUC for the FAMTM predicting discharge disposition (home vs not) was 0.66 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.58‐0.74]. After adjusting for confounders, higher FAMTM scores were independently associated with not being hospitalized, being discharged home, higher levels of education, younger age, and white race (see Supporting Table 1 in the online version of this article). Additionally, in the hospitalized subgroup, decreasing FAMTM score was significantly correlated with increasing errors on the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.27, P < 0.001), whereas the GCS score was not correlated with the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.05, P = 0.40) (Figure 1).
DISCUSSION
We demonstrated the utility of a rapid and accurate mobile application for assessment of mental status. The FAMTM was able to be quickly administered with a median time to completion of approximately 1 minute. The ability to detect mild alterations in mental status was shown through concurrent validity by FAMTM correlation with the SPMSQ and predictive validity with the association between the FAMTM and discharge disposition. Our study highlights the potential for the FAMTM to be used as a sensitive marker of AMS.
The novel design of the FAMTM presents unique advantages compared to current mental status testing. First, the FAMTM could allow patients with hearing impairment or language barriers to complete a mental status assessment. Additionally, the approximately 1‐minute median time to completion is much faster than other established mental status assessments including the SPMSQ (510 minutes). Compared to the SPMSQ taking 5 minutes, in a 400‐bed hospital, taken once per nursing shift, the FAMTM would save approximately 20,000 hours and 10 nursing full‐time equivalents per year.[5] Finally, many current mental status tests such as the Confusion Assessment Model utilize subjective mental status assessments.[2] However, the FAMTM is designed to be conducted through self‐assessment and, thus, could theoretically be free of observer bias. This potential for self‐administration expands beyond other proposed alternative testing mechanisms of the AMS such as ultrabrief assessments that include items such as asking subjects the months of the year backwards, and what is the day of the week?, and assessing arousal.[12, 13, 14]
In research settings and commonly in hospitals, the GCS and AVPU are used clinically for mental status assessment of hospitalized patients.[6, 15] However, similar to previous literature, our study found that the vast majority of hospitalized patients were defined as neurologically intact by the GCS, which is the more accurate predictor of the 2.[7] One major strength of the FAMTM was that it identified an extensive gradation of scores for patients previously labeled as merely alert, providing greater resolution than the GCS in quantifying mental status.
One of the key benefits of the FAMTM is that it can be measured longitudinally over the course of a patient's hospital stay. Therefore, once a baseline FAMTM score is established, variation from the patient's personal baseline could indicate mental status deterioration, which would not be affected by the patient's demographics, health status, or underlying neurocognitive deficits.
There were important limitations to this study. First, limited generalizability of these data may exist due to the single‐center setting and patient population. However, this initial study provides pilot data for further expansion into the potential broad applicability of the FAMTM to other patient populations and settings. Additionally, the cost of large‐scale implementation of the FAMTM is unknown and was beyond the scope of this pilot study. However, to reduce costs, the FAMTM technology could be integrated into existing hospital technology infrastructure. Finally, the scope of this study prevented a complete assessment of all validity measures or comparison to other mental status assessments such as the digit span or serial sevens tests. However, predictive and concurrent validity were assessed with comparison by discharge disposition, SPMSQ, and GCS scores.
In conclusion, this pilot study identifies the FAMTM application as a potentially clinically useful, novel, rapid, and feasible assessment tool of mental status in a general medicine inpatient setting.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Frank Zadravecz, MPH, for his support with this project.
Disclosures: This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIA 2T35AG029795‐07) and in part by career development awards granted to Dr. Churpek, Dr. Edelson, and Dr. Press by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080, K23 HL097157, and K23 HL118151, respectively). Dr. Churpek has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Altered mental status (AMS) is a complex spectrum of cognitive deficits that includes orientation, memory, language, visuospatial ability, and perception.[1] The clinical definitions of both delirium and dementia include AMS as a hallmark clinical prerequisite. Regardless of etiology, this broader AMS definition is particularly salient in the hospital setting, where AMS is present in up to 60% of inpatients and is associated with longer hospital stay as well as increased morbidity and mortality.[2, 3] Not surprisingly, due to the complexity of identifying and assessing changes in mental status, clinically relevant AMS is often undetected among inpatients.[2] However, when detected, the most common causes of AMS (infection, polypharmacy, and pain) are treatable, suggesting that early AMS identification could alert clinicians to early signs of clinical decompensation, potentially improving clinical outcomes.[4]
Because rapid and systemic clinical detection of AMS is limited by the complexity of mental status, a number of assessments have been created, each with their own advantages, limitations, and target populations. These assessments are often limited by time‐intensive administration, subjectivity of mental status assessment, and lack of sensitivity in general medicine patients. Time‐intensive measures, such as the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ) have utility in the research setting, whereas current common clinical risk stratification tools (eg, National Early Warning Score) utilize simpler measures such as the Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive (AVPU) and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) as measures of mental status.[2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
To address the need for a brief, clinically feasible, accurate tool in clinical detection of AMS, our group developed a mobile application for working memory testing, the Functional Assessment of Mentation (FAMTM). In this study, we aimed to identify baseline scoring distributions of the FAMTM in a nonhospitalized subgroup, as well as assess the correlation of the FAMTM to discharge disposition and compare it to the SPMSQ in inpatients.
METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a prospective observational study. Data were collected from both hospitalized and nonhospitalized adult participants as 2 distinct subgroups. Nonhospitalized adult subjects were recruited from a university medical campus (June 2013July 2013; IRB‐12‐0175). Hospitalized participants were recruited from the general medicine service as part of an ongoing study measuring quality of care and resource allocation at the same academic medical center (June 2014August 2014; IRB‐9967).[10]
FAMTM Application
The FAMTM application is a bedside tool for working memory assessment developed for the iPhone mobile operating system (Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA) and presented on an iPad mini (Apple). The application interface displays 4 colored rectangles individually labeled with a number (see Supporting Figure 1 in the online version of this article). The testing portion of the application presents a sequence of numbered rectangles, illuminated 1 at a time in random order. Subjects are prompted first to watch and remember the sequence and then repeat the sequence by touching the screen within each numbered rectangle. Successful reproduction of the sequence is followed by a distinct and longer sequence, whereas unsuccessful attempts are followed by a shorter sequence. The final FAMTM score corresponds to the longest sequence of rectangles successfully repeated by the subject.

Data Collection
In the nonhospitalized subject population, research assistants collected demographic data immediately prior to FAMTM administration. Among hospitalized subjects, GCS information was collected by nursing staff as part of standard clinical care. One research assistant administered the SPMSQ while a second assistant, blinded to the SPMSQ and GCS scores, administered the FAMTM. Clinical data were obtained from medical records (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI). Discharge disposition was dichotomized as discharged home or not.
Statistical Analyses
Demographic characteristics of the 2 subject populations were compared using Student t tests (continuous variables) and 2 tests (categorical variables). Score distribution and discharge disposition comparison was conducted with the Mann‐Whitney U test and area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) analysis, using the trapezoidal rule.[11] Multivariable linear regression was used to investigate the impact of age, race, education, discharge disposition, and hospitalization status on patient scores and times. Correlations between the FAMTM and SPMSQ scores and between the GCS and SPMSQ scores were calculated using the Spearman rank test. Significance was set at a 2‐sided P value of <0.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata version 13.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
A total of 931 subjects were enrolled in the study. In the nonhospitalized subgroup, 651 consented to study participation and 612 were included in final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they started but did not complete the application (n = 36) or were under the age of 18 years (n = 3). Of the 363 hospitalized subjects approached for enrollment, 319 were included in the final analysis. Subjects were excluded if they refused to participate (n = 23), were under the age of 18 (n = 2), had technical failures (n = 5), or had physical or visual limitations that precluded them from participation (n = 14). Within the hospitalized subgroup, 268 subjects were discharged home (85%). The table displays demographics and score distributions by subgroup.1
| Nonhospitalized Subjects, n = 612 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Home, n = 268 | Hospitalized Subjects Discharged Elsewhere, n = 48 | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Age, y | 52 18 | 52 19 | 62 17 | <0.001 |
| Female sex | 343 (56%) | 158 (59%) | 26 (54%) | 0.63 |
| Education | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school graduate | 31 (5%) | 32 (12%) | 7 (15%) | |
| High school graduate | 312 (51%) | 153 (57%) | 26 (54%) | |
| College graduate | 263 (43%) | 43 (16%) | 8 (17%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 40 (15%) | 7 (15%) | |
| Race | <0.001 | |||
| Black | 196 (32%) | 185 (69%) | 34 (71%) | |
| White | 324 (53%) | 75 (28%) | 13 (27%) | |
| Other | 86 (14%) | 4 (1%) | 4 (1%) | |
| Missing | 6 (1%) | 4 (1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| FAMTM score, median (IQR) | 5 (47) | 5 (36) | 3 (15) | <0.001 |
The median FAMTM score for the combined study population was 5 (interquartile range [IQR] 36), and median time to completion was 55 seconds (IQR 4567 seconds). A graded reduction was found in the FAMTM score for all stepwise comparisons between nonhospitalized subjects, hospitalized subjects discharged home, and hospitalized subjects not discharged home (median 5 [IQR 47] vs 5 [IQR 36] vs 3 [IQR 15]; P < 0.001 for all pairwise comparisons). The AUC for the FAMTM predicting discharge disposition (home vs not) was 0.66 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.58‐0.74]. After adjusting for confounders, higher FAMTM scores were independently associated with not being hospitalized, being discharged home, higher levels of education, younger age, and white race (see Supporting Table 1 in the online version of this article). Additionally, in the hospitalized subgroup, decreasing FAMTM score was significantly correlated with increasing errors on the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.27, P < 0.001), whereas the GCS score was not correlated with the SPMSQ (Spearman = 0.05, P = 0.40) (Figure 1).
DISCUSSION
We demonstrated the utility of a rapid and accurate mobile application for assessment of mental status. The FAMTM was able to be quickly administered with a median time to completion of approximately 1 minute. The ability to detect mild alterations in mental status was shown through concurrent validity by FAMTM correlation with the SPMSQ and predictive validity with the association between the FAMTM and discharge disposition. Our study highlights the potential for the FAMTM to be used as a sensitive marker of AMS.
The novel design of the FAMTM presents unique advantages compared to current mental status testing. First, the FAMTM could allow patients with hearing impairment or language barriers to complete a mental status assessment. Additionally, the approximately 1‐minute median time to completion is much faster than other established mental status assessments including the SPMSQ (510 minutes). Compared to the SPMSQ taking 5 minutes, in a 400‐bed hospital, taken once per nursing shift, the FAMTM would save approximately 20,000 hours and 10 nursing full‐time equivalents per year.[5] Finally, many current mental status tests such as the Confusion Assessment Model utilize subjective mental status assessments.[2] However, the FAMTM is designed to be conducted through self‐assessment and, thus, could theoretically be free of observer bias. This potential for self‐administration expands beyond other proposed alternative testing mechanisms of the AMS such as ultrabrief assessments that include items such as asking subjects the months of the year backwards, and what is the day of the week?, and assessing arousal.[12, 13, 14]
In research settings and commonly in hospitals, the GCS and AVPU are used clinically for mental status assessment of hospitalized patients.[6, 15] However, similar to previous literature, our study found that the vast majority of hospitalized patients were defined as neurologically intact by the GCS, which is the more accurate predictor of the 2.[7] One major strength of the FAMTM was that it identified an extensive gradation of scores for patients previously labeled as merely alert, providing greater resolution than the GCS in quantifying mental status.
One of the key benefits of the FAMTM is that it can be measured longitudinally over the course of a patient's hospital stay. Therefore, once a baseline FAMTM score is established, variation from the patient's personal baseline could indicate mental status deterioration, which would not be affected by the patient's demographics, health status, or underlying neurocognitive deficits.
There were important limitations to this study. First, limited generalizability of these data may exist due to the single‐center setting and patient population. However, this initial study provides pilot data for further expansion into the potential broad applicability of the FAMTM to other patient populations and settings. Additionally, the cost of large‐scale implementation of the FAMTM is unknown and was beyond the scope of this pilot study. However, to reduce costs, the FAMTM technology could be integrated into existing hospital technology infrastructure. Finally, the scope of this study prevented a complete assessment of all validity measures or comparison to other mental status assessments such as the digit span or serial sevens tests. However, predictive and concurrent validity were assessed with comparison by discharge disposition, SPMSQ, and GCS scores.
In conclusion, this pilot study identifies the FAMTM application as a potentially clinically useful, novel, rapid, and feasible assessment tool of mental status in a general medicine inpatient setting.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Frank Zadravecz, MPH, for his support with this project.
Disclosures: This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIA 2T35AG029795‐07) and in part by career development awards granted to Dr. Churpek, Dr. Edelson, and Dr. Press by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080, K23 HL097157, and K23 HL118151, respectively). Dr. Churpek has received honoraria from Chest for invited speaking engagements. Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. In addition, Dr. Edelson has received research support from Philips Healthcare (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), and Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
- , . Altered mental status in older patients in the emergency department. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013;29(1):101–136.
- , , , , , . Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113(12):941–948.
- , , , , . Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , . Early recognition of delirium: review of the literature. J Clin Nurs. 2001;10(6):721–729.
- . A short portable mental status questionnaire for the assessment of organic brain deficit in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975;23(10):433–441.
- , , , , . The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit admission, and death. Resuscitation. 2013;84(4):465–470.
- , , , et al. Comparison of mental‐status scales for predicting mortality on the general wards. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):658–663.
- , . Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness: a practical scale. Lancet. 1974;304(7872):81–84.
- , , , . Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire as a Screening Test for Dementia and Delirium Among the Elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987;35(5):412–416.
- , , , et al. Effects of physician experience on costs and outcomes on an academic general medicine service: results of a trial of hospitalists. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(11):866–874.
- , , . Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , , , et al. Preliminary development of an ultrabrief two‐item bedside test for delirium. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):645–650.
- , , , , , . The association between an ultrabrief cognitive screening in older adults and hospital outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):651–657.
- , , , et al. Selecting optimal screening items for delirium: an application of item response theory. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:8.
- , , . Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
- , . Altered mental status in older patients in the emergency department. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013;29(1):101–136.
- , , , , , . Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113(12):941–948.
- , , , , . Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , . Early recognition of delirium: review of the literature. J Clin Nurs. 2001;10(6):721–729.
- . A short portable mental status questionnaire for the assessment of organic brain deficit in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975;23(10):433–441.
- , , , , . The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit admission, and death. Resuscitation. 2013;84(4):465–470.
- , , , et al. Comparison of mental‐status scales for predicting mortality on the general wards. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):658–663.
- , . Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness: a practical scale. Lancet. 1974;304(7872):81–84.
- , , , . Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire as a Screening Test for Dementia and Delirium Among the Elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987;35(5):412–416.
- , , , et al. Effects of physician experience on costs and outcomes on an academic general medicine service: results of a trial of hospitalists. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(11):866–874.
- , , . Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , , , et al. Preliminary development of an ultrabrief two‐item bedside test for delirium. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):645–650.
- , , , , , . The association between an ultrabrief cognitive screening in older adults and hospital outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(10):651–657.
- , , , et al. Selecting optimal screening items for delirium: an application of item response theory. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:8.
- , , . Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
Mental Status to Predict Mortality
Altered mental status (AMS), characterized by abnormal changes in a patient's arousal and/or cognition, is a significant predictor of hospital mortality.[1, 2, 3] Yet despite its prevalence[3, 4, 5] and importance, up to three‐quarters of AMS events go unrecognized by caregivers.[6, 7, 8] Acute changes in mental status, often caused by delirium in the hospitalized patient,[3] can present nonspecifically, making it difficult to detect and distinguish from other diagnoses such as depression or dementia.[7, 9] Further complicating the recognition of AMS, numerous and imprecise qualitative descriptors such as confused and alert and oriented are used in clinical practice to describe the mental status of patients.[10] Thus, more objective measures may result in improved detection of altered mental status and in earlier diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
In critically ill patients, several scales have been widely adopted for quantifying mental status. The Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale (RASS) was created to optimize sedation.[11] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was developed for head‐trauma patients[12] and is now a standardized assessment tool in intensive care units,[13] the emergency department,[14] and the prehospital setting.[15] In addition, a simplified scale, AVPU (Alert, responsive to Verbal stimuli, responsive to Painful stimuli, and Unresponsive) was initially used in the primary survey of trauma patients[16] but is now a common component of early‐warning scores and rapid response activation criteria, such as the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS).[17, 18] In fact, in a systematic review of 72 distinct early‐warning scores, 89% of the scores used AVPU as the measure of mentation.[17] However, the utility of these 3 scales is not well established in the general‐ward setting. Our aim was therefore to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in hospitalized general‐ward patients to provide insight into the accuracy of these different scores for clinical deterioration.
METHODS
Study Setting and Protocol
We conducted an observational cohort study of consecutive adult general‐ward admissions from July 2011 through January 2013 at a 500‐bed, urban US teaching hospital. During the study period, no early‐warning scoring systems were in place on the hospital wards. Rapid response teams responding to altered mental status would do so without specific thresholds for activation. During this period, nurses on the general floors were expected to record each patient's GCS and RASS score in the electronic health record (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI) as part of the routine patient assessment at least once every 12‐hour shift. AVPU assessments were extracted from the eye component of the GCS. The letter A was assigned to a GCS Eye score of 4 (opens eyes spontaneously), V to a score of 3 (opens eyes in response to voice), P to a score of 2 (opens eyes in response to painful stimuli), and U to a score of 1 (does not open eyes). To avoid comparison of mental‐status scores at different time points, only concurrent GCS and RASS scores, documented within 10 minutes of one another, were included in the analysis.
Location and time‐stamped GCS and RASS scores, demographics, and in‐hospital mortality data were obtained from the hospital's Clinical Research Data Warehouse, which is maintained by the Center for Research Informatics at The University of Chicago. The study protocol and data‐collection mechanisms were approved by The University of Chicago Institutional Review Board (#16995A).
Statistical Analysis
Baseline admission characteristics were described using proportions (%) and measures of central tendency (mean, standard deviations [SD]; median, interquartile ranges [IQR]). Patient severity of illness at first ward observation was calculated using the MEWS.[19] All mental‐status observations during a patient's ward stay were included in the analysis. Odds ratios for 24‐hour mortality following an abnormal mental‐status score were calculated using generalized estimating equations, with an exchangeable correlation structure to account for the correlation of scores within the same patient, as more than 1 abnormal mental‐status score may have been documented within the 24 hours preceding death. Spearman's rank correlation coefficients () were used to estimate the correlation among AVPU, GCS, and RASS scores.
The predictive accuracies of AVPU, GCS, RASS, and the subscales of GCS were compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), with mortality within 24 hours of a mental‐status observation as the primary outcome and the mental‐status score as the predictor variable. Although AUCs are typically used as a measure of discriminative ability, this study used AUCs to summarize both sensitivity and specificity across a range of cutoffs, providing an overall measure of predictive accuracies across mental‐status scales. To estimate AUCs, the AVPU, GCS, and GCS subscales were entered into a logistic regression model as ordinal variables, whereas RASS was entered as a nominal variable due to its positive and negative components, and predicted probabilities were calculated. In addition, a combined model was fit where GCS and RASS were classified as categorical independent variables. AUCs were then calculated by utilizing the predicted probabilities from each logistic regression model using the trapezoidal rule.[20] A sensitivity analysis was performed to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model using 10‐fold cross‐validation.
Predefined subgroup analyses were performed that compared the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting 24‐hour mortality in patients above and below the median age of the study population, and between patients who underwent surgery during their admission or not (surgical vs medical). All tests of significance used a 2‐sided P value <0.05. All data analysis was performed using Stata version 13.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
During the study period, 313,577 complete GCS and 305,177 RASS scores were recorded in the electronic health record by nursing staff. A total of 26,806 (17,603 GCS and 9203 RASS) observations were excluded due to nonsimultaneous measurement of the other score, resulting in 295,974 paired mental‐status observations. These observations were obtained from 26,873 admissions in 17,660 unique patients, with a median MEWS at ward admission of 1 (IQR 11). The mean patient age was 57 years (SD 17), and 23% were surgical patients (Table 1). Patients spent a median 63.9 hours (IQR 26.7118.6) on the wards per admission and contributed a median of 3 paired observations (IQR 24) per day, with 91% of patients having at least 2 observations per day. A total of 417 (1.6%) general‐ward admissions resulted in death during the hospitalization, with 354 mental‐status observations occurring within 24 hours of a death. In addition, 26,618 (99.9%) admissions had at least 1 paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay.
| |
| Total no. of admissions | 26,873 |
| Total no. of unique patients | 17,660 |
| Age, y, mean (SD) | 57 (17) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 14,293 (53) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 10,516 (39) |
| Black | 12,580 (47) |
| Other/unknown | 3,777 (14) |
| Admission MEWS, median (IQR) | 1 (11) |
| Days on ward, median (IQR) | 5 (310) |
| Observations per person, per day, median (IQR) | 3 (24) |
| Underwent surgery during hospitalization, n (%) | 6,141 (23) |
| Deaths, n (%) | 417 (1.6) |
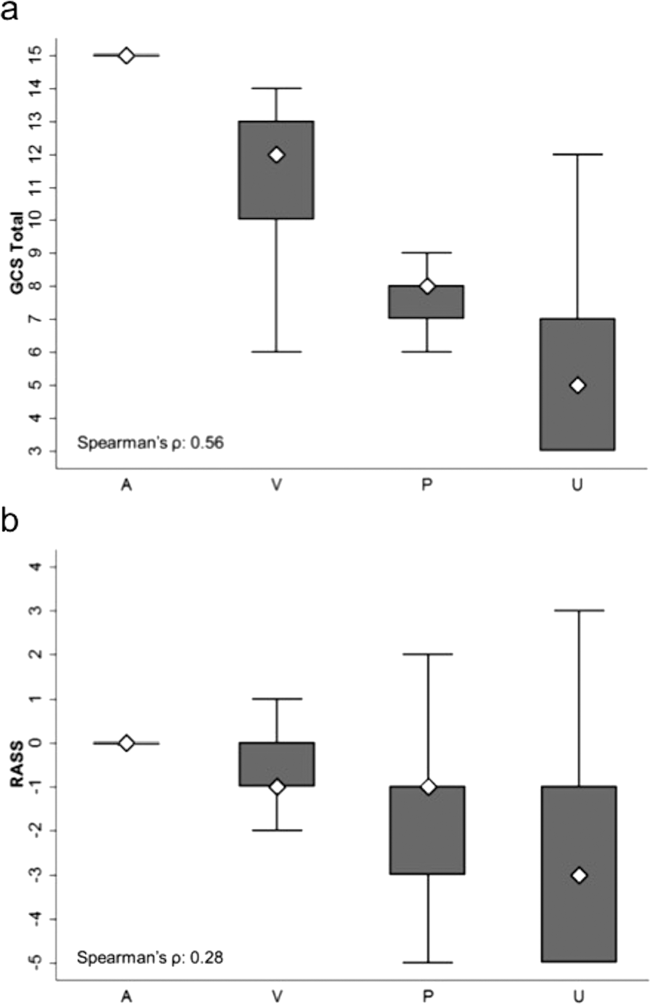
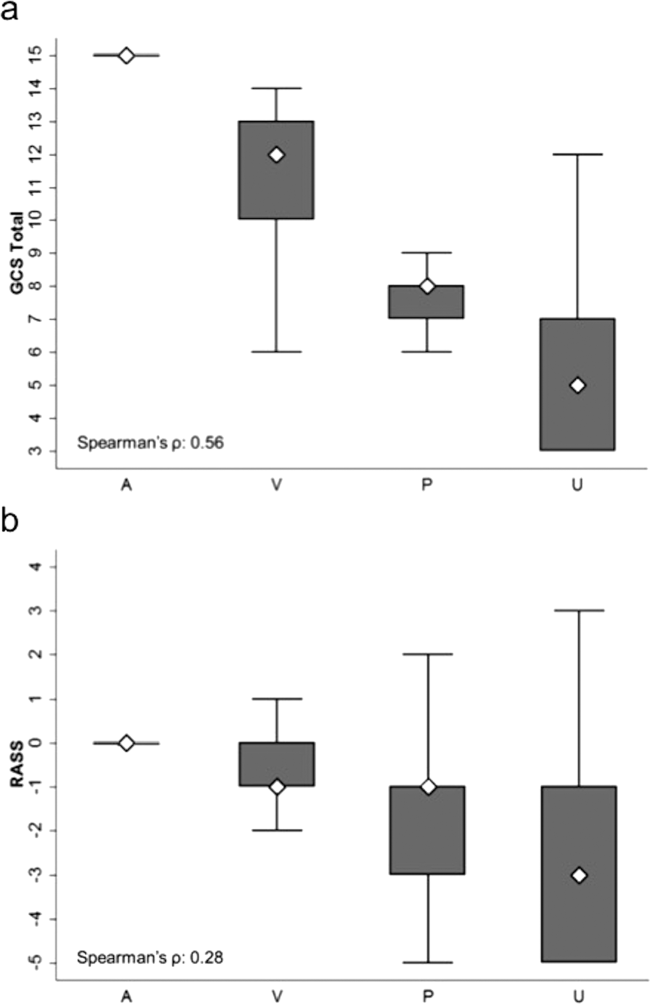
AVPU was moderately correlated with GCS (Spearman's =0.56) (Figure 1a) and weakly correlated with RASS (Spearman's =0.28) (Figure 1b). GCS scores were also weakly correlated to RASS (Spearman's =0.13, P<0.001). Notably, AVPU mapped to distinct levels of GCS, with Alert associated with a median GCS total score of 15, Voice a score of 12, Pain a score of 8, and Unresponsive a score of 5. Abnormal mental‐status scores on any scale were associated with significantly higher odds of death within 24 hours than normal mental‐status scores (Table 2). This association was consistent within the 3 subscales of GCS and for scores in both the sedation (<0) and agitation (>0) ranges of RASS.
| Mental‐status Score | Observations, n (%) | Odds Ratio for Mortality (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| ||
| GCS Eye (AVPU) | ||
| 4 (alert) | 289,857 (98) | Reference |
| <4 (not alert) | 6,117 (2) | 33.8 (23.947.9) |
| GCS Verbal | ||
| 5 | 277,862 (94) | Reference |
| 4 | 11,258 (4) | 4.7 (2.87.9) |
| <4 | 6,854 (2) | 52.7 (38.073.2) |
| GCS Motor | ||
| 6 | 287,441 (97) | Reference |
| <6 | 8,533 (3) | 41.8 (30.756.9) |
| GCS total | ||
| 15 | 276,042 (93) | Reference |
| 13, 14 | 12,437 (4) | 5.2 (3.38.3) |
| <13 | 7,495 (3) | 55.5 (40.077.1) |
| RASS | ||
| >0 | 6,867 (2) | 8.5 (5.613.0) |
| 0 | 275,708 (93) | Reference |
| <0 | 13,339 (5) | 25.8 (19.234.6) |
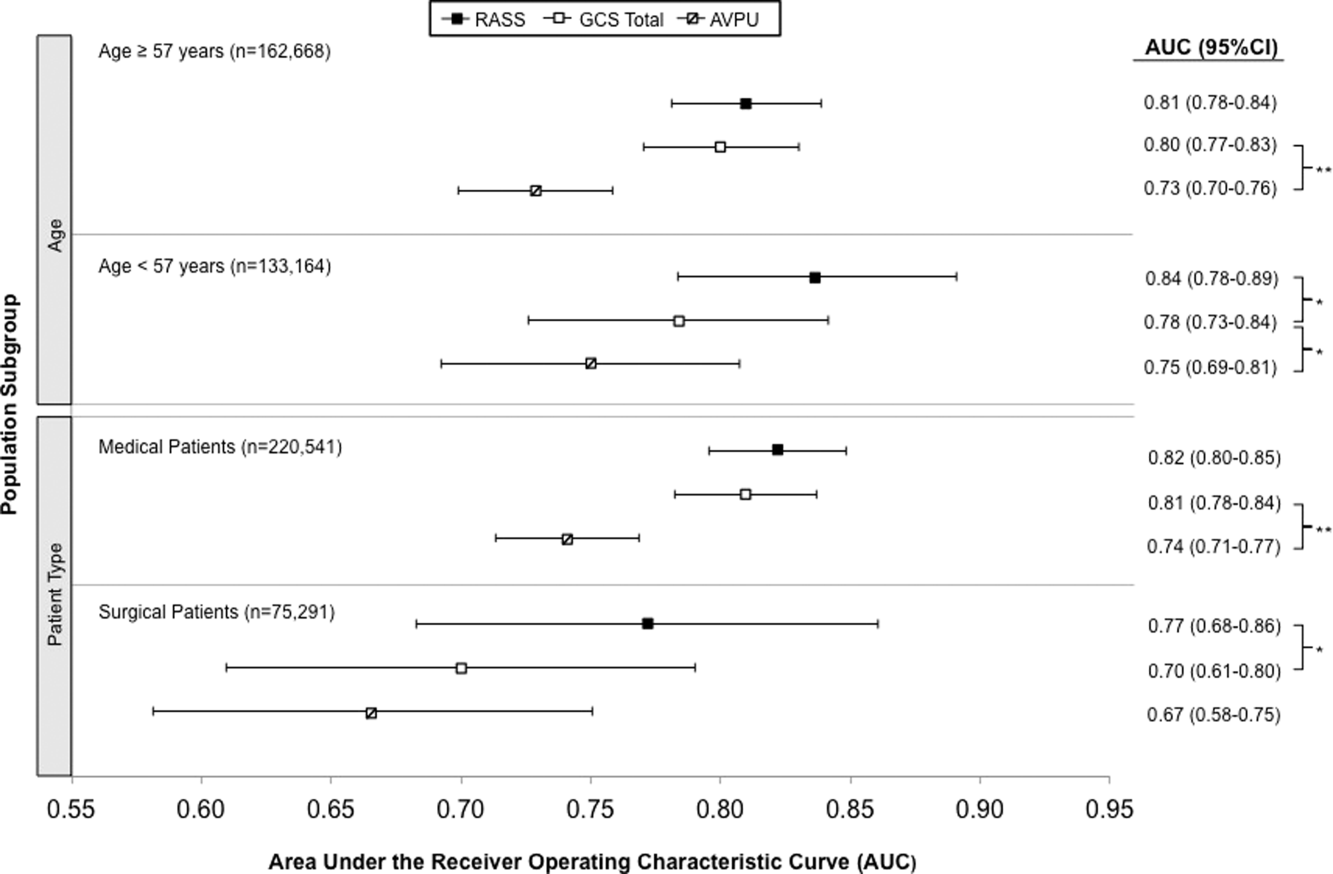
AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality (AUC 0.73 [95% confidence interval {CI}: 0.710.76]), whereas simultaneous use of GCS and RASS was the most accurate predictor (AUC 0.85 [95% CI: 0.820.87] (Figure 2). The accuracies of GCS and RASS were not significantly different from one another in the total study population (AUC 0.80 [95% CI: 0.770.83] and 0.82 [0.790.84], respectively, P=0.13). Ten‐fold cross‐validation to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model resulted in a lower AUC (0.78 [95% CI: 0.750.81]) for RASS as a predictor of 24‐hour mortality. Subgroup analysis indicated that RASS was more accurate than GCS in younger patients (<57 years old) and in surgical patients (Figure 3).
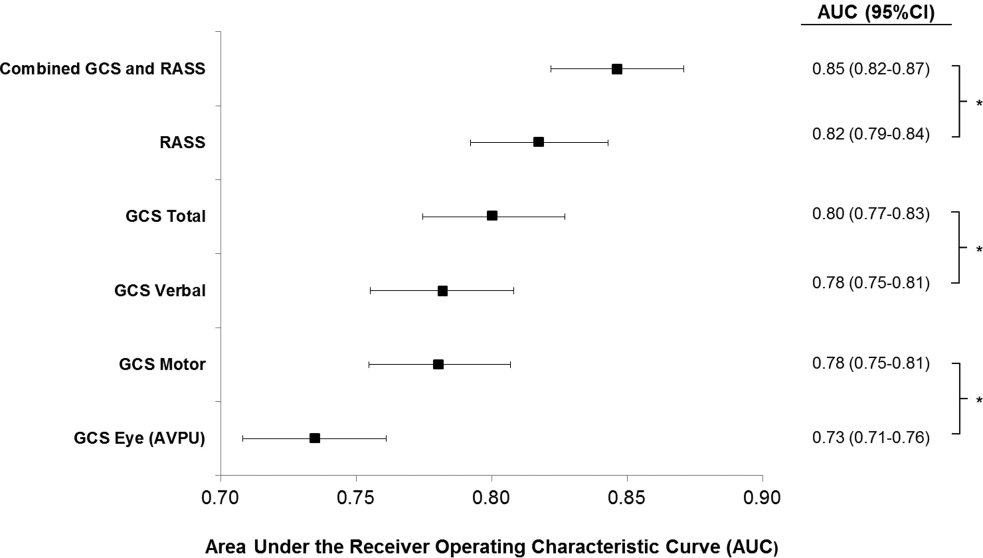
Removal of the 255 admissions missing a paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay resulted in no change in the AUC values. A sensitivity analysis for prediction of a combined secondary outcome of 24‐hour intensive care unit ICU transfer or cardiac arrest yielded lower AUCs for each mental‐status scale, with no change in the association among scales.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this study is the first to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in the general‐ward setting. Similar to McNarry and Goldhill, we demonstrated that AVPU scores mapped to distinct levels of GCS. Although our study reports the same median GCS scores of 15 and 8 for AVPU levels of Alert and Pain, respectively, we indicate slightly lower corresponding median GCS scores for AVPU scores of Voice (12 vs 13) and Unresponsive (5 vs 6) than their previous work.[21] We found that AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality within 24 hours of an observation, and the combination of GCS and RASS was the most accurate. RASS was at least as accurate a predictor for 24‐hour mortality in comparison to GCS total in the overall study population. However, the RASS score was the most accurate individual score in surgical and younger patients. These findings suggest that changing from the commonly used AVPU scale to the RASS and/or GCS would improve the prognostic ability of mental‐status assessments on the general wards.
Buist and colleagues have previously demonstrated altered mental status to be one of the strongest predictors of death on the wards. In that study, a GCS score of 3 and a decrease in GCS score by more than 2 points were independently associated with mortality (odds ratio 6.1 [95% CI: 3.111.8] and 5.5 [95% CI: 2.611.9], respectively).[22] We have also previously shown that after adjusting for vital signs, being unresponsive to pain was associated with a 4.5‐fold increase in the odds of death within 24 hours,[23]whereas Subbe and colleagues showed a relative risk ratio of 5.2 (95% CI: 1.518.1) for the combined endpoint of cardiac arrest, death at 60 days, or admission to the intensive care/high dependency unit.[19] In the current study, the magnitude of these associations was even stronger, with a GCS score <13 correlating with a 55‐fold increase in the odds of death, compared to a normal GCS, and not being alert being associated with a 33.8‐fold increase in the odds of death. This difference in magnitude is likely a product of the univariate nature of the current analysis, compared to both the Buist et al. and Churpek et al. studies, which adjusted for vital signs, thereby lessening the impact of any single predictor. Because this study was designed to compare mental‐status variables to one another for future model inclusion, and all the analyses were paired, confounding by additional predictors of death was not a concern.
One of the potential strengths of RASS over GCS and AVPU is its ability to measure agitation levels, in addition to depressed mentation, a feature that has been shown to be present in up to 60% of delirium episodes.[24] This may also explain why RASS was the most accurate predictor of mortality in our subset of younger patients and surgical patients, because hyperactive delirium is more common in younger and healthier patients, which surgical patients tend to be as compared to medical patients.[25, 26] In this study, we found negative RASS scores portending a worse prognosis than positive ones, which supports previous findings that hypoactive delirium had a higher association with mortality than hyperactive delirium at 6 months (hazard ratio 1.90 vs 1.37) and at 1 year (hazard ratio 1.60 vs 1.30) in elderly patients at postacute‐care facilities in 2 separate studies.[27, 28] However, a study of patients undergoing surgery for hip fracture found that patients with hyperactive delirium were more likely to die or be placed in a nursing home at 1 month follow‐up when compared to patients with purely hypoactive delirium (79% vs 32%, P=0.003).[29]
We found the assessment of RASS and GCS by ward nurses to be highly feasible. During the study period, nurses assessed mental status with the GCS and RASS scales at least once per 12‐hour shift in 91% of patients. GCS has been shown to be reliably and accurately recorded by experienced nurses (reliability coefficient=0.944 with 96.4% agreement with expert ratings).[30] RASS can take <30 seconds to administer, and in previous studies of the ICU setting has been shown to have over 94% nurse compliance for administration,[31] and good inter‐rater reliability (weighted kappa 0.66 and 0.89, respectively).[31, 32] Further, in a prior survey of 55 critical care nurses, 82% agreed that RASS was easy to score and clinically relevant.[31]
This study has several limitations. First, it was conducted in a single academic institution, which may limit generalizability to other hospitals. Second, baseline cognition and comorbidities were not available in the dataset, so we were unable to conduct additional subgroup analyses by these categories. However, we used age and hospital admission type as proxies. Third, the AVPU scores in this study were extracted from the Eye subset of the GCS scale, as AVPU was not directly assessed on our wards during the study period. Clinical assessment of mental status on the AVPU scale notes the presence of any active patient response (eg, eye opening, grunting, moaning, movement) to increasingly noxious stimuli. As such, our adaptation of AVPU using only eye‐opening criteria may underestimate the true number of patients correctly classified as alert, or responding to vocal/painful stimuli. However, a sensitivity analysis comparing directly assessed AVPU during a 3‐year period prior to the study implementation at our institution, and AVPU derived from the GCS Eye subscale for the study period, indicated no difference in predictive value for 24‐hour mortality. Fourth, we did not perform trend analyses for change from baseline mental status or evolution of AMS, which may more accurately predict 24‐hour mortality than discrete mental‐status observations. Finally, the 3 scales we compared differ in length, which may bias the AUC against AVPU, a 4‐point scale with a trapezoidal ROC curve compared to the smoother curve generated by the 15‐point GCS scale, for example. However, the lack of discrimination of the AVPU is the likely source of its lesser accuracy.
CONCLUSION
In the general‐ward setting, routine collection of GCS and RASS is feasible, and both are significantly more accurate for predicting mortality than the more commonly used AVPU scale. In addition, the combination of GCS and RASS has greater accuracy than any of the 3 individual scales. RASS may be particularly beneficial in the assessment of younger and/or surgical patients. Routine documentation and tracking of GCS and/or RASS by nurses may improve the detection of clinical deterioration in general‐ward patients. In addition, future early‐warning scores may benefit from the inclusion of GCS and/or RASS in lieu of AVPU.
Disclosures
Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080). Dr. Edelson has received research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K23 HL097157), Philips (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and Early Sense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
- , , , et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1753–1762.
- , , , , , Delirium in hospitalized older persons: outcomes and predictors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42(8):809–815.
- , , Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in‐patients: a systematic literature review. Age Ageing. 2006;35(4):350–364.
- , , , et al. Delirium. The occurrence and persistence of symptoms among elderly hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(2):334–340.
- , , Postoperative delirium. A review of 80 primary data‐collection studies. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(5):461–465.
- , , , , Nurses' recognition of delirium and its symptoms: comparison of nurse and researcher ratings. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(20):2467–2473.
- , , The misdiagnosis of delirium. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):433–439.
- , , , et al. Current opinions regarding the importance, diagnosis, and management of delirium in the intensive care unit: a survey of 912 healthcare professionals. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(1):106–112.
- , Misdiagnosing delirium as depression in medically ill elderly patients. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(22):2459–2464.
- Doctors and nurses use of the word confused. Br J Psychiatry. 1984;145:441–443.
- , , , et al. The Richmond Agitation‐Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–1344.
- , Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1976;34(1–4):45–55.
- , , , , Glasgow Coma Scale score in the evaluation of outcome in the intensive care unit: findings from the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III study. Crit Care Med. 1993;21(10):1459–1465.
- , , Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
- , , , Reliability of the Glasgow Coma Scale when used by emergency physicians and paramedics. J Trauma. 1993;34(1):46–48.
- , ; American College of Surgeons. Committee on Trauma. Advanced Trauma Life Support Program For Physicians: ATLS. 5th ed. Chicago, IL: American College of Surgeons; 1993.
- , , , Review and performance evaluation of aggregate weighted 'track and trigger' systems. Resuscitation. 2008;77(2):170–179.
- , , , , A review, and performance evaluation, of single‐parameter “track and trigger” systems. Resuscitation. 2008;79(1):11–21.
- , , , Validation of a modified Early Warning score in medical admissions. QJM. 2001;94(10):521–526.
- , , Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , Simple bedside assessment of level of consciousness: comparison of two simple assessment scales with the Glascow Coma Scale. Anaesthesia. 2004;59(1):34–37.
- , , , , Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , Predicting clinical deterioration in the hospital: the impact of outcome selection. Resuscitation. 2013;84(5):564–568.
- , , , et al. Delirium and its motoric subtypes: a study of 614 critically ill patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(3):479–484.
- , , , et al. Risk factors for delirium after major trauma. Am J Surg. 2008;196(6):864–869.
- , , , , Relationship between symptoms and motoric subtype of delirium. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2000;12(1):51–56.
- , , , et al. Phenomenological subtypes of delirium in older persons: patterns, prevalence, and prognosis. Psychosomatics. 2009;50(3):248–254.
- , , , Association between psychomotor activity delirium subtypes and mortality among newly admitted post‐acute facility patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62(2):174–179.
- , , , Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850–857.
- , Reliability and accuracy of the Glasgow Coma Scale with experienced and inexperienced users. Lancet. 1991;337(8740):535–538.
- , , , et al. Large‐scale implementation of sedation and delirium monitoring in the intensive care unit: a report from two medical centers. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(6):1199–1205.
- , , , et al. Delirium and sedation recognition using validated instruments: reliability of bedside intensive care unit nursing assessments from 2007 to 2010. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(suppl 2):S249–S255.
Altered mental status (AMS), characterized by abnormal changes in a patient's arousal and/or cognition, is a significant predictor of hospital mortality.[1, 2, 3] Yet despite its prevalence[3, 4, 5] and importance, up to three‐quarters of AMS events go unrecognized by caregivers.[6, 7, 8] Acute changes in mental status, often caused by delirium in the hospitalized patient,[3] can present nonspecifically, making it difficult to detect and distinguish from other diagnoses such as depression or dementia.[7, 9] Further complicating the recognition of AMS, numerous and imprecise qualitative descriptors such as confused and alert and oriented are used in clinical practice to describe the mental status of patients.[10] Thus, more objective measures may result in improved detection of altered mental status and in earlier diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
In critically ill patients, several scales have been widely adopted for quantifying mental status. The Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale (RASS) was created to optimize sedation.[11] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was developed for head‐trauma patients[12] and is now a standardized assessment tool in intensive care units,[13] the emergency department,[14] and the prehospital setting.[15] In addition, a simplified scale, AVPU (Alert, responsive to Verbal stimuli, responsive to Painful stimuli, and Unresponsive) was initially used in the primary survey of trauma patients[16] but is now a common component of early‐warning scores and rapid response activation criteria, such as the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS).[17, 18] In fact, in a systematic review of 72 distinct early‐warning scores, 89% of the scores used AVPU as the measure of mentation.[17] However, the utility of these 3 scales is not well established in the general‐ward setting. Our aim was therefore to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in hospitalized general‐ward patients to provide insight into the accuracy of these different scores for clinical deterioration.
METHODS
Study Setting and Protocol
We conducted an observational cohort study of consecutive adult general‐ward admissions from July 2011 through January 2013 at a 500‐bed, urban US teaching hospital. During the study period, no early‐warning scoring systems were in place on the hospital wards. Rapid response teams responding to altered mental status would do so without specific thresholds for activation. During this period, nurses on the general floors were expected to record each patient's GCS and RASS score in the electronic health record (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI) as part of the routine patient assessment at least once every 12‐hour shift. AVPU assessments were extracted from the eye component of the GCS. The letter A was assigned to a GCS Eye score of 4 (opens eyes spontaneously), V to a score of 3 (opens eyes in response to voice), P to a score of 2 (opens eyes in response to painful stimuli), and U to a score of 1 (does not open eyes). To avoid comparison of mental‐status scores at different time points, only concurrent GCS and RASS scores, documented within 10 minutes of one another, were included in the analysis.
Location and time‐stamped GCS and RASS scores, demographics, and in‐hospital mortality data were obtained from the hospital's Clinical Research Data Warehouse, which is maintained by the Center for Research Informatics at The University of Chicago. The study protocol and data‐collection mechanisms were approved by The University of Chicago Institutional Review Board (#16995A).
Statistical Analysis
Baseline admission characteristics were described using proportions (%) and measures of central tendency (mean, standard deviations [SD]; median, interquartile ranges [IQR]). Patient severity of illness at first ward observation was calculated using the MEWS.[19] All mental‐status observations during a patient's ward stay were included in the analysis. Odds ratios for 24‐hour mortality following an abnormal mental‐status score were calculated using generalized estimating equations, with an exchangeable correlation structure to account for the correlation of scores within the same patient, as more than 1 abnormal mental‐status score may have been documented within the 24 hours preceding death. Spearman's rank correlation coefficients () were used to estimate the correlation among AVPU, GCS, and RASS scores.
The predictive accuracies of AVPU, GCS, RASS, and the subscales of GCS were compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), with mortality within 24 hours of a mental‐status observation as the primary outcome and the mental‐status score as the predictor variable. Although AUCs are typically used as a measure of discriminative ability, this study used AUCs to summarize both sensitivity and specificity across a range of cutoffs, providing an overall measure of predictive accuracies across mental‐status scales. To estimate AUCs, the AVPU, GCS, and GCS subscales were entered into a logistic regression model as ordinal variables, whereas RASS was entered as a nominal variable due to its positive and negative components, and predicted probabilities were calculated. In addition, a combined model was fit where GCS and RASS were classified as categorical independent variables. AUCs were then calculated by utilizing the predicted probabilities from each logistic regression model using the trapezoidal rule.[20] A sensitivity analysis was performed to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model using 10‐fold cross‐validation.
Predefined subgroup analyses were performed that compared the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting 24‐hour mortality in patients above and below the median age of the study population, and between patients who underwent surgery during their admission or not (surgical vs medical). All tests of significance used a 2‐sided P value <0.05. All data analysis was performed using Stata version 13.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
During the study period, 313,577 complete GCS and 305,177 RASS scores were recorded in the electronic health record by nursing staff. A total of 26,806 (17,603 GCS and 9203 RASS) observations were excluded due to nonsimultaneous measurement of the other score, resulting in 295,974 paired mental‐status observations. These observations were obtained from 26,873 admissions in 17,660 unique patients, with a median MEWS at ward admission of 1 (IQR 11). The mean patient age was 57 years (SD 17), and 23% were surgical patients (Table 1). Patients spent a median 63.9 hours (IQR 26.7118.6) on the wards per admission and contributed a median of 3 paired observations (IQR 24) per day, with 91% of patients having at least 2 observations per day. A total of 417 (1.6%) general‐ward admissions resulted in death during the hospitalization, with 354 mental‐status observations occurring within 24 hours of a death. In addition, 26,618 (99.9%) admissions had at least 1 paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay.
| |
| Total no. of admissions | 26,873 |
| Total no. of unique patients | 17,660 |
| Age, y, mean (SD) | 57 (17) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 14,293 (53) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 10,516 (39) |
| Black | 12,580 (47) |
| Other/unknown | 3,777 (14) |
| Admission MEWS, median (IQR) | 1 (11) |
| Days on ward, median (IQR) | 5 (310) |
| Observations per person, per day, median (IQR) | 3 (24) |
| Underwent surgery during hospitalization, n (%) | 6,141 (23) |
| Deaths, n (%) | 417 (1.6) |
AVPU was moderately correlated with GCS (Spearman's =0.56) (Figure 1a) and weakly correlated with RASS (Spearman's =0.28) (Figure 1b). GCS scores were also weakly correlated to RASS (Spearman's =0.13, P<0.001). Notably, AVPU mapped to distinct levels of GCS, with Alert associated with a median GCS total score of 15, Voice a score of 12, Pain a score of 8, and Unresponsive a score of 5. Abnormal mental‐status scores on any scale were associated with significantly higher odds of death within 24 hours than normal mental‐status scores (Table 2). This association was consistent within the 3 subscales of GCS and for scores in both the sedation (<0) and agitation (>0) ranges of RASS.

| Mental‐status Score | Observations, n (%) | Odds Ratio for Mortality (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| ||
| GCS Eye (AVPU) | ||
| 4 (alert) | 289,857 (98) | Reference |
| <4 (not alert) | 6,117 (2) | 33.8 (23.947.9) |
| GCS Verbal | ||
| 5 | 277,862 (94) | Reference |
| 4 | 11,258 (4) | 4.7 (2.87.9) |
| <4 | 6,854 (2) | 52.7 (38.073.2) |
| GCS Motor | ||
| 6 | 287,441 (97) | Reference |
| <6 | 8,533 (3) | 41.8 (30.756.9) |
| GCS total | ||
| 15 | 276,042 (93) | Reference |
| 13, 14 | 12,437 (4) | 5.2 (3.38.3) |
| <13 | 7,495 (3) | 55.5 (40.077.1) |
| RASS | ||
| >0 | 6,867 (2) | 8.5 (5.613.0) |
| 0 | 275,708 (93) | Reference |
| <0 | 13,339 (5) | 25.8 (19.234.6) |
AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality (AUC 0.73 [95% confidence interval {CI}: 0.710.76]), whereas simultaneous use of GCS and RASS was the most accurate predictor (AUC 0.85 [95% CI: 0.820.87] (Figure 2). The accuracies of GCS and RASS were not significantly different from one another in the total study population (AUC 0.80 [95% CI: 0.770.83] and 0.82 [0.790.84], respectively, P=0.13). Ten‐fold cross‐validation to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model resulted in a lower AUC (0.78 [95% CI: 0.750.81]) for RASS as a predictor of 24‐hour mortality. Subgroup analysis indicated that RASS was more accurate than GCS in younger patients (<57 years old) and in surgical patients (Figure 3).


Removal of the 255 admissions missing a paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay resulted in no change in the AUC values. A sensitivity analysis for prediction of a combined secondary outcome of 24‐hour intensive care unit ICU transfer or cardiac arrest yielded lower AUCs for each mental‐status scale, with no change in the association among scales.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this study is the first to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in the general‐ward setting. Similar to McNarry and Goldhill, we demonstrated that AVPU scores mapped to distinct levels of GCS. Although our study reports the same median GCS scores of 15 and 8 for AVPU levels of Alert and Pain, respectively, we indicate slightly lower corresponding median GCS scores for AVPU scores of Voice (12 vs 13) and Unresponsive (5 vs 6) than their previous work.[21] We found that AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality within 24 hours of an observation, and the combination of GCS and RASS was the most accurate. RASS was at least as accurate a predictor for 24‐hour mortality in comparison to GCS total in the overall study population. However, the RASS score was the most accurate individual score in surgical and younger patients. These findings suggest that changing from the commonly used AVPU scale to the RASS and/or GCS would improve the prognostic ability of mental‐status assessments on the general wards.
Buist and colleagues have previously demonstrated altered mental status to be one of the strongest predictors of death on the wards. In that study, a GCS score of 3 and a decrease in GCS score by more than 2 points were independently associated with mortality (odds ratio 6.1 [95% CI: 3.111.8] and 5.5 [95% CI: 2.611.9], respectively).[22] We have also previously shown that after adjusting for vital signs, being unresponsive to pain was associated with a 4.5‐fold increase in the odds of death within 24 hours,[23]whereas Subbe and colleagues showed a relative risk ratio of 5.2 (95% CI: 1.518.1) for the combined endpoint of cardiac arrest, death at 60 days, or admission to the intensive care/high dependency unit.[19] In the current study, the magnitude of these associations was even stronger, with a GCS score <13 correlating with a 55‐fold increase in the odds of death, compared to a normal GCS, and not being alert being associated with a 33.8‐fold increase in the odds of death. This difference in magnitude is likely a product of the univariate nature of the current analysis, compared to both the Buist et al. and Churpek et al. studies, which adjusted for vital signs, thereby lessening the impact of any single predictor. Because this study was designed to compare mental‐status variables to one another for future model inclusion, and all the analyses were paired, confounding by additional predictors of death was not a concern.
One of the potential strengths of RASS over GCS and AVPU is its ability to measure agitation levels, in addition to depressed mentation, a feature that has been shown to be present in up to 60% of delirium episodes.[24] This may also explain why RASS was the most accurate predictor of mortality in our subset of younger patients and surgical patients, because hyperactive delirium is more common in younger and healthier patients, which surgical patients tend to be as compared to medical patients.[25, 26] In this study, we found negative RASS scores portending a worse prognosis than positive ones, which supports previous findings that hypoactive delirium had a higher association with mortality than hyperactive delirium at 6 months (hazard ratio 1.90 vs 1.37) and at 1 year (hazard ratio 1.60 vs 1.30) in elderly patients at postacute‐care facilities in 2 separate studies.[27, 28] However, a study of patients undergoing surgery for hip fracture found that patients with hyperactive delirium were more likely to die or be placed in a nursing home at 1 month follow‐up when compared to patients with purely hypoactive delirium (79% vs 32%, P=0.003).[29]
We found the assessment of RASS and GCS by ward nurses to be highly feasible. During the study period, nurses assessed mental status with the GCS and RASS scales at least once per 12‐hour shift in 91% of patients. GCS has been shown to be reliably and accurately recorded by experienced nurses (reliability coefficient=0.944 with 96.4% agreement with expert ratings).[30] RASS can take <30 seconds to administer, and in previous studies of the ICU setting has been shown to have over 94% nurse compliance for administration,[31] and good inter‐rater reliability (weighted kappa 0.66 and 0.89, respectively).[31, 32] Further, in a prior survey of 55 critical care nurses, 82% agreed that RASS was easy to score and clinically relevant.[31]
This study has several limitations. First, it was conducted in a single academic institution, which may limit generalizability to other hospitals. Second, baseline cognition and comorbidities were not available in the dataset, so we were unable to conduct additional subgroup analyses by these categories. However, we used age and hospital admission type as proxies. Third, the AVPU scores in this study were extracted from the Eye subset of the GCS scale, as AVPU was not directly assessed on our wards during the study period. Clinical assessment of mental status on the AVPU scale notes the presence of any active patient response (eg, eye opening, grunting, moaning, movement) to increasingly noxious stimuli. As such, our adaptation of AVPU using only eye‐opening criteria may underestimate the true number of patients correctly classified as alert, or responding to vocal/painful stimuli. However, a sensitivity analysis comparing directly assessed AVPU during a 3‐year period prior to the study implementation at our institution, and AVPU derived from the GCS Eye subscale for the study period, indicated no difference in predictive value for 24‐hour mortality. Fourth, we did not perform trend analyses for change from baseline mental status or evolution of AMS, which may more accurately predict 24‐hour mortality than discrete mental‐status observations. Finally, the 3 scales we compared differ in length, which may bias the AUC against AVPU, a 4‐point scale with a trapezoidal ROC curve compared to the smoother curve generated by the 15‐point GCS scale, for example. However, the lack of discrimination of the AVPU is the likely source of its lesser accuracy.
CONCLUSION
In the general‐ward setting, routine collection of GCS and RASS is feasible, and both are significantly more accurate for predicting mortality than the more commonly used AVPU scale. In addition, the combination of GCS and RASS has greater accuracy than any of the 3 individual scales. RASS may be particularly beneficial in the assessment of younger and/or surgical patients. Routine documentation and tracking of GCS and/or RASS by nurses may improve the detection of clinical deterioration in general‐ward patients. In addition, future early‐warning scores may benefit from the inclusion of GCS and/or RASS in lieu of AVPU.
Disclosures
Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080). Dr. Edelson has received research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K23 HL097157), Philips (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and Early Sense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Altered mental status (AMS), characterized by abnormal changes in a patient's arousal and/or cognition, is a significant predictor of hospital mortality.[1, 2, 3] Yet despite its prevalence[3, 4, 5] and importance, up to three‐quarters of AMS events go unrecognized by caregivers.[6, 7, 8] Acute changes in mental status, often caused by delirium in the hospitalized patient,[3] can present nonspecifically, making it difficult to detect and distinguish from other diagnoses such as depression or dementia.[7, 9] Further complicating the recognition of AMS, numerous and imprecise qualitative descriptors such as confused and alert and oriented are used in clinical practice to describe the mental status of patients.[10] Thus, more objective measures may result in improved detection of altered mental status and in earlier diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
In critically ill patients, several scales have been widely adopted for quantifying mental status. The Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale (RASS) was created to optimize sedation.[11] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was developed for head‐trauma patients[12] and is now a standardized assessment tool in intensive care units,[13] the emergency department,[14] and the prehospital setting.[15] In addition, a simplified scale, AVPU (Alert, responsive to Verbal stimuli, responsive to Painful stimuli, and Unresponsive) was initially used in the primary survey of trauma patients[16] but is now a common component of early‐warning scores and rapid response activation criteria, such as the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS).[17, 18] In fact, in a systematic review of 72 distinct early‐warning scores, 89% of the scores used AVPU as the measure of mentation.[17] However, the utility of these 3 scales is not well established in the general‐ward setting. Our aim was therefore to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in hospitalized general‐ward patients to provide insight into the accuracy of these different scores for clinical deterioration.
METHODS
Study Setting and Protocol
We conducted an observational cohort study of consecutive adult general‐ward admissions from July 2011 through January 2013 at a 500‐bed, urban US teaching hospital. During the study period, no early‐warning scoring systems were in place on the hospital wards. Rapid response teams responding to altered mental status would do so without specific thresholds for activation. During this period, nurses on the general floors were expected to record each patient's GCS and RASS score in the electronic health record (EPIC Systems Corp., Verona, WI) as part of the routine patient assessment at least once every 12‐hour shift. AVPU assessments were extracted from the eye component of the GCS. The letter A was assigned to a GCS Eye score of 4 (opens eyes spontaneously), V to a score of 3 (opens eyes in response to voice), P to a score of 2 (opens eyes in response to painful stimuli), and U to a score of 1 (does not open eyes). To avoid comparison of mental‐status scores at different time points, only concurrent GCS and RASS scores, documented within 10 minutes of one another, were included in the analysis.
Location and time‐stamped GCS and RASS scores, demographics, and in‐hospital mortality data were obtained from the hospital's Clinical Research Data Warehouse, which is maintained by the Center for Research Informatics at The University of Chicago. The study protocol and data‐collection mechanisms were approved by The University of Chicago Institutional Review Board (#16995A).
Statistical Analysis
Baseline admission characteristics were described using proportions (%) and measures of central tendency (mean, standard deviations [SD]; median, interquartile ranges [IQR]). Patient severity of illness at first ward observation was calculated using the MEWS.[19] All mental‐status observations during a patient's ward stay were included in the analysis. Odds ratios for 24‐hour mortality following an abnormal mental‐status score were calculated using generalized estimating equations, with an exchangeable correlation structure to account for the correlation of scores within the same patient, as more than 1 abnormal mental‐status score may have been documented within the 24 hours preceding death. Spearman's rank correlation coefficients () were used to estimate the correlation among AVPU, GCS, and RASS scores.
The predictive accuracies of AVPU, GCS, RASS, and the subscales of GCS were compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), with mortality within 24 hours of a mental‐status observation as the primary outcome and the mental‐status score as the predictor variable. Although AUCs are typically used as a measure of discriminative ability, this study used AUCs to summarize both sensitivity and specificity across a range of cutoffs, providing an overall measure of predictive accuracies across mental‐status scales. To estimate AUCs, the AVPU, GCS, and GCS subscales were entered into a logistic regression model as ordinal variables, whereas RASS was entered as a nominal variable due to its positive and negative components, and predicted probabilities were calculated. In addition, a combined model was fit where GCS and RASS were classified as categorical independent variables. AUCs were then calculated by utilizing the predicted probabilities from each logistic regression model using the trapezoidal rule.[20] A sensitivity analysis was performed to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model using 10‐fold cross‐validation.
Predefined subgroup analyses were performed that compared the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting 24‐hour mortality in patients above and below the median age of the study population, and between patients who underwent surgery during their admission or not (surgical vs medical). All tests of significance used a 2‐sided P value <0.05. All data analysis was performed using Stata version 13.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
RESULTS
During the study period, 313,577 complete GCS and 305,177 RASS scores were recorded in the electronic health record by nursing staff. A total of 26,806 (17,603 GCS and 9203 RASS) observations were excluded due to nonsimultaneous measurement of the other score, resulting in 295,974 paired mental‐status observations. These observations were obtained from 26,873 admissions in 17,660 unique patients, with a median MEWS at ward admission of 1 (IQR 11). The mean patient age was 57 years (SD 17), and 23% were surgical patients (Table 1). Patients spent a median 63.9 hours (IQR 26.7118.6) on the wards per admission and contributed a median of 3 paired observations (IQR 24) per day, with 91% of patients having at least 2 observations per day. A total of 417 (1.6%) general‐ward admissions resulted in death during the hospitalization, with 354 mental‐status observations occurring within 24 hours of a death. In addition, 26,618 (99.9%) admissions had at least 1 paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay.
| |
| Total no. of admissions | 26,873 |
| Total no. of unique patients | 17,660 |
| Age, y, mean (SD) | 57 (17) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 14,293 (53) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 10,516 (39) |
| Black | 12,580 (47) |
| Other/unknown | 3,777 (14) |
| Admission MEWS, median (IQR) | 1 (11) |
| Days on ward, median (IQR) | 5 (310) |
| Observations per person, per day, median (IQR) | 3 (24) |
| Underwent surgery during hospitalization, n (%) | 6,141 (23) |
| Deaths, n (%) | 417 (1.6) |
AVPU was moderately correlated with GCS (Spearman's =0.56) (Figure 1a) and weakly correlated with RASS (Spearman's =0.28) (Figure 1b). GCS scores were also weakly correlated to RASS (Spearman's =0.13, P<0.001). Notably, AVPU mapped to distinct levels of GCS, with Alert associated with a median GCS total score of 15, Voice a score of 12, Pain a score of 8, and Unresponsive a score of 5. Abnormal mental‐status scores on any scale were associated with significantly higher odds of death within 24 hours than normal mental‐status scores (Table 2). This association was consistent within the 3 subscales of GCS and for scores in both the sedation (<0) and agitation (>0) ranges of RASS.

| Mental‐status Score | Observations, n (%) | Odds Ratio for Mortality (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| ||
| GCS Eye (AVPU) | ||
| 4 (alert) | 289,857 (98) | Reference |
| <4 (not alert) | 6,117 (2) | 33.8 (23.947.9) |
| GCS Verbal | ||
| 5 | 277,862 (94) | Reference |
| 4 | 11,258 (4) | 4.7 (2.87.9) |
| <4 | 6,854 (2) | 52.7 (38.073.2) |
| GCS Motor | ||
| 6 | 287,441 (97) | Reference |
| <6 | 8,533 (3) | 41.8 (30.756.9) |
| GCS total | ||
| 15 | 276,042 (93) | Reference |
| 13, 14 | 12,437 (4) | 5.2 (3.38.3) |
| <13 | 7,495 (3) | 55.5 (40.077.1) |
| RASS | ||
| >0 | 6,867 (2) | 8.5 (5.613.0) |
| 0 | 275,708 (93) | Reference |
| <0 | 13,339 (5) | 25.8 (19.234.6) |
AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality (AUC 0.73 [95% confidence interval {CI}: 0.710.76]), whereas simultaneous use of GCS and RASS was the most accurate predictor (AUC 0.85 [95% CI: 0.820.87] (Figure 2). The accuracies of GCS and RASS were not significantly different from one another in the total study population (AUC 0.80 [95% CI: 0.770.83] and 0.82 [0.790.84], respectively, P=0.13). Ten‐fold cross‐validation to estimate the internal validity of the RASS model resulted in a lower AUC (0.78 [95% CI: 0.750.81]) for RASS as a predictor of 24‐hour mortality. Subgroup analysis indicated that RASS was more accurate than GCS in younger patients (<57 years old) and in surgical patients (Figure 3).


Removal of the 255 admissions missing a paired mental‐status observation within the last 24 hours of their ward stay resulted in no change in the AUC values. A sensitivity analysis for prediction of a combined secondary outcome of 24‐hour intensive care unit ICU transfer or cardiac arrest yielded lower AUCs for each mental‐status scale, with no change in the association among scales.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this study is the first to compare the accuracies of AVPU, GCS, and RASS for predicting mortality in the general‐ward setting. Similar to McNarry and Goldhill, we demonstrated that AVPU scores mapped to distinct levels of GCS. Although our study reports the same median GCS scores of 15 and 8 for AVPU levels of Alert and Pain, respectively, we indicate slightly lower corresponding median GCS scores for AVPU scores of Voice (12 vs 13) and Unresponsive (5 vs 6) than their previous work.[21] We found that AVPU was the least accurate predictor of mortality within 24 hours of an observation, and the combination of GCS and RASS was the most accurate. RASS was at least as accurate a predictor for 24‐hour mortality in comparison to GCS total in the overall study population. However, the RASS score was the most accurate individual score in surgical and younger patients. These findings suggest that changing from the commonly used AVPU scale to the RASS and/or GCS would improve the prognostic ability of mental‐status assessments on the general wards.
Buist and colleagues have previously demonstrated altered mental status to be one of the strongest predictors of death on the wards. In that study, a GCS score of 3 and a decrease in GCS score by more than 2 points were independently associated with mortality (odds ratio 6.1 [95% CI: 3.111.8] and 5.5 [95% CI: 2.611.9], respectively).[22] We have also previously shown that after adjusting for vital signs, being unresponsive to pain was associated with a 4.5‐fold increase in the odds of death within 24 hours,[23]whereas Subbe and colleagues showed a relative risk ratio of 5.2 (95% CI: 1.518.1) for the combined endpoint of cardiac arrest, death at 60 days, or admission to the intensive care/high dependency unit.[19] In the current study, the magnitude of these associations was even stronger, with a GCS score <13 correlating with a 55‐fold increase in the odds of death, compared to a normal GCS, and not being alert being associated with a 33.8‐fold increase in the odds of death. This difference in magnitude is likely a product of the univariate nature of the current analysis, compared to both the Buist et al. and Churpek et al. studies, which adjusted for vital signs, thereby lessening the impact of any single predictor. Because this study was designed to compare mental‐status variables to one another for future model inclusion, and all the analyses were paired, confounding by additional predictors of death was not a concern.
One of the potential strengths of RASS over GCS and AVPU is its ability to measure agitation levels, in addition to depressed mentation, a feature that has been shown to be present in up to 60% of delirium episodes.[24] This may also explain why RASS was the most accurate predictor of mortality in our subset of younger patients and surgical patients, because hyperactive delirium is more common in younger and healthier patients, which surgical patients tend to be as compared to medical patients.[25, 26] In this study, we found negative RASS scores portending a worse prognosis than positive ones, which supports previous findings that hypoactive delirium had a higher association with mortality than hyperactive delirium at 6 months (hazard ratio 1.90 vs 1.37) and at 1 year (hazard ratio 1.60 vs 1.30) in elderly patients at postacute‐care facilities in 2 separate studies.[27, 28] However, a study of patients undergoing surgery for hip fracture found that patients with hyperactive delirium were more likely to die or be placed in a nursing home at 1 month follow‐up when compared to patients with purely hypoactive delirium (79% vs 32%, P=0.003).[29]
We found the assessment of RASS and GCS by ward nurses to be highly feasible. During the study period, nurses assessed mental status with the GCS and RASS scales at least once per 12‐hour shift in 91% of patients. GCS has been shown to be reliably and accurately recorded by experienced nurses (reliability coefficient=0.944 with 96.4% agreement with expert ratings).[30] RASS can take <30 seconds to administer, and in previous studies of the ICU setting has been shown to have over 94% nurse compliance for administration,[31] and good inter‐rater reliability (weighted kappa 0.66 and 0.89, respectively).[31, 32] Further, in a prior survey of 55 critical care nurses, 82% agreed that RASS was easy to score and clinically relevant.[31]
This study has several limitations. First, it was conducted in a single academic institution, which may limit generalizability to other hospitals. Second, baseline cognition and comorbidities were not available in the dataset, so we were unable to conduct additional subgroup analyses by these categories. However, we used age and hospital admission type as proxies. Third, the AVPU scores in this study were extracted from the Eye subset of the GCS scale, as AVPU was not directly assessed on our wards during the study period. Clinical assessment of mental status on the AVPU scale notes the presence of any active patient response (eg, eye opening, grunting, moaning, movement) to increasingly noxious stimuli. As such, our adaptation of AVPU using only eye‐opening criteria may underestimate the true number of patients correctly classified as alert, or responding to vocal/painful stimuli. However, a sensitivity analysis comparing directly assessed AVPU during a 3‐year period prior to the study implementation at our institution, and AVPU derived from the GCS Eye subscale for the study period, indicated no difference in predictive value for 24‐hour mortality. Fourth, we did not perform trend analyses for change from baseline mental status or evolution of AMS, which may more accurately predict 24‐hour mortality than discrete mental‐status observations. Finally, the 3 scales we compared differ in length, which may bias the AUC against AVPU, a 4‐point scale with a trapezoidal ROC curve compared to the smoother curve generated by the 15‐point GCS scale, for example. However, the lack of discrimination of the AVPU is the likely source of its lesser accuracy.
CONCLUSION
In the general‐ward setting, routine collection of GCS and RASS is feasible, and both are significantly more accurate for predicting mortality than the more commonly used AVPU scale. In addition, the combination of GCS and RASS has greater accuracy than any of the 3 individual scales. RASS may be particularly beneficial in the assessment of younger and/or surgical patients. Routine documentation and tracking of GCS and/or RASS by nurses may improve the detection of clinical deterioration in general‐ward patients. In addition, future early‐warning scores may benefit from the inclusion of GCS and/or RASS in lieu of AVPU.
Disclosures
Drs. Churpek and Edelson have a patent pending (ARCD. P0535US.P2) for risk stratification algorithms for hospitalized patients. Dr. Churpek is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K08 HL121080). Dr. Edelson has received research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K23 HL097157), Philips (Andover, MA), the American Heart Association (Dallas, TX), Laerdal Medical (Stavanger, Norway), and Early Sense (Tel Aviv, Israel). She has ownership interest in Quant HC (Chicago, IL), which is developing products for risk stratification of hospitalized patients. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
- , , , et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1753–1762.
- , , , , , Delirium in hospitalized older persons: outcomes and predictors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42(8):809–815.
- , , Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in‐patients: a systematic literature review. Age Ageing. 2006;35(4):350–364.
- , , , et al. Delirium. The occurrence and persistence of symptoms among elderly hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(2):334–340.
- , , Postoperative delirium. A review of 80 primary data‐collection studies. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(5):461–465.
- , , , , Nurses' recognition of delirium and its symptoms: comparison of nurse and researcher ratings. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(20):2467–2473.
- , , The misdiagnosis of delirium. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):433–439.
- , , , et al. Current opinions regarding the importance, diagnosis, and management of delirium in the intensive care unit: a survey of 912 healthcare professionals. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(1):106–112.
- , Misdiagnosing delirium as depression in medically ill elderly patients. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(22):2459–2464.
- Doctors and nurses use of the word confused. Br J Psychiatry. 1984;145:441–443.
- , , , et al. The Richmond Agitation‐Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–1344.
- , Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1976;34(1–4):45–55.
- , , , , Glasgow Coma Scale score in the evaluation of outcome in the intensive care unit: findings from the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III study. Crit Care Med. 1993;21(10):1459–1465.
- , , Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
- , , , Reliability of the Glasgow Coma Scale when used by emergency physicians and paramedics. J Trauma. 1993;34(1):46–48.
- , ; American College of Surgeons. Committee on Trauma. Advanced Trauma Life Support Program For Physicians: ATLS. 5th ed. Chicago, IL: American College of Surgeons; 1993.
- , , , Review and performance evaluation of aggregate weighted 'track and trigger' systems. Resuscitation. 2008;77(2):170–179.
- , , , , A review, and performance evaluation, of single‐parameter “track and trigger” systems. Resuscitation. 2008;79(1):11–21.
- , , , Validation of a modified Early Warning score in medical admissions. QJM. 2001;94(10):521–526.
- , , Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , Simple bedside assessment of level of consciousness: comparison of two simple assessment scales with the Glascow Coma Scale. Anaesthesia. 2004;59(1):34–37.
- , , , , Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , Predicting clinical deterioration in the hospital: the impact of outcome selection. Resuscitation. 2013;84(5):564–568.
- , , , et al. Delirium and its motoric subtypes: a study of 614 critically ill patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(3):479–484.
- , , , et al. Risk factors for delirium after major trauma. Am J Surg. 2008;196(6):864–869.
- , , , , Relationship between symptoms and motoric subtype of delirium. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2000;12(1):51–56.
- , , , et al. Phenomenological subtypes of delirium in older persons: patterns, prevalence, and prognosis. Psychosomatics. 2009;50(3):248–254.
- , , , Association between psychomotor activity delirium subtypes and mortality among newly admitted post‐acute facility patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62(2):174–179.
- , , , Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850–857.
- , Reliability and accuracy of the Glasgow Coma Scale with experienced and inexperienced users. Lancet. 1991;337(8740):535–538.
- , , , et al. Large‐scale implementation of sedation and delirium monitoring in the intensive care unit: a report from two medical centers. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(6):1199–1205.
- , , , et al. Delirium and sedation recognition using validated instruments: reliability of bedside intensive care unit nursing assessments from 2007 to 2010. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(suppl 2):S249–S255.
- , , , et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1753–1762.
- , , , , , Delirium in hospitalized older persons: outcomes and predictors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42(8):809–815.
- , , Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in‐patients: a systematic literature review. Age Ageing. 2006;35(4):350–364.
- , , , et al. Delirium. The occurrence and persistence of symptoms among elderly hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(2):334–340.
- , , Postoperative delirium. A review of 80 primary data‐collection studies. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(5):461–465.
- , , , , Nurses' recognition of delirium and its symptoms: comparison of nurse and researcher ratings. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(20):2467–2473.
- , , The misdiagnosis of delirium. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):433–439.
- , , , et al. Current opinions regarding the importance, diagnosis, and management of delirium in the intensive care unit: a survey of 912 healthcare professionals. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(1):106–112.
- , Misdiagnosing delirium as depression in medically ill elderly patients. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(22):2459–2464.
- Doctors and nurses use of the word confused. Br J Psychiatry. 1984;145:441–443.
- , , , et al. The Richmond Agitation‐Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–1344.
- , Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1976;34(1–4):45–55.
- , , , , Glasgow Coma Scale score in the evaluation of outcome in the intensive care unit: findings from the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III study. Crit Care Med. 1993;21(10):1459–1465.
- , , Variability in agreement between physicians and nurses when measuring the Glasgow Coma Scale in the emergency department limits its clinical usefulness. Emerg Med Australas. 2006;18(4):379–384.
- , , , Reliability of the Glasgow Coma Scale when used by emergency physicians and paramedics. J Trauma. 1993;34(1):46–48.
- , ; American College of Surgeons. Committee on Trauma. Advanced Trauma Life Support Program For Physicians: ATLS. 5th ed. Chicago, IL: American College of Surgeons; 1993.
- , , , Review and performance evaluation of aggregate weighted 'track and trigger' systems. Resuscitation. 2008;77(2):170–179.
- , , , , A review, and performance evaluation, of single‐parameter “track and trigger” systems. Resuscitation. 2008;79(1):11–21.
- , , , Validation of a modified Early Warning score in medical admissions. QJM. 2001;94(10):521–526.
- , , Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845.
- , Simple bedside assessment of level of consciousness: comparison of two simple assessment scales with the Glascow Coma Scale. Anaesthesia. 2004;59(1):34–37.
- , , , , Association between clinically abnormal observations and subsequent in‐hospital mortality: a prospective study. Resuscitation. 2004;62(2):137–141.
- , , Predicting clinical deterioration in the hospital: the impact of outcome selection. Resuscitation. 2013;84(5):564–568.
- , , , et al. Delirium and its motoric subtypes: a study of 614 critically ill patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(3):479–484.
- , , , et al. Risk factors for delirium after major trauma. Am J Surg. 2008;196(6):864–869.
- , , , , Relationship between symptoms and motoric subtype of delirium. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2000;12(1):51–56.
- , , , et al. Phenomenological subtypes of delirium in older persons: patterns, prevalence, and prognosis. Psychosomatics. 2009;50(3):248–254.
- , , , Association between psychomotor activity delirium subtypes and mortality among newly admitted post‐acute facility patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62(2):174–179.
- , , , Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850–857.
- , Reliability and accuracy of the Glasgow Coma Scale with experienced and inexperienced users. Lancet. 1991;337(8740):535–538.
- , , , et al. Large‐scale implementation of sedation and delirium monitoring in the intensive care unit: a report from two medical centers. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(6):1199–1205.
- , , , et al. Delirium and sedation recognition using validated instruments: reliability of bedside intensive care unit nursing assessments from 2007 to 2010. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(suppl 2):S249–S255.
© 2015 Society of Hospital Medicine