User login
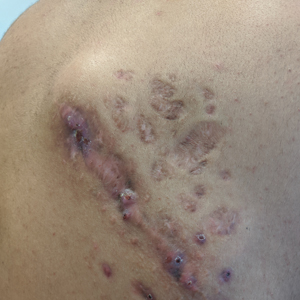
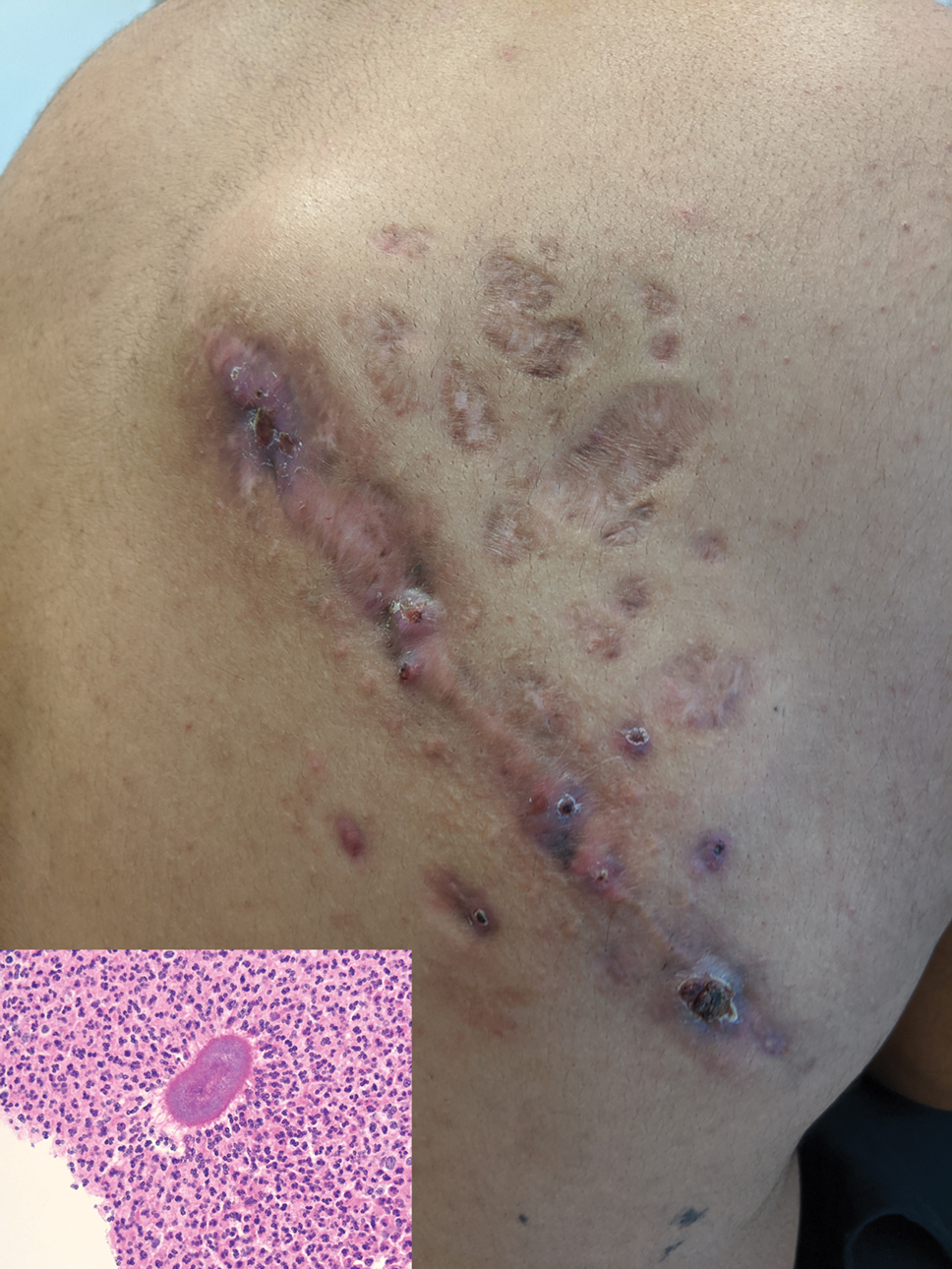
Indurated Mass on the Right Central Back
The Diagnosis: Actinomycetoma
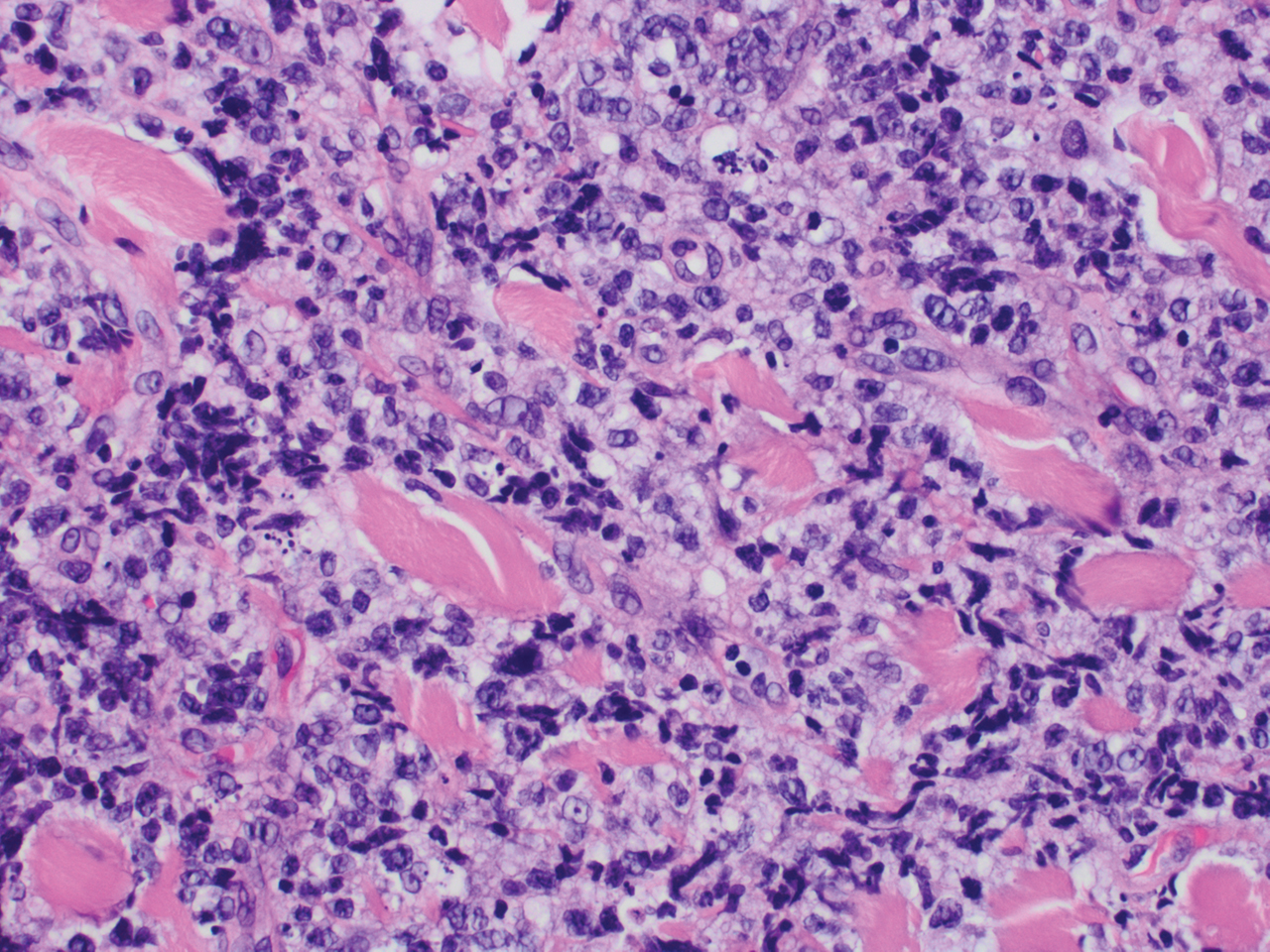
Histopathology revealed evidence of an actinomycete organism within the suppuration, consistent with actinomycosis (quiz image [inset]). Given the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings, our patient was diagnosed with actinomycetoma.
Actinomycetoma is an indolent, progressive, subcutaneous infection characterized by a well-known clinical triad of tumefaction/subcutaneous mass, draining sinuses, and an exudate containing grains on microscopy. The sinus tracts are formed from the chronic infectious process that destroys tissue, creating tunnels. This infectious disease of soft tissue is a clinical subset of mycetoma, which is categorized as eumycetoma (fungal) and actinomycetoma (bacterial). Actinomycetoma resembles the behavior of insidious and chronic fungal infections; however, most mycetoma infections are bacterial.1,2 Actinomycetoma may be confused with actinomycosis, which is caused by Actinomycoses species, commensal organisms commonly located on the teeth and oral mucosa in association with other microorganisms that may pathogenically cause cervicofacial actinomycosis.3,4 Actinomycetoma can be caused by Nocardia, Streptomyces, and Actinomadura. 2,5 The foot is the most common location of involvement followed by the thoracic region. It is more common in tropical or equatorial locations and may be contracted through exposure to soil or wood.5 Mycetoma is considered a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization.1 In tropical countries, this disease may go undiagnosed or untreated for so long that surgical amputation may be the only effective treatment.
Actinomycetoma commonly is identifiable by direct microscopy, Gram stain, or bacterial culture, with Gram stain being more sensitive than bacterial culture.3 It is important to indicate the suspected organism to the microbiology laboratory because common bacterial pathogens are detected within 24 to 48 hours, but the causative microorganism in actinomycetoma may require up to 4 weeks for culture,2 leading to possible false negatives due to inadequate culture time.3 Histopathology of actinomycotic infections will demonstrate granulomatous inflammation, focal suppuration, and the presence of grains (ie, a colony of filamentous bacteria in a stellate shaped mass)(quiz image [inset]).
The gold standard of treatment is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for up to several years.4,5 Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, dapsone, amikacin, streptomycin, and beta-lactams have been used successfully.2,5 The treatment course is dependent on clinical severity and location of the disease. The cure rate with appropriate antibiotics can be as high as 90%,2,5 and thus surgical intervention can be avoided.
In the differential, cutaneous tuberculosis would show tuberculoid granulomas with epithelioid histiocytes with possible caseation on histopathology, typically alongside positive tuberculosis screening. Botryomycosis has a similar clinical presentation of a swollen or indurated lesion with draining sinus tracts, but it less commonly occurs on the trunk. Histopathology also is a close mimic of actinomycetoma with a small grain inside a suppurative infiltrate; however, it has no filamentous bacteria. A foreign body reaction would not histologically present with suppuration or grains, and draining sinuses typically would not be seen on clinical presentation. Sarcoma is a neoplastic process and most commonly would show a proliferation of cells with soft tissue or bone origin on histopathology and not primarily an inflammatory cell process.6
- Verma P, Jha A. Mycetoma: reviewing a neglected disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:123-129.
- Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197.
- Bennhoff DF. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:1198-1217.
- Welsh O, Vera-Cabrera L, Welsh E, et al. Actinomycetoma and advances in its treatment. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:372-381.
- Arenas R, Fernandez Martinez RF, Torres-Guerrero E, et al. Actinomycetoma: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Cutis. 2017;99:E11-E15.
- Weedon D. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
The Diagnosis: Actinomycetoma
Histopathology revealed evidence of an actinomycete organism within the suppuration, consistent with actinomycosis (quiz image [inset]). Given the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings, our patient was diagnosed with actinomycetoma.
Actinomycetoma is an indolent, progressive, subcutaneous infection characterized by a well-known clinical triad of tumefaction/subcutaneous mass, draining sinuses, and an exudate containing grains on microscopy. The sinus tracts are formed from the chronic infectious process that destroys tissue, creating tunnels. This infectious disease of soft tissue is a clinical subset of mycetoma, which is categorized as eumycetoma (fungal) and actinomycetoma (bacterial). Actinomycetoma resembles the behavior of insidious and chronic fungal infections; however, most mycetoma infections are bacterial.1,2 Actinomycetoma may be confused with actinomycosis, which is caused by Actinomycoses species, commensal organisms commonly located on the teeth and oral mucosa in association with other microorganisms that may pathogenically cause cervicofacial actinomycosis.3,4 Actinomycetoma can be caused by Nocardia, Streptomyces, and Actinomadura. 2,5 The foot is the most common location of involvement followed by the thoracic region. It is more common in tropical or equatorial locations and may be contracted through exposure to soil or wood.5 Mycetoma is considered a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization.1 In tropical countries, this disease may go undiagnosed or untreated for so long that surgical amputation may be the only effective treatment.
Actinomycetoma commonly is identifiable by direct microscopy, Gram stain, or bacterial culture, with Gram stain being more sensitive than bacterial culture.3 It is important to indicate the suspected organism to the microbiology laboratory because common bacterial pathogens are detected within 24 to 48 hours, but the causative microorganism in actinomycetoma may require up to 4 weeks for culture,2 leading to possible false negatives due to inadequate culture time.3 Histopathology of actinomycotic infections will demonstrate granulomatous inflammation, focal suppuration, and the presence of grains (ie, a colony of filamentous bacteria in a stellate shaped mass)(quiz image [inset]).
The gold standard of treatment is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for up to several years.4,5 Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, dapsone, amikacin, streptomycin, and beta-lactams have been used successfully.2,5 The treatment course is dependent on clinical severity and location of the disease. The cure rate with appropriate antibiotics can be as high as 90%,2,5 and thus surgical intervention can be avoided.
In the differential, cutaneous tuberculosis would show tuberculoid granulomas with epithelioid histiocytes with possible caseation on histopathology, typically alongside positive tuberculosis screening. Botryomycosis has a similar clinical presentation of a swollen or indurated lesion with draining sinus tracts, but it less commonly occurs on the trunk. Histopathology also is a close mimic of actinomycetoma with a small grain inside a suppurative infiltrate; however, it has no filamentous bacteria. A foreign body reaction would not histologically present with suppuration or grains, and draining sinuses typically would not be seen on clinical presentation. Sarcoma is a neoplastic process and most commonly would show a proliferation of cells with soft tissue or bone origin on histopathology and not primarily an inflammatory cell process.6
The Diagnosis: Actinomycetoma
Histopathology revealed evidence of an actinomycete organism within the suppuration, consistent with actinomycosis (quiz image [inset]). Given the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings, our patient was diagnosed with actinomycetoma.
Actinomycetoma is an indolent, progressive, subcutaneous infection characterized by a well-known clinical triad of tumefaction/subcutaneous mass, draining sinuses, and an exudate containing grains on microscopy. The sinus tracts are formed from the chronic infectious process that destroys tissue, creating tunnels. This infectious disease of soft tissue is a clinical subset of mycetoma, which is categorized as eumycetoma (fungal) and actinomycetoma (bacterial). Actinomycetoma resembles the behavior of insidious and chronic fungal infections; however, most mycetoma infections are bacterial.1,2 Actinomycetoma may be confused with actinomycosis, which is caused by Actinomycoses species, commensal organisms commonly located on the teeth and oral mucosa in association with other microorganisms that may pathogenically cause cervicofacial actinomycosis.3,4 Actinomycetoma can be caused by Nocardia, Streptomyces, and Actinomadura. 2,5 The foot is the most common location of involvement followed by the thoracic region. It is more common in tropical or equatorial locations and may be contracted through exposure to soil or wood.5 Mycetoma is considered a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization.1 In tropical countries, this disease may go undiagnosed or untreated for so long that surgical amputation may be the only effective treatment.
Actinomycetoma commonly is identifiable by direct microscopy, Gram stain, or bacterial culture, with Gram stain being more sensitive than bacterial culture.3 It is important to indicate the suspected organism to the microbiology laboratory because common bacterial pathogens are detected within 24 to 48 hours, but the causative microorganism in actinomycetoma may require up to 4 weeks for culture,2 leading to possible false negatives due to inadequate culture time.3 Histopathology of actinomycotic infections will demonstrate granulomatous inflammation, focal suppuration, and the presence of grains (ie, a colony of filamentous bacteria in a stellate shaped mass)(quiz image [inset]).
The gold standard of treatment is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for up to several years.4,5 Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, dapsone, amikacin, streptomycin, and beta-lactams have been used successfully.2,5 The treatment course is dependent on clinical severity and location of the disease. The cure rate with appropriate antibiotics can be as high as 90%,2,5 and thus surgical intervention can be avoided.
In the differential, cutaneous tuberculosis would show tuberculoid granulomas with epithelioid histiocytes with possible caseation on histopathology, typically alongside positive tuberculosis screening. Botryomycosis has a similar clinical presentation of a swollen or indurated lesion with draining sinus tracts, but it less commonly occurs on the trunk. Histopathology also is a close mimic of actinomycetoma with a small grain inside a suppurative infiltrate; however, it has no filamentous bacteria. A foreign body reaction would not histologically present with suppuration or grains, and draining sinuses typically would not be seen on clinical presentation. Sarcoma is a neoplastic process and most commonly would show a proliferation of cells with soft tissue or bone origin on histopathology and not primarily an inflammatory cell process.6
- Verma P, Jha A. Mycetoma: reviewing a neglected disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:123-129.
- Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197.
- Bennhoff DF. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:1198-1217.
- Welsh O, Vera-Cabrera L, Welsh E, et al. Actinomycetoma and advances in its treatment. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:372-381.
- Arenas R, Fernandez Martinez RF, Torres-Guerrero E, et al. Actinomycetoma: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Cutis. 2017;99:E11-E15.
- Weedon D. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
- Verma P, Jha A. Mycetoma: reviewing a neglected disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:123-129.
- Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197.
- Bennhoff DF. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:1198-1217.
- Welsh O, Vera-Cabrera L, Welsh E, et al. Actinomycetoma and advances in its treatment. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:372-381.
- Arenas R, Fernandez Martinez RF, Torres-Guerrero E, et al. Actinomycetoma: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Cutis. 2017;99:E11-E15.
- Weedon D. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
A 26-year-old Guatemalan man who was a former carpenter presented with an indurated, nontender, nonpruritic, subcutaneous mass on the right central back with multiple draining sinus tracts on the surface and several depressed circular atrophic scars on the periphery of the mass. He noticed that the lesion began as a pustule 1.5 years prior and gradually enlarged. He denied any trauma, insect bites, fever, chills, headaches, weight loss, or travel history (he relocated to the United States 3.5 years ago) prior to the skin eruption. A biopsy was performed by an outside dermatologist 1 year prior to the current presentation, with a diagnosis of Pityrosporum folliculitis. Throughout his clinical course, treatment with oral antifungals, oral doxycycline, and topical clindamycin all failed. The mass was removed by plastic surgery 1 year prior.
A tissue biopsy for histology and culture was obtained at presentation to our institution. Laboratory findings showed that the basic metabolic panel was within reference range. Chest radiography indicated no active disease. A tuberculosis screening was negative. A bacterial culture of the lesion identified no growth after 48 hours. Our tissue biopsy revealed fibrosing granulation tissue, but the surgical pathology from a prior mass excision revealed sinus tracts with suppuration, evidence of scarring, foreign body giant cell reaction, and a characteristic finding (inset: H&E, original magnification ×200).
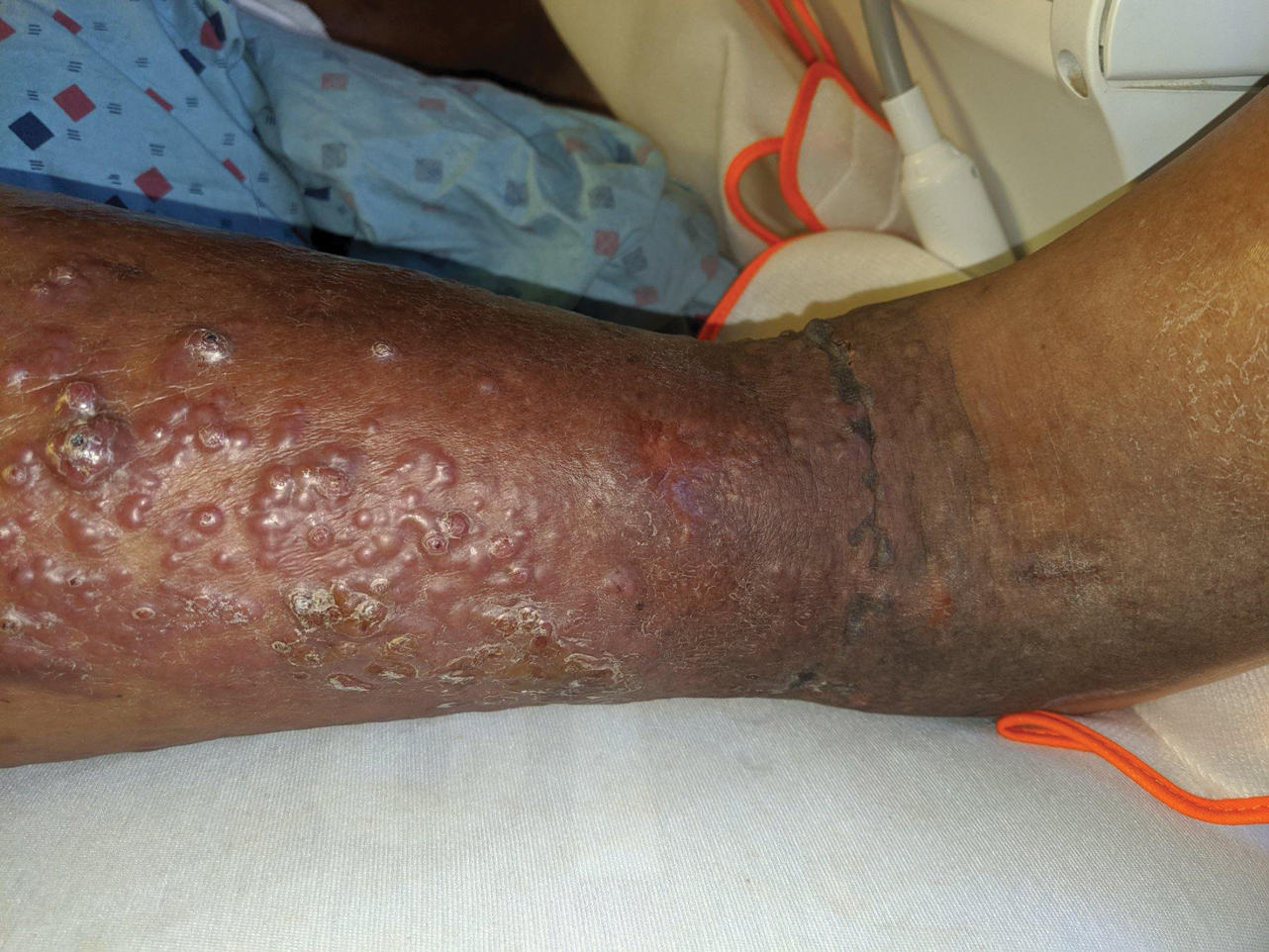
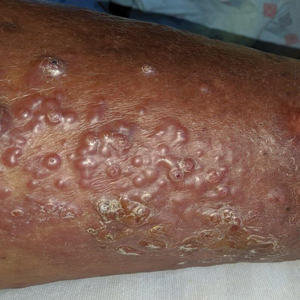
Vesicles and Bullae on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
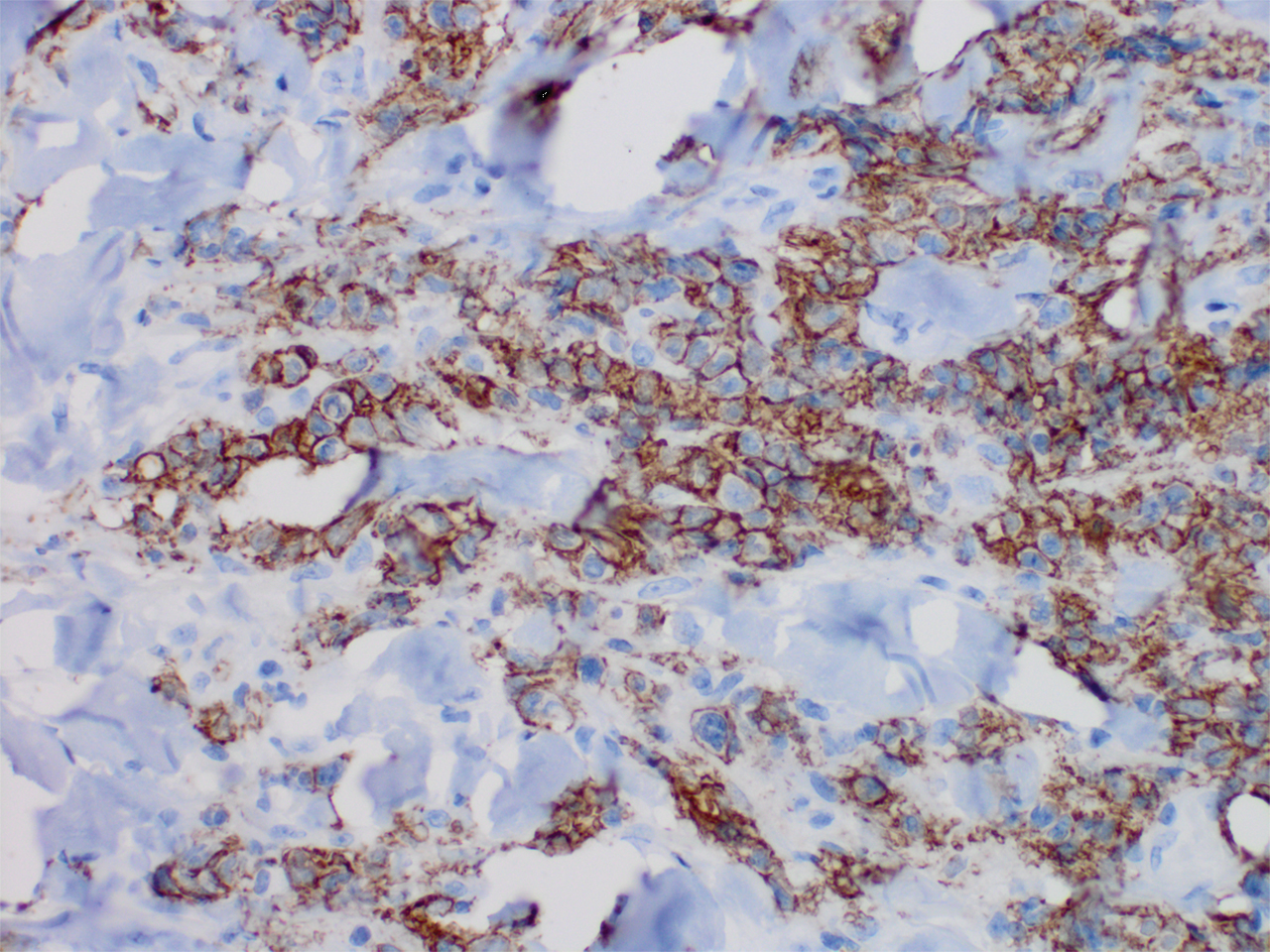
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).
Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).

Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).

Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
A 60-year-old man presented to the emergency department with slowly progressing edema of the lower legs of 3 months’ duration. In the week prior to presentation to the emergency department, he noticed a sudden eruption of vesicles and bullae on the right leg that drained clear fluid and healed with brown crust. The lesions were associated with mild burning, pruritus, and pain. He denied fever, chills, recent travel, or injury. His medical history was notable for poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, hyperlipidemia, and chronic anemia. Physical examination revealed multiple scattered erythematous vesicles and bullae on the right leg on a background of hyperpigmentation. Bilateral 2+ pitting edema of the legs also was present. A punch biopsy of a lesion was performed.