User login
Global Quest to Cut CAR T Costs
In the United States, a stand-alone device could greatly reduce the expense of producing modified immune cells. In India, researchers hope homegrown technology is the key to getting costs under control. In Latin America, a partnership between the Brazilian government and a US nonprofit may be just the ticket.
At stake is expanded access to CAR T-cell therapy, a form of immunotherapy that in just the past few years has revolutionized the care of hematologic cancers.
“Among patients with lymphoma, leukemia, and myeloma, anywhere between 30% to 50% reach long-term remission after one CAR T-cell infusion,” Mayo Clinic–Rochester hematologist/oncologist Saad J. Kenderian, MB, ChB, said in an interview. “It’s such an important therapy.”
However, only a small percentage of eligible patients in the United States — perhaps 20% or fewer — are receiving the treatment, he added.
A 2024 report suggested that many patients in the United States who may benefit aren’t being treated because of a range of possible reasons, including high prices, manufacturing logistics, and far distance from the limited number of institutions offering the therapy.
“Taken together, the real-world cost of CAR T-cell therapy can range from $700,000 to $1 million, which may make the treatment unaffordable to those patients without robust financial and/or social support,” the report authors noted.
Outside Western countries, access to the therapy is even more limited, because of its exorbitant price. The 2024 report noted that “there is a wide use of CAR T-cell therapy in Europe and China, but access is limited in developing countries in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America.”
Harnessing the Power of T-Cells
Several types of CAR T-cell therapy have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with relapsed/refractory blood cancers such as follicular lymphoma, large B-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A 2023 review analyzed clinical trials and reported that complete response rates were 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B-cell lymphoma.
Pediatric hematologist/oncologist Kirsten Williams, MD, who specializes in pediatric blood and marrow transplant and cellular therapy at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, described CAR T-cell therapy as “a very unique form of immunotherapy” that harnesses the power of the immune system’s T-cells.
These cells are effective tumor killers, but they typically aren’t assigned to control cancer, she said in an interview. “We have very few of them, and most of our T cells are focused on killing various viruses,” she said. The therapy “allows us to take the T cell that would have killed the flu or mono and instead target leukemia, B-cell leukemia, or lymphoma.”
As she explained, “T cells are collected by a machine that reserves white blood cells and gives back the rest of the blood to the patient. We insert a gene into the T cells that encodes for a B-cell receptor. This receptor acts as a GPS signal, pulling T cells to the cancer so that they can kill it.”
In addition, “with this genetic change, we also add some things that allow the T cell to be stronger, to have a higher signal to kill the cancer cell once it locks on.”
The therapy is unique for each patient, Dr. Williams said. “We have collected and modified your specific T cells, and they can now only be infused into you. If we try to give your product to someone else, those cells would either cause harm by attacking the patient or would be immediately killed by that patient’s own immune system. This is very different than all the other kinds of therapies. When you take other medicines, it doesn’t matter who receives that pill.”
Treatment: Individual, Complex, and Costly
Why is CAR T-cell therapy so expensive? While only a single treatment is needed, the T cells have to go through an “individualized, bespoke manufacturing” process that’s “highly technical,” pediatric oncologist Stephan A. Grupp, MD, PhD, section chief of the Cellular Therapy and Transplant Section at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. As he explained, the cells for a single patient have to go through the same testing as with a drug that might be given to 1,000 people.
“The first thing we need to do is collect the cells from a patient,” said Dr. Williams. “For adults, that process involves putting in two big IVs — one in each arm — and then pulling the blood through a machine. This typically involves an 8-hour collection in the hospital and very highly specialized people to oversee the collection process.”
Secondly, at some institutions, “the cells get sent to a company where they undergo the process where the gene is inserted,” she said. “This process needs to be done in a very sterile environment so there’s no infections, and it needs to have a lot of oversight.”
Finally, “after the cells are generated, they are typically frozen and shipped back to the site where the patient is at the hospital,” she said. “Then we give chemotherapy to the patient, which prepares the patient’s blood system. It removes some of the T-cells that are there, allowing for the T cells that we’re about to infuse to quickly be activated, find the cancer, and kill it.”
Side effects can boost costs even more. “Unfortunately, some significant toxicities can occur after we infuse these cells,” Dr. Williams noted. “Patients can have trouble breathing and sometimes need ventilatory support. They can have trouble maintaining their blood pressure and become swollen as fluid seeps into tissues. Or they can have high fevers and organ dysfunction. Many of those patients go to the intensive care unit, which is obviously expensive as well.”
Taking Gene Therapy In-House
As Dr. Williams explained, one way to reduce costs is to “perform the genetic manipulation and expansion of the cells outside of a company.” Several academic institutions in the United States are embracing this approach, including Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, which is experimenting with an automated device developed by the German company Miltenyi Biotec and known as the CliniMACS Prodigy machine.
“The current manufacturing process is very manual and requires a lot of interaction with the product and highly trained personnel,” Dr. Grupp said. “If you have an automated device, you have those cells in the device over the 7 to 12 days that you actually need to grow the cells. There’s much less interaction, so you need fewer trained personnel.”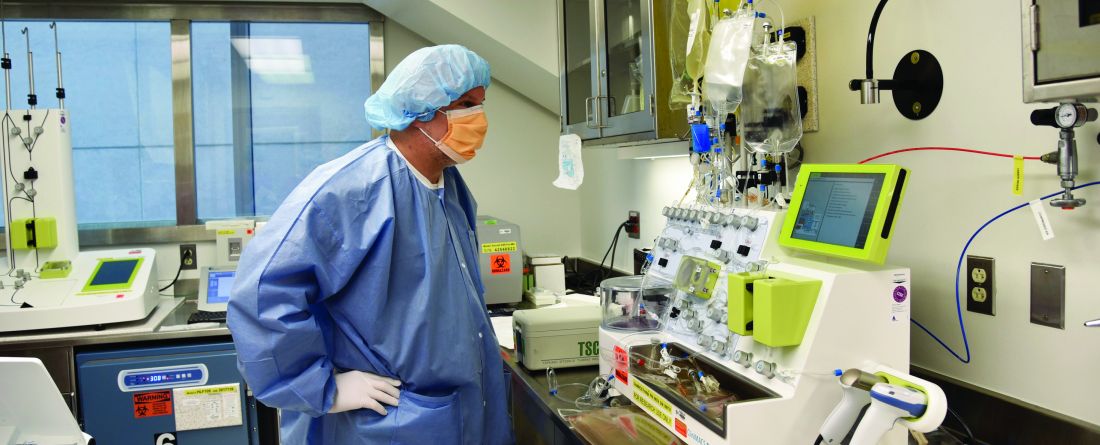
The device is experimental and not yet FDA approved, Dr. Grupp noted, so that patients are all in clinical trials. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia has treated more than a dozen patients with the device, he said.
Another member of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s CAR T-cell team told WHYY-FM that a single patient’s treatment would run about $30,000 for labor and testing, but not other expenses such as facility costs.
Dr. Grupp estimated that about half a dozen of these devices are in use in the United States, and many more worldwide. “They’re all just like we are — at the absolute beginning. We’ve only been doing this for about a year.”
In the big picture, Dr. Grupp said, “this is where cell therapy is going. Whether it’s point of care or not, automated cell manufacturing is the obvious next step.”
India: Big Hopes for Homegrown Technology
In India, researchers are hoping that their homegrown approach to CAR T-cell therapy will expand access by greatly lowering treatment prices.
Last fall, India’s equivalent of the FDA-granted approval for actalycabtagene autoleucel (NexCAR19), which was developed by Indian scientists who worked closely with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). The therapy’s developer is a company called ImmunoACT.
In an interview, ImmunoACT founder Rahul Purwar, PhD, MSc, associate professor at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, said the treatment costs about $40,000. The price is much lower than in the United States because staffing, facility construction, and maintenance are less expensive in India, he said.
Results of small early clinical trials have been promising, with complete responses in 68% of 38 lymphoma patients and 72% of 15 leukemia patients. Updated data will be presented at the annual American Society of Hematology meeting in December 2024, Dr. Purwar said.
According to the NIH, at first ImmunoACT hopes to treat about 1,200 patients a year. The immediate goal is to “focus and stabilize our operation in India,” Dr. Purwar said. “Then, if opportunities come, we will try to bring CAR T to all who might benefit from these technologies. A majority of countries don’t have access to these technologies.”
A US-Brazil Partnership Holds Promise
Meanwhile, a US nonprofit known as Caring Cross announced this year that it has partnered with Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz), a Brazilian government foundation, to manufacture CAR T cells at point-of-care in South America.
“Our model is different than traditional biotech/pharma,” Boro Dropulic, PhD, MBA, cofounder and executive director of Caring Cross, said in an interview. “Our goal is to develop technologies and transfer them to organizations like Fiocruz to enable them to manufacture these transformative therapies for patients in their regions. We believe this model is an important solution for therapies that are priced so high that they are not accessible to many patients that need them, particularly underserved populations and those in low- and middle-income countries.”
According to Dr. Dropulic: “We have developed a production process where the material cost is about $20,000 per dose.” When labor and infrastructure costs are added, the total expense won’t be more than $37,000-$47,500, he said.
The research process for the CAR T-cell technology is at an earlier stage than in India. Scientists plan to start clinical trials of the technology in the United States by the end of 2024 and then begin them in Brazil in 2025, after safety and efficacy have been demonstrated. The first trial, a phase I/II study, will enroll about 20 patients, Dr. Dropulic said.
Dr. Kenderian reported ties with Novartis, Capstan Bio, Kite/Gilead, Juno/BMS, Humanigen, Tolero, Leah Labs, Lentigen, Luminary, Sunesis/Viracta, Morphosys, Troque, Carisma, Sendero, and LifEngine. Dr. Williams disclosed grants from National Institutes of Health and philanthropic organizations. Dr. Grupp reported relationships with Novartis, Kite, Vertex and Servier, Roche, GSK, Humanigen, CBMG, Eureka, Janssen/JNJ, Jazz, Adaptimmune, TCR2, Cellectis, Juno, Allogene, and Cabaletta. Dr. Purwar is the founder of ImmunoACT. Dr. Dropulic serves as executive director of Caring Cross and CEO of Vector BioMed, which provides vectors for gene therapy.
In the United States, a stand-alone device could greatly reduce the expense of producing modified immune cells. In India, researchers hope homegrown technology is the key to getting costs under control. In Latin America, a partnership between the Brazilian government and a US nonprofit may be just the ticket.
At stake is expanded access to CAR T-cell therapy, a form of immunotherapy that in just the past few years has revolutionized the care of hematologic cancers.
“Among patients with lymphoma, leukemia, and myeloma, anywhere between 30% to 50% reach long-term remission after one CAR T-cell infusion,” Mayo Clinic–Rochester hematologist/oncologist Saad J. Kenderian, MB, ChB, said in an interview. “It’s such an important therapy.”
However, only a small percentage of eligible patients in the United States — perhaps 20% or fewer — are receiving the treatment, he added.
A 2024 report suggested that many patients in the United States who may benefit aren’t being treated because of a range of possible reasons, including high prices, manufacturing logistics, and far distance from the limited number of institutions offering the therapy.
“Taken together, the real-world cost of CAR T-cell therapy can range from $700,000 to $1 million, which may make the treatment unaffordable to those patients without robust financial and/or social support,” the report authors noted.
Outside Western countries, access to the therapy is even more limited, because of its exorbitant price. The 2024 report noted that “there is a wide use of CAR T-cell therapy in Europe and China, but access is limited in developing countries in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America.”
Harnessing the Power of T-Cells
Several types of CAR T-cell therapy have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with relapsed/refractory blood cancers such as follicular lymphoma, large B-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A 2023 review analyzed clinical trials and reported that complete response rates were 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B-cell lymphoma.
Pediatric hematologist/oncologist Kirsten Williams, MD, who specializes in pediatric blood and marrow transplant and cellular therapy at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, described CAR T-cell therapy as “a very unique form of immunotherapy” that harnesses the power of the immune system’s T-cells.
These cells are effective tumor killers, but they typically aren’t assigned to control cancer, she said in an interview. “We have very few of them, and most of our T cells are focused on killing various viruses,” she said. The therapy “allows us to take the T cell that would have killed the flu or mono and instead target leukemia, B-cell leukemia, or lymphoma.”
As she explained, “T cells are collected by a machine that reserves white blood cells and gives back the rest of the blood to the patient. We insert a gene into the T cells that encodes for a B-cell receptor. This receptor acts as a GPS signal, pulling T cells to the cancer so that they can kill it.”
In addition, “with this genetic change, we also add some things that allow the T cell to be stronger, to have a higher signal to kill the cancer cell once it locks on.”
The therapy is unique for each patient, Dr. Williams said. “We have collected and modified your specific T cells, and they can now only be infused into you. If we try to give your product to someone else, those cells would either cause harm by attacking the patient or would be immediately killed by that patient’s own immune system. This is very different than all the other kinds of therapies. When you take other medicines, it doesn’t matter who receives that pill.”
Treatment: Individual, Complex, and Costly
Why is CAR T-cell therapy so expensive? While only a single treatment is needed, the T cells have to go through an “individualized, bespoke manufacturing” process that’s “highly technical,” pediatric oncologist Stephan A. Grupp, MD, PhD, section chief of the Cellular Therapy and Transplant Section at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. As he explained, the cells for a single patient have to go through the same testing as with a drug that might be given to 1,000 people.
“The first thing we need to do is collect the cells from a patient,” said Dr. Williams. “For adults, that process involves putting in two big IVs — one in each arm — and then pulling the blood through a machine. This typically involves an 8-hour collection in the hospital and very highly specialized people to oversee the collection process.”
Secondly, at some institutions, “the cells get sent to a company where they undergo the process where the gene is inserted,” she said. “This process needs to be done in a very sterile environment so there’s no infections, and it needs to have a lot of oversight.”
Finally, “after the cells are generated, they are typically frozen and shipped back to the site where the patient is at the hospital,” she said. “Then we give chemotherapy to the patient, which prepares the patient’s blood system. It removes some of the T-cells that are there, allowing for the T cells that we’re about to infuse to quickly be activated, find the cancer, and kill it.”
Side effects can boost costs even more. “Unfortunately, some significant toxicities can occur after we infuse these cells,” Dr. Williams noted. “Patients can have trouble breathing and sometimes need ventilatory support. They can have trouble maintaining their blood pressure and become swollen as fluid seeps into tissues. Or they can have high fevers and organ dysfunction. Many of those patients go to the intensive care unit, which is obviously expensive as well.”
Taking Gene Therapy In-House
As Dr. Williams explained, one way to reduce costs is to “perform the genetic manipulation and expansion of the cells outside of a company.” Several academic institutions in the United States are embracing this approach, including Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, which is experimenting with an automated device developed by the German company Miltenyi Biotec and known as the CliniMACS Prodigy machine.
“The current manufacturing process is very manual and requires a lot of interaction with the product and highly trained personnel,” Dr. Grupp said. “If you have an automated device, you have those cells in the device over the 7 to 12 days that you actually need to grow the cells. There’s much less interaction, so you need fewer trained personnel.”
The device is experimental and not yet FDA approved, Dr. Grupp noted, so that patients are all in clinical trials. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia has treated more than a dozen patients with the device, he said.
Another member of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s CAR T-cell team told WHYY-FM that a single patient’s treatment would run about $30,000 for labor and testing, but not other expenses such as facility costs.
Dr. Grupp estimated that about half a dozen of these devices are in use in the United States, and many more worldwide. “They’re all just like we are — at the absolute beginning. We’ve only been doing this for about a year.”
In the big picture, Dr. Grupp said, “this is where cell therapy is going. Whether it’s point of care or not, automated cell manufacturing is the obvious next step.”
India: Big Hopes for Homegrown Technology
In India, researchers are hoping that their homegrown approach to CAR T-cell therapy will expand access by greatly lowering treatment prices.
Last fall, India’s equivalent of the FDA-granted approval for actalycabtagene autoleucel (NexCAR19), which was developed by Indian scientists who worked closely with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). The therapy’s developer is a company called ImmunoACT.
In an interview, ImmunoACT founder Rahul Purwar, PhD, MSc, associate professor at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, said the treatment costs about $40,000. The price is much lower than in the United States because staffing, facility construction, and maintenance are less expensive in India, he said.
Results of small early clinical trials have been promising, with complete responses in 68% of 38 lymphoma patients and 72% of 15 leukemia patients. Updated data will be presented at the annual American Society of Hematology meeting in December 2024, Dr. Purwar said.
According to the NIH, at first ImmunoACT hopes to treat about 1,200 patients a year. The immediate goal is to “focus and stabilize our operation in India,” Dr. Purwar said. “Then, if opportunities come, we will try to bring CAR T to all who might benefit from these technologies. A majority of countries don’t have access to these technologies.”
A US-Brazil Partnership Holds Promise
Meanwhile, a US nonprofit known as Caring Cross announced this year that it has partnered with Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz), a Brazilian government foundation, to manufacture CAR T cells at point-of-care in South America.
“Our model is different than traditional biotech/pharma,” Boro Dropulic, PhD, MBA, cofounder and executive director of Caring Cross, said in an interview. “Our goal is to develop technologies and transfer them to organizations like Fiocruz to enable them to manufacture these transformative therapies for patients in their regions. We believe this model is an important solution for therapies that are priced so high that they are not accessible to many patients that need them, particularly underserved populations and those in low- and middle-income countries.”
According to Dr. Dropulic: “We have developed a production process where the material cost is about $20,000 per dose.” When labor and infrastructure costs are added, the total expense won’t be more than $37,000-$47,500, he said.
The research process for the CAR T-cell technology is at an earlier stage than in India. Scientists plan to start clinical trials of the technology in the United States by the end of 2024 and then begin them in Brazil in 2025, after safety and efficacy have been demonstrated. The first trial, a phase I/II study, will enroll about 20 patients, Dr. Dropulic said.
Dr. Kenderian reported ties with Novartis, Capstan Bio, Kite/Gilead, Juno/BMS, Humanigen, Tolero, Leah Labs, Lentigen, Luminary, Sunesis/Viracta, Morphosys, Troque, Carisma, Sendero, and LifEngine. Dr. Williams disclosed grants from National Institutes of Health and philanthropic organizations. Dr. Grupp reported relationships with Novartis, Kite, Vertex and Servier, Roche, GSK, Humanigen, CBMG, Eureka, Janssen/JNJ, Jazz, Adaptimmune, TCR2, Cellectis, Juno, Allogene, and Cabaletta. Dr. Purwar is the founder of ImmunoACT. Dr. Dropulic serves as executive director of Caring Cross and CEO of Vector BioMed, which provides vectors for gene therapy.
In the United States, a stand-alone device could greatly reduce the expense of producing modified immune cells. In India, researchers hope homegrown technology is the key to getting costs under control. In Latin America, a partnership between the Brazilian government and a US nonprofit may be just the ticket.
At stake is expanded access to CAR T-cell therapy, a form of immunotherapy that in just the past few years has revolutionized the care of hematologic cancers.
“Among patients with lymphoma, leukemia, and myeloma, anywhere between 30% to 50% reach long-term remission after one CAR T-cell infusion,” Mayo Clinic–Rochester hematologist/oncologist Saad J. Kenderian, MB, ChB, said in an interview. “It’s such an important therapy.”
However, only a small percentage of eligible patients in the United States — perhaps 20% or fewer — are receiving the treatment, he added.
A 2024 report suggested that many patients in the United States who may benefit aren’t being treated because of a range of possible reasons, including high prices, manufacturing logistics, and far distance from the limited number of institutions offering the therapy.
“Taken together, the real-world cost of CAR T-cell therapy can range from $700,000 to $1 million, which may make the treatment unaffordable to those patients without robust financial and/or social support,” the report authors noted.
Outside Western countries, access to the therapy is even more limited, because of its exorbitant price. The 2024 report noted that “there is a wide use of CAR T-cell therapy in Europe and China, but access is limited in developing countries in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America.”
Harnessing the Power of T-Cells
Several types of CAR T-cell therapy have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with relapsed/refractory blood cancers such as follicular lymphoma, large B-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A 2023 review analyzed clinical trials and reported that complete response rates were 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B-cell lymphoma.
Pediatric hematologist/oncologist Kirsten Williams, MD, who specializes in pediatric blood and marrow transplant and cellular therapy at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, described CAR T-cell therapy as “a very unique form of immunotherapy” that harnesses the power of the immune system’s T-cells.
These cells are effective tumor killers, but they typically aren’t assigned to control cancer, she said in an interview. “We have very few of them, and most of our T cells are focused on killing various viruses,” she said. The therapy “allows us to take the T cell that would have killed the flu or mono and instead target leukemia, B-cell leukemia, or lymphoma.”
As she explained, “T cells are collected by a machine that reserves white blood cells and gives back the rest of the blood to the patient. We insert a gene into the T cells that encodes for a B-cell receptor. This receptor acts as a GPS signal, pulling T cells to the cancer so that they can kill it.”
In addition, “with this genetic change, we also add some things that allow the T cell to be stronger, to have a higher signal to kill the cancer cell once it locks on.”
The therapy is unique for each patient, Dr. Williams said. “We have collected and modified your specific T cells, and they can now only be infused into you. If we try to give your product to someone else, those cells would either cause harm by attacking the patient or would be immediately killed by that patient’s own immune system. This is very different than all the other kinds of therapies. When you take other medicines, it doesn’t matter who receives that pill.”
Treatment: Individual, Complex, and Costly
Why is CAR T-cell therapy so expensive? While only a single treatment is needed, the T cells have to go through an “individualized, bespoke manufacturing” process that’s “highly technical,” pediatric oncologist Stephan A. Grupp, MD, PhD, section chief of the Cellular Therapy and Transplant Section at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. As he explained, the cells for a single patient have to go through the same testing as with a drug that might be given to 1,000 people.
“The first thing we need to do is collect the cells from a patient,” said Dr. Williams. “For adults, that process involves putting in two big IVs — one in each arm — and then pulling the blood through a machine. This typically involves an 8-hour collection in the hospital and very highly specialized people to oversee the collection process.”
Secondly, at some institutions, “the cells get sent to a company where they undergo the process where the gene is inserted,” she said. “This process needs to be done in a very sterile environment so there’s no infections, and it needs to have a lot of oversight.”
Finally, “after the cells are generated, they are typically frozen and shipped back to the site where the patient is at the hospital,” she said. “Then we give chemotherapy to the patient, which prepares the patient’s blood system. It removes some of the T-cells that are there, allowing for the T cells that we’re about to infuse to quickly be activated, find the cancer, and kill it.”
Side effects can boost costs even more. “Unfortunately, some significant toxicities can occur after we infuse these cells,” Dr. Williams noted. “Patients can have trouble breathing and sometimes need ventilatory support. They can have trouble maintaining their blood pressure and become swollen as fluid seeps into tissues. Or they can have high fevers and organ dysfunction. Many of those patients go to the intensive care unit, which is obviously expensive as well.”
Taking Gene Therapy In-House
As Dr. Williams explained, one way to reduce costs is to “perform the genetic manipulation and expansion of the cells outside of a company.” Several academic institutions in the United States are embracing this approach, including Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, which is experimenting with an automated device developed by the German company Miltenyi Biotec and known as the CliniMACS Prodigy machine.
“The current manufacturing process is very manual and requires a lot of interaction with the product and highly trained personnel,” Dr. Grupp said. “If you have an automated device, you have those cells in the device over the 7 to 12 days that you actually need to grow the cells. There’s much less interaction, so you need fewer trained personnel.”
The device is experimental and not yet FDA approved, Dr. Grupp noted, so that patients are all in clinical trials. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia has treated more than a dozen patients with the device, he said.
Another member of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s CAR T-cell team told WHYY-FM that a single patient’s treatment would run about $30,000 for labor and testing, but not other expenses such as facility costs.
Dr. Grupp estimated that about half a dozen of these devices are in use in the United States, and many more worldwide. “They’re all just like we are — at the absolute beginning. We’ve only been doing this for about a year.”
In the big picture, Dr. Grupp said, “this is where cell therapy is going. Whether it’s point of care or not, automated cell manufacturing is the obvious next step.”
India: Big Hopes for Homegrown Technology
In India, researchers are hoping that their homegrown approach to CAR T-cell therapy will expand access by greatly lowering treatment prices.
Last fall, India’s equivalent of the FDA-granted approval for actalycabtagene autoleucel (NexCAR19), which was developed by Indian scientists who worked closely with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). The therapy’s developer is a company called ImmunoACT.
In an interview, ImmunoACT founder Rahul Purwar, PhD, MSc, associate professor at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, said the treatment costs about $40,000. The price is much lower than in the United States because staffing, facility construction, and maintenance are less expensive in India, he said.
Results of small early clinical trials have been promising, with complete responses in 68% of 38 lymphoma patients and 72% of 15 leukemia patients. Updated data will be presented at the annual American Society of Hematology meeting in December 2024, Dr. Purwar said.
According to the NIH, at first ImmunoACT hopes to treat about 1,200 patients a year. The immediate goal is to “focus and stabilize our operation in India,” Dr. Purwar said. “Then, if opportunities come, we will try to bring CAR T to all who might benefit from these technologies. A majority of countries don’t have access to these technologies.”
A US-Brazil Partnership Holds Promise
Meanwhile, a US nonprofit known as Caring Cross announced this year that it has partnered with Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz), a Brazilian government foundation, to manufacture CAR T cells at point-of-care in South America.
“Our model is different than traditional biotech/pharma,” Boro Dropulic, PhD, MBA, cofounder and executive director of Caring Cross, said in an interview. “Our goal is to develop technologies and transfer them to organizations like Fiocruz to enable them to manufacture these transformative therapies for patients in their regions. We believe this model is an important solution for therapies that are priced so high that they are not accessible to many patients that need them, particularly underserved populations and those in low- and middle-income countries.”
According to Dr. Dropulic: “We have developed a production process where the material cost is about $20,000 per dose.” When labor and infrastructure costs are added, the total expense won’t be more than $37,000-$47,500, he said.
The research process for the CAR T-cell technology is at an earlier stage than in India. Scientists plan to start clinical trials of the technology in the United States by the end of 2024 and then begin them in Brazil in 2025, after safety and efficacy have been demonstrated. The first trial, a phase I/II study, will enroll about 20 patients, Dr. Dropulic said.
Dr. Kenderian reported ties with Novartis, Capstan Bio, Kite/Gilead, Juno/BMS, Humanigen, Tolero, Leah Labs, Lentigen, Luminary, Sunesis/Viracta, Morphosys, Troque, Carisma, Sendero, and LifEngine. Dr. Williams disclosed grants from National Institutes of Health and philanthropic organizations. Dr. Grupp reported relationships with Novartis, Kite, Vertex and Servier, Roche, GSK, Humanigen, CBMG, Eureka, Janssen/JNJ, Jazz, Adaptimmune, TCR2, Cellectis, Juno, Allogene, and Cabaletta. Dr. Purwar is the founder of ImmunoACT. Dr. Dropulic serves as executive director of Caring Cross and CEO of Vector BioMed, which provides vectors for gene therapy.
New Trial Deepens Debate Over Late-Preterm Steroids
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Consider Skin Cancer, Infection Risks in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
SAN DIEGO — because of their suppressed immune systems.
“There are over 450,000 people with a solid organ transplant living in the United States. If you do the math, that works out to about 40 organ transplant recipients for every dermatologist, so there’s a lot of them out there for us to take care of,” Sean Christensen, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). “If we expand that umbrella to include all types of immunosuppression, that’s over 4 million adults in the US.”
Dr. Christensen encouraged dermatologists to be aware of the varying risks for immunosuppressive drugs and best screening practices for these patients, and to take advantage of a validated skin cancer risk assessment tool for transplant patients.
During his presentation, he highlighted five classes of immunosuppressive drugs and their associated skin cancer risks:
- Calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus or cyclosporine), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk. They may also cause gingival hyperplasia and sebaceous hyperplasia.
- Antimetabolites (mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine), which cause moderate to severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk.
- Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (sirolimus or everolimus), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a moderate skin cancer risk. They also impair wound healing.
- Corticosteroids (prednisone), which cause mild to severe immune suppression and pose a minimal skin cancer risk.
- A decoy receptor protein (belatacept), which causes severe immune suppression and poses a mild skin cancer risk.
“Most of our solid-organ transplant recipients will be on both a calcineurin inhibitor and an antimetabolite,” Dr. Christensen said. “In addition to the skin cancer risk associated with immunosuppression, there is an additive risk” that is a direct effect of these medications on the skin. “That means our transplant recipients have a severely and disproportionate increase in skin cancer,” he noted.
Up to half of solid-organ transplant recipients will develop skin cancer, Dr. Christensen said. These patients have a sixfold to 10-fold increased risk for basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a 35- to 65-fold increased risk for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a twofold to sevenfold increased risk for melanoma, and a 16- to 100-fold increased risk for Merkel cell carcinoma.
Transplant recipients with SCC, he said, have a twofold to threefold higher risk for metastasis (4%-8% nodal metastasis) and twofold to fivefold higher risk for death (2%-7% mortality) from SCC.
As for other kinds of immunosuppression, HIV positivity, treatment with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine (for inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis), and antitumor necrosis factor agents (for psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid arthritis) have been linked in studies to a higher risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Dr. Christensen also highlighted graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). “It does look like there is a disproportionate and increased risk of SCC of the oropharynx and of the skin in patients who have chronic GVHD. This is probably due to a combination of both the immunosuppressive medications that are required but also from chronic and ongoing inflammation in the skin.”
Chronic GVHD has been linked to a 5.3-fold increase in the risk for SCC and a twofold increase in the risk for BCC, he added.
Moreover, new medications for treating GVHD have been linked to an increased risk for SCC, including a 3.2-fold increased risk for SCC associated with ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in a study of patients with polycythemia vera and myelofibrosis; and a case report of SCC in a patient treated with belumosudil, a rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-2 kinase inhibitor, for chronic GVHD. Risk for SCC appears to increase based on duration of use with voriconazole, an antifungal, which, he said, is a potent photosynthesizer.
Dr. Christensen also noted the higher risk for infections in immunocompromised patients and added that these patients can develop inflammatory disease despite immunosuppression:
Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Dermatophytes are the most common skin pathogens in these patients. There’s a significantly increased risk for reactivation of herpes simplex, varicella-zoster viruses, and cytomegalovirus. Opportunistic and disseminated fungal infections, such as mycobacteria, Candida, histoplasma, cryptococcus, aspergillus, and mucormycosis, can also appear.
More than 80% of transplant recipients develop molluscum and verruca vulgaris/human papillomavirus infection. They may also develop noninfectious inflammatory dermatoses.
Risk Calculator
What can dermatologists do to help transplant patients? Dr. Christensen highlighted the Skin and UV Neoplasia Transplant Risk Assessment Calculator, which predicts skin cancer risk based on points given for race, gender, skin cancer history, age at transplant, and site of transplant.
The tool, validated in a 2023 study of transplant recipients in Europe, is available online and as an app. It makes recommendations to users about when patients should have initial skin screening exams. Those with the most risk — 45% at 5 years — should be screened within 6 months. “We can use [the tool] to triage these cases when we first meet them and get them plugged into the appropriate care,” Dr. Christensen said.
He recommended seeing high-risk patients at least annually. Patients with a prior SCC and a heavy burden of actinic keratosis should be followed more frequently, he said.
In regard to SCC, he highlighted a 2024 study of solid organ transplant recipients that found the risk for a second SCC after a first SCC was 74%, the risk for a third SCC after a second SCC was 83%, and the risk for another SCC after five SCCs was 92%.
Dr. Christensen disclosed relationships with Canfield Scientific Inc. (consulting), Inhibitor Therapeutics (advisory board), and Sol-Gel Technologies Ltd. (grants/research funding).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — because of their suppressed immune systems.
“There are over 450,000 people with a solid organ transplant living in the United States. If you do the math, that works out to about 40 organ transplant recipients for every dermatologist, so there’s a lot of them out there for us to take care of,” Sean Christensen, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). “If we expand that umbrella to include all types of immunosuppression, that’s over 4 million adults in the US.”
Dr. Christensen encouraged dermatologists to be aware of the varying risks for immunosuppressive drugs and best screening practices for these patients, and to take advantage of a validated skin cancer risk assessment tool for transplant patients.
During his presentation, he highlighted five classes of immunosuppressive drugs and their associated skin cancer risks:
- Calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus or cyclosporine), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk. They may also cause gingival hyperplasia and sebaceous hyperplasia.
- Antimetabolites (mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine), which cause moderate to severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk.
- Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (sirolimus or everolimus), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a moderate skin cancer risk. They also impair wound healing.
- Corticosteroids (prednisone), which cause mild to severe immune suppression and pose a minimal skin cancer risk.
- A decoy receptor protein (belatacept), which causes severe immune suppression and poses a mild skin cancer risk.
“Most of our solid-organ transplant recipients will be on both a calcineurin inhibitor and an antimetabolite,” Dr. Christensen said. “In addition to the skin cancer risk associated with immunosuppression, there is an additive risk” that is a direct effect of these medications on the skin. “That means our transplant recipients have a severely and disproportionate increase in skin cancer,” he noted.
Up to half of solid-organ transplant recipients will develop skin cancer, Dr. Christensen said. These patients have a sixfold to 10-fold increased risk for basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a 35- to 65-fold increased risk for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a twofold to sevenfold increased risk for melanoma, and a 16- to 100-fold increased risk for Merkel cell carcinoma.
Transplant recipients with SCC, he said, have a twofold to threefold higher risk for metastasis (4%-8% nodal metastasis) and twofold to fivefold higher risk for death (2%-7% mortality) from SCC.
As for other kinds of immunosuppression, HIV positivity, treatment with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine (for inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis), and antitumor necrosis factor agents (for psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid arthritis) have been linked in studies to a higher risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Dr. Christensen also highlighted graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). “It does look like there is a disproportionate and increased risk of SCC of the oropharynx and of the skin in patients who have chronic GVHD. This is probably due to a combination of both the immunosuppressive medications that are required but also from chronic and ongoing inflammation in the skin.”
Chronic GVHD has been linked to a 5.3-fold increase in the risk for SCC and a twofold increase in the risk for BCC, he added.
Moreover, new medications for treating GVHD have been linked to an increased risk for SCC, including a 3.2-fold increased risk for SCC associated with ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in a study of patients with polycythemia vera and myelofibrosis; and a case report of SCC in a patient treated with belumosudil, a rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-2 kinase inhibitor, for chronic GVHD. Risk for SCC appears to increase based on duration of use with voriconazole, an antifungal, which, he said, is a potent photosynthesizer.
Dr. Christensen also noted the higher risk for infections in immunocompromised patients and added that these patients can develop inflammatory disease despite immunosuppression:
Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Dermatophytes are the most common skin pathogens in these patients. There’s a significantly increased risk for reactivation of herpes simplex, varicella-zoster viruses, and cytomegalovirus. Opportunistic and disseminated fungal infections, such as mycobacteria, Candida, histoplasma, cryptococcus, aspergillus, and mucormycosis, can also appear.
More than 80% of transplant recipients develop molluscum and verruca vulgaris/human papillomavirus infection. They may also develop noninfectious inflammatory dermatoses.
Risk Calculator
What can dermatologists do to help transplant patients? Dr. Christensen highlighted the Skin and UV Neoplasia Transplant Risk Assessment Calculator, which predicts skin cancer risk based on points given for race, gender, skin cancer history, age at transplant, and site of transplant.
The tool, validated in a 2023 study of transplant recipients in Europe, is available online and as an app. It makes recommendations to users about when patients should have initial skin screening exams. Those with the most risk — 45% at 5 years — should be screened within 6 months. “We can use [the tool] to triage these cases when we first meet them and get them plugged into the appropriate care,” Dr. Christensen said.
He recommended seeing high-risk patients at least annually. Patients with a prior SCC and a heavy burden of actinic keratosis should be followed more frequently, he said.
In regard to SCC, he highlighted a 2024 study of solid organ transplant recipients that found the risk for a second SCC after a first SCC was 74%, the risk for a third SCC after a second SCC was 83%, and the risk for another SCC after five SCCs was 92%.
Dr. Christensen disclosed relationships with Canfield Scientific Inc. (consulting), Inhibitor Therapeutics (advisory board), and Sol-Gel Technologies Ltd. (grants/research funding).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — because of their suppressed immune systems.
“There are over 450,000 people with a solid organ transplant living in the United States. If you do the math, that works out to about 40 organ transplant recipients for every dermatologist, so there’s a lot of them out there for us to take care of,” Sean Christensen, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). “If we expand that umbrella to include all types of immunosuppression, that’s over 4 million adults in the US.”
Dr. Christensen encouraged dermatologists to be aware of the varying risks for immunosuppressive drugs and best screening practices for these patients, and to take advantage of a validated skin cancer risk assessment tool for transplant patients.
During his presentation, he highlighted five classes of immunosuppressive drugs and their associated skin cancer risks:
- Calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus or cyclosporine), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk. They may also cause gingival hyperplasia and sebaceous hyperplasia.
- Antimetabolites (mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine), which cause moderate to severe immune suppression and pose a severe skin cancer risk.
- Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (sirolimus or everolimus), which cause severe immune suppression and pose a moderate skin cancer risk. They also impair wound healing.
- Corticosteroids (prednisone), which cause mild to severe immune suppression and pose a minimal skin cancer risk.
- A decoy receptor protein (belatacept), which causes severe immune suppression and poses a mild skin cancer risk.
“Most of our solid-organ transplant recipients will be on both a calcineurin inhibitor and an antimetabolite,” Dr. Christensen said. “In addition to the skin cancer risk associated with immunosuppression, there is an additive risk” that is a direct effect of these medications on the skin. “That means our transplant recipients have a severely and disproportionate increase in skin cancer,” he noted.
Up to half of solid-organ transplant recipients will develop skin cancer, Dr. Christensen said. These patients have a sixfold to 10-fold increased risk for basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a 35- to 65-fold increased risk for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a twofold to sevenfold increased risk for melanoma, and a 16- to 100-fold increased risk for Merkel cell carcinoma.
Transplant recipients with SCC, he said, have a twofold to threefold higher risk for metastasis (4%-8% nodal metastasis) and twofold to fivefold higher risk for death (2%-7% mortality) from SCC.
As for other kinds of immunosuppression, HIV positivity, treatment with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine (for inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis), and antitumor necrosis factor agents (for psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid arthritis) have been linked in studies to a higher risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Dr. Christensen also highlighted graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). “It does look like there is a disproportionate and increased risk of SCC of the oropharynx and of the skin in patients who have chronic GVHD. This is probably due to a combination of both the immunosuppressive medications that are required but also from chronic and ongoing inflammation in the skin.”
Chronic GVHD has been linked to a 5.3-fold increase in the risk for SCC and a twofold increase in the risk for BCC, he added.
Moreover, new medications for treating GVHD have been linked to an increased risk for SCC, including a 3.2-fold increased risk for SCC associated with ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in a study of patients with polycythemia vera and myelofibrosis; and a case report of SCC in a patient treated with belumosudil, a rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-2 kinase inhibitor, for chronic GVHD. Risk for SCC appears to increase based on duration of use with voriconazole, an antifungal, which, he said, is a potent photosynthesizer.
Dr. Christensen also noted the higher risk for infections in immunocompromised patients and added that these patients can develop inflammatory disease despite immunosuppression:
Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Dermatophytes are the most common skin pathogens in these patients. There’s a significantly increased risk for reactivation of herpes simplex, varicella-zoster viruses, and cytomegalovirus. Opportunistic and disseminated fungal infections, such as mycobacteria, Candida, histoplasma, cryptococcus, aspergillus, and mucormycosis, can also appear.
More than 80% of transplant recipients develop molluscum and verruca vulgaris/human papillomavirus infection. They may also develop noninfectious inflammatory dermatoses.
Risk Calculator
What can dermatologists do to help transplant patients? Dr. Christensen highlighted the Skin and UV Neoplasia Transplant Risk Assessment Calculator, which predicts skin cancer risk based on points given for race, gender, skin cancer history, age at transplant, and site of transplant.
The tool, validated in a 2023 study of transplant recipients in Europe, is available online and as an app. It makes recommendations to users about when patients should have initial skin screening exams. Those with the most risk — 45% at 5 years — should be screened within 6 months. “We can use [the tool] to triage these cases when we first meet them and get them plugged into the appropriate care,” Dr. Christensen said.
He recommended seeing high-risk patients at least annually. Patients with a prior SCC and a heavy burden of actinic keratosis should be followed more frequently, he said.
In regard to SCC, he highlighted a 2024 study of solid organ transplant recipients that found the risk for a second SCC after a first SCC was 74%, the risk for a third SCC after a second SCC was 83%, and the risk for another SCC after five SCCs was 92%.
Dr. Christensen disclosed relationships with Canfield Scientific Inc. (consulting), Inhibitor Therapeutics (advisory board), and Sol-Gel Technologies Ltd. (grants/research funding).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
MS and Epstein-Barr Virus: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go From Here?
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is our constant companion, infecting an estimated 90%-95% of adults. Many of us are first infected as children, when the germ may trigger cold and flu symptoms. EBV also causes mononucleosis, or kissing disease, a glandular fever that has afflicted generations of amorous young people.
Post infection, EBV settles in for the long haul and remains in the body until death. It’s thought to be largely innocuous, but EBV is now implicated as a cause of several types of cancer — including lymphoma and nasopharyngeal tumors – and multiple sclerosis (MS). In 2022, a landmark study in Science suggested that previous EBV infection is the primary cause of MS.
While there aren’t many implications for current treatment, greater insight into the origin story of MS may eventually help neurologists better diagnose and treat patients, experts said. The goal is to uncover clues that “can help us understand MS a little bit better and reveal insights that could lead to new disease-modifying therapy,” Bruce Bebo, PhD, executive vice president of research with the National MS Society, said in an interview.
EBV Boosts MS Risk 32-Fold
EBV was first linked to MS back in 1981. For the 2022 study, researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed blood serum from 10 million active-duty members of the US military. They focused on 801 recruits with MS and matched them with more than 1500 controls. All but one of those with MS had been infected with EBV; infection appeared to boost the risk for MS 32-fold (95% CI, 4.3-245.3; P < .001).
Neurologist and associate professor Michael Levy, MD, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview that the findings are “groundbreaking” and confirm that EBV is “likely the primary cause of MS.”
According to Dr. Levy, there are two main theories about why EBV causes MS. The first hypothesis, known as the “molecular mimicry” theory, suggests that “EBV is a trigger of MS, possibly when the immune system mistakes a viral protein for a myelin protein and then attacks myelin,” Dr. Levy said. In MS, the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath and the axons it insulates.
“After that point, the virus is not necessary to maintain the disease state and eradicating the virus likely won’t have much effect since the immune response is already triggered,” he said.
The second theory is that “EBV is a driver of MS where there is an ongoing, lifelong immunological response to EBV that continuously causes damage in the central nervous system [CNS]. In theory, if we could eradicate the virus, the destructive immune response could also resolve. Thus, an EBV antiviral treatment could potentially treat and maybe cure MS,” Dr. Levy explained, noting that “removing the pathogenic antigen may be a more effective strategy than removing the immune response.”
However, “we don’t yet know which hypothesis is correct,” he said. But “there is preliminary evidence in favor of each one.”
‘Additional Fuses Must Be Ignited’
It’s also unclear why most people infected with EBV do not develop MS. It appears that “additional fuses must be ignited,” for MS to take hold, according to a commentary accompanying the landmark 2022 study.
“As far as clinical implications, knowing whether a patient has a medical or family history of mononucleosis may be a small clue, a small piece of evidence, to help with diagnosis,” Dr. Bebo said.
He agreed with Dr. Levy that an antiviral could be a promising approach “If the problem in MS is a dysfunctional immune response to EBV.”
Natalia Drosu, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard-MIT Biomedical Engineering Center, said that a clinical trial of a non-immunosuppressive antiviral targeting EBV in patients with MS would be a crucial step toward better understanding the MS-EBV connection. “If we learn that antivirals are effective in MS, we should develop non-immunosuppressive therapies for patients with MS as soon as possible,” she said.
Stanford University’s Lawrence Steinman, MD, professor of neurology and neurological sciences, pediatrics, and genetics, who coauthored the commentary on the original Science paper, agreed that it’s worth investigating whether antiviral therapies targeting EBV will benefit patients who already have MS. But he cautioned against clinicians experimenting on their own outside of a research study. “You’d want to use the right antiviral and a properly designed trial,” he said.
Antivirals May Place a Crucial Role in MS Control
While there are no approved therapies for EBV, several MS disease-modifying therapies have anti-EBV effects, Dr. Levy said, citing anti-CD20 therapy as a clear example. It depletes B cells from the circulation, and it depletes EBV because the virus lives in the B-cell compartment. “Some MS treatments may be inadvertent EBV antivirals,” he said.
Researchers are also thinking about how they might exploit the MS-EBV link to prevent MS from developing in the first place, but there are uncertainties on that front too.
Conceivably, there may be some way to intervene in patients to treat EBV and prevent MS, such as a unique treatment for infectious mononucleosis (IM), Dr. Levy said.
Researchers are especially intrigued by signs that the timing of infection may play a role, with people infected with EBV via IM after early childhood at especially a high risk of developing MS. A 2022 German study calculated that people who developed IM were almost twice as likely as those who didn’t to develop MS within 10 years, although the risks in both groups were very small. Subgroup analysis revealed the strongest association between IM and MS was in the group infected between age 14 and 20 years (hazard ratio, 3.52; 95% CI, 1.00-12.37). They also saw a stronger association in men than in women.
The authors of a 2023 review in Clinical & Translational Immunology wrote that “further understanding of IM may be critical in solving the mystery” of EBV’s role in MS.
Dr. Levy said this line of questioning is important.
However, “remember that while most of the world gets EBV infections, only 1 in 1000 will get MS. So, it might not be feasible to test everyone before neurological manifestations occur,” he said.
More Questions to Answer About EBV and MS
Researchers hope to answer several questions moving forward. For one, why is EBV uniquely connected to MS? “You would think that if there were cross-reactivity to myelin, there are many viruses that could cause MS. But the association seems to be very restricted to EBV,” Dr. Levy said. “It is probably due to the fact that EBV is one of the only human viruses that can infect B cells, which play important roles in controlling immune responses.”
The molecular mimicry theory also opens up a potential treatment pathway.
A 2022 study reported “high-affinity molecular mimicry between the EBV transcription factor EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) and the central nervous system protein glial cell adhesion molecule (GlialCAM)”. Antibodies against EBNA1 and GlialCAM are prevalent in patients with MS. In a mouse model of MS, the researchers showed that EBNA1 immunization exacerbates disease. The authors wrote that “Our results provide a mechanistic link for the association between MS and EBV and could guide the development of new MS therapies.”
Could an EBV Vaccine Be the Answer?
On the prevention front, perhaps the most obvious question is whether an EBV vaccine could eliminate MS for good?
Dr. Bebo, from the National MS Society, said it will be important to determine which kind of vaccine is best. Is it one that neutralizes infection with EBV? Or is it enough to simply prevent clinical manifestations?
Both types of vaccines are in development, and at least two clinical trials are now in the works. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is sponsoring a phase 1 study of an adjuvanted EBV gp350-Ferritin nanoparticle vaccine. Forty subjects aged 18-29 years will take part: 20 with EBV and 20 who are not infected. The study is expected to end in 2025.
There is also a phase 1 placebo-controlled study in progress testing an EBV vaccine based on mRNA-1189 in 422 subjects aged 12-30 years. This trial is also due to end in 2025.
“This is very exciting, but it may take a decade or two to determine whether a vaccine is effective at preventing MS,” Dr. Levy said.
Dr. Levy, Dr. Steinman, Dr. Drosu, and Dr. Bebo had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is our constant companion, infecting an estimated 90%-95% of adults. Many of us are first infected as children, when the germ may trigger cold and flu symptoms. EBV also causes mononucleosis, or kissing disease, a glandular fever that has afflicted generations of amorous young people.
Post infection, EBV settles in for the long haul and remains in the body until death. It’s thought to be largely innocuous, but EBV is now implicated as a cause of several types of cancer — including lymphoma and nasopharyngeal tumors – and multiple sclerosis (MS). In 2022, a landmark study in Science suggested that previous EBV infection is the primary cause of MS.
While there aren’t many implications for current treatment, greater insight into the origin story of MS may eventually help neurologists better diagnose and treat patients, experts said. The goal is to uncover clues that “can help us understand MS a little bit better and reveal insights that could lead to new disease-modifying therapy,” Bruce Bebo, PhD, executive vice president of research with the National MS Society, said in an interview.
EBV Boosts MS Risk 32-Fold
EBV was first linked to MS back in 1981. For the 2022 study, researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed blood serum from 10 million active-duty members of the US military. They focused on 801 recruits with MS and matched them with more than 1500 controls. All but one of those with MS had been infected with EBV; infection appeared to boost the risk for MS 32-fold (95% CI, 4.3-245.3; P < .001).
Neurologist and associate professor Michael Levy, MD, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview that the findings are “groundbreaking” and confirm that EBV is “likely the primary cause of MS.”
According to Dr. Levy, there are two main theories about why EBV causes MS. The first hypothesis, known as the “molecular mimicry” theory, suggests that “EBV is a trigger of MS, possibly when the immune system mistakes a viral protein for a myelin protein and then attacks myelin,” Dr. Levy said. In MS, the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath and the axons it insulates.
“After that point, the virus is not necessary to maintain the disease state and eradicating the virus likely won’t have much effect since the immune response is already triggered,” he said.
The second theory is that “EBV is a driver of MS where there is an ongoing, lifelong immunological response to EBV that continuously causes damage in the central nervous system [CNS]. In theory, if we could eradicate the virus, the destructive immune response could also resolve. Thus, an EBV antiviral treatment could potentially treat and maybe cure MS,” Dr. Levy explained, noting that “removing the pathogenic antigen may be a more effective strategy than removing the immune response.”
However, “we don’t yet know which hypothesis is correct,” he said. But “there is preliminary evidence in favor of each one.”
‘Additional Fuses Must Be Ignited’
It’s also unclear why most people infected with EBV do not develop MS. It appears that “additional fuses must be ignited,” for MS to take hold, according to a commentary accompanying the landmark 2022 study.
“As far as clinical implications, knowing whether a patient has a medical or family history of mononucleosis may be a small clue, a small piece of evidence, to help with diagnosis,” Dr. Bebo said.
He agreed with Dr. Levy that an antiviral could be a promising approach “If the problem in MS is a dysfunctional immune response to EBV.”
Natalia Drosu, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard-MIT Biomedical Engineering Center, said that a clinical trial of a non-immunosuppressive antiviral targeting EBV in patients with MS would be a crucial step toward better understanding the MS-EBV connection. “If we learn that antivirals are effective in MS, we should develop non-immunosuppressive therapies for patients with MS as soon as possible,” she said.
Stanford University’s Lawrence Steinman, MD, professor of neurology and neurological sciences, pediatrics, and genetics, who coauthored the commentary on the original Science paper, agreed that it’s worth investigating whether antiviral therapies targeting EBV will benefit patients who already have MS. But he cautioned against clinicians experimenting on their own outside of a research study. “You’d want to use the right antiviral and a properly designed trial,” he said.
Antivirals May Place a Crucial Role in MS Control
While there are no approved therapies for EBV, several MS disease-modifying therapies have anti-EBV effects, Dr. Levy said, citing anti-CD20 therapy as a clear example. It depletes B cells from the circulation, and it depletes EBV because the virus lives in the B-cell compartment. “Some MS treatments may be inadvertent EBV antivirals,” he said.
Researchers are also thinking about how they might exploit the MS-EBV link to prevent MS from developing in the first place, but there are uncertainties on that front too.
Conceivably, there may be some way to intervene in patients to treat EBV and prevent MS, such as a unique treatment for infectious mononucleosis (IM), Dr. Levy said.
Researchers are especially intrigued by signs that the timing of infection may play a role, with people infected with EBV via IM after early childhood at especially a high risk of developing MS. A 2022 German study calculated that people who developed IM were almost twice as likely as those who didn’t to develop MS within 10 years, although the risks in both groups were very small. Subgroup analysis revealed the strongest association between IM and MS was in the group infected between age 14 and 20 years (hazard ratio, 3.52; 95% CI, 1.00-12.37). They also saw a stronger association in men than in women.
The authors of a 2023 review in Clinical & Translational Immunology wrote that “further understanding of IM may be critical in solving the mystery” of EBV’s role in MS.
Dr. Levy said this line of questioning is important.
However, “remember that while most of the world gets EBV infections, only 1 in 1000 will get MS. So, it might not be feasible to test everyone before neurological manifestations occur,” he said.
More Questions to Answer About EBV and MS
Researchers hope to answer several questions moving forward. For one, why is EBV uniquely connected to MS? “You would think that if there were cross-reactivity to myelin, there are many viruses that could cause MS. But the association seems to be very restricted to EBV,” Dr. Levy said. “It is probably due to the fact that EBV is one of the only human viruses that can infect B cells, which play important roles in controlling immune responses.”
The molecular mimicry theory also opens up a potential treatment pathway.
A 2022 study reported “high-affinity molecular mimicry between the EBV transcription factor EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) and the central nervous system protein glial cell adhesion molecule (GlialCAM)”. Antibodies against EBNA1 and GlialCAM are prevalent in patients with MS. In a mouse model of MS, the researchers showed that EBNA1 immunization exacerbates disease. The authors wrote that “Our results provide a mechanistic link for the association between MS and EBV and could guide the development of new MS therapies.”
Could an EBV Vaccine Be the Answer?
On the prevention front, perhaps the most obvious question is whether an EBV vaccine could eliminate MS for good?
Dr. Bebo, from the National MS Society, said it will be important to determine which kind of vaccine is best. Is it one that neutralizes infection with EBV? Or is it enough to simply prevent clinical manifestations?
Both types of vaccines are in development, and at least two clinical trials are now in the works. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is sponsoring a phase 1 study of an adjuvanted EBV gp350-Ferritin nanoparticle vaccine. Forty subjects aged 18-29 years will take part: 20 with EBV and 20 who are not infected. The study is expected to end in 2025.
There is also a phase 1 placebo-controlled study in progress testing an EBV vaccine based on mRNA-1189 in 422 subjects aged 12-30 years. This trial is also due to end in 2025.
“This is very exciting, but it may take a decade or two to determine whether a vaccine is effective at preventing MS,” Dr. Levy said.
Dr. Levy, Dr. Steinman, Dr. Drosu, and Dr. Bebo had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is our constant companion, infecting an estimated 90%-95% of adults. Many of us are first infected as children, when the germ may trigger cold and flu symptoms. EBV also causes mononucleosis, or kissing disease, a glandular fever that has afflicted generations of amorous young people.
Post infection, EBV settles in for the long haul and remains in the body until death. It’s thought to be largely innocuous, but EBV is now implicated as a cause of several types of cancer — including lymphoma and nasopharyngeal tumors – and multiple sclerosis (MS). In 2022, a landmark study in Science suggested that previous EBV infection is the primary cause of MS.
While there aren’t many implications for current treatment, greater insight into the origin story of MS may eventually help neurologists better diagnose and treat patients, experts said. The goal is to uncover clues that “can help us understand MS a little bit better and reveal insights that could lead to new disease-modifying therapy,” Bruce Bebo, PhD, executive vice president of research with the National MS Society, said in an interview.
EBV Boosts MS Risk 32-Fold
EBV was first linked to MS back in 1981. For the 2022 study, researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed blood serum from 10 million active-duty members of the US military. They focused on 801 recruits with MS and matched them with more than 1500 controls. All but one of those with MS had been infected with EBV; infection appeared to boost the risk for MS 32-fold (95% CI, 4.3-245.3; P < .001).
Neurologist and associate professor Michael Levy, MD, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview that the findings are “groundbreaking” and confirm that EBV is “likely the primary cause of MS.”
According to Dr. Levy, there are two main theories about why EBV causes MS. The first hypothesis, known as the “molecular mimicry” theory, suggests that “EBV is a trigger of MS, possibly when the immune system mistakes a viral protein for a myelin protein and then attacks myelin,” Dr. Levy said. In MS, the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath and the axons it insulates.
“After that point, the virus is not necessary to maintain the disease state and eradicating the virus likely won’t have much effect since the immune response is already triggered,” he said.
The second theory is that “EBV is a driver of MS where there is an ongoing, lifelong immunological response to EBV that continuously causes damage in the central nervous system [CNS]. In theory, if we could eradicate the virus, the destructive immune response could also resolve. Thus, an EBV antiviral treatment could potentially treat and maybe cure MS,” Dr. Levy explained, noting that “removing the pathogenic antigen may be a more effective strategy than removing the immune response.”
However, “we don’t yet know which hypothesis is correct,” he said. But “there is preliminary evidence in favor of each one.”
‘Additional Fuses Must Be Ignited’
It’s also unclear why most people infected with EBV do not develop MS. It appears that “additional fuses must be ignited,” for MS to take hold, according to a commentary accompanying the landmark 2022 study.
“As far as clinical implications, knowing whether a patient has a medical or family history of mononucleosis may be a small clue, a small piece of evidence, to help with diagnosis,” Dr. Bebo said.
He agreed with Dr. Levy that an antiviral could be a promising approach “If the problem in MS is a dysfunctional immune response to EBV.”
Natalia Drosu, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard-MIT Biomedical Engineering Center, said that a clinical trial of a non-immunosuppressive antiviral targeting EBV in patients with MS would be a crucial step toward better understanding the MS-EBV connection. “If we learn that antivirals are effective in MS, we should develop non-immunosuppressive therapies for patients with MS as soon as possible,” she said.
Stanford University’s Lawrence Steinman, MD, professor of neurology and neurological sciences, pediatrics, and genetics, who coauthored the commentary on the original Science paper, agreed that it’s worth investigating whether antiviral therapies targeting EBV will benefit patients who already have MS. But he cautioned against clinicians experimenting on their own outside of a research study. “You’d want to use the right antiviral and a properly designed trial,” he said.
Antivirals May Place a Crucial Role in MS Control
While there are no approved therapies for EBV, several MS disease-modifying therapies have anti-EBV effects, Dr. Levy said, citing anti-CD20 therapy as a clear example. It depletes B cells from the circulation, and it depletes EBV because the virus lives in the B-cell compartment. “Some MS treatments may be inadvertent EBV antivirals,” he said.
Researchers are also thinking about how they might exploit the MS-EBV link to prevent MS from developing in the first place, but there are uncertainties on that front too.
Conceivably, there may be some way to intervene in patients to treat EBV and prevent MS, such as a unique treatment for infectious mononucleosis (IM), Dr. Levy said.
Researchers are especially intrigued by signs that the timing of infection may play a role, with people infected with EBV via IM after early childhood at especially a high risk of developing MS. A 2022 German study calculated that people who developed IM were almost twice as likely as those who didn’t to develop MS within 10 years, although the risks in both groups were very small. Subgroup analysis revealed the strongest association between IM and MS was in the group infected between age 14 and 20 years (hazard ratio, 3.52; 95% CI, 1.00-12.37). They also saw a stronger association in men than in women.
The authors of a 2023 review in Clinical & Translational Immunology wrote that “further understanding of IM may be critical in solving the mystery” of EBV’s role in MS.
Dr. Levy said this line of questioning is important.
However, “remember that while most of the world gets EBV infections, only 1 in 1000 will get MS. So, it might not be feasible to test everyone before neurological manifestations occur,” he said.
More Questions to Answer About EBV and MS
Researchers hope to answer several questions moving forward. For one, why is EBV uniquely connected to MS? “You would think that if there were cross-reactivity to myelin, there are many viruses that could cause MS. But the association seems to be very restricted to EBV,” Dr. Levy said. “It is probably due to the fact that EBV is one of the only human viruses that can infect B cells, which play important roles in controlling immune responses.”
The molecular mimicry theory also opens up a potential treatment pathway.
A 2022 study reported “high-affinity molecular mimicry between the EBV transcription factor EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) and the central nervous system protein glial cell adhesion molecule (GlialCAM)”. Antibodies against EBNA1 and GlialCAM are prevalent in patients with MS. In a mouse model of MS, the researchers showed that EBNA1 immunization exacerbates disease. The authors wrote that “Our results provide a mechanistic link for the association between MS and EBV and could guide the development of new MS therapies.”
Could an EBV Vaccine Be the Answer?
On the prevention front, perhaps the most obvious question is whether an EBV vaccine could eliminate MS for good?
Dr. Bebo, from the National MS Society, said it will be important to determine which kind of vaccine is best. Is it one that neutralizes infection with EBV? Or is it enough to simply prevent clinical manifestations?
Both types of vaccines are in development, and at least two clinical trials are now in the works. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is sponsoring a phase 1 study of an adjuvanted EBV gp350-Ferritin nanoparticle vaccine. Forty subjects aged 18-29 years will take part: 20 with EBV and 20 who are not infected. The study is expected to end in 2025.
There is also a phase 1 placebo-controlled study in progress testing an EBV vaccine based on mRNA-1189 in 422 subjects aged 12-30 years. This trial is also due to end in 2025.
“This is very exciting, but it may take a decade or two to determine whether a vaccine is effective at preventing MS,” Dr. Levy said.
Dr. Levy, Dr. Steinman, Dr. Drosu, and Dr. Bebo had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Blood Cancer Emergencies: Hematologists’ Late-Night Calls
When a patient with a blood-cancer crisis comes in, “I can recognize what’s going on, and I can initiate treatment. But if you do have a true hematologic emergency, then you need a hematologist to be able to contribute to your care,” Molly Estes, MD, an emergency physician with California’s Loma Linda University, said in an interview.
In situations such as a patient with an extraordinarily high white blood count, “you’ll be calling your hematologist for treatment recommendations and calling your nephrologist for assistance managing electrolyte disorders,” Megan Boysen-Osborn, MD, an emergency physician with the University of California at Irvine, said in an interview.
Here’s a look at three emergency hematologic conditions that lead to late-night phone calls:
Leukocytosis
Blood cancers can cause white blood cell counts to skyrocket, a condition known as leukocytosis, but a high count is not necessarily an emergency. The key is to figure out whether the high count is normal for the patient — perhaps due to the disease or the medical treatment — or a sign of an internal medical crisis, Dr. Estes said.
“Let’s say you stubbed your toe in the night, and I happened to get blood work on you and incidentally notice that your white blood cells are high. But they’re the same high level that they always are,” Dr. Estes said. “That’s a completely different scenario than if I’m seeing you for fever, vomiting, and stomach pain.”
Indeed, there’s no cut-off that differentiates a dangerously high white blood count from one that’s acceptable, Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of hematology at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Health System, said in an interview.
“In the past, I’ve taken care of a couple of patients who had chronic lymphocytic leukemia and white blood cell counts that were 200,000 or 300,000 [white blood cells per microliter] and worked out in the gym every day,” he said. “It didn’t negatively affect them. On the flip side, I have also taken care of patients with acute myeloid leukemia with a white blood cell count of 50,000. That landed them in the intensive care unit.”
Dr. Estes said that her first impulse in cases of high white blood cell count is to give IV fluids to dilute the blood and prevent the cells from turning blood into sludge via hyperviscosity syndrome. Dr. Sekeres said this makes sense, since the condition can lead to blockages in vessels and cause heart attacks and strokes.
There are other options, depending on the severity of the case. Hydroxyurea can be administered to lower white blood cell counts along with allopurinol to protect the kidneys, Dr. Sekeres said. In some situations, he said, “we’ll consider initiating chemotherapy immediately to reduce the level of the white blood cells. Or we will consider placing a patient on dialysis to take off some of those white blood cells.”
Tumor lysis syndrome
While it’s rare, tumor lysis syndrome can occur when tumors release their content into blood stream. According to Dr. Sekeres, this can happen when “cancers that grow so quickly that they can start to outgrow their own blood supply and start dying before we even treat patients. When this happens, it causes electrolyte disarray.”
It’s crucial to understand the potential for patients to quickly get worse, he said. He advises clinicians to aggressively check lab values for electrolyte abnormalities and aggressively administer IV fluids and electrolyte replacement when needed. “It’s also important to let the intensive care unit know that they may need to be activated,” he said. Fortunately, he noted, patients can often be stabilized.
Differentiation syndrome
According to the Cleveland Clinic, medications used to treat acute myeloid leukemia and acute promyelocytic leukemia cause cancer cells to differentiate from immature states to mature normal states. But the process can go awry when fluid leaks out of blood vessels in a condition called differentiation syndrome. This can cause multiple problems, Dr. Sekeres said.
A 2020 report noted the potential for “acute end-organ damage with peripheral edema, hypotension, acute renal failure, and interstitial pulmonary infiltrates.”
In these cases, aggressive supportive management is key, Dr. Sekeres said. If a patient is having difficulty breathing, for example, they’ll need electrolyte management and perhaps support via a respirator, he said.
“Most people with acute promyelocytic leukemia can fully recover from differentiation syndrome with prompt, effective treatment,” the Cleveland Clinic notes. It adds that the disease is “highly curable.”
In all of these emergent crises, Dr. Sekeres said, it’s important for hematologists understand that “patients can get very sick very quickly,” and it’s important to intervene early and often.
Dr. Sekeres serves on advisory boards for BMS and Curium Pharma. Dr. Estes and Dr. Boysen-Osborn have no disclosures.
When a patient with a blood-cancer crisis comes in, “I can recognize what’s going on, and I can initiate treatment. But if you do have a true hematologic emergency, then you need a hematologist to be able to contribute to your care,” Molly Estes, MD, an emergency physician with California’s Loma Linda University, said in an interview.
In situations such as a patient with an extraordinarily high white blood count, “you’ll be calling your hematologist for treatment recommendations and calling your nephrologist for assistance managing electrolyte disorders,” Megan Boysen-Osborn, MD, an emergency physician with the University of California at Irvine, said in an interview.
Here’s a look at three emergency hematologic conditions that lead to late-night phone calls:
Leukocytosis
Blood cancers can cause white blood cell counts to skyrocket, a condition known as leukocytosis, but a high count is not necessarily an emergency. The key is to figure out whether the high count is normal for the patient — perhaps due to the disease or the medical treatment — or a sign of an internal medical crisis, Dr. Estes said.
“Let’s say you stubbed your toe in the night, and I happened to get blood work on you and incidentally notice that your white blood cells are high. But they’re the same high level that they always are,” Dr. Estes said. “That’s a completely different scenario than if I’m seeing you for fever, vomiting, and stomach pain.”
Indeed, there’s no cut-off that differentiates a dangerously high white blood count from one that’s acceptable, Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of hematology at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Health System, said in an interview.
“In the past, I’ve taken care of a couple of patients who had chronic lymphocytic leukemia and white blood cell counts that were 200,000 or 300,000 [white blood cells per microliter] and worked out in the gym every day,” he said. “It didn’t negatively affect them. On the flip side, I have also taken care of patients with acute myeloid leukemia with a white blood cell count of 50,000. That landed them in the intensive care unit.”
Dr. Estes said that her first impulse in cases of high white blood cell count is to give IV fluids to dilute the blood and prevent the cells from turning blood into sludge via hyperviscosity syndrome. Dr. Sekeres said this makes sense, since the condition can lead to blockages in vessels and cause heart attacks and strokes.
There are other options, depending on the severity of the case. Hydroxyurea can be administered to lower white blood cell counts along with allopurinol to protect the kidneys, Dr. Sekeres said. In some situations, he said, “we’ll consider initiating chemotherapy immediately to reduce the level of the white blood cells. Or we will consider placing a patient on dialysis to take off some of those white blood cells.”
Tumor lysis syndrome
While it’s rare, tumor lysis syndrome can occur when tumors release their content into blood stream. According to Dr. Sekeres, this can happen when “cancers that grow so quickly that they can start to outgrow their own blood supply and start dying before we even treat patients. When this happens, it causes electrolyte disarray.”
It’s crucial to understand the potential for patients to quickly get worse, he said. He advises clinicians to aggressively check lab values for electrolyte abnormalities and aggressively administer IV fluids and electrolyte replacement when needed. “It’s also important to let the intensive care unit know that they may need to be activated,” he said. Fortunately, he noted, patients can often be stabilized.
Differentiation syndrome
According to the Cleveland Clinic, medications used to treat acute myeloid leukemia and acute promyelocytic leukemia cause cancer cells to differentiate from immature states to mature normal states. But the process can go awry when fluid leaks out of blood vessels in a condition called differentiation syndrome. This can cause multiple problems, Dr. Sekeres said.
A 2020 report noted the potential for “acute end-organ damage with peripheral edema, hypotension, acute renal failure, and interstitial pulmonary infiltrates.”
In these cases, aggressive supportive management is key, Dr. Sekeres said. If a patient is having difficulty breathing, for example, they’ll need electrolyte management and perhaps support via a respirator, he said.
“Most people with acute promyelocytic leukemia can fully recover from differentiation syndrome with prompt, effective treatment,” the Cleveland Clinic notes. It adds that the disease is “highly curable.”
In all of these emergent crises, Dr. Sekeres said, it’s important for hematologists understand that “patients can get very sick very quickly,” and it’s important to intervene early and often.
Dr. Sekeres serves on advisory boards for BMS and Curium Pharma. Dr. Estes and Dr. Boysen-Osborn have no disclosures.
When a patient with a blood-cancer crisis comes in, “I can recognize what’s going on, and I can initiate treatment. But if you do have a true hematologic emergency, then you need a hematologist to be able to contribute to your care,” Molly Estes, MD, an emergency physician with California’s Loma Linda University, said in an interview.
In situations such as a patient with an extraordinarily high white blood count, “you’ll be calling your hematologist for treatment recommendations and calling your nephrologist for assistance managing electrolyte disorders,” Megan Boysen-Osborn, MD, an emergency physician with the University of California at Irvine, said in an interview.
Here’s a look at three emergency hematologic conditions that lead to late-night phone calls:
Leukocytosis
Blood cancers can cause white blood cell counts to skyrocket, a condition known as leukocytosis, but a high count is not necessarily an emergency. The key is to figure out whether the high count is normal for the patient — perhaps due to the disease or the medical treatment — or a sign of an internal medical crisis, Dr. Estes said.
“Let’s say you stubbed your toe in the night, and I happened to get blood work on you and incidentally notice that your white blood cells are high. But they’re the same high level that they always are,” Dr. Estes said. “That’s a completely different scenario than if I’m seeing you for fever, vomiting, and stomach pain.”
Indeed, there’s no cut-off that differentiates a dangerously high white blood count from one that’s acceptable, Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of hematology at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Health System, said in an interview.
“In the past, I’ve taken care of a couple of patients who had chronic lymphocytic leukemia and white blood cell counts that were 200,000 or 300,000 [white blood cells per microliter] and worked out in the gym every day,” he said. “It didn’t negatively affect them. On the flip side, I have also taken care of patients with acute myeloid leukemia with a white blood cell count of 50,000. That landed them in the intensive care unit.”
Dr. Estes said that her first impulse in cases of high white blood cell count is to give IV fluids to dilute the blood and prevent the cells from turning blood into sludge via hyperviscosity syndrome. Dr. Sekeres said this makes sense, since the condition can lead to blockages in vessels and cause heart attacks and strokes.
There are other options, depending on the severity of the case. Hydroxyurea can be administered to lower white blood cell counts along with allopurinol to protect the kidneys, Dr. Sekeres said. In some situations, he said, “we’ll consider initiating chemotherapy immediately to reduce the level of the white blood cells. Or we will consider placing a patient on dialysis to take off some of those white blood cells.”
Tumor lysis syndrome
While it’s rare, tumor lysis syndrome can occur when tumors release their content into blood stream. According to Dr. Sekeres, this can happen when “cancers that grow so quickly that they can start to outgrow their own blood supply and start dying before we even treat patients. When this happens, it causes electrolyte disarray.”
It’s crucial to understand the potential for patients to quickly get worse, he said. He advises clinicians to aggressively check lab values for electrolyte abnormalities and aggressively administer IV fluids and electrolyte replacement when needed. “It’s also important to let the intensive care unit know that they may need to be activated,” he said. Fortunately, he noted, patients can often be stabilized.
Differentiation syndrome
According to the Cleveland Clinic, medications used to treat acute myeloid leukemia and acute promyelocytic leukemia cause cancer cells to differentiate from immature states to mature normal states. But the process can go awry when fluid leaks out of blood vessels in a condition called differentiation syndrome. This can cause multiple problems, Dr. Sekeres said.
A 2020 report noted the potential for “acute end-organ damage with peripheral edema, hypotension, acute renal failure, and interstitial pulmonary infiltrates.”
In these cases, aggressive supportive management is key, Dr. Sekeres said. If a patient is having difficulty breathing, for example, they’ll need electrolyte management and perhaps support via a respirator, he said.
“Most people with acute promyelocytic leukemia can fully recover from differentiation syndrome with prompt, effective treatment,” the Cleveland Clinic notes. It adds that the disease is “highly curable.”
In all of these emergent crises, Dr. Sekeres said, it’s important for hematologists understand that “patients can get very sick very quickly,” and it’s important to intervene early and often.
Dr. Sekeres serves on advisory boards for BMS and Curium Pharma. Dr. Estes and Dr. Boysen-Osborn have no disclosures.
Acne in Transmasculine Patients: Management Recommendations
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Topical Roflumilast Effective in 4 Weeks for Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
SAN DIEGO — Treatment with (AD), according to the results of a phase 3 study reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Among patients treated with roflumilast cream, 0.05%, 25.4% reached the primary endpoint of “clear” or “almost clear” plus a two-grade improvement from baseline at week 4 vs 10.7% among those in the vehicle group (P < .0001) in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial of children. The findings were released in a late-breaker session at the meeting.
Roflumilast cream, 0.3% (Zoryve), is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating psoriasis in patients 6 years and older, and lower doses are being evaluated for AD: 0.15% for adults and children ages 6 and older, and 0.05% for ages 2-5. Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor. In 2023, the FDA accepted a supplemental drug application from the manufacturer, Arcutis, for roflumilast, 0.15%, for treating AD in patients ages 6 and older, based on the results from two recently published phase 3 trials, INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2.
The study of younger children, INTEGUMENT-PED, recruited 652 patients aged 2-5 with mild to moderate AD, with a Validated Investigator Global Assessment scale for AD (vlGA-AD) score of 2 or 3, a mean body surface area of 22% overall (range, 3%-82%), and an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of at least 5. Of the patients enrolled, 437 were assigned to 0.05% roflumilast cream, applied once a day for 4 weeks (mean age, 3.3 years; 51.6% male; 67.4% White; 15.6% Black; 8.5% Asian; 8.5% other or more than one race; 80.5% not Latino/Hispanic). The remaining 215 children were assigned to vehicle cream and had similar characteristics.
About 52% of the patients in both groups had an inadequate response, intolerance, or contraindications to topical corticosteroids (and about 17% for topical calcineurin inhibitors and about 9% for crisaborole).
The proportions of patients who reached “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) on the vlGA-AD scale were 35.4% and 14.6%, respectively, at week 4 (P < .0001) for roflumilast and vehicle, respectively, according to the lead author of the study, Lawrence M. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, who presented the results at the meeting. In addition, 39.4% and 20.6% achieved an EASI-75 (a secondary endpoint), respectively (P < .0001), and itch also improved within 24 hours of starting treatment.
With regard to safety, 29.7% of patients taking roflumilast had treatment-emergent adverse effects (including upper respiratory tract infections in 4.1%) vs 21.9% of those in the vehicle arm (including upper respiratory tract infections in 1.4%). Reports of pain at the administration site were low (1.6% for roflumilast vs 1.9% for vehicle). Only one patient, a 2-year-old girl, had a treatment-emergent serious adverse event. The child, who was in the roflumilast group, had cellulitis involving noneczematous skin and was treated with antibiotics in the hospital for 3 days. The event was not attributed to roflumilast, which was stopped for 5 days, according to Dr. Eichenfield.
In an interview, Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist Brittany Craiglow, MD, who was not involved in the study, said topical roflumilast would be an “important” new treatment because there are still few nonsteroidal options for the treatment of AD in children under 12. “The excellent local tolerability combined with early improvements in itch and skin clearance will make this a particularly attractive option, if approved,” she said.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed multiple relationships with various drugmakers. He and several other study authors are investigators and/or consultants for Arcutis and received grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Two authors are Arcutis employees. Other disclosure information for the authors was not immediately available. Dr. Craiglow had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
SAN DIEGO — Treatment with (AD), according to the results of a phase 3 study reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Among patients treated with roflumilast cream, 0.05%, 25.4% reached the primary endpoint of “clear” or “almost clear” plus a two-grade improvement from baseline at week 4 vs 10.7% among those in the vehicle group (P < .0001) in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial of children. The findings were released in a late-breaker session at the meeting.
Roflumilast cream, 0.3% (Zoryve), is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating psoriasis in patients 6 years and older, and lower doses are being evaluated for AD: 0.15% for adults and children ages 6 and older, and 0.05% for ages 2-5. Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor. In 2023, the FDA accepted a supplemental drug application from the manufacturer, Arcutis, for roflumilast, 0.15%, for treating AD in patients ages 6 and older, based on the results from two recently published phase 3 trials, INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2.
The study of younger children, INTEGUMENT-PED, recruited 652 patients aged 2-5 with mild to moderate AD, with a Validated Investigator Global Assessment scale for AD (vlGA-AD) score of 2 or 3, a mean body surface area of 22% overall (range, 3%-82%), and an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of at least 5. Of the patients enrolled, 437 were assigned to 0.05% roflumilast cream, applied once a day for 4 weeks (mean age, 3.3 years; 51.6% male; 67.4% White; 15.6% Black; 8.5% Asian; 8.5% other or more than one race; 80.5% not Latino/Hispanic). The remaining 215 children were assigned to vehicle cream and had similar characteristics.
About 52% of the patients in both groups had an inadequate response, intolerance, or contraindications to topical corticosteroids (and about 17% for topical calcineurin inhibitors and about 9% for crisaborole).
The proportions of patients who reached “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) on the vlGA-AD scale were 35.4% and 14.6%, respectively, at week 4 (P < .0001) for roflumilast and vehicle, respectively, according to the lead author of the study, Lawrence M. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, who presented the results at the meeting. In addition, 39.4% and 20.6% achieved an EASI-75 (a secondary endpoint), respectively (P < .0001), and itch also improved within 24 hours of starting treatment.
With regard to safety, 29.7% of patients taking roflumilast had treatment-emergent adverse effects (including upper respiratory tract infections in 4.1%) vs 21.9% of those in the vehicle arm (including upper respiratory tract infections in 1.4%). Reports of pain at the administration site were low (1.6% for roflumilast vs 1.9% for vehicle). Only one patient, a 2-year-old girl, had a treatment-emergent serious adverse event. The child, who was in the roflumilast group, had cellulitis involving noneczematous skin and was treated with antibiotics in the hospital for 3 days. The event was not attributed to roflumilast, which was stopped for 5 days, according to Dr. Eichenfield.
In an interview, Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist Brittany Craiglow, MD, who was not involved in the study, said topical roflumilast would be an “important” new treatment because there are still few nonsteroidal options for the treatment of AD in children under 12. “The excellent local tolerability combined with early improvements in itch and skin clearance will make this a particularly attractive option, if approved,” she said.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed multiple relationships with various drugmakers. He and several other study authors are investigators and/or consultants for Arcutis and received grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Two authors are Arcutis employees. Other disclosure information for the authors was not immediately available. Dr. Craiglow had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
SAN DIEGO — Treatment with (AD), according to the results of a phase 3 study reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Among patients treated with roflumilast cream, 0.05%, 25.4% reached the primary endpoint of “clear” or “almost clear” plus a two-grade improvement from baseline at week 4 vs 10.7% among those in the vehicle group (P < .0001) in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial of children. The findings were released in a late-breaker session at the meeting.
Roflumilast cream, 0.3% (Zoryve), is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating psoriasis in patients 6 years and older, and lower doses are being evaluated for AD: 0.15% for adults and children ages 6 and older, and 0.05% for ages 2-5. Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor. In 2023, the FDA accepted a supplemental drug application from the manufacturer, Arcutis, for roflumilast, 0.15%, for treating AD in patients ages 6 and older, based on the results from two recently published phase 3 trials, INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2.
The study of younger children, INTEGUMENT-PED, recruited 652 patients aged 2-5 with mild to moderate AD, with a Validated Investigator Global Assessment scale for AD (vlGA-AD) score of 2 or 3, a mean body surface area of 22% overall (range, 3%-82%), and an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of at least 5. Of the patients enrolled, 437 were assigned to 0.05% roflumilast cream, applied once a day for 4 weeks (mean age, 3.3 years; 51.6% male; 67.4% White; 15.6% Black; 8.5% Asian; 8.5% other or more than one race; 80.5% not Latino/Hispanic). The remaining 215 children were assigned to vehicle cream and had similar characteristics.
About 52% of the patients in both groups had an inadequate response, intolerance, or contraindications to topical corticosteroids (and about 17% for topical calcineurin inhibitors and about 9% for crisaborole).
The proportions of patients who reached “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) on the vlGA-AD scale were 35.4% and 14.6%, respectively, at week 4 (P < .0001) for roflumilast and vehicle, respectively, according to the lead author of the study, Lawrence M. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, who presented the results at the meeting. In addition, 39.4% and 20.6% achieved an EASI-75 (a secondary endpoint), respectively (P < .0001), and itch also improved within 24 hours of starting treatment.
With regard to safety, 29.7% of patients taking roflumilast had treatment-emergent adverse effects (including upper respiratory tract infections in 4.1%) vs 21.9% of those in the vehicle arm (including upper respiratory tract infections in 1.4%). Reports of pain at the administration site were low (1.6% for roflumilast vs 1.9% for vehicle). Only one patient, a 2-year-old girl, had a treatment-emergent serious adverse event. The child, who was in the roflumilast group, had cellulitis involving noneczematous skin and was treated with antibiotics in the hospital for 3 days. The event was not attributed to roflumilast, which was stopped for 5 days, according to Dr. Eichenfield.
In an interview, Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist Brittany Craiglow, MD, who was not involved in the study, said topical roflumilast would be an “important” new treatment because there are still few nonsteroidal options for the treatment of AD in children under 12. “The excellent local tolerability combined with early improvements in itch and skin clearance will make this a particularly attractive option, if approved,” she said.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed multiple relationships with various drugmakers. He and several other study authors are investigators and/or consultants for Arcutis and received grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Two authors are Arcutis employees. Other disclosure information for the authors was not immediately available. Dr. Craiglow had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM AAD 2024
In Unexpected Finding, Clemastine Fumarate Linked to Worsening Symptoms in MS
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2024
An Easy, Effective Solution to Exercise-Induced Heat Sensitivity in RRMS?
WEST PALM BEACH, CALIFORNIA — , results from a new phase 3 trial suggested.
The findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study could solve this common problem, known clinically as Uhthoff’s phenomenon, that causes temporary worsening of MS symptoms with heat exposure.
“This could be a game changer,” said study investigator Victoria M. Leavitt, PhD, assistant professor of neuropsychology of Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) and published online in the Journal of Neurology.
A Common Condition
Research suggested that 60%-80% of MS patients experience heat sensitivity. However, while the exact cause is unknown, some evidence suggested it may be related to hypothalamic dysregulation or lesions of the hypothalamus.
Researchers have explored cooling strategies such as liquid-cooled clothing, but available tools can be hard to find, expensive, and cumbersome. Although aspirin has been linked to some symptom improvement in MS, its utility and that of acetaminophen for the condition has not been studied, Dr. Leavitt said.
For the single-center study, researchers recruited 60 patients (81% female; average age, 42 years; 73% White individuals) between 2019 and 2022. Overall, 37 completed at least one study visit, and 29 completed two to three visits. The average disease duration was 6 years.
Participants received oral administration of 650 mg aspirin, acetaminophen, or placebo at each of three study visits over 3 weeks, separated by at least 1 week. At each visit, they took part in a maximal exercise test conducted on a cycle ergometer and were asked to cycle at 50-60 revolutions/min for as long as possible.
Compared with placebo, body temperature increase from baseline to exercise stoppage was significantly reduced with aspirin (0.006 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .001) and with acetaminophen (0.31 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .004)
Neither medication was associated with a significant difference in time to exhaustion, and there were no serious adverse events.
“This is really nice because some people might have an adverse reaction to aspirin,” such as gastrointestinal issues. Acetaminophen has a different side-effect profile,” Dr. Leavitt said.
Both medications are inexpensive and available over the counter. The 650-mg acetaminophen dose used in the study is available in an extended-release formula. Typically aspirin isn’t available in doses larger than 325 mg. The 650-mg dose used in the study is considered safe but large.
Dr. Leavitt said she would like to study daily aspirin in people with MS to see if it can boost physical activity. “That’s the test of whether this will meaningfully affect the lives of people with MS,” she said.
No Harm From Overheating
Commenting on the findings, Katherine Knox, MD, associate professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada, noted that “the intervention maybe be initially helpful for the person fearful of getting weaker when they get ‘hot’ with exercise.”
Dr. Knox, who wasn’t involved in the research, added that it’s important for patients with MS to overcome initial barriers and fears about exercise.
“However, for most people the effects of being warm with exercise are less concerning for them after education that the weakness is temporary and does not cause harm if one takes the right precautions such as planning ahead to avoid a fall,” she said. Also, inexpensive interventions such as a fan or a wet cotton headband can be helpful, she said.
The study “provides further evidence that the ‘overheating’ is not causing harm since the time to exhaustion was unchanged,” Dr. Knox added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no disclosures. Disclosure information for Dr. Knox was not available.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, CALIFORNIA — , results from a new phase 3 trial suggested.
The findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study could solve this common problem, known clinically as Uhthoff’s phenomenon, that causes temporary worsening of MS symptoms with heat exposure.
“This could be a game changer,” said study investigator Victoria M. Leavitt, PhD, assistant professor of neuropsychology of Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) and published online in the Journal of Neurology.
A Common Condition
Research suggested that 60%-80% of MS patients experience heat sensitivity. However, while the exact cause is unknown, some evidence suggested it may be related to hypothalamic dysregulation or lesions of the hypothalamus.
Researchers have explored cooling strategies such as liquid-cooled clothing, but available tools can be hard to find, expensive, and cumbersome. Although aspirin has been linked to some symptom improvement in MS, its utility and that of acetaminophen for the condition has not been studied, Dr. Leavitt said.
For the single-center study, researchers recruited 60 patients (81% female; average age, 42 years; 73% White individuals) between 2019 and 2022. Overall, 37 completed at least one study visit, and 29 completed two to three visits. The average disease duration was 6 years.
Participants received oral administration of 650 mg aspirin, acetaminophen, or placebo at each of three study visits over 3 weeks, separated by at least 1 week. At each visit, they took part in a maximal exercise test conducted on a cycle ergometer and were asked to cycle at 50-60 revolutions/min for as long as possible.
Compared with placebo, body temperature increase from baseline to exercise stoppage was significantly reduced with aspirin (0.006 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .001) and with acetaminophen (0.31 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .004)
Neither medication was associated with a significant difference in time to exhaustion, and there were no serious adverse events.
“This is really nice because some people might have an adverse reaction to aspirin,” such as gastrointestinal issues. Acetaminophen has a different side-effect profile,” Dr. Leavitt said.
Both medications are inexpensive and available over the counter. The 650-mg acetaminophen dose used in the study is available in an extended-release formula. Typically aspirin isn’t available in doses larger than 325 mg. The 650-mg dose used in the study is considered safe but large.
Dr. Leavitt said she would like to study daily aspirin in people with MS to see if it can boost physical activity. “That’s the test of whether this will meaningfully affect the lives of people with MS,” she said.
No Harm From Overheating
Commenting on the findings, Katherine Knox, MD, associate professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada, noted that “the intervention maybe be initially helpful for the person fearful of getting weaker when they get ‘hot’ with exercise.”
Dr. Knox, who wasn’t involved in the research, added that it’s important for patients with MS to overcome initial barriers and fears about exercise.
“However, for most people the effects of being warm with exercise are less concerning for them after education that the weakness is temporary and does not cause harm if one takes the right precautions such as planning ahead to avoid a fall,” she said. Also, inexpensive interventions such as a fan or a wet cotton headband can be helpful, she said.
The study “provides further evidence that the ‘overheating’ is not causing harm since the time to exhaustion was unchanged,” Dr. Knox added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no disclosures. Disclosure information for Dr. Knox was not available.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, CALIFORNIA — , results from a new phase 3 trial suggested.
The findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study could solve this common problem, known clinically as Uhthoff’s phenomenon, that causes temporary worsening of MS symptoms with heat exposure.
“This could be a game changer,” said study investigator Victoria M. Leavitt, PhD, assistant professor of neuropsychology of Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) and published online in the Journal of Neurology.
A Common Condition
Research suggested that 60%-80% of MS patients experience heat sensitivity. However, while the exact cause is unknown, some evidence suggested it may be related to hypothalamic dysregulation or lesions of the hypothalamus.
Researchers have explored cooling strategies such as liquid-cooled clothing, but available tools can be hard to find, expensive, and cumbersome. Although aspirin has been linked to some symptom improvement in MS, its utility and that of acetaminophen for the condition has not been studied, Dr. Leavitt said.
For the single-center study, researchers recruited 60 patients (81% female; average age, 42 years; 73% White individuals) between 2019 and 2022. Overall, 37 completed at least one study visit, and 29 completed two to three visits. The average disease duration was 6 years.
Participants received oral administration of 650 mg aspirin, acetaminophen, or placebo at each of three study visits over 3 weeks, separated by at least 1 week. At each visit, they took part in a maximal exercise test conducted on a cycle ergometer and were asked to cycle at 50-60 revolutions/min for as long as possible.
Compared with placebo, body temperature increase from baseline to exercise stoppage was significantly reduced with aspirin (0.006 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .001) and with acetaminophen (0.31 °F vs 0.68 °F; P < .004)
Neither medication was associated with a significant difference in time to exhaustion, and there were no serious adverse events.
“This is really nice because some people might have an adverse reaction to aspirin,” such as gastrointestinal issues. Acetaminophen has a different side-effect profile,” Dr. Leavitt said.
Both medications are inexpensive and available over the counter. The 650-mg acetaminophen dose used in the study is available in an extended-release formula. Typically aspirin isn’t available in doses larger than 325 mg. The 650-mg dose used in the study is considered safe but large.
Dr. Leavitt said she would like to study daily aspirin in people with MS to see if it can boost physical activity. “That’s the test of whether this will meaningfully affect the lives of people with MS,” she said.
No Harm From Overheating
Commenting on the findings, Katherine Knox, MD, associate professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada, noted that “the intervention maybe be initially helpful for the person fearful of getting weaker when they get ‘hot’ with exercise.”
Dr. Knox, who wasn’t involved in the research, added that it’s important for patients with MS to overcome initial barriers and fears about exercise.
“However, for most people the effects of being warm with exercise are less concerning for them after education that the weakness is temporary and does not cause harm if one takes the right precautions such as planning ahead to avoid a fall,” she said. Also, inexpensive interventions such as a fan or a wet cotton headband can be helpful, she said.
The study “provides further evidence that the ‘overheating’ is not causing harm since the time to exhaustion was unchanged,” Dr. Knox added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no disclosures. Disclosure information for Dr. Knox was not available.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2024
Inside the 2024 AAD Acne Guidelines: New Therapies Join Old Standbys
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024

