User login
Do ICDs still ‘work’ in primary prevention given today’s recommended HF meds?
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC CLINICAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Cardiologists concerned for patient safety after abortion ruling
Pregnancy termination for medical reasons had been part of the fabric of everyday health care in the United States since the Supreme Court’s 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, which the current high court overturned in a ruling announced on June 24.
That means many clinicians across specialties are entering uncharted territory with the country’s new patchwork of abortion legality. Some specialties, cardiology among them, may feel the impact more than others.
“We know that the rising maternal mortality rate is predominantly driven by cardiovascular disease, women having children at older ages, and ... risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity,” Jennifer H. Haythe, MD, told this news organization.
So the high court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned Roe v. Wade and leaves the legality of abortion up to the 50 separate state legislatures, “is very relevant to cardiologists specifically,” said Dr. Haythe, who is director of cardiology in the cardio-obstetrics program at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
The ruling “is going to have a huge effect on women who may not be able to tolerate pregnancy,” she said. Whether to terminate a pregnancy “is a relatively common discussion I have with women with bad heart failure about their risk of further decompensation, death, or needing a heart transplant or heart pump after delivery, or the risk of death in women with pulmonary hypertension.”
The high court’s decision “is a direct attack on the practice of medicine and really the sanctity of the patient-clinician relationship,” Rachel M. Bond, MD, director of Women’s Heart Health Systems Dignity Health of Arizona, told this news organization.
Physicians take an oath “that we should do no harm to our patients, and once the law or governance impacts that, it places us in a very vulnerable situation,” Dr. Bond said. “As a cardiologist who focuses a lot on high-risk pregnancies, I am worried and hesitant to give guidance to many of these patients in the states that may not have access to something that is a medical right, which at times is an abortion.”
She has colleagues in obstetrics in states where abortion is newly illegal who “don’t know what to do,” Dr. Bond said. Many have sought guidance from their legal teams, she said, “and many of them are now trying to figure out what is the best path.”
Pregnancy is “a very significant cardiovascular stress test, and women who may tolerate certain conditions reasonably well outside of the setting of pregnancy may have severe issues, not just for the mother, but for the baby as well,” Ki Park, MD, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said in an interview.
“As clinicians, none of us like recommending a medically indicated abortion. But it is health care, just like any other medication or treatment that we advise to our patients in cases where the risk of the mother is excessively high and mortality risk is elevated,” said Dr. Park, who is cochair of the American College of Cardiology Cardio-Obstetrics Work Group.
Some conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension and severe aortic valve stenosis, during pregnancy are well recognized as very high risk, and there are various scoring systems to help clinicians with risk stratification, she observed. “But there are also a lot of gray areas where patients don’t necessarily fit into these risk scores that we use.”
So physician-patient discussions in high-risk pregnancies “are already complicated,” Dr. Park said. “Patients want to have options, and they look to us as physicians for guidance with regard to their risks. And if abortion is not available as an option, then part of our toolbox is no longer available to help us care for the mother.”
In the new legal climate, clinicians in states where abortion is illegal may well want to put more emphasis on preconception counseling, so more of their patients with high-risk conditions are aware of the new barriers to pregnancy termination.
“Unfortunately,” Dr. Haythe said, “many of the states that are going to make or have made abortion illegal are not providing that kind of preconception counseling or good prenatal care to women.”
Cardiologists can provide such counseling to their female patients of childbearing age who have high-risk cardiac conditions, “but not everybody knows that they have a heart problem when they get pregnant, and not everybody is getting screened for heart problems when they’re of childbearing age,” Dr. Haythe said.
“Sometimes it’s not clear whether the problems could have been picked up until a woman is pregnant and has started to have symptoms.” For example, “a lot of women with poor access to health care have rheumatic heart disease. They may have no idea that they have severe aortic stenosis, and it’s not until their second trimester that they start to feel really short of breath.” Often that can be treated in the cath lab, “but again, that’s putting the woman and the baby at risk.”
Cardiologists in states where abortion is illegal will still present the option to their patients with high-risk pregnancies, noted Dr. Haythe. But the conversation may sound something like, “you are at very high risk, termination of the pregnancy takes that risk away, but you’ll have to find a state where it’s legal to do that.”
Dr. Park said such a situation, when abortion is recommended but locally unavailable, is much like any other in cardiology for which the patient may want a second opinion. If a center “doesn’t have the capability or the technology to offer a certain treatment, the patient can opt to seek another opinion at another center,” she said. “Patients will often travel out of state to get the care they need.”
A requirement for out-of-state travel to obtain abortions is likely to worsen socioeconomic disparities in health care, Dr. Bond observed, “because we know that those who are low-income won’t be able to afford that travel.”
Dr. Bond is cosignatory on a statement from the Association of Black Cardiologists (ABC) responding to the high court’s ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson. “This decision will isolate the poor, socioeconomically disadvantaged, and minority populations specifically, widening the already large gaps in health care for our most vulnerable communities,” it states.
“The loss of broad protections supporting the medical and often lifesaving procedure of abortions is likely to have a real impact on the maternal mortality rate, especially in those with congenital and/or acquired cardiovascular conditions where evidence-based guidelines advise at times on termination of such high-risk pregnancies.”
The ABC, it states, “believes that every woman, and every person, should be afforded the right to safe, accessible, legal, timely, patient-centered, equitable, and affordable health care.”
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) released a statement on the matter June 24, signed by its president, Edward T.A. Fry, MD, along with five former ACC presidents. “While the ACC has no official policy on abortion, clinical practice guidelines and other clinical guidance tools address the dangers of pregnancy in certain patient populations at higher risk of death or serious cardiac events.”
The college, it states, is “deeply concerned about the potential implications of the Supreme Court decision regarding Roe vs. Wade on the ability of patients and clinicians to engage in important shared discussions about maternal health, or to remove previously available health care options.”
Dr. Bond proposed that a “vocal stance” from medical societies involved in women’s health, “perhaps even a collective stance from our cardiovascular societies and our obstetrics societies,” would also perhaps reach “the masses of doctors in private practice who are dealing with these patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnancy termination for medical reasons had been part of the fabric of everyday health care in the United States since the Supreme Court’s 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, which the current high court overturned in a ruling announced on June 24.
That means many clinicians across specialties are entering uncharted territory with the country’s new patchwork of abortion legality. Some specialties, cardiology among them, may feel the impact more than others.
“We know that the rising maternal mortality rate is predominantly driven by cardiovascular disease, women having children at older ages, and ... risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity,” Jennifer H. Haythe, MD, told this news organization.
So the high court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned Roe v. Wade and leaves the legality of abortion up to the 50 separate state legislatures, “is very relevant to cardiologists specifically,” said Dr. Haythe, who is director of cardiology in the cardio-obstetrics program at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
The ruling “is going to have a huge effect on women who may not be able to tolerate pregnancy,” she said. Whether to terminate a pregnancy “is a relatively common discussion I have with women with bad heart failure about their risk of further decompensation, death, or needing a heart transplant or heart pump after delivery, or the risk of death in women with pulmonary hypertension.”
The high court’s decision “is a direct attack on the practice of medicine and really the sanctity of the patient-clinician relationship,” Rachel M. Bond, MD, director of Women’s Heart Health Systems Dignity Health of Arizona, told this news organization.
Physicians take an oath “that we should do no harm to our patients, and once the law or governance impacts that, it places us in a very vulnerable situation,” Dr. Bond said. “As a cardiologist who focuses a lot on high-risk pregnancies, I am worried and hesitant to give guidance to many of these patients in the states that may not have access to something that is a medical right, which at times is an abortion.”
She has colleagues in obstetrics in states where abortion is newly illegal who “don’t know what to do,” Dr. Bond said. Many have sought guidance from their legal teams, she said, “and many of them are now trying to figure out what is the best path.”
Pregnancy is “a very significant cardiovascular stress test, and women who may tolerate certain conditions reasonably well outside of the setting of pregnancy may have severe issues, not just for the mother, but for the baby as well,” Ki Park, MD, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said in an interview.
“As clinicians, none of us like recommending a medically indicated abortion. But it is health care, just like any other medication or treatment that we advise to our patients in cases where the risk of the mother is excessively high and mortality risk is elevated,” said Dr. Park, who is cochair of the American College of Cardiology Cardio-Obstetrics Work Group.
Some conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension and severe aortic valve stenosis, during pregnancy are well recognized as very high risk, and there are various scoring systems to help clinicians with risk stratification, she observed. “But there are also a lot of gray areas where patients don’t necessarily fit into these risk scores that we use.”
So physician-patient discussions in high-risk pregnancies “are already complicated,” Dr. Park said. “Patients want to have options, and they look to us as physicians for guidance with regard to their risks. And if abortion is not available as an option, then part of our toolbox is no longer available to help us care for the mother.”
In the new legal climate, clinicians in states where abortion is illegal may well want to put more emphasis on preconception counseling, so more of their patients with high-risk conditions are aware of the new barriers to pregnancy termination.
“Unfortunately,” Dr. Haythe said, “many of the states that are going to make or have made abortion illegal are not providing that kind of preconception counseling or good prenatal care to women.”
Cardiologists can provide such counseling to their female patients of childbearing age who have high-risk cardiac conditions, “but not everybody knows that they have a heart problem when they get pregnant, and not everybody is getting screened for heart problems when they’re of childbearing age,” Dr. Haythe said.
“Sometimes it’s not clear whether the problems could have been picked up until a woman is pregnant and has started to have symptoms.” For example, “a lot of women with poor access to health care have rheumatic heart disease. They may have no idea that they have severe aortic stenosis, and it’s not until their second trimester that they start to feel really short of breath.” Often that can be treated in the cath lab, “but again, that’s putting the woman and the baby at risk.”
Cardiologists in states where abortion is illegal will still present the option to their patients with high-risk pregnancies, noted Dr. Haythe. But the conversation may sound something like, “you are at very high risk, termination of the pregnancy takes that risk away, but you’ll have to find a state where it’s legal to do that.”
Dr. Park said such a situation, when abortion is recommended but locally unavailable, is much like any other in cardiology for which the patient may want a second opinion. If a center “doesn’t have the capability or the technology to offer a certain treatment, the patient can opt to seek another opinion at another center,” she said. “Patients will often travel out of state to get the care they need.”
A requirement for out-of-state travel to obtain abortions is likely to worsen socioeconomic disparities in health care, Dr. Bond observed, “because we know that those who are low-income won’t be able to afford that travel.”
Dr. Bond is cosignatory on a statement from the Association of Black Cardiologists (ABC) responding to the high court’s ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson. “This decision will isolate the poor, socioeconomically disadvantaged, and minority populations specifically, widening the already large gaps in health care for our most vulnerable communities,” it states.
“The loss of broad protections supporting the medical and often lifesaving procedure of abortions is likely to have a real impact on the maternal mortality rate, especially in those with congenital and/or acquired cardiovascular conditions where evidence-based guidelines advise at times on termination of such high-risk pregnancies.”
The ABC, it states, “believes that every woman, and every person, should be afforded the right to safe, accessible, legal, timely, patient-centered, equitable, and affordable health care.”
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) released a statement on the matter June 24, signed by its president, Edward T.A. Fry, MD, along with five former ACC presidents. “While the ACC has no official policy on abortion, clinical practice guidelines and other clinical guidance tools address the dangers of pregnancy in certain patient populations at higher risk of death or serious cardiac events.”
The college, it states, is “deeply concerned about the potential implications of the Supreme Court decision regarding Roe vs. Wade on the ability of patients and clinicians to engage in important shared discussions about maternal health, or to remove previously available health care options.”
Dr. Bond proposed that a “vocal stance” from medical societies involved in women’s health, “perhaps even a collective stance from our cardiovascular societies and our obstetrics societies,” would also perhaps reach “the masses of doctors in private practice who are dealing with these patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnancy termination for medical reasons had been part of the fabric of everyday health care in the United States since the Supreme Court’s 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, which the current high court overturned in a ruling announced on June 24.
That means many clinicians across specialties are entering uncharted territory with the country’s new patchwork of abortion legality. Some specialties, cardiology among them, may feel the impact more than others.
“We know that the rising maternal mortality rate is predominantly driven by cardiovascular disease, women having children at older ages, and ... risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity,” Jennifer H. Haythe, MD, told this news organization.
So the high court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned Roe v. Wade and leaves the legality of abortion up to the 50 separate state legislatures, “is very relevant to cardiologists specifically,” said Dr. Haythe, who is director of cardiology in the cardio-obstetrics program at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
The ruling “is going to have a huge effect on women who may not be able to tolerate pregnancy,” she said. Whether to terminate a pregnancy “is a relatively common discussion I have with women with bad heart failure about their risk of further decompensation, death, or needing a heart transplant or heart pump after delivery, or the risk of death in women with pulmonary hypertension.”
The high court’s decision “is a direct attack on the practice of medicine and really the sanctity of the patient-clinician relationship,” Rachel M. Bond, MD, director of Women’s Heart Health Systems Dignity Health of Arizona, told this news organization.
Physicians take an oath “that we should do no harm to our patients, and once the law or governance impacts that, it places us in a very vulnerable situation,” Dr. Bond said. “As a cardiologist who focuses a lot on high-risk pregnancies, I am worried and hesitant to give guidance to many of these patients in the states that may not have access to something that is a medical right, which at times is an abortion.”
She has colleagues in obstetrics in states where abortion is newly illegal who “don’t know what to do,” Dr. Bond said. Many have sought guidance from their legal teams, she said, “and many of them are now trying to figure out what is the best path.”
Pregnancy is “a very significant cardiovascular stress test, and women who may tolerate certain conditions reasonably well outside of the setting of pregnancy may have severe issues, not just for the mother, but for the baby as well,” Ki Park, MD, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said in an interview.
“As clinicians, none of us like recommending a medically indicated abortion. But it is health care, just like any other medication or treatment that we advise to our patients in cases where the risk of the mother is excessively high and mortality risk is elevated,” said Dr. Park, who is cochair of the American College of Cardiology Cardio-Obstetrics Work Group.
Some conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension and severe aortic valve stenosis, during pregnancy are well recognized as very high risk, and there are various scoring systems to help clinicians with risk stratification, she observed. “But there are also a lot of gray areas where patients don’t necessarily fit into these risk scores that we use.”
So physician-patient discussions in high-risk pregnancies “are already complicated,” Dr. Park said. “Patients want to have options, and they look to us as physicians for guidance with regard to their risks. And if abortion is not available as an option, then part of our toolbox is no longer available to help us care for the mother.”
In the new legal climate, clinicians in states where abortion is illegal may well want to put more emphasis on preconception counseling, so more of their patients with high-risk conditions are aware of the new barriers to pregnancy termination.
“Unfortunately,” Dr. Haythe said, “many of the states that are going to make or have made abortion illegal are not providing that kind of preconception counseling or good prenatal care to women.”
Cardiologists can provide such counseling to their female patients of childbearing age who have high-risk cardiac conditions, “but not everybody knows that they have a heart problem when they get pregnant, and not everybody is getting screened for heart problems when they’re of childbearing age,” Dr. Haythe said.
“Sometimes it’s not clear whether the problems could have been picked up until a woman is pregnant and has started to have symptoms.” For example, “a lot of women with poor access to health care have rheumatic heart disease. They may have no idea that they have severe aortic stenosis, and it’s not until their second trimester that they start to feel really short of breath.” Often that can be treated in the cath lab, “but again, that’s putting the woman and the baby at risk.”
Cardiologists in states where abortion is illegal will still present the option to their patients with high-risk pregnancies, noted Dr. Haythe. But the conversation may sound something like, “you are at very high risk, termination of the pregnancy takes that risk away, but you’ll have to find a state where it’s legal to do that.”
Dr. Park said such a situation, when abortion is recommended but locally unavailable, is much like any other in cardiology for which the patient may want a second opinion. If a center “doesn’t have the capability or the technology to offer a certain treatment, the patient can opt to seek another opinion at another center,” she said. “Patients will often travel out of state to get the care they need.”
A requirement for out-of-state travel to obtain abortions is likely to worsen socioeconomic disparities in health care, Dr. Bond observed, “because we know that those who are low-income won’t be able to afford that travel.”
Dr. Bond is cosignatory on a statement from the Association of Black Cardiologists (ABC) responding to the high court’s ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson. “This decision will isolate the poor, socioeconomically disadvantaged, and minority populations specifically, widening the already large gaps in health care for our most vulnerable communities,” it states.
“The loss of broad protections supporting the medical and often lifesaving procedure of abortions is likely to have a real impact on the maternal mortality rate, especially in those with congenital and/or acquired cardiovascular conditions where evidence-based guidelines advise at times on termination of such high-risk pregnancies.”
The ABC, it states, “believes that every woman, and every person, should be afforded the right to safe, accessible, legal, timely, patient-centered, equitable, and affordable health care.”
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) released a statement on the matter June 24, signed by its president, Edward T.A. Fry, MD, along with five former ACC presidents. “While the ACC has no official policy on abortion, clinical practice guidelines and other clinical guidance tools address the dangers of pregnancy in certain patient populations at higher risk of death or serious cardiac events.”
The college, it states, is “deeply concerned about the potential implications of the Supreme Court decision regarding Roe vs. Wade on the ability of patients and clinicians to engage in important shared discussions about maternal health, or to remove previously available health care options.”
Dr. Bond proposed that a “vocal stance” from medical societies involved in women’s health, “perhaps even a collective stance from our cardiovascular societies and our obstetrics societies,” would also perhaps reach “the masses of doctors in private practice who are dealing with these patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pig-heart transplant case published with new details, insights
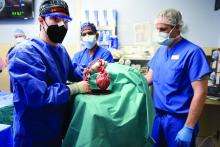
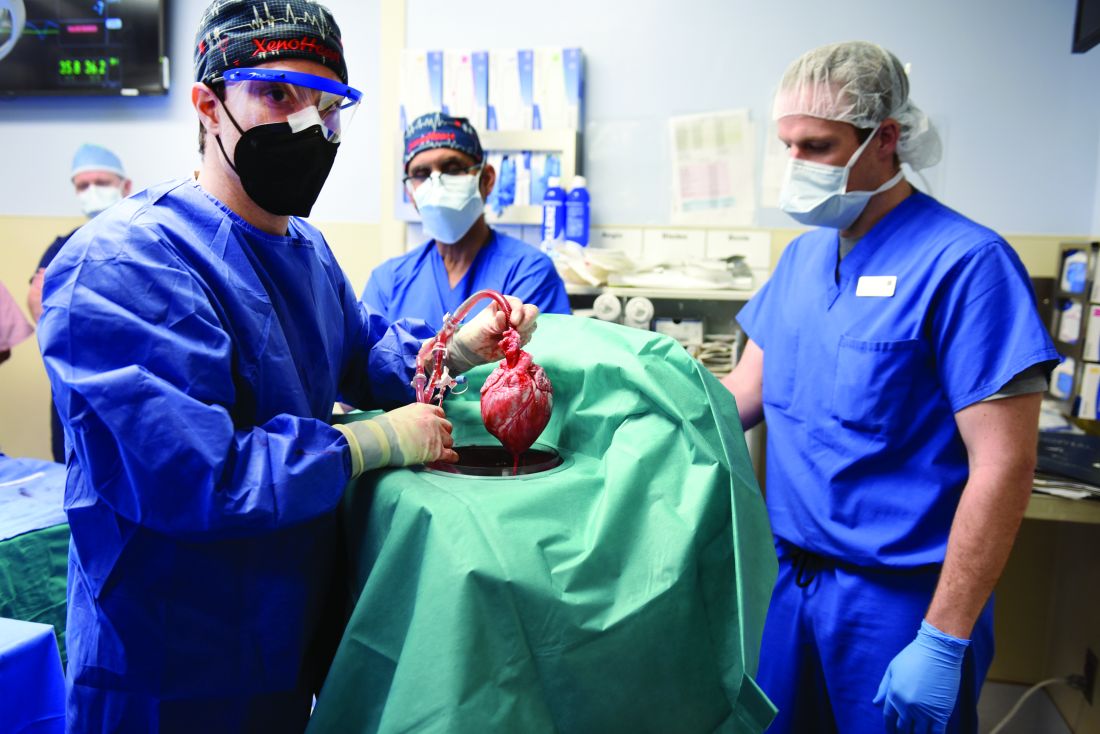
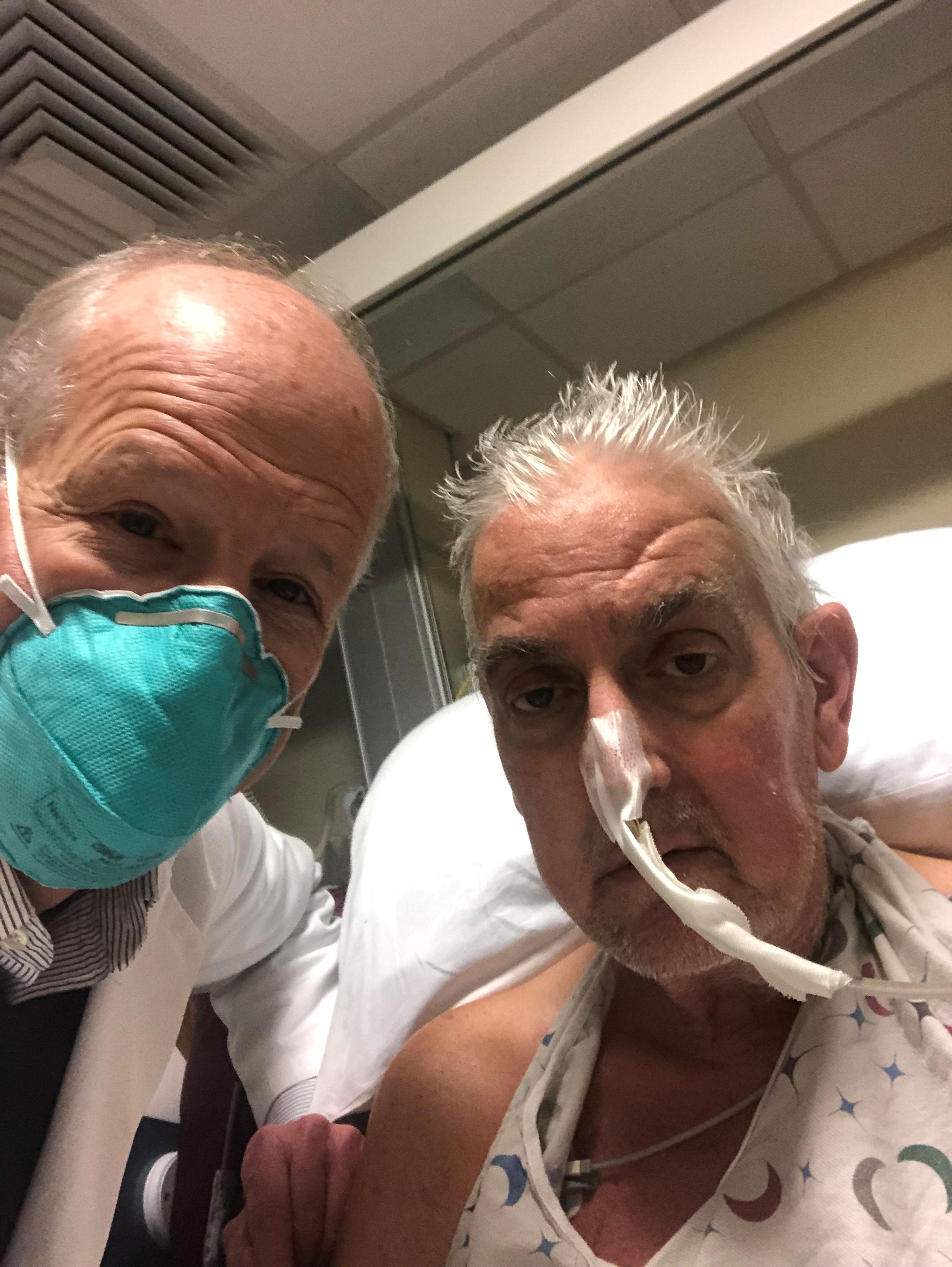
It’s a given that the case of David Bennett, Sr, and his transplanted, genetically modified porcine heart will have a lot to teach, and the peer-reviewed publication this week lends welcome authority to some of its earliest lessons.
Mr. Bennett lived for 2 months after receiving the heart in the pioneering surgery, and the new case report compiles the available clinical, anatomic, and histologic evidence and other potential clues to the underlying cause or causes of death.
It also describes a mystery that came to light at autopsy: a grossly enlarged heart attributable to pervasive interstitial edema, and at the cellular level, a peculiar pattern of myocardial damage that included microvascular deterioration and, potentially as a result, cellular necrosis, according to the new report.
The myocardium itself was described as “thickened and stiff,” consistent with the “diastolic heart failure” that characterized Mr. Bennett’s final 10 days and the likely convergence of several underlying processes. Missing, however, was any conventional sign of graft rejection as it is understood clinically or in animal models, the report states.
If a form of tissue rejection was the cause of graft failure, any implicating cellular evidence may simply have been unrecognizable, given the unprecedented nature of the first pig-to-human heart transplantation, the donor animal’s multiple anti-inflammatory gene deletions, and partly investigational immunosuppression regimen, speculated Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, College Park.
“I’m betting against it being a fulminant rejection,” he told this news organization, “because we saw nothing like the [characteristic] platelet deposition or thrombosis of the capillaries.”
Dr. Griffith, who performed the xenotransplant surgery and led Mr. Bennett’s postoperative care, is lead author on the case report published in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Additional studies are underway to characterize the pathophysiologic mechanisms that resulted in this damage,” the report states.
The report builds on recent meeting presentations on the case, which, as previously reported, gave cursory details regarding the organ damage and other clinical developments during and after the surgery, including evidence that the transplanted heart contained porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV).
Similar details also appeared in a third-person account based in part on personal communication with Dr. Griffith. The cardiac XTx review that focused on this University of Maryland experience was published June 15 in JACC: Basic to Translational Science, with lead author Jacinthe Boulet, MD, CM, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart, Boston.
“The question of how to move XTx forward remains uncertain, and appropriate selection of patients for experimental XTx will be one of the most important challenges to be addressed. The first issue we must contend with is whether we are ready to move to the next XTx in a human. We strongly believe this to be the case,” the review states. “Once early experience is gained, with successive iterations of XTx, the bar for success can be raised with maturation of the technology.”
Evidence has so far not implicated several other potential mechanisms underlying the graft failure that had been the focus of early speculations. For example, the transplanted pig heart was infected with PCMV, as previously reported. Mr. Bennett showed traces of PCMV DNA in his circulation, but no actual virus in his native cells. Still, PCMV remains a suspect.
Mr. Bennett also received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) on several occasions to fight rejection, and also severe infections, including a nasty episode of sepsis. A reaction to the IVIG, derived from pooled donor antibodies, could potentially have caused the unusual myocardial damage seen by the University of Maryland team, Dr. Griffith observed. Alternatively, the damage might have been partly related to the patient’s overall severely diminished condition even before the transplant surgery or his rocky postoperative clinical course.
Indeed, Mr. Bennett’s condition worsened dramatically on postoperative day 50, and echocardiography showed a striking degree of myocardial wall thickening and heart enlargement, determined to be from edema. “The heart got amazingly stiff but maintained a systolic function that wasn›t too terrible, even to the very end. But his heart seemed as though it had swollen overnight,” Dr. Griffith said. “We had never seen that type of process, the suddenness of this swelling, in our nonhuman primate studies.”
The damage to the heart muscle appeared irreversible, based on myocardial biopsy results, so the decision was made to withdraw life support 60 days after the transplant surgery, the report notes.
Among the experience’s apparent lessons for future cardiac xenotransplantation, Dr. Griffith said, would be to select patients for the surgery who are in a bit more robust condition than Mr. Bennett was, who are perhaps ambulatory, not sarcopenic, and not recently on prolonged mechanical circulatory support. “We’re going to try to pick a patient who, on the front end, is less critically ill but who is just as likely not to benefit from continued medical therapy” and who isn’t a candidate for conventional heart transplantation, he said.
Because of universal efforts to manage conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and vascular disease in the population, and “because these conditions cause many of the cases of organ failure and fuel demand for transplantation, one might wonder whether the advances reported by Dr. Griffith and colleagues presage a decreasing demand for organ transplantation,” speculates an accompanying editorialfrom Jeffrey L. Platt, MD, and Marilia Cascalho, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We think the answer is no. Since aging is associated with progressive decline in the function of the heart, kidneys, and other organs, advances that extend life expectancy will ultimately increase the prevalence of organ failure and potentially the demand for transplantation.”
The donor pig was developed and provided by Revivicor, and the investigational KPL-404 antibody drug used in the experience was provided by Kiniksa. Other disclosures for the case report and editorial from Dr. Platt and Dr. Cascalho are available at NEJM.com. Dr. Boulet reports no relevant relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in their report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a given that the case of David Bennett, Sr, and his transplanted, genetically modified porcine heart will have a lot to teach, and the peer-reviewed publication this week lends welcome authority to some of its earliest lessons.
Mr. Bennett lived for 2 months after receiving the heart in the pioneering surgery, and the new case report compiles the available clinical, anatomic, and histologic evidence and other potential clues to the underlying cause or causes of death.
It also describes a mystery that came to light at autopsy: a grossly enlarged heart attributable to pervasive interstitial edema, and at the cellular level, a peculiar pattern of myocardial damage that included microvascular deterioration and, potentially as a result, cellular necrosis, according to the new report.
The myocardium itself was described as “thickened and stiff,” consistent with the “diastolic heart failure” that characterized Mr. Bennett’s final 10 days and the likely convergence of several underlying processes. Missing, however, was any conventional sign of graft rejection as it is understood clinically or in animal models, the report states.
If a form of tissue rejection was the cause of graft failure, any implicating cellular evidence may simply have been unrecognizable, given the unprecedented nature of the first pig-to-human heart transplantation, the donor animal’s multiple anti-inflammatory gene deletions, and partly investigational immunosuppression regimen, speculated Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, College Park.
“I’m betting against it being a fulminant rejection,” he told this news organization, “because we saw nothing like the [characteristic] platelet deposition or thrombosis of the capillaries.”
Dr. Griffith, who performed the xenotransplant surgery and led Mr. Bennett’s postoperative care, is lead author on the case report published in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Additional studies are underway to characterize the pathophysiologic mechanisms that resulted in this damage,” the report states.
The report builds on recent meeting presentations on the case, which, as previously reported, gave cursory details regarding the organ damage and other clinical developments during and after the surgery, including evidence that the transplanted heart contained porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV).
Similar details also appeared in a third-person account based in part on personal communication with Dr. Griffith. The cardiac XTx review that focused on this University of Maryland experience was published June 15 in JACC: Basic to Translational Science, with lead author Jacinthe Boulet, MD, CM, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart, Boston.
“The question of how to move XTx forward remains uncertain, and appropriate selection of patients for experimental XTx will be one of the most important challenges to be addressed. The first issue we must contend with is whether we are ready to move to the next XTx in a human. We strongly believe this to be the case,” the review states. “Once early experience is gained, with successive iterations of XTx, the bar for success can be raised with maturation of the technology.”
Evidence has so far not implicated several other potential mechanisms underlying the graft failure that had been the focus of early speculations. For example, the transplanted pig heart was infected with PCMV, as previously reported. Mr. Bennett showed traces of PCMV DNA in his circulation, but no actual virus in his native cells. Still, PCMV remains a suspect.
Mr. Bennett also received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) on several occasions to fight rejection, and also severe infections, including a nasty episode of sepsis. A reaction to the IVIG, derived from pooled donor antibodies, could potentially have caused the unusual myocardial damage seen by the University of Maryland team, Dr. Griffith observed. Alternatively, the damage might have been partly related to the patient’s overall severely diminished condition even before the transplant surgery or his rocky postoperative clinical course.
Indeed, Mr. Bennett’s condition worsened dramatically on postoperative day 50, and echocardiography showed a striking degree of myocardial wall thickening and heart enlargement, determined to be from edema. “The heart got amazingly stiff but maintained a systolic function that wasn›t too terrible, even to the very end. But his heart seemed as though it had swollen overnight,” Dr. Griffith said. “We had never seen that type of process, the suddenness of this swelling, in our nonhuman primate studies.”
The damage to the heart muscle appeared irreversible, based on myocardial biopsy results, so the decision was made to withdraw life support 60 days after the transplant surgery, the report notes.
Among the experience’s apparent lessons for future cardiac xenotransplantation, Dr. Griffith said, would be to select patients for the surgery who are in a bit more robust condition than Mr. Bennett was, who are perhaps ambulatory, not sarcopenic, and not recently on prolonged mechanical circulatory support. “We’re going to try to pick a patient who, on the front end, is less critically ill but who is just as likely not to benefit from continued medical therapy” and who isn’t a candidate for conventional heart transplantation, he said.
Because of universal efforts to manage conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and vascular disease in the population, and “because these conditions cause many of the cases of organ failure and fuel demand for transplantation, one might wonder whether the advances reported by Dr. Griffith and colleagues presage a decreasing demand for organ transplantation,” speculates an accompanying editorialfrom Jeffrey L. Platt, MD, and Marilia Cascalho, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We think the answer is no. Since aging is associated with progressive decline in the function of the heart, kidneys, and other organs, advances that extend life expectancy will ultimately increase the prevalence of organ failure and potentially the demand for transplantation.”
The donor pig was developed and provided by Revivicor, and the investigational KPL-404 antibody drug used in the experience was provided by Kiniksa. Other disclosures for the case report and editorial from Dr. Platt and Dr. Cascalho are available at NEJM.com. Dr. Boulet reports no relevant relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in their report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a given that the case of David Bennett, Sr, and his transplanted, genetically modified porcine heart will have a lot to teach, and the peer-reviewed publication this week lends welcome authority to some of its earliest lessons.
Mr. Bennett lived for 2 months after receiving the heart in the pioneering surgery, and the new case report compiles the available clinical, anatomic, and histologic evidence and other potential clues to the underlying cause or causes of death.
It also describes a mystery that came to light at autopsy: a grossly enlarged heart attributable to pervasive interstitial edema, and at the cellular level, a peculiar pattern of myocardial damage that included microvascular deterioration and, potentially as a result, cellular necrosis, according to the new report.
The myocardium itself was described as “thickened and stiff,” consistent with the “diastolic heart failure” that characterized Mr. Bennett’s final 10 days and the likely convergence of several underlying processes. Missing, however, was any conventional sign of graft rejection as it is understood clinically or in animal models, the report states.
If a form of tissue rejection was the cause of graft failure, any implicating cellular evidence may simply have been unrecognizable, given the unprecedented nature of the first pig-to-human heart transplantation, the donor animal’s multiple anti-inflammatory gene deletions, and partly investigational immunosuppression regimen, speculated Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, College Park.
“I’m betting against it being a fulminant rejection,” he told this news organization, “because we saw nothing like the [characteristic] platelet deposition or thrombosis of the capillaries.”
Dr. Griffith, who performed the xenotransplant surgery and led Mr. Bennett’s postoperative care, is lead author on the case report published in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Additional studies are underway to characterize the pathophysiologic mechanisms that resulted in this damage,” the report states.
The report builds on recent meeting presentations on the case, which, as previously reported, gave cursory details regarding the organ damage and other clinical developments during and after the surgery, including evidence that the transplanted heart contained porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV).
Similar details also appeared in a third-person account based in part on personal communication with Dr. Griffith. The cardiac XTx review that focused on this University of Maryland experience was published June 15 in JACC: Basic to Translational Science, with lead author Jacinthe Boulet, MD, CM, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart, Boston.
“The question of how to move XTx forward remains uncertain, and appropriate selection of patients for experimental XTx will be one of the most important challenges to be addressed. The first issue we must contend with is whether we are ready to move to the next XTx in a human. We strongly believe this to be the case,” the review states. “Once early experience is gained, with successive iterations of XTx, the bar for success can be raised with maturation of the technology.”
Evidence has so far not implicated several other potential mechanisms underlying the graft failure that had been the focus of early speculations. For example, the transplanted pig heart was infected with PCMV, as previously reported. Mr. Bennett showed traces of PCMV DNA in his circulation, but no actual virus in his native cells. Still, PCMV remains a suspect.
Mr. Bennett also received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) on several occasions to fight rejection, and also severe infections, including a nasty episode of sepsis. A reaction to the IVIG, derived from pooled donor antibodies, could potentially have caused the unusual myocardial damage seen by the University of Maryland team, Dr. Griffith observed. Alternatively, the damage might have been partly related to the patient’s overall severely diminished condition even before the transplant surgery or his rocky postoperative clinical course.
Indeed, Mr. Bennett’s condition worsened dramatically on postoperative day 50, and echocardiography showed a striking degree of myocardial wall thickening and heart enlargement, determined to be from edema. “The heart got amazingly stiff but maintained a systolic function that wasn›t too terrible, even to the very end. But his heart seemed as though it had swollen overnight,” Dr. Griffith said. “We had never seen that type of process, the suddenness of this swelling, in our nonhuman primate studies.”
The damage to the heart muscle appeared irreversible, based on myocardial biopsy results, so the decision was made to withdraw life support 60 days after the transplant surgery, the report notes.
Among the experience’s apparent lessons for future cardiac xenotransplantation, Dr. Griffith said, would be to select patients for the surgery who are in a bit more robust condition than Mr. Bennett was, who are perhaps ambulatory, not sarcopenic, and not recently on prolonged mechanical circulatory support. “We’re going to try to pick a patient who, on the front end, is less critically ill but who is just as likely not to benefit from continued medical therapy” and who isn’t a candidate for conventional heart transplantation, he said.
Because of universal efforts to manage conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and vascular disease in the population, and “because these conditions cause many of the cases of organ failure and fuel demand for transplantation, one might wonder whether the advances reported by Dr. Griffith and colleagues presage a decreasing demand for organ transplantation,” speculates an accompanying editorialfrom Jeffrey L. Platt, MD, and Marilia Cascalho, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We think the answer is no. Since aging is associated with progressive decline in the function of the heart, kidneys, and other organs, advances that extend life expectancy will ultimately increase the prevalence of organ failure and potentially the demand for transplantation.”
The donor pig was developed and provided by Revivicor, and the investigational KPL-404 antibody drug used in the experience was provided by Kiniksa. Other disclosures for the case report and editorial from Dr. Platt and Dr. Cascalho are available at NEJM.com. Dr. Boulet reports no relevant relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in their report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Add AFib to noncardiac surgery risk evaluation: New support
Practice has gone back and forth on whether atrial fibrillation (AFib) should be considered in the preoperative cardiovascular risk (CV) evaluation of patients slated for noncardiac surgery, and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI), currently widely used as an assessment tool, doesn’t include the arrhythmia.
But consideration of preexisting AFib along with the RCRI predicted 30-day mortality more sharply than the RCRI alone in an analysis of data covering several million patients slated for such procedures.
Indeed, AFib emerged as a significant, independent risk factor for a number of bad postoperative outcomes. Mortality within a month of the procedure climbed about 30% for patients with AFib before the noncardiac surgery. Their 30-day risks for stroke and for heart failure hospitalization went up similarly.
The addition of AFib to the RCRI significantly improved its ability to discriminate 30-day postoperative risk levels regardless of age, sex, and type of noncardiac surgery, Amgad Mentias, MD, Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization. And “it was able to correctly up-classify patients to high risk, if AFib was there, and it was able to down-classify some patients to lower risk if it wasn’t there.”
“I think [the findings] are convincing evidence that atrial fib should at least be part of the thought process for the surgical team and the medical team taking care of the patient,” said Dr. Mentias, who is senior author on the study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Sameer Prasada, MD, also of the Cleveland Clinic.
The results “call for incorporating AFib as a risk factor in perioperative risk scores for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” the published report states.
Supraventricular arrhythmias had been part of the Goldman Risk Index once widely used preoperatively to assess cardiac risk before practice adopted the RCRI in the past decade, observe Anne B. Curtis, MD, and Sai Krishna C. Korada, MD, University at Buffalo, New York, in an accompanying editorial.
The current findings “demonstrate improved prediction of adverse postsurgical outcomes” from supplementing the RCRI with AFib, they write. Given associations between preexisting AFib and serious cardiac events, “it is time to ‘re-revise’ the RCRI and acknowledge the importance of AFib in predicting adverse outcomes” after noncardiac surgery.
The new findings, however, aren’t all straightforward. In one result that remains a bit of a head-scratcher, postoperative risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with preexisting AFib went in the opposite direction of risk for death and other CV outcomes, falling by almost 20%.
That is “hard to explain with the available data,” the report states, but “the use of anticoagulation, whether oral or parenteral (as a bridge therapy in the perioperative period), is a plausible explanation” given the frequent role of thrombosis in triggering MIs.
Consistent with such a mechanism, the group argues, the MI risk reduction was seen primarily among patients with AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or higher – that is, those at highest risk for stroke and therefore most likely to be on oral anticoagulation. The MI risk reduction wasn’t seen in such patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 or 1.
“I think that’s part of the explanation, that anticoagulation can reduce risk of MI. But it’s not the whole explanation,” Dr. Mentias said in an interview. If it were the sole mechanism, he said, then the same oral anticoagulation that protected against MI should have also cut the postoperative stroke risk. Yet that risk climbed 40% among patients with preexisting AFib.
The analysis started with 8.6 million Medicare patients with planned noncardiac surgery, seen from 2015 to 2019, of whom 16.4% had preexisting AFib. Propensity matching for demographics, urgency and type of surgery, CHA2DS2-VASc score, and RCRI index created two cohorts for comparison: 1.13 million patients with and 1.92 million without preexisting AFib.
Preexisting AFib was associated with a higher 30-day risk for death from any cause, the primary endpoint being 8.3% versus 5.8% for those without such AFib (P < .001), for an odds ratio of 1.31 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.32).
Corresponding 30-day ORs for other events, all significant at P < .001, were:
- 1.31 (95% CI, 1.30-1.33) for heart failure
- 1.40 (95% CI, 1.37-1.43) for stroke
- 1.59 (95% CI, 1.43-1.75) for systemic embolism
- 1.14 (95% CI, 1.13-1.16) for major bleeding
- 0.81 (95% CI, 0.79-0.82) for MI
Those with preexisting AFib also had longer hospitalizations at a median 5 days, compared with 4 days for those without such AFib (P < .001).
The study has the limitations of most any retrospective cohort analysis. Other limitations, the report notes, include lack of information on any antiarrhythmic meds given during hospitalization or type of AFib.
For example, AFib that is permanent – compared with paroxysmal or persistent – may be associated with more atrial fibrosis, greater atrial dilatation, “and probably higher pressures inside the heart,” Dr. Mentias observed.
“That’s not always the case, but that’s the notion. So presumably people with persistent or permanent atrial fib would have more advanced heart disease, and that could imply more risk. But we did not have that kind of data.”
Dr. Mentias and Dr. Prasada report no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Curtis discloses serving on advisory boards for Abbott, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Milestone Pharmaceuticals; receiving honoraria for speaking from Medtronic and Zoll; and serving on a data-monitoring board for Medtronic. Dr. Korada reports he has no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Practice has gone back and forth on whether atrial fibrillation (AFib) should be considered in the preoperative cardiovascular risk (CV) evaluation of patients slated for noncardiac surgery, and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI), currently widely used as an assessment tool, doesn’t include the arrhythmia.
But consideration of preexisting AFib along with the RCRI predicted 30-day mortality more sharply than the RCRI alone in an analysis of data covering several million patients slated for such procedures.
Indeed, AFib emerged as a significant, independent risk factor for a number of bad postoperative outcomes. Mortality within a month of the procedure climbed about 30% for patients with AFib before the noncardiac surgery. Their 30-day risks for stroke and for heart failure hospitalization went up similarly.
The addition of AFib to the RCRI significantly improved its ability to discriminate 30-day postoperative risk levels regardless of age, sex, and type of noncardiac surgery, Amgad Mentias, MD, Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization. And “it was able to correctly up-classify patients to high risk, if AFib was there, and it was able to down-classify some patients to lower risk if it wasn’t there.”
“I think [the findings] are convincing evidence that atrial fib should at least be part of the thought process for the surgical team and the medical team taking care of the patient,” said Dr. Mentias, who is senior author on the study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Sameer Prasada, MD, also of the Cleveland Clinic.
The results “call for incorporating AFib as a risk factor in perioperative risk scores for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” the published report states.
Supraventricular arrhythmias had been part of the Goldman Risk Index once widely used preoperatively to assess cardiac risk before practice adopted the RCRI in the past decade, observe Anne B. Curtis, MD, and Sai Krishna C. Korada, MD, University at Buffalo, New York, in an accompanying editorial.
The current findings “demonstrate improved prediction of adverse postsurgical outcomes” from supplementing the RCRI with AFib, they write. Given associations between preexisting AFib and serious cardiac events, “it is time to ‘re-revise’ the RCRI and acknowledge the importance of AFib in predicting adverse outcomes” after noncardiac surgery.
The new findings, however, aren’t all straightforward. In one result that remains a bit of a head-scratcher, postoperative risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with preexisting AFib went in the opposite direction of risk for death and other CV outcomes, falling by almost 20%.
That is “hard to explain with the available data,” the report states, but “the use of anticoagulation, whether oral or parenteral (as a bridge therapy in the perioperative period), is a plausible explanation” given the frequent role of thrombosis in triggering MIs.
Consistent with such a mechanism, the group argues, the MI risk reduction was seen primarily among patients with AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or higher – that is, those at highest risk for stroke and therefore most likely to be on oral anticoagulation. The MI risk reduction wasn’t seen in such patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 or 1.
“I think that’s part of the explanation, that anticoagulation can reduce risk of MI. But it’s not the whole explanation,” Dr. Mentias said in an interview. If it were the sole mechanism, he said, then the same oral anticoagulation that protected against MI should have also cut the postoperative stroke risk. Yet that risk climbed 40% among patients with preexisting AFib.
The analysis started with 8.6 million Medicare patients with planned noncardiac surgery, seen from 2015 to 2019, of whom 16.4% had preexisting AFib. Propensity matching for demographics, urgency and type of surgery, CHA2DS2-VASc score, and RCRI index created two cohorts for comparison: 1.13 million patients with and 1.92 million without preexisting AFib.
Preexisting AFib was associated with a higher 30-day risk for death from any cause, the primary endpoint being 8.3% versus 5.8% for those without such AFib (P < .001), for an odds ratio of 1.31 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.32).
Corresponding 30-day ORs for other events, all significant at P < .001, were:
- 1.31 (95% CI, 1.30-1.33) for heart failure
- 1.40 (95% CI, 1.37-1.43) for stroke
- 1.59 (95% CI, 1.43-1.75) for systemic embolism
- 1.14 (95% CI, 1.13-1.16) for major bleeding
- 0.81 (95% CI, 0.79-0.82) for MI
Those with preexisting AFib also had longer hospitalizations at a median 5 days, compared with 4 days for those without such AFib (P < .001).
The study has the limitations of most any retrospective cohort analysis. Other limitations, the report notes, include lack of information on any antiarrhythmic meds given during hospitalization or type of AFib.
For example, AFib that is permanent – compared with paroxysmal or persistent – may be associated with more atrial fibrosis, greater atrial dilatation, “and probably higher pressures inside the heart,” Dr. Mentias observed.
“That’s not always the case, but that’s the notion. So presumably people with persistent or permanent atrial fib would have more advanced heart disease, and that could imply more risk. But we did not have that kind of data.”
Dr. Mentias and Dr. Prasada report no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Curtis discloses serving on advisory boards for Abbott, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Milestone Pharmaceuticals; receiving honoraria for speaking from Medtronic and Zoll; and serving on a data-monitoring board for Medtronic. Dr. Korada reports he has no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Practice has gone back and forth on whether atrial fibrillation (AFib) should be considered in the preoperative cardiovascular risk (CV) evaluation of patients slated for noncardiac surgery, and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI), currently widely used as an assessment tool, doesn’t include the arrhythmia.
But consideration of preexisting AFib along with the RCRI predicted 30-day mortality more sharply than the RCRI alone in an analysis of data covering several million patients slated for such procedures.
Indeed, AFib emerged as a significant, independent risk factor for a number of bad postoperative outcomes. Mortality within a month of the procedure climbed about 30% for patients with AFib before the noncardiac surgery. Their 30-day risks for stroke and for heart failure hospitalization went up similarly.
The addition of AFib to the RCRI significantly improved its ability to discriminate 30-day postoperative risk levels regardless of age, sex, and type of noncardiac surgery, Amgad Mentias, MD, Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization. And “it was able to correctly up-classify patients to high risk, if AFib was there, and it was able to down-classify some patients to lower risk if it wasn’t there.”
“I think [the findings] are convincing evidence that atrial fib should at least be part of the thought process for the surgical team and the medical team taking care of the patient,” said Dr. Mentias, who is senior author on the study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Sameer Prasada, MD, also of the Cleveland Clinic.
The results “call for incorporating AFib as a risk factor in perioperative risk scores for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” the published report states.
Supraventricular arrhythmias had been part of the Goldman Risk Index once widely used preoperatively to assess cardiac risk before practice adopted the RCRI in the past decade, observe Anne B. Curtis, MD, and Sai Krishna C. Korada, MD, University at Buffalo, New York, in an accompanying editorial.
The current findings “demonstrate improved prediction of adverse postsurgical outcomes” from supplementing the RCRI with AFib, they write. Given associations between preexisting AFib and serious cardiac events, “it is time to ‘re-revise’ the RCRI and acknowledge the importance of AFib in predicting adverse outcomes” after noncardiac surgery.
The new findings, however, aren’t all straightforward. In one result that remains a bit of a head-scratcher, postoperative risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with preexisting AFib went in the opposite direction of risk for death and other CV outcomes, falling by almost 20%.
That is “hard to explain with the available data,” the report states, but “the use of anticoagulation, whether oral or parenteral (as a bridge therapy in the perioperative period), is a plausible explanation” given the frequent role of thrombosis in triggering MIs.
Consistent with such a mechanism, the group argues, the MI risk reduction was seen primarily among patients with AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or higher – that is, those at highest risk for stroke and therefore most likely to be on oral anticoagulation. The MI risk reduction wasn’t seen in such patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 or 1.
“I think that’s part of the explanation, that anticoagulation can reduce risk of MI. But it’s not the whole explanation,” Dr. Mentias said in an interview. If it were the sole mechanism, he said, then the same oral anticoagulation that protected against MI should have also cut the postoperative stroke risk. Yet that risk climbed 40% among patients with preexisting AFib.
The analysis started with 8.6 million Medicare patients with planned noncardiac surgery, seen from 2015 to 2019, of whom 16.4% had preexisting AFib. Propensity matching for demographics, urgency and type of surgery, CHA2DS2-VASc score, and RCRI index created two cohorts for comparison: 1.13 million patients with and 1.92 million without preexisting AFib.
Preexisting AFib was associated with a higher 30-day risk for death from any cause, the primary endpoint being 8.3% versus 5.8% for those without such AFib (P < .001), for an odds ratio of 1.31 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.32).
Corresponding 30-day ORs for other events, all significant at P < .001, were:
- 1.31 (95% CI, 1.30-1.33) for heart failure
- 1.40 (95% CI, 1.37-1.43) for stroke
- 1.59 (95% CI, 1.43-1.75) for systemic embolism
- 1.14 (95% CI, 1.13-1.16) for major bleeding
- 0.81 (95% CI, 0.79-0.82) for MI
Those with preexisting AFib also had longer hospitalizations at a median 5 days, compared with 4 days for those without such AFib (P < .001).
The study has the limitations of most any retrospective cohort analysis. Other limitations, the report notes, include lack of information on any antiarrhythmic meds given during hospitalization or type of AFib.
For example, AFib that is permanent – compared with paroxysmal or persistent – may be associated with more atrial fibrosis, greater atrial dilatation, “and probably higher pressures inside the heart,” Dr. Mentias observed.
“That’s not always the case, but that’s the notion. So presumably people with persistent or permanent atrial fib would have more advanced heart disease, and that could imply more risk. But we did not have that kind of data.”
Dr. Mentias and Dr. Prasada report no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Curtis discloses serving on advisory boards for Abbott, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Milestone Pharmaceuticals; receiving honoraria for speaking from Medtronic and Zoll; and serving on a data-monitoring board for Medtronic. Dr. Korada reports he has no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cause of death in pig heart recipient: New clues
The underlying cause of David Bennett’s death on March 8, two months after he received the heart of a genetically altered pig, remains unknown and is only slightly less mysterious for what can likely be ruled out, suggests a progress report on the case from the director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program where the pioneering surgery took place.
Mr. Bennett died in “diastolic heart failure,” reported Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MBBS, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, “but the mechanism is still under investigation.”
Although the immediate cause could have been single or multiple, evidence so far does not point to immune rejection nor does it support a role for a recently proposed suspect, infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV), Dr. Mohiuddin observed in front of a standing-room-only audience June 6 at the American Transplant Congress (ATC) in Boston. The congress is a joint meeting of the American Society of Transplant Surgeons (ASTS) and the American Society of Transplantation (AST).
Rocky clinical course
Early characterizations of the patient’s death focused more on his diminished, end-stage clinical condition at the time of the surgery than on immune rejection or other direct effects of the xenograft or on the first-of-its-kind procedure itself.
The 57-year-old Mr. Bennett had presented to the University of Maryland team with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, on multiple inotropes, and requiring an intra-aortic balloon pump, Dr. Mohiuddin said in his ATC presentation. The patient had suffered multiple arrests and resuscitations, and by the time of surgery had been hospitalized for almost 2 months, including 40 days on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
The transplant procedure itself went as planned until removal of the aortic cross clamp, which triggered a type-A aortic dissection. “We put a graft in the ascending aorta and a stent in the descending aorta. Even after 2 days, we found the dissection extending to the renal artery, so we had to go back and also put a stent in the renal artery,” Dr. Mohiuddin said.
Mr. Bennett also underwent two exploratory laparotomies in the first 10 days after transplantation, after CT imaging revealed signs of possible bowel inflammation and ischemia.
Further, he had to fight back a series of infections that led to major changes to his experimental drug regimen, which included immunosuppressants methylprednisolone and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), the investigational anti-CD40 antibody KPL-404 (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals), and the anti-inflammatories etanercept (Enbrel) and tocilizumab (Actemra).
One episode of sepsis, in particular, forced temporary withdrawal of MMF and a reduction in methylprednisolone dosage. It’s unknown whether the 30-day MMF suspension played a role in Mr. Bennett’s ultimate clinical deterioration and death, but it’s “highly possible,” Dr. Mohiuddin said in an interview.
Realistically, Mr. Bennett’s death was likely “multifactorial,” Dr. Mohiuddin said. He was in such poor clinical condition going into the procedure, and afterward confronted so many clinical challenges, that “it’s very difficult to say that one thing caused it.”
That hasn’t lessened speculation that the patient’s heart failed secondary to immunologic rejection or PCMV infection, either in Mr. Bennett or the donor pig.
A role for PCMV?
Weeks after Mr. Bennett’s death, as previously reported, his surgeon announced at a public forum that PCMV had been identified in the transplanted heart and in tissues of the donor pig. Mr. Bennett’s circulation showed traces of the viral DNA but not of the virus itself.
The presence of PCMV in transplanted porcine hearts is a well-recognized potential hazard in animal models but is considered avoidable with proper screening. In Mr. Bennett’s case, preoperative screening of the pig donor missed signs of the virus.
Still, PCMV could potentially have contributed to Mr. Bennett’s death, acknowledged Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland School of Medicine, who had announced the PCMV finding in an AST-sponsored April 20 webcast.
Preclinical evidence does suggest that PCMV can harm a xenograft organ, observed David H. Sachs, MD, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, from the audience during the comment period after Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
“Each species has a CMV, and they’re quite species-specific,” observed the renowned surgeon and xenotransplantation immunologist. “We showed almost 10 years ago that if PCMV was in a pig kidney, it led to a much shortened survival of the pig kidney in a baboon. There was never any evidence, however, that the CMV infected the baboon or any baboon cells.”
Dr. Sachs asked Dr. Mohiuddin for confirmation that Mr. Bennett displayed no more than DNAemia, circulating cell-free PCMV DNA presumably shed from the porcine heart, but no sign of the virus itself outside of the heart’s porcine cells.
Cell-free DNA had shown up in Mr. Bennett’s circulation about 20 days after the surgery, with concentrations rising until at least day 50. Post-hoc polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing disclosed PCMV only in the pig’s spleen and porcine cells of the transplanted heart, Dr. Mohiuddin noted.
“We have not found any evidence that the patient was infected by PCMV,” nor was there evidence of any disease related to PCMV, Dr. Mohiuddin replied.
Nor of ongoing rejection
Mr. Bennett’s new heart passed a critical test in the first post-implantation hours by avoiding acute rejection, a potentially disastrous outcome that three of the pig’s 10 gene edits had been designed to prevent.
Although chronic immune rejection was always a concern despite Mr. Bennett’s novel immunosuppressant regimen, myocardial biopsy on postoperative days 34, 50, and 56 and necropsy showed “no signs of typical xenograft rejection,” Dr. Mohiuddin said at the ATC presentation. But “there’s a chance of atypical rejection which we were not accustomed to.”
By day 50, his diastolic function showed echocardiographic signs of deterioration, and “we started seeing interstitial edema with some extravasation of red blood cells, which we thought would resolve over a period of time,” he said. Eventually, however, “we saw that turn into fibroblasts and scar tissue.”
Mr. Bennett once again went on veno-arterial ECMO but died 10 days later. Once they had seen histologic evidence of fibrosis, Dr. Mohiuddin told this news organization, the team believed the myocardial injury was irreversible. “That was the reason we gave up on recovery.”
Mr. Bennett’s xenotransplantation journey has taught the field a lot, he said. “By no means was this a failure; we consider this a huge success. You can do all the experiments in animal models, but you won’t find out the true mechanism of rejection unless you do these kinds of human experiments.”
Looking ahead to clinical trials
Research involving humans is always subject to vagaries of human nature, including degree of adherence to prescribed therapy and – in xenotransplantation – precautions in place to mitigate any risks to public health. Such risks theoretically include transfer of porcine viruses or other pathogens to the patient and subsequent release into the general population.
Looking ahead to the possibility of clinical trials after this successful xenotransplantation experience, transplant nephrologist and epidemiologist Peter P. Reese, MD, PhD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the potentially controversial issue in discussion following Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
It’s known that Mr. Bennett had been repeatedly turned down for a conventional allograft transplant primarily because of his history of treatment noncompliance. Should such a record, Dr. Reese asked, be a relative contraindication to enrollment in any future xenotransplantation trials? Or does the field need a standardized gauge of a patient’s readiness, once discharged, to adhere not only to all medications – including those that fight infection – but also with rules established for public safety, such as routine contact reporting?
“It makes me wonder about choosing a noncompliant patient for these trials,” Dr. Reese said. “If we discharge a patient from the hospital who is at risk for a zoonotic infection that could spread if they basically refuse to cooperate with us or with public health authorities, it really could have negative consequences for the reputation of the field.”
Dr. Mohiuddin agreed such concerns are valid. Mr. Bennett “and all his immediate contacts” signed consent forms acknowledging their willingness to be followed should he be discharged. Mr. Bennett himself “signed a consent to inform us if he has any other intimate contact with someone,” he said in an interview.
“But those are only on paper.” Had Mr. Bennett survived to be discharged, Dr. Mohuiddin said, “no one knows how he would have behaved.”
Dr. Mohiuddin said the research staff had prepared to monitor Mr. Bennett at his home if that’s what it took. “We were ready to follow him as long as we could. There was a surveillance plan in place.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The underlying cause of David Bennett’s death on March 8, two months after he received the heart of a genetically altered pig, remains unknown and is only slightly less mysterious for what can likely be ruled out, suggests a progress report on the case from the director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program where the pioneering surgery took place.
Mr. Bennett died in “diastolic heart failure,” reported Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MBBS, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, “but the mechanism is still under investigation.”
Although the immediate cause could have been single or multiple, evidence so far does not point to immune rejection nor does it support a role for a recently proposed suspect, infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV), Dr. Mohiuddin observed in front of a standing-room-only audience June 6 at the American Transplant Congress (ATC) in Boston. The congress is a joint meeting of the American Society of Transplant Surgeons (ASTS) and the American Society of Transplantation (AST).
Rocky clinical course
Early characterizations of the patient’s death focused more on his diminished, end-stage clinical condition at the time of the surgery than on immune rejection or other direct effects of the xenograft or on the first-of-its-kind procedure itself.
The 57-year-old Mr. Bennett had presented to the University of Maryland team with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, on multiple inotropes, and requiring an intra-aortic balloon pump, Dr. Mohiuddin said in his ATC presentation. The patient had suffered multiple arrests and resuscitations, and by the time of surgery had been hospitalized for almost 2 months, including 40 days on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
The transplant procedure itself went as planned until removal of the aortic cross clamp, which triggered a type-A aortic dissection. “We put a graft in the ascending aorta and a stent in the descending aorta. Even after 2 days, we found the dissection extending to the renal artery, so we had to go back and also put a stent in the renal artery,” Dr. Mohiuddin said.
Mr. Bennett also underwent two exploratory laparotomies in the first 10 days after transplantation, after CT imaging revealed signs of possible bowel inflammation and ischemia.
Further, he had to fight back a series of infections that led to major changes to his experimental drug regimen, which included immunosuppressants methylprednisolone and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), the investigational anti-CD40 antibody KPL-404 (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals), and the anti-inflammatories etanercept (Enbrel) and tocilizumab (Actemra).
One episode of sepsis, in particular, forced temporary withdrawal of MMF and a reduction in methylprednisolone dosage. It’s unknown whether the 30-day MMF suspension played a role in Mr. Bennett’s ultimate clinical deterioration and death, but it’s “highly possible,” Dr. Mohiuddin said in an interview.
Realistically, Mr. Bennett’s death was likely “multifactorial,” Dr. Mohiuddin said. He was in such poor clinical condition going into the procedure, and afterward confronted so many clinical challenges, that “it’s very difficult to say that one thing caused it.”
That hasn’t lessened speculation that the patient’s heart failed secondary to immunologic rejection or PCMV infection, either in Mr. Bennett or the donor pig.
A role for PCMV?
Weeks after Mr. Bennett’s death, as previously reported, his surgeon announced at a public forum that PCMV had been identified in the transplanted heart and in tissues of the donor pig. Mr. Bennett’s circulation showed traces of the viral DNA but not of the virus itself.
The presence of PCMV in transplanted porcine hearts is a well-recognized potential hazard in animal models but is considered avoidable with proper screening. In Mr. Bennett’s case, preoperative screening of the pig donor missed signs of the virus.
Still, PCMV could potentially have contributed to Mr. Bennett’s death, acknowledged Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland School of Medicine, who had announced the PCMV finding in an AST-sponsored April 20 webcast.
Preclinical evidence does suggest that PCMV can harm a xenograft organ, observed David H. Sachs, MD, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, from the audience during the comment period after Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
“Each species has a CMV, and they’re quite species-specific,” observed the renowned surgeon and xenotransplantation immunologist. “We showed almost 10 years ago that if PCMV was in a pig kidney, it led to a much shortened survival of the pig kidney in a baboon. There was never any evidence, however, that the CMV infected the baboon or any baboon cells.”
Dr. Sachs asked Dr. Mohiuddin for confirmation that Mr. Bennett displayed no more than DNAemia, circulating cell-free PCMV DNA presumably shed from the porcine heart, but no sign of the virus itself outside of the heart’s porcine cells.
Cell-free DNA had shown up in Mr. Bennett’s circulation about 20 days after the surgery, with concentrations rising until at least day 50. Post-hoc polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing disclosed PCMV only in the pig’s spleen and porcine cells of the transplanted heart, Dr. Mohiuddin noted.
“We have not found any evidence that the patient was infected by PCMV,” nor was there evidence of any disease related to PCMV, Dr. Mohiuddin replied.
Nor of ongoing rejection
Mr. Bennett’s new heart passed a critical test in the first post-implantation hours by avoiding acute rejection, a potentially disastrous outcome that three of the pig’s 10 gene edits had been designed to prevent.
Although chronic immune rejection was always a concern despite Mr. Bennett’s novel immunosuppressant regimen, myocardial biopsy on postoperative days 34, 50, and 56 and necropsy showed “no signs of typical xenograft rejection,” Dr. Mohiuddin said at the ATC presentation. But “there’s a chance of atypical rejection which we were not accustomed to.”
By day 50, his diastolic function showed echocardiographic signs of deterioration, and “we started seeing interstitial edema with some extravasation of red blood cells, which we thought would resolve over a period of time,” he said. Eventually, however, “we saw that turn into fibroblasts and scar tissue.”
Mr. Bennett once again went on veno-arterial ECMO but died 10 days later. Once they had seen histologic evidence of fibrosis, Dr. Mohiuddin told this news organization, the team believed the myocardial injury was irreversible. “That was the reason we gave up on recovery.”
Mr. Bennett’s xenotransplantation journey has taught the field a lot, he said. “By no means was this a failure; we consider this a huge success. You can do all the experiments in animal models, but you won’t find out the true mechanism of rejection unless you do these kinds of human experiments.”
Looking ahead to clinical trials
Research involving humans is always subject to vagaries of human nature, including degree of adherence to prescribed therapy and – in xenotransplantation – precautions in place to mitigate any risks to public health. Such risks theoretically include transfer of porcine viruses or other pathogens to the patient and subsequent release into the general population.
Looking ahead to the possibility of clinical trials after this successful xenotransplantation experience, transplant nephrologist and epidemiologist Peter P. Reese, MD, PhD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the potentially controversial issue in discussion following Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
It’s known that Mr. Bennett had been repeatedly turned down for a conventional allograft transplant primarily because of his history of treatment noncompliance. Should such a record, Dr. Reese asked, be a relative contraindication to enrollment in any future xenotransplantation trials? Or does the field need a standardized gauge of a patient’s readiness, once discharged, to adhere not only to all medications – including those that fight infection – but also with rules established for public safety, such as routine contact reporting?
“It makes me wonder about choosing a noncompliant patient for these trials,” Dr. Reese said. “If we discharge a patient from the hospital who is at risk for a zoonotic infection that could spread if they basically refuse to cooperate with us or with public health authorities, it really could have negative consequences for the reputation of the field.”
Dr. Mohiuddin agreed such concerns are valid. Mr. Bennett “and all his immediate contacts” signed consent forms acknowledging their willingness to be followed should he be discharged. Mr. Bennett himself “signed a consent to inform us if he has any other intimate contact with someone,” he said in an interview.
“But those are only on paper.” Had Mr. Bennett survived to be discharged, Dr. Mohuiddin said, “no one knows how he would have behaved.”
Dr. Mohiuddin said the research staff had prepared to monitor Mr. Bennett at his home if that’s what it took. “We were ready to follow him as long as we could. There was a surveillance plan in place.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The underlying cause of David Bennett’s death on March 8, two months after he received the heart of a genetically altered pig, remains unknown and is only slightly less mysterious for what can likely be ruled out, suggests a progress report on the case from the director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program where the pioneering surgery took place.
Mr. Bennett died in “diastolic heart failure,” reported Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MBBS, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, “but the mechanism is still under investigation.”
Although the immediate cause could have been single or multiple, evidence so far does not point to immune rejection nor does it support a role for a recently proposed suspect, infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV), Dr. Mohiuddin observed in front of a standing-room-only audience June 6 at the American Transplant Congress (ATC) in Boston. The congress is a joint meeting of the American Society of Transplant Surgeons (ASTS) and the American Society of Transplantation (AST).
Rocky clinical course
Early characterizations of the patient’s death focused more on his diminished, end-stage clinical condition at the time of the surgery than on immune rejection or other direct effects of the xenograft or on the first-of-its-kind procedure itself.
The 57-year-old Mr. Bennett had presented to the University of Maryland team with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, on multiple inotropes, and requiring an intra-aortic balloon pump, Dr. Mohiuddin said in his ATC presentation. The patient had suffered multiple arrests and resuscitations, and by the time of surgery had been hospitalized for almost 2 months, including 40 days on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
The transplant procedure itself went as planned until removal of the aortic cross clamp, which triggered a type-A aortic dissection. “We put a graft in the ascending aorta and a stent in the descending aorta. Even after 2 days, we found the dissection extending to the renal artery, so we had to go back and also put a stent in the renal artery,” Dr. Mohiuddin said.
Mr. Bennett also underwent two exploratory laparotomies in the first 10 days after transplantation, after CT imaging revealed signs of possible bowel inflammation and ischemia.
Further, he had to fight back a series of infections that led to major changes to his experimental drug regimen, which included immunosuppressants methylprednisolone and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), the investigational anti-CD40 antibody KPL-404 (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals), and the anti-inflammatories etanercept (Enbrel) and tocilizumab (Actemra).
One episode of sepsis, in particular, forced temporary withdrawal of MMF and a reduction in methylprednisolone dosage. It’s unknown whether the 30-day MMF suspension played a role in Mr. Bennett’s ultimate clinical deterioration and death, but it’s “highly possible,” Dr. Mohiuddin said in an interview.
Realistically, Mr. Bennett’s death was likely “multifactorial,” Dr. Mohiuddin said. He was in such poor clinical condition going into the procedure, and afterward confronted so many clinical challenges, that “it’s very difficult to say that one thing caused it.”
That hasn’t lessened speculation that the patient’s heart failed secondary to immunologic rejection or PCMV infection, either in Mr. Bennett or the donor pig.
A role for PCMV?
Weeks after Mr. Bennett’s death, as previously reported, his surgeon announced at a public forum that PCMV had been identified in the transplanted heart and in tissues of the donor pig. Mr. Bennett’s circulation showed traces of the viral DNA but not of the virus itself.
The presence of PCMV in transplanted porcine hearts is a well-recognized potential hazard in animal models but is considered avoidable with proper screening. In Mr. Bennett’s case, preoperative screening of the pig donor missed signs of the virus.
Still, PCMV could potentially have contributed to Mr. Bennett’s death, acknowledged Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland School of Medicine, who had announced the PCMV finding in an AST-sponsored April 20 webcast.
Preclinical evidence does suggest that PCMV can harm a xenograft organ, observed David H. Sachs, MD, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, from the audience during the comment period after Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
“Each species has a CMV, and they’re quite species-specific,” observed the renowned surgeon and xenotransplantation immunologist. “We showed almost 10 years ago that if PCMV was in a pig kidney, it led to a much shortened survival of the pig kidney in a baboon. There was never any evidence, however, that the CMV infected the baboon or any baboon cells.”
Dr. Sachs asked Dr. Mohiuddin for confirmation that Mr. Bennett displayed no more than DNAemia, circulating cell-free PCMV DNA presumably shed from the porcine heart, but no sign of the virus itself outside of the heart’s porcine cells.
Cell-free DNA had shown up in Mr. Bennett’s circulation about 20 days after the surgery, with concentrations rising until at least day 50. Post-hoc polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing disclosed PCMV only in the pig’s spleen and porcine cells of the transplanted heart, Dr. Mohiuddin noted.
“We have not found any evidence that the patient was infected by PCMV,” nor was there evidence of any disease related to PCMV, Dr. Mohiuddin replied.
Nor of ongoing rejection
Mr. Bennett’s new heart passed a critical test in the first post-implantation hours by avoiding acute rejection, a potentially disastrous outcome that three of the pig’s 10 gene edits had been designed to prevent.
Although chronic immune rejection was always a concern despite Mr. Bennett’s novel immunosuppressant regimen, myocardial biopsy on postoperative days 34, 50, and 56 and necropsy showed “no signs of typical xenograft rejection,” Dr. Mohiuddin said at the ATC presentation. But “there’s a chance of atypical rejection which we were not accustomed to.”
By day 50, his diastolic function showed echocardiographic signs of deterioration, and “we started seeing interstitial edema with some extravasation of red blood cells, which we thought would resolve over a period of time,” he said. Eventually, however, “we saw that turn into fibroblasts and scar tissue.”
Mr. Bennett once again went on veno-arterial ECMO but died 10 days later. Once they had seen histologic evidence of fibrosis, Dr. Mohiuddin told this news organization, the team believed the myocardial injury was irreversible. “That was the reason we gave up on recovery.”
Mr. Bennett’s xenotransplantation journey has taught the field a lot, he said. “By no means was this a failure; we consider this a huge success. You can do all the experiments in animal models, but you won’t find out the true mechanism of rejection unless you do these kinds of human experiments.”
Looking ahead to clinical trials
Research involving humans is always subject to vagaries of human nature, including degree of adherence to prescribed therapy and – in xenotransplantation – precautions in place to mitigate any risks to public health. Such risks theoretically include transfer of porcine viruses or other pathogens to the patient and subsequent release into the general population.
Looking ahead to the possibility of clinical trials after this successful xenotransplantation experience, transplant nephrologist and epidemiologist Peter P. Reese, MD, PhD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the potentially controversial issue in discussion following Dr. Mohiuddin’s presentation.
It’s known that Mr. Bennett had been repeatedly turned down for a conventional allograft transplant primarily because of his history of treatment noncompliance. Should such a record, Dr. Reese asked, be a relative contraindication to enrollment in any future xenotransplantation trials? Or does the field need a standardized gauge of a patient’s readiness, once discharged, to adhere not only to all medications – including those that fight infection – but also with rules established for public safety, such as routine contact reporting?
“It makes me wonder about choosing a noncompliant patient for these trials,” Dr. Reese said. “If we discharge a patient from the hospital who is at risk for a zoonotic infection that could spread if they basically refuse to cooperate with us or with public health authorities, it really could have negative consequences for the reputation of the field.”
Dr. Mohiuddin agreed such concerns are valid. Mr. Bennett “and all his immediate contacts” signed consent forms acknowledging their willingness to be followed should he be discharged. Mr. Bennett himself “signed a consent to inform us if he has any other intimate contact with someone,” he said in an interview.
“But those are only on paper.” Had Mr. Bennett survived to be discharged, Dr. Mohuiddin said, “no one knows how he would have behaved.”
Dr. Mohiuddin said the research staff had prepared to monitor Mr. Bennett at his home if that’s what it took. “We were ready to follow him as long as we could. There was a surveillance plan in place.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paradigm-challenging heart failure treatment strategy hopeful in early trial
A small group of patients with heart failure (HF) who underwent a novel transcatheter nerve-ablation procedure seemed to benefit with improved hemodynamics, symptoms, and quality of life in an admittedly limited observational series.
All had HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and remained on guideline-directed medical therapy during the study.
The open-label experience has launched a randomized trial, featuring a sham control group, that could ultimately challenge dogma about volume overload in patients with chronic and acute HF and the perceived essential role of diuretics.
Researchers see transvenous ablation of the right greater splanchnic nerve (GSN) as potentially appropriate for patients with HF, regardless of ventricular function or acuity. But the ongoing REBALANCE-HF trial aims to enroll up to 80 patients with chronic HFpEF.
Meanwhile, the current 18 patients with elevated resting or exertional pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), given the procedure as part of the main trial’s “roll-in” phase, showed declines in exercise PCWP after 1 month (P = .007) and improved quality-of-life scores at both 1 and 3 months (P < .01). Also at 1 month, a third of the patients improved by at least one step in NYHA functional class.
The procedure, called splanchnic ablation for volume management (SAVM), could potentially be used “across the spectrum of acute and chronic heart failure, maybe even with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and preserved ejection fraction,” Marat Fudim, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
However, “for outcomes, we’ve really only looked in the ambulatory setting,” and only at symptomatic and functional responses. To that extent, based on the current experience and a few small previous studies, Dr. Fudim said, SAVM seems to benefit patients with HF in general who have dyspnea at exercise. Beyond that, the kind of patient who may be most suitable for it “is something I hope we will be able answer once the randomized dataset is in.”
Dr. Fudim reported the REBALANCE-HF roll-in results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2022 sessions, held virtually and live in Madrid. He is also lead author on the same-day publication in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
A different treatment paradigm
Splanchnic-nerve blockade as a possible HF treatment is based on growing evidence that volume overload in patients with HF is not always the cause, at least not a main cause, of congestion and dyspnea. Rather, those classic HF signs and symptoms may often be triggered by adverse redistribution of stable fluid volume from primarily the splanchnic vascular compartment to the intrathoracic space.
In other words, what might seem like classic volume overload calling for diuresis often might actually be euvolemic redistribution of fluid from the abdomen to the chest, raising intracardiac pressures and causing dyspnea.
In that scenario, loop diuretics might only dehydrate the patient and potentially put the kidneys at risk, Dr. Fudim proposed. His recent experience with HF patients implanted with a pulmonary-artery pressure monitor, he said, suggests many who received standard volume-overload therapy had actually been normo- or hypovolemic.
More then half the patients “did not have high volume, they just had high pressures,” he said. “So there is a significant portion of the population that has pathological processes leading to high pressures, but it’s not volume overload. Diuresing those patients would probably not be the right decision.”
The unilateral SAVM procedure appears to attenuate sympathetically mediated splanchnic volume redistribution to the heart and lungs, but as it doesn’t affect the left GSN, preserves some normal sympathetic response.
Sometimes in studies of surgical or catheter-based SAVM, Dr. Fudim said, “we have observationally seen that people discontinued diuretics or decreased doses in the treatment arm.”
‘Beyond our classical thinking’
It’s “impressive” that such right-GSN ablation seemed to reduce exercise-filling pressures, but one should be circumspect because “it’s way beyond our classical thinking,” Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Hospital Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, said as a panelist after Dr. Fudim’s presentation.
“These are invasive procedures,” he noted, “and our physiological understanding does not always match up with what we’re doing in real life, if you look at other interventional procedures, like renal denervation, which showed neutral effects, or if you look at even interatrial shunt devices, which might even be dangerous.”
The field should be “very prudent” before using SAVM in practice, which shouldn’t be “before we have sufficient data to support the efficacy and safety,” Dr. Mullens said. “It remains to be seen how treatment success will be defined. Is it during exercise? How long does the treatment last? What is the effect of the treatment over time; is it not harmful? These are things that we don’t know yet.”
The procedure was considered successful in all 18 patients, 14 of whom were women and 16 of whom were in NYHA class 3. Their average age was 75, and their mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at baseline was 61%. The primary efficacy endpoints were a reduction in PCWP at rest, with legs raised, and at 20W exercise at 1 month. Their baseline invasively measured peak exercise PCWP was at least 25 mm Hg.
At 1 month, mean PCWP at 20W exercise fell from 36.4 mm Hg to 28.9 mm Hg (P = .007) and peak PCWP declined from 39.5 mm Hg to 31.9 mm Hg (P = .013); resting PCWP wasn’t significantly affected. Twelve patients improved by at least one NYHA functional class (P = .02).
Scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), which assesses quality of life, improved by 22 points at 1 month and 18.3 points at 3 months (P < .01 for both differences).
No significant effects on 6-minute walk distance or natriuretic peptide levels were observed, nor were any observed on LVEF or echocardiographic measures of diastolic function, left ventricular (LV) atrial volume, or LV mass at 3 months.
Three “nonserious” device-related adverse events were observed, including one case of acute decompensation early in the experience, ostensibly due to excessive saline administration, Dr. Fudim reported. There was also one case of transient periprocedural hypertension and one instance of postprocedure back pain.
The SAVM procedure is performed transvenously and in general is technically “really not that challenging,” Dr. Fudim said. In most cases, the necessary skills would be accessible not only to interventional cardiologists but also heart failure specialists. “I have performed this procedure myself, and I’m a heart failure guy.”
The REBALANCE-HF roll-in phase and main trial are supported by Axon Therapies. Dr. Fudim discloses receiving support from Bayer, Bodyport, and BTG Specialty Pharmaceuticals; and consulting fees from Abbott, Audicor, Axon Therapies, Bodyguide, Bodyport, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Daxor, Edwards LifeSciences, Feldschuh Foundation, Fire1, Gradient, Intershunt, NXT Biomedical, Pharmacosmos, PreHealth, Splendo, Vironix, Viscardia, and Zoll. Dr. Mullens discloses receiving fees for speaking from Medtronic, Abbott, Novartis, Boston Scientific, AstraZeneca, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A small group of patients with heart failure (HF) who underwent a novel transcatheter nerve-ablation procedure seemed to benefit with improved hemodynamics, symptoms, and quality of life in an admittedly limited observational series.
All had HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and remained on guideline-directed medical therapy during the study.
The open-label experience has launched a randomized trial, featuring a sham control group, that could ultimately challenge dogma about volume overload in patients with chronic and acute HF and the perceived essential role of diuretics.
Researchers see transvenous ablation of the right greater splanchnic nerve (GSN) as potentially appropriate for patients with HF, regardless of ventricular function or acuity. But the ongoing REBALANCE-HF trial aims to enroll up to 80 patients with chronic HFpEF.
Meanwhile, the current 18 patients with elevated resting or exertional pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), given the procedure as part of the main trial’s “roll-in” phase, showed declines in exercise PCWP after 1 month (P = .007) and improved quality-of-life scores at both 1 and 3 months (P < .01). Also at 1 month, a third of the patients improved by at least one step in NYHA functional class.
The procedure, called splanchnic ablation for volume management (SAVM), could potentially be used “across the spectrum of acute and chronic heart failure, maybe even with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and preserved ejection fraction,” Marat Fudim, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
However, “for outcomes, we’ve really only looked in the ambulatory setting,” and only at symptomatic and functional responses. To that extent, based on the current experience and a few small previous studies, Dr. Fudim said, SAVM seems to benefit patients with HF in general who have dyspnea at exercise. Beyond that, the kind of patient who may be most suitable for it “is something I hope we will be able answer once the randomized dataset is in.”
Dr. Fudim reported the REBALANCE-HF roll-in results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2022 sessions, held virtually and live in Madrid. He is also lead author on the same-day publication in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
A different treatment paradigm
Splanchnic-nerve blockade as a possible HF treatment is based on growing evidence that volume overload in patients with HF is not always the cause, at least not a main cause, of congestion and dyspnea. Rather, those classic HF signs and symptoms may often be triggered by adverse redistribution of stable fluid volume from primarily the splanchnic vascular compartment to the intrathoracic space.
In other words, what might seem like classic volume overload calling for diuresis often might actually be euvolemic redistribution of fluid from the abdomen to the chest, raising intracardiac pressures and causing dyspnea.
In that scenario, loop diuretics might only dehydrate the patient and potentially put the kidneys at risk, Dr. Fudim proposed. His recent experience with HF patients implanted with a pulmonary-artery pressure monitor, he said, suggests many who received standard volume-overload therapy had actually been normo- or hypovolemic.
More then half the patients “did not have high volume, they just had high pressures,” he said. “So there is a significant portion of the population that has pathological processes leading to high pressures, but it’s not volume overload. Diuresing those patients would probably not be the right decision.”
The unilateral SAVM procedure appears to attenuate sympathetically mediated splanchnic volume redistribution to the heart and lungs, but as it doesn’t affect the left GSN, preserves some normal sympathetic response.
Sometimes in studies of surgical or catheter-based SAVM, Dr. Fudim said, “we have observationally seen that people discontinued diuretics or decreased doses in the treatment arm.”
‘Beyond our classical thinking’
It’s “impressive” that such right-GSN ablation seemed to reduce exercise-filling pressures, but one should be circumspect because “it’s way beyond our classical thinking,” Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Hospital Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, said as a panelist after Dr. Fudim’s presentation.
“These are invasive procedures,” he noted, “and our physiological understanding does not always match up with what we’re doing in real life, if you look at other interventional procedures, like renal denervation, which showed neutral effects, or if you look at even interatrial shunt devices, which might even be dangerous.”
The field should be “very prudent” before using SAVM in practice, which shouldn’t be “before we have sufficient data to support the efficacy and safety,” Dr. Mullens said. “It remains to be seen how treatment success will be defined. Is it during exercise? How long does the treatment last? What is the effect of the treatment over time; is it not harmful? These are things that we don’t know yet.”
The procedure was considered successful in all 18 patients, 14 of whom were women and 16 of whom were in NYHA class 3. Their average age was 75, and their mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at baseline was 61%. The primary efficacy endpoints were a reduction in PCWP at rest, with legs raised, and at 20W exercise at 1 month. Their baseline invasively measured peak exercise PCWP was at least 25 mm Hg.
At 1 month, mean PCWP at 20W exercise fell from 36.4 mm Hg to 28.9 mm Hg (P = .007) and peak PCWP declined from 39.5 mm Hg to 31.9 mm Hg (P = .013); resting PCWP wasn’t significantly affected. Twelve patients improved by at least one NYHA functional class (P = .02).
Scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), which assesses quality of life, improved by 22 points at 1 month and 18.3 points at 3 months (P < .01 for both differences).
No significant effects on 6-minute walk distance or natriuretic peptide levels were observed, nor were any observed on LVEF or echocardiographic measures of diastolic function, left ventricular (LV) atrial volume, or LV mass at 3 months.
Three “nonserious” device-related adverse events were observed, including one case of acute decompensation early in the experience, ostensibly due to excessive saline administration, Dr. Fudim reported. There was also one case of transient periprocedural hypertension and one instance of postprocedure back pain.
The SAVM procedure is performed transvenously and in general is technically “really not that challenging,” Dr. Fudim said. In most cases, the necessary skills would be accessible not only to interventional cardiologists but also heart failure specialists. “I have performed this procedure myself, and I’m a heart failure guy.”
The REBALANCE-HF roll-in phase and main trial are supported by Axon Therapies. Dr. Fudim discloses receiving support from Bayer, Bodyport, and BTG Specialty Pharmaceuticals; and consulting fees from Abbott, Audicor, Axon Therapies, Bodyguide, Bodyport, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Daxor, Edwards LifeSciences, Feldschuh Foundation, Fire1, Gradient, Intershunt, NXT Biomedical, Pharmacosmos, PreHealth, Splendo, Vironix, Viscardia, and Zoll. Dr. Mullens discloses receiving fees for speaking from Medtronic, Abbott, Novartis, Boston Scientific, AstraZeneca, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A small group of patients with heart failure (HF) who underwent a novel transcatheter nerve-ablation procedure seemed to benefit with improved hemodynamics, symptoms, and quality of life in an admittedly limited observational series.
All had HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and remained on guideline-directed medical therapy during the study.
The open-label experience has launched a randomized trial, featuring a sham control group, that could ultimately challenge dogma about volume overload in patients with chronic and acute HF and the perceived essential role of diuretics.
Researchers see transvenous ablation of the right greater splanchnic nerve (GSN) as potentially appropriate for patients with HF, regardless of ventricular function or acuity. But the ongoing REBALANCE-HF trial aims to enroll up to 80 patients with chronic HFpEF.
Meanwhile, the current 18 patients with elevated resting or exertional pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), given the procedure as part of the main trial’s “roll-in” phase, showed declines in exercise PCWP after 1 month (P = .007) and improved quality-of-life scores at both 1 and 3 months (P < .01). Also at 1 month, a third of the patients improved by at least one step in NYHA functional class.
The procedure, called splanchnic ablation for volume management (SAVM), could potentially be used “across the spectrum of acute and chronic heart failure, maybe even with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and preserved ejection fraction,” Marat Fudim, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
However, “for outcomes, we’ve really only looked in the ambulatory setting,” and only at symptomatic and functional responses. To that extent, based on the current experience and a few small previous studies, Dr. Fudim said, SAVM seems to benefit patients with HF in general who have dyspnea at exercise. Beyond that, the kind of patient who may be most suitable for it “is something I hope we will be able answer once the randomized dataset is in.”
Dr. Fudim reported the REBALANCE-HF roll-in results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2022 sessions, held virtually and live in Madrid. He is also lead author on the same-day publication in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
A different treatment paradigm
Splanchnic-nerve blockade as a possible HF treatment is based on growing evidence that volume overload in patients with HF is not always the cause, at least not a main cause, of congestion and dyspnea. Rather, those classic HF signs and symptoms may often be triggered by adverse redistribution of stable fluid volume from primarily the splanchnic vascular compartment to the intrathoracic space.
In other words, what might seem like classic volume overload calling for diuresis often might actually be euvolemic redistribution of fluid from the abdomen to the chest, raising intracardiac pressures and causing dyspnea.
In that scenario, loop diuretics might only dehydrate the patient and potentially put the kidneys at risk, Dr. Fudim proposed. His recent experience with HF patients implanted with a pulmonary-artery pressure monitor, he said, suggests many who received standard volume-overload therapy had actually been normo- or hypovolemic.
More then half the patients “did not have high volume, they just had high pressures,” he said. “So there is a significant portion of the population that has pathological processes leading to high pressures, but it’s not volume overload. Diuresing those patients would probably not be the right decision.”
The unilateral SAVM procedure appears to attenuate sympathetically mediated splanchnic volume redistribution to the heart and lungs, but as it doesn’t affect the left GSN, preserves some normal sympathetic response.
Sometimes in studies of surgical or catheter-based SAVM, Dr. Fudim said, “we have observationally seen that people discontinued diuretics or decreased doses in the treatment arm.”
‘Beyond our classical thinking’
It’s “impressive” that such right-GSN ablation seemed to reduce exercise-filling pressures, but one should be circumspect because “it’s way beyond our classical thinking,” Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Hospital Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, said as a panelist after Dr. Fudim’s presentation.
“These are invasive procedures,” he noted, “and our physiological understanding does not always match up with what we’re doing in real life, if you look at other interventional procedures, like renal denervation, which showed neutral effects, or if you look at even interatrial shunt devices, which might even be dangerous.”
The field should be “very prudent” before using SAVM in practice, which shouldn’t be “before we have sufficient data to support the efficacy and safety,” Dr. Mullens said. “It remains to be seen how treatment success will be defined. Is it during exercise? How long does the treatment last? What is the effect of the treatment over time; is it not harmful? These are things that we don’t know yet.”
The procedure was considered successful in all 18 patients, 14 of whom were women and 16 of whom were in NYHA class 3. Their average age was 75, and their mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at baseline was 61%. The primary efficacy endpoints were a reduction in PCWP at rest, with legs raised, and at 20W exercise at 1 month. Their baseline invasively measured peak exercise PCWP was at least 25 mm Hg.
At 1 month, mean PCWP at 20W exercise fell from 36.4 mm Hg to 28.9 mm Hg (P = .007) and peak PCWP declined from 39.5 mm Hg to 31.9 mm Hg (P = .013); resting PCWP wasn’t significantly affected. Twelve patients improved by at least one NYHA functional class (P = .02).
Scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), which assesses quality of life, improved by 22 points at 1 month and 18.3 points at 3 months (P < .01 for both differences).
No significant effects on 6-minute walk distance or natriuretic peptide levels were observed, nor were any observed on LVEF or echocardiographic measures of diastolic function, left ventricular (LV) atrial volume, or LV mass at 3 months.
Three “nonserious” device-related adverse events were observed, including one case of acute decompensation early in the experience, ostensibly due to excessive saline administration, Dr. Fudim reported. There was also one case of transient periprocedural hypertension and one instance of postprocedure back pain.
The SAVM procedure is performed transvenously and in general is technically “really not that challenging,” Dr. Fudim said. In most cases, the necessary skills would be accessible not only to interventional cardiologists but also heart failure specialists. “I have performed this procedure myself, and I’m a heart failure guy.”
The REBALANCE-HF roll-in phase and main trial are supported by Axon Therapies. Dr. Fudim discloses receiving support from Bayer, Bodyport, and BTG Specialty Pharmaceuticals; and consulting fees from Abbott, Audicor, Axon Therapies, Bodyguide, Bodyport, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Daxor, Edwards LifeSciences, Feldschuh Foundation, Fire1, Gradient, Intershunt, NXT Biomedical, Pharmacosmos, PreHealth, Splendo, Vironix, Viscardia, and Zoll. Dr. Mullens discloses receiving fees for speaking from Medtronic, Abbott, Novartis, Boston Scientific, AstraZeneca, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2022
Voice-analysis app promising as early warning system for heart failure decompensation
A voice can carry a long distance, but in patients with heart failure (HF) a voice can also carry otherwise hidden signs useful for predicting short-term risk for worsening disease, even acute decompensation. Potentially, it only has to reach a smartphone to do it, suggests a preliminary study of a mobile app designed to alert patients and clinicians to such looming HF events, if possible in time to avert them.
The proprietary app and analysis system (HearO, Cordio Medical), used daily at home by 180 patients with stable HF, demonstrated 82% accuracy in picking out vocal signals of early congestion that would soon be followed by a need for intensified therapy or acute decompensation.
In practice, clinicians receiving the system’s alerts about altered fluid status would intervene with medication adjustments before the patient deteriorates and possibly heads for the ED. That would be the plan; there were no interventions in the current study, which was designed only to explore the strategy’s feasibility and accuracy.
The system could emerge as “a useful tool in remote monitoring of heart failure patients, providing early warning of worsening heart failure,” said William Abraham, MD, from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. “It has the potential to reduce acute decompensated heart failure hospitalizations and improve patient quality of life and economic outcomes. But, of course, we have to show that now in larger and randomized clinical studies.”
Abraham presented the Cordio HearO Community Study preliminary results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology sessions. It follows a recent small study that showed the same app could identify vocal signals linked to altered fluid status in patients with HF hospitalized with acute decompensation.
In the current study, researchers prospectively tracked any worsening HF events that hit patients within a month after the system sent them an alert suggesting early changes in fluid status. Then, they retrospectively assessed the strategy’s predictive accuracy for an initial episode.
The system correctly predicted 32 of 39 first HF events, for an 82% sensitivity and a false-positive rate of 18%. On an annualized basis, Dr. Abraham said, the patients experienced an estimated two to three false alarms per year, alerts that were not followed by HF events. For context, the standard practice of monitoring the patient’s weight “has a sensitivity of about 10%-20%. So this performs very well as a noninvasive technology.”
On average, Dr. Abraham said, “we were able to detect future events about 18 days prior to the worsening heart failure event,” which in practice would provide “a pretty broad window for intervention.”
The false positives were not a surprise. Lung fluid status can change in conditions other than heart failure, he observed, and the HearO system alerts aren’t meant to be followed blindly.
“I don’t know that we clearly understand what those false-positives represent just yet,” Dr. Abraham said. “The bottom line is, as with any diagnostic tool, you have to use the totality of clinical information you have available. If you get an alert and the patient has a fever and a cough, you might think of pneumonia before worsening heart failure.”
“The false positives don’t appear to be alarming,” agreed Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Badalona, Spain, and Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
The study suggests that the HearO system, combined with sound clinical judgment, “has the potential to identify early congestion that may allow for treatment management, and then avoiding hospital admission,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who isn’t connected with the study, said in an interview.
The entirely noninvasive, smartphone-based app would be more appealing than implanted devices that, for example, measure thoracic bioimpedance or pulmonary artery pressure and are also intended as congestion early-warning systems, he proposed. “Its scalability makes it very attractive as well.”
But all that “would have to be validated in a large clinical trial,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who comoderated the conference session featuring Dr. Abraham’s presentation, said when interviewed.
The ongoing study has enrolled 430 clinically stable adult patients with HF in New York Heart Association functional class II or III, regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction, who were cared for by teams at eight centers in Israel. At the outset, during a period of stability, each patient spoke a few sentences into the app to establish a vocal-pattern baseline.
Once home, their assignment was to speak the same sentences into their phones once a day. The app, working through a cloud-based, artificial intelligence–derived processing system, compared each day’s vocal signature with the baseline and alerted researchers when it detected signs of altered fluid status.
About 460,000 recordings were collected from the 180 patients in the current analysis, of whom about 27% were women. They used the app for a mean of 512 days.
The system seems to work well regardless of language or dialect, Dr. Abraham said. About 70% of the current study’s patients spoke Hebrew, and most of the rest spoke either Russian or Arabic.
Most patients (almost 80%) used the app at least 70% of the prescribed time. Only 14 patients used the app less than 60% of the time, he reported.
Dr. Bayés-Genís proposed that, in practice, unfamiliarity with or resistance to smartphone technology would be unlikely to figure greatly in any nonadherence with the daily app regimen, except “maybe for the eldest of the eldest.” The current cohort’s mean age was 70 years. In his experience, he said, most older persons younger than age 80 use a smartphone, at least in more developed countries.
Dr. Abraham disclosed serving on an advisory board for and receiving consulting fees from Cordio Medical; receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Edwards Lifesciences, and Respicardia; receiving salary from V-Wave Medical; and receiving research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bayés-Genís reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Vifor-Fresenius, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, and Critical Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A voice can carry a long distance, but in patients with heart failure (HF) a voice can also carry otherwise hidden signs useful for predicting short-term risk for worsening disease, even acute decompensation. Potentially, it only has to reach a smartphone to do it, suggests a preliminary study of a mobile app designed to alert patients and clinicians to such looming HF events, if possible in time to avert them.
The proprietary app and analysis system (HearO, Cordio Medical), used daily at home by 180 patients with stable HF, demonstrated 82% accuracy in picking out vocal signals of early congestion that would soon be followed by a need for intensified therapy or acute decompensation.
In practice, clinicians receiving the system’s alerts about altered fluid status would intervene with medication adjustments before the patient deteriorates and possibly heads for the ED. That would be the plan; there were no interventions in the current study, which was designed only to explore the strategy’s feasibility and accuracy.
The system could emerge as “a useful tool in remote monitoring of heart failure patients, providing early warning of worsening heart failure,” said William Abraham, MD, from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. “It has the potential to reduce acute decompensated heart failure hospitalizations and improve patient quality of life and economic outcomes. But, of course, we have to show that now in larger and randomized clinical studies.”
Abraham presented the Cordio HearO Community Study preliminary results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology sessions. It follows a recent small study that showed the same app could identify vocal signals linked to altered fluid status in patients with HF hospitalized with acute decompensation.
In the current study, researchers prospectively tracked any worsening HF events that hit patients within a month after the system sent them an alert suggesting early changes in fluid status. Then, they retrospectively assessed the strategy’s predictive accuracy for an initial episode.
The system correctly predicted 32 of 39 first HF events, for an 82% sensitivity and a false-positive rate of 18%. On an annualized basis, Dr. Abraham said, the patients experienced an estimated two to three false alarms per year, alerts that were not followed by HF events. For context, the standard practice of monitoring the patient’s weight “has a sensitivity of about 10%-20%. So this performs very well as a noninvasive technology.”
On average, Dr. Abraham said, “we were able to detect future events about 18 days prior to the worsening heart failure event,” which in practice would provide “a pretty broad window for intervention.”
The false positives were not a surprise. Lung fluid status can change in conditions other than heart failure, he observed, and the HearO system alerts aren’t meant to be followed blindly.
“I don’t know that we clearly understand what those false-positives represent just yet,” Dr. Abraham said. “The bottom line is, as with any diagnostic tool, you have to use the totality of clinical information you have available. If you get an alert and the patient has a fever and a cough, you might think of pneumonia before worsening heart failure.”
“The false positives don’t appear to be alarming,” agreed Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Badalona, Spain, and Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
The study suggests that the HearO system, combined with sound clinical judgment, “has the potential to identify early congestion that may allow for treatment management, and then avoiding hospital admission,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who isn’t connected with the study, said in an interview.
The entirely noninvasive, smartphone-based app would be more appealing than implanted devices that, for example, measure thoracic bioimpedance or pulmonary artery pressure and are also intended as congestion early-warning systems, he proposed. “Its scalability makes it very attractive as well.”
But all that “would have to be validated in a large clinical trial,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who comoderated the conference session featuring Dr. Abraham’s presentation, said when interviewed.
The ongoing study has enrolled 430 clinically stable adult patients with HF in New York Heart Association functional class II or III, regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction, who were cared for by teams at eight centers in Israel. At the outset, during a period of stability, each patient spoke a few sentences into the app to establish a vocal-pattern baseline.
Once home, their assignment was to speak the same sentences into their phones once a day. The app, working through a cloud-based, artificial intelligence–derived processing system, compared each day’s vocal signature with the baseline and alerted researchers when it detected signs of altered fluid status.
About 460,000 recordings were collected from the 180 patients in the current analysis, of whom about 27% were women. They used the app for a mean of 512 days.
The system seems to work well regardless of language or dialect, Dr. Abraham said. About 70% of the current study’s patients spoke Hebrew, and most of the rest spoke either Russian or Arabic.
Most patients (almost 80%) used the app at least 70% of the prescribed time. Only 14 patients used the app less than 60% of the time, he reported.
Dr. Bayés-Genís proposed that, in practice, unfamiliarity with or resistance to smartphone technology would be unlikely to figure greatly in any nonadherence with the daily app regimen, except “maybe for the eldest of the eldest.” The current cohort’s mean age was 70 years. In his experience, he said, most older persons younger than age 80 use a smartphone, at least in more developed countries.
Dr. Abraham disclosed serving on an advisory board for and receiving consulting fees from Cordio Medical; receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Edwards Lifesciences, and Respicardia; receiving salary from V-Wave Medical; and receiving research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bayés-Genís reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Vifor-Fresenius, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, and Critical Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A voice can carry a long distance, but in patients with heart failure (HF) a voice can also carry otherwise hidden signs useful for predicting short-term risk for worsening disease, even acute decompensation. Potentially, it only has to reach a smartphone to do it, suggests a preliminary study of a mobile app designed to alert patients and clinicians to such looming HF events, if possible in time to avert them.
The proprietary app and analysis system (HearO, Cordio Medical), used daily at home by 180 patients with stable HF, demonstrated 82% accuracy in picking out vocal signals of early congestion that would soon be followed by a need for intensified therapy or acute decompensation.
In practice, clinicians receiving the system’s alerts about altered fluid status would intervene with medication adjustments before the patient deteriorates and possibly heads for the ED. That would be the plan; there were no interventions in the current study, which was designed only to explore the strategy’s feasibility and accuracy.
The system could emerge as “a useful tool in remote monitoring of heart failure patients, providing early warning of worsening heart failure,” said William Abraham, MD, from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. “It has the potential to reduce acute decompensated heart failure hospitalizations and improve patient quality of life and economic outcomes. But, of course, we have to show that now in larger and randomized clinical studies.”
Abraham presented the Cordio HearO Community Study preliminary results at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology sessions. It follows a recent small study that showed the same app could identify vocal signals linked to altered fluid status in patients with HF hospitalized with acute decompensation.
In the current study, researchers prospectively tracked any worsening HF events that hit patients within a month after the system sent them an alert suggesting early changes in fluid status. Then, they retrospectively assessed the strategy’s predictive accuracy for an initial episode.
The system correctly predicted 32 of 39 first HF events, for an 82% sensitivity and a false-positive rate of 18%. On an annualized basis, Dr. Abraham said, the patients experienced an estimated two to three false alarms per year, alerts that were not followed by HF events. For context, the standard practice of monitoring the patient’s weight “has a sensitivity of about 10%-20%. So this performs very well as a noninvasive technology.”
On average, Dr. Abraham said, “we were able to detect future events about 18 days prior to the worsening heart failure event,” which in practice would provide “a pretty broad window for intervention.”
The false positives were not a surprise. Lung fluid status can change in conditions other than heart failure, he observed, and the HearO system alerts aren’t meant to be followed blindly.
“I don’t know that we clearly understand what those false-positives represent just yet,” Dr. Abraham said. “The bottom line is, as with any diagnostic tool, you have to use the totality of clinical information you have available. If you get an alert and the patient has a fever and a cough, you might think of pneumonia before worsening heart failure.”
“The false positives don’t appear to be alarming,” agreed Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Badalona, Spain, and Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
The study suggests that the HearO system, combined with sound clinical judgment, “has the potential to identify early congestion that may allow for treatment management, and then avoiding hospital admission,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who isn’t connected with the study, said in an interview.
The entirely noninvasive, smartphone-based app would be more appealing than implanted devices that, for example, measure thoracic bioimpedance or pulmonary artery pressure and are also intended as congestion early-warning systems, he proposed. “Its scalability makes it very attractive as well.”
But all that “would have to be validated in a large clinical trial,” Dr. Bayés-Genís, who comoderated the conference session featuring Dr. Abraham’s presentation, said when interviewed.
The ongoing study has enrolled 430 clinically stable adult patients with HF in New York Heart Association functional class II or III, regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction, who were cared for by teams at eight centers in Israel. At the outset, during a period of stability, each patient spoke a few sentences into the app to establish a vocal-pattern baseline.
Once home, their assignment was to speak the same sentences into their phones once a day. The app, working through a cloud-based, artificial intelligence–derived processing system, compared each day’s vocal signature with the baseline and alerted researchers when it detected signs of altered fluid status.
About 460,000 recordings were collected from the 180 patients in the current analysis, of whom about 27% were women. They used the app for a mean of 512 days.
The system seems to work well regardless of language or dialect, Dr. Abraham said. About 70% of the current study’s patients spoke Hebrew, and most of the rest spoke either Russian or Arabic.
Most patients (almost 80%) used the app at least 70% of the prescribed time. Only 14 patients used the app less than 60% of the time, he reported.
Dr. Bayés-Genís proposed that, in practice, unfamiliarity with or resistance to smartphone technology would be unlikely to figure greatly in any nonadherence with the daily app regimen, except “maybe for the eldest of the eldest.” The current cohort’s mean age was 70 years. In his experience, he said, most older persons younger than age 80 use a smartphone, at least in more developed countries.
Dr. Abraham disclosed serving on an advisory board for and receiving consulting fees from Cordio Medical; receiving consulting fees from Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Edwards Lifesciences, and Respicardia; receiving salary from V-Wave Medical; and receiving research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bayés-Genís reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Vifor-Fresenius, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, and Critical Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2022
Porcine virus a suspect in man’s death after pig heart transplant
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MIT TECHNOLOGY REVIEW
Cutting dementia risk in AFib: Does rhythm control strategy matter?
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cutting dementia risk in atrial fibrillation: Does rhythm control strategy matter?
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. But a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD alone at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler disclosed consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. But a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD alone at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler disclosed consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. But a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD alone at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler disclosed consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HEART RHYTHM 2022