Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction that usually manifests with eczematous lesions within hours to days after exposure to a contact allergen. The primary treatment of ACD consists of allergen avoidance, but medications also may be necessary to manage symptoms, particularly in cases where avoidance alone does not lead to resolution of dermatitis. At present, no medical therapies are explicitly approved for use in the management of ACD. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a class of small molecule inhibitors that are used for the treatment of a range of inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Several oral and topical JAK inhibitors also have recently been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for atopic dermatitis (AD). In this article, we discuss this important class of medications and the role that they may play in the off-label management of refractory ACD.
JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
The JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway plays a crucial role in many biologic processes. Notably, JAK/STAT signaling is involved in the development and regulation of the immune system.1 The cascade begins when a particular transmembrane receptor binds a ligand, such as an interferon or interleukin.2 Upon ligand binding, the receptor dimerizes or oligomerizes, bringing the relevant JAK proteins into close approximation to each other.3 This allows the JAK proteins to autophosphorylate or transphosphorylate.2-4 Phosphorylation activates the JAK proteins and increases their kinase activity.3 In humans, there are 4 JAK proteins: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2.4 When activated, the JAK proteins phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor, which creates a docking site for STAT proteins. After binding, the STAT proteins then are phosphorylated, leading to their dimerization and translocation to the nucleus.2,3 Once in the nucleus, the STAT proteins act as transcription factors for target genes.3
JAK Inhibitors
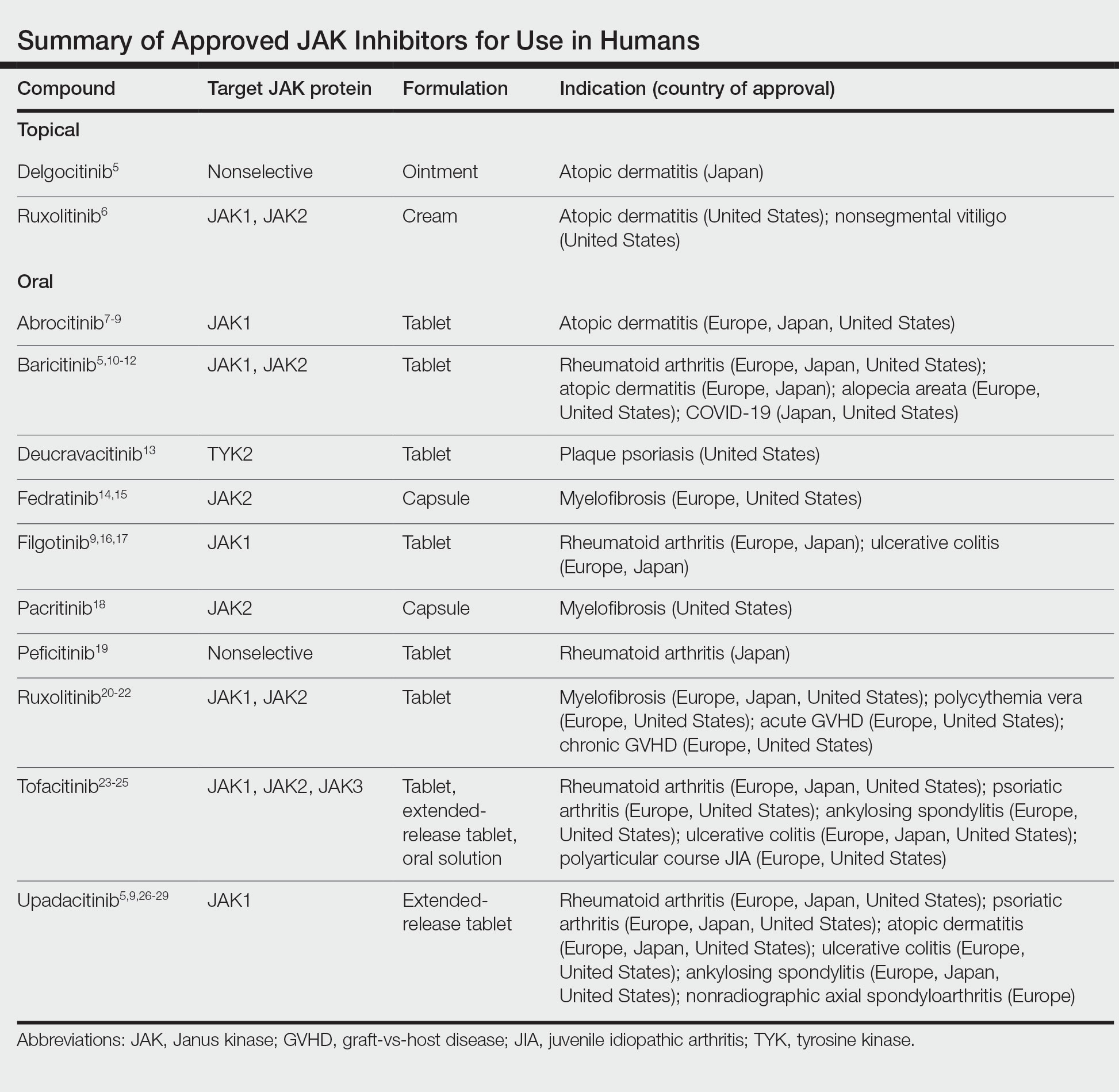
Janus kinase inhibitors are immunomodulatory medications that work through inhibition of 1 or more of the JAK proteins in the JAK/STAT pathway. Through this mechanism, JAK inhibitors can impede the activity of proinflammatory cytokines and T cells.4 A brief overview of the commercially available JAK inhibitors in Europe, Japan, and the United States is provided in the Table.5-29
Of the approved JAK inhibitors, more than 40% are indicated for AD. The first JAK inhibitor to be approved in the topical form was delgocitinib in 2020 in Japan.5 In a phase 3 trial, delgocitinib demonstrated significant reductions in modified Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score (P<.001) as well as Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) when compared with vehicle.30 Topical ruxolitinib soon followed when its approval for AD was announced by the FDA in 2021.31 Results from 2 phase 3 trials found that significantly more patients achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) treatment success (P<.0001) and a significant reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) with topical ruxolitinib vs vehicle.32
The first oral JAK inhibitor to attain approval for AD was baricitinib in Europe and Japan, but it is not currently approved for this indication in the United States by the FDA.11,12,33 Consistent findings across phase 3 trials revealed that baricitinib was more effective at achieving IGA treatment success and improved EASI scores compared with placebo.33
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK inhibitor, was subsequently approved for AD in Europe and Japan in 2021 and in the United States in early 2022.5,9,26,27 Two replicate phase 3 trials demonstrated significant improvement in EASI score, itch, and quality of life with upadacitinib compared with placebo (P<.0001).34 Abrocitinib was granted FDA approval for AD in the same time period, with phase 3 trials exhibiting greater responses in IGA and EASI scores vs placebo.35
Potential for Use in ACD
Given the successful use of JAK inhibitors in the management of AD, there is optimism that these medications also may have potential application in ACD. Recent literature suggests that the 2 conditions may be more closely related mechanistically than previously understood. As a result, AD and ACD often are managed with the same therapeutic agents.36