User login
Lanolin: The 2023 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Practice Points
- Lanolin is a common ingredient in personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial materials.
- Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin appears to be most common in patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis, and perianal/genital dermatitis.
- There is no single best lanolin patch test formulation. Patch testing and repeat open application testing to PCPs containing lanolin also may be of benefit.
Is Laundry Detergent a Common Cause of Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Laundry detergent, a cleaning agent ubiquitous in the modern household, often is suspected as a cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
We provide a summary of the evidence for the potential allergenicity of laundry detergent, including common allergens present in laundry detergent, the role of machine washing, and the differential diagnosis for laundry detergent–associated ACD.
Allergenic Ingredients in Laundry Detergent
Potential allergens present in laundry detergent include fragrances, preservatives, surfactants, emulsifiers, bleaches, brighteners, enzymes, and dyes.6-8 In an analysis of allergens present in laundry detergents available in the United States, fragrances and preservatives were most common (eTable).7,8 Contact allergy to fragrances occurs in approximately 3.5% of the general population9 and is detected in as many as 9.2% of patients referred for patch testing in North America.10 Preservatives commonly found in laundry detergent include isothiazolinones, such as methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI)/methylisothiazolinone (MI), MI alone, and benzisothiazolinone (BIT). Methylisothiazolinone has gained attention for causing an ACD epidemic beginning in the early 2000s and peaking in Europe between 2013 and 2014 and decreasing thereafter due to consumer personal care product regulatory changes enacted in the European Union.11 In contrast, rates of MI allergy in North America have continued to increase (reaching as high as 15% of patch tested patients in 2017-2018) due to a lack of similar regulation.10,12 More recently, the prevalence of positive patch tests to BIT has been rising, though it often is difficult to ascertain relevant sources of exposure, and some cases could represent cross-reactions to MCI/MI.10,13
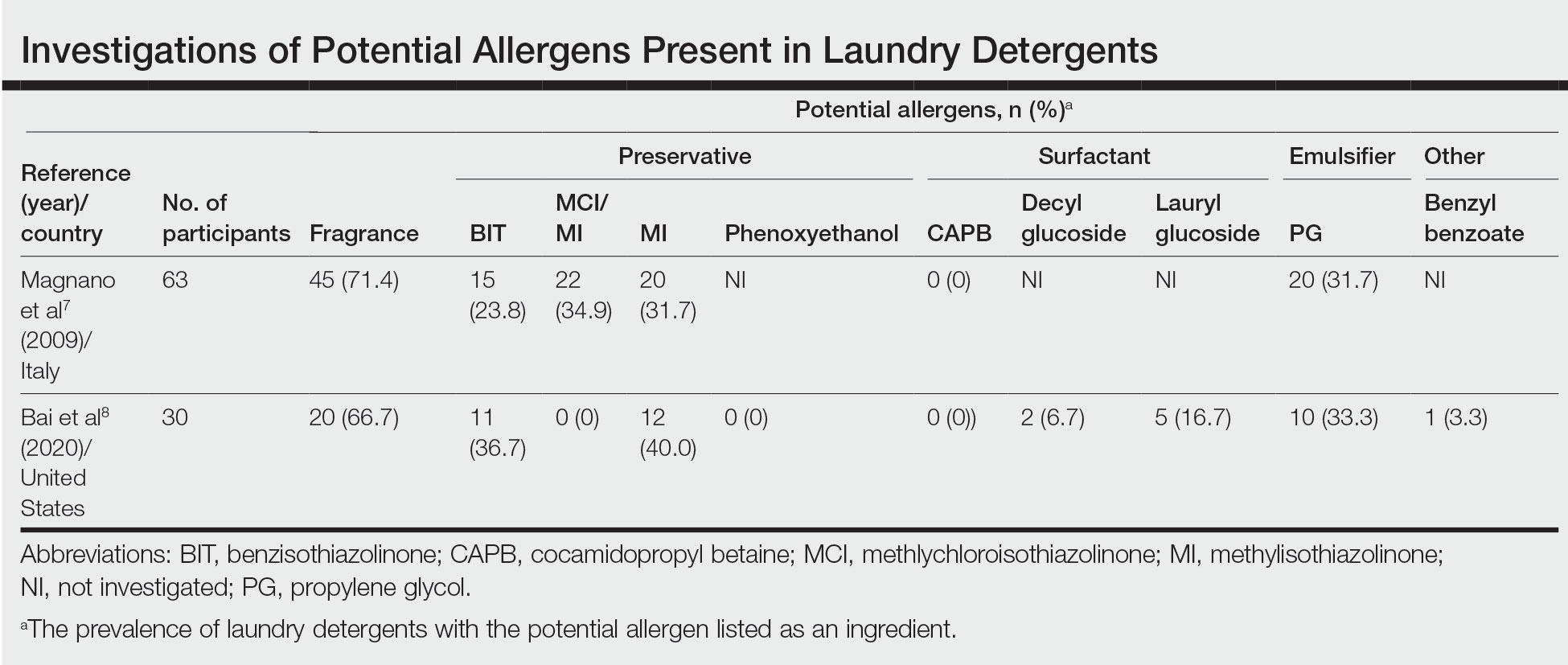
Other allergens that may be present in laundry detergent include surfactants and propylene glycol. Alkyl glucosides such as decyl glucoside and lauryl glucoside are considered gentle surfactants and often are included in products marketed as safe for sensitive skin,14 such as “free and gentle” detergents.8 However, they actually may pose an increased risk for sensitization in patients with atopic dermatitis.14 In addition to being allergenic, surfactants and emulsifiers are known irritants.6,15 Although pathologically distinct, ACD and irritant contact dermatitis can be indistinguishable on clinical presentation.
How Commonly Does Laundry Detergent Cause ACD?
The mere presence of a contact allergen in laundry detergent does not necessarily imply that it is likely to cause ACD. To do so, the chemical in question must exceed the exposure thresholds for primary sensitization (ie, induction of contact allergy) and/or elicitation (ie, development of ACD in sensitized individuals). These depend on a complex interplay of product- and patient-specific factors, among them the concentration of the chemical in the detergent, the method of use, and the amount of detergent residue remaining on clothing after washing.
In the 1990s, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) attempted to determine the prevalence of ACD caused by laundry detergent.1 Among 738 patients patch tested to aqueous dilutions of granular and liquid laundry detergents, only 5 (0.7%) had a possible allergic patch test reaction. It was unclear what the culprit allergens in the detergents may have been; only 1 of the patients also tested positive to fragrance. Two patients underwent further testing to additional detergent dilutions, and the results called into question whether their initial reactions had truly been allergic (positive) or were actually irritant (negative). The investigators concluded that the prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD in this large group of patients was at most 0.7%, and possibly lower.1
Importantly, patch testing to laundry detergents should not be undertaken in routine clinical practice. Laundry detergents should never be tested “as is” (ie, undiluted) on the skin; they are inherently irritating and have a high likelihood of producing misleading false-positive reactions. Careful dilutions and testing of control subjects are necessary if patch testing with these products is to be appropriately conducted.
Isothiazolinones in Laundry Detergent
The extremely low prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD reported by the NACDG was determined prior to the start of the worldwide MI allergy epidemic, raising the possibility that laundry detergents containing isothiazolinones may be associated with ACD. There is no consensus about the minimum level at which isothiazolinones pose no risk to consumers,16-19 but the US Expert Panel for Cosmetic Ingredient Safety declared that MI is “safe for use in rinse-off cosmetic products at concentrations up to 100 ppm and safe in leave-on cosmetic products when they are formulated to be nonsensitizing.”18,19 Although ingredient lists do not always reveal when isothiazolinones are present, analyses of commercially available laundry detergents have shown MI concentrations ranging from undetectable to 65.7 ppm.20-23
Published reports suggest that MCI/MI in laundry detergent can elicit ACD in sensitized individuals. In one case, a 7-year-old girl with chronic truncal dermatitis (atopic history unspecified) was patch tested, revealing a strongly positive reaction to MCI/MI.24 Her laundry detergent was the only personal product found to contain MI. The dermatitis completely resolved after switching detergents and flared after wearing a jacket that had been washed in the implicated detergent, further supporting the relevance of the positive patch test. The investigators suspected initial sensitization to MI from wet wipes used earlier in childhood.24 In another case involving occupational exposure, a 39-year-old nonatopic factory worker was responsible for directly adding MI to laundry detergent.25 Although he wore disposable work gloves, he developed severe hand dermatitis, eczematous pretibial patches, and generalized pruritus. Patch testing revealed positive reactions to MCI/MI and MI, and he experienced improvement when reassigned to different work duties. It was hypothesized that the leg dermatitis and generalized pruritus may have been related to exposure to small concentrations of MI in work clothes washed with an MI-containing detergent.25 Notably, this patient’s level of exposure was much greater than that encountered by individuals in day-to-day life outside of specialized occupational settings.
Regarding other isothiazolinones, a toxicologic study estimated that BIT in laundry detergent would be unlikely to induce sensitization, even at the maximal acceptable concentration, as recommended by preservative manufacturers, and accounting for undiluted detergent spilling directly onto the skin.26
Does Machine Washing Impact Allergen Concentrations?
Two recent investigations have suggested that machine washing reduces concentrations of isothiazolinones to levels that are likely below clinical relevance. In the first study, 3 fabrics—cotton, polyester, cotton-polyester—were machine washed and line dried.27 A standard detergent was used with MI added at different concentrations: less than 1 ppm, 100 ppm, and 1000 ppm. This process was either performed once or 10 times. Following laundering and line drying, MI was undetectable in all fabrics regardless of MI concentration or number of times washed (detection limit, 0.5 ppm).27 In the second study, 4 fabrics—cotton, wool, polyester, linen—were washed with standard laundry detergent in 1 of 4 ways: handwashing (positive control), standard machine washing, standard machine washing with fabric softener, and standard machine washing with a double rinse.28 After laundering and line drying, concentrations of MI, MCI, and BIT were low or undetectable regardless of fabric type or method of laundering. The highest levels detected were in handwashed garments at a maximum of 0.5 ppm of MI. The study authors postulated that chemical concentrations near these maximum residual levels may pose a risk for eliciting ACD in highly sensitized individuals. Therefore, handwashing can be considered a much higher risk activity for isothiazolinone ACD compared with machine washing.28
It is intriguing that machine washing appears to reduce isothiazolinones to low concentrations that may have limited likelihood of causing ACD. Similar findings have been reported regarding fragrances. A quantitative risk assessment performed on 24 of 26 fragrance allergens regulated by the European Union determined that the amount of fragrance deposited on the skin from laundered garments would be less than the threshold for causing sensitization.29 Although this risk assessment was unable to address the threshold of elicitation, another study conducted in Europe investigated whether fragrance residues present on fabric, such as those deposited from laundry detergent, are present at high enough concentrations to elicit ACD in previously sensitized individuals.30 When 36 individuals were patch tested with increasing concentrations of a fragrance to which they were already sensitized, only 2 (5.6%) had a weakly positive reaction and then only to the highest concentration, which was estimated to be 20-fold higher than the level of skin exposure after normal laundering. No patient reacted at lower concentrations.30
Although machine washing may decrease isothiazolinone and/or fragrance concentrations in laundry detergent to below clinically relevant levels, these findings should not necessarily be extrapolated to all chemicals in laundry detergent. Indeed, a prior study observed that after washing cotton cloths in a detergent solution for 10 minutes, detergent residue was present at concentrations ranging from 139 to 2820 ppm and required a subsequent 20 to 22 washes in water to become undetectable.31 Another study produced a mathematical model of the residual concentration of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), a surfactant and known irritant, in laundered clothing.32 It was estimated that after machine washing, the residual concentration of SDS on clothes would be too low to cause irritation; however, as the clothes dry (ie, as moisture evaporates but solutes remain), the concentration of SDS on the fabric’s surface would increase to potentially irritating levels. The extensive drying that is possible with electric dryers may further enhance this solute-concentrating effect.
Differential Diagnosis of Laundry Detergent ACD
The propensity for laundry detergent to cause ACD is a question that is nowhere near settled, but the prevalence of allergy likely is far less common than is generally suspected. In our experience, many patients presenting for patch testing have already made the change to “free and clear” detergents without noticeable improvement in their dermatitis, which could possibly relate to the ongoing presence of contact allergens in these “gentle” formulations.7 However, to avoid anchoring bias, more frequent causes of dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis. Textile ACD presents beneath clothing with accentuation at areas of closest contact with the skin, classically involving the axillary rim but sparing the vault. The most frequently implicated allergens in textile ACD are disperse dyes and less commonly textile resins.33,34 Between 2017 and 2018, 2.3% of 4882 patients patch tested by the NACDG reacted positively to disperse dye mix.10 There is evidence to suggest that the actual prevalence of disperse dye allergy might be higher due to inadequacy of screening allergens on baseline patch test series.35 Additional diagnoses that should be distinguished from presumed detergent contact dermatitis include atopic dermatitis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Final Interpretation
Although many patients and physicians consider laundry detergent to be a major cause of ACD, there is limited high-quality evidence to support this belief. Contact allergy to laundry detergent is probably much less common than is widely supposed. Although laundry detergents can contain common allergens such as fragrances and preservatives, evidence suggests that they are likely reduced to below clinically relevant levels during routine machine washing; however, we cannot assume that we are in the “free and clear,” as uncertainty remains about the impact of these low concentrationson individuals with strong contact allergy, and large studies of patch testing to modern detergents have yet to be carried out.
- Belsito DV, Fransway AF, Fowler JF, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to detergents: a multicenter study to assess prevalence. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:200-206. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.119665
- Dallas MJ, Wilson PA, Burns LD, et al. Dermatological and other health problems attributed by consumers to contact with laundry products. Home Econ Res J. 1992;21:34-49. doi:10.1177/1077727X9202100103
- Bailey A. An overview of laundry detergent allergies. Verywell Health. September 16, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.verywellhealth.com/laundry-detergent-allergies-signs-symptoms-and-treatment-5198934
- Fasanella K. How to tell if you laundry detergent is messing with your skin. Allure. June 15, 2019. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.allure.com/story/laundry-detergent-allergy-skin-reaction
- Oykhman P, Dookie J, Al-Rammahy et al. Dietary elimination for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Immunol Pract. 2022;10:2657-2666.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2022.06.044
- Kwon S, Holland D, Kern P. Skin safety evaluation of laundry detergent products. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009;72:1369-1379. doi:10.1080/1528739090321675
- Magnano M, Silvani S, Vincenzi C, et al. Contact allergens and irritants in household washing and cleaning products. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:337-341. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01647.x
- Bai H, Tam I, Yu J. Contact allergens in top-selling textile-care products. Dermatitis. 2020;31:53-58. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000566
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Havmose M, Thyssen JP, Zachariae C, et al. The epidemic of contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone–an analysis of Danish consecutive patients patch tested between 2005 and 2019. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:254-262. doi:10.1111/cod.13717
- Atwater AR, Petty AJ, Liu B, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with preservatives: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994 through 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:965-976. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.059
- King N, Latheef F, Wilkinson M. Trends in preservative allergy: benzisothiazolinone emerges from the pack. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:637-642. doi:10.1111/cod.13968
- Sasseville D. Alkyl glucosides: 2017 “allergen of the year.” Dermatitis. 2017;28:296. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000290
- McGowan MA, Scheman A, Jacob SE. Propylene glycol in contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2018;29:6-12. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000307
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Health and Consumers. Opinion on methylisothiazolinone (P94) submission II (sensitisation only). Revised March 27, 2014. Accessed March 21, 2023. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_145.pdf
- Cosmetic ingredient hotlist: list of ingredients that are restricted for use in cosmetic products. Government of Canada website. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/hotlist.html#tbl2
- Burnett CL, Boyer I, Bergfeld WF, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2019;38(1 suppl):70S-84S. doi:10.1177/1091581819838792
- Burnett CL, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2021;40(1 suppl):5S-19S. doi:10.1177/10915818211015795
- Aerts O, Meert H, Goossens A, et al. Methylisothiazolinone in selected consumer products in Belgium: adding fuel to the fire? Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:142-149. doi:10.1111/cod.12449
- Garcia-Hidalgo E, Sottas V, von Goetz N, et al. Occurrence and concentrations of isothiazolinones in detergents and cosmetics in Switzerland. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:96-106. doi:10.1111/cod.12700
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Antuña AG, et al. Isothiazolinones in cleaning products: analysis with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry of samples from sensitized patients and markets. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:94-100. doi:10.1111/cod.13430
- Alvarez-Rivera G, Dagnac T, Lores M, et al. Determination of isothiazolinone preservatives in cosmetics and household products by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1270:41-50. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.10.063
- Cotton CH, Duah CG, Matiz C. Allergic contact dermatitis due to methylisothiazolinone in a young girl’s laundry detergent. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:486-487. doi:10.1111/pde.13122
- Sandvik A, Holm JO. Severe allergic contact dermatitis in a detergent production worker caused by exposure to methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:243-245. doi:10.1111/cod.13182
- Novick RM, Nelson ML, Unice KM, et al. Estimation of safe use concentrations of the preservative 1,2-benziosothiazolin-3-one (BIT) in consumer cleaning products and sunscreens. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;56:60-66. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.006
- Hofmann MA, Giménez-Arnau A, Aberer W, et al. MI (2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one) contained in detergents is not detectable in machine washed textiles. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:1. doi:10.1186/s13601-017-0187-2
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Atuña AG, et al. Persistence of isothiazolinones in clothes after machine washing. Dermatitis. 2021;32:298-300. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000603
- Corea NV, Basketter DA, Clapp C, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the risk from washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:48-53. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00872.x
- Basketter DA, Pons-Guiraud A, van Asten A, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the safety of washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2010;62:349-354. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2010.01728.x
- Agarwal C, Gupta BN, Mathur AK, et al. Residue analysis of detergent in crockery and clothes. Environmentalist. 1986;4:240-243.
- Broadbridge P, Tilley BS. Diffusion of dermatological irritant in drying laundered cloth. Math Med Biol. 2021;38:474-489. doi:10.1093/imammb/dqab014
- Lisi P, Stingeni L, Cristaudo A, et al. Clinical and epidemiological features of textile contact dermatitis: an Italian multicentre study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:344-350. doi:10.1111/cod.12179
- Mobolaji-Lawal M, Nedorost S. The role of textiles in dermatitis: an update. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015;15:17. doi:10.1007/s11882-015-0518-0
- Nijman L, Rustemeyer T, Franken SM, et al. The prevalence and relevance of patch testing with textile dyes [published online December 3, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14260
Laundry detergent, a cleaning agent ubiquitous in the modern household, often is suspected as a cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
We provide a summary of the evidence for the potential allergenicity of laundry detergent, including common allergens present in laundry detergent, the role of machine washing, and the differential diagnosis for laundry detergent–associated ACD.
Allergenic Ingredients in Laundry Detergent
Potential allergens present in laundry detergent include fragrances, preservatives, surfactants, emulsifiers, bleaches, brighteners, enzymes, and dyes.6-8 In an analysis of allergens present in laundry detergents available in the United States, fragrances and preservatives were most common (eTable).7,8 Contact allergy to fragrances occurs in approximately 3.5% of the general population9 and is detected in as many as 9.2% of patients referred for patch testing in North America.10 Preservatives commonly found in laundry detergent include isothiazolinones, such as methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI)/methylisothiazolinone (MI), MI alone, and benzisothiazolinone (BIT). Methylisothiazolinone has gained attention for causing an ACD epidemic beginning in the early 2000s and peaking in Europe between 2013 and 2014 and decreasing thereafter due to consumer personal care product regulatory changes enacted in the European Union.11 In contrast, rates of MI allergy in North America have continued to increase (reaching as high as 15% of patch tested patients in 2017-2018) due to a lack of similar regulation.10,12 More recently, the prevalence of positive patch tests to BIT has been rising, though it often is difficult to ascertain relevant sources of exposure, and some cases could represent cross-reactions to MCI/MI.10,13

Other allergens that may be present in laundry detergent include surfactants and propylene glycol. Alkyl glucosides such as decyl glucoside and lauryl glucoside are considered gentle surfactants and often are included in products marketed as safe for sensitive skin,14 such as “free and gentle” detergents.8 However, they actually may pose an increased risk for sensitization in patients with atopic dermatitis.14 In addition to being allergenic, surfactants and emulsifiers are known irritants.6,15 Although pathologically distinct, ACD and irritant contact dermatitis can be indistinguishable on clinical presentation.
How Commonly Does Laundry Detergent Cause ACD?
The mere presence of a contact allergen in laundry detergent does not necessarily imply that it is likely to cause ACD. To do so, the chemical in question must exceed the exposure thresholds for primary sensitization (ie, induction of contact allergy) and/or elicitation (ie, development of ACD in sensitized individuals). These depend on a complex interplay of product- and patient-specific factors, among them the concentration of the chemical in the detergent, the method of use, and the amount of detergent residue remaining on clothing after washing.
In the 1990s, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) attempted to determine the prevalence of ACD caused by laundry detergent.1 Among 738 patients patch tested to aqueous dilutions of granular and liquid laundry detergents, only 5 (0.7%) had a possible allergic patch test reaction. It was unclear what the culprit allergens in the detergents may have been; only 1 of the patients also tested positive to fragrance. Two patients underwent further testing to additional detergent dilutions, and the results called into question whether their initial reactions had truly been allergic (positive) or were actually irritant (negative). The investigators concluded that the prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD in this large group of patients was at most 0.7%, and possibly lower.1
Importantly, patch testing to laundry detergents should not be undertaken in routine clinical practice. Laundry detergents should never be tested “as is” (ie, undiluted) on the skin; they are inherently irritating and have a high likelihood of producing misleading false-positive reactions. Careful dilutions and testing of control subjects are necessary if patch testing with these products is to be appropriately conducted.
Isothiazolinones in Laundry Detergent
The extremely low prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD reported by the NACDG was determined prior to the start of the worldwide MI allergy epidemic, raising the possibility that laundry detergents containing isothiazolinones may be associated with ACD. There is no consensus about the minimum level at which isothiazolinones pose no risk to consumers,16-19 but the US Expert Panel for Cosmetic Ingredient Safety declared that MI is “safe for use in rinse-off cosmetic products at concentrations up to 100 ppm and safe in leave-on cosmetic products when they are formulated to be nonsensitizing.”18,19 Although ingredient lists do not always reveal when isothiazolinones are present, analyses of commercially available laundry detergents have shown MI concentrations ranging from undetectable to 65.7 ppm.20-23
Published reports suggest that MCI/MI in laundry detergent can elicit ACD in sensitized individuals. In one case, a 7-year-old girl with chronic truncal dermatitis (atopic history unspecified) was patch tested, revealing a strongly positive reaction to MCI/MI.24 Her laundry detergent was the only personal product found to contain MI. The dermatitis completely resolved after switching detergents and flared after wearing a jacket that had been washed in the implicated detergent, further supporting the relevance of the positive patch test. The investigators suspected initial sensitization to MI from wet wipes used earlier in childhood.24 In another case involving occupational exposure, a 39-year-old nonatopic factory worker was responsible for directly adding MI to laundry detergent.25 Although he wore disposable work gloves, he developed severe hand dermatitis, eczematous pretibial patches, and generalized pruritus. Patch testing revealed positive reactions to MCI/MI and MI, and he experienced improvement when reassigned to different work duties. It was hypothesized that the leg dermatitis and generalized pruritus may have been related to exposure to small concentrations of MI in work clothes washed with an MI-containing detergent.25 Notably, this patient’s level of exposure was much greater than that encountered by individuals in day-to-day life outside of specialized occupational settings.
Regarding other isothiazolinones, a toxicologic study estimated that BIT in laundry detergent would be unlikely to induce sensitization, even at the maximal acceptable concentration, as recommended by preservative manufacturers, and accounting for undiluted detergent spilling directly onto the skin.26
Does Machine Washing Impact Allergen Concentrations?
Two recent investigations have suggested that machine washing reduces concentrations of isothiazolinones to levels that are likely below clinical relevance. In the first study, 3 fabrics—cotton, polyester, cotton-polyester—were machine washed and line dried.27 A standard detergent was used with MI added at different concentrations: less than 1 ppm, 100 ppm, and 1000 ppm. This process was either performed once or 10 times. Following laundering and line drying, MI was undetectable in all fabrics regardless of MI concentration or number of times washed (detection limit, 0.5 ppm).27 In the second study, 4 fabrics—cotton, wool, polyester, linen—were washed with standard laundry detergent in 1 of 4 ways: handwashing (positive control), standard machine washing, standard machine washing with fabric softener, and standard machine washing with a double rinse.28 After laundering and line drying, concentrations of MI, MCI, and BIT were low or undetectable regardless of fabric type or method of laundering. The highest levels detected were in handwashed garments at a maximum of 0.5 ppm of MI. The study authors postulated that chemical concentrations near these maximum residual levels may pose a risk for eliciting ACD in highly sensitized individuals. Therefore, handwashing can be considered a much higher risk activity for isothiazolinone ACD compared with machine washing.28
It is intriguing that machine washing appears to reduce isothiazolinones to low concentrations that may have limited likelihood of causing ACD. Similar findings have been reported regarding fragrances. A quantitative risk assessment performed on 24 of 26 fragrance allergens regulated by the European Union determined that the amount of fragrance deposited on the skin from laundered garments would be less than the threshold for causing sensitization.29 Although this risk assessment was unable to address the threshold of elicitation, another study conducted in Europe investigated whether fragrance residues present on fabric, such as those deposited from laundry detergent, are present at high enough concentrations to elicit ACD in previously sensitized individuals.30 When 36 individuals were patch tested with increasing concentrations of a fragrance to which they were already sensitized, only 2 (5.6%) had a weakly positive reaction and then only to the highest concentration, which was estimated to be 20-fold higher than the level of skin exposure after normal laundering. No patient reacted at lower concentrations.30
Although machine washing may decrease isothiazolinone and/or fragrance concentrations in laundry detergent to below clinically relevant levels, these findings should not necessarily be extrapolated to all chemicals in laundry detergent. Indeed, a prior study observed that after washing cotton cloths in a detergent solution for 10 minutes, detergent residue was present at concentrations ranging from 139 to 2820 ppm and required a subsequent 20 to 22 washes in water to become undetectable.31 Another study produced a mathematical model of the residual concentration of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), a surfactant and known irritant, in laundered clothing.32 It was estimated that after machine washing, the residual concentration of SDS on clothes would be too low to cause irritation; however, as the clothes dry (ie, as moisture evaporates but solutes remain), the concentration of SDS on the fabric’s surface would increase to potentially irritating levels. The extensive drying that is possible with electric dryers may further enhance this solute-concentrating effect.
Differential Diagnosis of Laundry Detergent ACD
The propensity for laundry detergent to cause ACD is a question that is nowhere near settled, but the prevalence of allergy likely is far less common than is generally suspected. In our experience, many patients presenting for patch testing have already made the change to “free and clear” detergents without noticeable improvement in their dermatitis, which could possibly relate to the ongoing presence of contact allergens in these “gentle” formulations.7 However, to avoid anchoring bias, more frequent causes of dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis. Textile ACD presents beneath clothing with accentuation at areas of closest contact with the skin, classically involving the axillary rim but sparing the vault. The most frequently implicated allergens in textile ACD are disperse dyes and less commonly textile resins.33,34 Between 2017 and 2018, 2.3% of 4882 patients patch tested by the NACDG reacted positively to disperse dye mix.10 There is evidence to suggest that the actual prevalence of disperse dye allergy might be higher due to inadequacy of screening allergens on baseline patch test series.35 Additional diagnoses that should be distinguished from presumed detergent contact dermatitis include atopic dermatitis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Final Interpretation
Although many patients and physicians consider laundry detergent to be a major cause of ACD, there is limited high-quality evidence to support this belief. Contact allergy to laundry detergent is probably much less common than is widely supposed. Although laundry detergents can contain common allergens such as fragrances and preservatives, evidence suggests that they are likely reduced to below clinically relevant levels during routine machine washing; however, we cannot assume that we are in the “free and clear,” as uncertainty remains about the impact of these low concentrationson individuals with strong contact allergy, and large studies of patch testing to modern detergents have yet to be carried out.
Laundry detergent, a cleaning agent ubiquitous in the modern household, often is suspected as a cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
We provide a summary of the evidence for the potential allergenicity of laundry detergent, including common allergens present in laundry detergent, the role of machine washing, and the differential diagnosis for laundry detergent–associated ACD.
Allergenic Ingredients in Laundry Detergent
Potential allergens present in laundry detergent include fragrances, preservatives, surfactants, emulsifiers, bleaches, brighteners, enzymes, and dyes.6-8 In an analysis of allergens present in laundry detergents available in the United States, fragrances and preservatives were most common (eTable).7,8 Contact allergy to fragrances occurs in approximately 3.5% of the general population9 and is detected in as many as 9.2% of patients referred for patch testing in North America.10 Preservatives commonly found in laundry detergent include isothiazolinones, such as methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI)/methylisothiazolinone (MI), MI alone, and benzisothiazolinone (BIT). Methylisothiazolinone has gained attention for causing an ACD epidemic beginning in the early 2000s and peaking in Europe between 2013 and 2014 and decreasing thereafter due to consumer personal care product regulatory changes enacted in the European Union.11 In contrast, rates of MI allergy in North America have continued to increase (reaching as high as 15% of patch tested patients in 2017-2018) due to a lack of similar regulation.10,12 More recently, the prevalence of positive patch tests to BIT has been rising, though it often is difficult to ascertain relevant sources of exposure, and some cases could represent cross-reactions to MCI/MI.10,13

Other allergens that may be present in laundry detergent include surfactants and propylene glycol. Alkyl glucosides such as decyl glucoside and lauryl glucoside are considered gentle surfactants and often are included in products marketed as safe for sensitive skin,14 such as “free and gentle” detergents.8 However, they actually may pose an increased risk for sensitization in patients with atopic dermatitis.14 In addition to being allergenic, surfactants and emulsifiers are known irritants.6,15 Although pathologically distinct, ACD and irritant contact dermatitis can be indistinguishable on clinical presentation.
How Commonly Does Laundry Detergent Cause ACD?
The mere presence of a contact allergen in laundry detergent does not necessarily imply that it is likely to cause ACD. To do so, the chemical in question must exceed the exposure thresholds for primary sensitization (ie, induction of contact allergy) and/or elicitation (ie, development of ACD in sensitized individuals). These depend on a complex interplay of product- and patient-specific factors, among them the concentration of the chemical in the detergent, the method of use, and the amount of detergent residue remaining on clothing after washing.
In the 1990s, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) attempted to determine the prevalence of ACD caused by laundry detergent.1 Among 738 patients patch tested to aqueous dilutions of granular and liquid laundry detergents, only 5 (0.7%) had a possible allergic patch test reaction. It was unclear what the culprit allergens in the detergents may have been; only 1 of the patients also tested positive to fragrance. Two patients underwent further testing to additional detergent dilutions, and the results called into question whether their initial reactions had truly been allergic (positive) or were actually irritant (negative). The investigators concluded that the prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD in this large group of patients was at most 0.7%, and possibly lower.1
Importantly, patch testing to laundry detergents should not be undertaken in routine clinical practice. Laundry detergents should never be tested “as is” (ie, undiluted) on the skin; they are inherently irritating and have a high likelihood of producing misleading false-positive reactions. Careful dilutions and testing of control subjects are necessary if patch testing with these products is to be appropriately conducted.
Isothiazolinones in Laundry Detergent
The extremely low prevalence of laundry detergent–associated ACD reported by the NACDG was determined prior to the start of the worldwide MI allergy epidemic, raising the possibility that laundry detergents containing isothiazolinones may be associated with ACD. There is no consensus about the minimum level at which isothiazolinones pose no risk to consumers,16-19 but the US Expert Panel for Cosmetic Ingredient Safety declared that MI is “safe for use in rinse-off cosmetic products at concentrations up to 100 ppm and safe in leave-on cosmetic products when they are formulated to be nonsensitizing.”18,19 Although ingredient lists do not always reveal when isothiazolinones are present, analyses of commercially available laundry detergents have shown MI concentrations ranging from undetectable to 65.7 ppm.20-23
Published reports suggest that MCI/MI in laundry detergent can elicit ACD in sensitized individuals. In one case, a 7-year-old girl with chronic truncal dermatitis (atopic history unspecified) was patch tested, revealing a strongly positive reaction to MCI/MI.24 Her laundry detergent was the only personal product found to contain MI. The dermatitis completely resolved after switching detergents and flared after wearing a jacket that had been washed in the implicated detergent, further supporting the relevance of the positive patch test. The investigators suspected initial sensitization to MI from wet wipes used earlier in childhood.24 In another case involving occupational exposure, a 39-year-old nonatopic factory worker was responsible for directly adding MI to laundry detergent.25 Although he wore disposable work gloves, he developed severe hand dermatitis, eczematous pretibial patches, and generalized pruritus. Patch testing revealed positive reactions to MCI/MI and MI, and he experienced improvement when reassigned to different work duties. It was hypothesized that the leg dermatitis and generalized pruritus may have been related to exposure to small concentrations of MI in work clothes washed with an MI-containing detergent.25 Notably, this patient’s level of exposure was much greater than that encountered by individuals in day-to-day life outside of specialized occupational settings.
Regarding other isothiazolinones, a toxicologic study estimated that BIT in laundry detergent would be unlikely to induce sensitization, even at the maximal acceptable concentration, as recommended by preservative manufacturers, and accounting for undiluted detergent spilling directly onto the skin.26
Does Machine Washing Impact Allergen Concentrations?
Two recent investigations have suggested that machine washing reduces concentrations of isothiazolinones to levels that are likely below clinical relevance. In the first study, 3 fabrics—cotton, polyester, cotton-polyester—were machine washed and line dried.27 A standard detergent was used with MI added at different concentrations: less than 1 ppm, 100 ppm, and 1000 ppm. This process was either performed once or 10 times. Following laundering and line drying, MI was undetectable in all fabrics regardless of MI concentration or number of times washed (detection limit, 0.5 ppm).27 In the second study, 4 fabrics—cotton, wool, polyester, linen—were washed with standard laundry detergent in 1 of 4 ways: handwashing (positive control), standard machine washing, standard machine washing with fabric softener, and standard machine washing with a double rinse.28 After laundering and line drying, concentrations of MI, MCI, and BIT were low or undetectable regardless of fabric type or method of laundering. The highest levels detected were in handwashed garments at a maximum of 0.5 ppm of MI. The study authors postulated that chemical concentrations near these maximum residual levels may pose a risk for eliciting ACD in highly sensitized individuals. Therefore, handwashing can be considered a much higher risk activity for isothiazolinone ACD compared with machine washing.28
It is intriguing that machine washing appears to reduce isothiazolinones to low concentrations that may have limited likelihood of causing ACD. Similar findings have been reported regarding fragrances. A quantitative risk assessment performed on 24 of 26 fragrance allergens regulated by the European Union determined that the amount of fragrance deposited on the skin from laundered garments would be less than the threshold for causing sensitization.29 Although this risk assessment was unable to address the threshold of elicitation, another study conducted in Europe investigated whether fragrance residues present on fabric, such as those deposited from laundry detergent, are present at high enough concentrations to elicit ACD in previously sensitized individuals.30 When 36 individuals were patch tested with increasing concentrations of a fragrance to which they were already sensitized, only 2 (5.6%) had a weakly positive reaction and then only to the highest concentration, which was estimated to be 20-fold higher than the level of skin exposure after normal laundering. No patient reacted at lower concentrations.30
Although machine washing may decrease isothiazolinone and/or fragrance concentrations in laundry detergent to below clinically relevant levels, these findings should not necessarily be extrapolated to all chemicals in laundry detergent. Indeed, a prior study observed that after washing cotton cloths in a detergent solution for 10 minutes, detergent residue was present at concentrations ranging from 139 to 2820 ppm and required a subsequent 20 to 22 washes in water to become undetectable.31 Another study produced a mathematical model of the residual concentration of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), a surfactant and known irritant, in laundered clothing.32 It was estimated that after machine washing, the residual concentration of SDS on clothes would be too low to cause irritation; however, as the clothes dry (ie, as moisture evaporates but solutes remain), the concentration of SDS on the fabric’s surface would increase to potentially irritating levels. The extensive drying that is possible with electric dryers may further enhance this solute-concentrating effect.
Differential Diagnosis of Laundry Detergent ACD
The propensity for laundry detergent to cause ACD is a question that is nowhere near settled, but the prevalence of allergy likely is far less common than is generally suspected. In our experience, many patients presenting for patch testing have already made the change to “free and clear” detergents without noticeable improvement in their dermatitis, which could possibly relate to the ongoing presence of contact allergens in these “gentle” formulations.7 However, to avoid anchoring bias, more frequent causes of dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis. Textile ACD presents beneath clothing with accentuation at areas of closest contact with the skin, classically involving the axillary rim but sparing the vault. The most frequently implicated allergens in textile ACD are disperse dyes and less commonly textile resins.33,34 Between 2017 and 2018, 2.3% of 4882 patients patch tested by the NACDG reacted positively to disperse dye mix.10 There is evidence to suggest that the actual prevalence of disperse dye allergy might be higher due to inadequacy of screening allergens on baseline patch test series.35 Additional diagnoses that should be distinguished from presumed detergent contact dermatitis include atopic dermatitis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Final Interpretation
Although many patients and physicians consider laundry detergent to be a major cause of ACD, there is limited high-quality evidence to support this belief. Contact allergy to laundry detergent is probably much less common than is widely supposed. Although laundry detergents can contain common allergens such as fragrances and preservatives, evidence suggests that they are likely reduced to below clinically relevant levels during routine machine washing; however, we cannot assume that we are in the “free and clear,” as uncertainty remains about the impact of these low concentrationson individuals with strong contact allergy, and large studies of patch testing to modern detergents have yet to be carried out.
- Belsito DV, Fransway AF, Fowler JF, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to detergents: a multicenter study to assess prevalence. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:200-206. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.119665
- Dallas MJ, Wilson PA, Burns LD, et al. Dermatological and other health problems attributed by consumers to contact with laundry products. Home Econ Res J. 1992;21:34-49. doi:10.1177/1077727X9202100103
- Bailey A. An overview of laundry detergent allergies. Verywell Health. September 16, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.verywellhealth.com/laundry-detergent-allergies-signs-symptoms-and-treatment-5198934
- Fasanella K. How to tell if you laundry detergent is messing with your skin. Allure. June 15, 2019. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.allure.com/story/laundry-detergent-allergy-skin-reaction
- Oykhman P, Dookie J, Al-Rammahy et al. Dietary elimination for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Immunol Pract. 2022;10:2657-2666.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2022.06.044
- Kwon S, Holland D, Kern P. Skin safety evaluation of laundry detergent products. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009;72:1369-1379. doi:10.1080/1528739090321675
- Magnano M, Silvani S, Vincenzi C, et al. Contact allergens and irritants in household washing and cleaning products. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:337-341. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01647.x
- Bai H, Tam I, Yu J. Contact allergens in top-selling textile-care products. Dermatitis. 2020;31:53-58. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000566
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Havmose M, Thyssen JP, Zachariae C, et al. The epidemic of contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone–an analysis of Danish consecutive patients patch tested between 2005 and 2019. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:254-262. doi:10.1111/cod.13717
- Atwater AR, Petty AJ, Liu B, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with preservatives: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994 through 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:965-976. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.059
- King N, Latheef F, Wilkinson M. Trends in preservative allergy: benzisothiazolinone emerges from the pack. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:637-642. doi:10.1111/cod.13968
- Sasseville D. Alkyl glucosides: 2017 “allergen of the year.” Dermatitis. 2017;28:296. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000290
- McGowan MA, Scheman A, Jacob SE. Propylene glycol in contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2018;29:6-12. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000307
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Health and Consumers. Opinion on methylisothiazolinone (P94) submission II (sensitisation only). Revised March 27, 2014. Accessed March 21, 2023. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_145.pdf
- Cosmetic ingredient hotlist: list of ingredients that are restricted for use in cosmetic products. Government of Canada website. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/hotlist.html#tbl2
- Burnett CL, Boyer I, Bergfeld WF, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2019;38(1 suppl):70S-84S. doi:10.1177/1091581819838792
- Burnett CL, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2021;40(1 suppl):5S-19S. doi:10.1177/10915818211015795
- Aerts O, Meert H, Goossens A, et al. Methylisothiazolinone in selected consumer products in Belgium: adding fuel to the fire? Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:142-149. doi:10.1111/cod.12449
- Garcia-Hidalgo E, Sottas V, von Goetz N, et al. Occurrence and concentrations of isothiazolinones in detergents and cosmetics in Switzerland. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:96-106. doi:10.1111/cod.12700
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Antuña AG, et al. Isothiazolinones in cleaning products: analysis with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry of samples from sensitized patients and markets. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:94-100. doi:10.1111/cod.13430
- Alvarez-Rivera G, Dagnac T, Lores M, et al. Determination of isothiazolinone preservatives in cosmetics and household products by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1270:41-50. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.10.063
- Cotton CH, Duah CG, Matiz C. Allergic contact dermatitis due to methylisothiazolinone in a young girl’s laundry detergent. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:486-487. doi:10.1111/pde.13122
- Sandvik A, Holm JO. Severe allergic contact dermatitis in a detergent production worker caused by exposure to methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:243-245. doi:10.1111/cod.13182
- Novick RM, Nelson ML, Unice KM, et al. Estimation of safe use concentrations of the preservative 1,2-benziosothiazolin-3-one (BIT) in consumer cleaning products and sunscreens. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;56:60-66. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.006
- Hofmann MA, Giménez-Arnau A, Aberer W, et al. MI (2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one) contained in detergents is not detectable in machine washed textiles. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:1. doi:10.1186/s13601-017-0187-2
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Atuña AG, et al. Persistence of isothiazolinones in clothes after machine washing. Dermatitis. 2021;32:298-300. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000603
- Corea NV, Basketter DA, Clapp C, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the risk from washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:48-53. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00872.x
- Basketter DA, Pons-Guiraud A, van Asten A, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the safety of washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2010;62:349-354. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2010.01728.x
- Agarwal C, Gupta BN, Mathur AK, et al. Residue analysis of detergent in crockery and clothes. Environmentalist. 1986;4:240-243.
- Broadbridge P, Tilley BS. Diffusion of dermatological irritant in drying laundered cloth. Math Med Biol. 2021;38:474-489. doi:10.1093/imammb/dqab014
- Lisi P, Stingeni L, Cristaudo A, et al. Clinical and epidemiological features of textile contact dermatitis: an Italian multicentre study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:344-350. doi:10.1111/cod.12179
- Mobolaji-Lawal M, Nedorost S. The role of textiles in dermatitis: an update. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015;15:17. doi:10.1007/s11882-015-0518-0
- Nijman L, Rustemeyer T, Franken SM, et al. The prevalence and relevance of patch testing with textile dyes [published online December 3, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14260
- Belsito DV, Fransway AF, Fowler JF, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to detergents: a multicenter study to assess prevalence. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:200-206. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.119665
- Dallas MJ, Wilson PA, Burns LD, et al. Dermatological and other health problems attributed by consumers to contact with laundry products. Home Econ Res J. 1992;21:34-49. doi:10.1177/1077727X9202100103
- Bailey A. An overview of laundry detergent allergies. Verywell Health. September 16, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.verywellhealth.com/laundry-detergent-allergies-signs-symptoms-and-treatment-5198934
- Fasanella K. How to tell if you laundry detergent is messing with your skin. Allure. June 15, 2019. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.allure.com/story/laundry-detergent-allergy-skin-reaction
- Oykhman P, Dookie J, Al-Rammahy et al. Dietary elimination for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Immunol Pract. 2022;10:2657-2666.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2022.06.044
- Kwon S, Holland D, Kern P. Skin safety evaluation of laundry detergent products. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009;72:1369-1379. doi:10.1080/1528739090321675
- Magnano M, Silvani S, Vincenzi C, et al. Contact allergens and irritants in household washing and cleaning products. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:337-341. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01647.x
- Bai H, Tam I, Yu J. Contact allergens in top-selling textile-care products. Dermatitis. 2020;31:53-58. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000566
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Havmose M, Thyssen JP, Zachariae C, et al. The epidemic of contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone–an analysis of Danish consecutive patients patch tested between 2005 and 2019. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:254-262. doi:10.1111/cod.13717
- Atwater AR, Petty AJ, Liu B, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with preservatives: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994 through 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:965-976. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.059
- King N, Latheef F, Wilkinson M. Trends in preservative allergy: benzisothiazolinone emerges from the pack. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:637-642. doi:10.1111/cod.13968
- Sasseville D. Alkyl glucosides: 2017 “allergen of the year.” Dermatitis. 2017;28:296. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000290
- McGowan MA, Scheman A, Jacob SE. Propylene glycol in contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2018;29:6-12. doi:10.1097/DER0000000000000307
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Health and Consumers. Opinion on methylisothiazolinone (P94) submission II (sensitisation only). Revised March 27, 2014. Accessed March 21, 2023. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_145.pdf
- Cosmetic ingredient hotlist: list of ingredients that are restricted for use in cosmetic products. Government of Canada website. Accessed March 21, 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/hotlist.html#tbl2
- Burnett CL, Boyer I, Bergfeld WF, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2019;38(1 suppl):70S-84S. doi:10.1177/1091581819838792
- Burnett CL, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, et al. Amended safety assessment of methylisothiazolinone as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2021;40(1 suppl):5S-19S. doi:10.1177/10915818211015795
- Aerts O, Meert H, Goossens A, et al. Methylisothiazolinone in selected consumer products in Belgium: adding fuel to the fire? Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:142-149. doi:10.1111/cod.12449
- Garcia-Hidalgo E, Sottas V, von Goetz N, et al. Occurrence and concentrations of isothiazolinones in detergents and cosmetics in Switzerland. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:96-106. doi:10.1111/cod.12700
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Antuña AG, et al. Isothiazolinones in cleaning products: analysis with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry of samples from sensitized patients and markets. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:94-100. doi:10.1111/cod.13430
- Alvarez-Rivera G, Dagnac T, Lores M, et al. Determination of isothiazolinone preservatives in cosmetics and household products by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1270:41-50. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.10.063
- Cotton CH, Duah CG, Matiz C. Allergic contact dermatitis due to methylisothiazolinone in a young girl’s laundry detergent. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:486-487. doi:10.1111/pde.13122
- Sandvik A, Holm JO. Severe allergic contact dermatitis in a detergent production worker caused by exposure to methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:243-245. doi:10.1111/cod.13182
- Novick RM, Nelson ML, Unice KM, et al. Estimation of safe use concentrations of the preservative 1,2-benziosothiazolin-3-one (BIT) in consumer cleaning products and sunscreens. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;56:60-66. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.006
- Hofmann MA, Giménez-Arnau A, Aberer W, et al. MI (2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one) contained in detergents is not detectable in machine washed textiles. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:1. doi:10.1186/s13601-017-0187-2
- Marrero-Alemán G, Borrego L, Atuña AG, et al. Persistence of isothiazolinones in clothes after machine washing. Dermatitis. 2021;32:298-300. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000603
- Corea NV, Basketter DA, Clapp C, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the risk from washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:48-53. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00872.x
- Basketter DA, Pons-Guiraud A, van Asten A, et al. Fragrance allergy: assessing the safety of washed fabrics. Contact Dermatitis. 2010;62:349-354. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2010.01728.x
- Agarwal C, Gupta BN, Mathur AK, et al. Residue analysis of detergent in crockery and clothes. Environmentalist. 1986;4:240-243.
- Broadbridge P, Tilley BS. Diffusion of dermatological irritant in drying laundered cloth. Math Med Biol. 2021;38:474-489. doi:10.1093/imammb/dqab014
- Lisi P, Stingeni L, Cristaudo A, et al. Clinical and epidemiological features of textile contact dermatitis: an Italian multicentre study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:344-350. doi:10.1111/cod.12179
- Mobolaji-Lawal M, Nedorost S. The role of textiles in dermatitis: an update. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015;15:17. doi:10.1007/s11882-015-0518-0
- Nijman L, Rustemeyer T, Franken SM, et al. The prevalence and relevance of patch testing with textile dyes [published online December 3, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14260
Practice Points
- Although laundry detergent commonly is believed to be a cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), the actual prevalence is quite low (<1%).
- Common allergens present in laundry detergent such as fragrances and isothiazolinone preservatives likely are reduced to clinically irrelevant levels during routine machine washing.
- Other diagnoses to consider when laundry detergent–associated ACD is suspected include textile ACD, atopic dermatitis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Janus Kinase Inhibitors: A Promising Therapeutic Option for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction that usually manifests with eczematous lesions within hours to days after exposure to a contact allergen. The primary treatment of ACD consists of allergen avoidance, but medications also may be necessary to manage symptoms, particularly in cases where avoidance alone does not lead to resolution of dermatitis. At present, no medical therapies are explicitly approved for use in the management of ACD. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a class of small molecule inhibitors that are used for the treatment of a range of inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Several oral and topical JAK inhibitors also have recently been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for atopic dermatitis (AD). In this article, we discuss this important class of medications and the role that they may play in the off-label management of refractory ACD.
JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
The JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway plays a crucial role in many biologic processes. Notably, JAK/STAT signaling is involved in the development and regulation of the immune system.1 The cascade begins when a particular transmembrane receptor binds a ligand, such as an interferon or interleukin.2 Upon ligand binding, the receptor dimerizes or oligomerizes, bringing the relevant JAK proteins into close approximation to each other.3 This allows the JAK proteins to autophosphorylate or transphosphorylate.2-4 Phosphorylation activates the JAK proteins and increases their kinase activity.3 In humans, there are 4 JAK proteins: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2.4 When activated, the JAK proteins phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor, which creates a docking site for STAT proteins. After binding, the STAT proteins then are phosphorylated, leading to their dimerization and translocation to the nucleus.2,3 Once in the nucleus, the STAT proteins act as transcription factors for target genes.3
JAK Inhibitors
Janus kinase inhibitors are immunomodulatory medications that work through inhibition of 1 or more of the JAK proteins in the JAK/STAT pathway. Through this mechanism, JAK inhibitors can impede the activity of proinflammatory cytokines and T cells.4 A brief overview of the commercially available JAK inhibitors in Europe, Japan, and the United States is provided in the Table.5-29
Of the approved JAK inhibitors, more than 40% are indicated for AD. The first JAK inhibitor to be approved in the topical form was delgocitinib in 2020 in Japan.5 In a phase 3 trial, delgocitinib demonstrated significant reductions in modified Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score (P<.001) as well as Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) when compared with vehicle.30 Topical ruxolitinib soon followed when its approval for AD was announced by the FDA in 2021.31 Results from 2 phase 3 trials found that significantly more patients achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) treatment success (P<.0001) and a significant reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) with topical ruxolitinib vs vehicle.32
The first oral JAK inhibitor to attain approval for AD was baricitinib in Europe and Japan, but it is not currently approved for this indication in the United States by the FDA.11,12,33 Consistent findings across phase 3 trials revealed that baricitinib was more effective at achieving IGA treatment success and improved EASI scores compared with placebo.33
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK inhibitor, was subsequently approved for AD in Europe and Japan in 2021 and in the United States in early 2022.5,9,26,27 Two replicate phase 3 trials demonstrated significant improvement in EASI score, itch, and quality of life with upadacitinib compared with placebo (P<.0001).34 Abrocitinib was granted FDA approval for AD in the same time period, with phase 3 trials exhibiting greater responses in IGA and EASI scores vs placebo.35
Potential for Use in ACD
Given the successful use of JAK inhibitors in the management of AD, there is optimism that these medications also may have potential application in ACD. Recent literature suggests that the 2 conditions may be more closely related mechanistically than previously understood. As a result, AD and ACD often are managed with the same therapeutic agents.36
Although the exact etiology of ACD is still being elucidated, activation of T cells and cytokines plays an important role.37 Notably, more than 40 cytokines exert their effects through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, including IL-2, IL-6, IL-17, IL-22, and IFN-γ.37,38 A study on nickel contact allergy revealed that JAK/STAT activation may regulate the balance between IL-12 and IL-23 and increase type 1 T-helper (TH1) polarization.39 Skin inflammation and chronic pruritus, which are major components of ACD, also are thought to be mediated in part by JAK signaling.34,40
Animal studies have suggested that JAK inhibitors may show benefit in the management of ACD. Rats with oxazolone-induced ACD were found to have less swelling and epidermal thickening in the area of induced dermatitis after treatment with oral tofacitinib, comparable to the effects of cyclosporine. Tofacitinib was presumed to exert its effects through cytokine suppression, particularly that of IFN-γ, IL-22, and tumor necrosis factor α.41 In a separate study on mice with toluene-2,4-diisocyanate–induced ACD, both tofacitinib and another JAK inhibitor, oclacitinib, demonstrated inhibition of cytokine production, migration, and maturation of bone marrow–derived dendritic cells. Both topical and oral formulations of these 2 JAK inhibitors also were found to decrease scratching behavior; only the topicals improved ear thickness (used as a marker of skin inflammation), suggesting potential benefits to local application.42 In a murine model, oral delgocitinib also attenuated contact hypersensitivity via inhibition of antigen-specific T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.37 Finally, in a randomized clinical trial conducted on dogs with allergic dermatitis (of which 10% were presumed to be from contact allergy), oral oclacitinib significantly reduced pruritus and clinical severity scores vs placebo (P<.0001).43
There also are early clinical studies and case reports highlighting the effective use of JAK inhibitors in the management of ACD in humans. A 37-year-old man with occupational airborne ACD to Compositae saw full clearance of his dermatitis with daily oral abrocitinib after topical corticosteroids and dupilumab failed.44 Another patient, a 57-year-old woman, had near-complete resolution of chronic Parthenium-induced airborne ACD after starting twice-daily oral tofacitinib. Allergen avoidance, as well as multiple medications, including topical and oral corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, and azathioprine, previously failed in this patient.45 Finally, a phase 2 study on patients with irritant and nonirritant chronic hand eczema found that significantly more patients achieved treatment success (as measured by the physician global assessment) with topical delgocitinib vs vehicle (P=.009).46 Chronic hand eczema may be due to a variety of causes, including AD, irritant contact dermatitis, and ACD. Thus, these studies begin to highlight the potential role for JAK inhibitors in the management of refractory ACD.
Side Effects of JAK Inhibitors
The safety profile of JAK inhibitors must be taken into consideration. In general, topical JAK inhibitors are safe and well tolerated, with the majority of adverse events (AEs) seen in clinical trials considered mild or unrelated to the medication.30,32 Nasopharyngitis, local skin infection, and acne were reported; a systematic review found no increased risk of AEs with topical JAK inhibitors compared with placebo.30,32,47 Application-site reactions, a common concern among the existing topical calcineurin and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, were rare (approximately 2% of patients).47 The most frequent AEs seen in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors included acne, nasopharyngitis/upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and headache.33-35 Herpes simplex virus infection and worsening of AD also were seen. Although elevations in creatine phosphokinase levels were reported, patients often were asymptomatic and elevations were related to exercise or resolved without treatment interruption.33-35
As a class, JAK inhibitors carry a boxed warning for serious infections, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, thrombosis, and mortality. The FDA placed this label on JAK inhibitors because of the results of a randomized controlled trial of oral tofacitinib vs tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors in RA.48,49 Notably, participants in the trial had to be 50 years or older and have at least 1 additional cardiovascular risk factor. Postmarket safety data are still being collected for patients with AD and other dermatologic conditions, but the findings of safety analyses have been reassuring to date.50,51 Regular follow-up and routine laboratory monitoring are recommended for any patient started on an oral JAK inhibitor, which often includes monitoring of the complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and lipids, as well as baseline screening for tuberculosis and hepatitis.52,53 For topical JAK inhibitors, no specific laboratory monitoring is recommended.
Finally, it must be considered that the challenges of off-label prescribing combined with high costs may limit access to JAK inhibitors for use in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Early investigations, including studies on animals and humans, suggest that JAK inhibitors are a promising option in the management of treatment-refractory ACD. Patients and providers should be aware of both the benefits and known side effects of JAK inhibitors prior to treatment initiation.
- Ghoreschi K, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:273-287.
- Bousoik E, Montazeri Aliabadi H. “Do we know Jack” about JAK? a closer look at JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Front Oncol. 2018;8:287.
- Jatiani SS, Baker SJ, Silverman LR, et al. Jak/STAT pathways in cytokine signaling and myeloproliferative disorders: approaches for targeted therapies. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:979-993.
- Seif F, Khoshmirsafa M, Aazami H, et al. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15:23.
- Traidl S, Freimooser S, Werfel T. Janus kinase inhibitors for the therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2021;5:293-304.
- Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215309s001lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/213871s000lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 17, 2021. Updated November 10, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cibinqo
- New drugs approved in FY 2021. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000246734.pdf
- Olumiant (baricitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/207924s007lbl.pdf
- Olumiant. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 16, 2017. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/olumiant
- Review report: Olumiant. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. April 21, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000243207.pdf
- Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214958s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic (fedratinib) capsules. Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212327s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 3, 2021. Updated December 8, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/inrebic
- Jyseleca. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published September 28, 2020. Updated November 9, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/jyseleca-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Jyseleca. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. September 8, 2020. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000247830.pdf
- Vonjo (pacritinib) capsules. Prescribing information. CTI BioPharma Corp; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208712s000lbl.pdf
- Review report: Smyraf. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. February 28, 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000233074.pdf
- Jakafi (ruxolitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/202192s023lbl.pdf
- Jakavi. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published October 4, 2012. Updated May 18, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/jakavi
- New drugs approved in FY 2014. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000229076.pdf
- Xeljanz (tofacitinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/203214s028,208246s013,213082s003lbl.pdf
- Xeljanz. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xeljanz-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Xeljanz. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000237584.pdf
- Rinvoq (upadacitinib) extended-release tablets. Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/211675s003lbl.pdf
- Rinvoq. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 18, 2019. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/rinvoq
- New drugs approved in FY 2019. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000235289.pdfs
- New drugs approved in May 2022. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000248626.pdf
- Nakagawa H, Nemoto O, Igarashi A, et al. Delgocitinib ointment, a topical Janus kinase inhibitor, in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study and an open-label, long-term extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:823-831. Erratum appears in J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1069.
- Sideris N, Paschou E, Bakirtzi K, et al. New and upcoming topical treatments for atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Clin Med. 2022;11:4974.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Radi G, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Baricitinib: the first Jak inhibitor approved in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9:1575.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. Erratum appears in Lancet. 2021;397:2150.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142.
- Amano W, Nakajima S, Yamamoto Y, et al. JAK inhibitor JTE-052 regulates contact hypersensitivity by downmodulating T cell activation and differentiation. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84:258-265.
- O’Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV, et al. The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:311-328.
- Bechara R, Antonios D, Azouri H, et al. Nickel sulfate promotes IL-17A producing CD4+ T cells by an IL-23-dependent mechanism regulated by TLR4 and JAK-STAT pathways. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2140-2148.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- Fujii Y, Sengoku T. Effects of the Janus kinase inhibitor CP-690550 (tofacitinib) in a rat model of oxazolone-induced chronic dermatitis. Pharmacology. 2013;91:207-213.
- Fukuyama T, Ehling S, Cook E, et al. Topically administered Janus-kinase inhibitors tofacitinib and oclacitinib display impressive antipruritic and anti-inflammatory responses in a model of allergic dermatitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;354:394-405.
- Cosgrove SB, Wren JA, Cleaver DM, et al. Efficacy and safety of oclacitinib for the control of pruritus and associated skin lesions in dogs with canine allergic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2013;24:479, E114.
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544.
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis [published online October 12, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Worm M, Bauer A, Elsner P, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical delgocitinib in patients with chronic hand eczema: data from a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled phase IIa study. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:1103-1110.
- Chen J, Cheng J, Yang H, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:495-496.
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. Updated December 7, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chen TL, Lee LL, Huang HK, et al. Association of risk of incident venous thromboembolism with atopic dermatitis and treatment with Janus kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:1254-1261.
- King B, Maari C, Lain E, et al. Extended safety analysis of baricitinib 2 mg in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: an integrated analysis from eight randomized clinical trials. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:395-405.
- Nash P, Kerschbaumer A, Dörner T, et al. Points to consider for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with Janus kinase inhibitors: a consensus statement. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:71-87.
- Narla S, Silverberg JI. The suitability of treating atopic dermatitis with Janus kinase inhibitors. Exp Rev Clin Immunol. 2022;18:439-459.
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction that usually manifests with eczematous lesions within hours to days after exposure to a contact allergen. The primary treatment of ACD consists of allergen avoidance, but medications also may be necessary to manage symptoms, particularly in cases where avoidance alone does not lead to resolution of dermatitis. At present, no medical therapies are explicitly approved for use in the management of ACD. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a class of small molecule inhibitors that are used for the treatment of a range of inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Several oral and topical JAK inhibitors also have recently been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for atopic dermatitis (AD). In this article, we discuss this important class of medications and the role that they may play in the off-label management of refractory ACD.
JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
The JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway plays a crucial role in many biologic processes. Notably, JAK/STAT signaling is involved in the development and regulation of the immune system.1 The cascade begins when a particular transmembrane receptor binds a ligand, such as an interferon or interleukin.2 Upon ligand binding, the receptor dimerizes or oligomerizes, bringing the relevant JAK proteins into close approximation to each other.3 This allows the JAK proteins to autophosphorylate or transphosphorylate.2-4 Phosphorylation activates the JAK proteins and increases their kinase activity.3 In humans, there are 4 JAK proteins: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2.4 When activated, the JAK proteins phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor, which creates a docking site for STAT proteins. After binding, the STAT proteins then are phosphorylated, leading to their dimerization and translocation to the nucleus.2,3 Once in the nucleus, the STAT proteins act as transcription factors for target genes.3
JAK Inhibitors
Janus kinase inhibitors are immunomodulatory medications that work through inhibition of 1 or more of the JAK proteins in the JAK/STAT pathway. Through this mechanism, JAK inhibitors can impede the activity of proinflammatory cytokines and T cells.4 A brief overview of the commercially available JAK inhibitors in Europe, Japan, and the United States is provided in the Table.5-29

Of the approved JAK inhibitors, more than 40% are indicated for AD. The first JAK inhibitor to be approved in the topical form was delgocitinib in 2020 in Japan.5 In a phase 3 trial, delgocitinib demonstrated significant reductions in modified Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score (P<.001) as well as Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) when compared with vehicle.30 Topical ruxolitinib soon followed when its approval for AD was announced by the FDA in 2021.31 Results from 2 phase 3 trials found that significantly more patients achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) treatment success (P<.0001) and a significant reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) with topical ruxolitinib vs vehicle.32
The first oral JAK inhibitor to attain approval for AD was baricitinib in Europe and Japan, but it is not currently approved for this indication in the United States by the FDA.11,12,33 Consistent findings across phase 3 trials revealed that baricitinib was more effective at achieving IGA treatment success and improved EASI scores compared with placebo.33
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK inhibitor, was subsequently approved for AD in Europe and Japan in 2021 and in the United States in early 2022.5,9,26,27 Two replicate phase 3 trials demonstrated significant improvement in EASI score, itch, and quality of life with upadacitinib compared with placebo (P<.0001).34 Abrocitinib was granted FDA approval for AD in the same time period, with phase 3 trials exhibiting greater responses in IGA and EASI scores vs placebo.35
Potential for Use in ACD
Given the successful use of JAK inhibitors in the management of AD, there is optimism that these medications also may have potential application in ACD. Recent literature suggests that the 2 conditions may be more closely related mechanistically than previously understood. As a result, AD and ACD often are managed with the same therapeutic agents.36
Although the exact etiology of ACD is still being elucidated, activation of T cells and cytokines plays an important role.37 Notably, more than 40 cytokines exert their effects through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, including IL-2, IL-6, IL-17, IL-22, and IFN-γ.37,38 A study on nickel contact allergy revealed that JAK/STAT activation may regulate the balance between IL-12 and IL-23 and increase type 1 T-helper (TH1) polarization.39 Skin inflammation and chronic pruritus, which are major components of ACD, also are thought to be mediated in part by JAK signaling.34,40
Animal studies have suggested that JAK inhibitors may show benefit in the management of ACD. Rats with oxazolone-induced ACD were found to have less swelling and epidermal thickening in the area of induced dermatitis after treatment with oral tofacitinib, comparable to the effects of cyclosporine. Tofacitinib was presumed to exert its effects through cytokine suppression, particularly that of IFN-γ, IL-22, and tumor necrosis factor α.41 In a separate study on mice with toluene-2,4-diisocyanate–induced ACD, both tofacitinib and another JAK inhibitor, oclacitinib, demonstrated inhibition of cytokine production, migration, and maturation of bone marrow–derived dendritic cells. Both topical and oral formulations of these 2 JAK inhibitors also were found to decrease scratching behavior; only the topicals improved ear thickness (used as a marker of skin inflammation), suggesting potential benefits to local application.42 In a murine model, oral delgocitinib also attenuated contact hypersensitivity via inhibition of antigen-specific T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.37 Finally, in a randomized clinical trial conducted on dogs with allergic dermatitis (of which 10% were presumed to be from contact allergy), oral oclacitinib significantly reduced pruritus and clinical severity scores vs placebo (P<.0001).43
There also are early clinical studies and case reports highlighting the effective use of JAK inhibitors in the management of ACD in humans. A 37-year-old man with occupational airborne ACD to Compositae saw full clearance of his dermatitis with daily oral abrocitinib after topical corticosteroids and dupilumab failed.44 Another patient, a 57-year-old woman, had near-complete resolution of chronic Parthenium-induced airborne ACD after starting twice-daily oral tofacitinib. Allergen avoidance, as well as multiple medications, including topical and oral corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, and azathioprine, previously failed in this patient.45 Finally, a phase 2 study on patients with irritant and nonirritant chronic hand eczema found that significantly more patients achieved treatment success (as measured by the physician global assessment) with topical delgocitinib vs vehicle (P=.009).46 Chronic hand eczema may be due to a variety of causes, including AD, irritant contact dermatitis, and ACD. Thus, these studies begin to highlight the potential role for JAK inhibitors in the management of refractory ACD.
Side Effects of JAK Inhibitors
The safety profile of JAK inhibitors must be taken into consideration. In general, topical JAK inhibitors are safe and well tolerated, with the majority of adverse events (AEs) seen in clinical trials considered mild or unrelated to the medication.30,32 Nasopharyngitis, local skin infection, and acne were reported; a systematic review found no increased risk of AEs with topical JAK inhibitors compared with placebo.30,32,47 Application-site reactions, a common concern among the existing topical calcineurin and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, were rare (approximately 2% of patients).47 The most frequent AEs seen in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors included acne, nasopharyngitis/upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and headache.33-35 Herpes simplex virus infection and worsening of AD also were seen. Although elevations in creatine phosphokinase levels were reported, patients often were asymptomatic and elevations were related to exercise or resolved without treatment interruption.33-35
As a class, JAK inhibitors carry a boxed warning for serious infections, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, thrombosis, and mortality. The FDA placed this label on JAK inhibitors because of the results of a randomized controlled trial of oral tofacitinib vs tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors in RA.48,49 Notably, participants in the trial had to be 50 years or older and have at least 1 additional cardiovascular risk factor. Postmarket safety data are still being collected for patients with AD and other dermatologic conditions, but the findings of safety analyses have been reassuring to date.50,51 Regular follow-up and routine laboratory monitoring are recommended for any patient started on an oral JAK inhibitor, which often includes monitoring of the complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and lipids, as well as baseline screening for tuberculosis and hepatitis.52,53 For topical JAK inhibitors, no specific laboratory monitoring is recommended.
Finally, it must be considered that the challenges of off-label prescribing combined with high costs may limit access to JAK inhibitors for use in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Early investigations, including studies on animals and humans, suggest that JAK inhibitors are a promising option in the management of treatment-refractory ACD. Patients and providers should be aware of both the benefits and known side effects of JAK inhibitors prior to treatment initiation.
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction that usually manifests with eczematous lesions within hours to days after exposure to a contact allergen. The primary treatment of ACD consists of allergen avoidance, but medications also may be necessary to manage symptoms, particularly in cases where avoidance alone does not lead to resolution of dermatitis. At present, no medical therapies are explicitly approved for use in the management of ACD. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a class of small molecule inhibitors that are used for the treatment of a range of inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Several oral and topical JAK inhibitors also have recently been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for atopic dermatitis (AD). In this article, we discuss this important class of medications and the role that they may play in the off-label management of refractory ACD.
JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
The JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway plays a crucial role in many biologic processes. Notably, JAK/STAT signaling is involved in the development and regulation of the immune system.1 The cascade begins when a particular transmembrane receptor binds a ligand, such as an interferon or interleukin.2 Upon ligand binding, the receptor dimerizes or oligomerizes, bringing the relevant JAK proteins into close approximation to each other.3 This allows the JAK proteins to autophosphorylate or transphosphorylate.2-4 Phosphorylation activates the JAK proteins and increases their kinase activity.3 In humans, there are 4 JAK proteins: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2.4 When activated, the JAK proteins phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor, which creates a docking site for STAT proteins. After binding, the STAT proteins then are phosphorylated, leading to their dimerization and translocation to the nucleus.2,3 Once in the nucleus, the STAT proteins act as transcription factors for target genes.3
JAK Inhibitors
Janus kinase inhibitors are immunomodulatory medications that work through inhibition of 1 or more of the JAK proteins in the JAK/STAT pathway. Through this mechanism, JAK inhibitors can impede the activity of proinflammatory cytokines and T cells.4 A brief overview of the commercially available JAK inhibitors in Europe, Japan, and the United States is provided in the Table.5-29

Of the approved JAK inhibitors, more than 40% are indicated for AD. The first JAK inhibitor to be approved in the topical form was delgocitinib in 2020 in Japan.5 In a phase 3 trial, delgocitinib demonstrated significant reductions in modified Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score (P<.001) as well as Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) when compared with vehicle.30 Topical ruxolitinib soon followed when its approval for AD was announced by the FDA in 2021.31 Results from 2 phase 3 trials found that significantly more patients achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) treatment success (P<.0001) and a significant reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (P<.001) with topical ruxolitinib vs vehicle.32
The first oral JAK inhibitor to attain approval for AD was baricitinib in Europe and Japan, but it is not currently approved for this indication in the United States by the FDA.11,12,33 Consistent findings across phase 3 trials revealed that baricitinib was more effective at achieving IGA treatment success and improved EASI scores compared with placebo.33
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK inhibitor, was subsequently approved for AD in Europe and Japan in 2021 and in the United States in early 2022.5,9,26,27 Two replicate phase 3 trials demonstrated significant improvement in EASI score, itch, and quality of life with upadacitinib compared with placebo (P<.0001).34 Abrocitinib was granted FDA approval for AD in the same time period, with phase 3 trials exhibiting greater responses in IGA and EASI scores vs placebo.35
Potential for Use in ACD
Given the successful use of JAK inhibitors in the management of AD, there is optimism that these medications also may have potential application in ACD. Recent literature suggests that the 2 conditions may be more closely related mechanistically than previously understood. As a result, AD and ACD often are managed with the same therapeutic agents.36
Although the exact etiology of ACD is still being elucidated, activation of T cells and cytokines plays an important role.37 Notably, more than 40 cytokines exert their effects through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, including IL-2, IL-6, IL-17, IL-22, and IFN-γ.37,38 A study on nickel contact allergy revealed that JAK/STAT activation may regulate the balance between IL-12 and IL-23 and increase type 1 T-helper (TH1) polarization.39 Skin inflammation and chronic pruritus, which are major components of ACD, also are thought to be mediated in part by JAK signaling.34,40
Animal studies have suggested that JAK inhibitors may show benefit in the management of ACD. Rats with oxazolone-induced ACD were found to have less swelling and epidermal thickening in the area of induced dermatitis after treatment with oral tofacitinib, comparable to the effects of cyclosporine. Tofacitinib was presumed to exert its effects through cytokine suppression, particularly that of IFN-γ, IL-22, and tumor necrosis factor α.41 In a separate study on mice with toluene-2,4-diisocyanate–induced ACD, both tofacitinib and another JAK inhibitor, oclacitinib, demonstrated inhibition of cytokine production, migration, and maturation of bone marrow–derived dendritic cells. Both topical and oral formulations of these 2 JAK inhibitors also were found to decrease scratching behavior; only the topicals improved ear thickness (used as a marker of skin inflammation), suggesting potential benefits to local application.42 In a murine model, oral delgocitinib also attenuated contact hypersensitivity via inhibition of antigen-specific T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.37 Finally, in a randomized clinical trial conducted on dogs with allergic dermatitis (of which 10% were presumed to be from contact allergy), oral oclacitinib significantly reduced pruritus and clinical severity scores vs placebo (P<.0001).43
There also are early clinical studies and case reports highlighting the effective use of JAK inhibitors in the management of ACD in humans. A 37-year-old man with occupational airborne ACD to Compositae saw full clearance of his dermatitis with daily oral abrocitinib after topical corticosteroids and dupilumab failed.44 Another patient, a 57-year-old woman, had near-complete resolution of chronic Parthenium-induced airborne ACD after starting twice-daily oral tofacitinib. Allergen avoidance, as well as multiple medications, including topical and oral corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, and azathioprine, previously failed in this patient.45 Finally, a phase 2 study on patients with irritant and nonirritant chronic hand eczema found that significantly more patients achieved treatment success (as measured by the physician global assessment) with topical delgocitinib vs vehicle (P=.009).46 Chronic hand eczema may be due to a variety of causes, including AD, irritant contact dermatitis, and ACD. Thus, these studies begin to highlight the potential role for JAK inhibitors in the management of refractory ACD.
Side Effects of JAK Inhibitors
The safety profile of JAK inhibitors must be taken into consideration. In general, topical JAK inhibitors are safe and well tolerated, with the majority of adverse events (AEs) seen in clinical trials considered mild or unrelated to the medication.30,32 Nasopharyngitis, local skin infection, and acne were reported; a systematic review found no increased risk of AEs with topical JAK inhibitors compared with placebo.30,32,47 Application-site reactions, a common concern among the existing topical calcineurin and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, were rare (approximately 2% of patients).47 The most frequent AEs seen in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors included acne, nasopharyngitis/upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and headache.33-35 Herpes simplex virus infection and worsening of AD also were seen. Although elevations in creatine phosphokinase levels were reported, patients often were asymptomatic and elevations were related to exercise or resolved without treatment interruption.33-35
As a class, JAK inhibitors carry a boxed warning for serious infections, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, thrombosis, and mortality. The FDA placed this label on JAK inhibitors because of the results of a randomized controlled trial of oral tofacitinib vs tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors in RA.48,49 Notably, participants in the trial had to be 50 years or older and have at least 1 additional cardiovascular risk factor. Postmarket safety data are still being collected for patients with AD and other dermatologic conditions, but the findings of safety analyses have been reassuring to date.50,51 Regular follow-up and routine laboratory monitoring are recommended for any patient started on an oral JAK inhibitor, which often includes monitoring of the complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and lipids, as well as baseline screening for tuberculosis and hepatitis.52,53 For topical JAK inhibitors, no specific laboratory monitoring is recommended.
Finally, it must be considered that the challenges of off-label prescribing combined with high costs may limit access to JAK inhibitors for use in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Early investigations, including studies on animals and humans, suggest that JAK inhibitors are a promising option in the management of treatment-refractory ACD. Patients and providers should be aware of both the benefits and known side effects of JAK inhibitors prior to treatment initiation.
- Ghoreschi K, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:273-287.
- Bousoik E, Montazeri Aliabadi H. “Do we know Jack” about JAK? a closer look at JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Front Oncol. 2018;8:287.
- Jatiani SS, Baker SJ, Silverman LR, et al. Jak/STAT pathways in cytokine signaling and myeloproliferative disorders: approaches for targeted therapies. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:979-993.
- Seif F, Khoshmirsafa M, Aazami H, et al. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15:23.
- Traidl S, Freimooser S, Werfel T. Janus kinase inhibitors for the therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2021;5:293-304.
- Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215309s001lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/213871s000lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 17, 2021. Updated November 10, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cibinqo
- New drugs approved in FY 2021. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000246734.pdf
- Olumiant (baricitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/207924s007lbl.pdf
- Olumiant. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 16, 2017. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/olumiant
- Review report: Olumiant. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. April 21, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000243207.pdf
- Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214958s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic (fedratinib) capsules. Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212327s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 3, 2021. Updated December 8, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/inrebic
- Jyseleca. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published September 28, 2020. Updated November 9, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/jyseleca-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Jyseleca. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. September 8, 2020. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000247830.pdf
- Vonjo (pacritinib) capsules. Prescribing information. CTI BioPharma Corp; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208712s000lbl.pdf
- Review report: Smyraf. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. February 28, 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000233074.pdf
- Jakafi (ruxolitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/202192s023lbl.pdf
- Jakavi. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published October 4, 2012. Updated May 18, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/jakavi
- New drugs approved in FY 2014. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000229076.pdf
- Xeljanz (tofacitinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/203214s028,208246s013,213082s003lbl.pdf
- Xeljanz. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xeljanz-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Xeljanz. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000237584.pdf
- Rinvoq (upadacitinib) extended-release tablets. Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/211675s003lbl.pdf
- Rinvoq. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 18, 2019. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/rinvoq
- New drugs approved in FY 2019. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000235289.pdfs
- New drugs approved in May 2022. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000248626.pdf
- Nakagawa H, Nemoto O, Igarashi A, et al. Delgocitinib ointment, a topical Janus kinase inhibitor, in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study and an open-label, long-term extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:823-831. Erratum appears in J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1069.
- Sideris N, Paschou E, Bakirtzi K, et al. New and upcoming topical treatments for atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Clin Med. 2022;11:4974.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Radi G, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Baricitinib: the first Jak inhibitor approved in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9:1575.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. Erratum appears in Lancet. 2021;397:2150.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142.
- Amano W, Nakajima S, Yamamoto Y, et al. JAK inhibitor JTE-052 regulates contact hypersensitivity by downmodulating T cell activation and differentiation. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84:258-265.
- O’Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV, et al. The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:311-328.
- Bechara R, Antonios D, Azouri H, et al. Nickel sulfate promotes IL-17A producing CD4+ T cells by an IL-23-dependent mechanism regulated by TLR4 and JAK-STAT pathways. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2140-2148.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- Fujii Y, Sengoku T. Effects of the Janus kinase inhibitor CP-690550 (tofacitinib) in a rat model of oxazolone-induced chronic dermatitis. Pharmacology. 2013;91:207-213.
- Fukuyama T, Ehling S, Cook E, et al. Topically administered Janus-kinase inhibitors tofacitinib and oclacitinib display impressive antipruritic and anti-inflammatory responses in a model of allergic dermatitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;354:394-405.
- Cosgrove SB, Wren JA, Cleaver DM, et al. Efficacy and safety of oclacitinib for the control of pruritus and associated skin lesions in dogs with canine allergic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2013;24:479, E114.
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544.
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis [published online October 12, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Worm M, Bauer A, Elsner P, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical delgocitinib in patients with chronic hand eczema: data from a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled phase IIa study. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:1103-1110.
- Chen J, Cheng J, Yang H, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:495-496.
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. Updated December 7, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chen TL, Lee LL, Huang HK, et al. Association of risk of incident venous thromboembolism with atopic dermatitis and treatment with Janus kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:1254-1261.
- King B, Maari C, Lain E, et al. Extended safety analysis of baricitinib 2 mg in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: an integrated analysis from eight randomized clinical trials. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:395-405.
- Nash P, Kerschbaumer A, Dörner T, et al. Points to consider for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with Janus kinase inhibitors: a consensus statement. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:71-87.
- Narla S, Silverberg JI. The suitability of treating atopic dermatitis with Janus kinase inhibitors. Exp Rev Clin Immunol. 2022;18:439-459.
- Ghoreschi K, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:273-287.
- Bousoik E, Montazeri Aliabadi H. “Do we know Jack” about JAK? a closer look at JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Front Oncol. 2018;8:287.
- Jatiani SS, Baker SJ, Silverman LR, et al. Jak/STAT pathways in cytokine signaling and myeloproliferative disorders: approaches for targeted therapies. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:979-993.
- Seif F, Khoshmirsafa M, Aazami H, et al. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15:23.
- Traidl S, Freimooser S, Werfel T. Janus kinase inhibitors for the therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2021;5:293-304.
- Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215309s001lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/213871s000lbl.pdf
- Cibinqo. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 17, 2021. Updated November 10, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cibinqo
- New drugs approved in FY 2021. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000246734.pdf
- Olumiant (baricitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/207924s007lbl.pdf
- Olumiant. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 16, 2017. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/olumiant
- Review report: Olumiant. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. April 21, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000243207.pdf
- Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214958s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic (fedratinib) capsules. Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212327s000lbl.pdf
- Inrebic. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published March 3, 2021. Updated December 8, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/inrebic
- Jyseleca. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published September 28, 2020. Updated November 9, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/jyseleca-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Jyseleca. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. September 8, 2020. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000247830.pdf
- Vonjo (pacritinib) capsules. Prescribing information. CTI BioPharma Corp; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208712s000lbl.pdf
- Review report: Smyraf. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. February 28, 2019. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000233074.pdf
- Jakafi (ruxolitinib) tablets. Prescribing information. Incyte Corporation; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/202192s023lbl.pdf
- Jakavi. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published October 4, 2012. Updated May 18, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/jakavi
- New drugs approved in FY 2014. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000229076.pdf
- Xeljanz (tofacitinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Labs; 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/203214s028,208246s013,213082s003lbl.pdf
- Xeljanz. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xeljanz-epar-product-information_en.pdf
- Review report: Xeljanz. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000237584.pdf
- Rinvoq (upadacitinib) extended-release tablets. Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/211675s003lbl.pdf
- Rinvoq. Product information. European Medicines Agency. Published December 18, 2019. Updated December 7, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/rinvoq
- New drugs approved in FY 2019. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000235289.pdfs
- New drugs approved in May 2022. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000248626.pdf
- Nakagawa H, Nemoto O, Igarashi A, et al. Delgocitinib ointment, a topical Janus kinase inhibitor, in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study and an open-label, long-term extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:823-831. Erratum appears in J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1069.
- Sideris N, Paschou E, Bakirtzi K, et al. New and upcoming topical treatments for atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Clin Med. 2022;11:4974.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Radi G, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Baricitinib: the first Jak inhibitor approved in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9:1575.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168. Erratum appears in Lancet. 2021;397:2150.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142.
- Amano W, Nakajima S, Yamamoto Y, et al. JAK inhibitor JTE-052 regulates contact hypersensitivity by downmodulating T cell activation and differentiation. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84:258-265.
- O’Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV, et al. The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:311-328.
- Bechara R, Antonios D, Azouri H, et al. Nickel sulfate promotes IL-17A producing CD4+ T cells by an IL-23-dependent mechanism regulated by TLR4 and JAK-STAT pathways. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2140-2148.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- Fujii Y, Sengoku T. Effects of the Janus kinase inhibitor CP-690550 (tofacitinib) in a rat model of oxazolone-induced chronic dermatitis. Pharmacology. 2013;91:207-213.
- Fukuyama T, Ehling S, Cook E, et al. Topically administered Janus-kinase inhibitors tofacitinib and oclacitinib display impressive antipruritic and anti-inflammatory responses in a model of allergic dermatitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;354:394-405.
- Cosgrove SB, Wren JA, Cleaver DM, et al. Efficacy and safety of oclacitinib for the control of pruritus and associated skin lesions in dogs with canine allergic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2013;24:479, E114.
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544.
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis [published online October 12, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Worm M, Bauer A, Elsner P, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical delgocitinib in patients with chronic hand eczema: data from a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled phase IIa study. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:1103-1110.
- Chen J, Cheng J, Yang H, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:495-496.
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. Updated December 7, 2021. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chen TL, Lee LL, Huang HK, et al. Association of risk of incident venous thromboembolism with atopic dermatitis and treatment with Janus kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:1254-1261.
- King B, Maari C, Lain E, et al. Extended safety analysis of baricitinib 2 mg in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: an integrated analysis from eight randomized clinical trials. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:395-405.
- Nash P, Kerschbaumer A, Dörner T, et al. Points to consider for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with Janus kinase inhibitors: a consensus statement. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:71-87.
- Narla S, Silverberg JI. The suitability of treating atopic dermatitis with Janus kinase inhibitors. Exp Rev Clin Immunol. 2022;18:439-459.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a novel class of small molecule inhibitors that modulate the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway.
- Select JAK inhibitors have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the management of atopic dermatitis. Their use in allergic contact dermatitis is under active investigation.
- Regular follow-up and laboratory monitoring for patients on oral JAK inhibitors is recommended, given the potential for treatment-related adverse effects.
Photoallergic Contact Dermatitis: No Fun in the Sun
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.
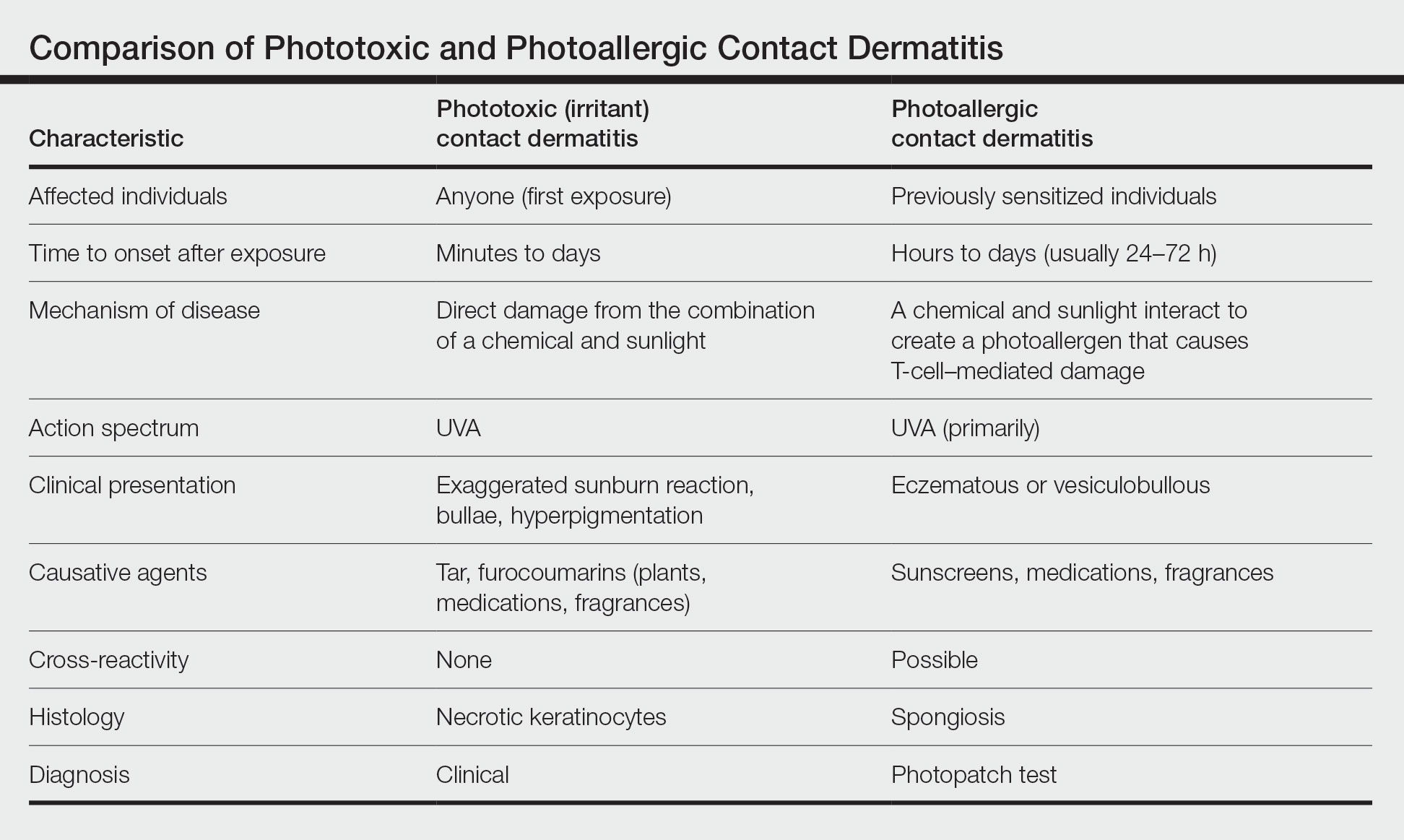
Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.

Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.

Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
Practice Points
- Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD) presents clinically and histologically similar to allergic contact dermatitis but is concentrated in sun-exposed body sites.
- Sunscreens currently are the most common photoallergens in North America, whereas topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are more common culprits in Europe.
- Photopatch testing is required to diagnose PACD; however, it is infrequently performed, and there currently are no North American consensus guidelines.
Can Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Contact Dermatitis Coexist?
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Practice Points
- Although it previously was thought that atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) could not coexist due to their polarized immune pathways, current evidence suggests otherwise.
- When both diagnoses are suspected, patch testing should be considered as well as therapeutic strategies that can treat both AD and ACD simultaneously.
Dupilumab for Allergic Contact Dermatitis: An Overview of Its Use and Impact on Patch Testing
Dupilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Through inhibition of the IL-4R α subunit, it prevents activation of the IL-4/IL-13 signaling cascade. This dampens the T H 2 inflammatory response, thereby improving the symptoms associated with atopic dermatitis. 1,2 Recent literature suggests that dupilumab may be useful in the treatment of other chronic dermatologic conditions, including allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) refractory to allergen avoidance and other treatments. Herein, we provide an overview of ACD, the role that dupilumab may play in its management, and its impact on patch testing results.
Pathogenesis of ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis is a cell-mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction that develops through 2 distinct stages. In the sensitization phase, an allergen penetrates the skin and subsequently is engulfed by a cutaneous antigen-presenting cell. The allergen is then combined with a peptide to form a complex that is presented to naïve T lymphocytes in regional lymph nodes. The result is clonal expansion of a T-cell population that recognizes the allergen. In the elicitation phase, repeat exposure to the allergen leads to the recruitment of primed T cells to the skin, followed by cytokine release, inflammation, and resultant dermatitis.3
Historically, ACD was thought to be primarily driven by the TH1 inflammatory response; however, it is now known that TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 also may play a role in its pathogenesis.4,5 Another key finding is that the immune response in ACD appears to be at least partially allergen specific. Molecular profiling has revealed that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, while allergens such as fragrance and rubber primarily induce a TH2 response.4
Management of ACD
Allergen avoidance is the mainstay of ACD treatment; however, in some patients, this approach does not always improve symptoms. In addition, eliminating the source of the allergen may not be possible in those with certain occupational, environmental, or medical exposures.
There are no FDA-approved treatments for ACD. When allergen avoidance alone is insufficient, first-line pharmacologic therapy typically includes topical or oral corticosteroids, the choice of which depends on the extent and severity of the dermatitis; however, a steroid-sparing agent often is preferred to avoid the unfavorable effects of long-term steroid use. Other systemic treatments for ACD include methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine.6 These agents are used for severe ACD and typically are chosen as a last resort due to their immunosuppressive activity.
Phototherapy is another option, often as an adjunct to other therapies. Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have both been used. Psoralen plus UVA tends to have more side effects; therefore, narrowband UVB often is preferred.7,8
Use of Dupilumab in ACD
Biologics are unique, as they can target a single step in the immune response to improve a wide variety of symptoms. Research investigating their role as a treatment modality for ACD is still evolving alongside our increasing knowledge of its pathophysiology.9 Of note, studies examining the anti–IL-17 biologic secukinumab revealed it to be ineffective against ACD,10,11 which suggests that targeting specific immune components may not always result in improvement of ACD symptoms, likely because its pathophysiology involves several pathways.
There have been multiple reports demonstrating the effectiveness of dupilumab in the treatment of ACD (eTable).12-20 The findings from these studies show that dupilumab can improve recalcitrant dermatitis caused by a broad range of contact allergens, including nickel. This highlights its ability to improve ACD caused by allergens with a TH1 bias, despite its primarily TH2-dampening effects. Notably, several studies have reported successful use of dupilumab for systemic ACD.12,18 In addition, dupilumab may be able to improve symptoms of ACD in as little as 1 to 4 weeks. Unlike some systemic therapies for ACD, dupilumab also benefits from its lack of notable immunosuppressive effects.9 A phase 4 clinical trial at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts) is recruiting participants, with a primary goal of investigating dupilumab’s impact on ACD in patients who have not improved despite allergen avoidance (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03935971).
There are a few potential disadvantages to dupilumab. Because it is not yet FDA approved for the treatment of ACD, insurance companies may deny coverage, making it likely to be unaffordable for most patients. Furthermore, the side-effect profile has not been fully characterized. In addition to ocular adverse effects, a growing number of studies have reported face and neck erythema after starting dupilumab. Although the cause is unclear, one theory is that the inhibition of IL-4/IL-13 leads to TH1/TH17 polarization, thereby worsening ACD caused by allergens that activate a TH1-predominant response.21 Finally, not all cases of ACD respond to dupilumab.22
Patch Testing While on Dupilumab
Diagnosing ACD is a challenging process. An accurate history and physical examination are critical, and patch testing remains the gold standard when it comes to identifying the source of the contact allergen(s).
There is ongoing debate among contact dermatitis experts regarding the diagnostic accuracy of patch testing for those on immunomodulators or immunosuppressants, as these medications can dampen positive results and increase the risk for false-negative readings.23 Consequently, some have questioned whether patch testing on dupilumab is accurate or feasible.24 Contact dermatitis experts have examined patch testing results before and after initiation of dupilumab to further investigate. Puza and Atwater25 established that patients are able to mount a positive patch test reaction while on dupilumab. Moreover, a retrospective review by Raffi et al26 found that out of 125 before therapy/on therapy patch test pairs, only 13 were lost after administration of dupilumab. Although this would suggest that dupilumab has little impact on patch testing, Jo et al27 found in a systematic review that patch test reactions may remain positive, change to negative, or become newly positive after dupilumab initiation.
This inconsistency in results may relate to the allergen-specific pathogenesis of ACD—one allergen may have a different response to the mechanism of dupilumab than another.28,29 More recently, de Wijs et al30 reported a series of 20 patients in whom more than two-thirds of prior positive patch test reactions were lost after retesting on dupilumab; there were no clear trends according to the immune polarity of the allergens. This finding suggests that patient-specific factors also should be considered, as this too could have an impact on the reliability of patch test findings after starting dupilumab.29
Final Interpretation
Given its overall excellent safety profile, dupilumab may be a feasible off-label option for patients with ACD that does not respond to allergen avoidance or for those who experience adverse effects from traditional therapies; however, it remains difficult to obtain through insurance because it is not yet FDA approved for ACD. Likewise, its impact on the accuracy of patch testing is not yet well defined. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the pathophysiology of ACD and to guide further use of dupilumab in its treatment.
- Harb H, Chatila TA. Mechanisms of dupilumab. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020;50:5-14. doi:10.1111/cea.13491
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Chan CX, Zug KA. Diagnosis and management of dermatitis, including atopic, contact, and hand eczemas. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:611-626. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.003
- Simons JR, Bohnen IJ, van der Valk PG. A left-right comparison of UVB phototherapy and topical photochemotherapy in bilateral chronic hand dermatitis after 6 weeks’ treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1997;22:7-10. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2230.1997.1640585.x
- Bhatia J, Sarin A, Wollina U, et al. Review of biologics in allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:179-181. doi:10.1111/cod.13584
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of anti-IL-17 treatment on the reaction to a nickel patch test in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E58-E61. doi:10.1111/ijd.14347
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Joshi SR, Khan DA. Effective use of dupilumab in managing systemic allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:282-284. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000409
- Goldminz AM, Scheinman PL. A case series of dupilumab-treated allergic contact dermatitis patients. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12701. doi:10.1111/dth.12701
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. Dupilumab as a treatment for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:347-348. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000414
- Zhu GA, Chen JK, Chiou A, et al. Repeat patch testing in a patient with allergic contact dermatitis improved on dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:336-338. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.023
- Machler BC, Sung CT, Darwin E, et al. Dupilumab use in allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:280-281.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.043
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. A retrospective review of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis patients with allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1166-1167. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.048
- Jacob SE, Sung CT, Machler BC. Dupilumab for systemic allergy syndrome with dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:164-167. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000446
- Ruge IF, Skov L, Zachariae C, et al. Dupilumab treatment in two patients with severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by sesquiterpene lactones. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:137-139. doi:10.1111/cod.13545
- Wilson B, Balogh E, Rayhan D, et al. Chromate-induced allergic contact dermatitis treated with dupilumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1340-1342. doi:10.36849/jdd.6246
- Jo CE, Finstad A, Georgakopoulos JR, et al. Facial and neck erythema associated with dupilumab treatment: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1339-1347. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.012
- Koblinski JE, Hamann D. Mixed occupational and iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in a hairdresser. Occup Med (Lond). 2020;70:523-526. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqaa152
- Levian B, Chan J, DeLeo VA, et al. Patch testing and immunosuppression: a comprehensive review. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:128-139.
- Shah P, Milam EC, Lo Sicco KI, et al. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis and implications for patch testing: irreconcilable differences. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E215-E216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.036
- Puza CJ, Atwater AR. Positive patch test reaction in a patient taking dupilumab. Dermatitis. 2018;29:89. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000346
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Botto N, et al. The impact of dupilumab on patch testing and the prevalence of comorbid allergic contact dermatitis in recalcitrant atopic dermatitis: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:132-138. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.09.028
- Jo CE, Mufti A, Sachdeva M, et al. Effect of dupilumab on allergic contact dermatitis and patch testing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1772-1776. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.044
- Raffi J, Botto N. Patch testing and allergen-specific inhibition in a patient taking dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:120-121. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4098
- Ludwig CM, Krase JM, Shi VY. T helper 2 inhibitors in allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2021;32:15-18. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000616
- de Wijs LEM, van der Waa JD, Nijsten T, et al. Effects of dupilumab treatment on patch test reactions: a retrospective evaluation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021;51:959-967. doi:10.1111/cea.13892
Dupilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Through inhibition of the IL-4R α subunit, it prevents activation of the IL-4/IL-13 signaling cascade. This dampens the T H 2 inflammatory response, thereby improving the symptoms associated with atopic dermatitis. 1,2 Recent literature suggests that dupilumab may be useful in the treatment of other chronic dermatologic conditions, including allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) refractory to allergen avoidance and other treatments. Herein, we provide an overview of ACD, the role that dupilumab may play in its management, and its impact on patch testing results.
Pathogenesis of ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis is a cell-mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction that develops through 2 distinct stages. In the sensitization phase, an allergen penetrates the skin and subsequently is engulfed by a cutaneous antigen-presenting cell. The allergen is then combined with a peptide to form a complex that is presented to naïve T lymphocytes in regional lymph nodes. The result is clonal expansion of a T-cell population that recognizes the allergen. In the elicitation phase, repeat exposure to the allergen leads to the recruitment of primed T cells to the skin, followed by cytokine release, inflammation, and resultant dermatitis.3
Historically, ACD was thought to be primarily driven by the TH1 inflammatory response; however, it is now known that TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 also may play a role in its pathogenesis.4,5 Another key finding is that the immune response in ACD appears to be at least partially allergen specific. Molecular profiling has revealed that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, while allergens such as fragrance and rubber primarily induce a TH2 response.4
Management of ACD
Allergen avoidance is the mainstay of ACD treatment; however, in some patients, this approach does not always improve symptoms. In addition, eliminating the source of the allergen may not be possible in those with certain occupational, environmental, or medical exposures.
There are no FDA-approved treatments for ACD. When allergen avoidance alone is insufficient, first-line pharmacologic therapy typically includes topical or oral corticosteroids, the choice of which depends on the extent and severity of the dermatitis; however, a steroid-sparing agent often is preferred to avoid the unfavorable effects of long-term steroid use. Other systemic treatments for ACD include methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine.6 These agents are used for severe ACD and typically are chosen as a last resort due to their immunosuppressive activity.
Phototherapy is another option, often as an adjunct to other therapies. Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have both been used. Psoralen plus UVA tends to have more side effects; therefore, narrowband UVB often is preferred.7,8
Use of Dupilumab in ACD
Biologics are unique, as they can target a single step in the immune response to improve a wide variety of symptoms. Research investigating their role as a treatment modality for ACD is still evolving alongside our increasing knowledge of its pathophysiology.9 Of note, studies examining the anti–IL-17 biologic secukinumab revealed it to be ineffective against ACD,10,11 which suggests that targeting specific immune components may not always result in improvement of ACD symptoms, likely because its pathophysiology involves several pathways.
There have been multiple reports demonstrating the effectiveness of dupilumab in the treatment of ACD (eTable).12-20 The findings from these studies show that dupilumab can improve recalcitrant dermatitis caused by a broad range of contact allergens, including nickel. This highlights its ability to improve ACD caused by allergens with a TH1 bias, despite its primarily TH2-dampening effects. Notably, several studies have reported successful use of dupilumab for systemic ACD.12,18 In addition, dupilumab may be able to improve symptoms of ACD in as little as 1 to 4 weeks. Unlike some systemic therapies for ACD, dupilumab also benefits from its lack of notable immunosuppressive effects.9 A phase 4 clinical trial at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts) is recruiting participants, with a primary goal of investigating dupilumab’s impact on ACD in patients who have not improved despite allergen avoidance (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03935971).
There are a few potential disadvantages to dupilumab. Because it is not yet FDA approved for the treatment of ACD, insurance companies may deny coverage, making it likely to be unaffordable for most patients. Furthermore, the side-effect profile has not been fully characterized. In addition to ocular adverse effects, a growing number of studies have reported face and neck erythema after starting dupilumab. Although the cause is unclear, one theory is that the inhibition of IL-4/IL-13 leads to TH1/TH17 polarization, thereby worsening ACD caused by allergens that activate a TH1-predominant response.21 Finally, not all cases of ACD respond to dupilumab.22
Patch Testing While on Dupilumab
Diagnosing ACD is a challenging process. An accurate history and physical examination are critical, and patch testing remains the gold standard when it comes to identifying the source of the contact allergen(s).
There is ongoing debate among contact dermatitis experts regarding the diagnostic accuracy of patch testing for those on immunomodulators or immunosuppressants, as these medications can dampen positive results and increase the risk for false-negative readings.23 Consequently, some have questioned whether patch testing on dupilumab is accurate or feasible.24 Contact dermatitis experts have examined patch testing results before and after initiation of dupilumab to further investigate. Puza and Atwater25 established that patients are able to mount a positive patch test reaction while on dupilumab. Moreover, a retrospective review by Raffi et al26 found that out of 125 before therapy/on therapy patch test pairs, only 13 were lost after administration of dupilumab. Although this would suggest that dupilumab has little impact on patch testing, Jo et al27 found in a systematic review that patch test reactions may remain positive, change to negative, or become newly positive after dupilumab initiation.
This inconsistency in results may relate to the allergen-specific pathogenesis of ACD—one allergen may have a different response to the mechanism of dupilumab than another.28,29 More recently, de Wijs et al30 reported a series of 20 patients in whom more than two-thirds of prior positive patch test reactions were lost after retesting on dupilumab; there were no clear trends according to the immune polarity of the allergens. This finding suggests that patient-specific factors also should be considered, as this too could have an impact on the reliability of patch test findings after starting dupilumab.29
Final Interpretation
Given its overall excellent safety profile, dupilumab may be a feasible off-label option for patients with ACD that does not respond to allergen avoidance or for those who experience adverse effects from traditional therapies; however, it remains difficult to obtain through insurance because it is not yet FDA approved for ACD. Likewise, its impact on the accuracy of patch testing is not yet well defined. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the pathophysiology of ACD and to guide further use of dupilumab in its treatment.
Dupilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Through inhibition of the IL-4R α subunit, it prevents activation of the IL-4/IL-13 signaling cascade. This dampens the T H 2 inflammatory response, thereby improving the symptoms associated with atopic dermatitis. 1,2 Recent literature suggests that dupilumab may be useful in the treatment of other chronic dermatologic conditions, including allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) refractory to allergen avoidance and other treatments. Herein, we provide an overview of ACD, the role that dupilumab may play in its management, and its impact on patch testing results.
Pathogenesis of ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis is a cell-mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction that develops through 2 distinct stages. In the sensitization phase, an allergen penetrates the skin and subsequently is engulfed by a cutaneous antigen-presenting cell. The allergen is then combined with a peptide to form a complex that is presented to naïve T lymphocytes in regional lymph nodes. The result is clonal expansion of a T-cell population that recognizes the allergen. In the elicitation phase, repeat exposure to the allergen leads to the recruitment of primed T cells to the skin, followed by cytokine release, inflammation, and resultant dermatitis.3
Historically, ACD was thought to be primarily driven by the TH1 inflammatory response; however, it is now known that TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 also may play a role in its pathogenesis.4,5 Another key finding is that the immune response in ACD appears to be at least partially allergen specific. Molecular profiling has revealed that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, while allergens such as fragrance and rubber primarily induce a TH2 response.4
Management of ACD
Allergen avoidance is the mainstay of ACD treatment; however, in some patients, this approach does not always improve symptoms. In addition, eliminating the source of the allergen may not be possible in those with certain occupational, environmental, or medical exposures.
There are no FDA-approved treatments for ACD. When allergen avoidance alone is insufficient, first-line pharmacologic therapy typically includes topical or oral corticosteroids, the choice of which depends on the extent and severity of the dermatitis; however, a steroid-sparing agent often is preferred to avoid the unfavorable effects of long-term steroid use. Other systemic treatments for ACD include methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine.6 These agents are used for severe ACD and typically are chosen as a last resort due to their immunosuppressive activity.
Phototherapy is another option, often as an adjunct to other therapies. Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have both been used. Psoralen plus UVA tends to have more side effects; therefore, narrowband UVB often is preferred.7,8
Use of Dupilumab in ACD
Biologics are unique, as they can target a single step in the immune response to improve a wide variety of symptoms. Research investigating their role as a treatment modality for ACD is still evolving alongside our increasing knowledge of its pathophysiology.9 Of note, studies examining the anti–IL-17 biologic secukinumab revealed it to be ineffective against ACD,10,11 which suggests that targeting specific immune components may not always result in improvement of ACD symptoms, likely because its pathophysiology involves several pathways.
There have been multiple reports demonstrating the effectiveness of dupilumab in the treatment of ACD (eTable).12-20 The findings from these studies show that dupilumab can improve recalcitrant dermatitis caused by a broad range of contact allergens, including nickel. This highlights its ability to improve ACD caused by allergens with a TH1 bias, despite its primarily TH2-dampening effects. Notably, several studies have reported successful use of dupilumab for systemic ACD.12,18 In addition, dupilumab may be able to improve symptoms of ACD in as little as 1 to 4 weeks. Unlike some systemic therapies for ACD, dupilumab also benefits from its lack of notable immunosuppressive effects.9 A phase 4 clinical trial at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts) is recruiting participants, with a primary goal of investigating dupilumab’s impact on ACD in patients who have not improved despite allergen avoidance (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03935971).
There are a few potential disadvantages to dupilumab. Because it is not yet FDA approved for the treatment of ACD, insurance companies may deny coverage, making it likely to be unaffordable for most patients. Furthermore, the side-effect profile has not been fully characterized. In addition to ocular adverse effects, a growing number of studies have reported face and neck erythema after starting dupilumab. Although the cause is unclear, one theory is that the inhibition of IL-4/IL-13 leads to TH1/TH17 polarization, thereby worsening ACD caused by allergens that activate a TH1-predominant response.21 Finally, not all cases of ACD respond to dupilumab.22
Patch Testing While on Dupilumab
Diagnosing ACD is a challenging process. An accurate history and physical examination are critical, and patch testing remains the gold standard when it comes to identifying the source of the contact allergen(s).
There is ongoing debate among contact dermatitis experts regarding the diagnostic accuracy of patch testing for those on immunomodulators or immunosuppressants, as these medications can dampen positive results and increase the risk for false-negative readings.23 Consequently, some have questioned whether patch testing on dupilumab is accurate or feasible.24 Contact dermatitis experts have examined patch testing results before and after initiation of dupilumab to further investigate. Puza and Atwater25 established that patients are able to mount a positive patch test reaction while on dupilumab. Moreover, a retrospective review by Raffi et al26 found that out of 125 before therapy/on therapy patch test pairs, only 13 were lost after administration of dupilumab. Although this would suggest that dupilumab has little impact on patch testing, Jo et al27 found in a systematic review that patch test reactions may remain positive, change to negative, or become newly positive after dupilumab initiation.
This inconsistency in results may relate to the allergen-specific pathogenesis of ACD—one allergen may have a different response to the mechanism of dupilumab than another.28,29 More recently, de Wijs et al30 reported a series of 20 patients in whom more than two-thirds of prior positive patch test reactions were lost after retesting on dupilumab; there were no clear trends according to the immune polarity of the allergens. This finding suggests that patient-specific factors also should be considered, as this too could have an impact on the reliability of patch test findings after starting dupilumab.29
Final Interpretation
Given its overall excellent safety profile, dupilumab may be a feasible off-label option for patients with ACD that does not respond to allergen avoidance or for those who experience adverse effects from traditional therapies; however, it remains difficult to obtain through insurance because it is not yet FDA approved for ACD. Likewise, its impact on the accuracy of patch testing is not yet well defined. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the pathophysiology of ACD and to guide further use of dupilumab in its treatment.
- Harb H, Chatila TA. Mechanisms of dupilumab. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020;50:5-14. doi:10.1111/cea.13491
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Chan CX, Zug KA. Diagnosis and management of dermatitis, including atopic, contact, and hand eczemas. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:611-626. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.003
- Simons JR, Bohnen IJ, van der Valk PG. A left-right comparison of UVB phototherapy and topical photochemotherapy in bilateral chronic hand dermatitis after 6 weeks’ treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1997;22:7-10. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2230.1997.1640585.x
- Bhatia J, Sarin A, Wollina U, et al. Review of biologics in allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:179-181. doi:10.1111/cod.13584
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of anti-IL-17 treatment on the reaction to a nickel patch test in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E58-E61. doi:10.1111/ijd.14347
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Joshi SR, Khan DA. Effective use of dupilumab in managing systemic allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:282-284. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000409
- Goldminz AM, Scheinman PL. A case series of dupilumab-treated allergic contact dermatitis patients. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12701. doi:10.1111/dth.12701
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. Dupilumab as a treatment for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:347-348. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000414
- Zhu GA, Chen JK, Chiou A, et al. Repeat patch testing in a patient with allergic contact dermatitis improved on dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:336-338. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.023
- Machler BC, Sung CT, Darwin E, et al. Dupilumab use in allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:280-281.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.043
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. A retrospective review of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis patients with allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1166-1167. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.048
- Jacob SE, Sung CT, Machler BC. Dupilumab for systemic allergy syndrome with dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:164-167. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000446
- Ruge IF, Skov L, Zachariae C, et al. Dupilumab treatment in two patients with severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by sesquiterpene lactones. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:137-139. doi:10.1111/cod.13545
- Wilson B, Balogh E, Rayhan D, et al. Chromate-induced allergic contact dermatitis treated with dupilumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1340-1342. doi:10.36849/jdd.6246
- Jo CE, Finstad A, Georgakopoulos JR, et al. Facial and neck erythema associated with dupilumab treatment: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1339-1347. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.012
- Koblinski JE, Hamann D. Mixed occupational and iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in a hairdresser. Occup Med (Lond). 2020;70:523-526. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqaa152
- Levian B, Chan J, DeLeo VA, et al. Patch testing and immunosuppression: a comprehensive review. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:128-139.
- Shah P, Milam EC, Lo Sicco KI, et al. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis and implications for patch testing: irreconcilable differences. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E215-E216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.036
- Puza CJ, Atwater AR. Positive patch test reaction in a patient taking dupilumab. Dermatitis. 2018;29:89. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000346
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Botto N, et al. The impact of dupilumab on patch testing and the prevalence of comorbid allergic contact dermatitis in recalcitrant atopic dermatitis: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:132-138. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.09.028
- Jo CE, Mufti A, Sachdeva M, et al. Effect of dupilumab on allergic contact dermatitis and patch testing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1772-1776. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.044
- Raffi J, Botto N. Patch testing and allergen-specific inhibition in a patient taking dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:120-121. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4098
- Ludwig CM, Krase JM, Shi VY. T helper 2 inhibitors in allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2021;32:15-18. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000616
- de Wijs LEM, van der Waa JD, Nijsten T, et al. Effects of dupilumab treatment on patch test reactions: a retrospective evaluation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021;51:959-967. doi:10.1111/cea.13892
- Harb H, Chatila TA. Mechanisms of dupilumab. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020;50:5-14. doi:10.1111/cea.13491
- Gooderham MJ, Hong HC, Eshtiaghi P, et al. Dupilumab: a review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S28-S36. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Chan CX, Zug KA. Diagnosis and management of dermatitis, including atopic, contact, and hand eczemas. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:611-626. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.003
- Simons JR, Bohnen IJ, van der Valk PG. A left-right comparison of UVB phototherapy and topical photochemotherapy in bilateral chronic hand dermatitis after 6 weeks’ treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1997;22:7-10. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2230.1997.1640585.x
- Bhatia J, Sarin A, Wollina U, et al. Review of biologics in allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:179-181. doi:10.1111/cod.13584
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of anti-IL-17 treatment on the reaction to a nickel patch test in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E58-E61. doi:10.1111/ijd.14347
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Joshi SR, Khan DA. Effective use of dupilumab in managing systemic allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:282-284. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000409
- Goldminz AM, Scheinman PL. A case series of dupilumab-treated allergic contact dermatitis patients. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12701. doi:10.1111/dth.12701
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. Dupilumab as a treatment for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2018;29:347-348. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000414
- Zhu GA, Chen JK, Chiou A, et al. Repeat patch testing in a patient with allergic contact dermatitis improved on dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:336-338. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.023
- Machler BC, Sung CT, Darwin E, et al. Dupilumab use in allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:280-281.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.043
- Chipalkatti N, Lee N, Zancanaro P, et al. A retrospective review of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis patients with allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1166-1167. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.048
- Jacob SE, Sung CT, Machler BC. Dupilumab for systemic allergy syndrome with dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:164-167. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000446
- Ruge IF, Skov L, Zachariae C, et al. Dupilumab treatment in two patients with severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by sesquiterpene lactones. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:137-139. doi:10.1111/cod.13545
- Wilson B, Balogh E, Rayhan D, et al. Chromate-induced allergic contact dermatitis treated with dupilumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1340-1342. doi:10.36849/jdd.6246
- Jo CE, Finstad A, Georgakopoulos JR, et al. Facial and neck erythema associated with dupilumab treatment: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1339-1347. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.012
- Koblinski JE, Hamann D. Mixed occupational and iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in a hairdresser. Occup Med (Lond). 2020;70:523-526. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqaa152
- Levian B, Chan J, DeLeo VA, et al. Patch testing and immunosuppression: a comprehensive review. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:128-139.
- Shah P, Milam EC, Lo Sicco KI, et al. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis and implications for patch testing: irreconcilable differences. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E215-E216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.036
- Puza CJ, Atwater AR. Positive patch test reaction in a patient taking dupilumab. Dermatitis. 2018;29:89. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000346
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Botto N, et al. The impact of dupilumab on patch testing and the prevalence of comorbid allergic contact dermatitis in recalcitrant atopic dermatitis: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:132-138. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.09.028
- Jo CE, Mufti A, Sachdeva M, et al. Effect of dupilumab on allergic contact dermatitis and patch testing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1772-1776. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.044
- Raffi J, Botto N. Patch testing and allergen-specific inhibition in a patient taking dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:120-121. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4098
- Ludwig CM, Krase JM, Shi VY. T helper 2 inhibitors in allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2021;32:15-18. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000616
- de Wijs LEM, van der Waa JD, Nijsten T, et al. Effects of dupilumab treatment on patch test reactions: a retrospective evaluation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021;51:959-967. doi:10.1111/cea.13892
Practice Points
- Dupilumab is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
- Multiple reports have suggested that dupilumab may be effective in the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis, and a phase 4 clinical trial is ongoing.
- The accuracy of patch testing after dupilumab initiation is unclear, as reactions may remain positive, change to negative, or become newly positive after its administration.