User login
Eyelid Dermatitis: Common Patterns and Contact Allergens
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic concern representing a broad group of inflammatory dermatoses and typically presenting as eczematous lesions on the eyelids.1 One of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis is thought to be allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), a type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction caused by exposure to external allergens.2 Although ACD can occur anywhere on the body, dermatitis on the face and eyelids is quite common.1,2 This article aims to explore the clinical manifestation, evaluation, and management of eyelid ACD.
Pathophysiology of Eyelid ACD
Studies have shown that ACD is the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, estimated to account for 46% to 72% of cases worldwide.3-6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction to external antigens that manifests as eczematous lesions at the site of contact with the allergen that may spread.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common condition, and it is estimated that at least 20% of the general worldwide population has a contact allergy.8,9 Histologically, ACD manifests as spongiotic dermatitis, though this is not unique and also may be seen in atopic dermatitis (AD) and irritant contact dermatitis.2 Allergic contact dermatitis is diagnosed via epicutaneous patch testing, and treatment involves allergen avoidance with or without adjuvant topical and/or systemic immunomodulatory treatments.7
The eyelids are uniquely prone to the development of ACD given their thinner epidermis and increased susceptibility to irritation. They frequently are exposed to allergens through the direct topical route as well as indirectly via airborne exposure, rinse-down products (eg, shampoos), and substances transferred from an individual’s own hands. The occluded skin folds of the eyelids facilitate increased exposure to trapped allergens.10,11 Additionally, the skin of the eyelids is thin, flexible, highly vascularized, and lacking in subcutaneous tissue, making this area more susceptible to antigen penetration than other locations on the body.1,2,10,12,13
Clinical Manifestations
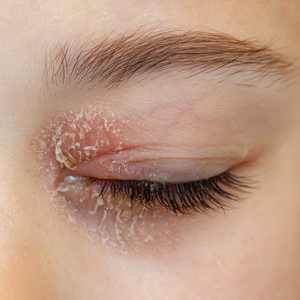
Eyelid ACD is more common in females than males, which is thought to be related to increased use of cosmetics and fragrances.1,3,12,14-16 Clinical manifestations may resemble eczematous papules and plaques.1 Eyelid ACD commonly spreads beyond the eyelid margin, which helps to differentiate it from AD and irritant contact dermatitis. Symptoms of ACD on the eyelids typically include pruritus, redness, swelling, tearing, scaling, and pain.2 Persistent untreated eyelid dermatitis can lead to eyelash loss, damage to meibomian glands, and hyperpigmentation.2,17,18
Patterns of Eyelid ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis on the eyelids can occur due to direct application of allergens onto the skin of the eyelids, runoff of products from the hair/scalp (eg, shampoo), transfer of allergens from the hands, or contact with airborne allergens.1,2,11,12 Some reports have suggested that eyelid ACD more often is caused by products applied to the scalp or face rather than those applied directly to the eyelids.11 Because the scalp and face are less reactive to contact allergens, in some cases the eyelids may be the only affected site.10,12,13
The specific pattern of dermatitis on or around the eyelids can provide clues to the allergenic source. Dermatitis present around the eyelids and periorbital region with involvement of the bilateral upper and lower eyelids suggests direct exposure to a contact allergen, such as makeup or other cosmetic products.1 Unilateral involvement of only 1 eyelid can occur with ectopic transfer of allergens from the hands or nails.1,19 Involvement of the fingers or nails in addition to the eyelids may further suggest ectopic transfer, such as from allergens in nail polish.10 Unilateral eyelid dermatitis also could be caused by unique exposures such as a microscope or camera eyepiece.19 Distribution around the lower eyelids and upper cheeks is indicative of a drip or runoff pattern, which may result from an ophthalmic solution such as eye drops or contact lens solution.1,19 Finally, dermatitis affecting the upper eyelids along with the nasolabial folds and upper chest may suggest airborne contact dermatitis to fragrances or household cleaning products.1,11
Common Culprits of Eyelid ACD
Common causes of eyelid ACD include cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry.10,13,20 Within the broader category of cosmetics, allergens may be found in makeup and makeup removers, cosmetic applicators and brushes, soaps and cleansers, creams and sunscreens, antiaging products, hair products, nail polish and files, and hair removal products, among many others.10,13,16,20 Additionally, ophthalmologic and topical medications are common sources of ACD, including eyedrops, contact lens solution, and topical antibiotics.10,13,21 Costume jewelry commonly contains allergenic metals, which also can be found in eyelash curlers, eyeglasses, toys, and other household items.22,23 Finally, contact allergens can be found in items such as goggles, gloves, textiles, and a variety of other occupational and household exposures.
Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids occurs predominantly—but not exclusively—in females.16,20,24 This finding has been attributed to the traditionally greater use of cosmetics and fragrances among women; however, the use of skin care products among men is increasing, and recent studies have shown the eyelids to be a common location of facial contact dermatitis among men.16,24 Although eyelid dermatitis has not been specifically analyzed by sex, a retrospective analysis of 1332 male patients with facial dermatitis found the most common sites to be the face (not otherwise specified)(48.9%), eyelids (23.5%), and lips (12.6%). In this cohort, the most common allergens were surfactants in shampoos and paraphenylenediamine in hair dyes.24
Common Allergens
Common contact allergens among patients with ACD of the eyelids include metals, fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications.3,10,16,20,25-27 Sources of common contact allergens are reviewed in Table 1.
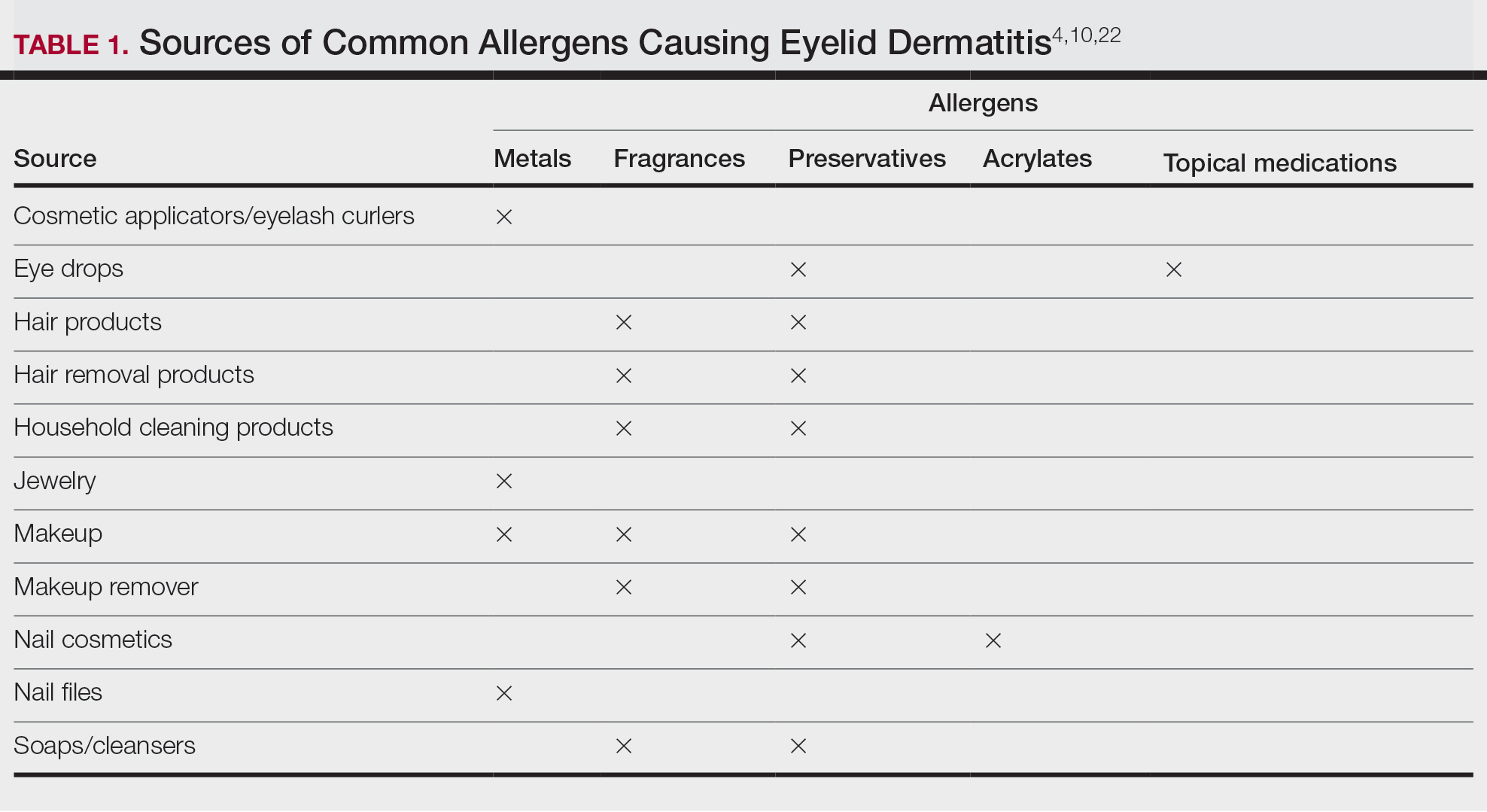
Metals—Metals are among the most common causes of ACD overall, and nickel frequently is reported as one of the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.16,27 A retrospective analysis of 2332 patients with eyelid dermatitis patch tested by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 1994 to 2016 found that 18.6% of patients with eyelid ACD had a clinically relevant nickel allergy. Sources of nickel exposure include jewelry, grooming devices, makeup and makeup applicators, and eyelash curlers, as well as direct transfer from the hands after contact with consumer products.16
Other metals that can cause ACD include cobalt (found in similar products to nickel) and gold. Gold often is associated with eyelid dermatitis, though its clinical relevance has been debated, as gold is a relatively inert metal that rarely is present in eye cosmetics and its ions are not displaced from objects and deposited on the skin via sweat in the same way as nickel.4,16,20,28-30 Despite this, studies have shown that gold is a common positive patch test reaction among patients with eyelid dermatitis, even in patients with no dermatitis at the site of contact with gold jewelry.20,29,31 Gold has been reported to be the most common allergen causing unilateral eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer.16,19,20,29 It has been proposed that titanium dioxide, present in many cosmetics and sunscreens, displaces gold allowing its release from jewelry, thereby liberating the fine gold ions and allowing them to desposit on the face and eyelids.30,31 Given the uncertain clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to gold, Warshaw at al16 recommend a 2- to 3-month trial of gold jewelry avoidance to establish relevance, and Ehrlich and Gold29 noted that avoidance of gold leads to improvement.
Fragrances—Fragrances represent a broad category of naturally occurring and man-made components that often are combined to produce a desired scent in personal care products.32 Essential oils and botanicals are both examples of natural fragrances.33 Fragrances are found in numerous products including makeup, hair products, and household cleaning supplies and represent some of the most common contact allergens.32 Common fragrance allergens include fragrance mixes I and II, hydroperoxides of linalool, and balsam of Peru.12,32,34 Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances typically manifests on the eyelids, face, or hands.33 Several studies have found fragrances to be among the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.3,12,20,25,34 Patch testing for fragrance allergy may include baseline series, supplemental fragrance series, and personal care products.32,35
Preservatives—Preservatives, including formaldehyde and formaldehyde releasers (eg, quaternium-15 and bronopol) and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone, may be found in personal care products such as makeup, makeup removers, emollients, shampoos, hair care products, and ophthalmologic solutions and are among the most common cosmetic sources of ACD.13,36-39 Preservatives are among the top allergens causing eyelid dermatitis.20 In particular, patch test positivity rates to methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone have been increasing in North America.40 Sensitization to preservatives may occur through direct skin contact or transfer from the hands.41
Acrylates—Acrylates are compounds derived from acrylic acid that may be found in acrylic and gel nails, eyelash extensions, and other adhesives and are frequent causes of eyelid ACD.4,10,42 Acrylate exposure may be cosmetic among consumers or occupational (eg, aestheticians).42,43 Acrylates on the nails may cause eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer from the hands and also may cause periungual dermatitis manifesting as nail bed erythema.10 Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is one of the more common eyelid ACD allergens, and studies have shown increasing prevalence of positive reaction rates to hydroxyethylmethacrylate.10,44Topical Medications—Contact allergies to topical medications are quite common, estimated to occur in 10% to 17% of patients undergoing patch testing.45 Both active and inactive ingredients of topical medications may be culprits in eyelid ACD. The most common topical medication allergens include antibiotics, steroids, local anesthetics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.45 Topical antibiotics such as neomycin and bacitracin represent some of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis4,10 and may be found in a variety of products, including antibacterial ointments and eye drops.1 Many ophthalmologic medications also contain corticosteroids, with the most common allergenic steroids being tixocortol pivalate (a marker for hydrocortisone allergy) and budesonide.10,20 Topical steroids pose a particular dilemma, as they can be either the source of or a treatment for ACD.10 Eye drops also may contain anesthetics, β-blockers, and antihistamines, as well as the preservative benzalkonium chloride, all of which may be contact allergens.21,39
Differential Diagnosis of Eyelid Dermatitis
Although ACD is reported to be the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, the differential diagnosis is broad, including endogenous inflammatory dermatoses and exogenous exposures (Table 2). Symptoms of eyelid ACD can be nonspecific (eg, erythema, pruritus), making diagnosis challenging.46
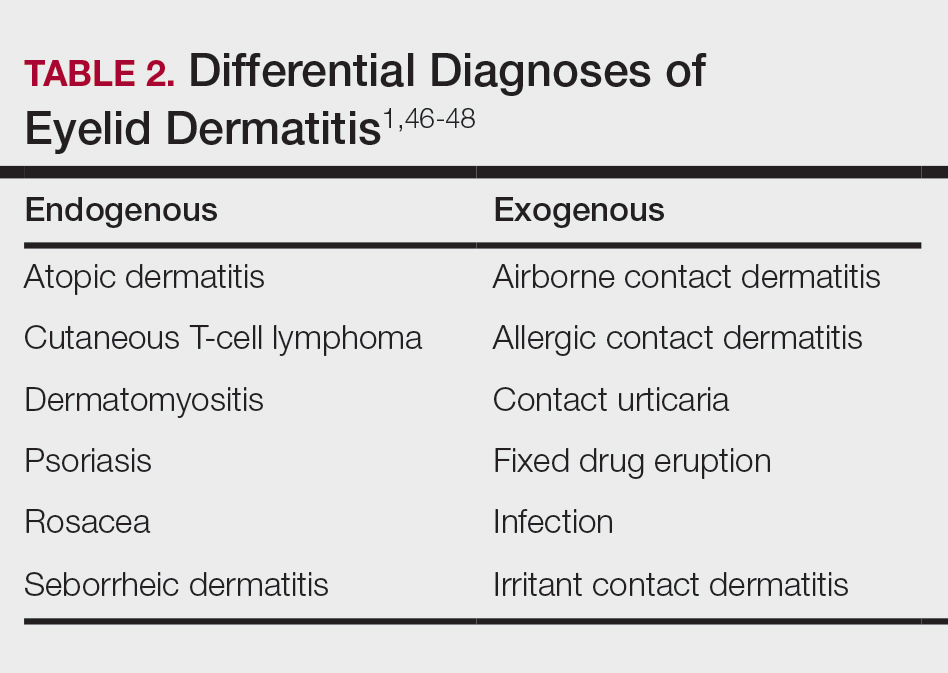
Atopic dermatitis represents another common cause of eyelid dermatitis, accounting for 14% to 39.5% of cases.3-5,49Atopic dermatitis of the eyelids classically manifests with lichenification of the medial aspects of the eyelids.50 Atopic dermatitis and ACD may be difficult to distinguish, as the 2 conditions appear clinically similar and can develop concomitantly.51 Additionally, atopic patients are likely to have comorbid allergic rhinitis and sensitivity to environmental allergens, which may lead to chronic eye scratching and lichenification.1,51 Clinical features of eyelid dermatitis suggesting allergic rhinitis and likely comorbid AD include creases in the lower eyelids (Dennie-Morgan lines) and periorbital hyperpigmentation (known as the allergic shiner) due to venous congestion.1,52
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction to Malassezia yeast that occurs in sebaceous areas such as the groin, scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, and nasolabial folds.1,53,54
Irritant contact dermatitis, a nonspecific inflammatory reaction caused by direct cell damage from external irritants, also may affect the eyelids and appear similar to ACD.1 It typically manifests with a burning or stinging sensation, as opposed to pruritus, and generally develops and resolves more rapidly than ACD.1 Personal care products are common causes of eyelid irritant contact dermatitis.16
Patch Testing for Eyelid ACD
The gold standard for diagnosis of ACD is patch testing, outlined by the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group.55-57 Patch testing generally is performed with standardized panels of allergens and can be customized either with supplemental panels based on unique exposures or with the patient’s own personal care products to increase the sensitivity of testing. Therefore, a thorough history is crucial to identifying potential allergens in a patient’s environment.
False negatives are possible, as the skin on the back may be thicker and less sensitive than the skin at the location of dermatitis.2,58 This is particularly relevant when using patch testing to diagnose ACD of the eyelids, where the skin is particularly thin and sensitive.2 Additionally, ingredients of ophthalmic medications are known to have an especially high false-negative rate with standard patch testing and may require repeated testing with higher drug concentrations or modified patch testing procedures (eg, open testing, scratch-patch testing).1,59
Treatment
Management of ACD involves allergen avoidance, typically dictated by patch test results.10 Allergen avoidance may be facilitated using online resources such as the Contact Allergen Management Program (https://www.acdscamp.org/) created by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.10,18 Patient counseling following patch testing is crucial to educating patients about sources of potential allergen exposures and strategies for avoidance. In the case of eyelid dermatitis, it is particularly important to consider exposure to airborne allergens such as fragrances.16 Fragrance avoidance is uniquely difficult, as labelling standards in the United States currently do not require disclosure of specific fragrance components.33 Additionally, products labelled as unscented may still contain fragrances. As such, some patients with fragrance allergy may need to carefully avoid all products containing fragrances.33
In addition to allergen avoidance, eyelid ACD may be treated with topical medications (eg, steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, Janus kinase inhibitors); however, these same topical medications also can cause ACD due to some ingredients such as propylene glycol.10 Topical steroids should be used with caution on the eyelids given the risk for atrophy, cataracts, and glaucoma.1
Final Interpretation
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic condition most frequently caused by ACD due to exposure to allergens in cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry, among many other potential sources. The most common allergens causing eyelid dermatitis include metals (particularly nickel), fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications. Eyelid ACD is diagnosed via patch testing, and the mainstay of treatment is strict allergen avoidance. Patient counseling is vital for successful allergen avoidance and resolution of eyelid ACD.
- Hine AM, Waldman RA, Grzybowski A, et al. Allergic disorders of the eyelid. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:476-480. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2023.08.002
- Turkiewicz M, Shah A, Yang YW, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids: an interdisciplinary review. Ocul Surf. 2023;28:124-130. doi:10.1016/j.jtos.2023.03.001
- Valsecchi R, Imberti G, Martino D, et al. Eyelid dermatitis: an evaluation of 150 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:143-147. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb05242.x
- Guin JD. Eyelid dermatitis: experience in 203 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:755-765. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.122736
- Nethercott JR, Nield G, Holness DL. A review of 79 cases of eyelid dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(2 pt 1):223-230. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70165-1
- Shah M, Lewis FM, Gawkrodger DJ. Facial dermatitis and eyelid dermatitis: a comparison of patch test results and final diagnoses. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:140-141. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02148.x
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- Adler BL, DeLeo VA. Allergic contact dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:364. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5639
- Huang CX, Yiannias JA, Killian JM, et al. Seven common allergen groups causing eyelid dermatitis: education and avoidance strategies. Clin Ophthalmol Auckl NZ. 2021;15:1477-1490. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S297754
- Rozas-Muñoz E, Gamé D, Serra-Baldrich E. Allergic contact dermatitis by anatomical regions: diagnostic clues. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas Engl Ed. 2018;109:485-507. doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2018.05.016
- Amin KA, Belsito DV. The aetiology of eyelid dermatitis: a 10-year retrospective analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:280-285. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00927.x
- Wolf R, Orion E, Tüzün Y. Periorbital (eyelid) dermatides. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:131-140. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.035
- Ockenfels HM, Seemann U, Goos M. Contact allergy in patients with periorbital eczema: an analysis of allergens. data recorded by the Information Network of the Departments of Dermatology. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1997;195:119-124. doi:10.1159/000245712
- Landeck L, John SM, Geier J. Periorbital dermatitis in 4779 patients—patch test results during a 10-year period. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:205-212. doi:10.1111/cod.12157
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Maibach HI, et al. Eyelid dermatitis in patients referred for patch testing: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:953-964. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.020
- McMonnies CW. Management of chronic habits of abnormal eye rubbing. Contact Lens Anterior Eye. 2008;31:95-102. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2007.07.008
- Chisholm SAM, Couch SM, Custer PL. Etiology and management of allergic eyelid dermatitis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33:248-250. doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000723
- Lewallen R, Feldman S, eds. Regional atlas of contact dermatitis. The Dermatologist. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://s3.amazonaws.com/HMP/hmp_ln/imported/Regional%20Atlas%20of%20Contact%20Dermatitis%20Book_lr.pdf
- Rietschel RL, Warshaw EM, Sasseville D, et al. Common contact allergens associated with eyelid dermatitis: data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2003-2004 study period. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2007;18:78-81. doi:10.2310/6620.2007.06041
- Mughal AA, Kalavala M. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:593-597; quiz 597-598. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04398.x
- Goossens A. Contact allergic reactions on the eyes and eyelids. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2004;292:11-17.
- Silverberg NB, Pelletier JL, Jacob SE, et al. Nickel allergic contact dermatitis: identification, treatment, and prevention. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20200628. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0628
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Maibach HI, et al. Facial dermatitis in male patients referred for patch testing. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:79-84. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3531
- Wenk KS, Ehrlich A. Fragrance series testing in eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:22-26. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d180f
- Crouse L, Ziemer C, Ziemer C, et al. Trends in eyelid dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2018;29:96-97. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000338
- Yazdanparast T, Nassiri Kashani M, Shamsipour M, et al. Contact allergens responsible for eyelid dermatitis in adults. J Dermatol. 2024;51:691-695. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.17140
- Fowler J, Taylor J, Storrs F, et al. Gold allergy in North America. Am J Contact Dermat. 2001;12:3-5.
- Ehrlich A, Belsito DV. Allergic contact dermatitis to gold. Cutis. 2000;65:323-326.
- Danesh M, Murase JE. Titanium dioxide induces eyelid dermatitis in patients allergic to gold. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E21. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.046
- Katta R. Common misconceptions in contact dermatitis counseling. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:2.
- De Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000463
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.009
- Warshaw EM, Zhang AJ, DeKoven JG, et al. Epidemiology of nickel sensitivity: retrospective cross-sectional analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data 1994-2014. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:701-713. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.058
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergen series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yim E, Baquerizo Nole KL, Tosti A. Contact dermatitis caused by preservatives. Dermatitis. 2014;25:215-231. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000061
- Alani JI, Davis MDP, Yiannias JA. Allergy to cosmetics. Dermatitis. 2013;24:283-290. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182a5d8bc
- Hamilton T, de Gannes GC. Allergic contact dermatitis to preservatives and fragrances in cosmetics. Skin Ther Lett. 2011;16:1-4.
- Ashton SJ, Mughal AA. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions: an update. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:480-483. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0033
- Reeder MJ, Warshaw E, Aravamuthan S, et al. Trends in the prevalence of methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in North America and Europe. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:267-274. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5991
- Herro EM, Elsaie ML, Nijhawan RI, et al. Recommendations for a screening series for allergic contact eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:17-21. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d191f
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Adv Dermatol Allergol Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Rodriguez I, George SE, Yu J, et al. Tackling acrylate allergy: the sticky truth. Cutis. 2023;112:282-286. doi:10.12788/cutis.0909
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019–2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.29017.jdk
- de Groot A. Allergic contact dermatitis from topical drugs: an overview. Dermatitis. 2021;32:197-213. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000737
- Zug KA, Palay DA, Rock B. Dermatologic diagnosis and treatment of itchy red eyelids. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996;40:293-306. doi:10.1016/s0039-6257(96)82004-2
- Beltrani VS. Eyelid dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001;1:380-388. doi:10.1007/s11882-001-0052-0
- Hirji SH, Maeng MM, Tran AQ, et al. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of the eyelid masquerading as dermatitis. Orbit Amst Neth. 2021;40:75-78. doi:10.1080/01676830.2020.1739080
- Svensson A, Möller H. Eyelid dermatitis: the role of atopy and contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1986;15:178-182. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1986.tb01321.x
- Papier A, Tuttle DJ, Mahar TJ. Differential diagnosis of the swollen red eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:1815-1824.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788cutis.0599
- Berger WE. Allergic rhinitis in children: diagnosis and management strategies. Paediatr Drugs. 2004;6:233-250. doi:10.2165/00148581-200406040-00003
- Singh A, Kansal NK, Kumawat D, et al. Ophthalmic manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis. Skinmed. 2023;21:397-401.
- Clark GW, Pope SM, Jaboori KA. Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91:185-190.
- Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI. Patch Testing and Prick Testing. Springer; 2012.
- Fregert S. Manual of Contact Dermatitis: On Behalf of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group. Munksgaard; 1974.
- Reeder M, Reck Atwater A. Patch testing 101, part 1: performing the test. Cutis. 2020;106:165-167. doi:10.12788/cutis.0093
- Wolf R, Perluk H. Failure of routine patch test results to detect eyelid dermatitis. Cutis. 1992;49:133-134.
- Grey KR, Warshaw EM. Allergic contact dermatitis to ophthalmic medications: relevant allergens and alternative testing methods. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:333-347. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000224
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic concern representing a broad group of inflammatory dermatoses and typically presenting as eczematous lesions on the eyelids.1 One of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis is thought to be allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), a type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction caused by exposure to external allergens.2 Although ACD can occur anywhere on the body, dermatitis on the face and eyelids is quite common.1,2 This article aims to explore the clinical manifestation, evaluation, and management of eyelid ACD.
Pathophysiology of Eyelid ACD
Studies have shown that ACD is the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, estimated to account for 46% to 72% of cases worldwide.3-6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction to external antigens that manifests as eczematous lesions at the site of contact with the allergen that may spread.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common condition, and it is estimated that at least 20% of the general worldwide population has a contact allergy.8,9 Histologically, ACD manifests as spongiotic dermatitis, though this is not unique and also may be seen in atopic dermatitis (AD) and irritant contact dermatitis.2 Allergic contact dermatitis is diagnosed via epicutaneous patch testing, and treatment involves allergen avoidance with or without adjuvant topical and/or systemic immunomodulatory treatments.7
The eyelids are uniquely prone to the development of ACD given their thinner epidermis and increased susceptibility to irritation. They frequently are exposed to allergens through the direct topical route as well as indirectly via airborne exposure, rinse-down products (eg, shampoos), and substances transferred from an individual’s own hands. The occluded skin folds of the eyelids facilitate increased exposure to trapped allergens.10,11 Additionally, the skin of the eyelids is thin, flexible, highly vascularized, and lacking in subcutaneous tissue, making this area more susceptible to antigen penetration than other locations on the body.1,2,10,12,13
Clinical Manifestations
Eyelid ACD is more common in females than males, which is thought to be related to increased use of cosmetics and fragrances.1,3,12,14-16 Clinical manifestations may resemble eczematous papules and plaques.1 Eyelid ACD commonly spreads beyond the eyelid margin, which helps to differentiate it from AD and irritant contact dermatitis. Symptoms of ACD on the eyelids typically include pruritus, redness, swelling, tearing, scaling, and pain.2 Persistent untreated eyelid dermatitis can lead to eyelash loss, damage to meibomian glands, and hyperpigmentation.2,17,18
Patterns of Eyelid ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis on the eyelids can occur due to direct application of allergens onto the skin of the eyelids, runoff of products from the hair/scalp (eg, shampoo), transfer of allergens from the hands, or contact with airborne allergens.1,2,11,12 Some reports have suggested that eyelid ACD more often is caused by products applied to the scalp or face rather than those applied directly to the eyelids.11 Because the scalp and face are less reactive to contact allergens, in some cases the eyelids may be the only affected site.10,12,13
The specific pattern of dermatitis on or around the eyelids can provide clues to the allergenic source. Dermatitis present around the eyelids and periorbital region with involvement of the bilateral upper and lower eyelids suggests direct exposure to a contact allergen, such as makeup or other cosmetic products.1 Unilateral involvement of only 1 eyelid can occur with ectopic transfer of allergens from the hands or nails.1,19 Involvement of the fingers or nails in addition to the eyelids may further suggest ectopic transfer, such as from allergens in nail polish.10 Unilateral eyelid dermatitis also could be caused by unique exposures such as a microscope or camera eyepiece.19 Distribution around the lower eyelids and upper cheeks is indicative of a drip or runoff pattern, which may result from an ophthalmic solution such as eye drops or contact lens solution.1,19 Finally, dermatitis affecting the upper eyelids along with the nasolabial folds and upper chest may suggest airborne contact dermatitis to fragrances or household cleaning products.1,11
Common Culprits of Eyelid ACD
Common causes of eyelid ACD include cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry.10,13,20 Within the broader category of cosmetics, allergens may be found in makeup and makeup removers, cosmetic applicators and brushes, soaps and cleansers, creams and sunscreens, antiaging products, hair products, nail polish and files, and hair removal products, among many others.10,13,16,20 Additionally, ophthalmologic and topical medications are common sources of ACD, including eyedrops, contact lens solution, and topical antibiotics.10,13,21 Costume jewelry commonly contains allergenic metals, which also can be found in eyelash curlers, eyeglasses, toys, and other household items.22,23 Finally, contact allergens can be found in items such as goggles, gloves, textiles, and a variety of other occupational and household exposures.
Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids occurs predominantly—but not exclusively—in females.16,20,24 This finding has been attributed to the traditionally greater use of cosmetics and fragrances among women; however, the use of skin care products among men is increasing, and recent studies have shown the eyelids to be a common location of facial contact dermatitis among men.16,24 Although eyelid dermatitis has not been specifically analyzed by sex, a retrospective analysis of 1332 male patients with facial dermatitis found the most common sites to be the face (not otherwise specified)(48.9%), eyelids (23.5%), and lips (12.6%). In this cohort, the most common allergens were surfactants in shampoos and paraphenylenediamine in hair dyes.24
Common Allergens
Common contact allergens among patients with ACD of the eyelids include metals, fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications.3,10,16,20,25-27 Sources of common contact allergens are reviewed in Table 1.

Metals—Metals are among the most common causes of ACD overall, and nickel frequently is reported as one of the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.16,27 A retrospective analysis of 2332 patients with eyelid dermatitis patch tested by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 1994 to 2016 found that 18.6% of patients with eyelid ACD had a clinically relevant nickel allergy. Sources of nickel exposure include jewelry, grooming devices, makeup and makeup applicators, and eyelash curlers, as well as direct transfer from the hands after contact with consumer products.16
Other metals that can cause ACD include cobalt (found in similar products to nickel) and gold. Gold often is associated with eyelid dermatitis, though its clinical relevance has been debated, as gold is a relatively inert metal that rarely is present in eye cosmetics and its ions are not displaced from objects and deposited on the skin via sweat in the same way as nickel.4,16,20,28-30 Despite this, studies have shown that gold is a common positive patch test reaction among patients with eyelid dermatitis, even in patients with no dermatitis at the site of contact with gold jewelry.20,29,31 Gold has been reported to be the most common allergen causing unilateral eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer.16,19,20,29 It has been proposed that titanium dioxide, present in many cosmetics and sunscreens, displaces gold allowing its release from jewelry, thereby liberating the fine gold ions and allowing them to desposit on the face and eyelids.30,31 Given the uncertain clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to gold, Warshaw at al16 recommend a 2- to 3-month trial of gold jewelry avoidance to establish relevance, and Ehrlich and Gold29 noted that avoidance of gold leads to improvement.
Fragrances—Fragrances represent a broad category of naturally occurring and man-made components that often are combined to produce a desired scent in personal care products.32 Essential oils and botanicals are both examples of natural fragrances.33 Fragrances are found in numerous products including makeup, hair products, and household cleaning supplies and represent some of the most common contact allergens.32 Common fragrance allergens include fragrance mixes I and II, hydroperoxides of linalool, and balsam of Peru.12,32,34 Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances typically manifests on the eyelids, face, or hands.33 Several studies have found fragrances to be among the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.3,12,20,25,34 Patch testing for fragrance allergy may include baseline series, supplemental fragrance series, and personal care products.32,35
Preservatives—Preservatives, including formaldehyde and formaldehyde releasers (eg, quaternium-15 and bronopol) and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone, may be found in personal care products such as makeup, makeup removers, emollients, shampoos, hair care products, and ophthalmologic solutions and are among the most common cosmetic sources of ACD.13,36-39 Preservatives are among the top allergens causing eyelid dermatitis.20 In particular, patch test positivity rates to methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone have been increasing in North America.40 Sensitization to preservatives may occur through direct skin contact or transfer from the hands.41
Acrylates—Acrylates are compounds derived from acrylic acid that may be found in acrylic and gel nails, eyelash extensions, and other adhesives and are frequent causes of eyelid ACD.4,10,42 Acrylate exposure may be cosmetic among consumers or occupational (eg, aestheticians).42,43 Acrylates on the nails may cause eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer from the hands and also may cause periungual dermatitis manifesting as nail bed erythema.10 Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is one of the more common eyelid ACD allergens, and studies have shown increasing prevalence of positive reaction rates to hydroxyethylmethacrylate.10,44Topical Medications—Contact allergies to topical medications are quite common, estimated to occur in 10% to 17% of patients undergoing patch testing.45 Both active and inactive ingredients of topical medications may be culprits in eyelid ACD. The most common topical medication allergens include antibiotics, steroids, local anesthetics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.45 Topical antibiotics such as neomycin and bacitracin represent some of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis4,10 and may be found in a variety of products, including antibacterial ointments and eye drops.1 Many ophthalmologic medications also contain corticosteroids, with the most common allergenic steroids being tixocortol pivalate (a marker for hydrocortisone allergy) and budesonide.10,20 Topical steroids pose a particular dilemma, as they can be either the source of or a treatment for ACD.10 Eye drops also may contain anesthetics, β-blockers, and antihistamines, as well as the preservative benzalkonium chloride, all of which may be contact allergens.21,39
Differential Diagnosis of Eyelid Dermatitis
Although ACD is reported to be the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, the differential diagnosis is broad, including endogenous inflammatory dermatoses and exogenous exposures (Table 2). Symptoms of eyelid ACD can be nonspecific (eg, erythema, pruritus), making diagnosis challenging.46

Atopic dermatitis represents another common cause of eyelid dermatitis, accounting for 14% to 39.5% of cases.3-5,49Atopic dermatitis of the eyelids classically manifests with lichenification of the medial aspects of the eyelids.50 Atopic dermatitis and ACD may be difficult to distinguish, as the 2 conditions appear clinically similar and can develop concomitantly.51 Additionally, atopic patients are likely to have comorbid allergic rhinitis and sensitivity to environmental allergens, which may lead to chronic eye scratching and lichenification.1,51 Clinical features of eyelid dermatitis suggesting allergic rhinitis and likely comorbid AD include creases in the lower eyelids (Dennie-Morgan lines) and periorbital hyperpigmentation (known as the allergic shiner) due to venous congestion.1,52
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction to Malassezia yeast that occurs in sebaceous areas such as the groin, scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, and nasolabial folds.1,53,54
Irritant contact dermatitis, a nonspecific inflammatory reaction caused by direct cell damage from external irritants, also may affect the eyelids and appear similar to ACD.1 It typically manifests with a burning or stinging sensation, as opposed to pruritus, and generally develops and resolves more rapidly than ACD.1 Personal care products are common causes of eyelid irritant contact dermatitis.16
Patch Testing for Eyelid ACD
The gold standard for diagnosis of ACD is patch testing, outlined by the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group.55-57 Patch testing generally is performed with standardized panels of allergens and can be customized either with supplemental panels based on unique exposures or with the patient’s own personal care products to increase the sensitivity of testing. Therefore, a thorough history is crucial to identifying potential allergens in a patient’s environment.
False negatives are possible, as the skin on the back may be thicker and less sensitive than the skin at the location of dermatitis.2,58 This is particularly relevant when using patch testing to diagnose ACD of the eyelids, where the skin is particularly thin and sensitive.2 Additionally, ingredients of ophthalmic medications are known to have an especially high false-negative rate with standard patch testing and may require repeated testing with higher drug concentrations or modified patch testing procedures (eg, open testing, scratch-patch testing).1,59
Treatment
Management of ACD involves allergen avoidance, typically dictated by patch test results.10 Allergen avoidance may be facilitated using online resources such as the Contact Allergen Management Program (https://www.acdscamp.org/) created by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.10,18 Patient counseling following patch testing is crucial to educating patients about sources of potential allergen exposures and strategies for avoidance. In the case of eyelid dermatitis, it is particularly important to consider exposure to airborne allergens such as fragrances.16 Fragrance avoidance is uniquely difficult, as labelling standards in the United States currently do not require disclosure of specific fragrance components.33 Additionally, products labelled as unscented may still contain fragrances. As such, some patients with fragrance allergy may need to carefully avoid all products containing fragrances.33
In addition to allergen avoidance, eyelid ACD may be treated with topical medications (eg, steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, Janus kinase inhibitors); however, these same topical medications also can cause ACD due to some ingredients such as propylene glycol.10 Topical steroids should be used with caution on the eyelids given the risk for atrophy, cataracts, and glaucoma.1
Final Interpretation
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic condition most frequently caused by ACD due to exposure to allergens in cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry, among many other potential sources. The most common allergens causing eyelid dermatitis include metals (particularly nickel), fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications. Eyelid ACD is diagnosed via patch testing, and the mainstay of treatment is strict allergen avoidance. Patient counseling is vital for successful allergen avoidance and resolution of eyelid ACD.
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic concern representing a broad group of inflammatory dermatoses and typically presenting as eczematous lesions on the eyelids.1 One of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis is thought to be allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), a type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction caused by exposure to external allergens.2 Although ACD can occur anywhere on the body, dermatitis on the face and eyelids is quite common.1,2 This article aims to explore the clinical manifestation, evaluation, and management of eyelid ACD.
Pathophysiology of Eyelid ACD
Studies have shown that ACD is the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, estimated to account for 46% to 72% of cases worldwide.3-6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a T cell–mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction to external antigens that manifests as eczematous lesions at the site of contact with the allergen that may spread.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common condition, and it is estimated that at least 20% of the general worldwide population has a contact allergy.8,9 Histologically, ACD manifests as spongiotic dermatitis, though this is not unique and also may be seen in atopic dermatitis (AD) and irritant contact dermatitis.2 Allergic contact dermatitis is diagnosed via epicutaneous patch testing, and treatment involves allergen avoidance with or without adjuvant topical and/or systemic immunomodulatory treatments.7
The eyelids are uniquely prone to the development of ACD given their thinner epidermis and increased susceptibility to irritation. They frequently are exposed to allergens through the direct topical route as well as indirectly via airborne exposure, rinse-down products (eg, shampoos), and substances transferred from an individual’s own hands. The occluded skin folds of the eyelids facilitate increased exposure to trapped allergens.10,11 Additionally, the skin of the eyelids is thin, flexible, highly vascularized, and lacking in subcutaneous tissue, making this area more susceptible to antigen penetration than other locations on the body.1,2,10,12,13
Clinical Manifestations
Eyelid ACD is more common in females than males, which is thought to be related to increased use of cosmetics and fragrances.1,3,12,14-16 Clinical manifestations may resemble eczematous papules and plaques.1 Eyelid ACD commonly spreads beyond the eyelid margin, which helps to differentiate it from AD and irritant contact dermatitis. Symptoms of ACD on the eyelids typically include pruritus, redness, swelling, tearing, scaling, and pain.2 Persistent untreated eyelid dermatitis can lead to eyelash loss, damage to meibomian glands, and hyperpigmentation.2,17,18
Patterns of Eyelid ACD
Allergic contact dermatitis on the eyelids can occur due to direct application of allergens onto the skin of the eyelids, runoff of products from the hair/scalp (eg, shampoo), transfer of allergens from the hands, or contact with airborne allergens.1,2,11,12 Some reports have suggested that eyelid ACD more often is caused by products applied to the scalp or face rather than those applied directly to the eyelids.11 Because the scalp and face are less reactive to contact allergens, in some cases the eyelids may be the only affected site.10,12,13
The specific pattern of dermatitis on or around the eyelids can provide clues to the allergenic source. Dermatitis present around the eyelids and periorbital region with involvement of the bilateral upper and lower eyelids suggests direct exposure to a contact allergen, such as makeup or other cosmetic products.1 Unilateral involvement of only 1 eyelid can occur with ectopic transfer of allergens from the hands or nails.1,19 Involvement of the fingers or nails in addition to the eyelids may further suggest ectopic transfer, such as from allergens in nail polish.10 Unilateral eyelid dermatitis also could be caused by unique exposures such as a microscope or camera eyepiece.19 Distribution around the lower eyelids and upper cheeks is indicative of a drip or runoff pattern, which may result from an ophthalmic solution such as eye drops or contact lens solution.1,19 Finally, dermatitis affecting the upper eyelids along with the nasolabial folds and upper chest may suggest airborne contact dermatitis to fragrances or household cleaning products.1,11
Common Culprits of Eyelid ACD
Common causes of eyelid ACD include cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry.10,13,20 Within the broader category of cosmetics, allergens may be found in makeup and makeup removers, cosmetic applicators and brushes, soaps and cleansers, creams and sunscreens, antiaging products, hair products, nail polish and files, and hair removal products, among many others.10,13,16,20 Additionally, ophthalmologic and topical medications are common sources of ACD, including eyedrops, contact lens solution, and topical antibiotics.10,13,21 Costume jewelry commonly contains allergenic metals, which also can be found in eyelash curlers, eyeglasses, toys, and other household items.22,23 Finally, contact allergens can be found in items such as goggles, gloves, textiles, and a variety of other occupational and household exposures.
Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids occurs predominantly—but not exclusively—in females.16,20,24 This finding has been attributed to the traditionally greater use of cosmetics and fragrances among women; however, the use of skin care products among men is increasing, and recent studies have shown the eyelids to be a common location of facial contact dermatitis among men.16,24 Although eyelid dermatitis has not been specifically analyzed by sex, a retrospective analysis of 1332 male patients with facial dermatitis found the most common sites to be the face (not otherwise specified)(48.9%), eyelids (23.5%), and lips (12.6%). In this cohort, the most common allergens were surfactants in shampoos and paraphenylenediamine in hair dyes.24
Common Allergens
Common contact allergens among patients with ACD of the eyelids include metals, fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications.3,10,16,20,25-27 Sources of common contact allergens are reviewed in Table 1.

Metals—Metals are among the most common causes of ACD overall, and nickel frequently is reported as one of the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.16,27 A retrospective analysis of 2332 patients with eyelid dermatitis patch tested by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 1994 to 2016 found that 18.6% of patients with eyelid ACD had a clinically relevant nickel allergy. Sources of nickel exposure include jewelry, grooming devices, makeup and makeup applicators, and eyelash curlers, as well as direct transfer from the hands after contact with consumer products.16
Other metals that can cause ACD include cobalt (found in similar products to nickel) and gold. Gold often is associated with eyelid dermatitis, though its clinical relevance has been debated, as gold is a relatively inert metal that rarely is present in eye cosmetics and its ions are not displaced from objects and deposited on the skin via sweat in the same way as nickel.4,16,20,28-30 Despite this, studies have shown that gold is a common positive patch test reaction among patients with eyelid dermatitis, even in patients with no dermatitis at the site of contact with gold jewelry.20,29,31 Gold has been reported to be the most common allergen causing unilateral eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer.16,19,20,29 It has been proposed that titanium dioxide, present in many cosmetics and sunscreens, displaces gold allowing its release from jewelry, thereby liberating the fine gold ions and allowing them to desposit on the face and eyelids.30,31 Given the uncertain clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to gold, Warshaw at al16 recommend a 2- to 3-month trial of gold jewelry avoidance to establish relevance, and Ehrlich and Gold29 noted that avoidance of gold leads to improvement.
Fragrances—Fragrances represent a broad category of naturally occurring and man-made components that often are combined to produce a desired scent in personal care products.32 Essential oils and botanicals are both examples of natural fragrances.33 Fragrances are found in numerous products including makeup, hair products, and household cleaning supplies and represent some of the most common contact allergens.32 Common fragrance allergens include fragrance mixes I and II, hydroperoxides of linalool, and balsam of Peru.12,32,34 Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances typically manifests on the eyelids, face, or hands.33 Several studies have found fragrances to be among the top contact allergens in patients with eyelid dermatitis.3,12,20,25,34 Patch testing for fragrance allergy may include baseline series, supplemental fragrance series, and personal care products.32,35
Preservatives—Preservatives, including formaldehyde and formaldehyde releasers (eg, quaternium-15 and bronopol) and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone, may be found in personal care products such as makeup, makeup removers, emollients, shampoos, hair care products, and ophthalmologic solutions and are among the most common cosmetic sources of ACD.13,36-39 Preservatives are among the top allergens causing eyelid dermatitis.20 In particular, patch test positivity rates to methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone have been increasing in North America.40 Sensitization to preservatives may occur through direct skin contact or transfer from the hands.41
Acrylates—Acrylates are compounds derived from acrylic acid that may be found in acrylic and gel nails, eyelash extensions, and other adhesives and are frequent causes of eyelid ACD.4,10,42 Acrylate exposure may be cosmetic among consumers or occupational (eg, aestheticians).42,43 Acrylates on the nails may cause eyelid dermatitis via ectopic transfer from the hands and also may cause periungual dermatitis manifesting as nail bed erythema.10 Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is one of the more common eyelid ACD allergens, and studies have shown increasing prevalence of positive reaction rates to hydroxyethylmethacrylate.10,44Topical Medications—Contact allergies to topical medications are quite common, estimated to occur in 10% to 17% of patients undergoing patch testing.45 Both active and inactive ingredients of topical medications may be culprits in eyelid ACD. The most common topical medication allergens include antibiotics, steroids, local anesthetics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.45 Topical antibiotics such as neomycin and bacitracin represent some of the most common causes of eyelid dermatitis4,10 and may be found in a variety of products, including antibacterial ointments and eye drops.1 Many ophthalmologic medications also contain corticosteroids, with the most common allergenic steroids being tixocortol pivalate (a marker for hydrocortisone allergy) and budesonide.10,20 Topical steroids pose a particular dilemma, as they can be either the source of or a treatment for ACD.10 Eye drops also may contain anesthetics, β-blockers, and antihistamines, as well as the preservative benzalkonium chloride, all of which may be contact allergens.21,39
Differential Diagnosis of Eyelid Dermatitis
Although ACD is reported to be the most common cause of eyelid dermatitis, the differential diagnosis is broad, including endogenous inflammatory dermatoses and exogenous exposures (Table 2). Symptoms of eyelid ACD can be nonspecific (eg, erythema, pruritus), making diagnosis challenging.46

Atopic dermatitis represents another common cause of eyelid dermatitis, accounting for 14% to 39.5% of cases.3-5,49Atopic dermatitis of the eyelids classically manifests with lichenification of the medial aspects of the eyelids.50 Atopic dermatitis and ACD may be difficult to distinguish, as the 2 conditions appear clinically similar and can develop concomitantly.51 Additionally, atopic patients are likely to have comorbid allergic rhinitis and sensitivity to environmental allergens, which may lead to chronic eye scratching and lichenification.1,51 Clinical features of eyelid dermatitis suggesting allergic rhinitis and likely comorbid AD include creases in the lower eyelids (Dennie-Morgan lines) and periorbital hyperpigmentation (known as the allergic shiner) due to venous congestion.1,52
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction to Malassezia yeast that occurs in sebaceous areas such as the groin, scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, and nasolabial folds.1,53,54
Irritant contact dermatitis, a nonspecific inflammatory reaction caused by direct cell damage from external irritants, also may affect the eyelids and appear similar to ACD.1 It typically manifests with a burning or stinging sensation, as opposed to pruritus, and generally develops and resolves more rapidly than ACD.1 Personal care products are common causes of eyelid irritant contact dermatitis.16
Patch Testing for Eyelid ACD
The gold standard for diagnosis of ACD is patch testing, outlined by the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group.55-57 Patch testing generally is performed with standardized panels of allergens and can be customized either with supplemental panels based on unique exposures or with the patient’s own personal care products to increase the sensitivity of testing. Therefore, a thorough history is crucial to identifying potential allergens in a patient’s environment.
False negatives are possible, as the skin on the back may be thicker and less sensitive than the skin at the location of dermatitis.2,58 This is particularly relevant when using patch testing to diagnose ACD of the eyelids, where the skin is particularly thin and sensitive.2 Additionally, ingredients of ophthalmic medications are known to have an especially high false-negative rate with standard patch testing and may require repeated testing with higher drug concentrations or modified patch testing procedures (eg, open testing, scratch-patch testing).1,59
Treatment
Management of ACD involves allergen avoidance, typically dictated by patch test results.10 Allergen avoidance may be facilitated using online resources such as the Contact Allergen Management Program (https://www.acdscamp.org/) created by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.10,18 Patient counseling following patch testing is crucial to educating patients about sources of potential allergen exposures and strategies for avoidance. In the case of eyelid dermatitis, it is particularly important to consider exposure to airborne allergens such as fragrances.16 Fragrance avoidance is uniquely difficult, as labelling standards in the United States currently do not require disclosure of specific fragrance components.33 Additionally, products labelled as unscented may still contain fragrances. As such, some patients with fragrance allergy may need to carefully avoid all products containing fragrances.33
In addition to allergen avoidance, eyelid ACD may be treated with topical medications (eg, steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, Janus kinase inhibitors); however, these same topical medications also can cause ACD due to some ingredients such as propylene glycol.10 Topical steroids should be used with caution on the eyelids given the risk for atrophy, cataracts, and glaucoma.1
Final Interpretation
Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic condition most frequently caused by ACD due to exposure to allergens in cosmetic products, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry, among many other potential sources. The most common allergens causing eyelid dermatitis include metals (particularly nickel), fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications. Eyelid ACD is diagnosed via patch testing, and the mainstay of treatment is strict allergen avoidance. Patient counseling is vital for successful allergen avoidance and resolution of eyelid ACD.
- Hine AM, Waldman RA, Grzybowski A, et al. Allergic disorders of the eyelid. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:476-480. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2023.08.002
- Turkiewicz M, Shah A, Yang YW, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids: an interdisciplinary review. Ocul Surf. 2023;28:124-130. doi:10.1016/j.jtos.2023.03.001
- Valsecchi R, Imberti G, Martino D, et al. Eyelid dermatitis: an evaluation of 150 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:143-147. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb05242.x
- Guin JD. Eyelid dermatitis: experience in 203 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:755-765. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.122736
- Nethercott JR, Nield G, Holness DL. A review of 79 cases of eyelid dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(2 pt 1):223-230. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70165-1
- Shah M, Lewis FM, Gawkrodger DJ. Facial dermatitis and eyelid dermatitis: a comparison of patch test results and final diagnoses. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:140-141. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02148.x
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- Adler BL, DeLeo VA. Allergic contact dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:364. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5639
- Huang CX, Yiannias JA, Killian JM, et al. Seven common allergen groups causing eyelid dermatitis: education and avoidance strategies. Clin Ophthalmol Auckl NZ. 2021;15:1477-1490. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S297754
- Rozas-Muñoz E, Gamé D, Serra-Baldrich E. Allergic contact dermatitis by anatomical regions: diagnostic clues. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas Engl Ed. 2018;109:485-507. doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2018.05.016
- Amin KA, Belsito DV. The aetiology of eyelid dermatitis: a 10-year retrospective analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:280-285. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00927.x
- Wolf R, Orion E, Tüzün Y. Periorbital (eyelid) dermatides. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:131-140. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.035
- Ockenfels HM, Seemann U, Goos M. Contact allergy in patients with periorbital eczema: an analysis of allergens. data recorded by the Information Network of the Departments of Dermatology. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1997;195:119-124. doi:10.1159/000245712
- Landeck L, John SM, Geier J. Periorbital dermatitis in 4779 patients—patch test results during a 10-year period. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:205-212. doi:10.1111/cod.12157
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Maibach HI, et al. Eyelid dermatitis in patients referred for patch testing: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:953-964. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.020
- McMonnies CW. Management of chronic habits of abnormal eye rubbing. Contact Lens Anterior Eye. 2008;31:95-102. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2007.07.008
- Chisholm SAM, Couch SM, Custer PL. Etiology and management of allergic eyelid dermatitis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33:248-250. doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000723
- Lewallen R, Feldman S, eds. Regional atlas of contact dermatitis. The Dermatologist. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://s3.amazonaws.com/HMP/hmp_ln/imported/Regional%20Atlas%20of%20Contact%20Dermatitis%20Book_lr.pdf
- Rietschel RL, Warshaw EM, Sasseville D, et al. Common contact allergens associated with eyelid dermatitis: data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2003-2004 study period. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2007;18:78-81. doi:10.2310/6620.2007.06041
- Mughal AA, Kalavala M. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:593-597; quiz 597-598. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04398.x
- Goossens A. Contact allergic reactions on the eyes and eyelids. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2004;292:11-17.
- Silverberg NB, Pelletier JL, Jacob SE, et al. Nickel allergic contact dermatitis: identification, treatment, and prevention. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20200628. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0628
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Maibach HI, et al. Facial dermatitis in male patients referred for patch testing. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:79-84. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3531
- Wenk KS, Ehrlich A. Fragrance series testing in eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:22-26. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d180f
- Crouse L, Ziemer C, Ziemer C, et al. Trends in eyelid dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2018;29:96-97. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000338
- Yazdanparast T, Nassiri Kashani M, Shamsipour M, et al. Contact allergens responsible for eyelid dermatitis in adults. J Dermatol. 2024;51:691-695. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.17140
- Fowler J, Taylor J, Storrs F, et al. Gold allergy in North America. Am J Contact Dermat. 2001;12:3-5.
- Ehrlich A, Belsito DV. Allergic contact dermatitis to gold. Cutis. 2000;65:323-326.
- Danesh M, Murase JE. Titanium dioxide induces eyelid dermatitis in patients allergic to gold. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E21. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.046
- Katta R. Common misconceptions in contact dermatitis counseling. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:2.
- De Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000463
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.009
- Warshaw EM, Zhang AJ, DeKoven JG, et al. Epidemiology of nickel sensitivity: retrospective cross-sectional analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data 1994-2014. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:701-713. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.058
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergen series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yim E, Baquerizo Nole KL, Tosti A. Contact dermatitis caused by preservatives. Dermatitis. 2014;25:215-231. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000061
- Alani JI, Davis MDP, Yiannias JA. Allergy to cosmetics. Dermatitis. 2013;24:283-290. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182a5d8bc
- Hamilton T, de Gannes GC. Allergic contact dermatitis to preservatives and fragrances in cosmetics. Skin Ther Lett. 2011;16:1-4.
- Ashton SJ, Mughal AA. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions: an update. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:480-483. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0033
- Reeder MJ, Warshaw E, Aravamuthan S, et al. Trends in the prevalence of methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in North America and Europe. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:267-274. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5991
- Herro EM, Elsaie ML, Nijhawan RI, et al. Recommendations for a screening series for allergic contact eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:17-21. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d191f
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Adv Dermatol Allergol Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Rodriguez I, George SE, Yu J, et al. Tackling acrylate allergy: the sticky truth. Cutis. 2023;112:282-286. doi:10.12788/cutis.0909
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019–2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.29017.jdk
- de Groot A. Allergic contact dermatitis from topical drugs: an overview. Dermatitis. 2021;32:197-213. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000737
- Zug KA, Palay DA, Rock B. Dermatologic diagnosis and treatment of itchy red eyelids. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996;40:293-306. doi:10.1016/s0039-6257(96)82004-2
- Beltrani VS. Eyelid dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001;1:380-388. doi:10.1007/s11882-001-0052-0
- Hirji SH, Maeng MM, Tran AQ, et al. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of the eyelid masquerading as dermatitis. Orbit Amst Neth. 2021;40:75-78. doi:10.1080/01676830.2020.1739080
- Svensson A, Möller H. Eyelid dermatitis: the role of atopy and contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1986;15:178-182. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1986.tb01321.x
- Papier A, Tuttle DJ, Mahar TJ. Differential diagnosis of the swollen red eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:1815-1824.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788cutis.0599
- Berger WE. Allergic rhinitis in children: diagnosis and management strategies. Paediatr Drugs. 2004;6:233-250. doi:10.2165/00148581-200406040-00003
- Singh A, Kansal NK, Kumawat D, et al. Ophthalmic manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis. Skinmed. 2023;21:397-401.
- Clark GW, Pope SM, Jaboori KA. Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91:185-190.
- Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI. Patch Testing and Prick Testing. Springer; 2012.
- Fregert S. Manual of Contact Dermatitis: On Behalf of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group. Munksgaard; 1974.
- Reeder M, Reck Atwater A. Patch testing 101, part 1: performing the test. Cutis. 2020;106:165-167. doi:10.12788/cutis.0093
- Wolf R, Perluk H. Failure of routine patch test results to detect eyelid dermatitis. Cutis. 1992;49:133-134.
- Grey KR, Warshaw EM. Allergic contact dermatitis to ophthalmic medications: relevant allergens and alternative testing methods. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:333-347. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000224
- Hine AM, Waldman RA, Grzybowski A, et al. Allergic disorders of the eyelid. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:476-480. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2023.08.002
- Turkiewicz M, Shah A, Yang YW, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids: an interdisciplinary review. Ocul Surf. 2023;28:124-130. doi:10.1016/j.jtos.2023.03.001
- Valsecchi R, Imberti G, Martino D, et al. Eyelid dermatitis: an evaluation of 150 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:143-147. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb05242.x
- Guin JD. Eyelid dermatitis: experience in 203 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:755-765. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.122736
- Nethercott JR, Nield G, Holness DL. A review of 79 cases of eyelid dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(2 pt 1):223-230. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70165-1
- Shah M, Lewis FM, Gawkrodger DJ. Facial dermatitis and eyelid dermatitis: a comparison of patch test results and final diagnoses. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:140-141. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02148.x
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- Adler BL, DeLeo VA. Allergic contact dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:364. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5639
- Huang CX, Yiannias JA, Killian JM, et al. Seven common allergen groups causing eyelid dermatitis: education and avoidance strategies. Clin Ophthalmol Auckl NZ. 2021;15:1477-1490. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S297754
- Rozas-Muñoz E, Gamé D, Serra-Baldrich E. Allergic contact dermatitis by anatomical regions: diagnostic clues. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas Engl Ed. 2018;109:485-507. doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2018.05.016
- Amin KA, Belsito DV. The aetiology of eyelid dermatitis: a 10-year retrospective analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;55:280-285. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00927.x
- Wolf R, Orion E, Tüzün Y. Periorbital (eyelid) dermatides. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:131-140. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.035
- Ockenfels HM, Seemann U, Goos M. Contact allergy in patients with periorbital eczema: an analysis of allergens. data recorded by the Information Network of the Departments of Dermatology. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1997;195:119-124. doi:10.1159/000245712
- Landeck L, John SM, Geier J. Periorbital dermatitis in 4779 patients—patch test results during a 10-year period. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:205-212. doi:10.1111/cod.12157
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Maibach HI, et al. Eyelid dermatitis in patients referred for patch testing: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1994-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:953-964. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.020
- McMonnies CW. Management of chronic habits of abnormal eye rubbing. Contact Lens Anterior Eye. 2008;31:95-102. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2007.07.008
- Chisholm SAM, Couch SM, Custer PL. Etiology and management of allergic eyelid dermatitis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33:248-250. doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000723
- Lewallen R, Feldman S, eds. Regional atlas of contact dermatitis. The Dermatologist. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://s3.amazonaws.com/HMP/hmp_ln/imported/Regional%20Atlas%20of%20Contact%20Dermatitis%20Book_lr.pdf
- Rietschel RL, Warshaw EM, Sasseville D, et al. Common contact allergens associated with eyelid dermatitis: data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2003-2004 study period. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2007;18:78-81. doi:10.2310/6620.2007.06041
- Mughal AA, Kalavala M. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:593-597; quiz 597-598. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04398.x
- Goossens A. Contact allergic reactions on the eyes and eyelids. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2004;292:11-17.
- Silverberg NB, Pelletier JL, Jacob SE, et al. Nickel allergic contact dermatitis: identification, treatment, and prevention. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20200628. doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0628
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Maibach HI, et al. Facial dermatitis in male patients referred for patch testing. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:79-84. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3531
- Wenk KS, Ehrlich A. Fragrance series testing in eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:22-26. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d180f
- Crouse L, Ziemer C, Ziemer C, et al. Trends in eyelid dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2018;29:96-97. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000338
- Yazdanparast T, Nassiri Kashani M, Shamsipour M, et al. Contact allergens responsible for eyelid dermatitis in adults. J Dermatol. 2024;51:691-695. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.17140
- Fowler J, Taylor J, Storrs F, et al. Gold allergy in North America. Am J Contact Dermat. 2001;12:3-5.
- Ehrlich A, Belsito DV. Allergic contact dermatitis to gold. Cutis. 2000;65:323-326.
- Danesh M, Murase JE. Titanium dioxide induces eyelid dermatitis in patients allergic to gold. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E21. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.046
- Katta R. Common misconceptions in contact dermatitis counseling. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:2.
- De Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000463
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.02.009
- Warshaw EM, Zhang AJ, DeKoven JG, et al. Epidemiology of nickel sensitivity: retrospective cross-sectional analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data 1994-2014. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:701-713. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.058
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergen series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yim E, Baquerizo Nole KL, Tosti A. Contact dermatitis caused by preservatives. Dermatitis. 2014;25:215-231. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000061
- Alani JI, Davis MDP, Yiannias JA. Allergy to cosmetics. Dermatitis. 2013;24:283-290. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182a5d8bc
- Hamilton T, de Gannes GC. Allergic contact dermatitis to preservatives and fragrances in cosmetics. Skin Ther Lett. 2011;16:1-4.
- Ashton SJ, Mughal AA. Contact dermatitis to ophthalmic solutions: an update. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:480-483. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0033
- Reeder MJ, Warshaw E, Aravamuthan S, et al. Trends in the prevalence of methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in North America and Europe. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:267-274. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5991
- Herro EM, Elsaie ML, Nijhawan RI, et al. Recommendations for a screening series for allergic contact eyelid dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2012;23:17-21. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31823d191f
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Adv Dermatol Allergol Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.95848
- Rodriguez I, George SE, Yu J, et al. Tackling acrylate allergy: the sticky truth. Cutis. 2023;112:282-286. doi:10.12788/cutis.0909
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019–2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.29017.jdk
- de Groot A. Allergic contact dermatitis from topical drugs: an overview. Dermatitis. 2021;32:197-213. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000737
- Zug KA, Palay DA, Rock B. Dermatologic diagnosis and treatment of itchy red eyelids. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996;40:293-306. doi:10.1016/s0039-6257(96)82004-2
- Beltrani VS. Eyelid dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001;1:380-388. doi:10.1007/s11882-001-0052-0
- Hirji SH, Maeng MM, Tran AQ, et al. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of the eyelid masquerading as dermatitis. Orbit Amst Neth. 2021;40:75-78. doi:10.1080/01676830.2020.1739080
- Svensson A, Möller H. Eyelid dermatitis: the role of atopy and contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1986;15:178-182. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1986.tb01321.x
- Papier A, Tuttle DJ, Mahar TJ. Differential diagnosis of the swollen red eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:1815-1824.
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788cutis.0599
- Berger WE. Allergic rhinitis in children: diagnosis and management strategies. Paediatr Drugs. 2004;6:233-250. doi:10.2165/00148581-200406040-00003
- Singh A, Kansal NK, Kumawat D, et al. Ophthalmic manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis. Skinmed. 2023;21:397-401.
- Clark GW, Pope SM, Jaboori KA. Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91:185-190.
- Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI. Patch Testing and Prick Testing. Springer; 2012.
- Fregert S. Manual of Contact Dermatitis: On Behalf of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group. Munksgaard; 1974.
- Reeder M, Reck Atwater A. Patch testing 101, part 1: performing the test. Cutis. 2020;106:165-167. doi:10.12788/cutis.0093
- Wolf R, Perluk H. Failure of routine patch test results to detect eyelid dermatitis. Cutis. 1992;49:133-134.
- Grey KR, Warshaw EM. Allergic contact dermatitis to ophthalmic medications: relevant allergens and alternative testing methods. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:333-347. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000224
Practice Points
- Eyelid dermatitis is a common dermatologic concern representing a broad range of inflammatory dermatoses, most often caused by allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
- The most common contact allergens associated with eyelid dermatitis are metals (particularly nickel), fragrances, preservatives, acrylates, and topical medications, which may be found in a variety of sources, including cosmetics, ophthalmic medications, nail lacquers, and jewelry.
- Eyelid ACD is diagnosed via patch testing, and management involves strict allergen avoidance.
A Whiff of Trouble: Navigating Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Fragrance
Fragrances are complex organic compounds that are sufficiently volatile to produce an odor—most often a pleasant one—or at times intended to neutralize unpleasant odors. They can be further divided into natural fragrances (eg, essential oils) and synthetic ones. Fragrances are found in abundance in our daily lives: in perfumes; colognes; lotions; shampoos; and an array of other personal, household, and even industrial products (Table). These exposures include products directly applied to the skin, rinsed off, or aerosolized. A single product often contains a multitude of different fragrances to create the scents we know and love. To many, fragrances can be an important part of everyday life or even a part of one’s identity. But that once-intoxicating aroma can transform into an itchy skin nightmare; fragrances are among the most common contact allergens.

Given the widespread prevalence of fragrances in so many products, understanding fragrance allergy and skillful avoidance is imperative. In this review, we explore important aspects of fragrance allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), including chemistry, epidemiology, patch test considerations, and management strategies for patients, with the goal of providing valuable clinical insights for treating physicians on how patients can embrace a fragrance-free lifestyle.
How Fragrances Act as Allergens
A plethora of chemicals emit odors, of which more than 2000 are used to create the fragranced products we see on our shelves today.1 For many of these fragrances, contact allergy develops because the fragrance acts as a hapten (ie, a small molecule that combines with a carrier protein to elicit an immune response).2 Some fragrance molecules require “activation” to be able to bind to proteins; these are known as prehaptens.3 For example, the natural fragrance linalool is generally considered nonallergenic in its initial form. However, once it is exposed to air, it may undergo oxidation to become linalool hydroperoxides, a well-established contact allergen. Some fragrances can become allergenic in the skin itself, often secondary to enzymatic reactions—these are known as prohaptens.3 However, most fragrances are directly reactive to skin proteins on the basis of chemical reactions such as Michael addition and Schiff base formation.4 In either case, the end result is that fragrance allergens, including essential oils, may cause skin sensitization and subsequent ACD.5,6
Epidemiology
Contact allergy to fragrances is not uncommon; in a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in 5 European countries, the prevalence in the general population was estimated to be as high as 2.6% and 1.9% among 3119 patients patch tested to fragrance mix I (FMI) and fragrance mix II (FMII), respectively.7 Studies in patients referred for patch testing have shown a higher 5% to 25% prevalence of fragrance allergy, largely depending on what population was evaluated.1 Factors such as sociocultural differences in frequency and types of fragrances used could contribute to this variation.
During patch testing, the primary fragrance screening allergens are FMI, FMII, and balsam of Peru (BOP)(Myroxylon pereirae resin).7 In recent years, hydroperoxides of linalool and limonene also have emerged as potentially important fragrance allergens.8 The frequencies of patch-test positivity of these allergens can be quite high in referral-based populations. In a study performed by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) from 2019 to 2020, frequencies of fragrance allergen positivity were 12.8% for FMI, 5.2% for FMII, 7.4% for BOP, 11.1% for hydroperoxides of linalool, and 3.5% for hydroperoxides of limonene.8 Additionally, it was noted that FMI and hydroperoxides of linalool were among the top 10 most frequently positive allergens.9 It should be kept in mind that NACDG studies are drawn from a referral population and not representative of the general population.
Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances can manifest anywhere on the body, but certain patterns are characteristic. A study by the NACDG analyzed fragrance and botanical patch test results in 24,246 patients and found that fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients more commonly had dermatitis involving the face (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.21), legs (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.06-1.41), and anal/genital areas (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52) and were less likely to have hand dermatitis (OR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95) compared with non–fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients.10 However, other studies have found that hand dermatitis is common among fragrance-allergic individuals.11-13
Fragrance allergy tends to be more common in women than men, which likely is attributable to differences in product use and exposure.10 The prevalence of fragrance allergy increases with age in both men and women, peaking at approximately 50 years of age, likely due to repeat exposure or age-related changes to the skin barrier or immune system.14
Occupational fragrance exposures are important to consider, and fragrance ACD is associated with hairdressers, beauticians, office workers exposed to aromatherapy diffusers, and food handlers.15 Less-obvious professions that involve exposure to fragrances used to cover up unwanted odors—such as working with industrial and cleaning chemicals or even metalworking—also have been reported to be associated with ACD.16
Patch Test Considerations
Patch testing is essential to confirm fragrance allergy and guide treatment, but because there are so many potential fragrance allergens, there is no perfect patch test strategy. In a standard patch test series, the most important screening allergens are considered to be FMI, FMII, and BOP; tested together, they are thought to detect a large proportion of cases of fragrance allergy. Strikingly, in a large European study (N=1951), patch testing with the fragrance markers in the baseline panel failed to detect more than 40% of cases of allergy compared to testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens.17 Other studies have reported that a smaller proportion of fragrance allergies are missed by using baseline screening allergens alone.18,19 Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides also are potentially important fragrance allergens to consider adding to the patch test panel, as unoxidized limonene and linalool commonly are used in many products and could theoretically undergo auto-oxidation under use conditions.8 However, because of the high number of irritant, questionable, and potentially false-positive reactions, the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology has recommended against adding these hydroperoxides to a standard screening tray for patch testing.20 It must be remembered that a positive patch test to a fragrance does not necessarily represent ACD unless the patient has a clinically relevant exposure to the allergen.21
In patients who test negative to the baseline fragrance-screening allergens and in whom a high degree of suspicion remains, further testing with supplemental fragrance allergens (commercially available from patch test suppliers) is warranted.17 The thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test (SmartPractice) includes FMI and BOP but not FMII or linalool or limonene hydroperoxides. More comprehensive patch test panels are available that include additional fragrances, such as the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series.22-24 It is important to remain vigilant and consider expanded patch testing if patients initially test negative but suspicion remains.
Furthermore, patch testing with the patient’s own products is an important consideration. Uter et al25 evaluated patch testing using patients’ perfumes, deodorants, and shaving lotions, and approximately 41% (53/129) of patients who tested positive to their own product tested negative for fragrance-screening allergens. Although it can be difficult to ascertain which exact component of a commercial product is the culprit, a positive patch test may still provide clinically relevant information for patients and treating physicians. In cases of questionable or weak-positive results, repeat testing or repeated open application tests can help re-evaluate suspected products.
Cross-reactivity should be considered when patch testing for fragrances. Atwater et al10 found that cross-reactivity between FMI, FMII, and BOP was common; for instance, approximately 40% of patients testing positive to FMII or BOP also had positive reactions to FMI (522/1182 and 768/1942, respectively). Understanding this concept is important because in some cases (as detailed below) patients will need to avoid all fragrances, not just the ones to which they have previously been exposed, given the limitations on fragrance labeling in the United States. However, this may change with the Modernization of Cosmetic Regulation Act of 2022.26
Avoiding Fragrances: Improving Patient Education and Outcomes
Once a relevant contact allergy to fragrance is established after patch testing, successful avoidance is critical but challenging, as there are numerous potential pitfalls. Missing just 1 hidden source of fragrance exposure will often be the difference between success or failure. Dermatologists play a crucial role in guiding patients through the intricate process of identifying and avoiding potential allergens.
Optimal Safety: Embracing a Fragrance-Free Lifestyle
For fragrance-allergic patients, it generally is safest to completely avoid fragrance.
First, if a patient only shows positive patch-test reactions to fragrance screening mixes (and not to the particular fragrances in these mixes), there is no way to be certain which fragrances the patient needs to avoid.
Second, even if specific fragrance allergens are identified, numerous chemically related fragrances to which the patient may be allergic are not commercially available for patch testing. One review provided evidence of 162 fragrance allergens that have been documented to cause contact allergy.1 Dermatologists generally patch test to screening mixtures and/or the 26 fragrance chemicals required on labels in European products (European Directive fragrance).27 Therefore, there are more than 100 known fragrance allergens that are not routinely tested to which patients could be allergic.
Third, certain fragrances, such as limonene and linalool, are found in many products with fragrance, and it is difficult to find products without these substances. Limonene and linalool themselves are not potent allergens; however, upon air exposure, they may auto-oxidize to hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool, which are increasingly common positive patch tests.19
Additionally, patients should be advised that many products labeled “fragrance free,” “unscented,” or “free and clear” are not truly fragrance free, and patients should not choose products based on these claims. There are no legal definitions for these claims in the United States, and industries are allowed to choose the definition they prefer. Numerous products labeled “unscented” use this term to indicate that the product had an odor, the company used a masking fragrance to hide the odor, and then the product can be considered unscented. In many holistic stores, most products labeled “fragrance free” are only free of artificial fragrances but contain essential oils. Of the 162 documented fragrance allergens, 80 are essential oils.6 Essential oils are perceived to be safe by the vast majority of the population because they are viewed as “natural” and “unprocessed” sources of fragrance.28 However, numerous allergenic terpenes have been discovered in essential oils, including functionalized variations of alcohols (eg, geraniol, bisabolol) and aldehydes (eg, citronellal).6 Essential oils also consist of nonterpenic compounds produced through the phenylpropanoids pathway, including eugenol and cinnamaldehyde. One review showed that most essential oils contain one or more European Directive fragrance.29 Therefore, many products labeled “unscented,” “fragrance free,” or “natural” are not free of fragrance and may be unsafe for fragrance-allergic patients.
Although not required, manufacturers sometimes voluntarily list one or more of the 162 currently identified fragrance allergens on product labels. Also, there are more than 50 potentially allergenic essential oils that can be listed on labels by their common names or by genus or species. In addition, there are synonyms for fragrance, such as aroma, parfum, perfume, and scent. Therefore, there are several hundred different ingredient names on labels that indicate the presence of fragrance, and patients are very unlikely to successfully identify fragrance-free products by trying to read product labels on their own.
Lastly, in the United States product labels only require products to state that they contain “fragrance” and do not mandate the listing of specific fragrances. If a patient is allergic to a specific fragrance, there is no way to determine if that fragrance is present in these products. This will change with the enactment of Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022, which empowers the US Food and Drug Administration to require manufacturers to disclose many, but not all, fragrance allergens on the labels of cosmetic and topical products.26
For all these reasons, patients should be advised to use a medical database to choose safe alternative products instead of trying to read labels themselves to avoid fragrance. The American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP) database (https://www.contactderm.org/resources/acds-camp) is designed to identify safe alternative products for patients with contact allergies. When CAMP is programmed to avoid “fragrance,” it will list only “safe” products free of all fragrances found in a comprehensive fragrance cross-reactor group.30 This customizable database is available as an application that can be downloaded onto a patient’s mobile device. Fragrance-allergic patients should be encouraged to use the CAMP application or other similar applications (eg, SkinSAFE)(https://www.skinsafeproducts.com/) to find all the products they use.
Potential Pitfalls in Fragrance Avoidance
Most physicians, even dermatologists, will not know which products on the market are fragrance free from a contact allergy standpoint. Patients should instruct their physicians to use the allergen-avoidance application of choice whenever recommending new topical products, whether prescription or nonprescription. In 2009, Nardelli and colleagues31 found that 10% of topical pharmaceutical products contained a total of 66 different fragrance substances.
Individuals who are allergic to fragrance also can react to fragrances used by close contacts (ie, consort dermatitis).32 Therefore, fragrance-allergic individuals who do not improve after changing their personal products should consider urging their spouses or significant others to choose their personal care products using an allergen-avoidance application. Also, physical contact with pets can cause reactions, and the use of a fragrance-free pet shampoo is recommended. Additionally, allergic individuals who are providing care for small children should select fragrance-free products for them.
Some of the most heavily fragranced products on the market are found at hair salons. One exposure to an allergen often can keep patients broken out for up to 4 weeks and occasionally longer, a typical frequency for salon visits—even if the individual is taking great care to avoid fragrance at home. Patients should be instructed to bring their own shampoo, conditioner, and styling products to the salon. These patients also should bring safe moisturizer and nail polish remover for manicures. Additionally, aromatherapy used in most massages can cause flare-ups, and it is recommended that allergic patients purchase fragrance-free massage oil to bring to their sessions.
Fragranced soaps and cleansers can leave a residue on the palmar surface of the hands and fingers. This residue may not meet the threshold for causing a reaction on the thick skin of these surfaces, but it is sufficient to passively transfer fragrance to other more sensitive areas, such as the eyelids. Passive transfer of fragrance can be a major source of allergen exposure and should not be overlooked. Allergic patients should be instructed to bring safe hand cleansers to friends’ houses, restaurants, or work.
Airborne fragrances in a patient’s environment can reach sufficient concentration to cause airborne contact dermatitis. In one case report, an Uber driver developed facial airborne ACD from a fragrance diffuser in his vehicle and his condition improved upon removing the diffuser.33 Therefore, patients should be instructed to avoid fragranced diffusers, scented candles, room deodorizers, incense, and wax melts.
Fragrance in household products also can be an issue. Fragrance-allergic patients should be instructed to choose fragrance-free cleaning products and to avoid fragranced wipes on surfaces that may be touched. In addition, they should be instructed to use fragrance-free laundry products. It is not required for household products in the United States to list their ingredients, and the majority do not have complete ingredient lists. Therefore, it is imperative that the patient use an allergen-avoidance application that identifies products that have full ingredient disclosure and are free of fragrance.
For individuals who enjoy perfume and/or cologne, it may be possible for them to resume use of these products in some cases after their condition has fully cleared with complete fragrance avoidance. They should avoid spraying products into the air or applying them directly onto the skin and should instead dip a cotton swab into the perfume/cologne and dab a small amount onto their clothing. This technique can sometimes satisfy the patient and improve compliance.
If a patient who is allergic to fragrance does not clear after 6 weeks of complete fragrance avoidance, it is worth considering systemic contact dermatitis due to ingestion of fragrance-related substances in foods.34 A large number of fragrance materials also are food flavorings. For patients allergic to a specific fragrance(s), systemic avoidance needs to be specific to the allergen, and the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association’s flavor ingredient library is most helpful (https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library). If the patient is allergic to the complex mixture BOP, a balsam-free diet can be attempted.35,36
Final Thoughts
Dermatologists must equip themselves with the knowledge to educate fragrance-allergic patients on proper avoidance. The multifaceted nature of fragrance avoidance requires a personalized approach, combining label scrutiny, utilization of a safe-product application, and tailored recommendations for specific situations. By guiding patients through these complexities, dermatologists can empower patients to manage their fragrance allergy and enhance their quality of life.
- de Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35.
- Uter W. Contact allergy to fragrances: current clinical and regulatory trends. Allergol Select. 2017;1:190-199.
- Karlberg AT, Börje A, Duus Johansen J, et al. Activation of non-sensitizing or low-sensitizing fragrance substances into potent sensitizers - prehaptens and prohaptens. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;69:323-334.
- Patlewicz GY, Wright ZM, Basketter DA, et al. Structure-activity relationships for selected fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:219-226. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470406
- Ward JM, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Essential oils debunked: separating fact from myth. Cutis. 2020;105:174-176.
- de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Essential oils, part IV: contact allergy. Dermatitis. 2016;27:170-175.
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch R, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of fragrance contact allergy in the general population of five European countries: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1411-1419
- Ogueta IA, Brared Christensson J, Giménez-Arnau E, et al. Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides review: pros and cons for routine patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:1-12.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019-2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104.
- Atwater AR, Ward JM, Liu B, et al. Fragrance- and botanical-related allergy and associated concomitant reactions: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data 2007-2016. Dermatitis. 2021;32:42-52.
- Tai V, Sharifah Rosniza SNC, Tang MM. Contact sensitization to fragrance allergen: a 5-year review in the Department of Dermatology, Hospital Kuala Lumpur. Med J Malaysia. 2023;78:583-588.
- Periyasamy MK, Sekar SC, Rai R. Analysis of hypersensitivity in fragrance series by patch testing. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:657-662.
- Heydorn S, Menné T, Johansen JD. Fragrance allergy and hand eczema - a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:59-66.
- Buckley DA, Rycroft RJG, White IR, et al. The frequency of fragrance allergy in patch-tested patients increases with their age. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:986-989.
- Montgomery RL, Agius R, Wilkinson SM, et al. UK trends of allergic occupational skin disease attributed to fragrances 1996-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:33-40.
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377.
- Mann J, McFadden JP, White JML, et al. Baseline series fragrance markers fail to predict contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:276-281.
- Vejanurug P, Tresukosol P, Sajjachareonpong P, et al. Fragrance allergy could be missed without patch testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;74:230-235.
- Sukakul T, Bruze M, Mowitz M, et al. Simultaneous patch testing with fragrance markers in the baseline series and the ingredients of fragrance mixes: an update from southern Sweden. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:514-523.
- Schubert S, Geier J, Brans R, et al; IVDK. Patch testing hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool in consecutive patients-results of the IVDK 2018-2020. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:85-94. doi:10.1111/cod.14332
- Storrs FJ. Fragrance. Dermatitis. 2007;18:3-7.
- T.R.U.E. test. SmartPractice website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.smartpractice.com/shop/category?id=581719&m=SPA ACDS
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32947457/
- North American 80 Comprehensive Series NAC-80. Chemotechnique MB Diagnostics AB website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.chemotechnique.se/products/national-series/north-american-80-comprehensive-series/
- Uter W, Geier J, Schnuch A, et al. Patch test results with patients’ own perfumes, deodorants and shaving lotions: results of the IVDK 1998-2002. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:374-379.
- Filley AR, Woodruff CM. The Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:629-631.
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2003/15/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 February 2003 amending Council Directive 76/768/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to cosmetic products (text with EEA relevance). November 3, 2003. Accessed June 7, 2024. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2003:066:0026:0035:en:PDF
- Sharmeen JB, Mahomoodally FM, Zengin G, et al. Essential oils as natural sources of fragrance compounds for cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021;26:666.
- Scheman A, Scheman N, Rakowski EM. European Directive fragrances in natural products. Dermatitis. 2014;25:51-55.
- Scheman A, Hipolito R, Severson D, et al. Contact allergy cross-reactions: retrospective clinical data and review of the literature. Dermatitis. 2017;28:128-140.
- Nardelli A, D’Hooghe E, Drieghe J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from fragrance components in specific topical pharmaceutical products in Belgium. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:303-313.
- Lee J, Guo S, Dinalo J, et al. Consort allergic contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2022;33:181-186.
- Perper M, Cervantes J, Eber AE, et al. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by fragrance diffusers in Uber cars. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:116-117.
- Nijhawan RI, Molenda M, Zirwas MJ, et al. Systemic contact dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:355-364.
- Salam TN, Fowler JF. Balsam-related systemic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:377-381.
- Scheman A, Rakowski EM, Chou V, et al. Balsam of Peru: past and future. Dermatitis. 2013;24:153-160.
Fragrances are complex organic compounds that are sufficiently volatile to produce an odor—most often a pleasant one—or at times intended to neutralize unpleasant odors. They can be further divided into natural fragrances (eg, essential oils) and synthetic ones. Fragrances are found in abundance in our daily lives: in perfumes; colognes; lotions; shampoos; and an array of other personal, household, and even industrial products (Table). These exposures include products directly applied to the skin, rinsed off, or aerosolized. A single product often contains a multitude of different fragrances to create the scents we know and love. To many, fragrances can be an important part of everyday life or even a part of one’s identity. But that once-intoxicating aroma can transform into an itchy skin nightmare; fragrances are among the most common contact allergens.

Given the widespread prevalence of fragrances in so many products, understanding fragrance allergy and skillful avoidance is imperative. In this review, we explore important aspects of fragrance allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), including chemistry, epidemiology, patch test considerations, and management strategies for patients, with the goal of providing valuable clinical insights for treating physicians on how patients can embrace a fragrance-free lifestyle.
How Fragrances Act as Allergens
A plethora of chemicals emit odors, of which more than 2000 are used to create the fragranced products we see on our shelves today.1 For many of these fragrances, contact allergy develops because the fragrance acts as a hapten (ie, a small molecule that combines with a carrier protein to elicit an immune response).2 Some fragrance molecules require “activation” to be able to bind to proteins; these are known as prehaptens.3 For example, the natural fragrance linalool is generally considered nonallergenic in its initial form. However, once it is exposed to air, it may undergo oxidation to become linalool hydroperoxides, a well-established contact allergen. Some fragrances can become allergenic in the skin itself, often secondary to enzymatic reactions—these are known as prohaptens.3 However, most fragrances are directly reactive to skin proteins on the basis of chemical reactions such as Michael addition and Schiff base formation.4 In either case, the end result is that fragrance allergens, including essential oils, may cause skin sensitization and subsequent ACD.5,6
Epidemiology
Contact allergy to fragrances is not uncommon; in a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in 5 European countries, the prevalence in the general population was estimated to be as high as 2.6% and 1.9% among 3119 patients patch tested to fragrance mix I (FMI) and fragrance mix II (FMII), respectively.7 Studies in patients referred for patch testing have shown a higher 5% to 25% prevalence of fragrance allergy, largely depending on what population was evaluated.1 Factors such as sociocultural differences in frequency and types of fragrances used could contribute to this variation.
During patch testing, the primary fragrance screening allergens are FMI, FMII, and balsam of Peru (BOP)(Myroxylon pereirae resin).7 In recent years, hydroperoxides of linalool and limonene also have emerged as potentially important fragrance allergens.8 The frequencies of patch-test positivity of these allergens can be quite high in referral-based populations. In a study performed by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) from 2019 to 2020, frequencies of fragrance allergen positivity were 12.8% for FMI, 5.2% for FMII, 7.4% for BOP, 11.1% for hydroperoxides of linalool, and 3.5% for hydroperoxides of limonene.8 Additionally, it was noted that FMI and hydroperoxides of linalool were among the top 10 most frequently positive allergens.9 It should be kept in mind that NACDG studies are drawn from a referral population and not representative of the general population.
Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances can manifest anywhere on the body, but certain patterns are characteristic. A study by the NACDG analyzed fragrance and botanical patch test results in 24,246 patients and found that fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients more commonly had dermatitis involving the face (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.21), legs (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.06-1.41), and anal/genital areas (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52) and were less likely to have hand dermatitis (OR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95) compared with non–fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients.10 However, other studies have found that hand dermatitis is common among fragrance-allergic individuals.11-13
Fragrance allergy tends to be more common in women than men, which likely is attributable to differences in product use and exposure.10 The prevalence of fragrance allergy increases with age in both men and women, peaking at approximately 50 years of age, likely due to repeat exposure or age-related changes to the skin barrier or immune system.14
Occupational fragrance exposures are important to consider, and fragrance ACD is associated with hairdressers, beauticians, office workers exposed to aromatherapy diffusers, and food handlers.15 Less-obvious professions that involve exposure to fragrances used to cover up unwanted odors—such as working with industrial and cleaning chemicals or even metalworking—also have been reported to be associated with ACD.16
Patch Test Considerations
Patch testing is essential to confirm fragrance allergy and guide treatment, but because there are so many potential fragrance allergens, there is no perfect patch test strategy. In a standard patch test series, the most important screening allergens are considered to be FMI, FMII, and BOP; tested together, they are thought to detect a large proportion of cases of fragrance allergy. Strikingly, in a large European study (N=1951), patch testing with the fragrance markers in the baseline panel failed to detect more than 40% of cases of allergy compared to testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens.17 Other studies have reported that a smaller proportion of fragrance allergies are missed by using baseline screening allergens alone.18,19 Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides also are potentially important fragrance allergens to consider adding to the patch test panel, as unoxidized limonene and linalool commonly are used in many products and could theoretically undergo auto-oxidation under use conditions.8 However, because of the high number of irritant, questionable, and potentially false-positive reactions, the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology has recommended against adding these hydroperoxides to a standard screening tray for patch testing.20 It must be remembered that a positive patch test to a fragrance does not necessarily represent ACD unless the patient has a clinically relevant exposure to the allergen.21
In patients who test negative to the baseline fragrance-screening allergens and in whom a high degree of suspicion remains, further testing with supplemental fragrance allergens (commercially available from patch test suppliers) is warranted.17 The thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test (SmartPractice) includes FMI and BOP but not FMII or linalool or limonene hydroperoxides. More comprehensive patch test panels are available that include additional fragrances, such as the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series.22-24 It is important to remain vigilant and consider expanded patch testing if patients initially test negative but suspicion remains.
Furthermore, patch testing with the patient’s own products is an important consideration. Uter et al25 evaluated patch testing using patients’ perfumes, deodorants, and shaving lotions, and approximately 41% (53/129) of patients who tested positive to their own product tested negative for fragrance-screening allergens. Although it can be difficult to ascertain which exact component of a commercial product is the culprit, a positive patch test may still provide clinically relevant information for patients and treating physicians. In cases of questionable or weak-positive results, repeat testing or repeated open application tests can help re-evaluate suspected products.
Cross-reactivity should be considered when patch testing for fragrances. Atwater et al10 found that cross-reactivity between FMI, FMII, and BOP was common; for instance, approximately 40% of patients testing positive to FMII or BOP also had positive reactions to FMI (522/1182 and 768/1942, respectively). Understanding this concept is important because in some cases (as detailed below) patients will need to avoid all fragrances, not just the ones to which they have previously been exposed, given the limitations on fragrance labeling in the United States. However, this may change with the Modernization of Cosmetic Regulation Act of 2022.26
Avoiding Fragrances: Improving Patient Education and Outcomes
Once a relevant contact allergy to fragrance is established after patch testing, successful avoidance is critical but challenging, as there are numerous potential pitfalls. Missing just 1 hidden source of fragrance exposure will often be the difference between success or failure. Dermatologists play a crucial role in guiding patients through the intricate process of identifying and avoiding potential allergens.
Optimal Safety: Embracing a Fragrance-Free Lifestyle
For fragrance-allergic patients, it generally is safest to completely avoid fragrance.
First, if a patient only shows positive patch-test reactions to fragrance screening mixes (and not to the particular fragrances in these mixes), there is no way to be certain which fragrances the patient needs to avoid.
Second, even if specific fragrance allergens are identified, numerous chemically related fragrances to which the patient may be allergic are not commercially available for patch testing. One review provided evidence of 162 fragrance allergens that have been documented to cause contact allergy.1 Dermatologists generally patch test to screening mixtures and/or the 26 fragrance chemicals required on labels in European products (European Directive fragrance).27 Therefore, there are more than 100 known fragrance allergens that are not routinely tested to which patients could be allergic.
Third, certain fragrances, such as limonene and linalool, are found in many products with fragrance, and it is difficult to find products without these substances. Limonene and linalool themselves are not potent allergens; however, upon air exposure, they may auto-oxidize to hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool, which are increasingly common positive patch tests.19
Additionally, patients should be advised that many products labeled “fragrance free,” “unscented,” or “free and clear” are not truly fragrance free, and patients should not choose products based on these claims. There are no legal definitions for these claims in the United States, and industries are allowed to choose the definition they prefer. Numerous products labeled “unscented” use this term to indicate that the product had an odor, the company used a masking fragrance to hide the odor, and then the product can be considered unscented. In many holistic stores, most products labeled “fragrance free” are only free of artificial fragrances but contain essential oils. Of the 162 documented fragrance allergens, 80 are essential oils.6 Essential oils are perceived to be safe by the vast majority of the population because they are viewed as “natural” and “unprocessed” sources of fragrance.28 However, numerous allergenic terpenes have been discovered in essential oils, including functionalized variations of alcohols (eg, geraniol, bisabolol) and aldehydes (eg, citronellal).6 Essential oils also consist of nonterpenic compounds produced through the phenylpropanoids pathway, including eugenol and cinnamaldehyde. One review showed that most essential oils contain one or more European Directive fragrance.29 Therefore, many products labeled “unscented,” “fragrance free,” or “natural” are not free of fragrance and may be unsafe for fragrance-allergic patients.
Although not required, manufacturers sometimes voluntarily list one or more of the 162 currently identified fragrance allergens on product labels. Also, there are more than 50 potentially allergenic essential oils that can be listed on labels by their common names or by genus or species. In addition, there are synonyms for fragrance, such as aroma, parfum, perfume, and scent. Therefore, there are several hundred different ingredient names on labels that indicate the presence of fragrance, and patients are very unlikely to successfully identify fragrance-free products by trying to read product labels on their own.
Lastly, in the United States product labels only require products to state that they contain “fragrance” and do not mandate the listing of specific fragrances. If a patient is allergic to a specific fragrance, there is no way to determine if that fragrance is present in these products. This will change with the enactment of Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022, which empowers the US Food and Drug Administration to require manufacturers to disclose many, but not all, fragrance allergens on the labels of cosmetic and topical products.26
For all these reasons, patients should be advised to use a medical database to choose safe alternative products instead of trying to read labels themselves to avoid fragrance. The American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP) database (https://www.contactderm.org/resources/acds-camp) is designed to identify safe alternative products for patients with contact allergies. When CAMP is programmed to avoid “fragrance,” it will list only “safe” products free of all fragrances found in a comprehensive fragrance cross-reactor group.30 This customizable database is available as an application that can be downloaded onto a patient’s mobile device. Fragrance-allergic patients should be encouraged to use the CAMP application or other similar applications (eg, SkinSAFE)(https://www.skinsafeproducts.com/) to find all the products they use.
Potential Pitfalls in Fragrance Avoidance
Most physicians, even dermatologists, will not know which products on the market are fragrance free from a contact allergy standpoint. Patients should instruct their physicians to use the allergen-avoidance application of choice whenever recommending new topical products, whether prescription or nonprescription. In 2009, Nardelli and colleagues31 found that 10% of topical pharmaceutical products contained a total of 66 different fragrance substances.
Individuals who are allergic to fragrance also can react to fragrances used by close contacts (ie, consort dermatitis).32 Therefore, fragrance-allergic individuals who do not improve after changing their personal products should consider urging their spouses or significant others to choose their personal care products using an allergen-avoidance application. Also, physical contact with pets can cause reactions, and the use of a fragrance-free pet shampoo is recommended. Additionally, allergic individuals who are providing care for small children should select fragrance-free products for them.
Some of the most heavily fragranced products on the market are found at hair salons. One exposure to an allergen often can keep patients broken out for up to 4 weeks and occasionally longer, a typical frequency for salon visits—even if the individual is taking great care to avoid fragrance at home. Patients should be instructed to bring their own shampoo, conditioner, and styling products to the salon. These patients also should bring safe moisturizer and nail polish remover for manicures. Additionally, aromatherapy used in most massages can cause flare-ups, and it is recommended that allergic patients purchase fragrance-free massage oil to bring to their sessions.
Fragranced soaps and cleansers can leave a residue on the palmar surface of the hands and fingers. This residue may not meet the threshold for causing a reaction on the thick skin of these surfaces, but it is sufficient to passively transfer fragrance to other more sensitive areas, such as the eyelids. Passive transfer of fragrance can be a major source of allergen exposure and should not be overlooked. Allergic patients should be instructed to bring safe hand cleansers to friends’ houses, restaurants, or work.
Airborne fragrances in a patient’s environment can reach sufficient concentration to cause airborne contact dermatitis. In one case report, an Uber driver developed facial airborne ACD from a fragrance diffuser in his vehicle and his condition improved upon removing the diffuser.33 Therefore, patients should be instructed to avoid fragranced diffusers, scented candles, room deodorizers, incense, and wax melts.
Fragrance in household products also can be an issue. Fragrance-allergic patients should be instructed to choose fragrance-free cleaning products and to avoid fragranced wipes on surfaces that may be touched. In addition, they should be instructed to use fragrance-free laundry products. It is not required for household products in the United States to list their ingredients, and the majority do not have complete ingredient lists. Therefore, it is imperative that the patient use an allergen-avoidance application that identifies products that have full ingredient disclosure and are free of fragrance.
For individuals who enjoy perfume and/or cologne, it may be possible for them to resume use of these products in some cases after their condition has fully cleared with complete fragrance avoidance. They should avoid spraying products into the air or applying them directly onto the skin and should instead dip a cotton swab into the perfume/cologne and dab a small amount onto their clothing. This technique can sometimes satisfy the patient and improve compliance.
If a patient who is allergic to fragrance does not clear after 6 weeks of complete fragrance avoidance, it is worth considering systemic contact dermatitis due to ingestion of fragrance-related substances in foods.34 A large number of fragrance materials also are food flavorings. For patients allergic to a specific fragrance(s), systemic avoidance needs to be specific to the allergen, and the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association’s flavor ingredient library is most helpful (https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library). If the patient is allergic to the complex mixture BOP, a balsam-free diet can be attempted.35,36
Final Thoughts
Dermatologists must equip themselves with the knowledge to educate fragrance-allergic patients on proper avoidance. The multifaceted nature of fragrance avoidance requires a personalized approach, combining label scrutiny, utilization of a safe-product application, and tailored recommendations for specific situations. By guiding patients through these complexities, dermatologists can empower patients to manage their fragrance allergy and enhance their quality of life.
Fragrances are complex organic compounds that are sufficiently volatile to produce an odor—most often a pleasant one—or at times intended to neutralize unpleasant odors. They can be further divided into natural fragrances (eg, essential oils) and synthetic ones. Fragrances are found in abundance in our daily lives: in perfumes; colognes; lotions; shampoos; and an array of other personal, household, and even industrial products (Table). These exposures include products directly applied to the skin, rinsed off, or aerosolized. A single product often contains a multitude of different fragrances to create the scents we know and love. To many, fragrances can be an important part of everyday life or even a part of one’s identity. But that once-intoxicating aroma can transform into an itchy skin nightmare; fragrances are among the most common contact allergens.

Given the widespread prevalence of fragrances in so many products, understanding fragrance allergy and skillful avoidance is imperative. In this review, we explore important aspects of fragrance allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), including chemistry, epidemiology, patch test considerations, and management strategies for patients, with the goal of providing valuable clinical insights for treating physicians on how patients can embrace a fragrance-free lifestyle.
How Fragrances Act as Allergens
A plethora of chemicals emit odors, of which more than 2000 are used to create the fragranced products we see on our shelves today.1 For many of these fragrances, contact allergy develops because the fragrance acts as a hapten (ie, a small molecule that combines with a carrier protein to elicit an immune response).2 Some fragrance molecules require “activation” to be able to bind to proteins; these are known as prehaptens.3 For example, the natural fragrance linalool is generally considered nonallergenic in its initial form. However, once it is exposed to air, it may undergo oxidation to become linalool hydroperoxides, a well-established contact allergen. Some fragrances can become allergenic in the skin itself, often secondary to enzymatic reactions—these are known as prohaptens.3 However, most fragrances are directly reactive to skin proteins on the basis of chemical reactions such as Michael addition and Schiff base formation.4 In either case, the end result is that fragrance allergens, including essential oils, may cause skin sensitization and subsequent ACD.5,6
Epidemiology
Contact allergy to fragrances is not uncommon; in a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in 5 European countries, the prevalence in the general population was estimated to be as high as 2.6% and 1.9% among 3119 patients patch tested to fragrance mix I (FMI) and fragrance mix II (FMII), respectively.7 Studies in patients referred for patch testing have shown a higher 5% to 25% prevalence of fragrance allergy, largely depending on what population was evaluated.1 Factors such as sociocultural differences in frequency and types of fragrances used could contribute to this variation.
During patch testing, the primary fragrance screening allergens are FMI, FMII, and balsam of Peru (BOP)(Myroxylon pereirae resin).7 In recent years, hydroperoxides of linalool and limonene also have emerged as potentially important fragrance allergens.8 The frequencies of patch-test positivity of these allergens can be quite high in referral-based populations. In a study performed by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) from 2019 to 2020, frequencies of fragrance allergen positivity were 12.8% for FMI, 5.2% for FMII, 7.4% for BOP, 11.1% for hydroperoxides of linalool, and 3.5% for hydroperoxides of limonene.8 Additionally, it was noted that FMI and hydroperoxides of linalool were among the top 10 most frequently positive allergens.9 It should be kept in mind that NACDG studies are drawn from a referral population and not representative of the general population.
Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances can manifest anywhere on the body, but certain patterns are characteristic. A study by the NACDG analyzed fragrance and botanical patch test results in 24,246 patients and found that fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients more commonly had dermatitis involving the face (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.21), legs (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.06-1.41), and anal/genital areas (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52) and were less likely to have hand dermatitis (OR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95) compared with non–fragrance/botanical-sensitive patients.10 However, other studies have found that hand dermatitis is common among fragrance-allergic individuals.11-13
Fragrance allergy tends to be more common in women than men, which likely is attributable to differences in product use and exposure.10 The prevalence of fragrance allergy increases with age in both men and women, peaking at approximately 50 years of age, likely due to repeat exposure or age-related changes to the skin barrier or immune system.14
Occupational fragrance exposures are important to consider, and fragrance ACD is associated with hairdressers, beauticians, office workers exposed to aromatherapy diffusers, and food handlers.15 Less-obvious professions that involve exposure to fragrances used to cover up unwanted odors—such as working with industrial and cleaning chemicals or even metalworking—also have been reported to be associated with ACD.16
Patch Test Considerations
Patch testing is essential to confirm fragrance allergy and guide treatment, but because there are so many potential fragrance allergens, there is no perfect patch test strategy. In a standard patch test series, the most important screening allergens are considered to be FMI, FMII, and BOP; tested together, they are thought to detect a large proportion of cases of fragrance allergy. Strikingly, in a large European study (N=1951), patch testing with the fragrance markers in the baseline panel failed to detect more than 40% of cases of allergy compared to testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens.17 Other studies have reported that a smaller proportion of fragrance allergies are missed by using baseline screening allergens alone.18,19 Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides also are potentially important fragrance allergens to consider adding to the patch test panel, as unoxidized limonene and linalool commonly are used in many products and could theoretically undergo auto-oxidation under use conditions.8 However, because of the high number of irritant, questionable, and potentially false-positive reactions, the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology has recommended against adding these hydroperoxides to a standard screening tray for patch testing.20 It must be remembered that a positive patch test to a fragrance does not necessarily represent ACD unless the patient has a clinically relevant exposure to the allergen.21
In patients who test negative to the baseline fragrance-screening allergens and in whom a high degree of suspicion remains, further testing with supplemental fragrance allergens (commercially available from patch test suppliers) is warranted.17 The thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test (SmartPractice) includes FMI and BOP but not FMII or linalool or limonene hydroperoxides. More comprehensive patch test panels are available that include additional fragrances, such as the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series.22-24 It is important to remain vigilant and consider expanded patch testing if patients initially test negative but suspicion remains.
Furthermore, patch testing with the patient’s own products is an important consideration. Uter et al25 evaluated patch testing using patients’ perfumes, deodorants, and shaving lotions, and approximately 41% (53/129) of patients who tested positive to their own product tested negative for fragrance-screening allergens. Although it can be difficult to ascertain which exact component of a commercial product is the culprit, a positive patch test may still provide clinically relevant information for patients and treating physicians. In cases of questionable or weak-positive results, repeat testing or repeated open application tests can help re-evaluate suspected products.
Cross-reactivity should be considered when patch testing for fragrances. Atwater et al10 found that cross-reactivity between FMI, FMII, and BOP was common; for instance, approximately 40% of patients testing positive to FMII or BOP also had positive reactions to FMI (522/1182 and 768/1942, respectively). Understanding this concept is important because in some cases (as detailed below) patients will need to avoid all fragrances, not just the ones to which they have previously been exposed, given the limitations on fragrance labeling in the United States. However, this may change with the Modernization of Cosmetic Regulation Act of 2022.26
Avoiding Fragrances: Improving Patient Education and Outcomes
Once a relevant contact allergy to fragrance is established after patch testing, successful avoidance is critical but challenging, as there are numerous potential pitfalls. Missing just 1 hidden source of fragrance exposure will often be the difference between success or failure. Dermatologists play a crucial role in guiding patients through the intricate process of identifying and avoiding potential allergens.
Optimal Safety: Embracing a Fragrance-Free Lifestyle
For fragrance-allergic patients, it generally is safest to completely avoid fragrance.
First, if a patient only shows positive patch-test reactions to fragrance screening mixes (and not to the particular fragrances in these mixes), there is no way to be certain which fragrances the patient needs to avoid.
Second, even if specific fragrance allergens are identified, numerous chemically related fragrances to which the patient may be allergic are not commercially available for patch testing. One review provided evidence of 162 fragrance allergens that have been documented to cause contact allergy.1 Dermatologists generally patch test to screening mixtures and/or the 26 fragrance chemicals required on labels in European products (European Directive fragrance).27 Therefore, there are more than 100 known fragrance allergens that are not routinely tested to which patients could be allergic.
Third, certain fragrances, such as limonene and linalool, are found in many products with fragrance, and it is difficult to find products without these substances. Limonene and linalool themselves are not potent allergens; however, upon air exposure, they may auto-oxidize to hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool, which are increasingly common positive patch tests.19
Additionally, patients should be advised that many products labeled “fragrance free,” “unscented,” or “free and clear” are not truly fragrance free, and patients should not choose products based on these claims. There are no legal definitions for these claims in the United States, and industries are allowed to choose the definition they prefer. Numerous products labeled “unscented” use this term to indicate that the product had an odor, the company used a masking fragrance to hide the odor, and then the product can be considered unscented. In many holistic stores, most products labeled “fragrance free” are only free of artificial fragrances but contain essential oils. Of the 162 documented fragrance allergens, 80 are essential oils.6 Essential oils are perceived to be safe by the vast majority of the population because they are viewed as “natural” and “unprocessed” sources of fragrance.28 However, numerous allergenic terpenes have been discovered in essential oils, including functionalized variations of alcohols (eg, geraniol, bisabolol) and aldehydes (eg, citronellal).6 Essential oils also consist of nonterpenic compounds produced through the phenylpropanoids pathway, including eugenol and cinnamaldehyde. One review showed that most essential oils contain one or more European Directive fragrance.29 Therefore, many products labeled “unscented,” “fragrance free,” or “natural” are not free of fragrance and may be unsafe for fragrance-allergic patients.
Although not required, manufacturers sometimes voluntarily list one or more of the 162 currently identified fragrance allergens on product labels. Also, there are more than 50 potentially allergenic essential oils that can be listed on labels by their common names or by genus or species. In addition, there are synonyms for fragrance, such as aroma, parfum, perfume, and scent. Therefore, there are several hundred different ingredient names on labels that indicate the presence of fragrance, and patients are very unlikely to successfully identify fragrance-free products by trying to read product labels on their own.
Lastly, in the United States product labels only require products to state that they contain “fragrance” and do not mandate the listing of specific fragrances. If a patient is allergic to a specific fragrance, there is no way to determine if that fragrance is present in these products. This will change with the enactment of Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022, which empowers the US Food and Drug Administration to require manufacturers to disclose many, but not all, fragrance allergens on the labels of cosmetic and topical products.26
For all these reasons, patients should be advised to use a medical database to choose safe alternative products instead of trying to read labels themselves to avoid fragrance. The American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP) database (https://www.contactderm.org/resources/acds-camp) is designed to identify safe alternative products for patients with contact allergies. When CAMP is programmed to avoid “fragrance,” it will list only “safe” products free of all fragrances found in a comprehensive fragrance cross-reactor group.30 This customizable database is available as an application that can be downloaded onto a patient’s mobile device. Fragrance-allergic patients should be encouraged to use the CAMP application or other similar applications (eg, SkinSAFE)(https://www.skinsafeproducts.com/) to find all the products they use.
Potential Pitfalls in Fragrance Avoidance
Most physicians, even dermatologists, will not know which products on the market are fragrance free from a contact allergy standpoint. Patients should instruct their physicians to use the allergen-avoidance application of choice whenever recommending new topical products, whether prescription or nonprescription. In 2009, Nardelli and colleagues31 found that 10% of topical pharmaceutical products contained a total of 66 different fragrance substances.
Individuals who are allergic to fragrance also can react to fragrances used by close contacts (ie, consort dermatitis).32 Therefore, fragrance-allergic individuals who do not improve after changing their personal products should consider urging their spouses or significant others to choose their personal care products using an allergen-avoidance application. Also, physical contact with pets can cause reactions, and the use of a fragrance-free pet shampoo is recommended. Additionally, allergic individuals who are providing care for small children should select fragrance-free products for them.
Some of the most heavily fragranced products on the market are found at hair salons. One exposure to an allergen often can keep patients broken out for up to 4 weeks and occasionally longer, a typical frequency for salon visits—even if the individual is taking great care to avoid fragrance at home. Patients should be instructed to bring their own shampoo, conditioner, and styling products to the salon. These patients also should bring safe moisturizer and nail polish remover for manicures. Additionally, aromatherapy used in most massages can cause flare-ups, and it is recommended that allergic patients purchase fragrance-free massage oil to bring to their sessions.
Fragranced soaps and cleansers can leave a residue on the palmar surface of the hands and fingers. This residue may not meet the threshold for causing a reaction on the thick skin of these surfaces, but it is sufficient to passively transfer fragrance to other more sensitive areas, such as the eyelids. Passive transfer of fragrance can be a major source of allergen exposure and should not be overlooked. Allergic patients should be instructed to bring safe hand cleansers to friends’ houses, restaurants, or work.
Airborne fragrances in a patient’s environment can reach sufficient concentration to cause airborne contact dermatitis. In one case report, an Uber driver developed facial airborne ACD from a fragrance diffuser in his vehicle and his condition improved upon removing the diffuser.33 Therefore, patients should be instructed to avoid fragranced diffusers, scented candles, room deodorizers, incense, and wax melts.
Fragrance in household products also can be an issue. Fragrance-allergic patients should be instructed to choose fragrance-free cleaning products and to avoid fragranced wipes on surfaces that may be touched. In addition, they should be instructed to use fragrance-free laundry products. It is not required for household products in the United States to list their ingredients, and the majority do not have complete ingredient lists. Therefore, it is imperative that the patient use an allergen-avoidance application that identifies products that have full ingredient disclosure and are free of fragrance.
For individuals who enjoy perfume and/or cologne, it may be possible for them to resume use of these products in some cases after their condition has fully cleared with complete fragrance avoidance. They should avoid spraying products into the air or applying them directly onto the skin and should instead dip a cotton swab into the perfume/cologne and dab a small amount onto their clothing. This technique can sometimes satisfy the patient and improve compliance.
If a patient who is allergic to fragrance does not clear after 6 weeks of complete fragrance avoidance, it is worth considering systemic contact dermatitis due to ingestion of fragrance-related substances in foods.34 A large number of fragrance materials also are food flavorings. For patients allergic to a specific fragrance(s), systemic avoidance needs to be specific to the allergen, and the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association’s flavor ingredient library is most helpful (https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library). If the patient is allergic to the complex mixture BOP, a balsam-free diet can be attempted.35,36
Final Thoughts
Dermatologists must equip themselves with the knowledge to educate fragrance-allergic patients on proper avoidance. The multifaceted nature of fragrance avoidance requires a personalized approach, combining label scrutiny, utilization of a safe-product application, and tailored recommendations for specific situations. By guiding patients through these complexities, dermatologists can empower patients to manage their fragrance allergy and enhance their quality of life.
- de Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35.
- Uter W. Contact allergy to fragrances: current clinical and regulatory trends. Allergol Select. 2017;1:190-199.
- Karlberg AT, Börje A, Duus Johansen J, et al. Activation of non-sensitizing or low-sensitizing fragrance substances into potent sensitizers - prehaptens and prohaptens. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;69:323-334.
- Patlewicz GY, Wright ZM, Basketter DA, et al. Structure-activity relationships for selected fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:219-226. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470406
- Ward JM, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Essential oils debunked: separating fact from myth. Cutis. 2020;105:174-176.
- de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Essential oils, part IV: contact allergy. Dermatitis. 2016;27:170-175.
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch R, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of fragrance contact allergy in the general population of five European countries: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1411-1419
- Ogueta IA, Brared Christensson J, Giménez-Arnau E, et al. Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides review: pros and cons for routine patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:1-12.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019-2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104.
- Atwater AR, Ward JM, Liu B, et al. Fragrance- and botanical-related allergy and associated concomitant reactions: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data 2007-2016. Dermatitis. 2021;32:42-52.
- Tai V, Sharifah Rosniza SNC, Tang MM. Contact sensitization to fragrance allergen: a 5-year review in the Department of Dermatology, Hospital Kuala Lumpur. Med J Malaysia. 2023;78:583-588.
- Periyasamy MK, Sekar SC, Rai R. Analysis of hypersensitivity in fragrance series by patch testing. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:657-662.
- Heydorn S, Menné T, Johansen JD. Fragrance allergy and hand eczema - a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:59-66.
- Buckley DA, Rycroft RJG, White IR, et al. The frequency of fragrance allergy in patch-tested patients increases with their age. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:986-989.
- Montgomery RL, Agius R, Wilkinson SM, et al. UK trends of allergic occupational skin disease attributed to fragrances 1996-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:33-40.
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377.
- Mann J, McFadden JP, White JML, et al. Baseline series fragrance markers fail to predict contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:276-281.
- Vejanurug P, Tresukosol P, Sajjachareonpong P, et al. Fragrance allergy could be missed without patch testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;74:230-235.
- Sukakul T, Bruze M, Mowitz M, et al. Simultaneous patch testing with fragrance markers in the baseline series and the ingredients of fragrance mixes: an update from southern Sweden. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:514-523.
- Schubert S, Geier J, Brans R, et al; IVDK. Patch testing hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool in consecutive patients-results of the IVDK 2018-2020. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:85-94. doi:10.1111/cod.14332
- Storrs FJ. Fragrance. Dermatitis. 2007;18:3-7.
- T.R.U.E. test. SmartPractice website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.smartpractice.com/shop/category?id=581719&m=SPA ACDS
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32947457/
- North American 80 Comprehensive Series NAC-80. Chemotechnique MB Diagnostics AB website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.chemotechnique.se/products/national-series/north-american-80-comprehensive-series/
- Uter W, Geier J, Schnuch A, et al. Patch test results with patients’ own perfumes, deodorants and shaving lotions: results of the IVDK 1998-2002. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:374-379.
- Filley AR, Woodruff CM. The Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:629-631.
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2003/15/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 February 2003 amending Council Directive 76/768/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to cosmetic products (text with EEA relevance). November 3, 2003. Accessed June 7, 2024. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2003:066:0026:0035:en:PDF
- Sharmeen JB, Mahomoodally FM, Zengin G, et al. Essential oils as natural sources of fragrance compounds for cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021;26:666.
- Scheman A, Scheman N, Rakowski EM. European Directive fragrances in natural products. Dermatitis. 2014;25:51-55.
- Scheman A, Hipolito R, Severson D, et al. Contact allergy cross-reactions: retrospective clinical data and review of the literature. Dermatitis. 2017;28:128-140.
- Nardelli A, D’Hooghe E, Drieghe J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from fragrance components in specific topical pharmaceutical products in Belgium. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:303-313.
- Lee J, Guo S, Dinalo J, et al. Consort allergic contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2022;33:181-186.
- Perper M, Cervantes J, Eber AE, et al. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by fragrance diffusers in Uber cars. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:116-117.
- Nijhawan RI, Molenda M, Zirwas MJ, et al. Systemic contact dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:355-364.
- Salam TN, Fowler JF. Balsam-related systemic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:377-381.
- Scheman A, Rakowski EM, Chou V, et al. Balsam of Peru: past and future. Dermatitis. 2013;24:153-160.
- de Groot AC. Fragrances: contact allergy and other adverse effects. Dermatitis. 2020;31:13-35.
- Uter W. Contact allergy to fragrances: current clinical and regulatory trends. Allergol Select. 2017;1:190-199.
- Karlberg AT, Börje A, Duus Johansen J, et al. Activation of non-sensitizing or low-sensitizing fragrance substances into potent sensitizers - prehaptens and prohaptens. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;69:323-334.
- Patlewicz GY, Wright ZM, Basketter DA, et al. Structure-activity relationships for selected fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:219-226. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470406
- Ward JM, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Essential oils debunked: separating fact from myth. Cutis. 2020;105:174-176.
- de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Essential oils, part IV: contact allergy. Dermatitis. 2016;27:170-175.
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch R, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of fragrance contact allergy in the general population of five European countries: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1411-1419
- Ogueta IA, Brared Christensson J, Giménez-Arnau E, et al. Limonene and linalool hydroperoxides review: pros and cons for routine patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:1-12.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019-2020. Dermatitis. 2023;34:90-104.
- Atwater AR, Ward JM, Liu B, et al. Fragrance- and botanical-related allergy and associated concomitant reactions: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data 2007-2016. Dermatitis. 2021;32:42-52.
- Tai V, Sharifah Rosniza SNC, Tang MM. Contact sensitization to fragrance allergen: a 5-year review in the Department of Dermatology, Hospital Kuala Lumpur. Med J Malaysia. 2023;78:583-588.
- Periyasamy MK, Sekar SC, Rai R. Analysis of hypersensitivity in fragrance series by patch testing. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:657-662.
- Heydorn S, Menné T, Johansen JD. Fragrance allergy and hand eczema - a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:59-66.
- Buckley DA, Rycroft RJG, White IR, et al. The frequency of fragrance allergy in patch-tested patients increases with their age. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:986-989.
- Montgomery RL, Agius R, Wilkinson SM, et al. UK trends of allergic occupational skin disease attributed to fragrances 1996-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:33-40.
- Reeder MJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to fragrances. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:371-377.
- Mann J, McFadden JP, White JML, et al. Baseline series fragrance markers fail to predict contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:276-281.
- Vejanurug P, Tresukosol P, Sajjachareonpong P, et al. Fragrance allergy could be missed without patch testing with 26 individual fragrance allergens. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;74:230-235.
- Sukakul T, Bruze M, Mowitz M, et al. Simultaneous patch testing with fragrance markers in the baseline series and the ingredients of fragrance mixes: an update from southern Sweden. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:514-523.
- Schubert S, Geier J, Brans R, et al; IVDK. Patch testing hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool in consecutive patients-results of the IVDK 2018-2020. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:85-94. doi:10.1111/cod.14332
- Storrs FJ. Fragrance. Dermatitis. 2007;18:3-7.
- T.R.U.E. test. SmartPractice website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.smartpractice.com/shop/category?id=581719&m=SPA ACDS
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32947457/
- North American 80 Comprehensive Series NAC-80. Chemotechnique MB Diagnostics AB website. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://www.chemotechnique.se/products/national-series/north-american-80-comprehensive-series/
- Uter W, Geier J, Schnuch A, et al. Patch test results with patients’ own perfumes, deodorants and shaving lotions: results of the IVDK 1998-2002. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:374-379.
- Filley AR, Woodruff CM. The Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:629-631.
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2003/15/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 February 2003 amending Council Directive 76/768/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to cosmetic products (text with EEA relevance). November 3, 2003. Accessed June 7, 2024. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2003:066:0026:0035:en:PDF
- Sharmeen JB, Mahomoodally FM, Zengin G, et al. Essential oils as natural sources of fragrance compounds for cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021;26:666.
- Scheman A, Scheman N, Rakowski EM. European Directive fragrances in natural products. Dermatitis. 2014;25:51-55.
- Scheman A, Hipolito R, Severson D, et al. Contact allergy cross-reactions: retrospective clinical data and review of the literature. Dermatitis. 2017;28:128-140.
- Nardelli A, D’Hooghe E, Drieghe J, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from fragrance components in specific topical pharmaceutical products in Belgium. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:303-313.
- Lee J, Guo S, Dinalo J, et al. Consort allergic contact dermatitis: a systematic review. Dermatitis. 2022;33:181-186.
- Perper M, Cervantes J, Eber AE, et al. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by fragrance diffusers in Uber cars. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:116-117.
- Nijhawan RI, Molenda M, Zirwas MJ, et al. Systemic contact dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:355-364.
- Salam TN, Fowler JF. Balsam-related systemic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:377-381.
- Scheman A, Rakowski EM, Chou V, et al. Balsam of Peru: past and future. Dermatitis. 2013;24:153-160.
Practice Points
- Fragrance allergy is common due to daily exposure from many sources, ranging from personal care products and cosmetics to cleaning products, foods/spices, and workplace materials.
- More than 100 different fragrances can cause contact allergy, but patch testing in routine practice usually is limited to a few key screening allergens with important limitations.
- Fragrance avoidance is challenging, and comprehensive patient education is critical, including the provision of a list of safe products that are truly fragrance free.
Tangled Truths: Unraveling the Link Between Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is an increasingly common diagnosis, especially in middle-aged women, and was first described by Kossard1 in 1994. It is a variant of lichen planopilaris (LPP), a progressive scarring cicatricial alopecia that affects the frontotemporal area of the scalp, eyebrows, and sometimes even body hair.1 Although its etiology remains unclear, genetic causes, drugs, hormones, and environmental exposures—including certain chemicals found in sunscreens—have been implicated in its pathogenesis.2,3 An association between contact allergy to ingredients in personal care products and FFA diagnosis has been suggested; however, there is no evidence of causality to date. In this article, we highlight the potential relationship between contact allergy and FFA as well as clinical considerations for management.
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Frontal fibrosing alopecia typically manifests with gradual symmetric recession of the frontal hairline leading to bandlike hair loss along the forehead, sometimes extending to the temporal region.4 Some patients may experience symptoms of scalp itching, burning, or tenderness that may precede or accompany the hair loss. Perifollicular erythema may be visible during the early stages and can be visualized on trichoscopy. The affected skin may appear pale and shiny and may have a smooth texture with a distinct lack of follicular openings. Aside from scalp involvement, other manifestations may include lichen planus pigmentosus, facial papules, body hair involvement, hypochromic lesions, diffuse redness on the face and neck, and prominent frontal veins.5 Although most FFA cases have characteristic clinical features and trichoscopic findings, biopsy for histopathologic examination is still recommended to confirm the diagnosis and ensure appropriate treatment.4 Classic histopathologic features include perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation, follicular destruction, and scarring.
Pathophysiology of FFA
The pathogenesis of FFA is thought to involve a variety of triggers, including immune-mediated inflammation, stress, genetics, hormones, and possibly environmental factors.6 Frontal fibrosing alopecia demonstrates considerable upregulation in cytotoxic helper T cells (TH1) and IFN-γ activity resulting in epithelial hair follicle stem cell apoptosis and replacement of normal epithelial tissue with fibrous tissue.7 There is some suspicion of genetic susceptibility in the onset of FFA as suggested by familial reports and genome-wide association studies.8-10 Hormonal and autoimmune factors also have been linked to FFA, including an increased risk for thyroid disease and the postmenopausal rise of androgen levels.6
Allergic Contact Dermatitis and FFA
Although they are 2 distinct conditions with differing etiologies, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) and FFA may share environmental triggers, especially in susceptible individuals. This may support the coexistence and potential association between ACD and FFA.
In one case report, a woman who developed facial eczema followed by FFA showed positive patch tests to the UV filters drometrizole trisiloxane and ethylhexyl salicylate, which were listed as ingredients in her sunscreens. Avoidance of these allergens reportedly led to notable improvement of the symptoms.11 Case-control studies have found an association between the use of facial sunscreen and risk for FFA.12 A 2016 questionnaire that assessed a wide range of lifestyle, social, and medical factors related to FFA found that the use of sunscreens was significantly higher in patients with FFA than controls (P<.001), pointing to sunscreens as a potential contributing factor, but further research has been inconclusive. A higher frequency of positive patch tests to hydroperoxides of linalool and balsam of Peru (BoP) in patients with FFA have been documented; however, a direct cause cannot be established.2
In a 2020 prospective study conducted at multiple international centers, 65% (13/20) of FFA patients and 37.5% (9/24) of the control group had a positive patch test reaction to one or more allergens (P=.003). The most common allergens that were identified included cobalt chloride (positive in 35% [7/20] of patients with FFA), nickel sulfate (25% [5/20]), and potassium dichromate (15% [3/20]).13 In a recent 2-year cohort study of 42 patients with FFA who were referred for patch testing, the most common allergens included gallates, hydroperoxides of linalool, and other fragrances.14 After a 3-month period of allergen avoidance, 70% (29/42) of patients had decreased scalp erythema on examination, indicating that avoiding relevant allergens may reduce local inflammation. Furthermore, 76.2% (32/42) of patients with FFA showed delayed-type hypersensitivity to allergens found in daily personal care products such as shampoos, sunscreens, and moisturizers, among others.14 Notably, the study lacked a control group. A case-control study of 36 Hispanic women conducted in Mexico also resulted in 83.3% (15/18) of patients with FFA and 55.5% (10/18) of controls having at least 1 positive patch test; in the FFA group, these included iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (16.7% [3/18]) and propolis (16.7% [3/18]).15
Most recently, a retrospective study conducted by Shtaynberger et al16 included 12 patients with LPP or FFA diagnosed via clinical findings or biopsy. It also included an age- and temporally matched control group tested with identical allergens. Among the 12 patients who had FFA/LPP, all had at least 1 allergen identified on patch testing. The most common allergens identified were propolis (positive in 50% [6/12] of patients with FFA/LPP), fragrance mix I (16%), and methylisothiazolinone (16% [2/12]). Follow-up data were available for 9 of these patients, of whom 6 (66.7%) experienced symptom improvement after 6 months of allergen avoidance. Four (44.4%) patients experienced decreased follicular redness or scaling, 2 (22.2%) patients experienced improved scalp pain/itch, 2 (22.2%) patients had stable/improved hair density, and 1 (1.1%) patient had decreased hair shedding. Although this suggests an environmental trigger for FFA/LPP, the authors stated that changes in patient treatment plans could have contributed to their improvement. The study also was limited by its small size and its overall generalizability.16
These studies have underscored the significance of patch testing in individuals diagnosed with FFA and have identified common allergens prevalent in this patient population. They have suggested that patients with FFA are more likely to have positive patch tests, and in some cases patients could experience improvements in scalp pruritus and erythema with allergen avoidance; however, we emphasize that a causal association between contact allergy and FFA remains unproven to date.
Most Common Allergens Pertinent to FFA
Preservatives—In some studies, patients with FFA have had positive patch tests to preservatives such as gallates and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI).14 Gallates are antioxidants that are used in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics due to their ability to inhibit oxidation and rancidity of fats and oils.17 The most common gallates include propyl gallate, octyl gallate, and dodecyl gallate. Propyl gallate is utilized in some waxy or oily cosmetics and personal care items including sunscreens, shampoos, conditioners, bar soaps, facial cleansers, and moisturizers.18 Typically, if patients have a positive patch test to one gallate, they should be advised to avoid all gallate compounds, as they can cross-react.
Similarly, MCI/MI can prevent product degradation through their antibacterial and antifungal properties. This combination of MCI and MI is used as an effective method of prolonging the shelf life of cosmetic products and commonly is found in sunscreens, facial moisturizing creams, shampoos, and conditioners19; it is banned from use in leave-on products in the European Union and Canada due to increased rates of contact allergy.20 In patients with FFA who commonly use facial sunscreen, preservatives can be a potential allergen exposure to consider.
Iodopropynyl butylcarbamate also is a preservative used in cosmetic formulations. Similar to MCI/MI, it is a potent fungicide and bactericide. This allergen can be found in hair care products, bodywashes, and other personal products.21
UV Light–Absorbing Agents—A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted in 2022 showed a significant (P<.001) association between sunscreen use and FFA.22 A majority of allergens identified on patch testing included UVA- and UVB-absorbing agents found in sunscreens and other products including cosmetics,11,12 such as drometrizole trisiloxane, ethylhexyl salicylate, avobenzone, and benzophenone-4. Drometrizole trisiloxane is a photostabilizer and a broad-spectrum UV filter that is not approved for use in sunscreens in the United States.23 It also is effective in stabilizing and preventing the degradation of avobenzone, a commonly used UVA filter.24
Fragrances—Fragrances are present in nearly every personal and cosmetic product, sometimes even in those advertised as being “fragrance free.” Hydroperoxides of linalool, BoP, and fragrance mix are common allergens that are found in a variety of personal care products including perfumes, cosmetics, and even household cleaning supplies.25 Simultaneous positive patch tests to BoP and fragrance mix are common due to shared components. Linalool can be found in various plants such as lavender, rose, bergamot, and jasmine.26 Upon air exposure, linalool auto-oxidizes to form allergenic hydroperoxides of linalool. Among patients with FFA, positive patch test reactions to fragrance chemicals are common and could be attributed to the use of fragranced hair products and facial cosmetics.
Hair Dyes and Bleaches—Allergic reactions to hair dyes and bleaches can result in severe ACD of the head/neck and, in rare cases, scarring alopecia.27 Chemicals found in these products include paraphenylenediamine (PPD) and ammonium persulfate. The most common hair dye allergen, PPD also is used in some rubbers and plastics. Ammonium persulfate is a chemical used in hair bleaches and to deodorize oils. One case study reported a patient with FFA who developed chemically induced vitiligo immediately after the use of a hair color product that contained PPD.28 However, without patch testing to confirm the presence of contact allergy, other patient-specific and environmental risk factors could have contributed to FFA in this case.
A Knot in the Truth
In this endeavor to untangle the truth, it should be remembered that at the time of writing, the purported association between FFA and ACD remains debatable. Contact dermatitis specialists have voiced that the association between FFA and ACD, especially with regard to sunscreen, cannot be supported due to the lack of sufficient evidence.29 A large majority of the research conducted on FFA and ACD is based on case reports and studies limited to a small sample size, and most of these patch test studies lack a control group. Felmingham et al30 noted that the recent epidemiology of FFA aligns with increased sunscreen use. They also highlighted the limitations of the aforementioned studies, which include misclassification of exposures in the control group2 and recall bias in questionnaire participants.2,12 The most pressing limitation that permeates through most of these studies is the temporal ambiguity associated with sunscreen use. A study by Dhana et al31 failed to specify whether increased sunscreen use preceded the diagnosis of FFA or if it stems from the need to protect more exposed skin as a consequence of disease. Broad sunscreen avoidance due to concern for a possible association with hair loss could have detrimental health implications by increasing the risk for photodamage and skin cancer.
FFA Patch Testing
The avoidance of pertinent allergens could be effective in reducing local inflammation, pruritus, and erythema in FFA.9,14,32 At our institution, we selectively patch test patients with FFA when there is a suspected contact allergy. Clinical features that may allude to a potential contact allergy include an erythematous or eczematous dermatitis or symptoms of pruritus along the scalp or eyebrows. If patients recall hair loss or symptoms after using a hair or facial product, then a potential contact allergy to these products could be considered. Patch testing in patients with FFA includes the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the cosmetic and hairdresser supplemental series, as well as an additional customized panel of 8 allergens as determined by patch testing experts at the University of Massachusetts, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Massachusetts General Hospital (private email communication, November 2017). Patch test readings are performed at 48 and 96 or 120 hours. Using the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program, patients are provided personalized safe product lists and avoidance strategies are discussed.
Final Interpretation
In a world where cosmetic products are ubiquitous, it is hard to define the potential role of contact allergens in the entangled pathogenesis of FFA and ACD. As evidenced by emerging literature that correlates the 2 conditions and their exacerbating factors, it is important for physicians to have a comprehensive diagnostic approach and heightened awareness for potential allergens at play in FFA (Table). The identification of certain chemicals and preservatives as potential triggers for FFA should emphasize the importance of patch testing in these patients; however, whether the positive reactions are relevant to the pathogenesis or disease course of FFA still is unknown. While these findings begin to unravel the intertwined causes of FFA and ACD, further research encompassing larger cohorts and prospective studies is imperative to solidify these associations, define concrete guidelines, and improve patient outcomes.

- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767. doi:10.1111/bjd.14535
- Debroy Kidambi A, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with facial moisturizers and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:260-261. doi:10.1111/bjd.15311
- Starace M, Orlando G, Iorizzo M, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic approaches to diagnosis of frontal fibrosing alopecia: results from a multicenter study of the International Dermoscopy Society. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:E2022080. doi:10.5826/dpc.1201a80
- Fechine COC, Valente NYS, Romiti R. Lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia: review and update of diagnostic and therapeutic features. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:348-357. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.08.008
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of disease pathogenesis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:911944. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.911944
- Del Duca E, Ruano Ruiz J, Pavel AB, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia shows robust T helper 1 and Janus kinase 3 skewing. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:1083-1093. doi:10.1111/bjd.19040
- Tziotzios C, Petridis C, Dand N, et al. Genome-wide association study in frontal fibrosing alopecia identifies four susceptibility loci including HLA-B*07:02. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1150. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09117-w
- Navarro‐Belmonte MR, Navarro‐López V, Ramírez‐Boscà A, et al. Case series of familial frontal fibrosing alopecia and a review of the literature. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:64-69. doi:10.1111/jocd.12125
- Cuenca-Barrales C, Ruiz-Villaverde R, Molina-Leyva A. Familial frontal fibrosing alopecia. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021;21:E320-E323. doi:10.18295/squmj.2021.21.02.025
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a woman thereafter diagnosed with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:215-217. doi:10.1111/cod.14370
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case–control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Rudnicka L, Rokni GR, Lotti T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: an international multi-center study. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13560. doi:10.1111/dth.13560
- Prasad S, Marks DH, Burns LJ, et al. Patch testing and contact allergen avoidance in patients with lichen planopilaris and/or frontal fibrosing alopecia: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:659-661. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.026
- Ocampo-Garza SS, Herz-Ruelas ME, Chavez-Alvarez S, et al. Association of frontal fibrosing alopecia and contact allergens in everyday skincare products in Hispanic females: a case-control study. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:776-778. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.09.013
- Shtaynberger B, Bruder P, Zippin JH. The prevalence of type iv hypersensitivity in patients with lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. Dermatitis. 2023;34:351-352. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000965
- Kahkeshani N, Farzaei F, Fotouhi M, et al. Pharmacological effects of gallic acid in health and diseases: a mechanistic review. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22:225-237. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2019.32806.7897
- Holcomb ZE, Van Noord MG, Atwater AR. Gallate contact dermatitis: product update and systematic review. Dermatitis. 2017;28:115-127. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000263
- Gorris A, Valencak J, Schremser V, et al. Contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone with three clinical presentations in one patient. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:162-164. doi:10.1111/cod.13384
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339. doi:10.1111/jdv.15875
- Batista M, Morgado F, Gonçalo M. Patch test reactivity to iodopropynyl butylcarbamate in consecutive patients during a period of 7 years. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:54-55. doi:10.1111/cod.13213
- Maghfour J, Ceresnie M, Olson J, et al. The association between frontal fibrosing alopecia, sunscreen, and moisturizers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:395-396. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.12.058
- Drometrizole trisiloxane. PubChem website. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9848888
- Hughes TM, Martin JA, Lewis VJ, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a sunscreen with concomitant sensitivities to other sunscreens. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:226-227. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.0566a.x
- de Groot AC. Myroxylon pereirae resin (balsam of Peru)—a critical review of the literature and assessment of the significance of positive patch test reactions and the usefulness of restrictive diets. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:335-353. doi:10.1111/cod.13263
- Sköld M, Börje A, Matura M, et al. Studies on the autoxidation and sensitizing capacity of the fragrance chemical linalool, identifying a linalool hydroperoxide. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;46:267-272. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.460504.x
- Dev T, Khan E, Patel U, et al. Cicatricial alopecia following allergic contact dermatitis from hair dyes: a rare clinical presentation. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:59-61. doi:10.1111/cod.13974
- De Souza B, Burns L, Senna MM. Frontal fibrosing alopecia preceding the development of vitiligo: a case report. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:154-155. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.011
- Abuav R, Shon W. Are sunscreen particles involved in frontal fibrosing alopecia?—a TEM-EDXS analysis on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded alopecia biopsies (pilot study). Am J Dermatopathol. 2022;44:E135. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000002317
- Felmingham C, Yip L, Tam M, et al. Allergy to sunscreen and leave-on facial products is not a likely causative mechanism in frontal fibrosing alopecia: perspective from contact allergy experts. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:481-482. doi:10.1111/bjd.18380
- Dhana A, Gumedze F, Khumalo N. Regarding “frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skincare products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study.” Br J Dermatol. 2016;176:836-837. doi:10.1111/bjd.15197
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Sensitization to benzyl salicylate and other allergens in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:423-430. doi:10.1111/cod.13763
- Rocha VB, Donati A, Contin LA, et al. Photopatch and patch testing in 63 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/bjd.16933
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is an increasingly common diagnosis, especially in middle-aged women, and was first described by Kossard1 in 1994. It is a variant of lichen planopilaris (LPP), a progressive scarring cicatricial alopecia that affects the frontotemporal area of the scalp, eyebrows, and sometimes even body hair.1 Although its etiology remains unclear, genetic causes, drugs, hormones, and environmental exposures—including certain chemicals found in sunscreens—have been implicated in its pathogenesis.2,3 An association between contact allergy to ingredients in personal care products and FFA diagnosis has been suggested; however, there is no evidence of causality to date. In this article, we highlight the potential relationship between contact allergy and FFA as well as clinical considerations for management.
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Frontal fibrosing alopecia typically manifests with gradual symmetric recession of the frontal hairline leading to bandlike hair loss along the forehead, sometimes extending to the temporal region.4 Some patients may experience symptoms of scalp itching, burning, or tenderness that may precede or accompany the hair loss. Perifollicular erythema may be visible during the early stages and can be visualized on trichoscopy. The affected skin may appear pale and shiny and may have a smooth texture with a distinct lack of follicular openings. Aside from scalp involvement, other manifestations may include lichen planus pigmentosus, facial papules, body hair involvement, hypochromic lesions, diffuse redness on the face and neck, and prominent frontal veins.5 Although most FFA cases have characteristic clinical features and trichoscopic findings, biopsy for histopathologic examination is still recommended to confirm the diagnosis and ensure appropriate treatment.4 Classic histopathologic features include perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation, follicular destruction, and scarring.
Pathophysiology of FFA
The pathogenesis of FFA is thought to involve a variety of triggers, including immune-mediated inflammation, stress, genetics, hormones, and possibly environmental factors.6 Frontal fibrosing alopecia demonstrates considerable upregulation in cytotoxic helper T cells (TH1) and IFN-γ activity resulting in epithelial hair follicle stem cell apoptosis and replacement of normal epithelial tissue with fibrous tissue.7 There is some suspicion of genetic susceptibility in the onset of FFA as suggested by familial reports and genome-wide association studies.8-10 Hormonal and autoimmune factors also have been linked to FFA, including an increased risk for thyroid disease and the postmenopausal rise of androgen levels.6
Allergic Contact Dermatitis and FFA
Although they are 2 distinct conditions with differing etiologies, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) and FFA may share environmental triggers, especially in susceptible individuals. This may support the coexistence and potential association between ACD and FFA.
In one case report, a woman who developed facial eczema followed by FFA showed positive patch tests to the UV filters drometrizole trisiloxane and ethylhexyl salicylate, which were listed as ingredients in her sunscreens. Avoidance of these allergens reportedly led to notable improvement of the symptoms.11 Case-control studies have found an association between the use of facial sunscreen and risk for FFA.12 A 2016 questionnaire that assessed a wide range of lifestyle, social, and medical factors related to FFA found that the use of sunscreens was significantly higher in patients with FFA than controls (P<.001), pointing to sunscreens as a potential contributing factor, but further research has been inconclusive. A higher frequency of positive patch tests to hydroperoxides of linalool and balsam of Peru (BoP) in patients with FFA have been documented; however, a direct cause cannot be established.2
In a 2020 prospective study conducted at multiple international centers, 65% (13/20) of FFA patients and 37.5% (9/24) of the control group had a positive patch test reaction to one or more allergens (P=.003). The most common allergens that were identified included cobalt chloride (positive in 35% [7/20] of patients with FFA), nickel sulfate (25% [5/20]), and potassium dichromate (15% [3/20]).13 In a recent 2-year cohort study of 42 patients with FFA who were referred for patch testing, the most common allergens included gallates, hydroperoxides of linalool, and other fragrances.14 After a 3-month period of allergen avoidance, 70% (29/42) of patients had decreased scalp erythema on examination, indicating that avoiding relevant allergens may reduce local inflammation. Furthermore, 76.2% (32/42) of patients with FFA showed delayed-type hypersensitivity to allergens found in daily personal care products such as shampoos, sunscreens, and moisturizers, among others.14 Notably, the study lacked a control group. A case-control study of 36 Hispanic women conducted in Mexico also resulted in 83.3% (15/18) of patients with FFA and 55.5% (10/18) of controls having at least 1 positive patch test; in the FFA group, these included iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (16.7% [3/18]) and propolis (16.7% [3/18]).15
Most recently, a retrospective study conducted by Shtaynberger et al16 included 12 patients with LPP or FFA diagnosed via clinical findings or biopsy. It also included an age- and temporally matched control group tested with identical allergens. Among the 12 patients who had FFA/LPP, all had at least 1 allergen identified on patch testing. The most common allergens identified were propolis (positive in 50% [6/12] of patients with FFA/LPP), fragrance mix I (16%), and methylisothiazolinone (16% [2/12]). Follow-up data were available for 9 of these patients, of whom 6 (66.7%) experienced symptom improvement after 6 months of allergen avoidance. Four (44.4%) patients experienced decreased follicular redness or scaling, 2 (22.2%) patients experienced improved scalp pain/itch, 2 (22.2%) patients had stable/improved hair density, and 1 (1.1%) patient had decreased hair shedding. Although this suggests an environmental trigger for FFA/LPP, the authors stated that changes in patient treatment plans could have contributed to their improvement. The study also was limited by its small size and its overall generalizability.16
These studies have underscored the significance of patch testing in individuals diagnosed with FFA and have identified common allergens prevalent in this patient population. They have suggested that patients with FFA are more likely to have positive patch tests, and in some cases patients could experience improvements in scalp pruritus and erythema with allergen avoidance; however, we emphasize that a causal association between contact allergy and FFA remains unproven to date.
Most Common Allergens Pertinent to FFA
Preservatives—In some studies, patients with FFA have had positive patch tests to preservatives such as gallates and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI).14 Gallates are antioxidants that are used in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics due to their ability to inhibit oxidation and rancidity of fats and oils.17 The most common gallates include propyl gallate, octyl gallate, and dodecyl gallate. Propyl gallate is utilized in some waxy or oily cosmetics and personal care items including sunscreens, shampoos, conditioners, bar soaps, facial cleansers, and moisturizers.18 Typically, if patients have a positive patch test to one gallate, they should be advised to avoid all gallate compounds, as they can cross-react.
Similarly, MCI/MI can prevent product degradation through their antibacterial and antifungal properties. This combination of MCI and MI is used as an effective method of prolonging the shelf life of cosmetic products and commonly is found in sunscreens, facial moisturizing creams, shampoos, and conditioners19; it is banned from use in leave-on products in the European Union and Canada due to increased rates of contact allergy.20 In patients with FFA who commonly use facial sunscreen, preservatives can be a potential allergen exposure to consider.
Iodopropynyl butylcarbamate also is a preservative used in cosmetic formulations. Similar to MCI/MI, it is a potent fungicide and bactericide. This allergen can be found in hair care products, bodywashes, and other personal products.21
UV Light–Absorbing Agents—A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted in 2022 showed a significant (P<.001) association between sunscreen use and FFA.22 A majority of allergens identified on patch testing included UVA- and UVB-absorbing agents found in sunscreens and other products including cosmetics,11,12 such as drometrizole trisiloxane, ethylhexyl salicylate, avobenzone, and benzophenone-4. Drometrizole trisiloxane is a photostabilizer and a broad-spectrum UV filter that is not approved for use in sunscreens in the United States.23 It also is effective in stabilizing and preventing the degradation of avobenzone, a commonly used UVA filter.24
Fragrances—Fragrances are present in nearly every personal and cosmetic product, sometimes even in those advertised as being “fragrance free.” Hydroperoxides of linalool, BoP, and fragrance mix are common allergens that are found in a variety of personal care products including perfumes, cosmetics, and even household cleaning supplies.25 Simultaneous positive patch tests to BoP and fragrance mix are common due to shared components. Linalool can be found in various plants such as lavender, rose, bergamot, and jasmine.26 Upon air exposure, linalool auto-oxidizes to form allergenic hydroperoxides of linalool. Among patients with FFA, positive patch test reactions to fragrance chemicals are common and could be attributed to the use of fragranced hair products and facial cosmetics.
Hair Dyes and Bleaches—Allergic reactions to hair dyes and bleaches can result in severe ACD of the head/neck and, in rare cases, scarring alopecia.27 Chemicals found in these products include paraphenylenediamine (PPD) and ammonium persulfate. The most common hair dye allergen, PPD also is used in some rubbers and plastics. Ammonium persulfate is a chemical used in hair bleaches and to deodorize oils. One case study reported a patient with FFA who developed chemically induced vitiligo immediately after the use of a hair color product that contained PPD.28 However, without patch testing to confirm the presence of contact allergy, other patient-specific and environmental risk factors could have contributed to FFA in this case.
A Knot in the Truth
In this endeavor to untangle the truth, it should be remembered that at the time of writing, the purported association between FFA and ACD remains debatable. Contact dermatitis specialists have voiced that the association between FFA and ACD, especially with regard to sunscreen, cannot be supported due to the lack of sufficient evidence.29 A large majority of the research conducted on FFA and ACD is based on case reports and studies limited to a small sample size, and most of these patch test studies lack a control group. Felmingham et al30 noted that the recent epidemiology of FFA aligns with increased sunscreen use. They also highlighted the limitations of the aforementioned studies, which include misclassification of exposures in the control group2 and recall bias in questionnaire participants.2,12 The most pressing limitation that permeates through most of these studies is the temporal ambiguity associated with sunscreen use. A study by Dhana et al31 failed to specify whether increased sunscreen use preceded the diagnosis of FFA or if it stems from the need to protect more exposed skin as a consequence of disease. Broad sunscreen avoidance due to concern for a possible association with hair loss could have detrimental health implications by increasing the risk for photodamage and skin cancer.
FFA Patch Testing
The avoidance of pertinent allergens could be effective in reducing local inflammation, pruritus, and erythema in FFA.9,14,32 At our institution, we selectively patch test patients with FFA when there is a suspected contact allergy. Clinical features that may allude to a potential contact allergy include an erythematous or eczematous dermatitis or symptoms of pruritus along the scalp or eyebrows. If patients recall hair loss or symptoms after using a hair or facial product, then a potential contact allergy to these products could be considered. Patch testing in patients with FFA includes the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the cosmetic and hairdresser supplemental series, as well as an additional customized panel of 8 allergens as determined by patch testing experts at the University of Massachusetts, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Massachusetts General Hospital (private email communication, November 2017). Patch test readings are performed at 48 and 96 or 120 hours. Using the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program, patients are provided personalized safe product lists and avoidance strategies are discussed.
Final Interpretation
In a world where cosmetic products are ubiquitous, it is hard to define the potential role of contact allergens in the entangled pathogenesis of FFA and ACD. As evidenced by emerging literature that correlates the 2 conditions and their exacerbating factors, it is important for physicians to have a comprehensive diagnostic approach and heightened awareness for potential allergens at play in FFA (Table). The identification of certain chemicals and preservatives as potential triggers for FFA should emphasize the importance of patch testing in these patients; however, whether the positive reactions are relevant to the pathogenesis or disease course of FFA still is unknown. While these findings begin to unravel the intertwined causes of FFA and ACD, further research encompassing larger cohorts and prospective studies is imperative to solidify these associations, define concrete guidelines, and improve patient outcomes.

Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is an increasingly common diagnosis, especially in middle-aged women, and was first described by Kossard1 in 1994. It is a variant of lichen planopilaris (LPP), a progressive scarring cicatricial alopecia that affects the frontotemporal area of the scalp, eyebrows, and sometimes even body hair.1 Although its etiology remains unclear, genetic causes, drugs, hormones, and environmental exposures—including certain chemicals found in sunscreens—have been implicated in its pathogenesis.2,3 An association between contact allergy to ingredients in personal care products and FFA diagnosis has been suggested; however, there is no evidence of causality to date. In this article, we highlight the potential relationship between contact allergy and FFA as well as clinical considerations for management.
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Frontal fibrosing alopecia typically manifests with gradual symmetric recession of the frontal hairline leading to bandlike hair loss along the forehead, sometimes extending to the temporal region.4 Some patients may experience symptoms of scalp itching, burning, or tenderness that may precede or accompany the hair loss. Perifollicular erythema may be visible during the early stages and can be visualized on trichoscopy. The affected skin may appear pale and shiny and may have a smooth texture with a distinct lack of follicular openings. Aside from scalp involvement, other manifestations may include lichen planus pigmentosus, facial papules, body hair involvement, hypochromic lesions, diffuse redness on the face and neck, and prominent frontal veins.5 Although most FFA cases have characteristic clinical features and trichoscopic findings, biopsy for histopathologic examination is still recommended to confirm the diagnosis and ensure appropriate treatment.4 Classic histopathologic features include perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation, follicular destruction, and scarring.
Pathophysiology of FFA
The pathogenesis of FFA is thought to involve a variety of triggers, including immune-mediated inflammation, stress, genetics, hormones, and possibly environmental factors.6 Frontal fibrosing alopecia demonstrates considerable upregulation in cytotoxic helper T cells (TH1) and IFN-γ activity resulting in epithelial hair follicle stem cell apoptosis and replacement of normal epithelial tissue with fibrous tissue.7 There is some suspicion of genetic susceptibility in the onset of FFA as suggested by familial reports and genome-wide association studies.8-10 Hormonal and autoimmune factors also have been linked to FFA, including an increased risk for thyroid disease and the postmenopausal rise of androgen levels.6
Allergic Contact Dermatitis and FFA
Although they are 2 distinct conditions with differing etiologies, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) and FFA may share environmental triggers, especially in susceptible individuals. This may support the coexistence and potential association between ACD and FFA.
In one case report, a woman who developed facial eczema followed by FFA showed positive patch tests to the UV filters drometrizole trisiloxane and ethylhexyl salicylate, which were listed as ingredients in her sunscreens. Avoidance of these allergens reportedly led to notable improvement of the symptoms.11 Case-control studies have found an association between the use of facial sunscreen and risk for FFA.12 A 2016 questionnaire that assessed a wide range of lifestyle, social, and medical factors related to FFA found that the use of sunscreens was significantly higher in patients with FFA than controls (P<.001), pointing to sunscreens as a potential contributing factor, but further research has been inconclusive. A higher frequency of positive patch tests to hydroperoxides of linalool and balsam of Peru (BoP) in patients with FFA have been documented; however, a direct cause cannot be established.2
In a 2020 prospective study conducted at multiple international centers, 65% (13/20) of FFA patients and 37.5% (9/24) of the control group had a positive patch test reaction to one or more allergens (P=.003). The most common allergens that were identified included cobalt chloride (positive in 35% [7/20] of patients with FFA), nickel sulfate (25% [5/20]), and potassium dichromate (15% [3/20]).13 In a recent 2-year cohort study of 42 patients with FFA who were referred for patch testing, the most common allergens included gallates, hydroperoxides of linalool, and other fragrances.14 After a 3-month period of allergen avoidance, 70% (29/42) of patients had decreased scalp erythema on examination, indicating that avoiding relevant allergens may reduce local inflammation. Furthermore, 76.2% (32/42) of patients with FFA showed delayed-type hypersensitivity to allergens found in daily personal care products such as shampoos, sunscreens, and moisturizers, among others.14 Notably, the study lacked a control group. A case-control study of 36 Hispanic women conducted in Mexico also resulted in 83.3% (15/18) of patients with FFA and 55.5% (10/18) of controls having at least 1 positive patch test; in the FFA group, these included iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (16.7% [3/18]) and propolis (16.7% [3/18]).15
Most recently, a retrospective study conducted by Shtaynberger et al16 included 12 patients with LPP or FFA diagnosed via clinical findings or biopsy. It also included an age- and temporally matched control group tested with identical allergens. Among the 12 patients who had FFA/LPP, all had at least 1 allergen identified on patch testing. The most common allergens identified were propolis (positive in 50% [6/12] of patients with FFA/LPP), fragrance mix I (16%), and methylisothiazolinone (16% [2/12]). Follow-up data were available for 9 of these patients, of whom 6 (66.7%) experienced symptom improvement after 6 months of allergen avoidance. Four (44.4%) patients experienced decreased follicular redness or scaling, 2 (22.2%) patients experienced improved scalp pain/itch, 2 (22.2%) patients had stable/improved hair density, and 1 (1.1%) patient had decreased hair shedding. Although this suggests an environmental trigger for FFA/LPP, the authors stated that changes in patient treatment plans could have contributed to their improvement. The study also was limited by its small size and its overall generalizability.16
These studies have underscored the significance of patch testing in individuals diagnosed with FFA and have identified common allergens prevalent in this patient population. They have suggested that patients with FFA are more likely to have positive patch tests, and in some cases patients could experience improvements in scalp pruritus and erythema with allergen avoidance; however, we emphasize that a causal association between contact allergy and FFA remains unproven to date.
Most Common Allergens Pertinent to FFA
Preservatives—In some studies, patients with FFA have had positive patch tests to preservatives such as gallates and methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI).14 Gallates are antioxidants that are used in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics due to their ability to inhibit oxidation and rancidity of fats and oils.17 The most common gallates include propyl gallate, octyl gallate, and dodecyl gallate. Propyl gallate is utilized in some waxy or oily cosmetics and personal care items including sunscreens, shampoos, conditioners, bar soaps, facial cleansers, and moisturizers.18 Typically, if patients have a positive patch test to one gallate, they should be advised to avoid all gallate compounds, as they can cross-react.
Similarly, MCI/MI can prevent product degradation through their antibacterial and antifungal properties. This combination of MCI and MI is used as an effective method of prolonging the shelf life of cosmetic products and commonly is found in sunscreens, facial moisturizing creams, shampoos, and conditioners19; it is banned from use in leave-on products in the European Union and Canada due to increased rates of contact allergy.20 In patients with FFA who commonly use facial sunscreen, preservatives can be a potential allergen exposure to consider.
Iodopropynyl butylcarbamate also is a preservative used in cosmetic formulations. Similar to MCI/MI, it is a potent fungicide and bactericide. This allergen can be found in hair care products, bodywashes, and other personal products.21
UV Light–Absorbing Agents—A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted in 2022 showed a significant (P<.001) association between sunscreen use and FFA.22 A majority of allergens identified on patch testing included UVA- and UVB-absorbing agents found in sunscreens and other products including cosmetics,11,12 such as drometrizole trisiloxane, ethylhexyl salicylate, avobenzone, and benzophenone-4. Drometrizole trisiloxane is a photostabilizer and a broad-spectrum UV filter that is not approved for use in sunscreens in the United States.23 It also is effective in stabilizing and preventing the degradation of avobenzone, a commonly used UVA filter.24
Fragrances—Fragrances are present in nearly every personal and cosmetic product, sometimes even in those advertised as being “fragrance free.” Hydroperoxides of linalool, BoP, and fragrance mix are common allergens that are found in a variety of personal care products including perfumes, cosmetics, and even household cleaning supplies.25 Simultaneous positive patch tests to BoP and fragrance mix are common due to shared components. Linalool can be found in various plants such as lavender, rose, bergamot, and jasmine.26 Upon air exposure, linalool auto-oxidizes to form allergenic hydroperoxides of linalool. Among patients with FFA, positive patch test reactions to fragrance chemicals are common and could be attributed to the use of fragranced hair products and facial cosmetics.
Hair Dyes and Bleaches—Allergic reactions to hair dyes and bleaches can result in severe ACD of the head/neck and, in rare cases, scarring alopecia.27 Chemicals found in these products include paraphenylenediamine (PPD) and ammonium persulfate. The most common hair dye allergen, PPD also is used in some rubbers and plastics. Ammonium persulfate is a chemical used in hair bleaches and to deodorize oils. One case study reported a patient with FFA who developed chemically induced vitiligo immediately after the use of a hair color product that contained PPD.28 However, without patch testing to confirm the presence of contact allergy, other patient-specific and environmental risk factors could have contributed to FFA in this case.
A Knot in the Truth
In this endeavor to untangle the truth, it should be remembered that at the time of writing, the purported association between FFA and ACD remains debatable. Contact dermatitis specialists have voiced that the association between FFA and ACD, especially with regard to sunscreen, cannot be supported due to the lack of sufficient evidence.29 A large majority of the research conducted on FFA and ACD is based on case reports and studies limited to a small sample size, and most of these patch test studies lack a control group. Felmingham et al30 noted that the recent epidemiology of FFA aligns with increased sunscreen use. They also highlighted the limitations of the aforementioned studies, which include misclassification of exposures in the control group2 and recall bias in questionnaire participants.2,12 The most pressing limitation that permeates through most of these studies is the temporal ambiguity associated with sunscreen use. A study by Dhana et al31 failed to specify whether increased sunscreen use preceded the diagnosis of FFA or if it stems from the need to protect more exposed skin as a consequence of disease. Broad sunscreen avoidance due to concern for a possible association with hair loss could have detrimental health implications by increasing the risk for photodamage and skin cancer.
FFA Patch Testing
The avoidance of pertinent allergens could be effective in reducing local inflammation, pruritus, and erythema in FFA.9,14,32 At our institution, we selectively patch test patients with FFA when there is a suspected contact allergy. Clinical features that may allude to a potential contact allergy include an erythematous or eczematous dermatitis or symptoms of pruritus along the scalp or eyebrows. If patients recall hair loss or symptoms after using a hair or facial product, then a potential contact allergy to these products could be considered. Patch testing in patients with FFA includes the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the cosmetic and hairdresser supplemental series, as well as an additional customized panel of 8 allergens as determined by patch testing experts at the University of Massachusetts, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Massachusetts General Hospital (private email communication, November 2017). Patch test readings are performed at 48 and 96 or 120 hours. Using the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program, patients are provided personalized safe product lists and avoidance strategies are discussed.
Final Interpretation
In a world where cosmetic products are ubiquitous, it is hard to define the potential role of contact allergens in the entangled pathogenesis of FFA and ACD. As evidenced by emerging literature that correlates the 2 conditions and their exacerbating factors, it is important for physicians to have a comprehensive diagnostic approach and heightened awareness for potential allergens at play in FFA (Table). The identification of certain chemicals and preservatives as potential triggers for FFA should emphasize the importance of patch testing in these patients; however, whether the positive reactions are relevant to the pathogenesis or disease course of FFA still is unknown. While these findings begin to unravel the intertwined causes of FFA and ACD, further research encompassing larger cohorts and prospective studies is imperative to solidify these associations, define concrete guidelines, and improve patient outcomes.

- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767. doi:10.1111/bjd.14535
- Debroy Kidambi A, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with facial moisturizers and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:260-261. doi:10.1111/bjd.15311
- Starace M, Orlando G, Iorizzo M, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic approaches to diagnosis of frontal fibrosing alopecia: results from a multicenter study of the International Dermoscopy Society. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:E2022080. doi:10.5826/dpc.1201a80
- Fechine COC, Valente NYS, Romiti R. Lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia: review and update of diagnostic and therapeutic features. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:348-357. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.08.008
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of disease pathogenesis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:911944. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.911944
- Del Duca E, Ruano Ruiz J, Pavel AB, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia shows robust T helper 1 and Janus kinase 3 skewing. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:1083-1093. doi:10.1111/bjd.19040
- Tziotzios C, Petridis C, Dand N, et al. Genome-wide association study in frontal fibrosing alopecia identifies four susceptibility loci including HLA-B*07:02. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1150. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09117-w
- Navarro‐Belmonte MR, Navarro‐López V, Ramírez‐Boscà A, et al. Case series of familial frontal fibrosing alopecia and a review of the literature. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:64-69. doi:10.1111/jocd.12125
- Cuenca-Barrales C, Ruiz-Villaverde R, Molina-Leyva A. Familial frontal fibrosing alopecia. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021;21:E320-E323. doi:10.18295/squmj.2021.21.02.025
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a woman thereafter diagnosed with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:215-217. doi:10.1111/cod.14370
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case–control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Rudnicka L, Rokni GR, Lotti T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: an international multi-center study. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13560. doi:10.1111/dth.13560
- Prasad S, Marks DH, Burns LJ, et al. Patch testing and contact allergen avoidance in patients with lichen planopilaris and/or frontal fibrosing alopecia: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:659-661. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.026
- Ocampo-Garza SS, Herz-Ruelas ME, Chavez-Alvarez S, et al. Association of frontal fibrosing alopecia and contact allergens in everyday skincare products in Hispanic females: a case-control study. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:776-778. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.09.013
- Shtaynberger B, Bruder P, Zippin JH. The prevalence of type iv hypersensitivity in patients with lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. Dermatitis. 2023;34:351-352. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000965
- Kahkeshani N, Farzaei F, Fotouhi M, et al. Pharmacological effects of gallic acid in health and diseases: a mechanistic review. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22:225-237. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2019.32806.7897
- Holcomb ZE, Van Noord MG, Atwater AR. Gallate contact dermatitis: product update and systematic review. Dermatitis. 2017;28:115-127. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000263
- Gorris A, Valencak J, Schremser V, et al. Contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone with three clinical presentations in one patient. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:162-164. doi:10.1111/cod.13384
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339. doi:10.1111/jdv.15875
- Batista M, Morgado F, Gonçalo M. Patch test reactivity to iodopropynyl butylcarbamate in consecutive patients during a period of 7 years. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:54-55. doi:10.1111/cod.13213
- Maghfour J, Ceresnie M, Olson J, et al. The association between frontal fibrosing alopecia, sunscreen, and moisturizers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:395-396. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.12.058
- Drometrizole trisiloxane. PubChem website. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9848888
- Hughes TM, Martin JA, Lewis VJ, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a sunscreen with concomitant sensitivities to other sunscreens. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:226-227. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.0566a.x
- de Groot AC. Myroxylon pereirae resin (balsam of Peru)—a critical review of the literature and assessment of the significance of positive patch test reactions and the usefulness of restrictive diets. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:335-353. doi:10.1111/cod.13263
- Sköld M, Börje A, Matura M, et al. Studies on the autoxidation and sensitizing capacity of the fragrance chemical linalool, identifying a linalool hydroperoxide. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;46:267-272. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.460504.x
- Dev T, Khan E, Patel U, et al. Cicatricial alopecia following allergic contact dermatitis from hair dyes: a rare clinical presentation. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:59-61. doi:10.1111/cod.13974
- De Souza B, Burns L, Senna MM. Frontal fibrosing alopecia preceding the development of vitiligo: a case report. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:154-155. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.011
- Abuav R, Shon W. Are sunscreen particles involved in frontal fibrosing alopecia?—a TEM-EDXS analysis on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded alopecia biopsies (pilot study). Am J Dermatopathol. 2022;44:E135. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000002317
- Felmingham C, Yip L, Tam M, et al. Allergy to sunscreen and leave-on facial products is not a likely causative mechanism in frontal fibrosing alopecia: perspective from contact allergy experts. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:481-482. doi:10.1111/bjd.18380
- Dhana A, Gumedze F, Khumalo N. Regarding “frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skincare products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study.” Br J Dermatol. 2016;176:836-837. doi:10.1111/bjd.15197
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Sensitization to benzyl salicylate and other allergens in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:423-430. doi:10.1111/cod.13763
- Rocha VB, Donati A, Contin LA, et al. Photopatch and patch testing in 63 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/bjd.16933
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767. doi:10.1111/bjd.14535
- Debroy Kidambi A, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with facial moisturizers and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:260-261. doi:10.1111/bjd.15311
- Starace M, Orlando G, Iorizzo M, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic approaches to diagnosis of frontal fibrosing alopecia: results from a multicenter study of the International Dermoscopy Society. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:E2022080. doi:10.5826/dpc.1201a80
- Fechine COC, Valente NYS, Romiti R. Lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia: review and update of diagnostic and therapeutic features. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:348-357. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.08.008
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of disease pathogenesis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:911944. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.911944
- Del Duca E, Ruano Ruiz J, Pavel AB, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia shows robust T helper 1 and Janus kinase 3 skewing. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:1083-1093. doi:10.1111/bjd.19040
- Tziotzios C, Petridis C, Dand N, et al. Genome-wide association study in frontal fibrosing alopecia identifies four susceptibility loci including HLA-B*07:02. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1150. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09117-w
- Navarro‐Belmonte MR, Navarro‐López V, Ramírez‐Boscà A, et al. Case series of familial frontal fibrosing alopecia and a review of the literature. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:64-69. doi:10.1111/jocd.12125
- Cuenca-Barrales C, Ruiz-Villaverde R, Molina-Leyva A. Familial frontal fibrosing alopecia. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021;21:E320-E323. doi:10.18295/squmj.2021.21.02.025
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a woman thereafter diagnosed with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;89:215-217. doi:10.1111/cod.14370
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case–control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Rudnicka L, Rokni GR, Lotti T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: an international multi-center study. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13560. doi:10.1111/dth.13560
- Prasad S, Marks DH, Burns LJ, et al. Patch testing and contact allergen avoidance in patients with lichen planopilaris and/or frontal fibrosing alopecia: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:659-661. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.026
- Ocampo-Garza SS, Herz-Ruelas ME, Chavez-Alvarez S, et al. Association of frontal fibrosing alopecia and contact allergens in everyday skincare products in Hispanic females: a case-control study. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:776-778. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.09.013
- Shtaynberger B, Bruder P, Zippin JH. The prevalence of type iv hypersensitivity in patients with lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. Dermatitis. 2023;34:351-352. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000965
- Kahkeshani N, Farzaei F, Fotouhi M, et al. Pharmacological effects of gallic acid in health and diseases: a mechanistic review. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22:225-237. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2019.32806.7897
- Holcomb ZE, Van Noord MG, Atwater AR. Gallate contact dermatitis: product update and systematic review. Dermatitis. 2017;28:115-127. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000263
- Gorris A, Valencak J, Schremser V, et al. Contact allergy to methylisothiazolinone with three clinical presentations in one patient. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;82:162-164. doi:10.1111/cod.13384
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339. doi:10.1111/jdv.15875
- Batista M, Morgado F, Gonçalo M. Patch test reactivity to iodopropynyl butylcarbamate in consecutive patients during a period of 7 years. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:54-55. doi:10.1111/cod.13213
- Maghfour J, Ceresnie M, Olson J, et al. The association between frontal fibrosing alopecia, sunscreen, and moisturizers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:395-396. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.12.058
- Drometrizole trisiloxane. PubChem website. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9848888
- Hughes TM, Martin JA, Lewis VJ, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to drometrizole trisiloxane in a sunscreen with concomitant sensitivities to other sunscreens. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:226-227. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.0566a.x
- de Groot AC. Myroxylon pereirae resin (balsam of Peru)—a critical review of the literature and assessment of the significance of positive patch test reactions and the usefulness of restrictive diets. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:335-353. doi:10.1111/cod.13263
- Sköld M, Börje A, Matura M, et al. Studies on the autoxidation and sensitizing capacity of the fragrance chemical linalool, identifying a linalool hydroperoxide. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;46:267-272. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.460504.x
- Dev T, Khan E, Patel U, et al. Cicatricial alopecia following allergic contact dermatitis from hair dyes: a rare clinical presentation. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:59-61. doi:10.1111/cod.13974
- De Souza B, Burns L, Senna MM. Frontal fibrosing alopecia preceding the development of vitiligo: a case report. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:154-155. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.011
- Abuav R, Shon W. Are sunscreen particles involved in frontal fibrosing alopecia?—a TEM-EDXS analysis on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded alopecia biopsies (pilot study). Am J Dermatopathol. 2022;44:E135. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000002317
- Felmingham C, Yip L, Tam M, et al. Allergy to sunscreen and leave-on facial products is not a likely causative mechanism in frontal fibrosing alopecia: perspective from contact allergy experts. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:481-482. doi:10.1111/bjd.18380
- Dhana A, Gumedze F, Khumalo N. Regarding “frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skincare products and sunscreens; a questionnaire study.” Br J Dermatol. 2016;176:836-837. doi:10.1111/bjd.15197
- Pastor-Nieto MA, Gatica-Ortega ME, Sánchez-Herreros C, et al. Sensitization to benzyl salicylate and other allergens in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:423-430. doi:10.1111/cod.13763
- Rocha VB, Donati A, Contin LA, et al. Photopatch and patch testing in 63 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case series. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/bjd.16933
Practice Points
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), a variant of lichen planopilaris (LPP), is an increasingly prevalent type of scarring alopecia that may have a closer relationship to contact allergy than was previously understood. However, there is no evidence of a causal association to date.
- When evaluating for FFA/LPP, clinicians should assess for use of cosmetic products or sunscreens that may have a potential impact on the disease course.
‘Real-World’ Registry Study of Upadacitinib Supports Clinical Trial Data
, results from an analysis of registry data showed.
“We know from clinical trials that upadacitinib is effective, but we have very little real-world experience on its effectiveness,” presenting study author Melinda Gooderham, MD, medical director of the Skin Center for Dermatology in Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference.
For the analysis, she and her coauthors evaluated the real-world clinical and patient-reported outcomes of 335 adults enrolled in the CorEvitas AD Registry from July 21, 2020, through Aug. 7, 2023. They included patients who were on upadacitinib for at least 4 weeks and persisted on the drug until the time of evaluation.
The CorEvitas AD Registry is a prospective, non-interventional registry of adults diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist or qualified dermatology practitioner. Outcomes measures included the proportion of patients who achieved skin clearance as defined by a Validated Investigators Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA) score of 0 or 1, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of 3 or less, a Peak Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 0 or 1, Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) scores of 0-2, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores of 0 or 1, or an Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT) score of <7.
The researchers evaluated cross-sectional data from three different cohorts: data from the last registry visit (the overall cohort), data from a visit within 1 month to less than 5 months of upadacitinib initiation (the 1-5 months cohort), and data from a visit within 5-9 months following upadacitinib initiation (the 5-9 months cohort). They also conducted subgroup analyses of patients with prior use of biologics for AD (bio-experience) and those with no such history (bio-naive). Safety events were not assessed in this analysis.
The mean age of the 335 patients was 45.6 years, 51.6% were female, 64.2% were White, 64.2% were based in the United States and the rest were based in Canada. Most patients (70.8%) were treated with the 15-mg dose of upadacitinib. The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months. Slightly more than one-quarter of patients (28.1%) reported concomitant use of topical corticosteroids for AD, while 45.4% reported prior use of dupilumab and 6% reported prior use of tralokinumab.
Dr. Gooderham reported that 57.5% of patients in the total cohort total cohort achieved clear or almost clear skin (a vIGA-AD score of 0 or 1), with slight differences between the bio-naive (60.6%) and bio-experienced (54.1%) subgroups.
The other outcomes were similarly close between the 176 bio-naive and 159 bio-experienced patients. Specifically, 74.8% in the total cohort, 79.4% in the bio-naive subgroup, and 69.6% in the bio-experienced subgroup achieved an EASI score of 3 or less. In the measure of the worst itch in the past 24 hours, 45.3%, 47.7%, and 42.8% respectively achieved a PP-NRS of 0 or 1. In the patient-reported disease burden, 36.4%, 41%, and 31.4% achieved a POEM score of 0-2. In the quality of life measure, 39.8%, 42.8%, and 36.5% achieved a DLQI score of 0 or 1. In the measure of disease control, 69.3%, 70.5%, and 67.9% achieved an ADCT score of <7. In a combination of skin clearance and itch control, 40.9%, 43.2%, and 38.4% of the total cohort, bio-naive, and bio-experienced respectively achieved both an EASI score of 3 or less and a PP-NRS of 0 or 1.
The study outcomes were similar between the 1-5 months cohort and the 5-9 months cohort, but there was a trend toward more clearance the longer patients were on therapy.
“The findings suggest that low levels of disease severity are observed in patients on upadacitinib in a real-world setting,” Dr. Gooderham concluded. “This confirms what we see in the clinical trials.”
She disclosed that she is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie.
, results from an analysis of registry data showed.
“We know from clinical trials that upadacitinib is effective, but we have very little real-world experience on its effectiveness,” presenting study author Melinda Gooderham, MD, medical director of the Skin Center for Dermatology in Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference.
For the analysis, she and her coauthors evaluated the real-world clinical and patient-reported outcomes of 335 adults enrolled in the CorEvitas AD Registry from July 21, 2020, through Aug. 7, 2023. They included patients who were on upadacitinib for at least 4 weeks and persisted on the drug until the time of evaluation.
The CorEvitas AD Registry is a prospective, non-interventional registry of adults diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist or qualified dermatology practitioner. Outcomes measures included the proportion of patients who achieved skin clearance as defined by a Validated Investigators Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA) score of 0 or 1, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of 3 or less, a Peak Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 0 or 1, Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) scores of 0-2, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores of 0 or 1, or an Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT) score of <7.
The researchers evaluated cross-sectional data from three different cohorts: data from the last registry visit (the overall cohort), data from a visit within 1 month to less than 5 months of upadacitinib initiation (the 1-5 months cohort), and data from a visit within 5-9 months following upadacitinib initiation (the 5-9 months cohort). They also conducted subgroup analyses of patients with prior use of biologics for AD (bio-experience) and those with no such history (bio-naive). Safety events were not assessed in this analysis.
The mean age of the 335 patients was 45.6 years, 51.6% were female, 64.2% were White, 64.2% were based in the United States and the rest were based in Canada. Most patients (70.8%) were treated with the 15-mg dose of upadacitinib. The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months. Slightly more than one-quarter of patients (28.1%) reported concomitant use of topical corticosteroids for AD, while 45.4% reported prior use of dupilumab and 6% reported prior use of tralokinumab.
Dr. Gooderham reported that 57.5% of patients in the total cohort total cohort achieved clear or almost clear skin (a vIGA-AD score of 0 or 1), with slight differences between the bio-naive (60.6%) and bio-experienced (54.1%) subgroups.
The other outcomes were similarly close between the 176 bio-naive and 159 bio-experienced patients. Specifically, 74.8% in the total cohort, 79.4% in the bio-naive subgroup, and 69.6% in the bio-experienced subgroup achieved an EASI score of 3 or less. In the measure of the worst itch in the past 24 hours, 45.3%, 47.7%, and 42.8% respectively achieved a PP-NRS of 0 or 1. In the patient-reported disease burden, 36.4%, 41%, and 31.4% achieved a POEM score of 0-2. In the quality of life measure, 39.8%, 42.8%, and 36.5% achieved a DLQI score of 0 or 1. In the measure of disease control, 69.3%, 70.5%, and 67.9% achieved an ADCT score of <7. In a combination of skin clearance and itch control, 40.9%, 43.2%, and 38.4% of the total cohort, bio-naive, and bio-experienced respectively achieved both an EASI score of 3 or less and a PP-NRS of 0 or 1.
The study outcomes were similar between the 1-5 months cohort and the 5-9 months cohort, but there was a trend toward more clearance the longer patients were on therapy.
“The findings suggest that low levels of disease severity are observed in patients on upadacitinib in a real-world setting,” Dr. Gooderham concluded. “This confirms what we see in the clinical trials.”
She disclosed that she is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie.
, results from an analysis of registry data showed.
“We know from clinical trials that upadacitinib is effective, but we have very little real-world experience on its effectiveness,” presenting study author Melinda Gooderham, MD, medical director of the Skin Center for Dermatology in Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference.
For the analysis, she and her coauthors evaluated the real-world clinical and patient-reported outcomes of 335 adults enrolled in the CorEvitas AD Registry from July 21, 2020, through Aug. 7, 2023. They included patients who were on upadacitinib for at least 4 weeks and persisted on the drug until the time of evaluation.
The CorEvitas AD Registry is a prospective, non-interventional registry of adults diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist or qualified dermatology practitioner. Outcomes measures included the proportion of patients who achieved skin clearance as defined by a Validated Investigators Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA) score of 0 or 1, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score of 3 or less, a Peak Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (PP-NRS) score of 0 or 1, Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) scores of 0-2, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores of 0 or 1, or an Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT) score of <7.
The researchers evaluated cross-sectional data from three different cohorts: data from the last registry visit (the overall cohort), data from a visit within 1 month to less than 5 months of upadacitinib initiation (the 1-5 months cohort), and data from a visit within 5-9 months following upadacitinib initiation (the 5-9 months cohort). They also conducted subgroup analyses of patients with prior use of biologics for AD (bio-experience) and those with no such history (bio-naive). Safety events were not assessed in this analysis.
The mean age of the 335 patients was 45.6 years, 51.6% were female, 64.2% were White, 64.2% were based in the United States and the rest were based in Canada. Most patients (70.8%) were treated with the 15-mg dose of upadacitinib. The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months. Slightly more than one-quarter of patients (28.1%) reported concomitant use of topical corticosteroids for AD, while 45.4% reported prior use of dupilumab and 6% reported prior use of tralokinumab.
Dr. Gooderham reported that 57.5% of patients in the total cohort total cohort achieved clear or almost clear skin (a vIGA-AD score of 0 or 1), with slight differences between the bio-naive (60.6%) and bio-experienced (54.1%) subgroups.
The other outcomes were similarly close between the 176 bio-naive and 159 bio-experienced patients. Specifically, 74.8% in the total cohort, 79.4% in the bio-naive subgroup, and 69.6% in the bio-experienced subgroup achieved an EASI score of 3 or less. In the measure of the worst itch in the past 24 hours, 45.3%, 47.7%, and 42.8% respectively achieved a PP-NRS of 0 or 1. In the patient-reported disease burden, 36.4%, 41%, and 31.4% achieved a POEM score of 0-2. In the quality of life measure, 39.8%, 42.8%, and 36.5% achieved a DLQI score of 0 or 1. In the measure of disease control, 69.3%, 70.5%, and 67.9% achieved an ADCT score of <7. In a combination of skin clearance and itch control, 40.9%, 43.2%, and 38.4% of the total cohort, bio-naive, and bio-experienced respectively achieved both an EASI score of 3 or less and a PP-NRS of 0 or 1.
The study outcomes were similar between the 1-5 months cohort and the 5-9 months cohort, but there was a trend toward more clearance the longer patients were on therapy.
“The findings suggest that low levels of disease severity are observed in patients on upadacitinib in a real-world setting,” Dr. Gooderham concluded. “This confirms what we see in the clinical trials.”
She disclosed that she is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie.
FROM RAD 2023
Tackling Acrylate Allergy: The Sticky Truth
Acrylates are a ubiquitous family of synthetic thermoplastic resins that are employed in a wide array of products. Since the discovery of acrylic acid in 1843 and its industrialization in the early 20th century, acrylates have been used by many different sectors of industry.1 Today, acrylates can be found in diverse sources such as adhesives, coatings, electronics, nail cosmetics, dental materials, and medical devices. Although these versatile compounds have revolutionized numerous sectors, their potential to trigger allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) has garnered considerable attention in recent years. In 2012, acrylates as a group were named Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society,2 and one member—isobornyl acrylate—also was given the infamous award in 2020.3 In this article, we highlight the chemistry of acrylates, the growing prevalence of acrylate contact allergy, common sources of exposure, patch testing considerations, and management/prevention strategies.
Chemistry and Uses of Acrylates
Acrylates are widely used due to their pliable and resilient properties.4 They begin as liquid monomers of (meth)acrylic acid or cyanoacrylic acid that are molded to the desired application before being cured or hardened by one of several means: spontaneously, using chemical catalysts, or with heat, UV light, or a light-emitting diode. Once cured, the final polymers (ie, [meth]acrylates, cyanoacrylates) serve a myriad of different purposes. Table 1 includes some of the more clinically relevant sources of acrylate exposure. Although this list is not comprehensive, it offers a glimpse into the vast array of uses for acrylates.
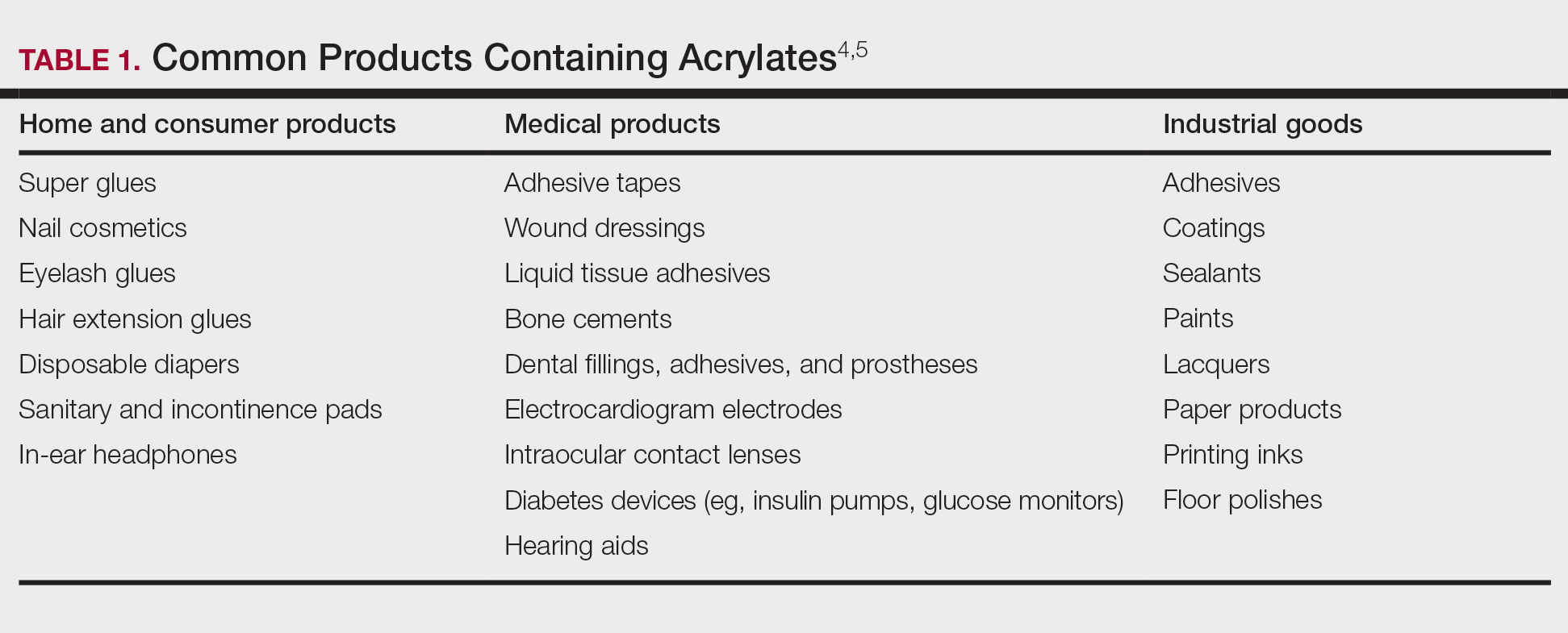
Acrylate Contact Allergy
Acrylic monomers are potent contact allergens, but the polymerized final products are not considered allergenic, assuming they are completely cured; however, ACD can occur with incomplete curing.6 It is of clinical importance that once an individual becomes sensitized to one type of acrylate, they may develop cross-reactions to others contained in different products. Notably, cyanoacrylates generally do not cross-react with (meth)acrylates; this has important implications for choosing safe alternative products in sensitized patients, though independent sensitization to cyanoacrylates is possible.7,8
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
The prevalence of acrylate allergy in the general population is unknown; however, there is a trend of increased patch test positivity in studies of patients referred for patch testing. A 2018 study by the European Environmental Contact Dermatitis Research Group reported positive patch tests to acrylates in 1.1% of 18,228 patients tested from 2013 to 2015.9 More recently, a multicenter European study (2019-2020) reported a 2.3% patch test positivity to 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) among 7675 tested individuals,10 and even higher HEMA positivity was reported in Spain (3.7% of 1884 patients in 2019-2020).11 In addition, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported positive patch test reactions to HEMA in 3.2% of 4111 patients tested from 2019 to 2020, a statistically significant increase compared with those tested in 2009 to 2018 (odds ratio, 1.25 [95% CI, 1.03-1.51]; P=.02).12
Historically, acrylate sensitization primarily stemmed from occupational exposure. A retrospective analysis of occupational dermatitis performed by the NACDG (2001-2016) showed that HEMA was among the top 10 most common occupational allergens (3.4% positivity [83/2461]) and had the fifth highest percentage of occupationally relevant reactions (73.5% [83/113]).13 High-risk occupations include dental providers and nail technicians. Dentistry utilizes many materials containing acrylates, including uncured plastic resins used in dental prostheses, dentin bonding materials, and glass ionomers.14 A retrospective analysis of 585 dental personnel who were patch tested by the NACDG (2001-2018) found that more than 20% of occupational ACD cases were related to acrylates.15 Nail technicians are another group routinely exposed to acrylates through a variety of modern nail cosmetics. In a 7-year study from Portugal evaluating acrylate ACD, 68% (25/37) of cases were attributed to occupation, 80% (20/25) of which were in nail technicians.16 Likewise, among 28 nail technicians in Sweden who were referred for patch testing, 57% (16/28) tested positive for at least 1 acrylate.17
Modern Sources of Acrylate Exposure
Once thought to be a predominantly occupational exposure, acrylates have rapidly made their way into everyday consumer products. Clinicians should be aware of several sources of clinically relevant acrylate exposure, including nail cosmetics, consumer electronics, and medical/surgical adhesives.
A 2016 study found a shift to nail cosmetics as the most common source of acrylate sensitization.18 Nail cosmetics that contain acrylates include traditional acrylic, gel (shellac), dipped, and press-on (false) nails.19 The NACDG found that the most common allergen in patients experiencing ACD associated with nail products (2001-2016) was HEMA (56.6% [273/482]), far ahead of the traditional nail polish allergen tosylamide (36.2% [273/755]). Over the study period, the frequency of positive patch tests statistically increased for HEMA (P=.0069) and decreased for tosylamide (P<.0001).20 There is concern that the use of home gel nail kits, which can be purchased online at the click of a button, may be associated with a risk for acrylate sensitization.21,22 A recent study surveyed a Facebook support group for individuals with self-reported reactions to nail cosmetics, finding that 78% of the 199 individuals had used at-home gel nail kits, and more than 80% of them first developed skin reactions after starting to use at-home kits.23 The risks for sensitization are thought to be greater when self-applying nail acrylates compared to having them done professionally because individuals are more likely to spill allergenic monomers onto the skin at home; it also is possible that home techniques could lead to incomplete curing. Table 2 reviews the different types of acrylic nail cosmetics.
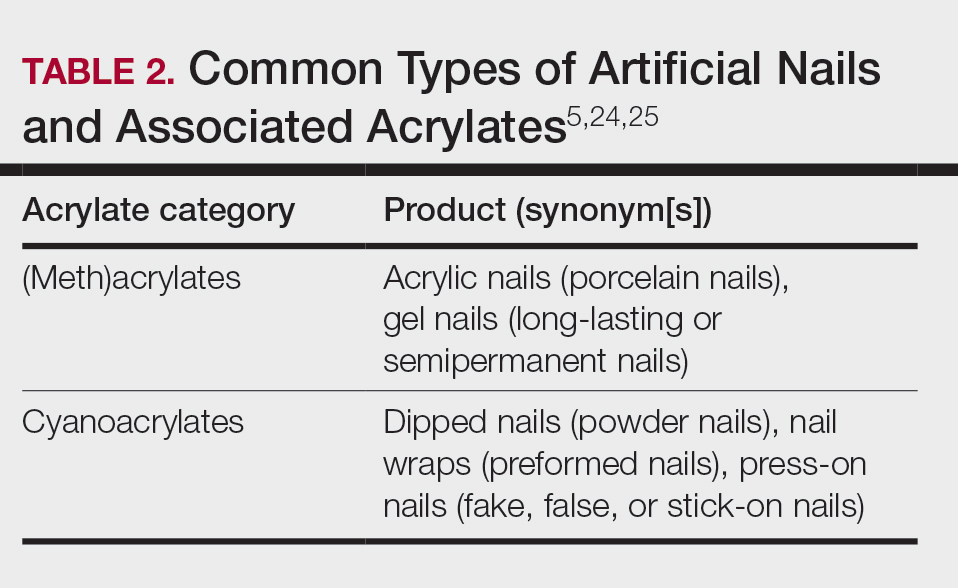
Medical adhesives and equipment are other important areas where acrylates can be encountered in abundance. A review by Spencer et al18 cautioned wound dressings as an up-and-coming source of sensitization, and this has been demonstrated in the literature as coming to fruition.26 Another study identified acrylates in 15 of 16 (94%) tested medical adhesives; among 7 medical adhesives labeled as hypoallergenic, 100% still contained acrylates and/or abietic acid.27 Multiple case reports have described ACD to adhesives of electrocardiogram electrodes containing acrylates.28-31 Physicians providing care to patients with diabetes mellitus also must be aware of acrylates in glucose monitors and insulin pumps, either found in the adhesives or leaching from the inside of the device to reach the skin.32 Isobornyl acrylate in particular has made quite the name for itself in this sector, being crowned the 2020 Allergen of the Year owing to its key role in cases of ACD to diabetes devices.3
Cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives (eg, 2‐octyl cyanoacrylate) are now well documented to cause postoperative ACD.33,34 Although robust prospective data are limited, studies suggest that 2% to 14% of patients develop postoperative skin reactions following 2-octyl cyanoacrylate application.35-37 It has been shown that sensitization to tissue adhesives often occurs after the first application, followed by an eruption of ACD as long as a month later, which can create confusion about the nature of the rash for patients and health care providers alike, who may for instance attribute it to infection rather than allergy.38 In the orthopedic literature, a woman with a known history of acrylic nail ACD had knee arthroplasty failure attributed to acrylic bone cement with resolution of the joint symptoms after changing to a cementless device.39
Awareness of the common use of acrylates is important to identify the cause of reactions from products that would otherwise seem nonallergenic. A case of occupational ACD to isobornyl acrylate in UV-cured phone screen protectors has been reported40; several cases of ACD to acrylates in headphones41,42 as well as one related to a wearable fitness device also have been reported.43 Given all these possible sources of exposure, ACD to acrylates should be on your radar.
When to Consider Acrylate ACD
When working up a patient with dermatitis, it is essential to ask about occupational history and hobbies to get a sense of potential contact allergen exposures. The typical presentation of occupational acrylate-associated ACD is hand eczema, specifically involving the fingertips.5,24,25,44 Acrylate ACD should be considered in patients with nail dystrophy and a history of wearing acrylic nails.45 There can even be involvement of the face and eyelids secondary to airborne contact or ectopic spread from the hands.24 Spreading vesicular eruptions associated with adhesives also should raise concern. The Figure depicts several possible presentations of ACD to acrylates. In a time of abundant access to products containing acrylates, dermatologists should consider this allergy in their differential diagnosis and consider patch testing.
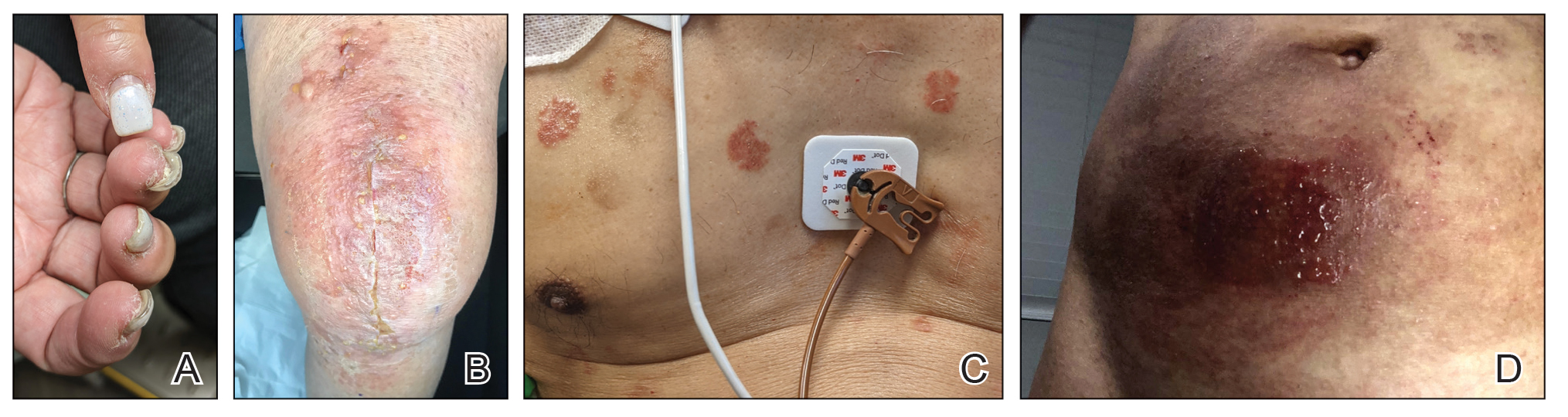
Patch Testing to Acrylates
The gold standard for ACD diagnosis is patch testing. It should be noted that no acrylates are included in the thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test series. Several acrylates are tested in expanded patch test series including the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen series and North American 80 Comprehensive Series. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is thought to be the most important screening allergen to test. Ramos et al16 reported a positive patch test to HEMA in 81% (30/37) of patients who had any type of acrylate allergy.
If initial testing to a limited number of acrylates is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, expanded acrylates/plastics and glue series also are available from commercial patch test suppliers. Testing to an expanded panel of acrylates is especially pertinent to consider in suspected occupational cases given the risk of workplace absenteeism and even disability that come with continued exposure to the allergen. Of note, isobornyl acrylate is not included in the baseline patch test series and must be tested separately, particularly because it usually does not cross-react with other acrylates, and therefore allergy could be missed if not tested on its own.
Acrylates are volatile substances that have been shown to degrade at room temperature and to a lesser degree when refrigerated. Ideally, they should be stored in a freezer and not used beyond their expiration date. Furthermore, it is advised that acrylate patch tests be prepared immediately prior to placement on the patient and to discard the initial extrusion from the syringe, as the concentration at the tip may be decreased.46,47
With regard to tissue adhesives, the actual product should be tested as-is because these are not commercially available patch test substances.48 Occasionally, patients who are sensitized to the tissue adhesive will not react when patch tested on intact skin. If clinical suspicion remains high, scratch patch testing may confirm contact allergy in cases of negative testing on intact skin.49
Management and Prevention
Once a diagnosis of ACD secondary to acrylates has been established, counseling patients on allergen avoidance strategies is essential. For (meth)acrylate-allergic patients who want to continue using modern nail products, cyanoacrylate-based options (eg, dipped, press-on nails) can be considered as an alternative, as they do not cross-react, though independent sensitization is still possible. However, traditional nail polish is the safest option to recommend.
The concern with acrylate sensitization extends beyond the immediate issue that brought the patient into your clinic. Dermatologists must counsel patients who are sensitized to acrylates on the possible sequelae of acrylate-containing dental or orthopedic procedures. Oral lichenoid lesions, denture stomatitis, burning mouth syndrome, or even acute facial swelling have been reported following dental work in patients with acrylate allergy.50-53 Dentists of patients with acrylate ACD should be informed of the diagnosis so acrylates can be avoided during dental work; if unavoidable, all possible steps should be taken to ensure complete curing of the monomers. In the surgical setting, patients sensitized to cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives should be offered wound closure alternatives such as sutures or staples.34
In patients with diabetes mellitus who develop ACD to their glucose monitor or insulin pump, ideally they should be switched to a device that does not contain acrylates. Problematically, these devices are constantly being reformulated, and manufacturers do not always divulge their components, which can make it challenging to determine safe alternative options.32,54 Various barrier products may help on a case-by-case basis.55Preventative measures should be implemented in workplaces that utilize acrylates, including dental practices and nail salons. Acrylic monomers have been shown to penetrate most gloves within minutes of exposure.56,57 Double gloving with nitrile gloves affords some protection for no longer than 60 minutes.6 4H gloves have been shown to provide true protection but result in a loss of dexterity.58 The fingerstall technique involves removing the fingers from a 4H glove, inserting them on the fingers, and applying a more flexible glove on top to hold them in place; this offers a hybrid between protection and finger dexterity.59
Final Interpretation
In a world characterized by technological advancements and increasing accessibility to acrylate-containing products, we hope this brief review serves as a resource and reminder to dermatologists to consider acrylates as a potential cause of ACD with diverse presentations and important future implications for affected individuals. The rising trend of acrylate allergy necessitates comprehensive assessment and shared decision-making between physicians and patients. As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of materials and technologies, clinicians must remain vigilant to avoid some potentially sticky situations for patients.
- Staehle HJ, Sekundo C. The origins of acrylates and adhesive technologies in dentistry. J Adhes Dent. 2021;23:397-406.
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergens of the Year 2000 to 2020. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320.
- Nath N, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Isobornyl acrylate and diabetic devices steal the show for the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Cutis. 2020;105:283-285.
- Ajekwene KK. Properties and applications of acrylates. In: Serrano-Aroca A, Deb S, eds. Acrylate Polymers for Advanced Applications. IntechOpen; 2020:35-46. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.89867
- Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Acrylates: new sources and new allergens. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45:277-283.
- Sasseville D. Acrylates in contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2012;23:6-16.
- Gardeen S, Hylwa S. A review of acrylates: super glue, nail adhesives, and diabetic pump adhesives increasing sensitization risk in women and children. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:263-267.
- Chou M, Dhingra N, Strugar TL. Contact sensitization to allergens in nail cosmetics. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2017;28:231-240.
- Gonçalo M, Pinho A, Agner T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by nail acrylates in Europe. an EECDRG study. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:254-260.
- Uter W, Wilkinson SM, Aerts O, et al. Patch test results with the European baseline series, 2019/20-Joint European results of the ESSCA and the EBS working groups of the ESCD, and the GEIDAC. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:343-355.
- Hernández-Fernández CP, Mercader-García P, Silvestre Salvador JF, et al. Candidate allergens for inclusion in the Spanish standard series based on data from the Spanish Contact Dermatitis Registry. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:798-805.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2019-2020. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:90-104.
- DeKoven JG, DeKoven BM, Warshaw EM, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:782-790.
- Heratizadeh A, Werfel T, Schubert S, et al. Contact sensitization in dental technicians with occupational contact dermatitis. data of the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology (IVDK) 2001-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:266-273.
- Warshaw EM, Ruggiero JL, Atwater AR, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis in dental personnel: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2018. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2022;33:80-90.
- Ramos L, Cabral R, Gonçalo M. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylates and methacrylates—a 7-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;71:102-107.
- Fisch A, Hamnerius N, Isaksson M. Dermatitis and occupational (meth)acrylate contact allergy in nail technicians—a 10-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:58-60.
- Spencer A, Gazzani P, Thompson DA. Acrylate and methacrylate contact allergy and allergic contact disease: a 13-year review. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:157-164.
- DeKoven S, DeKoven J, Holness DL. (Meth)acrylate occupational contact dermatitis in nail salon workers: a case series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:340-344.
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:191-201.
- Le Q, Cahill J, Palmer-Le A, et al. The rising trend in allergic contact dermatitis to acrylic nail products. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:221-223.
- Gatica-Ortega ME, Pastor-Nieto M. The present and future burden of contact dermatitis from acrylates in manicure. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2020;7:1-21.
- Guenther J, Norman T, Wee C, et al. A survey of skin reactions associated with acrylic nail cosmetics, with a focus on home kits: is there a need for regulation [published online October 16, 2023]? Dermatitis. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0204
- Calado R, Gomes T, Matos A, et al. Contact dermatitis to nail cosmetics. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:173-181.
- Draelos ZD. Nail cosmetics and adornment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:351-359.
- Mestach L, Huygens S, Goossens A, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylic-based medical dressings and adhesives. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;79:81-84.
- Tam I, Wang JX, Yu JD. Identifying acrylates in medical adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E40-E42.
- Stingeni L, Cerulli E, Spalletti A, et al. The role of acrylic acid impurity as a sensitizing component in electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:44-48.
- Ozkaya E, Kavlak Bozkurt P. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by self-adhesive electrocardiography electrodes: a rare case with concomitant roles of nickel and acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:121-123.
- Lyons G, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to methacrylates in ECG electrode dots. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:39-40.
- Jelen G. Acrylate, a hidden allergen of electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;45:315-316.
- Bembry R, Brys AK, Atwater AR. Medical device contact allergy: glucose monitors and insulin pumps. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2022;11:13-20.
- Liu T, Wan J, McKenna RA, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by Dermabond in a paediatric patient undergoing skin surgery. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:61-62.
- Ricciardo BM, Nixon RL, Tam MM, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to Dermabond Prineo after elective orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2020;43:E515-E522.
- Nigro LC, Parkerson J, Nunley J, et al. Should we stick with surgical glues? the incidence of dermatitis after 2-octyl cyanoacrylate exposure in 102 consecutive breast cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:32-37.
- Alotaibi NN, Ahmad T, Rabah SM, et al. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to Dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) in plastic surgical patients: a retrospective study. Plast Surg Oakv Ont. 2022;30:222-226.
- Durando D, Porubsky C, Winter S, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) after total knee arthroplasty. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2014;25:99-100.
- Asai C, Inomata N, Sato M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to the liquid skin adhesive Dermabond® predominantly occurs after the first exposure. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:103-108.
- Haughton AM, Belsito DV. Acrylate allergy induced by acrylic nails resulting in prosthesis failure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:S123-S124.
- Amat-Samaranch V, Garcia-Melendo C, Tubau C, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis to isobornyl acrylate present in cell phone screen protectors. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:352-354.
- Chan J, Rabi S, Adler BL. Allergic contact dermatitis to (meth)acrylates in Apple AirPods headphones. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E111-E112.
- Shaver RL, Buonomo M, Scherman JA, et al. Contact allergy to acrylates in Apple AirPods Pro® headphones: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E459-E461.
- Winston FK, Yan AC. Wearable health device dermatitis: a case of acrylate-related contact allergy. Cutis. 2017;100:97-99.
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560.
- Nanda S. Nail salon safety: from nail dystrophy to acrylate contact allergies. Cutis. 2022;110:E32-E33.
- Joy NM, Rice KR, Atwater AR. Stability of patch test allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2013;24:227-236.
- Jou PC, Siegel PD, Warshaw EM. Vapor pressure and predicted stability of American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:193-201.
- Cook KA, White AA, Shaw DW. Patch testing ingredients of Dermabond and other cyanoacrylate-containing adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2019;30:314-322.
- Patel K, Nixon R. Scratch patch testing to Dermabond in a patient with suspected allergic contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:250-251.
- Ditrichova D, Kapralova S, Tichy M, et al. Oral lichenoid lesions and allergy to dental materials. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov. 2007;151:333-339.
- Chen AYY, Zirwas MJ. Denture stomatitis. Skinmed. 2007;6:92-94.
- Marino R, Capaccio P, Pignataro L, et al. Burning mouth syndrome: the role of contact hypersensitivity. Oral Dis. 2009;15:255-258.
- Obayashi N, Shintani T, Kamegashira A, et al. A case report of allergic reaction with acute facial swelling: a rare complication of dental acrylic resin. J Int Med Res. 2023;51:3000605231187819.
- Cameli N, Silvestri M, Mariano M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis, an important skin reaction in diabetes device users: a systematic review. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 20221;33:110-115.
- Ng KL, Nixon RL, Grills C, et al. Solution using Stomahesive® wafers for allergic contact dermatitis caused by isobornyl acrylate in glucose monitoring sensors. Australas J Dermatol. 2022;63:E56-E59.
- Lönnroth EC, Wellendorf H, Ruyter E. Permeability of different types of medical protective gloves to acrylic monomers. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111:440-446.
- Sananez A, Sanchez A, Davis L, et al. Allergic reaction from dental bonding material through nitrile gloves: clinical case study and glove permeability testing. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2020;32:371-379.
- Andersson T, Bruze M, Björkner B. In vivo testing of the protection of gloves against acrylates in dentin-bonding systems on patients with known contact allergy to acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 1999;41:254-259.
- Roche E, Cuadra J, Alegre V. Sensitization to acrylates caused by artificial acrylic nails: review of 15 cases. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. 2009;99:788-794.
Acrylates are a ubiquitous family of synthetic thermoplastic resins that are employed in a wide array of products. Since the discovery of acrylic acid in 1843 and its industrialization in the early 20th century, acrylates have been used by many different sectors of industry.1 Today, acrylates can be found in diverse sources such as adhesives, coatings, electronics, nail cosmetics, dental materials, and medical devices. Although these versatile compounds have revolutionized numerous sectors, their potential to trigger allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) has garnered considerable attention in recent years. In 2012, acrylates as a group were named Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society,2 and one member—isobornyl acrylate—also was given the infamous award in 2020.3 In this article, we highlight the chemistry of acrylates, the growing prevalence of acrylate contact allergy, common sources of exposure, patch testing considerations, and management/prevention strategies.
Chemistry and Uses of Acrylates
Acrylates are widely used due to their pliable and resilient properties.4 They begin as liquid monomers of (meth)acrylic acid or cyanoacrylic acid that are molded to the desired application before being cured or hardened by one of several means: spontaneously, using chemical catalysts, or with heat, UV light, or a light-emitting diode. Once cured, the final polymers (ie, [meth]acrylates, cyanoacrylates) serve a myriad of different purposes. Table 1 includes some of the more clinically relevant sources of acrylate exposure. Although this list is not comprehensive, it offers a glimpse into the vast array of uses for acrylates.

Acrylate Contact Allergy
Acrylic monomers are potent contact allergens, but the polymerized final products are not considered allergenic, assuming they are completely cured; however, ACD can occur with incomplete curing.6 It is of clinical importance that once an individual becomes sensitized to one type of acrylate, they may develop cross-reactions to others contained in different products. Notably, cyanoacrylates generally do not cross-react with (meth)acrylates; this has important implications for choosing safe alternative products in sensitized patients, though independent sensitization to cyanoacrylates is possible.7,8
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
The prevalence of acrylate allergy in the general population is unknown; however, there is a trend of increased patch test positivity in studies of patients referred for patch testing. A 2018 study by the European Environmental Contact Dermatitis Research Group reported positive patch tests to acrylates in 1.1% of 18,228 patients tested from 2013 to 2015.9 More recently, a multicenter European study (2019-2020) reported a 2.3% patch test positivity to 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) among 7675 tested individuals,10 and even higher HEMA positivity was reported in Spain (3.7% of 1884 patients in 2019-2020).11 In addition, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported positive patch test reactions to HEMA in 3.2% of 4111 patients tested from 2019 to 2020, a statistically significant increase compared with those tested in 2009 to 2018 (odds ratio, 1.25 [95% CI, 1.03-1.51]; P=.02).12
Historically, acrylate sensitization primarily stemmed from occupational exposure. A retrospective analysis of occupational dermatitis performed by the NACDG (2001-2016) showed that HEMA was among the top 10 most common occupational allergens (3.4% positivity [83/2461]) and had the fifth highest percentage of occupationally relevant reactions (73.5% [83/113]).13 High-risk occupations include dental providers and nail technicians. Dentistry utilizes many materials containing acrylates, including uncured plastic resins used in dental prostheses, dentin bonding materials, and glass ionomers.14 A retrospective analysis of 585 dental personnel who were patch tested by the NACDG (2001-2018) found that more than 20% of occupational ACD cases were related to acrylates.15 Nail technicians are another group routinely exposed to acrylates through a variety of modern nail cosmetics. In a 7-year study from Portugal evaluating acrylate ACD, 68% (25/37) of cases were attributed to occupation, 80% (20/25) of which were in nail technicians.16 Likewise, among 28 nail technicians in Sweden who were referred for patch testing, 57% (16/28) tested positive for at least 1 acrylate.17
Modern Sources of Acrylate Exposure
Once thought to be a predominantly occupational exposure, acrylates have rapidly made their way into everyday consumer products. Clinicians should be aware of several sources of clinically relevant acrylate exposure, including nail cosmetics, consumer electronics, and medical/surgical adhesives.
A 2016 study found a shift to nail cosmetics as the most common source of acrylate sensitization.18 Nail cosmetics that contain acrylates include traditional acrylic, gel (shellac), dipped, and press-on (false) nails.19 The NACDG found that the most common allergen in patients experiencing ACD associated with nail products (2001-2016) was HEMA (56.6% [273/482]), far ahead of the traditional nail polish allergen tosylamide (36.2% [273/755]). Over the study period, the frequency of positive patch tests statistically increased for HEMA (P=.0069) and decreased for tosylamide (P<.0001).20 There is concern that the use of home gel nail kits, which can be purchased online at the click of a button, may be associated with a risk for acrylate sensitization.21,22 A recent study surveyed a Facebook support group for individuals with self-reported reactions to nail cosmetics, finding that 78% of the 199 individuals had used at-home gel nail kits, and more than 80% of them first developed skin reactions after starting to use at-home kits.23 The risks for sensitization are thought to be greater when self-applying nail acrylates compared to having them done professionally because individuals are more likely to spill allergenic monomers onto the skin at home; it also is possible that home techniques could lead to incomplete curing. Table 2 reviews the different types of acrylic nail cosmetics.

Medical adhesives and equipment are other important areas where acrylates can be encountered in abundance. A review by Spencer et al18 cautioned wound dressings as an up-and-coming source of sensitization, and this has been demonstrated in the literature as coming to fruition.26 Another study identified acrylates in 15 of 16 (94%) tested medical adhesives; among 7 medical adhesives labeled as hypoallergenic, 100% still contained acrylates and/or abietic acid.27 Multiple case reports have described ACD to adhesives of electrocardiogram electrodes containing acrylates.28-31 Physicians providing care to patients with diabetes mellitus also must be aware of acrylates in glucose monitors and insulin pumps, either found in the adhesives or leaching from the inside of the device to reach the skin.32 Isobornyl acrylate in particular has made quite the name for itself in this sector, being crowned the 2020 Allergen of the Year owing to its key role in cases of ACD to diabetes devices.3
Cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives (eg, 2‐octyl cyanoacrylate) are now well documented to cause postoperative ACD.33,34 Although robust prospective data are limited, studies suggest that 2% to 14% of patients develop postoperative skin reactions following 2-octyl cyanoacrylate application.35-37 It has been shown that sensitization to tissue adhesives often occurs after the first application, followed by an eruption of ACD as long as a month later, which can create confusion about the nature of the rash for patients and health care providers alike, who may for instance attribute it to infection rather than allergy.38 In the orthopedic literature, a woman with a known history of acrylic nail ACD had knee arthroplasty failure attributed to acrylic bone cement with resolution of the joint symptoms after changing to a cementless device.39
Awareness of the common use of acrylates is important to identify the cause of reactions from products that would otherwise seem nonallergenic. A case of occupational ACD to isobornyl acrylate in UV-cured phone screen protectors has been reported40; several cases of ACD to acrylates in headphones41,42 as well as one related to a wearable fitness device also have been reported.43 Given all these possible sources of exposure, ACD to acrylates should be on your radar.
When to Consider Acrylate ACD
When working up a patient with dermatitis, it is essential to ask about occupational history and hobbies to get a sense of potential contact allergen exposures. The typical presentation of occupational acrylate-associated ACD is hand eczema, specifically involving the fingertips.5,24,25,44 Acrylate ACD should be considered in patients with nail dystrophy and a history of wearing acrylic nails.45 There can even be involvement of the face and eyelids secondary to airborne contact or ectopic spread from the hands.24 Spreading vesicular eruptions associated with adhesives also should raise concern. The Figure depicts several possible presentations of ACD to acrylates. In a time of abundant access to products containing acrylates, dermatologists should consider this allergy in their differential diagnosis and consider patch testing.

Patch Testing to Acrylates
The gold standard for ACD diagnosis is patch testing. It should be noted that no acrylates are included in the thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test series. Several acrylates are tested in expanded patch test series including the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen series and North American 80 Comprehensive Series. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is thought to be the most important screening allergen to test. Ramos et al16 reported a positive patch test to HEMA in 81% (30/37) of patients who had any type of acrylate allergy.
If initial testing to a limited number of acrylates is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, expanded acrylates/plastics and glue series also are available from commercial patch test suppliers. Testing to an expanded panel of acrylates is especially pertinent to consider in suspected occupational cases given the risk of workplace absenteeism and even disability that come with continued exposure to the allergen. Of note, isobornyl acrylate is not included in the baseline patch test series and must be tested separately, particularly because it usually does not cross-react with other acrylates, and therefore allergy could be missed if not tested on its own.
Acrylates are volatile substances that have been shown to degrade at room temperature and to a lesser degree when refrigerated. Ideally, they should be stored in a freezer and not used beyond their expiration date. Furthermore, it is advised that acrylate patch tests be prepared immediately prior to placement on the patient and to discard the initial extrusion from the syringe, as the concentration at the tip may be decreased.46,47
With regard to tissue adhesives, the actual product should be tested as-is because these are not commercially available patch test substances.48 Occasionally, patients who are sensitized to the tissue adhesive will not react when patch tested on intact skin. If clinical suspicion remains high, scratch patch testing may confirm contact allergy in cases of negative testing on intact skin.49
Management and Prevention
Once a diagnosis of ACD secondary to acrylates has been established, counseling patients on allergen avoidance strategies is essential. For (meth)acrylate-allergic patients who want to continue using modern nail products, cyanoacrylate-based options (eg, dipped, press-on nails) can be considered as an alternative, as they do not cross-react, though independent sensitization is still possible. However, traditional nail polish is the safest option to recommend.
The concern with acrylate sensitization extends beyond the immediate issue that brought the patient into your clinic. Dermatologists must counsel patients who are sensitized to acrylates on the possible sequelae of acrylate-containing dental or orthopedic procedures. Oral lichenoid lesions, denture stomatitis, burning mouth syndrome, or even acute facial swelling have been reported following dental work in patients with acrylate allergy.50-53 Dentists of patients with acrylate ACD should be informed of the diagnosis so acrylates can be avoided during dental work; if unavoidable, all possible steps should be taken to ensure complete curing of the monomers. In the surgical setting, patients sensitized to cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives should be offered wound closure alternatives such as sutures or staples.34
In patients with diabetes mellitus who develop ACD to their glucose monitor or insulin pump, ideally they should be switched to a device that does not contain acrylates. Problematically, these devices are constantly being reformulated, and manufacturers do not always divulge their components, which can make it challenging to determine safe alternative options.32,54 Various barrier products may help on a case-by-case basis.55Preventative measures should be implemented in workplaces that utilize acrylates, including dental practices and nail salons. Acrylic monomers have been shown to penetrate most gloves within minutes of exposure.56,57 Double gloving with nitrile gloves affords some protection for no longer than 60 minutes.6 4H gloves have been shown to provide true protection but result in a loss of dexterity.58 The fingerstall technique involves removing the fingers from a 4H glove, inserting them on the fingers, and applying a more flexible glove on top to hold them in place; this offers a hybrid between protection and finger dexterity.59
Final Interpretation
In a world characterized by technological advancements and increasing accessibility to acrylate-containing products, we hope this brief review serves as a resource and reminder to dermatologists to consider acrylates as a potential cause of ACD with diverse presentations and important future implications for affected individuals. The rising trend of acrylate allergy necessitates comprehensive assessment and shared decision-making between physicians and patients. As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of materials and technologies, clinicians must remain vigilant to avoid some potentially sticky situations for patients.
Acrylates are a ubiquitous family of synthetic thermoplastic resins that are employed in a wide array of products. Since the discovery of acrylic acid in 1843 and its industrialization in the early 20th century, acrylates have been used by many different sectors of industry.1 Today, acrylates can be found in diverse sources such as adhesives, coatings, electronics, nail cosmetics, dental materials, and medical devices. Although these versatile compounds have revolutionized numerous sectors, their potential to trigger allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) has garnered considerable attention in recent years. In 2012, acrylates as a group were named Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society,2 and one member—isobornyl acrylate—also was given the infamous award in 2020.3 In this article, we highlight the chemistry of acrylates, the growing prevalence of acrylate contact allergy, common sources of exposure, patch testing considerations, and management/prevention strategies.
Chemistry and Uses of Acrylates
Acrylates are widely used due to their pliable and resilient properties.4 They begin as liquid monomers of (meth)acrylic acid or cyanoacrylic acid that are molded to the desired application before being cured or hardened by one of several means: spontaneously, using chemical catalysts, or with heat, UV light, or a light-emitting diode. Once cured, the final polymers (ie, [meth]acrylates, cyanoacrylates) serve a myriad of different purposes. Table 1 includes some of the more clinically relevant sources of acrylate exposure. Although this list is not comprehensive, it offers a glimpse into the vast array of uses for acrylates.

Acrylate Contact Allergy
Acrylic monomers are potent contact allergens, but the polymerized final products are not considered allergenic, assuming they are completely cured; however, ACD can occur with incomplete curing.6 It is of clinical importance that once an individual becomes sensitized to one type of acrylate, they may develop cross-reactions to others contained in different products. Notably, cyanoacrylates generally do not cross-react with (meth)acrylates; this has important implications for choosing safe alternative products in sensitized patients, though independent sensitization to cyanoacrylates is possible.7,8
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
The prevalence of acrylate allergy in the general population is unknown; however, there is a trend of increased patch test positivity in studies of patients referred for patch testing. A 2018 study by the European Environmental Contact Dermatitis Research Group reported positive patch tests to acrylates in 1.1% of 18,228 patients tested from 2013 to 2015.9 More recently, a multicenter European study (2019-2020) reported a 2.3% patch test positivity to 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) among 7675 tested individuals,10 and even higher HEMA positivity was reported in Spain (3.7% of 1884 patients in 2019-2020).11 In addition, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported positive patch test reactions to HEMA in 3.2% of 4111 patients tested from 2019 to 2020, a statistically significant increase compared with those tested in 2009 to 2018 (odds ratio, 1.25 [95% CI, 1.03-1.51]; P=.02).12
Historically, acrylate sensitization primarily stemmed from occupational exposure. A retrospective analysis of occupational dermatitis performed by the NACDG (2001-2016) showed that HEMA was among the top 10 most common occupational allergens (3.4% positivity [83/2461]) and had the fifth highest percentage of occupationally relevant reactions (73.5% [83/113]).13 High-risk occupations include dental providers and nail technicians. Dentistry utilizes many materials containing acrylates, including uncured plastic resins used in dental prostheses, dentin bonding materials, and glass ionomers.14 A retrospective analysis of 585 dental personnel who were patch tested by the NACDG (2001-2018) found that more than 20% of occupational ACD cases were related to acrylates.15 Nail technicians are another group routinely exposed to acrylates through a variety of modern nail cosmetics. In a 7-year study from Portugal evaluating acrylate ACD, 68% (25/37) of cases were attributed to occupation, 80% (20/25) of which were in nail technicians.16 Likewise, among 28 nail technicians in Sweden who were referred for patch testing, 57% (16/28) tested positive for at least 1 acrylate.17
Modern Sources of Acrylate Exposure
Once thought to be a predominantly occupational exposure, acrylates have rapidly made their way into everyday consumer products. Clinicians should be aware of several sources of clinically relevant acrylate exposure, including nail cosmetics, consumer electronics, and medical/surgical adhesives.
A 2016 study found a shift to nail cosmetics as the most common source of acrylate sensitization.18 Nail cosmetics that contain acrylates include traditional acrylic, gel (shellac), dipped, and press-on (false) nails.19 The NACDG found that the most common allergen in patients experiencing ACD associated with nail products (2001-2016) was HEMA (56.6% [273/482]), far ahead of the traditional nail polish allergen tosylamide (36.2% [273/755]). Over the study period, the frequency of positive patch tests statistically increased for HEMA (P=.0069) and decreased for tosylamide (P<.0001).20 There is concern that the use of home gel nail kits, which can be purchased online at the click of a button, may be associated with a risk for acrylate sensitization.21,22 A recent study surveyed a Facebook support group for individuals with self-reported reactions to nail cosmetics, finding that 78% of the 199 individuals had used at-home gel nail kits, and more than 80% of them first developed skin reactions after starting to use at-home kits.23 The risks for sensitization are thought to be greater when self-applying nail acrylates compared to having them done professionally because individuals are more likely to spill allergenic monomers onto the skin at home; it also is possible that home techniques could lead to incomplete curing. Table 2 reviews the different types of acrylic nail cosmetics.

Medical adhesives and equipment are other important areas where acrylates can be encountered in abundance. A review by Spencer et al18 cautioned wound dressings as an up-and-coming source of sensitization, and this has been demonstrated in the literature as coming to fruition.26 Another study identified acrylates in 15 of 16 (94%) tested medical adhesives; among 7 medical adhesives labeled as hypoallergenic, 100% still contained acrylates and/or abietic acid.27 Multiple case reports have described ACD to adhesives of electrocardiogram electrodes containing acrylates.28-31 Physicians providing care to patients with diabetes mellitus also must be aware of acrylates in glucose monitors and insulin pumps, either found in the adhesives or leaching from the inside of the device to reach the skin.32 Isobornyl acrylate in particular has made quite the name for itself in this sector, being crowned the 2020 Allergen of the Year owing to its key role in cases of ACD to diabetes devices.3
Cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives (eg, 2‐octyl cyanoacrylate) are now well documented to cause postoperative ACD.33,34 Although robust prospective data are limited, studies suggest that 2% to 14% of patients develop postoperative skin reactions following 2-octyl cyanoacrylate application.35-37 It has been shown that sensitization to tissue adhesives often occurs after the first application, followed by an eruption of ACD as long as a month later, which can create confusion about the nature of the rash for patients and health care providers alike, who may for instance attribute it to infection rather than allergy.38 In the orthopedic literature, a woman with a known history of acrylic nail ACD had knee arthroplasty failure attributed to acrylic bone cement with resolution of the joint symptoms after changing to a cementless device.39
Awareness of the common use of acrylates is important to identify the cause of reactions from products that would otherwise seem nonallergenic. A case of occupational ACD to isobornyl acrylate in UV-cured phone screen protectors has been reported40; several cases of ACD to acrylates in headphones41,42 as well as one related to a wearable fitness device also have been reported.43 Given all these possible sources of exposure, ACD to acrylates should be on your radar.
When to Consider Acrylate ACD
When working up a patient with dermatitis, it is essential to ask about occupational history and hobbies to get a sense of potential contact allergen exposures. The typical presentation of occupational acrylate-associated ACD is hand eczema, specifically involving the fingertips.5,24,25,44 Acrylate ACD should be considered in patients with nail dystrophy and a history of wearing acrylic nails.45 There can even be involvement of the face and eyelids secondary to airborne contact or ectopic spread from the hands.24 Spreading vesicular eruptions associated with adhesives also should raise concern. The Figure depicts several possible presentations of ACD to acrylates. In a time of abundant access to products containing acrylates, dermatologists should consider this allergy in their differential diagnosis and consider patch testing.

Patch Testing to Acrylates
The gold standard for ACD diagnosis is patch testing. It should be noted that no acrylates are included in the thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.) test series. Several acrylates are tested in expanded patch test series including the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen series and North American 80 Comprehensive Series. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is thought to be the most important screening allergen to test. Ramos et al16 reported a positive patch test to HEMA in 81% (30/37) of patients who had any type of acrylate allergy.
If initial testing to a limited number of acrylates is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, expanded acrylates/plastics and glue series also are available from commercial patch test suppliers. Testing to an expanded panel of acrylates is especially pertinent to consider in suspected occupational cases given the risk of workplace absenteeism and even disability that come with continued exposure to the allergen. Of note, isobornyl acrylate is not included in the baseline patch test series and must be tested separately, particularly because it usually does not cross-react with other acrylates, and therefore allergy could be missed if not tested on its own.
Acrylates are volatile substances that have been shown to degrade at room temperature and to a lesser degree when refrigerated. Ideally, they should be stored in a freezer and not used beyond their expiration date. Furthermore, it is advised that acrylate patch tests be prepared immediately prior to placement on the patient and to discard the initial extrusion from the syringe, as the concentration at the tip may be decreased.46,47
With regard to tissue adhesives, the actual product should be tested as-is because these are not commercially available patch test substances.48 Occasionally, patients who are sensitized to the tissue adhesive will not react when patch tested on intact skin. If clinical suspicion remains high, scratch patch testing may confirm contact allergy in cases of negative testing on intact skin.49
Management and Prevention
Once a diagnosis of ACD secondary to acrylates has been established, counseling patients on allergen avoidance strategies is essential. For (meth)acrylate-allergic patients who want to continue using modern nail products, cyanoacrylate-based options (eg, dipped, press-on nails) can be considered as an alternative, as they do not cross-react, though independent sensitization is still possible. However, traditional nail polish is the safest option to recommend.
The concern with acrylate sensitization extends beyond the immediate issue that brought the patient into your clinic. Dermatologists must counsel patients who are sensitized to acrylates on the possible sequelae of acrylate-containing dental or orthopedic procedures. Oral lichenoid lesions, denture stomatitis, burning mouth syndrome, or even acute facial swelling have been reported following dental work in patients with acrylate allergy.50-53 Dentists of patients with acrylate ACD should be informed of the diagnosis so acrylates can be avoided during dental work; if unavoidable, all possible steps should be taken to ensure complete curing of the monomers. In the surgical setting, patients sensitized to cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives should be offered wound closure alternatives such as sutures or staples.34
In patients with diabetes mellitus who develop ACD to their glucose monitor or insulin pump, ideally they should be switched to a device that does not contain acrylates. Problematically, these devices are constantly being reformulated, and manufacturers do not always divulge their components, which can make it challenging to determine safe alternative options.32,54 Various barrier products may help on a case-by-case basis.55Preventative measures should be implemented in workplaces that utilize acrylates, including dental practices and nail salons. Acrylic monomers have been shown to penetrate most gloves within minutes of exposure.56,57 Double gloving with nitrile gloves affords some protection for no longer than 60 minutes.6 4H gloves have been shown to provide true protection but result in a loss of dexterity.58 The fingerstall technique involves removing the fingers from a 4H glove, inserting them on the fingers, and applying a more flexible glove on top to hold them in place; this offers a hybrid between protection and finger dexterity.59
Final Interpretation
In a world characterized by technological advancements and increasing accessibility to acrylate-containing products, we hope this brief review serves as a resource and reminder to dermatologists to consider acrylates as a potential cause of ACD with diverse presentations and important future implications for affected individuals. The rising trend of acrylate allergy necessitates comprehensive assessment and shared decision-making between physicians and patients. As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of materials and technologies, clinicians must remain vigilant to avoid some potentially sticky situations for patients.
- Staehle HJ, Sekundo C. The origins of acrylates and adhesive technologies in dentistry. J Adhes Dent. 2021;23:397-406.
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergens of the Year 2000 to 2020. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320.
- Nath N, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Isobornyl acrylate and diabetic devices steal the show for the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Cutis. 2020;105:283-285.
- Ajekwene KK. Properties and applications of acrylates. In: Serrano-Aroca A, Deb S, eds. Acrylate Polymers for Advanced Applications. IntechOpen; 2020:35-46. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.89867
- Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Acrylates: new sources and new allergens. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45:277-283.
- Sasseville D. Acrylates in contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2012;23:6-16.
- Gardeen S, Hylwa S. A review of acrylates: super glue, nail adhesives, and diabetic pump adhesives increasing sensitization risk in women and children. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:263-267.
- Chou M, Dhingra N, Strugar TL. Contact sensitization to allergens in nail cosmetics. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2017;28:231-240.
- Gonçalo M, Pinho A, Agner T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by nail acrylates in Europe. an EECDRG study. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:254-260.
- Uter W, Wilkinson SM, Aerts O, et al. Patch test results with the European baseline series, 2019/20-Joint European results of the ESSCA and the EBS working groups of the ESCD, and the GEIDAC. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:343-355.
- Hernández-Fernández CP, Mercader-García P, Silvestre Salvador JF, et al. Candidate allergens for inclusion in the Spanish standard series based on data from the Spanish Contact Dermatitis Registry. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:798-805.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2019-2020. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:90-104.
- DeKoven JG, DeKoven BM, Warshaw EM, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:782-790.
- Heratizadeh A, Werfel T, Schubert S, et al. Contact sensitization in dental technicians with occupational contact dermatitis. data of the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology (IVDK) 2001-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:266-273.
- Warshaw EM, Ruggiero JL, Atwater AR, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis in dental personnel: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2018. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2022;33:80-90.
- Ramos L, Cabral R, Gonçalo M. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylates and methacrylates—a 7-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;71:102-107.
- Fisch A, Hamnerius N, Isaksson M. Dermatitis and occupational (meth)acrylate contact allergy in nail technicians—a 10-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:58-60.
- Spencer A, Gazzani P, Thompson DA. Acrylate and methacrylate contact allergy and allergic contact disease: a 13-year review. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:157-164.
- DeKoven S, DeKoven J, Holness DL. (Meth)acrylate occupational contact dermatitis in nail salon workers: a case series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:340-344.
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:191-201.
- Le Q, Cahill J, Palmer-Le A, et al. The rising trend in allergic contact dermatitis to acrylic nail products. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:221-223.
- Gatica-Ortega ME, Pastor-Nieto M. The present and future burden of contact dermatitis from acrylates in manicure. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2020;7:1-21.
- Guenther J, Norman T, Wee C, et al. A survey of skin reactions associated with acrylic nail cosmetics, with a focus on home kits: is there a need for regulation [published online October 16, 2023]? Dermatitis. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0204
- Calado R, Gomes T, Matos A, et al. Contact dermatitis to nail cosmetics. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:173-181.
- Draelos ZD. Nail cosmetics and adornment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:351-359.
- Mestach L, Huygens S, Goossens A, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylic-based medical dressings and adhesives. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;79:81-84.
- Tam I, Wang JX, Yu JD. Identifying acrylates in medical adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E40-E42.
- Stingeni L, Cerulli E, Spalletti A, et al. The role of acrylic acid impurity as a sensitizing component in electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:44-48.
- Ozkaya E, Kavlak Bozkurt P. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by self-adhesive electrocardiography electrodes: a rare case with concomitant roles of nickel and acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:121-123.
- Lyons G, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to methacrylates in ECG electrode dots. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:39-40.
- Jelen G. Acrylate, a hidden allergen of electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;45:315-316.
- Bembry R, Brys AK, Atwater AR. Medical device contact allergy: glucose monitors and insulin pumps. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2022;11:13-20.
- Liu T, Wan J, McKenna RA, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by Dermabond in a paediatric patient undergoing skin surgery. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:61-62.
- Ricciardo BM, Nixon RL, Tam MM, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to Dermabond Prineo after elective orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2020;43:E515-E522.
- Nigro LC, Parkerson J, Nunley J, et al. Should we stick with surgical glues? the incidence of dermatitis after 2-octyl cyanoacrylate exposure in 102 consecutive breast cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:32-37.
- Alotaibi NN, Ahmad T, Rabah SM, et al. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to Dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) in plastic surgical patients: a retrospective study. Plast Surg Oakv Ont. 2022;30:222-226.
- Durando D, Porubsky C, Winter S, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) after total knee arthroplasty. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2014;25:99-100.
- Asai C, Inomata N, Sato M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to the liquid skin adhesive Dermabond® predominantly occurs after the first exposure. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:103-108.
- Haughton AM, Belsito DV. Acrylate allergy induced by acrylic nails resulting in prosthesis failure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:S123-S124.
- Amat-Samaranch V, Garcia-Melendo C, Tubau C, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis to isobornyl acrylate present in cell phone screen protectors. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:352-354.
- Chan J, Rabi S, Adler BL. Allergic contact dermatitis to (meth)acrylates in Apple AirPods headphones. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E111-E112.
- Shaver RL, Buonomo M, Scherman JA, et al. Contact allergy to acrylates in Apple AirPods Pro® headphones: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E459-E461.
- Winston FK, Yan AC. Wearable health device dermatitis: a case of acrylate-related contact allergy. Cutis. 2017;100:97-99.
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560.
- Nanda S. Nail salon safety: from nail dystrophy to acrylate contact allergies. Cutis. 2022;110:E32-E33.
- Joy NM, Rice KR, Atwater AR. Stability of patch test allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2013;24:227-236.
- Jou PC, Siegel PD, Warshaw EM. Vapor pressure and predicted stability of American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:193-201.
- Cook KA, White AA, Shaw DW. Patch testing ingredients of Dermabond and other cyanoacrylate-containing adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2019;30:314-322.
- Patel K, Nixon R. Scratch patch testing to Dermabond in a patient with suspected allergic contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:250-251.
- Ditrichova D, Kapralova S, Tichy M, et al. Oral lichenoid lesions and allergy to dental materials. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov. 2007;151:333-339.
- Chen AYY, Zirwas MJ. Denture stomatitis. Skinmed. 2007;6:92-94.
- Marino R, Capaccio P, Pignataro L, et al. Burning mouth syndrome: the role of contact hypersensitivity. Oral Dis. 2009;15:255-258.
- Obayashi N, Shintani T, Kamegashira A, et al. A case report of allergic reaction with acute facial swelling: a rare complication of dental acrylic resin. J Int Med Res. 2023;51:3000605231187819.
- Cameli N, Silvestri M, Mariano M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis, an important skin reaction in diabetes device users: a systematic review. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 20221;33:110-115.
- Ng KL, Nixon RL, Grills C, et al. Solution using Stomahesive® wafers for allergic contact dermatitis caused by isobornyl acrylate in glucose monitoring sensors. Australas J Dermatol. 2022;63:E56-E59.
- Lönnroth EC, Wellendorf H, Ruyter E. Permeability of different types of medical protective gloves to acrylic monomers. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111:440-446.
- Sananez A, Sanchez A, Davis L, et al. Allergic reaction from dental bonding material through nitrile gloves: clinical case study and glove permeability testing. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2020;32:371-379.
- Andersson T, Bruze M, Björkner B. In vivo testing of the protection of gloves against acrylates in dentin-bonding systems on patients with known contact allergy to acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 1999;41:254-259.
- Roche E, Cuadra J, Alegre V. Sensitization to acrylates caused by artificial acrylic nails: review of 15 cases. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. 2009;99:788-794.
- Staehle HJ, Sekundo C. The origins of acrylates and adhesive technologies in dentistry. J Adhes Dent. 2021;23:397-406.
- Militello M, Hu S, Laughter M, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergens of the Year 2000 to 2020. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:309-320.
- Nath N, Reeder M, Atwater AR. Isobornyl acrylate and diabetic devices steal the show for the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Cutis. 2020;105:283-285.
- Ajekwene KK. Properties and applications of acrylates. In: Serrano-Aroca A, Deb S, eds. Acrylate Polymers for Advanced Applications. IntechOpen; 2020:35-46. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.89867
- Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Acrylates: new sources and new allergens. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45:277-283.
- Sasseville D. Acrylates in contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2012;23:6-16.
- Gardeen S, Hylwa S. A review of acrylates: super glue, nail adhesives, and diabetic pump adhesives increasing sensitization risk in women and children. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:263-267.
- Chou M, Dhingra N, Strugar TL. Contact sensitization to allergens in nail cosmetics. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2017;28:231-240.
- Gonçalo M, Pinho A, Agner T, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by nail acrylates in Europe. an EECDRG study. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:254-260.
- Uter W, Wilkinson SM, Aerts O, et al. Patch test results with the European baseline series, 2019/20-Joint European results of the ESSCA and the EBS working groups of the ESCD, and the GEIDAC. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:343-355.
- Hernández-Fernández CP, Mercader-García P, Silvestre Salvador JF, et al. Candidate allergens for inclusion in the Spanish standard series based on data from the Spanish Contact Dermatitis Registry. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:798-805.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2019-2020. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:90-104.
- DeKoven JG, DeKoven BM, Warshaw EM, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:782-790.
- Heratizadeh A, Werfel T, Schubert S, et al. Contact sensitization in dental technicians with occupational contact dermatitis. data of the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology (IVDK) 2001-2015. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:266-273.
- Warshaw EM, Ruggiero JL, Atwater AR, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis in dental personnel: a retrospective analysis of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001 to 2018. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2022;33:80-90.
- Ramos L, Cabral R, Gonçalo M. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylates and methacrylates—a 7-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;71:102-107.
- Fisch A, Hamnerius N, Isaksson M. Dermatitis and occupational (meth)acrylate contact allergy in nail technicians—a 10-year study. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:58-60.
- Spencer A, Gazzani P, Thompson DA. Acrylate and methacrylate contact allergy and allergic contact disease: a 13-year review. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:157-164.
- DeKoven S, DeKoven J, Holness DL. (Meth)acrylate occupational contact dermatitis in nail salon workers: a case series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:340-344.
- Warshaw EM, Voller LM, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis associated with nail care products: retrospective analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:191-201.
- Le Q, Cahill J, Palmer-Le A, et al. The rising trend in allergic contact dermatitis to acrylic nail products. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56:221-223.
- Gatica-Ortega ME, Pastor-Nieto M. The present and future burden of contact dermatitis from acrylates in manicure. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2020;7:1-21.
- Guenther J, Norman T, Wee C, et al. A survey of skin reactions associated with acrylic nail cosmetics, with a focus on home kits: is there a need for regulation [published online October 16, 2023]? Dermatitis. doi:10.1089/derm.2023.0204
- Calado R, Gomes T, Matos A, et al. Contact dermatitis to nail cosmetics. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:173-181.
- Draelos ZD. Nail cosmetics and adornment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:351-359.
- Mestach L, Huygens S, Goossens A, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by acrylic-based medical dressings and adhesives. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;79:81-84.
- Tam I, Wang JX, Yu JD. Identifying acrylates in medical adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E40-E42.
- Stingeni L, Cerulli E, Spalletti A, et al. The role of acrylic acid impurity as a sensitizing component in electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;73:44-48.
- Ozkaya E, Kavlak Bozkurt P. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by self-adhesive electrocardiography electrodes: a rare case with concomitant roles of nickel and acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:121-123.
- Lyons G, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to methacrylates in ECG electrode dots. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:39-40.
- Jelen G. Acrylate, a hidden allergen of electrocardiogram electrodes. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;45:315-316.
- Bembry R, Brys AK, Atwater AR. Medical device contact allergy: glucose monitors and insulin pumps. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2022;11:13-20.
- Liu T, Wan J, McKenna RA, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by Dermabond in a paediatric patient undergoing skin surgery. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:61-62.
- Ricciardo BM, Nixon RL, Tam MM, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to Dermabond Prineo after elective orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2020;43:E515-E522.
- Nigro LC, Parkerson J, Nunley J, et al. Should we stick with surgical glues? the incidence of dermatitis after 2-octyl cyanoacrylate exposure in 102 consecutive breast cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:32-37.
- Alotaibi NN, Ahmad T, Rabah SM, et al. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to Dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) in plastic surgical patients: a retrospective study. Plast Surg Oakv Ont. 2022;30:222-226.
- Durando D, Porubsky C, Winter S, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to dermabond (2-octyl cyanoacrylate) after total knee arthroplasty. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2014;25:99-100.
- Asai C, Inomata N, Sato M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis due to the liquid skin adhesive Dermabond® predominantly occurs after the first exposure. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:103-108.
- Haughton AM, Belsito DV. Acrylate allergy induced by acrylic nails resulting in prosthesis failure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:S123-S124.
- Amat-Samaranch V, Garcia-Melendo C, Tubau C, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis to isobornyl acrylate present in cell phone screen protectors. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:352-354.
- Chan J, Rabi S, Adler BL. Allergic contact dermatitis to (meth)acrylates in Apple AirPods headphones. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E111-E112.
- Shaver RL, Buonomo M, Scherman JA, et al. Contact allergy to acrylates in Apple AirPods Pro® headphones: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E459-E461.
- Winston FK, Yan AC. Wearable health device dermatitis: a case of acrylate-related contact allergy. Cutis. 2017;100:97-99.
- Kucharczyk M, Słowik-Rylska M, Cyran-Stemplewska S, et al. Acrylates as a significant cause of allergic contact dermatitis: new sources of exposure. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:555-560.
- Nanda S. Nail salon safety: from nail dystrophy to acrylate contact allergies. Cutis. 2022;110:E32-E33.
- Joy NM, Rice KR, Atwater AR. Stability of patch test allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2013;24:227-236.
- Jou PC, Siegel PD, Warshaw EM. Vapor pressure and predicted stability of American Contact Dermatitis Society core allergens. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2016;27:193-201.
- Cook KA, White AA, Shaw DW. Patch testing ingredients of Dermabond and other cyanoacrylate-containing adhesives. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2019;30:314-322.
- Patel K, Nixon R. Scratch patch testing to Dermabond in a patient with suspected allergic contact dermatitis. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2023;34:250-251.
- Ditrichova D, Kapralova S, Tichy M, et al. Oral lichenoid lesions and allergy to dental materials. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov. 2007;151:333-339.
- Chen AYY, Zirwas MJ. Denture stomatitis. Skinmed. 2007;6:92-94.
- Marino R, Capaccio P, Pignataro L, et al. Burning mouth syndrome: the role of contact hypersensitivity. Oral Dis. 2009;15:255-258.
- Obayashi N, Shintani T, Kamegashira A, et al. A case report of allergic reaction with acute facial swelling: a rare complication of dental acrylic resin. J Int Med Res. 2023;51:3000605231187819.
- Cameli N, Silvestri M, Mariano M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis, an important skin reaction in diabetes device users: a systematic review. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 20221;33:110-115.
- Ng KL, Nixon RL, Grills C, et al. Solution using Stomahesive® wafers for allergic contact dermatitis caused by isobornyl acrylate in glucose monitoring sensors. Australas J Dermatol. 2022;63:E56-E59.
- Lönnroth EC, Wellendorf H, Ruyter E. Permeability of different types of medical protective gloves to acrylic monomers. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111:440-446.
- Sananez A, Sanchez A, Davis L, et al. Allergic reaction from dental bonding material through nitrile gloves: clinical case study and glove permeability testing. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2020;32:371-379.
- Andersson T, Bruze M, Björkner B. In vivo testing of the protection of gloves against acrylates in dentin-bonding systems on patients with known contact allergy to acrylates. Contact Dermatitis. 1999;41:254-259.
- Roche E, Cuadra J, Alegre V. Sensitization to acrylates caused by artificial acrylic nails: review of 15 cases. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. 2009;99:788-794.
Practice Points
- Acrylates are thermoplastic resins used in a variety of products ranging from cosmetics to adhesives and industrial materials. Acrylic monomers are strong contact allergens, whereas fully polymerized forms are inert, provided they are completely cured.
- The use of home gel nail kits may increase the risk for sensitization to acrylates, which are the most common modern nail cosmetic allergens.
- When patch testing for suspected acrylate allergy, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is the most important screening allergen. Expanded testing to additional acrylates should be considered depending on the clinical scenario.
Lanolin: The 2023 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Practice Points
- Lanolin is a common ingredient in personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial materials.
- Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin appears to be most common in patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis, and perianal/genital dermatitis.
- There is no single best lanolin patch test formulation. Patch testing and repeat open application testing to PCPs containing lanolin also may be of benefit.
Dyshidroticlike Contact Dermatitis and Paronychia Resulting From a Dip Powder Manicure
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.
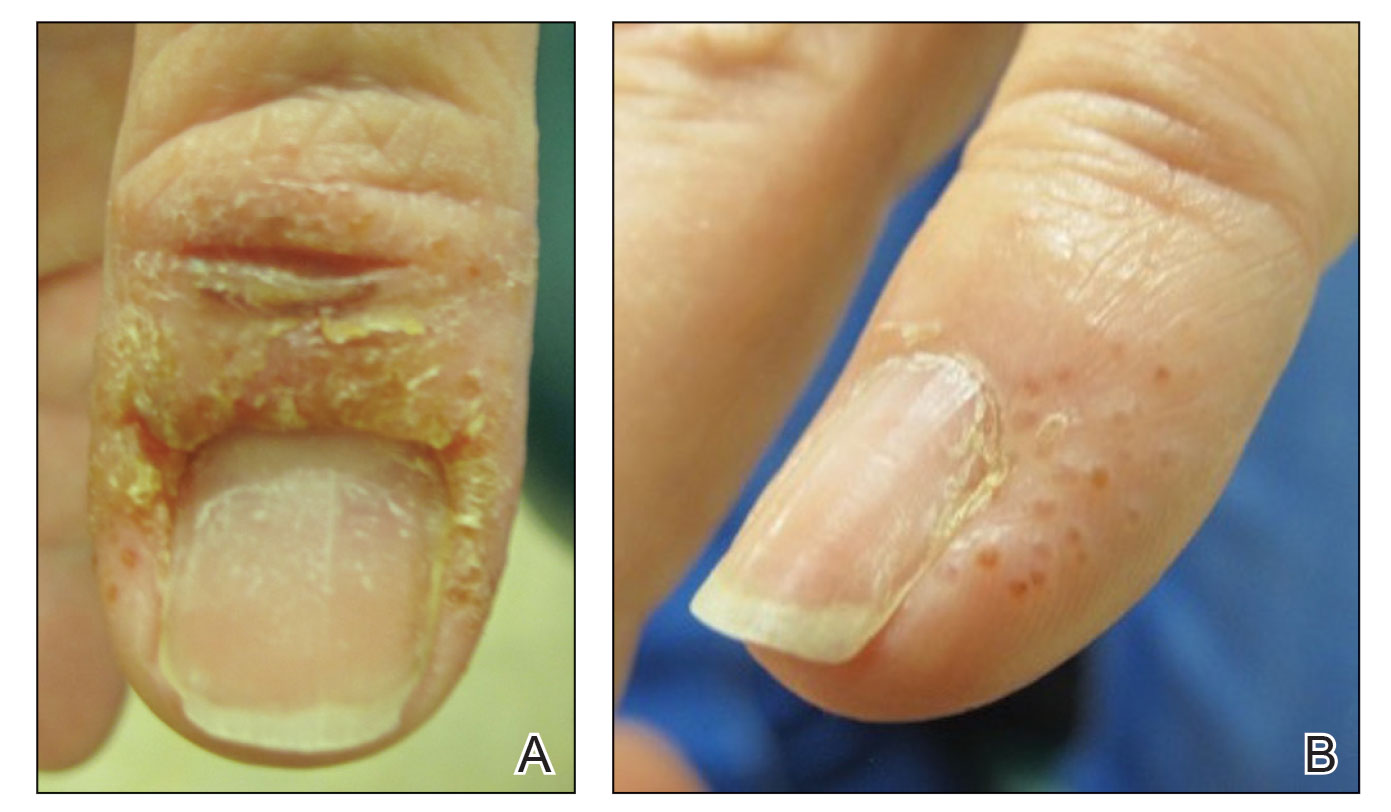
Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5
To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.

Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5

To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.

Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5

To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
Practice Points
- Manicures performed at nail salons have been associated with the development of paronychia due to inadequate sanitation practices and contact dermatitis caused by acrylates present in nail polish.
- The dip powder manicure is a relatively new manicure technique. The distribution of dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and are performed more frequently.
Photoallergic Contact Dermatitis: No Fun in the Sun
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.
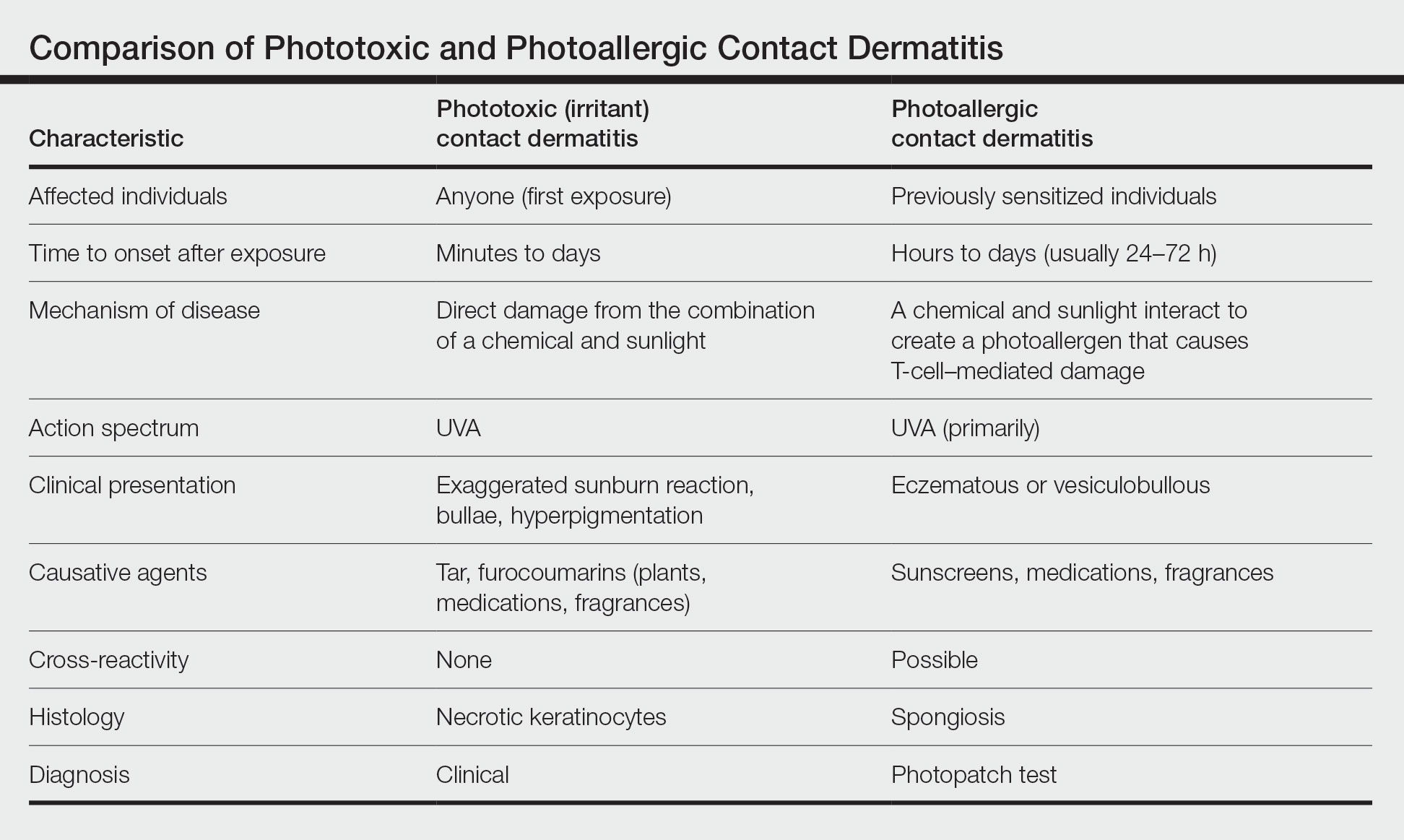
Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.

Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD), a subtype of allergic contact dermatitis that occurs because of the specific combination of exposure to an exogenous chemical applied topically to the skin and UV radiation, may be more common than was once thought.1 Although the incidence in the general population is unknown, current research points to approximately 20% to 40% of patients with suspected photosensitivity having a PACD diagnosis.2 Recently, the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) reported that 21% of 373 patients undergoing photopatch testing (PPT) were diagnosed with PACD2; however, PPT is not routinely performed, which may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Mechanism of Disease
Similar to allergic contact dermatitis, PACD is a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction; however, it only occurs when an exogenous chemical is applied topically to the skin with concomitant exposure to UV radiation, usually in the UVA range (315–400 nm).3,4 When exposed to UV radiation, it is thought that the exogenous chemical combines with a protein in the skin and transforms into a photoantigen. In the sensitization phase, the photoantigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and transported to local lymph nodes where antigen-specific T cells are generated.5 In the elicitation phase, the inflammatory reaction of PACD occurs upon subsequent exposure to the same chemical plus UV radiation.4 Development of PACD does not necessarily depend on the dose of the chemical or the amount of UV radiation.6 Why certain individuals may be more susceptible is unknown, though major histocompatibility complex haplotypes could be influential.7,8
Clinical Manifestations
Photoallergic contact dermatitis primarily presents in sun-exposed areas of the skin (eg, face, neck, V area of the chest, dorsal upper extremities) with sparing of naturally photoprotected sites, such as the upper eyelids and nasolabial and retroauricular folds. Other than its characteristic photodistribution, PACD often is clinically indistinguishable from routine allergic contact dermatitis. It manifests as a pruritic, poorly demarcated, eczematous or sometimes vesiculobullous eruption that develops in a delayed fashion—24 to 72 hours after sun exposure. The dermatitis may extend to other parts of the body either through spread of the chemical agent by the hands or clothing or due to the systemic nature of the immune response. The severity of the presentation can vary depending on multiple factors, such as concentration and absorption of the agent, length of exposure, intensity and duration of UV radiation exposure, and individual susceptibility.4 Chronic PACD may become lichenified. Generally, rashes resolve after discontinuation of the causative agent; however, long-term exposure may lead to development of chronic actinic dermatitis, with persistent photodistributed eczema regardless of contact with the initial inciting agent.9
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for patients presenting with photodistributed dermatitis is broad; therefore, taking a thorough history is important. Considerations include age of onset, timing and persistence of reactions, use of topical and systemic medications (both prescription and over-the-counter [OTC]), personal care products, occupation, and hobbies, as well as a thorough review of systems.
It is important to distinguish PACD from phototoxic contact dermatitis (PTCD)(also known as photoirritant contact dermatitis)(Table). Asking about the onset and timing of the eruption may be critical for distinction, as PTCD can occur within minutes to hours of the first exposure to a chemical and UV radiation, while there is a sensitization delay in PACD.6 Phytophotodermatitis is a well-known type of PTCD caused by exposure to furocoumarin-containing plants, most commonly limes.10 Other causes of PTCD include tar products and certain medications.11 Importantly, PPT to a known phototoxic chemical should never be performed because it will cause a strong reaction in anyone tested, regardless of exposure history.

Other diagnoses to consider include photoaggravated dermatoses (eg, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis) and idiopathic photodermatoses (eg, chronic actinic dermatitis, actinic prurigo, polymorphous light eruption). Although atopic dermatitis usually improves with UV light exposure, photoaggravated atopic dermatitis is suggested in eczema patients who flare with sun exposure, in a seasonal pattern, or after phototherapy; this condition is challenging to differentiate from PACD if PPT is not performed.12 The diagnosis of idiopathic photodermatoses is nuanced; however, asking about the timeline of the reaction including onset, duration, and persistence, as well as characterization of unique clinical features, can help in differentiation.13 In certain scenarios, a biopsy may be helpful. A thorough review of systems will help to assess for autoimmune connective tissue disorders, and relevant serologies should be checked as indicated.
Diagnosis
Histologically, PACD presents similarly to allergic contact dermatitis with spongiotic dermatitis; therefore, biopsy cannot be relied upon to make the diagnosis.6 Photopatch testing is required for definitive diagnosis. It is reasonable to perform PPT in any patient with chronic dermatitis primarily affecting sun-exposed areas without a clear alternative diagnosis.14,15 Of note, at present there are no North American consensus guidelines for PPT, but typically duplicate sets of photoallergens are applied to both sides of the patient’s back and one side is exposed to UVA radiation. The reactions are compared after 48 to 96 hours.15 A positive reaction only at the irradiated site is consistent with photoallergy, while a reaction of equal strength at both the irradiated and nonirradiated sites indicates regular contact allergy. The case of a reaction occurring at both sites with a stronger response at the irradiated site is known as photoaggravated contact allergy, which can be thought of as allergic contact dermatitis that worsens but does not solely occur with exposure to sunlight.
Although PPT is necessary for the accurate diagnosis of PACD, it is infrequently used. Two surveys of 112 and 117 American Contact Dermatitis Society members, respectively, have revealed that only around half performed PPT, most of them testing fewer than 20 times per year.16,17 Additionally, there was variability in the test methodology and allergens employed. Nevertheless, most respondents tested sunscreens, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), fragrances, and their patients’ own products.16,17 The most common reasons for not performing PPT were lack of equipment, insufficient skills, rare clinical suspicion, and cost. Dermatologists at academic centers performed more PPT than those in other practice settings, including multispecialty group practices and private offices.16 These findings highlight multiple factors that may contribute to reduced patient access to PPT and thus potential underdiagnosis of PACD.
Common Photoallergens
The most common photoallergens change over time in response to market trends; for example, fragrance was once a top photoallergen in the United States in the 1970s and 1980s but declined in prominence after musk ambrette—the primary allergen associated with PACD at the time—was removed as an ingredient in fragrances.18
In the largest and most recent PPT series from North America (1999-2009),2 sunscreens comprised 7 of the top 10 most common photoallergens, which is consistent with other studies showing sunscreens to be the most common North American photoallergens.19-22 The frequency of PACD due to sunscreens likely relates to their increasing use worldwide as awareness of photocarcinogenesis and photoaging grows, as well as the common use of UV filters in nonsunscreen personal care products, ranging from lip balms to perfumes and bodywashes. Chemical (organic) UV filters—in particular oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane)—are the most common sunscreen photoallergens.2,23 Para-aminobenzoic acid was once a common photoallergen, but it is no longer used in US sunscreens due to safety concerns.19,20 The physical (inorganic) UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are not known photosensitizers.
Methylisothiazolinone (MI) is a highly allergenic preservative commonly used in a wide array of personal care products, including sunscreens.24 In the most recent NACDG patch test data, MI was the second most common contact allergen.25 Allergic contact dermatitis caused by MI in sunscreen can mimic PACD.26 In addition, MI can cause photoaggravated contact dermatitis, with some affected patients experiencing ongoing photosensitivity even after avoiding this allergen.26-30 The European Union and Canada have introduced restrictions on the use of MI in personal care products, but no such regulatory measures have been taken in the United States to date.25,31,32
After sunscreens, another common cause of PACD are topical NSAIDs, which are frequently used for musculoskeletal pain relief. These are of particular concern in Europe, where a variety of formulations are widely available OTC.33 Ketoprofen and etofenamate are responsible for the largest number of PACD reactions in Europe.2,34,35 Meanwhile, the only OTC topical NSAID available in the United States is diclofenac gel, which was approved in 2020. Cases of PACD due to use of diclofenac gel have been reported in the literature, but testing in larger populations is needed.36-39
Notably, ketoprofen may co- or cross-react with certain UV filters—oxybenzone and octocrylene—and the lipid-lowering agent fenofibrate due to chemical similarities.40-43 Despite the relatively high number of photoallergic reactions to ketoprofen in the NACDG photopatch series, only 25% (5/20) were considered clinically relevant (ie, the allergen could not be verified as present in the known skin contactants of the patient, and the patient was not exposed to circumstances in which contact with materials known to contain the allergen would likely occur), which suggests that they likely represented cross-reactions in patients sensitized to sunscreens.2
Other agents that may cause PACD include antimicrobials, plants and plant derivatives, and pesticides.2,4,18 The antimicrobial fentichlor is a common cause of positive PPT reactions, but it rarely is clinically relevant.44
Treatment
The primary management of PACD centers on identification of the causative photoallergen to avoid future exposure. Patients should be educated on the various names by which the causative allergen can be identified on product labels and should be given a list of safe products that are free from relevant allergens and cross-reacting chemicals.45 Additionally, sun protection education should be provided. Exposure to UVA radiation can occur through windows, making the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing crucial. In cases of sunscreen-induced PACD, the responsible chemical UV filter(s) should be avoided, or alternatively, patients may use physical sunscreens containing only zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide as active ingredients, as these are not known to cause PACD.4
When avoidance alone is insufficient, topical corticosteroids are the usual first-line treatment for localized PACD. When steroid-sparing treatments are preferred, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be used. If PACD is more widespread and severe, systemic therapy using steroids or steroid-sparing agents may be necessary to provide symptomatic relief.4
Final Interpretation
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is not uncommon, particularly among photosensitive patients. Most cases are due to sunscreens or topical NSAIDs. Consideration of PPT should be given in any patient with a chronic photodistributed dermatitis to evaluate for the possibility of PACD.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
- Darvay A, White IR, Rycroft RJ, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is uncommon. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:597-601.
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291.
- Kerr A, Ferguson J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2010;26:56-65.
- As¸kın Ö, Cesur SK, Engin B, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2019;8:157-163.
- Wilm A, Berneburg M. Photoallergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:7-13.
- DeLeo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Imai S, Atarashi K, Ikesue K, et al. Establishment of murine model of allergic photocontact dermatitis to ketoprofen and characterization of pathogenic T cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:127-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Satoh T, et al. Inhibitory effect of melanin pigment on sensitization and elicitation of murine contact photosensitivity: mechanism of low responsiveness in C57BL/10 background mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:673-678.
- Stein KR, Scheinfeld NS. Drug-induced photoallergic and phototoxic reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6:431-443.
- Janusz SC, Schwartz RA. Botanical briefs: phytophotodermatitis is an occupational and recreational dermatosis in the limelight. Cutis. 2021;107:187-189.
- Atwal SK, Chen A, Adler BL. Phototoxic contact dermatitis from over-the-counter 8-methoxypsoralen. Cutis. 2022;109:E2-E3.
- Rutter KJ, Farrar MD, Marjanovic EJ, et al. Clinicophotobiological characterization of photoaggravated atopic dermatitis [published online July 27, 2022]. JAMA Dermatol. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2823
- Lecha M. Idiopathic photodermatoses: clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:499-505.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA. Contact & Occupational Dermatology. 4th ed. Jaypee Brothers; 2016.
- Bruynzeel DP, Ferguson J, Andersen K, et al. Photopatch testing: a consensus methodology for Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:679-682.
- Kim T, Taylor JS, Maibach HI, et al. Photopatch testing among members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society. Dermatitis. 2020;31:59-67.
- Asemota E, Crawford G, Kovarik C, et al. A survey examining photopatch test and phototest methodologies of contact dermatologists in the United States: platform for developing a consensus. Dermatitis. 2017;28:265-269.
- Scalf LA, Davis MD, Rohlinger AL, et al. Photopatch testing of 182 patients: a 6-year experience at the Mayo Clinic. Dermatitis. 2009;20:44-52.
- Greenspoon J, Ahluwalia R, Juma N, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis: a 10-year experience. Dermatitis. 2013;24:29-32.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Schauder S, Ippen H. Contact and photocontact sensitivity to sunscreens. review of a 15-year experience and of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:221-232.
- Collaris EJ, Frank J. Photoallergic contact dermatitis caused by ultraviolet filters in different sunscreens. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(suppl 1):35-37.
- Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, responsible irritants and allergens, clinical characteristics, and management. Dermatitis. 2014;25:289-326.
- Reeder M, Atwater AR. Methylisothiazolinone and isothiazolinone allergy. Cutis. 2019;104:94-96.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123.
- Kullberg SA, Voller LM, Warshaw EM. Methylisothiazolinone in “dermatology-recommended” sunscreens: an important mimicker of photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:366-370.
- Herman A, Aerts O, de Montjoye L, et al. Isothiazolinone derivatives and allergic contact dermatitis: a review and update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:267-276.
- Adler BL, Houle MC, Pratt M. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone and associated photosensitivity: a case series [published online January 25, 2022]. Dermatitis. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000833
- Aerts O, Goossens A, Marguery MC, et al. Photoaggravated allergic contact dermatitis and transient photosensitivity caused by methylisothiazolinone. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:241-245.
- Pirmez R, Fernandes AL, Melo MG. Photoaggravated contact dermatitis to Kathon CG (methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone): a novel pattern of involvement in a growing epidemic?. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1343-1344.
- Uter W, Aalto-Korte K, Agner T, et al. The epidemic of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy in Europe: follow-up on changing exposures.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:333-339.
- Government of Canada. Changes to the cosmetic ingredient hotlist. December 3, 2019. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredient-hotlist-prohibited-restricted-ingredients/changes.html
- Barkin RL. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the importance of drug, delivery, and therapeutic outcome. Am J Ther. 2015;22:388-407.
- European Multicentre Photopatch Test Study (EMCPPTS) Taskforce. A European multicentre photopatch test study. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1002-1009.
- Ophaswongse S, Maibach H. Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis and phototoxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;29:57-64.
- Kowalzick L, Ziegler H. Photoallergic contact dermatitis from topical diclofenac in Solaraze gel. Contact Dermatitis. 2006;54:348-349.
- Montoro J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac. Contact Dermatitis. 2003;48:115.
- Fernández-Jorge B, Goday-Buján JJ, Murga M, et al. Photoallergic contact dermatitis due to diclofenac with cross-reaction to aceclofenac: two case reports. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;61:236-237.
- Akat PB. Severe photosensitivity reaction induced by topical diclofenac. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45:408-409.
- Leroy D, Dompmartin A, Szczurko C, et al. Photodermatitis from ketoprofen with cross-reactivity to fenofibrate and benzophenones. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13:93-97.
- Devleeschouwer V, Roelandts R, Garmyn M, et al. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis from ketoprofen: results of (photo) patch testing and follow-up of 42 patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:159-166.
- Matsushita T, Kamide R. Five cases of photocontact dermatitisdue to topical ketoprofen: photopatch testing and cross-reaction study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2001;17:26-31.
- de Groot AC, Roberts DW. Contact and photocontact allergy to octocrylene: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 2014;70:193-204.
- Wolverton JE, Soter NA, Cohen DE. Fentichlor photocontact dermatitis: a persistent enigma. Dermatitis. 2013;24:77-81.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient management and education. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1043-1054.
Practice Points
- Photoallergic contact dermatitis (PACD) presents clinically and histologically similar to allergic contact dermatitis but is concentrated in sun-exposed body sites.
- Sunscreens currently are the most common photoallergens in North America, whereas topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are more common culprits in Europe.
- Photopatch testing is required to diagnose PACD; however, it is infrequently performed, and there currently are no North American consensus guidelines.
Can Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Contact Dermatitis Coexist?
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Practice Points
- Although it previously was thought that atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) could not coexist due to their polarized immune pathways, current evidence suggests otherwise.
- When both diagnoses are suspected, patch testing should be considered as well as therapeutic strategies that can treat both AD and ACD simultaneously.
Aluminum: The 2022 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year
No time of the year is more exciting than the unveiling of the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Sometimes the selected allergen represents a completely novel cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) with an unpronounceable chemical name. Not this time! The 2022 Allergen of the Year is likely to be lurking in your kitchen drawer at this very moment, as this year aluminum was chosen for this most prestigious honor.1 But do not throw out your aluminum foil just yet—aluminum allergy tends to be confined to specific scenarios. In this article, we highlight the growing recognition of aluminum contact allergy, particularly in the pediatric population, focusing on distinct presentations of aluminum ACD, unique sources of exposure, and nuances of patch testing to this metal.
Aluminum Is All Around Us
As the third most common element in the Earth’s crust, aluminum can be found quite literally everywhere.1 However, aluminum rarely is found in its pure elemental form; instead, it reacts with other elements around it, most commonly oxygen, to form aluminum-containing compounds. Known for their stability and safety, aluminum and its salts are incorporated in myriad products ranging from electronic equipment to foods and their packaging, medications, cosmetics, orthopedic and dental implants, and even tattoos. Aluminum also is found in the air and water supply and may even be encountered in certain workplaces, such as aircraft and machine industries. As such, contact with aluminum is all but certain in modern life.
The use of aluminum in consumer products is widely accepted as safe by public health agencies in the United States.2 Although there has been public concern that aluminum could be linked to development of breast cancer or Alzheimer disease, there is no clear evidence that these conditions are associated with routine aluminum exposure through ingestion or consumer products.3-5
Aluminum Contact Allergy
In part because of its ubiquity and in part because of the stability of aluminum-containing compounds, it was long thought that aluminum was nonallergenic. Contact allergy to elemental aluminum is rare; on the other hand, aluminum salts (the forms we are likely to encounter in daily life) are now recognized in the field of contact dermatitis as allergens of significance, particularly in the pediatric population.1,6
First reported as a possible occupational allergen in 1944,7 aluminum allergy came to prominence in the 1990s in association with vaccines. Aluminum is included in some vaccines as an adjuvant that bolsters the immune response8; the eTable lists currently available aluminum-containing vaccines in the United States; of note, none of the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the United States or Europe contain aluminum.11 Although the use of aluminum in vaccines is considered to be safe by the US Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,12,13 a small number of children become sensitized to aluminum through vaccines and may develop persistent pruritic subcutaneous nodules (also known as vaccination granulomas) at the injection site; however, the incidence of this adverse effect was less than 1% in large studies including as many as 76,000 children, suggesting that it is relatively rare.14,15 Upon patch testing, aluminum allergy has been detected in 77% to 95% of such cases.14 There is wide variation in the onset of the nodules ranging from weeks to years following vaccination.15 Due to pruritus, the examination may reveal accompanying excoriations, hyperpigmentation, and sometimes hypertrichosis at the injection site. Aluminum allergy related to vaccination also can manifest with widespread eruptions representing systemic contact dermatitis.16
Along with vaccines, the second major source of aluminum sensitization is allergen-specific immunotherapies administered by allergists/immunologists, many of which contain aluminum hydroxide.17,18
On the consumer product front, antiperspirants are the most common source of cutaneous exposure to aluminum. Aluminum complexes react with electrolytes in sweat to form plugs in eccrine ducts, thereby preventing sweat excretion.6 Allergic contact dermatitis to these products presents with axillary-vault dermatitis. There also have been reports of ACD to aluminum in sunscreen and toothpaste, with the latter implicated in causing systemic ACD.19,20
Prevalence of Sensitization to Aluminum
There have been a few large-scale studies evaluating rates of sensitization to aluminum in general patch-test patient populations; additionally, because of the complexities of testing this metal, investigators have utilized differing formulations for patch testing. A recent Swedish study found that 0.9% of 5448 adults and 5.1% of 196 children showed positive reactions to aluminum chloride hexahydrate (ACH) 10% in petrolatum and/or aluminum lactate 12% in petrolatum.21 Notably, there was a significant association between aluminum allergy and history of atopy for both adults (P=.0056) and children (P=.046), which remains to be further explored. A systematic review and meta-analysis found comparable rates of aluminum allergy in 0.4% of adults and 5.6% of children without vaccine granulomas who were tested.22 With this evidence in mind, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts that aluminum be included in pediatric baseline patch test series and also investigated for potential inclusion in baseline series for adults.1
Differential Diagnosis of Aluminum ACD
The differential diagnosis for subcutaneous nodules following vaccination is broad and includes various forms of panniculitis, sarcoidosis, foreign body reactions, vascular malformations, infections, and malignancies.23-25 The diagnosis may be obscured in cases with delayed onset. Biopsy is not mandatory to establish the diagnosis; although variable histopathologic findings have been reported, a common feature is histiocytes with abundant granular cytoplasm.26 It may be possible to demonstrate the presence of aluminum particles in tissue using electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis.
For those patients who present with axillary-vault dermatitis, the differential includes ACD to more common allergens in antiperspirants (eg, fragrance), as well as other axillary dermatoses including inverse psoriasis, erythrasma, Hailey-Hailey disease, and various forms of intertrigo. Dermatitis localized to the axillary rim suggests textile allergy.
Patch Testing to Aluminum
Due to its physicochemical properties, patch testing for aluminum allergy is complicated, and historically there has been a lack of consensus on the ideal test formulation.1,27,28 At this time, it appears that the most sensitive formulation for patch testing to aluminum is ACH 10% in petrolatum.1 Some contact dermatitis experts recommend that children younger than 8 years should be tested with ACH 2% in petrolatum to minimize the risk of extreme patch test reactions.29,30 In some patients sensitized to aluminum, the use of aluminum patch test chambers has been noted to produce false-positive reactions, taking the form of multiple ring-shaped reactions to the chambers themselves or reactions to certain allergens whose chemical properties cause corrosion of the aluminum within the chambers.31-33 Therefore, when testing for suspected aluminum allergy, plastic chambers should be used; given the higher prevalence of aluminum allergy in children, some clinics routinely use plastic chambers for all pediatric patch testing.34 Importantly, elemental aluminum, including empty aluminum test chambers or aluminum foil, alone is not sufficient for patch testing as it lacks sensitivity.1 Additionally, nearly 20% of positive tests will be missed if a day 7 reading is not performed, making delayed reading a must in cases with high suspicion for aluminum allergy.21
Management of Aluminum Allergy
The development of pruritic subcutaneous nodules is uncomfortable for children and their guardians alike and may be associated with prolonged symptoms that negatively impact quality of life35,36; nonetheless, expert authorities have determined that the preventive benefits of childhood vaccination far outweigh any risk posed by the presence of aluminum in vaccines.12,13,37 Because aluminum-free formulations may not be available for all vaccines, it is essential to educate patients and families who may be at risk for developing vaccine hesitancy or avoidance.35,36,38 Given the hypothesis that epidermal dendritic cells mediate aluminum sensitization, it has been proposed that vaccine administration via deep intramuscular rather than subcutaneous injection may mitigate the risk, but more evidence is needed to support this approach.39,40 The good news is that the nodules tend to fade with age, with a median time to resolution of 18 to 49 months.14 In addition, patients may experience loss of sensitization to aluminum over time41; in one study, 77% of 241 children lost patch test reactivity when retested 5 to 9 years later.42 The exact reason for this diminishment of reactivity is not well understood. Adjunctive treatments to relieve symptoms of vaccine granulomas include topical and intralesional corticosteroids and antihistamines.
For patients reacting to aluminum in antiperspirants, there are many aluminum-free formulations on the market as well as recipes for homemade antiperspirants.6 On a case-by-case basis, patients may need to avoid aluminum-containing medications, permanent tattoos, and orthopedic or dental implants. To the best of our knowledge, there is no evidence suggesting a need to avoid aluminum in foods and their containers in routine daily life; although some patients report exacerbations of their symptoms associated with food-related aluminum exposures (eg, canned food, dried fruit) and improvement with dietary modification, further investigation is needed to confirm the relevance of these sources of contact.36,38 For patients who require allergen-specific immunotherapy, aluminum-free allergen extracts are available.6
Final Interpretation
Exposure to aluminum is ubiquitous; although relatively uncommon, awareness of the potential for ACD to aluminum is increasingly important, particularly in children. Given the prevalence of aluminum contact allergy, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts for inclusion in baseline pediatric patch test series.1 Although it is a complex issue, the development of ACD in a small proportion of children exposed to aluminum in vaccines does not outweigh the benefit of vaccination for almost all children. When conducting patch testing to aluminum, studies support testing to ACH 10% in petrolatum for adults, and consider reducing the concentration to ACH 2% for children.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank Ian Fritz, MD (South Portland, Maine), for his critical input during preparation of this article.
- Bruze M, Netterlid E, Siemund I. Aluminum—Allergen of the Year 2022. Dermatitis. 2022;33:10-15.
- Toxicological profile for aluminum. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry website. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=191&tid=34
- Klotz K, Weistenhöfer W, Neff F, et al. The health effects of aluminum exposure. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114:653-659.
- Liszewski W, Zaidi AJ, Fournier E, et al. Review of aluminum, paraben, and sulfate product disclaimers on personal care products [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.06.840
- Van Dyke N, Yenugadhati N, Birkett NJ, et al. Association between aluminum in drinking water and incident Alzheimer’s disease in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging cohort. Neurotoxicology. 2021;83:157-165.
- Kullberg SA, Ward JM, Liou YL, et al. Cutaneous reactions to aluminum. Dermatitis. 2020;31:335-349.
- Hall AF. Occupational contact dermatitis among aircraft workers. J Am Med Assoc. 1944;125:179-185.
- HogenEsch H. Mechanism of immunopotentiation and safety of aluminum adjuvants. Front Immunol. 2012;3:406.
- Vaccine exipient summary. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Published November 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/downloads/appendices/b/excipient-table-2.pdf
- Vaccines licensed for use in the United States. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated January 31, 2022. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/vaccines-licensed-use-united-states
- Swenson A. US and EU COVID vaccines don’t contain aluminum. AP News. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://apnews.com/article/fact-checking-afs:Content:9991020426
- Adjuvants and vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated August 4, 2020. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/concerns/adjuvants.html
- Common ingredients in U.S. licensed vaccines. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2002. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/safety-availability-biologics/common-ingredients-us-licensed-vaccines
- Bergfors E, Hermansson G, Nyström Kronander U, et al. How common are long-lasting, intensely itching vaccination granulomas and contact allergy to aluminium induced by currently used pediatric vaccines? a prospective cohort study. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1297-1307.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B, Inerot A. Unexpectedly high incidence of persistent itching nodules and delayed hypersensitivity to aluminium in children after the use of adsorbed vaccines from a single manufacturer. Vaccine. 2003;22:64-69.
- Mistry BD, DeKoven JG. Widespread cutaneous eruption after aluminum-containing vaccination: a case report and review of current literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:872-874.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Björk J, et al. There is an association between contact allergy to aluminium and persistent subcutaneous nodules in children undergoing hyposensitization therapy. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:41-49.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Siemund I, et al. Does allergen-specific immunotherapy induce contact allergy to aluminium? Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:50-56.
- Hoffmann SS, Elberling J, Thyssen JP, et al. Does aluminium in sunscreens cause dermatitis in children with aluminium contact allergy: a repeated open application test study. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:9-14.
- Veien NK, Hattel T, Laurberg G. Systemically aggravated contact dermatitis caused by aluminium in toothpaste. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;28:199-200.
- Siemund I, Dahlin J, Hindsén M, et al. Contact allergy to two aluminum salts in consecutively patch-tested dermatitis patients. Dermatitis. 2022;33:31-35.
- Hoffmann SS, Wennervaldt M, Alinaghi F, et al. Aluminium contact allergy without vaccination granulomas: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:129-135.
- Bergfors E, Lundmark K, Kronander UN. Case report: a child with a long-standing, intensely itching subcutaneous nodule on a thigh: an uncommon (?) reaction to commonly used vaccines [published online January 13, 2013]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007779
- Mooser G, Gall H, Weber L, et al. Cold panniculitis—an unusual differential diagnosis from aluminium allergy in a patient hyposensitized with aluminium-precipitated antigen extract. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;44:366-375.
- Mulholland D, Joyce EA, Foran A, et al. The evaluation of palpable thigh nodularity in vaccination-age children—differentiating vaccination granulomas from other causes. J Med Ultrasound. 2021;29:129.
- Chong H, Brady K, Metze D, et al. Persistent nodules at injection sites (aluminium granuloma)—clinicopathological study of 14 cases with a diverse range of histological reaction patterns. Histopathology. 2006;48:182-188.
- Nikpour S, Hedberg YS. Using chemical speciation modelling to discuss variations in patch test reactions to different aluminium and chromium salts. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:415-420.
- Siemund I, Zimerson E, Hindsén M, et al. Establishing aluminium contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2012;67:162-170.
- Bergfors E, Inerot A, Falk L, et al. Patch testing children with aluminium chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum: a review and a recommendation. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:81-88.
- Bruze M, Mowitz M, Netterlid E, et al. Patch testing with aluminum chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:176-177.
- Hedberg YS, Wei Z, Matura M. Quantification of aluminium release from Finn Chambers under different in vitro test conditions of relevance for patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:380-386.
- King N, Moffitt D. Allergic contact dermatitis secondary to the use of aluminium Finn Chambers®. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:365-366.
- Rosholm Comstedt L, Dahlin J, Bruze M, et al. Patch testing with aluminium Finn Chambers could give false-positive reactions in patients with contact allergy to aluminium. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:407-414.
- Tran JM, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Patch testing in children: not just little adults. Cutis. 2019;104:288-290.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B. Sixty-four children with persistent itching nodules and contact allergy to aluminium after vaccination with aluminium-adsorbed vaccines-prognosis and outcome after booster vaccination. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172:171-177.
- Hoffmann SS, Thyssen JP, Elberling J, et al. Children with vaccination granulomas and aluminum contact allergy: evaluation of predispositions, avoidance behavior, and quality of life. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:99-107.
- Löffler P. Review: vaccine myth-buster-cleaning up with prejudices and dangerous misinformation [published online June 10, 2021]. Front Immunol. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663280
- Salik E, Løvik I, Andersen KE, et al. Persistent skin reactions and aluminium hypersensitivity induced by childhood vaccines. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016;96:967-971.
- Beveridge MG, Polcari IC, Burns JL, et al. Local vaccine site reactions and contact allergy to aluminum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012; 29:68-72.
- Frederiksen MS, Tofte H. Immunisation with aluminium-containing vaccine of a child with itching nodule following previous vaccination. Vaccine. 2004;23:1-2.
- Siemund I, Mowitz M, Zimerson E, et al. Variation in aluminium patch test reactivity over time. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:288-296.
- Lidholm AG, Bergfors E, Inerot A, et al. Unexpected loss of contact allergy to aluminium induced by vaccine. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;68:286.
No time of the year is more exciting than the unveiling of the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Sometimes the selected allergen represents a completely novel cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) with an unpronounceable chemical name. Not this time! The 2022 Allergen of the Year is likely to be lurking in your kitchen drawer at this very moment, as this year aluminum was chosen for this most prestigious honor.1 But do not throw out your aluminum foil just yet—aluminum allergy tends to be confined to specific scenarios. In this article, we highlight the growing recognition of aluminum contact allergy, particularly in the pediatric population, focusing on distinct presentations of aluminum ACD, unique sources of exposure, and nuances of patch testing to this metal.
Aluminum Is All Around Us
As the third most common element in the Earth’s crust, aluminum can be found quite literally everywhere.1 However, aluminum rarely is found in its pure elemental form; instead, it reacts with other elements around it, most commonly oxygen, to form aluminum-containing compounds. Known for their stability and safety, aluminum and its salts are incorporated in myriad products ranging from electronic equipment to foods and their packaging, medications, cosmetics, orthopedic and dental implants, and even tattoos. Aluminum also is found in the air and water supply and may even be encountered in certain workplaces, such as aircraft and machine industries. As such, contact with aluminum is all but certain in modern life.
The use of aluminum in consumer products is widely accepted as safe by public health agencies in the United States.2 Although there has been public concern that aluminum could be linked to development of breast cancer or Alzheimer disease, there is no clear evidence that these conditions are associated with routine aluminum exposure through ingestion or consumer products.3-5
Aluminum Contact Allergy
In part because of its ubiquity and in part because of the stability of aluminum-containing compounds, it was long thought that aluminum was nonallergenic. Contact allergy to elemental aluminum is rare; on the other hand, aluminum salts (the forms we are likely to encounter in daily life) are now recognized in the field of contact dermatitis as allergens of significance, particularly in the pediatric population.1,6
First reported as a possible occupational allergen in 1944,7 aluminum allergy came to prominence in the 1990s in association with vaccines. Aluminum is included in some vaccines as an adjuvant that bolsters the immune response8; the eTable lists currently available aluminum-containing vaccines in the United States; of note, none of the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the United States or Europe contain aluminum.11 Although the use of aluminum in vaccines is considered to be safe by the US Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,12,13 a small number of children become sensitized to aluminum through vaccines and may develop persistent pruritic subcutaneous nodules (also known as vaccination granulomas) at the injection site; however, the incidence of this adverse effect was less than 1% in large studies including as many as 76,000 children, suggesting that it is relatively rare.14,15 Upon patch testing, aluminum allergy has been detected in 77% to 95% of such cases.14 There is wide variation in the onset of the nodules ranging from weeks to years following vaccination.15 Due to pruritus, the examination may reveal accompanying excoriations, hyperpigmentation, and sometimes hypertrichosis at the injection site. Aluminum allergy related to vaccination also can manifest with widespread eruptions representing systemic contact dermatitis.16
Along with vaccines, the second major source of aluminum sensitization is allergen-specific immunotherapies administered by allergists/immunologists, many of which contain aluminum hydroxide.17,18
On the consumer product front, antiperspirants are the most common source of cutaneous exposure to aluminum. Aluminum complexes react with electrolytes in sweat to form plugs in eccrine ducts, thereby preventing sweat excretion.6 Allergic contact dermatitis to these products presents with axillary-vault dermatitis. There also have been reports of ACD to aluminum in sunscreen and toothpaste, with the latter implicated in causing systemic ACD.19,20
Prevalence of Sensitization to Aluminum
There have been a few large-scale studies evaluating rates of sensitization to aluminum in general patch-test patient populations; additionally, because of the complexities of testing this metal, investigators have utilized differing formulations for patch testing. A recent Swedish study found that 0.9% of 5448 adults and 5.1% of 196 children showed positive reactions to aluminum chloride hexahydrate (ACH) 10% in petrolatum and/or aluminum lactate 12% in petrolatum.21 Notably, there was a significant association between aluminum allergy and history of atopy for both adults (P=.0056) and children (P=.046), which remains to be further explored. A systematic review and meta-analysis found comparable rates of aluminum allergy in 0.4% of adults and 5.6% of children without vaccine granulomas who were tested.22 With this evidence in mind, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts that aluminum be included in pediatric baseline patch test series and also investigated for potential inclusion in baseline series for adults.1
Differential Diagnosis of Aluminum ACD
The differential diagnosis for subcutaneous nodules following vaccination is broad and includes various forms of panniculitis, sarcoidosis, foreign body reactions, vascular malformations, infections, and malignancies.23-25 The diagnosis may be obscured in cases with delayed onset. Biopsy is not mandatory to establish the diagnosis; although variable histopathologic findings have been reported, a common feature is histiocytes with abundant granular cytoplasm.26 It may be possible to demonstrate the presence of aluminum particles in tissue using electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis.
For those patients who present with axillary-vault dermatitis, the differential includes ACD to more common allergens in antiperspirants (eg, fragrance), as well as other axillary dermatoses including inverse psoriasis, erythrasma, Hailey-Hailey disease, and various forms of intertrigo. Dermatitis localized to the axillary rim suggests textile allergy.
Patch Testing to Aluminum
Due to its physicochemical properties, patch testing for aluminum allergy is complicated, and historically there has been a lack of consensus on the ideal test formulation.1,27,28 At this time, it appears that the most sensitive formulation for patch testing to aluminum is ACH 10% in petrolatum.1 Some contact dermatitis experts recommend that children younger than 8 years should be tested with ACH 2% in petrolatum to minimize the risk of extreme patch test reactions.29,30 In some patients sensitized to aluminum, the use of aluminum patch test chambers has been noted to produce false-positive reactions, taking the form of multiple ring-shaped reactions to the chambers themselves or reactions to certain allergens whose chemical properties cause corrosion of the aluminum within the chambers.31-33 Therefore, when testing for suspected aluminum allergy, plastic chambers should be used; given the higher prevalence of aluminum allergy in children, some clinics routinely use plastic chambers for all pediatric patch testing.34 Importantly, elemental aluminum, including empty aluminum test chambers or aluminum foil, alone is not sufficient for patch testing as it lacks sensitivity.1 Additionally, nearly 20% of positive tests will be missed if a day 7 reading is not performed, making delayed reading a must in cases with high suspicion for aluminum allergy.21
Management of Aluminum Allergy
The development of pruritic subcutaneous nodules is uncomfortable for children and their guardians alike and may be associated with prolonged symptoms that negatively impact quality of life35,36; nonetheless, expert authorities have determined that the preventive benefits of childhood vaccination far outweigh any risk posed by the presence of aluminum in vaccines.12,13,37 Because aluminum-free formulations may not be available for all vaccines, it is essential to educate patients and families who may be at risk for developing vaccine hesitancy or avoidance.35,36,38 Given the hypothesis that epidermal dendritic cells mediate aluminum sensitization, it has been proposed that vaccine administration via deep intramuscular rather than subcutaneous injection may mitigate the risk, but more evidence is needed to support this approach.39,40 The good news is that the nodules tend to fade with age, with a median time to resolution of 18 to 49 months.14 In addition, patients may experience loss of sensitization to aluminum over time41; in one study, 77% of 241 children lost patch test reactivity when retested 5 to 9 years later.42 The exact reason for this diminishment of reactivity is not well understood. Adjunctive treatments to relieve symptoms of vaccine granulomas include topical and intralesional corticosteroids and antihistamines.
For patients reacting to aluminum in antiperspirants, there are many aluminum-free formulations on the market as well as recipes for homemade antiperspirants.6 On a case-by-case basis, patients may need to avoid aluminum-containing medications, permanent tattoos, and orthopedic or dental implants. To the best of our knowledge, there is no evidence suggesting a need to avoid aluminum in foods and their containers in routine daily life; although some patients report exacerbations of their symptoms associated with food-related aluminum exposures (eg, canned food, dried fruit) and improvement with dietary modification, further investigation is needed to confirm the relevance of these sources of contact.36,38 For patients who require allergen-specific immunotherapy, aluminum-free allergen extracts are available.6
Final Interpretation
Exposure to aluminum is ubiquitous; although relatively uncommon, awareness of the potential for ACD to aluminum is increasingly important, particularly in children. Given the prevalence of aluminum contact allergy, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts for inclusion in baseline pediatric patch test series.1 Although it is a complex issue, the development of ACD in a small proportion of children exposed to aluminum in vaccines does not outweigh the benefit of vaccination for almost all children. When conducting patch testing to aluminum, studies support testing to ACH 10% in petrolatum for adults, and consider reducing the concentration to ACH 2% for children.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank Ian Fritz, MD (South Portland, Maine), for his critical input during preparation of this article.
No time of the year is more exciting than the unveiling of the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year. Sometimes the selected allergen represents a completely novel cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) with an unpronounceable chemical name. Not this time! The 2022 Allergen of the Year is likely to be lurking in your kitchen drawer at this very moment, as this year aluminum was chosen for this most prestigious honor.1 But do not throw out your aluminum foil just yet—aluminum allergy tends to be confined to specific scenarios. In this article, we highlight the growing recognition of aluminum contact allergy, particularly in the pediatric population, focusing on distinct presentations of aluminum ACD, unique sources of exposure, and nuances of patch testing to this metal.
Aluminum Is All Around Us
As the third most common element in the Earth’s crust, aluminum can be found quite literally everywhere.1 However, aluminum rarely is found in its pure elemental form; instead, it reacts with other elements around it, most commonly oxygen, to form aluminum-containing compounds. Known for their stability and safety, aluminum and its salts are incorporated in myriad products ranging from electronic equipment to foods and their packaging, medications, cosmetics, orthopedic and dental implants, and even tattoos. Aluminum also is found in the air and water supply and may even be encountered in certain workplaces, such as aircraft and machine industries. As such, contact with aluminum is all but certain in modern life.
The use of aluminum in consumer products is widely accepted as safe by public health agencies in the United States.2 Although there has been public concern that aluminum could be linked to development of breast cancer or Alzheimer disease, there is no clear evidence that these conditions are associated with routine aluminum exposure through ingestion or consumer products.3-5
Aluminum Contact Allergy
In part because of its ubiquity and in part because of the stability of aluminum-containing compounds, it was long thought that aluminum was nonallergenic. Contact allergy to elemental aluminum is rare; on the other hand, aluminum salts (the forms we are likely to encounter in daily life) are now recognized in the field of contact dermatitis as allergens of significance, particularly in the pediatric population.1,6
First reported as a possible occupational allergen in 1944,7 aluminum allergy came to prominence in the 1990s in association with vaccines. Aluminum is included in some vaccines as an adjuvant that bolsters the immune response8; the eTable lists currently available aluminum-containing vaccines in the United States; of note, none of the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the United States or Europe contain aluminum.11 Although the use of aluminum in vaccines is considered to be safe by the US Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,12,13 a small number of children become sensitized to aluminum through vaccines and may develop persistent pruritic subcutaneous nodules (also known as vaccination granulomas) at the injection site; however, the incidence of this adverse effect was less than 1% in large studies including as many as 76,000 children, suggesting that it is relatively rare.14,15 Upon patch testing, aluminum allergy has been detected in 77% to 95% of such cases.14 There is wide variation in the onset of the nodules ranging from weeks to years following vaccination.15 Due to pruritus, the examination may reveal accompanying excoriations, hyperpigmentation, and sometimes hypertrichosis at the injection site. Aluminum allergy related to vaccination also can manifest with widespread eruptions representing systemic contact dermatitis.16
Along with vaccines, the second major source of aluminum sensitization is allergen-specific immunotherapies administered by allergists/immunologists, many of which contain aluminum hydroxide.17,18
On the consumer product front, antiperspirants are the most common source of cutaneous exposure to aluminum. Aluminum complexes react with electrolytes in sweat to form plugs in eccrine ducts, thereby preventing sweat excretion.6 Allergic contact dermatitis to these products presents with axillary-vault dermatitis. There also have been reports of ACD to aluminum in sunscreen and toothpaste, with the latter implicated in causing systemic ACD.19,20
Prevalence of Sensitization to Aluminum
There have been a few large-scale studies evaluating rates of sensitization to aluminum in general patch-test patient populations; additionally, because of the complexities of testing this metal, investigators have utilized differing formulations for patch testing. A recent Swedish study found that 0.9% of 5448 adults and 5.1% of 196 children showed positive reactions to aluminum chloride hexahydrate (ACH) 10% in petrolatum and/or aluminum lactate 12% in petrolatum.21 Notably, there was a significant association between aluminum allergy and history of atopy for both adults (P=.0056) and children (P=.046), which remains to be further explored. A systematic review and meta-analysis found comparable rates of aluminum allergy in 0.4% of adults and 5.6% of children without vaccine granulomas who were tested.22 With this evidence in mind, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts that aluminum be included in pediatric baseline patch test series and also investigated for potential inclusion in baseline series for adults.1
Differential Diagnosis of Aluminum ACD
The differential diagnosis for subcutaneous nodules following vaccination is broad and includes various forms of panniculitis, sarcoidosis, foreign body reactions, vascular malformations, infections, and malignancies.23-25 The diagnosis may be obscured in cases with delayed onset. Biopsy is not mandatory to establish the diagnosis; although variable histopathologic findings have been reported, a common feature is histiocytes with abundant granular cytoplasm.26 It may be possible to demonstrate the presence of aluminum particles in tissue using electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis.
For those patients who present with axillary-vault dermatitis, the differential includes ACD to more common allergens in antiperspirants (eg, fragrance), as well as other axillary dermatoses including inverse psoriasis, erythrasma, Hailey-Hailey disease, and various forms of intertrigo. Dermatitis localized to the axillary rim suggests textile allergy.
Patch Testing to Aluminum
Due to its physicochemical properties, patch testing for aluminum allergy is complicated, and historically there has been a lack of consensus on the ideal test formulation.1,27,28 At this time, it appears that the most sensitive formulation for patch testing to aluminum is ACH 10% in petrolatum.1 Some contact dermatitis experts recommend that children younger than 8 years should be tested with ACH 2% in petrolatum to minimize the risk of extreme patch test reactions.29,30 In some patients sensitized to aluminum, the use of aluminum patch test chambers has been noted to produce false-positive reactions, taking the form of multiple ring-shaped reactions to the chambers themselves or reactions to certain allergens whose chemical properties cause corrosion of the aluminum within the chambers.31-33 Therefore, when testing for suspected aluminum allergy, plastic chambers should be used; given the higher prevalence of aluminum allergy in children, some clinics routinely use plastic chambers for all pediatric patch testing.34 Importantly, elemental aluminum, including empty aluminum test chambers or aluminum foil, alone is not sufficient for patch testing as it lacks sensitivity.1 Additionally, nearly 20% of positive tests will be missed if a day 7 reading is not performed, making delayed reading a must in cases with high suspicion for aluminum allergy.21
Management of Aluminum Allergy
The development of pruritic subcutaneous nodules is uncomfortable for children and their guardians alike and may be associated with prolonged symptoms that negatively impact quality of life35,36; nonetheless, expert authorities have determined that the preventive benefits of childhood vaccination far outweigh any risk posed by the presence of aluminum in vaccines.12,13,37 Because aluminum-free formulations may not be available for all vaccines, it is essential to educate patients and families who may be at risk for developing vaccine hesitancy or avoidance.35,36,38 Given the hypothesis that epidermal dendritic cells mediate aluminum sensitization, it has been proposed that vaccine administration via deep intramuscular rather than subcutaneous injection may mitigate the risk, but more evidence is needed to support this approach.39,40 The good news is that the nodules tend to fade with age, with a median time to resolution of 18 to 49 months.14 In addition, patients may experience loss of sensitization to aluminum over time41; in one study, 77% of 241 children lost patch test reactivity when retested 5 to 9 years later.42 The exact reason for this diminishment of reactivity is not well understood. Adjunctive treatments to relieve symptoms of vaccine granulomas include topical and intralesional corticosteroids and antihistamines.
For patients reacting to aluminum in antiperspirants, there are many aluminum-free formulations on the market as well as recipes for homemade antiperspirants.6 On a case-by-case basis, patients may need to avoid aluminum-containing medications, permanent tattoos, and orthopedic or dental implants. To the best of our knowledge, there is no evidence suggesting a need to avoid aluminum in foods and their containers in routine daily life; although some patients report exacerbations of their symptoms associated with food-related aluminum exposures (eg, canned food, dried fruit) and improvement with dietary modification, further investigation is needed to confirm the relevance of these sources of contact.36,38 For patients who require allergen-specific immunotherapy, aluminum-free allergen extracts are available.6
Final Interpretation
Exposure to aluminum is ubiquitous; although relatively uncommon, awareness of the potential for ACD to aluminum is increasingly important, particularly in children. Given the prevalence of aluminum contact allergy, it has been recommended by contact dermatitis experts for inclusion in baseline pediatric patch test series.1 Although it is a complex issue, the development of ACD in a small proportion of children exposed to aluminum in vaccines does not outweigh the benefit of vaccination for almost all children. When conducting patch testing to aluminum, studies support testing to ACH 10% in petrolatum for adults, and consider reducing the concentration to ACH 2% for children.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank Ian Fritz, MD (South Portland, Maine), for his critical input during preparation of this article.
- Bruze M, Netterlid E, Siemund I. Aluminum—Allergen of the Year 2022. Dermatitis. 2022;33:10-15.
- Toxicological profile for aluminum. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry website. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=191&tid=34
- Klotz K, Weistenhöfer W, Neff F, et al. The health effects of aluminum exposure. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114:653-659.
- Liszewski W, Zaidi AJ, Fournier E, et al. Review of aluminum, paraben, and sulfate product disclaimers on personal care products [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.06.840
- Van Dyke N, Yenugadhati N, Birkett NJ, et al. Association between aluminum in drinking water and incident Alzheimer’s disease in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging cohort. Neurotoxicology. 2021;83:157-165.
- Kullberg SA, Ward JM, Liou YL, et al. Cutaneous reactions to aluminum. Dermatitis. 2020;31:335-349.
- Hall AF. Occupational contact dermatitis among aircraft workers. J Am Med Assoc. 1944;125:179-185.
- HogenEsch H. Mechanism of immunopotentiation and safety of aluminum adjuvants. Front Immunol. 2012;3:406.
- Vaccine exipient summary. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Published November 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/downloads/appendices/b/excipient-table-2.pdf
- Vaccines licensed for use in the United States. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated January 31, 2022. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/vaccines-licensed-use-united-states
- Swenson A. US and EU COVID vaccines don’t contain aluminum. AP News. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://apnews.com/article/fact-checking-afs:Content:9991020426
- Adjuvants and vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated August 4, 2020. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/concerns/adjuvants.html
- Common ingredients in U.S. licensed vaccines. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2002. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/safety-availability-biologics/common-ingredients-us-licensed-vaccines
- Bergfors E, Hermansson G, Nyström Kronander U, et al. How common are long-lasting, intensely itching vaccination granulomas and contact allergy to aluminium induced by currently used pediatric vaccines? a prospective cohort study. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1297-1307.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B, Inerot A. Unexpectedly high incidence of persistent itching nodules and delayed hypersensitivity to aluminium in children after the use of adsorbed vaccines from a single manufacturer. Vaccine. 2003;22:64-69.
- Mistry BD, DeKoven JG. Widespread cutaneous eruption after aluminum-containing vaccination: a case report and review of current literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:872-874.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Björk J, et al. There is an association between contact allergy to aluminium and persistent subcutaneous nodules in children undergoing hyposensitization therapy. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:41-49.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Siemund I, et al. Does allergen-specific immunotherapy induce contact allergy to aluminium? Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:50-56.
- Hoffmann SS, Elberling J, Thyssen JP, et al. Does aluminium in sunscreens cause dermatitis in children with aluminium contact allergy: a repeated open application test study. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:9-14.
- Veien NK, Hattel T, Laurberg G. Systemically aggravated contact dermatitis caused by aluminium in toothpaste. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;28:199-200.
- Siemund I, Dahlin J, Hindsén M, et al. Contact allergy to two aluminum salts in consecutively patch-tested dermatitis patients. Dermatitis. 2022;33:31-35.
- Hoffmann SS, Wennervaldt M, Alinaghi F, et al. Aluminium contact allergy without vaccination granulomas: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:129-135.
- Bergfors E, Lundmark K, Kronander UN. Case report: a child with a long-standing, intensely itching subcutaneous nodule on a thigh: an uncommon (?) reaction to commonly used vaccines [published online January 13, 2013]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007779
- Mooser G, Gall H, Weber L, et al. Cold panniculitis—an unusual differential diagnosis from aluminium allergy in a patient hyposensitized with aluminium-precipitated antigen extract. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;44:366-375.
- Mulholland D, Joyce EA, Foran A, et al. The evaluation of palpable thigh nodularity in vaccination-age children—differentiating vaccination granulomas from other causes. J Med Ultrasound. 2021;29:129.
- Chong H, Brady K, Metze D, et al. Persistent nodules at injection sites (aluminium granuloma)—clinicopathological study of 14 cases with a diverse range of histological reaction patterns. Histopathology. 2006;48:182-188.
- Nikpour S, Hedberg YS. Using chemical speciation modelling to discuss variations in patch test reactions to different aluminium and chromium salts. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:415-420.
- Siemund I, Zimerson E, Hindsén M, et al. Establishing aluminium contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2012;67:162-170.
- Bergfors E, Inerot A, Falk L, et al. Patch testing children with aluminium chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum: a review and a recommendation. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:81-88.
- Bruze M, Mowitz M, Netterlid E, et al. Patch testing with aluminum chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:176-177.
- Hedberg YS, Wei Z, Matura M. Quantification of aluminium release from Finn Chambers under different in vitro test conditions of relevance for patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:380-386.
- King N, Moffitt D. Allergic contact dermatitis secondary to the use of aluminium Finn Chambers®. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:365-366.
- Rosholm Comstedt L, Dahlin J, Bruze M, et al. Patch testing with aluminium Finn Chambers could give false-positive reactions in patients with contact allergy to aluminium. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:407-414.
- Tran JM, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Patch testing in children: not just little adults. Cutis. 2019;104:288-290.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B. Sixty-four children with persistent itching nodules and contact allergy to aluminium after vaccination with aluminium-adsorbed vaccines-prognosis and outcome after booster vaccination. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172:171-177.
- Hoffmann SS, Thyssen JP, Elberling J, et al. Children with vaccination granulomas and aluminum contact allergy: evaluation of predispositions, avoidance behavior, and quality of life. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:99-107.
- Löffler P. Review: vaccine myth-buster-cleaning up with prejudices and dangerous misinformation [published online June 10, 2021]. Front Immunol. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663280
- Salik E, Løvik I, Andersen KE, et al. Persistent skin reactions and aluminium hypersensitivity induced by childhood vaccines. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016;96:967-971.
- Beveridge MG, Polcari IC, Burns JL, et al. Local vaccine site reactions and contact allergy to aluminum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012; 29:68-72.
- Frederiksen MS, Tofte H. Immunisation with aluminium-containing vaccine of a child with itching nodule following previous vaccination. Vaccine. 2004;23:1-2.
- Siemund I, Mowitz M, Zimerson E, et al. Variation in aluminium patch test reactivity over time. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:288-296.
- Lidholm AG, Bergfors E, Inerot A, et al. Unexpected loss of contact allergy to aluminium induced by vaccine. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;68:286.
- Bruze M, Netterlid E, Siemund I. Aluminum—Allergen of the Year 2022. Dermatitis. 2022;33:10-15.
- Toxicological profile for aluminum. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry website. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=191&tid=34
- Klotz K, Weistenhöfer W, Neff F, et al. The health effects of aluminum exposure. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114:653-659.
- Liszewski W, Zaidi AJ, Fournier E, et al. Review of aluminum, paraben, and sulfate product disclaimers on personal care products [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.06.840
- Van Dyke N, Yenugadhati N, Birkett NJ, et al. Association between aluminum in drinking water and incident Alzheimer’s disease in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging cohort. Neurotoxicology. 2021;83:157-165.
- Kullberg SA, Ward JM, Liou YL, et al. Cutaneous reactions to aluminum. Dermatitis. 2020;31:335-349.
- Hall AF. Occupational contact dermatitis among aircraft workers. J Am Med Assoc. 1944;125:179-185.
- HogenEsch H. Mechanism of immunopotentiation and safety of aluminum adjuvants. Front Immunol. 2012;3:406.
- Vaccine exipient summary. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Published November 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/downloads/appendices/b/excipient-table-2.pdf
- Vaccines licensed for use in the United States. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated January 31, 2022. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/vaccines-licensed-use-united-states
- Swenson A. US and EU COVID vaccines don’t contain aluminum. AP News. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://apnews.com/article/fact-checking-afs:Content:9991020426
- Adjuvants and vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated August 4, 2020. Accessed June 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/concerns/adjuvants.html
- Common ingredients in U.S. licensed vaccines. US Food and Drug Administration website. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2002. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/safety-availability-biologics/common-ingredients-us-licensed-vaccines
- Bergfors E, Hermansson G, Nyström Kronander U, et al. How common are long-lasting, intensely itching vaccination granulomas and contact allergy to aluminium induced by currently used pediatric vaccines? a prospective cohort study. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1297-1307.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B, Inerot A. Unexpectedly high incidence of persistent itching nodules and delayed hypersensitivity to aluminium in children after the use of adsorbed vaccines from a single manufacturer. Vaccine. 2003;22:64-69.
- Mistry BD, DeKoven JG. Widespread cutaneous eruption after aluminum-containing vaccination: a case report and review of current literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:872-874.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Björk J, et al. There is an association between contact allergy to aluminium and persistent subcutaneous nodules in children undergoing hyposensitization therapy. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:41-49.
- Netterlid E, Hindsén M, Siemund I, et al. Does allergen-specific immunotherapy induce contact allergy to aluminium? Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:50-56.
- Hoffmann SS, Elberling J, Thyssen JP, et al. Does aluminium in sunscreens cause dermatitis in children with aluminium contact allergy: a repeated open application test study. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:9-14.
- Veien NK, Hattel T, Laurberg G. Systemically aggravated contact dermatitis caused by aluminium in toothpaste. Contact Dermatitis. 1993;28:199-200.
- Siemund I, Dahlin J, Hindsén M, et al. Contact allergy to two aluminum salts in consecutively patch-tested dermatitis patients. Dermatitis. 2022;33:31-35.
- Hoffmann SS, Wennervaldt M, Alinaghi F, et al. Aluminium contact allergy without vaccination granulomas: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:129-135.
- Bergfors E, Lundmark K, Kronander UN. Case report: a child with a long-standing, intensely itching subcutaneous nodule on a thigh: an uncommon (?) reaction to commonly used vaccines [published online January 13, 2013]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007779
- Mooser G, Gall H, Weber L, et al. Cold panniculitis—an unusual differential diagnosis from aluminium allergy in a patient hyposensitized with aluminium-precipitated antigen extract. Contact Dermatitis. 2001;44:366-375.
- Mulholland D, Joyce EA, Foran A, et al. The evaluation of palpable thigh nodularity in vaccination-age children—differentiating vaccination granulomas from other causes. J Med Ultrasound. 2021;29:129.
- Chong H, Brady K, Metze D, et al. Persistent nodules at injection sites (aluminium granuloma)—clinicopathological study of 14 cases with a diverse range of histological reaction patterns. Histopathology. 2006;48:182-188.
- Nikpour S, Hedberg YS. Using chemical speciation modelling to discuss variations in patch test reactions to different aluminium and chromium salts. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:415-420.
- Siemund I, Zimerson E, Hindsén M, et al. Establishing aluminium contact allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 2012;67:162-170.
- Bergfors E, Inerot A, Falk L, et al. Patch testing children with aluminium chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum: a review and a recommendation. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:81-88.
- Bruze M, Mowitz M, Netterlid E, et al. Patch testing with aluminum chloride hexahydrate in petrolatum. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:176-177.
- Hedberg YS, Wei Z, Matura M. Quantification of aluminium release from Finn Chambers under different in vitro test conditions of relevance for patch testing. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:380-386.
- King N, Moffitt D. Allergic contact dermatitis secondary to the use of aluminium Finn Chambers®. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:365-366.
- Rosholm Comstedt L, Dahlin J, Bruze M, et al. Patch testing with aluminium Finn Chambers could give false-positive reactions in patients with contact allergy to aluminium. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:407-414.
- Tran JM, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Patch testing in children: not just little adults. Cutis. 2019;104:288-290.
- Bergfors E, Trollfors B. Sixty-four children with persistent itching nodules and contact allergy to aluminium after vaccination with aluminium-adsorbed vaccines-prognosis and outcome after booster vaccination. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172:171-177.
- Hoffmann SS, Thyssen JP, Elberling J, et al. Children with vaccination granulomas and aluminum contact allergy: evaluation of predispositions, avoidance behavior, and quality of life. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:99-107.
- Löffler P. Review: vaccine myth-buster-cleaning up with prejudices and dangerous misinformation [published online June 10, 2021]. Front Immunol. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663280
- Salik E, Løvik I, Andersen KE, et al. Persistent skin reactions and aluminium hypersensitivity induced by childhood vaccines. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016;96:967-971.
- Beveridge MG, Polcari IC, Burns JL, et al. Local vaccine site reactions and contact allergy to aluminum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012; 29:68-72.
- Frederiksen MS, Tofte H. Immunisation with aluminium-containing vaccine of a child with itching nodule following previous vaccination. Vaccine. 2004;23:1-2.
- Siemund I, Mowitz M, Zimerson E, et al. Variation in aluminium patch test reactivity over time. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:288-296.
- Lidholm AG, Bergfors E, Inerot A, et al. Unexpected loss of contact allergy to aluminium induced by vaccine. Contact Dermatitis. 2013;68:286.
Practice Points
- Aluminum is an allergen of significance relating to its use in vaccines, immunotherapies, and antiperspirants.
- There is a greater prevalence of aluminum contact allergy in children than in adults, affecting up to 5% of the pediatric patch-test population.
- The recommended patch test formulation is aluminum chloride hexahydrate 10% in petrolatum, with consideration of reducing the concentration to 2% in children younger than 8 years to avoid strong reactions.