The Diagnosis: Tumor of the Follicular Infundibulum
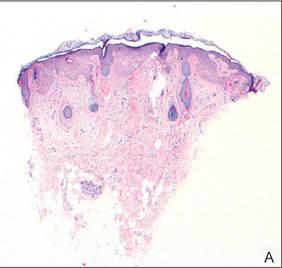
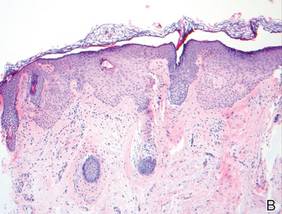
Histopathologic findings from a facial papule in our patient revealed multifocal hyperplasia of anastomosing follicular infundibular cells with multiple connections to the overlying epidermis (Figure). There was no atypia. Gomori methenamine-silver and periodic acid–Schiff stains for fungi were negative. The combined clinical presentation and histopathologic findings supported the diagnosis of multiple tumor of the follicular infundibulum (TFI).
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum was diagnosed based on a biopsy from the right cheek that revealed multifocal hyperplasia of anastomosing follicular infundibular cells with multiple connections to the overlying epidermis (A and B)(H&E, original magnifications ×40 and ×100). |
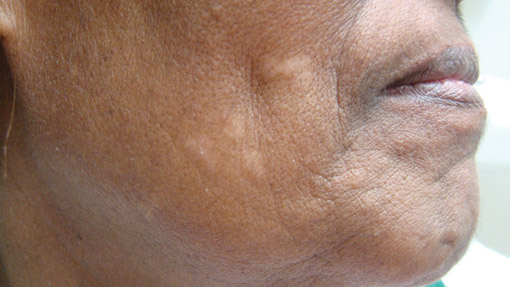
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum is an uncommon benign neoplasm that was first described in 1961 by Mehregan and Butler.1 The reported frequency is 10 per 100,000 biopsies.2 The majority of cases have been reported as solitary lesions, and multiple TFI are rare.3 Tumor of the follicular infundibulum affects middle-aged and elderly individuals with a female predominance.4 Multiple lesions generally range in number from 10 to 20, but there are few reports of more than 100 lesions.2,3,5,6 The solitary tumors often are initially misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) or seborrheic keratosis. Multiple TFI have been described variably as hypopigmented, flesh-colored and pink, flat and slightly depressed macules and thin papules. Sites of predilection include the scalp, face, neck, and upper trunk.2,3,5
There is no histopathologic difference between solitary and multiple TFI. Tumor of the follicular infundibulum displays a characteristic pale platelike proliferation of keratinocytes within the upper dermis attached to the overlying epidermis. The proliferating cells stain positive with periodic acid–Schiff, diastase-digestible glycogen is present in the cells at the base of the tumor, and a thickened network or brushlike pattern of elastic fibers surrounds the periphery of the tumor.1 Tumor of the follicular infundibulum is occasionally discovered incidentally on biopsy and has been observed in the margin of wide excisions of a variety of neoplasms including BCC.7 Based on the close association of TFI and BCC in the same specimens, Weyers et al7 concluded that TFI may be a nonaggressive type of BCC. Cribier and Grosshans2 reported 2 cases of TFI overlying a nevus sebaceous and a fibroma.
Treatment of TFI includes topical keratolytics, topical retinoic acid,5 imiquimod,8 topical steroids, and oral etretinate,6 all of which result in minimal improvement or incomplete resolution. Destructive treatments include cryotherapy, curettage, electrosurgery, laser ablation, and surgical excision, but all may lead to an unacceptable cosmetic result.