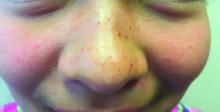
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.