User login
More evidence salt substitutes lower risk of CVD and death
Dietary salt substitutes not only lower blood pressure but also have a clear impact on hard clinical endpoints, lowering the risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and death from all causes and cardiovascular disease (CVD), a meta-analysis shows.
The blood pressure–mediated protective effects of salt substitutes on CVD and death are likely to apply to the roughly 1.28 billion people around the world who have high blood pressure, the researchers say.
“These findings are unlikely to reflect the play of chance and support the adoption of salt substitutes in clinical practice and public health policy as a strategy to reduce dietary sodium intake, increase dietary potassium intake, lower blood pressure, and prevent major cardiovascular events,” they write.
The study was published online in Heart.
Strong support for landmark study
In salt substitutes, a proportion of sodium chloride is replaced with potassium chloride. They are known to help lower blood pressure, but less is known about their impact on hard clinical endpoints, Maoyi Tian, PhD, with Harbin Medical University, China, and the George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, and colleagues note in their article.
In the landmark Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), salt substitutes cut the risk of MI, stroke, and early death, as reported previously by this news organization.
But SSaSS was conducted in China, and it was unclear whether these benefits would apply to people in other parts of the world.
To investigate, Dr. Tian and colleagues pooled data from 21 relevant parallel-group, step-wedge, or cluster randomized controlled trials published through August 2021, with 31,949 participants. The trials were conducted in Europe, the Western Pacific Region, the Americas, and South East Asia and reported the effect of a salt substitute on blood pressure or clinical outcomes.
A meta-analysis of blood pressure data from 19 trials that included 29,528 participants showed that salt substitutes lowered systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 4.61 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, −6.07 to −3.14) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) by 1.61 mm Hg (95% CI, −2.42 to −0.79).
The proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitutes varied from 33% to 75%; the proportion of potassium ranged from 25% to 65%.
Each 10% lower proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitute was associated with a 1.53 mm Hg (95% CI, −3.02 to −0.03; P = .045) greater reduction in SBP and a 0.95 mm Hg (95% CI, −1.78 to −0.12; P = .025) greater reduction in DBP.
Reductions in blood pressure appeared consistent, irrespective of country, age, sex, history of high blood pressure, weight, baseline blood pressure, and baseline levels of urinary sodium and potassium.
Clear benefit on hard outcomes
Pooled data on clinical outcomes from five trials that included 24,306 participants, mostly from the SSaSS, showed clear protective effects of salt substitutes on total mortality (risk ratio, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
Dr. Tian and colleagues say that “broader population use of salt substitute is supported by the absence of any detectable adverse effect of salt substitutes on hyperkalemia in this review.”
They note, however, that all of the trials took “pragmatic steps to exclude participants at elevated risk of hyperkalemia, seeking to exclude those with chronic kidney disease or using medications that elevate serum potassium.”
Offering perspective on the study, Harlan Krumholz, MD, with Yale New Haven Hospital and Yale School of Medicine, both in New Haven, Conn., said it provides “useful information by bringing together the trial evidence on salt substitutes. The evidence is dominated by the SSaSS, but the others add context.”
Dr. Krumholz said that at this point, he thinks salt substitutes “could be included in recommendations to patients.”
“SSaSS was conducted in villages in China, so that is where the evidence is strongest and most relevant, but this is a low-cost and seemingly safe strategy that could be tried by anyone without contraindications, such as kidney disease or taking a potassium-sparing medication or potassium supplement,” Dr. Krumholz told this news organization.
Johanna Contreras, MD, heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, agrees that in the absence of contraindications, salt substitutes should be recommended.
“Americans put salt on everything and don’t even think about it. The salt substitutes are very helpful,” Dr. Contreras said in an interview.
“People who don’t have high blood pressure should limit salt intake, because what we have seen is that if you have high blood pressure in your family – even if you don’t have high blood pressure in your 20s or 30s – you’re likely to develop high blood pressure,” Dr. Contreras said.
“Therefore, it’s wise early on to start protecting yourself and using low salt and salt substitutes,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Tian, Dr. Krumholz, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dietary salt substitutes not only lower blood pressure but also have a clear impact on hard clinical endpoints, lowering the risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and death from all causes and cardiovascular disease (CVD), a meta-analysis shows.
The blood pressure–mediated protective effects of salt substitutes on CVD and death are likely to apply to the roughly 1.28 billion people around the world who have high blood pressure, the researchers say.
“These findings are unlikely to reflect the play of chance and support the adoption of salt substitutes in clinical practice and public health policy as a strategy to reduce dietary sodium intake, increase dietary potassium intake, lower blood pressure, and prevent major cardiovascular events,” they write.
The study was published online in Heart.
Strong support for landmark study
In salt substitutes, a proportion of sodium chloride is replaced with potassium chloride. They are known to help lower blood pressure, but less is known about their impact on hard clinical endpoints, Maoyi Tian, PhD, with Harbin Medical University, China, and the George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, and colleagues note in their article.
In the landmark Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), salt substitutes cut the risk of MI, stroke, and early death, as reported previously by this news organization.
But SSaSS was conducted in China, and it was unclear whether these benefits would apply to people in other parts of the world.
To investigate, Dr. Tian and colleagues pooled data from 21 relevant parallel-group, step-wedge, or cluster randomized controlled trials published through August 2021, with 31,949 participants. The trials were conducted in Europe, the Western Pacific Region, the Americas, and South East Asia and reported the effect of a salt substitute on blood pressure or clinical outcomes.
A meta-analysis of blood pressure data from 19 trials that included 29,528 participants showed that salt substitutes lowered systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 4.61 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, −6.07 to −3.14) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) by 1.61 mm Hg (95% CI, −2.42 to −0.79).
The proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitutes varied from 33% to 75%; the proportion of potassium ranged from 25% to 65%.
Each 10% lower proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitute was associated with a 1.53 mm Hg (95% CI, −3.02 to −0.03; P = .045) greater reduction in SBP and a 0.95 mm Hg (95% CI, −1.78 to −0.12; P = .025) greater reduction in DBP.
Reductions in blood pressure appeared consistent, irrespective of country, age, sex, history of high blood pressure, weight, baseline blood pressure, and baseline levels of urinary sodium and potassium.
Clear benefit on hard outcomes
Pooled data on clinical outcomes from five trials that included 24,306 participants, mostly from the SSaSS, showed clear protective effects of salt substitutes on total mortality (risk ratio, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
Dr. Tian and colleagues say that “broader population use of salt substitute is supported by the absence of any detectable adverse effect of salt substitutes on hyperkalemia in this review.”
They note, however, that all of the trials took “pragmatic steps to exclude participants at elevated risk of hyperkalemia, seeking to exclude those with chronic kidney disease or using medications that elevate serum potassium.”
Offering perspective on the study, Harlan Krumholz, MD, with Yale New Haven Hospital and Yale School of Medicine, both in New Haven, Conn., said it provides “useful information by bringing together the trial evidence on salt substitutes. The evidence is dominated by the SSaSS, but the others add context.”
Dr. Krumholz said that at this point, he thinks salt substitutes “could be included in recommendations to patients.”
“SSaSS was conducted in villages in China, so that is where the evidence is strongest and most relevant, but this is a low-cost and seemingly safe strategy that could be tried by anyone without contraindications, such as kidney disease or taking a potassium-sparing medication or potassium supplement,” Dr. Krumholz told this news organization.
Johanna Contreras, MD, heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, agrees that in the absence of contraindications, salt substitutes should be recommended.
“Americans put salt on everything and don’t even think about it. The salt substitutes are very helpful,” Dr. Contreras said in an interview.
“People who don’t have high blood pressure should limit salt intake, because what we have seen is that if you have high blood pressure in your family – even if you don’t have high blood pressure in your 20s or 30s – you’re likely to develop high blood pressure,” Dr. Contreras said.
“Therefore, it’s wise early on to start protecting yourself and using low salt and salt substitutes,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Tian, Dr. Krumholz, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dietary salt substitutes not only lower blood pressure but also have a clear impact on hard clinical endpoints, lowering the risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and death from all causes and cardiovascular disease (CVD), a meta-analysis shows.
The blood pressure–mediated protective effects of salt substitutes on CVD and death are likely to apply to the roughly 1.28 billion people around the world who have high blood pressure, the researchers say.
“These findings are unlikely to reflect the play of chance and support the adoption of salt substitutes in clinical practice and public health policy as a strategy to reduce dietary sodium intake, increase dietary potassium intake, lower blood pressure, and prevent major cardiovascular events,” they write.
The study was published online in Heart.
Strong support for landmark study
In salt substitutes, a proportion of sodium chloride is replaced with potassium chloride. They are known to help lower blood pressure, but less is known about their impact on hard clinical endpoints, Maoyi Tian, PhD, with Harbin Medical University, China, and the George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, and colleagues note in their article.
In the landmark Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), salt substitutes cut the risk of MI, stroke, and early death, as reported previously by this news organization.
But SSaSS was conducted in China, and it was unclear whether these benefits would apply to people in other parts of the world.
To investigate, Dr. Tian and colleagues pooled data from 21 relevant parallel-group, step-wedge, or cluster randomized controlled trials published through August 2021, with 31,949 participants. The trials were conducted in Europe, the Western Pacific Region, the Americas, and South East Asia and reported the effect of a salt substitute on blood pressure or clinical outcomes.
A meta-analysis of blood pressure data from 19 trials that included 29,528 participants showed that salt substitutes lowered systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 4.61 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, −6.07 to −3.14) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) by 1.61 mm Hg (95% CI, −2.42 to −0.79).
The proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitutes varied from 33% to 75%; the proportion of potassium ranged from 25% to 65%.
Each 10% lower proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitute was associated with a 1.53 mm Hg (95% CI, −3.02 to −0.03; P = .045) greater reduction in SBP and a 0.95 mm Hg (95% CI, −1.78 to −0.12; P = .025) greater reduction in DBP.
Reductions in blood pressure appeared consistent, irrespective of country, age, sex, history of high blood pressure, weight, baseline blood pressure, and baseline levels of urinary sodium and potassium.
Clear benefit on hard outcomes
Pooled data on clinical outcomes from five trials that included 24,306 participants, mostly from the SSaSS, showed clear protective effects of salt substitutes on total mortality (risk ratio, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
Dr. Tian and colleagues say that “broader population use of salt substitute is supported by the absence of any detectable adverse effect of salt substitutes on hyperkalemia in this review.”
They note, however, that all of the trials took “pragmatic steps to exclude participants at elevated risk of hyperkalemia, seeking to exclude those with chronic kidney disease or using medications that elevate serum potassium.”
Offering perspective on the study, Harlan Krumholz, MD, with Yale New Haven Hospital and Yale School of Medicine, both in New Haven, Conn., said it provides “useful information by bringing together the trial evidence on salt substitutes. The evidence is dominated by the SSaSS, but the others add context.”
Dr. Krumholz said that at this point, he thinks salt substitutes “could be included in recommendations to patients.”
“SSaSS was conducted in villages in China, so that is where the evidence is strongest and most relevant, but this is a low-cost and seemingly safe strategy that could be tried by anyone without contraindications, such as kidney disease or taking a potassium-sparing medication or potassium supplement,” Dr. Krumholz told this news organization.
Johanna Contreras, MD, heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, agrees that in the absence of contraindications, salt substitutes should be recommended.
“Americans put salt on everything and don’t even think about it. The salt substitutes are very helpful,” Dr. Contreras said in an interview.
“People who don’t have high blood pressure should limit salt intake, because what we have seen is that if you have high blood pressure in your family – even if you don’t have high blood pressure in your 20s or 30s – you’re likely to develop high blood pressure,” Dr. Contreras said.
“Therefore, it’s wise early on to start protecting yourself and using low salt and salt substitutes,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Tian, Dr. Krumholz, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Social isolation, loneliness tied to death, MI, stroke: AHA
People who are socially isolated or lonely have an increased risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and death, independent of other factors, the American Heart Association concludes in a new scientific statement.
More than 4 decades of research have “clearly demonstrated that social isolation and loneliness are both associated with adverse health outcomes,” writing group chair Crystal Wiley Cené, MD, University of California San Diego Health, said in a news release.
“Given the prevalence of social disconnectedness across the United States, the public health impact is quite significant,” Dr. Cené added.
The writing group says more research is needed to develop, implement, and test interventions to improve cardiovascular (CV) and brain health in people who are socially isolated or lonely.
The scientific statement was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Common and potentially deadly
Social isolation is defined as having infrequent in-person contact with people and loneliness is when a person feels he or she is alone or has less connection with others than desired.
It’s estimated that one-quarter of community-dwelling Americans 65 years and older are socially isolated, with even more experiencing loneliness.
The problem is not limited to older adults, however. Research suggests that younger adults also experience social isolation and loneliness, which might be attributed to more social media use and less frequent in-person activities.
Dr. Cené and colleagues reviewed observational and intervention research on social isolation published through July 2021 to examine the impact of social isolation and loneliness on CV and brain health.
The evidence is most consistent for a direct association between social isolation, loneliness, and death from coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, they reported.
For example, one meta-analysis of 19 studies showed that social isolation and loneliness increase the risk for CHD by 29%; most of these studies focused on acute MI and/or CHD death as the measure of CHD.
A meta-analysis of eight longitudinal observational studies showed social isolation and loneliness were associated with a 32% increased risk for stroke, after adjustment for age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
The literature also suggests social isolation and loneliness are associated with worse prognoses in adults with existing CHD or history of stroke.
One systematic review showed that socially isolated people with CHD had a two- to threefold increase in illness and death over 6 years, independent of cardiac risk factors.
Other research suggests that socially isolated adults with three or fewer social contacts per month have a 40% increased risk for recurrent stroke or MI.
There are fewer and less robust data on the association between social isolation and loneliness with heart failure (HF), dementia, and cognitive impairment, the writing group noted.
It’s also unclear whether actually being isolated (social isolation) or feeling isolated (loneliness) matters most for cardiovascular and brain health, because only a few studies have examined both in the same sample, they pointed out.
However, a study published in Neurology in June showed that older adults who reported feeling socially isolated had worse cognitive function at baseline than did those who did not report social isolation, and were 26% more likely to have dementia at follow-up, as reported by this news organization.
Urgent need for interventions
“There is an urgent need to develop, implement, and evaluate programs and strategies to reduce the negative effects of social isolation and loneliness on cardiovascular and brain health, particularly for at-risk populations,” Dr. Cené said in the news release.
She encourages clinicians to ask patients about their social life and whether they are satisfied with their level of interactions with friends and family, and to be prepared to refer patients who are socially isolated or lonely, especially those with a history of CHD or stroke, to community resources to help them connect with others.
Fitness programs and recreational activities at senior centers, as well as interventions that address negative thoughts of self-worth and other negative thinking, have shown promise in reducing isolation and loneliness, the writing group said.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Social Determinants of Health Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; the Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology; and the Stroke Council.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing group have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who are socially isolated or lonely have an increased risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and death, independent of other factors, the American Heart Association concludes in a new scientific statement.
More than 4 decades of research have “clearly demonstrated that social isolation and loneliness are both associated with adverse health outcomes,” writing group chair Crystal Wiley Cené, MD, University of California San Diego Health, said in a news release.
“Given the prevalence of social disconnectedness across the United States, the public health impact is quite significant,” Dr. Cené added.
The writing group says more research is needed to develop, implement, and test interventions to improve cardiovascular (CV) and brain health in people who are socially isolated or lonely.
The scientific statement was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Common and potentially deadly
Social isolation is defined as having infrequent in-person contact with people and loneliness is when a person feels he or she is alone or has less connection with others than desired.
It’s estimated that one-quarter of community-dwelling Americans 65 years and older are socially isolated, with even more experiencing loneliness.
The problem is not limited to older adults, however. Research suggests that younger adults also experience social isolation and loneliness, which might be attributed to more social media use and less frequent in-person activities.
Dr. Cené and colleagues reviewed observational and intervention research on social isolation published through July 2021 to examine the impact of social isolation and loneliness on CV and brain health.
The evidence is most consistent for a direct association between social isolation, loneliness, and death from coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, they reported.
For example, one meta-analysis of 19 studies showed that social isolation and loneliness increase the risk for CHD by 29%; most of these studies focused on acute MI and/or CHD death as the measure of CHD.
A meta-analysis of eight longitudinal observational studies showed social isolation and loneliness were associated with a 32% increased risk for stroke, after adjustment for age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
The literature also suggests social isolation and loneliness are associated with worse prognoses in adults with existing CHD or history of stroke.
One systematic review showed that socially isolated people with CHD had a two- to threefold increase in illness and death over 6 years, independent of cardiac risk factors.
Other research suggests that socially isolated adults with three or fewer social contacts per month have a 40% increased risk for recurrent stroke or MI.
There are fewer and less robust data on the association between social isolation and loneliness with heart failure (HF), dementia, and cognitive impairment, the writing group noted.
It’s also unclear whether actually being isolated (social isolation) or feeling isolated (loneliness) matters most for cardiovascular and brain health, because only a few studies have examined both in the same sample, they pointed out.
However, a study published in Neurology in June showed that older adults who reported feeling socially isolated had worse cognitive function at baseline than did those who did not report social isolation, and were 26% more likely to have dementia at follow-up, as reported by this news organization.
Urgent need for interventions
“There is an urgent need to develop, implement, and evaluate programs and strategies to reduce the negative effects of social isolation and loneliness on cardiovascular and brain health, particularly for at-risk populations,” Dr. Cené said in the news release.
She encourages clinicians to ask patients about their social life and whether they are satisfied with their level of interactions with friends and family, and to be prepared to refer patients who are socially isolated or lonely, especially those with a history of CHD or stroke, to community resources to help them connect with others.
Fitness programs and recreational activities at senior centers, as well as interventions that address negative thoughts of self-worth and other negative thinking, have shown promise in reducing isolation and loneliness, the writing group said.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Social Determinants of Health Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; the Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology; and the Stroke Council.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing group have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who are socially isolated or lonely have an increased risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and death, independent of other factors, the American Heart Association concludes in a new scientific statement.
More than 4 decades of research have “clearly demonstrated that social isolation and loneliness are both associated with adverse health outcomes,” writing group chair Crystal Wiley Cené, MD, University of California San Diego Health, said in a news release.
“Given the prevalence of social disconnectedness across the United States, the public health impact is quite significant,” Dr. Cené added.
The writing group says more research is needed to develop, implement, and test interventions to improve cardiovascular (CV) and brain health in people who are socially isolated or lonely.
The scientific statement was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Common and potentially deadly
Social isolation is defined as having infrequent in-person contact with people and loneliness is when a person feels he or she is alone or has less connection with others than desired.
It’s estimated that one-quarter of community-dwelling Americans 65 years and older are socially isolated, with even more experiencing loneliness.
The problem is not limited to older adults, however. Research suggests that younger adults also experience social isolation and loneliness, which might be attributed to more social media use and less frequent in-person activities.
Dr. Cené and colleagues reviewed observational and intervention research on social isolation published through July 2021 to examine the impact of social isolation and loneliness on CV and brain health.
The evidence is most consistent for a direct association between social isolation, loneliness, and death from coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, they reported.
For example, one meta-analysis of 19 studies showed that social isolation and loneliness increase the risk for CHD by 29%; most of these studies focused on acute MI and/or CHD death as the measure of CHD.
A meta-analysis of eight longitudinal observational studies showed social isolation and loneliness were associated with a 32% increased risk for stroke, after adjustment for age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
The literature also suggests social isolation and loneliness are associated with worse prognoses in adults with existing CHD or history of stroke.
One systematic review showed that socially isolated people with CHD had a two- to threefold increase in illness and death over 6 years, independent of cardiac risk factors.
Other research suggests that socially isolated adults with three or fewer social contacts per month have a 40% increased risk for recurrent stroke or MI.
There are fewer and less robust data on the association between social isolation and loneliness with heart failure (HF), dementia, and cognitive impairment, the writing group noted.
It’s also unclear whether actually being isolated (social isolation) or feeling isolated (loneliness) matters most for cardiovascular and brain health, because only a few studies have examined both in the same sample, they pointed out.
However, a study published in Neurology in June showed that older adults who reported feeling socially isolated had worse cognitive function at baseline than did those who did not report social isolation, and were 26% more likely to have dementia at follow-up, as reported by this news organization.
Urgent need for interventions
“There is an urgent need to develop, implement, and evaluate programs and strategies to reduce the negative effects of social isolation and loneliness on cardiovascular and brain health, particularly for at-risk populations,” Dr. Cené said in the news release.
She encourages clinicians to ask patients about their social life and whether they are satisfied with their level of interactions with friends and family, and to be prepared to refer patients who are socially isolated or lonely, especially those with a history of CHD or stroke, to community resources to help them connect with others.
Fitness programs and recreational activities at senior centers, as well as interventions that address negative thoughts of self-worth and other negative thinking, have shown promise in reducing isolation and loneliness, the writing group said.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Social Determinants of Health Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; the Prevention Science Committee of the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; the Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology; and the Stroke Council.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing group have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Omecamtiv mecarbil fails to improve exercise capacity in HFrEF
Treatment with the novel agent omecamtiv mecarbil did not improve exercise capacity in people with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), in the METEORIC-HF trial.
The double-blind, phase 3 study failed to achieve its primary endpoint of change in peak oxygen uptake (VO2) after 20 weeks of treatment with omecamtiv mecarbil, compared with placebo.
There also was no benefit on secondary measures of total workload, ventilatory efficiency, and daily physical activity, according to results presented earlier this year at ACC 2022 and formally published this month in JAMA.
“These findings do not support the use of omecamtiv mecarbil for treatment of HFrEF for improvement of exercise capacity,” lead author Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues conclude in the paper.
Researchers had hoped that the oral selective myosin activator would prove useful in this subset of patients, having previously shown in the GALACTIC-HF trial to provide a significant improvement in heart failure (HF) events and cardiovascular death.
A prespecified subgroup analysis from that trial also found that HF patients with the lowest ejection fraction derived the greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
“The lack of effect of omecamtiv mecarbil on exercise performance is inconsistent with its known mechanism of action of directly enhancing ventricular performance and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events,” Dr. Lewis and colleagues observe.
The drug’s novel mechanism of action, direct activation of myosin, contrasts with that of currently available inotropic agents, such as dobutamine or milrinone. It is not yet approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration but is scheduled for an advisory committee meeting on Dec. 13, 2022, and has been assigned a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of Feb. 28, 2023.
METEORIC-HF randomly assigned 276 patients with New York Heart Association class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less to omecamtiv mecarbil (n = 185) or placebo (n = 91), given orally twice daily at a dose of 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg based on target plasma levels for 20 weeks, on top of guideline-directed medical therapy.
The patients’ median age was 64 years and 15% were women. The median ejection fraction was 28% and median baseline peak VO2 was 14.2 mL/kg per minute in the omecamtiv mecarbil group and 15.0 mL/kg per minute in the control group.
At 20 weeks, the mean change in peak VO2 in the omecamtiv mecarbil group was –0.24 mL/kg per minute and 0.21 mL/kg per minute in the placebo group (95% confidence interval, –1.02-0.13; P = .13).
For the secondary outcomes, the change in workload achieved on stress testing declined in the omecamtiv mecarbil group (–3.8 vs. 1.6). The drug had a neutral effect on minute ventilation relative to carbon dioxide production throughout exercise (0.28 vs. –0.14 VE/VCO2 slope) and average total daily activity units, measured over 2 weeks by accelerometer (–0.2 vs. –0.5).
The authors suggest that “one possible explanation for discordance between clinical events in a long-term follow-up study and exercise capacity improvement is that cardiac performance was not exclusively responsible for limiting exercise capacity in trial participants with HFrEF who were stable and very well treated with both pharmacologic and device HFrEF therapy.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mark H. Drazner, MD, MSc, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, writes that another possible explanation is that participants in METEORIC-HF had less severe heart failure, compared with participants in GALACTIC-HF, and so were less likely to benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
METEORIC-HF excluded participants who had a HF hospitalization that required intravenous diuretics in the preceding 3 months, whereas 25% of participants in GALACTIC-HF were inpatients for decompensated HF and 36% had a HF hospitalization within the preceding 3 months.
Another plausible explanation for the differing results is that a therapy that improves long-term clinical outcomes may not improve exercise capacity, Dr. Drazner writes. “The available data are persuasive to suggest this may be the case.”
Some pharmacologic therapies, such as flosequinan, improved exercise capacity in patients with HF yet increased long-term mortality, he noted. Several medications that have a class I recommendation in the 2022 Heart Failure Guideline for the treatment of HFrEF also have not been shown to improve exercise capacity, as measured by peak VO2 or by 6-minute walk distance.
In this context, Dr. Drazner said he doesn’t anticipate the METEORIC-HF findings to derail FDA approval. However, should the drug be approved, clinicians will have increasingly complex decisions to make about which therapies should be prescribed to which patients.
“Some clinicians may contemplate using omecamtiv mecarbil either in the subgroup of patients with very low ejection fractions or more severe disease, believing this strategy will maximize the benefits of this therapy, but those approaches should be pursued with caution given they are predicated on subgroup and post hoc analyses, respectively,” he wrote.
Dr. Drazner concludes that medications known to improve survival in patients with HFrEF are used at “disappointingly low rates and suboptimal doses in the United States. Implementation strategies to improve use of such therapies are needed, and those efforts should be prioritized before adoption of therapies that reduce morbidity but not cardiovascular mortality.”
The study was sponsored by Amgen and Cytokinetics. Dr. Lewis reports financial relationships with the National Institutes of Health, American Heart Association, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, SoniVie, Pfizer, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, American Regent, Cyclerion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and UpToDate. Dr. Drazner reports being a member of the writing committee of the 2022 Heart Failure guidelines; and that he is supported by the James M. Wooten Chair in Cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, which was a clinical site in METEORIC-HF. However, Dr. Drazner was not a study investigator in the trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with the novel agent omecamtiv mecarbil did not improve exercise capacity in people with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), in the METEORIC-HF trial.
The double-blind, phase 3 study failed to achieve its primary endpoint of change in peak oxygen uptake (VO2) after 20 weeks of treatment with omecamtiv mecarbil, compared with placebo.
There also was no benefit on secondary measures of total workload, ventilatory efficiency, and daily physical activity, according to results presented earlier this year at ACC 2022 and formally published this month in JAMA.
“These findings do not support the use of omecamtiv mecarbil for treatment of HFrEF for improvement of exercise capacity,” lead author Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues conclude in the paper.
Researchers had hoped that the oral selective myosin activator would prove useful in this subset of patients, having previously shown in the GALACTIC-HF trial to provide a significant improvement in heart failure (HF) events and cardiovascular death.
A prespecified subgroup analysis from that trial also found that HF patients with the lowest ejection fraction derived the greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
“The lack of effect of omecamtiv mecarbil on exercise performance is inconsistent with its known mechanism of action of directly enhancing ventricular performance and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events,” Dr. Lewis and colleagues observe.
The drug’s novel mechanism of action, direct activation of myosin, contrasts with that of currently available inotropic agents, such as dobutamine or milrinone. It is not yet approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration but is scheduled for an advisory committee meeting on Dec. 13, 2022, and has been assigned a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of Feb. 28, 2023.
METEORIC-HF randomly assigned 276 patients with New York Heart Association class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less to omecamtiv mecarbil (n = 185) or placebo (n = 91), given orally twice daily at a dose of 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg based on target plasma levels for 20 weeks, on top of guideline-directed medical therapy.
The patients’ median age was 64 years and 15% were women. The median ejection fraction was 28% and median baseline peak VO2 was 14.2 mL/kg per minute in the omecamtiv mecarbil group and 15.0 mL/kg per minute in the control group.
At 20 weeks, the mean change in peak VO2 in the omecamtiv mecarbil group was –0.24 mL/kg per minute and 0.21 mL/kg per minute in the placebo group (95% confidence interval, –1.02-0.13; P = .13).
For the secondary outcomes, the change in workload achieved on stress testing declined in the omecamtiv mecarbil group (–3.8 vs. 1.6). The drug had a neutral effect on minute ventilation relative to carbon dioxide production throughout exercise (0.28 vs. –0.14 VE/VCO2 slope) and average total daily activity units, measured over 2 weeks by accelerometer (–0.2 vs. –0.5).
The authors suggest that “one possible explanation for discordance between clinical events in a long-term follow-up study and exercise capacity improvement is that cardiac performance was not exclusively responsible for limiting exercise capacity in trial participants with HFrEF who were stable and very well treated with both pharmacologic and device HFrEF therapy.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mark H. Drazner, MD, MSc, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, writes that another possible explanation is that participants in METEORIC-HF had less severe heart failure, compared with participants in GALACTIC-HF, and so were less likely to benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
METEORIC-HF excluded participants who had a HF hospitalization that required intravenous diuretics in the preceding 3 months, whereas 25% of participants in GALACTIC-HF were inpatients for decompensated HF and 36% had a HF hospitalization within the preceding 3 months.
Another plausible explanation for the differing results is that a therapy that improves long-term clinical outcomes may not improve exercise capacity, Dr. Drazner writes. “The available data are persuasive to suggest this may be the case.”
Some pharmacologic therapies, such as flosequinan, improved exercise capacity in patients with HF yet increased long-term mortality, he noted. Several medications that have a class I recommendation in the 2022 Heart Failure Guideline for the treatment of HFrEF also have not been shown to improve exercise capacity, as measured by peak VO2 or by 6-minute walk distance.
In this context, Dr. Drazner said he doesn’t anticipate the METEORIC-HF findings to derail FDA approval. However, should the drug be approved, clinicians will have increasingly complex decisions to make about which therapies should be prescribed to which patients.
“Some clinicians may contemplate using omecamtiv mecarbil either in the subgroup of patients with very low ejection fractions or more severe disease, believing this strategy will maximize the benefits of this therapy, but those approaches should be pursued with caution given they are predicated on subgroup and post hoc analyses, respectively,” he wrote.
Dr. Drazner concludes that medications known to improve survival in patients with HFrEF are used at “disappointingly low rates and suboptimal doses in the United States. Implementation strategies to improve use of such therapies are needed, and those efforts should be prioritized before adoption of therapies that reduce morbidity but not cardiovascular mortality.”
The study was sponsored by Amgen and Cytokinetics. Dr. Lewis reports financial relationships with the National Institutes of Health, American Heart Association, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, SoniVie, Pfizer, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, American Regent, Cyclerion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and UpToDate. Dr. Drazner reports being a member of the writing committee of the 2022 Heart Failure guidelines; and that he is supported by the James M. Wooten Chair in Cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, which was a clinical site in METEORIC-HF. However, Dr. Drazner was not a study investigator in the trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with the novel agent omecamtiv mecarbil did not improve exercise capacity in people with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), in the METEORIC-HF trial.
The double-blind, phase 3 study failed to achieve its primary endpoint of change in peak oxygen uptake (VO2) after 20 weeks of treatment with omecamtiv mecarbil, compared with placebo.
There also was no benefit on secondary measures of total workload, ventilatory efficiency, and daily physical activity, according to results presented earlier this year at ACC 2022 and formally published this month in JAMA.
“These findings do not support the use of omecamtiv mecarbil for treatment of HFrEF for improvement of exercise capacity,” lead author Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues conclude in the paper.
Researchers had hoped that the oral selective myosin activator would prove useful in this subset of patients, having previously shown in the GALACTIC-HF trial to provide a significant improvement in heart failure (HF) events and cardiovascular death.
A prespecified subgroup analysis from that trial also found that HF patients with the lowest ejection fraction derived the greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
“The lack of effect of omecamtiv mecarbil on exercise performance is inconsistent with its known mechanism of action of directly enhancing ventricular performance and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events,” Dr. Lewis and colleagues observe.
The drug’s novel mechanism of action, direct activation of myosin, contrasts with that of currently available inotropic agents, such as dobutamine or milrinone. It is not yet approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration but is scheduled for an advisory committee meeting on Dec. 13, 2022, and has been assigned a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of Feb. 28, 2023.
METEORIC-HF randomly assigned 276 patients with New York Heart Association class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less to omecamtiv mecarbil (n = 185) or placebo (n = 91), given orally twice daily at a dose of 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg based on target plasma levels for 20 weeks, on top of guideline-directed medical therapy.
The patients’ median age was 64 years and 15% were women. The median ejection fraction was 28% and median baseline peak VO2 was 14.2 mL/kg per minute in the omecamtiv mecarbil group and 15.0 mL/kg per minute in the control group.
At 20 weeks, the mean change in peak VO2 in the omecamtiv mecarbil group was –0.24 mL/kg per minute and 0.21 mL/kg per minute in the placebo group (95% confidence interval, –1.02-0.13; P = .13).
For the secondary outcomes, the change in workload achieved on stress testing declined in the omecamtiv mecarbil group (–3.8 vs. 1.6). The drug had a neutral effect on minute ventilation relative to carbon dioxide production throughout exercise (0.28 vs. –0.14 VE/VCO2 slope) and average total daily activity units, measured over 2 weeks by accelerometer (–0.2 vs. –0.5).
The authors suggest that “one possible explanation for discordance between clinical events in a long-term follow-up study and exercise capacity improvement is that cardiac performance was not exclusively responsible for limiting exercise capacity in trial participants with HFrEF who were stable and very well treated with both pharmacologic and device HFrEF therapy.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mark H. Drazner, MD, MSc, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, writes that another possible explanation is that participants in METEORIC-HF had less severe heart failure, compared with participants in GALACTIC-HF, and so were less likely to benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil.
METEORIC-HF excluded participants who had a HF hospitalization that required intravenous diuretics in the preceding 3 months, whereas 25% of participants in GALACTIC-HF were inpatients for decompensated HF and 36% had a HF hospitalization within the preceding 3 months.
Another plausible explanation for the differing results is that a therapy that improves long-term clinical outcomes may not improve exercise capacity, Dr. Drazner writes. “The available data are persuasive to suggest this may be the case.”
Some pharmacologic therapies, such as flosequinan, improved exercise capacity in patients with HF yet increased long-term mortality, he noted. Several medications that have a class I recommendation in the 2022 Heart Failure Guideline for the treatment of HFrEF also have not been shown to improve exercise capacity, as measured by peak VO2 or by 6-minute walk distance.
In this context, Dr. Drazner said he doesn’t anticipate the METEORIC-HF findings to derail FDA approval. However, should the drug be approved, clinicians will have increasingly complex decisions to make about which therapies should be prescribed to which patients.
“Some clinicians may contemplate using omecamtiv mecarbil either in the subgroup of patients with very low ejection fractions or more severe disease, believing this strategy will maximize the benefits of this therapy, but those approaches should be pursued with caution given they are predicated on subgroup and post hoc analyses, respectively,” he wrote.
Dr. Drazner concludes that medications known to improve survival in patients with HFrEF are used at “disappointingly low rates and suboptimal doses in the United States. Implementation strategies to improve use of such therapies are needed, and those efforts should be prioritized before adoption of therapies that reduce morbidity but not cardiovascular mortality.”
The study was sponsored by Amgen and Cytokinetics. Dr. Lewis reports financial relationships with the National Institutes of Health, American Heart Association, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, SoniVie, Pfizer, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, American Regent, Cyclerion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and UpToDate. Dr. Drazner reports being a member of the writing committee of the 2022 Heart Failure guidelines; and that he is supported by the James M. Wooten Chair in Cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, which was a clinical site in METEORIC-HF. However, Dr. Drazner was not a study investigator in the trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Staggering’ CVD rise projected in U.S., especially in minorities
A new analysis projects steep increases by 2060 in the prevalence of cardiovascular (CV) risk factors and disease that will disproportionately affect non-White populations who have limited access to health care.
The study by Reza Mohebi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Even though several assumptions underlie these projections, the importance of this work cannot be overestimated,” Andreas P. Kalogeropoulos, MD, MPH, PhD, and Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “The absolute numbers are staggering.”
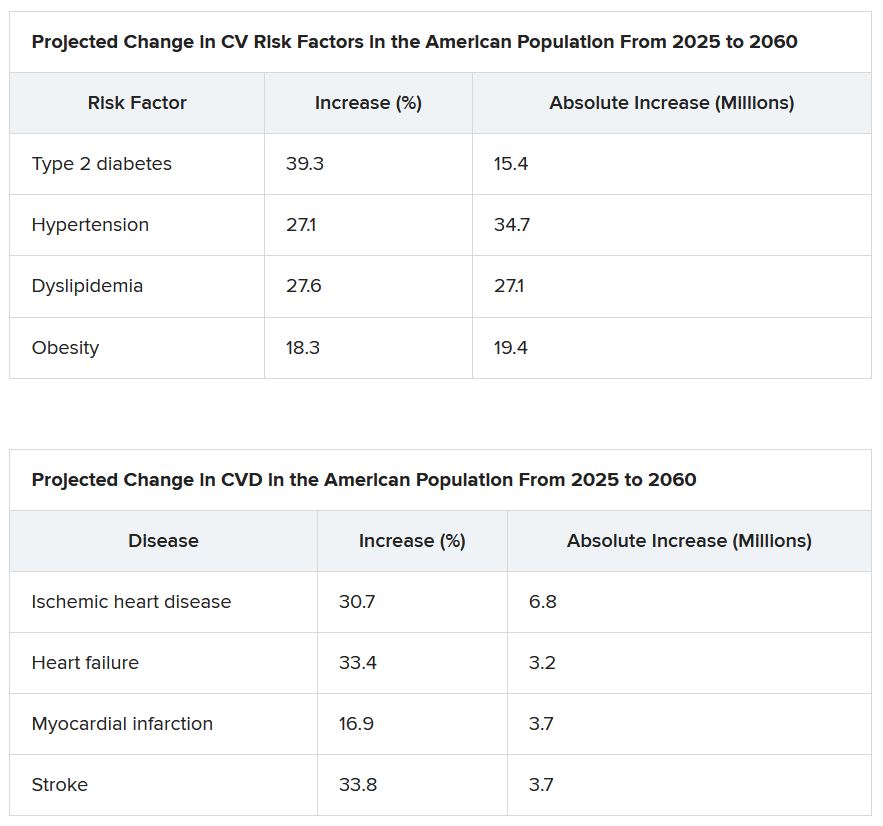
From 2025 to 2060, the number of people with any one of four CV risk factors – type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity – is projected to increase by 15.4 million, to 34.7 million.
And the number of people with of any one of four CV disease types – ischemic heart disease, heart failure, MI, and stroke – is projected to increase by 3.2 million, to 6.8 million.
Although the model predicts that the prevalence of CV risk factors will gradually decrease among White Americans, the highest prevalence of CV risk factors will be among the White population because of its overall size.
Conversely, the projected prevalence of CV risk factors is expected to increase in Black, Hispanic, Asian, and other race/ethnicity populations.
In parallel, the prevalence of CV disease is projected to decrease in the White population and increase among all other race/ethnicities, particularly in the Black and Hispanic populations.
“Our results project a worrisome increase with a particularly ominous increase in risk factors and disease in our most vulnerable patients, including Blacks and Hispanics,” senior author James L. Januzzi Jr., MD, summarized in a video issued by the society.
“The steep rise in CV risk factors and disease reflects the generally higher prevalence in populations projected to increase in the United States, owing to immigration and growth, including Black or Hispanic individuals,” Dr. Januzzi, also from Massachusetts General and Harvard, said in an interview.
“The disproportionate size of the risk is expected in a sense, as minority populations are disproportionately disadvantaged with respect to their health care,” he said. “But whether it is expected or not, the increase in projected prevalence is, nonetheless, concerning and a call to action.”
This study identifies “areas of opportunity for change in the U.S. health care system,” he continued. “Business as usual will result in us encountering a huge number of individuals with CV risk factors and diseases.”
The results from the current analysis assume there will be no modification in health care policies or changes in access to care for at-risk populations, Dr. Mohebi and colleagues noted.
To “stem the rising tide of CV disease in at-risk individuals,” would require strategies such as “emphasis on education regarding CV risk factors, improving access to quality healthcare, and facilitating lower-cost access to effective therapies for treatment of CV risk factors,” according to the researchers.
“Such advances need to be applied in a more equitable way throughout the United States, however,” they cautioned.
Census plus NHANES data
The researchers used 2020 U.S. census data and projected growth and 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Survey data to estimate the number of people with CV risk factors and CV disease from 2025 to 2060.
The estimates are based on a growing population and a fixed frequency.
The projected changes in CV risk factors and disease over time were similar in men and women.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the assumption that the prevalence patterns for CV risk factors and disease will be stable.
“To the extent the frequency of risk factors and disease are not likely to remain static, that assumption may reduce the accuracy of the projections,” Dr. Januzzi said. “However, we would point out that the goals of our analysis were to set general trends, and not to seek to project exact figures.”
Also, they did not take into account the effect of COVID-19. CV diseases were also based on self-report and CV risk factors could have been underestimated in minority populations that do not access health care.
Changing demographic landscape
It is “striking” that the numbers of non-White individuals with CV risk factors is projected to surpass the number of White individuals over time, and the number of non-White individuals with CV disease will be almost as many as White individuals by the year 2060, the editorialists noted.
“From a policy perspective, this means that unless appropriate, targeted action is taken, disparities in the burden of cardiovascular disease are only going to be exacerbated over time,” wrote Dr. Kalogeropoulos, from Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, and Dr. Butler, from Baylor College of Medicine, Dallas.
“On the positive side,” they continued, “the absolute increase in the percent prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and conditions is projected to lie within a manageable range,” assuming that specific prevention policies are implemented.
“This is an opportunity for professional societies, including the cardiovascular care community, to re-evaluate priorities and strategies, for both training and practice, to best match the growing demands of a changing demographic landscape in the United States,” Dr. Kalogeropoulos and Dr. Butler concluded.
Dr. Mohebi is supported by the Barry Fellowship. Dr. Januzzi is supported by the Hutter Family Professorship; is a Trustee of the American College of Cardiology; is a board member of Imbria Pharmaceuticals; has received grant support from Abbott Diagnostics, Applied Therapeutics, Innolife, and Novartis; has received consulting income from Abbott Diagnostics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and participates in clinical endpoint committees/data safety monitoring boards for AbbVie, Siemens, Takeda, and Vifor. Dr. Kalogeropoulos has received research funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the American Heart Association; and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Butler has been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis projects steep increases by 2060 in the prevalence of cardiovascular (CV) risk factors and disease that will disproportionately affect non-White populations who have limited access to health care.
The study by Reza Mohebi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Even though several assumptions underlie these projections, the importance of this work cannot be overestimated,” Andreas P. Kalogeropoulos, MD, MPH, PhD, and Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “The absolute numbers are staggering.”
From 2025 to 2060, the number of people with any one of four CV risk factors – type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity – is projected to increase by 15.4 million, to 34.7 million.
And the number of people with of any one of four CV disease types – ischemic heart disease, heart failure, MI, and stroke – is projected to increase by 3.2 million, to 6.8 million.
Although the model predicts that the prevalence of CV risk factors will gradually decrease among White Americans, the highest prevalence of CV risk factors will be among the White population because of its overall size.
Conversely, the projected prevalence of CV risk factors is expected to increase in Black, Hispanic, Asian, and other race/ethnicity populations.
In parallel, the prevalence of CV disease is projected to decrease in the White population and increase among all other race/ethnicities, particularly in the Black and Hispanic populations.
“Our results project a worrisome increase with a particularly ominous increase in risk factors and disease in our most vulnerable patients, including Blacks and Hispanics,” senior author James L. Januzzi Jr., MD, summarized in a video issued by the society.
“The steep rise in CV risk factors and disease reflects the generally higher prevalence in populations projected to increase in the United States, owing to immigration and growth, including Black or Hispanic individuals,” Dr. Januzzi, also from Massachusetts General and Harvard, said in an interview.
“The disproportionate size of the risk is expected in a sense, as minority populations are disproportionately disadvantaged with respect to their health care,” he said. “But whether it is expected or not, the increase in projected prevalence is, nonetheless, concerning and a call to action.”
This study identifies “areas of opportunity for change in the U.S. health care system,” he continued. “Business as usual will result in us encountering a huge number of individuals with CV risk factors and diseases.”
The results from the current analysis assume there will be no modification in health care policies or changes in access to care for at-risk populations, Dr. Mohebi and colleagues noted.
To “stem the rising tide of CV disease in at-risk individuals,” would require strategies such as “emphasis on education regarding CV risk factors, improving access to quality healthcare, and facilitating lower-cost access to effective therapies for treatment of CV risk factors,” according to the researchers.
“Such advances need to be applied in a more equitable way throughout the United States, however,” they cautioned.
Census plus NHANES data
The researchers used 2020 U.S. census data and projected growth and 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Survey data to estimate the number of people with CV risk factors and CV disease from 2025 to 2060.
The estimates are based on a growing population and a fixed frequency.
The projected changes in CV risk factors and disease over time were similar in men and women.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the assumption that the prevalence patterns for CV risk factors and disease will be stable.
“To the extent the frequency of risk factors and disease are not likely to remain static, that assumption may reduce the accuracy of the projections,” Dr. Januzzi said. “However, we would point out that the goals of our analysis were to set general trends, and not to seek to project exact figures.”
Also, they did not take into account the effect of COVID-19. CV diseases were also based on self-report and CV risk factors could have been underestimated in minority populations that do not access health care.
Changing demographic landscape
It is “striking” that the numbers of non-White individuals with CV risk factors is projected to surpass the number of White individuals over time, and the number of non-White individuals with CV disease will be almost as many as White individuals by the year 2060, the editorialists noted.
“From a policy perspective, this means that unless appropriate, targeted action is taken, disparities in the burden of cardiovascular disease are only going to be exacerbated over time,” wrote Dr. Kalogeropoulos, from Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, and Dr. Butler, from Baylor College of Medicine, Dallas.
“On the positive side,” they continued, “the absolute increase in the percent prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and conditions is projected to lie within a manageable range,” assuming that specific prevention policies are implemented.
“This is an opportunity for professional societies, including the cardiovascular care community, to re-evaluate priorities and strategies, for both training and practice, to best match the growing demands of a changing demographic landscape in the United States,” Dr. Kalogeropoulos and Dr. Butler concluded.
Dr. Mohebi is supported by the Barry Fellowship. Dr. Januzzi is supported by the Hutter Family Professorship; is a Trustee of the American College of Cardiology; is a board member of Imbria Pharmaceuticals; has received grant support from Abbott Diagnostics, Applied Therapeutics, Innolife, and Novartis; has received consulting income from Abbott Diagnostics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and participates in clinical endpoint committees/data safety monitoring boards for AbbVie, Siemens, Takeda, and Vifor. Dr. Kalogeropoulos has received research funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the American Heart Association; and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Butler has been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis projects steep increases by 2060 in the prevalence of cardiovascular (CV) risk factors and disease that will disproportionately affect non-White populations who have limited access to health care.
The study by Reza Mohebi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Even though several assumptions underlie these projections, the importance of this work cannot be overestimated,” Andreas P. Kalogeropoulos, MD, MPH, PhD, and Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “The absolute numbers are staggering.”
From 2025 to 2060, the number of people with any one of four CV risk factors – type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity – is projected to increase by 15.4 million, to 34.7 million.
And the number of people with of any one of four CV disease types – ischemic heart disease, heart failure, MI, and stroke – is projected to increase by 3.2 million, to 6.8 million.
Although the model predicts that the prevalence of CV risk factors will gradually decrease among White Americans, the highest prevalence of CV risk factors will be among the White population because of its overall size.
Conversely, the projected prevalence of CV risk factors is expected to increase in Black, Hispanic, Asian, and other race/ethnicity populations.
In parallel, the prevalence of CV disease is projected to decrease in the White population and increase among all other race/ethnicities, particularly in the Black and Hispanic populations.
“Our results project a worrisome increase with a particularly ominous increase in risk factors and disease in our most vulnerable patients, including Blacks and Hispanics,” senior author James L. Januzzi Jr., MD, summarized in a video issued by the society.
“The steep rise in CV risk factors and disease reflects the generally higher prevalence in populations projected to increase in the United States, owing to immigration and growth, including Black or Hispanic individuals,” Dr. Januzzi, also from Massachusetts General and Harvard, said in an interview.
“The disproportionate size of the risk is expected in a sense, as minority populations are disproportionately disadvantaged with respect to their health care,” he said. “But whether it is expected or not, the increase in projected prevalence is, nonetheless, concerning and a call to action.”
This study identifies “areas of opportunity for change in the U.S. health care system,” he continued. “Business as usual will result in us encountering a huge number of individuals with CV risk factors and diseases.”
The results from the current analysis assume there will be no modification in health care policies or changes in access to care for at-risk populations, Dr. Mohebi and colleagues noted.
To “stem the rising tide of CV disease in at-risk individuals,” would require strategies such as “emphasis on education regarding CV risk factors, improving access to quality healthcare, and facilitating lower-cost access to effective therapies for treatment of CV risk factors,” according to the researchers.
“Such advances need to be applied in a more equitable way throughout the United States, however,” they cautioned.
Census plus NHANES data
The researchers used 2020 U.S. census data and projected growth and 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Survey data to estimate the number of people with CV risk factors and CV disease from 2025 to 2060.
The estimates are based on a growing population and a fixed frequency.
The projected changes in CV risk factors and disease over time were similar in men and women.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the assumption that the prevalence patterns for CV risk factors and disease will be stable.
“To the extent the frequency of risk factors and disease are not likely to remain static, that assumption may reduce the accuracy of the projections,” Dr. Januzzi said. “However, we would point out that the goals of our analysis were to set general trends, and not to seek to project exact figures.”
Also, they did not take into account the effect of COVID-19. CV diseases were also based on self-report and CV risk factors could have been underestimated in minority populations that do not access health care.
Changing demographic landscape
It is “striking” that the numbers of non-White individuals with CV risk factors is projected to surpass the number of White individuals over time, and the number of non-White individuals with CV disease will be almost as many as White individuals by the year 2060, the editorialists noted.
“From a policy perspective, this means that unless appropriate, targeted action is taken, disparities in the burden of cardiovascular disease are only going to be exacerbated over time,” wrote Dr. Kalogeropoulos, from Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, and Dr. Butler, from Baylor College of Medicine, Dallas.
“On the positive side,” they continued, “the absolute increase in the percent prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and conditions is projected to lie within a manageable range,” assuming that specific prevention policies are implemented.
“This is an opportunity for professional societies, including the cardiovascular care community, to re-evaluate priorities and strategies, for both training and practice, to best match the growing demands of a changing demographic landscape in the United States,” Dr. Kalogeropoulos and Dr. Butler concluded.
Dr. Mohebi is supported by the Barry Fellowship. Dr. Januzzi is supported by the Hutter Family Professorship; is a Trustee of the American College of Cardiology; is a board member of Imbria Pharmaceuticals; has received grant support from Abbott Diagnostics, Applied Therapeutics, Innolife, and Novartis; has received consulting income from Abbott Diagnostics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and participates in clinical endpoint committees/data safety monitoring boards for AbbVie, Siemens, Takeda, and Vifor. Dr. Kalogeropoulos has received research funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the American Heart Association; and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Butler has been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Topline results for novel drug in ATTR amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy
The RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutic patisiran (Onpattro, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals) led to statistically significant improvement in functional capacity and quality of life in adults with transthyretin-mediated (ATTR) amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy in the phase 3 APOLLO-B study, according to topline results released Aug. 3.
“We are thrilled that APOLLO-B successfully met all its major objectives, which we believe for the first time validates the hypothesis that TTR silencing by an RNAi therapeutic can be an effective approach for treating the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis,” Pushkal Garg, MD, Alnylam chief medical officer, said in a news release.
The Food and Drug Administration approved patisiran in 2018 for polyneuropathy caused by hereditary ATTR in adults on the basis of results of the APOLLO phase 3 trial, as reported by this news organization.
APOLLO-B enrolled 360 adults with ATTR amyloidosis (hereditary or wild-type) with cardiomyopathy at 69 centers in 21 countries. Half were randomly allocated to 0.3 mg/kg of patisiran or placebo administered intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 months.
The study met the primary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in the 6-minute walk test at 12 months compared with placebo (P = .0162), the company said.
The study also met the first secondary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in quality of life compared with placebo, as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (P = .0397).
The patisiran and placebo groups had similar frequencies of adverse events (91% and 94%, respectively) and serious adverse events (34% and 35%, respectively).
“ATTR amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy is an increasingly recognized cause of heart failure, affecting greater than 250,000 patients around the world. These patients have limited treatment options, and disease progression is common. As such, we are encouraged to see the potential of patisiran to improve the functional capacity and quality of life of patients living with this fatal, multisystem disease,” Dr. Garg said in the release.
Full results from APOLLO-B will be presented at a late-breaker session at the 18th International Symposium on Amyloidosis in September in Heidelberg, Germany.
Based on these results, the company plans to file a supplementary new drug application (sNDA) for patisiran for this indication with the FDA later this year, the release noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutic patisiran (Onpattro, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals) led to statistically significant improvement in functional capacity and quality of life in adults with transthyretin-mediated (ATTR) amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy in the phase 3 APOLLO-B study, according to topline results released Aug. 3.
“We are thrilled that APOLLO-B successfully met all its major objectives, which we believe for the first time validates the hypothesis that TTR silencing by an RNAi therapeutic can be an effective approach for treating the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis,” Pushkal Garg, MD, Alnylam chief medical officer, said in a news release.
The Food and Drug Administration approved patisiran in 2018 for polyneuropathy caused by hereditary ATTR in adults on the basis of results of the APOLLO phase 3 trial, as reported by this news organization.
APOLLO-B enrolled 360 adults with ATTR amyloidosis (hereditary or wild-type) with cardiomyopathy at 69 centers in 21 countries. Half were randomly allocated to 0.3 mg/kg of patisiran or placebo administered intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 months.
The study met the primary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in the 6-minute walk test at 12 months compared with placebo (P = .0162), the company said.
The study also met the first secondary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in quality of life compared with placebo, as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (P = .0397).
The patisiran and placebo groups had similar frequencies of adverse events (91% and 94%, respectively) and serious adverse events (34% and 35%, respectively).
“ATTR amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy is an increasingly recognized cause of heart failure, affecting greater than 250,000 patients around the world. These patients have limited treatment options, and disease progression is common. As such, we are encouraged to see the potential of patisiran to improve the functional capacity and quality of life of patients living with this fatal, multisystem disease,” Dr. Garg said in the release.
Full results from APOLLO-B will be presented at a late-breaker session at the 18th International Symposium on Amyloidosis in September in Heidelberg, Germany.
Based on these results, the company plans to file a supplementary new drug application (sNDA) for patisiran for this indication with the FDA later this year, the release noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutic patisiran (Onpattro, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals) led to statistically significant improvement in functional capacity and quality of life in adults with transthyretin-mediated (ATTR) amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy in the phase 3 APOLLO-B study, according to topline results released Aug. 3.
“We are thrilled that APOLLO-B successfully met all its major objectives, which we believe for the first time validates the hypothesis that TTR silencing by an RNAi therapeutic can be an effective approach for treating the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis,” Pushkal Garg, MD, Alnylam chief medical officer, said in a news release.
The Food and Drug Administration approved patisiran in 2018 for polyneuropathy caused by hereditary ATTR in adults on the basis of results of the APOLLO phase 3 trial, as reported by this news organization.
APOLLO-B enrolled 360 adults with ATTR amyloidosis (hereditary or wild-type) with cardiomyopathy at 69 centers in 21 countries. Half were randomly allocated to 0.3 mg/kg of patisiran or placebo administered intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 months.
The study met the primary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in the 6-minute walk test at 12 months compared with placebo (P = .0162), the company said.
The study also met the first secondary endpoint of a statistically significant improvement from baseline in quality of life compared with placebo, as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (P = .0397).
The patisiran and placebo groups had similar frequencies of adverse events (91% and 94%, respectively) and serious adverse events (34% and 35%, respectively).
“ATTR amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy is an increasingly recognized cause of heart failure, affecting greater than 250,000 patients around the world. These patients have limited treatment options, and disease progression is common. As such, we are encouraged to see the potential of patisiran to improve the functional capacity and quality of life of patients living with this fatal, multisystem disease,” Dr. Garg said in the release.
Full results from APOLLO-B will be presented at a late-breaker session at the 18th International Symposium on Amyloidosis in September in Heidelberg, Germany.
Based on these results, the company plans to file a supplementary new drug application (sNDA) for patisiran for this indication with the FDA later this year, the release noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do ICDs still ‘work’ in primary prevention given today’s recommended HF meds?
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contemporary guidelines highly recommend patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) be on all four drug classes that together have shown clinical clout, including improved survival, in major randomized trials.
Although many such patients don’t receive all four drug classes, the more that are prescribed to those with primary-prevention implantable defibrillators (ICD), the better their odds of survival, a new analysis suggests.
The cohort study of almost 5,000 patients with HFrEF and such devices saw their all-cause mortality risk improve stepwise with each additional prescription they were given toward the full quadruple drug combo at the core of modern HFrEF guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). The four classes are sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors.
That inverse relation between risk and number of GDMT medications held whether patients had solo-ICD or defibrillating cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) implants, and were independent of device-implantation year and comorbidities, regardless of HFrEF etiology.
“If anybody had doubts about really pushing forward as much of these guideline-directed medical therapies as the patient tolerates, these data confirm that, by doing so, we definitely do better than with two medications or one medication,” Samir Saba, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
The analysis begs an old and challenging question: Do primary-prevention ICDs confer clinically important survival gains over those provided by increasingly life-preserving recommended HFrEF medical therapy?
Given the study’s incremental survival bumps with each added GDMT med, “one ought to consider whether ICD therapy can still have an impact on overall survival in this population,” proposes a report published online in JACC Clinical Electrophysiology, with Dr. Saba as senior author.
In the adjusted analysis, the 2-year risk for death from any cause in HFrEF patients with primary-prevention devices fell 36% in those with ICDs and 30% in those with CRT-D devices for each added prescribed GDMT drug, from none up to either three or four such agents (P < .001 in both cases).
Only so much can be made of nonrandomized study results, Saba observed in an interview. But they are enough to justify asking whether primary-prevention ICDs are “still valuable” in HFrEF given current GDMT. One interpretation of the study, the published report noted, is that contemporary GDMT improves HFrEF survival so much that it eclipses any such benefit from a primary-prevention ICD.
Both defibrillators and the four core drug therapies boost survival in such cases, “so the fundamental question is, are they additive. Do we save more lives by having a defibrillator on top of the medications, or is it overlapping?” Dr. Saba asked. “We don’t know the answer.”
For now, at least, the findings could reassure clinicians as they consider whether to recommended a primary-prevention ICD when there might be reasons not to, as long there is full GDMT on board, “especially what we today define as quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Recently announced North American guidelines defining an HFrEF quadruple regimen prefer – beyond a beta-blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor – that the selected RAS inhibitor be sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) as a substitute, if needed.
Nearly identical European guidelines on HFrEF quad therapy, unveiled in 2021, include but do not necessarily prefer sacubitril/valsartan over ACE inhibitors as the RAS inhibitor of choice.
GDMT a moving target
Primary-prevention defibrillators entered practice at a time when expected background GDMT consisted of beta-blockers and either ACE inhibitors or ARBs, the current report notes. In practice, many patients receive the devices without both drug classes optimally on board. Moreover, many who otherwise meet guidelines for such ICDs won’t tolerate the kind of maximally tolerated GDMT used in the major primary-prevention device trials.
Yet current guidelines give such devices a class I recommendation, based on the highest level of evidence, in HFrEF patients who remain symptomatic despite quad GDMT, observed Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center.
The current analysis “further reinforces the importance of providing all four foundational GDMTs” to all eligible HFrEF patients without contraindications who can tolerate them, he said in an interview. Such quad therapy “is associated with incremental 1-year survival advantages” in patients with primary-prevention devices. And in the major trials, “there were reductions in sudden deaths, as well as progressive heart failure deaths.”
But the current study also suggests that in practice “very few patients can actually get to all four drugs on GDMT,” Roderick Tung, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview. Optimized GDMT in randomized trials probably represents the best-case scenario. “There is a difference between randomized data and real-world data, which is why we need both.”
And it asserts that “the more GDMT you’re on, the better you do,” he said. “But does that obviate the need for an ICD? I think that’s not clear,” in part because of potential confounding in the analysis. For example, patients who can take all four agents tend to be less sick than those who cannot.
“The ones who can get up to four are preselected, because they’re healthier,” Dr. Tung said. “There are real limitations – such as metabolic disturbances, acute kidney injury and cardiorenal syndrome, and hypotension – that actually make it difficult to initiate and titrate these medications.”
Indeed, the major primary-prevention ICD trials usually excluded the sickest patients with the most comorbidities, Dr. Saba observed, which raises issues about their relevance to clinical practice. But his group’s study controlled for many potential confounders by adjusting for, among other things, Elixhauser comorbidity score, ejection fraction, type of cardiomyopathy, and year of device implantation.
“We tried to level the playing field that way, to see if – despite all of this adjustment – the incremental number of heart failure medicines stills make a difference,” Dr. Saba said. “And our results suggest that yes, they still do.”
GDMT coverage in the real world
The analysis of patients with HFrEF involved 3,210 with ICD-only implants and 1,762 with CRT-D devices for primary prevention at a major medical center from 2010 to 2021. Of the total, 5% had not been prescribed any of the four GDMT agents, 20% had been prescribed only one, 52% were prescribed two, and 23% were prescribed three or four. Only 113 patients had been prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors, which have only recently been indicated for HFrEF.
Adjusted hazard ratios for death from any cause at 2 years for each added GDMT drug (P < .001 in each case), were 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.74) for ICD recipients, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.58-0.86) for those with a CRT-D device, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60-0.81) for those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, and 0.61 (95% CI, 0.51-0.73) for patients with nonischemic disease.
The results “raise questions rather than answers,” Dr. Saba said. “At some point, someone will need to take patients who are optimized on their heart failure medications and then randomize them to defibrillator versus no defibrillator to see whether there is still an additive impact.”
Current best evidence suggests that primary-prevention ICDs in patients with guideline-based indications confer benefits that far outweigh any risks. But if the major primary-prevention ICD trials were to be repeated in patients on contemporary quad-therapy GDMT, Dr. Tung said, “would the benefit of ICD be attenuated? I think most of us believe it likely would.”
Still, he said, a background of modern GDMT could potentially “optimize” such trials by attenuating mortality from heart failure progression and thereby expanding the proportion of deaths that are arrhythmic, “which the defibrillator can prevent.”
Dr. Saba discloses receiving research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and serving on advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific. The other authors reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Tung has disclosed receiving speaker fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. Dr. Fonarow has reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC CLINICAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
‘Striking’ disparities in CVD deaths persist across COVID waves
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS
Boosting hypertension screening, treatment would cut global mortality 7%
If 80% of individuals with hypertension were screened, 80% received treatment, and 80% then reached guideline-specified targets, up to 200 million cases of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and 130 million deaths could be averted by 2050, a modeling study suggests.
Achievement of the 80-80-80 target “could be one of the single most important global public health accomplishments of the coming decades,” according to the authors.
“We need to reprioritize hypertension care in our practices,” principal investigator David A. Watkins, MD, MPH, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization. “Only about one in five persons with hypertension around the world has their blood pressure well controlled. Oftentimes, clinicians are focused on addressing patients’ other health needs, many of which can be pressing in the short term, and we forget to talk about blood pressure, which has more than earned its reputation as ‘the silent killer.’ ”
The modeling study was published online in Nature Medicine, with lead author Sarah J. Pickersgill, MPH, also from the University of Washington.
Two interventions, three scenarios
Dr. Watkins and colleagues based their analysis on two approaches to blood pressure (BP) control shown to be beneficial: drug treatment to a systolic BP of either 130 mm Hg or 140 mm Hg or less, depending on local guidelines, and dietary sodium reduction, as recommended by the World Health Organization.
The team modeled the impacts of these interventions in 182 countries according to three scenarios:
- Business as usual (control): allowing hypertension to increase at historic rates of change and mean sodium intake to remain at current levels
- Progress: matching historically high-performing countries (for example, accelerating hypertension control by about 3% per year at intermediate levels of intervention coverage) while lowering mean sodium intake by 15% by 2030
- Aspirational: hypertension control achieved faster than historically high-performing countries (about 4% per year) and mean sodium intake decreased by 30% by 2027
The analysis suggests that in the progressive scenario, all countries could achieve 80-80-80 targets by 2050 and most countries by 2040; the aspirational scenario would have all countries meeting them by 2040. That would result in reductions in all-cause mortality of 4%-7% (76 million to 130 million deaths averted) with progressive and aspirational interventions, respectively, compared with the control scenario.
There would also be a slower rise in expected CVD from population growth and aging (110 million to 200 million cases averted). That is, the probability of dying from any CVD cause between the ages of 30 and 80 years would be reduced by 16% in the progressive scenario and 26% in the aspirational scenario.
Of note, about 83%-85% of the potential mortality reductions would result from scaling up hypertension treatment in the progressive and aspirational scenarios, respectively, with the remaining 15%-17% coming from sodium reduction, the researchers state.
Further, they propose, scaling up BP interventions could reduce CVD inequalities across countries, with low-income and lower-middle-income countries likely experiencing the largest reductions in disease rates and mortality.
Implementation barriers
“Health systems in many low- and middle-income countries have not traditionally been set up to succeed in chronic disease management in primary care,” Dr. Watkins noted. For interventions to be successful, he said, “several barriers need to be addressed, including: low population awareness of chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes, which leads to low rates of screening and treatment; high out-of-pocket cost and low availability of medicines for chronic diseases; and need for adherence support and provider incentives for improving quality of chronic disease care in primary care settings.”
“Based on the analysis, achieving the 80-80-80 seems feasible, though actually getting there may be much more complicated. I wonder whether countries have the resources to implement the needed policies,” Rodrigo M. Carrillo-Larco, MD, researcher, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, told this news organization.
“It may be challenging, particularly after COVID-19, which revealed deficiencies in many health care systems, and care for hypertension may have been disturbed,” said Dr. Carrillo-Larco, who is not connected with the analysis.
That said, simplified BP screening approaches could help maximize the number of people screened overall, potentially identifying those with hypertension and raising awareness, he proposed. His team’s recent study showed that such approaches vary from country to country but are generally reliable and can be used effectively for population screening.
In addition, Dr. Carrillo-Larco said, any efforts by clinicians to improve adherence and help patients achieve BP control “would also have positive effects at the population level.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, with additional funding by a grant to Dr. Watkins from Resolve to Save Lives. No conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If 80% of individuals with hypertension were screened, 80% received treatment, and 80% then reached guideline-specified targets, up to 200 million cases of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and 130 million deaths could be averted by 2050, a modeling study suggests.
Achievement of the 80-80-80 target “could be one of the single most important global public health accomplishments of the coming decades,” according to the authors.
“We need to reprioritize hypertension care in our practices,” principal investigator David A. Watkins, MD, MPH, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization. “Only about one in five persons with hypertension around the world has their blood pressure well controlled. Oftentimes, clinicians are focused on addressing patients’ other health needs, many of which can be pressing in the short term, and we forget to talk about blood pressure, which has more than earned its reputation as ‘the silent killer.’ ”
The modeling study was published online in Nature Medicine, with lead author Sarah J. Pickersgill, MPH, also from the University of Washington.
Two interventions, three scenarios
Dr. Watkins and colleagues based their analysis on two approaches to blood pressure (BP) control shown to be beneficial: drug treatment to a systolic BP of either 130 mm Hg or 140 mm Hg or less, depending on local guidelines, and dietary sodium reduction, as recommended by the World Health Organization.
The team modeled the impacts of these interventions in 182 countries according to three scenarios:
- Business as usual (control): allowing hypertension to increase at historic rates of change and mean sodium intake to remain at current levels
- Progress: matching historically high-performing countries (for example, accelerating hypertension control by about 3% per year at intermediate levels of intervention coverage) while lowering mean sodium intake by 15% by 2030
- Aspirational: hypertension control achieved faster than historically high-performing countries (about 4% per year) and mean sodium intake decreased by 30% by 2027
The analysis suggests that in the progressive scenario, all countries could achieve 80-80-80 targets by 2050 and most countries by 2040; the aspirational scenario would have all countries meeting them by 2040. That would result in reductions in all-cause mortality of 4%-7% (76 million to 130 million deaths averted) with progressive and aspirational interventions, respectively, compared with the control scenario.
There would also be a slower rise in expected CVD from population growth and aging (110 million to 200 million cases averted). That is, the probability of dying from any CVD cause between the ages of 30 and 80 years would be reduced by 16% in the progressive scenario and 26% in the aspirational scenario.
Of note, about 83%-85% of the potential mortality reductions would result from scaling up hypertension treatment in the progressive and aspirational scenarios, respectively, with the remaining 15%-17% coming from sodium reduction, the researchers state.
Further, they propose, scaling up BP interventions could reduce CVD inequalities across countries, with low-income and lower-middle-income countries likely experiencing the largest reductions in disease rates and mortality.
Implementation barriers
“Health systems in many low- and middle-income countries have not traditionally been set up to succeed in chronic disease management in primary care,” Dr. Watkins noted. For interventions to be successful, he said, “several barriers need to be addressed, including: low population awareness of chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes, which leads to low rates of screening and treatment; high out-of-pocket cost and low availability of medicines for chronic diseases; and need for adherence support and provider incentives for improving quality of chronic disease care in primary care settings.”
“Based on the analysis, achieving the 80-80-80 seems feasible, though actually getting there may be much more complicated. I wonder whether countries have the resources to implement the needed policies,” Rodrigo M. Carrillo-Larco, MD, researcher, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, told this news organization.
“It may be challenging, particularly after COVID-19, which revealed deficiencies in many health care systems, and care for hypertension may have been disturbed,” said Dr. Carrillo-Larco, who is not connected with the analysis.
That said, simplified BP screening approaches could help maximize the number of people screened overall, potentially identifying those with hypertension and raising awareness, he proposed. His team’s recent study showed that such approaches vary from country to country but are generally reliable and can be used effectively for population screening.
In addition, Dr. Carrillo-Larco said, any efforts by clinicians to improve adherence and help patients achieve BP control “would also have positive effects at the population level.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, with additional funding by a grant to Dr. Watkins from Resolve to Save Lives. No conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If 80% of individuals with hypertension were screened, 80% received treatment, and 80% then reached guideline-specified targets, up to 200 million cases of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and 130 million deaths could be averted by 2050, a modeling study suggests.
Achievement of the 80-80-80 target “could be one of the single most important global public health accomplishments of the coming decades,” according to the authors.
“We need to reprioritize hypertension care in our practices,” principal investigator David A. Watkins, MD, MPH, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization. “Only about one in five persons with hypertension around the world has their blood pressure well controlled. Oftentimes, clinicians are focused on addressing patients’ other health needs, many of which can be pressing in the short term, and we forget to talk about blood pressure, which has more than earned its reputation as ‘the silent killer.’ ”
The modeling study was published online in Nature Medicine, with lead author Sarah J. Pickersgill, MPH, also from the University of Washington.
Two interventions, three scenarios
Dr. Watkins and colleagues based their analysis on two approaches to blood pressure (BP) control shown to be beneficial: drug treatment to a systolic BP of either 130 mm Hg or 140 mm Hg or less, depending on local guidelines, and dietary sodium reduction, as recommended by the World Health Organization.
The team modeled the impacts of these interventions in 182 countries according to three scenarios:
- Business as usual (control): allowing hypertension to increase at historic rates of change and mean sodium intake to remain at current levels
- Progress: matching historically high-performing countries (for example, accelerating hypertension control by about 3% per year at intermediate levels of intervention coverage) while lowering mean sodium intake by 15% by 2030
- Aspirational: hypertension control achieved faster than historically high-performing countries (about 4% per year) and mean sodium intake decreased by 30% by 2027
The analysis suggests that in the progressive scenario, all countries could achieve 80-80-80 targets by 2050 and most countries by 2040; the aspirational scenario would have all countries meeting them by 2040. That would result in reductions in all-cause mortality of 4%-7% (76 million to 130 million deaths averted) with progressive and aspirational interventions, respectively, compared with the control scenario.
There would also be a slower rise in expected CVD from population growth and aging (110 million to 200 million cases averted). That is, the probability of dying from any CVD cause between the ages of 30 and 80 years would be reduced by 16% in the progressive scenario and 26% in the aspirational scenario.
Of note, about 83%-85% of the potential mortality reductions would result from scaling up hypertension treatment in the progressive and aspirational scenarios, respectively, with the remaining 15%-17% coming from sodium reduction, the researchers state.
Further, they propose, scaling up BP interventions could reduce CVD inequalities across countries, with low-income and lower-middle-income countries likely experiencing the largest reductions in disease rates and mortality.
Implementation barriers
“Health systems in many low- and middle-income countries have not traditionally been set up to succeed in chronic disease management in primary care,” Dr. Watkins noted. For interventions to be successful, he said, “several barriers need to be addressed, including: low population awareness of chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes, which leads to low rates of screening and treatment; high out-of-pocket cost and low availability of medicines for chronic diseases; and need for adherence support and provider incentives for improving quality of chronic disease care in primary care settings.”
“Based on the analysis, achieving the 80-80-80 seems feasible, though actually getting there may be much more complicated. I wonder whether countries have the resources to implement the needed policies,” Rodrigo M. Carrillo-Larco, MD, researcher, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, told this news organization.
“It may be challenging, particularly after COVID-19, which revealed deficiencies in many health care systems, and care for hypertension may have been disturbed,” said Dr. Carrillo-Larco, who is not connected with the analysis.
That said, simplified BP screening approaches could help maximize the number of people screened overall, potentially identifying those with hypertension and raising awareness, he proposed. His team’s recent study showed that such approaches vary from country to country but are generally reliable and can be used effectively for population screening.
In addition, Dr. Carrillo-Larco said, any efforts by clinicians to improve adherence and help patients achieve BP control “would also have positive effects at the population level.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, with additional funding by a grant to Dr. Watkins from Resolve to Save Lives. No conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two distinct phenotypes of COVID-related myocarditis emerge
Researchers from France have identified two distinct phenotypes of fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis in adults, with different clinical presentations, immunologic profiles, and outcomes.
Differentiation between the two bioclinical entities is important to understand for patient management and further pathophysiological studies, they said.
The first phenotype occurs early (within a few days) in acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, with active viral replication (polymerase chain reaction positive) in adults who meet criteria for multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-A+).
In this early phenotype, there is “limited systemic inflammation without skin and mucosal involvement, but myocardial dysfunction is fulminant and frequently associated with large pericardial effusions. These cases more often require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO],” Guy Gorochov, MD, PhD, Sorbonne University, Paris, said in an interview.
The second is a delayed, postinfectious, immune-driven phenotype that occurs in adults who fail to meet the criteria for MIS-A (MIS-A–).
This phenotype occurs weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection, usually beyond detectable active viral replication (PCR–) in the context of specific immune response and severe systemic inflammation with skin and mucosal involvement. Myocardial dysfunction is more progressive and rarely associated with large pericardial effusions, Dr. Gorochov explained.
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Evolving understanding
The findings are based on a retrospective analysis of 38 patients without a history of COVID-19 vaccination who were admitted to the intensive care unit from March 2020 to June 2021 for suspected fulminant COVID-19 myocarditis.
Patients were confirmed to have SARS-CoV-2 infection by PCR and/or by serologic testing. As noted in other studies, the patients were predominantly young men (66%; median age, 27.5 years). Twenty-five (66%) patients were MIS-A+ and 13 (34%) were MIS-A–.
In general, the MIS-A– patients were sicker and had worse outcomes.
Specifically, compared with the MIS-A+ patients, MIS-A– patients had a shorter time between the onset of COVID-19 symptoms and the development of myocarditis, a shorter time to ICU admission, and more severe presentations assessed using lower left ventricular ejection fraction and sequential organ failure assessment scores.
MIS-A– patients also had higher lactate levels, were more likely to need venoarterial ECMO (92% vs 16%), had higher ICU mortality (31% vs. 4%), and a had lower probability of survival at 3 months (68% vs. 96%), compared with their MIS-A+ peers.
Immunologic differences
The immunologic profiles of these two distinct clinical phenotypes also differed.
In MIS-A– early-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are frequently positive and serum levels of antiviral interferon-alpha and granulocyte-attracting interleukin-8 are elevated.
In contrast, in MIS-A+ delayed-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are negative and serum levels of IL-17 and IL-22 are highly elevated.
“We suggest that IL-17 and IL-22 are novel criteria that should help to assess in adults the recently recognized MIS-A,” Dr. Gorochov told this news organization. “It should be tested whether IL-17 and IL-22 are also elevated in children with MIS-C.”
The researchers also observed “extremely” high serum IL-10 levels in both patient groups. This has been previously associated with severe myocardial injury and an increase in the risk for death in severe COVID-19 patients.
The researchers said the phenotypic clustering of patients with fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis “seems relevant” for their management.
MIS-A– cases, owing to the high risk for evolution toward refractory cardiogenic shock, should be “urgently” referred to a center with venoarterial ECMO and closely monitored to prevent a “too-late” cannulation, especially under cardiopulmonary resuscitation, known to be associated with poor outcomes, they advised.
They noted that the five patients who died in their series had late venoarterial ECMO implantation, while undergoing multiple organ failures or resuscitation.
Conversely, the risk for evolution to refractory cardiogenic shock is lower in MIS-A+ cases. However, identifying MIS-A+ cases is “all the more important given that numerous data support the efficacy of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulins in MIS-C,” Dr. Gorochov and colleagues wrote.
The authors of a linked editorial said the French team should be “commended on their work in furthering our understanding of fulminant myocarditis related to COVID-19 infection.”
Ajith Nair, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Anita Deswal, MD, MPH, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, both in Houston, noted that fulminant myocarditis is rare and can result from either of two mechanisms: viral tropism or an immune-mediated mechanism.
“It remains to be seen whether using antiviral therapy versus immunomodulatory therapy on the basis of clinical and cytokine profiles will yield benefits,” they wrote.
“Fulminant myocarditis invariably requires hemodynamic support and carries a high mortality risk if it is recognized late. However, the long-term prognosis in patients who survive the critical period is favorable, with recovery of myocardial function,” they added.
“This study highlights the ever-shifting understanding of the pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches to fulminant myocarditis,” Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal concluded.
This research was supported in part by the Foundation of France, French National Research Agency, Sorbonne University, and Clinical Research Hospital. The researchers have filed a patent application based on these results. Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers from France have identified two distinct phenotypes of fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis in adults, with different clinical presentations, immunologic profiles, and outcomes.
Differentiation between the two bioclinical entities is important to understand for patient management and further pathophysiological studies, they said.
The first phenotype occurs early (within a few days) in acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, with active viral replication (polymerase chain reaction positive) in adults who meet criteria for multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-A+).
In this early phenotype, there is “limited systemic inflammation without skin and mucosal involvement, but myocardial dysfunction is fulminant and frequently associated with large pericardial effusions. These cases more often require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO],” Guy Gorochov, MD, PhD, Sorbonne University, Paris, said in an interview.
The second is a delayed, postinfectious, immune-driven phenotype that occurs in adults who fail to meet the criteria for MIS-A (MIS-A–).
This phenotype occurs weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection, usually beyond detectable active viral replication (PCR–) in the context of specific immune response and severe systemic inflammation with skin and mucosal involvement. Myocardial dysfunction is more progressive and rarely associated with large pericardial effusions, Dr. Gorochov explained.
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Evolving understanding
The findings are based on a retrospective analysis of 38 patients without a history of COVID-19 vaccination who were admitted to the intensive care unit from March 2020 to June 2021 for suspected fulminant COVID-19 myocarditis.
Patients were confirmed to have SARS-CoV-2 infection by PCR and/or by serologic testing. As noted in other studies, the patients were predominantly young men (66%; median age, 27.5 years). Twenty-five (66%) patients were MIS-A+ and 13 (34%) were MIS-A–.
In general, the MIS-A– patients were sicker and had worse outcomes.
Specifically, compared with the MIS-A+ patients, MIS-A– patients had a shorter time between the onset of COVID-19 symptoms and the development of myocarditis, a shorter time to ICU admission, and more severe presentations assessed using lower left ventricular ejection fraction and sequential organ failure assessment scores.
MIS-A– patients also had higher lactate levels, were more likely to need venoarterial ECMO (92% vs 16%), had higher ICU mortality (31% vs. 4%), and a had lower probability of survival at 3 months (68% vs. 96%), compared with their MIS-A+ peers.
Immunologic differences
The immunologic profiles of these two distinct clinical phenotypes also differed.
In MIS-A– early-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are frequently positive and serum levels of antiviral interferon-alpha and granulocyte-attracting interleukin-8 are elevated.
In contrast, in MIS-A+ delayed-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are negative and serum levels of IL-17 and IL-22 are highly elevated.
“We suggest that IL-17 and IL-22 are novel criteria that should help to assess in adults the recently recognized MIS-A,” Dr. Gorochov told this news organization. “It should be tested whether IL-17 and IL-22 are also elevated in children with MIS-C.”
The researchers also observed “extremely” high serum IL-10 levels in both patient groups. This has been previously associated with severe myocardial injury and an increase in the risk for death in severe COVID-19 patients.
The researchers said the phenotypic clustering of patients with fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis “seems relevant” for their management.
MIS-A– cases, owing to the high risk for evolution toward refractory cardiogenic shock, should be “urgently” referred to a center with venoarterial ECMO and closely monitored to prevent a “too-late” cannulation, especially under cardiopulmonary resuscitation, known to be associated with poor outcomes, they advised.
They noted that the five patients who died in their series had late venoarterial ECMO implantation, while undergoing multiple organ failures or resuscitation.
Conversely, the risk for evolution to refractory cardiogenic shock is lower in MIS-A+ cases. However, identifying MIS-A+ cases is “all the more important given that numerous data support the efficacy of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulins in MIS-C,” Dr. Gorochov and colleagues wrote.
The authors of a linked editorial said the French team should be “commended on their work in furthering our understanding of fulminant myocarditis related to COVID-19 infection.”
Ajith Nair, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Anita Deswal, MD, MPH, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, both in Houston, noted that fulminant myocarditis is rare and can result from either of two mechanisms: viral tropism or an immune-mediated mechanism.
“It remains to be seen whether using antiviral therapy versus immunomodulatory therapy on the basis of clinical and cytokine profiles will yield benefits,” they wrote.
“Fulminant myocarditis invariably requires hemodynamic support and carries a high mortality risk if it is recognized late. However, the long-term prognosis in patients who survive the critical period is favorable, with recovery of myocardial function,” they added.
“This study highlights the ever-shifting understanding of the pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches to fulminant myocarditis,” Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal concluded.
This research was supported in part by the Foundation of France, French National Research Agency, Sorbonne University, and Clinical Research Hospital. The researchers have filed a patent application based on these results. Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers from France have identified two distinct phenotypes of fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis in adults, with different clinical presentations, immunologic profiles, and outcomes.
Differentiation between the two bioclinical entities is important to understand for patient management and further pathophysiological studies, they said.
The first phenotype occurs early (within a few days) in acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, with active viral replication (polymerase chain reaction positive) in adults who meet criteria for multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-A+).
In this early phenotype, there is “limited systemic inflammation without skin and mucosal involvement, but myocardial dysfunction is fulminant and frequently associated with large pericardial effusions. These cases more often require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO],” Guy Gorochov, MD, PhD, Sorbonne University, Paris, said in an interview.
The second is a delayed, postinfectious, immune-driven phenotype that occurs in adults who fail to meet the criteria for MIS-A (MIS-A–).
This phenotype occurs weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection, usually beyond detectable active viral replication (PCR–) in the context of specific immune response and severe systemic inflammation with skin and mucosal involvement. Myocardial dysfunction is more progressive and rarely associated with large pericardial effusions, Dr. Gorochov explained.
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Evolving understanding
The findings are based on a retrospective analysis of 38 patients without a history of COVID-19 vaccination who were admitted to the intensive care unit from March 2020 to June 2021 for suspected fulminant COVID-19 myocarditis.
Patients were confirmed to have SARS-CoV-2 infection by PCR and/or by serologic testing. As noted in other studies, the patients were predominantly young men (66%; median age, 27.5 years). Twenty-five (66%) patients were MIS-A+ and 13 (34%) were MIS-A–.
In general, the MIS-A– patients were sicker and had worse outcomes.
Specifically, compared with the MIS-A+ patients, MIS-A– patients had a shorter time between the onset of COVID-19 symptoms and the development of myocarditis, a shorter time to ICU admission, and more severe presentations assessed using lower left ventricular ejection fraction and sequential organ failure assessment scores.
MIS-A– patients also had higher lactate levels, were more likely to need venoarterial ECMO (92% vs 16%), had higher ICU mortality (31% vs. 4%), and a had lower probability of survival at 3 months (68% vs. 96%), compared with their MIS-A+ peers.
Immunologic differences
The immunologic profiles of these two distinct clinical phenotypes also differed.
In MIS-A– early-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are frequently positive and serum levels of antiviral interferon-alpha and granulocyte-attracting interleukin-8 are elevated.
In contrast, in MIS-A+ delayed-type COVID-19 myocarditis, RNA polymerase III autoantibodies are negative and serum levels of IL-17 and IL-22 are highly elevated.
“We suggest that IL-17 and IL-22 are novel criteria that should help to assess in adults the recently recognized MIS-A,” Dr. Gorochov told this news organization. “It should be tested whether IL-17 and IL-22 are also elevated in children with MIS-C.”
The researchers also observed “extremely” high serum IL-10 levels in both patient groups. This has been previously associated with severe myocardial injury and an increase in the risk for death in severe COVID-19 patients.
The researchers said the phenotypic clustering of patients with fulminant COVID-19–related myocarditis “seems relevant” for their management.
MIS-A– cases, owing to the high risk for evolution toward refractory cardiogenic shock, should be “urgently” referred to a center with venoarterial ECMO and closely monitored to prevent a “too-late” cannulation, especially under cardiopulmonary resuscitation, known to be associated with poor outcomes, they advised.
They noted that the five patients who died in their series had late venoarterial ECMO implantation, while undergoing multiple organ failures or resuscitation.
Conversely, the risk for evolution to refractory cardiogenic shock is lower in MIS-A+ cases. However, identifying MIS-A+ cases is “all the more important given that numerous data support the efficacy of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulins in MIS-C,” Dr. Gorochov and colleagues wrote.
The authors of a linked editorial said the French team should be “commended on their work in furthering our understanding of fulminant myocarditis related to COVID-19 infection.”
Ajith Nair, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Anita Deswal, MD, MPH, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, both in Houston, noted that fulminant myocarditis is rare and can result from either of two mechanisms: viral tropism or an immune-mediated mechanism.
“It remains to be seen whether using antiviral therapy versus immunomodulatory therapy on the basis of clinical and cytokine profiles will yield benefits,” they wrote.
“Fulminant myocarditis invariably requires hemodynamic support and carries a high mortality risk if it is recognized late. However, the long-term prognosis in patients who survive the critical period is favorable, with recovery of myocardial function,” they added.
“This study highlights the ever-shifting understanding of the pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches to fulminant myocarditis,” Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal concluded.
This research was supported in part by the Foundation of France, French National Research Agency, Sorbonne University, and Clinical Research Hospital. The researchers have filed a patent application based on these results. Dr. Nair and Dr. Deswal have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Hypertension heightens risk for severe COVID-19, even in the fully vaxxed
Adults with hypertension who were vaccinated for COVID-19 with at least one booster were more than twice as likely as vaccinated and boosted individuals without hypertension to be hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to data from more than 900 individuals.
“We were surprised to learn that many people who were hospitalized with COVID-19 had hypertension and no other risk factors,” said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Research on Healthy Aging in the department of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles, and a senior author of the study. “This is concerning when you consider that almost half of American adults have high blood pressure.”
COVID-19 vaccines demonstrated ability to reduce death and some of the most severe side effects from the infection in the early stages of the pandemic. Although the Omicron surge prompted recommendations for a third mRNA vaccine dose, “a proportion of individuals who received three mRNA vaccine doses still required hospitalization for COVID-19 during the Omicron surge,” and the characteristics associated with severe illness in vaccinated and boosted patients have not been explored, Joseph Ebinger, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote.
Previous research has shown an association between high blood pressure an increased risk for developing severe COVID-19 compared to several other chronic health conditions, including kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and heart failure, the researchers noted.
In a study published in Hypertension, the researchers identified 912 adults who received at least three doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and were later diagnosed with COVID-19 during the surge in infections from the Omicron variant between December 2021 and April 2022.
A total of 145 of the individuals were hospitalized (16%); of these, 125 (86%) had hypertension.
Patients with hypertension were the most likely to be hospitalized, with an odds ratio of 2.9. In addition to high blood pressure, factors including older age (OR, 1.3), chronic kidney disease (OR, 2.2), prior myocardial infarction or heart failure (OR, 2.2), and longer time since the last vaccination and COVID-19 infection were associated with increased risk of hospitalization in a multivariate analysis.
However, the increased risk of severe illness and hospitalization associated with high blood pressure persisted, with an OR of 2.6, in the absence of comorbid conditions such as type 2 diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, the researchers emphasized.
“Although the mechanism for hypertension-associated COVID-19 risk remains unclear, prior studies have identified delayed SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and prolonged inflammatory response among hypertensive patients, which may contribute to greater disease severity,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of data from a single center and lack of information on which Omicron variants and subvariants were behind the infections, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more research on how to reduce the risks of severe COVID-19 in vulnerable populations, and on the mechanism for a potential connection between high blood pressure and severe COVID-19, they said.
Given the high prevalence of hypertension worldwide, increased understanding of the hypertension-specific risks and identification of individual and population-level risk reduction strategies will be important to the transition of COVID-19 from pandemic to endemic, they concluded.
Omicron changes the game
“When the pandemic initially started, many conditions were seen to increase risk for more severe COVID illness, and hypertension was one of those factors – and then things changed,” lead author Dr. Ebinger said in an interview. “First, vaccines arrived on the scene and substantially reduced risk of severe COVID for everyone who received them. Second, Omicron arrived and, while more transmissible, this variant has been less likely to cause severe COVID. On the one hand, we have vaccines and boosters that we want to think of as ‘the great equalizer’ when it comes to preexisting conditions. On the other hand, we have a dominant set of SARS-CoV-2 subvariants that seem less virulent in most people.
“Taken together, we have been hoping and even assuming that we have been doing pretty well with minimizing risks. Unfortunately, our study results indicate this is not exactly the case,” he said.
“Although vaccines and boosters appear to have equalized or minimized the risks of severe COVID for some people, this has not happened for others – even in the setting of the milder Omicron variant. Of individuals who were fully vaccinated and boosted, having hypertension increased the odds of needing to be hospitalized after getting infected with Omicron by 2.6-fold, even when accounting for or in the absence of having any major chronic disease that might otherwise predispose to more severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Ebinger added.
“So, while the originally seen risks of having obesity or diabetes seem to have been minimized during this current era of pandemic, the risk of having hypertension has persisted. We found this both surprising and concerning, because hypertension is very common and present in over half of people over age 50.”
Surprisingly, “we found that a fair number of people, even after being fully vaccinated plus a having gotten a booster, will not only catch Omicron but get sick enough to need hospital care,” Dr. Ebinger emphasized. “Moreover, it is not just older adults with major comorbid conditions who are vulnerable. Our data show that this can happen to an adult of any age and especially if a person has only hypertension and otherwise no major chronic disease.”
The first takeaway message for clinicians at this time is to raise awareness, Dr. Ebinger stressed in the interview. “We need to raise understanding around the fact that receiving three doses of vaccine may not prevent severe COVID-19 illness in everyone, even when the circulating viral variant is presumed to be causing only mild disease in most people. Moreover, the people who are most at risk are not whom we might think they are. They are not the sickest of the sick. They include people who might not have major conditions such as heart disease or kidney disease, but they do have hypertension.”
Second, “we need more research to understand out why there is this link between hypertension and excess risk for the more severe forms of COVID-19, despite it arising from a supposedly milder variant,” said Dr. Ebinger.
“Third, we need to determine how to reduce these risks, whether through more tailored vaccine regimens or novel therapeutics or a combination approach,” he said.
Looking ahead, “the biological mechanism underpinning the association between hypertension and severe COVID-19 remains underexplored. Future work should focus on understanding the factors linking hypertension to severe COVID-19, as this may elucidate both information on how SARS-CoV-2 effects the body and potential targets for intervention,” Dr. Ebinger added.
The study was supported in part by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the Erika J. Glazer Family Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with hypertension who were vaccinated for COVID-19 with at least one booster were more than twice as likely as vaccinated and boosted individuals without hypertension to be hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to data from more than 900 individuals.
“We were surprised to learn that many people who were hospitalized with COVID-19 had hypertension and no other risk factors,” said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Research on Healthy Aging in the department of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles, and a senior author of the study. “This is concerning when you consider that almost half of American adults have high blood pressure.”
COVID-19 vaccines demonstrated ability to reduce death and some of the most severe side effects from the infection in the early stages of the pandemic. Although the Omicron surge prompted recommendations for a third mRNA vaccine dose, “a proportion of individuals who received three mRNA vaccine doses still required hospitalization for COVID-19 during the Omicron surge,” and the characteristics associated with severe illness in vaccinated and boosted patients have not been explored, Joseph Ebinger, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote.
Previous research has shown an association between high blood pressure an increased risk for developing severe COVID-19 compared to several other chronic health conditions, including kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and heart failure, the researchers noted.
In a study published in Hypertension, the researchers identified 912 adults who received at least three doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and were later diagnosed with COVID-19 during the surge in infections from the Omicron variant between December 2021 and April 2022.
A total of 145 of the individuals were hospitalized (16%); of these, 125 (86%) had hypertension.
Patients with hypertension were the most likely to be hospitalized, with an odds ratio of 2.9. In addition to high blood pressure, factors including older age (OR, 1.3), chronic kidney disease (OR, 2.2), prior myocardial infarction or heart failure (OR, 2.2), and longer time since the last vaccination and COVID-19 infection were associated with increased risk of hospitalization in a multivariate analysis.
However, the increased risk of severe illness and hospitalization associated with high blood pressure persisted, with an OR of 2.6, in the absence of comorbid conditions such as type 2 diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, the researchers emphasized.
“Although the mechanism for hypertension-associated COVID-19 risk remains unclear, prior studies have identified delayed SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and prolonged inflammatory response among hypertensive patients, which may contribute to greater disease severity,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of data from a single center and lack of information on which Omicron variants and subvariants were behind the infections, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more research on how to reduce the risks of severe COVID-19 in vulnerable populations, and on the mechanism for a potential connection between high blood pressure and severe COVID-19, they said.
Given the high prevalence of hypertension worldwide, increased understanding of the hypertension-specific risks and identification of individual and population-level risk reduction strategies will be important to the transition of COVID-19 from pandemic to endemic, they concluded.
Omicron changes the game
“When the pandemic initially started, many conditions were seen to increase risk for more severe COVID illness, and hypertension was one of those factors – and then things changed,” lead author Dr. Ebinger said in an interview. “First, vaccines arrived on the scene and substantially reduced risk of severe COVID for everyone who received them. Second, Omicron arrived and, while more transmissible, this variant has been less likely to cause severe COVID. On the one hand, we have vaccines and boosters that we want to think of as ‘the great equalizer’ when it comes to preexisting conditions. On the other hand, we have a dominant set of SARS-CoV-2 subvariants that seem less virulent in most people.
“Taken together, we have been hoping and even assuming that we have been doing pretty well with minimizing risks. Unfortunately, our study results indicate this is not exactly the case,” he said.
“Although vaccines and boosters appear to have equalized or minimized the risks of severe COVID for some people, this has not happened for others – even in the setting of the milder Omicron variant. Of individuals who were fully vaccinated and boosted, having hypertension increased the odds of needing to be hospitalized after getting infected with Omicron by 2.6-fold, even when accounting for or in the absence of having any major chronic disease that might otherwise predispose to more severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Ebinger added.
“So, while the originally seen risks of having obesity or diabetes seem to have been minimized during this current era of pandemic, the risk of having hypertension has persisted. We found this both surprising and concerning, because hypertension is very common and present in over half of people over age 50.”
Surprisingly, “we found that a fair number of people, even after being fully vaccinated plus a having gotten a booster, will not only catch Omicron but get sick enough to need hospital care,” Dr. Ebinger emphasized. “Moreover, it is not just older adults with major comorbid conditions who are vulnerable. Our data show that this can happen to an adult of any age and especially if a person has only hypertension and otherwise no major chronic disease.”
The first takeaway message for clinicians at this time is to raise awareness, Dr. Ebinger stressed in the interview. “We need to raise understanding around the fact that receiving three doses of vaccine may not prevent severe COVID-19 illness in everyone, even when the circulating viral variant is presumed to be causing only mild disease in most people. Moreover, the people who are most at risk are not whom we might think they are. They are not the sickest of the sick. They include people who might not have major conditions such as heart disease or kidney disease, but they do have hypertension.”
Second, “we need more research to understand out why there is this link between hypertension and excess risk for the more severe forms of COVID-19, despite it arising from a supposedly milder variant,” said Dr. Ebinger.
“Third, we need to determine how to reduce these risks, whether through more tailored vaccine regimens or novel therapeutics or a combination approach,” he said.
Looking ahead, “the biological mechanism underpinning the association between hypertension and severe COVID-19 remains underexplored. Future work should focus on understanding the factors linking hypertension to severe COVID-19, as this may elucidate both information on how SARS-CoV-2 effects the body and potential targets for intervention,” Dr. Ebinger added.
The study was supported in part by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the Erika J. Glazer Family Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with hypertension who were vaccinated for COVID-19 with at least one booster were more than twice as likely as vaccinated and boosted individuals without hypertension to be hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to data from more than 900 individuals.
“We were surprised to learn that many people who were hospitalized with COVID-19 had hypertension and no other risk factors,” said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Research on Healthy Aging in the department of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles, and a senior author of the study. “This is concerning when you consider that almost half of American adults have high blood pressure.”
COVID-19 vaccines demonstrated ability to reduce death and some of the most severe side effects from the infection in the early stages of the pandemic. Although the Omicron surge prompted recommendations for a third mRNA vaccine dose, “a proportion of individuals who received three mRNA vaccine doses still required hospitalization for COVID-19 during the Omicron surge,” and the characteristics associated with severe illness in vaccinated and boosted patients have not been explored, Joseph Ebinger, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote.
Previous research has shown an association between high blood pressure an increased risk for developing severe COVID-19 compared to several other chronic health conditions, including kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and heart failure, the researchers noted.
In a study published in Hypertension, the researchers identified 912 adults who received at least three doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and were later diagnosed with COVID-19 during the surge in infections from the Omicron variant between December 2021 and April 2022.
A total of 145 of the individuals were hospitalized (16%); of these, 125 (86%) had hypertension.
Patients with hypertension were the most likely to be hospitalized, with an odds ratio of 2.9. In addition to high blood pressure, factors including older age (OR, 1.3), chronic kidney disease (OR, 2.2), prior myocardial infarction or heart failure (OR, 2.2), and longer time since the last vaccination and COVID-19 infection were associated with increased risk of hospitalization in a multivariate analysis.
However, the increased risk of severe illness and hospitalization associated with high blood pressure persisted, with an OR of 2.6, in the absence of comorbid conditions such as type 2 diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, the researchers emphasized.
“Although the mechanism for hypertension-associated COVID-19 risk remains unclear, prior studies have identified delayed SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and prolonged inflammatory response among hypertensive patients, which may contribute to greater disease severity,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of data from a single center and lack of information on which Omicron variants and subvariants were behind the infections, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more research on how to reduce the risks of severe COVID-19 in vulnerable populations, and on the mechanism for a potential connection between high blood pressure and severe COVID-19, they said.
Given the high prevalence of hypertension worldwide, increased understanding of the hypertension-specific risks and identification of individual and population-level risk reduction strategies will be important to the transition of COVID-19 from pandemic to endemic, they concluded.
Omicron changes the game
“When the pandemic initially started, many conditions were seen to increase risk for more severe COVID illness, and hypertension was one of those factors – and then things changed,” lead author Dr. Ebinger said in an interview. “First, vaccines arrived on the scene and substantially reduced risk of severe COVID for everyone who received them. Second, Omicron arrived and, while more transmissible, this variant has been less likely to cause severe COVID. On the one hand, we have vaccines and boosters that we want to think of as ‘the great equalizer’ when it comes to preexisting conditions. On the other hand, we have a dominant set of SARS-CoV-2 subvariants that seem less virulent in most people.
“Taken together, we have been hoping and even assuming that we have been doing pretty well with minimizing risks. Unfortunately, our study results indicate this is not exactly the case,” he said.
“Although vaccines and boosters appear to have equalized or minimized the risks of severe COVID for some people, this has not happened for others – even in the setting of the milder Omicron variant. Of individuals who were fully vaccinated and boosted, having hypertension increased the odds of needing to be hospitalized after getting infected with Omicron by 2.6-fold, even when accounting for or in the absence of having any major chronic disease that might otherwise predispose to more severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Ebinger added.
“So, while the originally seen risks of having obesity or diabetes seem to have been minimized during this current era of pandemic, the risk of having hypertension has persisted. We found this both surprising and concerning, because hypertension is very common and present in over half of people over age 50.”
Surprisingly, “we found that a fair number of people, even after being fully vaccinated plus a having gotten a booster, will not only catch Omicron but get sick enough to need hospital care,” Dr. Ebinger emphasized. “Moreover, it is not just older adults with major comorbid conditions who are vulnerable. Our data show that this can happen to an adult of any age and especially if a person has only hypertension and otherwise no major chronic disease.”
The first takeaway message for clinicians at this time is to raise awareness, Dr. Ebinger stressed in the interview. “We need to raise understanding around the fact that receiving three doses of vaccine may not prevent severe COVID-19 illness in everyone, even when the circulating viral variant is presumed to be causing only mild disease in most people. Moreover, the people who are most at risk are not whom we might think they are. They are not the sickest of the sick. They include people who might not have major conditions such as heart disease or kidney disease, but they do have hypertension.”
Second, “we need more research to understand out why there is this link between hypertension and excess risk for the more severe forms of COVID-19, despite it arising from a supposedly milder variant,” said Dr. Ebinger.
“Third, we need to determine how to reduce these risks, whether through more tailored vaccine regimens or novel therapeutics or a combination approach,” he said.
Looking ahead, “the biological mechanism underpinning the association between hypertension and severe COVID-19 remains underexplored. Future work should focus on understanding the factors linking hypertension to severe COVID-19, as this may elucidate both information on how SARS-CoV-2 effects the body and potential targets for intervention,” Dr. Ebinger added.
The study was supported in part by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the Erika J. Glazer Family Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM HYPERTENSION