User login
Unleashing Our Immune Response to Quash Cancer
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The new obesity breakthrough drugs
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.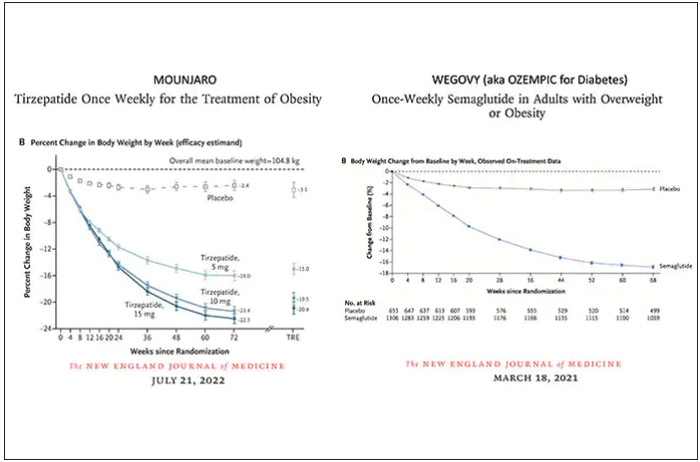
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction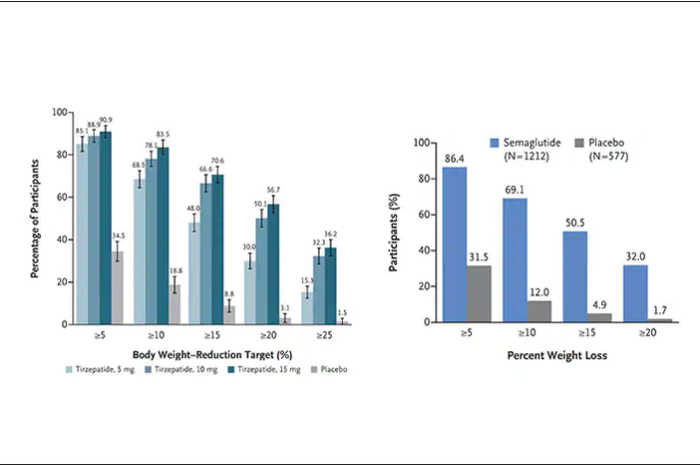
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.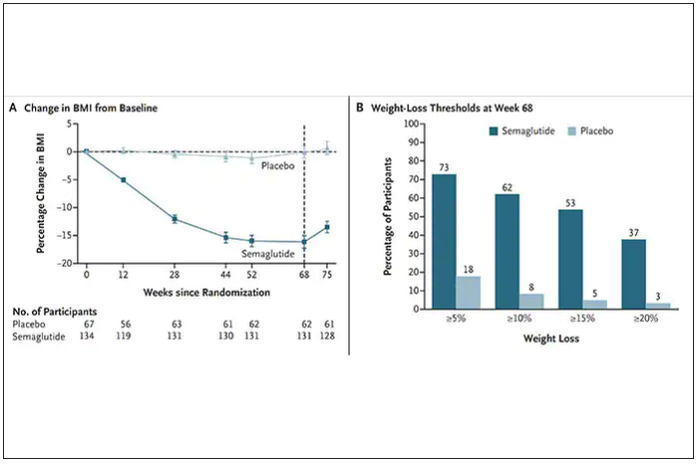
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.
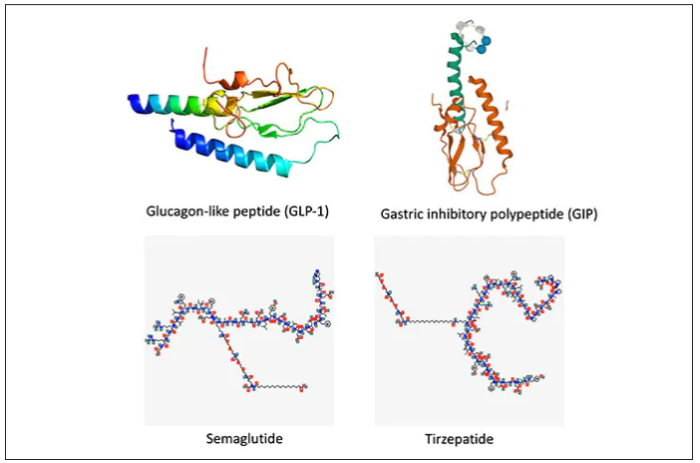
These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.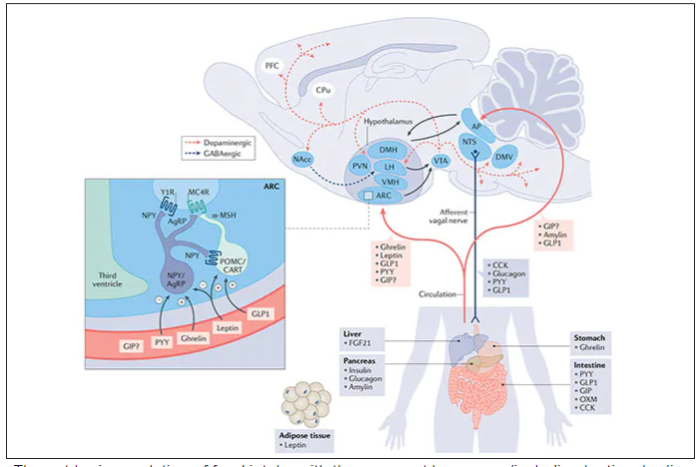
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.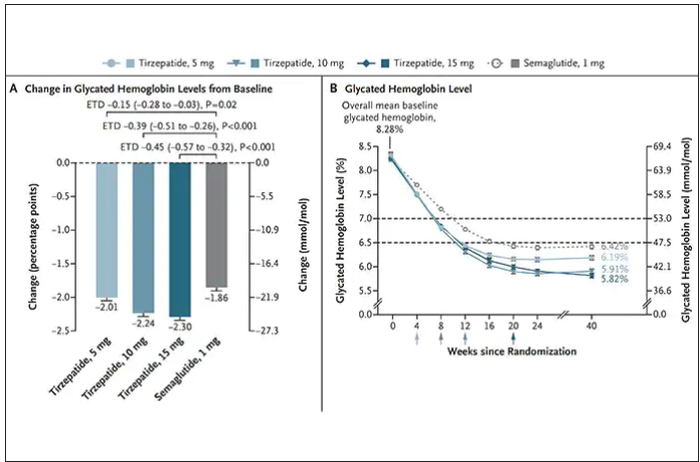
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.
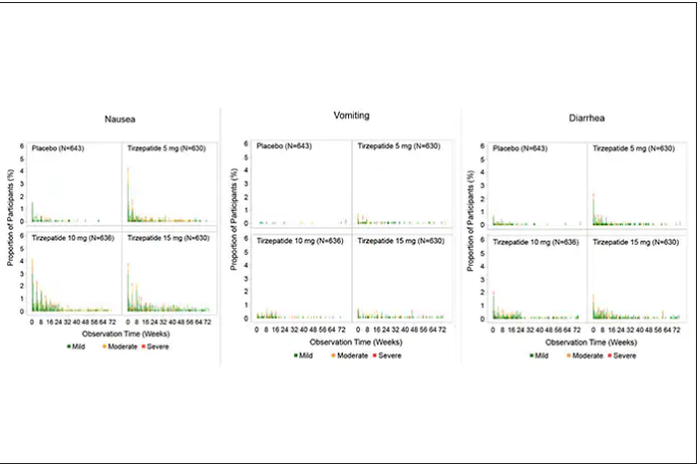
Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.

These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.

Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.

These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.

Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The body of evidence for Paxlovid therapy
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.