User login
U.S. reports first death from COVID-19, possible outbreak at long-term care facility
The first death in the United States from the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was a Washington state man in his 50s who had underlying health conditions, state health officials announced on Feb 29. At the same time, officials there are investigating a possible COVID-19 outbreak at a long-term care facility.
Washington state officials reported two other presumptive positive cases of COVID-19, both of whom are associated with LifeCare of Kirkland, Washington. One is a woman in her 70s who is a resident at the facility and the other is a woman in her 40s who is a health care worker at the facility.
Additionally, many residents and staff members at the facility have reported respiratory symptoms, according to Jeff Duchin, MD, health officer for public health in Seattle and King County. Among the more than 100 residents at the facility, 27 have respiratory symptoms; while among the 180 staff members, 25 have reported symptoms.
Overall, these reports bring the total number of U.S. COVID-19 cases detected by the public health system to 22, though that number is expected to climb as these investigations continue.
The general risk to the American public is still low, including residents in long-term care facilities, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during the Feb. 29 press briefing. Older people are are higher risk, however, and long-term care facilities should emphasize handwashing and the early identification of individuals with symptoms.
Dr. Duchin added that health care workers who are sick should stay home and that visitors should be screened for symptoms, the same advice offered to limit the spread of influenza at long-term care facilities.
The CDC briefing comes after President Trump held his own press conference at the White House where he identified the person who had died as being a woman in her 50s who was medically at risk.
During that press conference, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said that the current pattern of disease with COVID-19 suggests that 75%-80% of patients will have mild illness and recover, while 15%-20% will require advanced medical care.
For the most part, the more serious cases will occur in those who are elderly or have underlying medical conditions. There is “no indication” that individuals who recover from the virus are becoming re-infected, Dr. Fauci said.
The administration also announced a series of actions aimed at slowing the spread of the virus and responding to it. On March 2, President Trump will meet with leaders in the pharmaceutical industry at the White House to discuss vaccine development. The administration is also working to ensure an adequate supply of face masks. Vice President Mike Pence said there are currently more than 40 million masks available, but that the administration has received promises of 35 million more masks per month from manufacturers. Access to masks will be prioritized for high-risk health care workers, Vice President Pence said. “The average American does not need to go out and buy a mask,” he added.
Additionally, Vice President Pence announced new travel restrictions with Iran that would bar entry to the United States for any foreign national who visited Iran in the last 14 days. The federal government is also advising Americans not to travel to the regions in Italy and South Korea that have been most affected by COVID-19. The government is also working with officials in Italy and South Korea to conduct medical screening of anyone coming into the United States from those countries.
The first death in the United States from the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was a Washington state man in his 50s who had underlying health conditions, state health officials announced on Feb 29. At the same time, officials there are investigating a possible COVID-19 outbreak at a long-term care facility.
Washington state officials reported two other presumptive positive cases of COVID-19, both of whom are associated with LifeCare of Kirkland, Washington. One is a woman in her 70s who is a resident at the facility and the other is a woman in her 40s who is a health care worker at the facility.
Additionally, many residents and staff members at the facility have reported respiratory symptoms, according to Jeff Duchin, MD, health officer for public health in Seattle and King County. Among the more than 100 residents at the facility, 27 have respiratory symptoms; while among the 180 staff members, 25 have reported symptoms.
Overall, these reports bring the total number of U.S. COVID-19 cases detected by the public health system to 22, though that number is expected to climb as these investigations continue.
The general risk to the American public is still low, including residents in long-term care facilities, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during the Feb. 29 press briefing. Older people are are higher risk, however, and long-term care facilities should emphasize handwashing and the early identification of individuals with symptoms.
Dr. Duchin added that health care workers who are sick should stay home and that visitors should be screened for symptoms, the same advice offered to limit the spread of influenza at long-term care facilities.
The CDC briefing comes after President Trump held his own press conference at the White House where he identified the person who had died as being a woman in her 50s who was medically at risk.
During that press conference, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said that the current pattern of disease with COVID-19 suggests that 75%-80% of patients will have mild illness and recover, while 15%-20% will require advanced medical care.
For the most part, the more serious cases will occur in those who are elderly or have underlying medical conditions. There is “no indication” that individuals who recover from the virus are becoming re-infected, Dr. Fauci said.
The administration also announced a series of actions aimed at slowing the spread of the virus and responding to it. On March 2, President Trump will meet with leaders in the pharmaceutical industry at the White House to discuss vaccine development. The administration is also working to ensure an adequate supply of face masks. Vice President Mike Pence said there are currently more than 40 million masks available, but that the administration has received promises of 35 million more masks per month from manufacturers. Access to masks will be prioritized for high-risk health care workers, Vice President Pence said. “The average American does not need to go out and buy a mask,” he added.
Additionally, Vice President Pence announced new travel restrictions with Iran that would bar entry to the United States for any foreign national who visited Iran in the last 14 days. The federal government is also advising Americans not to travel to the regions in Italy and South Korea that have been most affected by COVID-19. The government is also working with officials in Italy and South Korea to conduct medical screening of anyone coming into the United States from those countries.
The first death in the United States from the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was a Washington state man in his 50s who had underlying health conditions, state health officials announced on Feb 29. At the same time, officials there are investigating a possible COVID-19 outbreak at a long-term care facility.
Washington state officials reported two other presumptive positive cases of COVID-19, both of whom are associated with LifeCare of Kirkland, Washington. One is a woman in her 70s who is a resident at the facility and the other is a woman in her 40s who is a health care worker at the facility.
Additionally, many residents and staff members at the facility have reported respiratory symptoms, according to Jeff Duchin, MD, health officer for public health in Seattle and King County. Among the more than 100 residents at the facility, 27 have respiratory symptoms; while among the 180 staff members, 25 have reported symptoms.
Overall, these reports bring the total number of U.S. COVID-19 cases detected by the public health system to 22, though that number is expected to climb as these investigations continue.
The general risk to the American public is still low, including residents in long-term care facilities, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during the Feb. 29 press briefing. Older people are are higher risk, however, and long-term care facilities should emphasize handwashing and the early identification of individuals with symptoms.
Dr. Duchin added that health care workers who are sick should stay home and that visitors should be screened for symptoms, the same advice offered to limit the spread of influenza at long-term care facilities.
The CDC briefing comes after President Trump held his own press conference at the White House where he identified the person who had died as being a woman in her 50s who was medically at risk.
During that press conference, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said that the current pattern of disease with COVID-19 suggests that 75%-80% of patients will have mild illness and recover, while 15%-20% will require advanced medical care.
For the most part, the more serious cases will occur in those who are elderly or have underlying medical conditions. There is “no indication” that individuals who recover from the virus are becoming re-infected, Dr. Fauci said.
The administration also announced a series of actions aimed at slowing the spread of the virus and responding to it. On March 2, President Trump will meet with leaders in the pharmaceutical industry at the White House to discuss vaccine development. The administration is also working to ensure an adequate supply of face masks. Vice President Mike Pence said there are currently more than 40 million masks available, but that the administration has received promises of 35 million more masks per month from manufacturers. Access to masks will be prioritized for high-risk health care workers, Vice President Pence said. “The average American does not need to go out and buy a mask,” he added.
Additionally, Vice President Pence announced new travel restrictions with Iran that would bar entry to the United States for any foreign national who visited Iran in the last 14 days. The federal government is also advising Americans not to travel to the regions in Italy and South Korea that have been most affected by COVID-19. The government is also working with officials in Italy and South Korea to conduct medical screening of anyone coming into the United States from those countries.
Experts break down latest CAR T-cell advances in lymphoma
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019
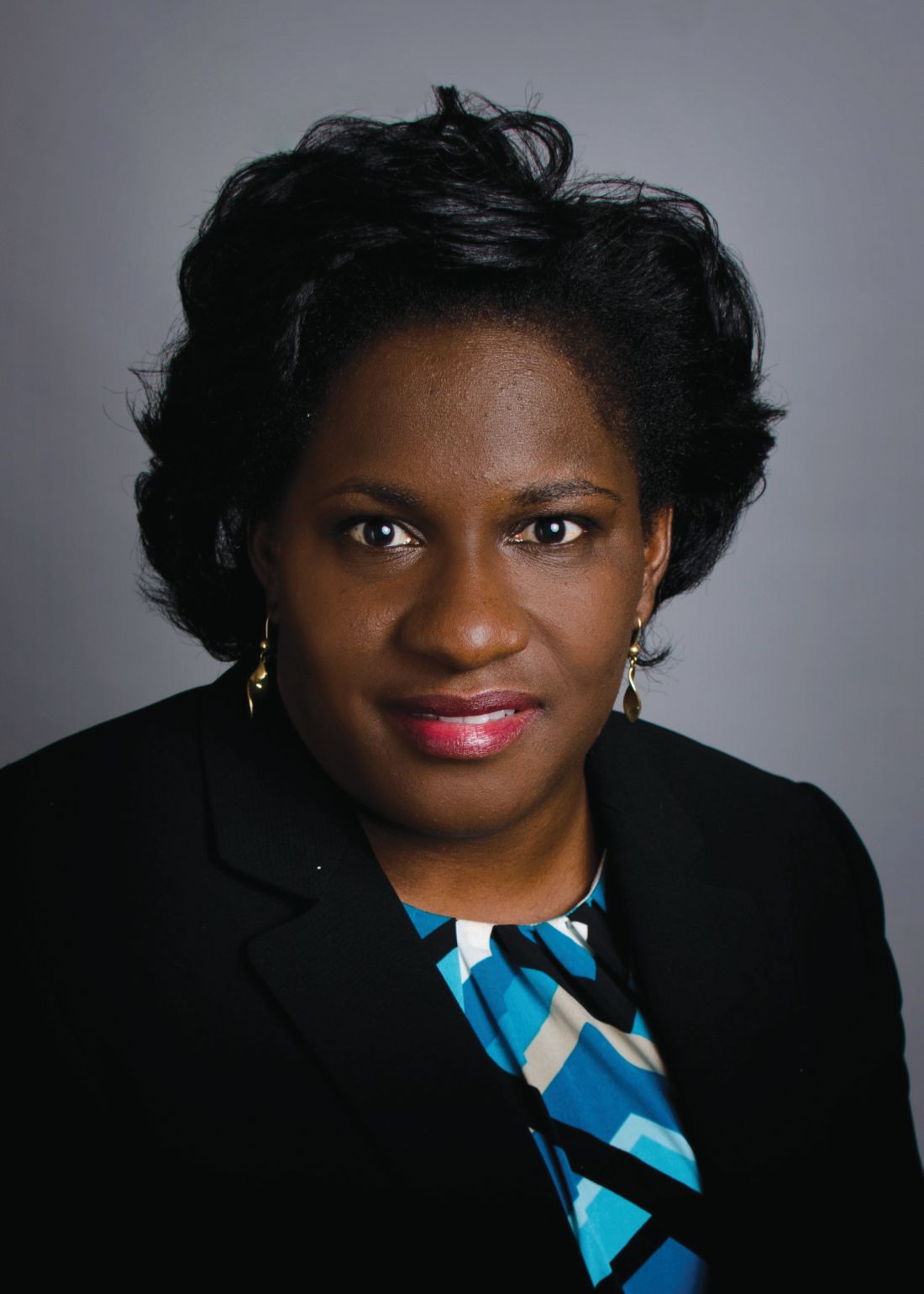
Hematology News welcomes Dr. Ify Osunkwo as editor in chief
Hematology News welcomes Ifeyinwa (Ify) Osunkwo, MD, MPH, as the new editor in chief.
Dr. Osunkwo is a professor of medicine at Atrium Health and the director of the Sickle Cell Enterprise at the Levine Cancer Institute, part of Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
She has made it her personal mission to improve the quality of life for patients with sickle cell disease, a passion that began during time spent in Nigeria as a child, where 150,000 children are born each year with the condition. In 2014, Dr. Osunkwo created a comprehensive sickle cell center in Charlotte with a multidisciplinary team of providers that includes physicians, nurses, social workers, psychologists, and nurse managers. She has also been an instrumental part of the Carolinas Sickle Cell Collaborative, which seeks to match sickle cell patients in the community with blood donors who have similar blood characteristics.
“As a practicing hematologist and researcher, I have a deep appreciation for the timely and relevant content provided by Hematology News,” Dr. Osunkwo said. “I hope to use my experience to help make this publication even better.”
She is a member of the National Adult Sickle Cell Provider Network and leads the Transition/Medical Home Committee for the Southeast Regional Genetics Network. Her interests include health literacy, adolescent transition of care, and chronic pain management.
Dr. Osunkwo graduated from medical school at the University of Nigeria, Enugu, performed her residency at the New Jersey Medical School, Newark, and completed her fellowship training at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. Osunkwo takes the reigns at Hematology News from Matt Kalaycio, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center. Dr. Kalaycio was the first editor in chief of Hematology News and held the post for 3 years.
Hematology News welcomes Ifeyinwa (Ify) Osunkwo, MD, MPH, as the new editor in chief.
Dr. Osunkwo is a professor of medicine at Atrium Health and the director of the Sickle Cell Enterprise at the Levine Cancer Institute, part of Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
She has made it her personal mission to improve the quality of life for patients with sickle cell disease, a passion that began during time spent in Nigeria as a child, where 150,000 children are born each year with the condition. In 2014, Dr. Osunkwo created a comprehensive sickle cell center in Charlotte with a multidisciplinary team of providers that includes physicians, nurses, social workers, psychologists, and nurse managers. She has also been an instrumental part of the Carolinas Sickle Cell Collaborative, which seeks to match sickle cell patients in the community with blood donors who have similar blood characteristics.
“As a practicing hematologist and researcher, I have a deep appreciation for the timely and relevant content provided by Hematology News,” Dr. Osunkwo said. “I hope to use my experience to help make this publication even better.”
She is a member of the National Adult Sickle Cell Provider Network and leads the Transition/Medical Home Committee for the Southeast Regional Genetics Network. Her interests include health literacy, adolescent transition of care, and chronic pain management.
Dr. Osunkwo graduated from medical school at the University of Nigeria, Enugu, performed her residency at the New Jersey Medical School, Newark, and completed her fellowship training at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. Osunkwo takes the reigns at Hematology News from Matt Kalaycio, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center. Dr. Kalaycio was the first editor in chief of Hematology News and held the post for 3 years.
Hematology News welcomes Ifeyinwa (Ify) Osunkwo, MD, MPH, as the new editor in chief.
Dr. Osunkwo is a professor of medicine at Atrium Health and the director of the Sickle Cell Enterprise at the Levine Cancer Institute, part of Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
She has made it her personal mission to improve the quality of life for patients with sickle cell disease, a passion that began during time spent in Nigeria as a child, where 150,000 children are born each year with the condition. In 2014, Dr. Osunkwo created a comprehensive sickle cell center in Charlotte with a multidisciplinary team of providers that includes physicians, nurses, social workers, psychologists, and nurse managers. She has also been an instrumental part of the Carolinas Sickle Cell Collaborative, which seeks to match sickle cell patients in the community with blood donors who have similar blood characteristics.
“As a practicing hematologist and researcher, I have a deep appreciation for the timely and relevant content provided by Hematology News,” Dr. Osunkwo said. “I hope to use my experience to help make this publication even better.”
She is a member of the National Adult Sickle Cell Provider Network and leads the Transition/Medical Home Committee for the Southeast Regional Genetics Network. Her interests include health literacy, adolescent transition of care, and chronic pain management.
Dr. Osunkwo graduated from medical school at the University of Nigeria, Enugu, performed her residency at the New Jersey Medical School, Newark, and completed her fellowship training at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. Osunkwo takes the reigns at Hematology News from Matt Kalaycio, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center. Dr. Kalaycio was the first editor in chief of Hematology News and held the post for 3 years.
Think twice: Choosing Wisely recommendations on testing to avoid in pediatric hematology
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
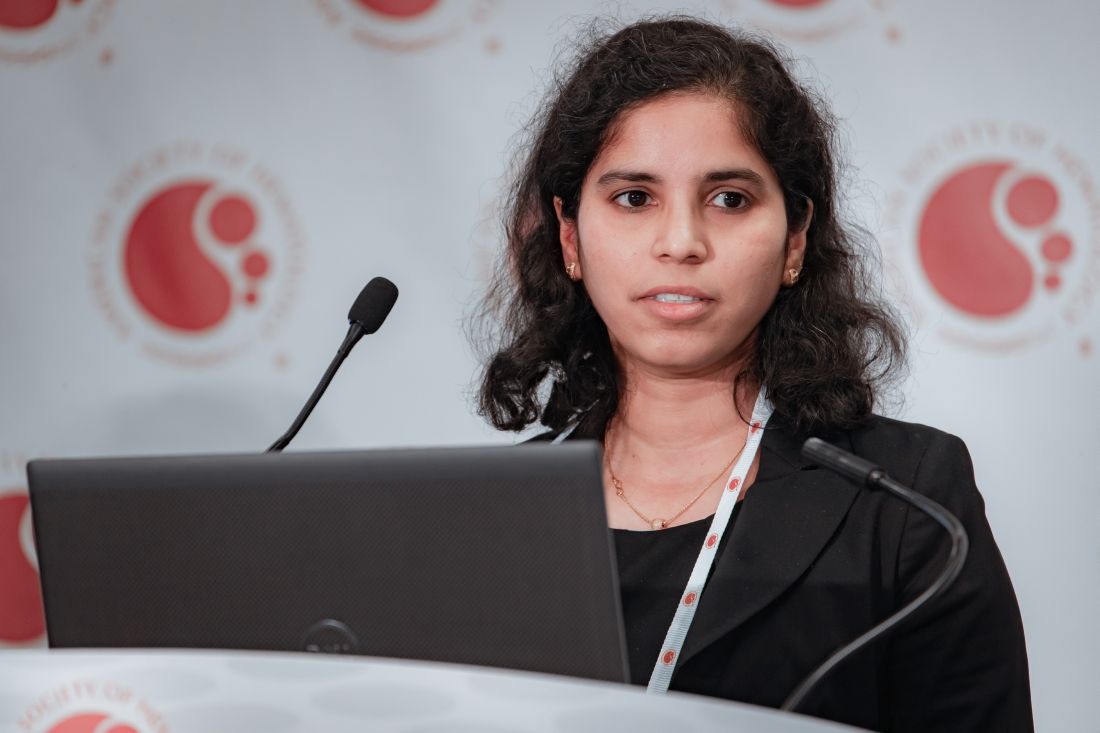
Myeloma patients over age 70 can benefit from auto-HC transplant
ORLANDO – Age 70 may be the new 60, at least when it comes to outcomes following autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (auto-HCT) in multiple myeloma.
A large-scale study looking at transplant outcomes across age groups in multiple myeloma patients found similar rates of nonrelapse mortality, relapse/progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival between patients who were aged 70 years and older and those who were aged 60-69 years.
“Age has no implication in terms of the antimyeloma effect of transplant,” Anita D’Souza, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The study analyzed outcomes from 15,999 multiple myeloma patients aged 20 years or older in the United States who received a single auto-HCT with melphalan conditioning within 12 months of diagnosis between 2013 and 2017. Within that dataset, the researchers compared outcomes from 7,032 patients aged 60-69 years and 2,092 patients aged 70 years and older.
This is the largest study of auto-HCT in older adults with multiple myeloma, the researchers said, and provides important data about the benefit of transplant at any age.
Univariate analysis showed that 100-day nonrelapse mortality was higher in patients aged 70 years and older – at 1% – compared with younger patients (P less than .01). Also, 2-year overall survival was lower in older adults – at 86% – compared with 60- to 69-year-olds (P less than .01).
However, on multivariate analysis with 60- to 69-year-olds as the reference group, patients older than age 70 years had similar nonrelapse mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 1.3, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1, 1.7, P = .06). The same trends were seen for relapse/progression (HR 1.0, 95% CI, 0.9-1, P = .6), progression-free survival (HR 1.1, 95% CI 1-1.2, P = .2), and overall survival (HR 1.2, 95% CI 1-1.4, P = .03). Given the large sample size, a P value of .01 was considered statistically significant.
Over the course of the study period, the percentage of patients aged 70 and older who received a transplant grew each year, rising to 28% by 2017. But Dr. D’Souza said that number is still too low given the safety and efficacy of auto-HCT in these patients.
“Every patient with myeloma should be referred to a transplant center,” she said.
Dr. D’Souza reported financial disclosures related to EDO-Mundapharma, Merck, Prothena, Sanofi, TeneoBio, Prothena, Pfizer, Imbrium, and Akcea. Other study authors reported financial relationships with multiple companies including Celgene, Takeda, BMS, and Janssen.
SOURCE: Munshi PN et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 782.
ORLANDO – Age 70 may be the new 60, at least when it comes to outcomes following autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (auto-HCT) in multiple myeloma.
A large-scale study looking at transplant outcomes across age groups in multiple myeloma patients found similar rates of nonrelapse mortality, relapse/progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival between patients who were aged 70 years and older and those who were aged 60-69 years.
“Age has no implication in terms of the antimyeloma effect of transplant,” Anita D’Souza, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The study analyzed outcomes from 15,999 multiple myeloma patients aged 20 years or older in the United States who received a single auto-HCT with melphalan conditioning within 12 months of diagnosis between 2013 and 2017. Within that dataset, the researchers compared outcomes from 7,032 patients aged 60-69 years and 2,092 patients aged 70 years and older.
This is the largest study of auto-HCT in older adults with multiple myeloma, the researchers said, and provides important data about the benefit of transplant at any age.
Univariate analysis showed that 100-day nonrelapse mortality was higher in patients aged 70 years and older – at 1% – compared with younger patients (P less than .01). Also, 2-year overall survival was lower in older adults – at 86% – compared with 60- to 69-year-olds (P less than .01).
However, on multivariate analysis with 60- to 69-year-olds as the reference group, patients older than age 70 years had similar nonrelapse mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 1.3, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1, 1.7, P = .06). The same trends were seen for relapse/progression (HR 1.0, 95% CI, 0.9-1, P = .6), progression-free survival (HR 1.1, 95% CI 1-1.2, P = .2), and overall survival (HR 1.2, 95% CI 1-1.4, P = .03). Given the large sample size, a P value of .01 was considered statistically significant.
Over the course of the study period, the percentage of patients aged 70 and older who received a transplant grew each year, rising to 28% by 2017. But Dr. D’Souza said that number is still too low given the safety and efficacy of auto-HCT in these patients.
“Every patient with myeloma should be referred to a transplant center,” she said.
Dr. D’Souza reported financial disclosures related to EDO-Mundapharma, Merck, Prothena, Sanofi, TeneoBio, Prothena, Pfizer, Imbrium, and Akcea. Other study authors reported financial relationships with multiple companies including Celgene, Takeda, BMS, and Janssen.
SOURCE: Munshi PN et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 782.
ORLANDO – Age 70 may be the new 60, at least when it comes to outcomes following autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (auto-HCT) in multiple myeloma.
A large-scale study looking at transplant outcomes across age groups in multiple myeloma patients found similar rates of nonrelapse mortality, relapse/progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival between patients who were aged 70 years and older and those who were aged 60-69 years.
“Age has no implication in terms of the antimyeloma effect of transplant,” Anita D’Souza, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The study analyzed outcomes from 15,999 multiple myeloma patients aged 20 years or older in the United States who received a single auto-HCT with melphalan conditioning within 12 months of diagnosis between 2013 and 2017. Within that dataset, the researchers compared outcomes from 7,032 patients aged 60-69 years and 2,092 patients aged 70 years and older.
This is the largest study of auto-HCT in older adults with multiple myeloma, the researchers said, and provides important data about the benefit of transplant at any age.
Univariate analysis showed that 100-day nonrelapse mortality was higher in patients aged 70 years and older – at 1% – compared with younger patients (P less than .01). Also, 2-year overall survival was lower in older adults – at 86% – compared with 60- to 69-year-olds (P less than .01).
However, on multivariate analysis with 60- to 69-year-olds as the reference group, patients older than age 70 years had similar nonrelapse mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 1.3, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1, 1.7, P = .06). The same trends were seen for relapse/progression (HR 1.0, 95% CI, 0.9-1, P = .6), progression-free survival (HR 1.1, 95% CI 1-1.2, P = .2), and overall survival (HR 1.2, 95% CI 1-1.4, P = .03). Given the large sample size, a P value of .01 was considered statistically significant.
Over the course of the study period, the percentage of patients aged 70 and older who received a transplant grew each year, rising to 28% by 2017. But Dr. D’Souza said that number is still too low given the safety and efficacy of auto-HCT in these patients.
“Every patient with myeloma should be referred to a transplant center,” she said.
Dr. D’Souza reported financial disclosures related to EDO-Mundapharma, Merck, Prothena, Sanofi, TeneoBio, Prothena, Pfizer, Imbrium, and Akcea. Other study authors reported financial relationships with multiple companies including Celgene, Takeda, BMS, and Janssen.
SOURCE: Munshi PN et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 782.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
FDA approves treatment for sickle cell pain crises
The Food and Drug Administration has approved crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo) to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crisis, a common complication of sickle cell disease.
The drug is approved for patients aged 16 years and older. It was approved on the strength of the SUSTAIN trial, which randomized 198 patients with sickle cell disease and a history of vaso-occlusive crisis to crizanlizumab or placebo. Patients who received crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for vaso-occlusive crises, compared with patients who received placebo and had a median annual rate of 2.98 visits. The drug also delayed the first vaso-occlusive crisis after starting treatment from 1.4 months to 4.1 months, according to the FDA.
“Adakveo is the first targeted therapy approved for sickle cell disease, specifically inhibiting selectin, a substance that contributes to cells sticking together and leads to vaso-occlusive crisis,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a statement. “Vaso-occlusive crisis can be extremely painful and is a frequent reason for emergency department visits and hospitalization for patients with sickle cell disease.”
Common adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. The FDA advised physicians to monitor patients for infusion-related reactions.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo) to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crisis, a common complication of sickle cell disease.
The drug is approved for patients aged 16 years and older. It was approved on the strength of the SUSTAIN trial, which randomized 198 patients with sickle cell disease and a history of vaso-occlusive crisis to crizanlizumab or placebo. Patients who received crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for vaso-occlusive crises, compared with patients who received placebo and had a median annual rate of 2.98 visits. The drug also delayed the first vaso-occlusive crisis after starting treatment from 1.4 months to 4.1 months, according to the FDA.
“Adakveo is the first targeted therapy approved for sickle cell disease, specifically inhibiting selectin, a substance that contributes to cells sticking together and leads to vaso-occlusive crisis,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a statement. “Vaso-occlusive crisis can be extremely painful and is a frequent reason for emergency department visits and hospitalization for patients with sickle cell disease.”
Common adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. The FDA advised physicians to monitor patients for infusion-related reactions.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo) to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crisis, a common complication of sickle cell disease.
The drug is approved for patients aged 16 years and older. It was approved on the strength of the SUSTAIN trial, which randomized 198 patients with sickle cell disease and a history of vaso-occlusive crisis to crizanlizumab or placebo. Patients who received crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for vaso-occlusive crises, compared with patients who received placebo and had a median annual rate of 2.98 visits. The drug also delayed the first vaso-occlusive crisis after starting treatment from 1.4 months to 4.1 months, according to the FDA.
“Adakveo is the first targeted therapy approved for sickle cell disease, specifically inhibiting selectin, a substance that contributes to cells sticking together and leads to vaso-occlusive crisis,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a statement. “Vaso-occlusive crisis can be extremely painful and is a frequent reason for emergency department visits and hospitalization for patients with sickle cell disease.”
Common adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. The FDA advised physicians to monitor patients for infusion-related reactions.
FDA approves anemia treatment for transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia patients
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
ASCO to award $50,000 young investigator grant to study MCL
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Hematopoietic cell transplant offers realistic cure in secondary AML
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
FROM BIOLOGY OF BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
FDA gives nod to earlier use of Nplate in adults with ITP
Romiplostim (Nplate) earned a new indication from the Food and Drug Administration, allowing for earlier usage in adult patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
The new indication is for newly diagnosed and persistent adult patients.
Romiplostim is already approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 year and older who have had ITP for at least 6 months and had an insufficient response to other treatments, as well as for adults patients with chronic ITP who had insufficient response to other therapies.
The latest approval is based on positive results from a single-arm, phase 2 trial in adults with ITP who had an insufficient response to first-line treatment. The study met its primary endpoint – platelet response (50 x 109/L or greater). The median number of months with platelet response was 11 months during a 12-month treatment period. The median time to first platelet response was just over 2 weeks.
Adverse events of at least 5% incidence in patients taking romiplostim with an ITP duration up to 12 months included bronchitis, sinusitis, vomiting, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, dizziness, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, cough, nausea, and oropharyngeal pain. There was a 2% incidence of thrombocytosis among adults with an ITP duration up to 12 months.
Romiplostim (Nplate) earned a new indication from the Food and Drug Administration, allowing for earlier usage in adult patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
The new indication is for newly diagnosed and persistent adult patients.
Romiplostim is already approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 year and older who have had ITP for at least 6 months and had an insufficient response to other treatments, as well as for adults patients with chronic ITP who had insufficient response to other therapies.
The latest approval is based on positive results from a single-arm, phase 2 trial in adults with ITP who had an insufficient response to first-line treatment. The study met its primary endpoint – platelet response (50 x 109/L or greater). The median number of months with platelet response was 11 months during a 12-month treatment period. The median time to first platelet response was just over 2 weeks.
Adverse events of at least 5% incidence in patients taking romiplostim with an ITP duration up to 12 months included bronchitis, sinusitis, vomiting, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, dizziness, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, cough, nausea, and oropharyngeal pain. There was a 2% incidence of thrombocytosis among adults with an ITP duration up to 12 months.
Romiplostim (Nplate) earned a new indication from the Food and Drug Administration, allowing for earlier usage in adult patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
The new indication is for newly diagnosed and persistent adult patients.
Romiplostim is already approved for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 year and older who have had ITP for at least 6 months and had an insufficient response to other treatments, as well as for adults patients with chronic ITP who had insufficient response to other therapies.
The latest approval is based on positive results from a single-arm, phase 2 trial in adults with ITP who had an insufficient response to first-line treatment. The study met its primary endpoint – platelet response (50 x 109/L or greater). The median number of months with platelet response was 11 months during a 12-month treatment period. The median time to first platelet response was just over 2 weeks.
Adverse events of at least 5% incidence in patients taking romiplostim with an ITP duration up to 12 months included bronchitis, sinusitis, vomiting, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, dizziness, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, cough, nausea, and oropharyngeal pain. There was a 2% incidence of thrombocytosis among adults with an ITP duration up to 12 months.