User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Energy-Restricted Diet Twice Weekly Tops Exercise in T2D
TOPLINE:
Two days a week of a medically supervised energy-restricted diet may lower blood glucose levels in adults with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Daily calorie restrictions and increased physical activity improve glycemic control and induce diabetes remission in patients with T2D, but these approaches are challenging to adhere to.
- Researchers tested whether 2 days a week (a 5:2 regimen) of either a very low-calorie formula diet or a “weekend warrior” physical activity pattern would be effective and more convenient.
- The three-arm IDEATE study enrolled 326 Asian participants with overweight or mild obesity (body mass index, 25.0-39.9) and T2D (diagnosed within prior 2 years; A1c, 7.0-8.9%; not on insulin) and randomly assigned them to receive a diet intervention, an exercise intervention, or routine lifestyle education (control group) for 12 weeks.
- The diet intervention group received an energy-restricted diet of 790 kcal/d on 2 days each week, and the exercise intervention group performed high-intensity interval training (4 minutes of aerobic activity, with a 10-minute total warm-up and cool-down) and resistance training twice a week (four exercises, two sets of eight to 12 repetitions).
- The primary outcome was the change in glycemic control between the diet or exercise intervention group and the control group after 12 weeks. Follow-up continued up to 1 year after intervention.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the control group, patients in the diet intervention group achieved greater reductions in A1c after 12 weeks (difference, -0.34; P =.007), whereas A1c reductions in the exercise intervention group did not differ significantly from the control group.
- The likelihood of achieving diabetes remission was higher in the diet intervention vs the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 3.60; P = .008) but not in the exercise intervention group (P =.52).
- Body weight, body mass index, and high-density lipoprtein cholesterol levels were more effectively controlled in the diet intervention group only.
- However, participants in both the diet and exercise intervention groups showed reduced adiposity, liver fat content, and diastolic blood pressure compared with those in the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The diet intervention group experienced a greater energy deficit with a more pronounced metabolic benefit,” the authors wrote. “Our study suggests that a medically supervised 5:2 energy-restricted diet could serve as an alternative strategy for improving glycemic control.”
SOURCE:
Mian Li, of the Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, led the study, which was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Body composition was analyzed using bioelectrical impedance analysis, which is a less accurate technique than dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. The study used finger-prick tests to monitor blood glucose levels, which could have underestimated both hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic episodes. No information was collected on whether the participants maintained the diet or exercise regimen during the postintervention follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Rising Star Program grant, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Two days a week of a medically supervised energy-restricted diet may lower blood glucose levels in adults with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Daily calorie restrictions and increased physical activity improve glycemic control and induce diabetes remission in patients with T2D, but these approaches are challenging to adhere to.
- Researchers tested whether 2 days a week (a 5:2 regimen) of either a very low-calorie formula diet or a “weekend warrior” physical activity pattern would be effective and more convenient.
- The three-arm IDEATE study enrolled 326 Asian participants with overweight or mild obesity (body mass index, 25.0-39.9) and T2D (diagnosed within prior 2 years; A1c, 7.0-8.9%; not on insulin) and randomly assigned them to receive a diet intervention, an exercise intervention, or routine lifestyle education (control group) for 12 weeks.
- The diet intervention group received an energy-restricted diet of 790 kcal/d on 2 days each week, and the exercise intervention group performed high-intensity interval training (4 minutes of aerobic activity, with a 10-minute total warm-up and cool-down) and resistance training twice a week (four exercises, two sets of eight to 12 repetitions).
- The primary outcome was the change in glycemic control between the diet or exercise intervention group and the control group after 12 weeks. Follow-up continued up to 1 year after intervention.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the control group, patients in the diet intervention group achieved greater reductions in A1c after 12 weeks (difference, -0.34; P =.007), whereas A1c reductions in the exercise intervention group did not differ significantly from the control group.
- The likelihood of achieving diabetes remission was higher in the diet intervention vs the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 3.60; P = .008) but not in the exercise intervention group (P =.52).
- Body weight, body mass index, and high-density lipoprtein cholesterol levels were more effectively controlled in the diet intervention group only.
- However, participants in both the diet and exercise intervention groups showed reduced adiposity, liver fat content, and diastolic blood pressure compared with those in the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The diet intervention group experienced a greater energy deficit with a more pronounced metabolic benefit,” the authors wrote. “Our study suggests that a medically supervised 5:2 energy-restricted diet could serve as an alternative strategy for improving glycemic control.”
SOURCE:
Mian Li, of the Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, led the study, which was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Body composition was analyzed using bioelectrical impedance analysis, which is a less accurate technique than dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. The study used finger-prick tests to monitor blood glucose levels, which could have underestimated both hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic episodes. No information was collected on whether the participants maintained the diet or exercise regimen during the postintervention follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Rising Star Program grant, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Two days a week of a medically supervised energy-restricted diet may lower blood glucose levels in adults with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Daily calorie restrictions and increased physical activity improve glycemic control and induce diabetes remission in patients with T2D, but these approaches are challenging to adhere to.
- Researchers tested whether 2 days a week (a 5:2 regimen) of either a very low-calorie formula diet or a “weekend warrior” physical activity pattern would be effective and more convenient.
- The three-arm IDEATE study enrolled 326 Asian participants with overweight or mild obesity (body mass index, 25.0-39.9) and T2D (diagnosed within prior 2 years; A1c, 7.0-8.9%; not on insulin) and randomly assigned them to receive a diet intervention, an exercise intervention, or routine lifestyle education (control group) for 12 weeks.
- The diet intervention group received an energy-restricted diet of 790 kcal/d on 2 days each week, and the exercise intervention group performed high-intensity interval training (4 minutes of aerobic activity, with a 10-minute total warm-up and cool-down) and resistance training twice a week (four exercises, two sets of eight to 12 repetitions).
- The primary outcome was the change in glycemic control between the diet or exercise intervention group and the control group after 12 weeks. Follow-up continued up to 1 year after intervention.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the control group, patients in the diet intervention group achieved greater reductions in A1c after 12 weeks (difference, -0.34; P =.007), whereas A1c reductions in the exercise intervention group did not differ significantly from the control group.
- The likelihood of achieving diabetes remission was higher in the diet intervention vs the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 3.60; P = .008) but not in the exercise intervention group (P =.52).
- Body weight, body mass index, and high-density lipoprtein cholesterol levels were more effectively controlled in the diet intervention group only.
- However, participants in both the diet and exercise intervention groups showed reduced adiposity, liver fat content, and diastolic blood pressure compared with those in the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The diet intervention group experienced a greater energy deficit with a more pronounced metabolic benefit,” the authors wrote. “Our study suggests that a medically supervised 5:2 energy-restricted diet could serve as an alternative strategy for improving glycemic control.”
SOURCE:
Mian Li, of the Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, led the study, which was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Body composition was analyzed using bioelectrical impedance analysis, which is a less accurate technique than dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. The study used finger-prick tests to monitor blood glucose levels, which could have underestimated both hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic episodes. No information was collected on whether the participants maintained the diet or exercise regimen during the postintervention follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Rising Star Program grant, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Managing Obesity Can Lead to Sarcopenia: A ‘Hidden’ Problem
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic Fat Is the Main Driver for Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreatic Diseases
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Plus HIV Ups Risk for CVD but Not Liver Disease
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Working Hard or Work Addiction — Have You Crossed the Line?
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Oregon Physician Assistants Get Name Change
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 4, Oregon’s Governor Tina Kotek signed a bill into law that officially changed the title of “physician assistants” to “physician associates” in the state.
In the Medscape Physician Assistant Career Satisfaction Report 2023, a diverse range of opinions on the title switch was reflected. Only 40% of PAs favored the name change at the time, 45% neither opposed nor favored it, and 15% opposed the name change, reflecting the complexity of the issue.
According to the AAPA, the change came about to better reflect the work PAs do in not just “assisting” physicians but in working independently with patients. Some also felt that the word “assistant” implies dependence. However, despite associate’s more accurate reflection of the job, PAs mostly remain split on whether they want the new moniker.
Many say that the name change will be confusing for the public and their patients, while others say that physician assistant was already not well understood, as patients often thought of the profession as a doctor’s helper or an assistant, like a medical assistant.
Yet many long-time PAs say that they prefer the title they’ve always had and that explaining to patients the new associate title will be equally confusing. Some mentioned patients may think they’re a business associate of the physician.
Oregon PAs won’t immediately switch to the new name. The new law takes effect on June 6, 2024. The Oregon Medical Board will establish regulations and guidance before PAs adopt the new name in their practices.
The law only changes the name of PAs in Oregon, not in other states. In fact, prematurely using the title of physician associate could subject a PA to regulatory challenges or disciplinary actions.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Evening May Be the Best Time for Exercise
TOPLINE:
Moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity performed in the evening is associated with the lowest risk for mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and microvascular disease (MVD) in adults with obesity, including those with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Bouts of moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity are widely recognized to improve cardiometabolic risk factors, but whether morning, afternoon, or evening timing may lead to greater improvements is unclear.
- Researchers analyzed UK Biobank data of 29,836 participants with obesity (body mass index, › 30; mean age, 62.2 years; 53.2% women), including 2995 also diagnosed with T2D, all enrolled in 2006-2010.
- Aerobic activity was defined as bouts lasting ≥ 3 minutes, and the intensity of activity was classified as light, moderate, or vigorous using accelerometer data collected from participants.
- Participants were stratified into the morning (6 a.m. to < 12 p.m.), afternoon (12 p.m. to < 6 p.m.), and evening (6 p.m. to < 12 a.m.) groups based on when > 50% of their total moderate to vigorous activity occurred, and those with no aerobic bouts were considered the reference group.
- The association between the timing of aerobic physical activity and risk for all-cause mortality, CVD (defined as circulatory, such as hypertension), and MVD (neuropathy, nephropathy, or retinopathy) was evaluated over a median follow-up of 7.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Mortality risk was lower in the afternoon (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.51-0.71) and morning (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.56-0.79) activity groups than in the reference group, but this association was weaker than that observed in the evening activity group.
- The evening moderate to vigorous activity group had a lower risk for CVD (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.75) and MVD (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.63-0.92) than the reference group.
- Among participants with obesity and T2D, moderate to vigorous physical activity in the evening was associated with a lower risk for mortality, CVD, and MVD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “The results of this study emphasize that beyond the total volume of MVPA [moderate to vigorous physical activity], its timing, particularly in the evening, was consistently associated with the lowest risk of mortality relative to other timing windows.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Angelo Sabag, PhD, Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney, Australia, was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this was an observational study, the possibility of reverse causation from prodromal disease and unaccounted confounding factors could not have been ruled out. There was a lag of a median of 5.5 years between the UK Biobank baseline, when covariate measurements were taken, and the accelerometry study. Moreover, the response rate of the UK Biobank was low.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant and the National Heart Foundation of Australia Postdoctoral Fellowship. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity performed in the evening is associated with the lowest risk for mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and microvascular disease (MVD) in adults with obesity, including those with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Bouts of moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity are widely recognized to improve cardiometabolic risk factors, but whether morning, afternoon, or evening timing may lead to greater improvements is unclear.
- Researchers analyzed UK Biobank data of 29,836 participants with obesity (body mass index, › 30; mean age, 62.2 years; 53.2% women), including 2995 also diagnosed with T2D, all enrolled in 2006-2010.
- Aerobic activity was defined as bouts lasting ≥ 3 minutes, and the intensity of activity was classified as light, moderate, or vigorous using accelerometer data collected from participants.
- Participants were stratified into the morning (6 a.m. to < 12 p.m.), afternoon (12 p.m. to < 6 p.m.), and evening (6 p.m. to < 12 a.m.) groups based on when > 50% of their total moderate to vigorous activity occurred, and those with no aerobic bouts were considered the reference group.
- The association between the timing of aerobic physical activity and risk for all-cause mortality, CVD (defined as circulatory, such as hypertension), and MVD (neuropathy, nephropathy, or retinopathy) was evaluated over a median follow-up of 7.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Mortality risk was lower in the afternoon (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.51-0.71) and morning (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.56-0.79) activity groups than in the reference group, but this association was weaker than that observed in the evening activity group.
- The evening moderate to vigorous activity group had a lower risk for CVD (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.75) and MVD (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.63-0.92) than the reference group.
- Among participants with obesity and T2D, moderate to vigorous physical activity in the evening was associated with a lower risk for mortality, CVD, and MVD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “The results of this study emphasize that beyond the total volume of MVPA [moderate to vigorous physical activity], its timing, particularly in the evening, was consistently associated with the lowest risk of mortality relative to other timing windows.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Angelo Sabag, PhD, Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney, Australia, was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this was an observational study, the possibility of reverse causation from prodromal disease and unaccounted confounding factors could not have been ruled out. There was a lag of a median of 5.5 years between the UK Biobank baseline, when covariate measurements were taken, and the accelerometry study. Moreover, the response rate of the UK Biobank was low.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant and the National Heart Foundation of Australia Postdoctoral Fellowship. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity performed in the evening is associated with the lowest risk for mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and microvascular disease (MVD) in adults with obesity, including those with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Bouts of moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity are widely recognized to improve cardiometabolic risk factors, but whether morning, afternoon, or evening timing may lead to greater improvements is unclear.
- Researchers analyzed UK Biobank data of 29,836 participants with obesity (body mass index, › 30; mean age, 62.2 years; 53.2% women), including 2995 also diagnosed with T2D, all enrolled in 2006-2010.
- Aerobic activity was defined as bouts lasting ≥ 3 minutes, and the intensity of activity was classified as light, moderate, or vigorous using accelerometer data collected from participants.
- Participants were stratified into the morning (6 a.m. to < 12 p.m.), afternoon (12 p.m. to < 6 p.m.), and evening (6 p.m. to < 12 a.m.) groups based on when > 50% of their total moderate to vigorous activity occurred, and those with no aerobic bouts were considered the reference group.
- The association between the timing of aerobic physical activity and risk for all-cause mortality, CVD (defined as circulatory, such as hypertension), and MVD (neuropathy, nephropathy, or retinopathy) was evaluated over a median follow-up of 7.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Mortality risk was lower in the afternoon (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.51-0.71) and morning (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.56-0.79) activity groups than in the reference group, but this association was weaker than that observed in the evening activity group.
- The evening moderate to vigorous activity group had a lower risk for CVD (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.75) and MVD (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.63-0.92) than the reference group.
- Among participants with obesity and T2D, moderate to vigorous physical activity in the evening was associated with a lower risk for mortality, CVD, and MVD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “The results of this study emphasize that beyond the total volume of MVPA [moderate to vigorous physical activity], its timing, particularly in the evening, was consistently associated with the lowest risk of mortality relative to other timing windows.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Angelo Sabag, PhD, Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney, Australia, was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this was an observational study, the possibility of reverse causation from prodromal disease and unaccounted confounding factors could not have been ruled out. There was a lag of a median of 5.5 years between the UK Biobank baseline, when covariate measurements were taken, and the accelerometry study. Moreover, the response rate of the UK Biobank was low.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant and the National Heart Foundation of Australia Postdoctoral Fellowship. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How These Young MDs Impressed the Hell Out of Their Bosses
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Safe to say that anyone undertaking the physician journey does so with intense motivation and book smarts. Still, it can be incredibly hard to stand out. Everyone’s a go-getter, but what’s the X factor?
Here’s what they said ...
Lesson #1: Never Be Scared to Ask
Brien Barnewolt, MD, chairman and chief of the Department of Emergency Medicine at Tufts Medical Center, was very much surprised when a resident named Scott G. Weiner did something unexpected: Go after a job in the fall of his junior year residency instead of following the typical senior year trajectory.
“It’s very unusual for a trainee to apply for a job virtually a year ahead of schedule. But he knew what he wanted,” said Dr. Barnewolt. “I’d never had anybody come to me in that same scenario, and I’ve been doing this a long time.”
Under normal circumstances it would’ve been easy for Dr. Barnewolt to say no. But the unexpected request made him and his colleagues take a closer look, and they were impressed with Dr. Weiner’s skills. That, paired with his ambition and demeanor, compelled them to offer him an early job. But there’s more.
As the next year approached, Dr. Weiner explained he had an opportunity to work in emergency medicine in Tuscany and asked if he could take a 1-year delayed start for the position he applied a year early for.
The department held his position, and upon his return, Dr. Weiner made a lasting impact at Tufts before eventually moving on. “He outgrew us, which is nice to see,” Dr. Barnewolt said. (Dr. Weiner is currently McGraw Distinguished Chair in Emergency Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School.)
Bottom line: Why did Dr. Barnewolt and his colleagues do so much to accommodate a young candidate? Yes, Dr. Weiner was talented, but he was also up-front about his ambitions from the get-go. Dr. Barnewolt said that kind of initiative can only be looked at positively.
“My advice would be, if you see an opportunity or a potential place where you might want to work, put out those feelers, start those conversations,” he said. “It’s not too early, especially in certain specialties, where the job market is very tight. Then, when circumstances change, be open about it and have that conversation. The worst that somebody can say is no, so it never hurts to be honest and open about where you want to go and what you want to be.”
Lesson #2: Chase Your Passion ‘Relentlessly’
Vance G. Fowler, MD, MHS, an infectious disease specialist at Duke University School of Medicine, runs a laboratory that researches methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Over the years, he’s mentored many doctors but understands the ambitions of young trainees don’t always align with the little free time that they have. “Many of them drop away when you give them a [side] project,” he said.
So when Tori Kinamon asked him to work on an MRSA project — in her first year — he gave her one that focused on researching vertebral osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can coincide with S aureus. What Dr. Fowler didn’t know: Kinamon (now MD) had been a competitive gymnast at Brown and battled her own life-threatening infection with MRSA.
“To my absolute astonishment, not only did she stick to it, but she was able to compile a presentation on the science and gave an oral presentation within a year of walking in the door,” said Dr. Fowler.
She went on to lead an initiative between the National Institutes of Health and US Food and Drug Administration to create endpoints for clinical drug trials, all of which occurred before starting her residency, which she’s about to embark upon.
Dr. Kinamon’s a good example, he said, of what happens when you add genuine passion to book smarts. Those who do always stand out because you can’t fake that. “Find your passion, and then chase it down relentlessly,” he said. “Once you’ve found your passion, things get easy because it stops being work and it starts being something else.”
If you haven’t identified a focus area, Dr. Fowler said to “be agnostic and observant. Keep your eyes open and your options open because you may surprise yourself. It may turn out that you end up liking something a whole lot more than you thought you did.”
Lesson #3: When You Say You’ve Always Wanted to Do Something, Do Something
As the chief of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, Scott Budinger, MD, often hears lip service from doctors who want to put their skills to use in their local communities. One of his students actually did it.
Justin Fiala, MD, a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep specialist at Northwestern Medicine, joined Northwestern as a pulmonary fellow with a big interest in addressing health equity issues.
Dr. Fiala began volunteering with CommunityHealth during his fellowship and saw that many patients of the free Chicago-area clinic needed help with sleep disorders. He launched the organization’s first sleep clinic and its Patient-Centered Apnea Protocols Initiative.
“He developed a plan with some of the partners of the sleep apnea equipment to do home sleep testing for these patients that’s free of cost,” said Dr. Budinger.
Dr. Fiala goes in on Saturdays and runs a free clinic conducting sleep studies for patients and outfits them with devices that they need to improve their conditions, said Dr. Budinger.
“And these patients are the severest of the severe patients,” he said. “These are people that have severe sleep apnea that are driving around the roads, oftentimes don’t have insurance because they’re also precluded from having auto insurance. So, this is really something that not just benefits these patients but benefits our whole community.”
The fact that Dr. Fiala followed through on something that all doctors aspire to do — and in the middle of a very busy training program — is something that Dr. Budinger said makes him stand out in a big way.
“If you talk to any of our trainees or young faculty, everybody’s interested in addressing the issue of health disparities,” said Dr. Budinger. “Justin looked at that and said, ‘Well, you know, I’m not interested in talking about it. What can I do about this problem? And how can I actually get boots on the ground and help?’ That requires a big activation energy that many people don’t have.”
Lesson #4: Be a People-Person and a Patient-Person
When hiring employees at American Family Care in Portland, Oregon, Andrew Miller, MD, director of provider training, is always on the lookout for young MDs with emotional intelligence and a good bedside manner. He has been recently blown away, however, by a young physician’s assistant named Joseph Van Bindsbergen, PA-C, who was described as “all-around wonderful” during his reference check.
“Having less than 6 months of experience out of school, he is our highest ranked provider, whether it’s a nurse practitioner, PA, or doctor, in terms of patient satisfaction,” said Dr. Miller. The young PA has an “unprecedented perfect score” on his NPS rating.
Why? Patients said they’ve never felt as heard as they felt with Van Bindsbergen.
“That’s the thing I think that the up-and-coming providers should be focusing on is making your patients feel heard,” explained Dr. Miller. Van Bindsbergen is great at building rapport with a patient, whether they are 6 or 96. “He doesn’t just ask about sore throat symptoms. He asks, ‘what is the impact on your life of the sore throat? How does it affect your family or your work? What do you think this could be besides just strep? What are your concerns?’ ”
Dr. Miller said the magic of Van Bindsbergen is that he has an innate ability to look at patients “not just as a diagnosis but as a person, which they love.”
Lesson #5: Remember to Make That Difference With Each Patient
Doctors are used to swooping in and seeing a patient, ordering further testing if needed, and then moving on to the next patient. But one young intern at the start of his medical career broke this mold by giving a very anxious patient some much-needed support.
“There was a resident who was working overnight, and this poor young woman came in who had a new diagnosis of an advanced illness and a lot of anxiety around her condition, the newness of it, and the impact this is going to have on her family and her life,” said Elizabeth Horn Prsic, MD, assistant professor at Yale School of Medicine and firm chief for medical oncology and the director of Adult Inpatient Palliative Care.
Dr. Prsic found out the next morning that this trainee accompanied the patient to the MRI and held her hand as much as he was allowed to throughout the entire experience. “I was like, ‘wait you went down with her to radiology?’ And he’s like, ‘Yes, I was there the whole time,’ ” she recalled.
This gesture not only helped the patient feel calmer after receiving a potentially life-altering diagnosis but also helped ensure the test results were as clear as possible.
“If the study is not done well and a patient is moving or uncomfortable, it has to be stopped early or paused,” said Dr. Prsic. “Then the study is not very useful. In situations like these, medical decisions may be made based on imperfect data. The fact that we had this full complete good quality scan helped us get the care that she needed in a much timelier manner to help her and to move along the care that she that was medically appropriate for her.”
Dr. Prsic got emotional reflecting on the experience. Working at Yale, she saw a ton of intelligent doctors come through the ranks. But this gesture, she said, should serve as a reminder that “you don’t need to be the smartest person in the room to just be there for a patient. It was pure empathic presence and human connection. It gave me hope in the next generation of physicians.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.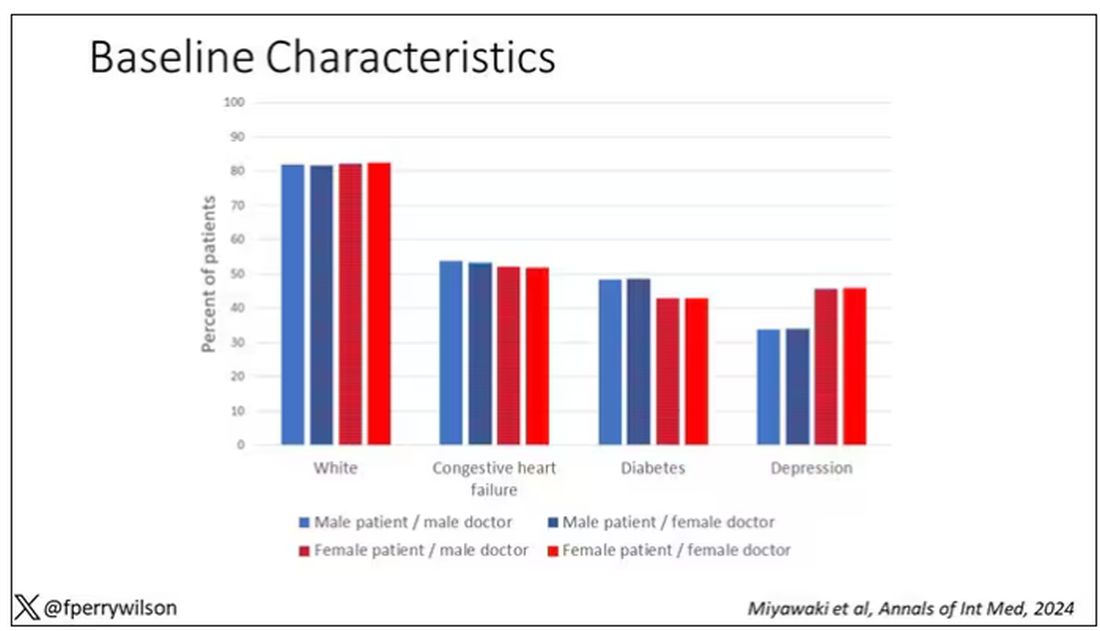
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 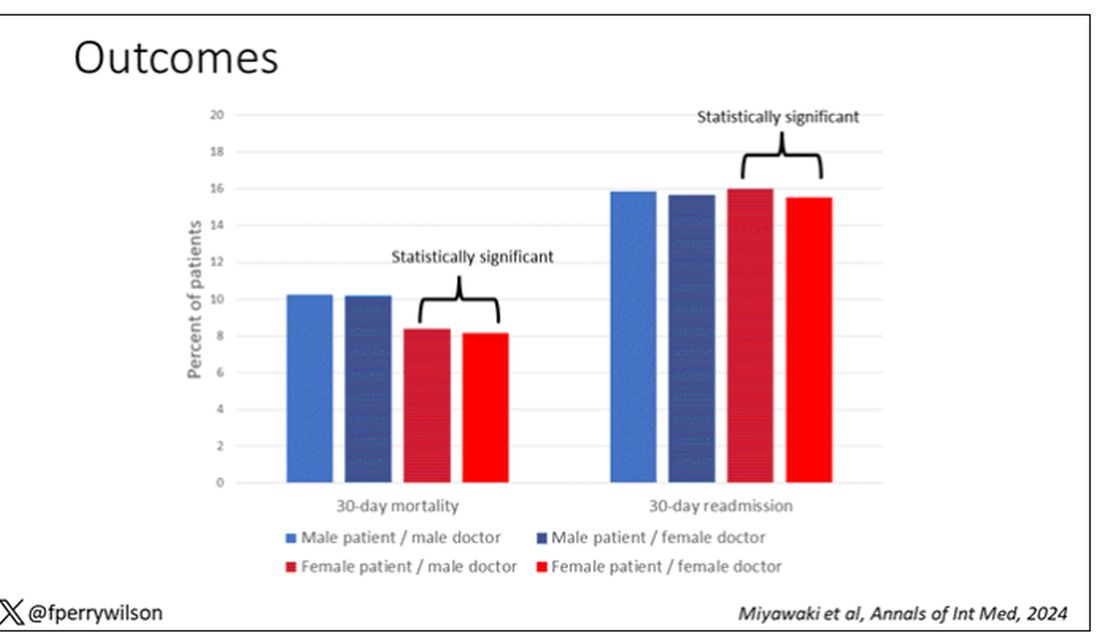
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.