Photo Challenge
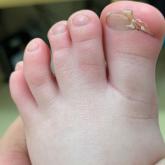
Congenital Defect of the Toenail
An 18-month-old girl presented for evaluation of nail dystrophy. The patient’s parents stated that the left great toenail had been dystrophic...
Dr. Gall is from the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland. Drs. Willett and Peters are from the Naval Medical Center San Diego, California.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not reflect the official position of the institution; the Departments of the Navy, Army, and Air Force; the Department of Defense; or the US Government.
Correspondence: Ryan Gall, MD, Transitional Medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, 8901 Wisconsin Ave, Bethesda MD 20889 (ryan.gall.md@gmail.com).

A 71-year-old man presented with an inflamed erythematous papule on the right subcostal region of 12 months’ duration. It began as a small pimplelike bump that slowly enlarged. The patient did not report any pain or pruritus, but the lesion intermittently drained purulent fluid. The patient had a pacemaker and a history of severe aortic stenosis for which he underwent bioprosthetic aortic valve repair approximately 3 years prior to presentation. His postoperative course was complicated by sternal wound infection and sepsis, prompting surgical replacement of the graft and the pacemaker. He then developed aortitis secondary to bacterial endocarditis with multiple associated septic emboli and is now on lifelong levofloxacin and minocycline therapy. Physical examination revealed a 1.5-cm, erythematous, soft, protuberant nodule with surrounding skin dimpling on the right subcostal region adjacent to a well-healed surgical scar. Approximately 1 to 2 mL of purulent fluid was expressed.
A delayed foreign body reaction is a rare complication of retained temporary pacing wires following cardiovascular surgery. These epicardial pacing wires are important for the management of postoperative arrhythmia and normally are removed by external traction after normal rhythm has been re-established. However, it is not uncommon for these wires to be cut at the skin surface in the setting of difficult removal, as retained pacing wires generally are viewed as benign.1 These reactions often take years after placement of the pacing wire to present themselves and most often resolve with either complete removal of the wire or resection of the distal end.2
Our patient was referred to dermatology and underwent a shave biopsy. Results were consistent with chronic inflammatory granulation tissue. Bacterial tissue culture grew Staphylococcus epidermidis. Cultures for acid-fast bacilli and fungi were negative. The patient was referred to cardiothoracic surgery. Computed tomography identified a retained temporary pacing wire extending to the base of the lesion. The lesion was excised and the distal aspect of the pacing wire was removed, which resulted in resolution of the nodule.
The differential diagnosis includes pyoderma gangrenosum, nodular basal cell carcinoma, Sister Mary Joseph nodule, and pyogenic granuloma. Pyoderma gangrenosum is a neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a rapidly progressing, painful, necrotic ulcer. It is classically associated with inflammatory bowel disease and other systemic diseases but also can occur in isolation.3
Nodular basal cell carcinomas often develop in chronically sun-exposed areas of the body. Morphologically, they present as pink, pearl appearing papules with rolled borders and overlying arborizing telangiectasia. Nodular basal cell carcinomas may present with recurrent bleeding but typically do not have continuous drainage.4
Sister Mary Joseph nodule represents a periumbilical lymphatic metastasis from an underlying (usually intra-abdominal) malignancy. It typically presents as an umbilical or periumbilical nodule measuring 0.5 to 15 cm in diameter. The nodules often are painful and discharge a serous fluid. It is estimated that they are present in 1% to 3% of cases of abdominopelvic malignancy, but Sister Mary Joseph nodules also have been reported in several other types of solid organ tumors.5
Pyogenic granuloma is a benign vascular lesion that classically develops rapidly over the course of a few weeks. It often presents as a single red, moist, friable papule with a collarette of scale and frequently is associated with pain, bleeding, and ulceration. Keratinized skin or mucosa can be affected, and pyogenic granuloma is most common in children and young adults.6

An 18-month-old girl presented for evaluation of nail dystrophy. The patient’s parents stated that the left great toenail had been dystrophic...
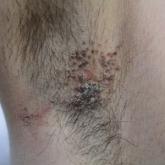
A 42-year-old man presented with pruritic axillary plaques of 6 months’ duration that were exacerbated by heat and friction. He maintained a very...
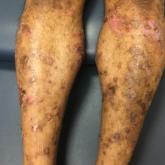
A 50-year-old man presented with a pruritic bullous dermatosis on the lower legs, arms, and back of 1 month’s duration. He had an 8-year history...
