User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
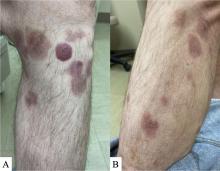
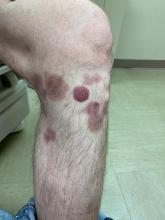
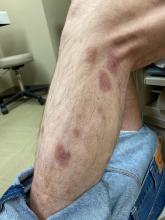
Study compares noninvasive treatments of cutaneous neurofibromas
PHOENIX – after only one treatment, according to preliminary results of an ongoing prospective trial that compared several treatment modalities.
“Neurofibromatosis type 1 is the most common single-gene disease of mankind, but there is so much we have yet to learn about it,” study author Patricia Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., said in an interview in advance of the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. Dr. Richey also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is working with R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center, on this project. In his words, she said, “the lack of better treatments for cNF is a ‘problem worth solving.’ ”
“The accepted and widely available treatments for cNF result in scars and hypopigmentation. Our treatments do not,” she added. Since the epidermis overlying cNF is normal, “there is no reason to use nonselective or surgical methods and destroy a perfectly good epidermis when you don’t need to.”
Four treatments vs. controls
For the study, Dr. Richey and colleagues enrolled 19 adults with a total of 307 cNFs measuring 2-4 mm in size to receive one of four treatments: electrocautery with an insulated radiofrequency needle; 755-nm alexandrite laser with negative pressure (8-mm spot size, 100 J/cm2 fluence, 3-ms pulse duration); 980-nm diode laser (delivered via 8-mm sapphire skin-contact window), and intratumoral injection of 10 mg/mL deoxycholic acid at a volume approximately equal to that of the tumor. The average age of the participants was 49 years and 15 were female.
The investigators applied 5% lidocaine/prilocaine for 40 minutes to treatment sites before randomizing the tumors to treatment or to the control arm (no treatment). They compared safety, tolerability (including pain scores), and efficacy of each modality as measured by the change in cNF volume/height via three-dimensional imaging and clinical improvement via physician assessment at 6 months. All 19 participants have completed the 6-month assessment.
All modalities reduced or eliminated some of the cNFs by 6 months after treatment, with statistically significant reductions in height and volume across all four treatments. A wide variation of responses was observed. Specifically, the mean tumor volume changes for each modality, compared with controls, were –33.4% versus –5.1% among those treated with the 755-nm alexandrite laser; –24.9% versus –9.2% among those treated with the 980-nm diode laser, –23.3% versus –0.8% among those treated with insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation, and –29.4% versus –3.7% among those treated with deoxycholic acid.
The variation in responses “may be due to histologic diversity of cNF or may indicate a need for more fine-tuned dosimetry, or a combination,” Dr. Richey said. “Our future trials will address this. We will also be treating all skin types in our upcoming trials.”
No adverse events categorized as higher than grade 2 occurred in any of the treatment groups, and no signs of regrowth or growth stimulation have been observed to date.
Tolerability of treatments
As for general tolerability, the 980-nm laser treatment caused moderate to severe pain; the alexandrite laser caused mild pain; insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation caused mild pain, though more than deoxycholic acid injections or alexandrite laser, and pain associated with the deoxycholic acid injections was minimal.
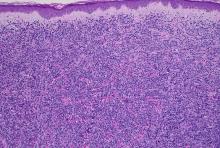
When residual neurofibroma tumor was present histologically, its appearance was similar to that of untreated tumors in controls. There was no evidence of atypia, mitosis, or tumor inflammation, and mild fibrosis was present at the sites of prior tumor.
“It was surprising that all four modalities did work to some extent,” Dr. Richey said, noting that the lack of ulceration with deoxycholic acid injection “was pleasantly surprising.” Treatment with the 980-nm diode laser “was a bit more painful than we anticipated.”
The positive results of this trial has raised “more questions for us to answer. We have three additional trials in the works to fine tune these treatments and optimize dose/delivery, with the end goal of treating younger people.”
Dr. Richey said that she was “amazed” by how motivated the enrollees were to participate in the trial, noting that many patients with cNF undergo general anesthesia to have dozens of tumors surgically removed at once. “They pay $10,000-$20,000 on average out of pocket, as this surgery is considered cosmetic,” she said.
“This very important study could lead to effective, relatively noninvasive, therapy for small neurofibromas,” said Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the results.
“Remarkably, all four treatments worked to varying degrees, but of all the treatments, the selective alexandrite laser appeared to achieve the best results. Further study will be needed to see just how effective these treatments are, and to determine the best and safest treatment parameters. Given how common this autosomal dominant disease is, and how disfiguring neurofibromas become as they enlarge, a well-tolerated noninvasive nonsurgical treatment with limited side effects is highly sought after.”
The study, which was named the best clinical abstract at the meeting, was supported by the Neurofibromatosis Therapeutic Acceleration Program. Dr. Anderson is supported in part as the Lancer Endowed Chair in Dermatology at MGH. Dr. Dover reported having no relevant disclosures.
PHOENIX – after only one treatment, according to preliminary results of an ongoing prospective trial that compared several treatment modalities.
“Neurofibromatosis type 1 is the most common single-gene disease of mankind, but there is so much we have yet to learn about it,” study author Patricia Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., said in an interview in advance of the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. Dr. Richey also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is working with R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center, on this project. In his words, she said, “the lack of better treatments for cNF is a ‘problem worth solving.’ ”
“The accepted and widely available treatments for cNF result in scars and hypopigmentation. Our treatments do not,” she added. Since the epidermis overlying cNF is normal, “there is no reason to use nonselective or surgical methods and destroy a perfectly good epidermis when you don’t need to.”
Four treatments vs. controls
For the study, Dr. Richey and colleagues enrolled 19 adults with a total of 307 cNFs measuring 2-4 mm in size to receive one of four treatments: electrocautery with an insulated radiofrequency needle; 755-nm alexandrite laser with negative pressure (8-mm spot size, 100 J/cm2 fluence, 3-ms pulse duration); 980-nm diode laser (delivered via 8-mm sapphire skin-contact window), and intratumoral injection of 10 mg/mL deoxycholic acid at a volume approximately equal to that of the tumor. The average age of the participants was 49 years and 15 were female.
The investigators applied 5% lidocaine/prilocaine for 40 minutes to treatment sites before randomizing the tumors to treatment or to the control arm (no treatment). They compared safety, tolerability (including pain scores), and efficacy of each modality as measured by the change in cNF volume/height via three-dimensional imaging and clinical improvement via physician assessment at 6 months. All 19 participants have completed the 6-month assessment.
All modalities reduced or eliminated some of the cNFs by 6 months after treatment, with statistically significant reductions in height and volume across all four treatments. A wide variation of responses was observed. Specifically, the mean tumor volume changes for each modality, compared with controls, were –33.4% versus –5.1% among those treated with the 755-nm alexandrite laser; –24.9% versus –9.2% among those treated with the 980-nm diode laser, –23.3% versus –0.8% among those treated with insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation, and –29.4% versus –3.7% among those treated with deoxycholic acid.
The variation in responses “may be due to histologic diversity of cNF or may indicate a need for more fine-tuned dosimetry, or a combination,” Dr. Richey said. “Our future trials will address this. We will also be treating all skin types in our upcoming trials.”
No adverse events categorized as higher than grade 2 occurred in any of the treatment groups, and no signs of regrowth or growth stimulation have been observed to date.
Tolerability of treatments
As for general tolerability, the 980-nm laser treatment caused moderate to severe pain; the alexandrite laser caused mild pain; insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation caused mild pain, though more than deoxycholic acid injections or alexandrite laser, and pain associated with the deoxycholic acid injections was minimal.
When residual neurofibroma tumor was present histologically, its appearance was similar to that of untreated tumors in controls. There was no evidence of atypia, mitosis, or tumor inflammation, and mild fibrosis was present at the sites of prior tumor.
“It was surprising that all four modalities did work to some extent,” Dr. Richey said, noting that the lack of ulceration with deoxycholic acid injection “was pleasantly surprising.” Treatment with the 980-nm diode laser “was a bit more painful than we anticipated.”
The positive results of this trial has raised “more questions for us to answer. We have three additional trials in the works to fine tune these treatments and optimize dose/delivery, with the end goal of treating younger people.”
Dr. Richey said that she was “amazed” by how motivated the enrollees were to participate in the trial, noting that many patients with cNF undergo general anesthesia to have dozens of tumors surgically removed at once. “They pay $10,000-$20,000 on average out of pocket, as this surgery is considered cosmetic,” she said.
“This very important study could lead to effective, relatively noninvasive, therapy for small neurofibromas,” said Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the results.
“Remarkably, all four treatments worked to varying degrees, but of all the treatments, the selective alexandrite laser appeared to achieve the best results. Further study will be needed to see just how effective these treatments are, and to determine the best and safest treatment parameters. Given how common this autosomal dominant disease is, and how disfiguring neurofibromas become as they enlarge, a well-tolerated noninvasive nonsurgical treatment with limited side effects is highly sought after.”
The study, which was named the best clinical abstract at the meeting, was supported by the Neurofibromatosis Therapeutic Acceleration Program. Dr. Anderson is supported in part as the Lancer Endowed Chair in Dermatology at MGH. Dr. Dover reported having no relevant disclosures.
PHOENIX – after only one treatment, according to preliminary results of an ongoing prospective trial that compared several treatment modalities.
“Neurofibromatosis type 1 is the most common single-gene disease of mankind, but there is so much we have yet to learn about it,” study author Patricia Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., said in an interview in advance of the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. Dr. Richey also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is working with R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center, on this project. In his words, she said, “the lack of better treatments for cNF is a ‘problem worth solving.’ ”
“The accepted and widely available treatments for cNF result in scars and hypopigmentation. Our treatments do not,” she added. Since the epidermis overlying cNF is normal, “there is no reason to use nonselective or surgical methods and destroy a perfectly good epidermis when you don’t need to.”
Four treatments vs. controls
For the study, Dr. Richey and colleagues enrolled 19 adults with a total of 307 cNFs measuring 2-4 mm in size to receive one of four treatments: electrocautery with an insulated radiofrequency needle; 755-nm alexandrite laser with negative pressure (8-mm spot size, 100 J/cm2 fluence, 3-ms pulse duration); 980-nm diode laser (delivered via 8-mm sapphire skin-contact window), and intratumoral injection of 10 mg/mL deoxycholic acid at a volume approximately equal to that of the tumor. The average age of the participants was 49 years and 15 were female.
The investigators applied 5% lidocaine/prilocaine for 40 minutes to treatment sites before randomizing the tumors to treatment or to the control arm (no treatment). They compared safety, tolerability (including pain scores), and efficacy of each modality as measured by the change in cNF volume/height via three-dimensional imaging and clinical improvement via physician assessment at 6 months. All 19 participants have completed the 6-month assessment.
All modalities reduced or eliminated some of the cNFs by 6 months after treatment, with statistically significant reductions in height and volume across all four treatments. A wide variation of responses was observed. Specifically, the mean tumor volume changes for each modality, compared with controls, were –33.4% versus –5.1% among those treated with the 755-nm alexandrite laser; –24.9% versus –9.2% among those treated with the 980-nm diode laser, –23.3% versus –0.8% among those treated with insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation, and –29.4% versus –3.7% among those treated with deoxycholic acid.
The variation in responses “may be due to histologic diversity of cNF or may indicate a need for more fine-tuned dosimetry, or a combination,” Dr. Richey said. “Our future trials will address this. We will also be treating all skin types in our upcoming trials.”
No adverse events categorized as higher than grade 2 occurred in any of the treatment groups, and no signs of regrowth or growth stimulation have been observed to date.
Tolerability of treatments
As for general tolerability, the 980-nm laser treatment caused moderate to severe pain; the alexandrite laser caused mild pain; insulated-needle radiofrequency coagulation caused mild pain, though more than deoxycholic acid injections or alexandrite laser, and pain associated with the deoxycholic acid injections was minimal.
When residual neurofibroma tumor was present histologically, its appearance was similar to that of untreated tumors in controls. There was no evidence of atypia, mitosis, or tumor inflammation, and mild fibrosis was present at the sites of prior tumor.
“It was surprising that all four modalities did work to some extent,” Dr. Richey said, noting that the lack of ulceration with deoxycholic acid injection “was pleasantly surprising.” Treatment with the 980-nm diode laser “was a bit more painful than we anticipated.”
The positive results of this trial has raised “more questions for us to answer. We have three additional trials in the works to fine tune these treatments and optimize dose/delivery, with the end goal of treating younger people.”
Dr. Richey said that she was “amazed” by how motivated the enrollees were to participate in the trial, noting that many patients with cNF undergo general anesthesia to have dozens of tumors surgically removed at once. “They pay $10,000-$20,000 on average out of pocket, as this surgery is considered cosmetic,” she said.
“This very important study could lead to effective, relatively noninvasive, therapy for small neurofibromas,” said Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the results.
“Remarkably, all four treatments worked to varying degrees, but of all the treatments, the selective alexandrite laser appeared to achieve the best results. Further study will be needed to see just how effective these treatments are, and to determine the best and safest treatment parameters. Given how common this autosomal dominant disease is, and how disfiguring neurofibromas become as they enlarge, a well-tolerated noninvasive nonsurgical treatment with limited side effects is highly sought after.”
The study, which was named the best clinical abstract at the meeting, was supported by the Neurofibromatosis Therapeutic Acceleration Program. Dr. Anderson is supported in part as the Lancer Endowed Chair in Dermatology at MGH. Dr. Dover reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2023
Study suggests narrow excision margins safe in early melanoma resection
Current U.S., European, and Australian or melanoma-specific mortality (MSM), results of a retrospective study suggest.
Among 1,179 patients with stage T1a melanomas near the face, scalp, external genitalia, or other critical areas, the weighted 10-year local recurrence rate for patients who underwent resection with 10-mm margins was 5.7%, compared with 6.7% for those who had resections with 5-mm margins, a nonsignificant difference.
Weighted 10-year melanoma-specific mortality was 1.8% for patients treated with wide margins, vs. 4.2% for those treated with narrow margins, also a nonsignificant difference. Patients treated with narrow margins did have significantly fewer reconstructive surgeries than patients treated with wide margins, reported Andrea Maurichi, MD, and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute of Italy in Milan.
“Because this association was found in melanomas of the head and neck, acral, and genital sites, there is no plausible reason why it could not be extrapolated to other locations. The findings also support the need for prospective randomized clinical trials to definitively answer the important question about appropriate excision margins for T1a melanoma,” they wrote in the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
The authors also found, however, that Breslow thickness greater than 0.4 mm and mitotic rate greater than 1/mm2 were associated with worse MSM, and that acral lentiginous melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and increasing Breslow thickness were associated with a higher incidence of local recurrence.
A melanoma expert who was not involved in the study said that despite these findings, wider margins are always preferable.
“There is always a conversation around these general [critical] areas, but as a rule we try to get larger margins,” said Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
In an interview, Dr. Sullivan said that the finding about lower frequency of reconstructive procedures in the narrow margins groups may be more of a concern for younger patients than for the elderly.
Study design
The investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive patients aged 18 or older at the National Cancer Institute of Milan who were diagnosed with T1a cutaneous melanoma close to critical areas from 2001 through 2020.
Patients with primary cutaneous melanoma of the head and face areas with functional or cosmetic considerations, acral areas (plantar, palmar, digital and interdigital areas), external genitalia, or periumbilical and perineal areas were eligible for inclusion.
The cohort comprised 1,179 patients with a median age of 50 and equal sex distribution. Of these patients, 626 (53%) had a wide excision, of whom 434 had a linear repair, and 192 had a flap of graft reconstruction. The remaining 553 patients had narrow excisions, 491 with linear repair, and 62 with flap or graft reconstruction.
Analyses were adjusted to account for imbalances between the surgical groups.
The study was supported by the nonprofit foundation Emme Rouge. The authors and Dr. Sullivan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Current U.S., European, and Australian or melanoma-specific mortality (MSM), results of a retrospective study suggest.
Among 1,179 patients with stage T1a melanomas near the face, scalp, external genitalia, or other critical areas, the weighted 10-year local recurrence rate for patients who underwent resection with 10-mm margins was 5.7%, compared with 6.7% for those who had resections with 5-mm margins, a nonsignificant difference.
Weighted 10-year melanoma-specific mortality was 1.8% for patients treated with wide margins, vs. 4.2% for those treated with narrow margins, also a nonsignificant difference. Patients treated with narrow margins did have significantly fewer reconstructive surgeries than patients treated with wide margins, reported Andrea Maurichi, MD, and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute of Italy in Milan.
“Because this association was found in melanomas of the head and neck, acral, and genital sites, there is no plausible reason why it could not be extrapolated to other locations. The findings also support the need for prospective randomized clinical trials to definitively answer the important question about appropriate excision margins for T1a melanoma,” they wrote in the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
The authors also found, however, that Breslow thickness greater than 0.4 mm and mitotic rate greater than 1/mm2 were associated with worse MSM, and that acral lentiginous melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and increasing Breslow thickness were associated with a higher incidence of local recurrence.
A melanoma expert who was not involved in the study said that despite these findings, wider margins are always preferable.
“There is always a conversation around these general [critical] areas, but as a rule we try to get larger margins,” said Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
In an interview, Dr. Sullivan said that the finding about lower frequency of reconstructive procedures in the narrow margins groups may be more of a concern for younger patients than for the elderly.
Study design
The investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive patients aged 18 or older at the National Cancer Institute of Milan who were diagnosed with T1a cutaneous melanoma close to critical areas from 2001 through 2020.
Patients with primary cutaneous melanoma of the head and face areas with functional or cosmetic considerations, acral areas (plantar, palmar, digital and interdigital areas), external genitalia, or periumbilical and perineal areas were eligible for inclusion.
The cohort comprised 1,179 patients with a median age of 50 and equal sex distribution. Of these patients, 626 (53%) had a wide excision, of whom 434 had a linear repair, and 192 had a flap of graft reconstruction. The remaining 553 patients had narrow excisions, 491 with linear repair, and 62 with flap or graft reconstruction.
Analyses were adjusted to account for imbalances between the surgical groups.
The study was supported by the nonprofit foundation Emme Rouge. The authors and Dr. Sullivan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Current U.S., European, and Australian or melanoma-specific mortality (MSM), results of a retrospective study suggest.
Among 1,179 patients with stage T1a melanomas near the face, scalp, external genitalia, or other critical areas, the weighted 10-year local recurrence rate for patients who underwent resection with 10-mm margins was 5.7%, compared with 6.7% for those who had resections with 5-mm margins, a nonsignificant difference.
Weighted 10-year melanoma-specific mortality was 1.8% for patients treated with wide margins, vs. 4.2% for those treated with narrow margins, also a nonsignificant difference. Patients treated with narrow margins did have significantly fewer reconstructive surgeries than patients treated with wide margins, reported Andrea Maurichi, MD, and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute of Italy in Milan.
“Because this association was found in melanomas of the head and neck, acral, and genital sites, there is no plausible reason why it could not be extrapolated to other locations. The findings also support the need for prospective randomized clinical trials to definitively answer the important question about appropriate excision margins for T1a melanoma,” they wrote in the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
The authors also found, however, that Breslow thickness greater than 0.4 mm and mitotic rate greater than 1/mm2 were associated with worse MSM, and that acral lentiginous melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and increasing Breslow thickness were associated with a higher incidence of local recurrence.
A melanoma expert who was not involved in the study said that despite these findings, wider margins are always preferable.
“There is always a conversation around these general [critical] areas, but as a rule we try to get larger margins,” said Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
In an interview, Dr. Sullivan said that the finding about lower frequency of reconstructive procedures in the narrow margins groups may be more of a concern for younger patients than for the elderly.
Study design
The investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive patients aged 18 or older at the National Cancer Institute of Milan who were diagnosed with T1a cutaneous melanoma close to critical areas from 2001 through 2020.
Patients with primary cutaneous melanoma of the head and face areas with functional or cosmetic considerations, acral areas (plantar, palmar, digital and interdigital areas), external genitalia, or periumbilical and perineal areas were eligible for inclusion.
The cohort comprised 1,179 patients with a median age of 50 and equal sex distribution. Of these patients, 626 (53%) had a wide excision, of whom 434 had a linear repair, and 192 had a flap of graft reconstruction. The remaining 553 patients had narrow excisions, 491 with linear repair, and 62 with flap or graft reconstruction.
Analyses were adjusted to account for imbalances between the surgical groups.
The study was supported by the nonprofit foundation Emme Rouge. The authors and Dr. Sullivan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
What happens to melanocytic nevi during laser hair removal?
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
AT ASLMS 2023
Alzheimer’s drug may ease hair pulling, skin-picking disorders
Results from the double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that 61% of participants who received memantine were “much or very much improved,” versus 8% in the placebo group.
“Memantine was far more effective than placebo,” lead investigator Jon Grant, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said in an interview. “However, while subjects responded favorably, that didn’t necessarily mean there were no symptoms.”
The study was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underrecognized, disabling
The investigators noted that trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder are underrecognized and are often disabling conditions. However, the researchers pointed out that with prevalence rates of 1.7% for trichotillomania and 2.1% for skin-picking disorder, they are not uncommon.
Behavioral therapy that attempts to reverse these habits is considered first-line treatment, but trained therapists are difficult to find. In addition, the investigators wrote that currently, there are no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for either disorder, and pharmacologic clinical trials are relatively uncommon.
The existing data from double-blind, placebo-controlled studies support the use of the antipsychotic olanzapine, the tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine, and the supplement N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Dr. Grant also noted that previous drug trials involving patients with trichotillomania have been very short in duration.
Prior research has implicated the glutamate system in repetitive motor habits and the urges that drive them. Memantine, a glutamate receptor antagonist, targets excessive glutamatergic drive. To investigate whether this medication may be beneficial for patients with trichotillomania and skin-picking disorders, the investigators conducted a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
The study included 100 adults (86 women; mean age, 31.4) with trichotillomania, skin-picking disorder, or both; participants received memantine (n = 55) or placebo (n = 45) for 8 weeks; they received memantine 10 mg or placebo for the first 2 weeks, then 20 mg for the next 6 weeks.
The researchers, who were blinded to assignment, assessed participants every 2 weeks using the National Institute of Mental Health Trichotillomania Symptom Severity Scale, which was modified to include questions for skin-picking disorder.
The team also tracked symptoms and behaviors using additional scales, including the Sheehan Disability Scale and the Clinical Global Impressions severity scale.
At the study’s conclusion, 79 patients remained. Of those, 26 of the 43 participants in the memantine group were “very much” or “much” improved (61%), versus 3 of 36 (8%) in the placebo group. (P < .0001)
Six participants in the memantine group experienced complete remission of symptoms, compared with one in the placebo group. There were no differences between the study groups in terms of adverse events.
Study limitations included the relatively short length of the trial for what should be considered a chronic disease, as well as the inclusion of only mildly to moderately symptomatic participants.
Dr. Grant said that he would like to study how memantine works in combination with behavioral therapy.
‘Two great options’
Katharine Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has been using memantine for “quite some time” to treat her patients with skin-picking disorder, adding that she uses higher doses of the drug than were tested in the study.
She noted that both NAC and memantine affect glutamate, an amino acid in the brain that is likely involved in repetitive physical or motor habits, such as hair pulling and skin picking.
“The good news is that we have two great options” for the treatment of trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder, said Dr. Phillips, and that both are easy to tolerate.
Future research should focus on longer trials of memantine and at higher doses, as well as other glutamate modulators, she said.
The study was funded by departmental research funds at the University of Chicago. Dr. Grant reported receiving research funding from Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and Janssen, as well as yearly compensation from Springer Publishing for his role as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Gambling Studies. He has also received royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing, McGraw Hill, Oxford University Press, and WW Norton. Dr. Phillips reported receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing and an honorarium from the Merck Manual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from the double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that 61% of participants who received memantine were “much or very much improved,” versus 8% in the placebo group.
“Memantine was far more effective than placebo,” lead investigator Jon Grant, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said in an interview. “However, while subjects responded favorably, that didn’t necessarily mean there were no symptoms.”
The study was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underrecognized, disabling
The investigators noted that trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder are underrecognized and are often disabling conditions. However, the researchers pointed out that with prevalence rates of 1.7% for trichotillomania and 2.1% for skin-picking disorder, they are not uncommon.
Behavioral therapy that attempts to reverse these habits is considered first-line treatment, but trained therapists are difficult to find. In addition, the investigators wrote that currently, there are no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for either disorder, and pharmacologic clinical trials are relatively uncommon.
The existing data from double-blind, placebo-controlled studies support the use of the antipsychotic olanzapine, the tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine, and the supplement N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Dr. Grant also noted that previous drug trials involving patients with trichotillomania have been very short in duration.
Prior research has implicated the glutamate system in repetitive motor habits and the urges that drive them. Memantine, a glutamate receptor antagonist, targets excessive glutamatergic drive. To investigate whether this medication may be beneficial for patients with trichotillomania and skin-picking disorders, the investigators conducted a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
The study included 100 adults (86 women; mean age, 31.4) with trichotillomania, skin-picking disorder, or both; participants received memantine (n = 55) or placebo (n = 45) for 8 weeks; they received memantine 10 mg or placebo for the first 2 weeks, then 20 mg for the next 6 weeks.
The researchers, who were blinded to assignment, assessed participants every 2 weeks using the National Institute of Mental Health Trichotillomania Symptom Severity Scale, which was modified to include questions for skin-picking disorder.
The team also tracked symptoms and behaviors using additional scales, including the Sheehan Disability Scale and the Clinical Global Impressions severity scale.
At the study’s conclusion, 79 patients remained. Of those, 26 of the 43 participants in the memantine group were “very much” or “much” improved (61%), versus 3 of 36 (8%) in the placebo group. (P < .0001)
Six participants in the memantine group experienced complete remission of symptoms, compared with one in the placebo group. There were no differences between the study groups in terms of adverse events.
Study limitations included the relatively short length of the trial for what should be considered a chronic disease, as well as the inclusion of only mildly to moderately symptomatic participants.
Dr. Grant said that he would like to study how memantine works in combination with behavioral therapy.
‘Two great options’
Katharine Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has been using memantine for “quite some time” to treat her patients with skin-picking disorder, adding that she uses higher doses of the drug than were tested in the study.
She noted that both NAC and memantine affect glutamate, an amino acid in the brain that is likely involved in repetitive physical or motor habits, such as hair pulling and skin picking.
“The good news is that we have two great options” for the treatment of trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder, said Dr. Phillips, and that both are easy to tolerate.
Future research should focus on longer trials of memantine and at higher doses, as well as other glutamate modulators, she said.
The study was funded by departmental research funds at the University of Chicago. Dr. Grant reported receiving research funding from Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and Janssen, as well as yearly compensation from Springer Publishing for his role as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Gambling Studies. He has also received royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing, McGraw Hill, Oxford University Press, and WW Norton. Dr. Phillips reported receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing and an honorarium from the Merck Manual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from the double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that 61% of participants who received memantine were “much or very much improved,” versus 8% in the placebo group.
“Memantine was far more effective than placebo,” lead investigator Jon Grant, MD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said in an interview. “However, while subjects responded favorably, that didn’t necessarily mean there were no symptoms.”
The study was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underrecognized, disabling
The investigators noted that trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder are underrecognized and are often disabling conditions. However, the researchers pointed out that with prevalence rates of 1.7% for trichotillomania and 2.1% for skin-picking disorder, they are not uncommon.
Behavioral therapy that attempts to reverse these habits is considered first-line treatment, but trained therapists are difficult to find. In addition, the investigators wrote that currently, there are no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for either disorder, and pharmacologic clinical trials are relatively uncommon.
The existing data from double-blind, placebo-controlled studies support the use of the antipsychotic olanzapine, the tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine, and the supplement N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Dr. Grant also noted that previous drug trials involving patients with trichotillomania have been very short in duration.
Prior research has implicated the glutamate system in repetitive motor habits and the urges that drive them. Memantine, a glutamate receptor antagonist, targets excessive glutamatergic drive. To investigate whether this medication may be beneficial for patients with trichotillomania and skin-picking disorders, the investigators conducted a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
The study included 100 adults (86 women; mean age, 31.4) with trichotillomania, skin-picking disorder, or both; participants received memantine (n = 55) or placebo (n = 45) for 8 weeks; they received memantine 10 mg or placebo for the first 2 weeks, then 20 mg for the next 6 weeks.
The researchers, who were blinded to assignment, assessed participants every 2 weeks using the National Institute of Mental Health Trichotillomania Symptom Severity Scale, which was modified to include questions for skin-picking disorder.
The team also tracked symptoms and behaviors using additional scales, including the Sheehan Disability Scale and the Clinical Global Impressions severity scale.
At the study’s conclusion, 79 patients remained. Of those, 26 of the 43 participants in the memantine group were “very much” or “much” improved (61%), versus 3 of 36 (8%) in the placebo group. (P < .0001)
Six participants in the memantine group experienced complete remission of symptoms, compared with one in the placebo group. There were no differences between the study groups in terms of adverse events.
Study limitations included the relatively short length of the trial for what should be considered a chronic disease, as well as the inclusion of only mildly to moderately symptomatic participants.
Dr. Grant said that he would like to study how memantine works in combination with behavioral therapy.
‘Two great options’
Katharine Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has been using memantine for “quite some time” to treat her patients with skin-picking disorder, adding that she uses higher doses of the drug than were tested in the study.
She noted that both NAC and memantine affect glutamate, an amino acid in the brain that is likely involved in repetitive physical or motor habits, such as hair pulling and skin picking.
“The good news is that we have two great options” for the treatment of trichotillomania and skin-picking disorder, said Dr. Phillips, and that both are easy to tolerate.
Future research should focus on longer trials of memantine and at higher doses, as well as other glutamate modulators, she said.
The study was funded by departmental research funds at the University of Chicago. Dr. Grant reported receiving research funding from Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and Janssen, as well as yearly compensation from Springer Publishing for his role as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Gambling Studies. He has also received royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing, McGraw Hill, Oxford University Press, and WW Norton. Dr. Phillips reported receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Publishing and an honorarium from the Merck Manual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
FDA clears first patch to treat axillary hyperhidrosis
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Health care in America: Let that tapeworm grow
In my most recent column, “ ‘They All Laughed When I Spoke of Greedy Doctors,’ ” I attempted to provide a global understanding of some of the economic forces that have made American medicine what it is, how that happened, and why it is still happening.
I did not propose a fix. I have been proposing fixes for more than 30 years, on the pages of JAMA until 1999 and then for this news organization, most recently in 2019 with “Healthcare for All in a Land of Special Interests.”
Where you stand depends a lot on where you sit.
Is this good news or bad news? When William Hubbard was the dean of the University of Michigan School of Medicine in 1969, he said that “an academic medical center is the most efficient energy and resource trapping device that has ever been created” (personal communication, 1969).
To me as a faculty member of an academic medical center for many years, that was great news. We could grow faculty, erect buildings, take the best care of sick people, churn out research papers, mint new physicians and specialists, and get paid well in the process for doing “the Lord’s work.” What’s not to like? At that time, the proportion of the country’s gross national product expended for medical and health care was about 7%. And the predicted life span of an American at birth was 70.5 years.
Is this good news or bad news? In 2021, the proportion of our annual gross domestic product (GDP) consumed by health care was 18.3%, totaling $4.3 trillion, or $12,914 per person. For perspective, in 2021, the median income per capita was $37,638. Because quite a few Americans have very high incomes, the mean income per capita is much higher: $63,444. Predicted life span in 2021 was 76.4 years.
Thus, in a span of 53 years (1969-2022), only 5.9 years of life were gained per person born, for how many trillions of dollars expended? To me as a tax-paying citizen and payer of medical insurance premiums, that is bad news.
Is this good news or bad news? If we compare developed societies globally, our medical system does a whole lot of things very well indeed. But we spend a great deal more than any other country for health care and objectively achieve poorer outcomes. Thus, we are neither efficient nor effective. We keep a lot of workers very busy doing stuff, and they are generally well paid. As a worker, that’s good news; as a manager who values efficiency, it’s bad news indeed.
Is this good news or bad news? We’re the leader at finding money to pay people to do “health care work.” More Americans work in health care than any other field. In 2019, the United States employed some 21,000,000 people doing “health care and social assistance.” Among others, these occupations include physicians, dentists, dental hygienists and assistants, pharmacists, registered nurses, LVNs/LPNs, nursing aides, technologists and technicians, home health aides, respiratory therapists, occupational and speech therapists, social workers, childcare workers, and personal and home care aides. For a patient, parent, grandparent, and great-grandparent, it is good news to have all those folks available to take care of us when we need it.
So, while I have cringed at the frequent exposés from Roy Poses of what seem to me to be massive societal betrayals by American health care industry giants, it doesn’t have to be that way. Might it still be possible to do well while doing good?
A jobs program
Consider such common medical procedures as coronary artery stents or bypass grafts for stable angina (when optimal medical therapy is as good, or better than, and much less expensive); PSAs on asymptomatic men followed by unnecessary surgery for localized cancer; excess surgery for low back pain; and the jobs created by managing the people caught up in medical complications of the obesity epidemic.
Don’t forget the number of people employed simply to “follow the money” within our byzantine cockamamie medical billing system. In 2009, this prompted me to describe the bloated system as a “health care bubble” not unlike Enron, the submarket real estate financing debacle, or the dot-com boom and bust. I warned of the downside of bursting that bubble, particularly lost jobs.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provided health insurance to some 35 million Americans who had been uninsured. It retarded health care inflation. But it did nothing to trim administrative costs or very high pay for nonclinical executives, or shareholder profits in those companies that were for-profit, or drug and device prices. Without the support of all those groups, the ACA would never have passed Congress. The ACA has clearly been a mixed blessing.
If any large American constituency were ever serious about reducing the percentage of our GDP expended on health care, we have excellent ways to do that while improving the health and well-being of the American people. But remember, one person’s liability (unnecessary work) is another person’s asset (needed job).
The MBAization of medicine
Meanwhile, back at Dean Hubbard’s voracious academic medical center, the high intellect and driven nature of those who are attracted to medicine as a career has had other effects. The resulting organizations reflect not only the glorious calling of caring for the sick and the availability of lots of money to recruit and compensate leaders, but also the necessity to develop strong executive types who won’t be “eaten alive” by the high-powered workforce of demanding physicians and the surrounding environment.
Thus, it came as no great surprise that in its 2021 determination of America’s top 25 Best Large Employers, Forbes included five health care organizations and seven universities. Beating out such giants as NASA, Cisco, Microsoft, Netflix, and Google, the University of Alabama Birmingham Hospital was ranked first. Mayo Clinic and Yale University came in third and fifth, respectively, and at the other end of the list were Duke (23), MIT (24), and MD Anderson (25).
My goodness! Well done.
Yet, as a country attempting to be balanced, Warren Buffett’s descriptive entreaty on the 2021 failure of Haven, the Amazon-Chase-Berkshire Hathaway joint initiative, remains troubling. Calling upon Haven to change the U.S. health care system, Buffet said, “We learned a lot about the difficulty of changing around an industry that’s 17% of the GDP. We were fighting a tapeworm in the American economy, and the tapeworm won.” They had failed to tame the American health care cost beast.
I am on record as despising the “MBAization” of American medicine. Unfairly, I blamed a professional and technical discipline for what I considered misuse. I hereby repent and renounce my earlier condemnations.
Take it all over?
Here’s an idea: If you can’t beat them, join them.
Medical care is important, especially for acute illnesses and injuries, early cancer therapy, and many chronic conditions. But the real determinants of health writ large are social: wealth, education, housing, nutritious food, childcare, climate, clean air and water, meaningful employment, safety from violence, exercise schemes, vaccinations, and so on.
Why doesn’t the American medical-industrial complex simply bestow the label of “health care” on all health-related social determinants? Take it all over. Good “health care” jobs for everyone. Medical professionals will still be blamed for the low health quality and poor outcome scores, the main social determinants of health over which we have no control or influence.
Let that tapeworm grow to encompass all social determinants of health, and measure results by length and quality of life, national human happiness, and, of course, jobs. We can do it. Let that bubble glow. Party time.
And that’s the way it is. That’s my opinion.
George Lundberg, MD, is editor-in-chief at Cancer Commons, president of the Lundberg Institute, executive advisor at Cureus, and a clinical professor of pathology at Northwestern University. Previously, he served as editor-in-chief of JAMA (including 10 specialty journals), American Medical News, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In my most recent column, “ ‘They All Laughed When I Spoke of Greedy Doctors,’ ” I attempted to provide a global understanding of some of the economic forces that have made American medicine what it is, how that happened, and why it is still happening.
I did not propose a fix. I have been proposing fixes for more than 30 years, on the pages of JAMA until 1999 and then for this news organization, most recently in 2019 with “Healthcare for All in a Land of Special Interests.”
Where you stand depends a lot on where you sit.
Is this good news or bad news? When William Hubbard was the dean of the University of Michigan School of Medicine in 1969, he said that “an academic medical center is the most efficient energy and resource trapping device that has ever been created” (personal communication, 1969).
To me as a faculty member of an academic medical center for many years, that was great news. We could grow faculty, erect buildings, take the best care of sick people, churn out research papers, mint new physicians and specialists, and get paid well in the process for doing “the Lord’s work.” What’s not to like? At that time, the proportion of the country’s gross national product expended for medical and health care was about 7%. And the predicted life span of an American at birth was 70.5 years.
Is this good news or bad news? In 2021, the proportion of our annual gross domestic product (GDP) consumed by health care was 18.3%, totaling $4.3 trillion, or $12,914 per person. For perspective, in 2021, the median income per capita was $37,638. Because quite a few Americans have very high incomes, the mean income per capita is much higher: $63,444. Predicted life span in 2021 was 76.4 years.
Thus, in a span of 53 years (1969-2022), only 5.9 years of life were gained per person born, for how many trillions of dollars expended? To me as a tax-paying citizen and payer of medical insurance premiums, that is bad news.
Is this good news or bad news? If we compare developed societies globally, our medical system does a whole lot of things very well indeed. But we spend a great deal more than any other country for health care and objectively achieve poorer outcomes. Thus, we are neither efficient nor effective. We keep a lot of workers very busy doing stuff, and they are generally well paid. As a worker, that’s good news; as a manager who values efficiency, it’s bad news indeed.
Is this good news or bad news? We’re the leader at finding money to pay people to do “health care work.” More Americans work in health care than any other field. In 2019, the United States employed some 21,000,000 people doing “health care and social assistance.” Among others, these occupations include physicians, dentists, dental hygienists and assistants, pharmacists, registered nurses, LVNs/LPNs, nursing aides, technologists and technicians, home health aides, respiratory therapists, occupational and speech therapists, social workers, childcare workers, and personal and home care aides. For a patient, parent, grandparent, and great-grandparent, it is good news to have all those folks available to take care of us when we need it.
So, while I have cringed at the frequent exposés from Roy Poses of what seem to me to be massive societal betrayals by American health care industry giants, it doesn’t have to be that way. Might it still be possible to do well while doing good?
A jobs program
Consider such common medical procedures as coronary artery stents or bypass grafts for stable angina (when optimal medical therapy is as good, or better than, and much less expensive); PSAs on asymptomatic men followed by unnecessary surgery for localized cancer; excess surgery for low back pain; and the jobs created by managing the people caught up in medical complications of the obesity epidemic.
Don’t forget the number of people employed simply to “follow the money” within our byzantine cockamamie medical billing system. In 2009, this prompted me to describe the bloated system as a “health care bubble” not unlike Enron, the submarket real estate financing debacle, or the dot-com boom and bust. I warned of the downside of bursting that bubble, particularly lost jobs.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provided health insurance to some 35 million Americans who had been uninsured. It retarded health care inflation. But it did nothing to trim administrative costs or very high pay for nonclinical executives, or shareholder profits in those companies that were for-profit, or drug and device prices. Without the support of all those groups, the ACA would never have passed Congress. The ACA has clearly been a mixed blessing.
If any large American constituency were ever serious about reducing the percentage of our GDP expended on health care, we have excellent ways to do that while improving the health and well-being of the American people. But remember, one person’s liability (unnecessary work) is another person’s asset (needed job).
The MBAization of medicine
Meanwhile, back at Dean Hubbard’s voracious academic medical center, the high intellect and driven nature of those who are attracted to medicine as a career has had other effects. The resulting organizations reflect not only the glorious calling of caring for the sick and the availability of lots of money to recruit and compensate leaders, but also the necessity to develop strong executive types who won’t be “eaten alive” by the high-powered workforce of demanding physicians and the surrounding environment.
Thus, it came as no great surprise that in its 2021 determination of America’s top 25 Best Large Employers, Forbes included five health care organizations and seven universities. Beating out such giants as NASA, Cisco, Microsoft, Netflix, and Google, the University of Alabama Birmingham Hospital was ranked first. Mayo Clinic and Yale University came in third and fifth, respectively, and at the other end of the list were Duke (23), MIT (24), and MD Anderson (25).
My goodness! Well done.
Yet, as a country attempting to be balanced, Warren Buffett’s descriptive entreaty on the 2021 failure of Haven, the Amazon-Chase-Berkshire Hathaway joint initiative, remains troubling. Calling upon Haven to change the U.S. health care system, Buffet said, “We learned a lot about the difficulty of changing around an industry that’s 17% of the GDP. We were fighting a tapeworm in the American economy, and the tapeworm won.” They had failed to tame the American health care cost beast.
I am on record as despising the “MBAization” of American medicine. Unfairly, I blamed a professional and technical discipline for what I considered misuse. I hereby repent and renounce my earlier condemnations.
Take it all over?
Here’s an idea: If you can’t beat them, join them.
Medical care is important, especially for acute illnesses and injuries, early cancer therapy, and many chronic conditions. But the real determinants of health writ large are social: wealth, education, housing, nutritious food, childcare, climate, clean air and water, meaningful employment, safety from violence, exercise schemes, vaccinations, and so on.
Why doesn’t the American medical-industrial complex simply bestow the label of “health care” on all health-related social determinants? Take it all over. Good “health care” jobs for everyone. Medical professionals will still be blamed for the low health quality and poor outcome scores, the main social determinants of health over which we have no control or influence.
Let that tapeworm grow to encompass all social determinants of health, and measure results by length and quality of life, national human happiness, and, of course, jobs. We can do it. Let that bubble glow. Party time.
And that’s the way it is. That’s my opinion.
George Lundberg, MD, is editor-in-chief at Cancer Commons, president of the Lundberg Institute, executive advisor at Cureus, and a clinical professor of pathology at Northwestern University. Previously, he served as editor-in-chief of JAMA (including 10 specialty journals), American Medical News, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In my most recent column, “ ‘They All Laughed When I Spoke of Greedy Doctors,’ ” I attempted to provide a global understanding of some of the economic forces that have made American medicine what it is, how that happened, and why it is still happening.
I did not propose a fix. I have been proposing fixes for more than 30 years, on the pages of JAMA until 1999 and then for this news organization, most recently in 2019 with “Healthcare for All in a Land of Special Interests.”
Where you stand depends a lot on where you sit.
Is this good news or bad news? When William Hubbard was the dean of the University of Michigan School of Medicine in 1969, he said that “an academic medical center is the most efficient energy and resource trapping device that has ever been created” (personal communication, 1969).
To me as a faculty member of an academic medical center for many years, that was great news. We could grow faculty, erect buildings, take the best care of sick people, churn out research papers, mint new physicians and specialists, and get paid well in the process for doing “the Lord’s work.” What’s not to like? At that time, the proportion of the country’s gross national product expended for medical and health care was about 7%. And the predicted life span of an American at birth was 70.5 years.
Is this good news or bad news? In 2021, the proportion of our annual gross domestic product (GDP) consumed by health care was 18.3%, totaling $4.3 trillion, or $12,914 per person. For perspective, in 2021, the median income per capita was $37,638. Because quite a few Americans have very high incomes, the mean income per capita is much higher: $63,444. Predicted life span in 2021 was 76.4 years.
Thus, in a span of 53 years (1969-2022), only 5.9 years of life were gained per person born, for how many trillions of dollars expended? To me as a tax-paying citizen and payer of medical insurance premiums, that is bad news.
Is this good news or bad news? If we compare developed societies globally, our medical system does a whole lot of things very well indeed. But we spend a great deal more than any other country for health care and objectively achieve poorer outcomes. Thus, we are neither efficient nor effective. We keep a lot of workers very busy doing stuff, and they are generally well paid. As a worker, that’s good news; as a manager who values efficiency, it’s bad news indeed.
Is this good news or bad news? We’re the leader at finding money to pay people to do “health care work.” More Americans work in health care than any other field. In 2019, the United States employed some 21,000,000 people doing “health care and social assistance.” Among others, these occupations include physicians, dentists, dental hygienists and assistants, pharmacists, registered nurses, LVNs/LPNs, nursing aides, technologists and technicians, home health aides, respiratory therapists, occupational and speech therapists, social workers, childcare workers, and personal and home care aides. For a patient, parent, grandparent, and great-grandparent, it is good news to have all those folks available to take care of us when we need it.
So, while I have cringed at the frequent exposés from Roy Poses of what seem to me to be massive societal betrayals by American health care industry giants, it doesn’t have to be that way. Might it still be possible to do well while doing good?
A jobs program
Consider such common medical procedures as coronary artery stents or bypass grafts for stable angina (when optimal medical therapy is as good, or better than, and much less expensive); PSAs on asymptomatic men followed by unnecessary surgery for localized cancer; excess surgery for low back pain; and the jobs created by managing the people caught up in medical complications of the obesity epidemic.
Don’t forget the number of people employed simply to “follow the money” within our byzantine cockamamie medical billing system. In 2009, this prompted me to describe the bloated system as a “health care bubble” not unlike Enron, the submarket real estate financing debacle, or the dot-com boom and bust. I warned of the downside of bursting that bubble, particularly lost jobs.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provided health insurance to some 35 million Americans who had been uninsured. It retarded health care inflation. But it did nothing to trim administrative costs or very high pay for nonclinical executives, or shareholder profits in those companies that were for-profit, or drug and device prices. Without the support of all those groups, the ACA would never have passed Congress. The ACA has clearly been a mixed blessing.
If any large American constituency were ever serious about reducing the percentage of our GDP expended on health care, we have excellent ways to do that while improving the health and well-being of the American people. But remember, one person’s liability (unnecessary work) is another person’s asset (needed job).
The MBAization of medicine
Meanwhile, back at Dean Hubbard’s voracious academic medical center, the high intellect and driven nature of those who are attracted to medicine as a career has had other effects. The resulting organizations reflect not only the glorious calling of caring for the sick and the availability of lots of money to recruit and compensate leaders, but also the necessity to develop strong executive types who won’t be “eaten alive” by the high-powered workforce of demanding physicians and the surrounding environment.
Thus, it came as no great surprise that in its 2021 determination of America’s top 25 Best Large Employers, Forbes included five health care organizations and seven universities. Beating out such giants as NASA, Cisco, Microsoft, Netflix, and Google, the University of Alabama Birmingham Hospital was ranked first. Mayo Clinic and Yale University came in third and fifth, respectively, and at the other end of the list were Duke (23), MIT (24), and MD Anderson (25).
My goodness! Well done.
Yet, as a country attempting to be balanced, Warren Buffett’s descriptive entreaty on the 2021 failure of Haven, the Amazon-Chase-Berkshire Hathaway joint initiative, remains troubling. Calling upon Haven to change the U.S. health care system, Buffet said, “We learned a lot about the difficulty of changing around an industry that’s 17% of the GDP. We were fighting a tapeworm in the American economy, and the tapeworm won.” They had failed to tame the American health care cost beast.
I am on record as despising the “MBAization” of American medicine. Unfairly, I blamed a professional and technical discipline for what I considered misuse. I hereby repent and renounce my earlier condemnations.
Take it all over?
Here’s an idea: If you can’t beat them, join them.
Medical care is important, especially for acute illnesses and injuries, early cancer therapy, and many chronic conditions. But the real determinants of health writ large are social: wealth, education, housing, nutritious food, childcare, climate, clean air and water, meaningful employment, safety from violence, exercise schemes, vaccinations, and so on.
Why doesn’t the American medical-industrial complex simply bestow the label of “health care” on all health-related social determinants? Take it all over. Good “health care” jobs for everyone. Medical professionals will still be blamed for the low health quality and poor outcome scores, the main social determinants of health over which we have no control or influence.
Let that tapeworm grow to encompass all social determinants of health, and measure results by length and quality of life, national human happiness, and, of course, jobs. We can do it. Let that bubble glow. Party time.
And that’s the way it is. That’s my opinion.
George Lundberg, MD, is editor-in-chief at Cancer Commons, president of the Lundberg Institute, executive advisor at Cureus, and a clinical professor of pathology at Northwestern University. Previously, he served as editor-in-chief of JAMA (including 10 specialty journals), American Medical News, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Previously unknown viral families hide in the darnedest places
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
A 50-year-old White male presented with a 4- to 5-year history of progressively growing violaceous lesions on his left lower extremity
with scarce T-cells, classically presenting as rapidly progressive, plum-colored lesions on the lower extremities.1,2 CBCLs, with PCDLBCL-LT accounting for 4%, make up the minority of cutaneous lymphomas in the Western world.1-3 The leg type variant, typically demonstrating a female predominance and median age of onset in the 70s, is clinically aggressive and associated with a poorer prognosis, increased recurrence rate, and 40%-60% 5-year survival rate.1-5
Histologically, this variant demonstrates a diffuse sheet-like growth of enlarged atypical B-cells distinctively separated from the epidermis by a prominent grenz zone. Classic PCDLBCL-LT immunophenotype includes B-cell markers CD20 and IgM; triple expressor phenotype indicating c-MYC, BCL-2, and BCL-6 positivity; as well as CD10 negativity, lack of BCL-2 rearrangement, and presence of a positive MYD-88 molecular result.
Other characteristic histopathological findings include positivity for post-germinal markers IRF4/MUM-1 and FOXP-1, positivity for additional B-cell markers, including CD79 and PAX5, and negativity of t(14;18) (q32;21).1,3-5
This case is of significant interest as it falls within the approximately 10% of PCDLBCL-LT cases demonstrating weak to negative MUM-1 staining, in addition to its presentation in a younger male individual.
While MUM-1 positivity is common in this subtype, its presence, or lack thereof, should not be looked at in isolation when evaluating diagnostic criteria, nor has it been shown to have a statistically significant effect on survival rate – in contrast to factors like lesion location on the leg versus non-leg lesions, multiple lesions at diagnosis, and dissemination to other sites.2,6
PCDLBCL-LT can uncommonly present in non-leg locations and only 10% depict associated B-symptoms, such as fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, or lymphadenopathy.2,6 First-line treatment is with the R-CHOP chemotherapy regimen – consisting of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone – although radiotherapy is sometimes considered in patients with a single small lesion.1,2
Because of possible cutaneous involvement beyond the legs, common lack of systemic symptoms, and variable immunophenotypes, this case of MUM-1 negative PCDLBCL-LT highlights the importance of a clinicopathological approach to differentiate the subtypes of CBCLs, allowing for proper and individualized stratification of risk, prognosis, and treatment.
This case was submitted and written by Marlee Hill, BS, Michael Franzetti, MD, Jeffrey McBride, MD, and Allison Hood, MD, of the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. They also provided the photos. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2019;133(16):1703-14.
2. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2005;105(10):3768-85.
3. Sukswai N et al. Pathology. 2020;52(1):53-67.
4. Hristov AC. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(8):876-81.
5. Sokol L et al. Cancer Control. 2012;19(3):236-44.
6. Grange F et al. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1144-50.
with scarce T-cells, classically presenting as rapidly progressive, plum-colored lesions on the lower extremities.1,2 CBCLs, with PCDLBCL-LT accounting for 4%, make up the minority of cutaneous lymphomas in the Western world.1-3 The leg type variant, typically demonstrating a female predominance and median age of onset in the 70s, is clinically aggressive and associated with a poorer prognosis, increased recurrence rate, and 40%-60% 5-year survival rate.1-5
Histologically, this variant demonstrates a diffuse sheet-like growth of enlarged atypical B-cells distinctively separated from the epidermis by a prominent grenz zone. Classic PCDLBCL-LT immunophenotype includes B-cell markers CD20 and IgM; triple expressor phenotype indicating c-MYC, BCL-2, and BCL-6 positivity; as well as CD10 negativity, lack of BCL-2 rearrangement, and presence of a positive MYD-88 molecular result.
Other characteristic histopathological findings include positivity for post-germinal markers IRF4/MUM-1 and FOXP-1, positivity for additional B-cell markers, including CD79 and PAX5, and negativity of t(14;18) (q32;21).1,3-5
This case is of significant interest as it falls within the approximately 10% of PCDLBCL-LT cases demonstrating weak to negative MUM-1 staining, in addition to its presentation in a younger male individual.
While MUM-1 positivity is common in this subtype, its presence, or lack thereof, should not be looked at in isolation when evaluating diagnostic criteria, nor has it been shown to have a statistically significant effect on survival rate – in contrast to factors like lesion location on the leg versus non-leg lesions, multiple lesions at diagnosis, and dissemination to other sites.2,6
PCDLBCL-LT can uncommonly present in non-leg locations and only 10% depict associated B-symptoms, such as fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, or lymphadenopathy.2,6 First-line treatment is with the R-CHOP chemotherapy regimen – consisting of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone – although radiotherapy is sometimes considered in patients with a single small lesion.1,2
Because of possible cutaneous involvement beyond the legs, common lack of systemic symptoms, and variable immunophenotypes, this case of MUM-1 negative PCDLBCL-LT highlights the importance of a clinicopathological approach to differentiate the subtypes of CBCLs, allowing for proper and individualized stratification of risk, prognosis, and treatment.
This case was submitted and written by Marlee Hill, BS, Michael Franzetti, MD, Jeffrey McBride, MD, and Allison Hood, MD, of the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. They also provided the photos. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2019;133(16):1703-14.
2. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2005;105(10):3768-85.
3. Sukswai N et al. Pathology. 2020;52(1):53-67.
4. Hristov AC. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(8):876-81.
5. Sokol L et al. Cancer Control. 2012;19(3):236-44.
6. Grange F et al. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1144-50.
with scarce T-cells, classically presenting as rapidly progressive, plum-colored lesions on the lower extremities.1,2 CBCLs, with PCDLBCL-LT accounting for 4%, make up the minority of cutaneous lymphomas in the Western world.1-3 The leg type variant, typically demonstrating a female predominance and median age of onset in the 70s, is clinically aggressive and associated with a poorer prognosis, increased recurrence rate, and 40%-60% 5-year survival rate.1-5
Histologically, this variant demonstrates a diffuse sheet-like growth of enlarged atypical B-cells distinctively separated from the epidermis by a prominent grenz zone. Classic PCDLBCL-LT immunophenotype includes B-cell markers CD20 and IgM; triple expressor phenotype indicating c-MYC, BCL-2, and BCL-6 positivity; as well as CD10 negativity, lack of BCL-2 rearrangement, and presence of a positive MYD-88 molecular result.
Other characteristic histopathological findings include positivity for post-germinal markers IRF4/MUM-1 and FOXP-1, positivity for additional B-cell markers, including CD79 and PAX5, and negativity of t(14;18) (q32;21).1,3-5
This case is of significant interest as it falls within the approximately 10% of PCDLBCL-LT cases demonstrating weak to negative MUM-1 staining, in addition to its presentation in a younger male individual.
While MUM-1 positivity is common in this subtype, its presence, or lack thereof, should not be looked at in isolation when evaluating diagnostic criteria, nor has it been shown to have a statistically significant effect on survival rate – in contrast to factors like lesion location on the leg versus non-leg lesions, multiple lesions at diagnosis, and dissemination to other sites.2,6
PCDLBCL-LT can uncommonly present in non-leg locations and only 10% depict associated B-symptoms, such as fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, or lymphadenopathy.2,6 First-line treatment is with the R-CHOP chemotherapy regimen – consisting of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone – although radiotherapy is sometimes considered in patients with a single small lesion.1,2
Because of possible cutaneous involvement beyond the legs, common lack of systemic symptoms, and variable immunophenotypes, this case of MUM-1 negative PCDLBCL-LT highlights the importance of a clinicopathological approach to differentiate the subtypes of CBCLs, allowing for proper and individualized stratification of risk, prognosis, and treatment.
This case was submitted and written by Marlee Hill, BS, Michael Franzetti, MD, Jeffrey McBride, MD, and Allison Hood, MD, of the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. They also provided the photos. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2019;133(16):1703-14.
2. Willemze R et al. Blood. 2005;105(10):3768-85.
3. Sukswai N et al. Pathology. 2020;52(1):53-67.
4. Hristov AC. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(8):876-81.
5. Sokol L et al. Cancer Control. 2012;19(3):236-44.
6. Grange F et al. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1144-50.
There was no cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymphadenopathy.
New 46-week PsA data released for IL-17A inhibitor izokibep
out to 46 weeks, according to an announcement reporting some of the long-term data by the drug’s developer, Acelyrin.
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic designed to inhibit IL-17A that the company says has “high potency and the potential for robust tissue penetration due to its small molecular size, about one-tenth the size of a monoclonal antibody.”
“Patients want both rapid and meaningful improvement of their symptoms, as well as lasting – and ideally improving – resolution of disease over time. Building on the 16-week data for izokibep reported at EULAR and ACR [American College of Rheumatology] last year, the 46-week data now show not only continued but marked improvements over time in key areas of psoriatic arthritis including joint pain, skin psoriasis, and enthesitis,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center and clinical professor at the University of Washington, both in Seattle, and an investigator in the izokibep PsA program, said in the announcement.
The phase 2 trial tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active PsA. For inclusion in the trial, patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and an inadequate response to prior therapy including NSAIDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. At week 16, the placebo group transitioned to 80 mg izokibep every 2 weeks and the trial treatment period continued for up to 46 weeks.
The trial’s primary endpoint of a 50% or higher level of improvement in ACR response criteria (ACR 50) was achieved by 48% of those on the 40 mg dose at week 16 and by 50% at week 46. For the 80-mg group, this rate rose from 52% to 79%. In the group that went from placebo to 80 mg, the ACR 50 rose from 13% with placebo to 73% with izokibep at week 46.
Resolution of enthesitis, measured by the Leeds Enthesitis Index, among those on the 40 mg dose, was achieved by 63% at week 16 and 83% at week 46, and among those on the 80 mg dose, 88% at week 16 and 89% at week 46. Those on placebo who switched to 80 mg of izokibep at week 16 had an 80% rate of enthesitis resolution at week 46.
Total resolution of skin involvement – 100% clearance of psoriasis based on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) – was observed at 46 weeks in 50% of those on 40 mg, 71% of those on 80 mg, and 67% of those on 80 mg after week 16.
In its announcement, Acelyrin did not report withdrawal rates from the study after 16 weeks and through 46 weeks, although the statement said that izokibep “was generally well tolerated through 46 weeks, which is in line with previous trials of izokibep.” The most common adverse event was localized injection site reactions, with the majority graded mild to moderate in severity. They were generally the size of a quarter to half-dollar, and typically presented within the first few injections, after which they declined in incidence. In the trial, a case of vulvar cancer was determined to be potentially drug related, the company said.
Acelyrin is currently conducting a phase 2b/3 trial in PsA evaluating a range of doses, including significantly higher doses than in the phase 2 trial, that the company said “could potentially result in better ACR, PASI, and enthesitis resolution responses.”
The drug has been tested at doses up to 160 mg, in some cases for up to 3 years, in more than 400 patients with psoriasis, spondyloarthritis, noninfective uveitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
The full 46-week data from this trial will be presented at a future scientific meeting, according to the company.
out to 46 weeks, according to an announcement reporting some of the long-term data by the drug’s developer, Acelyrin.
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic designed to inhibit IL-17A that the company says has “high potency and the potential for robust tissue penetration due to its small molecular size, about one-tenth the size of a monoclonal antibody.”
“Patients want both rapid and meaningful improvement of their symptoms, as well as lasting – and ideally improving – resolution of disease over time. Building on the 16-week data for izokibep reported at EULAR and ACR [American College of Rheumatology] last year, the 46-week data now show not only continued but marked improvements over time in key areas of psoriatic arthritis including joint pain, skin psoriasis, and enthesitis,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center and clinical professor at the University of Washington, both in Seattle, and an investigator in the izokibep PsA program, said in the announcement.
The phase 2 trial tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active PsA. For inclusion in the trial, patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and an inadequate response to prior therapy including NSAIDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. At week 16, the placebo group transitioned to 80 mg izokibep every 2 weeks and the trial treatment period continued for up to 46 weeks.
The trial’s primary endpoint of a 50% or higher level of improvement in ACR response criteria (ACR 50) was achieved by 48% of those on the 40 mg dose at week 16 and by 50% at week 46. For the 80-mg group, this rate rose from 52% to 79%. In the group that went from placebo to 80 mg, the ACR 50 rose from 13% with placebo to 73% with izokibep at week 46.
Resolution of enthesitis, measured by the Leeds Enthesitis Index, among those on the 40 mg dose, was achieved by 63% at week 16 and 83% at week 46, and among those on the 80 mg dose, 88% at week 16 and 89% at week 46. Those on placebo who switched to 80 mg of izokibep at week 16 had an 80% rate of enthesitis resolution at week 46.
Total resolution of skin involvement – 100% clearance of psoriasis based on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) – was observed at 46 weeks in 50% of those on 40 mg, 71% of those on 80 mg, and 67% of those on 80 mg after week 16.
In its announcement, Acelyrin did not report withdrawal rates from the study after 16 weeks and through 46 weeks, although the statement said that izokibep “was generally well tolerated through 46 weeks, which is in line with previous trials of izokibep.” The most common adverse event was localized injection site reactions, with the majority graded mild to moderate in severity. They were generally the size of a quarter to half-dollar, and typically presented within the first few injections, after which they declined in incidence. In the trial, a case of vulvar cancer was determined to be potentially drug related, the company said.
Acelyrin is currently conducting a phase 2b/3 trial in PsA evaluating a range of doses, including significantly higher doses than in the phase 2 trial, that the company said “could potentially result in better ACR, PASI, and enthesitis resolution responses.”
The drug has been tested at doses up to 160 mg, in some cases for up to 3 years, in more than 400 patients with psoriasis, spondyloarthritis, noninfective uveitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
The full 46-week data from this trial will be presented at a future scientific meeting, according to the company.
out to 46 weeks, according to an announcement reporting some of the long-term data by the drug’s developer, Acelyrin.
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic designed to inhibit IL-17A that the company says has “high potency and the potential for robust tissue penetration due to its small molecular size, about one-tenth the size of a monoclonal antibody.”
“Patients want both rapid and meaningful improvement of their symptoms, as well as lasting – and ideally improving – resolution of disease over time. Building on the 16-week data for izokibep reported at EULAR and ACR [American College of Rheumatology] last year, the 46-week data now show not only continued but marked improvements over time in key areas of psoriatic arthritis including joint pain, skin psoriasis, and enthesitis,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center and clinical professor at the University of Washington, both in Seattle, and an investigator in the izokibep PsA program, said in the announcement.
The phase 2 trial tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active PsA. For inclusion in the trial, patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and an inadequate response to prior therapy including NSAIDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. At week 16, the placebo group transitioned to 80 mg izokibep every 2 weeks and the trial treatment period continued for up to 46 weeks.
The trial’s primary endpoint of a 50% or higher level of improvement in ACR response criteria (ACR 50) was achieved by 48% of those on the 40 mg dose at week 16 and by 50% at week 46. For the 80-mg group, this rate rose from 52% to 79%. In the group that went from placebo to 80 mg, the ACR 50 rose from 13% with placebo to 73% with izokibep at week 46.
Resolution of enthesitis, measured by the Leeds Enthesitis Index, among those on the 40 mg dose, was achieved by 63% at week 16 and 83% at week 46, and among those on the 80 mg dose, 88% at week 16 and 89% at week 46. Those on placebo who switched to 80 mg of izokibep at week 16 had an 80% rate of enthesitis resolution at week 46.
Total resolution of skin involvement – 100% clearance of psoriasis based on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) – was observed at 46 weeks in 50% of those on 40 mg, 71% of those on 80 mg, and 67% of those on 80 mg after week 16.
In its announcement, Acelyrin did not report withdrawal rates from the study after 16 weeks and through 46 weeks, although the statement said that izokibep “was generally well tolerated through 46 weeks, which is in line with previous trials of izokibep.” The most common adverse event was localized injection site reactions, with the majority graded mild to moderate in severity. They were generally the size of a quarter to half-dollar, and typically presented within the first few injections, after which they declined in incidence. In the trial, a case of vulvar cancer was determined to be potentially drug related, the company said.
Acelyrin is currently conducting a phase 2b/3 trial in PsA evaluating a range of doses, including significantly higher doses than in the phase 2 trial, that the company said “could potentially result in better ACR, PASI, and enthesitis resolution responses.”
The drug has been tested at doses up to 160 mg, in some cases for up to 3 years, in more than 400 patients with psoriasis, spondyloarthritis, noninfective uveitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
The full 46-week data from this trial will be presented at a future scientific meeting, according to the company.
The earlier baricitinib for severe alopecia areata is started, the better
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
AT AAD 2023