User login
Semaglutide ‘a new pathway’ to CVD risk reduction: SELECT
over the approximately 3-year follow-up in patients with overweight or obesity and cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“This is a very exciting set of results. I think it is going to have a big impact on a large number of people,” lead investigator A. Michael Lincoff, MD, vice chair for research in the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“And from a scientific standpoint, these data show that we now have a new pathway or a new modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease that we can use in our patients who have overweight or obesity,” he added.
The trial involved 17,604 patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and a body mass index of 27 kg/m2 or above (mean BMI was 33), who were randomly assigned to the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide, given by subcutaneous injection once weekly at a gradually escalating dose up to 2.4 mg daily by week 16, or placebo. The mean baseline glycated hemoglobin level was 5.8% and 66.4% of patients met the criteria for prediabetes.
Patients lost a mean of 9.4% of body weight over the first 2 years with semaglutide versus 0.88% with placebo.
The primary cardiovascular endpoint – a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke – was reduced significantly, with a hazard ratio of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.90; P < .001).
Death from cardiovascular causes, the first confirmatory secondary endpoint, showed a 15% reduction (HR, 0.85; P = .07) but this missed meeting criteria for statistical significance, and because of the hierarchical design of the trial, this meant that superiority testing was not performed for the remaining confirmatory secondary endpoints.
However, results showed reductions of around 20% for the heart failure composite endpoint and for all-cause mortality, with confidence intervals that did not cross 1.0, and directionally consistent effects were observed for all supportive secondary endpoints.
The HR for the heart failure composite endpoint was 0.82 (95% CI, 0.71-0.96), and the HR for death from any cause was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.71-0.93). Nonfatal MI was reduced by 28% (HR 0.72; 95% CI, 0.61-0.85).
The effects of semaglutide on the primary endpoint appeared to be similar across all prespecified subgroups.
Adverse events leading to discontinuation of treatment occurred in 16.6% in the semaglutide group, mostly gastrointestinal effects, and in 8.2% in the placebo group.
The trial results were presented by Dr. Lincoff at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association . They were also simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Lincoff explained that there is a growing pandemic of overweight and obesity worldwide with clear evidence for years that these conditions increase the risk of cardiovascular events – and yet there has been no evidence, until now, that any pharmacologic or lifestyle therapy can reduce the increased risk conferred by overweight/obesity.
“Patients in the trial were already taking standard of care therapies for other risk factors, such as hypertension and cholesterol, so this drug is giving additional benefit,” he said.
Dr. Lincoff believes these data will lead to a large increase in use of semaglutide, which is already available for the treatment of obesity and diabetes but can be difficult to get reimbursed.
“There is a lot of difficulty getting payors to pay for this drug for weight management. But with this new data from the SELECT trial there should be more willingness – at least in the population with a history of cardiovascular disease,” he commented. In diabetes, where it is already established that there is a cardiovascular risk reduction, it is easier to get these drugs reimbursed, he noted.
On the outcome data, Dr. Lincoff said he could not explain why cardiovascular death was not significantly reduced while all-cause mortality appeared to be cut more definitively.
“The cardiovascular death curves separated, then merged, then separated again. We don’t really know what is going on there. It may be that some deaths were misclassified. This trial was conducted through the COVID era and there may have been less information available on some patients because of that.”
But he added: “The all-cause mortality is more reassuring, as it doesn’t depend on classifying cause of death. Because of the design of the trial, we can’t formally claim a reduction in all-cause mortality, but the results do suggest there is an effect on this endpoint. And all the different types of cardiovascular events were similarly reduced in a consistent way, with similar effects seen across all subgroups. That is very reassuring.”
‘A new era’ for patients with obesity
Outside experts in the field were also impressed with the data.
Designated discussant of the trial at the AHA meeting, Ania Jastreboff, MD, associate professor medicine (endocrinology) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the SELECT trial was “a turning point in the treatment of obesity and a call to action.
“Now is the time to treat obesity to improve health outcomes in people with cardiovascular disease,” she said.
Dr. Jastreboff noted that high BMI was estimated to have accounted for 4 million deaths worldwide in 2015, two-thirds of which were caused by cardiovascular disease. And she presented data showing that U.S. individuals meeting the SELECT criteria increased from 4.3 million in 2011-12 to 6.6 million in 2017-18.
She highlighted one major limitation of the SELECT trial: it enrolled a low number of women (38%) and ethnic minorities, with only 12% of the trial population being Black.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, director of Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, described the SELECT results as “altogether a compelling package of data.”
“These results are even better than I had expected,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview. “There is a significant reduction in MI as I had anticipated, but additionally, there is a reduction in all-cause death. One can debate the statistics, though on a common-sense level, I think it is a real finding,” he noted.
“Given that MI, heart failure, nephropathy, and revascularization are all reduced, and even stroke is numerically lower, it makes sense that all-cause mortality would be reduced,” he said. “To me, apart from the GI side effects, this counts as a home run.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Cleveland Clinic’s Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, was similarly upbeat.
“These data prove what many of us have long suspected – that losing weight can reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. This is great news for patients living with obesity. The obesity epidemic is out of control,” he added. “We need to have therapies that improve cardiovascular outcomes caused by obesity and this shows that semaglutide can do that. I think this is the beginning of a whole new era for patients with obesity.”
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, called the results of SELECT “both intriguing and compelling. Certainly, these findings lend further support to the use of semaglutide in a much broader secondary prevention population of individuals with obesity.”
Christie Ballantyne, MD, director of the center for cardiometabolic disease prevention at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, described the SELECT study as “a landmark trial which will change the practice of medicine in regard to how we treat obesity.”
He compared it with the landmark 4S trial in 1994, the first study in the area of cholesterol lowering therapy to show a clear benefit in reducing cardiovascular events and total mortality, and “began a drastic change in the way that physicians approached treatment of cholesterol.”
On the more robust reduction in all-cause death, compared with cardiovascular death,
Dr. Ballantyne pointed out: “Adjudication of dead or alive is something that everyone gets right. In contrast, the cause of death is sometime difficult to ascertain. Most importantly, the benefit on total mortality also provides assurance that this therapy does not have some adverse effect on increasing noncardiovascular deaths.”
Gastrointestinal adverse effects
On the side effects seen with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff reported that 10% of patients in the semaglutide group discontinued treatment because of GI side effects versus 2% in the placebo arm. He said this was “an expected issue.”
“GI effects, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, are known side effects of this whole class of drugs. The dose is slowly escalated to manage these adverse effects but there will be a proportion of patients who can’t tolerate it, although the vast majority are able to continue.”
He noted that, while dose reduction was allowed, of the patients who were still on the drug at 2 years, 77% were on the full dose, and 23% were on a reduced dose.
Dr. Lincoff pointed out that there were no serious adverse events with semaglutide. “This is the largest database by far now on the drug with a long-term follow up and we didn’t see the emergence of any new safety signals, which is very reassuring.”
Dr. Nissen said the 16% rate of patients stopping the drug because of tolerability “is not a trivial number.”
He noted that the semaglutide dose used in this study was larger than that used in diabetes.
“They did this to try to achieve more weight loss but then you get more issues with tolerability. It’s a trade-off. If patients are experiencing adverse effects, the dose can be reduced, but then you will lose some effect. All the GLP-1 agonists have GI side effects – it’s part of the way that they work.”
Just weight loss or other actions too?
Speculating on the mechanism behind the reduction in cardiovascular events with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff does not think it is just weight reduction.
“The event curves start to diverge very soon after the start of the trial and yet the maximum weight loss doesn’t occur until about 65 weeks. I think something else is going on.”
In the paper, the researchers noted that GLP-1 agonists have been shown in animal studies to reduce inflammation, improve endothelial and left ventricular function, promote plaque stability, and decrease platelet aggregation. In this trial, semaglutide was associated with changes in multiple biomarkers of cardiovascular risk, including blood pressure, waist circumference, glycemic control, nephropathy, and levels of lipids and C-reactive protein.
Dr. Lincoff also pointed out that similar benefits were seen in patients with different levels of overweight, and in those who were prediabetic and those who weren’t, so benefit was not dependent on baseline BMI or glycated hemoglobin levels.
Dr. O’Donoghue agreed that other effects, as well as weight loss, could be involved. “The reduction in events with semaglutide appeared very early after initiation and far preceded the drug’s maximal effects on weight reduction. This might suggest that the drug offers other cardioprotective effects through pathways independent of weight loss. Certainly, semaglutide and the other GLP-1 agonists appear to attenuate inflammation, and the patterns of redistribution of adipose tissue may also be of interest.”
She also pointed out that the reduction in cardiovascular events appeared even earlier in this population of obese nondiabetic patients with cardiovascular disease than in prior studies of patients with diabetes. “It may suggest that there is particular benefit for this type of therapy in patients with an inflammatory milieu. I look forward to seeing further analyses to help tease apart the correlation between changes in inflammation, observed weight loss and cardiovascular benefit.”
Effect on clinical practice
With the majority of patients with cardiovascular disease being overweight, these results are obviously going to increase demand for semaglutide, but cost and availability are going to be an issue.
Dr. Bhatt noted that semaglutide is already very popular. “Weight loss drugs are somewhat different from other medications. I can spend 30 minutes trying to convince a patient to take a statin, but here people realize it’s going to cause weight loss and they come in asking for it even if they don’t strictly need it. I think it’s good to have cardiovascular outcome data because now at least for this population of patients, we have evidence to prescribe it.”
He agreed with Dr. Lincoff that these new data should encourage insurance companies to cover the drug, because in reducing cardiovascular events it should also improve downstream health care costs.
“It is providing clear cardiovascular and kidney benefit, so it is in the best interest to the health care system to fund this drug,” he said. “I hope insurers look at it rationally in this way, but they may also be frightened of the explosion of patients wanting this drug and now doctors wanting to prescribe it and how that would affect their shorter-term costs.”
Dr. Lincoff said it would not be easy to prioritize certain groups. “We couldn’t identify any subgroup who showed particularly more benefit than any others. But in the evolution of any therapy, there is a time period where it is in short supply and prohibitively expensive, then over time when there is some competition and pricing deals occur as more people are advocating for it, they become more available.”
‘A welcome treatment option’
In an editorial accompanying publication of the trial, Amit Khera, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Tiffany Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, noted that baseline risk factors such as LDL cholesterol (78 mg/dL) and systolic blood pressure (131 mm Hg) were not ideal in the semaglutide group in this trial, and they suggest that the benefits of semaglutide may be attenuated when these measures are better controlled.
But given that more than 20 million people in the United States have coronary artery disease, with the majority having overweight or obesity and only approximately 30% having concomitant diabetes, they said that, even in the context of well-controlled risk factors and very low LDL cholesterol levels, the residual risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in these persons is unacceptably high. “Thus, the SELECT trial provides a welcome treatment option that can be extended to millions of additional patients.”
However, the editorialists cautioned that semaglutide at current pricing comes with a significant cost to both patients and society, which makes this treatment inaccessible for many.
They added that intensive lifestyle interventions and bariatric surgery remain effective but underutilized options for obesity, and that the prevention of obesity before it develops should be the primary goal.
The SELECT trial was supported by Novo Nordisk, and several coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Lincoff is a consultant for Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Nissen are involved in a cardiovascular outcomes trial with a new investigational weight loss drug from Lilly. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Ballantyne are also investigators in a Novo Nordisk trial of a new anti-inflammatory drug.
over the approximately 3-year follow-up in patients with overweight or obesity and cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“This is a very exciting set of results. I think it is going to have a big impact on a large number of people,” lead investigator A. Michael Lincoff, MD, vice chair for research in the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“And from a scientific standpoint, these data show that we now have a new pathway or a new modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease that we can use in our patients who have overweight or obesity,” he added.
The trial involved 17,604 patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and a body mass index of 27 kg/m2 or above (mean BMI was 33), who were randomly assigned to the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide, given by subcutaneous injection once weekly at a gradually escalating dose up to 2.4 mg daily by week 16, or placebo. The mean baseline glycated hemoglobin level was 5.8% and 66.4% of patients met the criteria for prediabetes.
Patients lost a mean of 9.4% of body weight over the first 2 years with semaglutide versus 0.88% with placebo.
The primary cardiovascular endpoint – a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke – was reduced significantly, with a hazard ratio of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.90; P < .001).
Death from cardiovascular causes, the first confirmatory secondary endpoint, showed a 15% reduction (HR, 0.85; P = .07) but this missed meeting criteria for statistical significance, and because of the hierarchical design of the trial, this meant that superiority testing was not performed for the remaining confirmatory secondary endpoints.
However, results showed reductions of around 20% for the heart failure composite endpoint and for all-cause mortality, with confidence intervals that did not cross 1.0, and directionally consistent effects were observed for all supportive secondary endpoints.
The HR for the heart failure composite endpoint was 0.82 (95% CI, 0.71-0.96), and the HR for death from any cause was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.71-0.93). Nonfatal MI was reduced by 28% (HR 0.72; 95% CI, 0.61-0.85).
The effects of semaglutide on the primary endpoint appeared to be similar across all prespecified subgroups.
Adverse events leading to discontinuation of treatment occurred in 16.6% in the semaglutide group, mostly gastrointestinal effects, and in 8.2% in the placebo group.
The trial results were presented by Dr. Lincoff at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association . They were also simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Lincoff explained that there is a growing pandemic of overweight and obesity worldwide with clear evidence for years that these conditions increase the risk of cardiovascular events – and yet there has been no evidence, until now, that any pharmacologic or lifestyle therapy can reduce the increased risk conferred by overweight/obesity.
“Patients in the trial were already taking standard of care therapies for other risk factors, such as hypertension and cholesterol, so this drug is giving additional benefit,” he said.
Dr. Lincoff believes these data will lead to a large increase in use of semaglutide, which is already available for the treatment of obesity and diabetes but can be difficult to get reimbursed.
“There is a lot of difficulty getting payors to pay for this drug for weight management. But with this new data from the SELECT trial there should be more willingness – at least in the population with a history of cardiovascular disease,” he commented. In diabetes, where it is already established that there is a cardiovascular risk reduction, it is easier to get these drugs reimbursed, he noted.
On the outcome data, Dr. Lincoff said he could not explain why cardiovascular death was not significantly reduced while all-cause mortality appeared to be cut more definitively.
“The cardiovascular death curves separated, then merged, then separated again. We don’t really know what is going on there. It may be that some deaths were misclassified. This trial was conducted through the COVID era and there may have been less information available on some patients because of that.”
But he added: “The all-cause mortality is more reassuring, as it doesn’t depend on classifying cause of death. Because of the design of the trial, we can’t formally claim a reduction in all-cause mortality, but the results do suggest there is an effect on this endpoint. And all the different types of cardiovascular events were similarly reduced in a consistent way, with similar effects seen across all subgroups. That is very reassuring.”
‘A new era’ for patients with obesity
Outside experts in the field were also impressed with the data.
Designated discussant of the trial at the AHA meeting, Ania Jastreboff, MD, associate professor medicine (endocrinology) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the SELECT trial was “a turning point in the treatment of obesity and a call to action.
“Now is the time to treat obesity to improve health outcomes in people with cardiovascular disease,” she said.
Dr. Jastreboff noted that high BMI was estimated to have accounted for 4 million deaths worldwide in 2015, two-thirds of which were caused by cardiovascular disease. And she presented data showing that U.S. individuals meeting the SELECT criteria increased from 4.3 million in 2011-12 to 6.6 million in 2017-18.
She highlighted one major limitation of the SELECT trial: it enrolled a low number of women (38%) and ethnic minorities, with only 12% of the trial population being Black.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, director of Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, described the SELECT results as “altogether a compelling package of data.”
“These results are even better than I had expected,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview. “There is a significant reduction in MI as I had anticipated, but additionally, there is a reduction in all-cause death. One can debate the statistics, though on a common-sense level, I think it is a real finding,” he noted.
“Given that MI, heart failure, nephropathy, and revascularization are all reduced, and even stroke is numerically lower, it makes sense that all-cause mortality would be reduced,” he said. “To me, apart from the GI side effects, this counts as a home run.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Cleveland Clinic’s Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, was similarly upbeat.
“These data prove what many of us have long suspected – that losing weight can reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. This is great news for patients living with obesity. The obesity epidemic is out of control,” he added. “We need to have therapies that improve cardiovascular outcomes caused by obesity and this shows that semaglutide can do that. I think this is the beginning of a whole new era for patients with obesity.”
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, called the results of SELECT “both intriguing and compelling. Certainly, these findings lend further support to the use of semaglutide in a much broader secondary prevention population of individuals with obesity.”
Christie Ballantyne, MD, director of the center for cardiometabolic disease prevention at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, described the SELECT study as “a landmark trial which will change the practice of medicine in regard to how we treat obesity.”
He compared it with the landmark 4S trial in 1994, the first study in the area of cholesterol lowering therapy to show a clear benefit in reducing cardiovascular events and total mortality, and “began a drastic change in the way that physicians approached treatment of cholesterol.”
On the more robust reduction in all-cause death, compared with cardiovascular death,
Dr. Ballantyne pointed out: “Adjudication of dead or alive is something that everyone gets right. In contrast, the cause of death is sometime difficult to ascertain. Most importantly, the benefit on total mortality also provides assurance that this therapy does not have some adverse effect on increasing noncardiovascular deaths.”
Gastrointestinal adverse effects
On the side effects seen with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff reported that 10% of patients in the semaglutide group discontinued treatment because of GI side effects versus 2% in the placebo arm. He said this was “an expected issue.”
“GI effects, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, are known side effects of this whole class of drugs. The dose is slowly escalated to manage these adverse effects but there will be a proportion of patients who can’t tolerate it, although the vast majority are able to continue.”
He noted that, while dose reduction was allowed, of the patients who were still on the drug at 2 years, 77% were on the full dose, and 23% were on a reduced dose.
Dr. Lincoff pointed out that there were no serious adverse events with semaglutide. “This is the largest database by far now on the drug with a long-term follow up and we didn’t see the emergence of any new safety signals, which is very reassuring.”
Dr. Nissen said the 16% rate of patients stopping the drug because of tolerability “is not a trivial number.”
He noted that the semaglutide dose used in this study was larger than that used in diabetes.
“They did this to try to achieve more weight loss but then you get more issues with tolerability. It’s a trade-off. If patients are experiencing adverse effects, the dose can be reduced, but then you will lose some effect. All the GLP-1 agonists have GI side effects – it’s part of the way that they work.”
Just weight loss or other actions too?
Speculating on the mechanism behind the reduction in cardiovascular events with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff does not think it is just weight reduction.
“The event curves start to diverge very soon after the start of the trial and yet the maximum weight loss doesn’t occur until about 65 weeks. I think something else is going on.”
In the paper, the researchers noted that GLP-1 agonists have been shown in animal studies to reduce inflammation, improve endothelial and left ventricular function, promote plaque stability, and decrease platelet aggregation. In this trial, semaglutide was associated with changes in multiple biomarkers of cardiovascular risk, including blood pressure, waist circumference, glycemic control, nephropathy, and levels of lipids and C-reactive protein.
Dr. Lincoff also pointed out that similar benefits were seen in patients with different levels of overweight, and in those who were prediabetic and those who weren’t, so benefit was not dependent on baseline BMI or glycated hemoglobin levels.
Dr. O’Donoghue agreed that other effects, as well as weight loss, could be involved. “The reduction in events with semaglutide appeared very early after initiation and far preceded the drug’s maximal effects on weight reduction. This might suggest that the drug offers other cardioprotective effects through pathways independent of weight loss. Certainly, semaglutide and the other GLP-1 agonists appear to attenuate inflammation, and the patterns of redistribution of adipose tissue may also be of interest.”
She also pointed out that the reduction in cardiovascular events appeared even earlier in this population of obese nondiabetic patients with cardiovascular disease than in prior studies of patients with diabetes. “It may suggest that there is particular benefit for this type of therapy in patients with an inflammatory milieu. I look forward to seeing further analyses to help tease apart the correlation between changes in inflammation, observed weight loss and cardiovascular benefit.”
Effect on clinical practice
With the majority of patients with cardiovascular disease being overweight, these results are obviously going to increase demand for semaglutide, but cost and availability are going to be an issue.
Dr. Bhatt noted that semaglutide is already very popular. “Weight loss drugs are somewhat different from other medications. I can spend 30 minutes trying to convince a patient to take a statin, but here people realize it’s going to cause weight loss and they come in asking for it even if they don’t strictly need it. I think it’s good to have cardiovascular outcome data because now at least for this population of patients, we have evidence to prescribe it.”
He agreed with Dr. Lincoff that these new data should encourage insurance companies to cover the drug, because in reducing cardiovascular events it should also improve downstream health care costs.
“It is providing clear cardiovascular and kidney benefit, so it is in the best interest to the health care system to fund this drug,” he said. “I hope insurers look at it rationally in this way, but they may also be frightened of the explosion of patients wanting this drug and now doctors wanting to prescribe it and how that would affect their shorter-term costs.”
Dr. Lincoff said it would not be easy to prioritize certain groups. “We couldn’t identify any subgroup who showed particularly more benefit than any others. But in the evolution of any therapy, there is a time period where it is in short supply and prohibitively expensive, then over time when there is some competition and pricing deals occur as more people are advocating for it, they become more available.”
‘A welcome treatment option’
In an editorial accompanying publication of the trial, Amit Khera, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Tiffany Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, noted that baseline risk factors such as LDL cholesterol (78 mg/dL) and systolic blood pressure (131 mm Hg) were not ideal in the semaglutide group in this trial, and they suggest that the benefits of semaglutide may be attenuated when these measures are better controlled.
But given that more than 20 million people in the United States have coronary artery disease, with the majority having overweight or obesity and only approximately 30% having concomitant diabetes, they said that, even in the context of well-controlled risk factors and very low LDL cholesterol levels, the residual risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in these persons is unacceptably high. “Thus, the SELECT trial provides a welcome treatment option that can be extended to millions of additional patients.”
However, the editorialists cautioned that semaglutide at current pricing comes with a significant cost to both patients and society, which makes this treatment inaccessible for many.
They added that intensive lifestyle interventions and bariatric surgery remain effective but underutilized options for obesity, and that the prevention of obesity before it develops should be the primary goal.
The SELECT trial was supported by Novo Nordisk, and several coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Lincoff is a consultant for Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Nissen are involved in a cardiovascular outcomes trial with a new investigational weight loss drug from Lilly. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Ballantyne are also investigators in a Novo Nordisk trial of a new anti-inflammatory drug.
over the approximately 3-year follow-up in patients with overweight or obesity and cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“This is a very exciting set of results. I think it is going to have a big impact on a large number of people,” lead investigator A. Michael Lincoff, MD, vice chair for research in the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“And from a scientific standpoint, these data show that we now have a new pathway or a new modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease that we can use in our patients who have overweight or obesity,” he added.
The trial involved 17,604 patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and a body mass index of 27 kg/m2 or above (mean BMI was 33), who were randomly assigned to the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide, given by subcutaneous injection once weekly at a gradually escalating dose up to 2.4 mg daily by week 16, or placebo. The mean baseline glycated hemoglobin level was 5.8% and 66.4% of patients met the criteria for prediabetes.
Patients lost a mean of 9.4% of body weight over the first 2 years with semaglutide versus 0.88% with placebo.
The primary cardiovascular endpoint – a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke – was reduced significantly, with a hazard ratio of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.90; P < .001).
Death from cardiovascular causes, the first confirmatory secondary endpoint, showed a 15% reduction (HR, 0.85; P = .07) but this missed meeting criteria for statistical significance, and because of the hierarchical design of the trial, this meant that superiority testing was not performed for the remaining confirmatory secondary endpoints.
However, results showed reductions of around 20% for the heart failure composite endpoint and for all-cause mortality, with confidence intervals that did not cross 1.0, and directionally consistent effects were observed for all supportive secondary endpoints.
The HR for the heart failure composite endpoint was 0.82 (95% CI, 0.71-0.96), and the HR for death from any cause was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.71-0.93). Nonfatal MI was reduced by 28% (HR 0.72; 95% CI, 0.61-0.85).
The effects of semaglutide on the primary endpoint appeared to be similar across all prespecified subgroups.
Adverse events leading to discontinuation of treatment occurred in 16.6% in the semaglutide group, mostly gastrointestinal effects, and in 8.2% in the placebo group.
The trial results were presented by Dr. Lincoff at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association . They were also simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Lincoff explained that there is a growing pandemic of overweight and obesity worldwide with clear evidence for years that these conditions increase the risk of cardiovascular events – and yet there has been no evidence, until now, that any pharmacologic or lifestyle therapy can reduce the increased risk conferred by overweight/obesity.
“Patients in the trial were already taking standard of care therapies for other risk factors, such as hypertension and cholesterol, so this drug is giving additional benefit,” he said.
Dr. Lincoff believes these data will lead to a large increase in use of semaglutide, which is already available for the treatment of obesity and diabetes but can be difficult to get reimbursed.
“There is a lot of difficulty getting payors to pay for this drug for weight management. But with this new data from the SELECT trial there should be more willingness – at least in the population with a history of cardiovascular disease,” he commented. In diabetes, where it is already established that there is a cardiovascular risk reduction, it is easier to get these drugs reimbursed, he noted.
On the outcome data, Dr. Lincoff said he could not explain why cardiovascular death was not significantly reduced while all-cause mortality appeared to be cut more definitively.
“The cardiovascular death curves separated, then merged, then separated again. We don’t really know what is going on there. It may be that some deaths were misclassified. This trial was conducted through the COVID era and there may have been less information available on some patients because of that.”
But he added: “The all-cause mortality is more reassuring, as it doesn’t depend on classifying cause of death. Because of the design of the trial, we can’t formally claim a reduction in all-cause mortality, but the results do suggest there is an effect on this endpoint. And all the different types of cardiovascular events were similarly reduced in a consistent way, with similar effects seen across all subgroups. That is very reassuring.”
‘A new era’ for patients with obesity
Outside experts in the field were also impressed with the data.
Designated discussant of the trial at the AHA meeting, Ania Jastreboff, MD, associate professor medicine (endocrinology) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said the SELECT trial was “a turning point in the treatment of obesity and a call to action.
“Now is the time to treat obesity to improve health outcomes in people with cardiovascular disease,” she said.
Dr. Jastreboff noted that high BMI was estimated to have accounted for 4 million deaths worldwide in 2015, two-thirds of which were caused by cardiovascular disease. And she presented data showing that U.S. individuals meeting the SELECT criteria increased from 4.3 million in 2011-12 to 6.6 million in 2017-18.
She highlighted one major limitation of the SELECT trial: it enrolled a low number of women (38%) and ethnic minorities, with only 12% of the trial population being Black.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, director of Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, described the SELECT results as “altogether a compelling package of data.”
“These results are even better than I had expected,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview. “There is a significant reduction in MI as I had anticipated, but additionally, there is a reduction in all-cause death. One can debate the statistics, though on a common-sense level, I think it is a real finding,” he noted.
“Given that MI, heart failure, nephropathy, and revascularization are all reduced, and even stroke is numerically lower, it makes sense that all-cause mortality would be reduced,” he said. “To me, apart from the GI side effects, this counts as a home run.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Cleveland Clinic’s Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, was similarly upbeat.
“These data prove what many of us have long suspected – that losing weight can reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. This is great news for patients living with obesity. The obesity epidemic is out of control,” he added. “We need to have therapies that improve cardiovascular outcomes caused by obesity and this shows that semaglutide can do that. I think this is the beginning of a whole new era for patients with obesity.”
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, called the results of SELECT “both intriguing and compelling. Certainly, these findings lend further support to the use of semaglutide in a much broader secondary prevention population of individuals with obesity.”
Christie Ballantyne, MD, director of the center for cardiometabolic disease prevention at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, described the SELECT study as “a landmark trial which will change the practice of medicine in regard to how we treat obesity.”
He compared it with the landmark 4S trial in 1994, the first study in the area of cholesterol lowering therapy to show a clear benefit in reducing cardiovascular events and total mortality, and “began a drastic change in the way that physicians approached treatment of cholesterol.”
On the more robust reduction in all-cause death, compared with cardiovascular death,
Dr. Ballantyne pointed out: “Adjudication of dead or alive is something that everyone gets right. In contrast, the cause of death is sometime difficult to ascertain. Most importantly, the benefit on total mortality also provides assurance that this therapy does not have some adverse effect on increasing noncardiovascular deaths.”
Gastrointestinal adverse effects
On the side effects seen with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff reported that 10% of patients in the semaglutide group discontinued treatment because of GI side effects versus 2% in the placebo arm. He said this was “an expected issue.”
“GI effects, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, are known side effects of this whole class of drugs. The dose is slowly escalated to manage these adverse effects but there will be a proportion of patients who can’t tolerate it, although the vast majority are able to continue.”
He noted that, while dose reduction was allowed, of the patients who were still on the drug at 2 years, 77% were on the full dose, and 23% were on a reduced dose.
Dr. Lincoff pointed out that there were no serious adverse events with semaglutide. “This is the largest database by far now on the drug with a long-term follow up and we didn’t see the emergence of any new safety signals, which is very reassuring.”
Dr. Nissen said the 16% rate of patients stopping the drug because of tolerability “is not a trivial number.”
He noted that the semaglutide dose used in this study was larger than that used in diabetes.
“They did this to try to achieve more weight loss but then you get more issues with tolerability. It’s a trade-off. If patients are experiencing adverse effects, the dose can be reduced, but then you will lose some effect. All the GLP-1 agonists have GI side effects – it’s part of the way that they work.”
Just weight loss or other actions too?
Speculating on the mechanism behind the reduction in cardiovascular events with semaglutide, Dr. Lincoff does not think it is just weight reduction.
“The event curves start to diverge very soon after the start of the trial and yet the maximum weight loss doesn’t occur until about 65 weeks. I think something else is going on.”
In the paper, the researchers noted that GLP-1 agonists have been shown in animal studies to reduce inflammation, improve endothelial and left ventricular function, promote plaque stability, and decrease platelet aggregation. In this trial, semaglutide was associated with changes in multiple biomarkers of cardiovascular risk, including blood pressure, waist circumference, glycemic control, nephropathy, and levels of lipids and C-reactive protein.
Dr. Lincoff also pointed out that similar benefits were seen in patients with different levels of overweight, and in those who were prediabetic and those who weren’t, so benefit was not dependent on baseline BMI or glycated hemoglobin levels.
Dr. O’Donoghue agreed that other effects, as well as weight loss, could be involved. “The reduction in events with semaglutide appeared very early after initiation and far preceded the drug’s maximal effects on weight reduction. This might suggest that the drug offers other cardioprotective effects through pathways independent of weight loss. Certainly, semaglutide and the other GLP-1 agonists appear to attenuate inflammation, and the patterns of redistribution of adipose tissue may also be of interest.”
She also pointed out that the reduction in cardiovascular events appeared even earlier in this population of obese nondiabetic patients with cardiovascular disease than in prior studies of patients with diabetes. “It may suggest that there is particular benefit for this type of therapy in patients with an inflammatory milieu. I look forward to seeing further analyses to help tease apart the correlation between changes in inflammation, observed weight loss and cardiovascular benefit.”
Effect on clinical practice
With the majority of patients with cardiovascular disease being overweight, these results are obviously going to increase demand for semaglutide, but cost and availability are going to be an issue.
Dr. Bhatt noted that semaglutide is already very popular. “Weight loss drugs are somewhat different from other medications. I can spend 30 minutes trying to convince a patient to take a statin, but here people realize it’s going to cause weight loss and they come in asking for it even if they don’t strictly need it. I think it’s good to have cardiovascular outcome data because now at least for this population of patients, we have evidence to prescribe it.”
He agreed with Dr. Lincoff that these new data should encourage insurance companies to cover the drug, because in reducing cardiovascular events it should also improve downstream health care costs.
“It is providing clear cardiovascular and kidney benefit, so it is in the best interest to the health care system to fund this drug,” he said. “I hope insurers look at it rationally in this way, but they may also be frightened of the explosion of patients wanting this drug and now doctors wanting to prescribe it and how that would affect their shorter-term costs.”
Dr. Lincoff said it would not be easy to prioritize certain groups. “We couldn’t identify any subgroup who showed particularly more benefit than any others. But in the evolution of any therapy, there is a time period where it is in short supply and prohibitively expensive, then over time when there is some competition and pricing deals occur as more people are advocating for it, they become more available.”
‘A welcome treatment option’
In an editorial accompanying publication of the trial, Amit Khera, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Tiffany Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, noted that baseline risk factors such as LDL cholesterol (78 mg/dL) and systolic blood pressure (131 mm Hg) were not ideal in the semaglutide group in this trial, and they suggest that the benefits of semaglutide may be attenuated when these measures are better controlled.
But given that more than 20 million people in the United States have coronary artery disease, with the majority having overweight or obesity and only approximately 30% having concomitant diabetes, they said that, even in the context of well-controlled risk factors and very low LDL cholesterol levels, the residual risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in these persons is unacceptably high. “Thus, the SELECT trial provides a welcome treatment option that can be extended to millions of additional patients.”
However, the editorialists cautioned that semaglutide at current pricing comes with a significant cost to both patients and society, which makes this treatment inaccessible for many.
They added that intensive lifestyle interventions and bariatric surgery remain effective but underutilized options for obesity, and that the prevention of obesity before it develops should be the primary goal.
The SELECT trial was supported by Novo Nordisk, and several coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Lincoff is a consultant for Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Nissen are involved in a cardiovascular outcomes trial with a new investigational weight loss drug from Lilly. Dr. Bhatt and Dr. Ballantyne are also investigators in a Novo Nordisk trial of a new anti-inflammatory drug.
FROM AHA 2023
Angioplasty finally proven beneficial in stable angina: ORBITA-2
PHILADELPHIA – Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) reduces angina frequency, increases exercise capacity, and improves quality of life, results of a placebo-controlled, randomized trial show, confirming advantages that have never before been proven.
reported Christopher A. Rajkumar, MBBS, an interventional cardiology registrar at the Imperial College Healthcare Trust, London.
Results of the trial, ORBITA-2, were presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Symptom relief has long been a justification for PCI in patients with stable CAD, but the evidence has been derived from uncontrolled studies, Dr. Rajkumar said. However, the first ORBITA trial, which was also placebo controlled and randomized, failed to show benefit.
Dr. Rajkumar acknowledged that the benefit of PCI in ORBITA-2 was lower than previously reported in nonrandomized trials. He also noted that 59% of patients still had at least some angina symptoms following PCI.
Even though ORBITA-2 proves that PCI is better than no PCI, he agreed that well-informed patients, such as those who wish to avoid an invasive procedure, might still reasonably select antianginal medication over PCI. Current guidelines recommend PCI for patients with refractory angina despite medical therapy.
While Dr. Rajkumar was unwilling to speculate on how these data might change guidelines, he did say that patients with stable CAD and angina “now have a choice of two first-line evidence-based pathways.”
‘Remarkable’ trial
“ORBITA 2 is a rather remarkable trial because my surgical colleagues have been asking me for many decades whether PCI actually works,” said Martin B. Leon, MD, professor of medicine, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “Now I can say with confidence on the basis of a placebo-controlled trial that PCI certainly does have a favorable impact in patients with documented angina, severe coronary stenosis, and demonstrated ischemia.”
The key enrollment criteria for ORBITA-2 were angina, severe coronary stenosis in at least one vessel, and ischemia on stress imaging or invasive physiology. Unlike the previous ORBITA trial, which was limited to single-vessel disease and did not require objective evidence of ischemia, ORBITA 2 employed change in angina, rather than improved exercise capacity, as its primary endpoint.
Relative to sham PCI, patients randomly assigned to an interventional procedure had a more than twofold increase in the odds ratio of improved angina control (OR, 2.2; P < .001) based on a patient scoring system that captured angina symptoms as well as angina medication use on a smartphone application.
The advantage of PCI over sham PCI was also significant for all secondary outcomes. These included a nearly fourfold greater (OR, 3.76; P < .001) likelihood of improvement in the Canadian Cardiovascular Society angina grade and a 1-minute increase (from 10 min. 40 seconds to 11 min. 40 seconds) in treadmill exercise time (P = .008).
On quality of life measured with the self-assessment questionnaire and the EQ-5D-5L, almost all endpoints were highly statistically significant in favor of PCI (typically on the level of P < .001).
The study had a bold design: At enrollment patients stopped all antianginal medications to undergo dobutamine echocardiography and other baseline tests. They were stopped again 2 weeks later, when patients were randomized.
With a study protocol that enrolled patients off medication, “we intentionally diverged from the clinical guidelines,” Dr. Rajkumar said.
Of the 439 patients enrolled, 301 were randomly assigned at the end of the 2-week period, when patients were already sedated. Control patients remained sedated for at least 15 minutes. All 151 of those randomized to PCI and the 150 control patients were available for the intent-to-treat analysis at the end of 12 weeks.
The novel angina symptom burden score was created from daily angina episodes and units of daily antianginal medication captured on the smartphone app. On an ordinal scale, a score of 0 on any given day represented no anginal symptoms and no antianginal medication.
As angina severity or medication use increased, it raised the daily scores. If there was unacceptable angina (requiring the patient to be removed from the blind), acute coronary syndrome, or death, it produced the highest scores, which reached a maximum of 79.
The favorable OR for a lower symptom burden in the PCI group reflected a relative reduction in angina observed the first day after the procedure. Over the entire follow-up, more patients in the PCI group had an angina score of 0 and more of those who had angina did not take antianginal medications.
This objective evidence that PCI reduces symptoms and improves quality of life in patients with angina and stable CAD was met at the AHA late-breaking session with a sustained ovation.
ORBITA-2 addresses ORBITA criticisms
Connie N. Hess, MD, the AHA-invited discussant and an interventional cardiologist at the University of Colorado Medicine, Aurora, provided perspective on the differences between ORBITA 2 and ORBITA, which she said “addressed a fundamentally different hypothesis” by focusing on angina rather than exercise capacity.
Of the criticisms of the original ORBITA, which Dr. Hess noted was the first sham-controlled PCI trial ever conducted in stable CAD, one is that patients with multivessel disease were excluded, another was that objectively proven ischemia was not required, and a third was that the study of 6 weeks had a short duration.
“ORBITA 2 addressed many of these concerns,” Dr. Hess said, but, when noting that 80% of patients in the newer trial still had single vessel disease, she questioned whether the true effect of PCI for improving symptoms might still be underestimated.
ORBITA-2 was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Imperial Biomedical Research Centre, the Medical Research Council, NIHR, the British Heart Foundation, Philips, and St. Mary’s Coronary Flow Trust. Dr. Rajkumar reported relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leon reported financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Anteris, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Foldax, and Medtronic. Dr. Hess has financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, but none related specifically to this presentation.
PHILADELPHIA – Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) reduces angina frequency, increases exercise capacity, and improves quality of life, results of a placebo-controlled, randomized trial show, confirming advantages that have never before been proven.
reported Christopher A. Rajkumar, MBBS, an interventional cardiology registrar at the Imperial College Healthcare Trust, London.
Results of the trial, ORBITA-2, were presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Symptom relief has long been a justification for PCI in patients with stable CAD, but the evidence has been derived from uncontrolled studies, Dr. Rajkumar said. However, the first ORBITA trial, which was also placebo controlled and randomized, failed to show benefit.
Dr. Rajkumar acknowledged that the benefit of PCI in ORBITA-2 was lower than previously reported in nonrandomized trials. He also noted that 59% of patients still had at least some angina symptoms following PCI.
Even though ORBITA-2 proves that PCI is better than no PCI, he agreed that well-informed patients, such as those who wish to avoid an invasive procedure, might still reasonably select antianginal medication over PCI. Current guidelines recommend PCI for patients with refractory angina despite medical therapy.
While Dr. Rajkumar was unwilling to speculate on how these data might change guidelines, he did say that patients with stable CAD and angina “now have a choice of two first-line evidence-based pathways.”
‘Remarkable’ trial
“ORBITA 2 is a rather remarkable trial because my surgical colleagues have been asking me for many decades whether PCI actually works,” said Martin B. Leon, MD, professor of medicine, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “Now I can say with confidence on the basis of a placebo-controlled trial that PCI certainly does have a favorable impact in patients with documented angina, severe coronary stenosis, and demonstrated ischemia.”
The key enrollment criteria for ORBITA-2 were angina, severe coronary stenosis in at least one vessel, and ischemia on stress imaging or invasive physiology. Unlike the previous ORBITA trial, which was limited to single-vessel disease and did not require objective evidence of ischemia, ORBITA 2 employed change in angina, rather than improved exercise capacity, as its primary endpoint.
Relative to sham PCI, patients randomly assigned to an interventional procedure had a more than twofold increase in the odds ratio of improved angina control (OR, 2.2; P < .001) based on a patient scoring system that captured angina symptoms as well as angina medication use on a smartphone application.
The advantage of PCI over sham PCI was also significant for all secondary outcomes. These included a nearly fourfold greater (OR, 3.76; P < .001) likelihood of improvement in the Canadian Cardiovascular Society angina grade and a 1-minute increase (from 10 min. 40 seconds to 11 min. 40 seconds) in treadmill exercise time (P = .008).
On quality of life measured with the self-assessment questionnaire and the EQ-5D-5L, almost all endpoints were highly statistically significant in favor of PCI (typically on the level of P < .001).
The study had a bold design: At enrollment patients stopped all antianginal medications to undergo dobutamine echocardiography and other baseline tests. They were stopped again 2 weeks later, when patients were randomized.
With a study protocol that enrolled patients off medication, “we intentionally diverged from the clinical guidelines,” Dr. Rajkumar said.
Of the 439 patients enrolled, 301 were randomly assigned at the end of the 2-week period, when patients were already sedated. Control patients remained sedated for at least 15 minutes. All 151 of those randomized to PCI and the 150 control patients were available for the intent-to-treat analysis at the end of 12 weeks.
The novel angina symptom burden score was created from daily angina episodes and units of daily antianginal medication captured on the smartphone app. On an ordinal scale, a score of 0 on any given day represented no anginal symptoms and no antianginal medication.
As angina severity or medication use increased, it raised the daily scores. If there was unacceptable angina (requiring the patient to be removed from the blind), acute coronary syndrome, or death, it produced the highest scores, which reached a maximum of 79.
The favorable OR for a lower symptom burden in the PCI group reflected a relative reduction in angina observed the first day after the procedure. Over the entire follow-up, more patients in the PCI group had an angina score of 0 and more of those who had angina did not take antianginal medications.
This objective evidence that PCI reduces symptoms and improves quality of life in patients with angina and stable CAD was met at the AHA late-breaking session with a sustained ovation.
ORBITA-2 addresses ORBITA criticisms
Connie N. Hess, MD, the AHA-invited discussant and an interventional cardiologist at the University of Colorado Medicine, Aurora, provided perspective on the differences between ORBITA 2 and ORBITA, which she said “addressed a fundamentally different hypothesis” by focusing on angina rather than exercise capacity.
Of the criticisms of the original ORBITA, which Dr. Hess noted was the first sham-controlled PCI trial ever conducted in stable CAD, one is that patients with multivessel disease were excluded, another was that objectively proven ischemia was not required, and a third was that the study of 6 weeks had a short duration.
“ORBITA 2 addressed many of these concerns,” Dr. Hess said, but, when noting that 80% of patients in the newer trial still had single vessel disease, she questioned whether the true effect of PCI for improving symptoms might still be underestimated.
ORBITA-2 was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Imperial Biomedical Research Centre, the Medical Research Council, NIHR, the British Heart Foundation, Philips, and St. Mary’s Coronary Flow Trust. Dr. Rajkumar reported relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leon reported financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Anteris, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Foldax, and Medtronic. Dr. Hess has financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, but none related specifically to this presentation.
PHILADELPHIA – Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) reduces angina frequency, increases exercise capacity, and improves quality of life, results of a placebo-controlled, randomized trial show, confirming advantages that have never before been proven.
reported Christopher A. Rajkumar, MBBS, an interventional cardiology registrar at the Imperial College Healthcare Trust, London.
Results of the trial, ORBITA-2, were presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Symptom relief has long been a justification for PCI in patients with stable CAD, but the evidence has been derived from uncontrolled studies, Dr. Rajkumar said. However, the first ORBITA trial, which was also placebo controlled and randomized, failed to show benefit.
Dr. Rajkumar acknowledged that the benefit of PCI in ORBITA-2 was lower than previously reported in nonrandomized trials. He also noted that 59% of patients still had at least some angina symptoms following PCI.
Even though ORBITA-2 proves that PCI is better than no PCI, he agreed that well-informed patients, such as those who wish to avoid an invasive procedure, might still reasonably select antianginal medication over PCI. Current guidelines recommend PCI for patients with refractory angina despite medical therapy.
While Dr. Rajkumar was unwilling to speculate on how these data might change guidelines, he did say that patients with stable CAD and angina “now have a choice of two first-line evidence-based pathways.”
‘Remarkable’ trial
“ORBITA 2 is a rather remarkable trial because my surgical colleagues have been asking me for many decades whether PCI actually works,” said Martin B. Leon, MD, professor of medicine, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. “Now I can say with confidence on the basis of a placebo-controlled trial that PCI certainly does have a favorable impact in patients with documented angina, severe coronary stenosis, and demonstrated ischemia.”
The key enrollment criteria for ORBITA-2 were angina, severe coronary stenosis in at least one vessel, and ischemia on stress imaging or invasive physiology. Unlike the previous ORBITA trial, which was limited to single-vessel disease and did not require objective evidence of ischemia, ORBITA 2 employed change in angina, rather than improved exercise capacity, as its primary endpoint.
Relative to sham PCI, patients randomly assigned to an interventional procedure had a more than twofold increase in the odds ratio of improved angina control (OR, 2.2; P < .001) based on a patient scoring system that captured angina symptoms as well as angina medication use on a smartphone application.
The advantage of PCI over sham PCI was also significant for all secondary outcomes. These included a nearly fourfold greater (OR, 3.76; P < .001) likelihood of improvement in the Canadian Cardiovascular Society angina grade and a 1-minute increase (from 10 min. 40 seconds to 11 min. 40 seconds) in treadmill exercise time (P = .008).
On quality of life measured with the self-assessment questionnaire and the EQ-5D-5L, almost all endpoints were highly statistically significant in favor of PCI (typically on the level of P < .001).
The study had a bold design: At enrollment patients stopped all antianginal medications to undergo dobutamine echocardiography and other baseline tests. They were stopped again 2 weeks later, when patients were randomized.
With a study protocol that enrolled patients off medication, “we intentionally diverged from the clinical guidelines,” Dr. Rajkumar said.
Of the 439 patients enrolled, 301 were randomly assigned at the end of the 2-week period, when patients were already sedated. Control patients remained sedated for at least 15 minutes. All 151 of those randomized to PCI and the 150 control patients were available for the intent-to-treat analysis at the end of 12 weeks.
The novel angina symptom burden score was created from daily angina episodes and units of daily antianginal medication captured on the smartphone app. On an ordinal scale, a score of 0 on any given day represented no anginal symptoms and no antianginal medication.
As angina severity or medication use increased, it raised the daily scores. If there was unacceptable angina (requiring the patient to be removed from the blind), acute coronary syndrome, or death, it produced the highest scores, which reached a maximum of 79.
The favorable OR for a lower symptom burden in the PCI group reflected a relative reduction in angina observed the first day after the procedure. Over the entire follow-up, more patients in the PCI group had an angina score of 0 and more of those who had angina did not take antianginal medications.
This objective evidence that PCI reduces symptoms and improves quality of life in patients with angina and stable CAD was met at the AHA late-breaking session with a sustained ovation.
ORBITA-2 addresses ORBITA criticisms
Connie N. Hess, MD, the AHA-invited discussant and an interventional cardiologist at the University of Colorado Medicine, Aurora, provided perspective on the differences between ORBITA 2 and ORBITA, which she said “addressed a fundamentally different hypothesis” by focusing on angina rather than exercise capacity.
Of the criticisms of the original ORBITA, which Dr. Hess noted was the first sham-controlled PCI trial ever conducted in stable CAD, one is that patients with multivessel disease were excluded, another was that objectively proven ischemia was not required, and a third was that the study of 6 weeks had a short duration.
“ORBITA 2 addressed many of these concerns,” Dr. Hess said, but, when noting that 80% of patients in the newer trial still had single vessel disease, she questioned whether the true effect of PCI for improving symptoms might still be underestimated.
ORBITA-2 was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Imperial Biomedical Research Centre, the Medical Research Council, NIHR, the British Heart Foundation, Philips, and St. Mary’s Coronary Flow Trust. Dr. Rajkumar reported relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leon reported financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Anteris, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Foldax, and Medtronic. Dr. Hess has financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, but none related specifically to this presentation.
AT AHA 2023
In MI with anemia, results may favor liberal transfusion: MINT
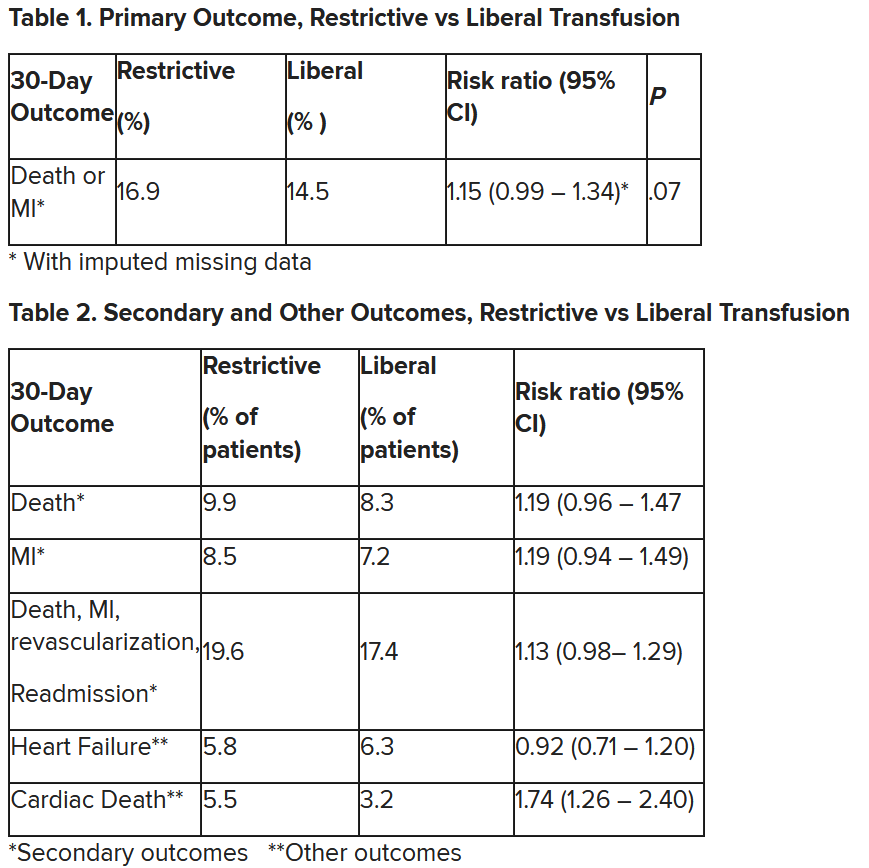
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Women have worse outcomes in cardiogenic shock
“These data identify the need for us to continue working to identify barriers in terms of diagnosis, management, and technological innovations for women in cardiogenic shock to resolve these issues and improve outcomes,” the senior author of the study, Navin Kapur, MD, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview.
The study is said to be the one of the largest contemporary analyses of real-world registry data on the characteristics and outcomes of women in comparison with men with cardiogenic shock.
It showed sex-specific differences in outcomes that were primarily driven by differences in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock. Women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had more severe cardiogenic shock, worse survival at discharge, and more vascular complications than men. Outcomes in cardiogenic shock related to MI were similar for men and women.
The study, which will be presented at the upcoming annual meeting of the American Heart Association, was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Dr. Kapur founded the Cardiogenic Shock Working Group in 2017 to collect quality data on the condition.
“We realized our patients were dying, and we didn’t have enough data on how best to manage them. So, we started this registry, and now have detailed data on close to 9,000 patients with cardiogenic shock from 45 hospitals in the U.S., Mexico, Australia, and Japan,” he explained.
“The primary goal is to try to investigate the questions related to cardiogenic shock that can inform management, and one of the key questions that came up was differences in how men and women present with cardiogenic shock and what their outcomes may be. This is what we are reporting in this paper,” he added.
Cardiogenic shock is defined as having a low cardiac output most commonly because of MI or an episode of acute heart failure, Dr. Kapur said. Patients with cardiogenic shock are identified by their low blood pressure or hypoperfusion evidenced by clinical exam or biomarkers, such as elevated lactate levels.
“In this analysis, we’re looking at patients presenting with cardiogenic shock, so were not looking at the incidence of the condition in men versus women,” Dr. Kapur noted. “However, we believe that cardiogenic shock is probably more underrepresented in women, who may present with an MI or acute heart failure and may or may not be identified as having low cardiac output states until quite late. The likelihood is that the incidence is similar in men and women, but women are more often undiagnosed.”
For the current study, the authors analyzed data on 5,083 patients with cardiogenic shock in the registry, of whom 1,522 (30%) were women. Compared with men, women had slightly higher body mass index (BMI) and smaller body surface area.
Results showed that women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had worse survival at discharge than men (69.9% vs. 74.4%) and a higher rate of refractory shock (SCAI stage E; 26% vs. 21%). Women were also less likely to undergo pulmonary artery catheterization (52.9% vs. 54.6%), heart transplantation (6.5% vs. 10.3%), or left ventricular assist device implantation (7.8% vs. 10%).
Regardless of cardiogenic shock etiology, women had more vascular complications (8.8% vs. 5.7%), bleeding (7.1% vs. 5.2%), and limb ischemia (6.8% vs. 4.5%).
“This analysis is quite revealing. We identified some important distinctions between men and women,” Dr. Kapur commented.
For many patients who present with MI-related cardiogenic shock, many of the baseline characteristics in men and women were quite similar, he said. “But in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock, we saw more differences, with typical comorbidities associated with cardiogenic shock [e.g., diabetes, chronic kidney disease, hypertension] being less common in women than in men. This suggests there may be phenotypic differences as to why women present with heart failure shock versus men.”
Dr. Kapur pointed out that differences in BMI or body surface area between men and women may play into some of the management decision-making.
“Women having a smaller stature may lead to a selection bias where we don’t want to use large-bore pumps or devices because we’re worried about causing complications. We found in the analysis that vascular complications such as bleeding or ischemia of the lower extremity where these devices typically go were more frequent in women,” he noted.
“We also found that women were less likely to receive invasive therapies in general, including pulmonary artery catheters, temporary mechanical support, and heart replacements, such as LVAD or transplants,” he added.
Further results showed that, after propensity score matching, some of the gender differences disappeared, but women continued to have a higher rate of vascular complications (10.4% women vs. 7.4% men).
But Dr. Kapur warned that the propensity-matched analysis had some caveats.
“Essentially what we are doing with propensity matching is creating two populations that are as similar as possible, and this reduced the number of patients in the analysis down to 25% of the original population,” he said. “One of the things we had to match was body surface area, and in doing this, we are taking out one of the most important differences between men and women, and as a result, a lot of the differences in outcomes go away.
“In this respect, propensity matching can be a bit of a double-edge sword,” he added. “I think the non–propensity-matched results are more interesting, as they are more of a reflection of the real world.”
Dr. Kapur concluded that these findings are compelling enough to suggest that there are important differences between women and men with cardiogenic shock in terms of outcomes as well as complication rates.
“Our decision-making around women seems to be different to that around men. I think this paper should start to trigger more awareness of that.”
Dr. Kapur also emphasized the importance of paying attention to vascular complications in women.
“The higher rates of bleeding and limb ischemia issues in women may explain the rationale for being less aggressive with invasive therapies in women,” he said. “But we need to come up with better solutions or technologies so they can be used more effectively in women. This could include adapting technology for smaller vascular sizes, which should lead to better outcome and fewer complications in women.”
He added that further granular data on this issue are needed. “We have very limited datasets in cardiogenic shock. There are few randomized controlled trials, and women are not well represented in such trials. We need to make sure we enroll women in randomized trials.”
Dr. Kapur said more women physicians who treat cardiogenic shock are also required, which would include cardiologists, critical care specialists, cardiac surgeons, and anesthesia personnel.
He pointed out that the two first authors of the current study are women – Van-Khue Ton, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Manreet Kanwar, MD, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
“We worked hard to involve women as principal investigators. They led the effort. These are investigations led by women, on women, to advance the care of women,” he commented.
Gender-related inequality
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study, Sara Kalantari, MD, and Jonathan Grinstein, MD, University of Chicago, and Robert O. Roswell, MD, Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said these results “provide valuable information about gender-related inequality in care and outcomes in the management of cardiogenic shock, although the exact mechanisms driving these observed differences still need to be elucidated.
“Broadly speaking, barriers in the care of women with heart failure and cardiogenic shock include a reduced awareness among both patients and providers, a deficiency of sex-specific objective criteria for guiding therapy, and unfavorable temporary mechanical circulatory support devices with higher rates of hemocompatibility-related complications in women,” they added.
“In the era of the multidisciplinary shock team and shock pathways with protocolized management algorithms, it is imperative that we still allow for personalization of care to match the physiologic needs of the patient in order for us to continue to close the gender gap in the care of patients presenting with cardiogenic shock,” the editorialists concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“These data identify the need for us to continue working to identify barriers in terms of diagnosis, management, and technological innovations for women in cardiogenic shock to resolve these issues and improve outcomes,” the senior author of the study, Navin Kapur, MD, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview.
The study is said to be the one of the largest contemporary analyses of real-world registry data on the characteristics and outcomes of women in comparison with men with cardiogenic shock.
It showed sex-specific differences in outcomes that were primarily driven by differences in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock. Women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had more severe cardiogenic shock, worse survival at discharge, and more vascular complications than men. Outcomes in cardiogenic shock related to MI were similar for men and women.
The study, which will be presented at the upcoming annual meeting of the American Heart Association, was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Dr. Kapur founded the Cardiogenic Shock Working Group in 2017 to collect quality data on the condition.
“We realized our patients were dying, and we didn’t have enough data on how best to manage them. So, we started this registry, and now have detailed data on close to 9,000 patients with cardiogenic shock from 45 hospitals in the U.S., Mexico, Australia, and Japan,” he explained.
“The primary goal is to try to investigate the questions related to cardiogenic shock that can inform management, and one of the key questions that came up was differences in how men and women present with cardiogenic shock and what their outcomes may be. This is what we are reporting in this paper,” he added.
Cardiogenic shock is defined as having a low cardiac output most commonly because of MI or an episode of acute heart failure, Dr. Kapur said. Patients with cardiogenic shock are identified by their low blood pressure or hypoperfusion evidenced by clinical exam or biomarkers, such as elevated lactate levels.
“In this analysis, we’re looking at patients presenting with cardiogenic shock, so were not looking at the incidence of the condition in men versus women,” Dr. Kapur noted. “However, we believe that cardiogenic shock is probably more underrepresented in women, who may present with an MI or acute heart failure and may or may not be identified as having low cardiac output states until quite late. The likelihood is that the incidence is similar in men and women, but women are more often undiagnosed.”
For the current study, the authors analyzed data on 5,083 patients with cardiogenic shock in the registry, of whom 1,522 (30%) were women. Compared with men, women had slightly higher body mass index (BMI) and smaller body surface area.
Results showed that women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had worse survival at discharge than men (69.9% vs. 74.4%) and a higher rate of refractory shock (SCAI stage E; 26% vs. 21%). Women were also less likely to undergo pulmonary artery catheterization (52.9% vs. 54.6%), heart transplantation (6.5% vs. 10.3%), or left ventricular assist device implantation (7.8% vs. 10%).
Regardless of cardiogenic shock etiology, women had more vascular complications (8.8% vs. 5.7%), bleeding (7.1% vs. 5.2%), and limb ischemia (6.8% vs. 4.5%).
“This analysis is quite revealing. We identified some important distinctions between men and women,” Dr. Kapur commented.
For many patients who present with MI-related cardiogenic shock, many of the baseline characteristics in men and women were quite similar, he said. “But in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock, we saw more differences, with typical comorbidities associated with cardiogenic shock [e.g., diabetes, chronic kidney disease, hypertension] being less common in women than in men. This suggests there may be phenotypic differences as to why women present with heart failure shock versus men.”
Dr. Kapur pointed out that differences in BMI or body surface area between men and women may play into some of the management decision-making.
“Women having a smaller stature may lead to a selection bias where we don’t want to use large-bore pumps or devices because we’re worried about causing complications. We found in the analysis that vascular complications such as bleeding or ischemia of the lower extremity where these devices typically go were more frequent in women,” he noted.
“We also found that women were less likely to receive invasive therapies in general, including pulmonary artery catheters, temporary mechanical support, and heart replacements, such as LVAD or transplants,” he added.
Further results showed that, after propensity score matching, some of the gender differences disappeared, but women continued to have a higher rate of vascular complications (10.4% women vs. 7.4% men).
But Dr. Kapur warned that the propensity-matched analysis had some caveats.
“Essentially what we are doing with propensity matching is creating two populations that are as similar as possible, and this reduced the number of patients in the analysis down to 25% of the original population,” he said. “One of the things we had to match was body surface area, and in doing this, we are taking out one of the most important differences between men and women, and as a result, a lot of the differences in outcomes go away.
“In this respect, propensity matching can be a bit of a double-edge sword,” he added. “I think the non–propensity-matched results are more interesting, as they are more of a reflection of the real world.”
Dr. Kapur concluded that these findings are compelling enough to suggest that there are important differences between women and men with cardiogenic shock in terms of outcomes as well as complication rates.
“Our decision-making around women seems to be different to that around men. I think this paper should start to trigger more awareness of that.”
Dr. Kapur also emphasized the importance of paying attention to vascular complications in women.
“The higher rates of bleeding and limb ischemia issues in women may explain the rationale for being less aggressive with invasive therapies in women,” he said. “But we need to come up with better solutions or technologies so they can be used more effectively in women. This could include adapting technology for smaller vascular sizes, which should lead to better outcome and fewer complications in women.”
He added that further granular data on this issue are needed. “We have very limited datasets in cardiogenic shock. There are few randomized controlled trials, and women are not well represented in such trials. We need to make sure we enroll women in randomized trials.”
Dr. Kapur said more women physicians who treat cardiogenic shock are also required, which would include cardiologists, critical care specialists, cardiac surgeons, and anesthesia personnel.
He pointed out that the two first authors of the current study are women – Van-Khue Ton, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Manreet Kanwar, MD, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
“We worked hard to involve women as principal investigators. They led the effort. These are investigations led by women, on women, to advance the care of women,” he commented.
Gender-related inequality
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study, Sara Kalantari, MD, and Jonathan Grinstein, MD, University of Chicago, and Robert O. Roswell, MD, Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said these results “provide valuable information about gender-related inequality in care and outcomes in the management of cardiogenic shock, although the exact mechanisms driving these observed differences still need to be elucidated.
“Broadly speaking, barriers in the care of women with heart failure and cardiogenic shock include a reduced awareness among both patients and providers, a deficiency of sex-specific objective criteria for guiding therapy, and unfavorable temporary mechanical circulatory support devices with higher rates of hemocompatibility-related complications in women,” they added.
“In the era of the multidisciplinary shock team and shock pathways with protocolized management algorithms, it is imperative that we still allow for personalization of care to match the physiologic needs of the patient in order for us to continue to close the gender gap in the care of patients presenting with cardiogenic shock,” the editorialists concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“These data identify the need for us to continue working to identify barriers in terms of diagnosis, management, and technological innovations for women in cardiogenic shock to resolve these issues and improve outcomes,” the senior author of the study, Navin Kapur, MD, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview.
The study is said to be the one of the largest contemporary analyses of real-world registry data on the characteristics and outcomes of women in comparison with men with cardiogenic shock.
It showed sex-specific differences in outcomes that were primarily driven by differences in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock. Women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had more severe cardiogenic shock, worse survival at discharge, and more vascular complications than men. Outcomes in cardiogenic shock related to MI were similar for men and women.
The study, which will be presented at the upcoming annual meeting of the American Heart Association, was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Dr. Kapur founded the Cardiogenic Shock Working Group in 2017 to collect quality data on the condition.
“We realized our patients were dying, and we didn’t have enough data on how best to manage them. So, we started this registry, and now have detailed data on close to 9,000 patients with cardiogenic shock from 45 hospitals in the U.S., Mexico, Australia, and Japan,” he explained.
“The primary goal is to try to investigate the questions related to cardiogenic shock that can inform management, and one of the key questions that came up was differences in how men and women present with cardiogenic shock and what their outcomes may be. This is what we are reporting in this paper,” he added.
Cardiogenic shock is defined as having a low cardiac output most commonly because of MI or an episode of acute heart failure, Dr. Kapur said. Patients with cardiogenic shock are identified by their low blood pressure or hypoperfusion evidenced by clinical exam or biomarkers, such as elevated lactate levels.
“In this analysis, we’re looking at patients presenting with cardiogenic shock, so were not looking at the incidence of the condition in men versus women,” Dr. Kapur noted. “However, we believe that cardiogenic shock is probably more underrepresented in women, who may present with an MI or acute heart failure and may or may not be identified as having low cardiac output states until quite late. The likelihood is that the incidence is similar in men and women, but women are more often undiagnosed.”
For the current study, the authors analyzed data on 5,083 patients with cardiogenic shock in the registry, of whom 1,522 (30%) were women. Compared with men, women had slightly higher body mass index (BMI) and smaller body surface area.
Results showed that women with heart failure–related cardiogenic shock had worse survival at discharge than men (69.9% vs. 74.4%) and a higher rate of refractory shock (SCAI stage E; 26% vs. 21%). Women were also less likely to undergo pulmonary artery catheterization (52.9% vs. 54.6%), heart transplantation (6.5% vs. 10.3%), or left ventricular assist device implantation (7.8% vs. 10%).
Regardless of cardiogenic shock etiology, women had more vascular complications (8.8% vs. 5.7%), bleeding (7.1% vs. 5.2%), and limb ischemia (6.8% vs. 4.5%).
“This analysis is quite revealing. We identified some important distinctions between men and women,” Dr. Kapur commented.
For many patients who present with MI-related cardiogenic shock, many of the baseline characteristics in men and women were quite similar, he said. “But in heart failure–related cardiogenic shock, we saw more differences, with typical comorbidities associated with cardiogenic shock [e.g., diabetes, chronic kidney disease, hypertension] being less common in women than in men. This suggests there may be phenotypic differences as to why women present with heart failure shock versus men.”
Dr. Kapur pointed out that differences in BMI or body surface area between men and women may play into some of the management decision-making.
“Women having a smaller stature may lead to a selection bias where we don’t want to use large-bore pumps or devices because we’re worried about causing complications. We found in the analysis that vascular complications such as bleeding or ischemia of the lower extremity where these devices typically go were more frequent in women,” he noted.
“We also found that women were less likely to receive invasive therapies in general, including pulmonary artery catheters, temporary mechanical support, and heart replacements, such as LVAD or transplants,” he added.
Further results showed that, after propensity score matching, some of the gender differences disappeared, but women continued to have a higher rate of vascular complications (10.4% women vs. 7.4% men).
But Dr. Kapur warned that the propensity-matched analysis had some caveats.
“Essentially what we are doing with propensity matching is creating two populations that are as similar as possible, and this reduced the number of patients in the analysis down to 25% of the original population,” he said. “One of the things we had to match was body surface area, and in doing this, we are taking out one of the most important differences between men and women, and as a result, a lot of the differences in outcomes go away.
“In this respect, propensity matching can be a bit of a double-edge sword,” he added. “I think the non–propensity-matched results are more interesting, as they are more of a reflection of the real world.”
Dr. Kapur concluded that these findings are compelling enough to suggest that there are important differences between women and men with cardiogenic shock in terms of outcomes as well as complication rates.
“Our decision-making around women seems to be different to that around men. I think this paper should start to trigger more awareness of that.”
Dr. Kapur also emphasized the importance of paying attention to vascular complications in women.
“The higher rates of bleeding and limb ischemia issues in women may explain the rationale for being less aggressive with invasive therapies in women,” he said. “But we need to come up with better solutions or technologies so they can be used more effectively in women. This could include adapting technology for smaller vascular sizes, which should lead to better outcome and fewer complications in women.”
He added that further granular data on this issue are needed. “We have very limited datasets in cardiogenic shock. There are few randomized controlled trials, and women are not well represented in such trials. We need to make sure we enroll women in randomized trials.”
Dr. Kapur said more women physicians who treat cardiogenic shock are also required, which would include cardiologists, critical care specialists, cardiac surgeons, and anesthesia personnel.
He pointed out that the two first authors of the current study are women – Van-Khue Ton, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Manreet Kanwar, MD, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
“We worked hard to involve women as principal investigators. They led the effort. These are investigations led by women, on women, to advance the care of women,” he commented.
Gender-related inequality
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study, Sara Kalantari, MD, and Jonathan Grinstein, MD, University of Chicago, and Robert O. Roswell, MD, Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said these results “provide valuable information about gender-related inequality in care and outcomes in the management of cardiogenic shock, although the exact mechanisms driving these observed differences still need to be elucidated.
“Broadly speaking, barriers in the care of women with heart failure and cardiogenic shock include a reduced awareness among both patients and providers, a deficiency of sex-specific objective criteria for guiding therapy, and unfavorable temporary mechanical circulatory support devices with higher rates of hemocompatibility-related complications in women,” they added.
“In the era of the multidisciplinary shock team and shock pathways with protocolized management algorithms, it is imperative that we still allow for personalization of care to match the physiologic needs of the patient in order for us to continue to close the gender gap in the care of patients presenting with cardiogenic shock,” the editorialists concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Cardiovascular disease deaths rise on and after high-pollution days
Cardiovascular disease deaths were significantly more common on days of high pollution and for the following 2 days, compared with other days, based on data from nearly 88,000 deaths over a 5-year period.
Previous research has shown the harmful effect of air pollution on human health in highly polluted areas, but Eastern Poland, a region with so-called “Polish smog” has exceptionally high levels of pollution. However, the specific impact of Polish smog, caused primarily by burning coal, on cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality has not been well studied, said Michal Swieczkowski, MD, of the Medical University of Bialystok (Poland) in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Swieczkowski and colleagues reviewed all-cause deaths from five main cities in Eastern Poland during 2016-2020 for associations with pollution levels and days when deaths occurred. Mortality data were obtained from the Central Statistical Office. Air pollution concentrations for two types of particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) and nitrogen oxide were collected from the Voivodeship Inspectorate for Environmental Protection. The main sources of the pollutants were road traffic and household heaters using coal or wood.
The final analysis included nearly 6 million person-years of follow-up. The researchers used a time-stratified case-crossover design. For each participant, the researchers compared levels of each pollutant on the day of the week a death occurred (such as a Wednesday) with pollutant levels on the same day of the week without any deaths in the same month (the remaining Wednesdays of that month). This design eliminated the potential confounding effects of participant characteristics, including other cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking and hyperlipidemia, and time trends. Essentially, participants “served as their own controls,” Dr. Swieczkowski said. The researchers conducted similar analyses for pollution levels 1 day and 2 days before a death occurred.
Overall, 87,990 deaths were identified during the study period; of these, 34,907 were from CVD, 9,688 from acute coronary syndromes, and 3,776 from ischemic stroke.
“Exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 was associated with increased mortality on the day of exposure, the next day, and up to 2 days after exposure,” said Dr. Swieczkowski.
Overall, an increase of 10 mcg/m3 in the three pollutants was significantly associated with increase in CVD mortality on the day of exposure to the increased pollution levels, with odds ratios of 1.034, 1.033, and 1.083 for PM2.5, PM10, and NO2, respectively (all P < .001).
The risks of dying from CVD were similar 1 and 2 days after the polluted day.
An increase in PM levels, but not NO2, was significantly associated with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) on the day of exposure to increased pollutants (ORs, 1.029 for PM2.5 [P = .002] and 1.015 [P = .049] for PM10). Both ischemic stroke and ACS mortality were significantly higher at 1 day after exposure, compared with other days. Ischemic stroke was associated with increases in PM2.5 and PM10, while ACS was associated with increases in PM2.5, PM10, and NO2.
When stratified by gender, the effects were more noticeable in women, Dr. Swieczkowski said. “Exposure to both types of particulate caused increased mortality due to acute coronary syndrome as well as ischemic stroke.” Among men, only death from acute coronary syndrome was significantly associated with exposure to increased particulate matter.
In a head-to-head comparison, women were more vulnerable to air pollution by up to 2.5%, he added.
When stratified by age, the effects of all three pollutants were associated with increased risk of death from ischemic stroke and ACS in participants older than 65 years. For those aged 65 years and younger, the only significant association was between ACS-associated mortality and ischemic stroke.
The results suggest “a special need for developing calculators to estimate the risk of CVD incidence depending on the place of residence that could be used for everyday practice,” said Dr. Swieczkowski. “Systemic changes should become a priority for policy makers, and, simultaneously, we as physicians should educate and protect our patients, especially those with high risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Gender differences rooted in anatomy
When asked for an explanation of the difference in the impact of pollution on mortality between men and women, Dr. Swieczkowski explained that women are likely more vulnerable because of differences in anatomy of the pharynx and larynx, and breathing patterns. Previous studies have shown that air pollution causes more oxidative stress in women. Also, in the current study, the mean age of the women was 8 to 9 years older, he said.
The study design was an “elegant way to take away the impact of other cardiovascular risk factors,” noted session moderator Maryam Kavousi, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The study was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Cardiovascular disease deaths were significantly more common on days of high pollution and for the following 2 days, compared with other days, based on data from nearly 88,000 deaths over a 5-year period.
Previous research has shown the harmful effect of air pollution on human health in highly polluted areas, but Eastern Poland, a region with so-called “Polish smog” has exceptionally high levels of pollution. However, the specific impact of Polish smog, caused primarily by burning coal, on cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality has not been well studied, said Michal Swieczkowski, MD, of the Medical University of Bialystok (Poland) in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Swieczkowski and colleagues reviewed all-cause deaths from five main cities in Eastern Poland during 2016-2020 for associations with pollution levels and days when deaths occurred. Mortality data were obtained from the Central Statistical Office. Air pollution concentrations for two types of particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) and nitrogen oxide were collected from the Voivodeship Inspectorate for Environmental Protection. The main sources of the pollutants were road traffic and household heaters using coal or wood.
The final analysis included nearly 6 million person-years of follow-up. The researchers used a time-stratified case-crossover design. For each participant, the researchers compared levels of each pollutant on the day of the week a death occurred (such as a Wednesday) with pollutant levels on the same day of the week without any deaths in the same month (the remaining Wednesdays of that month). This design eliminated the potential confounding effects of participant characteristics, including other cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking and hyperlipidemia, and time trends. Essentially, participants “served as their own controls,” Dr. Swieczkowski said. The researchers conducted similar analyses for pollution levels 1 day and 2 days before a death occurred.
Overall, 87,990 deaths were identified during the study period; of these, 34,907 were from CVD, 9,688 from acute coronary syndromes, and 3,776 from ischemic stroke.
“Exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 was associated with increased mortality on the day of exposure, the next day, and up to 2 days after exposure,” said Dr. Swieczkowski.
Overall, an increase of 10 mcg/m3 in the three pollutants was significantly associated with increase in CVD mortality on the day of exposure to the increased pollution levels, with odds ratios of 1.034, 1.033, and 1.083 for PM2.5, PM10, and NO2, respectively (all P < .001).
The risks of dying from CVD were similar 1 and 2 days after the polluted day.
An increase in PM levels, but not NO2, was significantly associated with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) on the day of exposure to increased pollutants (ORs, 1.029 for PM2.5 [P = .002] and 1.015 [P = .049] for PM10). Both ischemic stroke and ACS mortality were significantly higher at 1 day after exposure, compared with other days. Ischemic stroke was associated with increases in PM2.5 and PM10, while ACS was associated with increases in PM2.5, PM10, and NO2.
When stratified by gender, the effects were more noticeable in women, Dr. Swieczkowski said. “Exposure to both types of particulate caused increased mortality due to acute coronary syndrome as well as ischemic stroke.” Among men, only death from acute coronary syndrome was significantly associated with exposure to increased particulate matter.
In a head-to-head comparison, women were more vulnerable to air pollution by up to 2.5%, he added.
When stratified by age, the effects of all three pollutants were associated with increased risk of death from ischemic stroke and ACS in participants older than 65 years. For those aged 65 years and younger, the only significant association was between ACS-associated mortality and ischemic stroke.
The results suggest “a special need for developing calculators to estimate the risk of CVD incidence depending on the place of residence that could be used for everyday practice,” said Dr. Swieczkowski. “Systemic changes should become a priority for policy makers, and, simultaneously, we as physicians should educate and protect our patients, especially those with high risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Gender differences rooted in anatomy
When asked for an explanation of the difference in the impact of pollution on mortality between men and women, Dr. Swieczkowski explained that women are likely more vulnerable because of differences in anatomy of the pharynx and larynx, and breathing patterns. Previous studies have shown that air pollution causes more oxidative stress in women. Also, in the current study, the mean age of the women was 8 to 9 years older, he said.
The study design was an “elegant way to take away the impact of other cardiovascular risk factors,” noted session moderator Maryam Kavousi, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The study was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Cardiovascular disease deaths were significantly more common on days of high pollution and for the following 2 days, compared with other days, based on data from nearly 88,000 deaths over a 5-year period.
Previous research has shown the harmful effect of air pollution on human health in highly polluted areas, but Eastern Poland, a region with so-called “Polish smog” has exceptionally high levels of pollution. However, the specific impact of Polish smog, caused primarily by burning coal, on cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality has not been well studied, said Michal Swieczkowski, MD, of the Medical University of Bialystok (Poland) in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Swieczkowski and colleagues reviewed all-cause deaths from five main cities in Eastern Poland during 2016-2020 for associations with pollution levels and days when deaths occurred. Mortality data were obtained from the Central Statistical Office. Air pollution concentrations for two types of particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) and nitrogen oxide were collected from the Voivodeship Inspectorate for Environmental Protection. The main sources of the pollutants were road traffic and household heaters using coal or wood.
The final analysis included nearly 6 million person-years of follow-up. The researchers used a time-stratified case-crossover design. For each participant, the researchers compared levels of each pollutant on the day of the week a death occurred (such as a Wednesday) with pollutant levels on the same day of the week without any deaths in the same month (the remaining Wednesdays of that month). This design eliminated the potential confounding effects of participant characteristics, including other cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking and hyperlipidemia, and time trends. Essentially, participants “served as their own controls,” Dr. Swieczkowski said. The researchers conducted similar analyses for pollution levels 1 day and 2 days before a death occurred.
Overall, 87,990 deaths were identified during the study period; of these, 34,907 were from CVD, 9,688 from acute coronary syndromes, and 3,776 from ischemic stroke.
“Exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 was associated with increased mortality on the day of exposure, the next day, and up to 2 days after exposure,” said Dr. Swieczkowski.
Overall, an increase of 10 mcg/m3 in the three pollutants was significantly associated with increase in CVD mortality on the day of exposure to the increased pollution levels, with odds ratios of 1.034, 1.033, and 1.083 for PM2.5, PM10, and NO2, respectively (all P < .001).
The risks of dying from CVD were similar 1 and 2 days after the polluted day.
An increase in PM levels, but not NO2, was significantly associated with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) on the day of exposure to increased pollutants (ORs, 1.029 for PM2.5 [P = .002] and 1.015 [P = .049] for PM10). Both ischemic stroke and ACS mortality were significantly higher at 1 day after exposure, compared with other days. Ischemic stroke was associated with increases in PM2.5 and PM10, while ACS was associated with increases in PM2.5, PM10, and NO2.
When stratified by gender, the effects were more noticeable in women, Dr. Swieczkowski said. “Exposure to both types of particulate caused increased mortality due to acute coronary syndrome as well as ischemic stroke.” Among men, only death from acute coronary syndrome was significantly associated with exposure to increased particulate matter.
In a head-to-head comparison, women were more vulnerable to air pollution by up to 2.5%, he added.
When stratified by age, the effects of all three pollutants were associated with increased risk of death from ischemic stroke and ACS in participants older than 65 years. For those aged 65 years and younger, the only significant association was between ACS-associated mortality and ischemic stroke.
The results suggest “a special need for developing calculators to estimate the risk of CVD incidence depending on the place of residence that could be used for everyday practice,” said Dr. Swieczkowski. “Systemic changes should become a priority for policy makers, and, simultaneously, we as physicians should educate and protect our patients, especially those with high risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Gender differences rooted in anatomy
When asked for an explanation of the difference in the impact of pollution on mortality between men and women, Dr. Swieczkowski explained that women are likely more vulnerable because of differences in anatomy of the pharynx and larynx, and breathing patterns. Previous studies have shown that air pollution causes more oxidative stress in women. Also, in the current study, the mean age of the women was 8 to 9 years older, he said.
The study design was an “elegant way to take away the impact of other cardiovascular risk factors,” noted session moderator Maryam Kavousi, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The study was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2023