User login
Ragweed SLIT tablets improve asthma outcome scores in patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
FROM AAAAI
FDA approves first generic albuterol inhaler
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
Asthma: Newer Tx options mean more targeted therapy
Recent advances in our understanding of asthma pathophysiology have led to the development of new treatment approaches to this chronic respiratory condition, which affects 25 million Americans or nearly 8% of the population.1 As a result, asthma treatment options have expanded from just simple inhalers and corticosteroids to include
The pathophysiology of asthma provides key targets for therapy
There are 2 basic phenotypes of asthma—neutrophilic predominant and eosinophilic predominant—and 3 key components to its pathophysiology2:
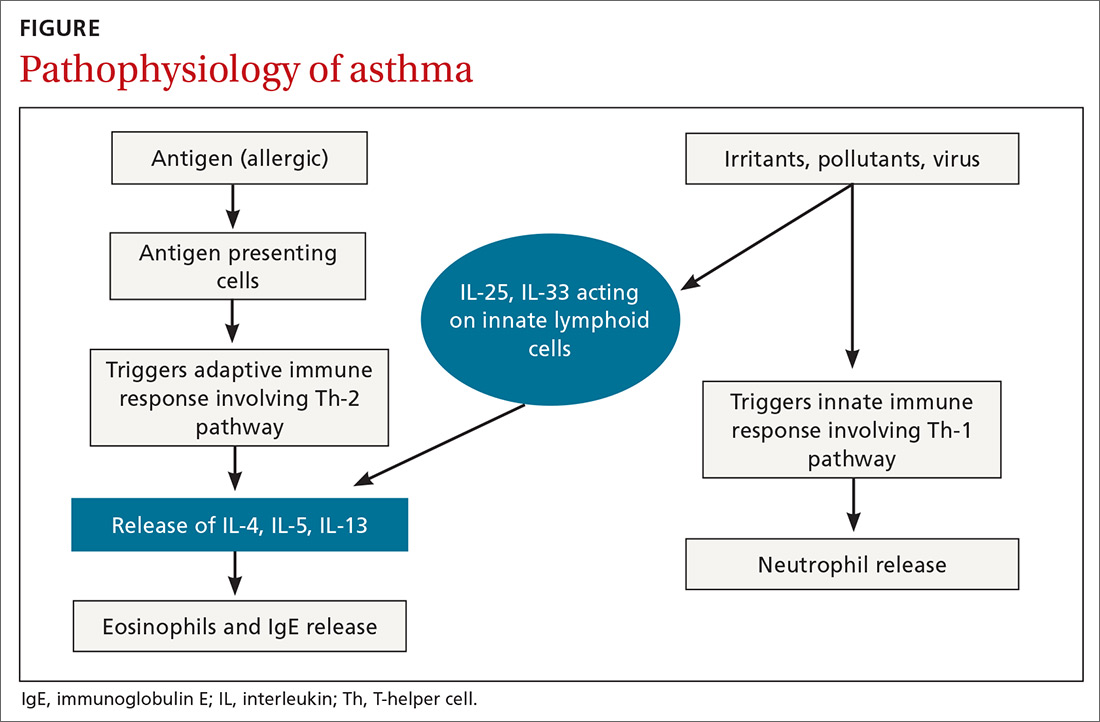
Airway inflammation. Asthma is mediated through either a type 1 T-helper (Th-1) cell or a type 2 T-helper (Th-2) cell response, the pathways of which have a fair amount of overlap (FIGURE). In the neutrophilic-predominant phenotype, irritants, pollutants, and viruses trigger an innate Th-1 cell–mediated pathway that leads to subsequent neutrophil release. This asthma phenotype responds poorly to standard asthma therapy.2-4
In the eosinophilic-predominant phenotype, environmental allergic antigens induce a Th-2 cell–mediated response in the airways of patients with asthma.5-7 This creates a downstream effect on the release of interleukins (IL) including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. IL-4 triggers immunoglobulin (Ig) E release, which subsequently induces mast cells to release inflammatory cytokines, while IL-5 and IL-13 are responsible for eosinophilic response. These cytokines and eosinophils induce airway hyperresponsiveness, remodeling, and mucus production. Through repeated exposure, chronic inflammation develops and subsequently causes structural changes related to increased smooth muscle mass, goblet cell hyperplasia, and thickening of lamina reticularis.8,9 Understanding of this pathobiological pathway has led to the development of anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 drugs (to be discussed shortly).
Airway obstruction. Early asthmatic response is due to acute bronchoconstriction secondary to IgE; this is followed by airway edema occurring 6 to 24 hours after an acute event (called late asthmatic response). The obstruction is worsened by an overproduction of mucus, which may take weeks to resolve.10 Longstanding inflammation can lead to structural changes and reduced airflow reversibility.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is induced by various forms of allergens, pollutants, or viral upper respiratory infections. Sympathetic control in the airway is mediated via beta-2 adrenoceptors expressed on airway smooth muscle, which are responsible for the effect of bronchodilation in response to albuterol.11,12 Cholinergic pathways may further contribute to bronchial hyperresponsiveness and form the basis for the efficacy of anticholinergic therapy.12,13
What we’ve learned about asthma can inform treatment decisions
Presentation may vary, as asthma has many forms including cough-variant asthma and exercise-induced asthma. Airflow limitation is typically identified through spirometry and characterized by reduced (< 70% in adults) forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC) or bronchodilator response positivity (an increase in post-bronchodilator FEV1 > 12% or FVC > 200 mL from baseline).2 If spirometry is not diagnostic but suspicion for asthma remains, bronchial provocation testing or exercise challenge testing may be needed.
Continue to: Additional diagnostic considerations...
Additional diagnostic considerations may impact the treatment plan for patients with asthma:
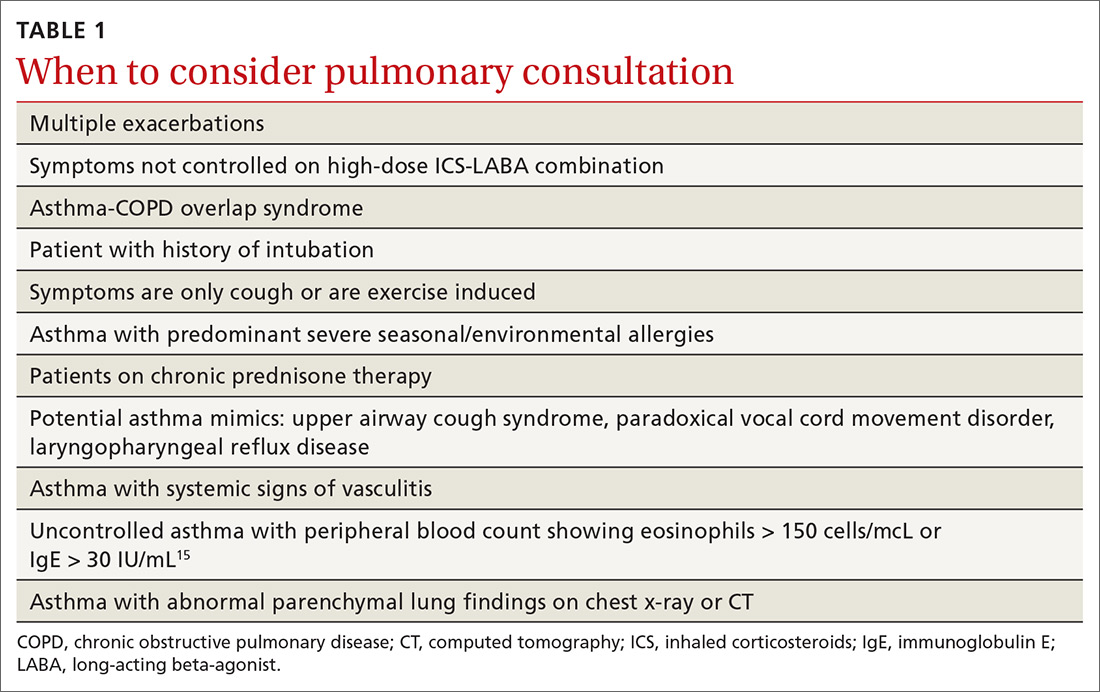
Asthma and COPD. A history of smoking is a key factor in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)—but many patients with asthma are also smokers. This subgroup may have asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). It is important to determine whether these patients are asthma predominant or COPD predominant, because appropriate first-line treatment will differ. Patients who are COPD predominant demonstrate reduced diffusion capacity (DLCO) and abnormal PaCO2 on arterial blood gas. They also may show more structural damage on chest computed tomography (CT) than patients with asthma do. Asthma-predominant patients are more likely to have eosinophilia.14
Patients with severe persistent asthma or frequent exacerbations, or those receiving step-up therapy, may require additional serologic testing. Specialized testing for IgE and eosinophil count, as well as a sensitized allergy panel, may help clinicians in selecting specific biological therapies for treatment of severe asthma (further discussion to follow). We recommend using a serum allergy panel, as it is a quick and easy way to identify patients with extrinsic allergies, whereas skin-based testing is often time consuming and may require referral to a specialist.2,5,15
Aspergillus. An additional consideration is testing for Aspergillus antibodies. Aspergillus is a ubiquitous fungus found in the airways of humans. In patients with asthma, however, it can trigger an intense inflammatory response known as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. ABPA is not an infection. It should be considered in patients who have lived in a damp, old housing environment with possible mold exposure. Treatment of ABPA involves oral corticosteroids; there are varying reports of efficacy with voriconazole or itraconazole as suppressive therapy or steroid-sparing treatment.16-18
Getting a handle on an ever-expanding asthma Tx arsenal
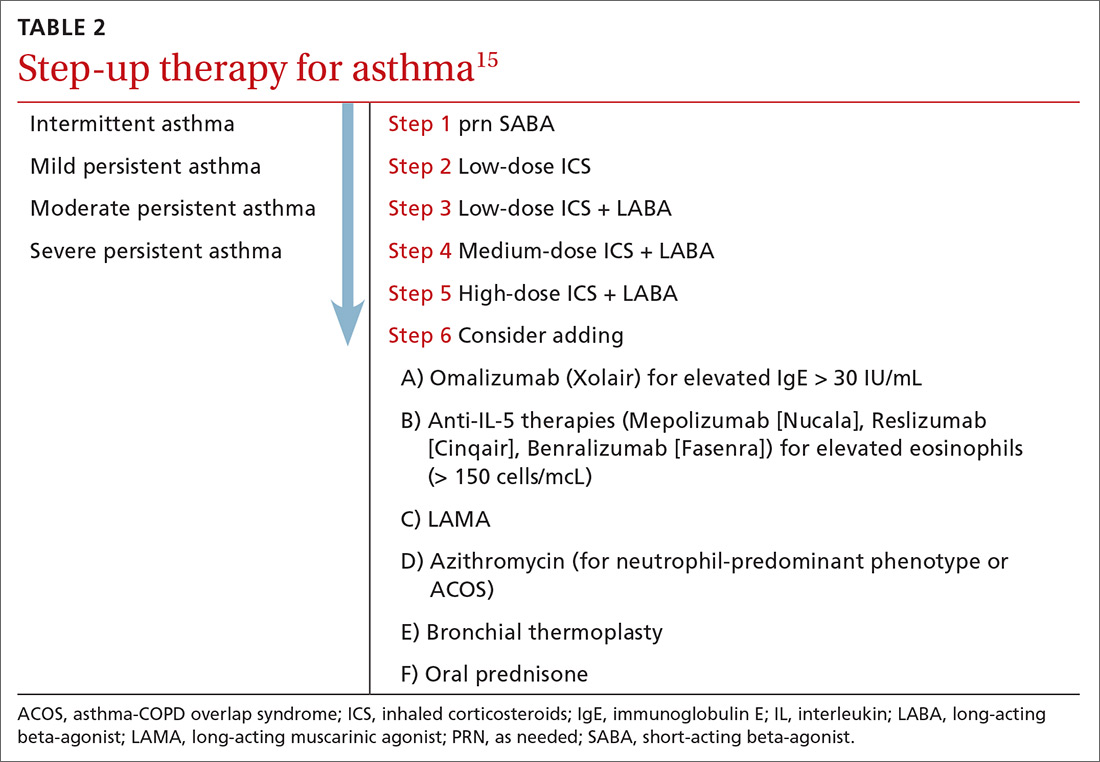
The goals of asthma treatment are symptom control and risk minimization. Treatment choices are dictated in part by disease severity (mild, moderate, severe) and classification (intermittent, persistent). Asthma therapy is traditionally described as step-up and step-down; TABLE 2 summarizes available pharmacotherapy for asthma and provides a framework for add-on therapy as the disease advances.
Continue to: Over the past decade...
Over the past decade, a number of therapeutic options have been introduced or added to the pantheon of asthma treatment.
Inhaled medications
This category includes inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), which are recommended for use alone or in combination with long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) or with long-acting
ICS is the first choice for long-term control of persistent asthma.2 Its molecular effects include activating anti-inflammatory genes, switching off inflammatory genes, and inhibiting inflammatory cells, combined with enhancement of beta-2-adrenergic receptor expression. The cumulative effect is reduction in airway responsiveness in asthma patients.19-22
LABAs are next in line in the step-up, step-down model of symptom management. LABAs should not be prescribed as stand-alone therapy in patients with asthma, as they have received a black box warning from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for an increase in asthma-related death23—a concern that has not been demonstrated with the combination of ICS-LABA.
LABAs cause smooth muscle relaxation in the lungs.24 There are 3 combination products currently available: once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (Breo), twice-daily fluticasone propionate/salmeterol (Advair), and twice-daily budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort).
Continue to: Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol...
Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol has been shown to improve mean FEV1.25 In a 24-week, open-label, multicenter randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of all 3 combination ICS-LABAs, preliminary results indicated that—at least in a tightly controlled setting—once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol provides asthma control similar to the twice-daily combinations and is well tolerated.26
Two ultra-long-acting (24-hour) LABAs, olodaterol (Striverdi Respimat) and indacaterol (Arcapta Neohaler), are being studied for possible use in asthma treatment. In a phase 2 trial investigating therapy for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma, 24-hour FEV1 improved with olodeaterol when compared to placebo.27
Another ongoing clinical trial is studying the effects of ultra-long-acting bronchodilator therapy (olodaterol vs combination olodaterol/tiotropium) in asthma patients who smoke and who are already using ICS (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02682862). Indacaterol has been shown to be effective in the treatment of moderate-to-severe asthma in a once-a-day dosing regimen.28 However, when compared to mometasone alone, a combination of indacaterol and mometasone demonstrated no statistically significant reduction in time to serious exacerbation.29
The LAMA tiotropium is recommended as add-on therapy for patients whose asthma is uncontrolled despite use of low-dose ICS-LABA or as an alternative to high-dose ICS-LABA, per Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2019 guidelines.15
Tiotropium induces bronchodilation by selectively inhibiting the action of acetylcholine at muscarinic (M) receptors in bronchial smooth muscles; it has a longer duration of action because of its slower dissociation from receptor types M1 and M3.30 Tiotropium respimat (Spiriva, Tiova) has been approved for COPD for many years; in 2013, it was shown to prevent worsening of symptomatic asthma and increase time to first severe exacerbation.13 The FDA subsequently approved tiotropium as an add-on treatment for patients with uncontrolled asthma despite use of ICS-LABA.
Continue to: Glycopyrronium bromide...
Glycopyrronium bromide (glycopyrrolate, multiple brand names) and umeclidinium (Incruse Ellipta) are LAMAs that are approved for COPD treatment but have not yet been approved for patients who have asthma only.31
Biological therapies
In the past few years, improved understanding of asthma’s pathophysiology has led to the development of biological therapy for severe asthma. This therapy is directed at Th-2 inflammatory pathways (FIGURE) and targets various inflammatory markers, such as IgE, IL-5, and eosinophils.
Biologicals are not the first-line therapy for the management of severe asthma. Ideal candidates for this therapy are patients who have exhausted other forms of severe asthma treatment, including ICS-LABA, LAMA, leukotriene receptor antagonists, and mucus-clearing agents. Patients with frequent exacerbations who need continuous steroids or need steroids at least twice a year should be considered for biologicals.32
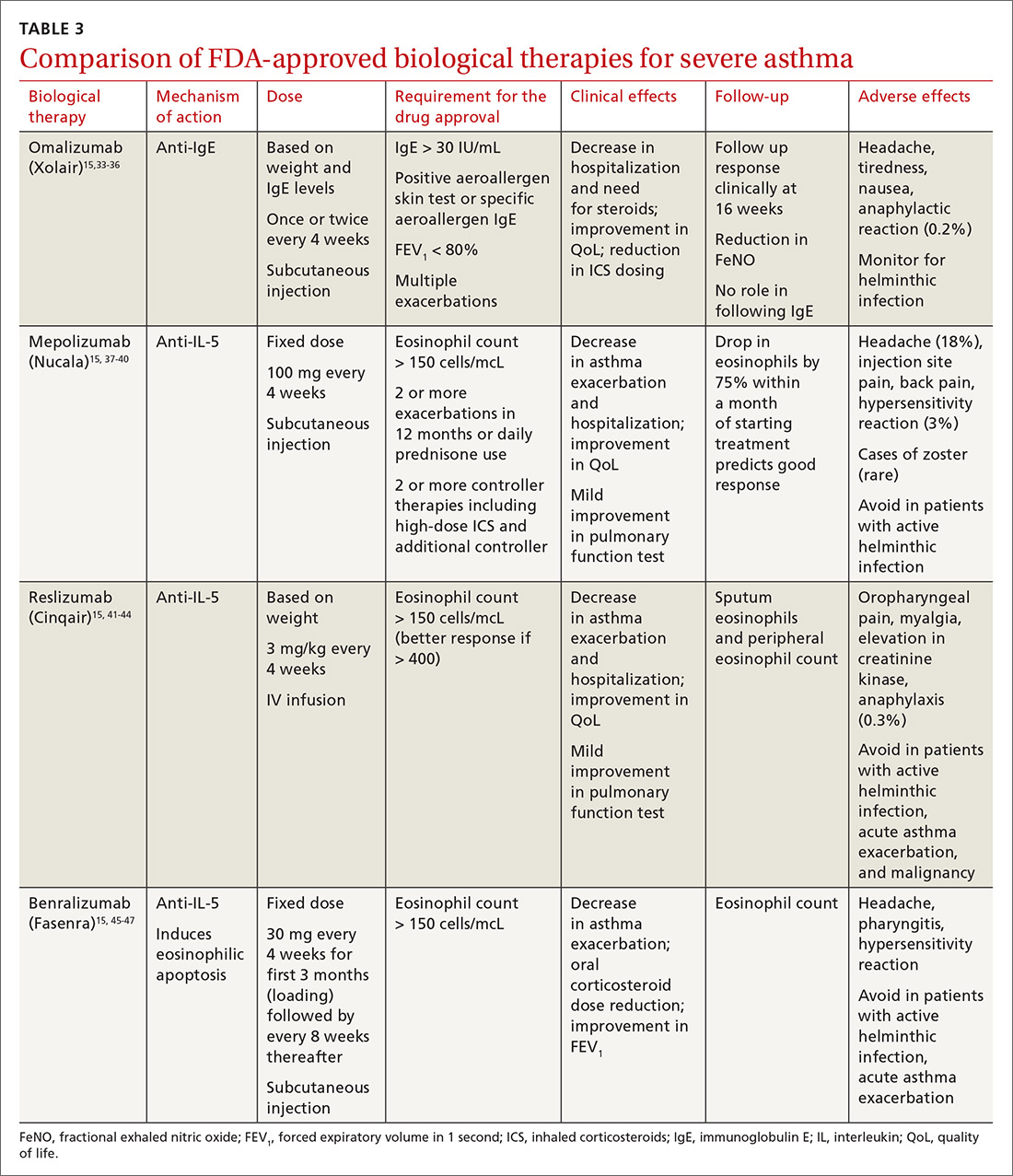
All biological therapies must be administered in a clinical setting, as they carry risk for anaphylaxis. TABLE 315,33-47 summarizes all approved biologicals for the management of severe asthma.
Anti-IgE therapy. Omalizumab (Xolair) was the first approved biological therapy for severe asthma (in 2003). It is a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to free IgE and down regulates the inflammatory cascade. It is therefore best suited for patients with early-onset allergic asthma with a high IgE count. The dose and frequency (once or twice per month) of omalizumab are based on IgE levels and patient weight. Omalizumab reduces asthma exacerbation (up to 45%) and hospitalization (up to 85%).34 Omalizumab also reduces the need for high-dose ICS-LABA therapy and improves quality of life (QoL).33,34
Continue to: Its efficacy and safety...
Its efficacy and safety have been proven outside the clinical trial setting. Treatment response should be assessed over a 3- to 4-month period, using fractional exhalation of nitric oxide (FeNO); serial measurement of IgE levels is not recommended for this purpose. Once started, treatment should be considered long term, as discontinuation of treatment has been shown to lead to recurrence of symptoms and exacerbation.35,36 Of note, the GINA guidelines recommend omalizumab over prednisone as add-on therapy for severe persistent asthma.15
Anti-IL-5 therapy. IL-5 is the main cytokine for growth, differentiation, and activation of eosinophils in the Th-2-mediated inflammatory cascade. Mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab are 3 FDA-approved anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody therapies for severe eosinophilic asthma. Mepolizumab has been the most commonly studied anti-IL-5 therapy, while benralizumab, the latest of the 3, has a unique property of inducing eosinophilic apoptosis. There has been no direct comparison of the different anti-IL-5 therapies.
Mepolizumab (Nucala) is a mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-5 and prevents it from binding to IL-5 receptors on the eosinophil surface. Mepolizumab should be considered in patients with a peripheral eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL; it has shown a trend of greater benefit in patients with a very high eosinophil count (75% reduction in exacerbation with blood eosinophil count > 500 cells/mcL compared to 56% exacerbation reduction with blood eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL).37
Mepolizumab has consistently been shown to reduce asthma exacerbation (by about 50%) and emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalization (60%), when compared with placebo in clinical trials.37,38 It also reduces the need for oral corticosteroids, an effect sustained for up to 52 weeks.39,40 The Mepolizumab adjUnctive therapy in subjects with Severe eosinophiliC Asthma (MUSCA) study showed that mepolizumab was associated with significant improvement of health-related QoL, lung function, and asthma symptoms in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.38
GINA guidelines recommend mepolizumab as an add-on therapy for severe asthma. Mepolizumab is given as a fixed dose of 100 mg every 4 weeks. A 300-mg dose has also been approved for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Monitoring with serial eosinophils might be of value in determining the efficacy of the drug. Mepolizumab is currently in clinical trials for a broad spectrum of diseases, including COPD, hyper-eosinophilic syndrome, and ABPA.
Continue to: Reslizumab (Cinqair)...
Reslizumab (Cinqair) is a rat anti-human monoclonal antibody of the IgG4κ subtype that binds to a small region of IL-5 and subsequently blocks IL-5 from binding to the IL-5 receptor complex on the cell surface of eosinophils. It is currently approved for use as a 3-mg/kg IV infusion every 4 weeks. In large clinical trials,41-43 reslizumab decreased asthma exacerbation and improved QoL, asthma control, and lung function. Most of the study populations had an eosinophil count > 400 cells/mcL. A small study also suggested patients with severe eosinophilic asthma with prednisone dependency (10 mg/d) had better sputum eosinophilia suppression and asthma control with reslizumab when compared with mepolizumab.44
Benralizumab (Fasenra) is a humanized IgG1 anti-IL-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody derived from mice. It induces apoptosis of eosinophils and, to a lesser extent, of basophils.45 In clinical trials, it demonstrated a reduction in asthma exacerbation rate and improvement in prebronchodilator FEV1 and asthma symptoms.46,47 It does not need reconstitution, as the drug is dispensed as prefilled syringes with fixed non-weight-based dosing. Another potential advantage to benralizumab is that after the loading dose, subsequent doses are given every 8 weeks.
Bronchial thermoplasty
Bronchial thermoplasty (BT) is a novel nonpharmacologic intervention that entails the delivery of controlled radiofrequency-generated heat via a catheter inserted into the bronchial tree of the lungs through a flexible bronchoscope. The potential mechanism of action is reduction in airway smooth muscle mass and inflammatory markers.
Evidence for BT started with the Asthma Intervention Research (AIR) and Research in Severe Asthma (RISA) trials.48,49 In the AIR study, BT was shown to reduce the rate of mild exacerbations and improve morning peak expiratory flow and asthma scores at 12 months.48 In the RISA trial, BT resulted in improvements in Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) score and need for rescue medication at 52 weeks, as well as a trend toward decrease in steroid use.49
However, these studies were criticized for not having a placebo group—an issue addressed in the AIR2 trial, which compared bronchial thermoplasty with a sham procedure. AIR2 demonstrated improvements in AQLQ score and a 32% reduction in severe exacerbations and 84% fewer ED visits in the post-treatment period (up to 1 year post treatment).50
Continue to: Both treatment groups...
Both treatment groups experienced an increase in respiratory adverse events: during the treatment period (up to 6 weeks post procedure), 16 subjects (8.4%) in the BT group required 19 hospitalizations for respiratory symptoms and 2 subjects (2%) in the sham group required 2 hospitalizations. A follow-up observational study involving a cohort of AIR2 patients demonstrated long-lasting effects of BT in asthma exacerbation frequency, ED visits, and stabilization of FEV1 for up to 5 years.51
The Post-market Post-FDA Approval Clinical Trial Evaluating Bronchial Thermoplasty in Severe Persistent Asthma (PAS2) showed similar beneficial effects of BT on asthma control despite enrolling subjects who may have had poorer asthma control in the “real world” setting.52
In summary, BT results in modest improvements in AQLQ scores and clinically worthwhile reductions in severe exacerbations and ED visits in the year post treatment, which may persist for up to 5 years. BT causes short-term increases in asthma-related morbidity, including hospital admissions. While there is encouraging data and the scope is increasing, BT remains limited to carefully selected (by a specialist) patients with severe asthma that is poorly controlled despite maximal inhaled therapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy for allergic disease is aimed at inducing immune tolerance to an allergen and alleviating allergic symptoms. This is done by administration of the allergen to which the patient is sensitive. There are 2 approaches: subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT; a dissolvable tablet under the tongue or an aqueous or liquid extract).
Immunotherapy is generally reserved for patients who have allergic symptoms with exposure to a trigger and evidence (through skin or serum testing) of specific IgE to that trigger, especially if there is poor response to pharmacotherapy and allergen avoidance. Overall, evidence in this field is limited: Most studies have included patients with mild asthma, and few studies have compared immunotherapy with pharmacologic therapy or used standardized outcomes, such as exacerbations.
Continue to: SCIT
SCIT. A 2010 Cochrane review concluded that SCIT reduces asthma symptoms and use of asthma medications and improves bronchial hyperreactivity. Adverse effects include uncommon anaphylactic reactions, which may be life-threatening.53
SLIT has advantages over SCIT as it can be administered by patients or caregivers, does not require injections, and carries a much lower risk for anaphylaxis. Modest benefits have been seen in adults and children, but there is concern about the design of many early studies.
A 2015 Cochrane review of SLIT in asthma recommended further research using validated scales and important outcomes for patients and decision makers so that SLIT can be properly assessed as a clinical treatment for asthma.54 A subsequently published study of SLIT for house dust mites (HDM) in patients with asthma and HDM allergic rhinitis demonstrated a modest reduction in use of ICS with high-dose SLIT.55
In another recent study, among adults with HDM allergy-related asthma not well controlled by ICS, the addition of HDM SLIT to maintenance medications improved time to first moderate-or-severe asthma exacerbation during ICS reduction.56 Additional studies are needed to assess long-term efficacy and safety. However, for patients who experience exacerbations despite use of a low-dose or medium-dose ICS-LABA combination, SLIT can now be considered as an add-on therapy.
Per the GINA guidelines, the potential benefits of allergen immunotherapy must be weighed against the risk for adverse effects, including anaphylaxis, and the inconvenience and cost of the prolonged course of therapy.15
Continue to: Azithromycin
Azithromycin
Macrolides have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects in addition to their antibacterial effects. Maintenance treatment with macrolides such as azithromycin has been proven to be effective in chronic neutrophilic airway diseases (FIGURE). There have been attempts to assess whether this therapy can be useful in asthma management, as well. Some randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have shown conflicting results, and early studies were limited by lack of data, heterogeneous results, and inadequate study designs.
The AZithromycin Against pLacebo in Exacerbations of Asthma (AZALEA) study was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in the United Kingdom among patients requiring emergency care for acute asthma exacerbations. Azithromycin added to standard care for asthma attacks did not result in clinical benefit.57 While azithromycin in acute exacerbation is not currently recommended, recent trials in outpatient settings have shown promise.
The AZIthromycin in Severe ASThma study (AZISAST) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in subjects with exacerbation-prone severe asthma in Belgium. Low-dose azithromycin (250 mg 3 times a week) as an add-on treatment to combination ICS-LABA therapy for 6 months did not reduce the rate of severe asthma exacerbations or lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI). However, subjects with a non-eosinophilic variant (neutrophilic phenotype) experienced significant reduction in the rate of exacerbation and LRTI.58
The recently published Asthma and Macrolides: the AZithromycin Efficacy and Safety Study (AMAZES) shows promise for chronic azithromycin therapy as an add-on to medium-to-high-dose inhaled steroids and a long-acting bronchodilator in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma. This was a large multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial in New Zealand and Australia. Patients were excluded if they had hearing impairment or abnormally prolonged QTc. Azithromycin at a dose of 500 mg 3 times a week for 48 months reduced asthma exacerbations and improved QoL compared to placebo. The effect was sustained between subgroups based on phenotypes (eosinophilic vs noneosinophilic; frequent exacerbators vs nonfrequent exacerbators) and even among those with symptom differences at baseline (eg, cough or sputum positivity). The rate of antibiotic courses for respiratory infectious episodes was significantly reduced in the azithromycin-treated group.59
The take-away: Chronic azithromycin might prove to be a useful agent in the long-term management of asthma patients whose disease is not well controlled on inhaled therapy. Further studies on mechanism and effects of prolonged antibiotic use will shed more light. For more information, see When guideline treatment of asthma fails, consider a macrolide antibiotic; http://bit.ly/2vDAWc6.
Continue to: A new era
A new era
We have entered an exciting era of asthma management, with the introduction of several novel modalities, such as biological therapy and bronchial thermoplasty, as well as use of known drugs such as macrolides, immunotherapy, and LAMA. This was made possible through a better understanding of the biological pathways of asthma. Asthma management has moved toward more personalized, targeted therapy based on asthma phenotypes.
It’s important to remember, however, that pharmacological and nonpharmacological aspects of management—including inhaler techniques, adherence to inhaler therapy, vaccinations, control of asthma triggers, and smoking cessation—remain the foundation of optimal asthma management and need to be aggressively addressed before embarking on advanced treatment options. Patients whose asthma is not well controlled with inhaled medications or who have frequent exacerbations (requiring use of steroids) should be comanaged by an expert asthma specialist to explore all possible therapies.
CORRESPONDENCE
Mayur Rali, MD, 995 Newbridge Road, Bellmore, NY 11710; mrali@northwell.edu
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Most recent national asthma data. Updated May 2019. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm. Accessed March 6, 2020.
2. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma—summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(5 suppl):S94-S138.
3. Woodruff PG, Modrek B, Choy DF, et al. T-helper type 2-driven inflammation defines major subphenotypes of asthma [published correction appears in Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(8):796]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:388–395.
4. Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma—present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:57–65.
5. Busse WW. Inflammation in asthma: the cornerstone of the disease and target of therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102(4 pt 2):S17-S22.
6. Lane SJ, Lee TH. Mast cell effector mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(5 pt 2):S67-S71.
7. Robinson DS, Bentley AM, Hartnell A, et al. Activated memory T helper cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with atopic asthma: relation to asthma symptoms, lung function, and bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1993;48:26-32.
8. Grigoraş A, Grigoraş CC, Giuşcă SE, et al. Remodeling of basement membrane in patients with asthma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57:115-119.
9. Huang SK, Xiao HQ, Kleine-Tebbe J, et al. IL-13 expression at the sites of allergen challenge in patients with asthma. J Immunol. 1995;155:2688-2694.
10. Hansbro PM, Starkey MR, Mattes J, et al. Pulmonary immunity during respiratory infections in early life and the development of severe asthma. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11 suppl 5:S297-S302.
11. Apter AJ, Reisine ST, Willard A, et al. The effect of inhaled albuterol in moderate to severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98:295-301.
12. Peters SP, Kunselman SJ, Icitovic N, et al. Tiotropium bromide step-up therapy for adults with uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1715-1726.
13. Kerstjens HA, O’Byrne PM. Tiotropium for the treatment of asthma: a drug safety evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15:1115-1124.
14. Global Initiative for Asthma. Diagnosis of diseases of chronic air flow limitation: asthma, COPD and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) 2014. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GINA_GOLD_ACOS_2014-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
15. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2019. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
16. Khanbabaee G, Enayat J, Chavoshzadeh Z, et al. Serum level of specific IgG antibody for aspergillus and its association with severity of asthma in asthmatic children. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2012;59:43-50.
17. Agbetile J, Bourne M, Fairs A, et al. Effectiveness of voriconazole in the treatment of aspergillus fumigatus-associated asthma (EVITA3 study). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:33-39.
18. Stevens DA, Schwartz HJ, Lee JY, et al. A randomized trial of itraconazole in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:756-762.
19. Barnes PJ. Glucocorticosteroids: current and future directions. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:29-43.
20. Oakley RH, Cidlowski JA. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: new signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1033-1044.
21. Barnes PJ. Scientific rationale for inhaled combination therapy with long-acting beta2-agonists and corticosteroids. Eur Respir J. 2002;19:182-191.
22. Newton R, Giembycz MA. Understanding how long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance the clinical efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma—an update. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:3405-3430.
23. Wijesinghe M, Perrin K, Harwood M, et al. The risk of asthma mortality with inhaled long acting beta-agonists. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:467-472.
24. Cazzola M, Page CP, Rogliani P, et al. β2-agonist therapy in lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:690-696.
25. Bernstein DI, Bateman ED, Woodcock A, et al. Fluticasone furoate (FF)/vilanterol (100/25 mcg or 200/25 mcg) or FF (100 mcg) in persistent asthma. J Asthma. 2015;52:1073-1083.
26. Devillier P, Humbert M, Boye A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (FF/VI) versus twice-daily inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β2-agonists (ICS/LABA) in patients with uncontrolled asthma: an open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Respir Med. 2018;141:111-120.
27. Beeh KM, LaForce C, Gahlemann M, et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study to investigate different dosing regimens of olodaterol delivered via Respimat(R) in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma. Respir Res. 2015;16:87.
28. LaForce C, Alexander M, Deckelmann R, et al. Indacaterol provides sustained 24 h bronchodilation on once-daily dosing in asthma: a 7-day dose-ranging study. Allergy. 2008;63:103-111.
29. Beasley RW, Donohue JF, Mehta R, et al. Effect of once-daily indacaterol maleate/mometasone furoate on exacerbation risk in adolescent and adult asthma: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e006131.
30. Aalbers R, Park HS. Positioning of long-acting muscarinic antagonists in the management of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9:386-393.
31. Lee LA, Briggs A, Edwards LD, et al. A randomized, three-period crossover study of umeclidinium as monotherapy in adult patients with asthma. Respir Med. 2015;109:63-73.
32. Israel E, Reddel HK. Severe and difficult-to-treat asthma in adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:965-976.
33. Normansell R, Walker S, Milan SJ, et al. Omalizumab for asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(1):CD003559.
34. Hanania NA, Wenzel S, Rosen K, et al. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: an analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:804-811.
35. Slavin RG, Ferioli C, Tannenbaum SJ, et al. Asthma symptom re-emergence after omalizumab withdrawal correlates well with increasing IgE and decreasing pharmacokinetic concentrations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:107-113.e3.
36. Ledford D, Busse W, Trzaskoma B, et al. A randomized multicenter study evaluating Xolair persistence of response after long-term therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:162-169.e2.
37. Ortega HG, Liu MC, Pavord ID, et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1198-1207.
38. Chupp GL, Bradford ES, Albers FC, et al. Efficacy of mepolizumab add-on therapy on health-related quality of life and markers of asthma control in severe eosinophilic asthma (MUSCA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:390-400.
39. Lugogo N, Domingo C, Chanez P, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: a multi-center, open-label, phase IIIb study. Clin Ther. 2016;38:2058-2070.e1.
40. Bel EH, Wenzel SE, Thompson PJ, et al. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1189-1197.
41. Castro M, Zangrilli J, Wechsler ME. Corrections. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:e15.
42. Bjermer L, Lemiere C, Maspero J, et al. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil levels: a randomized phase 3 study. Chest. 2016;150:789-798.
43. Corren J, Weinstein S, Janka L, et al. Phase 3 study of reslizumab in patients with poorly controlled asthma: Effects across a broad range of eosinophil counts. Chest. 2016;150:799-810.
44. Mukherjee M, Aleman Paramo F, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Weight-adjusted intravenous reslizumab in severe asthma with inadequate response to fixed-dose subcutaneous mepolizumab. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197:38-46.
45. Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:1344-1353.e2.
46. Bleecker ER, FitzGerald JM, Chanez P, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2115-2127.
47. FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Nair P, et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2128-2141.
48. Cox G, Thomson NC, Rubin AS, et al. Asthma control during the year after bronchial thermoplasty. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1327-1337.
49. Pavord ID, Cox G, Thomson NC, et al. Safety and efficacy of bronchial thermoplasty in symptomatic, severe asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:1185-1191.
50. Castro M, Rubin AS, Laviolette M, et al. Effectiveness and safety of bronchial thermoplasty in the treatment of severe asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:116-124.
51. Wechsler ME, Laviolette M, Rubin AS, et al. Bronchial thermoplasty: Long-term safety and effectiveness in patients with severe persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1295-1302.
52. Chupp G, Laviolette M, Cohn L, et al. Long-term outcomes of bronchial thermoplasty in subjects with severe asthma: A comparison of 3-year follow-up results from two prospective multicentre studies. Eur Respir J. 2017;50:1700017.
53. Abramson MJ, Puy RM, Weiner JM. Injection allergen immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(8):CD001186.
54. Normansell R, Kew KM, Bridgman AL. Sublingual immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(8):CD011293.
55. Mosbech H, Deckelmann R, de Blay F, et al. Standardized quality (SQ) house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet (ALK) reduces inhaled corticosteroid use while maintaining asthma control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:568575.e7.
56. Virchow JC, Backer V, Kuna P, et al. Efficacy of a house dust mite sublingual allergen immunotherapy tablet in adults with allergic asthma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:1715-1725.
57. Johnston SL, Szigeti M, Cross M, et al. Azithromycin for acute exacerbations of asthma : the AZALEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1630-1637.
58. Brusselle GG, Vanderstichele C, Jordens P, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations in severe asthma (AZISAST): a multicentre randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Thorax. 2013;68:322-329.
59. Gibson PG, Yang IA, Upham JW, et al. Effect of azithromycin on asthma exacerbations and quality of life in adults with persistent uncontrolled asthma (AMAZES): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;390:659-668.
Recent advances in our understanding of asthma pathophysiology have led to the development of new treatment approaches to this chronic respiratory condition, which affects 25 million Americans or nearly 8% of the population.1 As a result, asthma treatment options have expanded from just simple inhalers and corticosteroids to include
The pathophysiology of asthma provides key targets for therapy
There are 2 basic phenotypes of asthma—neutrophilic predominant and eosinophilic predominant—and 3 key components to its pathophysiology2:
Airway inflammation. Asthma is mediated through either a type 1 T-helper (Th-1) cell or a type 2 T-helper (Th-2) cell response, the pathways of which have a fair amount of overlap (FIGURE). In the neutrophilic-predominant phenotype, irritants, pollutants, and viruses trigger an innate Th-1 cell–mediated pathway that leads to subsequent neutrophil release. This asthma phenotype responds poorly to standard asthma therapy.2-4
In the eosinophilic-predominant phenotype, environmental allergic antigens induce a Th-2 cell–mediated response in the airways of patients with asthma.5-7 This creates a downstream effect on the release of interleukins (IL) including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. IL-4 triggers immunoglobulin (Ig) E release, which subsequently induces mast cells to release inflammatory cytokines, while IL-5 and IL-13 are responsible for eosinophilic response. These cytokines and eosinophils induce airway hyperresponsiveness, remodeling, and mucus production. Through repeated exposure, chronic inflammation develops and subsequently causes structural changes related to increased smooth muscle mass, goblet cell hyperplasia, and thickening of lamina reticularis.8,9 Understanding of this pathobiological pathway has led to the development of anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 drugs (to be discussed shortly).
Airway obstruction. Early asthmatic response is due to acute bronchoconstriction secondary to IgE; this is followed by airway edema occurring 6 to 24 hours after an acute event (called late asthmatic response). The obstruction is worsened by an overproduction of mucus, which may take weeks to resolve.10 Longstanding inflammation can lead to structural changes and reduced airflow reversibility.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is induced by various forms of allergens, pollutants, or viral upper respiratory infections. Sympathetic control in the airway is mediated via beta-2 adrenoceptors expressed on airway smooth muscle, which are responsible for the effect of bronchodilation in response to albuterol.11,12 Cholinergic pathways may further contribute to bronchial hyperresponsiveness and form the basis for the efficacy of anticholinergic therapy.12,13
What we’ve learned about asthma can inform treatment decisions
Presentation may vary, as asthma has many forms including cough-variant asthma and exercise-induced asthma. Airflow limitation is typically identified through spirometry and characterized by reduced (< 70% in adults) forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC) or bronchodilator response positivity (an increase in post-bronchodilator FEV1 > 12% or FVC > 200 mL from baseline).2 If spirometry is not diagnostic but suspicion for asthma remains, bronchial provocation testing or exercise challenge testing may be needed.
Continue to: Additional diagnostic considerations...
Additional diagnostic considerations may impact the treatment plan for patients with asthma:
Asthma and COPD. A history of smoking is a key factor in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)—but many patients with asthma are also smokers. This subgroup may have asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). It is important to determine whether these patients are asthma predominant or COPD predominant, because appropriate first-line treatment will differ. Patients who are COPD predominant demonstrate reduced diffusion capacity (DLCO) and abnormal PaCO2 on arterial blood gas. They also may show more structural damage on chest computed tomography (CT) than patients with asthma do. Asthma-predominant patients are more likely to have eosinophilia.14
Patients with severe persistent asthma or frequent exacerbations, or those receiving step-up therapy, may require additional serologic testing. Specialized testing for IgE and eosinophil count, as well as a sensitized allergy panel, may help clinicians in selecting specific biological therapies for treatment of severe asthma (further discussion to follow). We recommend using a serum allergy panel, as it is a quick and easy way to identify patients with extrinsic allergies, whereas skin-based testing is often time consuming and may require referral to a specialist.2,5,15
Aspergillus. An additional consideration is testing for Aspergillus antibodies. Aspergillus is a ubiquitous fungus found in the airways of humans. In patients with asthma, however, it can trigger an intense inflammatory response known as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. ABPA is not an infection. It should be considered in patients who have lived in a damp, old housing environment with possible mold exposure. Treatment of ABPA involves oral corticosteroids; there are varying reports of efficacy with voriconazole or itraconazole as suppressive therapy or steroid-sparing treatment.16-18
Getting a handle on an ever-expanding asthma Tx arsenal
The goals of asthma treatment are symptom control and risk minimization. Treatment choices are dictated in part by disease severity (mild, moderate, severe) and classification (intermittent, persistent). Asthma therapy is traditionally described as step-up and step-down; TABLE 2 summarizes available pharmacotherapy for asthma and provides a framework for add-on therapy as the disease advances.
Continue to: Over the past decade...
Over the past decade, a number of therapeutic options have been introduced or added to the pantheon of asthma treatment.
Inhaled medications
This category includes inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), which are recommended for use alone or in combination with long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) or with long-acting
ICS is the first choice for long-term control of persistent asthma.2 Its molecular effects include activating anti-inflammatory genes, switching off inflammatory genes, and inhibiting inflammatory cells, combined with enhancement of beta-2-adrenergic receptor expression. The cumulative effect is reduction in airway responsiveness in asthma patients.19-22
LABAs are next in line in the step-up, step-down model of symptom management. LABAs should not be prescribed as stand-alone therapy in patients with asthma, as they have received a black box warning from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for an increase in asthma-related death23—a concern that has not been demonstrated with the combination of ICS-LABA.
LABAs cause smooth muscle relaxation in the lungs.24 There are 3 combination products currently available: once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (Breo), twice-daily fluticasone propionate/salmeterol (Advair), and twice-daily budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort).
Continue to: Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol...
Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol has been shown to improve mean FEV1.25 In a 24-week, open-label, multicenter randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of all 3 combination ICS-LABAs, preliminary results indicated that—at least in a tightly controlled setting—once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol provides asthma control similar to the twice-daily combinations and is well tolerated.26
Two ultra-long-acting (24-hour) LABAs, olodaterol (Striverdi Respimat) and indacaterol (Arcapta Neohaler), are being studied for possible use in asthma treatment. In a phase 2 trial investigating therapy for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma, 24-hour FEV1 improved with olodeaterol when compared to placebo.27
Another ongoing clinical trial is studying the effects of ultra-long-acting bronchodilator therapy (olodaterol vs combination olodaterol/tiotropium) in asthma patients who smoke and who are already using ICS (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02682862). Indacaterol has been shown to be effective in the treatment of moderate-to-severe asthma in a once-a-day dosing regimen.28 However, when compared to mometasone alone, a combination of indacaterol and mometasone demonstrated no statistically significant reduction in time to serious exacerbation.29
The LAMA tiotropium is recommended as add-on therapy for patients whose asthma is uncontrolled despite use of low-dose ICS-LABA or as an alternative to high-dose ICS-LABA, per Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2019 guidelines.15
Tiotropium induces bronchodilation by selectively inhibiting the action of acetylcholine at muscarinic (M) receptors in bronchial smooth muscles; it has a longer duration of action because of its slower dissociation from receptor types M1 and M3.30 Tiotropium respimat (Spiriva, Tiova) has been approved for COPD for many years; in 2013, it was shown to prevent worsening of symptomatic asthma and increase time to first severe exacerbation.13 The FDA subsequently approved tiotropium as an add-on treatment for patients with uncontrolled asthma despite use of ICS-LABA.
Continue to: Glycopyrronium bromide...
Glycopyrronium bromide (glycopyrrolate, multiple brand names) and umeclidinium (Incruse Ellipta) are LAMAs that are approved for COPD treatment but have not yet been approved for patients who have asthma only.31
Biological therapies
In the past few years, improved understanding of asthma’s pathophysiology has led to the development of biological therapy for severe asthma. This therapy is directed at Th-2 inflammatory pathways (FIGURE) and targets various inflammatory markers, such as IgE, IL-5, and eosinophils.
Biologicals are not the first-line therapy for the management of severe asthma. Ideal candidates for this therapy are patients who have exhausted other forms of severe asthma treatment, including ICS-LABA, LAMA, leukotriene receptor antagonists, and mucus-clearing agents. Patients with frequent exacerbations who need continuous steroids or need steroids at least twice a year should be considered for biologicals.32
All biological therapies must be administered in a clinical setting, as they carry risk for anaphylaxis. TABLE 315,33-47 summarizes all approved biologicals for the management of severe asthma.
Anti-IgE therapy. Omalizumab (Xolair) was the first approved biological therapy for severe asthma (in 2003). It is a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to free IgE and down regulates the inflammatory cascade. It is therefore best suited for patients with early-onset allergic asthma with a high IgE count. The dose and frequency (once or twice per month) of omalizumab are based on IgE levels and patient weight. Omalizumab reduces asthma exacerbation (up to 45%) and hospitalization (up to 85%).34 Omalizumab also reduces the need for high-dose ICS-LABA therapy and improves quality of life (QoL).33,34
Continue to: Its efficacy and safety...
Its efficacy and safety have been proven outside the clinical trial setting. Treatment response should be assessed over a 3- to 4-month period, using fractional exhalation of nitric oxide (FeNO); serial measurement of IgE levels is not recommended for this purpose. Once started, treatment should be considered long term, as discontinuation of treatment has been shown to lead to recurrence of symptoms and exacerbation.35,36 Of note, the GINA guidelines recommend omalizumab over prednisone as add-on therapy for severe persistent asthma.15
Anti-IL-5 therapy. IL-5 is the main cytokine for growth, differentiation, and activation of eosinophils in the Th-2-mediated inflammatory cascade. Mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab are 3 FDA-approved anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody therapies for severe eosinophilic asthma. Mepolizumab has been the most commonly studied anti-IL-5 therapy, while benralizumab, the latest of the 3, has a unique property of inducing eosinophilic apoptosis. There has been no direct comparison of the different anti-IL-5 therapies.
Mepolizumab (Nucala) is a mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-5 and prevents it from binding to IL-5 receptors on the eosinophil surface. Mepolizumab should be considered in patients with a peripheral eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL; it has shown a trend of greater benefit in patients with a very high eosinophil count (75% reduction in exacerbation with blood eosinophil count > 500 cells/mcL compared to 56% exacerbation reduction with blood eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL).37
Mepolizumab has consistently been shown to reduce asthma exacerbation (by about 50%) and emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalization (60%), when compared with placebo in clinical trials.37,38 It also reduces the need for oral corticosteroids, an effect sustained for up to 52 weeks.39,40 The Mepolizumab adjUnctive therapy in subjects with Severe eosinophiliC Asthma (MUSCA) study showed that mepolizumab was associated with significant improvement of health-related QoL, lung function, and asthma symptoms in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.38
GINA guidelines recommend mepolizumab as an add-on therapy for severe asthma. Mepolizumab is given as a fixed dose of 100 mg every 4 weeks. A 300-mg dose has also been approved for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Monitoring with serial eosinophils might be of value in determining the efficacy of the drug. Mepolizumab is currently in clinical trials for a broad spectrum of diseases, including COPD, hyper-eosinophilic syndrome, and ABPA.
Continue to: Reslizumab (Cinqair)...
Reslizumab (Cinqair) is a rat anti-human monoclonal antibody of the IgG4κ subtype that binds to a small region of IL-5 and subsequently blocks IL-5 from binding to the IL-5 receptor complex on the cell surface of eosinophils. It is currently approved for use as a 3-mg/kg IV infusion every 4 weeks. In large clinical trials,41-43 reslizumab decreased asthma exacerbation and improved QoL, asthma control, and lung function. Most of the study populations had an eosinophil count > 400 cells/mcL. A small study also suggested patients with severe eosinophilic asthma with prednisone dependency (10 mg/d) had better sputum eosinophilia suppression and asthma control with reslizumab when compared with mepolizumab.44
Benralizumab (Fasenra) is a humanized IgG1 anti-IL-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody derived from mice. It induces apoptosis of eosinophils and, to a lesser extent, of basophils.45 In clinical trials, it demonstrated a reduction in asthma exacerbation rate and improvement in prebronchodilator FEV1 and asthma symptoms.46,47 It does not need reconstitution, as the drug is dispensed as prefilled syringes with fixed non-weight-based dosing. Another potential advantage to benralizumab is that after the loading dose, subsequent doses are given every 8 weeks.
Bronchial thermoplasty
Bronchial thermoplasty (BT) is a novel nonpharmacologic intervention that entails the delivery of controlled radiofrequency-generated heat via a catheter inserted into the bronchial tree of the lungs through a flexible bronchoscope. The potential mechanism of action is reduction in airway smooth muscle mass and inflammatory markers.
Evidence for BT started with the Asthma Intervention Research (AIR) and Research in Severe Asthma (RISA) trials.48,49 In the AIR study, BT was shown to reduce the rate of mild exacerbations and improve morning peak expiratory flow and asthma scores at 12 months.48 In the RISA trial, BT resulted in improvements in Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) score and need for rescue medication at 52 weeks, as well as a trend toward decrease in steroid use.49
However, these studies were criticized for not having a placebo group—an issue addressed in the AIR2 trial, which compared bronchial thermoplasty with a sham procedure. AIR2 demonstrated improvements in AQLQ score and a 32% reduction in severe exacerbations and 84% fewer ED visits in the post-treatment period (up to 1 year post treatment).50
Continue to: Both treatment groups...
Both treatment groups experienced an increase in respiratory adverse events: during the treatment period (up to 6 weeks post procedure), 16 subjects (8.4%) in the BT group required 19 hospitalizations for respiratory symptoms and 2 subjects (2%) in the sham group required 2 hospitalizations. A follow-up observational study involving a cohort of AIR2 patients demonstrated long-lasting effects of BT in asthma exacerbation frequency, ED visits, and stabilization of FEV1 for up to 5 years.51
The Post-market Post-FDA Approval Clinical Trial Evaluating Bronchial Thermoplasty in Severe Persistent Asthma (PAS2) showed similar beneficial effects of BT on asthma control despite enrolling subjects who may have had poorer asthma control in the “real world” setting.52
In summary, BT results in modest improvements in AQLQ scores and clinically worthwhile reductions in severe exacerbations and ED visits in the year post treatment, which may persist for up to 5 years. BT causes short-term increases in asthma-related morbidity, including hospital admissions. While there is encouraging data and the scope is increasing, BT remains limited to carefully selected (by a specialist) patients with severe asthma that is poorly controlled despite maximal inhaled therapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy for allergic disease is aimed at inducing immune tolerance to an allergen and alleviating allergic symptoms. This is done by administration of the allergen to which the patient is sensitive. There are 2 approaches: subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT; a dissolvable tablet under the tongue or an aqueous or liquid extract).
Immunotherapy is generally reserved for patients who have allergic symptoms with exposure to a trigger and evidence (through skin or serum testing) of specific IgE to that trigger, especially if there is poor response to pharmacotherapy and allergen avoidance. Overall, evidence in this field is limited: Most studies have included patients with mild asthma, and few studies have compared immunotherapy with pharmacologic therapy or used standardized outcomes, such as exacerbations.
Continue to: SCIT
SCIT. A 2010 Cochrane review concluded that SCIT reduces asthma symptoms and use of asthma medications and improves bronchial hyperreactivity. Adverse effects include uncommon anaphylactic reactions, which may be life-threatening.53
SLIT has advantages over SCIT as it can be administered by patients or caregivers, does not require injections, and carries a much lower risk for anaphylaxis. Modest benefits have been seen in adults and children, but there is concern about the design of many early studies.
A 2015 Cochrane review of SLIT in asthma recommended further research using validated scales and important outcomes for patients and decision makers so that SLIT can be properly assessed as a clinical treatment for asthma.54 A subsequently published study of SLIT for house dust mites (HDM) in patients with asthma and HDM allergic rhinitis demonstrated a modest reduction in use of ICS with high-dose SLIT.55
In another recent study, among adults with HDM allergy-related asthma not well controlled by ICS, the addition of HDM SLIT to maintenance medications improved time to first moderate-or-severe asthma exacerbation during ICS reduction.56 Additional studies are needed to assess long-term efficacy and safety. However, for patients who experience exacerbations despite use of a low-dose or medium-dose ICS-LABA combination, SLIT can now be considered as an add-on therapy.
Per the GINA guidelines, the potential benefits of allergen immunotherapy must be weighed against the risk for adverse effects, including anaphylaxis, and the inconvenience and cost of the prolonged course of therapy.15
Continue to: Azithromycin
Azithromycin
Macrolides have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects in addition to their antibacterial effects. Maintenance treatment with macrolides such as azithromycin has been proven to be effective in chronic neutrophilic airway diseases (FIGURE). There have been attempts to assess whether this therapy can be useful in asthma management, as well. Some randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have shown conflicting results, and early studies were limited by lack of data, heterogeneous results, and inadequate study designs.
The AZithromycin Against pLacebo in Exacerbations of Asthma (AZALEA) study was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in the United Kingdom among patients requiring emergency care for acute asthma exacerbations. Azithromycin added to standard care for asthma attacks did not result in clinical benefit.57 While azithromycin in acute exacerbation is not currently recommended, recent trials in outpatient settings have shown promise.
The AZIthromycin in Severe ASThma study (AZISAST) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in subjects with exacerbation-prone severe asthma in Belgium. Low-dose azithromycin (250 mg 3 times a week) as an add-on treatment to combination ICS-LABA therapy for 6 months did not reduce the rate of severe asthma exacerbations or lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI). However, subjects with a non-eosinophilic variant (neutrophilic phenotype) experienced significant reduction in the rate of exacerbation and LRTI.58
The recently published Asthma and Macrolides: the AZithromycin Efficacy and Safety Study (AMAZES) shows promise for chronic azithromycin therapy as an add-on to medium-to-high-dose inhaled steroids and a long-acting bronchodilator in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma. This was a large multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial in New Zealand and Australia. Patients were excluded if they had hearing impairment or abnormally prolonged QTc. Azithromycin at a dose of 500 mg 3 times a week for 48 months reduced asthma exacerbations and improved QoL compared to placebo. The effect was sustained between subgroups based on phenotypes (eosinophilic vs noneosinophilic; frequent exacerbators vs nonfrequent exacerbators) and even among those with symptom differences at baseline (eg, cough or sputum positivity). The rate of antibiotic courses for respiratory infectious episodes was significantly reduced in the azithromycin-treated group.59
The take-away: Chronic azithromycin might prove to be a useful agent in the long-term management of asthma patients whose disease is not well controlled on inhaled therapy. Further studies on mechanism and effects of prolonged antibiotic use will shed more light. For more information, see When guideline treatment of asthma fails, consider a macrolide antibiotic; http://bit.ly/2vDAWc6.
Continue to: A new era
A new era
We have entered an exciting era of asthma management, with the introduction of several novel modalities, such as biological therapy and bronchial thermoplasty, as well as use of known drugs such as macrolides, immunotherapy, and LAMA. This was made possible through a better understanding of the biological pathways of asthma. Asthma management has moved toward more personalized, targeted therapy based on asthma phenotypes.
It’s important to remember, however, that pharmacological and nonpharmacological aspects of management—including inhaler techniques, adherence to inhaler therapy, vaccinations, control of asthma triggers, and smoking cessation—remain the foundation of optimal asthma management and need to be aggressively addressed before embarking on advanced treatment options. Patients whose asthma is not well controlled with inhaled medications or who have frequent exacerbations (requiring use of steroids) should be comanaged by an expert asthma specialist to explore all possible therapies.
CORRESPONDENCE
Mayur Rali, MD, 995 Newbridge Road, Bellmore, NY 11710; mrali@northwell.edu
Recent advances in our understanding of asthma pathophysiology have led to the development of new treatment approaches to this chronic respiratory condition, which affects 25 million Americans or nearly 8% of the population.1 As a result, asthma treatment options have expanded from just simple inhalers and corticosteroids to include
The pathophysiology of asthma provides key targets for therapy
There are 2 basic phenotypes of asthma—neutrophilic predominant and eosinophilic predominant—and 3 key components to its pathophysiology2:
Airway inflammation. Asthma is mediated through either a type 1 T-helper (Th-1) cell or a type 2 T-helper (Th-2) cell response, the pathways of which have a fair amount of overlap (FIGURE). In the neutrophilic-predominant phenotype, irritants, pollutants, and viruses trigger an innate Th-1 cell–mediated pathway that leads to subsequent neutrophil release. This asthma phenotype responds poorly to standard asthma therapy.2-4
In the eosinophilic-predominant phenotype, environmental allergic antigens induce a Th-2 cell–mediated response in the airways of patients with asthma.5-7 This creates a downstream effect on the release of interleukins (IL) including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. IL-4 triggers immunoglobulin (Ig) E release, which subsequently induces mast cells to release inflammatory cytokines, while IL-5 and IL-13 are responsible for eosinophilic response. These cytokines and eosinophils induce airway hyperresponsiveness, remodeling, and mucus production. Through repeated exposure, chronic inflammation develops and subsequently causes structural changes related to increased smooth muscle mass, goblet cell hyperplasia, and thickening of lamina reticularis.8,9 Understanding of this pathobiological pathway has led to the development of anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 drugs (to be discussed shortly).
Airway obstruction. Early asthmatic response is due to acute bronchoconstriction secondary to IgE; this is followed by airway edema occurring 6 to 24 hours after an acute event (called late asthmatic response). The obstruction is worsened by an overproduction of mucus, which may take weeks to resolve.10 Longstanding inflammation can lead to structural changes and reduced airflow reversibility.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is induced by various forms of allergens, pollutants, or viral upper respiratory infections. Sympathetic control in the airway is mediated via beta-2 adrenoceptors expressed on airway smooth muscle, which are responsible for the effect of bronchodilation in response to albuterol.11,12 Cholinergic pathways may further contribute to bronchial hyperresponsiveness and form the basis for the efficacy of anticholinergic therapy.12,13
What we’ve learned about asthma can inform treatment decisions
Presentation may vary, as asthma has many forms including cough-variant asthma and exercise-induced asthma. Airflow limitation is typically identified through spirometry and characterized by reduced (< 70% in adults) forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC) or bronchodilator response positivity (an increase in post-bronchodilator FEV1 > 12% or FVC > 200 mL from baseline).2 If spirometry is not diagnostic but suspicion for asthma remains, bronchial provocation testing or exercise challenge testing may be needed.
Continue to: Additional diagnostic considerations...
Additional diagnostic considerations may impact the treatment plan for patients with asthma:
Asthma and COPD. A history of smoking is a key factor in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)—but many patients with asthma are also smokers. This subgroup may have asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). It is important to determine whether these patients are asthma predominant or COPD predominant, because appropriate first-line treatment will differ. Patients who are COPD predominant demonstrate reduced diffusion capacity (DLCO) and abnormal PaCO2 on arterial blood gas. They also may show more structural damage on chest computed tomography (CT) than patients with asthma do. Asthma-predominant patients are more likely to have eosinophilia.14
Patients with severe persistent asthma or frequent exacerbations, or those receiving step-up therapy, may require additional serologic testing. Specialized testing for IgE and eosinophil count, as well as a sensitized allergy panel, may help clinicians in selecting specific biological therapies for treatment of severe asthma (further discussion to follow). We recommend using a serum allergy panel, as it is a quick and easy way to identify patients with extrinsic allergies, whereas skin-based testing is often time consuming and may require referral to a specialist.2,5,15
Aspergillus. An additional consideration is testing for Aspergillus antibodies. Aspergillus is a ubiquitous fungus found in the airways of humans. In patients with asthma, however, it can trigger an intense inflammatory response known as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. ABPA is not an infection. It should be considered in patients who have lived in a damp, old housing environment with possible mold exposure. Treatment of ABPA involves oral corticosteroids; there are varying reports of efficacy with voriconazole or itraconazole as suppressive therapy or steroid-sparing treatment.16-18
Getting a handle on an ever-expanding asthma Tx arsenal
The goals of asthma treatment are symptom control and risk minimization. Treatment choices are dictated in part by disease severity (mild, moderate, severe) and classification (intermittent, persistent). Asthma therapy is traditionally described as step-up and step-down; TABLE 2 summarizes available pharmacotherapy for asthma and provides a framework for add-on therapy as the disease advances.
Continue to: Over the past decade...
Over the past decade, a number of therapeutic options have been introduced or added to the pantheon of asthma treatment.
Inhaled medications
This category includes inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), which are recommended for use alone or in combination with long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) or with long-acting
ICS is the first choice for long-term control of persistent asthma.2 Its molecular effects include activating anti-inflammatory genes, switching off inflammatory genes, and inhibiting inflammatory cells, combined with enhancement of beta-2-adrenergic receptor expression. The cumulative effect is reduction in airway responsiveness in asthma patients.19-22
LABAs are next in line in the step-up, step-down model of symptom management. LABAs should not be prescribed as stand-alone therapy in patients with asthma, as they have received a black box warning from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for an increase in asthma-related death23—a concern that has not been demonstrated with the combination of ICS-LABA.
LABAs cause smooth muscle relaxation in the lungs.24 There are 3 combination products currently available: once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (Breo), twice-daily fluticasone propionate/salmeterol (Advair), and twice-daily budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort).
Continue to: Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol...
Once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol has been shown to improve mean FEV1.25 In a 24-week, open-label, multicenter randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of all 3 combination ICS-LABAs, preliminary results indicated that—at least in a tightly controlled setting—once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol provides asthma control similar to the twice-daily combinations and is well tolerated.26
Two ultra-long-acting (24-hour) LABAs, olodaterol (Striverdi Respimat) and indacaterol (Arcapta Neohaler), are being studied for possible use in asthma treatment. In a phase 2 trial investigating therapy for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma, 24-hour FEV1 improved with olodeaterol when compared to placebo.27
Another ongoing clinical trial is studying the effects of ultra-long-acting bronchodilator therapy (olodaterol vs combination olodaterol/tiotropium) in asthma patients who smoke and who are already using ICS (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02682862). Indacaterol has been shown to be effective in the treatment of moderate-to-severe asthma in a once-a-day dosing regimen.28 However, when compared to mometasone alone, a combination of indacaterol and mometasone demonstrated no statistically significant reduction in time to serious exacerbation.29
The LAMA tiotropium is recommended as add-on therapy for patients whose asthma is uncontrolled despite use of low-dose ICS-LABA or as an alternative to high-dose ICS-LABA, per Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2019 guidelines.15
Tiotropium induces bronchodilation by selectively inhibiting the action of acetylcholine at muscarinic (M) receptors in bronchial smooth muscles; it has a longer duration of action because of its slower dissociation from receptor types M1 and M3.30 Tiotropium respimat (Spiriva, Tiova) has been approved for COPD for many years; in 2013, it was shown to prevent worsening of symptomatic asthma and increase time to first severe exacerbation.13 The FDA subsequently approved tiotropium as an add-on treatment for patients with uncontrolled asthma despite use of ICS-LABA.
Continue to: Glycopyrronium bromide...
Glycopyrronium bromide (glycopyrrolate, multiple brand names) and umeclidinium (Incruse Ellipta) are LAMAs that are approved for COPD treatment but have not yet been approved for patients who have asthma only.31
Biological therapies
In the past few years, improved understanding of asthma’s pathophysiology has led to the development of biological therapy for severe asthma. This therapy is directed at Th-2 inflammatory pathways (FIGURE) and targets various inflammatory markers, such as IgE, IL-5, and eosinophils.
Biologicals are not the first-line therapy for the management of severe asthma. Ideal candidates for this therapy are patients who have exhausted other forms of severe asthma treatment, including ICS-LABA, LAMA, leukotriene receptor antagonists, and mucus-clearing agents. Patients with frequent exacerbations who need continuous steroids or need steroids at least twice a year should be considered for biologicals.32
All biological therapies must be administered in a clinical setting, as they carry risk for anaphylaxis. TABLE 315,33-47 summarizes all approved biologicals for the management of severe asthma.
Anti-IgE therapy. Omalizumab (Xolair) was the first approved biological therapy for severe asthma (in 2003). It is a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to free IgE and down regulates the inflammatory cascade. It is therefore best suited for patients with early-onset allergic asthma with a high IgE count. The dose and frequency (once or twice per month) of omalizumab are based on IgE levels and patient weight. Omalizumab reduces asthma exacerbation (up to 45%) and hospitalization (up to 85%).34 Omalizumab also reduces the need for high-dose ICS-LABA therapy and improves quality of life (QoL).33,34
Continue to: Its efficacy and safety...
Its efficacy and safety have been proven outside the clinical trial setting. Treatment response should be assessed over a 3- to 4-month period, using fractional exhalation of nitric oxide (FeNO); serial measurement of IgE levels is not recommended for this purpose. Once started, treatment should be considered long term, as discontinuation of treatment has been shown to lead to recurrence of symptoms and exacerbation.35,36 Of note, the GINA guidelines recommend omalizumab over prednisone as add-on therapy for severe persistent asthma.15
Anti-IL-5 therapy. IL-5 is the main cytokine for growth, differentiation, and activation of eosinophils in the Th-2-mediated inflammatory cascade. Mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab are 3 FDA-approved anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody therapies for severe eosinophilic asthma. Mepolizumab has been the most commonly studied anti-IL-5 therapy, while benralizumab, the latest of the 3, has a unique property of inducing eosinophilic apoptosis. There has been no direct comparison of the different anti-IL-5 therapies.
Mepolizumab (Nucala) is a mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-5 and prevents it from binding to IL-5 receptors on the eosinophil surface. Mepolizumab should be considered in patients with a peripheral eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL; it has shown a trend of greater benefit in patients with a very high eosinophil count (75% reduction in exacerbation with blood eosinophil count > 500 cells/mcL compared to 56% exacerbation reduction with blood eosinophil count > 150 cells/mcL).37
Mepolizumab has consistently been shown to reduce asthma exacerbation (by about 50%) and emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalization (60%), when compared with placebo in clinical trials.37,38 It also reduces the need for oral corticosteroids, an effect sustained for up to 52 weeks.39,40 The Mepolizumab adjUnctive therapy in subjects with Severe eosinophiliC Asthma (MUSCA) study showed that mepolizumab was associated with significant improvement of health-related QoL, lung function, and asthma symptoms in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.38
GINA guidelines recommend mepolizumab as an add-on therapy for severe asthma. Mepolizumab is given as a fixed dose of 100 mg every 4 weeks. A 300-mg dose has also been approved for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Monitoring with serial eosinophils might be of value in determining the efficacy of the drug. Mepolizumab is currently in clinical trials for a broad spectrum of diseases, including COPD, hyper-eosinophilic syndrome, and ABPA.
Continue to: Reslizumab (Cinqair)...
Reslizumab (Cinqair) is a rat anti-human monoclonal antibody of the IgG4κ subtype that binds to a small region of IL-5 and subsequently blocks IL-5 from binding to the IL-5 receptor complex on the cell surface of eosinophils. It is currently approved for use as a 3-mg/kg IV infusion every 4 weeks. In large clinical trials,41-43 reslizumab decreased asthma exacerbation and improved QoL, asthma control, and lung function. Most of the study populations had an eosinophil count > 400 cells/mcL. A small study also suggested patients with severe eosinophilic asthma with prednisone dependency (10 mg/d) had better sputum eosinophilia suppression and asthma control with reslizumab when compared with mepolizumab.44
Benralizumab (Fasenra) is a humanized IgG1 anti-IL-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody derived from mice. It induces apoptosis of eosinophils and, to a lesser extent, of basophils.45 In clinical trials, it demonstrated a reduction in asthma exacerbation rate and improvement in prebronchodilator FEV1 and asthma symptoms.46,47 It does not need reconstitution, as the drug is dispensed as prefilled syringes with fixed non-weight-based dosing. Another potential advantage to benralizumab is that after the loading dose, subsequent doses are given every 8 weeks.
Bronchial thermoplasty
Bronchial thermoplasty (BT) is a novel nonpharmacologic intervention that entails the delivery of controlled radiofrequency-generated heat via a catheter inserted into the bronchial tree of the lungs through a flexible bronchoscope. The potential mechanism of action is reduction in airway smooth muscle mass and inflammatory markers.
Evidence for BT started with the Asthma Intervention Research (AIR) and Research in Severe Asthma (RISA) trials.48,49 In the AIR study, BT was shown to reduce the rate of mild exacerbations and improve morning peak expiratory flow and asthma scores at 12 months.48 In the RISA trial, BT resulted in improvements in Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) score and need for rescue medication at 52 weeks, as well as a trend toward decrease in steroid use.49
However, these studies were criticized for not having a placebo group—an issue addressed in the AIR2 trial, which compared bronchial thermoplasty with a sham procedure. AIR2 demonstrated improvements in AQLQ score and a 32% reduction in severe exacerbations and 84% fewer ED visits in the post-treatment period (up to 1 year post treatment).50
Continue to: Both treatment groups...
Both treatment groups experienced an increase in respiratory adverse events: during the treatment period (up to 6 weeks post procedure), 16 subjects (8.4%) in the BT group required 19 hospitalizations for respiratory symptoms and 2 subjects (2%) in the sham group required 2 hospitalizations. A follow-up observational study involving a cohort of AIR2 patients demonstrated long-lasting effects of BT in asthma exacerbation frequency, ED visits, and stabilization of FEV1 for up to 5 years.51
The Post-market Post-FDA Approval Clinical Trial Evaluating Bronchial Thermoplasty in Severe Persistent Asthma (PAS2) showed similar beneficial effects of BT on asthma control despite enrolling subjects who may have had poorer asthma control in the “real world” setting.52
In summary, BT results in modest improvements in AQLQ scores and clinically worthwhile reductions in severe exacerbations and ED visits in the year post treatment, which may persist for up to 5 years. BT causes short-term increases in asthma-related morbidity, including hospital admissions. While there is encouraging data and the scope is increasing, BT remains limited to carefully selected (by a specialist) patients with severe asthma that is poorly controlled despite maximal inhaled therapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy for allergic disease is aimed at inducing immune tolerance to an allergen and alleviating allergic symptoms. This is done by administration of the allergen to which the patient is sensitive. There are 2 approaches: subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT; a dissolvable tablet under the tongue or an aqueous or liquid extract).
Immunotherapy is generally reserved for patients who have allergic symptoms with exposure to a trigger and evidence (through skin or serum testing) of specific IgE to that trigger, especially if there is poor response to pharmacotherapy and allergen avoidance. Overall, evidence in this field is limited: Most studies have included patients with mild asthma, and few studies have compared immunotherapy with pharmacologic therapy or used standardized outcomes, such as exacerbations.
Continue to: SCIT
SCIT. A 2010 Cochrane review concluded that SCIT reduces asthma symptoms and use of asthma medications and improves bronchial hyperreactivity. Adverse effects include uncommon anaphylactic reactions, which may be life-threatening.53
SLIT has advantages over SCIT as it can be administered by patients or caregivers, does not require injections, and carries a much lower risk for anaphylaxis. Modest benefits have been seen in adults and children, but there is concern about the design of many early studies.
A 2015 Cochrane review of SLIT in asthma recommended further research using validated scales and important outcomes for patients and decision makers so that SLIT can be properly assessed as a clinical treatment for asthma.54 A subsequently published study of SLIT for house dust mites (HDM) in patients with asthma and HDM allergic rhinitis demonstrated a modest reduction in use of ICS with high-dose SLIT.55
In another recent study, among adults with HDM allergy-related asthma not well controlled by ICS, the addition of HDM SLIT to maintenance medications improved time to first moderate-or-severe asthma exacerbation during ICS reduction.56 Additional studies are needed to assess long-term efficacy and safety. However, for patients who experience exacerbations despite use of a low-dose or medium-dose ICS-LABA combination, SLIT can now be considered as an add-on therapy.
Per the GINA guidelines, the potential benefits of allergen immunotherapy must be weighed against the risk for adverse effects, including anaphylaxis, and the inconvenience and cost of the prolonged course of therapy.15
Continue to: Azithromycin
Azithromycin
Macrolides have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects in addition to their antibacterial effects. Maintenance treatment with macrolides such as azithromycin has been proven to be effective in chronic neutrophilic airway diseases (FIGURE). There have been attempts to assess whether this therapy can be useful in asthma management, as well. Some randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have shown conflicting results, and early studies were limited by lack of data, heterogeneous results, and inadequate study designs.
The AZithromycin Against pLacebo in Exacerbations of Asthma (AZALEA) study was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in the United Kingdom among patients requiring emergency care for acute asthma exacerbations. Azithromycin added to standard care for asthma attacks did not result in clinical benefit.57 While azithromycin in acute exacerbation is not currently recommended, recent trials in outpatient settings have shown promise.
The AZIthromycin in Severe ASThma study (AZISAST) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in subjects with exacerbation-prone severe asthma in Belgium. Low-dose azithromycin (250 mg 3 times a week) as an add-on treatment to combination ICS-LABA therapy for 6 months did not reduce the rate of severe asthma exacerbations or lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI). However, subjects with a non-eosinophilic variant (neutrophilic phenotype) experienced significant reduction in the rate of exacerbation and LRTI.58
The recently published Asthma and Macrolides: the AZithromycin Efficacy and Safety Study (AMAZES) shows promise for chronic azithromycin therapy as an add-on to medium-to-high-dose inhaled steroids and a long-acting bronchodilator in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma. This was a large multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial in New Zealand and Australia. Patients were excluded if they had hearing impairment or abnormally prolonged QTc. Azithromycin at a dose of 500 mg 3 times a week for 48 months reduced asthma exacerbations and improved QoL compared to placebo. The effect was sustained between subgroups based on phenotypes (eosinophilic vs noneosinophilic; frequent exacerbators vs nonfrequent exacerbators) and even among those with symptom differences at baseline (eg, cough or sputum positivity). The rate of antibiotic courses for respiratory infectious episodes was significantly reduced in the azithromycin-treated group.59
The take-away: Chronic azithromycin might prove to be a useful agent in the long-term management of asthma patients whose disease is not well controlled on inhaled therapy. Further studies on mechanism and effects of prolonged antibiotic use will shed more light. For more information, see When guideline treatment of asthma fails, consider a macrolide antibiotic; http://bit.ly/2vDAWc6.
Continue to: A new era
A new era
We have entered an exciting era of asthma management, with the introduction of several novel modalities, such as biological therapy and bronchial thermoplasty, as well as use of known drugs such as macrolides, immunotherapy, and LAMA. This was made possible through a better understanding of the biological pathways of asthma. Asthma management has moved toward more personalized, targeted therapy based on asthma phenotypes.
It’s important to remember, however, that pharmacological and nonpharmacological aspects of management—including inhaler techniques, adherence to inhaler therapy, vaccinations, control of asthma triggers, and smoking cessation—remain the foundation of optimal asthma management and need to be aggressively addressed before embarking on advanced treatment options. Patients whose asthma is not well controlled with inhaled medications or who have frequent exacerbations (requiring use of steroids) should be comanaged by an expert asthma specialist to explore all possible therapies.
CORRESPONDENCE
Mayur Rali, MD, 995 Newbridge Road, Bellmore, NY 11710; mrali@northwell.edu
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Most recent national asthma data. Updated May 2019. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm. Accessed March 6, 2020.
2. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma—summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(5 suppl):S94-S138.
3. Woodruff PG, Modrek B, Choy DF, et al. T-helper type 2-driven inflammation defines major subphenotypes of asthma [published correction appears in Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(8):796]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:388–395.
4. Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma—present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:57–65.
5. Busse WW. Inflammation in asthma: the cornerstone of the disease and target of therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102(4 pt 2):S17-S22.
6. Lane SJ, Lee TH. Mast cell effector mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(5 pt 2):S67-S71.
7. Robinson DS, Bentley AM, Hartnell A, et al. Activated memory T helper cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with atopic asthma: relation to asthma symptoms, lung function, and bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1993;48:26-32.
8. Grigoraş A, Grigoraş CC, Giuşcă SE, et al. Remodeling of basement membrane in patients with asthma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57:115-119.
9. Huang SK, Xiao HQ, Kleine-Tebbe J, et al. IL-13 expression at the sites of allergen challenge in patients with asthma. J Immunol. 1995;155:2688-2694.
10. Hansbro PM, Starkey MR, Mattes J, et al. Pulmonary immunity during respiratory infections in early life and the development of severe asthma. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11 suppl 5:S297-S302.
11. Apter AJ, Reisine ST, Willard A, et al. The effect of inhaled albuterol in moderate to severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98:295-301.
12. Peters SP, Kunselman SJ, Icitovic N, et al. Tiotropium bromide step-up therapy for adults with uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1715-1726.
13. Kerstjens HA, O’Byrne PM. Tiotropium for the treatment of asthma: a drug safety evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15:1115-1124.
14. Global Initiative for Asthma. Diagnosis of diseases of chronic air flow limitation: asthma, COPD and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) 2014. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GINA_GOLD_ACOS_2014-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
15. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2019. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
16. Khanbabaee G, Enayat J, Chavoshzadeh Z, et al. Serum level of specific IgG antibody for aspergillus and its association with severity of asthma in asthmatic children. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2012;59:43-50.
17. Agbetile J, Bourne M, Fairs A, et al. Effectiveness of voriconazole in the treatment of aspergillus fumigatus-associated asthma (EVITA3 study). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:33-39.
18. Stevens DA, Schwartz HJ, Lee JY, et al. A randomized trial of itraconazole in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:756-762.
19. Barnes PJ. Glucocorticosteroids: current and future directions. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:29-43.
20. Oakley RH, Cidlowski JA. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: new signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1033-1044.
21. Barnes PJ. Scientific rationale for inhaled combination therapy with long-acting beta2-agonists and corticosteroids. Eur Respir J. 2002;19:182-191.
22. Newton R, Giembycz MA. Understanding how long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance the clinical efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma—an update. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:3405-3430.
23. Wijesinghe M, Perrin K, Harwood M, et al. The risk of asthma mortality with inhaled long acting beta-agonists. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:467-472.
24. Cazzola M, Page CP, Rogliani P, et al. β2-agonist therapy in lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:690-696.
25. Bernstein DI, Bateman ED, Woodcock A, et al. Fluticasone furoate (FF)/vilanterol (100/25 mcg or 200/25 mcg) or FF (100 mcg) in persistent asthma. J Asthma. 2015;52:1073-1083.
26. Devillier P, Humbert M, Boye A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (FF/VI) versus twice-daily inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β2-agonists (ICS/LABA) in patients with uncontrolled asthma: an open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Respir Med. 2018;141:111-120.
27. Beeh KM, LaForce C, Gahlemann M, et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study to investigate different dosing regimens of olodaterol delivered via Respimat(R) in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma. Respir Res. 2015;16:87.
28. LaForce C, Alexander M, Deckelmann R, et al. Indacaterol provides sustained 24 h bronchodilation on once-daily dosing in asthma: a 7-day dose-ranging study. Allergy. 2008;63:103-111.
29. Beasley RW, Donohue JF, Mehta R, et al. Effect of once-daily indacaterol maleate/mometasone furoate on exacerbation risk in adolescent and adult asthma: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e006131.
30. Aalbers R, Park HS. Positioning of long-acting muscarinic antagonists in the management of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9:386-393.
31. Lee LA, Briggs A, Edwards LD, et al. A randomized, three-period crossover study of umeclidinium as monotherapy in adult patients with asthma. Respir Med. 2015;109:63-73.
32. Israel E, Reddel HK. Severe and difficult-to-treat asthma in adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:965-976.
33. Normansell R, Walker S, Milan SJ, et al. Omalizumab for asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(1):CD003559.
34. Hanania NA, Wenzel S, Rosen K, et al. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: an analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:804-811.
35. Slavin RG, Ferioli C, Tannenbaum SJ, et al. Asthma symptom re-emergence after omalizumab withdrawal correlates well with increasing IgE and decreasing pharmacokinetic concentrations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:107-113.e3.
36. Ledford D, Busse W, Trzaskoma B, et al. A randomized multicenter study evaluating Xolair persistence of response after long-term therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:162-169.e2.
37. Ortega HG, Liu MC, Pavord ID, et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1198-1207.
38. Chupp GL, Bradford ES, Albers FC, et al. Efficacy of mepolizumab add-on therapy on health-related quality of life and markers of asthma control in severe eosinophilic asthma (MUSCA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:390-400.
39. Lugogo N, Domingo C, Chanez P, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: a multi-center, open-label, phase IIIb study. Clin Ther. 2016;38:2058-2070.e1.
40. Bel EH, Wenzel SE, Thompson PJ, et al. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1189-1197.
41. Castro M, Zangrilli J, Wechsler ME. Corrections. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:e15.
42. Bjermer L, Lemiere C, Maspero J, et al. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil levels: a randomized phase 3 study. Chest. 2016;150:789-798.
43. Corren J, Weinstein S, Janka L, et al. Phase 3 study of reslizumab in patients with poorly controlled asthma: Effects across a broad range of eosinophil counts. Chest. 2016;150:799-810.
44. Mukherjee M, Aleman Paramo F, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Weight-adjusted intravenous reslizumab in severe asthma with inadequate response to fixed-dose subcutaneous mepolizumab. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197:38-46.
45. Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:1344-1353.e2.
46. Bleecker ER, FitzGerald JM, Chanez P, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2115-2127.
47. FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Nair P, et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2128-2141.
48. Cox G, Thomson NC, Rubin AS, et al. Asthma control during the year after bronchial thermoplasty. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1327-1337.
49. Pavord ID, Cox G, Thomson NC, et al. Safety and efficacy of bronchial thermoplasty in symptomatic, severe asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:1185-1191.
50. Castro M, Rubin AS, Laviolette M, et al. Effectiveness and safety of bronchial thermoplasty in the treatment of severe asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:116-124.
51. Wechsler ME, Laviolette M, Rubin AS, et al. Bronchial thermoplasty: Long-term safety and effectiveness in patients with severe persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1295-1302.
52. Chupp G, Laviolette M, Cohn L, et al. Long-term outcomes of bronchial thermoplasty in subjects with severe asthma: A comparison of 3-year follow-up results from two prospective multicentre studies. Eur Respir J. 2017;50:1700017.
53. Abramson MJ, Puy RM, Weiner JM. Injection allergen immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(8):CD001186.
54. Normansell R, Kew KM, Bridgman AL. Sublingual immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(8):CD011293.
55. Mosbech H, Deckelmann R, de Blay F, et al. Standardized quality (SQ) house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet (ALK) reduces inhaled corticosteroid use while maintaining asthma control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:568575.e7.
56. Virchow JC, Backer V, Kuna P, et al. Efficacy of a house dust mite sublingual allergen immunotherapy tablet in adults with allergic asthma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:1715-1725.
57. Johnston SL, Szigeti M, Cross M, et al. Azithromycin for acute exacerbations of asthma : the AZALEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1630-1637.
58. Brusselle GG, Vanderstichele C, Jordens P, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations in severe asthma (AZISAST): a multicentre randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Thorax. 2013;68:322-329.
59. Gibson PG, Yang IA, Upham JW, et al. Effect of azithromycin on asthma exacerbations and quality of life in adults with persistent uncontrolled asthma (AMAZES): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;390:659-668.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Most recent national asthma data. Updated May 2019. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm. Accessed March 6, 2020.
2. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma—summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(5 suppl):S94-S138.
3. Woodruff PG, Modrek B, Choy DF, et al. T-helper type 2-driven inflammation defines major subphenotypes of asthma [published correction appears in Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(8):796]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:388–395.
4. Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma—present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:57–65.
5. Busse WW. Inflammation in asthma: the cornerstone of the disease and target of therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102(4 pt 2):S17-S22.
6. Lane SJ, Lee TH. Mast cell effector mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(5 pt 2):S67-S71.
7. Robinson DS, Bentley AM, Hartnell A, et al. Activated memory T helper cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with atopic asthma: relation to asthma symptoms, lung function, and bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1993;48:26-32.
8. Grigoraş A, Grigoraş CC, Giuşcă SE, et al. Remodeling of basement membrane in patients with asthma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57:115-119.
9. Huang SK, Xiao HQ, Kleine-Tebbe J, et al. IL-13 expression at the sites of allergen challenge in patients with asthma. J Immunol. 1995;155:2688-2694.
10. Hansbro PM, Starkey MR, Mattes J, et al. Pulmonary immunity during respiratory infections in early life and the development of severe asthma. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11 suppl 5:S297-S302.
11. Apter AJ, Reisine ST, Willard A, et al. The effect of inhaled albuterol in moderate to severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98:295-301.
12. Peters SP, Kunselman SJ, Icitovic N, et al. Tiotropium bromide step-up therapy for adults with uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1715-1726.
13. Kerstjens HA, O’Byrne PM. Tiotropium for the treatment of asthma: a drug safety evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15:1115-1124.
14. Global Initiative for Asthma. Diagnosis of diseases of chronic air flow limitation: asthma, COPD and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) 2014. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GINA_GOLD_ACOS_2014-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
15. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2019. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 12, 2020.
16. Khanbabaee G, Enayat J, Chavoshzadeh Z, et al. Serum level of specific IgG antibody for aspergillus and its association with severity of asthma in asthmatic children. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2012;59:43-50.
17. Agbetile J, Bourne M, Fairs A, et al. Effectiveness of voriconazole in the treatment of aspergillus fumigatus-associated asthma (EVITA3 study). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:33-39.
18. Stevens DA, Schwartz HJ, Lee JY, et al. A randomized trial of itraconazole in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:756-762.
19. Barnes PJ. Glucocorticosteroids: current and future directions. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:29-43.
20. Oakley RH, Cidlowski JA. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: new signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1033-1044.
21. Barnes PJ. Scientific rationale for inhaled combination therapy with long-acting beta2-agonists and corticosteroids. Eur Respir J. 2002;19:182-191.
22. Newton R, Giembycz MA. Understanding how long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance the clinical efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma—an update. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:3405-3430.
23. Wijesinghe M, Perrin K, Harwood M, et al. The risk of asthma mortality with inhaled long acting beta-agonists. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:467-472.
24. Cazzola M, Page CP, Rogliani P, et al. β2-agonist therapy in lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:690-696.
25. Bernstein DI, Bateman ED, Woodcock A, et al. Fluticasone furoate (FF)/vilanterol (100/25 mcg or 200/25 mcg) or FF (100 mcg) in persistent asthma. J Asthma. 2015;52:1073-1083.
26. Devillier P, Humbert M, Boye A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (FF/VI) versus twice-daily inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β2-agonists (ICS/LABA) in patients with uncontrolled asthma: an open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Respir Med. 2018;141:111-120.
27. Beeh KM, LaForce C, Gahlemann M, et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study to investigate different dosing regimens of olodaterol delivered via Respimat(R) in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma. Respir Res. 2015;16:87.
28. LaForce C, Alexander M, Deckelmann R, et al. Indacaterol provides sustained 24 h bronchodilation on once-daily dosing in asthma: a 7-day dose-ranging study. Allergy. 2008;63:103-111.
29. Beasley RW, Donohue JF, Mehta R, et al. Effect of once-daily indacaterol maleate/mometasone furoate on exacerbation risk in adolescent and adult asthma: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e006131.
30. Aalbers R, Park HS. Positioning of long-acting muscarinic antagonists in the management of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9:386-393.
31. Lee LA, Briggs A, Edwards LD, et al. A randomized, three-period crossover study of umeclidinium as monotherapy in adult patients with asthma. Respir Med. 2015;109:63-73.
32. Israel E, Reddel HK. Severe and difficult-to-treat asthma in adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:965-976.
33. Normansell R, Walker S, Milan SJ, et al. Omalizumab for asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(1):CD003559.
34. Hanania NA, Wenzel S, Rosen K, et al. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: an analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:804-811.
35. Slavin RG, Ferioli C, Tannenbaum SJ, et al. Asthma symptom re-emergence after omalizumab withdrawal correlates well with increasing IgE and decreasing pharmacokinetic concentrations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:107-113.e3.
36. Ledford D, Busse W, Trzaskoma B, et al. A randomized multicenter study evaluating Xolair persistence of response after long-term therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:162-169.e2.
37. Ortega HG, Liu MC, Pavord ID, et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1198-1207.
38. Chupp GL, Bradford ES, Albers FC, et al. Efficacy of mepolizumab add-on therapy on health-related quality of life and markers of asthma control in severe eosinophilic asthma (MUSCA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:390-400.
39. Lugogo N, Domingo C, Chanez P, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: a multi-center, open-label, phase IIIb study. Clin Ther. 2016;38:2058-2070.e1.
40. Bel EH, Wenzel SE, Thompson PJ, et al. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1189-1197.
41. Castro M, Zangrilli J, Wechsler ME. Corrections. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:e15.
42. Bjermer L, Lemiere C, Maspero J, et al. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil levels: a randomized phase 3 study. Chest. 2016;150:789-798.
43. Corren J, Weinstein S, Janka L, et al. Phase 3 study of reslizumab in patients with poorly controlled asthma: Effects across a broad range of eosinophil counts. Chest. 2016;150:799-810.
44. Mukherjee M, Aleman Paramo F, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Weight-adjusted intravenous reslizumab in severe asthma with inadequate response to fixed-dose subcutaneous mepolizumab. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197:38-46.
45. Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:1344-1353.e2.
46. Bleecker ER, FitzGerald JM, Chanez P, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2115-2127.
47. FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Nair P, et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2128-2141.
48. Cox G, Thomson NC, Rubin AS, et al. Asthma control during the year after bronchial thermoplasty. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1327-1337.
49. Pavord ID, Cox G, Thomson NC, et al. Safety and efficacy of bronchial thermoplasty in symptomatic, severe asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:1185-1191.
50. Castro M, Rubin AS, Laviolette M, et al. Effectiveness and safety of bronchial thermoplasty in the treatment of severe asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:116-124.
51. Wechsler ME, Laviolette M, Rubin AS, et al. Bronchial thermoplasty: Long-term safety and effectiveness in patients with severe persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1295-1302.
52. Chupp G, Laviolette M, Cohn L, et al. Long-term outcomes of bronchial thermoplasty in subjects with severe asthma: A comparison of 3-year follow-up results from two prospective multicentre studies. Eur Respir J. 2017;50:1700017.
53. Abramson MJ, Puy RM, Weiner JM. Injection allergen immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(8):CD001186.
54. Normansell R, Kew KM, Bridgman AL. Sublingual immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(8):CD011293.
55. Mosbech H, Deckelmann R, de Blay F, et al. Standardized quality (SQ) house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet (ALK) reduces inhaled corticosteroid use while maintaining asthma control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:568575.e7.
56. Virchow JC, Backer V, Kuna P, et al. Efficacy of a house dust mite sublingual allergen immunotherapy tablet in adults with allergic asthma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:1715-1725.
57. Johnston SL, Szigeti M, Cross M, et al. Azithromycin for acute exacerbations of asthma : the AZALEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1630-1637.
58. Brusselle GG, Vanderstichele C, Jordens P, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations in severe asthma (AZISAST): a multicentre randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Thorax. 2013;68:322-329.
59. Gibson PG, Yang IA, Upham JW, et al. Effect of azithromycin on asthma exacerbations and quality of life in adults with persistent uncontrolled asthma (AMAZES): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;390:659-668.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Consider inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) as your first choice for a long-term control agent to treat asthma; add a long-acting beta agonist (LABA) when needed. A
› Use long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) as add-on therapy for patients whose asthma is uncontrolled despite the use of low-dose ICS-LABA, or as an alternative to high-dose ICS-LABA. A
› Consider biological therapies for patients with asthma exacerbations that require steroids at least twice a year. B
› Use azithromycin as an add-on therapy to ICS-LABA for a select group of patients with uncontrolled persistent asthma (neutrophilic phenotype). C
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Peanut OIT-induced eosinophilia may eventually resolve
Almost all patients who develop gastrointestinal side effects from oral immunotherapy for severe food allergies develop some degree of esophageal eosinophilia, but that eventually resolves in most of them after a year of treatment, according to results of a pilot study that was to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings may help identify biomarkers of persistent eosinophilia despite oral immunotherapy.
In January of this year the Food and Drug Administration approved oral immunotherapy (OIT), known as peanut allergen powder-dnfp, or peanut OIT (POIT), for severe food allergies. In an interview, lead study author Benjamin Wright, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, said OIT is a “promising proactive” treatment for food allergies. “But questions regarding the safety of immunotherapy remain,” he said. “About 30% of patients can develop GI side effects, including abdominal pain and vomiting; most concerning is that some patients develop eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).”
The pilot study was a mechanistic substudy of 20 adult patients with immunoglobulin E–mediated peanut allergies enrolled in the phase 2 Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Safety, Efficacy and Discovery trial (POISED), with 15 randomized to treatment and the remainder to placebo. They had serial gastrointestinal biopsies at baseline (n = 20), 1 year (n = 7 treatment, 3 placebo) and 2 years (n = 7 treatment, 4 placebo) to evaluate eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf).
Baseline characteristics between the treatment and placebo groups were similar, with some having signs of preexisting disease. About 14% of them had clinically significant EoE, represented as a measure of more than 15 eos/hpf, Dr. Wright said. “One of the findings that was really fascinating to us was that all of the subjects had evidence of dilated intercellular spaces at baseline,” he said. “This indicates that all the subjects have some degree of epithelial barrier dysfunction before they start OIT.” Dilated intercellular spaces are a marker of inflammation.
Four patients in the treatment group had mild endoscopic findings at weeks 52 and 104, as did one patient on placebo, Dr. Wright said. A plot of eosinophil counts showed a peak at 52 weeks but near resolution at 104 weeks for all but one patient on OIT. “One of the most interesting trends that we noted was that, for most of patients, OIT-induced eosinophilia was transient and not fixed,” he said. “We noted a triangle pattern where tissue eosinophilia peaks and then resolves with the continuation of therapy.” EoE Histologic scoring system results followed a similar pattern in these patients, he added.
Also, results of the comprehensive GI Symptom Questionnaire, which assessed symptoms such as abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, refusal to eat, and vomiting, showed that patient-reported GI symptoms did not correlate with tissue eosinophilia, Dr. Wright said. “To us, that suggests that perhaps eosinophils are not central to disease pathology or symptom development in these patients,” he said.
However, the findings validate that, in a small number of patients, OIT induces EoE, Dr. Wright said. He used a treadmill analogy to explain how OIT influences epithelial remodeling in some patients. “We’re constantly renewing our esophageal epithelium every 2 weeks, and when you challenge it with an antigen (i.e., OIT), the treadmill speeds up,” he said. “There may be some patients who will fall if the treadmill gets too fast, and they develop disease.”
He added, “Distinguishing someone’s fitness before they get on the treadmill is really going be a key moving forward in determining which subjects are good participants for OIT or how to dose OIT.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from the Arizona Biomedical Research Consortium and Phoenix Children’s Hospital Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Consortium for Food Allergy Research, as well as relationships with Aimmune Therapeutics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Consortium for Food Allergy Research, DBV Technologies, Astellas, AnaptysBio, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Wright B et al. AAAAI, Session 2605, Abstract No. 259.
Almost all patients who develop gastrointestinal side effects from oral immunotherapy for severe food allergies develop some degree of esophageal eosinophilia, but that eventually resolves in most of them after a year of treatment, according to results of a pilot study that was to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings may help identify biomarkers of persistent eosinophilia despite oral immunotherapy.
In January of this year the Food and Drug Administration approved oral immunotherapy (OIT), known as peanut allergen powder-dnfp, or peanut OIT (POIT), for severe food allergies. In an interview, lead study author Benjamin Wright, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, said OIT is a “promising proactive” treatment for food allergies. “But questions regarding the safety of immunotherapy remain,” he said. “About 30% of patients can develop GI side effects, including abdominal pain and vomiting; most concerning is that some patients develop eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).”
The pilot study was a mechanistic substudy of 20 adult patients with immunoglobulin E–mediated peanut allergies enrolled in the phase 2 Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Safety, Efficacy and Discovery trial (POISED), with 15 randomized to treatment and the remainder to placebo. They had serial gastrointestinal biopsies at baseline (n = 20), 1 year (n = 7 treatment, 3 placebo) and 2 years (n = 7 treatment, 4 placebo) to evaluate eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf).
Baseline characteristics between the treatment and placebo groups were similar, with some having signs of preexisting disease. About 14% of them had clinically significant EoE, represented as a measure of more than 15 eos/hpf, Dr. Wright said. “One of the findings that was really fascinating to us was that all of the subjects had evidence of dilated intercellular spaces at baseline,” he said. “This indicates that all the subjects have some degree of epithelial barrier dysfunction before they start OIT.” Dilated intercellular spaces are a marker of inflammation.
Four patients in the treatment group had mild endoscopic findings at weeks 52 and 104, as did one patient on placebo, Dr. Wright said. A plot of eosinophil counts showed a peak at 52 weeks but near resolution at 104 weeks for all but one patient on OIT. “One of the most interesting trends that we noted was that, for most of patients, OIT-induced eosinophilia was transient and not fixed,” he said. “We noted a triangle pattern where tissue eosinophilia peaks and then resolves with the continuation of therapy.” EoE Histologic scoring system results followed a similar pattern in these patients, he added.
Also, results of the comprehensive GI Symptom Questionnaire, which assessed symptoms such as abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, refusal to eat, and vomiting, showed that patient-reported GI symptoms did not correlate with tissue eosinophilia, Dr. Wright said. “To us, that suggests that perhaps eosinophils are not central to disease pathology or symptom development in these patients,” he said.
However, the findings validate that, in a small number of patients, OIT induces EoE, Dr. Wright said. He used a treadmill analogy to explain how OIT influences epithelial remodeling in some patients. “We’re constantly renewing our esophageal epithelium every 2 weeks, and when you challenge it with an antigen (i.e., OIT), the treadmill speeds up,” he said. “There may be some patients who will fall if the treadmill gets too fast, and they develop disease.”
He added, “Distinguishing someone’s fitness before they get on the treadmill is really going be a key moving forward in determining which subjects are good participants for OIT or how to dose OIT.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from the Arizona Biomedical Research Consortium and Phoenix Children’s Hospital Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Consortium for Food Allergy Research, as well as relationships with Aimmune Therapeutics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Consortium for Food Allergy Research, DBV Technologies, Astellas, AnaptysBio, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Wright B et al. AAAAI, Session 2605, Abstract No. 259.
Almost all patients who develop gastrointestinal side effects from oral immunotherapy for severe food allergies develop some degree of esophageal eosinophilia, but that eventually resolves in most of them after a year of treatment, according to results of a pilot study that was to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings may help identify biomarkers of persistent eosinophilia despite oral immunotherapy.
In January of this year the Food and Drug Administration approved oral immunotherapy (OIT), known as peanut allergen powder-dnfp, or peanut OIT (POIT), for severe food allergies. In an interview, lead study author Benjamin Wright, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, said OIT is a “promising proactive” treatment for food allergies. “But questions regarding the safety of immunotherapy remain,” he said. “About 30% of patients can develop GI side effects, including abdominal pain and vomiting; most concerning is that some patients develop eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).”
The pilot study was a mechanistic substudy of 20 adult patients with immunoglobulin E–mediated peanut allergies enrolled in the phase 2 Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Safety, Efficacy and Discovery trial (POISED), with 15 randomized to treatment and the remainder to placebo. They had serial gastrointestinal biopsies at baseline (n = 20), 1 year (n = 7 treatment, 3 placebo) and 2 years (n = 7 treatment, 4 placebo) to evaluate eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf).
Baseline characteristics between the treatment and placebo groups were similar, with some having signs of preexisting disease. About 14% of them had clinically significant EoE, represented as a measure of more than 15 eos/hpf, Dr. Wright said. “One of the findings that was really fascinating to us was that all of the subjects had evidence of dilated intercellular spaces at baseline,” he said. “This indicates that all the subjects have some degree of epithelial barrier dysfunction before they start OIT.” Dilated intercellular spaces are a marker of inflammation.
Four patients in the treatment group had mild endoscopic findings at weeks 52 and 104, as did one patient on placebo, Dr. Wright said. A plot of eosinophil counts showed a peak at 52 weeks but near resolution at 104 weeks for all but one patient on OIT. “One of the most interesting trends that we noted was that, for most of patients, OIT-induced eosinophilia was transient and not fixed,” he said. “We noted a triangle pattern where tissue eosinophilia peaks and then resolves with the continuation of therapy.” EoE Histologic scoring system results followed a similar pattern in these patients, he added.
Also, results of the comprehensive GI Symptom Questionnaire, which assessed symptoms such as abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, refusal to eat, and vomiting, showed that patient-reported GI symptoms did not correlate with tissue eosinophilia, Dr. Wright said. “To us, that suggests that perhaps eosinophils are not central to disease pathology or symptom development in these patients,” he said.
However, the findings validate that, in a small number of patients, OIT induces EoE, Dr. Wright said. He used a treadmill analogy to explain how OIT influences epithelial remodeling in some patients. “We’re constantly renewing our esophageal epithelium every 2 weeks, and when you challenge it with an antigen (i.e., OIT), the treadmill speeds up,” he said. “There may be some patients who will fall if the treadmill gets too fast, and they develop disease.”
He added, “Distinguishing someone’s fitness before they get on the treadmill is really going be a key moving forward in determining which subjects are good participants for OIT or how to dose OIT.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from the Arizona Biomedical Research Consortium and Phoenix Children’s Hospital Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Consortium for Food Allergy Research, as well as relationships with Aimmune Therapeutics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Consortium for Food Allergy Research, DBV Technologies, Astellas, AnaptysBio, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Wright B et al. AAAAI, Session 2605, Abstract No. 259.
FROM AAAAI
Gene-targeting therapy shown to reduce mastocytosis symptoms
by about 30%, according to early results of a clinical trial scheduled to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
“This correlates with reduction from very severe to moderate or from moderate to mild category, and all the reductions in symptoms were statistically significant,” Cem Akin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. He reported on part 1 of the phase 2 PIONEER trial of the kinase inhibitor avapritinib, described as a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the KIT D816V mutation that affects 90% of patients with systemic mastocytosis.
Currently, Dr. Akin noted, patients with indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis must rely on over-the-counter antihistamines used for seasonal allergies. “These patients use antihistamines in higher doses because mastocytosis patients have higher counts of mast cells that release histamines that cause a variety of symptoms,” he said. Symptoms, which can occur suddenly, include flushing and reactions that resemble allergic or anaphylactic reactions.
The purpose of the part 1 study was to evaluate three different dosing levels of avapritinib vs. placebo: 25, 50, and 100 mg. Ten patients were in each dosing group and nine were in the placebo group. The primary outcome was reduction in total symptom scores at 16 weeks as measured by the Indolent SM Symptom Assessment Form. “All three dose groups showed significant reductions in total symptom scores as well as specific symptoms that were most bothersome to the patient, whether skin symptoms or GI or neurocognitive symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. “All three doses were effective; the average reduction was about 30% compared to baseline.” Specifically, 25-mg dosing showed an average 30% reduction, 50-mg dosing showed an average 19% reduction, and 100-mg dosing showed an average 35% reduction.
The researchers determined that the 25-mg daily dose was the most effective and safest, with no patients on the dose reporting grade 3 adverse events, Dr. Akin said. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 AEs, according to study results.* The 25-mg daily dose will be evaluated in part 2 of the trial. The trial is estimated to enroll 112 total patients, according to the ClinicalTrials.gov filing. In part 3, patients who complete parts 1 or 2, including those initially randomized to placebo, may participate in a long-term open-label extension, receiving 25 mg avapritinib plus best supportive care.
“This is targeting a population whose symptoms are not controlled by antihistamines, based on a minimum total symptom score according to diaries they fill out, and they have to be on at least two different systemic medications – antihistamine or proton-pump inhibitor and leukotriene inhibitor – and they still have significant symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. He estimated that this describes about two-thirds of his patients with indolent or smoldering systematic mastocytosis.
“This is a disease that also takes a psychological toll,” he said. “This is a problem that starts in the bone marrow; it is similar to a hematological stem-cell disorder that affects the mast cell progenitor and it’s caused by a mutation that has not been particularly targeted until this drug,” he said. While most of these patients live with a benign mastocytosis their entire lives, the symptoms can be debilitating to the point where the disease disrupts and restricts social activities and comprises their quality of life, he said.
“This is a groundbreaking therapy that will change the way we think about mastocytosis treatment going forward,” Dr. Akin said. “It’s the first time we are actually targeting the underlying mutation that’s causing the disease, in terms of reducing directly that mutation as opposed to just treating the symptoms in indolent disease.”
Scheduled session moderator Anil Nanda, MD, of the Asthma and Allergy Center in Lewisville, Texas, said the findings are encouraging. “As a practicing allergist and immunologist in the community, it is very exciting to have a potential new treatment option for indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis,” he said via email. “Patients appreciate new options in therapy.”
Dr. Akin, the primary investigator, receives funding from and serves as a consultant for Blueprint Medicines, which sponsored the trial. He also disclosed a financial relationship with Novartis.
SOURCE: Akin C et al. AAAAI 2020, Presentation L5.
*Correction, 4/6/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the percentage of grade 3 adverse events. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 adverse events.
by about 30%, according to early results of a clinical trial scheduled to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
“This correlates with reduction from very severe to moderate or from moderate to mild category, and all the reductions in symptoms were statistically significant,” Cem Akin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. He reported on part 1 of the phase 2 PIONEER trial of the kinase inhibitor avapritinib, described as a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the KIT D816V mutation that affects 90% of patients with systemic mastocytosis.
Currently, Dr. Akin noted, patients with indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis must rely on over-the-counter antihistamines used for seasonal allergies. “These patients use antihistamines in higher doses because mastocytosis patients have higher counts of mast cells that release histamines that cause a variety of symptoms,” he said. Symptoms, which can occur suddenly, include flushing and reactions that resemble allergic or anaphylactic reactions.
The purpose of the part 1 study was to evaluate three different dosing levels of avapritinib vs. placebo: 25, 50, and 100 mg. Ten patients were in each dosing group and nine were in the placebo group. The primary outcome was reduction in total symptom scores at 16 weeks as measured by the Indolent SM Symptom Assessment Form. “All three dose groups showed significant reductions in total symptom scores as well as specific symptoms that were most bothersome to the patient, whether skin symptoms or GI or neurocognitive symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. “All three doses were effective; the average reduction was about 30% compared to baseline.” Specifically, 25-mg dosing showed an average 30% reduction, 50-mg dosing showed an average 19% reduction, and 100-mg dosing showed an average 35% reduction.
The researchers determined that the 25-mg daily dose was the most effective and safest, with no patients on the dose reporting grade 3 adverse events, Dr. Akin said. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 AEs, according to study results.* The 25-mg daily dose will be evaluated in part 2 of the trial. The trial is estimated to enroll 112 total patients, according to the ClinicalTrials.gov filing. In part 3, patients who complete parts 1 or 2, including those initially randomized to placebo, may participate in a long-term open-label extension, receiving 25 mg avapritinib plus best supportive care.
“This is targeting a population whose symptoms are not controlled by antihistamines, based on a minimum total symptom score according to diaries they fill out, and they have to be on at least two different systemic medications – antihistamine or proton-pump inhibitor and leukotriene inhibitor – and they still have significant symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. He estimated that this describes about two-thirds of his patients with indolent or smoldering systematic mastocytosis.
“This is a disease that also takes a psychological toll,” he said. “This is a problem that starts in the bone marrow; it is similar to a hematological stem-cell disorder that affects the mast cell progenitor and it’s caused by a mutation that has not been particularly targeted until this drug,” he said. While most of these patients live with a benign mastocytosis their entire lives, the symptoms can be debilitating to the point where the disease disrupts and restricts social activities and comprises their quality of life, he said.
“This is a groundbreaking therapy that will change the way we think about mastocytosis treatment going forward,” Dr. Akin said. “It’s the first time we are actually targeting the underlying mutation that’s causing the disease, in terms of reducing directly that mutation as opposed to just treating the symptoms in indolent disease.”
Scheduled session moderator Anil Nanda, MD, of the Asthma and Allergy Center in Lewisville, Texas, said the findings are encouraging. “As a practicing allergist and immunologist in the community, it is very exciting to have a potential new treatment option for indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis,” he said via email. “Patients appreciate new options in therapy.”
Dr. Akin, the primary investigator, receives funding from and serves as a consultant for Blueprint Medicines, which sponsored the trial. He also disclosed a financial relationship with Novartis.
SOURCE: Akin C et al. AAAAI 2020, Presentation L5.
*Correction, 4/6/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the percentage of grade 3 adverse events. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 adverse events.
by about 30%, according to early results of a clinical trial scheduled to be presented at the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled the meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
“This correlates with reduction from very severe to moderate or from moderate to mild category, and all the reductions in symptoms were statistically significant,” Cem Akin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. He reported on part 1 of the phase 2 PIONEER trial of the kinase inhibitor avapritinib, described as a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the KIT D816V mutation that affects 90% of patients with systemic mastocytosis.
Currently, Dr. Akin noted, patients with indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis must rely on over-the-counter antihistamines used for seasonal allergies. “These patients use antihistamines in higher doses because mastocytosis patients have higher counts of mast cells that release histamines that cause a variety of symptoms,” he said. Symptoms, which can occur suddenly, include flushing and reactions that resemble allergic or anaphylactic reactions.
The purpose of the part 1 study was to evaluate three different dosing levels of avapritinib vs. placebo: 25, 50, and 100 mg. Ten patients were in each dosing group and nine were in the placebo group. The primary outcome was reduction in total symptom scores at 16 weeks as measured by the Indolent SM Symptom Assessment Form. “All three dose groups showed significant reductions in total symptom scores as well as specific symptoms that were most bothersome to the patient, whether skin symptoms or GI or neurocognitive symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. “All three doses were effective; the average reduction was about 30% compared to baseline.” Specifically, 25-mg dosing showed an average 30% reduction, 50-mg dosing showed an average 19% reduction, and 100-mg dosing showed an average 35% reduction.
The researchers determined that the 25-mg daily dose was the most effective and safest, with no patients on the dose reporting grade 3 adverse events, Dr. Akin said. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 AEs, according to study results.* The 25-mg daily dose will be evaluated in part 2 of the trial. The trial is estimated to enroll 112 total patients, according to the ClinicalTrials.gov filing. In part 3, patients who complete parts 1 or 2, including those initially randomized to placebo, may participate in a long-term open-label extension, receiving 25 mg avapritinib plus best supportive care.
“This is targeting a population whose symptoms are not controlled by antihistamines, based on a minimum total symptom score according to diaries they fill out, and they have to be on at least two different systemic medications – antihistamine or proton-pump inhibitor and leukotriene inhibitor – and they still have significant symptoms,” Dr. Akin said. He estimated that this describes about two-thirds of his patients with indolent or smoldering systematic mastocytosis.
“This is a disease that also takes a psychological toll,” he said. “This is a problem that starts in the bone marrow; it is similar to a hematological stem-cell disorder that affects the mast cell progenitor and it’s caused by a mutation that has not been particularly targeted until this drug,” he said. While most of these patients live with a benign mastocytosis their entire lives, the symptoms can be debilitating to the point where the disease disrupts and restricts social activities and comprises their quality of life, he said.
“This is a groundbreaking therapy that will change the way we think about mastocytosis treatment going forward,” Dr. Akin said. “It’s the first time we are actually targeting the underlying mutation that’s causing the disease, in terms of reducing directly that mutation as opposed to just treating the symptoms in indolent disease.”
Scheduled session moderator Anil Nanda, MD, of the Asthma and Allergy Center in Lewisville, Texas, said the findings are encouraging. “As a practicing allergist and immunologist in the community, it is very exciting to have a potential new treatment option for indolent or smoldering systemic mastocytosis,” he said via email. “Patients appreciate new options in therapy.”
Dr. Akin, the primary investigator, receives funding from and serves as a consultant for Blueprint Medicines, which sponsored the trial. He also disclosed a financial relationship with Novartis.
SOURCE: Akin C et al. AAAAI 2020, Presentation L5.
*Correction, 4/6/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the percentage of grade 3 adverse events. In total 20% and 40% of the 50- and 100-mg dose groups, respectively, reported grade 3 adverse events.
FROM AAAAI
Acid-suppressant medications in infants with bronchiolitis raises later allergy risk
Infants who are hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis and receive acid-suppressant medications may be at risk of developing allergic disease by age 3 years, according to recent research released as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) Annual Meeting.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage
“Among children with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy, exposure to acid-suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years,” Lacey B. Robinson, MD, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology in the department of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Bronchiolitis is a risk factor in infants for developing conditions such as recurrent wheeze and childhood asthma in early childhood. Acid-suppressant medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) may further increase the risk of allergic disease. One study by Mitre et al. published in JAMA Pediatrics showed use of acid-suppressant medications in infants up to 6 months raised the risk of allergic disease (JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172[6]:e180315). Some studies suggest between 30% and 50% of infants diagnosed with bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization will develop asthma by age 5 years (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017 Jan - Feb;5[1]:92-6).
“Children with severe bronchiolitis during infancy are at a high risk of developing recurrent wheeze and subsequent asthma. There is limited evidence to suggest that exposure to acid suppressant medications [such as proton pump inhibitors and histamine-2 receptor antagonists] prenatally and during early childhood increases the risk of childhood asthma,” Dr. Robinson said. “It is not known if exposure to acid suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze among high-risk children, such as in those with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy.”
Dr. Robinson and colleagues performed a multicenter, prospective cohort study of 921 infants who were hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis between 2011 and 2014. The investigators reviewed the medical records of the infants for acid suppressant medication use, as well as parent report of acid suppressant medication use, during an infant’s first 12 months. Overall, 879 children were analyzed after excluding for patients who developed recurrent wheeze prior to receiving acid suppressant medications, as well as patients with incomplete data. The investigators used the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3) to define recurrent wheeze. A Cox-proportional hazard model was used to analyze the time to event, which was stratified by age and adjusted for confounders.
Infants with a history of severe bronchiolitis were at greater risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years after being exposed to acid-suppressant medications, compared with infants who were not exposed, Dr. Robinson said. Of the 879 infants in the final analysis, 159 (18%) received acid-suppressant medications, and 68 of 159 patients (43%) went on to develop recurrent wheeze, compared with 206 of 720 infants (29%) who were not exposed (unadjusted hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-2.14).
After adjustment for confounders such as gender, race and ethnicity; gestational age; delivery type; severity of bronchiolitis; respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection status; maternal atopy; use of acid-suppressant medications during pregnancy; median household income; and insurance status, the association between recurrent wheeze and acid-suppressant medication use during infancy remained (adjusted HR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.15-2.07).
“More research is needed on this important topic including studies in other populations,” such as in healthy children, Dr. Robinson said. “We encourage future research on this important and understudied topic, including further research on the potential underlying mechanisms of this association.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson L. AAAAI 2020, Abstract L1
Infants who are hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis and receive acid-suppressant medications may be at risk of developing allergic disease by age 3 years, according to recent research released as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) Annual Meeting.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage
“Among children with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy, exposure to acid-suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years,” Lacey B. Robinson, MD, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology in the department of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Bronchiolitis is a risk factor in infants for developing conditions such as recurrent wheeze and childhood asthma in early childhood. Acid-suppressant medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) may further increase the risk of allergic disease. One study by Mitre et al. published in JAMA Pediatrics showed use of acid-suppressant medications in infants up to 6 months raised the risk of allergic disease (JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172[6]:e180315). Some studies suggest between 30% and 50% of infants diagnosed with bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization will develop asthma by age 5 years (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017 Jan - Feb;5[1]:92-6).
“Children with severe bronchiolitis during infancy are at a high risk of developing recurrent wheeze and subsequent asthma. There is limited evidence to suggest that exposure to acid suppressant medications [such as proton pump inhibitors and histamine-2 receptor antagonists] prenatally and during early childhood increases the risk of childhood asthma,” Dr. Robinson said. “It is not known if exposure to acid suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze among high-risk children, such as in those with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy.”
Dr. Robinson and colleagues performed a multicenter, prospective cohort study of 921 infants who were hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis between 2011 and 2014. The investigators reviewed the medical records of the infants for acid suppressant medication use, as well as parent report of acid suppressant medication use, during an infant’s first 12 months. Overall, 879 children were analyzed after excluding for patients who developed recurrent wheeze prior to receiving acid suppressant medications, as well as patients with incomplete data. The investigators used the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3) to define recurrent wheeze. A Cox-proportional hazard model was used to analyze the time to event, which was stratified by age and adjusted for confounders.
Infants with a history of severe bronchiolitis were at greater risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years after being exposed to acid-suppressant medications, compared with infants who were not exposed, Dr. Robinson said. Of the 879 infants in the final analysis, 159 (18%) received acid-suppressant medications, and 68 of 159 patients (43%) went on to develop recurrent wheeze, compared with 206 of 720 infants (29%) who were not exposed (unadjusted hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-2.14).
After adjustment for confounders such as gender, race and ethnicity; gestational age; delivery type; severity of bronchiolitis; respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection status; maternal atopy; use of acid-suppressant medications during pregnancy; median household income; and insurance status, the association between recurrent wheeze and acid-suppressant medication use during infancy remained (adjusted HR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.15-2.07).
“More research is needed on this important topic including studies in other populations,” such as in healthy children, Dr. Robinson said. “We encourage future research on this important and understudied topic, including further research on the potential underlying mechanisms of this association.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson L. AAAAI 2020, Abstract L1
Infants who are hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis and receive acid-suppressant medications may be at risk of developing allergic disease by age 3 years, according to recent research released as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) Annual Meeting.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage
“Among children with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy, exposure to acid-suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years,” Lacey B. Robinson, MD, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology in the department of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Bronchiolitis is a risk factor in infants for developing conditions such as recurrent wheeze and childhood asthma in early childhood. Acid-suppressant medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) may further increase the risk of allergic disease. One study by Mitre et al. published in JAMA Pediatrics showed use of acid-suppressant medications in infants up to 6 months raised the risk of allergic disease (JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172[6]:e180315). Some studies suggest between 30% and 50% of infants diagnosed with bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization will develop asthma by age 5 years (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017 Jan - Feb;5[1]:92-6).
“Children with severe bronchiolitis during infancy are at a high risk of developing recurrent wheeze and subsequent asthma. There is limited evidence to suggest that exposure to acid suppressant medications [such as proton pump inhibitors and histamine-2 receptor antagonists] prenatally and during early childhood increases the risk of childhood asthma,” Dr. Robinson said. “It is not known if exposure to acid suppressant medications during infancy further increases the risk of developing recurrent wheeze among high-risk children, such as in those with a history of severe bronchiolitis during infancy.”
Dr. Robinson and colleagues performed a multicenter, prospective cohort study of 921 infants who were hospitalized for severe bronchiolitis between 2011 and 2014. The investigators reviewed the medical records of the infants for acid suppressant medication use, as well as parent report of acid suppressant medication use, during an infant’s first 12 months. Overall, 879 children were analyzed after excluding for patients who developed recurrent wheeze prior to receiving acid suppressant medications, as well as patients with incomplete data. The investigators used the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3) to define recurrent wheeze. A Cox-proportional hazard model was used to analyze the time to event, which was stratified by age and adjusted for confounders.
Infants with a history of severe bronchiolitis were at greater risk of developing recurrent wheeze by age 3 years after being exposed to acid-suppressant medications, compared with infants who were not exposed, Dr. Robinson said. Of the 879 infants in the final analysis, 159 (18%) received acid-suppressant medications, and 68 of 159 patients (43%) went on to develop recurrent wheeze, compared with 206 of 720 infants (29%) who were not exposed (unadjusted hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-2.14).
After adjustment for confounders such as gender, race and ethnicity; gestational age; delivery type; severity of bronchiolitis; respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection status; maternal atopy; use of acid-suppressant medications during pregnancy; median household income; and insurance status, the association between recurrent wheeze and acid-suppressant medication use during infancy remained (adjusted HR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.15-2.07).
“More research is needed on this important topic including studies in other populations,” such as in healthy children, Dr. Robinson said. “We encourage future research on this important and understudied topic, including further research on the potential underlying mechanisms of this association.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson L. AAAAI 2020, Abstract L1
REPORTING FROM AAAAI 2020
Stronger links forged between RA and asthma, COPD
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were both linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a recent large, prospective cohort study, researchers have reported, which adds to a growing body of evidence that airway inflammation is implicated in the development of this disease.
RA risk was increased by about 50% among asthma patients, even when excluding those who had ever smoked, according to the study’s results, which were based on more than 200,000 women in the Nurses’ Health Study I and II.
Risk of RA nearly doubled among those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with an even stronger association seen in older ever-smokers, according to authors of the study.
The findings not only strengthen the case for the potential role of obstructive lung diseases in RA development, according to the study’s authors, but also suggest that health care providers need to lower the bar for evaluation of patients with lung diseases and inflammatory joint symptoms.
“If these patients develop arthralgias, then the clinicians taking care of them should have a low threshold to consider RA, and perhaps refer, or check these patients with a diagnostic test for RA,” said researcher Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
What’s perhaps not as clear now is whether screening obstructive lung disease patients in the absence of early RA signs would be warranted: “I don’t know if we’re quite at the point where we would need to screen these patients if they’re not symptomatic,” Dr. Sparks said in an interview.
The study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is, by far, not the first study to implicate asthma or other lung conditions in RA development. However, most previous studies are retrospective, and interpretation of the findings has been subject to limitations such as inadequate power to detect an increased risk or lack of adjustment for important confounding factors, such as smoking.
As such, the study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is believed to be the first-ever prospective study to evaluate asthma and COPD as risk factors for RA, study authors reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Researchers were able to identify 1,060 incident RA cases that developed in 15,148 women with asthma and 3,573 with COPD in the study with more than 4 million person-years of follow-up.
The association between asthma and increased RA risk was seen not only for the asthma population as a whole (hazard ratio, 1.53; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.88), but also for the subset of women who had never smoked, to a similar degree (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.14-2.05), the report shows.
COPD’s association with RA risk was apparent overall (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.31-2.75) and even more so in the subgroup of ever-smokers 55 years of age and older (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.38-3.51), the data further show.
Findings of studies looking at the inflammation of airways and other mucosal sites are “critically important to understand” when it comes to trying to prevent RA, said Kevin Deane, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver at Aurora.
“If we indeed are trying to prevent rheumatoid arthritis in terms of the joint disease, we may need to look at these mucosal sites in individuals who don’t yet have joint disease as potential sites to target for prevention, or at least areas to study to understand how prevention may work,” said Dr. Deane, principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded Strategy for the Prevention of RA (StopRA) trial.
With that in mind, it’s conceivable targeting a lung process might prevent joint disease in a patient with asthma or airway inflammation and blood markers that indicate a risk of RA, Dr. Deane said in an interview.
Blood markers of RA have been evaluated in some recent studies, with findings that provide further evidence of a link between lung diseases and RA, and vice versa.
In particular, anti–citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are clearly central to RA pathogenesis. And while asthma is increasingly linked to RA risk, there have been relatively little data on any potential links between ACPA and asthma.
That research gap led to a case-control study of the Nurses’ Health Study I and II (on which Dr. Sparks was senior author) showing that asthma was strongly linked to elevated ACPA in blood drawn from patients prior to a diagnosis of RA.
Results, published last year in Arthritis Research & Therapy, showed a significant association between asthma and pre-RA ACPA elevation (odds ratio, 3.57; 95% CI, 1.58-8.04), after adjustment for smoking and other potentially confounding factors. Investigators said the findings provided evidence that chronic mucosal airway inflammation is a factor in the development of ACPA and in the pathogenesis of RA.
In a follow-up study published more recently in Arthritis Care & Research, investigators showed that, among women in the Nurses Health Study I and II, pre-RA ACPA elevation was linked to increased risk of COPD, compared with controls (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.33-7.00), while the risk for development of asthma was similar in women with or without elevated pre-RA ACPA.
That study was in part an attempt to establish a “timeline” related to antibodies, lung diseases, and RA onset, Dr. Sparks said in the interview.
“We think that probably the asthma is more important in developing the antibody, but that once you have the antibody, if you didn’t have asthma by then, you’re unlikely to develop it,” he said. “So asthma seems to be something that could happen before the antibody production, whereas COPD seems to happen after – but ACPA seems to be the common link in both of these obstructive lung diseases.”
The study in Arthritis & Rheumatology linking asthma and COPD to risk of incident RA was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sparks reported grant support from Amgen and Bristol Myers Squibb and consulting fees from Inova and Optum. Coauthors provided disclosures related to GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Merck, Neutrolis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Ford JA et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1002/art.41194.
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were both linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a recent large, prospective cohort study, researchers have reported, which adds to a growing body of evidence that airway inflammation is implicated in the development of this disease.
RA risk was increased by about 50% among asthma patients, even when excluding those who had ever smoked, according to the study’s results, which were based on more than 200,000 women in the Nurses’ Health Study I and II.
Risk of RA nearly doubled among those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with an even stronger association seen in older ever-smokers, according to authors of the study.
The findings not only strengthen the case for the potential role of obstructive lung diseases in RA development, according to the study’s authors, but also suggest that health care providers need to lower the bar for evaluation of patients with lung diseases and inflammatory joint symptoms.
“If these patients develop arthralgias, then the clinicians taking care of them should have a low threshold to consider RA, and perhaps refer, or check these patients with a diagnostic test for RA,” said researcher Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
What’s perhaps not as clear now is whether screening obstructive lung disease patients in the absence of early RA signs would be warranted: “I don’t know if we’re quite at the point where we would need to screen these patients if they’re not symptomatic,” Dr. Sparks said in an interview.
The study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is, by far, not the first study to implicate asthma or other lung conditions in RA development. However, most previous studies are retrospective, and interpretation of the findings has been subject to limitations such as inadequate power to detect an increased risk or lack of adjustment for important confounding factors, such as smoking.
As such, the study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is believed to be the first-ever prospective study to evaluate asthma and COPD as risk factors for RA, study authors reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Researchers were able to identify 1,060 incident RA cases that developed in 15,148 women with asthma and 3,573 with COPD in the study with more than 4 million person-years of follow-up.
The association between asthma and increased RA risk was seen not only for the asthma population as a whole (hazard ratio, 1.53; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.88), but also for the subset of women who had never smoked, to a similar degree (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.14-2.05), the report shows.
COPD’s association with RA risk was apparent overall (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.31-2.75) and even more so in the subgroup of ever-smokers 55 years of age and older (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.38-3.51), the data further show.
Findings of studies looking at the inflammation of airways and other mucosal sites are “critically important to understand” when it comes to trying to prevent RA, said Kevin Deane, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver at Aurora.
“If we indeed are trying to prevent rheumatoid arthritis in terms of the joint disease, we may need to look at these mucosal sites in individuals who don’t yet have joint disease as potential sites to target for prevention, or at least areas to study to understand how prevention may work,” said Dr. Deane, principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded Strategy for the Prevention of RA (StopRA) trial.
With that in mind, it’s conceivable targeting a lung process might prevent joint disease in a patient with asthma or airway inflammation and blood markers that indicate a risk of RA, Dr. Deane said in an interview.
Blood markers of RA have been evaluated in some recent studies, with findings that provide further evidence of a link between lung diseases and RA, and vice versa.
In particular, anti–citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are clearly central to RA pathogenesis. And while asthma is increasingly linked to RA risk, there have been relatively little data on any potential links between ACPA and asthma.
That research gap led to a case-control study of the Nurses’ Health Study I and II (on which Dr. Sparks was senior author) showing that asthma was strongly linked to elevated ACPA in blood drawn from patients prior to a diagnosis of RA.
Results, published last year in Arthritis Research & Therapy, showed a significant association between asthma and pre-RA ACPA elevation (odds ratio, 3.57; 95% CI, 1.58-8.04), after adjustment for smoking and other potentially confounding factors. Investigators said the findings provided evidence that chronic mucosal airway inflammation is a factor in the development of ACPA and in the pathogenesis of RA.
In a follow-up study published more recently in Arthritis Care & Research, investigators showed that, among women in the Nurses Health Study I and II, pre-RA ACPA elevation was linked to increased risk of COPD, compared with controls (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.33-7.00), while the risk for development of asthma was similar in women with or without elevated pre-RA ACPA.
That study was in part an attempt to establish a “timeline” related to antibodies, lung diseases, and RA onset, Dr. Sparks said in the interview.
“We think that probably the asthma is more important in developing the antibody, but that once you have the antibody, if you didn’t have asthma by then, you’re unlikely to develop it,” he said. “So asthma seems to be something that could happen before the antibody production, whereas COPD seems to happen after – but ACPA seems to be the common link in both of these obstructive lung diseases.”
The study in Arthritis & Rheumatology linking asthma and COPD to risk of incident RA was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sparks reported grant support from Amgen and Bristol Myers Squibb and consulting fees from Inova and Optum. Coauthors provided disclosures related to GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Merck, Neutrolis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Ford JA et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1002/art.41194.
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were both linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a recent large, prospective cohort study, researchers have reported, which adds to a growing body of evidence that airway inflammation is implicated in the development of this disease.
RA risk was increased by about 50% among asthma patients, even when excluding those who had ever smoked, according to the study’s results, which were based on more than 200,000 women in the Nurses’ Health Study I and II.
Risk of RA nearly doubled among those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with an even stronger association seen in older ever-smokers, according to authors of the study.
The findings not only strengthen the case for the potential role of obstructive lung diseases in RA development, according to the study’s authors, but also suggest that health care providers need to lower the bar for evaluation of patients with lung diseases and inflammatory joint symptoms.
“If these patients develop arthralgias, then the clinicians taking care of them should have a low threshold to consider RA, and perhaps refer, or check these patients with a diagnostic test for RA,” said researcher Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
What’s perhaps not as clear now is whether screening obstructive lung disease patients in the absence of early RA signs would be warranted: “I don’t know if we’re quite at the point where we would need to screen these patients if they’re not symptomatic,” Dr. Sparks said in an interview.
The study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is, by far, not the first study to implicate asthma or other lung conditions in RA development. However, most previous studies are retrospective, and interpretation of the findings has been subject to limitations such as inadequate power to detect an increased risk or lack of adjustment for important confounding factors, such as smoking.
As such, the study by Dr. Sparks and colleagues is believed to be the first-ever prospective study to evaluate asthma and COPD as risk factors for RA, study authors reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Researchers were able to identify 1,060 incident RA cases that developed in 15,148 women with asthma and 3,573 with COPD in the study with more than 4 million person-years of follow-up.
The association between asthma and increased RA risk was seen not only for the asthma population as a whole (hazard ratio, 1.53; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-1.88), but also for the subset of women who had never smoked, to a similar degree (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.14-2.05), the report shows.
COPD’s association with RA risk was apparent overall (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.31-2.75) and even more so in the subgroup of ever-smokers 55 years of age and older (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.38-3.51), the data further show.
Findings of studies looking at the inflammation of airways and other mucosal sites are “critically important to understand” when it comes to trying to prevent RA, said Kevin Deane, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver at Aurora.
“If we indeed are trying to prevent rheumatoid arthritis in terms of the joint disease, we may need to look at these mucosal sites in individuals who don’t yet have joint disease as potential sites to target for prevention, or at least areas to study to understand how prevention may work,” said Dr. Deane, principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded Strategy for the Prevention of RA (StopRA) trial.
With that in mind, it’s conceivable targeting a lung process might prevent joint disease in a patient with asthma or airway inflammation and blood markers that indicate a risk of RA, Dr. Deane said in an interview.
Blood markers of RA have been evaluated in some recent studies, with findings that provide further evidence of a link between lung diseases and RA, and vice versa.
In particular, anti–citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are clearly central to RA pathogenesis. And while asthma is increasingly linked to RA risk, there have been relatively little data on any potential links between ACPA and asthma.
That research gap led to a case-control study of the Nurses’ Health Study I and II (on which Dr. Sparks was senior author) showing that asthma was strongly linked to elevated ACPA in blood drawn from patients prior to a diagnosis of RA.
Results, published last year in Arthritis Research & Therapy, showed a significant association between asthma and pre-RA ACPA elevation (odds ratio, 3.57; 95% CI, 1.58-8.04), after adjustment for smoking and other potentially confounding factors. Investigators said the findings provided evidence that chronic mucosal airway inflammation is a factor in the development of ACPA and in the pathogenesis of RA.
In a follow-up study published more recently in Arthritis Care & Research, investigators showed that, among women in the Nurses Health Study I and II, pre-RA ACPA elevation was linked to increased risk of COPD, compared with controls (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.33-7.00), while the risk for development of asthma was similar in women with or without elevated pre-RA ACPA.
That study was in part an attempt to establish a “timeline” related to antibodies, lung diseases, and RA onset, Dr. Sparks said in the interview.
“We think that probably the asthma is more important in developing the antibody, but that once you have the antibody, if you didn’t have asthma by then, you’re unlikely to develop it,” he said. “So asthma seems to be something that could happen before the antibody production, whereas COPD seems to happen after – but ACPA seems to be the common link in both of these obstructive lung diseases.”
The study in Arthritis & Rheumatology linking asthma and COPD to risk of incident RA was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sparks reported grant support from Amgen and Bristol Myers Squibb and consulting fees from Inova and Optum. Coauthors provided disclosures related to GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Merck, Neutrolis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Ford JA et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1002/art.41194.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Study: Delays filling biologic prescriptions have consequences
Insurance and specialty pharmacy delays in authorizing new biologic prescriptions for severe allergies leave waiting patients at risk of asthma attacks, hospitalizations, emergency department visits and prednisone shots and their known side effects, according to a single-center study that was to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The study of 80 patients in State College, Pa., found that they waited an average of 44 days from when their doctor submitted the preauthorization request to the insurance company until the practice received the shipment for dispensing to the patient, investigator Faoud Ishmael, MD, PhD, of Mount Nittany Medical Group said in an interview. “The implication here is that these are really the most severe patients who, you would argue, need their medications the quickest, and it’s taking longer to get them than it would an inhaler,” Dr. Ishmael said.
The study focused on patients with severe asthma (n = 60) or urticarial (n = 20) who received a new prescription of monoclonal antibody therapy from March 2014 to August 2019. For asthma treatments, the average time was 45.8 days; for urticaria, 40.6 days (P = .573), Dr. Ishmael said. The researchers divided the total amount of time into two components: insurance plan review and approval (P = .654, and specialty pharmacy review and dispensing of the medicine, each of which averaged 22.8 days (P = .384), he said.
He also noted wide disparity in the range of approval times. “The shortest approval time was 1 day, and the longest 97 days,” Dr. Ishmael said. “It’s interesting that we had this really broad spread.”
What’s more, the study found no trend for the delays among insurers and specialty pharmacies, Dr. Ishmael added. “When these prescriptions get submitted, it’s like a black box,” he said. “It really seems arbitrary why some of them take so long and some of them don’t.” The findings were independent of type of coverage, whether commercial or government, or even specific insurance plans. “It’s more the process that is flawed rather than one insurance company being the bad guy,” he said.
The study also looked at what happened to patients while they were waiting for their prescriptions to be delivered. “What we found is that over half of asthmatics had an exacerbation – 51% had at least one asthma attack where they needed prednisone,” Dr. Ishmael said (P = .0015), “and we had three patients admitted to the hospital over that time frame when they were waiting for the drugs.” One of those patients had been admitted twice, making four total hospitalizations. Preliminary data analysis showed that about 40% of the patients who had attacks went to the emergency department.
For asthmatics who needed prednisone, the average dose was 480 mg (P = .284) – “a pretty substantial number,” in Dr. Ishmael’s words. He noted that a large portion of the study patients were obese, with a mean body mass index of 33 kg/m2. Other comorbidities prevalent in the study population were hypertension and type 2 diabetes. “Prednisone is something that could worsen all of those conditions, so it’s not a trivial issue,” he said.
The study, however, didn’t evaluate costs of the interventions during the delay period vs. the costs of the medications themselves. Of the 80 prescriptions Dr. Ishmael and coauthors submitted, only one was rejected, that person being a smoker, he said. “I understand these are expensive medicines, but it’s counterproductive to delay them because in the long run the insurance company ends up paying for the hospitalization and the drug rather than just the drug,” he said.
Timothy Craig, DO, of Penn State Health Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology and professor of medicine and pediatrics at Penn State College of Medicine, both in Hershey, said he was surprised at the brevity of the delays reported in Dr. Ishmael’s study. “They do much better than we do with preauthorization,” he said, noting that, in his experience, these approvals take much longer. He added that his own research has found faulty insurance plan algorithms are at the heart of these delays. “We need more studies to clarify how much this is interfering with patient care and how much risk they’re putting patients in,” he said.
The COVID-19 pandemic poses a double-edged sword for physicians managing patients with severe asthma, Dr. Craig noted. “Their asthma care is important, especially if they do test for COVID-19,” he said. On the other hand, doctors and nurses attending to COVID-19 patients will have less time to haggle with payers to expedite coverage for biologics for their severe asthma patients, he said. “I hope the flexibility is there, especially at this time to allow people to get on the biologics and stay on them,” he said.
Dr. Ishmael said these findings have serious implications because biologics are getting prescribed ever more frequently for asthma and hives. Steps his practice has taken to streamline the process include following the payer’s approval guidelines as closely as possible. This sometimes can mean making sure a patient with severe asthma has been maximized on controller medications before submitting the biologic prescription, he said. Another step is to use drug company programs to remove barriers to coverage.
Nonetheless, the approval process can be daunting even when taking those steps, he said. “Those guidelines that constitute approval may vary a lot from one insurer to another; and sometimes those guidelines are different from the criteria that studies may have used when these drugs were being evaluated in clinical trials,” he said. It would be helpful, he said, if payers used the National Heart, Lung and Blood institute and the Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines for biologics.
One of the goals of the researchers is to present their findings to payers, “to let them know, here are some of the hang-ups and the real risks associated with delaying these medications,” Dr. Ishmael said.
“When specialists especially prescribe these therapies, there’s usually a valid reason,” he said. “We really need to do something about the current process – if there are ways to make it more transparent, faster.”
Dr. Ishmael has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ishmael F et al. AAAAI 2020. Session 3609, Presentation 558.
Insurance and specialty pharmacy delays in authorizing new biologic prescriptions for severe allergies leave waiting patients at risk of asthma attacks, hospitalizations, emergency department visits and prednisone shots and their known side effects, according to a single-center study that was to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The study of 80 patients in State College, Pa., found that they waited an average of 44 days from when their doctor submitted the preauthorization request to the insurance company until the practice received the shipment for dispensing to the patient, investigator Faoud Ishmael, MD, PhD, of Mount Nittany Medical Group said in an interview. “The implication here is that these are really the most severe patients who, you would argue, need their medications the quickest, and it’s taking longer to get them than it would an inhaler,” Dr. Ishmael said.
The study focused on patients with severe asthma (n = 60) or urticarial (n = 20) who received a new prescription of monoclonal antibody therapy from March 2014 to August 2019. For asthma treatments, the average time was 45.8 days; for urticaria, 40.6 days (P = .573), Dr. Ishmael said. The researchers divided the total amount of time into two components: insurance plan review and approval (P = .654, and specialty pharmacy review and dispensing of the medicine, each of which averaged 22.8 days (P = .384), he said.
He also noted wide disparity in the range of approval times. “The shortest approval time was 1 day, and the longest 97 days,” Dr. Ishmael said. “It’s interesting that we had this really broad spread.”
What’s more, the study found no trend for the delays among insurers and specialty pharmacies, Dr. Ishmael added. “When these prescriptions get submitted, it’s like a black box,” he said. “It really seems arbitrary why some of them take so long and some of them don’t.” The findings were independent of type of coverage, whether commercial or government, or even specific insurance plans. “It’s more the process that is flawed rather than one insurance company being the bad guy,” he said.
The study also looked at what happened to patients while they were waiting for their prescriptions to be delivered. “What we found is that over half of asthmatics had an exacerbation – 51% had at least one asthma attack where they needed prednisone,” Dr. Ishmael said (P = .0015), “and we had three patients admitted to the hospital over that time frame when they were waiting for the drugs.” One of those patients had been admitted twice, making four total hospitalizations. Preliminary data analysis showed that about 40% of the patients who had attacks went to the emergency department.
For asthmatics who needed prednisone, the average dose was 480 mg (P = .284) – “a pretty substantial number,” in Dr. Ishmael’s words. He noted that a large portion of the study patients were obese, with a mean body mass index of 33 kg/m2. Other comorbidities prevalent in the study population were hypertension and type 2 diabetes. “Prednisone is something that could worsen all of those conditions, so it’s not a trivial issue,” he said.
The study, however, didn’t evaluate costs of the interventions during the delay period vs. the costs of the medications themselves. Of the 80 prescriptions Dr. Ishmael and coauthors submitted, only one was rejected, that person being a smoker, he said. “I understand these are expensive medicines, but it’s counterproductive to delay them because in the long run the insurance company ends up paying for the hospitalization and the drug rather than just the drug,” he said.
Timothy Craig, DO, of Penn State Health Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology and professor of medicine and pediatrics at Penn State College of Medicine, both in Hershey, said he was surprised at the brevity of the delays reported in Dr. Ishmael’s study. “They do much better than we do with preauthorization,” he said, noting that, in his experience, these approvals take much longer. He added that his own research has found faulty insurance plan algorithms are at the heart of these delays. “We need more studies to clarify how much this is interfering with patient care and how much risk they’re putting patients in,” he said.
The COVID-19 pandemic poses a double-edged sword for physicians managing patients with severe asthma, Dr. Craig noted. “Their asthma care is important, especially if they do test for COVID-19,” he said. On the other hand, doctors and nurses attending to COVID-19 patients will have less time to haggle with payers to expedite coverage for biologics for their severe asthma patients, he said. “I hope the flexibility is there, especially at this time to allow people to get on the biologics and stay on them,” he said.
Dr. Ishmael said these findings have serious implications because biologics are getting prescribed ever more frequently for asthma and hives. Steps his practice has taken to streamline the process include following the payer’s approval guidelines as closely as possible. This sometimes can mean making sure a patient with severe asthma has been maximized on controller medications before submitting the biologic prescription, he said. Another step is to use drug company programs to remove barriers to coverage.
Nonetheless, the approval process can be daunting even when taking those steps, he said. “Those guidelines that constitute approval may vary a lot from one insurer to another; and sometimes those guidelines are different from the criteria that studies may have used when these drugs were being evaluated in clinical trials,” he said. It would be helpful, he said, if payers used the National Heart, Lung and Blood institute and the Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines for biologics.
One of the goals of the researchers is to present their findings to payers, “to let them know, here are some of the hang-ups and the real risks associated with delaying these medications,” Dr. Ishmael said.
“When specialists especially prescribe these therapies, there’s usually a valid reason,” he said. “We really need to do something about the current process – if there are ways to make it more transparent, faster.”
Dr. Ishmael has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ishmael F et al. AAAAI 2020. Session 3609, Presentation 558.
Insurance and specialty pharmacy delays in authorizing new biologic prescriptions for severe allergies leave waiting patients at risk of asthma attacks, hospitalizations, emergency department visits and prednisone shots and their known side effects, according to a single-center study that was to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.
The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The study of 80 patients in State College, Pa., found that they waited an average of 44 days from when their doctor submitted the preauthorization request to the insurance company until the practice received the shipment for dispensing to the patient, investigator Faoud Ishmael, MD, PhD, of Mount Nittany Medical Group said in an interview. “The implication here is that these are really the most severe patients who, you would argue, need their medications the quickest, and it’s taking longer to get them than it would an inhaler,” Dr. Ishmael said.
The study focused on patients with severe asthma (n = 60) or urticarial (n = 20) who received a new prescription of monoclonal antibody therapy from March 2014 to August 2019. For asthma treatments, the average time was 45.8 days; for urticaria, 40.6 days (P = .573), Dr. Ishmael said. The researchers divided the total amount of time into two components: insurance plan review and approval (P = .654, and specialty pharmacy review and dispensing of the medicine, each of which averaged 22.8 days (P = .384), he said.
He also noted wide disparity in the range of approval times. “The shortest approval time was 1 day, and the longest 97 days,” Dr. Ishmael said. “It’s interesting that we had this really broad spread.”
What’s more, the study found no trend for the delays among insurers and specialty pharmacies, Dr. Ishmael added. “When these prescriptions get submitted, it’s like a black box,” he said. “It really seems arbitrary why some of them take so long and some of them don’t.” The findings were independent of type of coverage, whether commercial or government, or even specific insurance plans. “It’s more the process that is flawed rather than one insurance company being the bad guy,” he said.
The study also looked at what happened to patients while they were waiting for their prescriptions to be delivered. “What we found is that over half of asthmatics had an exacerbation – 51% had at least one asthma attack where they needed prednisone,” Dr. Ishmael said (P = .0015), “and we had three patients admitted to the hospital over that time frame when they were waiting for the drugs.” One of those patients had been admitted twice, making four total hospitalizations. Preliminary data analysis showed that about 40% of the patients who had attacks went to the emergency department.
For asthmatics who needed prednisone, the average dose was 480 mg (P = .284) – “a pretty substantial number,” in Dr. Ishmael’s words. He noted that a large portion of the study patients were obese, with a mean body mass index of 33 kg/m2. Other comorbidities prevalent in the study population were hypertension and type 2 diabetes. “Prednisone is something that could worsen all of those conditions, so it’s not a trivial issue,” he said.
The study, however, didn’t evaluate costs of the interventions during the delay period vs. the costs of the medications themselves. Of the 80 prescriptions Dr. Ishmael and coauthors submitted, only one was rejected, that person being a smoker, he said. “I understand these are expensive medicines, but it’s counterproductive to delay them because in the long run the insurance company ends up paying for the hospitalization and the drug rather than just the drug,” he said.
Timothy Craig, DO, of Penn State Health Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology and professor of medicine and pediatrics at Penn State College of Medicine, both in Hershey, said he was surprised at the brevity of the delays reported in Dr. Ishmael’s study. “They do much better than we do with preauthorization,” he said, noting that, in his experience, these approvals take much longer. He added that his own research has found faulty insurance plan algorithms are at the heart of these delays. “We need more studies to clarify how much this is interfering with patient care and how much risk they’re putting patients in,” he said.
The COVID-19 pandemic poses a double-edged sword for physicians managing patients with severe asthma, Dr. Craig noted. “Their asthma care is important, especially if they do test for COVID-19,” he said. On the other hand, doctors and nurses attending to COVID-19 patients will have less time to haggle with payers to expedite coverage for biologics for their severe asthma patients, he said. “I hope the flexibility is there, especially at this time to allow people to get on the biologics and stay on them,” he said.
Dr. Ishmael said these findings have serious implications because biologics are getting prescribed ever more frequently for asthma and hives. Steps his practice has taken to streamline the process include following the payer’s approval guidelines as closely as possible. This sometimes can mean making sure a patient with severe asthma has been maximized on controller medications before submitting the biologic prescription, he said. Another step is to use drug company programs to remove barriers to coverage.
Nonetheless, the approval process can be daunting even when taking those steps, he said. “Those guidelines that constitute approval may vary a lot from one insurer to another; and sometimes those guidelines are different from the criteria that studies may have used when these drugs were being evaluated in clinical trials,” he said. It would be helpful, he said, if payers used the National Heart, Lung and Blood institute and the Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines for biologics.
One of the goals of the researchers is to present their findings to payers, “to let them know, here are some of the hang-ups and the real risks associated with delaying these medications,” Dr. Ishmael said.
“When specialists especially prescribe these therapies, there’s usually a valid reason,” he said. “We really need to do something about the current process – if there are ways to make it more transparent, faster.”
Dr. Ishmael has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ishmael F et al. AAAAI 2020. Session 3609, Presentation 558.
REPORTING FROM AAAAI
Study links GLP-1R agonists, lower inflammatory biomarker levels
Patients with both type 2 diabetes and asthma who were on glucagonlike peptide receptor–1 (GLP-1R) agonists for glucose control had lower levels of a key biomarker of airway inflammation than similar patients on other types of glucose-control medications, according to results of a study to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Asthma, Allergy, and Immunology. The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings from this study potentially replicated findings in humans that have been reported in preclinical trials.
“Our work showed that type 2 diabetics with asthma who were treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists had lower levels of periostin, and this provides really one of the first human data to show that these drugs may impact key inflammation pathways in the airway,” Dinah Foer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. She described periostin as “a known critical inducer of airway mucous production and airway responsiveness.”
The study retrospectively evaluated serum samples from the Partners HealthCare Biobank of 161 adults with both asthma and type 2 diabetes, 42 of whom were on GLP-1R agonists and 119 of whom were taking non-GLP-1R agonist diabetes medications. The study used the Partners Healthcare EHR to identify eligible patients.
The study found that periostin levels were significantly decreased in GLP-1R agonist users: 19.1 ng/mL (standard deviation, +8.7) versus 27.4 ng/mL (SD, +14) in the non-GLP-1R agonist group (P = .001), Dr. Foer said. The other known mediators of asthma inflammatory pathways that were measured – interleukin-6, IL-8, sCD163, total IgE, and sST2 (soluble suppression of tumorigenesis–2) – showed no differences between the two groups, Dr. Foer said.
She said that this was the first human study to show similar results to preclinical models of asthma pathways. “What was interesting to us was that our findings were robust even when we controlled for covariates,” she added.
These findings lay the groundwork for further research into the potential therapeutic role GLP-1R agonists in asthma, Dr. Foer said. “This supports using periostin as a biomarker for novel therapeutic use of GLP-1R [agonists] in asthma,” she said. “At this point further study is needed to understand the clinical impact of GPL-1R [agonists] in asthma both for patients with type 2 diabetes and potentially in the future for patients who don’t have type 2 diabetes or metabolic disease.”
She added: “I don’t think we’re there yet; this is just one foot forward.”
The next step for researchers involves analyzing outcomes in asthmatics with type 2 diabetes on GLP-1R agonist therapy using a larger sample size as well as patients with asthma and metabolic disease, Dr. Foer said. The goal would be to identify corresponding biomarkers.
“There’s a terrific conversation in the field about the relationships between metabolism and asthma,” she said. “What our data contributes to that is, it suggests a role for metabolic pathways, specifically as it’s related GLP-1R [agonist] signaling pathways in regulating airway inflammation.”
Mark Moss, MD, associate professor of allergy & immunology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, who was to serve as the moderator of the session, was positive about the GLP-1R agonist findings. He said in an interview: “This is promising research that provides a possible new target for the treatment of asthma.”
Dr. Foer disclosed that she has no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Foer D et al. AAAAI Session 462, Abstract 784.
Patients with both type 2 diabetes and asthma who were on glucagonlike peptide receptor–1 (GLP-1R) agonists for glucose control had lower levels of a key biomarker of airway inflammation than similar patients on other types of glucose-control medications, according to results of a study to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Asthma, Allergy, and Immunology. The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings from this study potentially replicated findings in humans that have been reported in preclinical trials.
“Our work showed that type 2 diabetics with asthma who were treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists had lower levels of periostin, and this provides really one of the first human data to show that these drugs may impact key inflammation pathways in the airway,” Dinah Foer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. She described periostin as “a known critical inducer of airway mucous production and airway responsiveness.”
The study retrospectively evaluated serum samples from the Partners HealthCare Biobank of 161 adults with both asthma and type 2 diabetes, 42 of whom were on GLP-1R agonists and 119 of whom were taking non-GLP-1R agonist diabetes medications. The study used the Partners Healthcare EHR to identify eligible patients.
The study found that periostin levels were significantly decreased in GLP-1R agonist users: 19.1 ng/mL (standard deviation, +8.7) versus 27.4 ng/mL (SD, +14) in the non-GLP-1R agonist group (P = .001), Dr. Foer said. The other known mediators of asthma inflammatory pathways that were measured – interleukin-6, IL-8, sCD163, total IgE, and sST2 (soluble suppression of tumorigenesis–2) – showed no differences between the two groups, Dr. Foer said.
She said that this was the first human study to show similar results to preclinical models of asthma pathways. “What was interesting to us was that our findings were robust even when we controlled for covariates,” she added.
These findings lay the groundwork for further research into the potential therapeutic role GLP-1R agonists in asthma, Dr. Foer said. “This supports using periostin as a biomarker for novel therapeutic use of GLP-1R [agonists] in asthma,” she said. “At this point further study is needed to understand the clinical impact of GPL-1R [agonists] in asthma both for patients with type 2 diabetes and potentially in the future for patients who don’t have type 2 diabetes or metabolic disease.”
She added: “I don’t think we’re there yet; this is just one foot forward.”
The next step for researchers involves analyzing outcomes in asthmatics with type 2 diabetes on GLP-1R agonist therapy using a larger sample size as well as patients with asthma and metabolic disease, Dr. Foer said. The goal would be to identify corresponding biomarkers.
“There’s a terrific conversation in the field about the relationships between metabolism and asthma,” she said. “What our data contributes to that is, it suggests a role for metabolic pathways, specifically as it’s related GLP-1R [agonist] signaling pathways in regulating airway inflammation.”
Mark Moss, MD, associate professor of allergy & immunology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, who was to serve as the moderator of the session, was positive about the GLP-1R agonist findings. He said in an interview: “This is promising research that provides a possible new target for the treatment of asthma.”
Dr. Foer disclosed that she has no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Foer D et al. AAAAI Session 462, Abstract 784.
Patients with both type 2 diabetes and asthma who were on glucagonlike peptide receptor–1 (GLP-1R) agonists for glucose control had lower levels of a key biomarker of airway inflammation than similar patients on other types of glucose-control medications, according to results of a study to have been presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Asthma, Allergy, and Immunology. The AAAAI canceled their annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
The findings from this study potentially replicated findings in humans that have been reported in preclinical trials.
“Our work showed that type 2 diabetics with asthma who were treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists had lower levels of periostin, and this provides really one of the first human data to show that these drugs may impact key inflammation pathways in the airway,” Dinah Foer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. She described periostin as “a known critical inducer of airway mucous production and airway responsiveness.”
The study retrospectively evaluated serum samples from the Partners HealthCare Biobank of 161 adults with both asthma and type 2 diabetes, 42 of whom were on GLP-1R agonists and 119 of whom were taking non-GLP-1R agonist diabetes medications. The study used the Partners Healthcare EHR to identify eligible patients.
The study found that periostin levels were significantly decreased in GLP-1R agonist users: 19.1 ng/mL (standard deviation, +8.7) versus 27.4 ng/mL (SD, +14) in the non-GLP-1R agonist group (P = .001), Dr. Foer said. The other known mediators of asthma inflammatory pathways that were measured – interleukin-6, IL-8, sCD163, total IgE, and sST2 (soluble suppression of tumorigenesis–2) – showed no differences between the two groups, Dr. Foer said.
She said that this was the first human study to show similar results to preclinical models of asthma pathways. “What was interesting to us was that our findings were robust even when we controlled for covariates,” she added.
These findings lay the groundwork for further research into the potential therapeutic role GLP-1R agonists in asthma, Dr. Foer said. “This supports using periostin as a biomarker for novel therapeutic use of GLP-1R [agonists] in asthma,” she said. “At this point further study is needed to understand the clinical impact of GPL-1R [agonists] in asthma both for patients with type 2 diabetes and potentially in the future for patients who don’t have type 2 diabetes or metabolic disease.”
She added: “I don’t think we’re there yet; this is just one foot forward.”
The next step for researchers involves analyzing outcomes in asthmatics with type 2 diabetes on GLP-1R agonist therapy using a larger sample size as well as patients with asthma and metabolic disease, Dr. Foer said. The goal would be to identify corresponding biomarkers.
“There’s a terrific conversation in the field about the relationships between metabolism and asthma,” she said. “What our data contributes to that is, it suggests a role for metabolic pathways, specifically as it’s related GLP-1R [agonist] signaling pathways in regulating airway inflammation.”
Mark Moss, MD, associate professor of allergy & immunology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, who was to serve as the moderator of the session, was positive about the GLP-1R agonist findings. He said in an interview: “This is promising research that provides a possible new target for the treatment of asthma.”
Dr. Foer disclosed that she has no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Foer D et al. AAAAI Session 462, Abstract 784.
FDA issues stronger warning on neuropsychiatric event risk linked to montelukast
The Food and Drug Administration has issued , a prescription drug for asthma and allergy.
The new boxed warning advises health care providers to avoid prescribing montelukast for patients with mild symptoms, particularly those with allergic rhinitis, the FDA said in a press release. The drug was first approved in 1998, and the product labeling was updated in 2008 to include information about neuropsychiatric adverse events reported with usage of montelukast.
While the Sentinel study, along with other observational studies, did not find an increased risk of mental health side effects with montelukast treatment, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, those studies had limitations that may have affected results, the FDA said in the Drug Safety Communication. However, the FDA has continued to receive reports of neuropsychiatric events – including agitation, depression, sleeping problems, and suicidal thoughts and actions – in patients receiving the medication.
“The incidence of neuropsychiatric events associated with montelukast is unknown, but some reports are serious, and many patients and health care professionals are not fully aware of these risks,” Sally Seymour, MD, director of the division of pulmonary, allergy and rheumatology products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release. “There are many other safe and effective medications to treat allergies with extensive history of use and safety, such that many products are available over the counter without a prescription.”
In addition to the boxed warning, the FDA now requires a new medication guide to be given to patients with each montelukast prescription, the FDA said.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued , a prescription drug for asthma and allergy.
The new boxed warning advises health care providers to avoid prescribing montelukast for patients with mild symptoms, particularly those with allergic rhinitis, the FDA said in a press release. The drug was first approved in 1998, and the product labeling was updated in 2008 to include information about neuropsychiatric adverse events reported with usage of montelukast.
While the Sentinel study, along with other observational studies, did not find an increased risk of mental health side effects with montelukast treatment, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, those studies had limitations that may have affected results, the FDA said in the Drug Safety Communication. However, the FDA has continued to receive reports of neuropsychiatric events – including agitation, depression, sleeping problems, and suicidal thoughts and actions – in patients receiving the medication.
“The incidence of neuropsychiatric events associated with montelukast is unknown, but some reports are serious, and many patients and health care professionals are not fully aware of these risks,” Sally Seymour, MD, director of the division of pulmonary, allergy and rheumatology products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release. “There are many other safe and effective medications to treat allergies with extensive history of use and safety, such that many products are available over the counter without a prescription.”
In addition to the boxed warning, the FDA now requires a new medication guide to be given to patients with each montelukast prescription, the FDA said.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued , a prescription drug for asthma and allergy.
The new boxed warning advises health care providers to avoid prescribing montelukast for patients with mild symptoms, particularly those with allergic rhinitis, the FDA said in a press release. The drug was first approved in 1998, and the product labeling was updated in 2008 to include information about neuropsychiatric adverse events reported with usage of montelukast.
While the Sentinel study, along with other observational studies, did not find an increased risk of mental health side effects with montelukast treatment, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, those studies had limitations that may have affected results, the FDA said in the Drug Safety Communication. However, the FDA has continued to receive reports of neuropsychiatric events – including agitation, depression, sleeping problems, and suicidal thoughts and actions – in patients receiving the medication.
“The incidence of neuropsychiatric events associated with montelukast is unknown, but some reports are serious, and many patients and health care professionals are not fully aware of these risks,” Sally Seymour, MD, director of the division of pulmonary, allergy and rheumatology products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release. “There are many other safe and effective medications to treat allergies with extensive history of use and safety, such that many products are available over the counter without a prescription.”
In addition to the boxed warning, the FDA now requires a new medication guide to be given to patients with each montelukast prescription, the FDA said.