User login
Oophorectomies continue to dominate torsion treatment
Prompt surgical management is essential in cases of ovarian torsion in order to salvage ovarian function, and recent studies have shown that conservative management with detorsion does not increase postoperative complications, compared with oophorectomy, wrote Hannah Ryles, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists issued practice guidelines in November 2016 that recommended ovarian conservation rather than oophorectomy to manage adnexal torsion in women wishing to preserve fertility. However, the impact of this guideline on clinical practice and surgical patterns remains unclear, the researchers said.
In a study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from 402 patients who underwent surgeries before the updated ACOG guidelines (2008-2016) and 1,389 who underwent surgeries after the guidelines (2017-2020). Surgery data came from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database. The study population included women aged 18-50 years who underwent adnexal torsion surgery and were identified as having either oophorectomy or ovarian conservation surgery.
A total of 1,791 surgeries performed for adnexal torsion were included in the study; 542 (30.3%) involved ovarian conservation and 1,249 (69.7%) involved oophorectomy.
The proportion of oophorectomies was similar during the periods before and after the guidelines (71.9% vs. 69.1%; P = .16). However, the proportion of oophorectomies changed significantly across the entire study period, by approximately –1.6% each year.
Factors significantly associated with oophorectomy compared with ovarian conservation included older age (35 years vs. 28 years), higher body mass index (29.2 kg/m2 vs. 27.5 kg/m2), anemia (12.2% vs. 7.2%), hypertension (10.4% vs. 3.1%), and higher American Society of Anesthesiologists classification.
“There remains no defined acceptable rate of oophorectomy; this decision involves multiple factors, such as fertility and other patient desires after a risk and benefit discussion, menopausal status, concern for malignancy, and safety and feasibility of conservative procedures,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, in emergency situations, it may be difficult to determine a patient’s preferences, and a lack of desire for future fertility may be presumed, which may contribute to the relatively high oophorectomy rates over time, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of data on surgical history, histopathology, and intraoperative appearance of the ovary, as well as lack of clinical data including the time from presentation to diagnosis or surgery, the researchers noted. “Although we were also unable to determine obstetric history and fertility desires, our median age of 32 years reflects a young cohort that was limited to women of reproductive age,” they added.
However, the results reflect studies suggesting that clinical practice often lags behind updated guidelines, and the findings were strengthened by the use of the NSQIP database and reflect a need for greater efforts to promote ovarian conservation in accordance with the current guidelines, the researchers concluded.
Consider unilateral oophorectomy
The current study highlights the discrepancy between the ACOG guidelines and clinical practice, with “disappointingly low” rates of ovarian preservation in the adult population, wrote Riley J. Young, MD, and Kimberly A. Kho, MD, both of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, in an accompanying editorial. The reasons for the discrepancy include clinical concerns for conserving a torsed ovary and the difficulty of assessing fertility desires in an emergency situation, they said.
However, consideration of unilateral oophorectomy as an option should be part of clinical decision-making, according to the editorialists. Previous studies suggest that retention of a single ovarian may still allow for a successful pregnancy, and the effects of unilateral oophorectomy have been studied in infertility and assisted reproductive technology settings.
Women with a single ovary have fewer eggs and require higher amounts of gonadotropins, but pregnancy is possible, the editorialists said. However, the long-term effects of unilateral oophorectomy are uncertain, and potential detrimental outcomes include increased mortality and cognitive impairment; therefore “we aim for premenopausal ovaries simply to be conserved, whether fertility is the stated goal or not,” they noted. This may include consideration of unilateral oophorectomy. “Each ovary conserved at midnight moves us closer to a more acceptable ovarian conservation rate,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kho disclosed funding to her institution from Hologic for being on an investigator-initiated study, Dr. Young had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Prompt surgical management is essential in cases of ovarian torsion in order to salvage ovarian function, and recent studies have shown that conservative management with detorsion does not increase postoperative complications, compared with oophorectomy, wrote Hannah Ryles, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists issued practice guidelines in November 2016 that recommended ovarian conservation rather than oophorectomy to manage adnexal torsion in women wishing to preserve fertility. However, the impact of this guideline on clinical practice and surgical patterns remains unclear, the researchers said.
In a study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from 402 patients who underwent surgeries before the updated ACOG guidelines (2008-2016) and 1,389 who underwent surgeries after the guidelines (2017-2020). Surgery data came from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database. The study population included women aged 18-50 years who underwent adnexal torsion surgery and were identified as having either oophorectomy or ovarian conservation surgery.
A total of 1,791 surgeries performed for adnexal torsion were included in the study; 542 (30.3%) involved ovarian conservation and 1,249 (69.7%) involved oophorectomy.
The proportion of oophorectomies was similar during the periods before and after the guidelines (71.9% vs. 69.1%; P = .16). However, the proportion of oophorectomies changed significantly across the entire study period, by approximately –1.6% each year.
Factors significantly associated with oophorectomy compared with ovarian conservation included older age (35 years vs. 28 years), higher body mass index (29.2 kg/m2 vs. 27.5 kg/m2), anemia (12.2% vs. 7.2%), hypertension (10.4% vs. 3.1%), and higher American Society of Anesthesiologists classification.
“There remains no defined acceptable rate of oophorectomy; this decision involves multiple factors, such as fertility and other patient desires after a risk and benefit discussion, menopausal status, concern for malignancy, and safety and feasibility of conservative procedures,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, in emergency situations, it may be difficult to determine a patient’s preferences, and a lack of desire for future fertility may be presumed, which may contribute to the relatively high oophorectomy rates over time, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of data on surgical history, histopathology, and intraoperative appearance of the ovary, as well as lack of clinical data including the time from presentation to diagnosis or surgery, the researchers noted. “Although we were also unable to determine obstetric history and fertility desires, our median age of 32 years reflects a young cohort that was limited to women of reproductive age,” they added.
However, the results reflect studies suggesting that clinical practice often lags behind updated guidelines, and the findings were strengthened by the use of the NSQIP database and reflect a need for greater efforts to promote ovarian conservation in accordance with the current guidelines, the researchers concluded.
Consider unilateral oophorectomy
The current study highlights the discrepancy between the ACOG guidelines and clinical practice, with “disappointingly low” rates of ovarian preservation in the adult population, wrote Riley J. Young, MD, and Kimberly A. Kho, MD, both of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, in an accompanying editorial. The reasons for the discrepancy include clinical concerns for conserving a torsed ovary and the difficulty of assessing fertility desires in an emergency situation, they said.
However, consideration of unilateral oophorectomy as an option should be part of clinical decision-making, according to the editorialists. Previous studies suggest that retention of a single ovarian may still allow for a successful pregnancy, and the effects of unilateral oophorectomy have been studied in infertility and assisted reproductive technology settings.
Women with a single ovary have fewer eggs and require higher amounts of gonadotropins, but pregnancy is possible, the editorialists said. However, the long-term effects of unilateral oophorectomy are uncertain, and potential detrimental outcomes include increased mortality and cognitive impairment; therefore “we aim for premenopausal ovaries simply to be conserved, whether fertility is the stated goal or not,” they noted. This may include consideration of unilateral oophorectomy. “Each ovary conserved at midnight moves us closer to a more acceptable ovarian conservation rate,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kho disclosed funding to her institution from Hologic for being on an investigator-initiated study, Dr. Young had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Prompt surgical management is essential in cases of ovarian torsion in order to salvage ovarian function, and recent studies have shown that conservative management with detorsion does not increase postoperative complications, compared with oophorectomy, wrote Hannah Ryles, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists issued practice guidelines in November 2016 that recommended ovarian conservation rather than oophorectomy to manage adnexal torsion in women wishing to preserve fertility. However, the impact of this guideline on clinical practice and surgical patterns remains unclear, the researchers said.
In a study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from 402 patients who underwent surgeries before the updated ACOG guidelines (2008-2016) and 1,389 who underwent surgeries after the guidelines (2017-2020). Surgery data came from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database. The study population included women aged 18-50 years who underwent adnexal torsion surgery and were identified as having either oophorectomy or ovarian conservation surgery.
A total of 1,791 surgeries performed for adnexal torsion were included in the study; 542 (30.3%) involved ovarian conservation and 1,249 (69.7%) involved oophorectomy.
The proportion of oophorectomies was similar during the periods before and after the guidelines (71.9% vs. 69.1%; P = .16). However, the proportion of oophorectomies changed significantly across the entire study period, by approximately –1.6% each year.
Factors significantly associated with oophorectomy compared with ovarian conservation included older age (35 years vs. 28 years), higher body mass index (29.2 kg/m2 vs. 27.5 kg/m2), anemia (12.2% vs. 7.2%), hypertension (10.4% vs. 3.1%), and higher American Society of Anesthesiologists classification.
“There remains no defined acceptable rate of oophorectomy; this decision involves multiple factors, such as fertility and other patient desires after a risk and benefit discussion, menopausal status, concern for malignancy, and safety and feasibility of conservative procedures,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, in emergency situations, it may be difficult to determine a patient’s preferences, and a lack of desire for future fertility may be presumed, which may contribute to the relatively high oophorectomy rates over time, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of data on surgical history, histopathology, and intraoperative appearance of the ovary, as well as lack of clinical data including the time from presentation to diagnosis or surgery, the researchers noted. “Although we were also unable to determine obstetric history and fertility desires, our median age of 32 years reflects a young cohort that was limited to women of reproductive age,” they added.
However, the results reflect studies suggesting that clinical practice often lags behind updated guidelines, and the findings were strengthened by the use of the NSQIP database and reflect a need for greater efforts to promote ovarian conservation in accordance with the current guidelines, the researchers concluded.
Consider unilateral oophorectomy
The current study highlights the discrepancy between the ACOG guidelines and clinical practice, with “disappointingly low” rates of ovarian preservation in the adult population, wrote Riley J. Young, MD, and Kimberly A. Kho, MD, both of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, in an accompanying editorial. The reasons for the discrepancy include clinical concerns for conserving a torsed ovary and the difficulty of assessing fertility desires in an emergency situation, they said.
However, consideration of unilateral oophorectomy as an option should be part of clinical decision-making, according to the editorialists. Previous studies suggest that retention of a single ovarian may still allow for a successful pregnancy, and the effects of unilateral oophorectomy have been studied in infertility and assisted reproductive technology settings.
Women with a single ovary have fewer eggs and require higher amounts of gonadotropins, but pregnancy is possible, the editorialists said. However, the long-term effects of unilateral oophorectomy are uncertain, and potential detrimental outcomes include increased mortality and cognitive impairment; therefore “we aim for premenopausal ovaries simply to be conserved, whether fertility is the stated goal or not,” they noted. This may include consideration of unilateral oophorectomy. “Each ovary conserved at midnight moves us closer to a more acceptable ovarian conservation rate,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kho disclosed funding to her institution from Hologic for being on an investigator-initiated study, Dr. Young had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Surgical management of borderline ovarian tumors, part 1
Borderline ovarian tumors (BOTs) are estimated to comprise 10%-15% of all epithelial tumors of the ovary. They are characterized by their behavior, which falls somewhere between benign ovarian masses and frank carcinomas. They have cytologic characteristics suggesting malignancy, such as higher cellular proliferation and more variable nuclear atypia, but, unlike carcinomas, they lack destructive stromal invasion. For decades after their recognition by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics in 1971, these tumors were classified as being of low malignant potential (and subsequently referred to as LMP tumors of the ovary). Beginning with the 2014 World Health Organization classification, the recommended terminology is now borderline tumor of the ovary.
The primary treatment for BOTs is surgery. With a mean age at diagnosis in the fifth decade, many patients with BOTs desire ovarian preservation to maintain fertility and/or prevent surgical menopause. This raises multiple questions regarding the use of fertility-sparing surgery for BOTs: What types of procedures are safe and should be offered? For those patients who undergo fertility-sparing surgery initially, is additional surgery indicated after completion of childbearing or at an age closer to natural menopause? What should this completion surgery include?
Ovarian-sparing surgery
The diagnosis of a BOT is frequently only confirmed after the decision for ovarian conservation has been made. What should be considered before electing to proceed with ovarian cystectomy instead of unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (USO)?
Is the risk of recurrence higher with cystectomy versus oophorectomy?
Yes. The risk of recurrence of BOT appears to be higher after cystectomy than it is after oophorectomy. There is a large range reported in the literature, with the risk of recurrence after cystectomy described as between 12% and 58%. Most studies report recurrences between 25% and 35% of patients who undergo cystectomy. In contrast, the risk of recurrence after USO is often reported to be approximately 10%. Higher risk of recurrence after cystectomy is speculated to be due to leaving some BOT at the time of initial surgery.
Multiple meta-analyses have found an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy. The risk of recurrence after unilateral cystectomy was 19.4%, compared with 9.1% after USO, in 2,145 patients included in a 2017 meta-analysis.1 Similarly, a 2021 meta-analysis found a significantly higher rate of BOT recurrence in patients who underwent unilateral or bilateral cystectomy compared with USO (odds ratio, 2.02; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.57).2
Does the higher recurrence risk translate into a difference in long-term outcomes?
No. Despite an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy, ovarian-sparing surgery does not appear to alter patients’ survival. The pooled mortality estimate was 1.6% for those undergoing fertility-sparing surgery (95% CI, 0.011-0.023), compared with 2.0% for those undergoing radical surgery (95% CI, 0.014-0.029), in a 2015 meta-analysis of over 5,100 patients. The analysis included studies in which patients underwent unilateral cystectomy, bilateral cystectomy, USO, or USO plus contralateral cystectomy. The low mortality rate did not allow for comparison between the different types of fertility-sparing surgeries.3
Do we accept a higher risk of recurrence with ovarian sparing surgery to improve fertility?
Data are mixed. When we examine studies describing fertility rates after conservative surgery, there are significant limitations to interpreting the data available. Some studies do not differentiate among patients who underwent fertility-sparing surgery, or between those who had cystectomy versus USO. Other studies do not report the number of patients who tried to achieve pregnancy after surgery. Conception rates are reported to be as high as 88.2%, which was in 116 patients who were able to be reached after fertility-sparing surgery (retained at least one ovary). Of the 51 patients who tried to conceive, 45 were successful.4
Multiple studies and meta-analyses have shown no difference in postoperative pregnancy rates when comparing oophorectomy to cystectomy. For instance, in a 2021 meta-analysis, there was no significant difference noted in pregnancy rates between patients who underwent USO versus cystectomy (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.60-1.42).
There are some data that support improved postoperative pregnancy rates in more conservative surgery, especially in the setting of bilateral BOT. In a small study of 32 patients who had laparoscopic staging for bilateral BOTs, patients were randomized to unilateral oophorectomy plus contralateral cystectomy or to bilateral cystectomy, which was referred to as ultraconservative surgery. The time to first recurrence was shorter in the ultraconservative group (although this lost significance when regression analysis was performed), but the time to first live birth was shorter and the relative chance of having a baby was higher in the bilateral cystectomy group.5
Ovarian-sparing procedures should be offered to patients in the setting of BOT. With ovarian-sparing surgery, it is important to counsel patients about the increased risk of recurrence and need for long-term follow-up. Pregnancy rates are generally good after fertility-sparing surgery. Surgery to conserve both ovaries does not seem to improve pregnancy rates in the setting of unilateral BOTs.
Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
References
1. Jiao X et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2017 Nov;27(9):1833-41.
2. Wang P and Fang L. World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Apr 21;19(1):132.
3. Vasconcelos I and de Sousa Mendes M. Eur J Cancer. 2015 Mar;51(5):620-31.
4. Song T et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 May;21(4):640-6.
5. Palomba S et al. Hum Reprod. 2010 Aug;25(8):1966-72.
Borderline ovarian tumors (BOTs) are estimated to comprise 10%-15% of all epithelial tumors of the ovary. They are characterized by their behavior, which falls somewhere between benign ovarian masses and frank carcinomas. They have cytologic characteristics suggesting malignancy, such as higher cellular proliferation and more variable nuclear atypia, but, unlike carcinomas, they lack destructive stromal invasion. For decades after their recognition by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics in 1971, these tumors were classified as being of low malignant potential (and subsequently referred to as LMP tumors of the ovary). Beginning with the 2014 World Health Organization classification, the recommended terminology is now borderline tumor of the ovary.
The primary treatment for BOTs is surgery. With a mean age at diagnosis in the fifth decade, many patients with BOTs desire ovarian preservation to maintain fertility and/or prevent surgical menopause. This raises multiple questions regarding the use of fertility-sparing surgery for BOTs: What types of procedures are safe and should be offered? For those patients who undergo fertility-sparing surgery initially, is additional surgery indicated after completion of childbearing or at an age closer to natural menopause? What should this completion surgery include?
Ovarian-sparing surgery
The diagnosis of a BOT is frequently only confirmed after the decision for ovarian conservation has been made. What should be considered before electing to proceed with ovarian cystectomy instead of unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (USO)?
Is the risk of recurrence higher with cystectomy versus oophorectomy?
Yes. The risk of recurrence of BOT appears to be higher after cystectomy than it is after oophorectomy. There is a large range reported in the literature, with the risk of recurrence after cystectomy described as between 12% and 58%. Most studies report recurrences between 25% and 35% of patients who undergo cystectomy. In contrast, the risk of recurrence after USO is often reported to be approximately 10%. Higher risk of recurrence after cystectomy is speculated to be due to leaving some BOT at the time of initial surgery.
Multiple meta-analyses have found an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy. The risk of recurrence after unilateral cystectomy was 19.4%, compared with 9.1% after USO, in 2,145 patients included in a 2017 meta-analysis.1 Similarly, a 2021 meta-analysis found a significantly higher rate of BOT recurrence in patients who underwent unilateral or bilateral cystectomy compared with USO (odds ratio, 2.02; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.57).2
Does the higher recurrence risk translate into a difference in long-term outcomes?
No. Despite an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy, ovarian-sparing surgery does not appear to alter patients’ survival. The pooled mortality estimate was 1.6% for those undergoing fertility-sparing surgery (95% CI, 0.011-0.023), compared with 2.0% for those undergoing radical surgery (95% CI, 0.014-0.029), in a 2015 meta-analysis of over 5,100 patients. The analysis included studies in which patients underwent unilateral cystectomy, bilateral cystectomy, USO, or USO plus contralateral cystectomy. The low mortality rate did not allow for comparison between the different types of fertility-sparing surgeries.3
Do we accept a higher risk of recurrence with ovarian sparing surgery to improve fertility?
Data are mixed. When we examine studies describing fertility rates after conservative surgery, there are significant limitations to interpreting the data available. Some studies do not differentiate among patients who underwent fertility-sparing surgery, or between those who had cystectomy versus USO. Other studies do not report the number of patients who tried to achieve pregnancy after surgery. Conception rates are reported to be as high as 88.2%, which was in 116 patients who were able to be reached after fertility-sparing surgery (retained at least one ovary). Of the 51 patients who tried to conceive, 45 were successful.4
Multiple studies and meta-analyses have shown no difference in postoperative pregnancy rates when comparing oophorectomy to cystectomy. For instance, in a 2021 meta-analysis, there was no significant difference noted in pregnancy rates between patients who underwent USO versus cystectomy (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.60-1.42).
There are some data that support improved postoperative pregnancy rates in more conservative surgery, especially in the setting of bilateral BOT. In a small study of 32 patients who had laparoscopic staging for bilateral BOTs, patients were randomized to unilateral oophorectomy plus contralateral cystectomy or to bilateral cystectomy, which was referred to as ultraconservative surgery. The time to first recurrence was shorter in the ultraconservative group (although this lost significance when regression analysis was performed), but the time to first live birth was shorter and the relative chance of having a baby was higher in the bilateral cystectomy group.5
Ovarian-sparing procedures should be offered to patients in the setting of BOT. With ovarian-sparing surgery, it is important to counsel patients about the increased risk of recurrence and need for long-term follow-up. Pregnancy rates are generally good after fertility-sparing surgery. Surgery to conserve both ovaries does not seem to improve pregnancy rates in the setting of unilateral BOTs.
Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
References
1. Jiao X et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2017 Nov;27(9):1833-41.
2. Wang P and Fang L. World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Apr 21;19(1):132.
3. Vasconcelos I and de Sousa Mendes M. Eur J Cancer. 2015 Mar;51(5):620-31.
4. Song T et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 May;21(4):640-6.
5. Palomba S et al. Hum Reprod. 2010 Aug;25(8):1966-72.
Borderline ovarian tumors (BOTs) are estimated to comprise 10%-15% of all epithelial tumors of the ovary. They are characterized by their behavior, which falls somewhere between benign ovarian masses and frank carcinomas. They have cytologic characteristics suggesting malignancy, such as higher cellular proliferation and more variable nuclear atypia, but, unlike carcinomas, they lack destructive stromal invasion. For decades after their recognition by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics in 1971, these tumors were classified as being of low malignant potential (and subsequently referred to as LMP tumors of the ovary). Beginning with the 2014 World Health Organization classification, the recommended terminology is now borderline tumor of the ovary.
The primary treatment for BOTs is surgery. With a mean age at diagnosis in the fifth decade, many patients with BOTs desire ovarian preservation to maintain fertility and/or prevent surgical menopause. This raises multiple questions regarding the use of fertility-sparing surgery for BOTs: What types of procedures are safe and should be offered? For those patients who undergo fertility-sparing surgery initially, is additional surgery indicated after completion of childbearing or at an age closer to natural menopause? What should this completion surgery include?
Ovarian-sparing surgery
The diagnosis of a BOT is frequently only confirmed after the decision for ovarian conservation has been made. What should be considered before electing to proceed with ovarian cystectomy instead of unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (USO)?
Is the risk of recurrence higher with cystectomy versus oophorectomy?
Yes. The risk of recurrence of BOT appears to be higher after cystectomy than it is after oophorectomy. There is a large range reported in the literature, with the risk of recurrence after cystectomy described as between 12% and 58%. Most studies report recurrences between 25% and 35% of patients who undergo cystectomy. In contrast, the risk of recurrence after USO is often reported to be approximately 10%. Higher risk of recurrence after cystectomy is speculated to be due to leaving some BOT at the time of initial surgery.
Multiple meta-analyses have found an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy. The risk of recurrence after unilateral cystectomy was 19.4%, compared with 9.1% after USO, in 2,145 patients included in a 2017 meta-analysis.1 Similarly, a 2021 meta-analysis found a significantly higher rate of BOT recurrence in patients who underwent unilateral or bilateral cystectomy compared with USO (odds ratio, 2.02; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.57).2
Does the higher recurrence risk translate into a difference in long-term outcomes?
No. Despite an increased risk of recurrence after cystectomy, ovarian-sparing surgery does not appear to alter patients’ survival. The pooled mortality estimate was 1.6% for those undergoing fertility-sparing surgery (95% CI, 0.011-0.023), compared with 2.0% for those undergoing radical surgery (95% CI, 0.014-0.029), in a 2015 meta-analysis of over 5,100 patients. The analysis included studies in which patients underwent unilateral cystectomy, bilateral cystectomy, USO, or USO plus contralateral cystectomy. The low mortality rate did not allow for comparison between the different types of fertility-sparing surgeries.3
Do we accept a higher risk of recurrence with ovarian sparing surgery to improve fertility?
Data are mixed. When we examine studies describing fertility rates after conservative surgery, there are significant limitations to interpreting the data available. Some studies do not differentiate among patients who underwent fertility-sparing surgery, or between those who had cystectomy versus USO. Other studies do not report the number of patients who tried to achieve pregnancy after surgery. Conception rates are reported to be as high as 88.2%, which was in 116 patients who were able to be reached after fertility-sparing surgery (retained at least one ovary). Of the 51 patients who tried to conceive, 45 were successful.4
Multiple studies and meta-analyses have shown no difference in postoperative pregnancy rates when comparing oophorectomy to cystectomy. For instance, in a 2021 meta-analysis, there was no significant difference noted in pregnancy rates between patients who underwent USO versus cystectomy (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.60-1.42).
There are some data that support improved postoperative pregnancy rates in more conservative surgery, especially in the setting of bilateral BOT. In a small study of 32 patients who had laparoscopic staging for bilateral BOTs, patients were randomized to unilateral oophorectomy plus contralateral cystectomy or to bilateral cystectomy, which was referred to as ultraconservative surgery. The time to first recurrence was shorter in the ultraconservative group (although this lost significance when regression analysis was performed), but the time to first live birth was shorter and the relative chance of having a baby was higher in the bilateral cystectomy group.5
Ovarian-sparing procedures should be offered to patients in the setting of BOT. With ovarian-sparing surgery, it is important to counsel patients about the increased risk of recurrence and need for long-term follow-up. Pregnancy rates are generally good after fertility-sparing surgery. Surgery to conserve both ovaries does not seem to improve pregnancy rates in the setting of unilateral BOTs.
Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
References
1. Jiao X et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2017 Nov;27(9):1833-41.
2. Wang P and Fang L. World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Apr 21;19(1):132.
3. Vasconcelos I and de Sousa Mendes M. Eur J Cancer. 2015 Mar;51(5):620-31.
4. Song T et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 May;21(4):640-6.
5. Palomba S et al. Hum Reprod. 2010 Aug;25(8):1966-72.
For young people on Medicare, a hysterectomy sometimes is more affordable than birth control
Sam Chavarría said her doctor was clear about the birth defects her medication could cause if she became pregnant but agreed to keep her on it as long as she had an IUD.
As she was waiting to get her contraceptive intrauterine device replaced at her local clinic, however, the billing nurse told her that her insurance wouldn’t cover the removal – or a new IUD. Chavarría didn’t understand why not.
“Then she said very delicately, ‘Well, people on this insurance typically tend to be older,’ ” Chavarría recalled.
Although Chavarría is 34, she is enrolled in Medicare, the government insurance program designed for those 65 and older. Chavarría, who lives in Houston, is disabled by fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and mental health issues. Medicare automatically enrolls anyone who has received Social Security disability benefits for two years and this was her first time getting an IUD while in the government program.
Without insurance, just removing her expired IUD would cost Chavarría $350 out of pocket; exchanging it for a new one would be $2,000. She left the clinic in tears.
Chavarría’s experience is not rare. Medicare was originally intended for people of retirement age. Over the years, the program has evolved to include new populations, such as those who have disabilities or are critically ill, said Jennifer Lea Huer, a public health expert at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In 2020, 1.7 million people ages 18-44 were enrolled in Medicare.
An estimated 70% of childbearing-age women on Medicare are also eligible for Medicaid, a state and federal program for those with low incomes, which should fill the gap for contraception. It’s not clear how many transgender or nonbinary people – who also might need contraception – are on Medicare or are eligible for Medicaid.
Medicaid, like the plans offered via the federal Affordable Care Act, mandates coverage of birth control. But those who aren’t eligible for Medicaid are left in the lurch – Medicare’s origins mean it does not require access to birth control.
Traditional Medicare includes two parts: Part A covers hospital costs, while Part B covers physicians’ care and certain other services, such as ambulance rides. Neither ordinarily includes contraception.
People can get contraception through a Medicare Advantage plan or Part D of Medicare, which covers prescription drugs, but those come at a cost. And even people who pay for Part D often aren’t covered for some types of birth control, such as IUDs.
“So, if you are disabled, if you are locked outside of the labor market, if you do not have the means or any other way to financially support yourself, you were likely still on traditional Medicare, which is Part A and Part B,” Huer said. “In which case, your access to contraception is incredibly difficult.”
Contraception for those with traditional Medicare is given on a case-by-case basis, Huer said. It can be covered only if a doctor can make a credible case that the patient needs it for medical reasons – because their body cannot sustain a pregnancy – as opposed to merely wanting to avoid one.
“You have to have a champion physician who’s willing to partner with you and make those arguments,” Huer said.
That’s what Chavarría’s doctor tried to do. Before she left the clinic, staffers there told her they would try to make the case she needed the IUD for medical reasons. The IUD exchange was scheduled almost 10 weeks later, but during those weeks, she got pregnant. Her body couldn’t sustain a pregnancy, so she and her partner rushed to get an abortion just before Texas tightened its rules Sept. 1, 2021.
“If Medicare had just covered the IUD removal or exchange to begin with, none of this would have happened,” Chavarría said. “It would have saved me having to make a really tough decision that I never thought I’d have to make.”
Women with disabilities often face a stigma from health care practitioners, especially when it comes to birth control, said Willi Horner-Johnson, a public health researcher specializing in disabilities at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. In her research, women with disabilities have described being treated like children or having to go to multiple doctors to find someone with whom they felt comfortable.
“We don’t want to acknowledge that disabled people have sex,” said Miriam Garber, a 36-year-old sex worker who lives in Rhode Island and is also on Medicare because of her disabilities. Garber got an IUD from Planned Parenthood because her insurance wouldn’t cover it.
Even those who pay for Part D to have their prescription drugs covered and have a “champion physician” face difficulties. Liz Moore, a nonbinary person in their 30s who lives in the Washington, D.C., area, could not get Medicare to pay for the Mirena IUD their doctor prescribed for their polycystic ovary syndrome. Moore is disabled with fibromyalgia and dysautonomia, a condition of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates breathing, heart rate, and more.
“After literally months of phone calls, it seemed like my Medicare Part D and original Medicare could not agree on who should pay for my IUD,” they wrote in a direct message. “Was it a prescription or durable medical equipment?”
When Moore finally learned it would cost $800 upfront, they said, they decided to get a hysterectomy – which Medicare would pay for – instead.
Chavarría’s doctor told her a tubal ligation also was more likely to be approved by Medicare than an IUD, because older people have that procedure more often. Like all surgeries, both come with risks of complications and recovery.
Even for those on both Medicare and Medicaid, getting contraception also isn’t always easy, as in Katie Elizabeth Walsh’s case.
Walsh, 34, who lives in northeastern Connecticut, is disabled by a traumatic brain injury, depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome. She got an IUD at an ob.gyn. clinic and was told there her insurance would cover it.
Then she got a bill for nearly $2,000.
Medicaid should cover contraceptive devices for dual-eligibility people, according to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy guidance, but when Walsh tried to get her bill covered, Medicare and Medicaid could not agree on which of them should pay.
“Every single time I have called one of the insurance offices, they are like, ‘Oh, no, you have to talk to the other one, and we don’t really talk to each other,’ ” Walsh said.
Walsh said the hassle to get her contraception covered feels like a kick in the stomach: “Like truly you do not have a place in this world, and your insurance is telling you that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Sam Chavarría said her doctor was clear about the birth defects her medication could cause if she became pregnant but agreed to keep her on it as long as she had an IUD.
As she was waiting to get her contraceptive intrauterine device replaced at her local clinic, however, the billing nurse told her that her insurance wouldn’t cover the removal – or a new IUD. Chavarría didn’t understand why not.
“Then she said very delicately, ‘Well, people on this insurance typically tend to be older,’ ” Chavarría recalled.
Although Chavarría is 34, she is enrolled in Medicare, the government insurance program designed for those 65 and older. Chavarría, who lives in Houston, is disabled by fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and mental health issues. Medicare automatically enrolls anyone who has received Social Security disability benefits for two years and this was her first time getting an IUD while in the government program.
Without insurance, just removing her expired IUD would cost Chavarría $350 out of pocket; exchanging it for a new one would be $2,000. She left the clinic in tears.
Chavarría’s experience is not rare. Medicare was originally intended for people of retirement age. Over the years, the program has evolved to include new populations, such as those who have disabilities or are critically ill, said Jennifer Lea Huer, a public health expert at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In 2020, 1.7 million people ages 18-44 were enrolled in Medicare.
An estimated 70% of childbearing-age women on Medicare are also eligible for Medicaid, a state and federal program for those with low incomes, which should fill the gap for contraception. It’s not clear how many transgender or nonbinary people – who also might need contraception – are on Medicare or are eligible for Medicaid.
Medicaid, like the plans offered via the federal Affordable Care Act, mandates coverage of birth control. But those who aren’t eligible for Medicaid are left in the lurch – Medicare’s origins mean it does not require access to birth control.
Traditional Medicare includes two parts: Part A covers hospital costs, while Part B covers physicians’ care and certain other services, such as ambulance rides. Neither ordinarily includes contraception.
People can get contraception through a Medicare Advantage plan or Part D of Medicare, which covers prescription drugs, but those come at a cost. And even people who pay for Part D often aren’t covered for some types of birth control, such as IUDs.
“So, if you are disabled, if you are locked outside of the labor market, if you do not have the means or any other way to financially support yourself, you were likely still on traditional Medicare, which is Part A and Part B,” Huer said. “In which case, your access to contraception is incredibly difficult.”
Contraception for those with traditional Medicare is given on a case-by-case basis, Huer said. It can be covered only if a doctor can make a credible case that the patient needs it for medical reasons – because their body cannot sustain a pregnancy – as opposed to merely wanting to avoid one.
“You have to have a champion physician who’s willing to partner with you and make those arguments,” Huer said.
That’s what Chavarría’s doctor tried to do. Before she left the clinic, staffers there told her they would try to make the case she needed the IUD for medical reasons. The IUD exchange was scheduled almost 10 weeks later, but during those weeks, she got pregnant. Her body couldn’t sustain a pregnancy, so she and her partner rushed to get an abortion just before Texas tightened its rules Sept. 1, 2021.
“If Medicare had just covered the IUD removal or exchange to begin with, none of this would have happened,” Chavarría said. “It would have saved me having to make a really tough decision that I never thought I’d have to make.”
Women with disabilities often face a stigma from health care practitioners, especially when it comes to birth control, said Willi Horner-Johnson, a public health researcher specializing in disabilities at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. In her research, women with disabilities have described being treated like children or having to go to multiple doctors to find someone with whom they felt comfortable.
“We don’t want to acknowledge that disabled people have sex,” said Miriam Garber, a 36-year-old sex worker who lives in Rhode Island and is also on Medicare because of her disabilities. Garber got an IUD from Planned Parenthood because her insurance wouldn’t cover it.
Even those who pay for Part D to have their prescription drugs covered and have a “champion physician” face difficulties. Liz Moore, a nonbinary person in their 30s who lives in the Washington, D.C., area, could not get Medicare to pay for the Mirena IUD their doctor prescribed for their polycystic ovary syndrome. Moore is disabled with fibromyalgia and dysautonomia, a condition of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates breathing, heart rate, and more.
“After literally months of phone calls, it seemed like my Medicare Part D and original Medicare could not agree on who should pay for my IUD,” they wrote in a direct message. “Was it a prescription or durable medical equipment?”
When Moore finally learned it would cost $800 upfront, they said, they decided to get a hysterectomy – which Medicare would pay for – instead.
Chavarría’s doctor told her a tubal ligation also was more likely to be approved by Medicare than an IUD, because older people have that procedure more often. Like all surgeries, both come with risks of complications and recovery.
Even for those on both Medicare and Medicaid, getting contraception also isn’t always easy, as in Katie Elizabeth Walsh’s case.
Walsh, 34, who lives in northeastern Connecticut, is disabled by a traumatic brain injury, depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome. She got an IUD at an ob.gyn. clinic and was told there her insurance would cover it.
Then she got a bill for nearly $2,000.
Medicaid should cover contraceptive devices for dual-eligibility people, according to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy guidance, but when Walsh tried to get her bill covered, Medicare and Medicaid could not agree on which of them should pay.
“Every single time I have called one of the insurance offices, they are like, ‘Oh, no, you have to talk to the other one, and we don’t really talk to each other,’ ” Walsh said.
Walsh said the hassle to get her contraception covered feels like a kick in the stomach: “Like truly you do not have a place in this world, and your insurance is telling you that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Sam Chavarría said her doctor was clear about the birth defects her medication could cause if she became pregnant but agreed to keep her on it as long as she had an IUD.
As she was waiting to get her contraceptive intrauterine device replaced at her local clinic, however, the billing nurse told her that her insurance wouldn’t cover the removal – or a new IUD. Chavarría didn’t understand why not.
“Then she said very delicately, ‘Well, people on this insurance typically tend to be older,’ ” Chavarría recalled.
Although Chavarría is 34, she is enrolled in Medicare, the government insurance program designed for those 65 and older. Chavarría, who lives in Houston, is disabled by fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and mental health issues. Medicare automatically enrolls anyone who has received Social Security disability benefits for two years and this was her first time getting an IUD while in the government program.
Without insurance, just removing her expired IUD would cost Chavarría $350 out of pocket; exchanging it for a new one would be $2,000. She left the clinic in tears.
Chavarría’s experience is not rare. Medicare was originally intended for people of retirement age. Over the years, the program has evolved to include new populations, such as those who have disabilities or are critically ill, said Jennifer Lea Huer, a public health expert at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In 2020, 1.7 million people ages 18-44 were enrolled in Medicare.
An estimated 70% of childbearing-age women on Medicare are also eligible for Medicaid, a state and federal program for those with low incomes, which should fill the gap for contraception. It’s not clear how many transgender or nonbinary people – who also might need contraception – are on Medicare or are eligible for Medicaid.
Medicaid, like the plans offered via the federal Affordable Care Act, mandates coverage of birth control. But those who aren’t eligible for Medicaid are left in the lurch – Medicare’s origins mean it does not require access to birth control.
Traditional Medicare includes two parts: Part A covers hospital costs, while Part B covers physicians’ care and certain other services, such as ambulance rides. Neither ordinarily includes contraception.
People can get contraception through a Medicare Advantage plan or Part D of Medicare, which covers prescription drugs, but those come at a cost. And even people who pay for Part D often aren’t covered for some types of birth control, such as IUDs.
“So, if you are disabled, if you are locked outside of the labor market, if you do not have the means or any other way to financially support yourself, you were likely still on traditional Medicare, which is Part A and Part B,” Huer said. “In which case, your access to contraception is incredibly difficult.”
Contraception for those with traditional Medicare is given on a case-by-case basis, Huer said. It can be covered only if a doctor can make a credible case that the patient needs it for medical reasons – because their body cannot sustain a pregnancy – as opposed to merely wanting to avoid one.
“You have to have a champion physician who’s willing to partner with you and make those arguments,” Huer said.
That’s what Chavarría’s doctor tried to do. Before she left the clinic, staffers there told her they would try to make the case she needed the IUD for medical reasons. The IUD exchange was scheduled almost 10 weeks later, but during those weeks, she got pregnant. Her body couldn’t sustain a pregnancy, so she and her partner rushed to get an abortion just before Texas tightened its rules Sept. 1, 2021.
“If Medicare had just covered the IUD removal or exchange to begin with, none of this would have happened,” Chavarría said. “It would have saved me having to make a really tough decision that I never thought I’d have to make.”
Women with disabilities often face a stigma from health care practitioners, especially when it comes to birth control, said Willi Horner-Johnson, a public health researcher specializing in disabilities at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. In her research, women with disabilities have described being treated like children or having to go to multiple doctors to find someone with whom they felt comfortable.
“We don’t want to acknowledge that disabled people have sex,” said Miriam Garber, a 36-year-old sex worker who lives in Rhode Island and is also on Medicare because of her disabilities. Garber got an IUD from Planned Parenthood because her insurance wouldn’t cover it.
Even those who pay for Part D to have their prescription drugs covered and have a “champion physician” face difficulties. Liz Moore, a nonbinary person in their 30s who lives in the Washington, D.C., area, could not get Medicare to pay for the Mirena IUD their doctor prescribed for their polycystic ovary syndrome. Moore is disabled with fibromyalgia and dysautonomia, a condition of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates breathing, heart rate, and more.
“After literally months of phone calls, it seemed like my Medicare Part D and original Medicare could not agree on who should pay for my IUD,” they wrote in a direct message. “Was it a prescription or durable medical equipment?”
When Moore finally learned it would cost $800 upfront, they said, they decided to get a hysterectomy – which Medicare would pay for – instead.
Chavarría’s doctor told her a tubal ligation also was more likely to be approved by Medicare than an IUD, because older people have that procedure more often. Like all surgeries, both come with risks of complications and recovery.
Even for those on both Medicare and Medicaid, getting contraception also isn’t always easy, as in Katie Elizabeth Walsh’s case.
Walsh, 34, who lives in northeastern Connecticut, is disabled by a traumatic brain injury, depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome. She got an IUD at an ob.gyn. clinic and was told there her insurance would cover it.
Then she got a bill for nearly $2,000.
Medicaid should cover contraceptive devices for dual-eligibility people, according to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy guidance, but when Walsh tried to get her bill covered, Medicare and Medicaid could not agree on which of them should pay.
“Every single time I have called one of the insurance offices, they are like, ‘Oh, no, you have to talk to the other one, and we don’t really talk to each other,’ ” Walsh said.
Walsh said the hassle to get her contraception covered feels like a kick in the stomach: “Like truly you do not have a place in this world, and your insurance is telling you that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty
When the Food and Drug Administration first approved the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, Calif.) for adult use in 2000, it altered the face of minimally invasive surgery across a multitude of specialties. Improved three-dimensional visualization and enhanced instrument articulation facilitates complex dissections and intracorporeal suturing. While the standard of care for gender-affirming vaginoplasty remains the single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty, robotic procedures are quickly emerging as alternative options for both primary and revisional surgeries.
The single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty requires an adequate amount of penoscrotal tissue not only to line a neovaginal canal that measures 12-15 cm, but also to create external vulvar structures. While this is often sufficient in most candidates, there is an increasing number of patients who are receiving puberty blockers, resulting in penoscrotal hypoplasia.
Alternatively, there are patients who experience loss of vaginal depth and vaginal stenosis who seek revisional surgeries. Additional donor sites for skin grafting are available and include the lower abdomen and thighs, although patients may not want these donor site scars. With these donor sites, there is also concern about graft contracture, which could lead to recurrent vaginal stenosis.1 Robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty and robotic enteric vaginoplasty can serve as additional options for patients seeking revisional surgery or who have insufficient genital skin. One benefit of using peritoneal flaps is that they are hairless and are well vascularized with minimal donor site morbidity.1 Currently, there are two predominant techniques that utilize peritoneal flaps: the modified Davydov procedure and the tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap.
The modified Davydov technique, which originated in the treatment of congenital vaginal agenesis in cisgender women, involves the creation of anterior and posterior peritoneal flaps. This type of peritoneal vaginoplasty is more commonly utilized for primary cases.
Ideally, there is a robotic surgeon (typically a urologist) working in tandem with the perineal surgeon. The robotic surgeon makes a horizontal incision along the peritoneal ridge at the rectovesical junction and continues the dissection within Denonvilliers fascia, between the prostate and rectum, to the pelvic floor. This dissection is like that performed in a robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy.
Simultaneously, the perineal surgeon will break through the pelvic floor with assistance of the robotic view. Peritoneal flaps are raised from the anterior rectum and posterior bladder.2,3 In primary cases, the penoscrotal flap is introduced into the abdomen from the perineum and sutured to the anterior and posterior peritoneum to create a circumferential canal. At the apex of the neovagina, these anterior and posterior flaps are then sutured together.2,3
The tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap technique is predominantly used for revision cases in patients who experienced neovaginal shortening and desire increased neovaginal depth. As peritoneal reach is limited, candidates for this procedure must have both adequate width and neovaginal canal depth.4 Once intra-abdominal access is achieved, an anterior peritoneal flap is mobilized to the level of the bladder and rotated 180 degrees inferiorly.4 The superior aspect of the flap is flipped is mobilized and is sutured to the peritoneum at the apex of the neovaginal canal.
The main benefit of these procedures, compared with traditional techniques, is increased neovaginal depth. The average vaginal length in patients undergoing peritoneal vaginoplasties is 14.2 cm, compared with 11.6 cm achieved in those using skin grafts.1,3 However, many surgeons report achieving 14-15 cm of depth with the traditional vaginoplasty. There are insufficient short- and long-term data for the peritoneal technique to recommend this as a first-line procedure.
Complications for peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures are similar to those of single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty cases but with additional operative risks associated with laparoscopic/robotic surgery. These risks include injury to viscera and major vessels during initial intra-abdominal access, intra-abdominal adhesions, port site hernias, need to convert to an open procedure, and equipment malfunction.2 Additional postoperative risks include pelvic abscess formation, dehiscence of the peritoneal-vaginal incision, and peritoneal perforation during dilation.2,3 Surgeons and institutions must also weigh the cost of using the robot versus the cost of additional revisional surgical procedures. While initial studies evaluating robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures have yielded promising preliminary results, additional studies are warranted.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Salibian AA et al. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;147(4):634e-43e.
2. Dy GW et al. In: Nikolavsky D and Blakely SA, eds. Urological care for the transgender patient: A comprehensive guide. Switzerland: Springer, 2021:237-48.
3. Jacoby A et al. J Urol. 2019;201(6):1171-5.
4. Smith SM et al. J Sex Med. 2022;10(6):100572.
When the Food and Drug Administration first approved the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, Calif.) for adult use in 2000, it altered the face of minimally invasive surgery across a multitude of specialties. Improved three-dimensional visualization and enhanced instrument articulation facilitates complex dissections and intracorporeal suturing. While the standard of care for gender-affirming vaginoplasty remains the single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty, robotic procedures are quickly emerging as alternative options for both primary and revisional surgeries.
The single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty requires an adequate amount of penoscrotal tissue not only to line a neovaginal canal that measures 12-15 cm, but also to create external vulvar structures. While this is often sufficient in most candidates, there is an increasing number of patients who are receiving puberty blockers, resulting in penoscrotal hypoplasia.
Alternatively, there are patients who experience loss of vaginal depth and vaginal stenosis who seek revisional surgeries. Additional donor sites for skin grafting are available and include the lower abdomen and thighs, although patients may not want these donor site scars. With these donor sites, there is also concern about graft contracture, which could lead to recurrent vaginal stenosis.1 Robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty and robotic enteric vaginoplasty can serve as additional options for patients seeking revisional surgery or who have insufficient genital skin. One benefit of using peritoneal flaps is that they are hairless and are well vascularized with minimal donor site morbidity.1 Currently, there are two predominant techniques that utilize peritoneal flaps: the modified Davydov procedure and the tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap.
The modified Davydov technique, which originated in the treatment of congenital vaginal agenesis in cisgender women, involves the creation of anterior and posterior peritoneal flaps. This type of peritoneal vaginoplasty is more commonly utilized for primary cases.
Ideally, there is a robotic surgeon (typically a urologist) working in tandem with the perineal surgeon. The robotic surgeon makes a horizontal incision along the peritoneal ridge at the rectovesical junction and continues the dissection within Denonvilliers fascia, between the prostate and rectum, to the pelvic floor. This dissection is like that performed in a robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy.
Simultaneously, the perineal surgeon will break through the pelvic floor with assistance of the robotic view. Peritoneal flaps are raised from the anterior rectum and posterior bladder.2,3 In primary cases, the penoscrotal flap is introduced into the abdomen from the perineum and sutured to the anterior and posterior peritoneum to create a circumferential canal. At the apex of the neovagina, these anterior and posterior flaps are then sutured together.2,3
The tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap technique is predominantly used for revision cases in patients who experienced neovaginal shortening and desire increased neovaginal depth. As peritoneal reach is limited, candidates for this procedure must have both adequate width and neovaginal canal depth.4 Once intra-abdominal access is achieved, an anterior peritoneal flap is mobilized to the level of the bladder and rotated 180 degrees inferiorly.4 The superior aspect of the flap is flipped is mobilized and is sutured to the peritoneum at the apex of the neovaginal canal.
The main benefit of these procedures, compared with traditional techniques, is increased neovaginal depth. The average vaginal length in patients undergoing peritoneal vaginoplasties is 14.2 cm, compared with 11.6 cm achieved in those using skin grafts.1,3 However, many surgeons report achieving 14-15 cm of depth with the traditional vaginoplasty. There are insufficient short- and long-term data for the peritoneal technique to recommend this as a first-line procedure.
Complications for peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures are similar to those of single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty cases but with additional operative risks associated with laparoscopic/robotic surgery. These risks include injury to viscera and major vessels during initial intra-abdominal access, intra-abdominal adhesions, port site hernias, need to convert to an open procedure, and equipment malfunction.2 Additional postoperative risks include pelvic abscess formation, dehiscence of the peritoneal-vaginal incision, and peritoneal perforation during dilation.2,3 Surgeons and institutions must also weigh the cost of using the robot versus the cost of additional revisional surgical procedures. While initial studies evaluating robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures have yielded promising preliminary results, additional studies are warranted.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Salibian AA et al. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;147(4):634e-43e.
2. Dy GW et al. In: Nikolavsky D and Blakely SA, eds. Urological care for the transgender patient: A comprehensive guide. Switzerland: Springer, 2021:237-48.
3. Jacoby A et al. J Urol. 2019;201(6):1171-5.
4. Smith SM et al. J Sex Med. 2022;10(6):100572.
When the Food and Drug Administration first approved the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, Calif.) for adult use in 2000, it altered the face of minimally invasive surgery across a multitude of specialties. Improved three-dimensional visualization and enhanced instrument articulation facilitates complex dissections and intracorporeal suturing. While the standard of care for gender-affirming vaginoplasty remains the single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty, robotic procedures are quickly emerging as alternative options for both primary and revisional surgeries.
The single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty requires an adequate amount of penoscrotal tissue not only to line a neovaginal canal that measures 12-15 cm, but also to create external vulvar structures. While this is often sufficient in most candidates, there is an increasing number of patients who are receiving puberty blockers, resulting in penoscrotal hypoplasia.
Alternatively, there are patients who experience loss of vaginal depth and vaginal stenosis who seek revisional surgeries. Additional donor sites for skin grafting are available and include the lower abdomen and thighs, although patients may not want these donor site scars. With these donor sites, there is also concern about graft contracture, which could lead to recurrent vaginal stenosis.1 Robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty and robotic enteric vaginoplasty can serve as additional options for patients seeking revisional surgery or who have insufficient genital skin. One benefit of using peritoneal flaps is that they are hairless and are well vascularized with minimal donor site morbidity.1 Currently, there are two predominant techniques that utilize peritoneal flaps: the modified Davydov procedure and the tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap.
The modified Davydov technique, which originated in the treatment of congenital vaginal agenesis in cisgender women, involves the creation of anterior and posterior peritoneal flaps. This type of peritoneal vaginoplasty is more commonly utilized for primary cases.
Ideally, there is a robotic surgeon (typically a urologist) working in tandem with the perineal surgeon. The robotic surgeon makes a horizontal incision along the peritoneal ridge at the rectovesical junction and continues the dissection within Denonvilliers fascia, between the prostate and rectum, to the pelvic floor. This dissection is like that performed in a robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy.
Simultaneously, the perineal surgeon will break through the pelvic floor with assistance of the robotic view. Peritoneal flaps are raised from the anterior rectum and posterior bladder.2,3 In primary cases, the penoscrotal flap is introduced into the abdomen from the perineum and sutured to the anterior and posterior peritoneum to create a circumferential canal. At the apex of the neovagina, these anterior and posterior flaps are then sutured together.2,3
The tubularized urachus-peritoneal hinge flap technique is predominantly used for revision cases in patients who experienced neovaginal shortening and desire increased neovaginal depth. As peritoneal reach is limited, candidates for this procedure must have both adequate width and neovaginal canal depth.4 Once intra-abdominal access is achieved, an anterior peritoneal flap is mobilized to the level of the bladder and rotated 180 degrees inferiorly.4 The superior aspect of the flap is flipped is mobilized and is sutured to the peritoneum at the apex of the neovaginal canal.
The main benefit of these procedures, compared with traditional techniques, is increased neovaginal depth. The average vaginal length in patients undergoing peritoneal vaginoplasties is 14.2 cm, compared with 11.6 cm achieved in those using skin grafts.1,3 However, many surgeons report achieving 14-15 cm of depth with the traditional vaginoplasty. There are insufficient short- and long-term data for the peritoneal technique to recommend this as a first-line procedure.
Complications for peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures are similar to those of single-stage penile inversion vaginoplasty cases but with additional operative risks associated with laparoscopic/robotic surgery. These risks include injury to viscera and major vessels during initial intra-abdominal access, intra-abdominal adhesions, port site hernias, need to convert to an open procedure, and equipment malfunction.2 Additional postoperative risks include pelvic abscess formation, dehiscence of the peritoneal-vaginal incision, and peritoneal perforation during dilation.2,3 Surgeons and institutions must also weigh the cost of using the robot versus the cost of additional revisional surgical procedures. While initial studies evaluating robotic peritoneal vaginoplasty procedures have yielded promising preliminary results, additional studies are warranted.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Salibian AA et al. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;147(4):634e-43e.
2. Dy GW et al. In: Nikolavsky D and Blakely SA, eds. Urological care for the transgender patient: A comprehensive guide. Switzerland: Springer, 2021:237-48.
3. Jacoby A et al. J Urol. 2019;201(6):1171-5.
4. Smith SM et al. J Sex Med. 2022;10(6):100572.
Prepare for endometriosis excision surgery with a multidisciplinary approach
Introduction: The preoperative evaluation for endometriosis – more than meets the eye
It is well known that it often takes 6-10 years for endometriosis to be diagnosed in patients who have the disease, depending on where the patient lives. I certainly am not surprised. During my residency at Parkland Memorial Hospital, if a patient had chronic pelvic pain and no fibroids, her diagnosis was usually pelvic inflammatory disease. Later, during my fellowship in reproductive endocrinology at the University of Pennsylvania, the diagnosis became endometriosis.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo – How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller, MD, FACOG, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. He has no conflicts of interest to report.
Patients with endometriosis and the all-too-often decade-long diagnostic delay have a variety of coexisting conditions that are pain generators – from painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor dysfunction to a small intestine bacterial system that is significantly upregulated and sensitized.
For optimal surgical outcomes, and to help our patients recover from years of this inflammatory, systemic disease, we must treat our patients holistically and work to downregulate their pain as much as possible before excision surgery. I work with patients a few months prior to surgery, often for 4-5 months, during which time they not only see me for informative follow-ups, but also pelvic floor physical therapists, gastroenterologists, mental health professionals, integrative nutritionists, and physiatrists or pain specialists, depending on their needs.1
By identifying coexisting conditions in an initial consult and employing a presurgical multidisciplinary approach to downregulate the pain generators, my patients recover well from excision surgery, with greater and faster relief from pain, compared with those using standard approaches, and with little to no use of opioids.
At a minimum, given the unfortunate time constraints and productivity demands of working within health systems – and considering that surgeries are often scheduled a couple of months out – the surgeon could ensure that patients are engaged in at least 6-8 weeks of pelvic floor physical therapy before surgery to sufficiently lengthen the pelvic muscles and loosen surrounding fascia.
Short, tight pelvic floor muscles are almost universal in patients with delayed diagnosis of endometriosis and are significant generators of pain.
Appreciating sequelae of diagnostic delay
After my fellowship in advanced laparoscopic and pelvic surgery with Harry Reich, MD, and C. Y. Liu, MD, pioneers of endometriosis excision surgery, and as I did my residency in the early 2000s, I noticed puzzlement in the literature about why some patients still had lasting pain after thorough excision.
I didn’t doubt the efficacy of excision. It is the cornerstone of treatment, and at least one randomized double-blind trial2 and a systematic review and meta-analysis3 have demonstrated its superior efficacy over ablation in symptom reduction. What I did doubt was any presumption that surgery alone was enough. I knew there was more to healing when a disease process wreaks havoc on the body for more than a decade and that there were other generators of pain in addition to the endometriosis implants themselves.
As I began to focus on endometriosis in my own surgical practice, I strove to detect and treat endometriosis in teens. But in those patients with longstanding disease, I recognized patterns and began to more fully appreciate the systemic sequelae of endometriosis.
To cope with dysmenorrhea, patients curl up and assume a fetal position, tensing the abdominal muscles, inner thigh muscles, and pelvic floor muscles. Over time, these muscles come to maintain a short, tight, and painful state. (Hence the need for physical therapy to undo this decade-long pattern.)
Endometriosis implants on or near the gastrointestinal tract tug on fascia and muscles and commonly cause constipation, leading women to further overwork the pelvic floor muscles. In the case of diarrhea-predominant dysfunction, our patients squeeze pelvic floor muscles to prevent leakage. And in the case of urinary urgency, they squeeze muscles to release urine that isn’t really there.
As the chronic inflammation of the disease grows, and as pain worsens, the patient is increasingly in sympathetic overdrive (also known as ”fight or flight”), as opposed to a parasympathetic state (also known as “rest and digest”). The bowel’s motility slows, allowing the bacteria of the small intestine to grow beyond what is normal, leading to SIBO, a condition increasingly recognized by gastroenterologists and others that can impede nutrient absorption and cause bloat and pain and exacerbate constipation and diarrhea.
Key to my conceptualization of pain was a review published in 2011 by Pam Stratton, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, and Karen J. Berkley, PhD, then of Florida State University, on chronic pain and endometriosis.4 They detailed how endometriotic lesions can develop their own nerve supply that interacts directly and in a two-way fashion with the CNS – and how the lesions can engage the nervous system in ways that create comorbid conditions and pain that becomes “independent of the disease itself.”
Sensitized peripheral nerve fibers innervating a deeply infiltrating lesion on the left uterosacral ligament, for instance, can sensitize neurons in the spinal sacral segment. Branches of these nerve fibers can extend to other segments of the spinal cord, and, once sensitized themselves, turn on neurons in these other segments. There is a resultant remodeling of the central nervous system, in essence, and what is called “remote central sensitization.” The CNS becomes independent from peripheral neural processes.
I now explain to both patients and physicians that those who have had endometriosis for years have had an enduring “hand on the stove,” with a persistent signal to the CNS. Tight muscles are a hand on the stove, painful bladder syndrome is another hand on the stove, and SIBO is yet another. So are anxiety and depression.
The CNS becomes so upregulated and overloaded that messages branch out through the spinal cord to other available pathways and to other organs, muscles, and nerves. The CNS also starts firing on its own – and once it becomes its own pain generator, taking one hand off the stove (for instance, excising implants) while leaving multiple other hands on the hot stove won’t remove all pain. We must downregulate the CNS more broadly.
As I began addressing pain generators and instigators of CNS sensitization – and waiting for excision surgery until the CNS had sufficiently cooled – I saw that my patients had a better chance of more significant and lasting pain relief.
Pearls for a multimodal approach
My initial physical exam includes an assessment of the pelvic floor for overly tight musculature. An abdominal exam will usually reveal whether there is asymmetry of the abdominal wall muscles, which typically informs me of the likelihood of tightness and pulling on either side of the pelvic anatomy. On the internal exam, then, the pelvic floor muscles can be palpated and assessed. These findings will guide my referrals and my discussions with patients about the value of pelvic floor physical therapy. The cervix should be in the midline of the vagina – equidistant from the left and right vaginal fornices. If the cervix is pulled away from this midline, and a palpation of a thickened uterosacral ligament reproduces pain, endometriosis is 90% likely.
Patients who report significant “burning” pain that’s suggestive of neuropathic pain should be referred to a physical medicine rehabilitation physician or a pain specialist who can help downregulate their CNS. And patients who have symptoms of depression, anxiety disorders (including obsessive-compulsive disorder), or posttraumatic stress disorder should be referred to pain therapists, psychologists, or other mental health professionals, preferably well before surgery. I will also often discuss mindfulness practices and give my patients “meditation challenges” to achieve during the presurgical phase.
Additional points of emphasis about a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach include:
Advanced pelvic floor therapy: Therapists with specialized training in pelvic health and manual therapy utilize a range of techniques and modalities to release tension in affected muscles, fascia, nerves, and bone, and in doing so, they help to downregulate the CNS. Myofascial release, myofascial trigger point release, neural mobilization, and visceral mobilization are among these techniques. In addition to using manual therapy, many of these therapists may also employ neuromuscular reeducation and other techniques that will be helpful for the longer term.
It is important to identify physical therapists who have training in this approach; women with endometriosis often have a history of treatment by physical therapists whose focus is on incontinence and muscle strengthening (that is, Kegel exercises), which is the opposite of what endometriosis patients need.
Treating SIBO: Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO often overlap with symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – namely constipation, diarrhea (or both), and bloating. Indeed, many patients with undiagnosed endometriosis have been diagnosed with IBS. I send every patient who has one of these symptoms for SIBO breath testing, which utilizes carbohydrate substrates (glucose or lactulose) and measures hydrogen and/or methane in the breath.
SIBO is typically treated with rifampin, which stays in the small bowel and will not negatively affect beneficial bacteria, with or without neomycin. Gastroenterologists with more integrative practices also consider the use of herbals in addition to – or instead of – antibiotics. It can sometimes take months or a couple of years to correct SIBO, depending on how long the patient has been affected, but with presurgical diagnosis and a start on treatment, we can remove or at least tone down another instigator of CNS sensitization.
I estimate that 80% of my patients have tested positive for SIBO. Notably, in a testament to the systemic nature of endometriosis, a study published in 2009 of 355 women undergoing operative laparoscopy for suspected endometriosis found that 90% had gastrointestinal symptoms, but only 7.6% of the vast majority whose endometriosis was confirmed were found to have endometrial implants on the bowel itself.5
Addressing bladder issues: I routinely administer the PUF (Pain, Urgency, Frequency) questionnaire as part of my intake package and follow it up with conversation. For just about every patient with painful bladder syndrome, pelvic floor physical therapy in combination with a low-acid, low-potassium diet will work effectively together to reduce symptoms and pain. The IC Network offers a helpful food list, and patients can be counseled to choose foods that are also anti-inflammatory. When referrals to a urologist for bladder instillations are possible, these can be helpful as well.
Our communication with patients
Our patients need to have their symptoms and pain validated and to understand why we’re recommending these measures before surgery. Some education is necessary. Few patients will go to an integrative nutritionist, for example, if we just write a referral without explaining how years of inflammation and disruption in the gut can affect the whole body – including mental health – and that it can be corrected over time.
Also necessary is an appreciation of the fact that patients with delayed diagnoses have lived with gastrointestinal and other symptoms and patterns for so long – and often have mothers whose endometriosis caused similar symptoms – that some of their own experiences can seem almost “normal.” A patient whose mother had bowel movements every 7 days may think that 4-5 day intervals are acceptable, for instance. This means we have to carefully consider how we ask our questions.
I always ask my patients as we’re going into surgery, what percentage better are you? I’ve long aimed for at least 30% improvement, but most of the time, with pelvic floor therapy and as many other pain-generator–focused measures as possible, we’re getting them 70% better.
Excision surgery will remove the inflammation that has helped fuel the SIBO and other coconditions. Then, everything done to prepare the body must continue for some time. Certain practices, such as eating an anti-inflammatory diet, should be lifelong.
One day, it is hoped, a pediatrician or other physician will suspect endometriosis early on. The patient will see the surgeon within several months of the onset of pain, and we won’t need to unravel layers of pain generation and CNS upregulation before operating. But until this happens and we shorten the diagnostic delay, we must consider the benefits of presurgical preparation.
References
1. Orbuch I, Stein A. Beating Endo: How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis. (New York: HarperCollins, 2019).
2. Healey M et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2014;21(6):999-1004.
3. Pundir J et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(5):747-56.
4. Stratton P, Berkley KJ. Hum Repro Update. 2011;17(3):327-46.
5. Maroun P et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;49(4):411-4.
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in endometriosis. She has no conflicts of interest to report.
Introduction: The preoperative evaluation for endometriosis – more than meets the eye
It is well known that it often takes 6-10 years for endometriosis to be diagnosed in patients who have the disease, depending on where the patient lives. I certainly am not surprised. During my residency at Parkland Memorial Hospital, if a patient had chronic pelvic pain and no fibroids, her diagnosis was usually pelvic inflammatory disease. Later, during my fellowship in reproductive endocrinology at the University of Pennsylvania, the diagnosis became endometriosis.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo – How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller, MD, FACOG, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. He has no conflicts of interest to report.
Patients with endometriosis and the all-too-often decade-long diagnostic delay have a variety of coexisting conditions that are pain generators – from painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor dysfunction to a small intestine bacterial system that is significantly upregulated and sensitized.
For optimal surgical outcomes, and to help our patients recover from years of this inflammatory, systemic disease, we must treat our patients holistically and work to downregulate their pain as much as possible before excision surgery. I work with patients a few months prior to surgery, often for 4-5 months, during which time they not only see me for informative follow-ups, but also pelvic floor physical therapists, gastroenterologists, mental health professionals, integrative nutritionists, and physiatrists or pain specialists, depending on their needs.1
By identifying coexisting conditions in an initial consult and employing a presurgical multidisciplinary approach to downregulate the pain generators, my patients recover well from excision surgery, with greater and faster relief from pain, compared with those using standard approaches, and with little to no use of opioids.
At a minimum, given the unfortunate time constraints and productivity demands of working within health systems – and considering that surgeries are often scheduled a couple of months out – the surgeon could ensure that patients are engaged in at least 6-8 weeks of pelvic floor physical therapy before surgery to sufficiently lengthen the pelvic muscles and loosen surrounding fascia.
Short, tight pelvic floor muscles are almost universal in patients with delayed diagnosis of endometriosis and are significant generators of pain.
Appreciating sequelae of diagnostic delay
After my fellowship in advanced laparoscopic and pelvic surgery with Harry Reich, MD, and C. Y. Liu, MD, pioneers of endometriosis excision surgery, and as I did my residency in the early 2000s, I noticed puzzlement in the literature about why some patients still had lasting pain after thorough excision.
I didn’t doubt the efficacy of excision. It is the cornerstone of treatment, and at least one randomized double-blind trial2 and a systematic review and meta-analysis3 have demonstrated its superior efficacy over ablation in symptom reduction. What I did doubt was any presumption that surgery alone was enough. I knew there was more to healing when a disease process wreaks havoc on the body for more than a decade and that there were other generators of pain in addition to the endometriosis implants themselves.
As I began to focus on endometriosis in my own surgical practice, I strove to detect and treat endometriosis in teens. But in those patients with longstanding disease, I recognized patterns and began to more fully appreciate the systemic sequelae of endometriosis.
To cope with dysmenorrhea, patients curl up and assume a fetal position, tensing the abdominal muscles, inner thigh muscles, and pelvic floor muscles. Over time, these muscles come to maintain a short, tight, and painful state. (Hence the need for physical therapy to undo this decade-long pattern.)
Endometriosis implants on or near the gastrointestinal tract tug on fascia and muscles and commonly cause constipation, leading women to further overwork the pelvic floor muscles. In the case of diarrhea-predominant dysfunction, our patients squeeze pelvic floor muscles to prevent leakage. And in the case of urinary urgency, they squeeze muscles to release urine that isn’t really there.
As the chronic inflammation of the disease grows, and as pain worsens, the patient is increasingly in sympathetic overdrive (also known as ”fight or flight”), as opposed to a parasympathetic state (also known as “rest and digest”). The bowel’s motility slows, allowing the bacteria of the small intestine to grow beyond what is normal, leading to SIBO, a condition increasingly recognized by gastroenterologists and others that can impede nutrient absorption and cause bloat and pain and exacerbate constipation and diarrhea.
Key to my conceptualization of pain was a review published in 2011 by Pam Stratton, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, and Karen J. Berkley, PhD, then of Florida State University, on chronic pain and endometriosis.4 They detailed how endometriotic lesions can develop their own nerve supply that interacts directly and in a two-way fashion with the CNS – and how the lesions can engage the nervous system in ways that create comorbid conditions and pain that becomes “independent of the disease itself.”
Sensitized peripheral nerve fibers innervating a deeply infiltrating lesion on the left uterosacral ligament, for instance, can sensitize neurons in the spinal sacral segment. Branches of these nerve fibers can extend to other segments of the spinal cord, and, once sensitized themselves, turn on neurons in these other segments. There is a resultant remodeling of the central nervous system, in essence, and what is called “remote central sensitization.” The CNS becomes independent from peripheral neural processes.
I now explain to both patients and physicians that those who have had endometriosis for years have had an enduring “hand on the stove,” with a persistent signal to the CNS. Tight muscles are a hand on the stove, painful bladder syndrome is another hand on the stove, and SIBO is yet another. So are anxiety and depression.
The CNS becomes so upregulated and overloaded that messages branch out through the spinal cord to other available pathways and to other organs, muscles, and nerves. The CNS also starts firing on its own – and once it becomes its own pain generator, taking one hand off the stove (for instance, excising implants) while leaving multiple other hands on the hot stove won’t remove all pain. We must downregulate the CNS more broadly.
As I began addressing pain generators and instigators of CNS sensitization – and waiting for excision surgery until the CNS had sufficiently cooled – I saw that my patients had a better chance of more significant and lasting pain relief.
Pearls for a multimodal approach
My initial physical exam includes an assessment of the pelvic floor for overly tight musculature. An abdominal exam will usually reveal whether there is asymmetry of the abdominal wall muscles, which typically informs me of the likelihood of tightness and pulling on either side of the pelvic anatomy. On the internal exam, then, the pelvic floor muscles can be palpated and assessed. These findings will guide my referrals and my discussions with patients about the value of pelvic floor physical therapy. The cervix should be in the midline of the vagina – equidistant from the left and right vaginal fornices. If the cervix is pulled away from this midline, and a palpation of a thickened uterosacral ligament reproduces pain, endometriosis is 90% likely.
Patients who report significant “burning” pain that’s suggestive of neuropathic pain should be referred to a physical medicine rehabilitation physician or a pain specialist who can help downregulate their CNS. And patients who have symptoms of depression, anxiety disorders (including obsessive-compulsive disorder), or posttraumatic stress disorder should be referred to pain therapists, psychologists, or other mental health professionals, preferably well before surgery. I will also often discuss mindfulness practices and give my patients “meditation challenges” to achieve during the presurgical phase.
Additional points of emphasis about a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach include:
Advanced pelvic floor therapy: Therapists with specialized training in pelvic health and manual therapy utilize a range of techniques and modalities to release tension in affected muscles, fascia, nerves, and bone, and in doing so, they help to downregulate the CNS. Myofascial release, myofascial trigger point release, neural mobilization, and visceral mobilization are among these techniques. In addition to using manual therapy, many of these therapists may also employ neuromuscular reeducation and other techniques that will be helpful for the longer term.
It is important to identify physical therapists who have training in this approach; women with endometriosis often have a history of treatment by physical therapists whose focus is on incontinence and muscle strengthening (that is, Kegel exercises), which is the opposite of what endometriosis patients need.
Treating SIBO: Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO often overlap with symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – namely constipation, diarrhea (or both), and bloating. Indeed, many patients with undiagnosed endometriosis have been diagnosed with IBS. I send every patient who has one of these symptoms for SIBO breath testing, which utilizes carbohydrate substrates (glucose or lactulose) and measures hydrogen and/or methane in the breath.
SIBO is typically treated with rifampin, which stays in the small bowel and will not negatively affect beneficial bacteria, with or without neomycin. Gastroenterologists with more integrative practices also consider the use of herbals in addition to – or instead of – antibiotics. It can sometimes take months or a couple of years to correct SIBO, depending on how long the patient has been affected, but with presurgical diagnosis and a start on treatment, we can remove or at least tone down another instigator of CNS sensitization.
I estimate that 80% of my patients have tested positive for SIBO. Notably, in a testament to the systemic nature of endometriosis, a study published in 2009 of 355 women undergoing operative laparoscopy for suspected endometriosis found that 90% had gastrointestinal symptoms, but only 7.6% of the vast majority whose endometriosis was confirmed were found to have endometrial implants on the bowel itself.5
Addressing bladder issues: I routinely administer the PUF (Pain, Urgency, Frequency) questionnaire as part of my intake package and follow it up with conversation. For just about every patient with painful bladder syndrome, pelvic floor physical therapy in combination with a low-acid, low-potassium diet will work effectively together to reduce symptoms and pain. The IC Network offers a helpful food list, and patients can be counseled to choose foods that are also anti-inflammatory. When referrals to a urologist for bladder instillations are possible, these can be helpful as well.
Our communication with patients
Our patients need to have their symptoms and pain validated and to understand why we’re recommending these measures before surgery. Some education is necessary. Few patients will go to an integrative nutritionist, for example, if we just write a referral without explaining how years of inflammation and disruption in the gut can affect the whole body – including mental health – and that it can be corrected over time.
Also necessary is an appreciation of the fact that patients with delayed diagnoses have lived with gastrointestinal and other symptoms and patterns for so long – and often have mothers whose endometriosis caused similar symptoms – that some of their own experiences can seem almost “normal.” A patient whose mother had bowel movements every 7 days may think that 4-5 day intervals are acceptable, for instance. This means we have to carefully consider how we ask our questions.
I always ask my patients as we’re going into surgery, what percentage better are you? I’ve long aimed for at least 30% improvement, but most of the time, with pelvic floor therapy and as many other pain-generator–focused measures as possible, we’re getting them 70% better.
Excision surgery will remove the inflammation that has helped fuel the SIBO and other coconditions. Then, everything done to prepare the body must continue for some time. Certain practices, such as eating an anti-inflammatory diet, should be lifelong.
One day, it is hoped, a pediatrician or other physician will suspect endometriosis early on. The patient will see the surgeon within several months of the onset of pain, and we won’t need to unravel layers of pain generation and CNS upregulation before operating. But until this happens and we shorten the diagnostic delay, we must consider the benefits of presurgical preparation.
References
1. Orbuch I, Stein A. Beating Endo: How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis. (New York: HarperCollins, 2019).
2. Healey M et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2014;21(6):999-1004.
3. Pundir J et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(5):747-56.
4. Stratton P, Berkley KJ. Hum Repro Update. 2011;17(3):327-46.
5. Maroun P et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;49(4):411-4.
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in endometriosis. She has no conflicts of interest to report.
Introduction: The preoperative evaluation for endometriosis – more than meets the eye
It is well known that it often takes 6-10 years for endometriosis to be diagnosed in patients who have the disease, depending on where the patient lives. I certainly am not surprised. During my residency at Parkland Memorial Hospital, if a patient had chronic pelvic pain and no fibroids, her diagnosis was usually pelvic inflammatory disease. Later, during my fellowship in reproductive endocrinology at the University of Pennsylvania, the diagnosis became endometriosis.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo – How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller, MD, FACOG, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. He has no conflicts of interest to report.
Patients with endometriosis and the all-too-often decade-long diagnostic delay have a variety of coexisting conditions that are pain generators – from painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor dysfunction to a small intestine bacterial system that is significantly upregulated and sensitized.
For optimal surgical outcomes, and to help our patients recover from years of this inflammatory, systemic disease, we must treat our patients holistically and work to downregulate their pain as much as possible before excision surgery. I work with patients a few months prior to surgery, often for 4-5 months, during which time they not only see me for informative follow-ups, but also pelvic floor physical therapists, gastroenterologists, mental health professionals, integrative nutritionists, and physiatrists or pain specialists, depending on their needs.1
By identifying coexisting conditions in an initial consult and employing a presurgical multidisciplinary approach to downregulate the pain generators, my patients recover well from excision surgery, with greater and faster relief from pain, compared with those using standard approaches, and with little to no use of opioids.
At a minimum, given the unfortunate time constraints and productivity demands of working within health systems – and considering that surgeries are often scheduled a couple of months out – the surgeon could ensure that patients are engaged in at least 6-8 weeks of pelvic floor physical therapy before surgery to sufficiently lengthen the pelvic muscles and loosen surrounding fascia.
Short, tight pelvic floor muscles are almost universal in patients with delayed diagnosis of endometriosis and are significant generators of pain.
Appreciating sequelae of diagnostic delay
After my fellowship in advanced laparoscopic and pelvic surgery with Harry Reich, MD, and C. Y. Liu, MD, pioneers of endometriosis excision surgery, and as I did my residency in the early 2000s, I noticed puzzlement in the literature about why some patients still had lasting pain after thorough excision.
I didn’t doubt the efficacy of excision. It is the cornerstone of treatment, and at least one randomized double-blind trial2 and a systematic review and meta-analysis3 have demonstrated its superior efficacy over ablation in symptom reduction. What I did doubt was any presumption that surgery alone was enough. I knew there was more to healing when a disease process wreaks havoc on the body for more than a decade and that there were other generators of pain in addition to the endometriosis implants themselves.
As I began to focus on endometriosis in my own surgical practice, I strove to detect and treat endometriosis in teens. But in those patients with longstanding disease, I recognized patterns and began to more fully appreciate the systemic sequelae of endometriosis.
To cope with dysmenorrhea, patients curl up and assume a fetal position, tensing the abdominal muscles, inner thigh muscles, and pelvic floor muscles. Over time, these muscles come to maintain a short, tight, and painful state. (Hence the need for physical therapy to undo this decade-long pattern.)
Endometriosis implants on or near the gastrointestinal tract tug on fascia and muscles and commonly cause constipation, leading women to further overwork the pelvic floor muscles. In the case of diarrhea-predominant dysfunction, our patients squeeze pelvic floor muscles to prevent leakage. And in the case of urinary urgency, they squeeze muscles to release urine that isn’t really there.
As the chronic inflammation of the disease grows, and as pain worsens, the patient is increasingly in sympathetic overdrive (also known as ”fight or flight”), as opposed to a parasympathetic state (also known as “rest and digest”). The bowel’s motility slows, allowing the bacteria of the small intestine to grow beyond what is normal, leading to SIBO, a condition increasingly recognized by gastroenterologists and others that can impede nutrient absorption and cause bloat and pain and exacerbate constipation and diarrhea.
Key to my conceptualization of pain was a review published in 2011 by Pam Stratton, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, and Karen J. Berkley, PhD, then of Florida State University, on chronic pain and endometriosis.4 They detailed how endometriotic lesions can develop their own nerve supply that interacts directly and in a two-way fashion with the CNS – and how the lesions can engage the nervous system in ways that create comorbid conditions and pain that becomes “independent of the disease itself.”
Sensitized peripheral nerve fibers innervating a deeply infiltrating lesion on the left uterosacral ligament, for instance, can sensitize neurons in the spinal sacral segment. Branches of these nerve fibers can extend to other segments of the spinal cord, and, once sensitized themselves, turn on neurons in these other segments. There is a resultant remodeling of the central nervous system, in essence, and what is called “remote central sensitization.” The CNS becomes independent from peripheral neural processes.
I now explain to both patients and physicians that those who have had endometriosis for years have had an enduring “hand on the stove,” with a persistent signal to the CNS. Tight muscles are a hand on the stove, painful bladder syndrome is another hand on the stove, and SIBO is yet another. So are anxiety and depression.
The CNS becomes so upregulated and overloaded that messages branch out through the spinal cord to other available pathways and to other organs, muscles, and nerves. The CNS also starts firing on its own – and once it becomes its own pain generator, taking one hand off the stove (for instance, excising implants) while leaving multiple other hands on the hot stove won’t remove all pain. We must downregulate the CNS more broadly.
As I began addressing pain generators and instigators of CNS sensitization – and waiting for excision surgery until the CNS had sufficiently cooled – I saw that my patients had a better chance of more significant and lasting pain relief.
Pearls for a multimodal approach
My initial physical exam includes an assessment of the pelvic floor for overly tight musculature. An abdominal exam will usually reveal whether there is asymmetry of the abdominal wall muscles, which typically informs me of the likelihood of tightness and pulling on either side of the pelvic anatomy. On the internal exam, then, the pelvic floor muscles can be palpated and assessed. These findings will guide my referrals and my discussions with patients about the value of pelvic floor physical therapy. The cervix should be in the midline of the vagina – equidistant from the left and right vaginal fornices. If the cervix is pulled away from this midline, and a palpation of a thickened uterosacral ligament reproduces pain, endometriosis is 90% likely.
Patients who report significant “burning” pain that’s suggestive of neuropathic pain should be referred to a physical medicine rehabilitation physician or a pain specialist who can help downregulate their CNS. And patients who have symptoms of depression, anxiety disorders (including obsessive-compulsive disorder), or posttraumatic stress disorder should be referred to pain therapists, psychologists, or other mental health professionals, preferably well before surgery. I will also often discuss mindfulness practices and give my patients “meditation challenges” to achieve during the presurgical phase.
Additional points of emphasis about a multidisciplinary, multimodal approach include:
Advanced pelvic floor therapy: Therapists with specialized training in pelvic health and manual therapy utilize a range of techniques and modalities to release tension in affected muscles, fascia, nerves, and bone, and in doing so, they help to downregulate the CNS. Myofascial release, myofascial trigger point release, neural mobilization, and visceral mobilization are among these techniques. In addition to using manual therapy, many of these therapists may also employ neuromuscular reeducation and other techniques that will be helpful for the longer term.
It is important to identify physical therapists who have training in this approach; women with endometriosis often have a history of treatment by physical therapists whose focus is on incontinence and muscle strengthening (that is, Kegel exercises), which is the opposite of what endometriosis patients need.
Treating SIBO: Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO often overlap with symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – namely constipation, diarrhea (or both), and bloating. Indeed, many patients with undiagnosed endometriosis have been diagnosed with IBS. I send every patient who has one of these symptoms for SIBO breath testing, which utilizes carbohydrate substrates (glucose or lactulose) and measures hydrogen and/or methane in the breath.
SIBO is typically treated with rifampin, which stays in the small bowel and will not negatively affect beneficial bacteria, with or without neomycin. Gastroenterologists with more integrative practices also consider the use of herbals in addition to – or instead of – antibiotics. It can sometimes take months or a couple of years to correct SIBO, depending on how long the patient has been affected, but with presurgical diagnosis and a start on treatment, we can remove or at least tone down another instigator of CNS sensitization.
I estimate that 80% of my patients have tested positive for SIBO. Notably, in a testament to the systemic nature of endometriosis, a study published in 2009 of 355 women undergoing operative laparoscopy for suspected endometriosis found that 90% had gastrointestinal symptoms, but only 7.6% of the vast majority whose endometriosis was confirmed were found to have endometrial implants on the bowel itself.5
Addressing bladder issues: I routinely administer the PUF (Pain, Urgency, Frequency) questionnaire as part of my intake package and follow it up with conversation. For just about every patient with painful bladder syndrome, pelvic floor physical therapy in combination with a low-acid, low-potassium diet will work effectively together to reduce symptoms and pain. The IC Network offers a helpful food list, and patients can be counseled to choose foods that are also anti-inflammatory. When referrals to a urologist for bladder instillations are possible, these can be helpful as well.
Our communication with patients
Our patients need to have their symptoms and pain validated and to understand why we’re recommending these measures before surgery. Some education is necessary. Few patients will go to an integrative nutritionist, for example, if we just write a referral without explaining how years of inflammation and disruption in the gut can affect the whole body – including mental health – and that it can be corrected over time.
Also necessary is an appreciation of the fact that patients with delayed diagnoses have lived with gastrointestinal and other symptoms and patterns for so long – and often have mothers whose endometriosis caused similar symptoms – that some of their own experiences can seem almost “normal.” A patient whose mother had bowel movements every 7 days may think that 4-5 day intervals are acceptable, for instance. This means we have to carefully consider how we ask our questions.
I always ask my patients as we’re going into surgery, what percentage better are you? I’ve long aimed for at least 30% improvement, but most of the time, with pelvic floor therapy and as many other pain-generator–focused measures as possible, we’re getting them 70% better.
Excision surgery will remove the inflammation that has helped fuel the SIBO and other coconditions. Then, everything done to prepare the body must continue for some time. Certain practices, such as eating an anti-inflammatory diet, should be lifelong.
One day, it is hoped, a pediatrician or other physician will suspect endometriosis early on. The patient will see the surgeon within several months of the onset of pain, and we won’t need to unravel layers of pain generation and CNS upregulation before operating. But until this happens and we shorten the diagnostic delay, we must consider the benefits of presurgical preparation.
References
1. Orbuch I, Stein A. Beating Endo: How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis. (New York: HarperCollins, 2019).
2. Healey M et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2014;21(6):999-1004.
3. Pundir J et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(5):747-56.
4. Stratton P, Berkley KJ. Hum Repro Update. 2011;17(3):327-46.
5. Maroun P et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;49(4):411-4.
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in endometriosis. She has no conflicts of interest to report.
Is there still a role for tubal surgery in the modern world of IVF?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions, in 2019 2.1% of all infants born in the United States were conceived by assisted reproductive technology (ART). Now 45 years old, ART, namely in vitro fertilization (IVF), is offered in nearly 500 clinics in the United States, contributing to over 300,000 treatment cycles per year.
A tubal factor is responsible for 30% of female infertility and may involve proximal and/or distal tubal occlusion, irrespective of pelvic adhesions.1 Before the advent of IVF, the sole approach to the treatment of a tubal factor had been surgery. Given its success and minimal invasiveness, IVF is increasingly being offered to circumvent a tubal factor for infertility. This month we examine the utility of surgical treatment of tubal factor infertility. The options for fertility with a history of bilateral tubal ligation was covered in a prior Reproductive Rounds column.
Tubal disease and pelvic adhesions prevent the normal transport of the oocyte and sperm through the fallopian tube. The primary etiology of tubal factor infertility is pelvic inflammatory disease, mainly caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea. Other conditions that may interfere with tubal transport include severe endometriosis, adhesions from previous surgery, or nontubal infection (for example, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease), pelvic tuberculosis, and salpingitis isthmica nodosa (that is, diverticulosis of the fallopian tube).
Proximal tubal occlusion
During a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), transient uterine cornual spasm can result if a woman experiences significant uterine cramping, thereby resulting in a false-positive diagnosis of proximal tubal occlusion. When a repeat HSG is gently performed with slow instillation of contrast, uterine cramping is less likely, and the tubal patency rate is 60%. PTO may also result from plugs of mucus and amorphous debris, but this is not true occlusion.2 In cases with unilateral PTO, controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with intrauterine insemination has resulted in pregnancy rates similar to those in patients with unexplained infertility.3
Reconstructive surgery for bilateral PTO has limited effectiveness and the risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancy is as high as 20%.4 A more successful option is fluoroscopic tubal catheterization (FTC), an outpatient procedure performed in a radiology or infertility center. FTC uses a coaxial catheter system where the outer catheter is guided through the tubal ostium and an inner catheter is atraumatically advanced to overcome the blockage. This procedure is 85% successful for tubal patency with 50% of patients conceiving in the first 12 months; one-third of time the tubes reocclude. After the reestablishment of patency with FTC, the chance of achieving a live birth is 22% and the risk of ectopic pregnancy is 4%.5
Treatment of distal tubal occlusion – the hydrosalpinx
Surgery for treating tubal factor infertility is most successful in women with distal tubal obstruction (DTO), often caused by a hydrosalpinx. Fimbrioplasty is the lysis of fimbrial adhesions or dilatation of fimbrial strictures; the tube is patent, but there are adhesive bands that surround the terminal end with preserved tubal rugae. Gentle introduction of an alligator laparoscopic forceps into the tubal ostium followed by opening and withdrawal of the forceps helps to stretch the tube and release minor degrees of fimbrial agglutination.6
A hydrosalpinx is diagnosed by DTO with dilation and intraluminal fluid accumulation along with the reduction/loss of endothelial cilia. Left untreated, a hydrosalpinx can lead to a 50% reduction in IVF pregnancy rates.7 Tube-sparing treatment involves neosalpingostomy to create a new tubal opening. A nonsurgical approach, ultrasound-guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges, has not been shown to significantly increase the rate of clinical pregnancy. Efficacy for improving fertility is generally poor, but depends upon tubal wall thickness, ampullary dilation, presence of mucosal folds, percentage of ciliated cells in the fimbrial end, and peritubal adhesions.8
Evidence supports that laparoscopic salpingectomy in women with hydrosalpinges improves the outcomes of IVF treatment, compared with no surgical intervention.9 The improvement in pregnancy and live birth rates likely stems from the elimination of the retrograde flow of embryotoxic fluid that disrupts implantation. Endometrial receptivity markers (endometrial cell adhesion molecules, integrins, and HOXA10) have been shown to be reduced in the presence of hydrosalpinx.10 A small, randomized trial demonstrated that bipolar diathermy prior to IVF improved pregnancy outcomes.11 PTO was not more effective than salpingectomy. Conceptions, without IVF, have been reported following salpingectomy for unilateral hydrosalpinx.12
In a series including 434 patients with DTO who underwent laparoscopic fimbrioplasty (enlargement of the ostium) or neosalpingostomy (creation of a new ostium) by a single surgeon, 5-year actuarial delivery rates decreased as the severity of tubal occlusion increased; the ectopic rate was stable at approximately 15%.13 A prospective study reported that the relative increase in the pregnancy rate after salpingectomy was greatest in women with a large hydrosalpinx visible on ultrasound.14
Because of the possible risks of decreased ovarian reserve secondary to interruption of ovarian blood supply, salpingectomy should be done with minimal thermal injury and very close to the fallopian tube.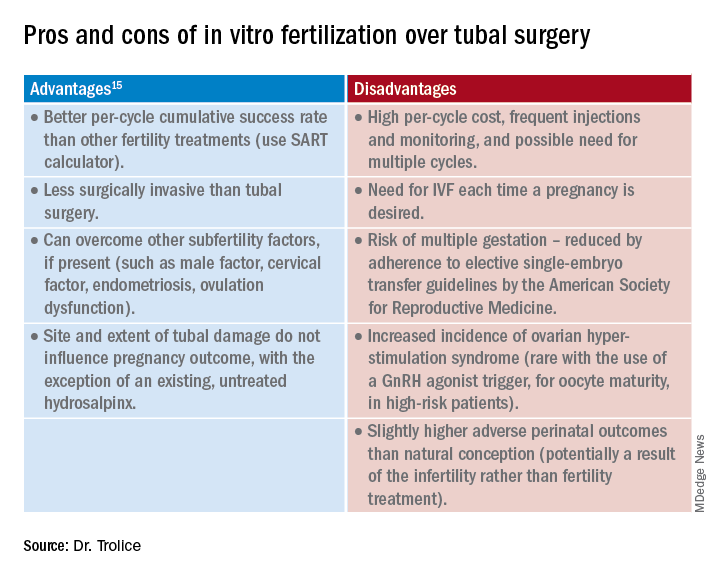
Summary
Surgery may be considered for young women with mild distal tubal disease as one surgical procedure can lead to several pregnancies whereas IVF must be performed each time pregnancy is desired. IVF is more likely than surgery to be successful in women with bilateral hydrosalpinx, in those with pelvic adhesions, in older reproductive aged women, and for both proximal and distal tubal occlusion.15 An online prediction calculator from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) can be helpful in counseling patients on personalized expectations for IVF pregnancy outcomes.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Ambildhuke K et al. Cureus. 2022;1:14(11):e30990.
2. Fatemeh Z et al. Br J Radiol. 2021 Jun 1;94(1122):20201386.
3. Farhi J et al. Fertil Steril. 2007 Aug;88(2):396.
4. Honoré GM et al. Fertil Steril. 1999;71(5):785.
5. De Silva PM et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32(4):836.
6. Namnoum A and Murphy A. “Diagnostic and Operative Laparoscopy,” in Te Linde’s Operative Gynecology, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997, pp. 389.
7. Camus E et al.Hum Reprod. 1999;14(5):1243.
8. Marana R et al. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(12):2991-5.
9. Johnson N et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD002125.
10. Savaris RF et al. Fertil Steril. 2006 Jan;85(1):188.
11. Kontoravdis A et al. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(6):1642.
12. Sagoskin AW et al. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(12):2634.
13. Audebert A et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(4):1203.
14. Bildirici I et al. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(11):2422.
15. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;97(3):539.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions, in 2019 2.1% of all infants born in the United States were conceived by assisted reproductive technology (ART). Now 45 years old, ART, namely in vitro fertilization (IVF), is offered in nearly 500 clinics in the United States, contributing to over 300,000 treatment cycles per year.
A tubal factor is responsible for 30% of female infertility and may involve proximal and/or distal tubal occlusion, irrespective of pelvic adhesions.1 Before the advent of IVF, the sole approach to the treatment of a tubal factor had been surgery. Given its success and minimal invasiveness, IVF is increasingly being offered to circumvent a tubal factor for infertility. This month we examine the utility of surgical treatment of tubal factor infertility. The options for fertility with a history of bilateral tubal ligation was covered in a prior Reproductive Rounds column.
Tubal disease and pelvic adhesions prevent the normal transport of the oocyte and sperm through the fallopian tube. The primary etiology of tubal factor infertility is pelvic inflammatory disease, mainly caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea. Other conditions that may interfere with tubal transport include severe endometriosis, adhesions from previous surgery, or nontubal infection (for example, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease), pelvic tuberculosis, and salpingitis isthmica nodosa (that is, diverticulosis of the fallopian tube).
Proximal tubal occlusion
During a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), transient uterine cornual spasm can result if a woman experiences significant uterine cramping, thereby resulting in a false-positive diagnosis of proximal tubal occlusion. When a repeat HSG is gently performed with slow instillation of contrast, uterine cramping is less likely, and the tubal patency rate is 60%. PTO may also result from plugs of mucus and amorphous debris, but this is not true occlusion.2 In cases with unilateral PTO, controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with intrauterine insemination has resulted in pregnancy rates similar to those in patients with unexplained infertility.3
Reconstructive surgery for bilateral PTO has limited effectiveness and the risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancy is as high as 20%.4 A more successful option is fluoroscopic tubal catheterization (FTC), an outpatient procedure performed in a radiology or infertility center. FTC uses a coaxial catheter system where the outer catheter is guided through the tubal ostium and an inner catheter is atraumatically advanced to overcome the blockage. This procedure is 85% successful for tubal patency with 50% of patients conceiving in the first 12 months; one-third of time the tubes reocclude. After the reestablishment of patency with FTC, the chance of achieving a live birth is 22% and the risk of ectopic pregnancy is 4%.5
Treatment of distal tubal occlusion – the hydrosalpinx
Surgery for treating tubal factor infertility is most successful in women with distal tubal obstruction (DTO), often caused by a hydrosalpinx. Fimbrioplasty is the lysis of fimbrial adhesions or dilatation of fimbrial strictures; the tube is patent, but there are adhesive bands that surround the terminal end with preserved tubal rugae. Gentle introduction of an alligator laparoscopic forceps into the tubal ostium followed by opening and withdrawal of the forceps helps to stretch the tube and release minor degrees of fimbrial agglutination.6
A hydrosalpinx is diagnosed by DTO with dilation and intraluminal fluid accumulation along with the reduction/loss of endothelial cilia. Left untreated, a hydrosalpinx can lead to a 50% reduction in IVF pregnancy rates.7 Tube-sparing treatment involves neosalpingostomy to create a new tubal opening. A nonsurgical approach, ultrasound-guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges, has not been shown to significantly increase the rate of clinical pregnancy. Efficacy for improving fertility is generally poor, but depends upon tubal wall thickness, ampullary dilation, presence of mucosal folds, percentage of ciliated cells in the fimbrial end, and peritubal adhesions.8
Evidence supports that laparoscopic salpingectomy in women with hydrosalpinges improves the outcomes of IVF treatment, compared with no surgical intervention.9 The improvement in pregnancy and live birth rates likely stems from the elimination of the retrograde flow of embryotoxic fluid that disrupts implantation. Endometrial receptivity markers (endometrial cell adhesion molecules, integrins, and HOXA10) have been shown to be reduced in the presence of hydrosalpinx.10 A small, randomized trial demonstrated that bipolar diathermy prior to IVF improved pregnancy outcomes.11 PTO was not more effective than salpingectomy. Conceptions, without IVF, have been reported following salpingectomy for unilateral hydrosalpinx.12
In a series including 434 patients with DTO who underwent laparoscopic fimbrioplasty (enlargement of the ostium) or neosalpingostomy (creation of a new ostium) by a single surgeon, 5-year actuarial delivery rates decreased as the severity of tubal occlusion increased; the ectopic rate was stable at approximately 15%.13 A prospective study reported that the relative increase in the pregnancy rate after salpingectomy was greatest in women with a large hydrosalpinx visible on ultrasound.14
Because of the possible risks of decreased ovarian reserve secondary to interruption of ovarian blood supply, salpingectomy should be done with minimal thermal injury and very close to the fallopian tube.
Summary
Surgery may be considered for young women with mild distal tubal disease as one surgical procedure can lead to several pregnancies whereas IVF must be performed each time pregnancy is desired. IVF is more likely than surgery to be successful in women with bilateral hydrosalpinx, in those with pelvic adhesions, in older reproductive aged women, and for both proximal and distal tubal occlusion.15 An online prediction calculator from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) can be helpful in counseling patients on personalized expectations for IVF pregnancy outcomes.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Ambildhuke K et al. Cureus. 2022;1:14(11):e30990.
2. Fatemeh Z et al. Br J Radiol. 2021 Jun 1;94(1122):20201386.
3. Farhi J et al. Fertil Steril. 2007 Aug;88(2):396.
4. Honoré GM et al. Fertil Steril. 1999;71(5):785.
5. De Silva PM et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32(4):836.
6. Namnoum A and Murphy A. “Diagnostic and Operative Laparoscopy,” in Te Linde’s Operative Gynecology, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997, pp. 389.
7. Camus E et al.Hum Reprod. 1999;14(5):1243.
8. Marana R et al. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(12):2991-5.
9. Johnson N et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD002125.
10. Savaris RF et al. Fertil Steril. 2006 Jan;85(1):188.
11. Kontoravdis A et al. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(6):1642.
12. Sagoskin AW et al. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(12):2634.
13. Audebert A et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(4):1203.
14. Bildirici I et al. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(11):2422.
15. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;97(3):539.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions, in 2019 2.1% of all infants born in the United States were conceived by assisted reproductive technology (ART). Now 45 years old, ART, namely in vitro fertilization (IVF), is offered in nearly 500 clinics in the United States, contributing to over 300,000 treatment cycles per year.
A tubal factor is responsible for 30% of female infertility and may involve proximal and/or distal tubal occlusion, irrespective of pelvic adhesions.1 Before the advent of IVF, the sole approach to the treatment of a tubal factor had been surgery. Given its success and minimal invasiveness, IVF is increasingly being offered to circumvent a tubal factor for infertility. This month we examine the utility of surgical treatment of tubal factor infertility. The options for fertility with a history of bilateral tubal ligation was covered in a prior Reproductive Rounds column.
Tubal disease and pelvic adhesions prevent the normal transport of the oocyte and sperm through the fallopian tube. The primary etiology of tubal factor infertility is pelvic inflammatory disease, mainly caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea. Other conditions that may interfere with tubal transport include severe endometriosis, adhesions from previous surgery, or nontubal infection (for example, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease), pelvic tuberculosis, and salpingitis isthmica nodosa (that is, diverticulosis of the fallopian tube).
Proximal tubal occlusion
During a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), transient uterine cornual spasm can result if a woman experiences significant uterine cramping, thereby resulting in a false-positive diagnosis of proximal tubal occlusion. When a repeat HSG is gently performed with slow instillation of contrast, uterine cramping is less likely, and the tubal patency rate is 60%. PTO may also result from plugs of mucus and amorphous debris, but this is not true occlusion.2 In cases with unilateral PTO, controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with intrauterine insemination has resulted in pregnancy rates similar to those in patients with unexplained infertility.3
Reconstructive surgery for bilateral PTO has limited effectiveness and the risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancy is as high as 20%.4 A more successful option is fluoroscopic tubal catheterization (FTC), an outpatient procedure performed in a radiology or infertility center. FTC uses a coaxial catheter system where the outer catheter is guided through the tubal ostium and an inner catheter is atraumatically advanced to overcome the blockage. This procedure is 85% successful for tubal patency with 50% of patients conceiving in the first 12 months; one-third of time the tubes reocclude. After the reestablishment of patency with FTC, the chance of achieving a live birth is 22% and the risk of ectopic pregnancy is 4%.5
Treatment of distal tubal occlusion – the hydrosalpinx
Surgery for treating tubal factor infertility is most successful in women with distal tubal obstruction (DTO), often caused by a hydrosalpinx. Fimbrioplasty is the lysis of fimbrial adhesions or dilatation of fimbrial strictures; the tube is patent, but there are adhesive bands that surround the terminal end with preserved tubal rugae. Gentle introduction of an alligator laparoscopic forceps into the tubal ostium followed by opening and withdrawal of the forceps helps to stretch the tube and release minor degrees of fimbrial agglutination.6
A hydrosalpinx is diagnosed by DTO with dilation and intraluminal fluid accumulation along with the reduction/loss of endothelial cilia. Left untreated, a hydrosalpinx can lead to a 50% reduction in IVF pregnancy rates.7 Tube-sparing treatment involves neosalpingostomy to create a new tubal opening. A nonsurgical approach, ultrasound-guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges, has not been shown to significantly increase the rate of clinical pregnancy. Efficacy for improving fertility is generally poor, but depends upon tubal wall thickness, ampullary dilation, presence of mucosal folds, percentage of ciliated cells in the fimbrial end, and peritubal adhesions.8
Evidence supports that laparoscopic salpingectomy in women with hydrosalpinges improves the outcomes of IVF treatment, compared with no surgical intervention.9 The improvement in pregnancy and live birth rates likely stems from the elimination of the retrograde flow of embryotoxic fluid that disrupts implantation. Endometrial receptivity markers (endometrial cell adhesion molecules, integrins, and HOXA10) have been shown to be reduced in the presence of hydrosalpinx.10 A small, randomized trial demonstrated that bipolar diathermy prior to IVF improved pregnancy outcomes.11 PTO was not more effective than salpingectomy. Conceptions, without IVF, have been reported following salpingectomy for unilateral hydrosalpinx.12
In a series including 434 patients with DTO who underwent laparoscopic fimbrioplasty (enlargement of the ostium) or neosalpingostomy (creation of a new ostium) by a single surgeon, 5-year actuarial delivery rates decreased as the severity of tubal occlusion increased; the ectopic rate was stable at approximately 15%.13 A prospective study reported that the relative increase in the pregnancy rate after salpingectomy was greatest in women with a large hydrosalpinx visible on ultrasound.14
Because of the possible risks of decreased ovarian reserve secondary to interruption of ovarian blood supply, salpingectomy should be done with minimal thermal injury and very close to the fallopian tube.
Summary
Surgery may be considered for young women with mild distal tubal disease as one surgical procedure can lead to several pregnancies whereas IVF must be performed each time pregnancy is desired. IVF is more likely than surgery to be successful in women with bilateral hydrosalpinx, in those with pelvic adhesions, in older reproductive aged women, and for both proximal and distal tubal occlusion.15 An online prediction calculator from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) can be helpful in counseling patients on personalized expectations for IVF pregnancy outcomes.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Ambildhuke K et al. Cureus. 2022;1:14(11):e30990.
2. Fatemeh Z et al. Br J Radiol. 2021 Jun 1;94(1122):20201386.
3. Farhi J et al. Fertil Steril. 2007 Aug;88(2):396.
4. Honoré GM et al. Fertil Steril. 1999;71(5):785.
5. De Silva PM et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32(4):836.
6. Namnoum A and Murphy A. “Diagnostic and Operative Laparoscopy,” in Te Linde’s Operative Gynecology, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997, pp. 389.
7. Camus E et al.Hum Reprod. 1999;14(5):1243.
8. Marana R et al. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(12):2991-5.
9. Johnson N et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD002125.
10. Savaris RF et al. Fertil Steril. 2006 Jan;85(1):188.
11. Kontoravdis A et al. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(6):1642.
12. Sagoskin AW et al. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(12):2634.
13. Audebert A et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(4):1203.
14. Bildirici I et al. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(11):2422.
15. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;97(3):539.
Renewed calls for fallopian tube removal to avoid ovarian cancer
All women, regardless of their risk profile, should consider prophylactic removal of the fallopian tubes at the same time as other pelvic surgery once they are finished having children, the Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance has advised.
The recommendation, announced Feb. 1, replaces the decades-old focus on symptom awareness and early detection and follows “sobering and deeply disappointing” results from a large U.K. study published 2 years ago, the organization said.
That was the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening published in The Lancet in 2021, which followed more than 200,000 women for a median 16 years. It showed that screening average-risk women with a CA-125 blood test and ultrasound does not reduce deaths from the disease, as reported at the time by this news organization.
“We all hoped that the trial would show that early detection was effective in changing mortality rates. When the results came out, it was very hard to accept,” Audra Moran, OCRA president and CEO, said in an interview.
“We have an obligation to let people know that symptom awareness and early detection will not save lives” but considering opportunistic salpingectomy “absolutely will,” said Ms. Moran. Hence the renewed call for women to consider having their fallopian tubes removed.
What sounds new about this call is that the group is directing fallopian tube removal to all women “who are undergoing pelvic surgeries for benign conditions,” irrespective of what perceived risk they have of developing ovarian cancer (for example, based on family history).
But this advice has been in place for years for women who are known to be at higher risk for the disease.
For instance, women at high risk for ovarian cancer based on Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome (HBOC) have long been recommended to undergo surgery to remove ovaries and fallopian tubes (risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy or RRBSO) once there is no longer a desire for pregnancy.
Approached for comment about the new messaging, Stephanie V. Blank, MD, president of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology, says that the new recommendation – that all women who are finished childbearing consider opportunistic salpingectomy at the time of other pelvic surgery for benign conditions – is “not aggressive.”
“It’s reasonable and makes sense,” Dr. Blank said in an interview.
And she pointed out that it’s actually not “new”; it is, however, getting “new attention” based on the disappointing U.K. screening study, said Dr. Blank, director of gynecologic oncology for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York and professor of gynecologic oncology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
She noted that the procedure of opportunistic salpingectomy has been endorsed by SGO since 2013 and by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists since 2015.
There is increasing evidence that most high-grade serous ovarian cancers arise from cells in the fallopian tubes, William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society, told this news organization.
“Indirect evidence suggests a fairly strong degree of risk reduction associated with opportunistic salpingectomy for the most prevalent type of ovarian cancer (serous), and some risk reduction of epithelial ovarian cancer. At this time, these discussions seem warranted,” Dr. Dahut said.
At this point, however, the fact that leading organizations advise “consideration” means that the evidence base has “not been judged to be sufficiently strong (in terms of what we can say about benefits and harms) to advise a direct recommendation for opportunistic salpingectomy,” Dr. Dahut added.
There is no current recommendation to have fallopian tubes removed as a stand-alone procedure, he pointed out. However, he commented that “the occasion of scheduled gynecologic surgery presents an opportunity to possibly reduce the risk of ovarian cancer without known adverse effects in women who have completed childbearing. Having the discussion seems to be justified by the current evidence,” Dr. Dahut said.
Deanna Gerber, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center-Long Island, agrees. “In women who are scheduled to have a gynecologic or pelvic procedure, clinicians should discuss the possibility of removing the fallopian tubes at that time. A salpingectomy is a relatively low-risk procedure and adds little time to the surgery,” Dr. Gerber said in an interview.
“Women should understand that there is still ongoing research on this topic, but this low-risk procedure may reduce their risk of developing an ovarian or fallopian tube cancer,” Dr. Gerber said.
OCRA also encourages all women (or anyone born with ovaries) to know their risk for ovarian cancer. To that end, the organization has launched a pilot program offering free, at-home genetic testing kits to people with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, uterine, or colorectal cancer.
Ms. Moran, Dr. Blank, Dr. Dahut, and Dr. Gerber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All women, regardless of their risk profile, should consider prophylactic removal of the fallopian tubes at the same time as other pelvic surgery once they are finished having children, the Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance has advised.
The recommendation, announced Feb. 1, replaces the decades-old focus on symptom awareness and early detection and follows “sobering and deeply disappointing” results from a large U.K. study published 2 years ago, the organization said.
That was the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening published in The Lancet in 2021, which followed more than 200,000 women for a median 16 years. It showed that screening average-risk women with a CA-125 blood test and ultrasound does not reduce deaths from the disease, as reported at the time by this news organization.
“We all hoped that the trial would show that early detection was effective in changing mortality rates. When the results came out, it was very hard to accept,” Audra Moran, OCRA president and CEO, said in an interview.
“We have an obligation to let people know that symptom awareness and early detection will not save lives” but considering opportunistic salpingectomy “absolutely will,” said Ms. Moran. Hence the renewed call for women to consider having their fallopian tubes removed.
What sounds new about this call is that the group is directing fallopian tube removal to all women “who are undergoing pelvic surgeries for benign conditions,” irrespective of what perceived risk they have of developing ovarian cancer (for example, based on family history).
But this advice has been in place for years for women who are known to be at higher risk for the disease.
For instance, women at high risk for ovarian cancer based on Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome (HBOC) have long been recommended to undergo surgery to remove ovaries and fallopian tubes (risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy or RRBSO) once there is no longer a desire for pregnancy.
Approached for comment about the new messaging, Stephanie V. Blank, MD, president of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology, says that the new recommendation – that all women who are finished childbearing consider opportunistic salpingectomy at the time of other pelvic surgery for benign conditions – is “not aggressive.”
“It’s reasonable and makes sense,” Dr. Blank said in an interview.
And she pointed out that it’s actually not “new”; it is, however, getting “new attention” based on the disappointing U.K. screening study, said Dr. Blank, director of gynecologic oncology for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York and professor of gynecologic oncology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
She noted that the procedure of opportunistic salpingectomy has been endorsed by SGO since 2013 and by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists since 2015.
There is increasing evidence that most high-grade serous ovarian cancers arise from cells in the fallopian tubes, William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society, told this news organization.
“Indirect evidence suggests a fairly strong degree of risk reduction associated with opportunistic salpingectomy for the most prevalent type of ovarian cancer (serous), and some risk reduction of epithelial ovarian cancer. At this time, these discussions seem warranted,” Dr. Dahut said.
At this point, however, the fact that leading organizations advise “consideration” means that the evidence base has “not been judged to be sufficiently strong (in terms of what we can say about benefits and harms) to advise a direct recommendation for opportunistic salpingectomy,” Dr. Dahut added.
There is no current recommendation to have fallopian tubes removed as a stand-alone procedure, he pointed out. However, he commented that “the occasion of scheduled gynecologic surgery presents an opportunity to possibly reduce the risk of ovarian cancer without known adverse effects in women who have completed childbearing. Having the discussion seems to be justified by the current evidence,” Dr. Dahut said.
Deanna Gerber, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center-Long Island, agrees. “In women who are scheduled to have a gynecologic or pelvic procedure, clinicians should discuss the possibility of removing the fallopian tubes at that time. A salpingectomy is a relatively low-risk procedure and adds little time to the surgery,” Dr. Gerber said in an interview.
“Women should understand that there is still ongoing research on this topic, but this low-risk procedure may reduce their risk of developing an ovarian or fallopian tube cancer,” Dr. Gerber said.
OCRA also encourages all women (or anyone born with ovaries) to know their risk for ovarian cancer. To that end, the organization has launched a pilot program offering free, at-home genetic testing kits to people with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, uterine, or colorectal cancer.
Ms. Moran, Dr. Blank, Dr. Dahut, and Dr. Gerber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All women, regardless of their risk profile, should consider prophylactic removal of the fallopian tubes at the same time as other pelvic surgery once they are finished having children, the Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance has advised.
The recommendation, announced Feb. 1, replaces the decades-old focus on symptom awareness and early detection and follows “sobering and deeply disappointing” results from a large U.K. study published 2 years ago, the organization said.
That was the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening published in The Lancet in 2021, which followed more than 200,000 women for a median 16 years. It showed that screening average-risk women with a CA-125 blood test and ultrasound does not reduce deaths from the disease, as reported at the time by this news organization.
“We all hoped that the trial would show that early detection was effective in changing mortality rates. When the results came out, it was very hard to accept,” Audra Moran, OCRA president and CEO, said in an interview.
“We have an obligation to let people know that symptom awareness and early detection will not save lives” but considering opportunistic salpingectomy “absolutely will,” said Ms. Moran. Hence the renewed call for women to consider having their fallopian tubes removed.
What sounds new about this call is that the group is directing fallopian tube removal to all women “who are undergoing pelvic surgeries for benign conditions,” irrespective of what perceived risk they have of developing ovarian cancer (for example, based on family history).
But this advice has been in place for years for women who are known to be at higher risk for the disease.
For instance, women at high risk for ovarian cancer based on Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome (HBOC) have long been recommended to undergo surgery to remove ovaries and fallopian tubes (risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy or RRBSO) once there is no longer a desire for pregnancy.
Approached for comment about the new messaging, Stephanie V. Blank, MD, president of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology, says that the new recommendation – that all women who are finished childbearing consider opportunistic salpingectomy at the time of other pelvic surgery for benign conditions – is “not aggressive.”
“It’s reasonable and makes sense,” Dr. Blank said in an interview.
And she pointed out that it’s actually not “new”; it is, however, getting “new attention” based on the disappointing U.K. screening study, said Dr. Blank, director of gynecologic oncology for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York and professor of gynecologic oncology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
She noted that the procedure of opportunistic salpingectomy has been endorsed by SGO since 2013 and by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists since 2015.
There is increasing evidence that most high-grade serous ovarian cancers arise from cells in the fallopian tubes, William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society, told this news organization.
“Indirect evidence suggests a fairly strong degree of risk reduction associated with opportunistic salpingectomy for the most prevalent type of ovarian cancer (serous), and some risk reduction of epithelial ovarian cancer. At this time, these discussions seem warranted,” Dr. Dahut said.
At this point, however, the fact that leading organizations advise “consideration” means that the evidence base has “not been judged to be sufficiently strong (in terms of what we can say about benefits and harms) to advise a direct recommendation for opportunistic salpingectomy,” Dr. Dahut added.
There is no current recommendation to have fallopian tubes removed as a stand-alone procedure, he pointed out. However, he commented that “the occasion of scheduled gynecologic surgery presents an opportunity to possibly reduce the risk of ovarian cancer without known adverse effects in women who have completed childbearing. Having the discussion seems to be justified by the current evidence,” Dr. Dahut said.
Deanna Gerber, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center-Long Island, agrees. “In women who are scheduled to have a gynecologic or pelvic procedure, clinicians should discuss the possibility of removing the fallopian tubes at that time. A salpingectomy is a relatively low-risk procedure and adds little time to the surgery,” Dr. Gerber said in an interview.
“Women should understand that there is still ongoing research on this topic, but this low-risk procedure may reduce their risk of developing an ovarian or fallopian tube cancer,” Dr. Gerber said.
OCRA also encourages all women (or anyone born with ovaries) to know their risk for ovarian cancer. To that end, the organization has launched a pilot program offering free, at-home genetic testing kits to people with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, uterine, or colorectal cancer.
Ms. Moran, Dr. Blank, Dr. Dahut, and Dr. Gerber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Decoding endometriosis: Recent research fosters hope
Roughly 4 decades after she first started menstruating, Elizabeth Flanagan finally underwent surgery to repair damage wreaked on her body by endometriosis. She’d spent years struggling with a variety of seemingly random symptoms, from migraines to excruciatingly painful periods to fatigue and irritable bowel syndrome. She’d worried about abnormal labs, including “extremely high” ANA, creatinine, and BUN blood test results that had been out of normal range for more than 10 years.
She was diagnosed with endometriosis in 2016, at age 47, after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. Still, it took 5 more years before she landed in the office of a surgeon with the proper training to excise the lesions that continued to cause her so much anguish. That physician, Matthew Siedhoff, MD, at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, explained why her creatinine and BUN results were so far out of range: The endometriosis was impinging on her ureters.
The appointment left Ms. Flanagan with a range of emotions. “I was shocked that no doctor had identified this before, relieved knowing that I was finally in the hands of an expert who understood my condition, and saddened by the dearth of knowledge and proper treatment of endometriosis,” she wrote in an email.
Although the disease afflicts at least 1 out of every 10 women, endometriosis remains a conundrum for patients and their physicians. It often masquerades as other problems, from mental health issues such as anxiety and depression to physical issues such as irritable bowel syndrome. It often coexists with autoimmune conditions. Short of performing surgery, it can be a diagnosis of exclusion. And the existing, state-of-the-art treatment – hormone therapy that shuts down the reproductive system – doesn’t work for every woman every time.
“It is no wonder that it takes 10 years on average, from the time someone has symptoms of endometriosis, until they get a definitive diagnosis,” said Hugh Taylor, MD, chair of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “It’s a combination of [physicians] not taking painful menses seriously and getting distracted by all these other manifestations of the disease throughout the whole body.”
Endometriosis, he said, “is a whole-body disease.”
But recent genetic research offers the tantalizing prospect of new diagnostic tools and treatments. In 5-10 years, scientists say, physicians may be able to diagnose the disease with a simple blood test, and treat it, for example, by preventing a gene receptor from initiating a cascade of inflammatory effects, or crafting treatments tailored to the molecular makeup of a patient’s disease.
“Tomorrow’s therapies will target specifically the molecular defects of endometriosis and be nonhormonal,” Dr. Taylor said.
Guidelines published last year by the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology detail the latest standards for diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis.
According to the guidelines, physicians should consider the diagnosis of endometriosis in individuals presenting with the following cyclical and noncyclical signs and symptoms: dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, dysuria, dyschezia, painful rectal bleeding or hematuria, shoulder tip pain, catamenial pneumothorax, cyclical cough/hemoptysis/chest pain, cyclical scar swelling, and pain, fatigue, and infertility.
A clinical exam should be considered, as well as imaging such as ultrasound and/or MRI, the guidelines state, although negative findings should not rule out a diagnosis. Laparoscopy is also an option, particularly for patients who desire a definitive diagnosis or cannot be diagnosed any other way, “although negative histology [of endometriotic lesions] does not entirely rule out the disease,” the guidelines state.
To treat the pain associated with endometriosis, the guidelines advise, as a first-line therapy, beginning with NSAIDs and combined hormonal contraceptives (in oral, vaginal, or transdermal form). Another option is progesterone, including progesterone-only contraceptives, with a recommendation to prescribe a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or an etonogestrel-releasing subdermal implant to reduce endometriosis-associated pain.
However, progestins and low-dose oral contraceptives are “unsuccessful in a third of women,” Dr. Taylor and his coauthors wrote in a paper published in 2021 in The Lancet.
Until recently, the gold standard for second-line treatment of endometriosis was oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. These manage the disease by inducing medical menopause – they downregulate pituitary GnRH receptors to create a hypoestrogenic state characterized by low serum levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). GnRH agonists may be administered nasally, or through daily, monthly, or trimonthly injections. But the Food and Drug Administration advises that, when used for longer than 6 months, GnRH agonists be paired with add-back hormone replacement therapy to reduce the risk of bone loss associated with the plunge in hormone levels. Also, treatment may not be appropriate for patients who, when suddenly forced into menopause, suffer from bothersome symptoms.
The latest treatment, GnRH antagonists, are new options for patients who either do not respond adequately to progestins and low-dose contraceptives or develop progesterone resistance, and want to avoid some of the risks and/or symptoms associated with GnRH agonists. Two advantages of GnRH antagonists for patients, Dr. Taylor said, are that they have a fast onset of action and are oral rather than injectable.
“These drugs [GnRH antagonists] cause competitive blockage of the GnRH receptor and hence dose-dependently suppress production of FSH and LH and inhibit secretion of ovarian steroid hormones without inducing a flare-up effect,” Belgian physicians and researchers Jacques Donnez, MD, and Marie-Madeleine Dolmans, MD, PhD, wrote in a paper published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine. “The mechanism is different from that of the GnRH agonist which, after a first phase of stimulation, desensitizes GnRH receptors, leading to full suppression of LH and FSH production and subsequently to complete suppression of [estrogen] to levels similar to those observed after bilateral oophorectomy.”
Patients who took Elagolix, the first oral nonpeptide GnRH antagonist available for the treatment of moderate to severe endometriosis-associated pain, had fewer vasomotor side effects and less bone density loss than those on the GnRH agonist leuprorelin, according to a 2018 study in Obstetrics and Gynecology. However, without add-back hormone-replacement therapy, GnRH antagonist use may need to be limited to 24 months, because of loss of bone density, a study in Cell Reports Medicine reported in 2022.
Attempting to explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis, and frustrated by the shortcomings of currently available therapies, researchers have turned to genetics for insight. A team of scientists led by Thomas Tapmeier, PhD, now a senior research fellow at Monash University in Australia, and Prof. Krina Zondervan at the University of Oxford, ran genetic analyses of families with a history of endometriosis, as well as rhesus macaques that spontaneously developed endometriosis. The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, identified NPSR1, the gene encoding neuropeptide S receptor 1, as one commonly associated with endometriosis. In trials with mouse models, they found that the NPSR1 inhibitor SHA 68R was able to reduce endometriosis-related inflammation and pain.
“It’s important to stress that there is no single gene that is responsible for endometriosis,” Dr. Tapmeier said in an interview. “This gene just has a higher frequency in people with endometriosis.”
The next step, then, would be to try to find a compound that would inhibit NPSR1 at some point, or a competitor to the ligand that binds to the receptor and blocks it, he said.
“We’re currently looking at compounds that might be able to inhibit the receptor signaling,” he said.
Such a therapy could potentially reduce the symptoms of endometriosis without interfering with the menstrual cycle and without introducing hormones that cause undesirable side effects in some patients.
“This might be a way to treat the pain and inflammation that goes with endometriosis, as well as leaving the possibility of pregnancy open,” he said.
Other researchers are searching for biomarkers of the disease, both to provide a definitive, nonsurgical diagnostic tool, and for potential, individualized treatment.
In a study published in Nature Genetics, researchers at Cedars-Sinai created a “cellular atlas” of endometriosis by analyzing nearly 400,000 individual cells from 21 patients, some of whom had the disease and some of whom did not. A new technology, single-cell genomics, allowed the scientists to profile the multiple cell types contributing to the disease.
“So the initial question we wanted to ask was about understanding how the cells look in endometriosis, compared to endometrium,” said Kate Lawrenson, PhD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Cedars-Sinai, and co–senior author of the study. “We know that they resemble the cells of the womb, but we really don’t understand if they behave the same. We had a good inkling that they would behave differently.”
It turned out they did: Cells of endometriosis interacted atypically with female hormones, compared with cells in the uterus, Dr. Lawrenson said.
“That helps us understand how, even when patients take contraceptive pills, which is a commonly prescribed therapy, it doesn’t always work, or sometimes it stops working after a while,” she said. The next step for researchers, she said, will be to pinpoint the specific causes of these altered interactions.
Meanwhile, the current research also points to diagnostic possibilities. “We were quite excited to see that multiple cell types and endometriosis are upregulating the same sets of genes,” she said. “That makes us optimistic that hopefully there are some protein gene products that are being made in abundance, and hopefully we can detect them in the blood stream. It might be that we could use that information to develop new biomarkers, or even risk stratification tools.”
In the future, a simple blood test could identify signs of endometriosis in at-risk patients and get them “fast-tracked to a specialist for evaluation,” she said. “Whereas now, they might go from PCP to gynecologist to a different gynecologist over the course of 5-10 years before they get that referral.”
This discovery, that endometrial cells use genes differently and cross-talk with nearby cells differently, presents new treatment possibilities. Maybe we can physically block how cells interact with nearby cells, Dr. Lawrenson said. One model for doing that, she said, would be antibody-based therapy, similar to the therapies now changing the treatment of cancer.
What’s most exciting, looking ahead 5-10 years, is that treatment for endometriosis in the future may be significantly more individualized, and less hormone-based, than it is today.
“What we need for endometriosis is more options for patients and something that is tailored to the molecular makeup of their disease rather than a process of trial and error,” she said.
Roughly 4 decades after she first started menstruating, Elizabeth Flanagan finally underwent surgery to repair damage wreaked on her body by endometriosis. She’d spent years struggling with a variety of seemingly random symptoms, from migraines to excruciatingly painful periods to fatigue and irritable bowel syndrome. She’d worried about abnormal labs, including “extremely high” ANA, creatinine, and BUN blood test results that had been out of normal range for more than 10 years.
She was diagnosed with endometriosis in 2016, at age 47, after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. Still, it took 5 more years before she landed in the office of a surgeon with the proper training to excise the lesions that continued to cause her so much anguish. That physician, Matthew Siedhoff, MD, at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, explained why her creatinine and BUN results were so far out of range: The endometriosis was impinging on her ureters.
The appointment left Ms. Flanagan with a range of emotions. “I was shocked that no doctor had identified this before, relieved knowing that I was finally in the hands of an expert who understood my condition, and saddened by the dearth of knowledge and proper treatment of endometriosis,” she wrote in an email.
Although the disease afflicts at least 1 out of every 10 women, endometriosis remains a conundrum for patients and their physicians. It often masquerades as other problems, from mental health issues such as anxiety and depression to physical issues such as irritable bowel syndrome. It often coexists with autoimmune conditions. Short of performing surgery, it can be a diagnosis of exclusion. And the existing, state-of-the-art treatment – hormone therapy that shuts down the reproductive system – doesn’t work for every woman every time.
“It is no wonder that it takes 10 years on average, from the time someone has symptoms of endometriosis, until they get a definitive diagnosis,” said Hugh Taylor, MD, chair of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “It’s a combination of [physicians] not taking painful menses seriously and getting distracted by all these other manifestations of the disease throughout the whole body.”
Endometriosis, he said, “is a whole-body disease.”
But recent genetic research offers the tantalizing prospect of new diagnostic tools and treatments. In 5-10 years, scientists say, physicians may be able to diagnose the disease with a simple blood test, and treat it, for example, by preventing a gene receptor from initiating a cascade of inflammatory effects, or crafting treatments tailored to the molecular makeup of a patient’s disease.
“Tomorrow’s therapies will target specifically the molecular defects of endometriosis and be nonhormonal,” Dr. Taylor said.
Guidelines published last year by the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology detail the latest standards for diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis.
According to the guidelines, physicians should consider the diagnosis of endometriosis in individuals presenting with the following cyclical and noncyclical signs and symptoms: dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, dysuria, dyschezia, painful rectal bleeding or hematuria, shoulder tip pain, catamenial pneumothorax, cyclical cough/hemoptysis/chest pain, cyclical scar swelling, and pain, fatigue, and infertility.
A clinical exam should be considered, as well as imaging such as ultrasound and/or MRI, the guidelines state, although negative findings should not rule out a diagnosis. Laparoscopy is also an option, particularly for patients who desire a definitive diagnosis or cannot be diagnosed any other way, “although negative histology [of endometriotic lesions] does not entirely rule out the disease,” the guidelines state.
To treat the pain associated with endometriosis, the guidelines advise, as a first-line therapy, beginning with NSAIDs and combined hormonal contraceptives (in oral, vaginal, or transdermal form). Another option is progesterone, including progesterone-only contraceptives, with a recommendation to prescribe a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or an etonogestrel-releasing subdermal implant to reduce endometriosis-associated pain.
However, progestins and low-dose oral contraceptives are “unsuccessful in a third of women,” Dr. Taylor and his coauthors wrote in a paper published in 2021 in The Lancet.
Until recently, the gold standard for second-line treatment of endometriosis was oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. These manage the disease by inducing medical menopause – they downregulate pituitary GnRH receptors to create a hypoestrogenic state characterized by low serum levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). GnRH agonists may be administered nasally, or through daily, monthly, or trimonthly injections. But the Food and Drug Administration advises that, when used for longer than 6 months, GnRH agonists be paired with add-back hormone replacement therapy to reduce the risk of bone loss associated with the plunge in hormone levels. Also, treatment may not be appropriate for patients who, when suddenly forced into menopause, suffer from bothersome symptoms.
The latest treatment, GnRH antagonists, are new options for patients who either do not respond adequately to progestins and low-dose contraceptives or develop progesterone resistance, and want to avoid some of the risks and/or symptoms associated with GnRH agonists. Two advantages of GnRH antagonists for patients, Dr. Taylor said, are that they have a fast onset of action and are oral rather than injectable.
“These drugs [GnRH antagonists] cause competitive blockage of the GnRH receptor and hence dose-dependently suppress production of FSH and LH and inhibit secretion of ovarian steroid hormones without inducing a flare-up effect,” Belgian physicians and researchers Jacques Donnez, MD, and Marie-Madeleine Dolmans, MD, PhD, wrote in a paper published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine. “The mechanism is different from that of the GnRH agonist which, after a first phase of stimulation, desensitizes GnRH receptors, leading to full suppression of LH and FSH production and subsequently to complete suppression of [estrogen] to levels similar to those observed after bilateral oophorectomy.”
Patients who took Elagolix, the first oral nonpeptide GnRH antagonist available for the treatment of moderate to severe endometriosis-associated pain, had fewer vasomotor side effects and less bone density loss than those on the GnRH agonist leuprorelin, according to a 2018 study in Obstetrics and Gynecology. However, without add-back hormone-replacement therapy, GnRH antagonist use may need to be limited to 24 months, because of loss of bone density, a study in Cell Reports Medicine reported in 2022.
Attempting to explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis, and frustrated by the shortcomings of currently available therapies, researchers have turned to genetics for insight. A team of scientists led by Thomas Tapmeier, PhD, now a senior research fellow at Monash University in Australia, and Prof. Krina Zondervan at the University of Oxford, ran genetic analyses of families with a history of endometriosis, as well as rhesus macaques that spontaneously developed endometriosis. The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, identified NPSR1, the gene encoding neuropeptide S receptor 1, as one commonly associated with endometriosis. In trials with mouse models, they found that the NPSR1 inhibitor SHA 68R was able to reduce endometriosis-related inflammation and pain.
“It’s important to stress that there is no single gene that is responsible for endometriosis,” Dr. Tapmeier said in an interview. “This gene just has a higher frequency in people with endometriosis.”
The next step, then, would be to try to find a compound that would inhibit NPSR1 at some point, or a competitor to the ligand that binds to the receptor and blocks it, he said.
“We’re currently looking at compounds that might be able to inhibit the receptor signaling,” he said.
Such a therapy could potentially reduce the symptoms of endometriosis without interfering with the menstrual cycle and without introducing hormones that cause undesirable side effects in some patients.
“This might be a way to treat the pain and inflammation that goes with endometriosis, as well as leaving the possibility of pregnancy open,” he said.
Other researchers are searching for biomarkers of the disease, both to provide a definitive, nonsurgical diagnostic tool, and for potential, individualized treatment.
In a study published in Nature Genetics, researchers at Cedars-Sinai created a “cellular atlas” of endometriosis by analyzing nearly 400,000 individual cells from 21 patients, some of whom had the disease and some of whom did not. A new technology, single-cell genomics, allowed the scientists to profile the multiple cell types contributing to the disease.
“So the initial question we wanted to ask was about understanding how the cells look in endometriosis, compared to endometrium,” said Kate Lawrenson, PhD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Cedars-Sinai, and co–senior author of the study. “We know that they resemble the cells of the womb, but we really don’t understand if they behave the same. We had a good inkling that they would behave differently.”
It turned out they did: Cells of endometriosis interacted atypically with female hormones, compared with cells in the uterus, Dr. Lawrenson said.
“That helps us understand how, even when patients take contraceptive pills, which is a commonly prescribed therapy, it doesn’t always work, or sometimes it stops working after a while,” she said. The next step for researchers, she said, will be to pinpoint the specific causes of these altered interactions.
Meanwhile, the current research also points to diagnostic possibilities. “We were quite excited to see that multiple cell types and endometriosis are upregulating the same sets of genes,” she said. “That makes us optimistic that hopefully there are some protein gene products that are being made in abundance, and hopefully we can detect them in the blood stream. It might be that we could use that information to develop new biomarkers, or even risk stratification tools.”
In the future, a simple blood test could identify signs of endometriosis in at-risk patients and get them “fast-tracked to a specialist for evaluation,” she said. “Whereas now, they might go from PCP to gynecologist to a different gynecologist over the course of 5-10 years before they get that referral.”
This discovery, that endometrial cells use genes differently and cross-talk with nearby cells differently, presents new treatment possibilities. Maybe we can physically block how cells interact with nearby cells, Dr. Lawrenson said. One model for doing that, she said, would be antibody-based therapy, similar to the therapies now changing the treatment of cancer.
What’s most exciting, looking ahead 5-10 years, is that treatment for endometriosis in the future may be significantly more individualized, and less hormone-based, than it is today.
“What we need for endometriosis is more options for patients and something that is tailored to the molecular makeup of their disease rather than a process of trial and error,” she said.
Roughly 4 decades after she first started menstruating, Elizabeth Flanagan finally underwent surgery to repair damage wreaked on her body by endometriosis. She’d spent years struggling with a variety of seemingly random symptoms, from migraines to excruciatingly painful periods to fatigue and irritable bowel syndrome. She’d worried about abnormal labs, including “extremely high” ANA, creatinine, and BUN blood test results that had been out of normal range for more than 10 years.
She was diagnosed with endometriosis in 2016, at age 47, after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. Still, it took 5 more years before she landed in the office of a surgeon with the proper training to excise the lesions that continued to cause her so much anguish. That physician, Matthew Siedhoff, MD, at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, explained why her creatinine and BUN results were so far out of range: The endometriosis was impinging on her ureters.
The appointment left Ms. Flanagan with a range of emotions. “I was shocked that no doctor had identified this before, relieved knowing that I was finally in the hands of an expert who understood my condition, and saddened by the dearth of knowledge and proper treatment of endometriosis,” she wrote in an email.
Although the disease afflicts at least 1 out of every 10 women, endometriosis remains a conundrum for patients and their physicians. It often masquerades as other problems, from mental health issues such as anxiety and depression to physical issues such as irritable bowel syndrome. It often coexists with autoimmune conditions. Short of performing surgery, it can be a diagnosis of exclusion. And the existing, state-of-the-art treatment – hormone therapy that shuts down the reproductive system – doesn’t work for every woman every time.
“It is no wonder that it takes 10 years on average, from the time someone has symptoms of endometriosis, until they get a definitive diagnosis,” said Hugh Taylor, MD, chair of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “It’s a combination of [physicians] not taking painful menses seriously and getting distracted by all these other manifestations of the disease throughout the whole body.”
Endometriosis, he said, “is a whole-body disease.”
But recent genetic research offers the tantalizing prospect of new diagnostic tools and treatments. In 5-10 years, scientists say, physicians may be able to diagnose the disease with a simple blood test, and treat it, for example, by preventing a gene receptor from initiating a cascade of inflammatory effects, or crafting treatments tailored to the molecular makeup of a patient’s disease.
“Tomorrow’s therapies will target specifically the molecular defects of endometriosis and be nonhormonal,” Dr. Taylor said.
Guidelines published last year by the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology detail the latest standards for diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis.
According to the guidelines, physicians should consider the diagnosis of endometriosis in individuals presenting with the following cyclical and noncyclical signs and symptoms: dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, dysuria, dyschezia, painful rectal bleeding or hematuria, shoulder tip pain, catamenial pneumothorax, cyclical cough/hemoptysis/chest pain, cyclical scar swelling, and pain, fatigue, and infertility.
A clinical exam should be considered, as well as imaging such as ultrasound and/or MRI, the guidelines state, although negative findings should not rule out a diagnosis. Laparoscopy is also an option, particularly for patients who desire a definitive diagnosis or cannot be diagnosed any other way, “although negative histology [of endometriotic lesions] does not entirely rule out the disease,” the guidelines state.
To treat the pain associated with endometriosis, the guidelines advise, as a first-line therapy, beginning with NSAIDs and combined hormonal contraceptives (in oral, vaginal, or transdermal form). Another option is progesterone, including progesterone-only contraceptives, with a recommendation to prescribe a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or an etonogestrel-releasing subdermal implant to reduce endometriosis-associated pain.
However, progestins and low-dose oral contraceptives are “unsuccessful in a third of women,” Dr. Taylor and his coauthors wrote in a paper published in 2021 in The Lancet.
Until recently, the gold standard for second-line treatment of endometriosis was oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. These manage the disease by inducing medical menopause – they downregulate pituitary GnRH receptors to create a hypoestrogenic state characterized by low serum levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). GnRH agonists may be administered nasally, or through daily, monthly, or trimonthly injections. But the Food and Drug Administration advises that, when used for longer than 6 months, GnRH agonists be paired with add-back hormone replacement therapy to reduce the risk of bone loss associated with the plunge in hormone levels. Also, treatment may not be appropriate for patients who, when suddenly forced into menopause, suffer from bothersome symptoms.
The latest treatment, GnRH antagonists, are new options for patients who either do not respond adequately to progestins and low-dose contraceptives or develop progesterone resistance, and want to avoid some of the risks and/or symptoms associated with GnRH agonists. Two advantages of GnRH antagonists for patients, Dr. Taylor said, are that they have a fast onset of action and are oral rather than injectable.
“These drugs [GnRH antagonists] cause competitive blockage of the GnRH receptor and hence dose-dependently suppress production of FSH and LH and inhibit secretion of ovarian steroid hormones without inducing a flare-up effect,” Belgian physicians and researchers Jacques Donnez, MD, and Marie-Madeleine Dolmans, MD, PhD, wrote in a paper published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine. “The mechanism is different from that of the GnRH agonist which, after a first phase of stimulation, desensitizes GnRH receptors, leading to full suppression of LH and FSH production and subsequently to complete suppression of [estrogen] to levels similar to those observed after bilateral oophorectomy.”
Patients who took Elagolix, the first oral nonpeptide GnRH antagonist available for the treatment of moderate to severe endometriosis-associated pain, had fewer vasomotor side effects and less bone density loss than those on the GnRH agonist leuprorelin, according to a 2018 study in Obstetrics and Gynecology. However, without add-back hormone-replacement therapy, GnRH antagonist use may need to be limited to 24 months, because of loss of bone density, a study in Cell Reports Medicine reported in 2022.
Attempting to explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis, and frustrated by the shortcomings of currently available therapies, researchers have turned to genetics for insight. A team of scientists led by Thomas Tapmeier, PhD, now a senior research fellow at Monash University in Australia, and Prof. Krina Zondervan at the University of Oxford, ran genetic analyses of families with a history of endometriosis, as well as rhesus macaques that spontaneously developed endometriosis. The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, identified NPSR1, the gene encoding neuropeptide S receptor 1, as one commonly associated with endometriosis. In trials with mouse models, they found that the NPSR1 inhibitor SHA 68R was able to reduce endometriosis-related inflammation and pain.
“It’s important to stress that there is no single gene that is responsible for endometriosis,” Dr. Tapmeier said in an interview. “This gene just has a higher frequency in people with endometriosis.”
The next step, then, would be to try to find a compound that would inhibit NPSR1 at some point, or a competitor to the ligand that binds to the receptor and blocks it, he said.
“We’re currently looking at compounds that might be able to inhibit the receptor signaling,” he said.
Such a therapy could potentially reduce the symptoms of endometriosis without interfering with the menstrual cycle and without introducing hormones that cause undesirable side effects in some patients.
“This might be a way to treat the pain and inflammation that goes with endometriosis, as well as leaving the possibility of pregnancy open,” he said.
Other researchers are searching for biomarkers of the disease, both to provide a definitive, nonsurgical diagnostic tool, and for potential, individualized treatment.
In a study published in Nature Genetics, researchers at Cedars-Sinai created a “cellular atlas” of endometriosis by analyzing nearly 400,000 individual cells from 21 patients, some of whom had the disease and some of whom did not. A new technology, single-cell genomics, allowed the scientists to profile the multiple cell types contributing to the disease.
“So the initial question we wanted to ask was about understanding how the cells look in endometriosis, compared to endometrium,” said Kate Lawrenson, PhD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Cedars-Sinai, and co–senior author of the study. “We know that they resemble the cells of the womb, but we really don’t understand if they behave the same. We had a good inkling that they would behave differently.”
It turned out they did: Cells of endometriosis interacted atypically with female hormones, compared with cells in the uterus, Dr. Lawrenson said.
“That helps us understand how, even when patients take contraceptive pills, which is a commonly prescribed therapy, it doesn’t always work, or sometimes it stops working after a while,” she said. The next step for researchers, she said, will be to pinpoint the specific causes of these altered interactions.
Meanwhile, the current research also points to diagnostic possibilities. “We were quite excited to see that multiple cell types and endometriosis are upregulating the same sets of genes,” she said. “That makes us optimistic that hopefully there are some protein gene products that are being made in abundance, and hopefully we can detect them in the blood stream. It might be that we could use that information to develop new biomarkers, or even risk stratification tools.”
In the future, a simple blood test could identify signs of endometriosis in at-risk patients and get them “fast-tracked to a specialist for evaluation,” she said. “Whereas now, they might go from PCP to gynecologist to a different gynecologist over the course of 5-10 years before they get that referral.”
This discovery, that endometrial cells use genes differently and cross-talk with nearby cells differently, presents new treatment possibilities. Maybe we can physically block how cells interact with nearby cells, Dr. Lawrenson said. One model for doing that, she said, would be antibody-based therapy, similar to the therapies now changing the treatment of cancer.
What’s most exciting, looking ahead 5-10 years, is that treatment for endometriosis in the future may be significantly more individualized, and less hormone-based, than it is today.
“What we need for endometriosis is more options for patients and something that is tailored to the molecular makeup of their disease rather than a process of trial and error,” she said.
Surgeon gender not associated with maternal morbidity and hemorrhage after C-section
Surgeon gender was not associated with maternal morbidity or severe blood loss after cesarean delivery, a large prospective cohort study from France reports. The results have important implications for the promotion of gender equality among surgeons, obstetricians in particular, wrote a team led by Hanane Bouchghoul, MD, PhD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Bordeaux (France) University Hospital. The report is in JAMA Surgery.
“Our findings are significant in that they add substantially to the string of studies contradicting the age-old dogma that men are better surgeons than women,” the authors wrote. Previous research has suggested slightly better outcomes with female surgeons or higher complication rates with male surgeons.
The results support those of a recent Canadian retrospective analysis suggesting that patients treated by male or female surgeons for various elective indications experience similar surgical outcomes but with a slight, statistically significant decrease in 30-day mortality when treated by female surgeons.
“Policy makers need to combat prejudice against women in surgical careers, particularly in obstetrics and gynecology, so that women no longer experience conscious or unconscious barriers or difficulties in their professional choices, training, and relationships with colleagues or patients,” study corresponding author Loïc Sentilhes, MD, PhD, of Bordeaux University Hospital, said in an interview.
Facing such barriers, women may doubt their ability to be surgeons, their legitimacy as surgeons, and may not consider this type of career, he continued. “Moreover a teacher may not be as involved in teaching young female surgeons as young male surgeons, or the doctor-patient relationship may be more complicated in the event of complications if the patient thinks that a female surgeon has less competence than a male surgeon.”
The analysis drew on data from the Tranexamic Acid for Preventing Postpartum Hemorrhage after Cesarean Delivery 2 trial, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted from March 2018 through January 2020 in mothers from 27 French maternity hospitals.
Eligible participants had a cesarean delivery before or during labor at or after 34 weeks’ gestation. The primary endpoint was the incidence of a composite maternal morbidity variable, and the secondary endpoint was the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage, defined by a calculated estimated blood loss exceeding 1,000 mL or transfusion by day 2.
Among the 4,244 women included, male surgeons performed 943 cesarean deliveries (22.2%) and female surgeons performed 3,301 (77.8%). The percentage who were attending obstetricians was higher for men at 441 of 929 (47.5%) than women at 687 of 3,239 (21.2%).
The observed risk of maternal morbidity did not differ between male and female surgeons: 119 of 837 (14.2%) vs. 476 of 2,928 (16.3%), for an adjusted risk ratio (aRR) of 0.92 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.77-1.13). Interaction between surgeon gender and level of experience with the risk of maternal morbidity was not statistically significant; nor did the groups differ specifically by risk for postpartum hemorrhage: aRR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.85-1.13).
Despite the longstanding stereotype that men perform surgery better than women, and the traditional preponderance of male surgeons, the authors noted, postoperative morbidity and mortality may be lower after various surgeries performed by women.
The TRAAP2 trial
In an accompanying editorial, Amanda Fader, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, and colleagues caution that the French study’s methodology may not fully account for the complex intersection of surgeon volume, experience, gender, clinical decision-making skills, and patient-level and clinical factors affecting outcomes.
That said, appraising surgical outcomes based on gender may be an essential step toward reducing implicit bias and dispelling engendered perceptions regarding gender and technical proficiency, the commentators stated. “To definitively dispel archaic, gender-based notions about performance in clinical or surgical settings, efforts must go beyond peer-reviewed research,” Dr. Fader said in an interview. “Medical institutions and leaders of clinical departments must make concerted efforts to recruit, mentor, support, and promote women and persons of all genders in medicine – as well as confront any discriminatory perceptions and experiences concerning sex, race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, or economic class.”
This study was supported by the French Ministry of Health under its Clinical Research Hospital Program. Dr. Sentilhes reported financial relationships with Dilafor, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sigvaris, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals. The editorial commentators disclosed no funding for their commentary or conflicts of interest.
Surgeon gender was not associated with maternal morbidity or severe blood loss after cesarean delivery, a large prospective cohort study from France reports. The results have important implications for the promotion of gender equality among surgeons, obstetricians in particular, wrote a team led by Hanane Bouchghoul, MD, PhD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Bordeaux (France) University Hospital. The report is in JAMA Surgery.
“Our findings are significant in that they add substantially to the string of studies contradicting the age-old dogma that men are better surgeons than women,” the authors wrote. Previous research has suggested slightly better outcomes with female surgeons or higher complication rates with male surgeons.
The results support those of a recent Canadian retrospective analysis suggesting that patients treated by male or female surgeons for various elective indications experience similar surgical outcomes but with a slight, statistically significant decrease in 30-day mortality when treated by female surgeons.
“Policy makers need to combat prejudice against women in surgical careers, particularly in obstetrics and gynecology, so that women no longer experience conscious or unconscious barriers or difficulties in their professional choices, training, and relationships with colleagues or patients,” study corresponding author Loïc Sentilhes, MD, PhD, of Bordeaux University Hospital, said in an interview.
Facing such barriers, women may doubt their ability to be surgeons, their legitimacy as surgeons, and may not consider this type of career, he continued. “Moreover a teacher may not be as involved in teaching young female surgeons as young male surgeons, or the doctor-patient relationship may be more complicated in the event of complications if the patient thinks that a female surgeon has less competence than a male surgeon.”
The analysis drew on data from the Tranexamic Acid for Preventing Postpartum Hemorrhage after Cesarean Delivery 2 trial, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted from March 2018 through January 2020 in mothers from 27 French maternity hospitals.
Eligible participants had a cesarean delivery before or during labor at or after 34 weeks’ gestation. The primary endpoint was the incidence of a composite maternal morbidity variable, and the secondary endpoint was the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage, defined by a calculated estimated blood loss exceeding 1,000 mL or transfusion by day 2.
Among the 4,244 women included, male surgeons performed 943 cesarean deliveries (22.2%) and female surgeons performed 3,301 (77.8%). The percentage who were attending obstetricians was higher for men at 441 of 929 (47.5%) than women at 687 of 3,239 (21.2%).
The observed risk of maternal morbidity did not differ between male and female surgeons: 119 of 837 (14.2%) vs. 476 of 2,928 (16.3%), for an adjusted risk ratio (aRR) of 0.92 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.77-1.13). Interaction between surgeon gender and level of experience with the risk of maternal morbidity was not statistically significant; nor did the groups differ specifically by risk for postpartum hemorrhage: aRR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.85-1.13).
Despite the longstanding stereotype that men perform surgery better than women, and the traditional preponderance of male surgeons, the authors noted, postoperative morbidity and mortality may be lower after various surgeries performed by women.
The TRAAP2 trial
In an accompanying editorial, Amanda Fader, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, and colleagues caution that the French study’s methodology may not fully account for the complex intersection of surgeon volume, experience, gender, clinical decision-making skills, and patient-level and clinical factors affecting outcomes.
That said, appraising surgical outcomes based on gender may be an essential step toward reducing implicit bias and dispelling engendered perceptions regarding gender and technical proficiency, the commentators stated. “To definitively dispel archaic, gender-based notions about performance in clinical or surgical settings, efforts must go beyond peer-reviewed research,” Dr. Fader said in an interview. “Medical institutions and leaders of clinical departments must make concerted efforts to recruit, mentor, support, and promote women and persons of all genders in medicine – as well as confront any discriminatory perceptions and experiences concerning sex, race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, or economic class.”
This study was supported by the French Ministry of Health under its Clinical Research Hospital Program. Dr. Sentilhes reported financial relationships with Dilafor, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sigvaris, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals. The editorial commentators disclosed no funding for their commentary or conflicts of interest.
Surgeon gender was not associated with maternal morbidity or severe blood loss after cesarean delivery, a large prospective cohort study from France reports. The results have important implications for the promotion of gender equality among surgeons, obstetricians in particular, wrote a team led by Hanane Bouchghoul, MD, PhD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Bordeaux (France) University Hospital. The report is in JAMA Surgery.
“Our findings are significant in that they add substantially to the string of studies contradicting the age-old dogma that men are better surgeons than women,” the authors wrote. Previous research has suggested slightly better outcomes with female surgeons or higher complication rates with male surgeons.
The results support those of a recent Canadian retrospective analysis suggesting that patients treated by male or female surgeons for various elective indications experience similar surgical outcomes but with a slight, statistically significant decrease in 30-day mortality when treated by female surgeons.
“Policy makers need to combat prejudice against women in surgical careers, particularly in obstetrics and gynecology, so that women no longer experience conscious or unconscious barriers or difficulties in their professional choices, training, and relationships with colleagues or patients,” study corresponding author Loïc Sentilhes, MD, PhD, of Bordeaux University Hospital, said in an interview.
Facing such barriers, women may doubt their ability to be surgeons, their legitimacy as surgeons, and may not consider this type of career, he continued. “Moreover a teacher may not be as involved in teaching young female surgeons as young male surgeons, or the doctor-patient relationship may be more complicated in the event of complications if the patient thinks that a female surgeon has less competence than a male surgeon.”
The analysis drew on data from the Tranexamic Acid for Preventing Postpartum Hemorrhage after Cesarean Delivery 2 trial, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted from March 2018 through January 2020 in mothers from 27 French maternity hospitals.
Eligible participants had a cesarean delivery before or during labor at or after 34 weeks’ gestation. The primary endpoint was the incidence of a composite maternal morbidity variable, and the secondary endpoint was the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage, defined by a calculated estimated blood loss exceeding 1,000 mL or transfusion by day 2.
Among the 4,244 women included, male surgeons performed 943 cesarean deliveries (22.2%) and female surgeons performed 3,301 (77.8%). The percentage who were attending obstetricians was higher for men at 441 of 929 (47.5%) than women at 687 of 3,239 (21.2%).
The observed risk of maternal morbidity did not differ between male and female surgeons: 119 of 837 (14.2%) vs. 476 of 2,928 (16.3%), for an adjusted risk ratio (aRR) of 0.92 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.77-1.13). Interaction between surgeon gender and level of experience with the risk of maternal morbidity was not statistically significant; nor did the groups differ specifically by risk for postpartum hemorrhage: aRR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.85-1.13).
Despite the longstanding stereotype that men perform surgery better than women, and the traditional preponderance of male surgeons, the authors noted, postoperative morbidity and mortality may be lower after various surgeries performed by women.
The TRAAP2 trial
In an accompanying editorial, Amanda Fader, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, and colleagues caution that the French study’s methodology may not fully account for the complex intersection of surgeon volume, experience, gender, clinical decision-making skills, and patient-level and clinical factors affecting outcomes.
That said, appraising surgical outcomes based on gender may be an essential step toward reducing implicit bias and dispelling engendered perceptions regarding gender and technical proficiency, the commentators stated. “To definitively dispel archaic, gender-based notions about performance in clinical or surgical settings, efforts must go beyond peer-reviewed research,” Dr. Fader said in an interview. “Medical institutions and leaders of clinical departments must make concerted efforts to recruit, mentor, support, and promote women and persons of all genders in medicine – as well as confront any discriminatory perceptions and experiences concerning sex, race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, or economic class.”
This study was supported by the French Ministry of Health under its Clinical Research Hospital Program. Dr. Sentilhes reported financial relationships with Dilafor, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sigvaris, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals. The editorial commentators disclosed no funding for their commentary or conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Update on secondary cytoreduction in recurrent ovarian cancer
Recurrent ovarian cancer is difficult to treat; it has high recurrence rates and poor targeted treatment options. Between 60% and 75% of patients initially diagnosed with advanced-stage ovarian cancer will relapse within 2-3 years.1 Survival for these patients is poor, with an average overall survival (OS) of 30-40 months from the time of recurrence.2 Historically, immunotherapy has shown poor efficacy for recurrent ovarian malignancy, leaving few options for patients and their providers. Given the lack of effective treatment options, secondary cytoreductive surgery (surgery at the time of recurrence) has been heavily studied as a potential therapeutic option.
The initial rationale for cytoreductive surgery (CRS) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer focused on palliation of symptoms from large, bulky disease that frequently caused obstructive symptoms and pain. Now, cytoreduction is a critical part of therapy. It decreases chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells, improves the immune response, and is thought to optimize perfusion of the residual cancer for systemic therapy. The survival benefit of surgery in the frontline setting, either with primary or interval debulking, is well established, and much of the data now demonstrate that complete resection of all macroscopic disease (also known as an R0 resection) has the greatest survival benefit.3 Given the benefits of an initial debulking surgery, secondary cytoreduction has been studied since the 1980s with mixed results. These data have demonstrated that the largest barrier to care has been appropriate patient selection for this often complex surgical procedure.
The 2020 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines list secondary CRS as a treatment option; however, the procedure should only be considered in patients who have platinum sensitive disease, a performance status of 0-1, no ascites, and an isolated focus or limited focus of disease that is amenable to complete resection. Numerous retrospective studies have suggested that secondary CRS is beneficial to patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, especially if complete cytoreduction can be accomplished. Many of these studies have similarly concluded that there are benefits, such as less ascites at the time of recurrence, smaller disease burden, and a longer disease-free interval. From that foundation, multiple groups used retrospective data to investigate prognostic models to determine who would benefit most from secondary cytoreduction.
The DESKTOP Group initially published their retrospective study in 2006 and created a scoring system assessing who would benefit from secondary CRS.4 Data demonstrated that a performance status of 0, FIGO stage of I/II at the time of initial diagnosis, no residual tumor after primary surgery, and ascites less than 500 mL were associated with improved survival after secondary cytoreduction. They created the AGO score out of these data, which is positive only if three criteria are met: a performance status of 0, R0 after primary debulk, and ascites less than 500 mL at the time of recurrence.
They prospectively tested this score in DESKTOP II, which validated their findings and showed that complete secondary CRS could be achieved in 76% of those with a positive AGO score.5 Many believed that the AGO score was too restrictive, and a second retrospective study performed by a group at Memorial Sloan Kettering showed that optimal secondary cytoreduction could be achieved to prolong survival by a median of 30 months in patients with a longer disease-free interval, a single site of recurrence, and residual disease measuring less than 5 mm at time of initial/first-line surgery.6 Many individuals now use this scoring system to determine candidacy for secondary debulking: disease-free interval, number of sites of recurrence (ideally oligometastatic disease), and residual disease less than 5 mm at the time of primary debulking.
Finally, the iMODEL was developed by a group from China and found that complete R0 secondary CRS was associated with a low initial FIGO stage, no residual disease after primary surgery, longer platinum-free interval, better Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, lower CA-125 levels, as well as no ascites at the time of recurrence. Based on these criteria, individuals received either high or low iMODEL scores, and those with a low score were said to be candidates for secondary CRS. Overall, these models demonstrate that the strongest predictive factor that suggests a survival benefit from secondary CRS is the ability to achieve a complete R0 resection at the time of surgery.
Secondary debulking surgery has been tested in three large randomized controlled trials. The DESKTOP investigators and the SOC-1 trial have been the most successful groups to publish on this topic with positive results. Both groups use prognostic models for their inclusion criteria to select candidates in whom an R0 resection is believed to be most feasible. The first randomized controlled trial to publish on this topic was GOG-213,7 which did not use prognostic modeling for their inclusion criteria. Patients were randomized to secondary cytoreduction followed by platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab versus chemotherapy alone. The median OS was 50.6 months in the surgery group and 64.7 months in the no-surgery group (P = .08), suggesting no survival benefit to secondary cytoreduction; however, an ad hoc exploratory analysis of the surgery arm showed that both overall and progression-free survival were significantly improved in the complete cytoreduction group, compared with those with residual disease at time of surgery.
The results from the GOG-213 group suggested that improved survival from secondary debulking might be achieved when prognostic modeling is used to select optimal surgical candidates. The SOC-1 trial, published in 2021, was a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial that used the iMODEL scoring system combined with PET/CT imaging for patient selection.8 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Complete cytoreduction was achieved in 73% of patients with a low iMODEL score, and these data showed improved OS in the surgery group of 58.1 months versus 53.9 months (P < .05) in the no-surgery group. Lastly, the DESKTOP group most recently published results on this topic in a large randomized, controlled trial.9 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Inclusion criteria were only met in patients with a positive AGO score. An improved OS of 7.7 months (53.7 vs. 46 months; P < .05) was demonstrated in patients that underwent surgery versus those exposed to only chemotherapy. Again, this group showed that overall survival was further improved when complete cytoreduction was achieved.
Given the results of these three trials, the Society for Gynecologic Oncology has released a statement on secondary cytoreduction in recurrent ovarian cancer (see Table).10 While it is important to use caution when comparing the three studies as study populations differed substantially, the most important takeaway the difference in survival outcomes in patients in whom complete gross resection was achieved versus no complete gross resection versus no surgery. This comparison highlights the benefit of complete cytoreduction as well as the potential harms of secondary debulking when an R0 resection cannot be achieved. Although not yet evaluated in this clinical setting, laparoscopic exploration may be useful to augment assessment of disease extent and possibility of disease resection, just as it is in frontline ovarian cancer surgery.
The importance of bevacizumab use in recurrent ovarian cancer is also highlighted in the SGO statement. In GOG-213, 84% of the total study population (in both the surgery and no surgery cohort) were treated with concurrent followed by maintenance bevacizumab with an improved survival outcome, which may suggest that this trial generalizes better than the others to contemporary management of platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer.
Overall, given the mixed data, the recommendation is for surgeons to consider all available data to guide them in treatment planning with a strong emphasis on using all available technology to assess whether complete cytoreduction can be achieved in the setting of recurrence so as to not delay the patient’s ability to receive chemotherapy.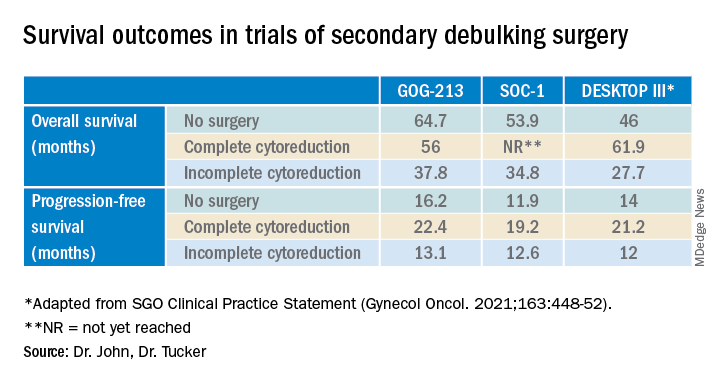
Dr. John is a gynecologic oncology fellow at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
1. du Bois A et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1320-9.
2. Wagner U et al. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:588-91.
3. Vergote I et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:943-53.
4. Harter P et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:1702-10.
5. Harter P et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21:289-95.
6. Chi DS et al. Cancer. 2006 106:1933-9.
7. Coleman RL et al. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:779-1.
8. Shi T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:439-49.
9. Harter P et al. N Engl J Med 2021;385:2123-31.
10. Harrison R, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2021;163:448-52.
Recurrent ovarian cancer is difficult to treat; it has high recurrence rates and poor targeted treatment options. Between 60% and 75% of patients initially diagnosed with advanced-stage ovarian cancer will relapse within 2-3 years.1 Survival for these patients is poor, with an average overall survival (OS) of 30-40 months from the time of recurrence.2 Historically, immunotherapy has shown poor efficacy for recurrent ovarian malignancy, leaving few options for patients and their providers. Given the lack of effective treatment options, secondary cytoreductive surgery (surgery at the time of recurrence) has been heavily studied as a potential therapeutic option.
The initial rationale for cytoreductive surgery (CRS) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer focused on palliation of symptoms from large, bulky disease that frequently caused obstructive symptoms and pain. Now, cytoreduction is a critical part of therapy. It decreases chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells, improves the immune response, and is thought to optimize perfusion of the residual cancer for systemic therapy. The survival benefit of surgery in the frontline setting, either with primary or interval debulking, is well established, and much of the data now demonstrate that complete resection of all macroscopic disease (also known as an R0 resection) has the greatest survival benefit.3 Given the benefits of an initial debulking surgery, secondary cytoreduction has been studied since the 1980s with mixed results. These data have demonstrated that the largest barrier to care has been appropriate patient selection for this often complex surgical procedure.
The 2020 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines list secondary CRS as a treatment option; however, the procedure should only be considered in patients who have platinum sensitive disease, a performance status of 0-1, no ascites, and an isolated focus or limited focus of disease that is amenable to complete resection. Numerous retrospective studies have suggested that secondary CRS is beneficial to patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, especially if complete cytoreduction can be accomplished. Many of these studies have similarly concluded that there are benefits, such as less ascites at the time of recurrence, smaller disease burden, and a longer disease-free interval. From that foundation, multiple groups used retrospective data to investigate prognostic models to determine who would benefit most from secondary cytoreduction.
The DESKTOP Group initially published their retrospective study in 2006 and created a scoring system assessing who would benefit from secondary CRS.4 Data demonstrated that a performance status of 0, FIGO stage of I/II at the time of initial diagnosis, no residual tumor after primary surgery, and ascites less than 500 mL were associated with improved survival after secondary cytoreduction. They created the AGO score out of these data, which is positive only if three criteria are met: a performance status of 0, R0 after primary debulk, and ascites less than 500 mL at the time of recurrence.
They prospectively tested this score in DESKTOP II, which validated their findings and showed that complete secondary CRS could be achieved in 76% of those with a positive AGO score.5 Many believed that the AGO score was too restrictive, and a second retrospective study performed by a group at Memorial Sloan Kettering showed that optimal secondary cytoreduction could be achieved to prolong survival by a median of 30 months in patients with a longer disease-free interval, a single site of recurrence, and residual disease measuring less than 5 mm at time of initial/first-line surgery.6 Many individuals now use this scoring system to determine candidacy for secondary debulking: disease-free interval, number of sites of recurrence (ideally oligometastatic disease), and residual disease less than 5 mm at the time of primary debulking.
Finally, the iMODEL was developed by a group from China and found that complete R0 secondary CRS was associated with a low initial FIGO stage, no residual disease after primary surgery, longer platinum-free interval, better Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, lower CA-125 levels, as well as no ascites at the time of recurrence. Based on these criteria, individuals received either high or low iMODEL scores, and those with a low score were said to be candidates for secondary CRS. Overall, these models demonstrate that the strongest predictive factor that suggests a survival benefit from secondary CRS is the ability to achieve a complete R0 resection at the time of surgery.
Secondary debulking surgery has been tested in three large randomized controlled trials. The DESKTOP investigators and the SOC-1 trial have been the most successful groups to publish on this topic with positive results. Both groups use prognostic models for their inclusion criteria to select candidates in whom an R0 resection is believed to be most feasible. The first randomized controlled trial to publish on this topic was GOG-213,7 which did not use prognostic modeling for their inclusion criteria. Patients were randomized to secondary cytoreduction followed by platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab versus chemotherapy alone. The median OS was 50.6 months in the surgery group and 64.7 months in the no-surgery group (P = .08), suggesting no survival benefit to secondary cytoreduction; however, an ad hoc exploratory analysis of the surgery arm showed that both overall and progression-free survival were significantly improved in the complete cytoreduction group, compared with those with residual disease at time of surgery.
The results from the GOG-213 group suggested that improved survival from secondary debulking might be achieved when prognostic modeling is used to select optimal surgical candidates. The SOC-1 trial, published in 2021, was a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial that used the iMODEL scoring system combined with PET/CT imaging for patient selection.8 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Complete cytoreduction was achieved in 73% of patients with a low iMODEL score, and these data showed improved OS in the surgery group of 58.1 months versus 53.9 months (P < .05) in the no-surgery group. Lastly, the DESKTOP group most recently published results on this topic in a large randomized, controlled trial.9 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Inclusion criteria were only met in patients with a positive AGO score. An improved OS of 7.7 months (53.7 vs. 46 months; P < .05) was demonstrated in patients that underwent surgery versus those exposed to only chemotherapy. Again, this group showed that overall survival was further improved when complete cytoreduction was achieved.
Given the results of these three trials, the Society for Gynecologic Oncology has released a statement on secondary cytoreduction in recurrent ovarian cancer (see Table).10 While it is important to use caution when comparing the three studies as study populations differed substantially, the most important takeaway the difference in survival outcomes in patients in whom complete gross resection was achieved versus no complete gross resection versus no surgery. This comparison highlights the benefit of complete cytoreduction as well as the potential harms of secondary debulking when an R0 resection cannot be achieved. Although not yet evaluated in this clinical setting, laparoscopic exploration may be useful to augment assessment of disease extent and possibility of disease resection, just as it is in frontline ovarian cancer surgery.
The importance of bevacizumab use in recurrent ovarian cancer is also highlighted in the SGO statement. In GOG-213, 84% of the total study population (in both the surgery and no surgery cohort) were treated with concurrent followed by maintenance bevacizumab with an improved survival outcome, which may suggest that this trial generalizes better than the others to contemporary management of platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer.
Overall, given the mixed data, the recommendation is for surgeons to consider all available data to guide them in treatment planning with a strong emphasis on using all available technology to assess whether complete cytoreduction can be achieved in the setting of recurrence so as to not delay the patient’s ability to receive chemotherapy.
Dr. John is a gynecologic oncology fellow at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
1. du Bois A et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1320-9.
2. Wagner U et al. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:588-91.
3. Vergote I et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:943-53.
4. Harter P et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:1702-10.
5. Harter P et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21:289-95.
6. Chi DS et al. Cancer. 2006 106:1933-9.
7. Coleman RL et al. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:779-1.
8. Shi T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:439-49.
9. Harter P et al. N Engl J Med 2021;385:2123-31.
10. Harrison R, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2021;163:448-52.
Recurrent ovarian cancer is difficult to treat; it has high recurrence rates and poor targeted treatment options. Between 60% and 75% of patients initially diagnosed with advanced-stage ovarian cancer will relapse within 2-3 years.1 Survival for these patients is poor, with an average overall survival (OS) of 30-40 months from the time of recurrence.2 Historically, immunotherapy has shown poor efficacy for recurrent ovarian malignancy, leaving few options for patients and their providers. Given the lack of effective treatment options, secondary cytoreductive surgery (surgery at the time of recurrence) has been heavily studied as a potential therapeutic option.
The initial rationale for cytoreductive surgery (CRS) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer focused on palliation of symptoms from large, bulky disease that frequently caused obstructive symptoms and pain. Now, cytoreduction is a critical part of therapy. It decreases chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells, improves the immune response, and is thought to optimize perfusion of the residual cancer for systemic therapy. The survival benefit of surgery in the frontline setting, either with primary or interval debulking, is well established, and much of the data now demonstrate that complete resection of all macroscopic disease (also known as an R0 resection) has the greatest survival benefit.3 Given the benefits of an initial debulking surgery, secondary cytoreduction has been studied since the 1980s with mixed results. These data have demonstrated that the largest barrier to care has been appropriate patient selection for this often complex surgical procedure.
The 2020 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines list secondary CRS as a treatment option; however, the procedure should only be considered in patients who have platinum sensitive disease, a performance status of 0-1, no ascites, and an isolated focus or limited focus of disease that is amenable to complete resection. Numerous retrospective studies have suggested that secondary CRS is beneficial to patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, especially if complete cytoreduction can be accomplished. Many of these studies have similarly concluded that there are benefits, such as less ascites at the time of recurrence, smaller disease burden, and a longer disease-free interval. From that foundation, multiple groups used retrospective data to investigate prognostic models to determine who would benefit most from secondary cytoreduction.
The DESKTOP Group initially published their retrospective study in 2006 and created a scoring system assessing who would benefit from secondary CRS.4 Data demonstrated that a performance status of 0, FIGO stage of I/II at the time of initial diagnosis, no residual tumor after primary surgery, and ascites less than 500 mL were associated with improved survival after secondary cytoreduction. They created the AGO score out of these data, which is positive only if three criteria are met: a performance status of 0, R0 after primary debulk, and ascites less than 500 mL at the time of recurrence.
They prospectively tested this score in DESKTOP II, which validated their findings and showed that complete secondary CRS could be achieved in 76% of those with a positive AGO score.5 Many believed that the AGO score was too restrictive, and a second retrospective study performed by a group at Memorial Sloan Kettering showed that optimal secondary cytoreduction could be achieved to prolong survival by a median of 30 months in patients with a longer disease-free interval, a single site of recurrence, and residual disease measuring less than 5 mm at time of initial/first-line surgery.6 Many individuals now use this scoring system to determine candidacy for secondary debulking: disease-free interval, number of sites of recurrence (ideally oligometastatic disease), and residual disease less than 5 mm at the time of primary debulking.
Finally, the iMODEL was developed by a group from China and found that complete R0 secondary CRS was associated with a low initial FIGO stage, no residual disease after primary surgery, longer platinum-free interval, better Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, lower CA-125 levels, as well as no ascites at the time of recurrence. Based on these criteria, individuals received either high or low iMODEL scores, and those with a low score were said to be candidates for secondary CRS. Overall, these models demonstrate that the strongest predictive factor that suggests a survival benefit from secondary CRS is the ability to achieve a complete R0 resection at the time of surgery.
Secondary debulking surgery has been tested in three large randomized controlled trials. The DESKTOP investigators and the SOC-1 trial have been the most successful groups to publish on this topic with positive results. Both groups use prognostic models for their inclusion criteria to select candidates in whom an R0 resection is believed to be most feasible. The first randomized controlled trial to publish on this topic was GOG-213,7 which did not use prognostic modeling for their inclusion criteria. Patients were randomized to secondary cytoreduction followed by platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab versus chemotherapy alone. The median OS was 50.6 months in the surgery group and 64.7 months in the no-surgery group (P = .08), suggesting no survival benefit to secondary cytoreduction; however, an ad hoc exploratory analysis of the surgery arm showed that both overall and progression-free survival were significantly improved in the complete cytoreduction group, compared with those with residual disease at time of surgery.
The results from the GOG-213 group suggested that improved survival from secondary debulking might be achieved when prognostic modeling is used to select optimal surgical candidates. The SOC-1 trial, published in 2021, was a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial that used the iMODEL scoring system combined with PET/CT imaging for patient selection.8 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Complete cytoreduction was achieved in 73% of patients with a low iMODEL score, and these data showed improved OS in the surgery group of 58.1 months versus 53.9 months (P < .05) in the no-surgery group. Lastly, the DESKTOP group most recently published results on this topic in a large randomized, controlled trial.9 Patients were again randomized to surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Inclusion criteria were only met in patients with a positive AGO score. An improved OS of 7.7 months (53.7 vs. 46 months; P < .05) was demonstrated in patients that underwent surgery versus those exposed to only chemotherapy. Again, this group showed that overall survival was further improved when complete cytoreduction was achieved.
Given the results of these three trials, the Society for Gynecologic Oncology has released a statement on secondary cytoreduction in recurrent ovarian cancer (see Table).10 While it is important to use caution when comparing the three studies as study populations differed substantially, the most important takeaway the difference in survival outcomes in patients in whom complete gross resection was achieved versus no complete gross resection versus no surgery. This comparison highlights the benefit of complete cytoreduction as well as the potential harms of secondary debulking when an R0 resection cannot be achieved. Although not yet evaluated in this clinical setting, laparoscopic exploration may be useful to augment assessment of disease extent and possibility of disease resection, just as it is in frontline ovarian cancer surgery.
The importance of bevacizumab use in recurrent ovarian cancer is also highlighted in the SGO statement. In GOG-213, 84% of the total study population (in both the surgery and no surgery cohort) were treated with concurrent followed by maintenance bevacizumab with an improved survival outcome, which may suggest that this trial generalizes better than the others to contemporary management of platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer.
Overall, given the mixed data, the recommendation is for surgeons to consider all available data to guide them in treatment planning with a strong emphasis on using all available technology to assess whether complete cytoreduction can be achieved in the setting of recurrence so as to not delay the patient’s ability to receive chemotherapy.
Dr. John is a gynecologic oncology fellow at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
1. du Bois A et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1320-9.
2. Wagner U et al. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:588-91.
3. Vergote I et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:943-53.
4. Harter P et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:1702-10.
5. Harter P et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21:289-95.
6. Chi DS et al. Cancer. 2006 106:1933-9.
7. Coleman RL et al. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:779-1.
8. Shi T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:439-49.
9. Harter P et al. N Engl J Med 2021;385:2123-31.
10. Harrison R, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2021;163:448-52.










