User login
Flu activity measures continue COVID-19–related divergence
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.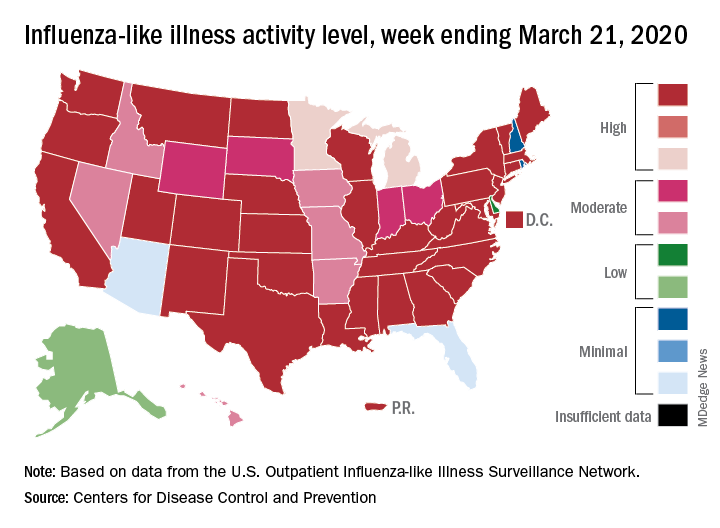
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.
Flu now riding on COVID-19’s coattails
The viral tsunami that is COVID-19 has hit the United States, and influenza appears to be riding the crest of the wave.
according to the Centers for Disease Control. Flu-related visits went from 5.2% of all outpatient visits the week before to 5.8% during the week ending March 14.
“The COVID-19 outbreak unfolding in the United States may affect healthcare seeking behavior which in turn would impact data from” the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the CDC explained.
Data from clinical laboratories show that, despite the increased activity, fewer respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza: 15.3% for the week of March 8-14, compared with 21.1% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division said in its latest FluView report.
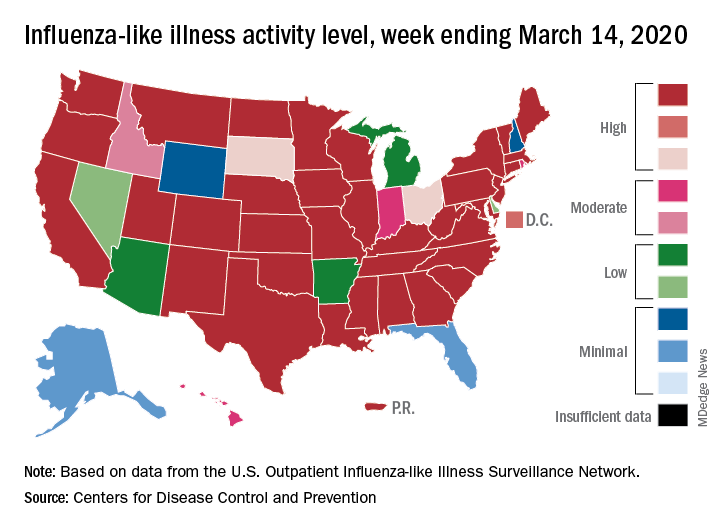
Influenza activity also increased slightly among the states, with 35 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, versus 34 states and Puerto Rico the previous week. The count was down to 33 for the last week of February, CDC data show.
Severity measures remain mixed as overall hospitalization continues to be moderate but rates for children aged 0-4 years and adults aged 18-49 years are the highest on record and rates for children aged 5-17 years are the highest since the 2009 pandemic, the influenza division said.
Mortality data present a similar picture: The overall death rate is low, but the 149 flu-related deaths reported among children is the most for this point of the season since 2009, the CDC said.
The viral tsunami that is COVID-19 has hit the United States, and influenza appears to be riding the crest of the wave.

according to the Centers for Disease Control. Flu-related visits went from 5.2% of all outpatient visits the week before to 5.8% during the week ending March 14.
“The COVID-19 outbreak unfolding in the United States may affect healthcare seeking behavior which in turn would impact data from” the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the CDC explained.
Data from clinical laboratories show that, despite the increased activity, fewer respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza: 15.3% for the week of March 8-14, compared with 21.1% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division said in its latest FluView report.
Influenza activity also increased slightly among the states, with 35 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, versus 34 states and Puerto Rico the previous week. The count was down to 33 for the last week of February, CDC data show.
Severity measures remain mixed as overall hospitalization continues to be moderate but rates for children aged 0-4 years and adults aged 18-49 years are the highest on record and rates for children aged 5-17 years are the highest since the 2009 pandemic, the influenza division said.
Mortality data present a similar picture: The overall death rate is low, but the 149 flu-related deaths reported among children is the most for this point of the season since 2009, the CDC said.
The viral tsunami that is COVID-19 has hit the United States, and influenza appears to be riding the crest of the wave.

according to the Centers for Disease Control. Flu-related visits went from 5.2% of all outpatient visits the week before to 5.8% during the week ending March 14.
“The COVID-19 outbreak unfolding in the United States may affect healthcare seeking behavior which in turn would impact data from” the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the CDC explained.
Data from clinical laboratories show that, despite the increased activity, fewer respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza: 15.3% for the week of March 8-14, compared with 21.1% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division said in its latest FluView report.
Influenza activity also increased slightly among the states, with 35 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, versus 34 states and Puerto Rico the previous week. The count was down to 33 for the last week of February, CDC data show.
Severity measures remain mixed as overall hospitalization continues to be moderate but rates for children aged 0-4 years and adults aged 18-49 years are the highest on record and rates for children aged 5-17 years are the highest since the 2009 pandemic, the influenza division said.
Mortality data present a similar picture: The overall death rate is low, but the 149 flu-related deaths reported among children is the most for this point of the season since 2009, the CDC said.
Inactivated flu vaccine succeeds among autoimmune rheumatic disease patients
Use of the inactivated influenza vaccine by adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases significantly reduced their risk of influenza-like illness, hospitalization for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and death from pneumonia, according to findings from an observational study of more than 30,000 patients in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Although the inactivated vaccine has been recommended for patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs), including rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis, the vaccine’s impact on patient outcomes including pneumonia, hospitalization, and death has not been well studied, wrote Georgina Nakafero, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 30,788 adults with AIRDs from the longitudinal Clinical Practice Research Datalink database in the United Kingdom. Of these, 66% were women, 76% had rheumatoid arthritis, and 61% had been prescribed methotrexate. The study included a total of 125,034 flu cycles between 2006 and 2009 and between 2010 and 2015.
Overall, vaccination with the inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) reduced the risk of primary care consultation for influenza-like illness (adjusted odds ratio, 0.70), hospitalization for pneumonia (aOR, 0.61), exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (aOR, 0.67), and death caused by pneumonia (aOR, 0.48) in the study population. In a propensity score–adjusted analysis, only protection from influenza-like illness lost statistical significance.
In addition, vaccination was associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality among AIRDs patients, but restricting the outcomes to the active influenza periods may have confounded this result, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including observational design, the use of a single vaccine efficacy estimate for each outcome, potential missed vaccination cycles, and potential confounding by indication and healthy user bias that could inflate the vaccine effectiveness, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, including a range of AIRDs, and the use of both diagnostic and prescription codes, they said.
“The findings of this study, together with the results of our previous study demonstrating the safety of IIV in people with AIRDs, provides evidence to promote seasonal flu vaccination in this population,” they concluded. They still emphasized that randomized, controlled trials are needed for an assessment of vaccine efficacy.
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis and the National Institute of Health Research. Lead author Dr. Nakafero had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with companies, including AstraZeneca, Roche, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Nakafero G et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Mar 11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa078.
Use of the inactivated influenza vaccine by adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases significantly reduced their risk of influenza-like illness, hospitalization for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and death from pneumonia, according to findings from an observational study of more than 30,000 patients in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Although the inactivated vaccine has been recommended for patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs), including rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis, the vaccine’s impact on patient outcomes including pneumonia, hospitalization, and death has not been well studied, wrote Georgina Nakafero, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 30,788 adults with AIRDs from the longitudinal Clinical Practice Research Datalink database in the United Kingdom. Of these, 66% were women, 76% had rheumatoid arthritis, and 61% had been prescribed methotrexate. The study included a total of 125,034 flu cycles between 2006 and 2009 and between 2010 and 2015.
Overall, vaccination with the inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) reduced the risk of primary care consultation for influenza-like illness (adjusted odds ratio, 0.70), hospitalization for pneumonia (aOR, 0.61), exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (aOR, 0.67), and death caused by pneumonia (aOR, 0.48) in the study population. In a propensity score–adjusted analysis, only protection from influenza-like illness lost statistical significance.
In addition, vaccination was associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality among AIRDs patients, but restricting the outcomes to the active influenza periods may have confounded this result, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including observational design, the use of a single vaccine efficacy estimate for each outcome, potential missed vaccination cycles, and potential confounding by indication and healthy user bias that could inflate the vaccine effectiveness, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, including a range of AIRDs, and the use of both diagnostic and prescription codes, they said.
“The findings of this study, together with the results of our previous study demonstrating the safety of IIV in people with AIRDs, provides evidence to promote seasonal flu vaccination in this population,” they concluded. They still emphasized that randomized, controlled trials are needed for an assessment of vaccine efficacy.
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis and the National Institute of Health Research. Lead author Dr. Nakafero had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with companies, including AstraZeneca, Roche, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Nakafero G et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Mar 11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa078.
Use of the inactivated influenza vaccine by adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases significantly reduced their risk of influenza-like illness, hospitalization for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and death from pneumonia, according to findings from an observational study of more than 30,000 patients in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Although the inactivated vaccine has been recommended for patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs), including rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis, the vaccine’s impact on patient outcomes including pneumonia, hospitalization, and death has not been well studied, wrote Georgina Nakafero, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 30,788 adults with AIRDs from the longitudinal Clinical Practice Research Datalink database in the United Kingdom. Of these, 66% were women, 76% had rheumatoid arthritis, and 61% had been prescribed methotrexate. The study included a total of 125,034 flu cycles between 2006 and 2009 and between 2010 and 2015.
Overall, vaccination with the inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) reduced the risk of primary care consultation for influenza-like illness (adjusted odds ratio, 0.70), hospitalization for pneumonia (aOR, 0.61), exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (aOR, 0.67), and death caused by pneumonia (aOR, 0.48) in the study population. In a propensity score–adjusted analysis, only protection from influenza-like illness lost statistical significance.
In addition, vaccination was associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality among AIRDs patients, but restricting the outcomes to the active influenza periods may have confounded this result, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including observational design, the use of a single vaccine efficacy estimate for each outcome, potential missed vaccination cycles, and potential confounding by indication and healthy user bias that could inflate the vaccine effectiveness, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, including a range of AIRDs, and the use of both diagnostic and prescription codes, they said.
“The findings of this study, together with the results of our previous study demonstrating the safety of IIV in people with AIRDs, provides evidence to promote seasonal flu vaccination in this population,” they concluded. They still emphasized that randomized, controlled trials are needed for an assessment of vaccine efficacy.
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis and the National Institute of Health Research. Lead author Dr. Nakafero had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with companies, including AstraZeneca, Roche, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Nakafero G et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Mar 11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa078.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases who received the inactivated flu vaccine had lower rates of flu-like illness, hospitalization, and death than did those not vaccinated.
Major finding: Vaccination significantly reduced the risk of flu-like illness, hospitalization for pneumonia or COPD exacerbation, and death from pneumonia by 30%, 39%, 33%, and 52%, respectively.
Study details: The data come from 30,788 adults with AIRD and included 125,034 influenza cycles.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Versus Arthritis and the National Institute of Health Research. Lead author Dr. Nakafero had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with companies, including AstraZeneca, Roche, and Pfizer.
Source: Nakafero G et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Mar 11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa078.
After weeks of decline, influenza activity increases slightly
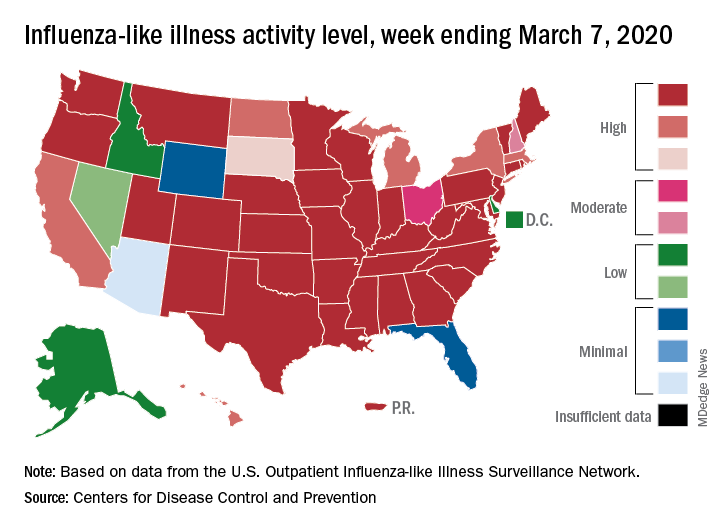
The two leading measures of influenza activity – the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza and the proportion of visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness (ILI) – had been following a similar downward path since mid-February. But during the week ending March 7, their paths diverged, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza dropped for the fourth consecutive week, falling from 26.1% to 21.5%, while the proportion of visits to health care providers for ILI increased from 5.1% to 5.2%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
One possible explanation for that rise: “The largest increases in ILI activity occurred in areas of the country where COVID-19 is most prevalent. More people may be seeking care for respiratory illness than usual at this time,” the influenza division said March 13 in its weekly Fluview report.
This week’s map puts 34 states and Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity, one more state than the week before, and 43 jurisdictions in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 42 the previous week, the CDC said.
Rates of hospitalizations associated with influenza “remain moderate compared to recent seasons, but rates for children 0-4 years and adults 18-49 years are now the highest CDC has on record for these age groups, surpassing rates reported during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic,” the Fluview report said. Rates for children aged 5-17 years “are higher than any recent regular season but remain lower than rates experienced by this age group during the pandemic.”
The number of pediatric deaths this season is now up to 144, equaling the total for all of the 2018-2019 season. This year’s count led the CDC to invoke 2009 again, since it “is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-2005, except for the 2009 pandemic.”
For the 2019-2020 season so far there have been 36 million flu illnesses, 370,000 hospitalizations, and 22,000 deaths from flu and pneumonia, the CDC estimated.

The two leading measures of influenza activity – the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza and the proportion of visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness (ILI) – had been following a similar downward path since mid-February. But during the week ending March 7, their paths diverged, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza dropped for the fourth consecutive week, falling from 26.1% to 21.5%, while the proportion of visits to health care providers for ILI increased from 5.1% to 5.2%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
One possible explanation for that rise: “The largest increases in ILI activity occurred in areas of the country where COVID-19 is most prevalent. More people may be seeking care for respiratory illness than usual at this time,” the influenza division said March 13 in its weekly Fluview report.
This week’s map puts 34 states and Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity, one more state than the week before, and 43 jurisdictions in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 42 the previous week, the CDC said.
Rates of hospitalizations associated with influenza “remain moderate compared to recent seasons, but rates for children 0-4 years and adults 18-49 years are now the highest CDC has on record for these age groups, surpassing rates reported during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic,” the Fluview report said. Rates for children aged 5-17 years “are higher than any recent regular season but remain lower than rates experienced by this age group during the pandemic.”
The number of pediatric deaths this season is now up to 144, equaling the total for all of the 2018-2019 season. This year’s count led the CDC to invoke 2009 again, since it “is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-2005, except for the 2009 pandemic.”
For the 2019-2020 season so far there have been 36 million flu illnesses, 370,000 hospitalizations, and 22,000 deaths from flu and pneumonia, the CDC estimated.

The two leading measures of influenza activity – the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza and the proportion of visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness (ILI) – had been following a similar downward path since mid-February. But during the week ending March 7, their paths diverged, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza dropped for the fourth consecutive week, falling from 26.1% to 21.5%, while the proportion of visits to health care providers for ILI increased from 5.1% to 5.2%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
One possible explanation for that rise: “The largest increases in ILI activity occurred in areas of the country where COVID-19 is most prevalent. More people may be seeking care for respiratory illness than usual at this time,” the influenza division said March 13 in its weekly Fluview report.
This week’s map puts 34 states and Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity, one more state than the week before, and 43 jurisdictions in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 42 the previous week, the CDC said.
Rates of hospitalizations associated with influenza “remain moderate compared to recent seasons, but rates for children 0-4 years and adults 18-49 years are now the highest CDC has on record for these age groups, surpassing rates reported during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic,” the Fluview report said. Rates for children aged 5-17 years “are higher than any recent regular season but remain lower than rates experienced by this age group during the pandemic.”
The number of pediatric deaths this season is now up to 144, equaling the total for all of the 2018-2019 season. This year’s count led the CDC to invoke 2009 again, since it “is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-2005, except for the 2009 pandemic.”
For the 2019-2020 season so far there have been 36 million flu illnesses, 370,000 hospitalizations, and 22,000 deaths from flu and pneumonia, the CDC estimated.
Flu activity declines again but remains high
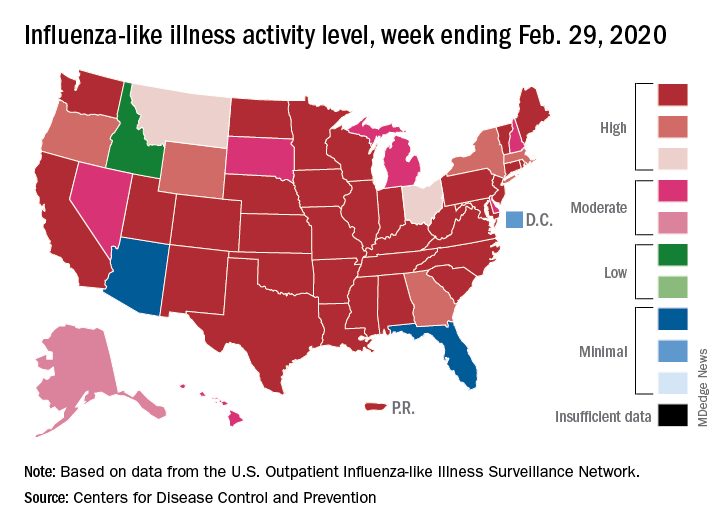
Outpatient visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness dropped from 5.5% the previous week to 5.3% of all visits for the week ending Feb. 29, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said on March 6.
The national baseline rate of 2.4% was first reached during the week of Nov. 9, 2019 – marking the start of flu season – and has remained at or above that level for 17 consecutive weeks. Last year’s season, which also was the longest in a decade, lasted 21 consecutive weeks but started 2 weeks later than the current season and had a lower outpatient-visit rate (4.5%) for the last week of February, CDC data show.
This season’s earlier start could mean that even a somewhat steep decline in visits to below the baseline rate – marking the end of the season – might take 5 or 6 weeks and would make 2019-2020 even longer than 2018-2019.
The activity situation on the state level reflects the small national decline. For the week ending Feb. 29, there were 33 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 activity scale, compared with 37 the week before, and a total of 40 in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 43 the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The other main measure of influenza activity, percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the third week in a row and is now at 24.3% after reaching a high of 30.3% during the week of Feb. 2-8, the influenza division said.
The overall cumulative hospitalization rate continues to remain at a fairly typical 57.9 per 100,000 population, but rates for school-aged children (84.9 per 100,000) and young adults (31.2 per 100,000) are among the highest ever recorded at this point in the season. Mortality among children – now at 136 for 2019-2020 – is higher than for any season since reporting began in 2004, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic, the CDC said.

Outpatient visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness dropped from 5.5% the previous week to 5.3% of all visits for the week ending Feb. 29, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said on March 6.
The national baseline rate of 2.4% was first reached during the week of Nov. 9, 2019 – marking the start of flu season – and has remained at or above that level for 17 consecutive weeks. Last year’s season, which also was the longest in a decade, lasted 21 consecutive weeks but started 2 weeks later than the current season and had a lower outpatient-visit rate (4.5%) for the last week of February, CDC data show.
This season’s earlier start could mean that even a somewhat steep decline in visits to below the baseline rate – marking the end of the season – might take 5 or 6 weeks and would make 2019-2020 even longer than 2018-2019.
The activity situation on the state level reflects the small national decline. For the week ending Feb. 29, there were 33 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 activity scale, compared with 37 the week before, and a total of 40 in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 43 the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The other main measure of influenza activity, percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the third week in a row and is now at 24.3% after reaching a high of 30.3% during the week of Feb. 2-8, the influenza division said.
The overall cumulative hospitalization rate continues to remain at a fairly typical 57.9 per 100,000 population, but rates for school-aged children (84.9 per 100,000) and young adults (31.2 per 100,000) are among the highest ever recorded at this point in the season. Mortality among children – now at 136 for 2019-2020 – is higher than for any season since reporting began in 2004, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic, the CDC said.

Outpatient visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness dropped from 5.5% the previous week to 5.3% of all visits for the week ending Feb. 29, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said on March 6.
The national baseline rate of 2.4% was first reached during the week of Nov. 9, 2019 – marking the start of flu season – and has remained at or above that level for 17 consecutive weeks. Last year’s season, which also was the longest in a decade, lasted 21 consecutive weeks but started 2 weeks later than the current season and had a lower outpatient-visit rate (4.5%) for the last week of February, CDC data show.
This season’s earlier start could mean that even a somewhat steep decline in visits to below the baseline rate – marking the end of the season – might take 5 or 6 weeks and would make 2019-2020 even longer than 2018-2019.
The activity situation on the state level reflects the small national decline. For the week ending Feb. 29, there were 33 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 activity scale, compared with 37 the week before, and a total of 40 in the “high” range of 8-10, compared with 43 the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The other main measure of influenza activity, percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the third week in a row and is now at 24.3% after reaching a high of 30.3% during the week of Feb. 2-8, the influenza division said.
The overall cumulative hospitalization rate continues to remain at a fairly typical 57.9 per 100,000 population, but rates for school-aged children (84.9 per 100,000) and young adults (31.2 per 100,000) are among the highest ever recorded at this point in the season. Mortality among children – now at 136 for 2019-2020 – is higher than for any season since reporting began in 2004, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic, the CDC said.
Children bearing the brunt of declining flu activity
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
ACIP: Flu vaccines for older adults show similar safety profiles
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that age-appropriate vaccines be used when possible, said Kenneth E. Schmader, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. However, no study to date had directly compared the safety of the trivalent high dose (HD-IIV3) and adjuvanted (aIIV3) vaccines or their impact on health-related quality of life. Dr. Schmader presented findings from a randomized trial at the February ACIP meeting.
To compare the safety of the vaccines, the researchers recruited community-dwelling volunteers aged 65 years and older who were cognitively intact, not immunosuppressed, and had no contraindications for influenza vaccination. A total of 378 individuals were randomized to aIIV3 and 379 to HD-IIV3. The average age was 72 years; 80 individuals in the aIIV3 group and 83 in the HDIIV3 group were 80 years and older. The primary outcome was moderate or severe injection site pain.
Overall, the proportion of participants with moderate or severe injection site pain was not significantly different after aIIV3 vs. HD-IIV3 (3.2% vs. 5.8%).
Nine participants in the aIIV3 group and three participants in the HD-IIV3 group experienced at least one serious adverse event, but no serious adverse events were deemed vaccine related, and the occurrence of serious adverse events was not significantly different between groups.
In addition, measures of short-term, postvaccination health-related quality of life were not significantly different between the groups. Changes in scores from day 1 prevaccination to day 3 postvaccination on the EuroQOL-5 dimensions-5 levels (EQ-5D-5L) were –0.05 for both groups.
The findings were limited in part by the lack of inclusion of older adults in nursing homes or similar settings, Dr. Schmader noted. However, the results suggest that “from the standpoint of safety, either vaccine is an acceptable option for the prevention of influenza in older adults.”
Studies comparing the immunogenicity of the vaccines are ongoing, and the data should be available within the next few months, he noted.
Dr. Schmader had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that age-appropriate vaccines be used when possible, said Kenneth E. Schmader, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. However, no study to date had directly compared the safety of the trivalent high dose (HD-IIV3) and adjuvanted (aIIV3) vaccines or their impact on health-related quality of life. Dr. Schmader presented findings from a randomized trial at the February ACIP meeting.
To compare the safety of the vaccines, the researchers recruited community-dwelling volunteers aged 65 years and older who were cognitively intact, not immunosuppressed, and had no contraindications for influenza vaccination. A total of 378 individuals were randomized to aIIV3 and 379 to HD-IIV3. The average age was 72 years; 80 individuals in the aIIV3 group and 83 in the HDIIV3 group were 80 years and older. The primary outcome was moderate or severe injection site pain.
Overall, the proportion of participants with moderate or severe injection site pain was not significantly different after aIIV3 vs. HD-IIV3 (3.2% vs. 5.8%).
Nine participants in the aIIV3 group and three participants in the HD-IIV3 group experienced at least one serious adverse event, but no serious adverse events were deemed vaccine related, and the occurrence of serious adverse events was not significantly different between groups.
In addition, measures of short-term, postvaccination health-related quality of life were not significantly different between the groups. Changes in scores from day 1 prevaccination to day 3 postvaccination on the EuroQOL-5 dimensions-5 levels (EQ-5D-5L) were –0.05 for both groups.
The findings were limited in part by the lack of inclusion of older adults in nursing homes or similar settings, Dr. Schmader noted. However, the results suggest that “from the standpoint of safety, either vaccine is an acceptable option for the prevention of influenza in older adults.”
Studies comparing the immunogenicity of the vaccines are ongoing, and the data should be available within the next few months, he noted.
Dr. Schmader had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that age-appropriate vaccines be used when possible, said Kenneth E. Schmader, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. However, no study to date had directly compared the safety of the trivalent high dose (HD-IIV3) and adjuvanted (aIIV3) vaccines or their impact on health-related quality of life. Dr. Schmader presented findings from a randomized trial at the February ACIP meeting.
To compare the safety of the vaccines, the researchers recruited community-dwelling volunteers aged 65 years and older who were cognitively intact, not immunosuppressed, and had no contraindications for influenza vaccination. A total of 378 individuals were randomized to aIIV3 and 379 to HD-IIV3. The average age was 72 years; 80 individuals in the aIIV3 group and 83 in the HDIIV3 group were 80 years and older. The primary outcome was moderate or severe injection site pain.
Overall, the proportion of participants with moderate or severe injection site pain was not significantly different after aIIV3 vs. HD-IIV3 (3.2% vs. 5.8%).
Nine participants in the aIIV3 group and three participants in the HD-IIV3 group experienced at least one serious adverse event, but no serious adverse events were deemed vaccine related, and the occurrence of serious adverse events was not significantly different between groups.
In addition, measures of short-term, postvaccination health-related quality of life were not significantly different between the groups. Changes in scores from day 1 prevaccination to day 3 postvaccination on the EuroQOL-5 dimensions-5 levels (EQ-5D-5L) were –0.05 for both groups.
The findings were limited in part by the lack of inclusion of older adults in nursing homes or similar settings, Dr. Schmader noted. However, the results suggest that “from the standpoint of safety, either vaccine is an acceptable option for the prevention of influenza in older adults.”
Studies comparing the immunogenicity of the vaccines are ongoing, and the data should be available within the next few months, he noted.
Dr. Schmader had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
Drop in flu activity suggests season may have peaked
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.
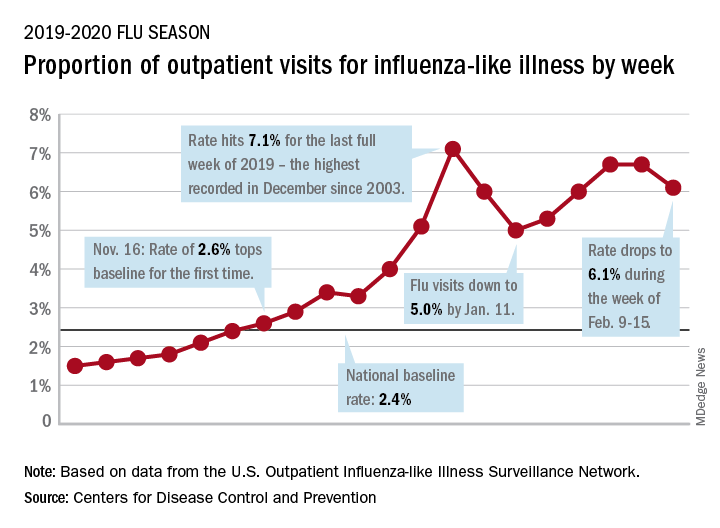
The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.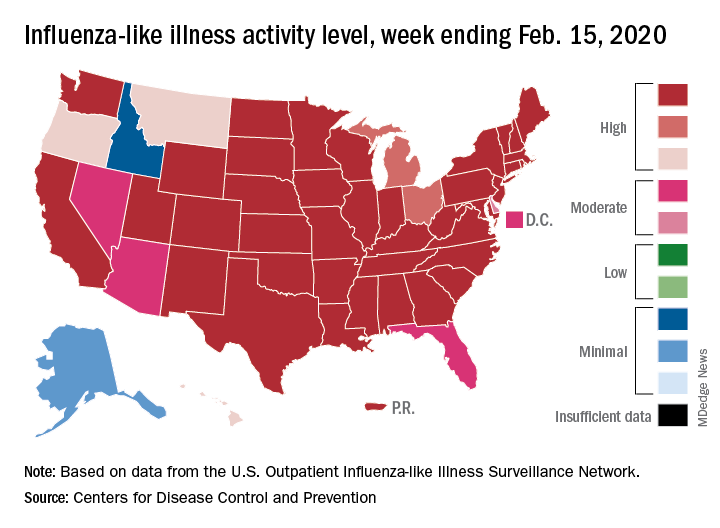
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.

The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.

The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
FROM THE CDC
Flu increases activity but not its severity

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.
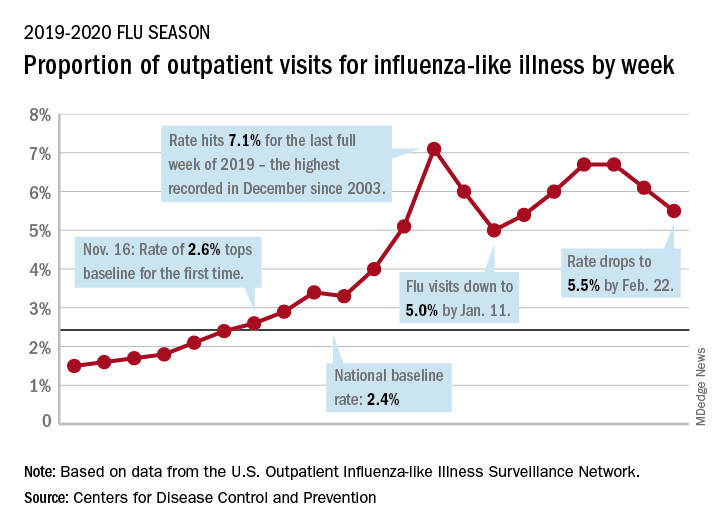
Flu activity increases for third straight week
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.
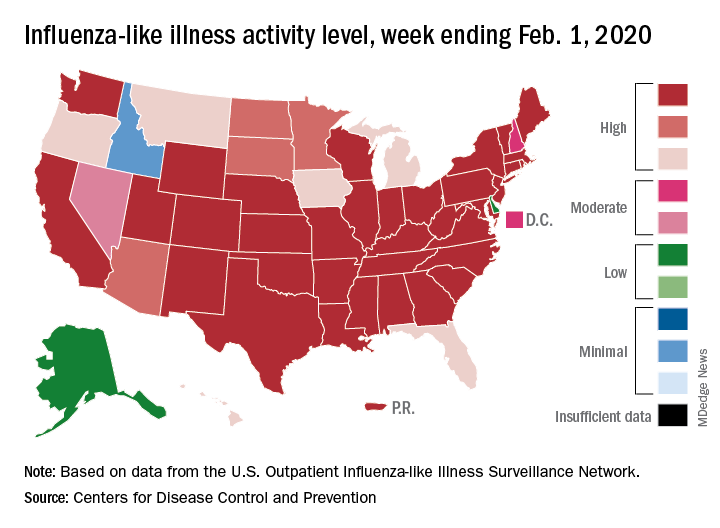
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.

The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.

The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.