User login
Liposomes boost bortezomib efficacy
Bortezomib treatment using liposome nanocarriers leads to decreased cell viability and greater apoptosis in vitro, compared with treatment with free bortezomib, according to a study in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Pharmacology.
Liposomes are lipid sacs with a watery compartment, which can be used to encapsulate and deliver a therapeutic cargo. The delivery method has been found to have improved efficacy with lesser side effects.
Ceramide liposomes are an attractive drug-delivery vehicle, the researchers said, because of their cell-permeability and because they’ve been found, on their own, to mediate apoptosis. Researchers said they believed this was the first time results have been reported on combining ceramide liposomes with an anticancer drug such as bortezomib. Cationic liposomes were picked because they’re known to destabilize cell membranes, helping with intracellular delivery of the drug.
Free bortezomib and bortezomib loaded into liposomes were tested for efficacy on mouse preosteoclast calvaria MC3T3 cells, mouse macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells, and human osteosarcoma U2OS cells.
On the RAW 264.7 cells, researchers found a significant difference in cell viability between free bortezomib and ceramide liposomes after 24 hours (P less than .01) and 48 hours (P less than .05) and between free bortezomib and cationic liposomes at 24 hours (P less than .01). They also reported a significant difference with cationic liposomes on MC3T3 cells and U2OS cells at 48 hours (both P less than .01).
One nanomolar (nM) of ceramide-loaded bortezomib induced significantly more apoptosis than did 1 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .01), and 10 nM of ceramide-loaded bortezomib brought about more cell death and apoptosis than did 10 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .05). These effects were likely the result of increased expression of proteins involved in apoptosis.
Liposomes might be able to boost the efficacy of bortezomib, according to the researchers, who are now studying the localization of these liposomes with confocal microscopes to better understand the mechanism of action.
“Such improvements,” they wrote, “offer the potential to reduce side effects known to occur with this chemotherapy, such as peripheral neuropathy, as well as to target Bort-resistant cancers.”
Bortezomib treatment using liposome nanocarriers leads to decreased cell viability and greater apoptosis in vitro, compared with treatment with free bortezomib, according to a study in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Pharmacology.
Liposomes are lipid sacs with a watery compartment, which can be used to encapsulate and deliver a therapeutic cargo. The delivery method has been found to have improved efficacy with lesser side effects.
Ceramide liposomes are an attractive drug-delivery vehicle, the researchers said, because of their cell-permeability and because they’ve been found, on their own, to mediate apoptosis. Researchers said they believed this was the first time results have been reported on combining ceramide liposomes with an anticancer drug such as bortezomib. Cationic liposomes were picked because they’re known to destabilize cell membranes, helping with intracellular delivery of the drug.
Free bortezomib and bortezomib loaded into liposomes were tested for efficacy on mouse preosteoclast calvaria MC3T3 cells, mouse macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells, and human osteosarcoma U2OS cells.
On the RAW 264.7 cells, researchers found a significant difference in cell viability between free bortezomib and ceramide liposomes after 24 hours (P less than .01) and 48 hours (P less than .05) and between free bortezomib and cationic liposomes at 24 hours (P less than .01). They also reported a significant difference with cationic liposomes on MC3T3 cells and U2OS cells at 48 hours (both P less than .01).
One nanomolar (nM) of ceramide-loaded bortezomib induced significantly more apoptosis than did 1 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .01), and 10 nM of ceramide-loaded bortezomib brought about more cell death and apoptosis than did 10 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .05). These effects were likely the result of increased expression of proteins involved in apoptosis.
Liposomes might be able to boost the efficacy of bortezomib, according to the researchers, who are now studying the localization of these liposomes with confocal microscopes to better understand the mechanism of action.
“Such improvements,” they wrote, “offer the potential to reduce side effects known to occur with this chemotherapy, such as peripheral neuropathy, as well as to target Bort-resistant cancers.”
Bortezomib treatment using liposome nanocarriers leads to decreased cell viability and greater apoptosis in vitro, compared with treatment with free bortezomib, according to a study in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Pharmacology.
Liposomes are lipid sacs with a watery compartment, which can be used to encapsulate and deliver a therapeutic cargo. The delivery method has been found to have improved efficacy with lesser side effects.
Ceramide liposomes are an attractive drug-delivery vehicle, the researchers said, because of their cell-permeability and because they’ve been found, on their own, to mediate apoptosis. Researchers said they believed this was the first time results have been reported on combining ceramide liposomes with an anticancer drug such as bortezomib. Cationic liposomes were picked because they’re known to destabilize cell membranes, helping with intracellular delivery of the drug.
Free bortezomib and bortezomib loaded into liposomes were tested for efficacy on mouse preosteoclast calvaria MC3T3 cells, mouse macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells, and human osteosarcoma U2OS cells.
On the RAW 264.7 cells, researchers found a significant difference in cell viability between free bortezomib and ceramide liposomes after 24 hours (P less than .01) and 48 hours (P less than .05) and between free bortezomib and cationic liposomes at 24 hours (P less than .01). They also reported a significant difference with cationic liposomes on MC3T3 cells and U2OS cells at 48 hours (both P less than .01).
One nanomolar (nM) of ceramide-loaded bortezomib induced significantly more apoptosis than did 1 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .01), and 10 nM of ceramide-loaded bortezomib brought about more cell death and apoptosis than did 10 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .05). These effects were likely the result of increased expression of proteins involved in apoptosis.
Liposomes might be able to boost the efficacy of bortezomib, according to the researchers, who are now studying the localization of these liposomes with confocal microscopes to better understand the mechanism of action.
“Such improvements,” they wrote, “offer the potential to reduce side effects known to occur with this chemotherapy, such as peripheral neuropathy, as well as to target Bort-resistant cancers.”
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES AND PHARMACOLOGY
Key clinical point: Ceramide and cationic liposomes loaded with bortezomib decreased cell viability and increased apoptosis in vitro, compared with bortezomib alone.
Major finding: One nanomolar (nM) of ceramide-loaded bortezomib induced significantly more apoptosis than did 1 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .01), and 10 nM of ceramide-loaded bortezomib brought about more cell death and apoptosis than did 10 nM of free bortezomib (P less than .05).
Data source: An in vitro study conducted at Midwestern University.
Disclosures: Researchers reported no conflicts of interest.
Early allo SCT advised for high-risk mantle cell lymphoma
High-risk patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have a matched related donor have a better chance for survival if they don’t delay allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo SCT), based on a small single-center study reported by Daniel Allen Kobrinski, DO, and his colleagues at Loyola University, Chicago.
They based the recommendation on the outcomes of 29 mantle cell lymphoma patients who underwent allo SCT at Loyola University Medical Center between Jan. 1, 1999 and Jan. 1, 2016. Before having allo SCT, 23 of 29 patients had three or more lines of treatment. Six had myeloablative conditioning and 23 had reduced-intensity conditioning; 15 had a related donor, 6 had a matched unrelated donor, and 8 had an unmatched cord blood donor.
Probability estimates for overall survival and non–relapse mortality at 5 years were calculated from the date of allo SCT to the date of patient death or last known follow-up. The 5-year rate of overall survival was 42% and the rate of non–relapse mortality was 53%. Based on a univariate analysis, the risk of death was lower in patients who received total body irradiation-based conditioning (hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.81; P = .03), and in those who had HLA-matched, related donor transplants (HR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.11-0.79; P = .02).
Patients who received more than three lines of prior treatment had a higher risk of death (HR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.05-7.34; P = .04).
Four of the patients had grade III/IV acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and four relapsed. Two patients died from acute GVHD, and most of the other deaths were from treatment-related toxicities.
Dr. Kobrinski had no relationships to disclose.
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mantle cell lymphoma in a heavily pretreated patient population. 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting Abstract No: 7558
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
High-risk patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have a matched related donor have a better chance for survival if they don’t delay allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo SCT), based on a small single-center study reported by Daniel Allen Kobrinski, DO, and his colleagues at Loyola University, Chicago.
They based the recommendation on the outcomes of 29 mantle cell lymphoma patients who underwent allo SCT at Loyola University Medical Center between Jan. 1, 1999 and Jan. 1, 2016. Before having allo SCT, 23 of 29 patients had three or more lines of treatment. Six had myeloablative conditioning and 23 had reduced-intensity conditioning; 15 had a related donor, 6 had a matched unrelated donor, and 8 had an unmatched cord blood donor.
Probability estimates for overall survival and non–relapse mortality at 5 years were calculated from the date of allo SCT to the date of patient death or last known follow-up. The 5-year rate of overall survival was 42% and the rate of non–relapse mortality was 53%. Based on a univariate analysis, the risk of death was lower in patients who received total body irradiation-based conditioning (hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.81; P = .03), and in those who had HLA-matched, related donor transplants (HR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.11-0.79; P = .02).
Patients who received more than three lines of prior treatment had a higher risk of death (HR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.05-7.34; P = .04).
Four of the patients had grade III/IV acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and four relapsed. Two patients died from acute GVHD, and most of the other deaths were from treatment-related toxicities.
Dr. Kobrinski had no relationships to disclose.
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mantle cell lymphoma in a heavily pretreated patient population. 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting Abstract No: 7558
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
High-risk patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have a matched related donor have a better chance for survival if they don’t delay allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo SCT), based on a small single-center study reported by Daniel Allen Kobrinski, DO, and his colleagues at Loyola University, Chicago.
They based the recommendation on the outcomes of 29 mantle cell lymphoma patients who underwent allo SCT at Loyola University Medical Center between Jan. 1, 1999 and Jan. 1, 2016. Before having allo SCT, 23 of 29 patients had three or more lines of treatment. Six had myeloablative conditioning and 23 had reduced-intensity conditioning; 15 had a related donor, 6 had a matched unrelated donor, and 8 had an unmatched cord blood donor.
Probability estimates for overall survival and non–relapse mortality at 5 years were calculated from the date of allo SCT to the date of patient death or last known follow-up. The 5-year rate of overall survival was 42% and the rate of non–relapse mortality was 53%. Based on a univariate analysis, the risk of death was lower in patients who received total body irradiation-based conditioning (hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.81; P = .03), and in those who had HLA-matched, related donor transplants (HR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.11-0.79; P = .02).
Patients who received more than three lines of prior treatment had a higher risk of death (HR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.05-7.34; P = .04).
Four of the patients had grade III/IV acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and four relapsed. Two patients died from acute GVHD, and most of the other deaths were from treatment-related toxicities.
Dr. Kobrinski had no relationships to disclose.
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mantle cell lymphoma in a heavily pretreated patient population. 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting Abstract No: 7558
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
FROM ASCO 2017 ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Based on a univariate analysis, the risk of death was lower in patients who received total body irradiation-based conditioning (HR, 0.1; 95% CI, 0.04-0.81; P = .03), and in those who had HLA-matched, related donor transplants (HR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.11-0.79; P = .02).
Data source: A retrospective study of all 29 patients who were treated with an allo stem cell transplant for mantle cell lymphoma at Loyola University Medical Center between Jan. 1, 1999 and Jan. 1, 2016.
Disclosures: Dr. Kobrinski had no relationships to disclose.
Citation: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mantle cell lymphoma in a heavily pretreated patient population. 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting Abstract No: 7558.
ALC/AMC prognostic in mantle cell lymphoma
The peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (ALC/AMC) was prognostic for overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma patients who have undergone induction therapy, based on a retrospective review study of 96 patients by Andre Goy, MD, of John Theurer Cancer Center, Hackensack (NJ) University, and his colleagues.
Overall survival was better when ALC/AMC was 2 or greater following induction therapy, the researchers wrote in an abstract published in conjunction with the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The finding indicates that novel maintenance programs, including targeting the microenvironment or immune response, might be appropriate when patients with mantle cell lymphoma have low ALC/AMC.
The researchers examined data for 96 consecutive mantle cell lymphoma patients. The ALC/AMC was determined from peripheral blood counts obtained approximately 30 days following completion of initial therapy or immediately prior to stem cell mobilization in patients who had first line stem cell transplants.
The ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 67 patients and was 2 or greater in 29 patients. The two patient cohorts were similar in median age, ethnicities, stage distributions, elevated beta-2-microglobulin, elevated lactate dehydrogenate, and Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores.
ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 10 of 13 transplanted patients and in 57 of 83 patients who did not undergo transplants. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the median overall survival has not been reached in either cohort.
The 5-year survival rate was 90% among patients with an ALC/AMC of 2 or greater and 68% in those with an ALC/AMC less than 2 (log-rank P less than .05).
Similar ALC/AMC 5-year survival trends were noted when subsetting to the 25 patients with high risk Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores (72% vs. 45%; P = .07).
Dr. Goy disclosed honoraria from Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; a consulting or advisory role with Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; and speakers’ bureaus participation for Pharmacyclics and Takeda.
Prognostic value of the absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte (ALC/AMC) ratio on overall survival among patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Published in conjunction with the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting. Abstract No: e19030.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
The peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (ALC/AMC) was prognostic for overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma patients who have undergone induction therapy, based on a retrospective review study of 96 patients by Andre Goy, MD, of John Theurer Cancer Center, Hackensack (NJ) University, and his colleagues.
Overall survival was better when ALC/AMC was 2 or greater following induction therapy, the researchers wrote in an abstract published in conjunction with the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The finding indicates that novel maintenance programs, including targeting the microenvironment or immune response, might be appropriate when patients with mantle cell lymphoma have low ALC/AMC.
The researchers examined data for 96 consecutive mantle cell lymphoma patients. The ALC/AMC was determined from peripheral blood counts obtained approximately 30 days following completion of initial therapy or immediately prior to stem cell mobilization in patients who had first line stem cell transplants.
The ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 67 patients and was 2 or greater in 29 patients. The two patient cohorts were similar in median age, ethnicities, stage distributions, elevated beta-2-microglobulin, elevated lactate dehydrogenate, and Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores.
ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 10 of 13 transplanted patients and in 57 of 83 patients who did not undergo transplants. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the median overall survival has not been reached in either cohort.
The 5-year survival rate was 90% among patients with an ALC/AMC of 2 or greater and 68% in those with an ALC/AMC less than 2 (log-rank P less than .05).
Similar ALC/AMC 5-year survival trends were noted when subsetting to the 25 patients with high risk Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores (72% vs. 45%; P = .07).
Dr. Goy disclosed honoraria from Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; a consulting or advisory role with Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; and speakers’ bureaus participation for Pharmacyclics and Takeda.
Prognostic value of the absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte (ALC/AMC) ratio on overall survival among patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Published in conjunction with the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting. Abstract No: e19030.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
The peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (ALC/AMC) was prognostic for overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma patients who have undergone induction therapy, based on a retrospective review study of 96 patients by Andre Goy, MD, of John Theurer Cancer Center, Hackensack (NJ) University, and his colleagues.
Overall survival was better when ALC/AMC was 2 or greater following induction therapy, the researchers wrote in an abstract published in conjunction with the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The finding indicates that novel maintenance programs, including targeting the microenvironment or immune response, might be appropriate when patients with mantle cell lymphoma have low ALC/AMC.
The researchers examined data for 96 consecutive mantle cell lymphoma patients. The ALC/AMC was determined from peripheral blood counts obtained approximately 30 days following completion of initial therapy or immediately prior to stem cell mobilization in patients who had first line stem cell transplants.
The ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 67 patients and was 2 or greater in 29 patients. The two patient cohorts were similar in median age, ethnicities, stage distributions, elevated beta-2-microglobulin, elevated lactate dehydrogenate, and Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores.
ALC/AMC was less than 2 in 10 of 13 transplanted patients and in 57 of 83 patients who did not undergo transplants. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the median overall survival has not been reached in either cohort.
The 5-year survival rate was 90% among patients with an ALC/AMC of 2 or greater and 68% in those with an ALC/AMC less than 2 (log-rank P less than .05).
Similar ALC/AMC 5-year survival trends were noted when subsetting to the 25 patients with high risk Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores (72% vs. 45%; P = .07).
Dr. Goy disclosed honoraria from Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; a consulting or advisory role with Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; and speakers’ bureaus participation for Pharmacyclics and Takeda.
Prognostic value of the absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte (ALC/AMC) ratio on overall survival among patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Published in conjunction with the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting. Abstract No: e19030.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
IN CONJUNCTION WITH ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 5-year survival rate was 90% among patients with an ALC/AMC of 2 or greater and 68% in those with an ALC/AMC less than 2 (log-rank P less than .05).
Data source: A retrospective review study of 96 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Goy disclosed honoraria from Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; a consulting or advisory role with Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; and speakers’ bureaus participation for Pharmacyclics and Takeda.
Citation: Prognostic value of the absolute lymphocyte-to-monocyte (ALC/AMC) ratio on overall survival among patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Published in conjunction with the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting. Abstract No: e19030.
CAR T-cell data expected soon in mantle cell lymphoma
Final data collection for primary outcome measures is anticipated in September for ZUMA-2, a Phase II multicenter study of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product KTE-C19 in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-2 (NCT02601313), with a planned enrollment of 70 patients, is expected to release the overall response rate at 12 months. Secondary outcome measures include duration of response, best objective response, and progression-free survival.
Subjects can have up to five prior regimens, which must include anthracycline or bendamustine-containing chemotherapy, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy, and ibrutinib. Study subjects cannot have received allogeneic stem cell transplantation, prior CD19 targeted therapy, or prior CAR or other genetically modified T cell therapy.
Trial participants must be adults with an Eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1, an absolute neutrophil count of at least 1000/µL, and a platelet count of at least 50,000/µL. All need to have adequate renal function, defined as a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL or less; adequate hepatic function, defined as a serum ALT/AST of 2.5 the upper limit of normal or less; and a total bilirubin of 1.5 mg/dL or less (except in subjects with Gilbert’s syndrome), and adequate cardiac function, defined as a cardiac ejection fraction of 50% or more with no evidence of pericardial effusion.
Exclusion criteria include a history of another cancer other than nonmelanomatous skin cancer or carcinoma in situ (for example, cervix, bladder, breast) unless disease free for at least 3 years, known infection with HIV or hepatitis B or C virus, metastases in cerebrospinal fluid or brain, and a history of a seizure disorder, cerebrovascular ischemia/hemorrhage, dementia, cerebellar disease, or any autoimmune disease with CNS involvement.
The study is sponsored by Kite Pharma, the makers of KTE-C19.
Final data collection for primary outcome measures is anticipated in September for ZUMA-2, a Phase II multicenter study of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product KTE-C19 in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-2 (NCT02601313), with a planned enrollment of 70 patients, is expected to release the overall response rate at 12 months. Secondary outcome measures include duration of response, best objective response, and progression-free survival.
Subjects can have up to five prior regimens, which must include anthracycline or bendamustine-containing chemotherapy, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy, and ibrutinib. Study subjects cannot have received allogeneic stem cell transplantation, prior CD19 targeted therapy, or prior CAR or other genetically modified T cell therapy.
Trial participants must be adults with an Eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1, an absolute neutrophil count of at least 1000/µL, and a platelet count of at least 50,000/µL. All need to have adequate renal function, defined as a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL or less; adequate hepatic function, defined as a serum ALT/AST of 2.5 the upper limit of normal or less; and a total bilirubin of 1.5 mg/dL or less (except in subjects with Gilbert’s syndrome), and adequate cardiac function, defined as a cardiac ejection fraction of 50% or more with no evidence of pericardial effusion.
Exclusion criteria include a history of another cancer other than nonmelanomatous skin cancer or carcinoma in situ (for example, cervix, bladder, breast) unless disease free for at least 3 years, known infection with HIV or hepatitis B or C virus, metastases in cerebrospinal fluid or brain, and a history of a seizure disorder, cerebrovascular ischemia/hemorrhage, dementia, cerebellar disease, or any autoimmune disease with CNS involvement.
The study is sponsored by Kite Pharma, the makers of KTE-C19.
Final data collection for primary outcome measures is anticipated in September for ZUMA-2, a Phase II multicenter study of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product KTE-C19 in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-2 (NCT02601313), with a planned enrollment of 70 patients, is expected to release the overall response rate at 12 months. Secondary outcome measures include duration of response, best objective response, and progression-free survival.
Subjects can have up to five prior regimens, which must include anthracycline or bendamustine-containing chemotherapy, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy, and ibrutinib. Study subjects cannot have received allogeneic stem cell transplantation, prior CD19 targeted therapy, or prior CAR or other genetically modified T cell therapy.
Trial participants must be adults with an Eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1, an absolute neutrophil count of at least 1000/µL, and a platelet count of at least 50,000/µL. All need to have adequate renal function, defined as a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL or less; adequate hepatic function, defined as a serum ALT/AST of 2.5 the upper limit of normal or less; and a total bilirubin of 1.5 mg/dL or less (except in subjects with Gilbert’s syndrome), and adequate cardiac function, defined as a cardiac ejection fraction of 50% or more with no evidence of pericardial effusion.
Exclusion criteria include a history of another cancer other than nonmelanomatous skin cancer or carcinoma in situ (for example, cervix, bladder, breast) unless disease free for at least 3 years, known infection with HIV or hepatitis B or C virus, metastases in cerebrospinal fluid or brain, and a history of a seizure disorder, cerebrovascular ischemia/hemorrhage, dementia, cerebellar disease, or any autoimmune disease with CNS involvement.
The study is sponsored by Kite Pharma, the makers of KTE-C19.
SUMMARY FROM CLINICALTRIALS.GOV
In mantle cell lymphoma, triple therapy proves too toxic
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of 11 patients, 8 were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit–level care.
Data source: Two phase I trials involving 11 patients.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
Newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma is ‘one of the hardest consultations’
NEW YORK – Relatively young patients with newly diagnosed, average-risk mantle cell lymphoma who go into remission on induction therapy face a difficult choice on their next management step: undergo immediate autologous stem cell transplantation or defer the stem cell transplant and continue on maintenance therapy.
The choice is especially difficult because both are currently considered reasonable options and each choice has certain attractions and downsides, experts highlighted in discussing this fork-in-the-road decision patients face.
Immediate autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has a good chance to allow the patient to remain treatment free and in remission for as long as about 10 years, but it involves intensive upfront treatment for 6-9 months, during which the patient will likely not be able to work or carry on many usual activities. Deferring the transplant with maintenance therapy puts off this life-disrupting initial period of intensive therapy for what may be several years, but relapse on maintenance therapy is inevitable and once it happens the patient may not have as successful an outcome from an ASCT. It also means several years of ongoing drug therapy with a maintenance regimen.
“I tell my fellows that patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma [are] one of the hardest consultations because, unlike most other lymphomas, there is no established standard therapy but a range of options,” Timothy S. Fenske, MD, said at the conference held by Imedex. “I go through the pros and cons with patients, and it comes down to the patient’s perceived quality of life and their lifestyle.”
“It’s a very difficult decision [for patients] because we don’t have the data we’d like to have,” observed Peter Martin, MD, director of the clinical research program in lymphoma at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There is a lot of upfront toxicity with transplantation, with 6-9 months out of work in my experience. Patients often tell me that they can’t afford to do that; they’ll lose their employment insurance and won’t be able to pay for replacement insurance. But then they will hopefully go 6-10 years without more treatment, which is a real benefit. With less intensive upfront treatment they have a chance for similar overall survival, but they’ll need more ongoing treatment. It’s pretty complicated and challenging” for patients to make a decision, he said. “It depends a lot on where patients are in their lives and what they are willing to accept,” Dr. Martin said.
In general, Dr. Martin took a more skeptical view of ASCT than Dr. Fenske. “There is no evidence that ASCT cures patients or prolongs their survival. It improves progression-free survival, but not necessarily overall survival,” Dr. Martin noted.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “if you have good biology it doesn’t matter what the treatment is, you will do well,” he explained.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “less intense therapy works just as well” as more intense therapy, as long as the patient has a favorable genetic profile, he explained.
In contrast, Dr. Fenske put a much more positive spin on more intensive treatment upfront with ASCT.
“There is not much debate that you get longer progression-free survival with the more intensive approach. The question is, does progression-free survival matter in mantle cell lymphoma? I argue that it does because relapse in patients with mantle cell lymphoma is no picnic. What you can expect in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma is a progression-free survival of about 1-2 years, and an overall survival of about 2-3 years,” said Dr. Fenske, head of the section of bone marrow transplant and hematologic malignancies at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
As an example of the poor prognosis of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma patients Dr. Fenske cited a review he coauthored of 97 patients treated with ibrutinib (Imbruvica. Their median duration of response was 17 months and median progression-free survival was 15 months. Once ibrutinib treatment failure occurred their median overall survival was less than 3 months. (Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 8.doi:10.1002/hon.2380).
“It’s easy to get carried away” when patients temporarily respond to a drug like ibrutinib or other new agents with a degree of efficacy for lymphomas, Dr. Fenske said, but these transient responses “don’t solve the problem. The patient is headed for trouble,” usually within a couple of years.
“I would argue that, especially for younger patients, the goal is to try to achieve the longest first remission, and that means an ASCT.” Dr. Fenske admitted that this strategy won’t work for very-high-risk patients, but for these patients no good treatment options currently exist.
He also stressed that research is just beginning to explore using measurement of negative minimal residual disease to identify patients with the best outcomes following initial induction treatment. It is possible that patients with undetectable minimal residual disease can avoid immediate ASCT and instead receive maintenance therapy, a hypothesis slated for testing in a randomized trial, he said.
Dr. Martin has been a consultant to Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Verastem. Dr. Fenske has been a consultant to Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics.
mzoler@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
This article was updated May 30, 2017 .
NEW YORK – Relatively young patients with newly diagnosed, average-risk mantle cell lymphoma who go into remission on induction therapy face a difficult choice on their next management step: undergo immediate autologous stem cell transplantation or defer the stem cell transplant and continue on maintenance therapy.
The choice is especially difficult because both are currently considered reasonable options and each choice has certain attractions and downsides, experts highlighted in discussing this fork-in-the-road decision patients face.
Immediate autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has a good chance to allow the patient to remain treatment free and in remission for as long as about 10 years, but it involves intensive upfront treatment for 6-9 months, during which the patient will likely not be able to work or carry on many usual activities. Deferring the transplant with maintenance therapy puts off this life-disrupting initial period of intensive therapy for what may be several years, but relapse on maintenance therapy is inevitable and once it happens the patient may not have as successful an outcome from an ASCT. It also means several years of ongoing drug therapy with a maintenance regimen.
“I tell my fellows that patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma [are] one of the hardest consultations because, unlike most other lymphomas, there is no established standard therapy but a range of options,” Timothy S. Fenske, MD, said at the conference held by Imedex. “I go through the pros and cons with patients, and it comes down to the patient’s perceived quality of life and their lifestyle.”
“It’s a very difficult decision [for patients] because we don’t have the data we’d like to have,” observed Peter Martin, MD, director of the clinical research program in lymphoma at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There is a lot of upfront toxicity with transplantation, with 6-9 months out of work in my experience. Patients often tell me that they can’t afford to do that; they’ll lose their employment insurance and won’t be able to pay for replacement insurance. But then they will hopefully go 6-10 years without more treatment, which is a real benefit. With less intensive upfront treatment they have a chance for similar overall survival, but they’ll need more ongoing treatment. It’s pretty complicated and challenging” for patients to make a decision, he said. “It depends a lot on where patients are in their lives and what they are willing to accept,” Dr. Martin said.
In general, Dr. Martin took a more skeptical view of ASCT than Dr. Fenske. “There is no evidence that ASCT cures patients or prolongs their survival. It improves progression-free survival, but not necessarily overall survival,” Dr. Martin noted.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “if you have good biology it doesn’t matter what the treatment is, you will do well,” he explained.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “less intense therapy works just as well” as more intense therapy, as long as the patient has a favorable genetic profile, he explained.
In contrast, Dr. Fenske put a much more positive spin on more intensive treatment upfront with ASCT.
“There is not much debate that you get longer progression-free survival with the more intensive approach. The question is, does progression-free survival matter in mantle cell lymphoma? I argue that it does because relapse in patients with mantle cell lymphoma is no picnic. What you can expect in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma is a progression-free survival of about 1-2 years, and an overall survival of about 2-3 years,” said Dr. Fenske, head of the section of bone marrow transplant and hematologic malignancies at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
As an example of the poor prognosis of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma patients Dr. Fenske cited a review he coauthored of 97 patients treated with ibrutinib (Imbruvica. Their median duration of response was 17 months and median progression-free survival was 15 months. Once ibrutinib treatment failure occurred their median overall survival was less than 3 months. (Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 8.doi:10.1002/hon.2380).
“It’s easy to get carried away” when patients temporarily respond to a drug like ibrutinib or other new agents with a degree of efficacy for lymphomas, Dr. Fenske said, but these transient responses “don’t solve the problem. The patient is headed for trouble,” usually within a couple of years.
“I would argue that, especially for younger patients, the goal is to try to achieve the longest first remission, and that means an ASCT.” Dr. Fenske admitted that this strategy won’t work for very-high-risk patients, but for these patients no good treatment options currently exist.
He also stressed that research is just beginning to explore using measurement of negative minimal residual disease to identify patients with the best outcomes following initial induction treatment. It is possible that patients with undetectable minimal residual disease can avoid immediate ASCT and instead receive maintenance therapy, a hypothesis slated for testing in a randomized trial, he said.
Dr. Martin has been a consultant to Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Verastem. Dr. Fenske has been a consultant to Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics.
mzoler@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
This article was updated May 30, 2017 .
NEW YORK – Relatively young patients with newly diagnosed, average-risk mantle cell lymphoma who go into remission on induction therapy face a difficult choice on their next management step: undergo immediate autologous stem cell transplantation or defer the stem cell transplant and continue on maintenance therapy.
The choice is especially difficult because both are currently considered reasonable options and each choice has certain attractions and downsides, experts highlighted in discussing this fork-in-the-road decision patients face.
Immediate autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has a good chance to allow the patient to remain treatment free and in remission for as long as about 10 years, but it involves intensive upfront treatment for 6-9 months, during which the patient will likely not be able to work or carry on many usual activities. Deferring the transplant with maintenance therapy puts off this life-disrupting initial period of intensive therapy for what may be several years, but relapse on maintenance therapy is inevitable and once it happens the patient may not have as successful an outcome from an ASCT. It also means several years of ongoing drug therapy with a maintenance regimen.
“I tell my fellows that patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma [are] one of the hardest consultations because, unlike most other lymphomas, there is no established standard therapy but a range of options,” Timothy S. Fenske, MD, said at the conference held by Imedex. “I go through the pros and cons with patients, and it comes down to the patient’s perceived quality of life and their lifestyle.”
“It’s a very difficult decision [for patients] because we don’t have the data we’d like to have,” observed Peter Martin, MD, director of the clinical research program in lymphoma at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“There is a lot of upfront toxicity with transplantation, with 6-9 months out of work in my experience. Patients often tell me that they can’t afford to do that; they’ll lose their employment insurance and won’t be able to pay for replacement insurance. But then they will hopefully go 6-10 years without more treatment, which is a real benefit. With less intensive upfront treatment they have a chance for similar overall survival, but they’ll need more ongoing treatment. It’s pretty complicated and challenging” for patients to make a decision, he said. “It depends a lot on where patients are in their lives and what they are willing to accept,” Dr. Martin said.
In general, Dr. Martin took a more skeptical view of ASCT than Dr. Fenske. “There is no evidence that ASCT cures patients or prolongs their survival. It improves progression-free survival, but not necessarily overall survival,” Dr. Martin noted.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “if you have good biology it doesn’t matter what the treatment is, you will do well,” he explained.
In fact, a report in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting (Blood. 2016 Dec 5;abstract 1095) suggested that “biology is the primary driver of outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma, not treatment,” said Dr. Martin. The results from a limited number of patients enrolled in the Nordic mantle cell lymphoma trials provided good but preliminary evidence that “less intense therapy works just as well” as more intense therapy, as long as the patient has a favorable genetic profile, he explained.
In contrast, Dr. Fenske put a much more positive spin on more intensive treatment upfront with ASCT.
“There is not much debate that you get longer progression-free survival with the more intensive approach. The question is, does progression-free survival matter in mantle cell lymphoma? I argue that it does because relapse in patients with mantle cell lymphoma is no picnic. What you can expect in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma is a progression-free survival of about 1-2 years, and an overall survival of about 2-3 years,” said Dr. Fenske, head of the section of bone marrow transplant and hematologic malignancies at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
As an example of the poor prognosis of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma patients Dr. Fenske cited a review he coauthored of 97 patients treated with ibrutinib (Imbruvica. Their median duration of response was 17 months and median progression-free survival was 15 months. Once ibrutinib treatment failure occurred their median overall survival was less than 3 months. (Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 8.doi:10.1002/hon.2380).
“It’s easy to get carried away” when patients temporarily respond to a drug like ibrutinib or other new agents with a degree of efficacy for lymphomas, Dr. Fenske said, but these transient responses “don’t solve the problem. The patient is headed for trouble,” usually within a couple of years.
“I would argue that, especially for younger patients, the goal is to try to achieve the longest first remission, and that means an ASCT.” Dr. Fenske admitted that this strategy won’t work for very-high-risk patients, but for these patients no good treatment options currently exist.
He also stressed that research is just beginning to explore using measurement of negative minimal residual disease to identify patients with the best outcomes following initial induction treatment. It is possible that patients with undetectable minimal residual disease can avoid immediate ASCT and instead receive maintenance therapy, a hypothesis slated for testing in a randomized trial, he said.
Dr. Martin has been a consultant to Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Verastem. Dr. Fenske has been a consultant to Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics.
mzoler@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
This article was updated May 30, 2017 .
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
MAGNIFY in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma
MAGNIFY is a phase IIIB randomized trial actively recruiting patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, based on studies posted at ClinicalTrials.gov.
MAGNIFY (NCT01996865) is a study of lenalidomide (CC-5013) plus rituximab maintenance therapy, followed by lenalidomide single-agent maintenance therapy, versus rituximab. Sponsored by Celgene, the maker of lenalidomide (Revlimid), the trial’s primary outcome measure is progression-free survival at up to 8 years.
The MAGNIFY trial includes patients with grades 1-3b or transformed follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma who had received at least one prior therapy and had stage I-IV measurable disease. About 500 patients are planned to enroll in 12 cycles of R2 induction, and slightly more than 300 patients are projected to be randomized after induction to the two maintenance arms. Induction includes oral lenalidomide 20 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle; plus intravenous rituximab 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 (28-day cycles).
Patients will then be randomized to maintenance lenalidomide 10 mg/day, given on days 1-21 per 28-day cycle for cycles 13-30; plus rituximab 375 mg/m2, given on day 1 of cycles 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, and 29 (R2, Arm A), or rituximab alone (same schedule, Arm B). Patients receiving R2 maintenance after 18 cycles may continue maintenance lenalidomide monotherapy at 10 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle, at the discretion of the patient and/or investigator, until disease progression as tolerated.
The primary endpoint is progression-free survival. Secondary endpoints include safety, overall survival, response rates, duration of response, and quality of life. Patients will be followed for at least 5 years after the last patient-initiated induction therapy. Enrollment in MAGNIFY began in March 2014; as of January 2016, 133 patients are enrolled, according to the study page at ClinicalTrials.gov.
MAGNIFY is a phase IIIB randomized trial actively recruiting patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, based on studies posted at ClinicalTrials.gov.
MAGNIFY (NCT01996865) is a study of lenalidomide (CC-5013) plus rituximab maintenance therapy, followed by lenalidomide single-agent maintenance therapy, versus rituximab. Sponsored by Celgene, the maker of lenalidomide (Revlimid), the trial’s primary outcome measure is progression-free survival at up to 8 years.
The MAGNIFY trial includes patients with grades 1-3b or transformed follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma who had received at least one prior therapy and had stage I-IV measurable disease. About 500 patients are planned to enroll in 12 cycles of R2 induction, and slightly more than 300 patients are projected to be randomized after induction to the two maintenance arms. Induction includes oral lenalidomide 20 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle; plus intravenous rituximab 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 (28-day cycles).
Patients will then be randomized to maintenance lenalidomide 10 mg/day, given on days 1-21 per 28-day cycle for cycles 13-30; plus rituximab 375 mg/m2, given on day 1 of cycles 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, and 29 (R2, Arm A), or rituximab alone (same schedule, Arm B). Patients receiving R2 maintenance after 18 cycles may continue maintenance lenalidomide monotherapy at 10 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle, at the discretion of the patient and/or investigator, until disease progression as tolerated.
The primary endpoint is progression-free survival. Secondary endpoints include safety, overall survival, response rates, duration of response, and quality of life. Patients will be followed for at least 5 years after the last patient-initiated induction therapy. Enrollment in MAGNIFY began in March 2014; as of January 2016, 133 patients are enrolled, according to the study page at ClinicalTrials.gov.
MAGNIFY is a phase IIIB randomized trial actively recruiting patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, based on studies posted at ClinicalTrials.gov.
MAGNIFY (NCT01996865) is a study of lenalidomide (CC-5013) plus rituximab maintenance therapy, followed by lenalidomide single-agent maintenance therapy, versus rituximab. Sponsored by Celgene, the maker of lenalidomide (Revlimid), the trial’s primary outcome measure is progression-free survival at up to 8 years.
The MAGNIFY trial includes patients with grades 1-3b or transformed follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma who had received at least one prior therapy and had stage I-IV measurable disease. About 500 patients are planned to enroll in 12 cycles of R2 induction, and slightly more than 300 patients are projected to be randomized after induction to the two maintenance arms. Induction includes oral lenalidomide 20 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle; plus intravenous rituximab 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 (28-day cycles).
Patients will then be randomized to maintenance lenalidomide 10 mg/day, given on days 1-21 per 28-day cycle for cycles 13-30; plus rituximab 375 mg/m2, given on day 1 of cycles 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, and 29 (R2, Arm A), or rituximab alone (same schedule, Arm B). Patients receiving R2 maintenance after 18 cycles may continue maintenance lenalidomide monotherapy at 10 mg/day, days 1-21 per 28-day cycle, at the discretion of the patient and/or investigator, until disease progression as tolerated.
The primary endpoint is progression-free survival. Secondary endpoints include safety, overall survival, response rates, duration of response, and quality of life. Patients will be followed for at least 5 years after the last patient-initiated induction therapy. Enrollment in MAGNIFY began in March 2014; as of January 2016, 133 patients are enrolled, according to the study page at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Unavoidable, random DNA replication errors are the most common cancer drivers
Up to two-thirds of the mutations that drive human cancers may be due to DNA replication errors in normally dividing stem cells, not by inherited or environmentally induced mutations, according to a mathematical modeling study.
The proportion of replication error-driven mutations varied widely among 17 cancers analyzed, but the overall attributable risk of these errors was remarkably consistent among 69 countries included in the study, said Cristian Tomasetti, PhD, a coauthor of the paper and a biostatistician at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The findings should be a game-changer in the cancer field, Dr. Tomasetti said during a press briefing sponsored by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Research dogma has long held that most cancers are related to lifestyle and environmental exposure, with a few primarily due to genetic factors.
“We have now determined that there is a third factor, and that it causes most of the mutations that drive cancer,” Dr. Tomasetti said. “We cannot ignore it and pretend it doesn’t exist. This is a complete paradigm shift in how we think of cancer and what causes it.”
The finding that 66% of cancer-driving mutations are based on unavoidable replication errors doesn’t challenge well-established epidemiology, said Dr. Tomasetti and his coauthor, Bert Vogelstein, MD. Rather, it fits perfectly with several key understandings of cancer: that about 40% of cases are preventable, that rapidly dividing tissues are more prone to develop cancers, and that cancer incidence rises exponentially as humans age.
“If we have as our starting point the assumption that 42% of cancers are preventable, we are completely consistent with that,” in finding that about 60% of cancers are unavoidable, Dr. Tomasetti said. “Those two numbers go perfectly together.”
The study also found that replication-error mutations (R) were most likely to drive cancers in tissues with rapid turnover, such as colorectal tissue. This makes intuitive sense, given that basal mutation rates hover at about three errors per cell replication cycle regardless of tissue type.
“The basal mutation rate in all cells is pretty even,” said Dr. Vogelstein, the Clayton Professor of Oncology and Pathology at John Hopkins University, Baltimore. “The difference is the number of stem cells. The more cells, the more divisions, and the more mistakes.”
R-mutations also contribute to age-related cancer incidence. As a person ages, more cell divisions accumulate, thus increasing the risk of a cancer-driving R-error. But these mutations also occur in children, who have rapid cell division in all their tissues. In fact, the colleagues suspect that R-errors are the main drivers of almost all pediatric cancers.
The new study bolsters the duo’s controversial 2015 work.
The theory sparked controversy among scholars and researchers. They challenged it on a number of technical fronts, from stem cell counts and division rates to charges that it didn’t adequately assess the interaction between R-mutations and environmental risks.
Some commentators, perceiving nihilism in the paper, expressed concern that clinicians and patients would get the idea that cancer prevention strategies were useless, since most cancers were simply a case of “bad luck.”
A pervading theme of these counter arguments was one familiar to any researcher: Correlation does not equal causation. The new study was an attempt to expand upon and strengthen the original findings, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“There are well-known environmental risk variations across the world, and there was a question of how our findings might change if we did this analysis in a different country. This paper is also the very first time that someone has ever looked at the proportions of mutations in each cancer type and assigned them to these factors.”
The new study employed a similar mathematical model, but comprised data from 423 cancer registries in 69 countries. The researchers examined the relationship between the lifetime risk of 17 cancers (including breast and prostate, which were not included in the 2015 study) and lifetime stem cell divisions for each tissue. The median correlation coefficient was 0.80; 89% of the countries examined had a correlation of greater than 0.70. This was “remarkably similar” to the correlation determined in the 2015 U.S.-only study.
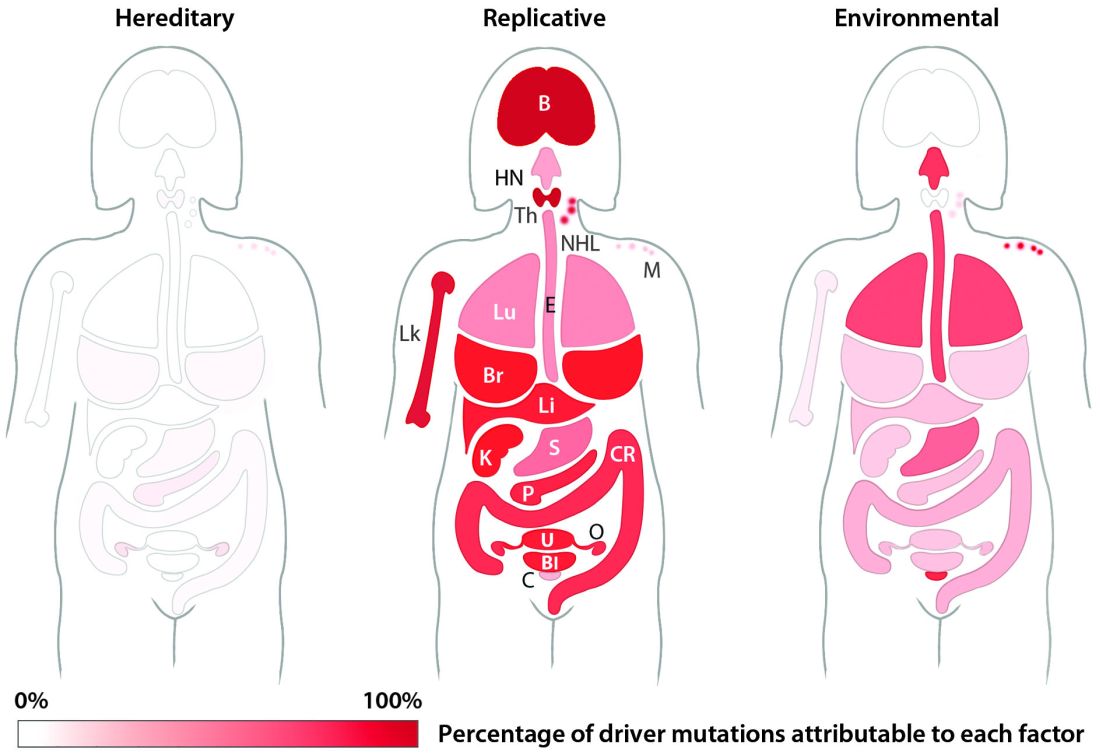
The team’s next step was to determine what fraction of cancer-driving mutations arose from R-errors, from environmental factors (E), and from hereditary factors (H). They examined these proportions in 32 different cancers in which environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors have been thoroughly studied. Overall, 29% of the driver mutations were due to environment, 5% to heredity, and 66% to R-errors.
The proportions of these drivers did vary widely between the cancer types, the team noted. For example, lung and esophageal cancers and melanoma were primarily driven by environmental factors (more than 60% each). However, they wrote, “even in lung adenocarcinomas, R contributes a third of the total mutations, with tobacco smoke [including secondhand smoke], diet, radiation, and occupational exposures contributing the remainder. In cancers that are less strongly associated with environmental factors, such as those of the pancreas, brain, bone, or prostate, the majority of the mutations are attributable to R.”
During the press briefing, Dr. Tomasetti and Dr. Vogelstein stressed that most of the inevitable R-errors don’t precipitate cancer – and that even if they do increase risk, that risk may not ever trip the disease process.
“Most of the time these replicative mutations do no harm,” Dr Vogelstein said. “They occur in junk DNA genes, or in areas that are unimportant with respect to cancer. That’s the good luck. Occasionally, they occur in a cancer driver gene, and that is bad luck.”
But even a dose of bad luck isn’t enough to cause cancer. Most cancers require multiple hits to develop – which makes primary prevention strategies more important than ever, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“In the case of lung cancer, for instance, three or more mutations are needed. We showed that these mutations are caused by a combination of environment and R-errors. In theory, then, all of these cancers are preventable because if we can prevent even one of the environmentally caused mutations, then that patient won’t develop cancer.”
However, he said, some cancers do appear to be entirely driven by E-errors and, thus, appear entirely unavoidable. This is an extremely difficult area for clinicians and patients to navigate, said Dr. Vogelstein, a former pediatrician.
“We hope that understanding this will offer some comfort to the literally millions of patients who develop cancer despite having lead a near-perfect life,” in terms of managing risk factors. “Cancer develops in people who haven’t smoked, who avoided the sun and wore sunscreen, who eat perfectly healthy diets and exercise regularly. This is a particularly important concept for parents of children who have cancer, who think ‘I either transmitted a bad gene or unknowingly exposed my child to an environmental agent that caused their cancer.’ They need to understand that these cancers would have occurred no matter what they did.”
Dr. Tomasetti had no disclosures. Dr. Vogelstein is on the scientific advisory boards of Morphotek, Exelixis GP, and Sysmex Inostics, and is a founder of PapGene and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
Up to two-thirds of the mutations that drive human cancers may be due to DNA replication errors in normally dividing stem cells, not by inherited or environmentally induced mutations, according to a mathematical modeling study.
The proportion of replication error-driven mutations varied widely among 17 cancers analyzed, but the overall attributable risk of these errors was remarkably consistent among 69 countries included in the study, said Cristian Tomasetti, PhD, a coauthor of the paper and a biostatistician at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The findings should be a game-changer in the cancer field, Dr. Tomasetti said during a press briefing sponsored by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Research dogma has long held that most cancers are related to lifestyle and environmental exposure, with a few primarily due to genetic factors.
“We have now determined that there is a third factor, and that it causes most of the mutations that drive cancer,” Dr. Tomasetti said. “We cannot ignore it and pretend it doesn’t exist. This is a complete paradigm shift in how we think of cancer and what causes it.”
The finding that 66% of cancer-driving mutations are based on unavoidable replication errors doesn’t challenge well-established epidemiology, said Dr. Tomasetti and his coauthor, Bert Vogelstein, MD. Rather, it fits perfectly with several key understandings of cancer: that about 40% of cases are preventable, that rapidly dividing tissues are more prone to develop cancers, and that cancer incidence rises exponentially as humans age.
“If we have as our starting point the assumption that 42% of cancers are preventable, we are completely consistent with that,” in finding that about 60% of cancers are unavoidable, Dr. Tomasetti said. “Those two numbers go perfectly together.”
The study also found that replication-error mutations (R) were most likely to drive cancers in tissues with rapid turnover, such as colorectal tissue. This makes intuitive sense, given that basal mutation rates hover at about three errors per cell replication cycle regardless of tissue type.
“The basal mutation rate in all cells is pretty even,” said Dr. Vogelstein, the Clayton Professor of Oncology and Pathology at John Hopkins University, Baltimore. “The difference is the number of stem cells. The more cells, the more divisions, and the more mistakes.”
R-mutations also contribute to age-related cancer incidence. As a person ages, more cell divisions accumulate, thus increasing the risk of a cancer-driving R-error. But these mutations also occur in children, who have rapid cell division in all their tissues. In fact, the colleagues suspect that R-errors are the main drivers of almost all pediatric cancers.
The new study bolsters the duo’s controversial 2015 work.
The theory sparked controversy among scholars and researchers. They challenged it on a number of technical fronts, from stem cell counts and division rates to charges that it didn’t adequately assess the interaction between R-mutations and environmental risks.
Some commentators, perceiving nihilism in the paper, expressed concern that clinicians and patients would get the idea that cancer prevention strategies were useless, since most cancers were simply a case of “bad luck.”
A pervading theme of these counter arguments was one familiar to any researcher: Correlation does not equal causation. The new study was an attempt to expand upon and strengthen the original findings, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“There are well-known environmental risk variations across the world, and there was a question of how our findings might change if we did this analysis in a different country. This paper is also the very first time that someone has ever looked at the proportions of mutations in each cancer type and assigned them to these factors.”
The new study employed a similar mathematical model, but comprised data from 423 cancer registries in 69 countries. The researchers examined the relationship between the lifetime risk of 17 cancers (including breast and prostate, which were not included in the 2015 study) and lifetime stem cell divisions for each tissue. The median correlation coefficient was 0.80; 89% of the countries examined had a correlation of greater than 0.70. This was “remarkably similar” to the correlation determined in the 2015 U.S.-only study.
The team’s next step was to determine what fraction of cancer-driving mutations arose from R-errors, from environmental factors (E), and from hereditary factors (H). They examined these proportions in 32 different cancers in which environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors have been thoroughly studied. Overall, 29% of the driver mutations were due to environment, 5% to heredity, and 66% to R-errors.
The proportions of these drivers did vary widely between the cancer types, the team noted. For example, lung and esophageal cancers and melanoma were primarily driven by environmental factors (more than 60% each). However, they wrote, “even in lung adenocarcinomas, R contributes a third of the total mutations, with tobacco smoke [including secondhand smoke], diet, radiation, and occupational exposures contributing the remainder. In cancers that are less strongly associated with environmental factors, such as those of the pancreas, brain, bone, or prostate, the majority of the mutations are attributable to R.”
During the press briefing, Dr. Tomasetti and Dr. Vogelstein stressed that most of the inevitable R-errors don’t precipitate cancer – and that even if they do increase risk, that risk may not ever trip the disease process.
“Most of the time these replicative mutations do no harm,” Dr Vogelstein said. “They occur in junk DNA genes, or in areas that are unimportant with respect to cancer. That’s the good luck. Occasionally, they occur in a cancer driver gene, and that is bad luck.”
But even a dose of bad luck isn’t enough to cause cancer. Most cancers require multiple hits to develop – which makes primary prevention strategies more important than ever, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“In the case of lung cancer, for instance, three or more mutations are needed. We showed that these mutations are caused by a combination of environment and R-errors. In theory, then, all of these cancers are preventable because if we can prevent even one of the environmentally caused mutations, then that patient won’t develop cancer.”
However, he said, some cancers do appear to be entirely driven by E-errors and, thus, appear entirely unavoidable. This is an extremely difficult area for clinicians and patients to navigate, said Dr. Vogelstein, a former pediatrician.
“We hope that understanding this will offer some comfort to the literally millions of patients who develop cancer despite having lead a near-perfect life,” in terms of managing risk factors. “Cancer develops in people who haven’t smoked, who avoided the sun and wore sunscreen, who eat perfectly healthy diets and exercise regularly. This is a particularly important concept for parents of children who have cancer, who think ‘I either transmitted a bad gene or unknowingly exposed my child to an environmental agent that caused their cancer.’ They need to understand that these cancers would have occurred no matter what they did.”
Dr. Tomasetti had no disclosures. Dr. Vogelstein is on the scientific advisory boards of Morphotek, Exelixis GP, and Sysmex Inostics, and is a founder of PapGene and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
Up to two-thirds of the mutations that drive human cancers may be due to DNA replication errors in normally dividing stem cells, not by inherited or environmentally induced mutations, according to a mathematical modeling study.
The proportion of replication error-driven mutations varied widely among 17 cancers analyzed, but the overall attributable risk of these errors was remarkably consistent among 69 countries included in the study, said Cristian Tomasetti, PhD, a coauthor of the paper and a biostatistician at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The findings should be a game-changer in the cancer field, Dr. Tomasetti said during a press briefing sponsored by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Research dogma has long held that most cancers are related to lifestyle and environmental exposure, with a few primarily due to genetic factors.
“We have now determined that there is a third factor, and that it causes most of the mutations that drive cancer,” Dr. Tomasetti said. “We cannot ignore it and pretend it doesn’t exist. This is a complete paradigm shift in how we think of cancer and what causes it.”
The finding that 66% of cancer-driving mutations are based on unavoidable replication errors doesn’t challenge well-established epidemiology, said Dr. Tomasetti and his coauthor, Bert Vogelstein, MD. Rather, it fits perfectly with several key understandings of cancer: that about 40% of cases are preventable, that rapidly dividing tissues are more prone to develop cancers, and that cancer incidence rises exponentially as humans age.
“If we have as our starting point the assumption that 42% of cancers are preventable, we are completely consistent with that,” in finding that about 60% of cancers are unavoidable, Dr. Tomasetti said. “Those two numbers go perfectly together.”
The study also found that replication-error mutations (R) were most likely to drive cancers in tissues with rapid turnover, such as colorectal tissue. This makes intuitive sense, given that basal mutation rates hover at about three errors per cell replication cycle regardless of tissue type.
“The basal mutation rate in all cells is pretty even,” said Dr. Vogelstein, the Clayton Professor of Oncology and Pathology at John Hopkins University, Baltimore. “The difference is the number of stem cells. The more cells, the more divisions, and the more mistakes.”
R-mutations also contribute to age-related cancer incidence. As a person ages, more cell divisions accumulate, thus increasing the risk of a cancer-driving R-error. But these mutations also occur in children, who have rapid cell division in all their tissues. In fact, the colleagues suspect that R-errors are the main drivers of almost all pediatric cancers.
The new study bolsters the duo’s controversial 2015 work.
The theory sparked controversy among scholars and researchers. They challenged it on a number of technical fronts, from stem cell counts and division rates to charges that it didn’t adequately assess the interaction between R-mutations and environmental risks.
Some commentators, perceiving nihilism in the paper, expressed concern that clinicians and patients would get the idea that cancer prevention strategies were useless, since most cancers were simply a case of “bad luck.”
A pervading theme of these counter arguments was one familiar to any researcher: Correlation does not equal causation. The new study was an attempt to expand upon and strengthen the original findings, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“There are well-known environmental risk variations across the world, and there was a question of how our findings might change if we did this analysis in a different country. This paper is also the very first time that someone has ever looked at the proportions of mutations in each cancer type and assigned them to these factors.”
The new study employed a similar mathematical model, but comprised data from 423 cancer registries in 69 countries. The researchers examined the relationship between the lifetime risk of 17 cancers (including breast and prostate, which were not included in the 2015 study) and lifetime stem cell divisions for each tissue. The median correlation coefficient was 0.80; 89% of the countries examined had a correlation of greater than 0.70. This was “remarkably similar” to the correlation determined in the 2015 U.S.-only study.
The team’s next step was to determine what fraction of cancer-driving mutations arose from R-errors, from environmental factors (E), and from hereditary factors (H). They examined these proportions in 32 different cancers in which environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors have been thoroughly studied. Overall, 29% of the driver mutations were due to environment, 5% to heredity, and 66% to R-errors.
The proportions of these drivers did vary widely between the cancer types, the team noted. For example, lung and esophageal cancers and melanoma were primarily driven by environmental factors (more than 60% each). However, they wrote, “even in lung adenocarcinomas, R contributes a third of the total mutations, with tobacco smoke [including secondhand smoke], diet, radiation, and occupational exposures contributing the remainder. In cancers that are less strongly associated with environmental factors, such as those of the pancreas, brain, bone, or prostate, the majority of the mutations are attributable to R.”
During the press briefing, Dr. Tomasetti and Dr. Vogelstein stressed that most of the inevitable R-errors don’t precipitate cancer – and that even if they do increase risk, that risk may not ever trip the disease process.
“Most of the time these replicative mutations do no harm,” Dr Vogelstein said. “They occur in junk DNA genes, or in areas that are unimportant with respect to cancer. That’s the good luck. Occasionally, they occur in a cancer driver gene, and that is bad luck.”
But even a dose of bad luck isn’t enough to cause cancer. Most cancers require multiple hits to develop – which makes primary prevention strategies more important than ever, Dr. Tomasetti said.
“In the case of lung cancer, for instance, three or more mutations are needed. We showed that these mutations are caused by a combination of environment and R-errors. In theory, then, all of these cancers are preventable because if we can prevent even one of the environmentally caused mutations, then that patient won’t develop cancer.”
However, he said, some cancers do appear to be entirely driven by E-errors and, thus, appear entirely unavoidable. This is an extremely difficult area for clinicians and patients to navigate, said Dr. Vogelstein, a former pediatrician.
“We hope that understanding this will offer some comfort to the literally millions of patients who develop cancer despite having lead a near-perfect life,” in terms of managing risk factors. “Cancer develops in people who haven’t smoked, who avoided the sun and wore sunscreen, who eat perfectly healthy diets and exercise regularly. This is a particularly important concept for parents of children who have cancer, who think ‘I either transmitted a bad gene or unknowingly exposed my child to an environmental agent that caused their cancer.’ They need to understand that these cancers would have occurred no matter what they did.”
Dr. Tomasetti had no disclosures. Dr. Vogelstein is on the scientific advisory boards of Morphotek, Exelixis GP, and Sysmex Inostics, and is a founder of PapGene and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Two-thirds (66%) of cancer drivers are replication errors, 29% are environmentally induced, and 5% are hereditary.
Data source: The researchers examined cancer mutation drivers in two cohorts that spanned 69 countries.
Disclosures: Dr. Tomasetti had no disclosures. Dr. Vogelstein is on the scientific advisory boards of Morphotek, Exelixis GP, and Sysmex Inostics, and is a founder of PapGene and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
Phase III trial: VZV protects auto-HCT patients
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
AT THE 2017 BMT TANDEM MEETINGS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Overall incidence of herpes zoster was 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years vs. 91.8/1,000 patient-years in patients in the vaccine and placebo groups, respectively.
Data source: A randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial involving 1,230 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
For mantle cell lymphoma, VR-CAP beat R-CHOP
For patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, duration and quality of response were superior with a regimen of bortezomib, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) when compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), based on a post hoc analysis of the randomized, phase III LYM-3002 trial.
The difference was especially evident among patients who had a low- or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index, Gregor Verhoef, MD, of University Hospital Leuven (Belgium) and his associates wrote in Haematologica.
In LYM-3002, 487 patients with newly diagnosed stage II-IV mantle cell lymphoma received six to eight 21-day cycles of intravenous VR-CAP or R-CHOP. Although overall response rates were similar for both groups, VR-CAP was associated with better duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) and extended time to next treatment. To further explore these differences, the post hoc analysis stratified outcomes by response categories and analyzed depth of response based on computed tomography (CT) scans. Patients had a median age of about 65 years, and most were white males with stage-IV disease at diagnosis and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 1 (Haematologica. 2017 Feb 9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.152496).The superiority of VR-CAP held up across response categories. Complete responders to VR-CAP had more than twice the median PFS as did complete responders to R-CHOP (40.9 vs. 19.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.84; P = .004). Among partial responders, median PFS was 17.1 vs. 11.7 months, respectively (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.89; P = .01). Respective median duration of overall response was 42.1 months for VR-CAP vs. 18.5 months among complete responders (HR, 0.42; P less than .001), and 20.2 vs. 9.6 months among partial responders (HR, 0.57; P = .006).
Median time to next treatment also favored VR-CAP over R-CHOP among both complete responders (not evaluable vs. 26.6 months; HR, 0.42; P less than .001) and partial responders (35.3 vs. 24.3 months; HR, 0.57; P = .006), the researchers said. Further, CT scans showed that proportionally more patients in each response category became lesion-negative on VR-CAP than on R-CHOP. Among complete responders, rates of lesion negativity were 72% and 59%, respectively. Among partial responders, rates were 48% and 28%.
The effects of VR-CAP were most evident among patients with a low or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index. Perhaps high-risk status signifies more rapidly proliferative disease, which negates the deeper responses with VR-CAP, compared with R-CHOP, they added.
The LYM-3002 study was supported by Janssen Research & Development and Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Verhoef had no disclosures. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Janssen, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
For patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, duration and quality of response were superior with a regimen of bortezomib, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) when compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), based on a post hoc analysis of the randomized, phase III LYM-3002 trial.
The difference was especially evident among patients who had a low- or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index, Gregor Verhoef, MD, of University Hospital Leuven (Belgium) and his associates wrote in Haematologica.
In LYM-3002, 487 patients with newly diagnosed stage II-IV mantle cell lymphoma received six to eight 21-day cycles of intravenous VR-CAP or R-CHOP. Although overall response rates were similar for both groups, VR-CAP was associated with better duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) and extended time to next treatment. To further explore these differences, the post hoc analysis stratified outcomes by response categories and analyzed depth of response based on computed tomography (CT) scans. Patients had a median age of about 65 years, and most were white males with stage-IV disease at diagnosis and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 1 (Haematologica. 2017 Feb 9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.152496).The superiority of VR-CAP held up across response categories. Complete responders to VR-CAP had more than twice the median PFS as did complete responders to R-CHOP (40.9 vs. 19.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.84; P = .004). Among partial responders, median PFS was 17.1 vs. 11.7 months, respectively (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.89; P = .01). Respective median duration of overall response was 42.1 months for VR-CAP vs. 18.5 months among complete responders (HR, 0.42; P less than .001), and 20.2 vs. 9.6 months among partial responders (HR, 0.57; P = .006).
Median time to next treatment also favored VR-CAP over R-CHOP among both complete responders (not evaluable vs. 26.6 months; HR, 0.42; P less than .001) and partial responders (35.3 vs. 24.3 months; HR, 0.57; P = .006), the researchers said. Further, CT scans showed that proportionally more patients in each response category became lesion-negative on VR-CAP than on R-CHOP. Among complete responders, rates of lesion negativity were 72% and 59%, respectively. Among partial responders, rates were 48% and 28%.
The effects of VR-CAP were most evident among patients with a low or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index. Perhaps high-risk status signifies more rapidly proliferative disease, which negates the deeper responses with VR-CAP, compared with R-CHOP, they added.
The LYM-3002 study was supported by Janssen Research & Development and Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Verhoef had no disclosures. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Janssen, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
For patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, duration and quality of response were superior with a regimen of bortezomib, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) when compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), based on a post hoc analysis of the randomized, phase III LYM-3002 trial.
The difference was especially evident among patients who had a low- or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index, Gregor Verhoef, MD, of University Hospital Leuven (Belgium) and his associates wrote in Haematologica.
In LYM-3002, 487 patients with newly diagnosed stage II-IV mantle cell lymphoma received six to eight 21-day cycles of intravenous VR-CAP or R-CHOP. Although overall response rates were similar for both groups, VR-CAP was associated with better duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) and extended time to next treatment. To further explore these differences, the post hoc analysis stratified outcomes by response categories and analyzed depth of response based on computed tomography (CT) scans. Patients had a median age of about 65 years, and most were white males with stage-IV disease at diagnosis and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 1 (Haematologica. 2017 Feb 9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.152496).The superiority of VR-CAP held up across response categories. Complete responders to VR-CAP had more than twice the median PFS as did complete responders to R-CHOP (40.9 vs. 19.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.84; P = .004). Among partial responders, median PFS was 17.1 vs. 11.7 months, respectively (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.89; P = .01). Respective median duration of overall response was 42.1 months for VR-CAP vs. 18.5 months among complete responders (HR, 0.42; P less than .001), and 20.2 vs. 9.6 months among partial responders (HR, 0.57; P = .006).
Median time to next treatment also favored VR-CAP over R-CHOP among both complete responders (not evaluable vs. 26.6 months; HR, 0.42; P less than .001) and partial responders (35.3 vs. 24.3 months; HR, 0.57; P = .006), the researchers said. Further, CT scans showed that proportionally more patients in each response category became lesion-negative on VR-CAP than on R-CHOP. Among complete responders, rates of lesion negativity were 72% and 59%, respectively. Among partial responders, rates were 48% and 28%.
The effects of VR-CAP were most evident among patients with a low or medium-risk mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index. Perhaps high-risk status signifies more rapidly proliferative disease, which negates the deeper responses with VR-CAP, compared with R-CHOP, they added.
The LYM-3002 study was supported by Janssen Research & Development and Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Verhoef had no disclosures. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Janssen, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Key clinical point: A regimen of bortezomib, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) led to superior duration and quality of response when compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma.
Major finding: Among complete responders, median progression-free survival on VR-CAP was nearly twice that of R-CHOP (40.9 vs. 19.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.84; P = .004).
Data source: A post hoc analysis of a phase III trial comparing VR-CAP with R-CHOP in 487 patients with newly diagnosed, measurable stage II-IV mantle cell lymphoma (LYM-3002).
Disclosures: The LYM-3002 study was supported by Janssen Research & Development and Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Verhoef had no disclosures. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Janssen, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.