User login
Testosterone Increases Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Trans Men
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
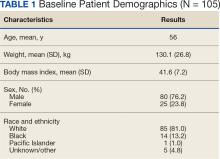
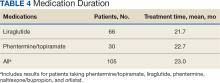
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The SOPHIA Project Conceives of Obesity Beyond BMI
During a lecture at the 2024 International Congress on Obesity in São Paulo, Brazil, Dr. Carel Le Roux, a South African researcher, reflected on the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Therapy (SOPHIA) project. The effort, of which Dr. Le Roux is a leader, involves using federated data and reframing obesity as a set of diseases, each with its own peculiarities and treatment needs.
A collaborative research initiative led by the European Union, the SOPHIA project is a public-private partnership that brings together healthcare professionals, universities, industry leaders, and patient organizations to rethink how we understand and treat obesity, considering factors beyond body mass index (BMI).
“We need to ask ourselves, ‘Is obesity a disease? Or, in fact, does ‘obesity’ refer to multiple diseases that lead to excess adipose tissue?’ ” Dr. Le Roux asked at the beginning of his presentation.
The researcher, who is also the director of the Obesity and Metabolic Medicine Group, stated that obesity can no longer be seen as a single homogeneous pathology but rather should be viewed as clinical conditions affecting various subpopulations that respond differently to treatments.
Patients are currently diagnosed with obesity based on BMI value or waist measurement, as recommended by current clinical guidelines, but this method contributes to treating obesity subtypes as if they were identical.
“By taking into account the patient’s specificities, we can identify individuals who are likely to progress rapidly with the disease and those who will respond well to targeted interventions,” said Dr. Le Roux, emphasizing that this approach also contributes to reducing public health system costs.
Researchers proposed creating a map that allows the visualization of the distinct characteristics of patients with obesity, such as the presence of associated diseases like hypertension and diabetes. One of the main challenges of the project was finding a way to share sensitive data among SOPHIA partners without compromising individual privacy. The solution was the creation of a federated database.
In practice, this system allows academic and industry partners to send data to a central server, which keeps them protected. “We wanted to reach the optimal point, where we can have maximum utility and maximum privacy protection using technology. Researchers can then obtain statistics, enabling the analysis of large data sets without compromising security,” Dr. Le Roux explained.
Most patients analyzed in the project fall into the main group, where “the higher the weight, the greater the risk” for associated diseases, he added. However, the project allows for specifically visualizing patients with alterations related to high blood pressure, liver function, lipid profile, blood glucose, and inflammation.
“Subclassifying diseases helps us better understand the various mechanisms by which these pathologies arise and why some individuals exhibit unexpected phenotypic patterns of increased susceptibility or resilience. For example, patients with inflammation changes have a much higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and liver failure,” said Dr. Le Roux.
In addition to visualizing the associated diseases of each participant, SOPHIA, in which 30 partners in Europe, the Middle East, and the United States participate, also features treatment overlap, which allows researchers to track individual responses to the treatment.
“With this overlap, we confirm something that many know: When treating people with type 2 diabetes, whether through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgery, weight loss is lower. But, to our surprise, we found that patients with inflammation-related changes had greater weight loss. This finding tells us that some groups benefit more, and others less,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This analysis is particularly interesting when it comes to bariatric surgery, he continued. “Often, the surgeon performs an incredibly well-done gastric bypass, and the response is not as expected. In this case, we can say that it is purely biology,” said Dr. Le Roux, who concluded the presentation by discussing the benefits of this approach for good patient counseling.
“When we talk about ‘obesities’ and not ‘obesity,’ we can also conduct our consultations more carefully by explaining to our patients that if they do not respond to treatment, it is not their fault, not because they did something wrong, but because of something that is not usually taken into account, such as the presence of comorbidities, or even personal characteristics and lifestyle, such as age and smoking,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a lecture at the 2024 International Congress on Obesity in São Paulo, Brazil, Dr. Carel Le Roux, a South African researcher, reflected on the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Therapy (SOPHIA) project. The effort, of which Dr. Le Roux is a leader, involves using federated data and reframing obesity as a set of diseases, each with its own peculiarities and treatment needs.
A collaborative research initiative led by the European Union, the SOPHIA project is a public-private partnership that brings together healthcare professionals, universities, industry leaders, and patient organizations to rethink how we understand and treat obesity, considering factors beyond body mass index (BMI).
“We need to ask ourselves, ‘Is obesity a disease? Or, in fact, does ‘obesity’ refer to multiple diseases that lead to excess adipose tissue?’ ” Dr. Le Roux asked at the beginning of his presentation.
The researcher, who is also the director of the Obesity and Metabolic Medicine Group, stated that obesity can no longer be seen as a single homogeneous pathology but rather should be viewed as clinical conditions affecting various subpopulations that respond differently to treatments.
Patients are currently diagnosed with obesity based on BMI value or waist measurement, as recommended by current clinical guidelines, but this method contributes to treating obesity subtypes as if they were identical.
“By taking into account the patient’s specificities, we can identify individuals who are likely to progress rapidly with the disease and those who will respond well to targeted interventions,” said Dr. Le Roux, emphasizing that this approach also contributes to reducing public health system costs.
Researchers proposed creating a map that allows the visualization of the distinct characteristics of patients with obesity, such as the presence of associated diseases like hypertension and diabetes. One of the main challenges of the project was finding a way to share sensitive data among SOPHIA partners without compromising individual privacy. The solution was the creation of a federated database.
In practice, this system allows academic and industry partners to send data to a central server, which keeps them protected. “We wanted to reach the optimal point, where we can have maximum utility and maximum privacy protection using technology. Researchers can then obtain statistics, enabling the analysis of large data sets without compromising security,” Dr. Le Roux explained.
Most patients analyzed in the project fall into the main group, where “the higher the weight, the greater the risk” for associated diseases, he added. However, the project allows for specifically visualizing patients with alterations related to high blood pressure, liver function, lipid profile, blood glucose, and inflammation.
“Subclassifying diseases helps us better understand the various mechanisms by which these pathologies arise and why some individuals exhibit unexpected phenotypic patterns of increased susceptibility or resilience. For example, patients with inflammation changes have a much higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and liver failure,” said Dr. Le Roux.
In addition to visualizing the associated diseases of each participant, SOPHIA, in which 30 partners in Europe, the Middle East, and the United States participate, also features treatment overlap, which allows researchers to track individual responses to the treatment.
“With this overlap, we confirm something that many know: When treating people with type 2 diabetes, whether through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgery, weight loss is lower. But, to our surprise, we found that patients with inflammation-related changes had greater weight loss. This finding tells us that some groups benefit more, and others less,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This analysis is particularly interesting when it comes to bariatric surgery, he continued. “Often, the surgeon performs an incredibly well-done gastric bypass, and the response is not as expected. In this case, we can say that it is purely biology,” said Dr. Le Roux, who concluded the presentation by discussing the benefits of this approach for good patient counseling.
“When we talk about ‘obesities’ and not ‘obesity,’ we can also conduct our consultations more carefully by explaining to our patients that if they do not respond to treatment, it is not their fault, not because they did something wrong, but because of something that is not usually taken into account, such as the presence of comorbidities, or even personal characteristics and lifestyle, such as age and smoking,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a lecture at the 2024 International Congress on Obesity in São Paulo, Brazil, Dr. Carel Le Roux, a South African researcher, reflected on the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Therapy (SOPHIA) project. The effort, of which Dr. Le Roux is a leader, involves using federated data and reframing obesity as a set of diseases, each with its own peculiarities and treatment needs.
A collaborative research initiative led by the European Union, the SOPHIA project is a public-private partnership that brings together healthcare professionals, universities, industry leaders, and patient organizations to rethink how we understand and treat obesity, considering factors beyond body mass index (BMI).
“We need to ask ourselves, ‘Is obesity a disease? Or, in fact, does ‘obesity’ refer to multiple diseases that lead to excess adipose tissue?’ ” Dr. Le Roux asked at the beginning of his presentation.
The researcher, who is also the director of the Obesity and Metabolic Medicine Group, stated that obesity can no longer be seen as a single homogeneous pathology but rather should be viewed as clinical conditions affecting various subpopulations that respond differently to treatments.
Patients are currently diagnosed with obesity based on BMI value or waist measurement, as recommended by current clinical guidelines, but this method contributes to treating obesity subtypes as if they were identical.
“By taking into account the patient’s specificities, we can identify individuals who are likely to progress rapidly with the disease and those who will respond well to targeted interventions,” said Dr. Le Roux, emphasizing that this approach also contributes to reducing public health system costs.
Researchers proposed creating a map that allows the visualization of the distinct characteristics of patients with obesity, such as the presence of associated diseases like hypertension and diabetes. One of the main challenges of the project was finding a way to share sensitive data among SOPHIA partners without compromising individual privacy. The solution was the creation of a federated database.
In practice, this system allows academic and industry partners to send data to a central server, which keeps them protected. “We wanted to reach the optimal point, where we can have maximum utility and maximum privacy protection using technology. Researchers can then obtain statistics, enabling the analysis of large data sets without compromising security,” Dr. Le Roux explained.
Most patients analyzed in the project fall into the main group, where “the higher the weight, the greater the risk” for associated diseases, he added. However, the project allows for specifically visualizing patients with alterations related to high blood pressure, liver function, lipid profile, blood glucose, and inflammation.
“Subclassifying diseases helps us better understand the various mechanisms by which these pathologies arise and why some individuals exhibit unexpected phenotypic patterns of increased susceptibility or resilience. For example, patients with inflammation changes have a much higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and liver failure,” said Dr. Le Roux.
In addition to visualizing the associated diseases of each participant, SOPHIA, in which 30 partners in Europe, the Middle East, and the United States participate, also features treatment overlap, which allows researchers to track individual responses to the treatment.
“With this overlap, we confirm something that many know: When treating people with type 2 diabetes, whether through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgery, weight loss is lower. But, to our surprise, we found that patients with inflammation-related changes had greater weight loss. This finding tells us that some groups benefit more, and others less,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This analysis is particularly interesting when it comes to bariatric surgery, he continued. “Often, the surgeon performs an incredibly well-done gastric bypass, and the response is not as expected. In this case, we can say that it is purely biology,” said Dr. Le Roux, who concluded the presentation by discussing the benefits of this approach for good patient counseling.
“When we talk about ‘obesities’ and not ‘obesity,’ we can also conduct our consultations more carefully by explaining to our patients that if they do not respond to treatment, it is not their fault, not because they did something wrong, but because of something that is not usually taken into account, such as the presence of comorbidities, or even personal characteristics and lifestyle, such as age and smoking,” said Dr. Le Roux.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Meet the Pregnancy Challenges of Women With Chronic Conditions
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Expanding Use of GLP-1 RAs for Weight Management
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mounjaro Beats Ozempic, So Why Isn’t It More Popular?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 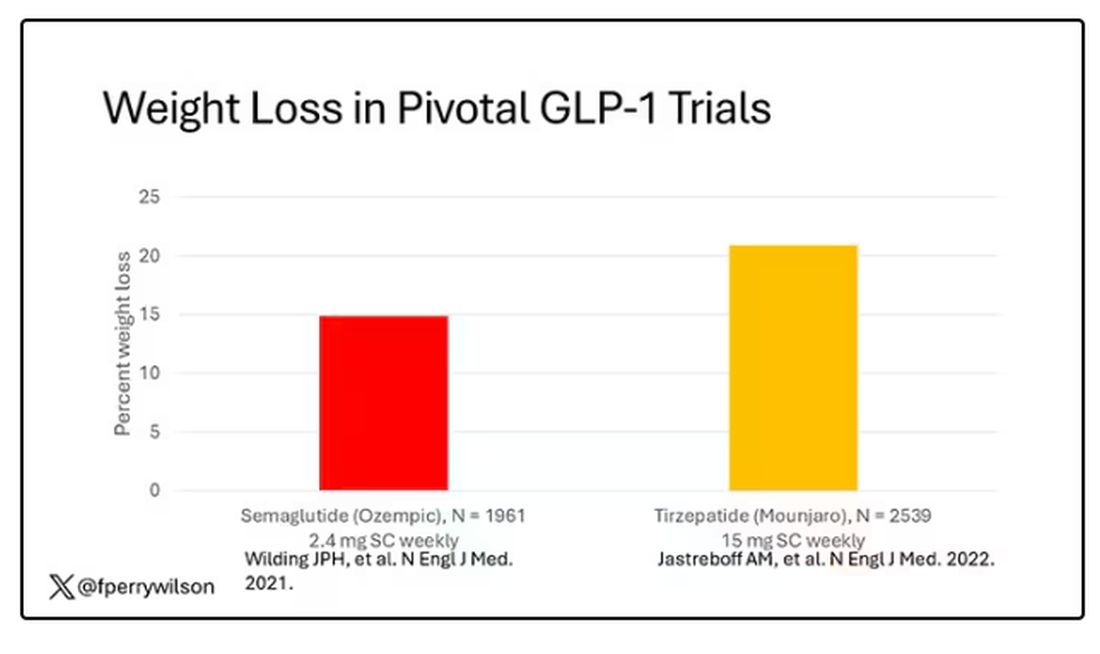
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
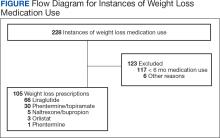
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 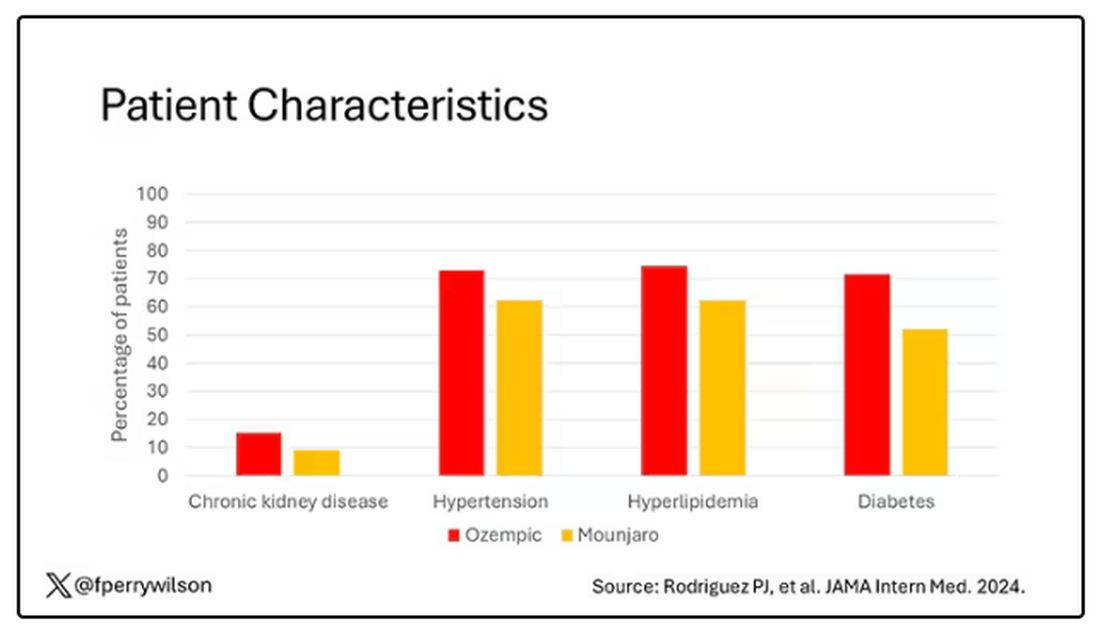
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.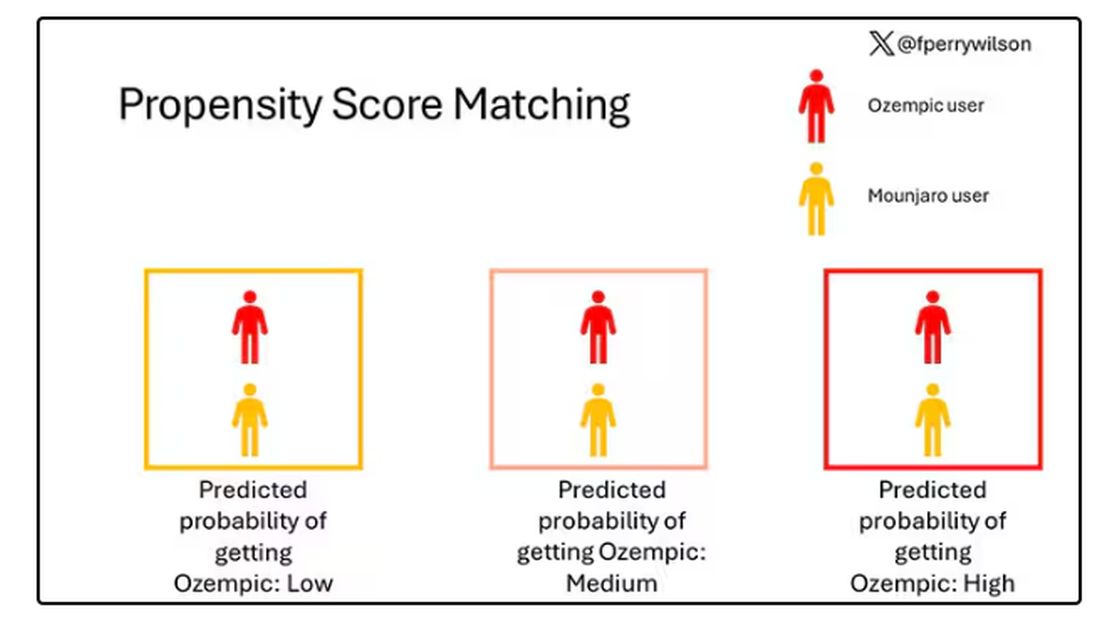
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.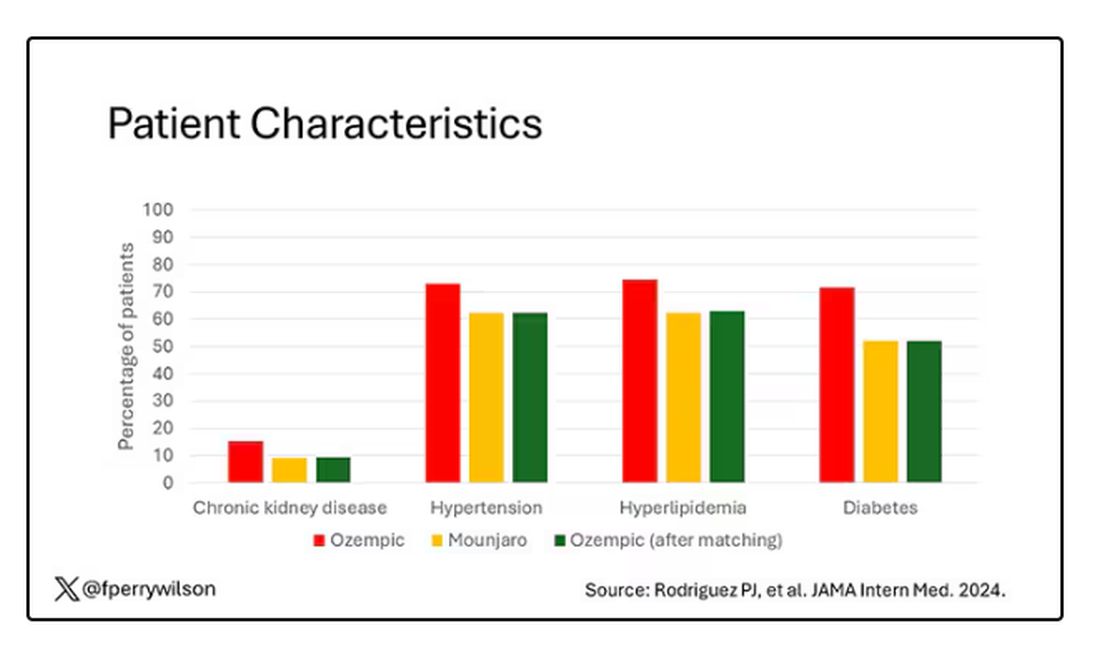
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 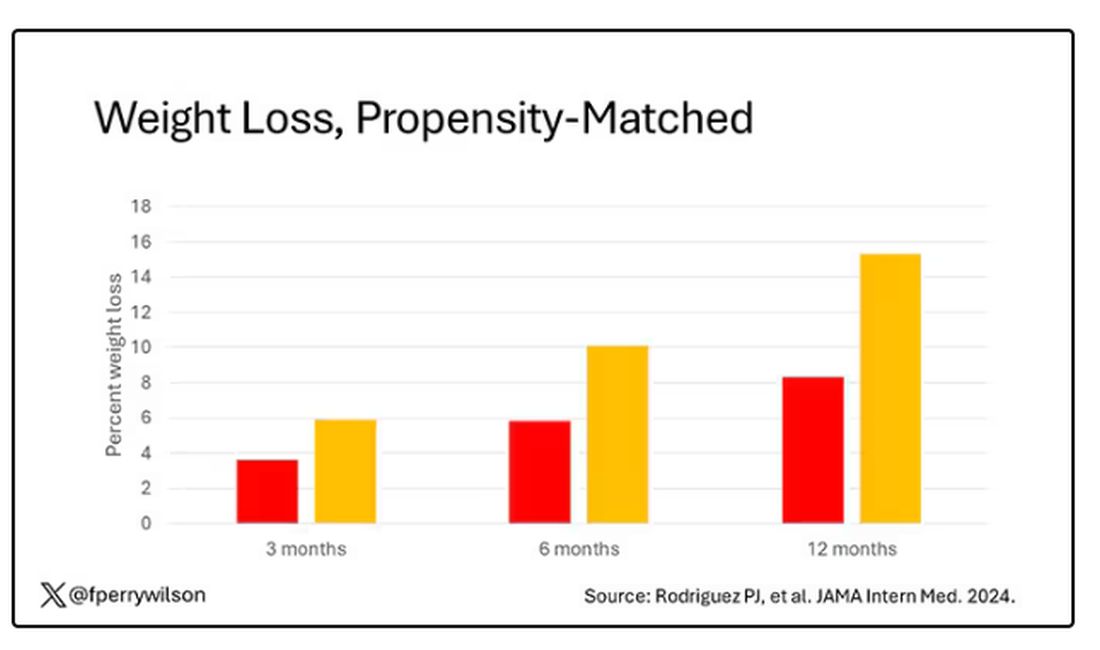
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.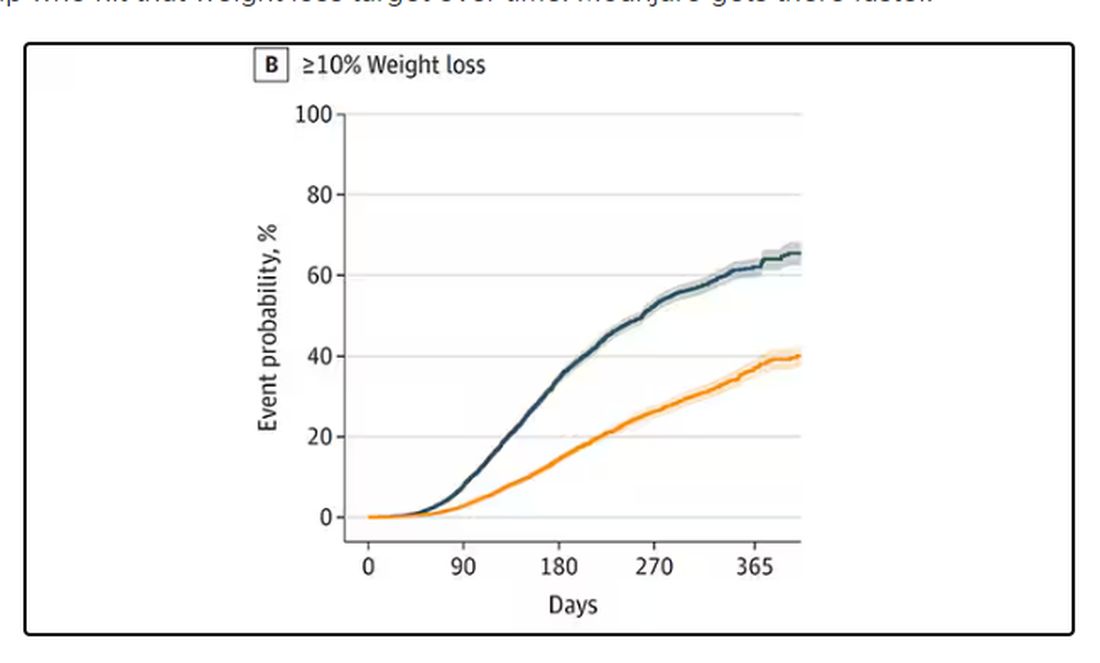
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether GLP-1 RAs Significantly Delay Gastric Emptying Called into Question
TOPLINE:
Patients taking a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) experience only a modest delay in gastric emptying of solid foods and no significant delay for liquids, compared with those receiving placebo, indicating that patients may not need to discontinue these medications before surgery.
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs, while effective in managing diabetes and obesity, are linked to delayed gastric emptying, which may pose risks during procedures requiring anesthesia or sedation due to potential aspiration of gastric contents.
- Researchers conducted a meta-analysis to quantify the duration of delay in gastric emptying caused by GLP-1 RAs in patients with diabetes and/or excessive body weight, which could guide periprocedural management decisions in the future.
- The primary outcome was halftime, the time required for 50% of solid gastric contents to empty, measured using scintigraphy. This analysis included data from five studies involving 247 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo.
- The secondary outcome was gastric emptying of liquids measured using the acetaminophen absorption test. Ten studies including 411 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo were included in this analysis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean gastric emptying halftime for solid foods was 138.4 minutes with a GLP-1 RA and 95.0 minutes with placebo, resulting in a pooled mean difference of 36.0 minutes (P < .01).
- Furthermore, the amount of gastric emptying noted at 4 or 5 hours on the acetaminophen absorption test was comparable between these groups.
- The gastric emptying time for both solids and liquids did not differ between GLP-1 RA formulations or between short-acting or long-acting GLP-1 RAs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on current evidence, a conservative approach with a liquid diet on the day before procedures while continuing GLP-1 RA therapy would represent the most sensible approach until more conclusive data on a solid diet are available,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Brent Hiramoto, MD, MPH, of the Center for Gastrointestinal Motility at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of studies utilizing some diagnostic modalities, such as breath testing, precluded a formal meta-analysis of these subgroups. The results could not be stratified by indication for GLP-1 RA (diabetes or obesity) because of insufficient studies in each category.
DISCLOSURES:
The lead author was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author declared serving on the advisory boards of three pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients taking a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) experience only a modest delay in gastric emptying of solid foods and no significant delay for liquids, compared with those receiving placebo, indicating that patients may not need to discontinue these medications before surgery.
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs, while effective in managing diabetes and obesity, are linked to delayed gastric emptying, which may pose risks during procedures requiring anesthesia or sedation due to potential aspiration of gastric contents.
- Researchers conducted a meta-analysis to quantify the duration of delay in gastric emptying caused by GLP-1 RAs in patients with diabetes and/or excessive body weight, which could guide periprocedural management decisions in the future.
- The primary outcome was halftime, the time required for 50% of solid gastric contents to empty, measured using scintigraphy. This analysis included data from five studies involving 247 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo.
- The secondary outcome was gastric emptying of liquids measured using the acetaminophen absorption test. Ten studies including 411 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo were included in this analysis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean gastric emptying halftime for solid foods was 138.4 minutes with a GLP-1 RA and 95.0 minutes with placebo, resulting in a pooled mean difference of 36.0 minutes (P < .01).
- Furthermore, the amount of gastric emptying noted at 4 or 5 hours on the acetaminophen absorption test was comparable between these groups.
- The gastric emptying time for both solids and liquids did not differ between GLP-1 RA formulations or between short-acting or long-acting GLP-1 RAs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on current evidence, a conservative approach with a liquid diet on the day before procedures while continuing GLP-1 RA therapy would represent the most sensible approach until more conclusive data on a solid diet are available,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Brent Hiramoto, MD, MPH, of the Center for Gastrointestinal Motility at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of studies utilizing some diagnostic modalities, such as breath testing, precluded a formal meta-analysis of these subgroups. The results could not be stratified by indication for GLP-1 RA (diabetes or obesity) because of insufficient studies in each category.
DISCLOSURES:
The lead author was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author declared serving on the advisory boards of three pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients taking a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) experience only a modest delay in gastric emptying of solid foods and no significant delay for liquids, compared with those receiving placebo, indicating that patients may not need to discontinue these medications before surgery.
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs, while effective in managing diabetes and obesity, are linked to delayed gastric emptying, which may pose risks during procedures requiring anesthesia or sedation due to potential aspiration of gastric contents.
- Researchers conducted a meta-analysis to quantify the duration of delay in gastric emptying caused by GLP-1 RAs in patients with diabetes and/or excessive body weight, which could guide periprocedural management decisions in the future.
- The primary outcome was halftime, the time required for 50% of solid gastric contents to empty, measured using scintigraphy. This analysis included data from five studies involving 247 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo.
- The secondary outcome was gastric emptying of liquids measured using the acetaminophen absorption test. Ten studies including 411 patients who received either a GLP-1 RA or placebo were included in this analysis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean gastric emptying halftime for solid foods was 138.4 minutes with a GLP-1 RA and 95.0 minutes with placebo, resulting in a pooled mean difference of 36.0 minutes (P < .01).
- Furthermore, the amount of gastric emptying noted at 4 or 5 hours on the acetaminophen absorption test was comparable between these groups.
- The gastric emptying time for both solids and liquids did not differ between GLP-1 RA formulations or between short-acting or long-acting GLP-1 RAs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on current evidence, a conservative approach with a liquid diet on the day before procedures while continuing GLP-1 RA therapy would represent the most sensible approach until more conclusive data on a solid diet are available,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Brent Hiramoto, MD, MPH, of the Center for Gastrointestinal Motility at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of studies utilizing some diagnostic modalities, such as breath testing, precluded a formal meta-analysis of these subgroups. The results could not be stratified by indication for GLP-1 RA (diabetes or obesity) because of insufficient studies in each category.
DISCLOSURES:
The lead author was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author declared serving on the advisory boards of three pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-Term Assessment of Weight Loss Medications in a Veteran Population
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classifies individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 29.9as overweight and those with a BMI > 30 as obese (obesity classes: I, BMI 30 to 34.9; II, BMI 35 to 39.9; and III, BMI ≥ 40).1 In 2011, the CDC estimated that 27.4% of adults in the United States were obese; less than a decade later, that number increased to 31.9%.1 In that same period, the percentage of adults in Indiana classified as obese increased from 30.8% to 36.8%.1 About 1 in 14 individuals in the US have class III obesity and 86% of veterans are either overweight or obese.2
High medical expenses can likely be attributed to the long-term health consequences of obesity. Compared to those with a healthy weight, individuals who are overweight or obese are at an increased risk for high blood pressure, high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), coronary heart disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, cancer, mental health disorders, body pain, low quality of life, and death.3 Many of these conditions lead to increased health care needs, medication needs, hospitalizations, and overall health care system use.
Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of obesity have been produced by the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and The Obesity Society; the Endocrine Society; the American Diabetes Association; and the US Departments of Veterans Affairs (VA) and Defense. Each follows a general algorithm to manage and prevent adverse effects (AEs) related to obesity. General practice is to assess a patient for elevated BMI (> 25), implement intense lifestyle modifications including calorie restriction and exercise, reassess for a maintained 5% to 10% weight loss for cardiovascular benefits, and potentially assess for pharmacological or surgical intervention to assist in weight loss.2,4-6
While some weight loss medications (eg, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and lorcaserin) tend to have unfavorable AEs or mixed efficacy, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have provided new options.7-10 Lorcaserin, for example, was removed from the market in 2020 due to its association with cancer risks.11 The GLP-1RAs liraglutide and semaglutide received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for weight loss in 2014 and 2021, respectively.12,13 GLP-1RAs have shown the greatest efficacy and benefits in reducing hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c); they are the preferred agents for patients who qualify for pharmacologic intervention for weight loss, especially those with T2DM. However, these studies have not evaluated the long-term outcomes of using these medications for weight loss and may not reflect the veteran population.14,15
At Veteran Health Indiana (VHI), clinicians may use several weight loss medications for patients to achieve 5% to 10% weight loss. The medications most often used include liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone. However, more research is needed to determine which weight loss medication is the most beneficial for veterans, particularly following FDA approval of GLP-1RAs. At VHI, phentermine/topiramate is the preferred first-line agent unless patients have contraindications for use, in which case naltrexone/bupropion is recommended. These are considered first-line due to their ease of use in pill form, lower cost, and comparable weight loss to the GLP-1 medication class.2 However, for patients with prediabetes, T2DM, BMI > 40, or BMI > 35 with specific comorbid conditions, liraglutide is preferred because of its beneficial effects for both weight loss and blood glucose control.2
This study aimed to expand on the 2021 Hood and colleagues study that examined total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage of baseline weight in patients with obesity at 3, 6, 12, and > 12 months of pharmacologic therapy by extending the time frame to 48 months.16 This study excluded semaglutide because few patients were prescribed the medication for weight loss during the study.
METHODS
We conducted a single-center, retrospective chart review of patients prescribed weight loss medications at VHI. A patient list was generated based on prescription fills from June 1, 2017, to July 31, 2021. Data were obtained from the Computerized Patient Record System; patients were not contacted. This study was approved by the Indiana University Health Institutional Review Board and VHI Research and Development Committee.
At the time of this study, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone were available at VHI for patients who met the clinical criteria for use. All patients must have been enrolled in dietary and lifestyle management programs, including the VA MOVE! program, to be approved for these medications. After the MOVE! orientation, patients could participate in group or individual 12-week programs that included weigh-ins, goal-setting strategies, meal planning, and habit modification support. If patients could not meet in person, phone and other telehealth opportunities were available.
Patients were included in the study if they were aged ≥ 18 years, received a prescription for any of the 5 available medications for weight loss during the enrollment period, and were on the medication for ≥ 6 consecutive months. Patients were excluded if they received a prescription, were treated outside the VA system, or were pregnant. The primary indication for the included medication was not weight loss; the primary indication for the GLP-1RA was T2DM, or the weight loss was attributed to another disease. Adherence was not a measured outcome of this study; if patients were filling the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. Data were collected for each instance of medication use; as a result, a few patients were included more than once. Data collection for a failed medication ended when failure was documented. New data points began when new medication was prescribed; all data were per medication, not per patient. This allowed us to account for medication failure and provide accurate weight loss results based on medication choice within VHI.
Primary outcomes included total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage ofbaseline weight during the study period at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of therapy. Secondary outcomes included the percentage of patients who lost 5% to 10% of their body weight from baseline; the percentage of patients who maintained ≥ 5% weight loss from baseline to 12, 24, 36, and 48 months if maintained on medication for that duration; duration of medication treatment in weeks; medication discontinuation rate; reason for medication discontinuation; enrollment in the MOVE! clinic and the time enrolled; percentage of patients with a BMI of 18 to 24.9 at the end of the study; and change in HbA1c at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months.
Demographic data included race, age, sex, baseline weight, height, baseline BMI, and comorbid conditions (collected based on the most recent primary care clinical note before initiating medication). Medication data collected included medications used to manage comorbidities. Data related to weight management medication included prescribing clinic, maintenance dose of medication, duration of medication during the study period, the reason for medication discontinuation, or bariatric surgery intervention if applicable.
Basic descriptive statistics were used to characterize study participants. For continuous data, analysis of variance tests were used; if those results were not normal, then nonparametric tests were used, followed by pairwise tests between medication groups if the overall test was significant using the Fisher significant differences test. For nominal data, χ2 or Fisher exact tests were used. For comparisons of primary and secondary outcomes, if the analyses needed to include adjustment for confounding variables, analysis of covariance was used for continuous data. A 2-sided 5% significance level was used for all tests.
RESULTS
A total of 228 instances of medication use were identified based on prescription fills; 123 did not meet inclusion criteria (117 for < 6 consecutive months of medication use) (Figure). The study included 105 participants with a mean age of 56 years; 80 were male (76.2%), and 85 identified as White race (81.0%). Mean (SD) weight was 130.1 kg (26.8) and BMI was 41.6 (7.2). The most common comorbid disease states among patients included hypertension, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, and T2DM (Table 1). The baseline characteristics were comparable to those of Hood and colleagues.16
Most patients at VHI started on liraglutide (63%) or phentermine/topiramate (28%). For primary and secondary outcomes, statistics were calculated to determine whether the results were statistically significant for comparing the liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate subgroups. Sample sizes were too small for statistical analysis for bupropion/naltrexone, phentermine, and orlistat.
Primary Outcomes
The mean (SD) weight of participants dropped 8.1% from 130.1 kg to 119.5 kg over the patient-specific duration of weight management medication therapy for an absolute difference of 10.6 kg (9.7). Duration of individual medication use varied from 6 to 48 months. Weight loss was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. Patient weight was not recorded after the medication was discontinued.
When classified by medication choice, the mean change in weight over the duration of the study was −23.9 kg for 2 patients using orlistat, −10.2 kg for 46 patients using liraglutide, −11.0 kg for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, -7.4 kg for 1 patient using phentermine, and -13.0 kg for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion. Patients without a weight documented at the end of their therapy or at the conclusion of the data collection period were not included in the total weight loss at the end of therapy. There were 78 documented instances of weight loss at the end of therapy (Table 2).
Body weight loss percentage was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. The mean (SD) body weight loss percentage over the duration of the study was 9.2% (11.2). When classified by medication choice, the mean percentage of body weight loss was 16.8% for 2 patients using orlistat, 9.4% for 46 patients using liraglutide, 8.2% for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, 6.0% for 1 patient using phentermine alone, and 10.6% for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion (Table 3).
Secondary Outcomes
While none of the secondary outcomes were statistically significant, the results of this study suggest that both medications may contribute to weight loss in many patients included in this study. Almost two-thirds of the included patients analyzed lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline while taking weight management medication. Sixty-six patients (63%) lost ≥ 5% of body weight at any time during the data collection period. When stratified by liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate, 41 patients (63%) taking liraglutide and 20 patients (67%) taking phentermine/topiramate lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline. Of the 66 patients who lost ≥ 5% of body weight from baseline, 36 (55%) lost ≥ 10% of body weight from baseline at any time during the data collection period.
The mean (SD) duration for weight management medication use was 23 months (14.9). Phentermine/topiramate was tolerated longer than liraglutide: 22.7 months vs 21.7 months, respectively (Table 4).
The average overall documented medication discontinuation rate was 35.2%. Reasons for discontinuation included 21 patient-elected discontinuations, 8 patients no longer met criteria for use, 4 medications were no longer indicated, and 4 patients experienced AEs. It is unknown whether weight management medication was discontinued or not in 18 patients (17.2%).
DISCUSSION
This study evaluated the use and outcomes of weight loss medications over a longer period (up to 48 months) than what was previously studied among patients at VHI (12 months). The study aimed to better understand the long-term effect of weight loss medications, determine which medication had better long-term outcomes, and examine the reasons for medication discontinuation.
The results of this study displayed some similarities and differences compared with the Hood and colleagues study.16 Both yielded similar results for 5% of body weight loss and 10% of body weight loss. The largest difference was mean weight loss over the study period. In this study, patients lost a mean 10.6 kg over the course of weight loss medication use compared to 15.8 kg found by Hood and colleagues.16 A reason patients in the current study lost less weight overall could be the difference in time frames. The current study encompassed the COVID-19 pandemic, meaning fewer overall in-person patient appointments, which led to patients being lost to follow-up, missing weigh-ins during the time period, and gaps in care. For some patients, the pandemic possibly contributed to depression, missed medication doses, and a more sedentary lifestyle, leading to more weight gain.17 Telemedicine services at VHI expanded during the pandemic in an attempt to increase patient monitoring and counseling. It is unclear whether this expansion was enough to replace the in-person contact necessary to promote a healthy lifestyle.
VA pharmacists now care for patients through telehealth and are more involved in weight loss management. Since the conclusion of the Hood and colleagues study and start of this research, 2 pharmacists at VHI have been assigned to follow patients for obesity management to help with adherence to medication and lifestyle changes, management of AEs, dispense logistics, interventions for medications that may cause weight gain, and case management of glycemic control and weight loss with GLP-1RAs. Care management by pharmacists at VHI helps improve the logistics of titratable orders and save money by improving the use of high-cost items like GLP-1RAs. VA clinical pharmacy practitioners already monitor GLP-1RAs for patients with T2DM, so they are prepared to educate and assist patients with these medications.
It is important to continue developing a standardized process for weight loss medication management across the VA to improve the quality of patient care and optimize prescription outcomes. VA facilities differ in how weight loss management care is delivered and the level at which pharmacists are involved. Given the high rate of obesity among patients at the VA, the advent of new prescription options for weight loss, and the high cost associated with these medications, there has been increased attention to obesity care. Some Veterans Integrated Service Networks are forming a weight management community of practice groups to create standard operating procedures and algorithms to standardize care. Developing consistent processes is necessary to improve weight loss and patient care for veterans regardless where they receive treatment.
Limitations
The data used in this study were dependent on clinician documentation. Because of a lack of documentation in many instances, it was difficult to determine the full efficacy of the medications studied due to missing weight recordings. The lack of documentation made it difficult to determine whether patients were enrolled and active in the MOVE! program. It is required that patients enroll in MOVE! to obtain medications, but many did not have any follow-up MOVE! visits after initially obtaining their weight loss medication.
In this study, differences in the outcomes of patients with and without T2DM were not compared. It is the VA standard of care to prefer liraglutide over phentermine/topiramate in patients with T2DM or prediabetes.2 This makes it difficult to assess whether phentermine/topiramate or liraglutide is more effective for weight loss in patients with T2DM. Weight gain after the discontinuation of weight loss medications was not assessed. Collecting this data may help determine whether a certain weight loss medication is less likely to cause rebound weight gain when discontinued.
Other limitations to this study consisted of excluding patients who discontinued therapy within 6 months, small sample sizes on some medications, and lack of data on adherence. Adherence was based on medication refills, which means that if a patient refilled the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. This is not always the case, and while accurate data on adherence is difficult to gather, it can impact how results may be interpreted. These additional limitations make it difficult to accurately determine the efficacy of the medications in this study.
CONCLUSIONS
This study found similar outcomes to what has been observed in larger clinical trials regarding weight loss medications. Nevertheless, there was a lack of accurate clinical documentation for most patients, which limits the conclusions. This lack of documentation potentially led to inaccurate results. It revealed that many patients at VHI did not uniformly receive consistent follow-up after starting a weight loss medication during the study period. With more standardized processes implemented at VA facilities, increased pharmacist involvement in weight loss medication management, and increased use of established telehealth services, patients could have the opportunity for closer follow-up that may lead to better weight loss outcomes. With these changes, there is more reason for additional studies to be conducted to assess follow-up, medication management, and weight loss overall.
1. Overweight & obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 21, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/index.html
2. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. The Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity Working Group. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/obesity/VADoDObesityCPGFinal5087242020.pdf
3. Health effects of overweight and obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 24, 2022. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/effects/index.html
4. Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2985-3023. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.004
5. Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-362. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-3415
6. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes and associated comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S39-S45. doi:10.2337/dc22-S003
7. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release. Package insert. Vivus, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://qsymia.com/patient/include/media/pdf/prescribing-information.pdf
8. Naltrexone and bupropion extended-release. Package insert. Orexigen Therapeutics, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://contrave.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Contrave-label-113023.pdf
9. Orlistat. Package insert. Roche Laboratories, Inc; 2009. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020766s026lbl.pdf
10. Lorcaserin. Package insert. Arena Pharmaceuticals; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/022529lbl.pdf
11. FDA requests the withdrawal of the weight-loss drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the market. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. February 13, 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requests-withdrawal-weight-loss-drug-belviq-belviq-xr-lorcaserin-market
12. Saxenda Injection (Liraglutide [rDNA origin]). Novo Nordisk, Inc. October 1, 2015. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/206321Orig1s000TOC.cfm
13. FDA approves new drug treatment for chronic weight management, first since 2014. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. June 4, 2021. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014
14. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
15. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. New Engl J Med 2021;384:989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
16. Hood SR, Berkeley AW, Moore EA. Evaluation of pharmacologic interventions for weight management in a veteran population. Fed Pract. 2021;38(5):220-226. doi:10.12788/fp.0117
17. Melamed OC, Selby P, Taylor VH. Mental health and obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Obes Rep. 2022;11(1):23-31. doi:10.1007/s13679-021-00466-6
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classifies individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 29.9as overweight and those with a BMI > 30 as obese (obesity classes: I, BMI 30 to 34.9; II, BMI 35 to 39.9; and III, BMI ≥ 40).1 In 2011, the CDC estimated that 27.4% of adults in the United States were obese; less than a decade later, that number increased to 31.9%.1 In that same period, the percentage of adults in Indiana classified as obese increased from 30.8% to 36.8%.1 About 1 in 14 individuals in the US have class III obesity and 86% of veterans are either overweight or obese.2
High medical expenses can likely be attributed to the long-term health consequences of obesity. Compared to those with a healthy weight, individuals who are overweight or obese are at an increased risk for high blood pressure, high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), coronary heart disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, cancer, mental health disorders, body pain, low quality of life, and death.3 Many of these conditions lead to increased health care needs, medication needs, hospitalizations, and overall health care system use.
Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of obesity have been produced by the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and The Obesity Society; the Endocrine Society; the American Diabetes Association; and the US Departments of Veterans Affairs (VA) and Defense. Each follows a general algorithm to manage and prevent adverse effects (AEs) related to obesity. General practice is to assess a patient for elevated BMI (> 25), implement intense lifestyle modifications including calorie restriction and exercise, reassess for a maintained 5% to 10% weight loss for cardiovascular benefits, and potentially assess for pharmacological or surgical intervention to assist in weight loss.2,4-6
While some weight loss medications (eg, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and lorcaserin) tend to have unfavorable AEs or mixed efficacy, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have provided new options.7-10 Lorcaserin, for example, was removed from the market in 2020 due to its association with cancer risks.11 The GLP-1RAs liraglutide and semaglutide received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for weight loss in 2014 and 2021, respectively.12,13 GLP-1RAs have shown the greatest efficacy and benefits in reducing hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c); they are the preferred agents for patients who qualify for pharmacologic intervention for weight loss, especially those with T2DM. However, these studies have not evaluated the long-term outcomes of using these medications for weight loss and may not reflect the veteran population.14,15
At Veteran Health Indiana (VHI), clinicians may use several weight loss medications for patients to achieve 5% to 10% weight loss. The medications most often used include liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone. However, more research is needed to determine which weight loss medication is the most beneficial for veterans, particularly following FDA approval of GLP-1RAs. At VHI, phentermine/topiramate is the preferred first-line agent unless patients have contraindications for use, in which case naltrexone/bupropion is recommended. These are considered first-line due to their ease of use in pill form, lower cost, and comparable weight loss to the GLP-1 medication class.2 However, for patients with prediabetes, T2DM, BMI > 40, or BMI > 35 with specific comorbid conditions, liraglutide is preferred because of its beneficial effects for both weight loss and blood glucose control.2
This study aimed to expand on the 2021 Hood and colleagues study that examined total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage of baseline weight in patients with obesity at 3, 6, 12, and > 12 months of pharmacologic therapy by extending the time frame to 48 months.16 This study excluded semaglutide because few patients were prescribed the medication for weight loss during the study.
METHODS
We conducted a single-center, retrospective chart review of patients prescribed weight loss medications at VHI. A patient list was generated based on prescription fills from June 1, 2017, to July 31, 2021. Data were obtained from the Computerized Patient Record System; patients were not contacted. This study was approved by the Indiana University Health Institutional Review Board and VHI Research and Development Committee.
At the time of this study, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone were available at VHI for patients who met the clinical criteria for use. All patients must have been enrolled in dietary and lifestyle management programs, including the VA MOVE! program, to be approved for these medications. After the MOVE! orientation, patients could participate in group or individual 12-week programs that included weigh-ins, goal-setting strategies, meal planning, and habit modification support. If patients could not meet in person, phone and other telehealth opportunities were available.
Patients were included in the study if they were aged ≥ 18 years, received a prescription for any of the 5 available medications for weight loss during the enrollment period, and were on the medication for ≥ 6 consecutive months. Patients were excluded if they received a prescription, were treated outside the VA system, or were pregnant. The primary indication for the included medication was not weight loss; the primary indication for the GLP-1RA was T2DM, or the weight loss was attributed to another disease. Adherence was not a measured outcome of this study; if patients were filling the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. Data were collected for each instance of medication use; as a result, a few patients were included more than once. Data collection for a failed medication ended when failure was documented. New data points began when new medication was prescribed; all data were per medication, not per patient. This allowed us to account for medication failure and provide accurate weight loss results based on medication choice within VHI.
Primary outcomes included total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage ofbaseline weight during the study period at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of therapy. Secondary outcomes included the percentage of patients who lost 5% to 10% of their body weight from baseline; the percentage of patients who maintained ≥ 5% weight loss from baseline to 12, 24, 36, and 48 months if maintained on medication for that duration; duration of medication treatment in weeks; medication discontinuation rate; reason for medication discontinuation; enrollment in the MOVE! clinic and the time enrolled; percentage of patients with a BMI of 18 to 24.9 at the end of the study; and change in HbA1c at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months.
Demographic data included race, age, sex, baseline weight, height, baseline BMI, and comorbid conditions (collected based on the most recent primary care clinical note before initiating medication). Medication data collected included medications used to manage comorbidities. Data related to weight management medication included prescribing clinic, maintenance dose of medication, duration of medication during the study period, the reason for medication discontinuation, or bariatric surgery intervention if applicable.
Basic descriptive statistics were used to characterize study participants. For continuous data, analysis of variance tests were used; if those results were not normal, then nonparametric tests were used, followed by pairwise tests between medication groups if the overall test was significant using the Fisher significant differences test. For nominal data, χ2 or Fisher exact tests were used. For comparisons of primary and secondary outcomes, if the analyses needed to include adjustment for confounding variables, analysis of covariance was used for continuous data. A 2-sided 5% significance level was used for all tests.
RESULTS
A total of 228 instances of medication use were identified based on prescription fills; 123 did not meet inclusion criteria (117 for < 6 consecutive months of medication use) (Figure). The study included 105 participants with a mean age of 56 years; 80 were male (76.2%), and 85 identified as White race (81.0%). Mean (SD) weight was 130.1 kg (26.8) and BMI was 41.6 (7.2). The most common comorbid disease states among patients included hypertension, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, and T2DM (Table 1). The baseline characteristics were comparable to those of Hood and colleagues.16
Most patients at VHI started on liraglutide (63%) or phentermine/topiramate (28%). For primary and secondary outcomes, statistics were calculated to determine whether the results were statistically significant for comparing the liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate subgroups. Sample sizes were too small for statistical analysis for bupropion/naltrexone, phentermine, and orlistat.
Primary Outcomes
The mean (SD) weight of participants dropped 8.1% from 130.1 kg to 119.5 kg over the patient-specific duration of weight management medication therapy for an absolute difference of 10.6 kg (9.7). Duration of individual medication use varied from 6 to 48 months. Weight loss was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. Patient weight was not recorded after the medication was discontinued.
When classified by medication choice, the mean change in weight over the duration of the study was −23.9 kg for 2 patients using orlistat, −10.2 kg for 46 patients using liraglutide, −11.0 kg for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, -7.4 kg for 1 patient using phentermine, and -13.0 kg for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion. Patients without a weight documented at the end of their therapy or at the conclusion of the data collection period were not included in the total weight loss at the end of therapy. There were 78 documented instances of weight loss at the end of therapy (Table 2).
Body weight loss percentage was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. The mean (SD) body weight loss percentage over the duration of the study was 9.2% (11.2). When classified by medication choice, the mean percentage of body weight loss was 16.8% for 2 patients using orlistat, 9.4% for 46 patients using liraglutide, 8.2% for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, 6.0% for 1 patient using phentermine alone, and 10.6% for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion (Table 3).
Secondary Outcomes
While none of the secondary outcomes were statistically significant, the results of this study suggest that both medications may contribute to weight loss in many patients included in this study. Almost two-thirds of the included patients analyzed lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline while taking weight management medication. Sixty-six patients (63%) lost ≥ 5% of body weight at any time during the data collection period. When stratified by liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate, 41 patients (63%) taking liraglutide and 20 patients (67%) taking phentermine/topiramate lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline. Of the 66 patients who lost ≥ 5% of body weight from baseline, 36 (55%) lost ≥ 10% of body weight from baseline at any time during the data collection period.
The mean (SD) duration for weight management medication use was 23 months (14.9). Phentermine/topiramate was tolerated longer than liraglutide: 22.7 months vs 21.7 months, respectively (Table 4).
The average overall documented medication discontinuation rate was 35.2%. Reasons for discontinuation included 21 patient-elected discontinuations, 8 patients no longer met criteria for use, 4 medications were no longer indicated, and 4 patients experienced AEs. It is unknown whether weight management medication was discontinued or not in 18 patients (17.2%).
DISCUSSION
This study evaluated the use and outcomes of weight loss medications over a longer period (up to 48 months) than what was previously studied among patients at VHI (12 months). The study aimed to better understand the long-term effect of weight loss medications, determine which medication had better long-term outcomes, and examine the reasons for medication discontinuation.
The results of this study displayed some similarities and differences compared with the Hood and colleagues study.16 Both yielded similar results for 5% of body weight loss and 10% of body weight loss. The largest difference was mean weight loss over the study period. In this study, patients lost a mean 10.6 kg over the course of weight loss medication use compared to 15.8 kg found by Hood and colleagues.16 A reason patients in the current study lost less weight overall could be the difference in time frames. The current study encompassed the COVID-19 pandemic, meaning fewer overall in-person patient appointments, which led to patients being lost to follow-up, missing weigh-ins during the time period, and gaps in care. For some patients, the pandemic possibly contributed to depression, missed medication doses, and a more sedentary lifestyle, leading to more weight gain.17 Telemedicine services at VHI expanded during the pandemic in an attempt to increase patient monitoring and counseling. It is unclear whether this expansion was enough to replace the in-person contact necessary to promote a healthy lifestyle.
VA pharmacists now care for patients through telehealth and are more involved in weight loss management. Since the conclusion of the Hood and colleagues study and start of this research, 2 pharmacists at VHI have been assigned to follow patients for obesity management to help with adherence to medication and lifestyle changes, management of AEs, dispense logistics, interventions for medications that may cause weight gain, and case management of glycemic control and weight loss with GLP-1RAs. Care management by pharmacists at VHI helps improve the logistics of titratable orders and save money by improving the use of high-cost items like GLP-1RAs. VA clinical pharmacy practitioners already monitor GLP-1RAs for patients with T2DM, so they are prepared to educate and assist patients with these medications.
It is important to continue developing a standardized process for weight loss medication management across the VA to improve the quality of patient care and optimize prescription outcomes. VA facilities differ in how weight loss management care is delivered and the level at which pharmacists are involved. Given the high rate of obesity among patients at the VA, the advent of new prescription options for weight loss, and the high cost associated with these medications, there has been increased attention to obesity care. Some Veterans Integrated Service Networks are forming a weight management community of practice groups to create standard operating procedures and algorithms to standardize care. Developing consistent processes is necessary to improve weight loss and patient care for veterans regardless where they receive treatment.
Limitations
The data used in this study were dependent on clinician documentation. Because of a lack of documentation in many instances, it was difficult to determine the full efficacy of the medications studied due to missing weight recordings. The lack of documentation made it difficult to determine whether patients were enrolled and active in the MOVE! program. It is required that patients enroll in MOVE! to obtain medications, but many did not have any follow-up MOVE! visits after initially obtaining their weight loss medication.
In this study, differences in the outcomes of patients with and without T2DM were not compared. It is the VA standard of care to prefer liraglutide over phentermine/topiramate in patients with T2DM or prediabetes.2 This makes it difficult to assess whether phentermine/topiramate or liraglutide is more effective for weight loss in patients with T2DM. Weight gain after the discontinuation of weight loss medications was not assessed. Collecting this data may help determine whether a certain weight loss medication is less likely to cause rebound weight gain when discontinued.
Other limitations to this study consisted of excluding patients who discontinued therapy within 6 months, small sample sizes on some medications, and lack of data on adherence. Adherence was based on medication refills, which means that if a patient refilled the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. This is not always the case, and while accurate data on adherence is difficult to gather, it can impact how results may be interpreted. These additional limitations make it difficult to accurately determine the efficacy of the medications in this study.
CONCLUSIONS
This study found similar outcomes to what has been observed in larger clinical trials regarding weight loss medications. Nevertheless, there was a lack of accurate clinical documentation for most patients, which limits the conclusions. This lack of documentation potentially led to inaccurate results. It revealed that many patients at VHI did not uniformly receive consistent follow-up after starting a weight loss medication during the study period. With more standardized processes implemented at VA facilities, increased pharmacist involvement in weight loss medication management, and increased use of established telehealth services, patients could have the opportunity for closer follow-up that may lead to better weight loss outcomes. With these changes, there is more reason for additional studies to be conducted to assess follow-up, medication management, and weight loss overall.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classifies individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 29.9as overweight and those with a BMI > 30 as obese (obesity classes: I, BMI 30 to 34.9; II, BMI 35 to 39.9; and III, BMI ≥ 40).1 In 2011, the CDC estimated that 27.4% of adults in the United States were obese; less than a decade later, that number increased to 31.9%.1 In that same period, the percentage of adults in Indiana classified as obese increased from 30.8% to 36.8%.1 About 1 in 14 individuals in the US have class III obesity and 86% of veterans are either overweight or obese.2
High medical expenses can likely be attributed to the long-term health consequences of obesity. Compared to those with a healthy weight, individuals who are overweight or obese are at an increased risk for high blood pressure, high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), coronary heart disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, cancer, mental health disorders, body pain, low quality of life, and death.3 Many of these conditions lead to increased health care needs, medication needs, hospitalizations, and overall health care system use.
Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of obesity have been produced by the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and The Obesity Society; the Endocrine Society; the American Diabetes Association; and the US Departments of Veterans Affairs (VA) and Defense. Each follows a general algorithm to manage and prevent adverse effects (AEs) related to obesity. General practice is to assess a patient for elevated BMI (> 25), implement intense lifestyle modifications including calorie restriction and exercise, reassess for a maintained 5% to 10% weight loss for cardiovascular benefits, and potentially assess for pharmacological or surgical intervention to assist in weight loss.2,4-6
While some weight loss medications (eg, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and lorcaserin) tend to have unfavorable AEs or mixed efficacy, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have provided new options.7-10 Lorcaserin, for example, was removed from the market in 2020 due to its association with cancer risks.11 The GLP-1RAs liraglutide and semaglutide received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for weight loss in 2014 and 2021, respectively.12,13 GLP-1RAs have shown the greatest efficacy and benefits in reducing hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c); they are the preferred agents for patients who qualify for pharmacologic intervention for weight loss, especially those with T2DM. However, these studies have not evaluated the long-term outcomes of using these medications for weight loss and may not reflect the veteran population.14,15
At Veteran Health Indiana (VHI), clinicians may use several weight loss medications for patients to achieve 5% to 10% weight loss. The medications most often used include liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone. However, more research is needed to determine which weight loss medication is the most beneficial for veterans, particularly following FDA approval of GLP-1RAs. At VHI, phentermine/topiramate is the preferred first-line agent unless patients have contraindications for use, in which case naltrexone/bupropion is recommended. These are considered first-line due to their ease of use in pill form, lower cost, and comparable weight loss to the GLP-1 medication class.2 However, for patients with prediabetes, T2DM, BMI > 40, or BMI > 35 with specific comorbid conditions, liraglutide is preferred because of its beneficial effects for both weight loss and blood glucose control.2
This study aimed to expand on the 2021 Hood and colleagues study that examined total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage of baseline weight in patients with obesity at 3, 6, 12, and > 12 months of pharmacologic therapy by extending the time frame to 48 months.16 This study excluded semaglutide because few patients were prescribed the medication for weight loss during the study.
METHODS
We conducted a single-center, retrospective chart review of patients prescribed weight loss medications at VHI. A patient list was generated based on prescription fills from June 1, 2017, to July 31, 2021. Data were obtained from the Computerized Patient Record System; patients were not contacted. This study was approved by the Indiana University Health Institutional Review Board and VHI Research and Development Committee.
At the time of this study, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, naltrexone/bupropion, orlistat, and phentermine alone were available at VHI for patients who met the clinical criteria for use. All patients must have been enrolled in dietary and lifestyle management programs, including the VA MOVE! program, to be approved for these medications. After the MOVE! orientation, patients could participate in group or individual 12-week programs that included weigh-ins, goal-setting strategies, meal planning, and habit modification support. If patients could not meet in person, phone and other telehealth opportunities were available.
Patients were included in the study if they were aged ≥ 18 years, received a prescription for any of the 5 available medications for weight loss during the enrollment period, and were on the medication for ≥ 6 consecutive months. Patients were excluded if they received a prescription, were treated outside the VA system, or were pregnant. The primary indication for the included medication was not weight loss; the primary indication for the GLP-1RA was T2DM, or the weight loss was attributed to another disease. Adherence was not a measured outcome of this study; if patients were filling the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. Data were collected for each instance of medication use; as a result, a few patients were included more than once. Data collection for a failed medication ended when failure was documented. New data points began when new medication was prescribed; all data were per medication, not per patient. This allowed us to account for medication failure and provide accurate weight loss results based on medication choice within VHI.
Primary outcomes included total weight loss and weight loss as a percentage ofbaseline weight during the study period at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of therapy. Secondary outcomes included the percentage of patients who lost 5% to 10% of their body weight from baseline; the percentage of patients who maintained ≥ 5% weight loss from baseline to 12, 24, 36, and 48 months if maintained on medication for that duration; duration of medication treatment in weeks; medication discontinuation rate; reason for medication discontinuation; enrollment in the MOVE! clinic and the time enrolled; percentage of patients with a BMI of 18 to 24.9 at the end of the study; and change in HbA1c at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months.
Demographic data included race, age, sex, baseline weight, height, baseline BMI, and comorbid conditions (collected based on the most recent primary care clinical note before initiating medication). Medication data collected included medications used to manage comorbidities. Data related to weight management medication included prescribing clinic, maintenance dose of medication, duration of medication during the study period, the reason for medication discontinuation, or bariatric surgery intervention if applicable.
Basic descriptive statistics were used to characterize study participants. For continuous data, analysis of variance tests were used; if those results were not normal, then nonparametric tests were used, followed by pairwise tests between medication groups if the overall test was significant using the Fisher significant differences test. For nominal data, χ2 or Fisher exact tests were used. For comparisons of primary and secondary outcomes, if the analyses needed to include adjustment for confounding variables, analysis of covariance was used for continuous data. A 2-sided 5% significance level was used for all tests.
RESULTS
A total of 228 instances of medication use were identified based on prescription fills; 123 did not meet inclusion criteria (117 for < 6 consecutive months of medication use) (Figure). The study included 105 participants with a mean age of 56 years; 80 were male (76.2%), and 85 identified as White race (81.0%). Mean (SD) weight was 130.1 kg (26.8) and BMI was 41.6 (7.2). The most common comorbid disease states among patients included hypertension, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, and T2DM (Table 1). The baseline characteristics were comparable to those of Hood and colleagues.16
Most patients at VHI started on liraglutide (63%) or phentermine/topiramate (28%). For primary and secondary outcomes, statistics were calculated to determine whether the results were statistically significant for comparing the liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate subgroups. Sample sizes were too small for statistical analysis for bupropion/naltrexone, phentermine, and orlistat.
Primary Outcomes
The mean (SD) weight of participants dropped 8.1% from 130.1 kg to 119.5 kg over the patient-specific duration of weight management medication therapy for an absolute difference of 10.6 kg (9.7). Duration of individual medication use varied from 6 to 48 months. Weight loss was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. Patient weight was not recorded after the medication was discontinued.
When classified by medication choice, the mean change in weight over the duration of the study was −23.9 kg for 2 patients using orlistat, −10.2 kg for 46 patients using liraglutide, −11.0 kg for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, -7.4 kg for 1 patient using phentermine, and -13.0 kg for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion. Patients without a weight documented at the end of their therapy or at the conclusion of the data collection period were not included in the total weight loss at the end of therapy. There were 78 documented instances of weight loss at the end of therapy (Table 2).
Body weight loss percentage was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 months of weight management therapy. The mean (SD) body weight loss percentage over the duration of the study was 9.2% (11.2). When classified by medication choice, the mean percentage of body weight loss was 16.8% for 2 patients using orlistat, 9.4% for 46 patients using liraglutide, 8.2% for 25 patients using phentermine/topiramate, 6.0% for 1 patient using phentermine alone, and 10.6% for 4 patients using naltrexone/bupropion (Table 3).
Secondary Outcomes
While none of the secondary outcomes were statistically significant, the results of this study suggest that both medications may contribute to weight loss in many patients included in this study. Almost two-thirds of the included patients analyzed lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline while taking weight management medication. Sixty-six patients (63%) lost ≥ 5% of body weight at any time during the data collection period. When stratified by liraglutide and phentermine/topiramate, 41 patients (63%) taking liraglutide and 20 patients (67%) taking phentermine/topiramate lost ≥ 5% of weight from baseline. Of the 66 patients who lost ≥ 5% of body weight from baseline, 36 (55%) lost ≥ 10% of body weight from baseline at any time during the data collection period.
The mean (SD) duration for weight management medication use was 23 months (14.9). Phentermine/topiramate was tolerated longer than liraglutide: 22.7 months vs 21.7 months, respectively (Table 4).
The average overall documented medication discontinuation rate was 35.2%. Reasons for discontinuation included 21 patient-elected discontinuations, 8 patients no longer met criteria for use, 4 medications were no longer indicated, and 4 patients experienced AEs. It is unknown whether weight management medication was discontinued or not in 18 patients (17.2%).
DISCUSSION
This study evaluated the use and outcomes of weight loss medications over a longer period (up to 48 months) than what was previously studied among patients at VHI (12 months). The study aimed to better understand the long-term effect of weight loss medications, determine which medication had better long-term outcomes, and examine the reasons for medication discontinuation.
The results of this study displayed some similarities and differences compared with the Hood and colleagues study.16 Both yielded similar results for 5% of body weight loss and 10% of body weight loss. The largest difference was mean weight loss over the study period. In this study, patients lost a mean 10.6 kg over the course of weight loss medication use compared to 15.8 kg found by Hood and colleagues.16 A reason patients in the current study lost less weight overall could be the difference in time frames. The current study encompassed the COVID-19 pandemic, meaning fewer overall in-person patient appointments, which led to patients being lost to follow-up, missing weigh-ins during the time period, and gaps in care. For some patients, the pandemic possibly contributed to depression, missed medication doses, and a more sedentary lifestyle, leading to more weight gain.17 Telemedicine services at VHI expanded during the pandemic in an attempt to increase patient monitoring and counseling. It is unclear whether this expansion was enough to replace the in-person contact necessary to promote a healthy lifestyle.
VA pharmacists now care for patients through telehealth and are more involved in weight loss management. Since the conclusion of the Hood and colleagues study and start of this research, 2 pharmacists at VHI have been assigned to follow patients for obesity management to help with adherence to medication and lifestyle changes, management of AEs, dispense logistics, interventions for medications that may cause weight gain, and case management of glycemic control and weight loss with GLP-1RAs. Care management by pharmacists at VHI helps improve the logistics of titratable orders and save money by improving the use of high-cost items like GLP-1RAs. VA clinical pharmacy practitioners already monitor GLP-1RAs for patients with T2DM, so they are prepared to educate and assist patients with these medications.
It is important to continue developing a standardized process for weight loss medication management across the VA to improve the quality of patient care and optimize prescription outcomes. VA facilities differ in how weight loss management care is delivered and the level at which pharmacists are involved. Given the high rate of obesity among patients at the VA, the advent of new prescription options for weight loss, and the high cost associated with these medications, there has been increased attention to obesity care. Some Veterans Integrated Service Networks are forming a weight management community of practice groups to create standard operating procedures and algorithms to standardize care. Developing consistent processes is necessary to improve weight loss and patient care for veterans regardless where they receive treatment.
Limitations
The data used in this study were dependent on clinician documentation. Because of a lack of documentation in many instances, it was difficult to determine the full efficacy of the medications studied due to missing weight recordings. The lack of documentation made it difficult to determine whether patients were enrolled and active in the MOVE! program. It is required that patients enroll in MOVE! to obtain medications, but many did not have any follow-up MOVE! visits after initially obtaining their weight loss medication.
In this study, differences in the outcomes of patients with and without T2DM were not compared. It is the VA standard of care to prefer liraglutide over phentermine/topiramate in patients with T2DM or prediabetes.2 This makes it difficult to assess whether phentermine/topiramate or liraglutide is more effective for weight loss in patients with T2DM. Weight gain after the discontinuation of weight loss medications was not assessed. Collecting this data may help determine whether a certain weight loss medication is less likely to cause rebound weight gain when discontinued.
Other limitations to this study consisted of excluding patients who discontinued therapy within 6 months, small sample sizes on some medications, and lack of data on adherence. Adherence was based on medication refills, which means that if a patient refilled the medication, it was assumed they were taking it. This is not always the case, and while accurate data on adherence is difficult to gather, it can impact how results may be interpreted. These additional limitations make it difficult to accurately determine the efficacy of the medications in this study.
CONCLUSIONS
This study found similar outcomes to what has been observed in larger clinical trials regarding weight loss medications. Nevertheless, there was a lack of accurate clinical documentation for most patients, which limits the conclusions. This lack of documentation potentially led to inaccurate results. It revealed that many patients at VHI did not uniformly receive consistent follow-up after starting a weight loss medication during the study period. With more standardized processes implemented at VA facilities, increased pharmacist involvement in weight loss medication management, and increased use of established telehealth services, patients could have the opportunity for closer follow-up that may lead to better weight loss outcomes. With these changes, there is more reason for additional studies to be conducted to assess follow-up, medication management, and weight loss overall.
1. Overweight & obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 21, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/index.html
2. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. The Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity Working Group. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/obesity/VADoDObesityCPGFinal5087242020.pdf
3. Health effects of overweight and obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 24, 2022. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/effects/index.html
4. Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2985-3023. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.004
5. Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-362. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-3415
6. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes and associated comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S39-S45. doi:10.2337/dc22-S003
7. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release. Package insert. Vivus, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://qsymia.com/patient/include/media/pdf/prescribing-information.pdf
8. Naltrexone and bupropion extended-release. Package insert. Orexigen Therapeutics, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://contrave.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Contrave-label-113023.pdf
9. Orlistat. Package insert. Roche Laboratories, Inc; 2009. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020766s026lbl.pdf
10. Lorcaserin. Package insert. Arena Pharmaceuticals; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/022529lbl.pdf
11. FDA requests the withdrawal of the weight-loss drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the market. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. February 13, 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requests-withdrawal-weight-loss-drug-belviq-belviq-xr-lorcaserin-market
12. Saxenda Injection (Liraglutide [rDNA origin]). Novo Nordisk, Inc. October 1, 2015. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/206321Orig1s000TOC.cfm
13. FDA approves new drug treatment for chronic weight management, first since 2014. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. June 4, 2021. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014
14. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
15. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. New Engl J Med 2021;384:989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
16. Hood SR, Berkeley AW, Moore EA. Evaluation of pharmacologic interventions for weight management in a veteran population. Fed Pract. 2021;38(5):220-226. doi:10.12788/fp.0117
17. Melamed OC, Selby P, Taylor VH. Mental health and obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Obes Rep. 2022;11(1):23-31. doi:10.1007/s13679-021-00466-6
1. Overweight & obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 21, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/index.html
2. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. The Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity Working Group. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Adult Overweight and Obesity. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/obesity/VADoDObesityCPGFinal5087242020.pdf
3. Health effects of overweight and obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated September 24, 2022. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/effects/index.html
4. Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2985-3023. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.004
5. Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-362. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-3415
6. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes and associated comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S39-S45. doi:10.2337/dc22-S003
7. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release. Package insert. Vivus, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://qsymia.com/patient/include/media/pdf/prescribing-information.pdf
8. Naltrexone and bupropion extended-release. Package insert. Orexigen Therapeutics, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://contrave.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Contrave-label-113023.pdf
9. Orlistat. Package insert. Roche Laboratories, Inc; 2009. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020766s026lbl.pdf
10. Lorcaserin. Package insert. Arena Pharmaceuticals; 2012. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/022529lbl.pdf
11. FDA requests the withdrawal of the weight-loss drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the market. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. February 13, 2020. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requests-withdrawal-weight-loss-drug-belviq-belviq-xr-lorcaserin-market
12. Saxenda Injection (Liraglutide [rDNA origin]). Novo Nordisk, Inc. October 1, 2015. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/206321Orig1s000TOC.cfm
13. FDA approves new drug treatment for chronic weight management, first since 2014. News release. US Food & Drug Administration. June 4, 2021. Accessed April 23, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014
14. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
15. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. New Engl J Med 2021;384:989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
16. Hood SR, Berkeley AW, Moore EA. Evaluation of pharmacologic interventions for weight management in a veteran population. Fed Pract. 2021;38(5):220-226. doi:10.12788/fp.0117
17. Melamed OC, Selby P, Taylor VH. Mental health and obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Obes Rep. 2022;11(1):23-31. doi:10.1007/s13679-021-00466-6
Common Antidepressants Ranked by Potential for Weight Gain
Eight commonly used antidepressants have been ranked by their weight gain potential.
Results of a large observational study showed small differences in short- and long-term weight change in patients prescribed one of eight antidepressants, with bupropion associated with the lowest weight gain and escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine associated with the greatest.
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with those taking sertraline, which was used as a comparator.
“Patients and their clinicians often have several options when starting an antidepressant for the first time. This study provides important real-world evidence regarding the amount of weight gain that should be expected after starting some of the most common antidepressants,” lead author Joshua Petimar, ScD, assistant professor of population medicine in the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Real-World Data
Though weight gain is a commonly reported side effect of antidepressant use and may lead to medication nonadherence and worse outcomes, there is a lack of real-world data about weight change across specific medications.
Investigators used electronic health records from eight health care systems across the United States spanning from 2010 to 2019. The analysis included information on 183,118 adults aged 20-80 years who were new users of one of eight common first-line antidepressants. Investigators measured their weight at baseline and at 6, 12, and 24 months after initiation to estimate intention-to-treat (ITT) effects of weight change.
At baseline, participants were randomly assigned to begin sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, bupropion, duloxetine, or venlafaxine.
The most common antidepressants prescribed were sertraline, citalopram, and bupropion. Approximately 36% of participants had a diagnosis of depression, and 39% were diagnosed with anxiety.
Among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), escitalopram and paroxetine were associated with the greatest 6-month weight gain, whereas bupropion was associated with the least weight gain across all analyses.
Using sertraline as a comparator, 6-month weight change was lower for bupropion (difference, 0.22 kg) and higher for escitalopram (difference, 0.41 kg), duloxetine (difference, 0.34 kg), paroxetine (difference, 0.37 kg), and venlafaxine (difference, 0.17 kg).
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with sertraline users.
Investigators noted little difference in adherence levels between medications during the study except at 6 months, when it was higher for those who took bupropion (41%) than for those taking other antidepressants (28%-36%).
The study included data only on prescriptions and investigators could not verify whether the medications were dispensed or taken as prescribed. Other limitations included missing weight information because most patients did not encounter the health system at exactly 6, 12, and 24 months; only 15%-30% had weight measurements in those months.
Finally, the low adherence rates made it difficult to attribute relative weight change at the 12- and 24-month time points to the specific medications of interest.
“Clinicians and patients could consider these differences when making decisions about specific antidepressants, especially given the complex relationships of obesity and depression with health, quality of life, and stigma,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Eight commonly used antidepressants have been ranked by their weight gain potential.
Results of a large observational study showed small differences in short- and long-term weight change in patients prescribed one of eight antidepressants, with bupropion associated with the lowest weight gain and escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine associated with the greatest.
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with those taking sertraline, which was used as a comparator.
“Patients and their clinicians often have several options when starting an antidepressant for the first time. This study provides important real-world evidence regarding the amount of weight gain that should be expected after starting some of the most common antidepressants,” lead author Joshua Petimar, ScD, assistant professor of population medicine in the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Real-World Data
Though weight gain is a commonly reported side effect of antidepressant use and may lead to medication nonadherence and worse outcomes, there is a lack of real-world data about weight change across specific medications.
Investigators used electronic health records from eight health care systems across the United States spanning from 2010 to 2019. The analysis included information on 183,118 adults aged 20-80 years who were new users of one of eight common first-line antidepressants. Investigators measured their weight at baseline and at 6, 12, and 24 months after initiation to estimate intention-to-treat (ITT) effects of weight change.
At baseline, participants were randomly assigned to begin sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, bupropion, duloxetine, or venlafaxine.
The most common antidepressants prescribed were sertraline, citalopram, and bupropion. Approximately 36% of participants had a diagnosis of depression, and 39% were diagnosed with anxiety.
Among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), escitalopram and paroxetine were associated with the greatest 6-month weight gain, whereas bupropion was associated with the least weight gain across all analyses.
Using sertraline as a comparator, 6-month weight change was lower for bupropion (difference, 0.22 kg) and higher for escitalopram (difference, 0.41 kg), duloxetine (difference, 0.34 kg), paroxetine (difference, 0.37 kg), and venlafaxine (difference, 0.17 kg).
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with sertraline users.
Investigators noted little difference in adherence levels between medications during the study except at 6 months, when it was higher for those who took bupropion (41%) than for those taking other antidepressants (28%-36%).
The study included data only on prescriptions and investigators could not verify whether the medications were dispensed or taken as prescribed. Other limitations included missing weight information because most patients did not encounter the health system at exactly 6, 12, and 24 months; only 15%-30% had weight measurements in those months.
Finally, the low adherence rates made it difficult to attribute relative weight change at the 12- and 24-month time points to the specific medications of interest.
“Clinicians and patients could consider these differences when making decisions about specific antidepressants, especially given the complex relationships of obesity and depression with health, quality of life, and stigma,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Eight commonly used antidepressants have been ranked by their weight gain potential.
Results of a large observational study showed small differences in short- and long-term weight change in patients prescribed one of eight antidepressants, with bupropion associated with the lowest weight gain and escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine associated with the greatest.
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with those taking sertraline, which was used as a comparator.
“Patients and their clinicians often have several options when starting an antidepressant for the first time. This study provides important real-world evidence regarding the amount of weight gain that should be expected after starting some of the most common antidepressants,” lead author Joshua Petimar, ScD, assistant professor of population medicine in the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Real-World Data
Though weight gain is a commonly reported side effect of antidepressant use and may lead to medication nonadherence and worse outcomes, there is a lack of real-world data about weight change across specific medications.
Investigators used electronic health records from eight health care systems across the United States spanning from 2010 to 2019. The analysis included information on 183,118 adults aged 20-80 years who were new users of one of eight common first-line antidepressants. Investigators measured their weight at baseline and at 6, 12, and 24 months after initiation to estimate intention-to-treat (ITT) effects of weight change.
At baseline, participants were randomly assigned to begin sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, bupropion, duloxetine, or venlafaxine.
The most common antidepressants prescribed were sertraline, citalopram, and bupropion. Approximately 36% of participants had a diagnosis of depression, and 39% were diagnosed with anxiety.
Among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), escitalopram and paroxetine were associated with the greatest 6-month weight gain, whereas bupropion was associated with the least weight gain across all analyses.
Using sertraline as a comparator, 6-month weight change was lower for bupropion (difference, 0.22 kg) and higher for escitalopram (difference, 0.41 kg), duloxetine (difference, 0.34 kg), paroxetine (difference, 0.37 kg), and venlafaxine (difference, 0.17 kg).
Escitalopram, paroxetine, and duloxetine users were 10%-15% more likely to gain at least 5% of their baseline weight compared with sertraline users.
Investigators noted little difference in adherence levels between medications during the study except at 6 months, when it was higher for those who took bupropion (41%) than for those taking other antidepressants (28%-36%).
The study included data only on prescriptions and investigators could not verify whether the medications were dispensed or taken as prescribed. Other limitations included missing weight information because most patients did not encounter the health system at exactly 6, 12, and 24 months; only 15%-30% had weight measurements in those months.
Finally, the low adherence rates made it difficult to attribute relative weight change at the 12- and 24-month time points to the specific medications of interest.
“Clinicians and patients could consider these differences when making decisions about specific antidepressants, especially given the complex relationships of obesity and depression with health, quality of life, and stigma,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide May Increase Risk of Disease Causing Vision Loss
TOPLINE:
Patients with type 2 diabetes, overweight, or obesity taking the glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) semaglutide appear to have an increased risk for an uncommon condition that can cause vision loss.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 16,827 patients at Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston.
- Their analysis focused on 710 patients with type 2 diabetes (194 of whom had been prescribed semaglutide) and 979 patients with overweight or obesity (361 prescribed semaglutide).
- The researchers compared patients prescribed semaglutide with those prescribed a medication other than a GLP-1 agent. They matched patients by factors such as age and sex and whether they had hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, or coronary artery disease.
- They assessed the cumulative incidence of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) during 36 months of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- Semaglutide use was associated with a higher risk for NAION in patients with type 2 diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 4.28; 95% CI, 1.62-11.29).
- In patients with overweight or obesity, semaglutide again was linked to a higher risk for NAION (HR, 7.64; 95% CI, 2.21-26.36).
- Among patients with type 2 diabetes, the cumulative incidence of NAION over 36 months was 8.9% for those prescribed semaglutide vs 1.8% among those taking non–GLP-1 medications.
IN PRACTICE:
Semaglutide has “provided very significant benefits in many ways, but future discussions between a patient and their physician should include NAION as a potential risk,” study leader Joseph Rizzo, MD, with Mass Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, said in a news release about the findings. “It is important to appreciate, however, that the increased risk relates to a disorder that is relatively uncommon.”
“Given the numbers of participants who have been recruited to clinical trials and the large number of people globally who use GLP-1 RAs, we should be confident that if corroborated, the absolute risk of developing NAION in direct relation to taking semaglutide must indeed be rare,” Susan P. Mollan, MBcHB, of University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, in England, wrote in a commentary published with the study.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on July 3 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The patients were seen at a hospital that specializes in ophthalmology and has a specialized neuro-ophthalmology service, so the results may not fully apply to other settings. The results were driven by a relatively small number of NAION cases in the patients exposed to semaglutide. The study does not establish that semaglutide directly causes NAION, the researchers noted. “The best approaches to confirm, refute, or refine our findings would be to conduct a much larger, retrospective, multicenter population-based cohort study; a prospective, randomized clinical study; or a postmarket analysis of all GLP-1 RA drugs,” they wrote.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from Research to Prevent Blindness.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with type 2 diabetes, overweight, or obesity taking the glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) semaglutide appear to have an increased risk for an uncommon condition that can cause vision loss.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 16,827 patients at Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston.
- Their analysis focused on 710 patients with type 2 diabetes (194 of whom had been prescribed semaglutide) and 979 patients with overweight or obesity (361 prescribed semaglutide).
- The researchers compared patients prescribed semaglutide with those prescribed a medication other than a GLP-1 agent. They matched patients by factors such as age and sex and whether they had hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, or coronary artery disease.
- They assessed the cumulative incidence of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) during 36 months of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- Semaglutide use was associated with a higher risk for NAION in patients with type 2 diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 4.28; 95% CI, 1.62-11.29).
- In patients with overweight or obesity, semaglutide again was linked to a higher risk for NAION (HR, 7.64; 95% CI, 2.21-26.36).
- Among patients with type 2 diabetes, the cumulative incidence of NAION over 36 months was 8.9% for those prescribed semaglutide vs 1.8% among those taking non–GLP-1 medications.
IN PRACTICE:
Semaglutide has “provided very significant benefits in many ways, but future discussions between a patient and their physician should include NAION as a potential risk,” study leader Joseph Rizzo, MD, with Mass Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, said in a news release about the findings. “It is important to appreciate, however, that the increased risk relates to a disorder that is relatively uncommon.”
“Given the numbers of participants who have been recruited to clinical trials and the large number of people globally who use GLP-1 RAs, we should be confident that if corroborated, the absolute risk of developing NAION in direct relation to taking semaglutide must indeed be rare,” Susan P. Mollan, MBcHB, of University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, in England, wrote in a commentary published with the study.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on July 3 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The patients were seen at a hospital that specializes in ophthalmology and has a specialized neuro-ophthalmology service, so the results may not fully apply to other settings. The results were driven by a relatively small number of NAION cases in the patients exposed to semaglutide. The study does not establish that semaglutide directly causes NAION, the researchers noted. “The best approaches to confirm, refute, or refine our findings would be to conduct a much larger, retrospective, multicenter population-based cohort study; a prospective, randomized clinical study; or a postmarket analysis of all GLP-1 RA drugs,” they wrote.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from Research to Prevent Blindness.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with type 2 diabetes, overweight, or obesity taking the glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) semaglutide appear to have an increased risk for an uncommon condition that can cause vision loss.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 16,827 patients at Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston.
- Their analysis focused on 710 patients with type 2 diabetes (194 of whom had been prescribed semaglutide) and 979 patients with overweight or obesity (361 prescribed semaglutide).
- The researchers compared patients prescribed semaglutide with those prescribed a medication other than a GLP-1 agent. They matched patients by factors such as age and sex and whether they had hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, or coronary artery disease.
- They assessed the cumulative incidence of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) during 36 months of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- Semaglutide use was associated with a higher risk for NAION in patients with type 2 diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 4.28; 95% CI, 1.62-11.29).
- In patients with overweight or obesity, semaglutide again was linked to a higher risk for NAION (HR, 7.64; 95% CI, 2.21-26.36).
- Among patients with type 2 diabetes, the cumulative incidence of NAION over 36 months was 8.9% for those prescribed semaglutide vs 1.8% among those taking non–GLP-1 medications.
IN PRACTICE:
Semaglutide has “provided very significant benefits in many ways, but future discussions between a patient and their physician should include NAION as a potential risk,” study leader Joseph Rizzo, MD, with Mass Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, said in a news release about the findings. “It is important to appreciate, however, that the increased risk relates to a disorder that is relatively uncommon.”
“Given the numbers of participants who have been recruited to clinical trials and the large number of people globally who use GLP-1 RAs, we should be confident that if corroborated, the absolute risk of developing NAION in direct relation to taking semaglutide must indeed be rare,” Susan P. Mollan, MBcHB, of University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, in England, wrote in a commentary published with the study.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on July 3 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The patients were seen at a hospital that specializes in ophthalmology and has a specialized neuro-ophthalmology service, so the results may not fully apply to other settings. The results were driven by a relatively small number of NAION cases in the patients exposed to semaglutide. The study does not establish that semaglutide directly causes NAION, the researchers noted. “The best approaches to confirm, refute, or refine our findings would be to conduct a much larger, retrospective, multicenter population-based cohort study; a prospective, randomized clinical study; or a postmarket analysis of all GLP-1 RA drugs,” they wrote.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from Research to Prevent Blindness.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Weight Loss Drugs Cut Cancer Risk in Diabetes Patients
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.