User login
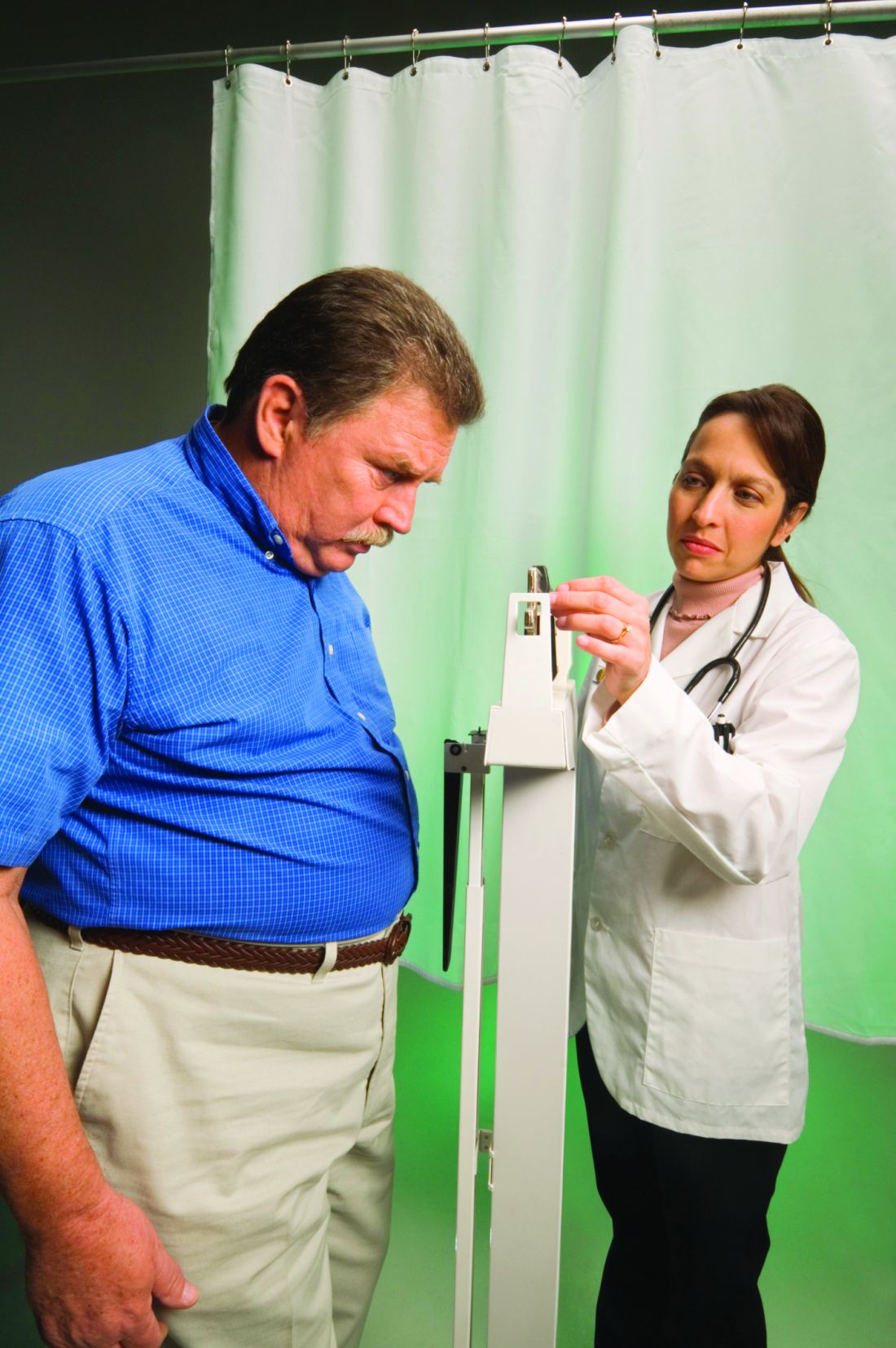
Will the doctor see you now? The health system’s changing landscape
Lucia Agajanian, a 25-year-old freelance film producer in Chicago, doesn’t have a specific primary care doctor, preferring the convenience of visiting a local clinic for flu shots or going online for video visits. “You say what you need, and there’s a 15-minute wait time,” she said, explaining how her appointments usually work. “I really liked that.”
But Olga Lucia Torres, a 52-year-old who teaches narrative medicine classes at Columbia University in New York, misses her longtime primary care doctor, who kept tabs for two decades on her conditions, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and made sure she was up to date on vaccines and screening tests. Two years ago, Torres received a letter informing her that he was changing to a “boutique practice” and would charge a retainer fee of $10,000 for her to stay on as a patient.
“I felt really sad and abandoned,” Ms. Torres said. “This was my PCP. I was like, ‘Dude, I thought we were in this together!’ ”
The two women reflect an ongoing reality: The primary care landscape is changing in ways that could shape patients’ access and quality of care now and for decades to come. A solid and enduring relationship with a primary care doctor – who knows a patient’s history and can monitor new problems – has long been regarded as the bedrock of a quality health care system. But investment in primary care in the U.S. lags behind that of other high-income countries, and America has a smaller share of primary care physicians than most of its European counterparts.
An estimated one-third of all physicians in the U.S. are primary care doctors – who include family medicine physicians, general internists, and pediatricians – according to the Robert Graham Center, a research and analysis organization that studies primary care. Other researchers say the numbers are lower, with the Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker reporting only 12% of U.S. doctors are generalists, compared with 23% in Germany and as many as 45% in the Netherlands.
That means it’s often hard to find a doctor and make an appointment that’s not weeks or months away.
“This is a problem that has been simmering and now beginning to erupt in some communities at a boil. It’s hard to find that front door of the health system,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit membership organization.
Today, a smaller percentage of physicians are entering the field than are practicing, suggesting that shortages will worsen over time.
Interest has waned partly because, in the U.S., primary care yields lower salaries than other medical and surgical specialties.
Some doctors now in practice also say they are burned out, facing cumbersome electronic health record systems and limits on appointment times, making it harder to get to know a patient and establish a relationship.
Others are retiring or selling their practices. Hospitals, insurers like Aetna-CVS Health, and other corporate entities like Amazon are on a buying spree, snapping up primary care practices, furthering a move away from the “Marcus Welby, M.D.”-style neighborhood doctor. About 48% of primary care physicians currently work in practices they do not own. Two-thirds of those doctors don’t work for other physicians but are employed by private equity investors or other corporate entities, according to data in the “Primary Care Chartbook,” which is collected and published by the Graham Center.
Patients who seek care at these offices may not be seen by the same doctor at every visit. Indeed, they may not be seen by a doctor at all but by a paraprofessional – a nurse practitioner or a physician assistant, for instance – who works under the doctor’s license. That trend has been accelerated by new state laws – as well as changes in Medicare policy – that loosen the requirements for physician supervisors and billing. And these jobs are expected to be among the decade’s fastest-growing in the health sector.
Overall, demand for primary care is up, spurred partly by record enrollment in Affordable Care Act plans. All those new patients, combined with the low supply of doctors, are contributing to a years-long downward trend in the number of people reporting they have a usual source of care, be it an individual doctor or a specific clinic or practice.
Researchers say that raises questions, including whether people can’t find a primary care doctor, can’t afford one, or simply no longer want an established relationship.
“Is it poor access or problems with the supply of providers? Does it reflect a societal disconnection, a go-it-alone phenomenon?” asked Christopher F. Koller, president of the Milbank Memorial Fund, a foundation whose nonpartisan analyses focus on state health policy.
For patients, frustrating wait times are one result. A recent survey by a physician staffing firm found it now takes an average of 21 days just to get in to see a doctor of family medicine, defined as a subgroup of primary care, which includes general internists and pediatricians. Those physicians are many patients’ first stop for health care. That runs counter to the trend in other countries, where patients complain of months- or years-long waits for elective procedures like hip replacements but generally experience short waits for primary care visits.
Another complication: All these factors are adding urgency to ongoing concerns about attracting new primary care physicians to the specialty.
When she was in medical school, Natalie A. Cameron, MD, specifically chose primary care because she enjoyed forming relationships with patients and because “I’m specifically interested in prevention and women’s health, and you do a lot of that in primary care.” The 33-year-old is currently an instructor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she also sees patients at a primary care practice.
Still, she understands why many of her colleagues chose something else. For some, it’s the pay differential. For others, it’s because of primary care’s reputation for involving “a lot of care and paperwork and coordinating a lot of issues that may not just be medical,” Dr. Cameron said.
The million-dollar question, then, is how much does having a usual source of care influence medical outcomes and cost? And for which kinds of patients is having a close relationship with a doctor important? While studies show that many young people value the convenience of visiting urgent care – especially when it takes so long to see a primary care doctor – will their long-term health suffer because of that strategy?
Many patients – particularly the young and generally healthy ones – shrug at the new normal, embracing alternatives that require less waiting. These options are particularly attractive to millennials, who tell focus groups that the convenience of a one-off video call or visit to a big-box store clinic trumps a long-standing relationship with a doctor, especially if they have to wait days, weeks, or longer for a traditional appointment.
“The doctor I have is a family friend, but definitely I would take access and ease over a relationship,” said Matt Degn, 24, who says it can take two to three months to book a routine appointment in Salt Lake City, where he lives.
Patients are increasingly turning to what are dubbed “retail clinics,” such as CVS’ Minute Clinics, which tout “in-person and virtual care 7 days a week.” CVS Health’s more than 1,000 clinics inside stores across the U.S. treated more than 5 million people last year, Creagh Milford, a physician and the company’s senior vice president of retail health, said in a written statement. He cited a recent study by a data products firm showing the use of retail clinics has grown 200% over the past five years.
Health policy experts say increased access to alternatives can be good, but forgoing an ongoing relationship to a regular provider is not, especially as people get older and are more likely to develop chronic conditions or other medical problems.
“There’s a lot of data that show communities with a lot of primary care have better health,” said Mr. Koller.
People with a regular primary care doctor or practice are more likely to get preventive care, such as cancer screenings or flu shots, studies show, and are less likely to die if they do suffer a heart attack.
Physicians who see patients regularly are better able to spot patterns of seemingly minor concerns that could add up to a serious health issue.
“What happens when you go to four different providers on four platforms for urinary tract infections because, well, they are just UTIs,” posed Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, a family physician practicing in Washington, and the director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But actually, you have a large kidney stone that’s causing your UTI or have some sort of immune deficiency like diabetes that’s causing frequent UTIs. But no one tested you.”
Most experts agree that figuring out how to coordinate care amid this changing landscape and make it more accessible without undermining quality – even when different doctors, locations, health systems, and electronic health records are involved – will be as complex as the pressures causing long waits and less interest in today’s primary care market.
And experiences sometimes lead patients to change their minds.
There’s something to be said for establishing a relationship, said Ms. Agajanian, in Chicago. She’s rethinking her decision to cobble together care, rather than have a specific primary care doctor or clinic, following an injury at work last year that led to shoulder surgery.
“As I’m getting older, even though I’m still young,” she said, “I have all these problems with my body, and it would be nice to have a consistent person who knows all my problems to talk with.”
KFF Health News’ Colleen DeGuzman contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Lucia Agajanian, a 25-year-old freelance film producer in Chicago, doesn’t have a specific primary care doctor, preferring the convenience of visiting a local clinic for flu shots or going online for video visits. “You say what you need, and there’s a 15-minute wait time,” she said, explaining how her appointments usually work. “I really liked that.”
But Olga Lucia Torres, a 52-year-old who teaches narrative medicine classes at Columbia University in New York, misses her longtime primary care doctor, who kept tabs for two decades on her conditions, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and made sure she was up to date on vaccines and screening tests. Two years ago, Torres received a letter informing her that he was changing to a “boutique practice” and would charge a retainer fee of $10,000 for her to stay on as a patient.
“I felt really sad and abandoned,” Ms. Torres said. “This was my PCP. I was like, ‘Dude, I thought we were in this together!’ ”
The two women reflect an ongoing reality: The primary care landscape is changing in ways that could shape patients’ access and quality of care now and for decades to come. A solid and enduring relationship with a primary care doctor – who knows a patient’s history and can monitor new problems – has long been regarded as the bedrock of a quality health care system. But investment in primary care in the U.S. lags behind that of other high-income countries, and America has a smaller share of primary care physicians than most of its European counterparts.
An estimated one-third of all physicians in the U.S. are primary care doctors – who include family medicine physicians, general internists, and pediatricians – according to the Robert Graham Center, a research and analysis organization that studies primary care. Other researchers say the numbers are lower, with the Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker reporting only 12% of U.S. doctors are generalists, compared with 23% in Germany and as many as 45% in the Netherlands.
That means it’s often hard to find a doctor and make an appointment that’s not weeks or months away.
“This is a problem that has been simmering and now beginning to erupt in some communities at a boil. It’s hard to find that front door of the health system,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit membership organization.
Today, a smaller percentage of physicians are entering the field than are practicing, suggesting that shortages will worsen over time.
Interest has waned partly because, in the U.S., primary care yields lower salaries than other medical and surgical specialties.
Some doctors now in practice also say they are burned out, facing cumbersome electronic health record systems and limits on appointment times, making it harder to get to know a patient and establish a relationship.
Others are retiring or selling their practices. Hospitals, insurers like Aetna-CVS Health, and other corporate entities like Amazon are on a buying spree, snapping up primary care practices, furthering a move away from the “Marcus Welby, M.D.”-style neighborhood doctor. About 48% of primary care physicians currently work in practices they do not own. Two-thirds of those doctors don’t work for other physicians but are employed by private equity investors or other corporate entities, according to data in the “Primary Care Chartbook,” which is collected and published by the Graham Center.
Patients who seek care at these offices may not be seen by the same doctor at every visit. Indeed, they may not be seen by a doctor at all but by a paraprofessional – a nurse practitioner or a physician assistant, for instance – who works under the doctor’s license. That trend has been accelerated by new state laws – as well as changes in Medicare policy – that loosen the requirements for physician supervisors and billing. And these jobs are expected to be among the decade’s fastest-growing in the health sector.
Overall, demand for primary care is up, spurred partly by record enrollment in Affordable Care Act plans. All those new patients, combined with the low supply of doctors, are contributing to a years-long downward trend in the number of people reporting they have a usual source of care, be it an individual doctor or a specific clinic or practice.
Researchers say that raises questions, including whether people can’t find a primary care doctor, can’t afford one, or simply no longer want an established relationship.
“Is it poor access or problems with the supply of providers? Does it reflect a societal disconnection, a go-it-alone phenomenon?” asked Christopher F. Koller, president of the Milbank Memorial Fund, a foundation whose nonpartisan analyses focus on state health policy.
For patients, frustrating wait times are one result. A recent survey by a physician staffing firm found it now takes an average of 21 days just to get in to see a doctor of family medicine, defined as a subgroup of primary care, which includes general internists and pediatricians. Those physicians are many patients’ first stop for health care. That runs counter to the trend in other countries, where patients complain of months- or years-long waits for elective procedures like hip replacements but generally experience short waits for primary care visits.
Another complication: All these factors are adding urgency to ongoing concerns about attracting new primary care physicians to the specialty.
When she was in medical school, Natalie A. Cameron, MD, specifically chose primary care because she enjoyed forming relationships with patients and because “I’m specifically interested in prevention and women’s health, and you do a lot of that in primary care.” The 33-year-old is currently an instructor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she also sees patients at a primary care practice.
Still, she understands why many of her colleagues chose something else. For some, it’s the pay differential. For others, it’s because of primary care’s reputation for involving “a lot of care and paperwork and coordinating a lot of issues that may not just be medical,” Dr. Cameron said.
The million-dollar question, then, is how much does having a usual source of care influence medical outcomes and cost? And for which kinds of patients is having a close relationship with a doctor important? While studies show that many young people value the convenience of visiting urgent care – especially when it takes so long to see a primary care doctor – will their long-term health suffer because of that strategy?
Many patients – particularly the young and generally healthy ones – shrug at the new normal, embracing alternatives that require less waiting. These options are particularly attractive to millennials, who tell focus groups that the convenience of a one-off video call or visit to a big-box store clinic trumps a long-standing relationship with a doctor, especially if they have to wait days, weeks, or longer for a traditional appointment.
“The doctor I have is a family friend, but definitely I would take access and ease over a relationship,” said Matt Degn, 24, who says it can take two to three months to book a routine appointment in Salt Lake City, where he lives.
Patients are increasingly turning to what are dubbed “retail clinics,” such as CVS’ Minute Clinics, which tout “in-person and virtual care 7 days a week.” CVS Health’s more than 1,000 clinics inside stores across the U.S. treated more than 5 million people last year, Creagh Milford, a physician and the company’s senior vice president of retail health, said in a written statement. He cited a recent study by a data products firm showing the use of retail clinics has grown 200% over the past five years.
Health policy experts say increased access to alternatives can be good, but forgoing an ongoing relationship to a regular provider is not, especially as people get older and are more likely to develop chronic conditions or other medical problems.
“There’s a lot of data that show communities with a lot of primary care have better health,” said Mr. Koller.
People with a regular primary care doctor or practice are more likely to get preventive care, such as cancer screenings or flu shots, studies show, and are less likely to die if they do suffer a heart attack.
Physicians who see patients regularly are better able to spot patterns of seemingly minor concerns that could add up to a serious health issue.
“What happens when you go to four different providers on four platforms for urinary tract infections because, well, they are just UTIs,” posed Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, a family physician practicing in Washington, and the director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But actually, you have a large kidney stone that’s causing your UTI or have some sort of immune deficiency like diabetes that’s causing frequent UTIs. But no one tested you.”
Most experts agree that figuring out how to coordinate care amid this changing landscape and make it more accessible without undermining quality – even when different doctors, locations, health systems, and electronic health records are involved – will be as complex as the pressures causing long waits and less interest in today’s primary care market.
And experiences sometimes lead patients to change their minds.
There’s something to be said for establishing a relationship, said Ms. Agajanian, in Chicago. She’s rethinking her decision to cobble together care, rather than have a specific primary care doctor or clinic, following an injury at work last year that led to shoulder surgery.
“As I’m getting older, even though I’m still young,” she said, “I have all these problems with my body, and it would be nice to have a consistent person who knows all my problems to talk with.”
KFF Health News’ Colleen DeGuzman contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Lucia Agajanian, a 25-year-old freelance film producer in Chicago, doesn’t have a specific primary care doctor, preferring the convenience of visiting a local clinic for flu shots or going online for video visits. “You say what you need, and there’s a 15-minute wait time,” she said, explaining how her appointments usually work. “I really liked that.”
But Olga Lucia Torres, a 52-year-old who teaches narrative medicine classes at Columbia University in New York, misses her longtime primary care doctor, who kept tabs for two decades on her conditions, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and made sure she was up to date on vaccines and screening tests. Two years ago, Torres received a letter informing her that he was changing to a “boutique practice” and would charge a retainer fee of $10,000 for her to stay on as a patient.
“I felt really sad and abandoned,” Ms. Torres said. “This was my PCP. I was like, ‘Dude, I thought we were in this together!’ ”
The two women reflect an ongoing reality: The primary care landscape is changing in ways that could shape patients’ access and quality of care now and for decades to come. A solid and enduring relationship with a primary care doctor – who knows a patient’s history and can monitor new problems – has long been regarded as the bedrock of a quality health care system. But investment in primary care in the U.S. lags behind that of other high-income countries, and America has a smaller share of primary care physicians than most of its European counterparts.
An estimated one-third of all physicians in the U.S. are primary care doctors – who include family medicine physicians, general internists, and pediatricians – according to the Robert Graham Center, a research and analysis organization that studies primary care. Other researchers say the numbers are lower, with the Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker reporting only 12% of U.S. doctors are generalists, compared with 23% in Germany and as many as 45% in the Netherlands.
That means it’s often hard to find a doctor and make an appointment that’s not weeks or months away.
“This is a problem that has been simmering and now beginning to erupt in some communities at a boil. It’s hard to find that front door of the health system,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit membership organization.
Today, a smaller percentage of physicians are entering the field than are practicing, suggesting that shortages will worsen over time.
Interest has waned partly because, in the U.S., primary care yields lower salaries than other medical and surgical specialties.
Some doctors now in practice also say they are burned out, facing cumbersome electronic health record systems and limits on appointment times, making it harder to get to know a patient and establish a relationship.
Others are retiring or selling their practices. Hospitals, insurers like Aetna-CVS Health, and other corporate entities like Amazon are on a buying spree, snapping up primary care practices, furthering a move away from the “Marcus Welby, M.D.”-style neighborhood doctor. About 48% of primary care physicians currently work in practices they do not own. Two-thirds of those doctors don’t work for other physicians but are employed by private equity investors or other corporate entities, according to data in the “Primary Care Chartbook,” which is collected and published by the Graham Center.
Patients who seek care at these offices may not be seen by the same doctor at every visit. Indeed, they may not be seen by a doctor at all but by a paraprofessional – a nurse practitioner or a physician assistant, for instance – who works under the doctor’s license. That trend has been accelerated by new state laws – as well as changes in Medicare policy – that loosen the requirements for physician supervisors and billing. And these jobs are expected to be among the decade’s fastest-growing in the health sector.
Overall, demand for primary care is up, spurred partly by record enrollment in Affordable Care Act plans. All those new patients, combined with the low supply of doctors, are contributing to a years-long downward trend in the number of people reporting they have a usual source of care, be it an individual doctor or a specific clinic or practice.
Researchers say that raises questions, including whether people can’t find a primary care doctor, can’t afford one, or simply no longer want an established relationship.
“Is it poor access or problems with the supply of providers? Does it reflect a societal disconnection, a go-it-alone phenomenon?” asked Christopher F. Koller, president of the Milbank Memorial Fund, a foundation whose nonpartisan analyses focus on state health policy.
For patients, frustrating wait times are one result. A recent survey by a physician staffing firm found it now takes an average of 21 days just to get in to see a doctor of family medicine, defined as a subgroup of primary care, which includes general internists and pediatricians. Those physicians are many patients’ first stop for health care. That runs counter to the trend in other countries, where patients complain of months- or years-long waits for elective procedures like hip replacements but generally experience short waits for primary care visits.
Another complication: All these factors are adding urgency to ongoing concerns about attracting new primary care physicians to the specialty.
When she was in medical school, Natalie A. Cameron, MD, specifically chose primary care because she enjoyed forming relationships with patients and because “I’m specifically interested in prevention and women’s health, and you do a lot of that in primary care.” The 33-year-old is currently an instructor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she also sees patients at a primary care practice.
Still, she understands why many of her colleagues chose something else. For some, it’s the pay differential. For others, it’s because of primary care’s reputation for involving “a lot of care and paperwork and coordinating a lot of issues that may not just be medical,” Dr. Cameron said.
The million-dollar question, then, is how much does having a usual source of care influence medical outcomes and cost? And for which kinds of patients is having a close relationship with a doctor important? While studies show that many young people value the convenience of visiting urgent care – especially when it takes so long to see a primary care doctor – will their long-term health suffer because of that strategy?
Many patients – particularly the young and generally healthy ones – shrug at the new normal, embracing alternatives that require less waiting. These options are particularly attractive to millennials, who tell focus groups that the convenience of a one-off video call or visit to a big-box store clinic trumps a long-standing relationship with a doctor, especially if they have to wait days, weeks, or longer for a traditional appointment.
“The doctor I have is a family friend, but definitely I would take access and ease over a relationship,” said Matt Degn, 24, who says it can take two to three months to book a routine appointment in Salt Lake City, where he lives.
Patients are increasingly turning to what are dubbed “retail clinics,” such as CVS’ Minute Clinics, which tout “in-person and virtual care 7 days a week.” CVS Health’s more than 1,000 clinics inside stores across the U.S. treated more than 5 million people last year, Creagh Milford, a physician and the company’s senior vice president of retail health, said in a written statement. He cited a recent study by a data products firm showing the use of retail clinics has grown 200% over the past five years.
Health policy experts say increased access to alternatives can be good, but forgoing an ongoing relationship to a regular provider is not, especially as people get older and are more likely to develop chronic conditions or other medical problems.
“There’s a lot of data that show communities with a lot of primary care have better health,” said Mr. Koller.
People with a regular primary care doctor or practice are more likely to get preventive care, such as cancer screenings or flu shots, studies show, and are less likely to die if they do suffer a heart attack.
Physicians who see patients regularly are better able to spot patterns of seemingly minor concerns that could add up to a serious health issue.
“What happens when you go to four different providers on four platforms for urinary tract infections because, well, they are just UTIs,” posed Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, a family physician practicing in Washington, and the director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But actually, you have a large kidney stone that’s causing your UTI or have some sort of immune deficiency like diabetes that’s causing frequent UTIs. But no one tested you.”
Most experts agree that figuring out how to coordinate care amid this changing landscape and make it more accessible without undermining quality – even when different doctors, locations, health systems, and electronic health records are involved – will be as complex as the pressures causing long waits and less interest in today’s primary care market.
And experiences sometimes lead patients to change their minds.
There’s something to be said for establishing a relationship, said Ms. Agajanian, in Chicago. She’s rethinking her decision to cobble together care, rather than have a specific primary care doctor or clinic, following an injury at work last year that led to shoulder surgery.
“As I’m getting older, even though I’m still young,” she said, “I have all these problems with my body, and it would be nice to have a consistent person who knows all my problems to talk with.”
KFF Health News’ Colleen DeGuzman contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Employers use patient assistance programs to offset their own costs
Anna Sutton was shocked when she received a letter from her husband’s job-based health plan stating that Humira, an expensive drug used to treat her daughter’s juvenile arthritis, was now on a long list of medications considered “nonessential benefits.”
The July 2021 letter said the family could either participate in a new effort overseen by a company called SaveOnSP and get the drug free of charge or be saddled with a monthly copayment that could top $1,000.
“It really gave us no choice,” said Mrs. Sutton, of Woodinville, Wash. She added that “every single [Food and Drug Administration]–approved medication for juvenile arthritis” was on the list of nonessential benefits.
Mrs. Sutton had unwittingly become part of a strategy that employers are using to deal with the high cost of drugs prescribed to treat conditions such as arthritis, psoriasis, cancer, and hemophilia.
Those employers are tapping into dollars provided through programs they have previously criticized: patient financial assistance initiatives set up by drugmakers, which some benefit managers have complained encourage patients to stay on expensive brand-name drugs when less expensive options might be available.
Now, though, employers, or the vendors and insurers they hire specifically to oversee such efforts, are seeking that money to offset their own costs. Drugmakers object, saying the money was intended primarily for patients. But some benefit brokers and companies like SaveOnSP say they can help trim employers’ spending on insurance – which, they say, could be the difference between an employer offering coverage to workers or not.
It’s the latest twist in a long-running dispute between the drug industry and insurers over which group is more to blame for rising costs to patients. And patients are, again, caught in the middle.
Patient advocates say the term “nonessential” stresses patients out even though it doesn’t mean the drugs – often called “specialty” drugs because of their high prices or the way they are made – are unnecessary.
Some advocates fear the new strategies could be “a way to weed out those with costly health care needs,” said Rachel Klein, deputy executive director of the AIDS Institute, a nonprofit advocacy group. Workers who rely on the drugs may feel pressured to change insurers or jobs.
Two versions of the new strategy are in play. Both are used mainly by self-insured employers that hire vendors, like SaveOnSP, which then work with the employers’ pharmacy benefit managers, such as Express Scripts/Cigna, to implement the strategy. There are also smaller vendors, like SHARx and Payer Matrix, some of which work directly with employers.
In one approach, insurers or employers continue to cover the drugs but designate them as “nonessential,” which allows the health plans to bypass annual limits set by the Affordable Care Act on how much patients can pay in out-of-pocket costs for drugs. The employer or hired vendor then raises the copay required of the worker, often sharply, but offers to substantially cut or eliminate that copay if the patient participates in the new effort. Workers who agree enroll in drugmaker financial assistance programs meant to cover the drug copays, and the vendor monitoring the effort aims to capture the maximum amount the drugmaker provides annually, according to a lawsuit filed in May by drugmaker Johnson & Johnson against SaveOnSP, which is based in Elma, N.Y.
The employer must still cover part of the cost of the drug, but the amount is reduced by the amount of copay assistance that is accessed. That assistance can vary widely and be as much as $20,000 a year for some drugs.
In the other approach, employers don’t bother naming drugs nonessential; they simply drop coverage for specific drugs or classes of drugs. Then, the outside vendor helps patients provide the financial and other information needed to apply for free medication from drugmakers through charity programs intended for uninsured patients.
“We’re seeing it in every state at this point,” said Becky Burns, chief operating officer and chief financial officer at the Bleeding and Clotting Disorders Institute in Peoria, Ill., a federally funded hemophilia treatment center.
The strategies are mostly being used in self-insured employer health plans, which are governed by federal laws that give broad flexibility to employers in designing health benefits.
Still, some patient advocates say these programs can lead to delays for patients in accessing medications while applications are processed – and sometimes unexpected bills for consumers.
“We have patients get billed after they max out their assistance,” said Kollet Koulianos, vice president of payer relations at the National Hemophilia Foundation. Once she gets involved, vendors often claim the bills were sent in error.
Even though only about 2% of the workforce needs the drugs, which can cost thousands of dollars a dose, they can lead to a hefty financial liability for self-insured employers, said Drew Mann, a benefits consultant in Knoxville, Tenn., whose clientele includes employers that use variations of these programs.
Before employer health plans took advantage of such assistance, patients often signed up for these programs on their own, receiving coupons that covered their share of the drug’s cost. In that circumstance, drugmakers often paid less than they do under the new employer schemes because a patient’s out-of-pocket costs were capped at lower amounts.
Brokers and the CEOs of firms offering the new programs say that in most cases patients continue to get their drugs, often with little or no out-of-pocket costs.
If workers do not qualify for charity because their income is too high, or for another reason, the employer might make an exception and pay the claim or look for an alternative solution, Mr. Mann said. Patient groups noted that some specialty drugs may not have any alternatives.
How this practice will play out in the long run remains uncertain. Drugmakers offer both copay assistance and charity care in part because they know many patients, even those with insurance, cannot afford their products. The programs are also good public relations and a tax write-off. But the new emphasis by some employers on maximizing the amount they or their insurers can collect from the programs could cause some drugmakers to take issue with the new strategies or even reconsider their programs.
“Even though our client, like most manufacturers, provides billions in discounts and rebates to health insurers as part of their negotiations, the insurers also want this additional pool of funds, which is meant to help people who can’t meet the copay,” said Harry Sandick, a lawyer representing J&J.
J&J’s lawsuit, filed in U.S. District Court in New Jersey, alleges that patients are “coerced” into participating in copay assistance programs after their drugs are deemed “nonessential” and therefore are “no longer subject to the ACA’s annual out-of-pocket maximum.”
Once patients enroll, the money from the drugmaker goes to the insurer or employer plan, with SaveOnSP retaining 25%, according to the lawsuit. It claims J&J has lost $100 million to these efforts.
None of that money counts toward patients’ deductibles or out-of-pocket maximums for the year.
In addition to the lawsuit over the copay assistance program efforts, there has been other reaction to the new employer strategies. In an October letter to physicians, the Johnson & Johnson Patient Assistance Foundation, a separate entity, said it will no longer offer free medications to patients with insurance starting in January, citing the rise of such “alternative funding programs.”
Still, J&J spokesperson L.D. Platt said the drugmaker has plans, also in January, to roll out other assistance to patients who may be “underinsured” so they won’t be affected by the foundation’s decision.
In a statement, SaveOnSP said that employers object to drug companies’ “using their employees’ ongoing need for these drugs as an excuse to keep hiking the drugs’ prices” and that the firm simply “advises these employers on how to fight back against rising prices while getting employees the drugs they need at no cost to the employees.”
In a court filing, SaveOnSP said drugmakers have another option if they don’t like efforts by insurers and employers to max out what they can get from the programs: reduce the amount of assistance available. J&J, the filing said, did just that when it recently cut its allotted amount of copay assistance for psoriasis drugs Stelara and Tremfya from $20,000 to $6,000 per participant annually. The filing noted that SaveOnSP participants would still have no copay for those drugs.
For Mrs. Sutton’s part, her family did participate in the program offered through her husband’s work-based insurance plan, agreeing to have SaveOnSP monitor their enrollment and payments from the drugmaker.
So far, her 15-year-old daughter has continued to get Humira, and she has not been billed a copay.
Even so, “the whole process seems kind of slimy to me,” she said. “The patients are caught in the middle between the drug industry and the insurance industry, each trying to get as much money as possible out of the other.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Anna Sutton was shocked when she received a letter from her husband’s job-based health plan stating that Humira, an expensive drug used to treat her daughter’s juvenile arthritis, was now on a long list of medications considered “nonessential benefits.”
The July 2021 letter said the family could either participate in a new effort overseen by a company called SaveOnSP and get the drug free of charge or be saddled with a monthly copayment that could top $1,000.
“It really gave us no choice,” said Mrs. Sutton, of Woodinville, Wash. She added that “every single [Food and Drug Administration]–approved medication for juvenile arthritis” was on the list of nonessential benefits.
Mrs. Sutton had unwittingly become part of a strategy that employers are using to deal with the high cost of drugs prescribed to treat conditions such as arthritis, psoriasis, cancer, and hemophilia.
Those employers are tapping into dollars provided through programs they have previously criticized: patient financial assistance initiatives set up by drugmakers, which some benefit managers have complained encourage patients to stay on expensive brand-name drugs when less expensive options might be available.
Now, though, employers, or the vendors and insurers they hire specifically to oversee such efforts, are seeking that money to offset their own costs. Drugmakers object, saying the money was intended primarily for patients. But some benefit brokers and companies like SaveOnSP say they can help trim employers’ spending on insurance – which, they say, could be the difference between an employer offering coverage to workers or not.
It’s the latest twist in a long-running dispute between the drug industry and insurers over which group is more to blame for rising costs to patients. And patients are, again, caught in the middle.
Patient advocates say the term “nonessential” stresses patients out even though it doesn’t mean the drugs – often called “specialty” drugs because of their high prices or the way they are made – are unnecessary.
Some advocates fear the new strategies could be “a way to weed out those with costly health care needs,” said Rachel Klein, deputy executive director of the AIDS Institute, a nonprofit advocacy group. Workers who rely on the drugs may feel pressured to change insurers or jobs.
Two versions of the new strategy are in play. Both are used mainly by self-insured employers that hire vendors, like SaveOnSP, which then work with the employers’ pharmacy benefit managers, such as Express Scripts/Cigna, to implement the strategy. There are also smaller vendors, like SHARx and Payer Matrix, some of which work directly with employers.
In one approach, insurers or employers continue to cover the drugs but designate them as “nonessential,” which allows the health plans to bypass annual limits set by the Affordable Care Act on how much patients can pay in out-of-pocket costs for drugs. The employer or hired vendor then raises the copay required of the worker, often sharply, but offers to substantially cut or eliminate that copay if the patient participates in the new effort. Workers who agree enroll in drugmaker financial assistance programs meant to cover the drug copays, and the vendor monitoring the effort aims to capture the maximum amount the drugmaker provides annually, according to a lawsuit filed in May by drugmaker Johnson & Johnson against SaveOnSP, which is based in Elma, N.Y.
The employer must still cover part of the cost of the drug, but the amount is reduced by the amount of copay assistance that is accessed. That assistance can vary widely and be as much as $20,000 a year for some drugs.
In the other approach, employers don’t bother naming drugs nonessential; they simply drop coverage for specific drugs or classes of drugs. Then, the outside vendor helps patients provide the financial and other information needed to apply for free medication from drugmakers through charity programs intended for uninsured patients.
“We’re seeing it in every state at this point,” said Becky Burns, chief operating officer and chief financial officer at the Bleeding and Clotting Disorders Institute in Peoria, Ill., a federally funded hemophilia treatment center.
The strategies are mostly being used in self-insured employer health plans, which are governed by federal laws that give broad flexibility to employers in designing health benefits.
Still, some patient advocates say these programs can lead to delays for patients in accessing medications while applications are processed – and sometimes unexpected bills for consumers.
“We have patients get billed after they max out their assistance,” said Kollet Koulianos, vice president of payer relations at the National Hemophilia Foundation. Once she gets involved, vendors often claim the bills were sent in error.
Even though only about 2% of the workforce needs the drugs, which can cost thousands of dollars a dose, they can lead to a hefty financial liability for self-insured employers, said Drew Mann, a benefits consultant in Knoxville, Tenn., whose clientele includes employers that use variations of these programs.
Before employer health plans took advantage of such assistance, patients often signed up for these programs on their own, receiving coupons that covered their share of the drug’s cost. In that circumstance, drugmakers often paid less than they do under the new employer schemes because a patient’s out-of-pocket costs were capped at lower amounts.
Brokers and the CEOs of firms offering the new programs say that in most cases patients continue to get their drugs, often with little or no out-of-pocket costs.
If workers do not qualify for charity because their income is too high, or for another reason, the employer might make an exception and pay the claim or look for an alternative solution, Mr. Mann said. Patient groups noted that some specialty drugs may not have any alternatives.
How this practice will play out in the long run remains uncertain. Drugmakers offer both copay assistance and charity care in part because they know many patients, even those with insurance, cannot afford their products. The programs are also good public relations and a tax write-off. But the new emphasis by some employers on maximizing the amount they or their insurers can collect from the programs could cause some drugmakers to take issue with the new strategies or even reconsider their programs.
“Even though our client, like most manufacturers, provides billions in discounts and rebates to health insurers as part of their negotiations, the insurers also want this additional pool of funds, which is meant to help people who can’t meet the copay,” said Harry Sandick, a lawyer representing J&J.
J&J’s lawsuit, filed in U.S. District Court in New Jersey, alleges that patients are “coerced” into participating in copay assistance programs after their drugs are deemed “nonessential” and therefore are “no longer subject to the ACA’s annual out-of-pocket maximum.”
Once patients enroll, the money from the drugmaker goes to the insurer or employer plan, with SaveOnSP retaining 25%, according to the lawsuit. It claims J&J has lost $100 million to these efforts.
None of that money counts toward patients’ deductibles or out-of-pocket maximums for the year.
In addition to the lawsuit over the copay assistance program efforts, there has been other reaction to the new employer strategies. In an October letter to physicians, the Johnson & Johnson Patient Assistance Foundation, a separate entity, said it will no longer offer free medications to patients with insurance starting in January, citing the rise of such “alternative funding programs.”
Still, J&J spokesperson L.D. Platt said the drugmaker has plans, also in January, to roll out other assistance to patients who may be “underinsured” so they won’t be affected by the foundation’s decision.
In a statement, SaveOnSP said that employers object to drug companies’ “using their employees’ ongoing need for these drugs as an excuse to keep hiking the drugs’ prices” and that the firm simply “advises these employers on how to fight back against rising prices while getting employees the drugs they need at no cost to the employees.”
In a court filing, SaveOnSP said drugmakers have another option if they don’t like efforts by insurers and employers to max out what they can get from the programs: reduce the amount of assistance available. J&J, the filing said, did just that when it recently cut its allotted amount of copay assistance for psoriasis drugs Stelara and Tremfya from $20,000 to $6,000 per participant annually. The filing noted that SaveOnSP participants would still have no copay for those drugs.
For Mrs. Sutton’s part, her family did participate in the program offered through her husband’s work-based insurance plan, agreeing to have SaveOnSP monitor their enrollment and payments from the drugmaker.
So far, her 15-year-old daughter has continued to get Humira, and she has not been billed a copay.
Even so, “the whole process seems kind of slimy to me,” she said. “The patients are caught in the middle between the drug industry and the insurance industry, each trying to get as much money as possible out of the other.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Anna Sutton was shocked when she received a letter from her husband’s job-based health plan stating that Humira, an expensive drug used to treat her daughter’s juvenile arthritis, was now on a long list of medications considered “nonessential benefits.”
The July 2021 letter said the family could either participate in a new effort overseen by a company called SaveOnSP and get the drug free of charge or be saddled with a monthly copayment that could top $1,000.
“It really gave us no choice,” said Mrs. Sutton, of Woodinville, Wash. She added that “every single [Food and Drug Administration]–approved medication for juvenile arthritis” was on the list of nonessential benefits.
Mrs. Sutton had unwittingly become part of a strategy that employers are using to deal with the high cost of drugs prescribed to treat conditions such as arthritis, psoriasis, cancer, and hemophilia.
Those employers are tapping into dollars provided through programs they have previously criticized: patient financial assistance initiatives set up by drugmakers, which some benefit managers have complained encourage patients to stay on expensive brand-name drugs when less expensive options might be available.
Now, though, employers, or the vendors and insurers they hire specifically to oversee such efforts, are seeking that money to offset their own costs. Drugmakers object, saying the money was intended primarily for patients. But some benefit brokers and companies like SaveOnSP say they can help trim employers’ spending on insurance – which, they say, could be the difference between an employer offering coverage to workers or not.
It’s the latest twist in a long-running dispute between the drug industry and insurers over which group is more to blame for rising costs to patients. And patients are, again, caught in the middle.
Patient advocates say the term “nonessential” stresses patients out even though it doesn’t mean the drugs – often called “specialty” drugs because of their high prices or the way they are made – are unnecessary.
Some advocates fear the new strategies could be “a way to weed out those with costly health care needs,” said Rachel Klein, deputy executive director of the AIDS Institute, a nonprofit advocacy group. Workers who rely on the drugs may feel pressured to change insurers or jobs.
Two versions of the new strategy are in play. Both are used mainly by self-insured employers that hire vendors, like SaveOnSP, which then work with the employers’ pharmacy benefit managers, such as Express Scripts/Cigna, to implement the strategy. There are also smaller vendors, like SHARx and Payer Matrix, some of which work directly with employers.
In one approach, insurers or employers continue to cover the drugs but designate them as “nonessential,” which allows the health plans to bypass annual limits set by the Affordable Care Act on how much patients can pay in out-of-pocket costs for drugs. The employer or hired vendor then raises the copay required of the worker, often sharply, but offers to substantially cut or eliminate that copay if the patient participates in the new effort. Workers who agree enroll in drugmaker financial assistance programs meant to cover the drug copays, and the vendor monitoring the effort aims to capture the maximum amount the drugmaker provides annually, according to a lawsuit filed in May by drugmaker Johnson & Johnson against SaveOnSP, which is based in Elma, N.Y.
The employer must still cover part of the cost of the drug, but the amount is reduced by the amount of copay assistance that is accessed. That assistance can vary widely and be as much as $20,000 a year for some drugs.
In the other approach, employers don’t bother naming drugs nonessential; they simply drop coverage for specific drugs or classes of drugs. Then, the outside vendor helps patients provide the financial and other information needed to apply for free medication from drugmakers through charity programs intended for uninsured patients.
“We’re seeing it in every state at this point,” said Becky Burns, chief operating officer and chief financial officer at the Bleeding and Clotting Disorders Institute in Peoria, Ill., a federally funded hemophilia treatment center.
The strategies are mostly being used in self-insured employer health plans, which are governed by federal laws that give broad flexibility to employers in designing health benefits.
Still, some patient advocates say these programs can lead to delays for patients in accessing medications while applications are processed – and sometimes unexpected bills for consumers.
“We have patients get billed after they max out their assistance,” said Kollet Koulianos, vice president of payer relations at the National Hemophilia Foundation. Once she gets involved, vendors often claim the bills were sent in error.
Even though only about 2% of the workforce needs the drugs, which can cost thousands of dollars a dose, they can lead to a hefty financial liability for self-insured employers, said Drew Mann, a benefits consultant in Knoxville, Tenn., whose clientele includes employers that use variations of these programs.
Before employer health plans took advantage of such assistance, patients often signed up for these programs on their own, receiving coupons that covered their share of the drug’s cost. In that circumstance, drugmakers often paid less than they do under the new employer schemes because a patient’s out-of-pocket costs were capped at lower amounts.
Brokers and the CEOs of firms offering the new programs say that in most cases patients continue to get their drugs, often with little or no out-of-pocket costs.
If workers do not qualify for charity because their income is too high, or for another reason, the employer might make an exception and pay the claim or look for an alternative solution, Mr. Mann said. Patient groups noted that some specialty drugs may not have any alternatives.
How this practice will play out in the long run remains uncertain. Drugmakers offer both copay assistance and charity care in part because they know many patients, even those with insurance, cannot afford their products. The programs are also good public relations and a tax write-off. But the new emphasis by some employers on maximizing the amount they or their insurers can collect from the programs could cause some drugmakers to take issue with the new strategies or even reconsider their programs.
“Even though our client, like most manufacturers, provides billions in discounts and rebates to health insurers as part of their negotiations, the insurers also want this additional pool of funds, which is meant to help people who can’t meet the copay,” said Harry Sandick, a lawyer representing J&J.
J&J’s lawsuit, filed in U.S. District Court in New Jersey, alleges that patients are “coerced” into participating in copay assistance programs after their drugs are deemed “nonessential” and therefore are “no longer subject to the ACA’s annual out-of-pocket maximum.”
Once patients enroll, the money from the drugmaker goes to the insurer or employer plan, with SaveOnSP retaining 25%, according to the lawsuit. It claims J&J has lost $100 million to these efforts.
None of that money counts toward patients’ deductibles or out-of-pocket maximums for the year.
In addition to the lawsuit over the copay assistance program efforts, there has been other reaction to the new employer strategies. In an October letter to physicians, the Johnson & Johnson Patient Assistance Foundation, a separate entity, said it will no longer offer free medications to patients with insurance starting in January, citing the rise of such “alternative funding programs.”
Still, J&J spokesperson L.D. Platt said the drugmaker has plans, also in January, to roll out other assistance to patients who may be “underinsured” so they won’t be affected by the foundation’s decision.
In a statement, SaveOnSP said that employers object to drug companies’ “using their employees’ ongoing need for these drugs as an excuse to keep hiking the drugs’ prices” and that the firm simply “advises these employers on how to fight back against rising prices while getting employees the drugs they need at no cost to the employees.”
In a court filing, SaveOnSP said drugmakers have another option if they don’t like efforts by insurers and employers to max out what they can get from the programs: reduce the amount of assistance available. J&J, the filing said, did just that when it recently cut its allotted amount of copay assistance for psoriasis drugs Stelara and Tremfya from $20,000 to $6,000 per participant annually. The filing noted that SaveOnSP participants would still have no copay for those drugs.
For Mrs. Sutton’s part, her family did participate in the program offered through her husband’s work-based insurance plan, agreeing to have SaveOnSP monitor their enrollment and payments from the drugmaker.
So far, her 15-year-old daughter has continued to get Humira, and she has not been billed a copay.
Even so, “the whole process seems kind of slimy to me,” she said. “The patients are caught in the middle between the drug industry and the insurance industry, each trying to get as much money as possible out of the other.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Three things to know about insurance coverage for abortion
Will your health plan pay for an abortion now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade?
Even before the June 24 ruling, insurance coverage for abortion varied widely. Now the issue is even more complex as states set varying rules – about half are expected to limit or ban abortion in almost all circumstances.
To be clear, though, the question of whether an insurance plan covers abortion is not the same as whether abortion is allowed in a state. Coverage issues are more complicated and governed by a wide variety of factors, including the level of abortion access a state allows.
How dense a thicket is it? Abortion may be covered by a health plan, but if no providers are available, patients don’t have access. However, people with insurance that does not cover abortion can still get one – but only if it’s available in their states or they can afford to travel and pay out of pocket. There are also a host of unanswered questions about whether states that restrict abortion will have the legal authority to target abortion coverage in employer plans.
The issues will likely be before the courts for years to come.
“States will pass laws, there will be some conflict, and then it goes to the courts,” said Erin Fuse Brown, director of the Center for Law, Health & Society at the Georgia State University, Atlanta. “It could be a while.”
In the meantime, here are answers to three common questions.
Are health plans – or employers – required to offer coverage for elective abortions?
The simple answer is “no.”
“There’s no law that requires any health plan, employer-based or anything else, to cover an elective abortion,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
Whether they do is more complicated.
Some job-based health plans cover elective abortions. Patients can search their plan documents or call their insurers directly to check.
Coverage is more likely in plans offered by self-insured employers because a federal pensions law generally preempts state regulation of those health plans. Self-funded employers, which tend to be the larger ones, pay the medical bills, although they generally hire third parties, sometimes health insurers, to handle claims and administrative work.
Still, millions of Americans work for smaller employers, which tend to buy plans directly from health insurers, which then pay the medical bills. Those plans, known as “fully insured,” are subject to state laws, whose approaches to abortion coverage have long varied.
Eleven states bar those private plans from covering abortion in most circumstances, according to KFF, although some of the states allow consumers to purchase an insurance rider that would cover abortion costs.
If you’re not sure what type of health plan you have, ask the administrators.
“There is no way to tell from the face of your insurance card if you are fully insured or self-funded,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
For the more than 14 million Americans who buy their coverage through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces, their state of residence is key.
Twenty-six states restrict abortion coverage in ACA plans, while seven states require it as a plan benefit, according to KFF. Those states are California, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, New York, Oregon, and Washington.
The rules for Medicaid, the federal-state health program for people with low incomes, also vary. Thirty-four states and the District of Columbia follow the so-called Hyde Amendment, which bars federal funds from paying for abortions, except in cases of rape or incest or to save the life of the mother, although some states allow coverage for other medically necessary abortions.
For all those reasons, it’s not surprising that research published in the journal Health Affairs noted that patients paid out-of-pocket for the majority of abortions (69% in one study). The researchers found that the median cost of a medication abortion was $560 and that abortion procedures ranged from a median of $575 in the first trimester to $895 in the second.
What about coverage for pregnancy-related complications that require treatment similar to abortion?
Insurance policies must cover care for essential health services, including medically necessary pregnancy care and abortion when carrying a pregnancy to term would endanger a patient’s life.
Under the Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 and other rules, Ms. Fuse Brown said, “pregnancy and prenatal care, including high-risk pregnancies, and obstetric care in general is required to be covered.”
In an ectopic pregnancy – when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus – the embryo is not viable, and the condition is generally life-threatening to the mother without medical treatment. Many other scenarios could come into play, including situations in which a woman has a miscarriage but not all the tissue is expelled, potentially leading to a dangerous infection.
Although all state laws that currently restrict abortion include an exception to save the life of the mother, what constitutes a life-threatening scenario is not always clear. That means physicians in abortion-ban states may have to weigh the pregnant person’s medical risk against possible legal ramifications.
“This is less of a coverage question and more of a question of whether providers in the states that ban abortion are going to provide the care,” said Katie Keith, a research faculty member at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University, Washington. “All of these laws are designed to chill behavior, to make it so unattractive or scary to providers to keep them from doing it at all.”
Can residents of states where abortion is illegal get coverage in other states or help with travel costs?
In recent weeks, many large employers – including Microsoft, Bank of America, Disney, and Netflix – have said they will set up programs to help pay travel costs so workers or other beneficiaries in states with bans can travel to get an abortion elsewhere.
But it isn’t as straightforward as it sounds. Employers will have to figure out whether workers will access this benefit through the health plan or some other reimbursement method. Protecting privacy, too, may be an issue. Some consultants also said employers will need to consider whether their travel reimbursement benefit conflicts with other rules. If an employer, for example, covers travel for abortion procedures but not for an eating disorder clinic, does that violate the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act? If a plan has no providers willing or able to do abortions, does it violate any state or federal network adequacy rules?
Lawmakers need to think about these conflicts, said Jessica Waltman, vice president for compliance at employee benefits company MZQ Consulting. “They could be putting all the employer group plans in their state in a very precarious position if that state law would prohibit them from complying with federal law,” particularly if they restrict access to benefits called for in the Pregnancy Discrimination Act.
There are other potential conflicts if an employer is in a state that allows abortion but a worker is in a state that restricts it. “If I’m an Oregon-based company, my insurance plan must provide for abortion coverage, but what do I do about an Oklahoma employee? I don’t know the answer,” said René Thorne, a principal at Jackson Lewis, where she oversees litigation that involves self-insured firms.
Also uncertain is whether state laws will take aim at insurers, employers, or others that offer benefits, including travel or televisits, for abortion services.
Laws that restrict abortion, Ms. Thorne wrote in a white paper for clients, generally apply to the medical provider and sometimes those who “aid or abet” the abortion. Some states, including Texas, allow private citizens to sue for $10,000 anyone who provides an illegal abortion or helps a person access an abortion.
Whether those laws will be applied to employers or insurers will undoubtedly end up in the courts.
“We are in uncharted territory here, as we’ve never before been in a situation where plans, as well as their employer sponsors and those administering the plans, might face criminal liability in connection with a plan benefit,” said Seth Perretta, a principal at the Groom Law Group, which advises employers.
Answers won’t come soon, but “there will be so much litigation around this,” said Ms. Thorne.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Will your health plan pay for an abortion now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade?
Even before the June 24 ruling, insurance coverage for abortion varied widely. Now the issue is even more complex as states set varying rules – about half are expected to limit or ban abortion in almost all circumstances.
To be clear, though, the question of whether an insurance plan covers abortion is not the same as whether abortion is allowed in a state. Coverage issues are more complicated and governed by a wide variety of factors, including the level of abortion access a state allows.
How dense a thicket is it? Abortion may be covered by a health plan, but if no providers are available, patients don’t have access. However, people with insurance that does not cover abortion can still get one – but only if it’s available in their states or they can afford to travel and pay out of pocket. There are also a host of unanswered questions about whether states that restrict abortion will have the legal authority to target abortion coverage in employer plans.
The issues will likely be before the courts for years to come.
“States will pass laws, there will be some conflict, and then it goes to the courts,” said Erin Fuse Brown, director of the Center for Law, Health & Society at the Georgia State University, Atlanta. “It could be a while.”
In the meantime, here are answers to three common questions.
Are health plans – or employers – required to offer coverage for elective abortions?
The simple answer is “no.”
“There’s no law that requires any health plan, employer-based or anything else, to cover an elective abortion,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
Whether they do is more complicated.
Some job-based health plans cover elective abortions. Patients can search their plan documents or call their insurers directly to check.
Coverage is more likely in plans offered by self-insured employers because a federal pensions law generally preempts state regulation of those health plans. Self-funded employers, which tend to be the larger ones, pay the medical bills, although they generally hire third parties, sometimes health insurers, to handle claims and administrative work.
Still, millions of Americans work for smaller employers, which tend to buy plans directly from health insurers, which then pay the medical bills. Those plans, known as “fully insured,” are subject to state laws, whose approaches to abortion coverage have long varied.
Eleven states bar those private plans from covering abortion in most circumstances, according to KFF, although some of the states allow consumers to purchase an insurance rider that would cover abortion costs.
If you’re not sure what type of health plan you have, ask the administrators.
“There is no way to tell from the face of your insurance card if you are fully insured or self-funded,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
For the more than 14 million Americans who buy their coverage through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces, their state of residence is key.
Twenty-six states restrict abortion coverage in ACA plans, while seven states require it as a plan benefit, according to KFF. Those states are California, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, New York, Oregon, and Washington.
The rules for Medicaid, the federal-state health program for people with low incomes, also vary. Thirty-four states and the District of Columbia follow the so-called Hyde Amendment, which bars federal funds from paying for abortions, except in cases of rape or incest or to save the life of the mother, although some states allow coverage for other medically necessary abortions.
For all those reasons, it’s not surprising that research published in the journal Health Affairs noted that patients paid out-of-pocket for the majority of abortions (69% in one study). The researchers found that the median cost of a medication abortion was $560 and that abortion procedures ranged from a median of $575 in the first trimester to $895 in the second.
What about coverage for pregnancy-related complications that require treatment similar to abortion?
Insurance policies must cover care for essential health services, including medically necessary pregnancy care and abortion when carrying a pregnancy to term would endanger a patient’s life.
Under the Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 and other rules, Ms. Fuse Brown said, “pregnancy and prenatal care, including high-risk pregnancies, and obstetric care in general is required to be covered.”
In an ectopic pregnancy – when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus – the embryo is not viable, and the condition is generally life-threatening to the mother without medical treatment. Many other scenarios could come into play, including situations in which a woman has a miscarriage but not all the tissue is expelled, potentially leading to a dangerous infection.
Although all state laws that currently restrict abortion include an exception to save the life of the mother, what constitutes a life-threatening scenario is not always clear. That means physicians in abortion-ban states may have to weigh the pregnant person’s medical risk against possible legal ramifications.
“This is less of a coverage question and more of a question of whether providers in the states that ban abortion are going to provide the care,” said Katie Keith, a research faculty member at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University, Washington. “All of these laws are designed to chill behavior, to make it so unattractive or scary to providers to keep them from doing it at all.”
Can residents of states where abortion is illegal get coverage in other states or help with travel costs?
In recent weeks, many large employers – including Microsoft, Bank of America, Disney, and Netflix – have said they will set up programs to help pay travel costs so workers or other beneficiaries in states with bans can travel to get an abortion elsewhere.
But it isn’t as straightforward as it sounds. Employers will have to figure out whether workers will access this benefit through the health plan or some other reimbursement method. Protecting privacy, too, may be an issue. Some consultants also said employers will need to consider whether their travel reimbursement benefit conflicts with other rules. If an employer, for example, covers travel for abortion procedures but not for an eating disorder clinic, does that violate the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act? If a plan has no providers willing or able to do abortions, does it violate any state or federal network adequacy rules?
Lawmakers need to think about these conflicts, said Jessica Waltman, vice president for compliance at employee benefits company MZQ Consulting. “They could be putting all the employer group plans in their state in a very precarious position if that state law would prohibit them from complying with federal law,” particularly if they restrict access to benefits called for in the Pregnancy Discrimination Act.
There are other potential conflicts if an employer is in a state that allows abortion but a worker is in a state that restricts it. “If I’m an Oregon-based company, my insurance plan must provide for abortion coverage, but what do I do about an Oklahoma employee? I don’t know the answer,” said René Thorne, a principal at Jackson Lewis, where she oversees litigation that involves self-insured firms.
Also uncertain is whether state laws will take aim at insurers, employers, or others that offer benefits, including travel or televisits, for abortion services.
Laws that restrict abortion, Ms. Thorne wrote in a white paper for clients, generally apply to the medical provider and sometimes those who “aid or abet” the abortion. Some states, including Texas, allow private citizens to sue for $10,000 anyone who provides an illegal abortion or helps a person access an abortion.
Whether those laws will be applied to employers or insurers will undoubtedly end up in the courts.
“We are in uncharted territory here, as we’ve never before been in a situation where plans, as well as their employer sponsors and those administering the plans, might face criminal liability in connection with a plan benefit,” said Seth Perretta, a principal at the Groom Law Group, which advises employers.
Answers won’t come soon, but “there will be so much litigation around this,” said Ms. Thorne.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Will your health plan pay for an abortion now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade?
Even before the June 24 ruling, insurance coverage for abortion varied widely. Now the issue is even more complex as states set varying rules – about half are expected to limit or ban abortion in almost all circumstances.
To be clear, though, the question of whether an insurance plan covers abortion is not the same as whether abortion is allowed in a state. Coverage issues are more complicated and governed by a wide variety of factors, including the level of abortion access a state allows.
How dense a thicket is it? Abortion may be covered by a health plan, but if no providers are available, patients don’t have access. However, people with insurance that does not cover abortion can still get one – but only if it’s available in their states or they can afford to travel and pay out of pocket. There are also a host of unanswered questions about whether states that restrict abortion will have the legal authority to target abortion coverage in employer plans.
The issues will likely be before the courts for years to come.
“States will pass laws, there will be some conflict, and then it goes to the courts,” said Erin Fuse Brown, director of the Center for Law, Health & Society at the Georgia State University, Atlanta. “It could be a while.”
In the meantime, here are answers to three common questions.
Are health plans – or employers – required to offer coverage for elective abortions?
The simple answer is “no.”
“There’s no law that requires any health plan, employer-based or anything else, to cover an elective abortion,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
Whether they do is more complicated.
Some job-based health plans cover elective abortions. Patients can search their plan documents or call their insurers directly to check.
Coverage is more likely in plans offered by self-insured employers because a federal pensions law generally preempts state regulation of those health plans. Self-funded employers, which tend to be the larger ones, pay the medical bills, although they generally hire third parties, sometimes health insurers, to handle claims and administrative work.
Still, millions of Americans work for smaller employers, which tend to buy plans directly from health insurers, which then pay the medical bills. Those plans, known as “fully insured,” are subject to state laws, whose approaches to abortion coverage have long varied.
Eleven states bar those private plans from covering abortion in most circumstances, according to KFF, although some of the states allow consumers to purchase an insurance rider that would cover abortion costs.
If you’re not sure what type of health plan you have, ask the administrators.
“There is no way to tell from the face of your insurance card if you are fully insured or self-funded,” Ms. Fuse Brown said.
For the more than 14 million Americans who buy their coverage through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces, their state of residence is key.
Twenty-six states restrict abortion coverage in ACA plans, while seven states require it as a plan benefit, according to KFF. Those states are California, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, New York, Oregon, and Washington.
The rules for Medicaid, the federal-state health program for people with low incomes, also vary. Thirty-four states and the District of Columbia follow the so-called Hyde Amendment, which bars federal funds from paying for abortions, except in cases of rape or incest or to save the life of the mother, although some states allow coverage for other medically necessary abortions.
For all those reasons, it’s not surprising that research published in the journal Health Affairs noted that patients paid out-of-pocket for the majority of abortions (69% in one study). The researchers found that the median cost of a medication abortion was $560 and that abortion procedures ranged from a median of $575 in the first trimester to $895 in the second.
What about coverage for pregnancy-related complications that require treatment similar to abortion?
Insurance policies must cover care for essential health services, including medically necessary pregnancy care and abortion when carrying a pregnancy to term would endanger a patient’s life.
Under the Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 and other rules, Ms. Fuse Brown said, “pregnancy and prenatal care, including high-risk pregnancies, and obstetric care in general is required to be covered.”
In an ectopic pregnancy – when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus – the embryo is not viable, and the condition is generally life-threatening to the mother without medical treatment. Many other scenarios could come into play, including situations in which a woman has a miscarriage but not all the tissue is expelled, potentially leading to a dangerous infection.
Although all state laws that currently restrict abortion include an exception to save the life of the mother, what constitutes a life-threatening scenario is not always clear. That means physicians in abortion-ban states may have to weigh the pregnant person’s medical risk against possible legal ramifications.
“This is less of a coverage question and more of a question of whether providers in the states that ban abortion are going to provide the care,” said Katie Keith, a research faculty member at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University, Washington. “All of these laws are designed to chill behavior, to make it so unattractive or scary to providers to keep them from doing it at all.”
Can residents of states where abortion is illegal get coverage in other states or help with travel costs?
In recent weeks, many large employers – including Microsoft, Bank of America, Disney, and Netflix – have said they will set up programs to help pay travel costs so workers or other beneficiaries in states with bans can travel to get an abortion elsewhere.
But it isn’t as straightforward as it sounds. Employers will have to figure out whether workers will access this benefit through the health plan or some other reimbursement method. Protecting privacy, too, may be an issue. Some consultants also said employers will need to consider whether their travel reimbursement benefit conflicts with other rules. If an employer, for example, covers travel for abortion procedures but not for an eating disorder clinic, does that violate the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act? If a plan has no providers willing or able to do abortions, does it violate any state or federal network adequacy rules?
Lawmakers need to think about these conflicts, said Jessica Waltman, vice president for compliance at employee benefits company MZQ Consulting. “They could be putting all the employer group plans in their state in a very precarious position if that state law would prohibit them from complying with federal law,” particularly if they restrict access to benefits called for in the Pregnancy Discrimination Act.
There are other potential conflicts if an employer is in a state that allows abortion but a worker is in a state that restricts it. “If I’m an Oregon-based company, my insurance plan must provide for abortion coverage, but what do I do about an Oklahoma employee? I don’t know the answer,” said René Thorne, a principal at Jackson Lewis, where she oversees litigation that involves self-insured firms.
Also uncertain is whether state laws will take aim at insurers, employers, or others that offer benefits, including travel or televisits, for abortion services.
Laws that restrict abortion, Ms. Thorne wrote in a white paper for clients, generally apply to the medical provider and sometimes those who “aid or abet” the abortion. Some states, including Texas, allow private citizens to sue for $10,000 anyone who provides an illegal abortion or helps a person access an abortion.
Whether those laws will be applied to employers or insurers will undoubtedly end up in the courts.
“We are in uncharted territory here, as we’ve never before been in a situation where plans, as well as their employer sponsors and those administering the plans, might face criminal liability in connection with a plan benefit,” said Seth Perretta, a principal at the Groom Law Group, which advises employers.
Answers won’t come soon, but “there will be so much litigation around this,” said Ms. Thorne.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
How much health insurers pay for almost everything is about to go public
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Diabetes drug’s new weight-loss indication fuels cost-benefit debate
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Post-COVID clinics get jump-start from patients with lingering illness
Clarence Troutman survived a 2-month hospital stay with COVID-19, then went home in early June. But he’s far from over the disease, still suffering from limited endurance, shortness of breath and hands that can be stiff and swollen.
“Before COVID, I was a 59-year-old, relatively healthy man,” said the broadband technician from Denver. “If I had to say where I’m at now, I’d say about 50% of where I was, but when I first went home, I was at 20%.”
He credits much of his progress to the “motivation and education” gleaned from a new program for post-COVID patients at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, one of a small but growing number of clinics aimed at treating and studying those who have had the unpredictable coronavirus.
As the election nears, much attention is focused on daily infection numbers or the climbing death toll, but another measure matters: Patients who survive but continue to wrestle with a range of physical or mental effects, including lung damage, heart or neurologic concerns, anxiety, and depression.
“We need to think about how we’re going to provide care for patients who may be recovering for years after the virus,” said Sarah Jolley, MD, a pulmonologist with UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and director of UCHealth’s Post-Covid Clinic, where Mr. Troutman is seen.
That need has jump-started post-COVID clinics, which bring together a range of specialists into a one-stop shop.
One of the first and largest such clinics is at Mount Sinai in New York City, but programs have also launched at the University of California,San Francisco; Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center; and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The Cleveland Clinic plans to open one early next year. And it’s not just academic medical centers: St. John’s Well Child and Family Center, part of a network of community clinics in south central Los Angeles, said this month it aims to test thousands of its patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 since March for long-term effects.
Mental health specialists are also involved, along with social workers and pharmacists. Many of the centers also do research studies, aiming to better understand why the virus hits certain patients so hard.
“Some of our patients, even those on a ventilator on death’s door, will come out remarkably unscathed,” said Lekshmi Santhosh, MD, an assistant professor of pulmonary critical care and a leader of the post-COVID program at UCSF, called the OPTIMAL clinic. “Others, even those who were never hospitalized, have disabling fatigue, ongoing chest pain, and shortness of breath, and there’s a whole spectrum in between.”
‘Staggering’ medical need
It’s too early to know how long the persistent medical effects and symptoms will linger, or to make accurate estimates on the percentage of patients affected.
Some early studies are sobering. An Austrian report released this month found that 76 of the first 86 patients studied had evidence of lung damage 6 weeks after hospital discharge, but that dropped to 48 patients at 12 weeks.
Some researchers and clinics say about 10% of U.S. COVID patients they see may have longer-running effects, said Zijian Chen, MD, medical director of the Center for Post-COVID Care at Mount Sinai, which has enrolled 400 patients so far.
If that estimate is correct – and Dr. Chen emphasized that more research is needed to make sure – it translates to patients entering the medical system in droves, often with multiple issues.
How health systems and insurers respond will be key, he said. More than 6.5 million U.S. residents have tested positive for the disease. If fewer than 10% – say 500,000 – already have long-lasting symptoms, “that number is staggering,” Dr. Chen said. “How much medical care will be needed for that?”
Though start-up costs could be a hurdle, the clinics themselves may eventually draw much-needed revenue to medical centers by attracting patients, many of whom have insurance to cover some or all of the cost of repeated visits.
Dr. Chen said the specialized centers can help lower health spending by providing more cost effective, coordinated care that avoids duplicative testing a patient might otherwise undergo.
“We’ve seen patients that when they come in, they’ve already had four MRI or CT scans and a stack of bloodwork,” he said.
The program consolidates those earlier results and determines if any additional testing is needed. Sometimes the answer to what’s causing patients’ long-lasting symptoms remains elusive. One problem for patients seeking help outside of dedicated clinics is that when there is no clear cause for their condition, they may be told the symptoms are imagined.
“I believe in the patients,” said Dr. Chen.
About half the clinic’s patients have received test results showing damage, said Dr. Chen, an endocrinologist and internal medicine physician. For those patients, the clinic can develop a treatment plan. But, frustratingly, the other half have inconclusive test results yet exhibit a range of symptoms.
“That makes it more difficult to treat,” said Dr. Chen.
Experts see parallels to a push in the past decade to establish special clinics to treat patients released from ICU wards, who may have problems related to long-term bed rest or the delirium many experience while hospitalized. Some of the current post-COVID clinics are modeled after the post-ICU clinics or are expanded versions of them.
The ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., for instance, which opened in 2012, is accepting post-COVID patients.
There are about a dozen post-ICU clinics nationally, some of which are also now working with COVID patients, said James Jackson, director of long-term outcomes at the Vanderbilt center. In addition, he’s heard of at least another dozen post-COVID centers in development.
The centers generally do an initial assessment a few weeks after a patient is diagnosed or discharged from the hospital, often by video call. Check-in and repeat visits are scheduled every month or so after that.
“In an ideal world, with these post-COVID clinics, you can identify the patients and get them into rehab,” he said. “Even if the primary thing these clinics did was to say to patients: ‘This is real, it is not all in your head,’ that impact would be important.”
A question of feasibility
Financing is the largest obstacle, program proponents said. Many hospitals lost substantial revenue to canceled elective procedures during stay-at-home periods.
“So, it’s not a great time to be pitching a new activity that requires a start-up subsidy,” said Glenn Melnick, PhD, a professor of health economics at the University of Southern California.
At UCSF, a select group of faculty members staff the post-COVID clinics and some mental health professionals volunteer their time, said Dr. Santhosh.
Dr. Chen said he was able to recruit team members and support staff from the ranks of those whose elective patient caseload had dropped.
Dr. Jackson said unfortunately there’s not been enough research into the cost-and-clinical effectiveness of post-ICU centers.
“In the early days, there may have been questions about how much value does this add,” he noted. “Now, the question is not so much is it a good idea, but is it feasible?”
Right now, the post-COVID centers are foremost a research effort, said Len Nichols, an economist and nonresident fellow at the Urban Institute. “If these guys get good at treating long-term symptoms, that’s good for all of us. There’s not enough patients to make it a business model yet, but if they become the place to go when you get it, it could become a business model for some of the elite institutions.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Clarence Troutman survived a 2-month hospital stay with COVID-19, then went home in early June. But he’s far from over the disease, still suffering from limited endurance, shortness of breath and hands that can be stiff and swollen.
“Before COVID, I was a 59-year-old, relatively healthy man,” said the broadband technician from Denver. “If I had to say where I’m at now, I’d say about 50% of where I was, but when I first went home, I was at 20%.”
He credits much of his progress to the “motivation and education” gleaned from a new program for post-COVID patients at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, one of a small but growing number of clinics aimed at treating and studying those who have had the unpredictable coronavirus.
As the election nears, much attention is focused on daily infection numbers or the climbing death toll, but another measure matters: Patients who survive but continue to wrestle with a range of physical or mental effects, including lung damage, heart or neurologic concerns, anxiety, and depression.
“We need to think about how we’re going to provide care for patients who may be recovering for years after the virus,” said Sarah Jolley, MD, a pulmonologist with UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and director of UCHealth’s Post-Covid Clinic, where Mr. Troutman is seen.
That need has jump-started post-COVID clinics, which bring together a range of specialists into a one-stop shop.
One of the first and largest such clinics is at Mount Sinai in New York City, but programs have also launched at the University of California,San Francisco; Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center; and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The Cleveland Clinic plans to open one early next year. And it’s not just academic medical centers: St. John’s Well Child and Family Center, part of a network of community clinics in south central Los Angeles, said this month it aims to test thousands of its patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 since March for long-term effects.
Mental health specialists are also involved, along with social workers and pharmacists. Many of the centers also do research studies, aiming to better understand why the virus hits certain patients so hard.
“Some of our patients, even those on a ventilator on death’s door, will come out remarkably unscathed,” said Lekshmi Santhosh, MD, an assistant professor of pulmonary critical care and a leader of the post-COVID program at UCSF, called the OPTIMAL clinic. “Others, even those who were never hospitalized, have disabling fatigue, ongoing chest pain, and shortness of breath, and there’s a whole spectrum in between.”
‘Staggering’ medical need
It’s too early to know how long the persistent medical effects and symptoms will linger, or to make accurate estimates on the percentage of patients affected.
Some early studies are sobering. An Austrian report released this month found that 76 of the first 86 patients studied had evidence of lung damage 6 weeks after hospital discharge, but that dropped to 48 patients at 12 weeks.
Some researchers and clinics say about 10% of U.S. COVID patients they see may have longer-running effects, said Zijian Chen, MD, medical director of the Center for Post-COVID Care at Mount Sinai, which has enrolled 400 patients so far.
If that estimate is correct – and Dr. Chen emphasized that more research is needed to make sure – it translates to patients entering the medical system in droves, often with multiple issues.
How health systems and insurers respond will be key, he said. More than 6.5 million U.S. residents have tested positive for the disease. If fewer than 10% – say 500,000 – already have long-lasting symptoms, “that number is staggering,” Dr. Chen said. “How much medical care will be needed for that?”
Though start-up costs could be a hurdle, the clinics themselves may eventually draw much-needed revenue to medical centers by attracting patients, many of whom have insurance to cover some or all of the cost of repeated visits.
Dr. Chen said the specialized centers can help lower health spending by providing more cost effective, coordinated care that avoids duplicative testing a patient might otherwise undergo.
“We’ve seen patients that when they come in, they’ve already had four MRI or CT scans and a stack of bloodwork,” he said.
The program consolidates those earlier results and determines if any additional testing is needed. Sometimes the answer to what’s causing patients’ long-lasting symptoms remains elusive. One problem for patients seeking help outside of dedicated clinics is that when there is no clear cause for their condition, they may be told the symptoms are imagined.
“I believe in the patients,” said Dr. Chen.
About half the clinic’s patients have received test results showing damage, said Dr. Chen, an endocrinologist and internal medicine physician. For those patients, the clinic can develop a treatment plan. But, frustratingly, the other half have inconclusive test results yet exhibit a range of symptoms.
“That makes it more difficult to treat,” said Dr. Chen.
Experts see parallels to a push in the past decade to establish special clinics to treat patients released from ICU wards, who may have problems related to long-term bed rest or the delirium many experience while hospitalized. Some of the current post-COVID clinics are modeled after the post-ICU clinics or are expanded versions of them.
The ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., for instance, which opened in 2012, is accepting post-COVID patients.
There are about a dozen post-ICU clinics nationally, some of which are also now working with COVID patients, said James Jackson, director of long-term outcomes at the Vanderbilt center. In addition, he’s heard of at least another dozen post-COVID centers in development.
The centers generally do an initial assessment a few weeks after a patient is diagnosed or discharged from the hospital, often by video call. Check-in and repeat visits are scheduled every month or so after that.
“In an ideal world, with these post-COVID clinics, you can identify the patients and get them into rehab,” he said. “Even if the primary thing these clinics did was to say to patients: ‘This is real, it is not all in your head,’ that impact would be important.”
A question of feasibility
Financing is the largest obstacle, program proponents said. Many hospitals lost substantial revenue to canceled elective procedures during stay-at-home periods.
“So, it’s not a great time to be pitching a new activity that requires a start-up subsidy,” said Glenn Melnick, PhD, a professor of health economics at the University of Southern California.
At UCSF, a select group of faculty members staff the post-COVID clinics and some mental health professionals volunteer their time, said Dr. Santhosh.
Dr. Chen said he was able to recruit team members and support staff from the ranks of those whose elective patient caseload had dropped.
Dr. Jackson said unfortunately there’s not been enough research into the cost-and-clinical effectiveness of post-ICU centers.
“In the early days, there may have been questions about how much value does this add,” he noted. “Now, the question is not so much is it a good idea, but is it feasible?”
Right now, the post-COVID centers are foremost a research effort, said Len Nichols, an economist and nonresident fellow at the Urban Institute. “If these guys get good at treating long-term symptoms, that’s good for all of us. There’s not enough patients to make it a business model yet, but if they become the place to go when you get it, it could become a business model for some of the elite institutions.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Clarence Troutman survived a 2-month hospital stay with COVID-19, then went home in early June. But he’s far from over the disease, still suffering from limited endurance, shortness of breath and hands that can be stiff and swollen.
“Before COVID, I was a 59-year-old, relatively healthy man,” said the broadband technician from Denver. “If I had to say where I’m at now, I’d say about 50% of where I was, but when I first went home, I was at 20%.”
He credits much of his progress to the “motivation and education” gleaned from a new program for post-COVID patients at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, one of a small but growing number of clinics aimed at treating and studying those who have had the unpredictable coronavirus.
As the election nears, much attention is focused on daily infection numbers or the climbing death toll, but another measure matters: Patients who survive but continue to wrestle with a range of physical or mental effects, including lung damage, heart or neurologic concerns, anxiety, and depression.
“We need to think about how we’re going to provide care for patients who may be recovering for years after the virus,” said Sarah Jolley, MD, a pulmonologist with UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and director of UCHealth’s Post-Covid Clinic, where Mr. Troutman is seen.
That need has jump-started post-COVID clinics, which bring together a range of specialists into a one-stop shop.
One of the first and largest such clinics is at Mount Sinai in New York City, but programs have also launched at the University of California,San Francisco; Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center; and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The Cleveland Clinic plans to open one early next year. And it’s not just academic medical centers: St. John’s Well Child and Family Center, part of a network of community clinics in south central Los Angeles, said this month it aims to test thousands of its patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 since March for long-term effects.
Mental health specialists are also involved, along with social workers and pharmacists. Many of the centers also do research studies, aiming to better understand why the virus hits certain patients so hard.
“Some of our patients, even those on a ventilator on death’s door, will come out remarkably unscathed,” said Lekshmi Santhosh, MD, an assistant professor of pulmonary critical care and a leader of the post-COVID program at UCSF, called the OPTIMAL clinic. “Others, even those who were never hospitalized, have disabling fatigue, ongoing chest pain, and shortness of breath, and there’s a whole spectrum in between.”
‘Staggering’ medical need
It’s too early to know how long the persistent medical effects and symptoms will linger, or to make accurate estimates on the percentage of patients affected.
Some early studies are sobering. An Austrian report released this month found that 76 of the first 86 patients studied had evidence of lung damage 6 weeks after hospital discharge, but that dropped to 48 patients at 12 weeks.
Some researchers and clinics say about 10% of U.S. COVID patients they see may have longer-running effects, said Zijian Chen, MD, medical director of the Center for Post-COVID Care at Mount Sinai, which has enrolled 400 patients so far.
If that estimate is correct – and Dr. Chen emphasized that more research is needed to make sure – it translates to patients entering the medical system in droves, often with multiple issues.
How health systems and insurers respond will be key, he said. More than 6.5 million U.S. residents have tested positive for the disease. If fewer than 10% – say 500,000 – already have long-lasting symptoms, “that number is staggering,” Dr. Chen said. “How much medical care will be needed for that?”
Though start-up costs could be a hurdle, the clinics themselves may eventually draw much-needed revenue to medical centers by attracting patients, many of whom have insurance to cover some or all of the cost of repeated visits.
Dr. Chen said the specialized centers can help lower health spending by providing more cost effective, coordinated care that avoids duplicative testing a patient might otherwise undergo.
“We’ve seen patients that when they come in, they’ve already had four MRI or CT scans and a stack of bloodwork,” he said.
The program consolidates those earlier results and determines if any additional testing is needed. Sometimes the answer to what’s causing patients’ long-lasting symptoms remains elusive. One problem for patients seeking help outside of dedicated clinics is that when there is no clear cause for their condition, they may be told the symptoms are imagined.
“I believe in the patients,” said Dr. Chen.
About half the clinic’s patients have received test results showing damage, said Dr. Chen, an endocrinologist and internal medicine physician. For those patients, the clinic can develop a treatment plan. But, frustratingly, the other half have inconclusive test results yet exhibit a range of symptoms.
“That makes it more difficult to treat,” said Dr. Chen.
Experts see parallels to a push in the past decade to establish special clinics to treat patients released from ICU wards, who may have problems related to long-term bed rest or the delirium many experience while hospitalized. Some of the current post-COVID clinics are modeled after the post-ICU clinics or are expanded versions of them.
The ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., for instance, which opened in 2012, is accepting post-COVID patients.
There are about a dozen post-ICU clinics nationally, some of which are also now working with COVID patients, said James Jackson, director of long-term outcomes at the Vanderbilt center. In addition, he’s heard of at least another dozen post-COVID centers in development.
The centers generally do an initial assessment a few weeks after a patient is diagnosed or discharged from the hospital, often by video call. Check-in and repeat visits are scheduled every month or so after that.
“In an ideal world, with these post-COVID clinics, you can identify the patients and get them into rehab,” he said. “Even if the primary thing these clinics did was to say to patients: ‘This is real, it is not all in your head,’ that impact would be important.”
A question of feasibility
Financing is the largest obstacle, program proponents said. Many hospitals lost substantial revenue to canceled elective procedures during stay-at-home periods.
“So, it’s not a great time to be pitching a new activity that requires a start-up subsidy,” said Glenn Melnick, PhD, a professor of health economics at the University of Southern California.
At UCSF, a select group of faculty members staff the post-COVID clinics and some mental health professionals volunteer their time, said Dr. Santhosh.
Dr. Chen said he was able to recruit team members and support staff from the ranks of those whose elective patient caseload had dropped.
Dr. Jackson said unfortunately there’s not been enough research into the cost-and-clinical effectiveness of post-ICU centers.
“In the early days, there may have been questions about how much value does this add,” he noted. “Now, the question is not so much is it a good idea, but is it feasible?”
Right now, the post-COVID centers are foremost a research effort, said Len Nichols, an economist and nonresident fellow at the Urban Institute. “If these guys get good at treating long-term symptoms, that’s good for all of us. There’s not enough patients to make it a business model yet, but if they become the place to go when you get it, it could become a business model for some of the elite institutions.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Trump administration seeks more health care cost details for consumers
Anyone who has tried to “shop” for hospital services knows one thing: It’s hard to get prices.
President Donald Trump on Monday signed an executive order he said would make it easier.
The order directs agencies to draw up rules requiring hospitals and insurers to make public more information on the negotiated prices they hammer out in contract negotiations. Also, hospitals and insurers would have to give estimates to patients on out-of-pocket costs before they go in for nonemergency medical care.
The move, which officials said will help address skyrocketing health care costs, comes amid other efforts by the administration to elicit more price transparency for medical care and initiatives by Congress to limit so-called surprise bills. These are the often-expensive bills consumers get when they unwittingly receive care that is not covered by their insurers.
“This will put American patients in control and address fundamental drivers of health care costs in a way no president has done before,” said Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar during a press briefing on Monday.
The proposal is likely to run into opposition from some hospitals and insurers who say disclosing negotiated rates could instead drive up costs.
Just how useful the effort will prove for consumers is unclear.
Much depends on how the administration writes the rules governing what information must be provided, such as whether it will include hospital-specific prices, regional averages, or other measures. While the administration calls for a “consumer-friendly” format, it’s not clear how such a massive amount of data – potentially negotiated price information from thousands of hospitals and insurers for tens of thousands of services – will be presented to consumers.
“It’s well intended, but may grossly overestimate the ability of the average patient to decipher this information overload,” said Dan Ward, a vice president at Waystar, a health care payments service.
So, does this new development advance efforts to better arm consumers with pricing information? Some key point to consider:
Q: What does the order do?
It may expand on price information consumers receive.
The order directs agencies to develop rules to require hospitals and insurers to provide information “based on negotiated rates” to the public.
Currently, such rates are hard to get, even for patients, until after medical care is provided. That’s when insured patients get an “explanation of benefits [EOBs],” which shows how much the hospital charged, how much of a discount their insurer received, and the amount a patient may owe.
In addition to consumers being unable to get price information upfront in many cases, hospital list prices and negotiated discount rates vary widely by hospital and insurer, even in a region. Uninsured patients often are charged the full amounts.
“People are sick and tired of hospitals playing these games with prices,” said George Nation, a business professor at Lehigh University in Bethlehem, Pa. who studies hospital contract law. “That’s what’s driving all of this.”
Some insurers and hospitals do provide online tools or apps that can help individual patients estimate out-of-pocket costs for a service or procedure ahead of time, but research shows few patients use such tools. Also, many medical services are needed without much notice – think of a heart attack or a broken leg – so shopping simply isn’t possible.
Administration officials say they want patients to have access to more information, including “advance EOBs” outlining anticipated costs before patients get nonemergency medical care. In theory, that would allow consumers to shop around for lower-cost care.
Q: Isn’t this information already available?
Not exactly. In January, new rules took effect under the Affordable Care Act that require hospitals to post online their “list prices,” which hospitals set themselves and have little relation to actual costs or what insurers actually pay.
What resulted are often confusing spreadsheets that contain thousands of a la carte charges – ranging from the price of medicines and sutures to room costs, among other things – that patients have to piece together if they can to estimate their total bill. Also, those list charges don’t reflect the discounted rates insurers have negotiated, so they are of little use to insured patients who might want to compare prices hospital to hospital.
The information that would result from President Trump’s executive order would provide more detail based on negotiated, discounted rates.
A senior administration official at the press briefing said details about whether the rates would be aggregated or relate to individual hospitals would be spelled out only when the administration puts forward proposed rules to implement the order later this year. It also is unclear how the administration would enforce the rules.
Another limitation: The order applies only to hospitals and the medical staff they employ. Many hospitals, however, are staffed by doctors who are not directly employed, or laboratories that are also separate. That means negotiated prices for services provided by such laboratories or physicians would not have to be disclosed.
Q: How could consumers use this information?
In theory, consumers could get information allowing them to compare prices for, say, a hip replacement or knee surgery in advance.
But that could prove difficult if the rates were not fairly hospital specific, or if they were not lumped in with all the care needed for a specific procedure or surgery.
“They could take the top 20 common procedures the hospital does, for example, and put negotiated prices on them,” said Mr. Nation. “It makes sense to do an average for that particular hospital, so I can see how much it’s going to cost to have my knee replaced at St. Joe’s versus St. Anne’s.”
Having advance notice of out-of-pocket costs could also help patients who have high-deductible plans.
“Patients are increasingly subject to insurance deductibles and other forms of substantial cost sharing. For a subset of so-called shoppable services, patients would benefit from price estimates in advance that allow them to compare options and plan financially for their care,” said John Rother, president and CEO at the advocacy group National Coalition on Health Care.
Q: Will this push consumers to shop for health care?
The short answer is maybe. Right now, it’s difficult, even with some of the tools available, said Lovisa Gustafsson, assistant vice president at the Commonwealth Fund, which has looked at whether patients use existing tools or the list price information hospitals must post online.
“The evidence to date shows patients aren’t necessarily the best shoppers, but we haven’t given them the best tools to be shoppers,” she said.
Posting negotiated rates might be a step forward, she said, but only if it is easily understandable.
It’s possible that insurers, physician offices, consumer groups, or online businesses may find ways to help direct patients to the most cost-effective locations for surgeries, tests or other procedures based on the information.
“Institutions like Consumer Reports or Consumer Checkbook could do some kind of high-level comparison between facilities or doctors, giving some general information that might be useful for consumers,” said Tim Jost, a professor emeritus at the Washington and Lee University School of Law in Lexington, Va.
But some hospitals and insurers maintain that disclosing specific rates could backfire.
Hospitals charging lower rates, for example, might raise them if they see competitors are getting higher reimbursement from insurers, they say. Insurers say they might be hampered in their ability to negotiate if rivals all know what they each pay.
“We also agree that patients should have accurate, real-time information about costs so they can make the best, most informed decisions about their care,” said a statement from lobbying group America’s Health Insurance Plans. “But publicly disclosing competitively negotiated, proprietary rates will reduce competition and push prices higher – not lower – for consumers, patients, and taxpayers.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Anyone who has tried to “shop” for hospital services knows one thing: It’s hard to get prices.
President Donald Trump on Monday signed an executive order he said would make it easier.
The order directs agencies to draw up rules requiring hospitals and insurers to make public more information on the negotiated prices they hammer out in contract negotiations. Also, hospitals and insurers would have to give estimates to patients on out-of-pocket costs before they go in for nonemergency medical care.
The move, which officials said will help address skyrocketing health care costs, comes amid other efforts by the administration to elicit more price transparency for medical care and initiatives by Congress to limit so-called surprise bills. These are the often-expensive bills consumers get when they unwittingly receive care that is not covered by their insurers.
“This will put American patients in control and address fundamental drivers of health care costs in a way no president has done before,” said Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar during a press briefing on Monday.
The proposal is likely to run into opposition from some hospitals and insurers who say disclosing negotiated rates could instead drive up costs.
Just how useful the effort will prove for consumers is unclear.
Much depends on how the administration writes the rules governing what information must be provided, such as whether it will include hospital-specific prices, regional averages, or other measures. While the administration calls for a “consumer-friendly” format, it’s not clear how such a massive amount of data – potentially negotiated price information from thousands of hospitals and insurers for tens of thousands of services – will be presented to consumers.
“It’s well intended, but may grossly overestimate the ability of the average patient to decipher this information overload,” said Dan Ward, a vice president at Waystar, a health care payments service.
So, does this new development advance efforts to better arm consumers with pricing information? Some key point to consider:
Q: What does the order do?
It may expand on price information consumers receive.
The order directs agencies to develop rules to require hospitals and insurers to provide information “based on negotiated rates” to the public.
Currently, such rates are hard to get, even for patients, until after medical care is provided. That’s when insured patients get an “explanation of benefits [EOBs],” which shows how much the hospital charged, how much of a discount their insurer received, and the amount a patient may owe.
In addition to consumers being unable to get price information upfront in many cases, hospital list prices and negotiated discount rates vary widely by hospital and insurer, even in a region. Uninsured patients often are charged the full amounts.
“People are sick and tired of hospitals playing these games with prices,” said George Nation, a business professor at Lehigh University in Bethlehem, Pa. who studies hospital contract law. “That’s what’s driving all of this.”
Some insurers and hospitals do provide online tools or apps that can help individual patients estimate out-of-pocket costs for a service or procedure ahead of time, but research shows few patients use such tools. Also, many medical services are needed without much notice – think of a heart attack or a broken leg – so shopping simply isn’t possible.
Administration officials say they want patients to have access to more information, including “advance EOBs” outlining anticipated costs before patients get nonemergency medical care. In theory, that would allow consumers to shop around for lower-cost care.
Q: Isn’t this information already available?
Not exactly. In January, new rules took effect under the Affordable Care Act that require hospitals to post online their “list prices,” which hospitals set themselves and have little relation to actual costs or what insurers actually pay.
What resulted are often confusing spreadsheets that contain thousands of a la carte charges – ranging from the price of medicines and sutures to room costs, among other things – that patients have to piece together if they can to estimate their total bill. Also, those list charges don’t reflect the discounted rates insurers have negotiated, so they are of little use to insured patients who might want to compare prices hospital to hospital.
The information that would result from President Trump’s executive order would provide more detail based on negotiated, discounted rates.
A senior administration official at the press briefing said details about whether the rates would be aggregated or relate to individual hospitals would be spelled out only when the administration puts forward proposed rules to implement the order later this year. It also is unclear how the administration would enforce the rules.
Another limitation: The order applies only to hospitals and the medical staff they employ. Many hospitals, however, are staffed by doctors who are not directly employed, or laboratories that are also separate. That means negotiated prices for services provided by such laboratories or physicians would not have to be disclosed.
Q: How could consumers use this information?
In theory, consumers could get information allowing them to compare prices for, say, a hip replacement or knee surgery in advance.
But that could prove difficult if the rates were not fairly hospital specific, or if they were not lumped in with all the care needed for a specific procedure or surgery.
“They could take the top 20 common procedures the hospital does, for example, and put negotiated prices on them,” said Mr. Nation. “It makes sense to do an average for that particular hospital, so I can see how much it’s going to cost to have my knee replaced at St. Joe’s versus St. Anne’s.”
Having advance notice of out-of-pocket costs could also help patients who have high-deductible plans.
“Patients are increasingly subject to insurance deductibles and other forms of substantial cost sharing. For a subset of so-called shoppable services, patients would benefit from price estimates in advance that allow them to compare options and plan financially for their care,” said John Rother, president and CEO at the advocacy group National Coalition on Health Care.
Q: Will this push consumers to shop for health care?
The short answer is maybe. Right now, it’s difficult, even with some of the tools available, said Lovisa Gustafsson, assistant vice president at the Commonwealth Fund, which has looked at whether patients use existing tools or the list price information hospitals must post online.
“The evidence to date shows patients aren’t necessarily the best shoppers, but we haven’t given them the best tools to be shoppers,” she said.
Posting negotiated rates might be a step forward, she said, but only if it is easily understandable.
It’s possible that insurers, physician offices, consumer groups, or online businesses may find ways to help direct patients to the most cost-effective locations for surgeries, tests or other procedures based on the information.
“Institutions like Consumer Reports or Consumer Checkbook could do some kind of high-level comparison between facilities or doctors, giving some general information that might be useful for consumers,” said Tim Jost, a professor emeritus at the Washington and Lee University School of Law in Lexington, Va.
But some hospitals and insurers maintain that disclosing specific rates could backfire.
Hospitals charging lower rates, for example, might raise them if they see competitors are getting higher reimbursement from insurers, they say. Insurers say they might be hampered in their ability to negotiate if rivals all know what they each pay.
“We also agree that patients should have accurate, real-time information about costs so they can make the best, most informed decisions about their care,” said a statement from lobbying group America’s Health Insurance Plans. “But publicly disclosing competitively negotiated, proprietary rates will reduce competition and push prices higher – not lower – for consumers, patients, and taxpayers.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Anyone who has tried to “shop” for hospital services knows one thing: It’s hard to get prices.
President Donald Trump on Monday signed an executive order he said would make it easier.
The order directs agencies to draw up rules requiring hospitals and insurers to make public more information on the negotiated prices they hammer out in contract negotiations. Also, hospitals and insurers would have to give estimates to patients on out-of-pocket costs before they go in for nonemergency medical care.
The move, which officials said will help address skyrocketing health care costs, comes amid other efforts by the administration to elicit more price transparency for medical care and initiatives by Congress to limit so-called surprise bills. These are the often-expensive bills consumers get when they unwittingly receive care that is not covered by their insurers.
“This will put American patients in control and address fundamental drivers of health care costs in a way no president has done before,” said Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar during a press briefing on Monday.
The proposal is likely to run into opposition from some hospitals and insurers who say disclosing negotiated rates could instead drive up costs.
Just how useful the effort will prove for consumers is unclear.
Much depends on how the administration writes the rules governing what information must be provided, such as whether it will include hospital-specific prices, regional averages, or other measures. While the administration calls for a “consumer-friendly” format, it’s not clear how such a massive amount of data – potentially negotiated price information from thousands of hospitals and insurers for tens of thousands of services – will be presented to consumers.
“It’s well intended, but may grossly overestimate the ability of the average patient to decipher this information overload,” said Dan Ward, a vice president at Waystar, a health care payments service.
So, does this new development advance efforts to better arm consumers with pricing information? Some key point to consider:
Q: What does the order do?
It may expand on price information consumers receive.
The order directs agencies to develop rules to require hospitals and insurers to provide information “based on negotiated rates” to the public.
Currently, such rates are hard to get, even for patients, until after medical care is provided. That’s when insured patients get an “explanation of benefits [EOBs],” which shows how much the hospital charged, how much of a discount their insurer received, and the amount a patient may owe.
In addition to consumers being unable to get price information upfront in many cases, hospital list prices and negotiated discount rates vary widely by hospital and insurer, even in a region. Uninsured patients often are charged the full amounts.
“People are sick and tired of hospitals playing these games with prices,” said George Nation, a business professor at Lehigh University in Bethlehem, Pa. who studies hospital contract law. “That’s what’s driving all of this.”
Some insurers and hospitals do provide online tools or apps that can help individual patients estimate out-of-pocket costs for a service or procedure ahead of time, but research shows few patients use such tools. Also, many medical services are needed without much notice – think of a heart attack or a broken leg – so shopping simply isn’t possible.
Administration officials say they want patients to have access to more information, including “advance EOBs” outlining anticipated costs before patients get nonemergency medical care. In theory, that would allow consumers to shop around for lower-cost care.
Q: Isn’t this information already available?
Not exactly. In January, new rules took effect under the Affordable Care Act that require hospitals to post online their “list prices,” which hospitals set themselves and have little relation to actual costs or what insurers actually pay.
What resulted are often confusing spreadsheets that contain thousands of a la carte charges – ranging from the price of medicines and sutures to room costs, among other things – that patients have to piece together if they can to estimate their total bill. Also, those list charges don’t reflect the discounted rates insurers have negotiated, so they are of little use to insured patients who might want to compare prices hospital to hospital.
The information that would result from President Trump’s executive order would provide more detail based on negotiated, discounted rates.
A senior administration official at the press briefing said details about whether the rates would be aggregated or relate to individual hospitals would be spelled out only when the administration puts forward proposed rules to implement the order later this year. It also is unclear how the administration would enforce the rules.
Another limitation: The order applies only to hospitals and the medical staff they employ. Many hospitals, however, are staffed by doctors who are not directly employed, or laboratories that are also separate. That means negotiated prices for services provided by such laboratories or physicians would not have to be disclosed.
Q: How could consumers use this information?
In theory, consumers could get information allowing them to compare prices for, say, a hip replacement or knee surgery in advance.
But that could prove difficult if the rates were not fairly hospital specific, or if they were not lumped in with all the care needed for a specific procedure or surgery.
“They could take the top 20 common procedures the hospital does, for example, and put negotiated prices on them,” said Mr. Nation. “It makes sense to do an average for that particular hospital, so I can see how much it’s going to cost to have my knee replaced at St. Joe’s versus St. Anne’s.”
Having advance notice of out-of-pocket costs could also help patients who have high-deductible plans.
“Patients are increasingly subject to insurance deductibles and other forms of substantial cost sharing. For a subset of so-called shoppable services, patients would benefit from price estimates in advance that allow them to compare options and plan financially for their care,” said John Rother, president and CEO at the advocacy group National Coalition on Health Care.
Q: Will this push consumers to shop for health care?
The short answer is maybe. Right now, it’s difficult, even with some of the tools available, said Lovisa Gustafsson, assistant vice president at the Commonwealth Fund, which has looked at whether patients use existing tools or the list price information hospitals must post online.
“The evidence to date shows patients aren’t necessarily the best shoppers, but we haven’t given them the best tools to be shoppers,” she said.
Posting negotiated rates might be a step forward, she said, but only if it is easily understandable.
It’s possible that insurers, physician offices, consumer groups, or online businesses may find ways to help direct patients to the most cost-effective locations for surgeries, tests or other procedures based on the information.
“Institutions like Consumer Reports or Consumer Checkbook could do some kind of high-level comparison between facilities or doctors, giving some general information that might be useful for consumers,” said Tim Jost, a professor emeritus at the Washington and Lee University School of Law in Lexington, Va.
But some hospitals and insurers maintain that disclosing specific rates could backfire.
Hospitals charging lower rates, for example, might raise them if they see competitors are getting higher reimbursement from insurers, they say. Insurers say they might be hampered in their ability to negotiate if rivals all know what they each pay.
“We also agree that patients should have accurate, real-time information about costs so they can make the best, most informed decisions about their care,” said a statement from lobbying group America’s Health Insurance Plans. “But publicly disclosing competitively negotiated, proprietary rates will reduce competition and push prices higher – not lower – for consumers, patients, and taxpayers.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Association insurance pushes on despite court ruling
When the Trump administration in June 2018 issued rules making it easier for small employers to band together to buy health insurance, “we started looking immediately,” recalled Scott Lyon, a top executive at the Small Business Association of Michigan.
Although he offered traditional small-group health insurance to his association’s employees and members, Mr. Lyon liked adding a new option for both: potentially less expensive coverage through an association health plan, which doesn’t have to meet all the rules of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Now, a few months in, “we’ve got 400 companies and a couple of thousand workers signed up,” said Mr. Lyon.
Most of the new enrollees joined through groups like Mr. Lyon’s or local chambers of commerce, farm bureaus, or agriculture-based cooperatives. Such groups see the plans not only as a way to offer insurance, but also as an enticement to boost membership.
In the first legal test, however, U.S. District Judge John Bates at the end of March sided with 11 states and the District of Columbia challenging the law. He invalidated a large chunk of those June rules, saying the administration issued them as an “end-run around the Affordable Care Act.”
So what now?
Unless the government seeks – which it has yet to do – and is granted a stay of the judge’s order, “plans formed under the vacated sections of the rule are illegal,” said Timothy Jost, an emeritus health law professor from Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Va.
Still, that won’t mean anything for existing plans if the states or federal regulators choose not to enforce the ruling, Mr. Jost said.
And that could cause more confusion in the marketplace.
While the states that brought the challenge are expected to enforce the ruling, some other states support broader access to association health plans, said Christopher Condeluci, an attorney who represents several such plans, including the one formed by Mr. Lyon’s group.
“These plans are not an end run around the ACA,” said Mr. Condeluci.
Association health plans already established under the administration’s rules cover “virtually” all the federal law’s essential health benefits, he said, with the exception of dental and vision care for children.
Local chamber of commerce plans are mainly continuing business as usual while watching to see if the government will appeal, said Katie Mahoney, vice president of health policy at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce.
A few, including a plan offered through the Las Vegas chamber, may limit new enrollment for sole proprietors, she said, as the judge sharply questioned whether they qualified as “employers” under federal laws.
Sole proprietors are generally individuals who own and operate their own businesses without any employees.
Judge Bates wrote that, in the regulation, the Department of Labor “stretches the definition of employer” beyond what federal law allows. The rule was designed to increase access to plans that “avoid the most stringent requirements” of the ACA.
The opinion by Judge Bates, who was appointed by President George W. Bush, is widely expected to be appealed, although the government has not yet done so.
The decision affects one pillar of a broader effort by the Trump administration to expand access to less expensive health insurance. Association plans have long been a favorite of Republicans, existing before the ACA. Supporters say they are one way to pool groups of businesses together to get better premium rates.
Still, some plans faced problems in the past, including bankruptcy or complaints that they misled consumers by not fully informing them about what is covered.
After the ACA took effect, enrollment fell, partly because many small businesses were buying new ACA plans and many existing association plans had to comply with ACA rules for small-group coverage anyway. People who ran their own businesses and had no employees qualified only for coverage through the ACA’s individual market.
But the Trump administration in June broadened the definition of those eligible to buy insurance through employer-based associations to include sole proprietors and also made it easier to form associations to offer coverage.
In addition, the changes allowed more association plans to be classified as large-employer coverage, which exempts them from some of the ACA’s requirements. For example, association plans don’t have to include all 10 of the ACA’s “essential” health benefits, such as mental health care and prescription drug coverage.
Also, unlike ACA plans, association insurers can set premium rates based on an employer’s industry, as well as taking into account the age range and gender makeup of their workforce.
In other words, association plans can charge less for companies with workforces that are generally younger and male in occupations that involve mainly desk work than for firms with mostly older workers or companies doing riskier work, such as cutting down trees or roofing.
Still, such plans must abide by other ACA provisions, including accepting people with preexisting medical conditions.
Critics, including the states that sued, say the new rules and other administration-backed changes will weaken the market for ACA plans by drawing out younger and healthier people. The states also argued that the new rules would be costly for them to administer, alleging they would have to devote more resources to preventing consumer fraud.
In Michigan, Mr. Lyon said the association his group formed, called Transcend, offers coverage to small employers and sole proprietors that is just as generous as large-group plans. It is a fully insured plan through the state’s Blue Cross Blue Shield carrier that covers a broad array of benefits, except children’s dental and vision.
“One thing we don’t want to do is sell a bag of air to our members,” said Mr. Lyon.
While some new members have reported large savings by enrolling, Mr. Lyon said association plans are not necessarily less expensive than small-group coverage. It all depends on the demographic and occupational makeup of the small business, he said.
“Our best estimate was association health plans would be the right solution for 30%-35% of the small-group world,” said Mr. Lyon. “It all has to come together. Age matters. Gender matters. It’s so specific to each company.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
When the Trump administration in June 2018 issued rules making it easier for small employers to band together to buy health insurance, “we started looking immediately,” recalled Scott Lyon, a top executive at the Small Business Association of Michigan.
Although he offered traditional small-group health insurance to his association’s employees and members, Mr. Lyon liked adding a new option for both: potentially less expensive coverage through an association health plan, which doesn’t have to meet all the rules of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Now, a few months in, “we’ve got 400 companies and a couple of thousand workers signed up,” said Mr. Lyon.
Most of the new enrollees joined through groups like Mr. Lyon’s or local chambers of commerce, farm bureaus, or agriculture-based cooperatives. Such groups see the plans not only as a way to offer insurance, but also as an enticement to boost membership.
In the first legal test, however, U.S. District Judge John Bates at the end of March sided with 11 states and the District of Columbia challenging the law. He invalidated a large chunk of those June rules, saying the administration issued them as an “end-run around the Affordable Care Act.”
So what now?
Unless the government seeks – which it has yet to do – and is granted a stay of the judge’s order, “plans formed under the vacated sections of the rule are illegal,” said Timothy Jost, an emeritus health law professor from Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Va.
Still, that won’t mean anything for existing plans if the states or federal regulators choose not to enforce the ruling, Mr. Jost said.
And that could cause more confusion in the marketplace.
While the states that brought the challenge are expected to enforce the ruling, some other states support broader access to association health plans, said Christopher Condeluci, an attorney who represents several such plans, including the one formed by Mr. Lyon’s group.
“These plans are not an end run around the ACA,” said Mr. Condeluci.
Association health plans already established under the administration’s rules cover “virtually” all the federal law’s essential health benefits, he said, with the exception of dental and vision care for children.
Local chamber of commerce plans are mainly continuing business as usual while watching to see if the government will appeal, said Katie Mahoney, vice president of health policy at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce.
A few, including a plan offered through the Las Vegas chamber, may limit new enrollment for sole proprietors, she said, as the judge sharply questioned whether they qualified as “employers” under federal laws.
Sole proprietors are generally individuals who own and operate their own businesses without any employees.
Judge Bates wrote that, in the regulation, the Department of Labor “stretches the definition of employer” beyond what federal law allows. The rule was designed to increase access to plans that “avoid the most stringent requirements” of the ACA.
The opinion by Judge Bates, who was appointed by President George W. Bush, is widely expected to be appealed, although the government has not yet done so.
The decision affects one pillar of a broader effort by the Trump administration to expand access to less expensive health insurance. Association plans have long been a favorite of Republicans, existing before the ACA. Supporters say they are one way to pool groups of businesses together to get better premium rates.
Still, some plans faced problems in the past, including bankruptcy or complaints that they misled consumers by not fully informing them about what is covered.
After the ACA took effect, enrollment fell, partly because many small businesses were buying new ACA plans and many existing association plans had to comply with ACA rules for small-group coverage anyway. People who ran their own businesses and had no employees qualified only for coverage through the ACA’s individual market.
But the Trump administration in June broadened the definition of those eligible to buy insurance through employer-based associations to include sole proprietors and also made it easier to form associations to offer coverage.
In addition, the changes allowed more association plans to be classified as large-employer coverage, which exempts them from some of the ACA’s requirements. For example, association plans don’t have to include all 10 of the ACA’s “essential” health benefits, such as mental health care and prescription drug coverage.
Also, unlike ACA plans, association insurers can set premium rates based on an employer’s industry, as well as taking into account the age range and gender makeup of their workforce.
In other words, association plans can charge less for companies with workforces that are generally younger and male in occupations that involve mainly desk work than for firms with mostly older workers or companies doing riskier work, such as cutting down trees or roofing.
Still, such plans must abide by other ACA provisions, including accepting people with preexisting medical conditions.
Critics, including the states that sued, say the new rules and other administration-backed changes will weaken the market for ACA plans by drawing out younger and healthier people. The states also argued that the new rules would be costly for them to administer, alleging they would have to devote more resources to preventing consumer fraud.
In Michigan, Mr. Lyon said the association his group formed, called Transcend, offers coverage to small employers and sole proprietors that is just as generous as large-group plans. It is a fully insured plan through the state’s Blue Cross Blue Shield carrier that covers a broad array of benefits, except children’s dental and vision.
“One thing we don’t want to do is sell a bag of air to our members,” said Mr. Lyon.
While some new members have reported large savings by enrolling, Mr. Lyon said association plans are not necessarily less expensive than small-group coverage. It all depends on the demographic and occupational makeup of the small business, he said.
“Our best estimate was association health plans would be the right solution for 30%-35% of the small-group world,” said Mr. Lyon. “It all has to come together. Age matters. Gender matters. It’s so specific to each company.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
When the Trump administration in June 2018 issued rules making it easier for small employers to band together to buy health insurance, “we started looking immediately,” recalled Scott Lyon, a top executive at the Small Business Association of Michigan.
Although he offered traditional small-group health insurance to his association’s employees and members, Mr. Lyon liked adding a new option for both: potentially less expensive coverage through an association health plan, which doesn’t have to meet all the rules of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Now, a few months in, “we’ve got 400 companies and a couple of thousand workers signed up,” said Mr. Lyon.
Most of the new enrollees joined through groups like Mr. Lyon’s or local chambers of commerce, farm bureaus, or agriculture-based cooperatives. Such groups see the plans not only as a way to offer insurance, but also as an enticement to boost membership.
In the first legal test, however, U.S. District Judge John Bates at the end of March sided with 11 states and the District of Columbia challenging the law. He invalidated a large chunk of those June rules, saying the administration issued them as an “end-run around the Affordable Care Act.”
So what now?
Unless the government seeks – which it has yet to do – and is granted a stay of the judge’s order, “plans formed under the vacated sections of the rule are illegal,” said Timothy Jost, an emeritus health law professor from Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Va.
Still, that won’t mean anything for existing plans if the states or federal regulators choose not to enforce the ruling, Mr. Jost said.
And that could cause more confusion in the marketplace.
While the states that brought the challenge are expected to enforce the ruling, some other states support broader access to association health plans, said Christopher Condeluci, an attorney who represents several such plans, including the one formed by Mr. Lyon’s group.
“These plans are not an end run around the ACA,” said Mr. Condeluci.
Association health plans already established under the administration’s rules cover “virtually” all the federal law’s essential health benefits, he said, with the exception of dental and vision care for children.
Local chamber of commerce plans are mainly continuing business as usual while watching to see if the government will appeal, said Katie Mahoney, vice president of health policy at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce.
A few, including a plan offered through the Las Vegas chamber, may limit new enrollment for sole proprietors, she said, as the judge sharply questioned whether they qualified as “employers” under federal laws.
Sole proprietors are generally individuals who own and operate their own businesses without any employees.
Judge Bates wrote that, in the regulation, the Department of Labor “stretches the definition of employer” beyond what federal law allows. The rule was designed to increase access to plans that “avoid the most stringent requirements” of the ACA.
The opinion by Judge Bates, who was appointed by President George W. Bush, is widely expected to be appealed, although the government has not yet done so.
The decision affects one pillar of a broader effort by the Trump administration to expand access to less expensive health insurance. Association plans have long been a favorite of Republicans, existing before the ACA. Supporters say they are one way to pool groups of businesses together to get better premium rates.
Still, some plans faced problems in the past, including bankruptcy or complaints that they misled consumers by not fully informing them about what is covered.
After the ACA took effect, enrollment fell, partly because many small businesses were buying new ACA plans and many existing association plans had to comply with ACA rules for small-group coverage anyway. People who ran their own businesses and had no employees qualified only for coverage through the ACA’s individual market.
But the Trump administration in June broadened the definition of those eligible to buy insurance through employer-based associations to include sole proprietors and also made it easier to form associations to offer coverage.
In addition, the changes allowed more association plans to be classified as large-employer coverage, which exempts them from some of the ACA’s requirements. For example, association plans don’t have to include all 10 of the ACA’s “essential” health benefits, such as mental health care and prescription drug coverage.
Also, unlike ACA plans, association insurers can set premium rates based on an employer’s industry, as well as taking into account the age range and gender makeup of their workforce.
In other words, association plans can charge less for companies with workforces that are generally younger and male in occupations that involve mainly desk work than for firms with mostly older workers or companies doing riskier work, such as cutting down trees or roofing.
Still, such plans must abide by other ACA provisions, including accepting people with preexisting medical conditions.
Critics, including the states that sued, say the new rules and other administration-backed changes will weaken the market for ACA plans by drawing out younger and healthier people. The states also argued that the new rules would be costly for them to administer, alleging they would have to devote more resources to preventing consumer fraud.
In Michigan, Mr. Lyon said the association his group formed, called Transcend, offers coverage to small employers and sole proprietors that is just as generous as large-group plans. It is a fully insured plan through the state’s Blue Cross Blue Shield carrier that covers a broad array of benefits, except children’s dental and vision.
“One thing we don’t want to do is sell a bag of air to our members,” said Mr. Lyon.
While some new members have reported large savings by enrolling, Mr. Lyon said association plans are not necessarily less expensive than small-group coverage. It all depends on the demographic and occupational makeup of the small business, he said.
“Our best estimate was association health plans would be the right solution for 30%-35% of the small-group world,” said Mr. Lyon. “It all has to come together. Age matters. Gender matters. It’s so specific to each company.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
With one hand, administration boosts ACA marketplaces, weakens them with another
In the span of less than 12 hours, the Trump administration took two seemingly contradictory actions that could have profound effects on the insurance marketplaces set up by the Affordable Care Act.
First, officials issued guidance on the morning of Oct. 22 that could weaken the exchanges set up for people who buy their own insurance. The new approach makes it easier for states to get around some ACA requirements, including allowing the use of federal subsidies for skimpier plans that can reject people with preexisting conditions.
Yet, the other move – a proposed rule unveiled that evening – could bolster ACA marketplaces by sending millions of people with job-based coverage there, armed with tax-free money from their employers to buy individual plans.
Both efforts play into the parallel narratives dominating the bitter political debate over the ACA.
The administration, frustrated that Congress did not repeal the law, say some critics and policy experts, is working to undermine it by weakening the marketplaces and the law’s consumer protections. Those efforts make it easier for insurers to offer skimpier policies that bypass the law’s rules, such as its ban on annual or lifetime limits or its protections for people with preexisting conditions. Congress also zeroed out the tax penalty for not having coverage, effective next year. Combined, the moves could reduce enrollment in ACA plans, potentially driving up premiums for those who remain.
The administration and Republicans in Congress say they are looking to assist those left behind by the ACA – people who don’t get subsidies to help them buy coverage and are desperate for less expensive options – even if that means purchasing less robust coverage.
“These are people who were buying insurance before [the law] and then the rules changed and they could not buy it because they could not afford it,” said Joe Antos, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute. “They have been slowly dropping out of insurance coverage altogether.”
The efforts are dramatically reshaping the ACA and the individual insurance market to one that looks more as it did before the 2010 law, when regulation, coverage, and consumer protections varied widely across the country.
“Some states will do everything they can to keep individual markets strong and stable. Others won’t,” said Sabrina Corlette, research professor at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University.
So what expectations should consumers have? Here are three key takeaways:
Protections for preexisting health problems are uncertain
Polls show that keeping the ACA’s guarantees on coverage for people with medical problems is a top concern for Americans, and Democrats have made their defense of the health law a key part of their midterm election campaigns.
Republicans have gotten that message and even those who voted to repeal the ACA or joined a lawsuit by 20 red states to overturn it now say they want to protect people with preexisting conditions. Still, GOP lawmakers have not introduced any plan that would be as protective as the current law.
In August, the administration released a rule allowing expanded use of short-term plans, which are less expensive than ACA policies. To get those lower prices, most of these plans do not cover prescription drugs, maternity care, mental health, or substance abuse treatments.
The move is unlikely to benefit people with health problems, as short-term plans can reject people with preexisting conditions or decline to cover care for those medical problems.
Under the rule, insurers can sell them starting in 2019 for up to a year’s duration, with an option to renew for up to 3 years, reversing an Obama-era directive that limited them to 90 days.
Administration officials estimate such plans could draw 600,000 new enrollees next year, and others have estimated the numbers could be far higher. The concern is if many healthy people in 2019 switch out of the ACA market and choose short-term plans, premiums will rise for those who remain, including those with preexisting conditions, or make the ACA market less attractive for insurers.
Where you live matters more
One of the biggest changes ushered in with the ACA was a standard set of rules across all states.
Before the law took effect, consumers buying their own coverage saw tremendous variation in what was offered and what protections they had, depending on the state where they lived.
Most states, for example, allowed insurers to reject people with medical conditions. A few states required insurers to charge similar premiums across the board, but most allowed wide variations based on age, gender or health. Some skimpy plans didn’t cover prescription drugs, chemotherapy, or other medical services.
By standardizing the rules and benefits, the ACA barred insurers from rejecting applicants with medical conditions or charging them more. Women and men get the same premium rates and insurers could charge older people no more than three times what they charged younger ones.
Under the new guidance issued this week giving states more flexibility on what is offered, consumers could again see a wide variation on coverage, premium rules, and even subsidy eligibility.
“It shifts pressure to state politicians,” said Caroline Pearson, a senior fellow at NORC, a nonpartisan research institution at the University of Chicago. That could play into the calculus of whether a state will seek to make broad changes to help people who cannot afford ACA plans, even if the trade-off affects people with medical conditions.
“You risk making some worse off by threatening those markets,” said Pearson. “That is always going to be hard.”
Millions more will join the “buy-your-own” ranks
The proposed rule released Oct. 23 allows employers to fund tax-free accounts – called health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) – that workers can use to buy their own coverage on the ACA marketplaces.
The administration estimates about 10 million people would do so by 2028 – a substantial boost for those exchanges, which policymakers say never hit the enrollment numbers needed to attract enough insurers and hold prices down.
John Barkett, senior director of policy affairs at Willis Towers Watson, a benefits consulting firm, said he expects employers to “seriously consider” the new market. The infusion of workers will improve options by attracting more insurers, he added.
“These people coming in will be employer-sponsored, they’ll have steady jobs,” Barkett noted, and will likely stick with coverage longer than those typically in the individual market.
Currently more than 14 million people buy their own insurance, with about 10 million of those using federal or state ACA marketplaces. The others buy private plans through brokers.
The proposed rule won’t be finalized for months, but it could result in new options by 2020.
If these workers seeking coverage are generally healthy, the infusion could slow premium increases in the overall ACA marketplace because it would improve the risk pool for insurers.
But, if employers with mainly higher-cost or older workers opt to move to the marketplaces, it could help drive up premiums.
In an odd twist, the administration notes in the proposed rule that the ACA has provisions that could protect the marketplace from that type of adverse selection, which can drive up prices. But most of the protective factors cited by the rule have been weakened, removed, or expired, such as the tax penalty for being uninsured and the federal subsidies for insurers to cover lower deductibles for certain low-income consumers.
Benefits consultants and policy experts are skeptical about how many companies will move to the HRA plan, given the tight labor market. Continued uncertainty about the fate of the ACA marketplace may keep them reluctant to send workers out on their own, they say.
Health benefits are a big factor in attracting and retaining workers, said Chris Condeluci, a Washington attorney who previously worked for Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa) and served as counsel to the Senate Finance Committee during the drafting of the ACA.
“Most employers believe their group health plan will provide better health coverage than an individual market plan,” he said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
In the span of less than 12 hours, the Trump administration took two seemingly contradictory actions that could have profound effects on the insurance marketplaces set up by the Affordable Care Act.
First, officials issued guidance on the morning of Oct. 22 that could weaken the exchanges set up for people who buy their own insurance. The new approach makes it easier for states to get around some ACA requirements, including allowing the use of federal subsidies for skimpier plans that can reject people with preexisting conditions.
Yet, the other move – a proposed rule unveiled that evening – could bolster ACA marketplaces by sending millions of people with job-based coverage there, armed with tax-free money from their employers to buy individual plans.
Both efforts play into the parallel narratives dominating the bitter political debate over the ACA.
The administration, frustrated that Congress did not repeal the law, say some critics and policy experts, is working to undermine it by weakening the marketplaces and the law’s consumer protections. Those efforts make it easier for insurers to offer skimpier policies that bypass the law’s rules, such as its ban on annual or lifetime limits or its protections for people with preexisting conditions. Congress also zeroed out the tax penalty for not having coverage, effective next year. Combined, the moves could reduce enrollment in ACA plans, potentially driving up premiums for those who remain.
The administration and Republicans in Congress say they are looking to assist those left behind by the ACA – people who don’t get subsidies to help them buy coverage and are desperate for less expensive options – even if that means purchasing less robust coverage.
“These are people who were buying insurance before [the law] and then the rules changed and they could not buy it because they could not afford it,” said Joe Antos, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute. “They have been slowly dropping out of insurance coverage altogether.”
The efforts are dramatically reshaping the ACA and the individual insurance market to one that looks more as it did before the 2010 law, when regulation, coverage, and consumer protections varied widely across the country.
“Some states will do everything they can to keep individual markets strong and stable. Others won’t,” said Sabrina Corlette, research professor at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University.
So what expectations should consumers have? Here are three key takeaways:
Protections for preexisting health problems are uncertain
Polls show that keeping the ACA’s guarantees on coverage for people with medical problems is a top concern for Americans, and Democrats have made their defense of the health law a key part of their midterm election campaigns.
Republicans have gotten that message and even those who voted to repeal the ACA or joined a lawsuit by 20 red states to overturn it now say they want to protect people with preexisting conditions. Still, GOP lawmakers have not introduced any plan that would be as protective as the current law.
In August, the administration released a rule allowing expanded use of short-term plans, which are less expensive than ACA policies. To get those lower prices, most of these plans do not cover prescription drugs, maternity care, mental health, or substance abuse treatments.
The move is unlikely to benefit people with health problems, as short-term plans can reject people with preexisting conditions or decline to cover care for those medical problems.
Under the rule, insurers can sell them starting in 2019 for up to a year’s duration, with an option to renew for up to 3 years, reversing an Obama-era directive that limited them to 90 days.
Administration officials estimate such plans could draw 600,000 new enrollees next year, and others have estimated the numbers could be far higher. The concern is if many healthy people in 2019 switch out of the ACA market and choose short-term plans, premiums will rise for those who remain, including those with preexisting conditions, or make the ACA market less attractive for insurers.
Where you live matters more
One of the biggest changes ushered in with the ACA was a standard set of rules across all states.
Before the law took effect, consumers buying their own coverage saw tremendous variation in what was offered and what protections they had, depending on the state where they lived.
Most states, for example, allowed insurers to reject people with medical conditions. A few states required insurers to charge similar premiums across the board, but most allowed wide variations based on age, gender or health. Some skimpy plans didn’t cover prescription drugs, chemotherapy, or other medical services.
By standardizing the rules and benefits, the ACA barred insurers from rejecting applicants with medical conditions or charging them more. Women and men get the same premium rates and insurers could charge older people no more than three times what they charged younger ones.
Under the new guidance issued this week giving states more flexibility on what is offered, consumers could again see a wide variation on coverage, premium rules, and even subsidy eligibility.
“It shifts pressure to state politicians,” said Caroline Pearson, a senior fellow at NORC, a nonpartisan research institution at the University of Chicago. That could play into the calculus of whether a state will seek to make broad changes to help people who cannot afford ACA plans, even if the trade-off affects people with medical conditions.
“You risk making some worse off by threatening those markets,” said Pearson. “That is always going to be hard.”
Millions more will join the “buy-your-own” ranks
The proposed rule released Oct. 23 allows employers to fund tax-free accounts – called health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) – that workers can use to buy their own coverage on the ACA marketplaces.
The administration estimates about 10 million people would do so by 2028 – a substantial boost for those exchanges, which policymakers say never hit the enrollment numbers needed to attract enough insurers and hold prices down.
John Barkett, senior director of policy affairs at Willis Towers Watson, a benefits consulting firm, said he expects employers to “seriously consider” the new market. The infusion of workers will improve options by attracting more insurers, he added.
“These people coming in will be employer-sponsored, they’ll have steady jobs,” Barkett noted, and will likely stick with coverage longer than those typically in the individual market.
Currently more than 14 million people buy their own insurance, with about 10 million of those using federal or state ACA marketplaces. The others buy private plans through brokers.
The proposed rule won’t be finalized for months, but it could result in new options by 2020.
If these workers seeking coverage are generally healthy, the infusion could slow premium increases in the overall ACA marketplace because it would improve the risk pool for insurers.
But, if employers with mainly higher-cost or older workers opt to move to the marketplaces, it could help drive up premiums.
In an odd twist, the administration notes in the proposed rule that the ACA has provisions that could protect the marketplace from that type of adverse selection, which can drive up prices. But most of the protective factors cited by the rule have been weakened, removed, or expired, such as the tax penalty for being uninsured and the federal subsidies for insurers to cover lower deductibles for certain low-income consumers.
Benefits consultants and policy experts are skeptical about how many companies will move to the HRA plan, given the tight labor market. Continued uncertainty about the fate of the ACA marketplace may keep them reluctant to send workers out on their own, they say.
Health benefits are a big factor in attracting and retaining workers, said Chris Condeluci, a Washington attorney who previously worked for Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa) and served as counsel to the Senate Finance Committee during the drafting of the ACA.
“Most employers believe their group health plan will provide better health coverage than an individual market plan,” he said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
In the span of less than 12 hours, the Trump administration took two seemingly contradictory actions that could have profound effects on the insurance marketplaces set up by the Affordable Care Act.
First, officials issued guidance on the morning of Oct. 22 that could weaken the exchanges set up for people who buy their own insurance. The new approach makes it easier for states to get around some ACA requirements, including allowing the use of federal subsidies for skimpier plans that can reject people with preexisting conditions.
Yet, the other move – a proposed rule unveiled that evening – could bolster ACA marketplaces by sending millions of people with job-based coverage there, armed with tax-free money from their employers to buy individual plans.
Both efforts play into the parallel narratives dominating the bitter political debate over the ACA.
The administration, frustrated that Congress did not repeal the law, say some critics and policy experts, is working to undermine it by weakening the marketplaces and the law’s consumer protections. Those efforts make it easier for insurers to offer skimpier policies that bypass the law’s rules, such as its ban on annual or lifetime limits or its protections for people with preexisting conditions. Congress also zeroed out the tax penalty for not having coverage, effective next year. Combined, the moves could reduce enrollment in ACA plans, potentially driving up premiums for those who remain.
The administration and Republicans in Congress say they are looking to assist those left behind by the ACA – people who don’t get subsidies to help them buy coverage and are desperate for less expensive options – even if that means purchasing less robust coverage.
“These are people who were buying insurance before [the law] and then the rules changed and they could not buy it because they could not afford it,” said Joe Antos, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute. “They have been slowly dropping out of insurance coverage altogether.”
The efforts are dramatically reshaping the ACA and the individual insurance market to one that looks more as it did before the 2010 law, when regulation, coverage, and consumer protections varied widely across the country.
“Some states will do everything they can to keep individual markets strong and stable. Others won’t,” said Sabrina Corlette, research professor at the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University.
So what expectations should consumers have? Here are three key takeaways:
Protections for preexisting health problems are uncertain
Polls show that keeping the ACA’s guarantees on coverage for people with medical problems is a top concern for Americans, and Democrats have made their defense of the health law a key part of their midterm election campaigns.
Republicans have gotten that message and even those who voted to repeal the ACA or joined a lawsuit by 20 red states to overturn it now say they want to protect people with preexisting conditions. Still, GOP lawmakers have not introduced any plan that would be as protective as the current law.
In August, the administration released a rule allowing expanded use of short-term plans, which are less expensive than ACA policies. To get those lower prices, most of these plans do not cover prescription drugs, maternity care, mental health, or substance abuse treatments.
The move is unlikely to benefit people with health problems, as short-term plans can reject people with preexisting conditions or decline to cover care for those medical problems.
Under the rule, insurers can sell them starting in 2019 for up to a year’s duration, with an option to renew for up to 3 years, reversing an Obama-era directive that limited them to 90 days.
Administration officials estimate such plans could draw 600,000 new enrollees next year, and others have estimated the numbers could be far higher. The concern is if many healthy people in 2019 switch out of the ACA market and choose short-term plans, premiums will rise for those who remain, including those with preexisting conditions, or make the ACA market less attractive for insurers.
Where you live matters more
One of the biggest changes ushered in with the ACA was a standard set of rules across all states.
Before the law took effect, consumers buying their own coverage saw tremendous variation in what was offered and what protections they had, depending on the state where they lived.
Most states, for example, allowed insurers to reject people with medical conditions. A few states required insurers to charge similar premiums across the board, but most allowed wide variations based on age, gender or health. Some skimpy plans didn’t cover prescription drugs, chemotherapy, or other medical services.
By standardizing the rules and benefits, the ACA barred insurers from rejecting applicants with medical conditions or charging them more. Women and men get the same premium rates and insurers could charge older people no more than three times what they charged younger ones.
Under the new guidance issued this week giving states more flexibility on what is offered, consumers could again see a wide variation on coverage, premium rules, and even subsidy eligibility.
“It shifts pressure to state politicians,” said Caroline Pearson, a senior fellow at NORC, a nonpartisan research institution at the University of Chicago. That could play into the calculus of whether a state will seek to make broad changes to help people who cannot afford ACA plans, even if the trade-off affects people with medical conditions.
“You risk making some worse off by threatening those markets,” said Pearson. “That is always going to be hard.”
Millions more will join the “buy-your-own” ranks
The proposed rule released Oct. 23 allows employers to fund tax-free accounts – called health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) – that workers can use to buy their own coverage on the ACA marketplaces.
The administration estimates about 10 million people would do so by 2028 – a substantial boost for those exchanges, which policymakers say never hit the enrollment numbers needed to attract enough insurers and hold prices down.
John Barkett, senior director of policy affairs at Willis Towers Watson, a benefits consulting firm, said he expects employers to “seriously consider” the new market. The infusion of workers will improve options by attracting more insurers, he added.
“These people coming in will be employer-sponsored, they’ll have steady jobs,” Barkett noted, and will likely stick with coverage longer than those typically in the individual market.
Currently more than 14 million people buy their own insurance, with about 10 million of those using federal or state ACA marketplaces. The others buy private plans through brokers.
The proposed rule won’t be finalized for months, but it could result in new options by 2020.
If these workers seeking coverage are generally healthy, the infusion could slow premium increases in the overall ACA marketplace because it would improve the risk pool for insurers.
But, if employers with mainly higher-cost or older workers opt to move to the marketplaces, it could help drive up premiums.
In an odd twist, the administration notes in the proposed rule that the ACA has provisions that could protect the marketplace from that type of adverse selection, which can drive up prices. But most of the protective factors cited by the rule have been weakened, removed, or expired, such as the tax penalty for being uninsured and the federal subsidies for insurers to cover lower deductibles for certain low-income consumers.
Benefits consultants and policy experts are skeptical about how many companies will move to the HRA plan, given the tight labor market. Continued uncertainty about the fate of the ACA marketplace may keep them reluctant to send workers out on their own, they say.
Health benefits are a big factor in attracting and retaining workers, said Chris Condeluci, a Washington attorney who previously worked for Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa) and served as counsel to the Senate Finance Committee during the drafting of the ACA.
“Most employers believe their group health plan will provide better health coverage than an individual market plan,” he said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Compounded topicals flagged on fears of Medicare fraud, risk
But a new report finds that officials are concerned about possible fraud and patient safety risks from products made at nearly a quarter of the pharmacies that fill the bulk of those prescriptions.
“Although some of this billing may be legitimate, all of these pharmacies warrant further scrutiny,” concludes the report from the Office of Inspector General for the Department of Health and Human Services.
In total, 547 pharmacies – nearly 23% of those that submit most of the bills to Medicare for making these creams – hit one or more of five red-flag markers set by investigators. Those included what the researchers called “extremely high” prices; large percentages of Medicare members getting identical drugs – 16 of the pharmacies billed for identical drugs for 200 or more customers; “greatly increased” year-over-year billing – 20 pharmacies increased their billing by more than 10,000%; or having a single medical provider writing more than 131 prescriptions. More than half of those pharmacies hit two or more measures – and 10 hit all five.
One Oregon pharmacy, for example, submitted claims for 91% of its customers. A pharmacy in New York submitted 5,342 prescriptions ordered by one podiatrist, while a Florida pharmacy saw its Medicare billing for such treatments go from $7,468 in 2015 to $1.8 million the following year.
Many of the pharmacies are clustered in four cities: Detroit, Houston, Los Angeles, and New York.
The report comes amid ongoing concern by Medicare officials about compounded drugs. In addition to questions like those raised in the report about overuse and pricing, safety has been a key issue in recent years. A meningitis outbreak in 2012 was linked to a Massachusetts pharmacy that did not maintain sterile conditions and sold tainted made-to-order injections that killed 64 Americans.
When done safely, pharmacy-made compounded drugs provide a legitimate option for patients whose medical needs can’t be met by commercially available products mass-produced by pharmaceutical companies. For example, a patient who can’t swallow a commercially available prescription pill might get a liquid version of a drug.
State boards of pharmacy generally oversee compounding pharmacies, and the drugs they produce are not considered approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The new report focuses on concerns with compounded topical medications.
Medicare spending for such treatments has skyrocketed, rising more than 2,350%, from $13.2 million in 2010 to $323.5 million in 2016. Price hikes and an increase in the number of prescriptions written drove the increase, the report said.
It is not the first time the inspector general has looked at compounded drugs. A 2016 report found that overall spending on all types of compounded drugs – not just topical medications – rose sharply. The U.S. Postal Service inspector general and the Department of Defense also have raised concerns about rising spending and possible fraud for compounded drugs.
In response to those previous reports, the International Academy of Compounding Pharmacists, the industry’s trade group, has said that legitimately compounded drugs “can dramatically improve a patient’s quality of life,” noting that proper billing controls need to be in place. The inspector general’s report in 2016, it added, found that “such controls are not in place.”
This report, which the compounding trade group has not yet reviewed, focuses on topical drugs and a subset of the 15,290 pharmacies that provide at least one such prescription each year. It looked at billing records from the 2,388 pharmacies that do at least 10 such prescriptions a year – providing 93% of all compounded topical drugs paid for by Medicare.
Most of the prescriptions were for pain treatment, made from ingredients such as lidocaine or diclofenac sodium.
On average, those compounds were more expensive than noncompounded drugs with the same ingredients.
For example, Medicare paid an average of $751 per tube of compounded lidocaine, and $1,506 for the diclofenac, according to the inspector general’s report. Noncompounded tubes of those drugs averaged $445 and $128, respectively.
FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, recently outlined new efforts his agency is taking to oversee compounded drugs in the wake of legislation passed by Congress following the meningitis outbreak.
“The FDA is inspecting compounding facilities to assess whether drugs that are essentially copies of FDA-approved drugs are being compounded for patients” who could otherwise take a product sold commercially, he said in a statement issued on June 28.
Dr. Gottlieb also said the FDA plans to make more information available to patients and their doctors about compounded topical pain creams, including information about their effectiveness and any potential safety risks.
Not being effective is a safety risk, noted Miriam Anderson, a researcher with the inspector general’s office who helped write the report.
The report urged the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to clarify some of its policies to emphasize that insurers can limit the use of compounded drugs by requiring prior authorization or other steps. The agency concurred with the recommendations, according to the report, including the need to “follow up on pharmacies with questionable Part D billing and the prescribers associated with these pharmacies.”
Ms. Anderson said the inspector general’s office is continuing to probe the issue.
“We will investigate a number of leads on specific pharmacies and prescribers who were identified as having these questionable patterns,” she said. “Whenever we see that kind of increase in spending, it raises concern about fraud, waste, and abuse.”
KHN’s coverage of prescription drug development, costs, and pricing is supported in part by the Laura and John Arnold Foundation.
Kaiser Health News (KHN) is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
But a new report finds that officials are concerned about possible fraud and patient safety risks from products made at nearly a quarter of the pharmacies that fill the bulk of those prescriptions.
“Although some of this billing may be legitimate, all of these pharmacies warrant further scrutiny,” concludes the report from the Office of Inspector General for the Department of Health and Human Services.
In total, 547 pharmacies – nearly 23% of those that submit most of the bills to Medicare for making these creams – hit one or more of five red-flag markers set by investigators. Those included what the researchers called “extremely high” prices; large percentages of Medicare members getting identical drugs – 16 of the pharmacies billed for identical drugs for 200 or more customers; “greatly increased” year-over-year billing – 20 pharmacies increased their billing by more than 10,000%; or having a single medical provider writing more than 131 prescriptions. More than half of those pharmacies hit two or more measures – and 10 hit all five.
One Oregon pharmacy, for example, submitted claims for 91% of its customers. A pharmacy in New York submitted 5,342 prescriptions ordered by one podiatrist, while a Florida pharmacy saw its Medicare billing for such treatments go from $7,468 in 2015 to $1.8 million the following year.
Many of the pharmacies are clustered in four cities: Detroit, Houston, Los Angeles, and New York.
The report comes amid ongoing concern by Medicare officials about compounded drugs. In addition to questions like those raised in the report about overuse and pricing, safety has been a key issue in recent years. A meningitis outbreak in 2012 was linked to a Massachusetts pharmacy that did not maintain sterile conditions and sold tainted made-to-order injections that killed 64 Americans.
When done safely, pharmacy-made compounded drugs provide a legitimate option for patients whose medical needs can’t be met by commercially available products mass-produced by pharmaceutical companies. For example, a patient who can’t swallow a commercially available prescription pill might get a liquid version of a drug.
State boards of pharmacy generally oversee compounding pharmacies, and the drugs they produce are not considered approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The new report focuses on concerns with compounded topical medications.
Medicare spending for such treatments has skyrocketed, rising more than 2,350%, from $13.2 million in 2010 to $323.5 million in 2016. Price hikes and an increase in the number of prescriptions written drove the increase, the report said.
It is not the first time the inspector general has looked at compounded drugs. A 2016 report found that overall spending on all types of compounded drugs – not just topical medications – rose sharply. The U.S. Postal Service inspector general and the Department of Defense also have raised concerns about rising spending and possible fraud for compounded drugs.
In response to those previous reports, the International Academy of Compounding Pharmacists, the industry’s trade group, has said that legitimately compounded drugs “can dramatically improve a patient’s quality of life,” noting that proper billing controls need to be in place. The inspector general’s report in 2016, it added, found that “such controls are not in place.”
This report, which the compounding trade group has not yet reviewed, focuses on topical drugs and a subset of the 15,290 pharmacies that provide at least one such prescription each year. It looked at billing records from the 2,388 pharmacies that do at least 10 such prescriptions a year – providing 93% of all compounded topical drugs paid for by Medicare.
Most of the prescriptions were for pain treatment, made from ingredients such as lidocaine or diclofenac sodium.
On average, those compounds were more expensive than noncompounded drugs with the same ingredients.
For example, Medicare paid an average of $751 per tube of compounded lidocaine, and $1,506 for the diclofenac, according to the inspector general’s report. Noncompounded tubes of those drugs averaged $445 and $128, respectively.
FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, recently outlined new efforts his agency is taking to oversee compounded drugs in the wake of legislation passed by Congress following the meningitis outbreak.
“The FDA is inspecting compounding facilities to assess whether drugs that are essentially copies of FDA-approved drugs are being compounded for patients” who could otherwise take a product sold commercially, he said in a statement issued on June 28.
Dr. Gottlieb also said the FDA plans to make more information available to patients and their doctors about compounded topical pain creams, including information about their effectiveness and any potential safety risks.
Not being effective is a safety risk, noted Miriam Anderson, a researcher with the inspector general’s office who helped write the report.
The report urged the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to clarify some of its policies to emphasize that insurers can limit the use of compounded drugs by requiring prior authorization or other steps. The agency concurred with the recommendations, according to the report, including the need to “follow up on pharmacies with questionable Part D billing and the prescribers associated with these pharmacies.”
Ms. Anderson said the inspector general’s office is continuing to probe the issue.
“We will investigate a number of leads on specific pharmacies and prescribers who were identified as having these questionable patterns,” she said. “Whenever we see that kind of increase in spending, it raises concern about fraud, waste, and abuse.”
KHN’s coverage of prescription drug development, costs, and pricing is supported in part by the Laura and John Arnold Foundation.
Kaiser Health News (KHN) is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
But a new report finds that officials are concerned about possible fraud and patient safety risks from products made at nearly a quarter of the pharmacies that fill the bulk of those prescriptions.
“Although some of this billing may be legitimate, all of these pharmacies warrant further scrutiny,” concludes the report from the Office of Inspector General for the Department of Health and Human Services.
In total, 547 pharmacies – nearly 23% of those that submit most of the bills to Medicare for making these creams – hit one or more of five red-flag markers set by investigators. Those included what the researchers called “extremely high” prices; large percentages of Medicare members getting identical drugs – 16 of the pharmacies billed for identical drugs for 200 or more customers; “greatly increased” year-over-year billing – 20 pharmacies increased their billing by more than 10,000%; or having a single medical provider writing more than 131 prescriptions. More than half of those pharmacies hit two or more measures – and 10 hit all five.
One Oregon pharmacy, for example, submitted claims for 91% of its customers. A pharmacy in New York submitted 5,342 prescriptions ordered by one podiatrist, while a Florida pharmacy saw its Medicare billing for such treatments go from $7,468 in 2015 to $1.8 million the following year.
Many of the pharmacies are clustered in four cities: Detroit, Houston, Los Angeles, and New York.
The report comes amid ongoing concern by Medicare officials about compounded drugs. In addition to questions like those raised in the report about overuse and pricing, safety has been a key issue in recent years. A meningitis outbreak in 2012 was linked to a Massachusetts pharmacy that did not maintain sterile conditions and sold tainted made-to-order injections that killed 64 Americans.
When done safely, pharmacy-made compounded drugs provide a legitimate option for patients whose medical needs can’t be met by commercially available products mass-produced by pharmaceutical companies. For example, a patient who can’t swallow a commercially available prescription pill might get a liquid version of a drug.
State boards of pharmacy generally oversee compounding pharmacies, and the drugs they produce are not considered approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The new report focuses on concerns with compounded topical medications.
Medicare spending for such treatments has skyrocketed, rising more than 2,350%, from $13.2 million in 2010 to $323.5 million in 2016. Price hikes and an increase in the number of prescriptions written drove the increase, the report said.
It is not the first time the inspector general has looked at compounded drugs. A 2016 report found that overall spending on all types of compounded drugs – not just topical medications – rose sharply. The U.S. Postal Service inspector general and the Department of Defense also have raised concerns about rising spending and possible fraud for compounded drugs.
In response to those previous reports, the International Academy of Compounding Pharmacists, the industry’s trade group, has said that legitimately compounded drugs “can dramatically improve a patient’s quality of life,” noting that proper billing controls need to be in place. The inspector general’s report in 2016, it added, found that “such controls are not in place.”
This report, which the compounding trade group has not yet reviewed, focuses on topical drugs and a subset of the 15,290 pharmacies that provide at least one such prescription each year. It looked at billing records from the 2,388 pharmacies that do at least 10 such prescriptions a year – providing 93% of all compounded topical drugs paid for by Medicare.
Most of the prescriptions were for pain treatment, made from ingredients such as lidocaine or diclofenac sodium.
On average, those compounds were more expensive than noncompounded drugs with the same ingredients.
For example, Medicare paid an average of $751 per tube of compounded lidocaine, and $1,506 for the diclofenac, according to the inspector general’s report. Noncompounded tubes of those drugs averaged $445 and $128, respectively.
FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, recently outlined new efforts his agency is taking to oversee compounded drugs in the wake of legislation passed by Congress following the meningitis outbreak.
“The FDA is inspecting compounding facilities to assess whether drugs that are essentially copies of FDA-approved drugs are being compounded for patients” who could otherwise take a product sold commercially, he said in a statement issued on June 28.
Dr. Gottlieb also said the FDA plans to make more information available to patients and their doctors about compounded topical pain creams, including information about their effectiveness and any potential safety risks.
Not being effective is a safety risk, noted Miriam Anderson, a researcher with the inspector general’s office who helped write the report.
The report urged the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to clarify some of its policies to emphasize that insurers can limit the use of compounded drugs by requiring prior authorization or other steps. The agency concurred with the recommendations, according to the report, including the need to “follow up on pharmacies with questionable Part D billing and the prescribers associated with these pharmacies.”
Ms. Anderson said the inspector general’s office is continuing to probe the issue.
“We will investigate a number of leads on specific pharmacies and prescribers who were identified as having these questionable patterns,” she said. “Whenever we see that kind of increase in spending, it raises concern about fraud, waste, and abuse.”
KHN’s coverage of prescription drug development, costs, and pricing is supported in part by the Laura and John Arnold Foundation.
Kaiser Health News (KHN) is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.