User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes: What’s the Link?
TOPLINE:
Patients who undergo surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) may have an increased risk of developing incident diabetes, showed a recent study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Diabetes has been shown to be a risk factor for CTS, the most common entrapment neuropathy, but it remains unclear whether CTS is associated with subsequent diabetes.
- Researchers used data from Danish national registries to evaluate the odds of developing diabetes in 83,466 patients (median age, 54 years; 67% women) who underwent surgery for CTS between January 1996 and December 2018.
- The study compared the risk of developing diabetes in patients who had CTS surgery with that of an age- and sex-matched cohort of individuals from the general population in a 1:5 ratio (n = 417,330).
- Patients were followed (median of 7.6 years) until either a diagnosis of diabetes during hospitalization or a prescription of a glucose-lowering drug, or until either death, emigration, or the end of the study period.
- Cause-specific Cox proportional hazard models were used to compare the odds of developing diabetes between the two groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cumulative incidence of diabetes was higher in the CTS group than in the age-matched controls (16.8% vs 10.3%).
- Patients who underwent surgery for CTS were at a higher risk of developing diabetes within 1 year of surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.72) and during the rest of the study period (> 1 year: HR, 1.66).
- The risk for incident diabetes after CTS surgery was higher among younger patients aged 18-39 years (adjusted HR, 2.77) than among older patients aged 70-79 years (adjusted HR, 1.29).
- Also, patients who had bilateral surgery had a higher risk of developing diabetes than the matched control population (adjusted HR, 1.86).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patients who are at risk of DM [diabetes mellitus] may mediate earlier initiation of preventive strategies. However, other factors, such as obesity and A1c levels, may affect the association,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study led by Jeppe Ravn Jacobsen, MB, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism .
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not find an association between CTS and a future diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, which may be attributed to the fact that patients younger than 18 years were excluded. A proportion of the patients who underwent CTS may have had undetected prediabetes or diabetes at the time of CTS surgery. Moreover, the registry lacked information on potential confounders such as body mass index, smoking history, and blood samples. The association between CTS and diabetes may be attributable to shared risk factors for both, such as obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an internal grant from the Department of Cardiology, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who undergo surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) may have an increased risk of developing incident diabetes, showed a recent study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Diabetes has been shown to be a risk factor for CTS, the most common entrapment neuropathy, but it remains unclear whether CTS is associated with subsequent diabetes.
- Researchers used data from Danish national registries to evaluate the odds of developing diabetes in 83,466 patients (median age, 54 years; 67% women) who underwent surgery for CTS between January 1996 and December 2018.
- The study compared the risk of developing diabetes in patients who had CTS surgery with that of an age- and sex-matched cohort of individuals from the general population in a 1:5 ratio (n = 417,330).
- Patients were followed (median of 7.6 years) until either a diagnosis of diabetes during hospitalization or a prescription of a glucose-lowering drug, or until either death, emigration, or the end of the study period.
- Cause-specific Cox proportional hazard models were used to compare the odds of developing diabetes between the two groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cumulative incidence of diabetes was higher in the CTS group than in the age-matched controls (16.8% vs 10.3%).
- Patients who underwent surgery for CTS were at a higher risk of developing diabetes within 1 year of surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.72) and during the rest of the study period (> 1 year: HR, 1.66).
- The risk for incident diabetes after CTS surgery was higher among younger patients aged 18-39 years (adjusted HR, 2.77) than among older patients aged 70-79 years (adjusted HR, 1.29).
- Also, patients who had bilateral surgery had a higher risk of developing diabetes than the matched control population (adjusted HR, 1.86).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patients who are at risk of DM [diabetes mellitus] may mediate earlier initiation of preventive strategies. However, other factors, such as obesity and A1c levels, may affect the association,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study led by Jeppe Ravn Jacobsen, MB, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism .
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not find an association between CTS and a future diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, which may be attributed to the fact that patients younger than 18 years were excluded. A proportion of the patients who underwent CTS may have had undetected prediabetes or diabetes at the time of CTS surgery. Moreover, the registry lacked information on potential confounders such as body mass index, smoking history, and blood samples. The association between CTS and diabetes may be attributable to shared risk factors for both, such as obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an internal grant from the Department of Cardiology, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who undergo surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) may have an increased risk of developing incident diabetes, showed a recent study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Diabetes has been shown to be a risk factor for CTS, the most common entrapment neuropathy, but it remains unclear whether CTS is associated with subsequent diabetes.
- Researchers used data from Danish national registries to evaluate the odds of developing diabetes in 83,466 patients (median age, 54 years; 67% women) who underwent surgery for CTS between January 1996 and December 2018.
- The study compared the risk of developing diabetes in patients who had CTS surgery with that of an age- and sex-matched cohort of individuals from the general population in a 1:5 ratio (n = 417,330).
- Patients were followed (median of 7.6 years) until either a diagnosis of diabetes during hospitalization or a prescription of a glucose-lowering drug, or until either death, emigration, or the end of the study period.
- Cause-specific Cox proportional hazard models were used to compare the odds of developing diabetes between the two groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cumulative incidence of diabetes was higher in the CTS group than in the age-matched controls (16.8% vs 10.3%).
- Patients who underwent surgery for CTS were at a higher risk of developing diabetes within 1 year of surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.72) and during the rest of the study period (> 1 year: HR, 1.66).
- The risk for incident diabetes after CTS surgery was higher among younger patients aged 18-39 years (adjusted HR, 2.77) than among older patients aged 70-79 years (adjusted HR, 1.29).
- Also, patients who had bilateral surgery had a higher risk of developing diabetes than the matched control population (adjusted HR, 1.86).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patients who are at risk of DM [diabetes mellitus] may mediate earlier initiation of preventive strategies. However, other factors, such as obesity and A1c levels, may affect the association,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study led by Jeppe Ravn Jacobsen, MB, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism .
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not find an association between CTS and a future diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, which may be attributed to the fact that patients younger than 18 years were excluded. A proportion of the patients who underwent CTS may have had undetected prediabetes or diabetes at the time of CTS surgery. Moreover, the registry lacked information on potential confounders such as body mass index, smoking history, and blood samples. The association between CTS and diabetes may be attributable to shared risk factors for both, such as obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by an internal grant from the Department of Cardiology, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What Do Sex Therapists Do? (Hint: It’s Not What You Think)
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Acne in Transmasculine Patients: Management Recommendations
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , a dermatologist told colleagues in a session at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In these patients, treatment of acne is crucial, said Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta. “These are patients who are suffering and reporting that they’re having mental health impacts” related to acne.
In transmasculine patients — those who were biologically female at birth but identify as masculine — testosterone therapy greatly boosts the risk for acne, even in adults who are long past adolescence, Dr. Yeung said. Data suggest that acne appears within the first 6 months after testosterone therapy begins, he said, “and the maximal and complete effect occurs within 1-2 years.”
A 2021 study tracked 988 transgender patients receiving testosterone at Fenway Health in Boston and found that 31% had a diagnosis of acne, up from 6.3% prior to taking hormones. And 2 years following the start of therapy, 25.1% had acne, with cases especially common among those aged 18-20.75 years (29.6%). Even among those aged 28.25-66.5 years, 17.1% had acne.
Transmasculine patients may develop acne in areas across the body “in places that you normally won’t see by just looking at the patient,” Dr. Yeung said. Excoriation in addition to comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules can be common, he added.
Dr. Yeung highlighted a 2019 study of transgender men that linked higher levels of acne to higher levels of serum testosterone, higher body mass index, and current smoking. And in a 2014 study, 6% of 50 transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne after an average of 10 years on testosterone therapy.
A 2020 study of 696 transgender adults surveyed in California and Georgia found that 14% of transmasculine patients had moderate to severe acne — two thirds attributed it to hormone therapy — vs 1% of transfeminine patients, said Dr. Yeung, the lead author of the study. However, transmasculine patients were less likely to have seen a dermatologist.
Dr. Yeung also highlighted a 2021 study he coauthored that linked current moderate to severe acne in transmasculine patients taking testosterone to higher levels of depression and anxiety vs counterparts who had never had those forms of acne.
Another factor affecting acne in transmasculine patients is the use of chest binders to reduce breast size. “Wearing a chest binder is really helpful for a lot of our patients and is associated with improved self-esteem, mood, mental health, and safety in public,” Dr. Yeung said. However, the binders can contribute to skin problems.
Dr. Yeung said he and his colleagues emphasize the importance of breathable material in binders and suggest to patients that they not wear them when they’re in “safe spaces.”
Isotretinoin, Contraception Considerations
As for treatment of acne in transgender patients, Dr. Yeung cautioned colleagues to not automatically reject isotretinoin as an option for transgender patients who have a history of depression. Dermatologists may be tempted to avoid the drug in these patients because of its link to suicide, he said. (This apparent association has long been debated.) But, Dr. Yeung said, it’s important to consider that many of these patients suffered from anxiety and depression because of the lack of access to proper gender-reassignment treatment.
When using isotretinoin, he emphasized, it’s crucial to consider whether transmasculine patients could become pregnant while on this therapy. Consider whether the patient has the organs needed to become pregnant and ask questions about the potential that they could be impregnated.
“Remember that sexual behavior is different from gender identity,” Dr. Yeung said. A transmasculine person with a uterus and vagina, for example, may still have vaginal intercourse with males and potentially become pregnant. “So, we need to assess what kind of sexual behavior our patients are taking part in.”
Contraceptives such as intrauterine devices, implants, and injectable options may be helpful for transmasculine patients because they can reduce menstrual symptoms like spotting that can be distressing to them, he said. By helping a patient take a contraceptive, “you may actually be helping with their gender dysphoria and helping them get on isotretinoin.”
Dr. Yeung disclosed fees from JAMA and American Academy of Dermatology; grants/research funding from the American Acne & Rosacea Society, Dermatology Foundation, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Eczema Association, and National Institutes of Health; and speaker/faculty education honoraria from Dermatology Digest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Debate Arises Over Ovarian Tissue Transplants to Delay Menopause
The transplantation of ovarian tissue is often performed to extend fertility among women and adolescents with cancer. But some reproductive specialists believe the procedure may have another role to play with much wider application: delaying, or even preventing, menopause in healthy women.
Kutluk Oktay, MD, director of the Laboratory of Molecular Reproduction and Fertility Preservation at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, has used ovarian tissue transplantation (OTT) in his own practice — Innovation Fertility Preservation & IVF — for several years. He said the approach can reduce health risks associated with menopause, such as the loss of bone density and cardiovascular disease.
“We have started offering [ovarian tissue transplantation] in carefully selected candidates, but the pace will accelerate now that we have a way to better inform the candidates on the potential of the procedure,” Dr. Oktay said. To date, he said he has performed the procedure on approximately 20 patients.
But Dr. Oktay’s vision of the future for OTT remains on the fringe of reproductive medicine.
“I think there are ethical considerations to take into account here,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, Medical Director for the North American Menopause Society. “You’re taking a perfectly healthy 25- to 30-year-old woman and putting her through surgery to take out a healthy organ. Let’s just think about that.”
The Promise and Risks of OTT
OTT involves removing part of the ovarian tissue, cryopreservation, and then transplanting it back into the body. The procedure has reversed early menopause in women who underwent cancer treatment and resulted in over 140 live births worldwide.
Dr. Oktay recently published a nonclinical study in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology using a mathematical model based on decades of clinical research on cancer patients and ovarian follicle counts in cadaver to forecast how OTT can delay the onset of menopause through restored ovarian function and hormonal shifts.
The model forecasts a delay in menopause of up to 47 years, depending on factors such as the age of tissue removal, a woman’s ovarian reserve, and an estimated number of primordial follicles — where tens to hundreds of thousands of undeveloped eggs can live — that survive the process of removal, freezing, and reimplantation.
OTT is currently associated with a survival rate of 40% for follicles, Dr. Oktay said. But technological advancements, including revascularization drugs and robotic surgery, are likely to extend the survival rate to 80% by the time reimplantation occurs, potentially 15-20 years after tissue removal, he said.
Prospective patients at Dr. Oktay’s practice can use an interactive tool to receive an estimate of their potential menopausal delay. Patients receive a clinical assessment, including tests for ovarian reserve markers, to determine their potential for the procedure.
The model predicted that harvesting tissue before age 30 could delay menopause significantly. A 25-year-old woman with an average ovarian reserve who preserved a quarter of one ovary would have a delay in menopause of 11.8 years if 40% of the follicles survived. Women around age 40, and especially those with a low ovarian reserve, would need a follicle survival rate of close to 100% to result in a delay significant enough to justify the procedure.
The procedure also comes with risks. Removing ovarian tissue can bring on early menopause, Dr. Oktay said. Removing part or all of the ovarian cortex — the outer part of the ovary that contains the follicles — can start menopause about 1.5 years earlier. But as long as the tissue is transplanted, a woman would gain many more years of fertility before menopause.
While potentially promising, some obstetrics and gynecology experts question the procedure, with no proven benefits.
“While theoretically possible, my biggest question is, how is this better than egg freezing in your 20s or 30s combined with hormone replacement for the aging benefits, given the risks associated with potentially multiple surgeries?” said Paula Amato, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Any risks associated with receiving hormone therapy through OTT rather than traditional hormone replacement therapy are also unknown, Dr. Amato said.
A UK clinic, ProFam, based in Birmingham, also offered the procedure but faced criticism in 2020 for being unnecessary and experimental. This news organization could not confirm if the clinic is still in operation.
Why Delay Menopause?
While the procedure may extend fertility, the goal of the procedure is not to enable patients to become pregnant at ages that are not safe, Dr. Oktay said. Rather, he said postponing menopause is medically beneficial.
Some research shows that women who have late menopause have a lower risk for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease but a higher risk for breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers.
Dr. Oktay said that delaying menopause could improve the quality of life for women by reducing menopausal symptoms like anxiety and depression. Clinicians could also use the procedure as preventive care for those who are at high risk for conditions associated with menopause, such as osteoporosis and dementia.
But Dr. Faubion is unconvinced that delaying menopause through OTT carries health benefits.
“Just because we can do this, should we?” she said. “And will it do the things that we think it will? Does preventing or delaying menopause delay the aging process? I think that’s what they’re trying to imply, and we don’t have evidence that that’s true.”
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation, U-Anschutz Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research Funds, SF Faculty Early Career Development Program, and the National Institutes of Health awards. The authors reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The transplantation of ovarian tissue is often performed to extend fertility among women and adolescents with cancer. But some reproductive specialists believe the procedure may have another role to play with much wider application: delaying, or even preventing, menopause in healthy women.
Kutluk Oktay, MD, director of the Laboratory of Molecular Reproduction and Fertility Preservation at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, has used ovarian tissue transplantation (OTT) in his own practice — Innovation Fertility Preservation & IVF — for several years. He said the approach can reduce health risks associated with menopause, such as the loss of bone density and cardiovascular disease.
“We have started offering [ovarian tissue transplantation] in carefully selected candidates, but the pace will accelerate now that we have a way to better inform the candidates on the potential of the procedure,” Dr. Oktay said. To date, he said he has performed the procedure on approximately 20 patients.
But Dr. Oktay’s vision of the future for OTT remains on the fringe of reproductive medicine.
“I think there are ethical considerations to take into account here,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, Medical Director for the North American Menopause Society. “You’re taking a perfectly healthy 25- to 30-year-old woman and putting her through surgery to take out a healthy organ. Let’s just think about that.”
The Promise and Risks of OTT
OTT involves removing part of the ovarian tissue, cryopreservation, and then transplanting it back into the body. The procedure has reversed early menopause in women who underwent cancer treatment and resulted in over 140 live births worldwide.
Dr. Oktay recently published a nonclinical study in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology using a mathematical model based on decades of clinical research on cancer patients and ovarian follicle counts in cadaver to forecast how OTT can delay the onset of menopause through restored ovarian function and hormonal shifts.
The model forecasts a delay in menopause of up to 47 years, depending on factors such as the age of tissue removal, a woman’s ovarian reserve, and an estimated number of primordial follicles — where tens to hundreds of thousands of undeveloped eggs can live — that survive the process of removal, freezing, and reimplantation.
OTT is currently associated with a survival rate of 40% for follicles, Dr. Oktay said. But technological advancements, including revascularization drugs and robotic surgery, are likely to extend the survival rate to 80% by the time reimplantation occurs, potentially 15-20 years after tissue removal, he said.
Prospective patients at Dr. Oktay’s practice can use an interactive tool to receive an estimate of their potential menopausal delay. Patients receive a clinical assessment, including tests for ovarian reserve markers, to determine their potential for the procedure.
The model predicted that harvesting tissue before age 30 could delay menopause significantly. A 25-year-old woman with an average ovarian reserve who preserved a quarter of one ovary would have a delay in menopause of 11.8 years if 40% of the follicles survived. Women around age 40, and especially those with a low ovarian reserve, would need a follicle survival rate of close to 100% to result in a delay significant enough to justify the procedure.
The procedure also comes with risks. Removing ovarian tissue can bring on early menopause, Dr. Oktay said. Removing part or all of the ovarian cortex — the outer part of the ovary that contains the follicles — can start menopause about 1.5 years earlier. But as long as the tissue is transplanted, a woman would gain many more years of fertility before menopause.
While potentially promising, some obstetrics and gynecology experts question the procedure, with no proven benefits.
“While theoretically possible, my biggest question is, how is this better than egg freezing in your 20s or 30s combined with hormone replacement for the aging benefits, given the risks associated with potentially multiple surgeries?” said Paula Amato, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Any risks associated with receiving hormone therapy through OTT rather than traditional hormone replacement therapy are also unknown, Dr. Amato said.
A UK clinic, ProFam, based in Birmingham, also offered the procedure but faced criticism in 2020 for being unnecessary and experimental. This news organization could not confirm if the clinic is still in operation.
Why Delay Menopause?
While the procedure may extend fertility, the goal of the procedure is not to enable patients to become pregnant at ages that are not safe, Dr. Oktay said. Rather, he said postponing menopause is medically beneficial.
Some research shows that women who have late menopause have a lower risk for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease but a higher risk for breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers.
Dr. Oktay said that delaying menopause could improve the quality of life for women by reducing menopausal symptoms like anxiety and depression. Clinicians could also use the procedure as preventive care for those who are at high risk for conditions associated with menopause, such as osteoporosis and dementia.
But Dr. Faubion is unconvinced that delaying menopause through OTT carries health benefits.
“Just because we can do this, should we?” she said. “And will it do the things that we think it will? Does preventing or delaying menopause delay the aging process? I think that’s what they’re trying to imply, and we don’t have evidence that that’s true.”
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation, U-Anschutz Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research Funds, SF Faculty Early Career Development Program, and the National Institutes of Health awards. The authors reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The transplantation of ovarian tissue is often performed to extend fertility among women and adolescents with cancer. But some reproductive specialists believe the procedure may have another role to play with much wider application: delaying, or even preventing, menopause in healthy women.
Kutluk Oktay, MD, director of the Laboratory of Molecular Reproduction and Fertility Preservation at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, has used ovarian tissue transplantation (OTT) in his own practice — Innovation Fertility Preservation & IVF — for several years. He said the approach can reduce health risks associated with menopause, such as the loss of bone density and cardiovascular disease.
“We have started offering [ovarian tissue transplantation] in carefully selected candidates, but the pace will accelerate now that we have a way to better inform the candidates on the potential of the procedure,” Dr. Oktay said. To date, he said he has performed the procedure on approximately 20 patients.
But Dr. Oktay’s vision of the future for OTT remains on the fringe of reproductive medicine.
“I think there are ethical considerations to take into account here,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, Medical Director for the North American Menopause Society. “You’re taking a perfectly healthy 25- to 30-year-old woman and putting her through surgery to take out a healthy organ. Let’s just think about that.”
The Promise and Risks of OTT
OTT involves removing part of the ovarian tissue, cryopreservation, and then transplanting it back into the body. The procedure has reversed early menopause in women who underwent cancer treatment and resulted in over 140 live births worldwide.
Dr. Oktay recently published a nonclinical study in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology using a mathematical model based on decades of clinical research on cancer patients and ovarian follicle counts in cadaver to forecast how OTT can delay the onset of menopause through restored ovarian function and hormonal shifts.
The model forecasts a delay in menopause of up to 47 years, depending on factors such as the age of tissue removal, a woman’s ovarian reserve, and an estimated number of primordial follicles — where tens to hundreds of thousands of undeveloped eggs can live — that survive the process of removal, freezing, and reimplantation.
OTT is currently associated with a survival rate of 40% for follicles, Dr. Oktay said. But technological advancements, including revascularization drugs and robotic surgery, are likely to extend the survival rate to 80% by the time reimplantation occurs, potentially 15-20 years after tissue removal, he said.
Prospective patients at Dr. Oktay’s practice can use an interactive tool to receive an estimate of their potential menopausal delay. Patients receive a clinical assessment, including tests for ovarian reserve markers, to determine their potential for the procedure.
The model predicted that harvesting tissue before age 30 could delay menopause significantly. A 25-year-old woman with an average ovarian reserve who preserved a quarter of one ovary would have a delay in menopause of 11.8 years if 40% of the follicles survived. Women around age 40, and especially those with a low ovarian reserve, would need a follicle survival rate of close to 100% to result in a delay significant enough to justify the procedure.
The procedure also comes with risks. Removing ovarian tissue can bring on early menopause, Dr. Oktay said. Removing part or all of the ovarian cortex — the outer part of the ovary that contains the follicles — can start menopause about 1.5 years earlier. But as long as the tissue is transplanted, a woman would gain many more years of fertility before menopause.
While potentially promising, some obstetrics and gynecology experts question the procedure, with no proven benefits.
“While theoretically possible, my biggest question is, how is this better than egg freezing in your 20s or 30s combined with hormone replacement for the aging benefits, given the risks associated with potentially multiple surgeries?” said Paula Amato, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Any risks associated with receiving hormone therapy through OTT rather than traditional hormone replacement therapy are also unknown, Dr. Amato said.
A UK clinic, ProFam, based in Birmingham, also offered the procedure but faced criticism in 2020 for being unnecessary and experimental. This news organization could not confirm if the clinic is still in operation.
Why Delay Menopause?
While the procedure may extend fertility, the goal of the procedure is not to enable patients to become pregnant at ages that are not safe, Dr. Oktay said. Rather, he said postponing menopause is medically beneficial.
Some research shows that women who have late menopause have a lower risk for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease but a higher risk for breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers.
Dr. Oktay said that delaying menopause could improve the quality of life for women by reducing menopausal symptoms like anxiety and depression. Clinicians could also use the procedure as preventive care for those who are at high risk for conditions associated with menopause, such as osteoporosis and dementia.
But Dr. Faubion is unconvinced that delaying menopause through OTT carries health benefits.
“Just because we can do this, should we?” she said. “And will it do the things that we think it will? Does preventing or delaying menopause delay the aging process? I think that’s what they’re trying to imply, and we don’t have evidence that that’s true.”
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation, U-Anschutz Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research Funds, SF Faculty Early Career Development Program, and the National Institutes of Health awards. The authors reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Clock Watchers
The following scenario was discussed during a forum at a meeting recently:
Two employees managing the front desk are clock watchers, always the first to leave at 11:59 a.m. for lunch and at 4:59 p.m. for the end of the day no matter what is happening. This leaves the other employees stuck with their work.
I have seen clock watching often enough to know that it is widely practiced, and widely reviled by coworkers and managers alike. Generally, clock watchers — sometimes referred to in modern parlance as “quiet quitters” — radiate a palpable sense of “I don’t want to be here.”
; if that involves working past the usual “quitting time,” so be it. So your first task in dealing with this problem is to determine its cause. The clock watcher label may be unfair. There may be legitimate reasons for certain employees to leave work at precisely 4:59 every day. Perhaps they must pick up children, or they have a second job to get to. The label usually comes from a pattern of consistent, repeated behavior. And if more than one employee is exhibiting the same behavior in the same office, the likelihood of a valid explanation decreases proportionally.
A common cause of clock watching is a lack of employees’ commitment to their jobs. They don’t see the point in putting in extra effort, so they run out the door as soon as possible. There are many reasons why this might be the case. For example, the workload in your office may be too large to be accomplished in the time available by the number of people you employ. The solution might be to simply hire additional personnel.
Another common cause is a lack of communication between physicians, managers, and lower-level employees. If staffers are raising concerns or potential solutions, and management is not listening to their opinions or ideas, they will stop offering them. Alternatively, other staff members may not be pulling their weight. When there is a large imbalance in the contribution of team members, the higher performers will stop trying.
Over my 40 plus years in practice, I have had my share of clock watchers. I try the best I can not to let employees’ time commitment practices impact my valuation of their work. I always attempt to focus on quality and productivity. It isn’t easy, but I always try to address the issues behind clock watching behavior. As such, I can’t recall ever having to fire anyone for clock watching. Here are some of the strategies that have worked for me over the years:
1. Set clear expectations. Clearly communicate job responsibilities and expectations regarding time management and patient care. Ensure that all staff understand the importance of dedicating the necessary time to each patient, regardless of the time of day.
2. Foster a patient-centered culture. Cultivate a work environment that prioritizes patient care above all. This can help shift the focus from watching the clock to ensuring high-quality patient care.
3. Provide adequate breaks. Ensure that staff schedules include sufficient breaks. Overworked staff are more likely to watch the clock. Adequate rest periods can help alleviate this issue.
4. Offer flexibility where possible. If feasible, offer some degree of scheduling flexibility. This can help staff manage their personal time more effectively, potentially reducing the tendency to watch the clock.
5. Implement time management training. Offer training sessions focused on time management and efficiency. This can help staff manage their duties more effectively, reducing the need to constantly check the time.
6. Encourage open communication. Create an environment where staff feel comfortable discussing their concerns, including issues related to workload and time management. This can help identify and address specific factors contributing to clock watching.
7. Monitor and provide feedback. Regularly monitor staff performance and provide constructive feedback. If clock watching is observed, discuss it directly with the employee, focusing on the impact on patient care and the work environment.
8. Recognize and reward. Acknowledge and reward staff who consistently provide high-quality care and demonstrate effective time management. Recognition can motivate others to adjust their behavior.
9. Evaluate workloads. Regularly assess staff workloads to ensure they are manageable. Overburdened employees are more likely to engage in clock watching.
10. Lead by example. Management should model the behavior they wish to see in their staff. Demonstrating a commitment to patient care and effective time management can set a positive example.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The following scenario was discussed during a forum at a meeting recently:
Two employees managing the front desk are clock watchers, always the first to leave at 11:59 a.m. for lunch and at 4:59 p.m. for the end of the day no matter what is happening. This leaves the other employees stuck with their work.
I have seen clock watching often enough to know that it is widely practiced, and widely reviled by coworkers and managers alike. Generally, clock watchers — sometimes referred to in modern parlance as “quiet quitters” — radiate a palpable sense of “I don’t want to be here.”
; if that involves working past the usual “quitting time,” so be it. So your first task in dealing with this problem is to determine its cause. The clock watcher label may be unfair. There may be legitimate reasons for certain employees to leave work at precisely 4:59 every day. Perhaps they must pick up children, or they have a second job to get to. The label usually comes from a pattern of consistent, repeated behavior. And if more than one employee is exhibiting the same behavior in the same office, the likelihood of a valid explanation decreases proportionally.
A common cause of clock watching is a lack of employees’ commitment to their jobs. They don’t see the point in putting in extra effort, so they run out the door as soon as possible. There are many reasons why this might be the case. For example, the workload in your office may be too large to be accomplished in the time available by the number of people you employ. The solution might be to simply hire additional personnel.
Another common cause is a lack of communication between physicians, managers, and lower-level employees. If staffers are raising concerns or potential solutions, and management is not listening to their opinions or ideas, they will stop offering them. Alternatively, other staff members may not be pulling their weight. When there is a large imbalance in the contribution of team members, the higher performers will stop trying.
Over my 40 plus years in practice, I have had my share of clock watchers. I try the best I can not to let employees’ time commitment practices impact my valuation of their work. I always attempt to focus on quality and productivity. It isn’t easy, but I always try to address the issues behind clock watching behavior. As such, I can’t recall ever having to fire anyone for clock watching. Here are some of the strategies that have worked for me over the years:
1. Set clear expectations. Clearly communicate job responsibilities and expectations regarding time management and patient care. Ensure that all staff understand the importance of dedicating the necessary time to each patient, regardless of the time of day.
2. Foster a patient-centered culture. Cultivate a work environment that prioritizes patient care above all. This can help shift the focus from watching the clock to ensuring high-quality patient care.
3. Provide adequate breaks. Ensure that staff schedules include sufficient breaks. Overworked staff are more likely to watch the clock. Adequate rest periods can help alleviate this issue.
4. Offer flexibility where possible. If feasible, offer some degree of scheduling flexibility. This can help staff manage their personal time more effectively, potentially reducing the tendency to watch the clock.
5. Implement time management training. Offer training sessions focused on time management and efficiency. This can help staff manage their duties more effectively, reducing the need to constantly check the time.
6. Encourage open communication. Create an environment where staff feel comfortable discussing their concerns, including issues related to workload and time management. This can help identify and address specific factors contributing to clock watching.
7. Monitor and provide feedback. Regularly monitor staff performance and provide constructive feedback. If clock watching is observed, discuss it directly with the employee, focusing on the impact on patient care and the work environment.
8. Recognize and reward. Acknowledge and reward staff who consistently provide high-quality care and demonstrate effective time management. Recognition can motivate others to adjust their behavior.
9. Evaluate workloads. Regularly assess staff workloads to ensure they are manageable. Overburdened employees are more likely to engage in clock watching.
10. Lead by example. Management should model the behavior they wish to see in their staff. Demonstrating a commitment to patient care and effective time management can set a positive example.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The following scenario was discussed during a forum at a meeting recently:
Two employees managing the front desk are clock watchers, always the first to leave at 11:59 a.m. for lunch and at 4:59 p.m. for the end of the day no matter what is happening. This leaves the other employees stuck with their work.
I have seen clock watching often enough to know that it is widely practiced, and widely reviled by coworkers and managers alike. Generally, clock watchers — sometimes referred to in modern parlance as “quiet quitters” — radiate a palpable sense of “I don’t want to be here.”
; if that involves working past the usual “quitting time,” so be it. So your first task in dealing with this problem is to determine its cause. The clock watcher label may be unfair. There may be legitimate reasons for certain employees to leave work at precisely 4:59 every day. Perhaps they must pick up children, or they have a second job to get to. The label usually comes from a pattern of consistent, repeated behavior. And if more than one employee is exhibiting the same behavior in the same office, the likelihood of a valid explanation decreases proportionally.
A common cause of clock watching is a lack of employees’ commitment to their jobs. They don’t see the point in putting in extra effort, so they run out the door as soon as possible. There are many reasons why this might be the case. For example, the workload in your office may be too large to be accomplished in the time available by the number of people you employ. The solution might be to simply hire additional personnel.
Another common cause is a lack of communication between physicians, managers, and lower-level employees. If staffers are raising concerns or potential solutions, and management is not listening to their opinions or ideas, they will stop offering them. Alternatively, other staff members may not be pulling their weight. When there is a large imbalance in the contribution of team members, the higher performers will stop trying.
Over my 40 plus years in practice, I have had my share of clock watchers. I try the best I can not to let employees’ time commitment practices impact my valuation of their work. I always attempt to focus on quality and productivity. It isn’t easy, but I always try to address the issues behind clock watching behavior. As such, I can’t recall ever having to fire anyone for clock watching. Here are some of the strategies that have worked for me over the years:
1. Set clear expectations. Clearly communicate job responsibilities and expectations regarding time management and patient care. Ensure that all staff understand the importance of dedicating the necessary time to each patient, regardless of the time of day.
2. Foster a patient-centered culture. Cultivate a work environment that prioritizes patient care above all. This can help shift the focus from watching the clock to ensuring high-quality patient care.
3. Provide adequate breaks. Ensure that staff schedules include sufficient breaks. Overworked staff are more likely to watch the clock. Adequate rest periods can help alleviate this issue.
4. Offer flexibility where possible. If feasible, offer some degree of scheduling flexibility. This can help staff manage their personal time more effectively, potentially reducing the tendency to watch the clock.
5. Implement time management training. Offer training sessions focused on time management and efficiency. This can help staff manage their duties more effectively, reducing the need to constantly check the time.
6. Encourage open communication. Create an environment where staff feel comfortable discussing their concerns, including issues related to workload and time management. This can help identify and address specific factors contributing to clock watching.
7. Monitor and provide feedback. Regularly monitor staff performance and provide constructive feedback. If clock watching is observed, discuss it directly with the employee, focusing on the impact on patient care and the work environment.
8. Recognize and reward. Acknowledge and reward staff who consistently provide high-quality care and demonstrate effective time management. Recognition can motivate others to adjust their behavior.
9. Evaluate workloads. Regularly assess staff workloads to ensure they are manageable. Overburdened employees are more likely to engage in clock watching.
10. Lead by example. Management should model the behavior they wish to see in their staff. Demonstrating a commitment to patient care and effective time management can set a positive example.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Weight Loss in Later-Life Women: More Than Diet, Exercise
Unwanted weight gain is a common problem for women after menopause. Primary care clinicians have likely heard from patients that attempts at shedding extra pounds are not working.
Aging does: Women gain about 1.5 pounds per year on average starting almost a decade prior to menopause to a decade after their final menstrual cycle, according to research.
“A lot of women are in tears because they have gained 10 or 15 pounds,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of The Menopause Society and director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
A shortage of obesity and menopause specialists means primary care clinicians must understand the intersection of weight management and how the body functions after menopause.
“The importance of weight management in midlife cannot be overemphasized,” Dr. Faubion said. “Excess weight around the middle increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease and that is directly related to the loss of estrogen.”
The loss of estrogen due to menopause also causes the redistribution of fat from the thighs, hips, and buttocks to the midsection, which can be more difficult to trim. And women naturally lose muscle mass as they age, in part because the hormone is important to muscle functioning, according to Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in Jacksonville, Florida.
“Menopause compounds the changes associated with aging: It makes them worse,” Dr. Hurtado Andrade said.
Mounting evidence has linked obesity-related systemic inflammation with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and vascular damage.
Michael Knight, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine and a weight loss specialist at the George Washington University in Washington, DC, estimated that more than half of his patients are postmenopausal women.
He recommended clinicians look for adipose tissue dysfunction, which can cause localized insulin resistance and affect metabolic health. Research suggests clinicians can perform a basic metabolic panel, in addition to testing for triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein, and renal function levels. Several other recent studies have pointed to using waist circumference, insulin resistance, or presence of metabolic syndrome to diagnose adipose tissue dysfunction.
Beyond Diet and Exercise
Physicians should ask their patients about physical activity, the type of foods they are eating, and changes in day-to-day movement, Dr. Knight advised.
Pharmacotherapy or surgical options should be considered for some patients, according to Karen Adams, MD, clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology and a lifestyle medicine specialist at Stanford Medicine in Palo Alto, California. Postmenopausal women who want to lose more than 5%-10% of their body weight likely will need another modality in addition to diet and exercise.
“What’s important is transitioning the patient from feeling like they’ve failed to a mindset of seeking help or seeking care for this condition,” she said. Dr. Adams, a certified menopause specialist, uses the idea of “good enough” with her patients and suggests they think of weight loss as a journey, which may require different tools at various points.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or tirzepatide are some of the most effective drugs for obesity, according to Dr. Knight.
In addition to these drugs, hormone replacement therapy in combination with the weight loss drug semaglutide may improve weight loss and reduce cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women compared with semaglutide alone, as reported in a study Dr. Hurtado Andrade and Dr. Faubion recently coauthored. Improving vasomotor symptoms improved sleep, physical activity, and quality of life, which all can affect efforts to lose weight.
Most patients who struggle to lose weight using diet and exercise methods alone usually do not maintain a healthy weight long term, according to Knight. Physicians need a comprehensive strategy to introduce options like medications or surgery when indicated for long-term, weight management solutions.
Tips for primary care clinicians in helping postmenopausal women lose weight:
- Develop an effective solution that works for your patient’s lifestyle. If you don’t have one, make a referral to a weight loss specialist.
- Educate patients about obesity and postmenopausal weight loss challenges, to help destigmatize the condition. Explain that obesity is a chronic disease, like hypertension or diabetes.
- Exercise suggestions should consider issues like walkable neighborhoods, access and affordability of gym membership, and home broadband access.
- Strength training should be recommended to counter loss of muscle mass that comes with aging.
- Consider a patient’s culture when discussing healthier alternatives to their usual diet.
- Suggest simple changes to start, like eliminating simple carbohydrates — white bread, pasta, and white rice — as a good place to start.
Body mass index was not designed to be a clinical tool and does not fully assess weight in many populations. Risk for chronic diseases and obesity varies depending on whether a person carries weight centrally or on the hips and thighs.
But well before menopause, clinicians can educate their female patients on what body changes to expect and be more mindful about which medications to not prescribe.
People in menopause or perimenopause are frequently prescribed weight-promoting drugs like antidepressants for mood swings or gabapentin for hot flashes. Clinicians should conduct a medication review and look for alternatives to drugs that are associated with weight gain.
The best approach is to try to avoid weight gain in the first place, which can be easier than trying to lose later, Dr. Faubion said. “You can’t just exercise your way out of it,” she said.
Dr. Adams, Dr. Faubion, and Dr. Hurtado Andrade reported no disclosures. Dr. Knight is a former consultant with Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unwanted weight gain is a common problem for women after menopause. Primary care clinicians have likely heard from patients that attempts at shedding extra pounds are not working.
Aging does: Women gain about 1.5 pounds per year on average starting almost a decade prior to menopause to a decade after their final menstrual cycle, according to research.
“A lot of women are in tears because they have gained 10 or 15 pounds,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of The Menopause Society and director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
A shortage of obesity and menopause specialists means primary care clinicians must understand the intersection of weight management and how the body functions after menopause.
“The importance of weight management in midlife cannot be overemphasized,” Dr. Faubion said. “Excess weight around the middle increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease and that is directly related to the loss of estrogen.”
The loss of estrogen due to menopause also causes the redistribution of fat from the thighs, hips, and buttocks to the midsection, which can be more difficult to trim. And women naturally lose muscle mass as they age, in part because the hormone is important to muscle functioning, according to Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in Jacksonville, Florida.
“Menopause compounds the changes associated with aging: It makes them worse,” Dr. Hurtado Andrade said.
Mounting evidence has linked obesity-related systemic inflammation with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and vascular damage.
Michael Knight, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine and a weight loss specialist at the George Washington University in Washington, DC, estimated that more than half of his patients are postmenopausal women.
He recommended clinicians look for adipose tissue dysfunction, which can cause localized insulin resistance and affect metabolic health. Research suggests clinicians can perform a basic metabolic panel, in addition to testing for triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein, and renal function levels. Several other recent studies have pointed to using waist circumference, insulin resistance, or presence of metabolic syndrome to diagnose adipose tissue dysfunction.
Beyond Diet and Exercise
Physicians should ask their patients about physical activity, the type of foods they are eating, and changes in day-to-day movement, Dr. Knight advised.
Pharmacotherapy or surgical options should be considered for some patients, according to Karen Adams, MD, clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology and a lifestyle medicine specialist at Stanford Medicine in Palo Alto, California. Postmenopausal women who want to lose more than 5%-10% of their body weight likely will need another modality in addition to diet and exercise.
“What’s important is transitioning the patient from feeling like they’ve failed to a mindset of seeking help or seeking care for this condition,” she said. Dr. Adams, a certified menopause specialist, uses the idea of “good enough” with her patients and suggests they think of weight loss as a journey, which may require different tools at various points.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or tirzepatide are some of the most effective drugs for obesity, according to Dr. Knight.
In addition to these drugs, hormone replacement therapy in combination with the weight loss drug semaglutide may improve weight loss and reduce cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women compared with semaglutide alone, as reported in a study Dr. Hurtado Andrade and Dr. Faubion recently coauthored. Improving vasomotor symptoms improved sleep, physical activity, and quality of life, which all can affect efforts to lose weight.
Most patients who struggle to lose weight using diet and exercise methods alone usually do not maintain a healthy weight long term, according to Knight. Physicians need a comprehensive strategy to introduce options like medications or surgery when indicated for long-term, weight management solutions.
Tips for primary care clinicians in helping postmenopausal women lose weight:
- Develop an effective solution that works for your patient’s lifestyle. If you don’t have one, make a referral to a weight loss specialist.
- Educate patients about obesity and postmenopausal weight loss challenges, to help destigmatize the condition. Explain that obesity is a chronic disease, like hypertension or diabetes.
- Exercise suggestions should consider issues like walkable neighborhoods, access and affordability of gym membership, and home broadband access.
- Strength training should be recommended to counter loss of muscle mass that comes with aging.
- Consider a patient’s culture when discussing healthier alternatives to their usual diet.
- Suggest simple changes to start, like eliminating simple carbohydrates — white bread, pasta, and white rice — as a good place to start.
Body mass index was not designed to be a clinical tool and does not fully assess weight in many populations. Risk for chronic diseases and obesity varies depending on whether a person carries weight centrally or on the hips and thighs.
But well before menopause, clinicians can educate their female patients on what body changes to expect and be more mindful about which medications to not prescribe.
People in menopause or perimenopause are frequently prescribed weight-promoting drugs like antidepressants for mood swings or gabapentin for hot flashes. Clinicians should conduct a medication review and look for alternatives to drugs that are associated with weight gain.
The best approach is to try to avoid weight gain in the first place, which can be easier than trying to lose later, Dr. Faubion said. “You can’t just exercise your way out of it,” she said.
Dr. Adams, Dr. Faubion, and Dr. Hurtado Andrade reported no disclosures. Dr. Knight is a former consultant with Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unwanted weight gain is a common problem for women after menopause. Primary care clinicians have likely heard from patients that attempts at shedding extra pounds are not working.
Aging does: Women gain about 1.5 pounds per year on average starting almost a decade prior to menopause to a decade after their final menstrual cycle, according to research.
“A lot of women are in tears because they have gained 10 or 15 pounds,” said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of The Menopause Society and director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
A shortage of obesity and menopause specialists means primary care clinicians must understand the intersection of weight management and how the body functions after menopause.
“The importance of weight management in midlife cannot be overemphasized,” Dr. Faubion said. “Excess weight around the middle increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease and that is directly related to the loss of estrogen.”
The loss of estrogen due to menopause also causes the redistribution of fat from the thighs, hips, and buttocks to the midsection, which can be more difficult to trim. And women naturally lose muscle mass as they age, in part because the hormone is important to muscle functioning, according to Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in Jacksonville, Florida.
“Menopause compounds the changes associated with aging: It makes them worse,” Dr. Hurtado Andrade said.
Mounting evidence has linked obesity-related systemic inflammation with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and vascular damage.
Michael Knight, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine and a weight loss specialist at the George Washington University in Washington, DC, estimated that more than half of his patients are postmenopausal women.
He recommended clinicians look for adipose tissue dysfunction, which can cause localized insulin resistance and affect metabolic health. Research suggests clinicians can perform a basic metabolic panel, in addition to testing for triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein, and renal function levels. Several other recent studies have pointed to using waist circumference, insulin resistance, or presence of metabolic syndrome to diagnose adipose tissue dysfunction.
Beyond Diet and Exercise
Physicians should ask their patients about physical activity, the type of foods they are eating, and changes in day-to-day movement, Dr. Knight advised.
Pharmacotherapy or surgical options should be considered for some patients, according to Karen Adams, MD, clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology and a lifestyle medicine specialist at Stanford Medicine in Palo Alto, California. Postmenopausal women who want to lose more than 5%-10% of their body weight likely will need another modality in addition to diet and exercise.
“What’s important is transitioning the patient from feeling like they’ve failed to a mindset of seeking help or seeking care for this condition,” she said. Dr. Adams, a certified menopause specialist, uses the idea of “good enough” with her patients and suggests they think of weight loss as a journey, which may require different tools at various points.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or tirzepatide are some of the most effective drugs for obesity, according to Dr. Knight.
In addition to these drugs, hormone replacement therapy in combination with the weight loss drug semaglutide may improve weight loss and reduce cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women compared with semaglutide alone, as reported in a study Dr. Hurtado Andrade and Dr. Faubion recently coauthored. Improving vasomotor symptoms improved sleep, physical activity, and quality of life, which all can affect efforts to lose weight.
Most patients who struggle to lose weight using diet and exercise methods alone usually do not maintain a healthy weight long term, according to Knight. Physicians need a comprehensive strategy to introduce options like medications or surgery when indicated for long-term, weight management solutions.
Tips for primary care clinicians in helping postmenopausal women lose weight:
- Develop an effective solution that works for your patient’s lifestyle. If you don’t have one, make a referral to a weight loss specialist.
- Educate patients about obesity and postmenopausal weight loss challenges, to help destigmatize the condition. Explain that obesity is a chronic disease, like hypertension or diabetes.
- Exercise suggestions should consider issues like walkable neighborhoods, access and affordability of gym membership, and home broadband access.
- Strength training should be recommended to counter loss of muscle mass that comes with aging.
- Consider a patient’s culture when discussing healthier alternatives to their usual diet.
- Suggest simple changes to start, like eliminating simple carbohydrates — white bread, pasta, and white rice — as a good place to start.
Body mass index was not designed to be a clinical tool and does not fully assess weight in many populations. Risk for chronic diseases and obesity varies depending on whether a person carries weight centrally or on the hips and thighs.
But well before menopause, clinicians can educate their female patients on what body changes to expect and be more mindful about which medications to not prescribe.
People in menopause or perimenopause are frequently prescribed weight-promoting drugs like antidepressants for mood swings or gabapentin for hot flashes. Clinicians should conduct a medication review and look for alternatives to drugs that are associated with weight gain.
The best approach is to try to avoid weight gain in the first place, which can be easier than trying to lose later, Dr. Faubion said. “You can’t just exercise your way out of it,” she said.
Dr. Adams, Dr. Faubion, and Dr. Hurtado Andrade reported no disclosures. Dr. Knight is a former consultant with Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is It Possible to Reverse Osteoporosis?
Fractures, particularly hip and spine fractures, are a major cause of mortality and morbidity among older individuals. The term “osteoporosis” indicates increased porosity of bones resulting in low bone density; increased bone fragility; and an increased risk for fracture, often with minimal trauma.
During the adolescent years, bone accrues at a rapid rate, and optimal bone accrual during this time is essential to attain optimal peak bone mass, typically achieved in the third decade of life. Bone mass then stays stable until the 40s-50s, after which it starts to decline. One’s peak bone mass sets the stage for both immediate and future bone health. Individuals with lower peak bone mass tend to have less optimal bone health throughout their lives, and this becomes particularly problematic in older men and in the postmenopausal years for women.
One’s genes have a major impact on bone density and are currently not modifiable.
Modifiable factors include mechanical loading of bones through exercise activity, maintaining a normal body weight, and ensuring adequate intake of micronutrients (including calcium and vitamin D) and macronutrients. Medications such as glucocorticoids that have deleterious effects on bones should be limited as far as possible. Endocrine, gastrointestinal, renal, and rheumatologic conditions and others, such as cancer, which are known to be associated with reduced bone density and increased fracture risk, should be managed appropriately.
A deficiency of the gonadal hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and high blood concentrations of cortisol are particularly deleterious to bone. Hormone replacement therapy in those with gonadal hormone deficiency and strategies to reduce cortisol levels in those with hypercortisolemia are essential to prevent osteoporosis and also improve bone density over time. The same applies to management of conditions such as anorexia nervosa, relative energy deficiency in sports, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and chronic arthritis.
Once osteoporosis has developed, depending on the cause, these strategies may not be sufficient to completely reverse the condition, and pharmacologic therapy may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk. This is particularly an issue with postmenopausal women and older men. In these individuals, medications that increase bone formation or reduce bone loss may be necessary.
Medications that reduce bone loss include bisphosphonates and denosumab; these are also called “antiresorptive medications” because they reduce bone resorption by cells called osteoclasts. Bisphosphonates include alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, pamidronate, and zoledronic acid, and these medications have direct effects on osteoclasts, reducing their activity. Some bisphosphonates, such as alendronate and risedronate, are taken orally (daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the medication and its strength), whereas others, such as pamidronate and zoledronic acid, are administered intravenously: every 3-4 months for pamidronate and every 6-12 months for zoledronic acid. Ibandronate is available both orally and intravenously.
Denosumab is a medication that inhibits the action of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa ligand 1 (RANKL), which otherwise increases osteoclast activity. It is administered as a subcutaneous injection every 6 months to treat osteoporosis. One concern with denosumab is a rapid increase in bone loss after its discontinuation.
Medications that increase bone formation are called bone anabolics and include teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab. Teriparatide is a synthetic form of parathyroid hormone (recombinant PTH1-34) administered daily for up to 2 years. Abaloparatide is a synthetic analog of parathyroid hormone–related peptide (PTHrP), which is also administered daily as a subcutaneous injection. Romosozumab inhibits sclerostin (a substance that otherwise reduces bone formation and increases bone resorption) and is administered as a subcutaneous injection once a month. Effects of these medications tend to be lost after they are discontinued.
In 2019, the Endocrine Society published guidelines for managing postmenopausal osteoporosis. The guidelines recommend lifestyle modifications, including attention to diet, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and weight-bearing exercise for all postmenopausal women. They also recommend assessing fracture risk using country-specific existing models.
Guidelines vary depending on whether fracture risk is low, moderate, or high. Patients at low risk are followed and reassessed every 2-4 years for fracture risk. Those at moderate risk may be followed similarly or prescribed bisphosphonates. Those at high risk are prescribed an antiresorptive, such as a bisphosphonate or denosumab, or a bone anabolic, such as teriparatide or abaloparatide (for up to 2 years) or romosozumab (for a year), with calcium and vitamin D and are reassessed at defined intervals for fracture risk; subsequent management then depends on the assessed fracture risk.
People who are on a bone anabolic should typically follow this with an antiresorptive medication to maintain the gains achieved with the former after that medication is discontinued. Patients who discontinue denosumab should be switched to bisphosphonates to prevent the increase in bone loss that typically occurs.
In postmenopausal women who are intolerant to or inappropriate for use of these medications, guidelines vary depending on age (younger or older than 60 years) and presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms (such as hot flashes). Options could include the use of calcium and vitamin D supplements; hormone replacement therapy with estrogen with or without a progestin; or selective estrogen receptor modulators (such as raloxifene or bazedoxifene), tibolone, or calcitonin.
It’s important to recognize that all pharmacologic therapy carries the risk for adverse events, and it’s essential to take the necessary steps to prevent, monitor for, and manage any adverse effects that may develop.
Managing osteoporosis in older men could include the use of bone anabolics and/or antiresorptives. In younger individuals, use of pharmacologic therapy is less common but sometimes necessary, particularly when bone density is very low and associated with a problematic fracture history — for example, in those with genetic conditions such as osteogenesis imperfecta. Furthermore, the occurrence of vertebral compression fractures often requires bisphosphonate treatment regardless of bone density, particularly in patients on chronic glucocorticoid therapy.
Preventing osteoporosis is best managed by paying attention to lifestyle; optimizing nutrition and calcium and vitamin D intake; and managing conditions and limiting the use of medications that reduce bone density.
However, in certain patients, these measures are not enough, and pharmacologic therapy with bone anabolics or antiresorptives may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
Dr. Misra, of the University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s Hospital, Charlottesville, disclosed ties with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Fractures, particularly hip and spine fractures, are a major cause of mortality and morbidity among older individuals. The term “osteoporosis” indicates increased porosity of bones resulting in low bone density; increased bone fragility; and an increased risk for fracture, often with minimal trauma.
During the adolescent years, bone accrues at a rapid rate, and optimal bone accrual during this time is essential to attain optimal peak bone mass, typically achieved in the third decade of life. Bone mass then stays stable until the 40s-50s, after which it starts to decline. One’s peak bone mass sets the stage for both immediate and future bone health. Individuals with lower peak bone mass tend to have less optimal bone health throughout their lives, and this becomes particularly problematic in older men and in the postmenopausal years for women.
One’s genes have a major impact on bone density and are currently not modifiable.
Modifiable factors include mechanical loading of bones through exercise activity, maintaining a normal body weight, and ensuring adequate intake of micronutrients (including calcium and vitamin D) and macronutrients. Medications such as glucocorticoids that have deleterious effects on bones should be limited as far as possible. Endocrine, gastrointestinal, renal, and rheumatologic conditions and others, such as cancer, which are known to be associated with reduced bone density and increased fracture risk, should be managed appropriately.
A deficiency of the gonadal hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and high blood concentrations of cortisol are particularly deleterious to bone. Hormone replacement therapy in those with gonadal hormone deficiency and strategies to reduce cortisol levels in those with hypercortisolemia are essential to prevent osteoporosis and also improve bone density over time. The same applies to management of conditions such as anorexia nervosa, relative energy deficiency in sports, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and chronic arthritis.
Once osteoporosis has developed, depending on the cause, these strategies may not be sufficient to completely reverse the condition, and pharmacologic therapy may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk. This is particularly an issue with postmenopausal women and older men. In these individuals, medications that increase bone formation or reduce bone loss may be necessary.
Medications that reduce bone loss include bisphosphonates and denosumab; these are also called “antiresorptive medications” because they reduce bone resorption by cells called osteoclasts. Bisphosphonates include alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, pamidronate, and zoledronic acid, and these medications have direct effects on osteoclasts, reducing their activity. Some bisphosphonates, such as alendronate and risedronate, are taken orally (daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the medication and its strength), whereas others, such as pamidronate and zoledronic acid, are administered intravenously: every 3-4 months for pamidronate and every 6-12 months for zoledronic acid. Ibandronate is available both orally and intravenously.
Denosumab is a medication that inhibits the action of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa ligand 1 (RANKL), which otherwise increases osteoclast activity. It is administered as a subcutaneous injection every 6 months to treat osteoporosis. One concern with denosumab is a rapid increase in bone loss after its discontinuation.
Medications that increase bone formation are called bone anabolics and include teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab. Teriparatide is a synthetic form of parathyroid hormone (recombinant PTH1-34) administered daily for up to 2 years. Abaloparatide is a synthetic analog of parathyroid hormone–related peptide (PTHrP), which is also administered daily as a subcutaneous injection. Romosozumab inhibits sclerostin (a substance that otherwise reduces bone formation and increases bone resorption) and is administered as a subcutaneous injection once a month. Effects of these medications tend to be lost after they are discontinued.
In 2019, the Endocrine Society published guidelines for managing postmenopausal osteoporosis. The guidelines recommend lifestyle modifications, including attention to diet, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and weight-bearing exercise for all postmenopausal women. They also recommend assessing fracture risk using country-specific existing models.
Guidelines vary depending on whether fracture risk is low, moderate, or high. Patients at low risk are followed and reassessed every 2-4 years for fracture risk. Those at moderate risk may be followed similarly or prescribed bisphosphonates. Those at high risk are prescribed an antiresorptive, such as a bisphosphonate or denosumab, or a bone anabolic, such as teriparatide or abaloparatide (for up to 2 years) or romosozumab (for a year), with calcium and vitamin D and are reassessed at defined intervals for fracture risk; subsequent management then depends on the assessed fracture risk.
People who are on a bone anabolic should typically follow this with an antiresorptive medication to maintain the gains achieved with the former after that medication is discontinued. Patients who discontinue denosumab should be switched to bisphosphonates to prevent the increase in bone loss that typically occurs.
In postmenopausal women who are intolerant to or inappropriate for use of these medications, guidelines vary depending on age (younger or older than 60 years) and presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms (such as hot flashes). Options could include the use of calcium and vitamin D supplements; hormone replacement therapy with estrogen with or without a progestin; or selective estrogen receptor modulators (such as raloxifene or bazedoxifene), tibolone, or calcitonin.
It’s important to recognize that all pharmacologic therapy carries the risk for adverse events, and it’s essential to take the necessary steps to prevent, monitor for, and manage any adverse effects that may develop.
Managing osteoporosis in older men could include the use of bone anabolics and/or antiresorptives. In younger individuals, use of pharmacologic therapy is less common but sometimes necessary, particularly when bone density is very low and associated with a problematic fracture history — for example, in those with genetic conditions such as osteogenesis imperfecta. Furthermore, the occurrence of vertebral compression fractures often requires bisphosphonate treatment regardless of bone density, particularly in patients on chronic glucocorticoid therapy.
Preventing osteoporosis is best managed by paying attention to lifestyle; optimizing nutrition and calcium and vitamin D intake; and managing conditions and limiting the use of medications that reduce bone density.
However, in certain patients, these measures are not enough, and pharmacologic therapy with bone anabolics or antiresorptives may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
Dr. Misra, of the University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s Hospital, Charlottesville, disclosed ties with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Fractures, particularly hip and spine fractures, are a major cause of mortality and morbidity among older individuals. The term “osteoporosis” indicates increased porosity of bones resulting in low bone density; increased bone fragility; and an increased risk for fracture, often with minimal trauma.
During the adolescent years, bone accrues at a rapid rate, and optimal bone accrual during this time is essential to attain optimal peak bone mass, typically achieved in the third decade of life. Bone mass then stays stable until the 40s-50s, after which it starts to decline. One’s peak bone mass sets the stage for both immediate and future bone health. Individuals with lower peak bone mass tend to have less optimal bone health throughout their lives, and this becomes particularly problematic in older men and in the postmenopausal years for women.
One’s genes have a major impact on bone density and are currently not modifiable.
Modifiable factors include mechanical loading of bones through exercise activity, maintaining a normal body weight, and ensuring adequate intake of micronutrients (including calcium and vitamin D) and macronutrients. Medications such as glucocorticoids that have deleterious effects on bones should be limited as far as possible. Endocrine, gastrointestinal, renal, and rheumatologic conditions and others, such as cancer, which are known to be associated with reduced bone density and increased fracture risk, should be managed appropriately.
A deficiency of the gonadal hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and high blood concentrations of cortisol are particularly deleterious to bone. Hormone replacement therapy in those with gonadal hormone deficiency and strategies to reduce cortisol levels in those with hypercortisolemia are essential to prevent osteoporosis and also improve bone density over time. The same applies to management of conditions such as anorexia nervosa, relative energy deficiency in sports, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and chronic arthritis.
Once osteoporosis has developed, depending on the cause, these strategies may not be sufficient to completely reverse the condition, and pharmacologic therapy may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk. This is particularly an issue with postmenopausal women and older men. In these individuals, medications that increase bone formation or reduce bone loss may be necessary.
Medications that reduce bone loss include bisphosphonates and denosumab; these are also called “antiresorptive medications” because they reduce bone resorption by cells called osteoclasts. Bisphosphonates include alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, pamidronate, and zoledronic acid, and these medications have direct effects on osteoclasts, reducing their activity. Some bisphosphonates, such as alendronate and risedronate, are taken orally (daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the medication and its strength), whereas others, such as pamidronate and zoledronic acid, are administered intravenously: every 3-4 months for pamidronate and every 6-12 months for zoledronic acid. Ibandronate is available both orally and intravenously.
Denosumab is a medication that inhibits the action of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa ligand 1 (RANKL), which otherwise increases osteoclast activity. It is administered as a subcutaneous injection every 6 months to treat osteoporosis. One concern with denosumab is a rapid increase in bone loss after its discontinuation.
Medications that increase bone formation are called bone anabolics and include teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab. Teriparatide is a synthetic form of parathyroid hormone (recombinant PTH1-34) administered daily for up to 2 years. Abaloparatide is a synthetic analog of parathyroid hormone–related peptide (PTHrP), which is also administered daily as a subcutaneous injection. Romosozumab inhibits sclerostin (a substance that otherwise reduces bone formation and increases bone resorption) and is administered as a subcutaneous injection once a month. Effects of these medications tend to be lost after they are discontinued.
In 2019, the Endocrine Society published guidelines for managing postmenopausal osteoporosis. The guidelines recommend lifestyle modifications, including attention to diet, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and weight-bearing exercise for all postmenopausal women. They also recommend assessing fracture risk using country-specific existing models.
Guidelines vary depending on whether fracture risk is low, moderate, or high. Patients at low risk are followed and reassessed every 2-4 years for fracture risk. Those at moderate risk may be followed similarly or prescribed bisphosphonates. Those at high risk are prescribed an antiresorptive, such as a bisphosphonate or denosumab, or a bone anabolic, such as teriparatide or abaloparatide (for up to 2 years) or romosozumab (for a year), with calcium and vitamin D and are reassessed at defined intervals for fracture risk; subsequent management then depends on the assessed fracture risk.
People who are on a bone anabolic should typically follow this with an antiresorptive medication to maintain the gains achieved with the former after that medication is discontinued. Patients who discontinue denosumab should be switched to bisphosphonates to prevent the increase in bone loss that typically occurs.
In postmenopausal women who are intolerant to or inappropriate for use of these medications, guidelines vary depending on age (younger or older than 60 years) and presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms (such as hot flashes). Options could include the use of calcium and vitamin D supplements; hormone replacement therapy with estrogen with or without a progestin; or selective estrogen receptor modulators (such as raloxifene or bazedoxifene), tibolone, or calcitonin.
It’s important to recognize that all pharmacologic therapy carries the risk for adverse events, and it’s essential to take the necessary steps to prevent, monitor for, and manage any adverse effects that may develop.
Managing osteoporosis in older men could include the use of bone anabolics and/or antiresorptives. In younger individuals, use of pharmacologic therapy is less common but sometimes necessary, particularly when bone density is very low and associated with a problematic fracture history — for example, in those with genetic conditions such as osteogenesis imperfecta. Furthermore, the occurrence of vertebral compression fractures often requires bisphosphonate treatment regardless of bone density, particularly in patients on chronic glucocorticoid therapy.
Preventing osteoporosis is best managed by paying attention to lifestyle; optimizing nutrition and calcium and vitamin D intake; and managing conditions and limiting the use of medications that reduce bone density.
However, in certain patients, these measures are not enough, and pharmacologic therapy with bone anabolics or antiresorptives may be necessary to improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
Dr. Misra, of the University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s Hospital, Charlottesville, disclosed ties with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Help Patients Avoid Weight Gain After Stopping GLP-1s
Weight loss drugs have surged in popularity — in part because they work. Patients on glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists like liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide (which is technically also a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist) can lose 10%, 20%, or even 25% of their body weight.
But if those patients stop taking GLP-1s, they tend to regain most of that weight within a year, studies showed.
“These drugs work inside the person from a biologic point of view to alter appetite,” said Robert Kushner, MD, an endocrinologist and professor at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, who specializes in obesity medicine. “And when the drug is gone, that disease comes back.”
Often, “patients are told by their insurers that they are no longer going to cover a GLP-1 for obesity,” said Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, Minnesota, who sees patients at the M Health Fairview weight management clinic.
Other barriers include side effects like nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain, and vomiting. Some patients simply don’t want to take a medication forever, instead choosing to take their chances keeping the weight off sans drug.
If your patient must stop GLP-1s, or really wants to, here’s how to help.
Find out why the patient wants to go off the GLP-1. Ask them to help you understand, suggested Jaime Almandoz, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and medical director of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center’s Weight Wellness Program. Sometimes, the patient or family members worry about safety, Dr. Almandoz said. “They may be concerned about the risks and may not have had an opportunity to ask questions.” Dr. Almandoz reviews the drug safety data and tells patients that studies show, on average, people gain back two-thirds of the weight they’ve lost within a year. You’re not trying to persuade them, only to equip them to make a well-informed choice.
Don’t let bias affect treatment decisions. Patients on GLP-1s often ask: How long will I have to take this? The reason: “We’re biased to believe that this is not a disease state, that this is a character flaw,” said Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for weight management in Burlington, Ontario, Canada. Remind your patient that obesity is not a personal failure but rather a complex mix of genetic and biological factors.
Give patients a primer on the biology of obesity. Science shows that when we lose weight, our bodies fight back, trying to return to our highest-ever fat mass. Changes in neurohormones, gut hormones, satiety mechanisms, metabolism, and muscle function all converge to promote weight recurrence, Dr. Almandoz said. To explain this to patients, Dr. Almandoz compares gaining fat to depositing money in a savings account. “When we try to lose weight, it isn’t as simple as withdrawing this money,” he’ll tell them. “It is almost like the money that we put into the savings account is now tied up in investments that we can’t liquidate easily.”
Prepare patients for an uptick in appetite. When patients stop GLP-1s, their hunger and food cravings tend to increase. “I explain that GLP-1 medications mimic a hormone that is released from our intestines when they sense we have eaten,” said Dr. Almandoz. This signals the brain and body that food is on board, decreasing appetite and cravings. Ask patients what hungry and full feel like on the medication, Dr. Almandoz suggested. “Many will report that their hunger and cravings are low, that they now have an indifference to foods,” said Dr. Almandoz. Such probing questions can help patients be more aware of the medication’s effects. “This positions a more informed conversation if medications are to be discontinued,” Dr. Almandoz said.
Help their body adjust. “Slowly wean down on the dose, if possible, to avoid a big rebound in hunger,” said Dr. Bramante. If your patient has the time — say, they received a letter from their insurance that coverage will end in 3 months — use it to taper the dose as low as possible before stopping. The slower and more gradual, the better. Dr. Almandoz checks in with patients every 4-8 weeks. If they›re maintaining weight well, he considers decreasing the dose again and repeating with follow-up visits.
Substitute one intervention for another. In general, maintaining weight loss requires some intervention, Dr. Wharton said. “But that intervention does not need to be the same as the intervention that got the weight down.” If the patient can›t continue a GLP-1, consider an alternate medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, or a combination of the two. When patients lose coverage for GLP-1s, Dr. Bramante sometimes prescribes an older, less-expensive weight loss drug, such as phentermine, topiramate, or metformin. And sometimes, insurers that don’t cover GLP-1s (like Medicare), do cover bariatric surgery, a potential option depending on the patient›s body mass index, overall health, and comorbidities, said Dr. Almandoz.
Create a habit template. Dr. Kushner asks patients who have successfully lost weight to take an inventory of everything they’re doing to support their efforts. He’ll have them describe how they plan their diet, what types of food they’re eating, how much they eat, and when they eat it. He’ll also ask about physical activity, exercise patterns, and sleep. He logs all the habits into a bulleted list in the patient’s after-visit summary and hands them a printout before they leave. “That’s your template,” he’ll tell them. “That’s what you’re going to try to maintain to the best of your ability because it’s working for you.”
Prescribe exercise. “Increasing exercise is not usually effective for initial weight loss, but it is important for maintaining weight loss,” said Dr. Bramante. Tell patients to start right away, ideally while they’re still on the drug. In a study published last month, patients on liraglutide (Saxenda) who exercised 4 days a week were much more likely to keep weight off after stopping the drug than those who didn’t work out. (The study was partially funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, the charitable arm of Saxenda’s maker, also the maker of semaglutide meds Ozempic and Wegovy.) By establishing strong exercise habits while on the medication, they were able to sustain higher physical activity levels after they stopped. Ask your patient to identify someone or something to help them stick to their plan, “whether it’s seeing a personal trainer or being accountable to a friend or family member or to themselves through record keeping,” said Dr. Kushner. Learn more about how to prescribe exercise to patients here.
Help them create a “microenvironment” for success. Dr. Kushner asks patients which of the recommended dietary habits for weight loss are hardest to follow: Eating more plant-based foods? Cutting back on ultra-processed foods, fatty foods, fast foods, and/or sugary beverages? Depending on the patient’s answers, he tries to recommend strategies — maybe going meatless a few days a week or keeping tempting foods out of the house. “If you go off medication, food may become more enticing, and you may not feel as content eating less,” Dr. Kushner said. “Make sure your own what we call microenvironment, your home environment, is filled with healthy foods.”
Rely on multidisciplinary expertise. Obesity is a complex, multifactorial disease, so call in reinforcements. “When I see someone, I’m always evaluating what other team members they would benefit from,” said Dr. Kushner. If the patient lacks nutrition knowledge, he refers them to a registered dietitian. If they struggle with self-blame, low self-esteem, and emotional eating, he’ll refer them to a psychologist. It can make a difference: A 2023 study showed that people who lost weight and received support from professionals like trainers, dietitians, and mental health therapists regained less weight over 2 years than those who did not receive the same help.
Reassure patients you will help them no matter what. Ask patients to follow-up within the first month of quitting medication or to call back sooner if they gain 5 pounds. People who stop taking GLP-1s often report less satisfaction with eating, or that they think about food more. That’s when Dr. Kushner asks whether they want to go back on the medication or focus on other strategies. Sometimes, patients who gain weight feel embarrassed and delay their follow-up visits. If that happens, welcome them back and let them know that all chronic conditions ebb and flow. “I constantly remind them that I am here to help you, and there are many tools or resources that will help you,” Dr. Kushner said. “And dispel the notion that it’s somehow your fault.”
Dr. Kushner reported participation on the medical advisory board or consultancy with Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Structure Therapeutics, and Altimmune. He added he does not own stock or participate in any speaker’s bureau. Dr. Almandoz reported participation on advisory boards with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Wharton reported participation on advisory boards and honoraria for academic talks and clinical research with Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Regeneron, and BioHaven.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Weight loss drugs have surged in popularity — in part because they work. Patients on glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists like liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide (which is technically also a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist) can lose 10%, 20%, or even 25% of their body weight.
But if those patients stop taking GLP-1s, they tend to regain most of that weight within a year, studies showed.
“These drugs work inside the person from a biologic point of view to alter appetite,” said Robert Kushner, MD, an endocrinologist and professor at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, who specializes in obesity medicine. “And when the drug is gone, that disease comes back.”
Often, “patients are told by their insurers that they are no longer going to cover a GLP-1 for obesity,” said Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, Minnesota, who sees patients at the M Health Fairview weight management clinic.
Other barriers include side effects like nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain, and vomiting. Some patients simply don’t want to take a medication forever, instead choosing to take their chances keeping the weight off sans drug.
If your patient must stop GLP-1s, or really wants to, here’s how to help.
Find out why the patient wants to go off the GLP-1. Ask them to help you understand, suggested Jaime Almandoz, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and medical director of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center’s Weight Wellness Program. Sometimes, the patient or family members worry about safety, Dr. Almandoz said. “They may be concerned about the risks and may not have had an opportunity to ask questions.” Dr. Almandoz reviews the drug safety data and tells patients that studies show, on average, people gain back two-thirds of the weight they’ve lost within a year. You’re not trying to persuade them, only to equip them to make a well-informed choice.
Don’t let bias affect treatment decisions. Patients on GLP-1s often ask: How long will I have to take this? The reason: “We’re biased to believe that this is not a disease state, that this is a character flaw,” said Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for weight management in Burlington, Ontario, Canada. Remind your patient that obesity is not a personal failure but rather a complex mix of genetic and biological factors.
Give patients a primer on the biology of obesity. Science shows that when we lose weight, our bodies fight back, trying to return to our highest-ever fat mass. Changes in neurohormones, gut hormones, satiety mechanisms, metabolism, and muscle function all converge to promote weight recurrence, Dr. Almandoz said. To explain this to patients, Dr. Almandoz compares gaining fat to depositing money in a savings account. “When we try to lose weight, it isn’t as simple as withdrawing this money,” he’ll tell them. “It is almost like the money that we put into the savings account is now tied up in investments that we can’t liquidate easily.”
Prepare patients for an uptick in appetite. When patients stop GLP-1s, their hunger and food cravings tend to increase. “I explain that GLP-1 medications mimic a hormone that is released from our intestines when they sense we have eaten,” said Dr. Almandoz. This signals the brain and body that food is on board, decreasing appetite and cravings. Ask patients what hungry and full feel like on the medication, Dr. Almandoz suggested. “Many will report that their hunger and cravings are low, that they now have an indifference to foods,” said Dr. Almandoz. Such probing questions can help patients be more aware of the medication’s effects. “This positions a more informed conversation if medications are to be discontinued,” Dr. Almandoz said.
Help their body adjust. “Slowly wean down on the dose, if possible, to avoid a big rebound in hunger,” said Dr. Bramante. If your patient has the time — say, they received a letter from their insurance that coverage will end in 3 months — use it to taper the dose as low as possible before stopping. The slower and more gradual, the better. Dr. Almandoz checks in with patients every 4-8 weeks. If they›re maintaining weight well, he considers decreasing the dose again and repeating with follow-up visits.
Substitute one intervention for another. In general, maintaining weight loss requires some intervention, Dr. Wharton said. “But that intervention does not need to be the same as the intervention that got the weight down.” If the patient can›t continue a GLP-1, consider an alternate medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, or a combination of the two. When patients lose coverage for GLP-1s, Dr. Bramante sometimes prescribes an older, less-expensive weight loss drug, such as phentermine, topiramate, or metformin. And sometimes, insurers that don’t cover GLP-1s (like Medicare), do cover bariatric surgery, a potential option depending on the patient›s body mass index, overall health, and comorbidities, said Dr. Almandoz.
Create a habit template. Dr. Kushner asks patients who have successfully lost weight to take an inventory of everything they’re doing to support their efforts. He’ll have them describe how they plan their diet, what types of food they’re eating, how much they eat, and when they eat it. He’ll also ask about physical activity, exercise patterns, and sleep. He logs all the habits into a bulleted list in the patient’s after-visit summary and hands them a printout before they leave. “That’s your template,” he’ll tell them. “That’s what you’re going to try to maintain to the best of your ability because it’s working for you.”
Prescribe exercise. “Increasing exercise is not usually effective for initial weight loss, but it is important for maintaining weight loss,” said Dr. Bramante. Tell patients to start right away, ideally while they’re still on the drug. In a study published last month, patients on liraglutide (Saxenda) who exercised 4 days a week were much more likely to keep weight off after stopping the drug than those who didn’t work out. (The study was partially funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, the charitable arm of Saxenda’s maker, also the maker of semaglutide meds Ozempic and Wegovy.) By establishing strong exercise habits while on the medication, they were able to sustain higher physical activity levels after they stopped. Ask your patient to identify someone or something to help them stick to their plan, “whether it’s seeing a personal trainer or being accountable to a friend or family member or to themselves through record keeping,” said Dr. Kushner. Learn more about how to prescribe exercise to patients here.
Help them create a “microenvironment” for success. Dr. Kushner asks patients which of the recommended dietary habits for weight loss are hardest to follow: Eating more plant-based foods? Cutting back on ultra-processed foods, fatty foods, fast foods, and/or sugary beverages? Depending on the patient’s answers, he tries to recommend strategies — maybe going meatless a few days a week or keeping tempting foods out of the house. “If you go off medication, food may become more enticing, and you may not feel as content eating less,” Dr. Kushner said. “Make sure your own what we call microenvironment, your home environment, is filled with healthy foods.”
Rely on multidisciplinary expertise. Obesity is a complex, multifactorial disease, so call in reinforcements. “When I see someone, I’m always evaluating what other team members they would benefit from,” said Dr. Kushner. If the patient lacks nutrition knowledge, he refers them to a registered dietitian. If they struggle with self-blame, low self-esteem, and emotional eating, he’ll refer them to a psychologist. It can make a difference: A 2023 study showed that people who lost weight and received support from professionals like trainers, dietitians, and mental health therapists regained less weight over 2 years than those who did not receive the same help.
Reassure patients you will help them no matter what. Ask patients to follow-up within the first month of quitting medication or to call back sooner if they gain 5 pounds. People who stop taking GLP-1s often report less satisfaction with eating, or that they think about food more. That’s when Dr. Kushner asks whether they want to go back on the medication or focus on other strategies. Sometimes, patients who gain weight feel embarrassed and delay their follow-up visits. If that happens, welcome them back and let them know that all chronic conditions ebb and flow. “I constantly remind them that I am here to help you, and there are many tools or resources that will help you,” Dr. Kushner said. “And dispel the notion that it’s somehow your fault.”
Dr. Kushner reported participation on the medical advisory board or consultancy with Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Structure Therapeutics, and Altimmune. He added he does not own stock or participate in any speaker’s bureau. Dr. Almandoz reported participation on advisory boards with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Wharton reported participation on advisory boards and honoraria for academic talks and clinical research with Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Regeneron, and BioHaven.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Weight loss drugs have surged in popularity — in part because they work. Patients on glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists like liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide (which is technically also a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist) can lose 10%, 20%, or even 25% of their body weight.
But if those patients stop taking GLP-1s, they tend to regain most of that weight within a year, studies showed.
“These drugs work inside the person from a biologic point of view to alter appetite,” said Robert Kushner, MD, an endocrinologist and professor at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, who specializes in obesity medicine. “And when the drug is gone, that disease comes back.”
Often, “patients are told by their insurers that they are no longer going to cover a GLP-1 for obesity,” said Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, Minnesota, who sees patients at the M Health Fairview weight management clinic.
Other barriers include side effects like nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain, and vomiting. Some patients simply don’t want to take a medication forever, instead choosing to take their chances keeping the weight off sans drug.
If your patient must stop GLP-1s, or really wants to, here’s how to help.
Find out why the patient wants to go off the GLP-1. Ask them to help you understand, suggested Jaime Almandoz, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and medical director of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center’s Weight Wellness Program. Sometimes, the patient or family members worry about safety, Dr. Almandoz said. “They may be concerned about the risks and may not have had an opportunity to ask questions.” Dr. Almandoz reviews the drug safety data and tells patients that studies show, on average, people gain back two-thirds of the weight they’ve lost within a year. You’re not trying to persuade them, only to equip them to make a well-informed choice.
Don’t let bias affect treatment decisions. Patients on GLP-1s often ask: How long will I have to take this? The reason: “We’re biased to believe that this is not a disease state, that this is a character flaw,” said Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for weight management in Burlington, Ontario, Canada. Remind your patient that obesity is not a personal failure but rather a complex mix of genetic and biological factors.
Give patients a primer on the biology of obesity. Science shows that when we lose weight, our bodies fight back, trying to return to our highest-ever fat mass. Changes in neurohormones, gut hormones, satiety mechanisms, metabolism, and muscle function all converge to promote weight recurrence, Dr. Almandoz said. To explain this to patients, Dr. Almandoz compares gaining fat to depositing money in a savings account. “When we try to lose weight, it isn’t as simple as withdrawing this money,” he’ll tell them. “It is almost like the money that we put into the savings account is now tied up in investments that we can’t liquidate easily.”
Prepare patients for an uptick in appetite. When patients stop GLP-1s, their hunger and food cravings tend to increase. “I explain that GLP-1 medications mimic a hormone that is released from our intestines when they sense we have eaten,” said Dr. Almandoz. This signals the brain and body that food is on board, decreasing appetite and cravings. Ask patients what hungry and full feel like on the medication, Dr. Almandoz suggested. “Many will report that their hunger and cravings are low, that they now have an indifference to foods,” said Dr. Almandoz. Such probing questions can help patients be more aware of the medication’s effects. “This positions a more informed conversation if medications are to be discontinued,” Dr. Almandoz said.
Help their body adjust. “Slowly wean down on the dose, if possible, to avoid a big rebound in hunger,” said Dr. Bramante. If your patient has the time — say, they received a letter from their insurance that coverage will end in 3 months — use it to taper the dose as low as possible before stopping. The slower and more gradual, the better. Dr. Almandoz checks in with patients every 4-8 weeks. If they›re maintaining weight well, he considers decreasing the dose again and repeating with follow-up visits.
Substitute one intervention for another. In general, maintaining weight loss requires some intervention, Dr. Wharton said. “But that intervention does not need to be the same as the intervention that got the weight down.” If the patient can›t continue a GLP-1, consider an alternate medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, or a combination of the two. When patients lose coverage for GLP-1s, Dr. Bramante sometimes prescribes an older, less-expensive weight loss drug, such as phentermine, topiramate, or metformin. And sometimes, insurers that don’t cover GLP-1s (like Medicare), do cover bariatric surgery, a potential option depending on the patient›s body mass index, overall health, and comorbidities, said Dr. Almandoz.
Create a habit template. Dr. Kushner asks patients who have successfully lost weight to take an inventory of everything they’re doing to support their efforts. He’ll have them describe how they plan their diet, what types of food they’re eating, how much they eat, and when they eat it. He’ll also ask about physical activity, exercise patterns, and sleep. He logs all the habits into a bulleted list in the patient’s after-visit summary and hands them a printout before they leave. “That’s your template,” he’ll tell them. “That’s what you’re going to try to maintain to the best of your ability because it’s working for you.”
Prescribe exercise. “Increasing exercise is not usually effective for initial weight loss, but it is important for maintaining weight loss,” said Dr. Bramante. Tell patients to start right away, ideally while they’re still on the drug. In a study published last month, patients on liraglutide (Saxenda) who exercised 4 days a week were much more likely to keep weight off after stopping the drug than those who didn’t work out. (The study was partially funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, the charitable arm of Saxenda’s maker, also the maker of semaglutide meds Ozempic and Wegovy.) By establishing strong exercise habits while on the medication, they were able to sustain higher physical activity levels after they stopped. Ask your patient to identify someone or something to help them stick to their plan, “whether it’s seeing a personal trainer or being accountable to a friend or family member or to themselves through record keeping,” said Dr. Kushner. Learn more about how to prescribe exercise to patients here.
Help them create a “microenvironment” for success. Dr. Kushner asks patients which of the recommended dietary habits for weight loss are hardest to follow: Eating more plant-based foods? Cutting back on ultra-processed foods, fatty foods, fast foods, and/or sugary beverages? Depending on the patient’s answers, he tries to recommend strategies — maybe going meatless a few days a week or keeping tempting foods out of the house. “If you go off medication, food may become more enticing, and you may not feel as content eating less,” Dr. Kushner said. “Make sure your own what we call microenvironment, your home environment, is filled with healthy foods.”
Rely on multidisciplinary expertise. Obesity is a complex, multifactorial disease, so call in reinforcements. “When I see someone, I’m always evaluating what other team members they would benefit from,” said Dr. Kushner. If the patient lacks nutrition knowledge, he refers them to a registered dietitian. If they struggle with self-blame, low self-esteem, and emotional eating, he’ll refer them to a psychologist. It can make a difference: A 2023 study showed that people who lost weight and received support from professionals like trainers, dietitians, and mental health therapists regained less weight over 2 years than those who did not receive the same help.
Reassure patients you will help them no matter what. Ask patients to follow-up within the first month of quitting medication or to call back sooner if they gain 5 pounds. People who stop taking GLP-1s often report less satisfaction with eating, or that they think about food more. That’s when Dr. Kushner asks whether they want to go back on the medication or focus on other strategies. Sometimes, patients who gain weight feel embarrassed and delay their follow-up visits. If that happens, welcome them back and let them know that all chronic conditions ebb and flow. “I constantly remind them that I am here to help you, and there are many tools or resources that will help you,” Dr. Kushner said. “And dispel the notion that it’s somehow your fault.”
Dr. Kushner reported participation on the medical advisory board or consultancy with Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Structure Therapeutics, and Altimmune. He added he does not own stock or participate in any speaker’s bureau. Dr. Almandoz reported participation on advisory boards with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Wharton reported participation on advisory boards and honoraria for academic talks and clinical research with Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Regeneron, and BioHaven.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ginger, Cinnamon, Cumin Improve Glycemic Control
TOPLINE:
The spices and aromatic herbs of the Mediterranean diet with significant benefits in improving glycemic health in type 2 diabetes are limited to ginger, cinnamon, black cumin, turmeric, and saffron, with ginger, black cumin, and cinnamon having the strongest effects on fasting glucose, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of research.
The meta-analysis also evaluated clove, thyme, turmeric, and various other spices and herbs common in the diet but showed no other correlations with glycemic benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the analysis of 77 studies, 45, involving 3050 participants, were included in the meta-analysis and 32 studies in the systematic review.
- The studies’ inclusion criteria included adult patients with type 2 diabetes, with data on fasting glucose and/or A1c and/or , and involving any supplementation with black cumin, clove, , saffron, thyme, ginger, black pepper, , curcumin, cinnamon, basil, and/or oregano.
- The number of studies involving clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, or oregano and their association with glycemic factors in people with type 2 diabetes was insufficient, hence the analysis primarily focused on the remaining five ingredients of cinnamon, curcumin, ginger, black cumin, saffron, and rosemary.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, the most significant decreases in fasting glucose, between 17 mg/dL and 27 mg/dL, occurred after supplementation with black cumin, followed by cinnamon and ginger.
- Notably, only ginger and black cumin were associated with a significant improvement in A1c.
- Only cinnamon and ginger were associated with a significant decrease in insulin values.
- Of the 11 studies including cinnamon in the meta-analysis, 6 reported significant differences in fasting glucose, while 4 had differences in A1c after the supplementation.
- However, ginger was the only component associated with a significant decrease in each of the 3 outcomes examined of fasting glucose, A1c, and insulin.
IN PRACTICE:
“The Mediterranean Diet is the dietary pattern par excellence for managing and preventing metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes,” the authors reported.
“As far as we are aware, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis aiming to evaluate the effect of aromatic herbs and spices included in the Mediterranean Diet, such as black cumin, clove [and others], on the glycemic profile of individuals with type 2 diabetes,” they added.
“When focusing on HbA1c, only ginger and black cumin demonstrated therapeutic effects,” the authors noted. “However, our meta-analysis highlights ginger as an herb with substantial translational potential for diabetes treatment, impacting all three glycemic parameters.”
“Regarding clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, and oregano, more studies are needed to analyze the effect of these herbs on the glycemic profile in type 2 diabetes subjects,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was published on March 7, 2024, in Nutrients. The first author was Maria Carmen Garza, PhD, of the Department of Human Anatomy and Histology, School Medicine, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the results, a variety of other factors can affect fasting glucose levels, including changes in body weight or body mass index, as well as the combination of spice or aromatic herb supplementation with physical activity or lifestyle changes, the authors noted.
Due to the studies’ differences, the determination of effective dosages of the herbs and spices was not possible.
Furthermore, the studies had wide variations in quality, with few studies including adequate statistical analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The spices and aromatic herbs of the Mediterranean diet with significant benefits in improving glycemic health in type 2 diabetes are limited to ginger, cinnamon, black cumin, turmeric, and saffron, with ginger, black cumin, and cinnamon having the strongest effects on fasting glucose, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of research.
The meta-analysis also evaluated clove, thyme, turmeric, and various other spices and herbs common in the diet but showed no other correlations with glycemic benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the analysis of 77 studies, 45, involving 3050 participants, were included in the meta-analysis and 32 studies in the systematic review.
- The studies’ inclusion criteria included adult patients with type 2 diabetes, with data on fasting glucose and/or A1c and/or , and involving any supplementation with black cumin, clove, , saffron, thyme, ginger, black pepper, , curcumin, cinnamon, basil, and/or oregano.
- The number of studies involving clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, or oregano and their association with glycemic factors in people with type 2 diabetes was insufficient, hence the analysis primarily focused on the remaining five ingredients of cinnamon, curcumin, ginger, black cumin, saffron, and rosemary.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, the most significant decreases in fasting glucose, between 17 mg/dL and 27 mg/dL, occurred after supplementation with black cumin, followed by cinnamon and ginger.
- Notably, only ginger and black cumin were associated with a significant improvement in A1c.
- Only cinnamon and ginger were associated with a significant decrease in insulin values.
- Of the 11 studies including cinnamon in the meta-analysis, 6 reported significant differences in fasting glucose, while 4 had differences in A1c after the supplementation.
- However, ginger was the only component associated with a significant decrease in each of the 3 outcomes examined of fasting glucose, A1c, and insulin.
IN PRACTICE:
“The Mediterranean Diet is the dietary pattern par excellence for managing and preventing metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes,” the authors reported.
“As far as we are aware, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis aiming to evaluate the effect of aromatic herbs and spices included in the Mediterranean Diet, such as black cumin, clove [and others], on the glycemic profile of individuals with type 2 diabetes,” they added.
“When focusing on HbA1c, only ginger and black cumin demonstrated therapeutic effects,” the authors noted. “However, our meta-analysis highlights ginger as an herb with substantial translational potential for diabetes treatment, impacting all three glycemic parameters.”
“Regarding clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, and oregano, more studies are needed to analyze the effect of these herbs on the glycemic profile in type 2 diabetes subjects,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was published on March 7, 2024, in Nutrients. The first author was Maria Carmen Garza, PhD, of the Department of Human Anatomy and Histology, School Medicine, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the results, a variety of other factors can affect fasting glucose levels, including changes in body weight or body mass index, as well as the combination of spice or aromatic herb supplementation with physical activity or lifestyle changes, the authors noted.
Due to the studies’ differences, the determination of effective dosages of the herbs and spices was not possible.
Furthermore, the studies had wide variations in quality, with few studies including adequate statistical analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The spices and aromatic herbs of the Mediterranean diet with significant benefits in improving glycemic health in type 2 diabetes are limited to ginger, cinnamon, black cumin, turmeric, and saffron, with ginger, black cumin, and cinnamon having the strongest effects on fasting glucose, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of research.
The meta-analysis also evaluated clove, thyme, turmeric, and various other spices and herbs common in the diet but showed no other correlations with glycemic benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the analysis of 77 studies, 45, involving 3050 participants, were included in the meta-analysis and 32 studies in the systematic review.
- The studies’ inclusion criteria included adult patients with type 2 diabetes, with data on fasting glucose and/or A1c and/or , and involving any supplementation with black cumin, clove, , saffron, thyme, ginger, black pepper, , curcumin, cinnamon, basil, and/or oregano.
- The number of studies involving clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, or oregano and their association with glycemic factors in people with type 2 diabetes was insufficient, hence the analysis primarily focused on the remaining five ingredients of cinnamon, curcumin, ginger, black cumin, saffron, and rosemary.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, the most significant decreases in fasting glucose, between 17 mg/dL and 27 mg/dL, occurred after supplementation with black cumin, followed by cinnamon and ginger.
- Notably, only ginger and black cumin were associated with a significant improvement in A1c.
- Only cinnamon and ginger were associated with a significant decrease in insulin values.
- Of the 11 studies including cinnamon in the meta-analysis, 6 reported significant differences in fasting glucose, while 4 had differences in A1c after the supplementation.
- However, ginger was the only component associated with a significant decrease in each of the 3 outcomes examined of fasting glucose, A1c, and insulin.
IN PRACTICE:
“The Mediterranean Diet is the dietary pattern par excellence for managing and preventing metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes,” the authors reported.
“As far as we are aware, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis aiming to evaluate the effect of aromatic herbs and spices included in the Mediterranean Diet, such as black cumin, clove [and others], on the glycemic profile of individuals with type 2 diabetes,” they added.
“When focusing on HbA1c, only ginger and black cumin demonstrated therapeutic effects,” the authors noted. “However, our meta-analysis highlights ginger as an herb with substantial translational potential for diabetes treatment, impacting all three glycemic parameters.”
“Regarding clove, parsley, thyme, black pepper, rosemary, basil, and oregano, more studies are needed to analyze the effect of these herbs on the glycemic profile in type 2 diabetes subjects,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was published on March 7, 2024, in Nutrients. The first author was Maria Carmen Garza, PhD, of the Department of Human Anatomy and Histology, School Medicine, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the results, a variety of other factors can affect fasting glucose levels, including changes in body weight or body mass index, as well as the combination of spice or aromatic herb supplementation with physical activity or lifestyle changes, the authors noted.
Due to the studies’ differences, the determination of effective dosages of the herbs and spices was not possible.
Furthermore, the studies had wide variations in quality, with few studies including adequate statistical analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Research Dissects Transgenerational Obesity and Diabetes
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 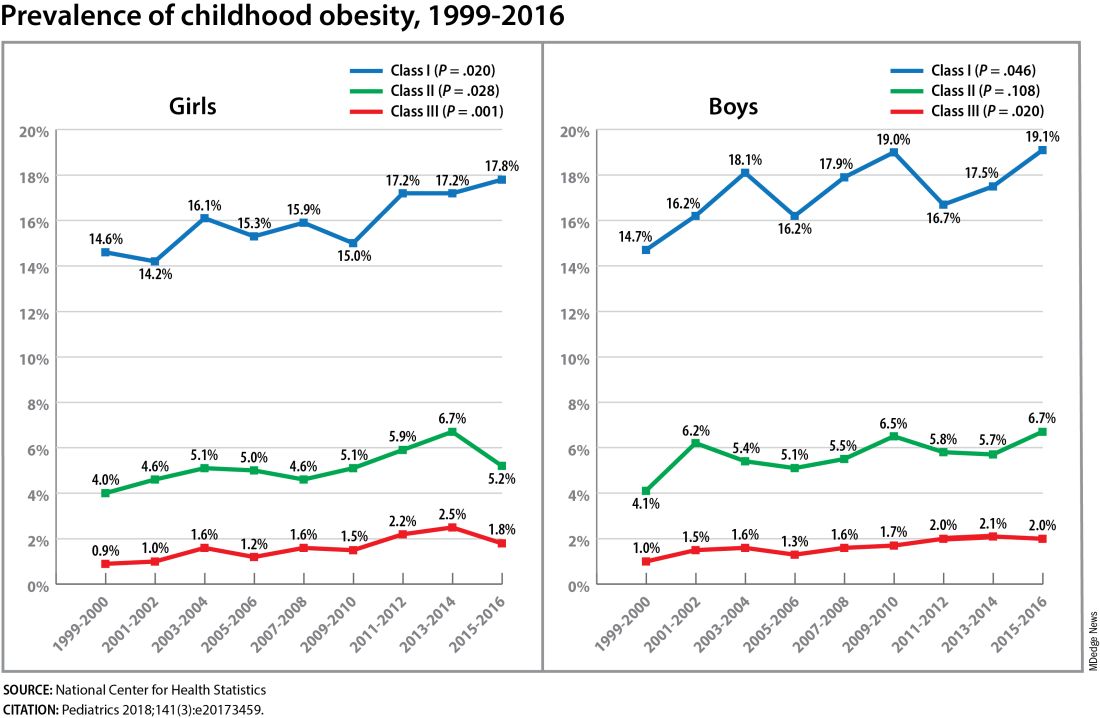
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FROM DPSG-NA 2023




