User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
FDA approves new drug for ulcerative colitis
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EMA warns that omega-3-acid ethyl esters may cause AFib
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Painful heels
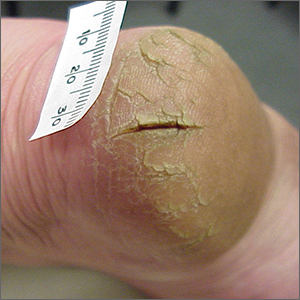
This patient was given a diagnosis of xerosis of the feet, commonly called fissured or cracked heels. Scaling and fissuring are also common in tinea pedis, but the location is often between the toes and there are finer splits and scale.
Xerosis is severely dry skin with hyperkeratosis due to abnormal keratinization;1 it leads to inflexibility and subsequent fissuring of the heel pads. The cracks can be painful and even bleed.
Although the condition is common, well-controlled trials and definitive evidence in the literature are sparse. The authors of one systematic review were unable to draw conclusions regarding the efficacy of various treatments due to wide variation in research methodologies and outcome measures; they did, however, note that urea-containing products (followed by ammonium lactate products) were studied the most.2
In clinical practice, frequently applied topical emollients are recommended. Exfoliating products, including prescription Lac-Hydrin (ammonium lactate 12% cream) and the over-the-counter version, Am-Lactin, may be helpful. Mechanical debridement with a file or pumice stone can be used (with caution) to reduce the hyperkeratotic plaques. If these measures fail, topical steroids may be added to the emollients. In addition, patients have used cyanoacrylate glues to hold the fissures together with a reported reduction in pain.3
This patient had already tried standard topical emollients. She was prescribed ammonium lactate cream to be used as an exfoliating moisturizer topically twice daily along with triamcinolone acetonide (TAC) 0.1% ointment to be applied twice daily. She was instructed to wean off the TAC once the xerosis was controlled with the ammonium lactate cream.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Mazereeuw J, Bonafé JL. La xérose [Xerosis]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002;129(1 Pt 2):137-142
2. Parker J, Scharfbillig R, Jones S. Moisturisers for the treatment of foot xerosis: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017;10:9. doi: 10.1186/s13047-017-0190-9
3. Hashimoto H. Superglue for the treatment of heel fissures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1999;89:434-435. doi: 10.7547/87507315-89-8-434

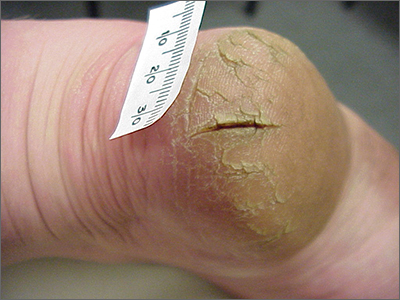
This patient was given a diagnosis of xerosis of the feet, commonly called fissured or cracked heels. Scaling and fissuring are also common in tinea pedis, but the location is often between the toes and there are finer splits and scale.
Xerosis is severely dry skin with hyperkeratosis due to abnormal keratinization;1 it leads to inflexibility and subsequent fissuring of the heel pads. The cracks can be painful and even bleed.
Although the condition is common, well-controlled trials and definitive evidence in the literature are sparse. The authors of one systematic review were unable to draw conclusions regarding the efficacy of various treatments due to wide variation in research methodologies and outcome measures; they did, however, note that urea-containing products (followed by ammonium lactate products) were studied the most.2
In clinical practice, frequently applied topical emollients are recommended. Exfoliating products, including prescription Lac-Hydrin (ammonium lactate 12% cream) and the over-the-counter version, Am-Lactin, may be helpful. Mechanical debridement with a file or pumice stone can be used (with caution) to reduce the hyperkeratotic plaques. If these measures fail, topical steroids may be added to the emollients. In addition, patients have used cyanoacrylate glues to hold the fissures together with a reported reduction in pain.3
This patient had already tried standard topical emollients. She was prescribed ammonium lactate cream to be used as an exfoliating moisturizer topically twice daily along with triamcinolone acetonide (TAC) 0.1% ointment to be applied twice daily. She was instructed to wean off the TAC once the xerosis was controlled with the ammonium lactate cream.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

This patient was given a diagnosis of xerosis of the feet, commonly called fissured or cracked heels. Scaling and fissuring are also common in tinea pedis, but the location is often between the toes and there are finer splits and scale.
Xerosis is severely dry skin with hyperkeratosis due to abnormal keratinization;1 it leads to inflexibility and subsequent fissuring of the heel pads. The cracks can be painful and even bleed.
Although the condition is common, well-controlled trials and definitive evidence in the literature are sparse. The authors of one systematic review were unable to draw conclusions regarding the efficacy of various treatments due to wide variation in research methodologies and outcome measures; they did, however, note that urea-containing products (followed by ammonium lactate products) were studied the most.2
In clinical practice, frequently applied topical emollients are recommended. Exfoliating products, including prescription Lac-Hydrin (ammonium lactate 12% cream) and the over-the-counter version, Am-Lactin, may be helpful. Mechanical debridement with a file or pumice stone can be used (with caution) to reduce the hyperkeratotic plaques. If these measures fail, topical steroids may be added to the emollients. In addition, patients have used cyanoacrylate glues to hold the fissures together with a reported reduction in pain.3
This patient had already tried standard topical emollients. She was prescribed ammonium lactate cream to be used as an exfoliating moisturizer topically twice daily along with triamcinolone acetonide (TAC) 0.1% ointment to be applied twice daily. She was instructed to wean off the TAC once the xerosis was controlled with the ammonium lactate cream.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Mazereeuw J, Bonafé JL. La xérose [Xerosis]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002;129(1 Pt 2):137-142
2. Parker J, Scharfbillig R, Jones S. Moisturisers for the treatment of foot xerosis: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017;10:9. doi: 10.1186/s13047-017-0190-9
3. Hashimoto H. Superglue for the treatment of heel fissures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1999;89:434-435. doi: 10.7547/87507315-89-8-434
1. Mazereeuw J, Bonafé JL. La xérose [Xerosis]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002;129(1 Pt 2):137-142
2. Parker J, Scharfbillig R, Jones S. Moisturisers for the treatment of foot xerosis: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017;10:9. doi: 10.1186/s13047-017-0190-9
3. Hashimoto H. Superglue for the treatment of heel fissures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1999;89:434-435. doi: 10.7547/87507315-89-8-434
High and low HDL cholesterol levels linked to dementia risk
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New RSV vaccine will cut hospitalizations, study shows
, according to research presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“With RSV maternal vaccination that is associated with clinical efficacy of 69% against severe RSV disease at 6 months, we estimated that up to 200,000 cases can be averted, and that is associated with almost $800 million in total,” presenting author Amy W. Law, PharmD, director of global value and evidence at Pfizer, pointed out during a news briefing.
“RSV is associated with a significant burden in the U.S. and this newly approved and recommended maternal RSV vaccine can have substantial impact in easing some of that burden,” Dr. Law explained.
This study is “particularly timely as we head into RSV peak season,” said briefing moderator Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The challenge, said Dr. Halasa, is that uptake of maternal vaccines and vaccines in general is “not optimal,” making increased awareness of this new maternal RSV vaccine important.
Strong efficacy data
Most children are infected with RSV at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
As reported previously by this news organization, in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study, Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine had an almost 82% efficacy against severe RSV infection in infants from birth through the first 90 days of life.
The vaccine also had a 69% efficacy against severe disease through the first 6 months of life. As part of the trial, a total of 7,400 women received a single dose of the vaccine in the late second or third trimester of their pregnancy. There were no signs of safety issues for the mothers or infants.
Based on the results, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the vaccine, known as Abrysvo, in August, to be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy.
New modeling study
Dr. Law and colleagues modeled the potential public health impact – both clinical and economic – of the maternal RSV vaccine among the population of all pregnant women and their infants born during a 12-month period in the United States. The model focused on severe RSV disease in babies that required medical attention.
According to their model, without widespread use of the maternal RSV vaccine, 48,246 hospitalizations, 144,495 emergency department encounters, and 399,313 outpatient clinic visits related to RSV are projected to occur annually among the U.S. birth cohort of 3.7 million infants younger than 12 months.
With widespread use of the vaccine, annual hospitalizations resulting from infant RSV would fall by 51%, emergency department encounters would decline by 32%, and outpatient clinic visits by 32% – corresponding to a decrease in direct medical costs of about $692 million and indirect nonmedical costs of roughly $110 million.
Dr. Law highlighted two important caveats to the data. “The protections are based on the year-round administration of the vaccine to pregnant women at 32 to 36 weeks’ gestational age, and this is also assuming 100% uptake. Of course, in reality, that most likely is not the case,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa noted that the peak age for severe RSV illness is 3 months and it’s tough to identify infants at highest risk for severe RSV.
Nearly 80% of infants with RSV who are hospitalized do not have an underlying medical condition, “so we don’t even know who those high-risk infants are. That’s why having this vaccine is so exciting,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa said it’s also important to note that infants with severe RSV typically make not just one but multiple visits to the clinic or emergency department, leading to missed days of work for the parent, not to mention the “emotional burden of having your otherwise healthy newborn or young infant in the hospital.”
In addition to Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine, the FDA in July approved AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody nirsevimab (Beyfortus) for the prevention of RSV in neonates and infants entering their first RSV season, and in children up to 24 months who remain vulnerable to severe RSV disease through their second RSV season.
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Law is employed by Pfizer. Dr. Halasa has received grant and research support from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to research presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“With RSV maternal vaccination that is associated with clinical efficacy of 69% against severe RSV disease at 6 months, we estimated that up to 200,000 cases can be averted, and that is associated with almost $800 million in total,” presenting author Amy W. Law, PharmD, director of global value and evidence at Pfizer, pointed out during a news briefing.
“RSV is associated with a significant burden in the U.S. and this newly approved and recommended maternal RSV vaccine can have substantial impact in easing some of that burden,” Dr. Law explained.
This study is “particularly timely as we head into RSV peak season,” said briefing moderator Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The challenge, said Dr. Halasa, is that uptake of maternal vaccines and vaccines in general is “not optimal,” making increased awareness of this new maternal RSV vaccine important.
Strong efficacy data
Most children are infected with RSV at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
As reported previously by this news organization, in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study, Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine had an almost 82% efficacy against severe RSV infection in infants from birth through the first 90 days of life.
The vaccine also had a 69% efficacy against severe disease through the first 6 months of life. As part of the trial, a total of 7,400 women received a single dose of the vaccine in the late second or third trimester of their pregnancy. There were no signs of safety issues for the mothers or infants.
Based on the results, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the vaccine, known as Abrysvo, in August, to be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy.
New modeling study
Dr. Law and colleagues modeled the potential public health impact – both clinical and economic – of the maternal RSV vaccine among the population of all pregnant women and their infants born during a 12-month period in the United States. The model focused on severe RSV disease in babies that required medical attention.
According to their model, without widespread use of the maternal RSV vaccine, 48,246 hospitalizations, 144,495 emergency department encounters, and 399,313 outpatient clinic visits related to RSV are projected to occur annually among the U.S. birth cohort of 3.7 million infants younger than 12 months.
With widespread use of the vaccine, annual hospitalizations resulting from infant RSV would fall by 51%, emergency department encounters would decline by 32%, and outpatient clinic visits by 32% – corresponding to a decrease in direct medical costs of about $692 million and indirect nonmedical costs of roughly $110 million.
Dr. Law highlighted two important caveats to the data. “The protections are based on the year-round administration of the vaccine to pregnant women at 32 to 36 weeks’ gestational age, and this is also assuming 100% uptake. Of course, in reality, that most likely is not the case,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa noted that the peak age for severe RSV illness is 3 months and it’s tough to identify infants at highest risk for severe RSV.
Nearly 80% of infants with RSV who are hospitalized do not have an underlying medical condition, “so we don’t even know who those high-risk infants are. That’s why having this vaccine is so exciting,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa said it’s also important to note that infants with severe RSV typically make not just one but multiple visits to the clinic or emergency department, leading to missed days of work for the parent, not to mention the “emotional burden of having your otherwise healthy newborn or young infant in the hospital.”
In addition to Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine, the FDA in July approved AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody nirsevimab (Beyfortus) for the prevention of RSV in neonates and infants entering their first RSV season, and in children up to 24 months who remain vulnerable to severe RSV disease through their second RSV season.
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Law is employed by Pfizer. Dr. Halasa has received grant and research support from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to research presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“With RSV maternal vaccination that is associated with clinical efficacy of 69% against severe RSV disease at 6 months, we estimated that up to 200,000 cases can be averted, and that is associated with almost $800 million in total,” presenting author Amy W. Law, PharmD, director of global value and evidence at Pfizer, pointed out during a news briefing.
“RSV is associated with a significant burden in the U.S. and this newly approved and recommended maternal RSV vaccine can have substantial impact in easing some of that burden,” Dr. Law explained.
This study is “particularly timely as we head into RSV peak season,” said briefing moderator Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The challenge, said Dr. Halasa, is that uptake of maternal vaccines and vaccines in general is “not optimal,” making increased awareness of this new maternal RSV vaccine important.
Strong efficacy data
Most children are infected with RSV at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
As reported previously by this news organization, in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study, Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine had an almost 82% efficacy against severe RSV infection in infants from birth through the first 90 days of life.
The vaccine also had a 69% efficacy against severe disease through the first 6 months of life. As part of the trial, a total of 7,400 women received a single dose of the vaccine in the late second or third trimester of their pregnancy. There were no signs of safety issues for the mothers or infants.
Based on the results, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the vaccine, known as Abrysvo, in August, to be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy.
New modeling study
Dr. Law and colleagues modeled the potential public health impact – both clinical and economic – of the maternal RSV vaccine among the population of all pregnant women and their infants born during a 12-month period in the United States. The model focused on severe RSV disease in babies that required medical attention.
According to their model, without widespread use of the maternal RSV vaccine, 48,246 hospitalizations, 144,495 emergency department encounters, and 399,313 outpatient clinic visits related to RSV are projected to occur annually among the U.S. birth cohort of 3.7 million infants younger than 12 months.
With widespread use of the vaccine, annual hospitalizations resulting from infant RSV would fall by 51%, emergency department encounters would decline by 32%, and outpatient clinic visits by 32% – corresponding to a decrease in direct medical costs of about $692 million and indirect nonmedical costs of roughly $110 million.
Dr. Law highlighted two important caveats to the data. “The protections are based on the year-round administration of the vaccine to pregnant women at 32 to 36 weeks’ gestational age, and this is also assuming 100% uptake. Of course, in reality, that most likely is not the case,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa noted that the peak age for severe RSV illness is 3 months and it’s tough to identify infants at highest risk for severe RSV.
Nearly 80% of infants with RSV who are hospitalized do not have an underlying medical condition, “so we don’t even know who those high-risk infants are. That’s why having this vaccine is so exciting,” she told the briefing.
Dr. Halasa said it’s also important to note that infants with severe RSV typically make not just one but multiple visits to the clinic or emergency department, leading to missed days of work for the parent, not to mention the “emotional burden of having your otherwise healthy newborn or young infant in the hospital.”
In addition to Pfizer’s maternal RSV vaccine, the FDA in July approved AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody nirsevimab (Beyfortus) for the prevention of RSV in neonates and infants entering their first RSV season, and in children up to 24 months who remain vulnerable to severe RSV disease through their second RSV season.
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Law is employed by Pfizer. Dr. Halasa has received grant and research support from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IDWEEK 2023
AI detects hidden, potentially curable pancreatic cancers
TOPLINE:
new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers utilized a diverse dataset of 3,014 CT scans: 1,105 diagnostic CT scans with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) and 1,909 control CT scans.
- Of the total, 696 diagnostic CT scans with PDA and 1,080 control CT scans were used as an AI model training subset, and 409 CT scans with PDA and 829 control CT scans were used as an intramural hold-out test subset.
- The model was also tested on a simulated cohort that evaluated the risk for PDA in new-onset diabetes; multicenter public datasets (194 CT scans with PDA and 80 controls); and a cohort of 100 prediagnostic CT scans, incidentally acquired 3-36 months prior to PDA being diagnosed, and 134 controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The model correctly classified 360 CT scans with PDA (88%) and 783 control CT scans (94%) in the intramural test subset. The mean accuracy was 0.92, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.97, sensitivity was 0.88, and specificity was 0.95.
- On heat maps, activation areas overlapped with the tumor in 350 of 360 CT scans (97%).
- Performance was high across tumor stages, with sensitivities of 0.80, 0.87, 0.95, and 1.0 on T1 through T4 stages, respectively. Performance was comparable for hypodense versus isodense tumors (sensitivity of 0.90 vs. 0.82, respectively), patient demographics, CT slice thicknesses, and vendors.
- Findings were generalizable on both the simulated cohort (accuracy, 0.95; area under the ROC curve, 0.97) and public datasets (accuracy, 0.86; AUROC, 0.9).
- Occult PDA was detected on prediagnostic CT scans at a median 475 days before clinical diagnosis. Accuracy was 0.84, AUROC was 0.91, sensitivity was 0.75, and specificity was 0.9.
IN PRACTICE:
“Artificial intelligence model could mitigate the inadequacies of imaging and the diagnostic errors in interpretation, which often contribute to delayed diagnosis of pancreas cancer. In combination with emerging blood-based biomarkers, such a model could be evaluated to screen for sporadic cancer in ongoing trials of high-risk cohorts such as the Early Detection Initiative (NCT04662879).”
SOURCE:
Panagiotis Korfiatis, PhD, of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., led the study, which was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design is prone to selection bias. Results are presented dichotomously as either cancer or control. These are preliminary insights, and prospective clinical trials that incorporate epidemiological risk factors and emerging blood-based biomarkers are needed to further evaluate the model’s performance.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the Centene Charitable Foundation, and the Champions for Hope Pancreatic Cancer Research Program of the Funk Zitiello Foundation. One author received an institutional research grant from Sofie Biosciences and Clovis Oncology, is on the BlueStar Genomics advisory board (ad hoc), and is a consultant for Bayer Healthcare, Candel Therapeutics, and UWorld. The remaining authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers utilized a diverse dataset of 3,014 CT scans: 1,105 diagnostic CT scans with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) and 1,909 control CT scans.
- Of the total, 696 diagnostic CT scans with PDA and 1,080 control CT scans were used as an AI model training subset, and 409 CT scans with PDA and 829 control CT scans were used as an intramural hold-out test subset.
- The model was also tested on a simulated cohort that evaluated the risk for PDA in new-onset diabetes; multicenter public datasets (194 CT scans with PDA and 80 controls); and a cohort of 100 prediagnostic CT scans, incidentally acquired 3-36 months prior to PDA being diagnosed, and 134 controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The model correctly classified 360 CT scans with PDA (88%) and 783 control CT scans (94%) in the intramural test subset. The mean accuracy was 0.92, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.97, sensitivity was 0.88, and specificity was 0.95.
- On heat maps, activation areas overlapped with the tumor in 350 of 360 CT scans (97%).
- Performance was high across tumor stages, with sensitivities of 0.80, 0.87, 0.95, and 1.0 on T1 through T4 stages, respectively. Performance was comparable for hypodense versus isodense tumors (sensitivity of 0.90 vs. 0.82, respectively), patient demographics, CT slice thicknesses, and vendors.
- Findings were generalizable on both the simulated cohort (accuracy, 0.95; area under the ROC curve, 0.97) and public datasets (accuracy, 0.86; AUROC, 0.9).
- Occult PDA was detected on prediagnostic CT scans at a median 475 days before clinical diagnosis. Accuracy was 0.84, AUROC was 0.91, sensitivity was 0.75, and specificity was 0.9.
IN PRACTICE:
“Artificial intelligence model could mitigate the inadequacies of imaging and the diagnostic errors in interpretation, which often contribute to delayed diagnosis of pancreas cancer. In combination with emerging blood-based biomarkers, such a model could be evaluated to screen for sporadic cancer in ongoing trials of high-risk cohorts such as the Early Detection Initiative (NCT04662879).”
SOURCE:
Panagiotis Korfiatis, PhD, of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., led the study, which was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design is prone to selection bias. Results are presented dichotomously as either cancer or control. These are preliminary insights, and prospective clinical trials that incorporate epidemiological risk factors and emerging blood-based biomarkers are needed to further evaluate the model’s performance.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the Centene Charitable Foundation, and the Champions for Hope Pancreatic Cancer Research Program of the Funk Zitiello Foundation. One author received an institutional research grant from Sofie Biosciences and Clovis Oncology, is on the BlueStar Genomics advisory board (ad hoc), and is a consultant for Bayer Healthcare, Candel Therapeutics, and UWorld. The remaining authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers utilized a diverse dataset of 3,014 CT scans: 1,105 diagnostic CT scans with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) and 1,909 control CT scans.
- Of the total, 696 diagnostic CT scans with PDA and 1,080 control CT scans were used as an AI model training subset, and 409 CT scans with PDA and 829 control CT scans were used as an intramural hold-out test subset.
- The model was also tested on a simulated cohort that evaluated the risk for PDA in new-onset diabetes; multicenter public datasets (194 CT scans with PDA and 80 controls); and a cohort of 100 prediagnostic CT scans, incidentally acquired 3-36 months prior to PDA being diagnosed, and 134 controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The model correctly classified 360 CT scans with PDA (88%) and 783 control CT scans (94%) in the intramural test subset. The mean accuracy was 0.92, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.97, sensitivity was 0.88, and specificity was 0.95.
- On heat maps, activation areas overlapped with the tumor in 350 of 360 CT scans (97%).
- Performance was high across tumor stages, with sensitivities of 0.80, 0.87, 0.95, and 1.0 on T1 through T4 stages, respectively. Performance was comparable for hypodense versus isodense tumors (sensitivity of 0.90 vs. 0.82, respectively), patient demographics, CT slice thicknesses, and vendors.
- Findings were generalizable on both the simulated cohort (accuracy, 0.95; area under the ROC curve, 0.97) and public datasets (accuracy, 0.86; AUROC, 0.9).
- Occult PDA was detected on prediagnostic CT scans at a median 475 days before clinical diagnosis. Accuracy was 0.84, AUROC was 0.91, sensitivity was 0.75, and specificity was 0.9.
IN PRACTICE:
“Artificial intelligence model could mitigate the inadequacies of imaging and the diagnostic errors in interpretation, which often contribute to delayed diagnosis of pancreas cancer. In combination with emerging blood-based biomarkers, such a model could be evaluated to screen for sporadic cancer in ongoing trials of high-risk cohorts such as the Early Detection Initiative (NCT04662879).”
SOURCE:
Panagiotis Korfiatis, PhD, of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., led the study, which was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design is prone to selection bias. Results are presented dichotomously as either cancer or control. These are preliminary insights, and prospective clinical trials that incorporate epidemiological risk factors and emerging blood-based biomarkers are needed to further evaluate the model’s performance.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the Centene Charitable Foundation, and the Champions for Hope Pancreatic Cancer Research Program of the Funk Zitiello Foundation. One author received an institutional research grant from Sofie Biosciences and Clovis Oncology, is on the BlueStar Genomics advisory board (ad hoc), and is a consultant for Bayer Healthcare, Candel Therapeutics, and UWorld. The remaining authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wastewater can signal upswing in flu, RSV
according to new research reported at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The analysis of wastewater in Calgary (Alta.) found a “positive correlation” between positivity rates for these three viruses in wastewater and weekly laboratory-confirmed clinical cases and test positivity rates, study investigator Kristine Du, with Cumming School of Medicine, University of Calgary, told this news organization.
Wastewater monitoring of viral activity has become an established tool for COVID-19 pandemic monitoring, providing a leading indicator to cases and hospitalizations. However, less is known about its potential for monitoring endemic respiratory viruses.
The new study shows that wastewater-based surveillance is a “robust and adaptable” tool for community-level surveillance of seasonal respiratory viruses – “one that can complement health care clinical testing because it’s independent from testing biases, and we can actually correlate our cases very well with it,” Ms. Du said during a preconference media briefing.
Tracking community trends
For the study, Ms. Du and colleagues assessed the occurrence of influenza A, influenza B, and RSV RNA in all three wastewater treatment plants in Calgary between March 2022 and April 2023 and its correlation with clinical disease.
They found that viral signals in Calgary’s wastewater for influenza A and B and RSV correlated significantly with weekly confirmed clinical cases in Calgary residents.
Influenza A peaked in Calgary’s wastewater between November and December 2022; influenza B peaked between February and April 2023; and RSV between November 2022 and February 2023.
“Wastewater gives us unbiased, objective, and comprehensive data. It can be used in addition to other testing for assessing the community burden that disease may have, and it is complementary to clinical testing,” Ms. Du said.
Their team, Ms. Du said, is continuing to proactively monitor wastewater for influenza and RSV, as well as other agents of “pandemic potential to make sure we know what could affect humans – and make sure everyone is aware of that.”
Commenting on the research, briefing moderator Belinda Ostrowsky, MD, MPH, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said, “Wastewater surveillance illustrates how understanding community levels of viral trends can identify hotspots, inform local public health decision-making, and prepare clinicians and hospitals for potential outreach. This topic is particularly timely as we head into the flu and RSV season.”
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Du and Dr. Ostrowsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research reported at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The analysis of wastewater in Calgary (Alta.) found a “positive correlation” between positivity rates for these three viruses in wastewater and weekly laboratory-confirmed clinical cases and test positivity rates, study investigator Kristine Du, with Cumming School of Medicine, University of Calgary, told this news organization.
Wastewater monitoring of viral activity has become an established tool for COVID-19 pandemic monitoring, providing a leading indicator to cases and hospitalizations. However, less is known about its potential for monitoring endemic respiratory viruses.
The new study shows that wastewater-based surveillance is a “robust and adaptable” tool for community-level surveillance of seasonal respiratory viruses – “one that can complement health care clinical testing because it’s independent from testing biases, and we can actually correlate our cases very well with it,” Ms. Du said during a preconference media briefing.
Tracking community trends
For the study, Ms. Du and colleagues assessed the occurrence of influenza A, influenza B, and RSV RNA in all three wastewater treatment plants in Calgary between March 2022 and April 2023 and its correlation with clinical disease.
They found that viral signals in Calgary’s wastewater for influenza A and B and RSV correlated significantly with weekly confirmed clinical cases in Calgary residents.
Influenza A peaked in Calgary’s wastewater between November and December 2022; influenza B peaked between February and April 2023; and RSV between November 2022 and February 2023.
“Wastewater gives us unbiased, objective, and comprehensive data. It can be used in addition to other testing for assessing the community burden that disease may have, and it is complementary to clinical testing,” Ms. Du said.
Their team, Ms. Du said, is continuing to proactively monitor wastewater for influenza and RSV, as well as other agents of “pandemic potential to make sure we know what could affect humans – and make sure everyone is aware of that.”
Commenting on the research, briefing moderator Belinda Ostrowsky, MD, MPH, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said, “Wastewater surveillance illustrates how understanding community levels of viral trends can identify hotspots, inform local public health decision-making, and prepare clinicians and hospitals for potential outreach. This topic is particularly timely as we head into the flu and RSV season.”
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Du and Dr. Ostrowsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research reported at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The analysis of wastewater in Calgary (Alta.) found a “positive correlation” between positivity rates for these three viruses in wastewater and weekly laboratory-confirmed clinical cases and test positivity rates, study investigator Kristine Du, with Cumming School of Medicine, University of Calgary, told this news organization.
Wastewater monitoring of viral activity has become an established tool for COVID-19 pandemic monitoring, providing a leading indicator to cases and hospitalizations. However, less is known about its potential for monitoring endemic respiratory viruses.
The new study shows that wastewater-based surveillance is a “robust and adaptable” tool for community-level surveillance of seasonal respiratory viruses – “one that can complement health care clinical testing because it’s independent from testing biases, and we can actually correlate our cases very well with it,” Ms. Du said during a preconference media briefing.
Tracking community trends
For the study, Ms. Du and colleagues assessed the occurrence of influenza A, influenza B, and RSV RNA in all three wastewater treatment plants in Calgary between March 2022 and April 2023 and its correlation with clinical disease.
They found that viral signals in Calgary’s wastewater for influenza A and B and RSV correlated significantly with weekly confirmed clinical cases in Calgary residents.
Influenza A peaked in Calgary’s wastewater between November and December 2022; influenza B peaked between February and April 2023; and RSV between November 2022 and February 2023.
“Wastewater gives us unbiased, objective, and comprehensive data. It can be used in addition to other testing for assessing the community burden that disease may have, and it is complementary to clinical testing,” Ms. Du said.
Their team, Ms. Du said, is continuing to proactively monitor wastewater for influenza and RSV, as well as other agents of “pandemic potential to make sure we know what could affect humans – and make sure everyone is aware of that.”
Commenting on the research, briefing moderator Belinda Ostrowsky, MD, MPH, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said, “Wastewater surveillance illustrates how understanding community levels of viral trends can identify hotspots, inform local public health decision-making, and prepare clinicians and hospitals for potential outreach. This topic is particularly timely as we head into the flu and RSV season.”
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Du and Dr. Ostrowsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IDWEEK 2023
Pragmatic solutions to ‘catastrophic’ global stroke burden
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY
Atopic dermatitis: Five things to know
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, pruritic inflammatory skin condition that typically affects the face (cheeks), neck, arms, and legs but usually spares the groin and axillary regions. AD usually starts in early infancy but also affects some adults. AD is often associated with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE). That it is the first disease to present in a series of allergic diseases – including food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, in order – and has given rise to the “atopic march” theory, which suggests that AD is part of a progression that may lead to subsequent allergic disease at other epithelial barrier surfaces.
.
1. Essential features of AD are pruritus and eczema
The diagnosis of AD is primarily observational. It is made on the basis of patient and family history, pattern of lesions, morphology, and clinical signs. No genetic features or biomarkers are specific enough to reliably aid in diagnosis or severity assessment. Many individual findings are used to diagnose AD, as summarized by the American Academy of Dermatology based on essential, important, associated, and exclusionary features:
- Essential features (must be present for diagnosis) are pruritus and eczema (acute, subacute, or chronic) with typical morphology and age-specific patterns and chronic or relapsing history.
- Important features (usually seen in AD and support the diagnosis) are early age of onset, atopy (personal/family history, IgE reactivity), and xerosis.
- Associated features (nonspecific but suggestive) are atypical vascular response (e.g., delayed blanch response); keratosis pilaris (and some others); ocular/periorbital changes; other regional findings (e.g., perioral changes); and perifollicular accentuation, lichenification, or prurigo lesions.
- Exclusionary conditions (must be excluded to make the AD diagnosis) are scabies, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, ichthyoses, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis, photosensitivity dermatoses, immune deficiency diseases, and erythroderma due to other causes.
AD should be differentiated from other red, scaly skin conditions. It is often difficult to separate AD from seborrheic dermatitis in infancy, and the two conditions may overlap in this age group. Particularly if the condition is not responding to therapy, the diagnosis of AD should be re-reviewed and other disorders considered, including more serious nutritional, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in children and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in adults. Allergic contact dermatitis may be both an alternative diagnosis to AD and an exacerbator of AD in some individuals.
2. Associated comorbidities of AD may exacerbate the condition and lead to other atopic disorders
Reported comorbidities of AD include other atopic or allergic conditions, autoimmune diseases, infections, metabolic conditions, mental health disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Certain aspects of AD, such as chronic pruritus, psychosocial distress, and inflammation, can lead to anxiety, depression, and suicidality. AD is associated with and may predispose to higher risk for other atopic disorders, including asthma, hay fever, food allergy, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Persons with AD also appear to be at higher risk for infectious diseases. The prevalence of cutaneous and systemic infections in patients with AD is significantly higher than those without AD. Infectious complications can include skin and soft-tissue infections, bacteremia, eczema herpeticum, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, and septic arthritis.
3. Climate change has a profound impact on AD
The incidence of AD has increased over the past several decades, and environmental factors such as climate change have been implicated as a potential mechanism. Climate change–related factors affect the skin’s capacity to maintain homeostasis, leading to various cutaneous diseases. AD, psoriasis, pemphigus, acne vulgaris, melasma, and photoaging are all associated with rising levels of air pollution. Elevated temperatures due to global warming induce disruption of the skin microbiome, thereby affecting AD.
Extreme weather events due to climate change, including floods and wildfires, are implicated in cutaneous injuries, skin infections, and acute worsening of inflammatory skin disorders.
4. The impact and appearance of AD varies in different racial groups
It was once believed that AD was just one single disease affecting people of many different races. More recently, it has been proposed that AD is in fact a group of different diseases. Both epidemiologic and genetic factors may play a role in influencing the main features of AD.
Spongiotic processes such as AD that would be pink or erythematous on white skin are often hypopigmented in individuals with darkly pigmented skin. AD has a higher prevalence and severity in Black and mixed-race populations, probably owing to a combination of environmental and intrinsic factors. Black skin has been shown to have increased transepidermal water loss and lower levels of ceramides, which are important components of the lipid barrier in the stratum corneum.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, along with the Allergy & Asthma Network, are partnering to create Eczema in Skin of Color, a website to aid physicians and patients in recognizing eczema in people with all skin types.
5. New and emerging therapies are poised to improve outcomes with AD treatment
Ruxolitinib cream, a topical Janus kinase (JAK)-1/JAK2 inhibitor, was approved for AD by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in September 2021. The approval was based on results from the Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in AD (TRuE-AD) clinical trial program, which consisted of phase 3 studies that investigated 1,249 patients aged greater than or equal to 12 years with mild to moderate AD (Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 2-3) with a body surface area of 3%-20% (excluding scalp). The 2023 AAD guidelines for topical treatment recommend ruxolitinib cream for adults with mild to moderate AD.
Tralokinumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the interleukin-13 cytokines, which prevents the release of cytokines, chemokines, and IgE. It was approved by the FDA in 2021 for treatment of moderate to severe AD. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. Approval was based on the phase 3 trials ECZTRA 1, 2, and 3, which assessed the efficacy of tralokinumab in 1,934 adults.
Abrocitinib is an oral, once-daily JAK1 inhibitor for treatment of adults living with refractory, moderate to severe AD. FDA approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale trial program of more than 1,600 patients. Across the trials, abrocitinib demonstrated a consistent safety profile and profound improvements in skin clearance, extent of disease, and severity, as well as rapid improvement in itch after 2 weeks, for some people living with AD vs placebo.
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK1 inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in January 2022 for refractory moderate to severe AD. Approval was based on three double-blind phase 3 trials (Measure Up 1, Measure Up 2, AD Up) in which 2,584 patients with moderate to severe AD were randomized to receive oral upadacitinib 15 mg/d and 30 mg/d. In Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2, upadacitinib was evaluated as monotherapy; in AD Up, upadacitinib was evaluated in combination with topical corticosteroids.
On the horizon
Baricitinib, an oral JAK1/2 inhibitor, is not yet approved by the FDA for AD. It is, however, approved for moderate to severe AD treatment in the European Union and many other countries. A 2022 review of studies evaluating baricitinib for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults (BREEZE-AD1, -AD2, -AD3, -AD4, -AD5, -AD6) reported that current evidence supports baricitinib, used as monotherapy or in combination with topical corticosteroids, as a safe and effective agent that can be used as an alternative to subcutaneous biologics in adults with moderate to severe AD.
Topical JAK inhibitors
A 2023 systematic review (19 studies, 3,600 participants) reported on several topical JAK inhibitors that are effective for treating AD. It suggests a stronger safety profile and better results, compared with systemic JAK inhibitors. The review focused on topical delgocitinib, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, cerdulatinib, and ifidancitinib. All agents were effective in treating AD. All of these topical JAK inhibitors had minimal risk for mild to moderate adverse effects.
Biologics
Lebrikizumab was evaluated in a phase 2b, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. After 16 weeks (280 participants), patients with moderate to severe AD showed a dose-dependent significant improvement in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo. Two phase 3 trials (ADvocate1, ADvocate2) evaluated the safety and efficacy of monotherapy with lebrikizumab in adults and adolescents with moderate to severe AD.
Nemolizumab, assessed in long-term phase 3 trials of AD-associated pruritus, resulted in clinically meaningful improvements from the beginning of treatment to week 68. Nemolizumab is being evaluated in two identical phase 3 studies (Arcadia 1, Arcadia 2) and a long-term extension study.
Dr. Kim is Professor and Vice Chair of Research in the department of dermatology, as well as Director of the Mark Lebwohl Center for Neuroinflammation and Sensation at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He reported conflicts of interest with 23andMe, Abrax Japan, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, and KiiRNA Biotech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, pruritic inflammatory skin condition that typically affects the face (cheeks), neck, arms, and legs but usually spares the groin and axillary regions. AD usually starts in early infancy but also affects some adults. AD is often associated with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE). That it is the first disease to present in a series of allergic diseases – including food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, in order – and has given rise to the “atopic march” theory, which suggests that AD is part of a progression that may lead to subsequent allergic disease at other epithelial barrier surfaces.
.
1. Essential features of AD are pruritus and eczema
The diagnosis of AD is primarily observational. It is made on the basis of patient and family history, pattern of lesions, morphology, and clinical signs. No genetic features or biomarkers are specific enough to reliably aid in diagnosis or severity assessment. Many individual findings are used to diagnose AD, as summarized by the American Academy of Dermatology based on essential, important, associated, and exclusionary features:
- Essential features (must be present for diagnosis) are pruritus and eczema (acute, subacute, or chronic) with typical morphology and age-specific patterns and chronic or relapsing history.
- Important features (usually seen in AD and support the diagnosis) are early age of onset, atopy (personal/family history, IgE reactivity), and xerosis.
- Associated features (nonspecific but suggestive) are atypical vascular response (e.g., delayed blanch response); keratosis pilaris (and some others); ocular/periorbital changes; other regional findings (e.g., perioral changes); and perifollicular accentuation, lichenification, or prurigo lesions.
- Exclusionary conditions (must be excluded to make the AD diagnosis) are scabies, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, ichthyoses, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis, photosensitivity dermatoses, immune deficiency diseases, and erythroderma due to other causes.
AD should be differentiated from other red, scaly skin conditions. It is often difficult to separate AD from seborrheic dermatitis in infancy, and the two conditions may overlap in this age group. Particularly if the condition is not responding to therapy, the diagnosis of AD should be re-reviewed and other disorders considered, including more serious nutritional, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in children and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in adults. Allergic contact dermatitis may be both an alternative diagnosis to AD and an exacerbator of AD in some individuals.
2. Associated comorbidities of AD may exacerbate the condition and lead to other atopic disorders
Reported comorbidities of AD include other atopic or allergic conditions, autoimmune diseases, infections, metabolic conditions, mental health disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Certain aspects of AD, such as chronic pruritus, psychosocial distress, and inflammation, can lead to anxiety, depression, and suicidality. AD is associated with and may predispose to higher risk for other atopic disorders, including asthma, hay fever, food allergy, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Persons with AD also appear to be at higher risk for infectious diseases. The prevalence of cutaneous and systemic infections in patients with AD is significantly higher than those without AD. Infectious complications can include skin and soft-tissue infections, bacteremia, eczema herpeticum, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, and septic arthritis.
3. Climate change has a profound impact on AD
The incidence of AD has increased over the past several decades, and environmental factors such as climate change have been implicated as a potential mechanism. Climate change–related factors affect the skin’s capacity to maintain homeostasis, leading to various cutaneous diseases. AD, psoriasis, pemphigus, acne vulgaris, melasma, and photoaging are all associated with rising levels of air pollution. Elevated temperatures due to global warming induce disruption of the skin microbiome, thereby affecting AD.
Extreme weather events due to climate change, including floods and wildfires, are implicated in cutaneous injuries, skin infections, and acute worsening of inflammatory skin disorders.
4. The impact and appearance of AD varies in different racial groups
It was once believed that AD was just one single disease affecting people of many different races. More recently, it has been proposed that AD is in fact a group of different diseases. Both epidemiologic and genetic factors may play a role in influencing the main features of AD.
Spongiotic processes such as AD that would be pink or erythematous on white skin are often hypopigmented in individuals with darkly pigmented skin. AD has a higher prevalence and severity in Black and mixed-race populations, probably owing to a combination of environmental and intrinsic factors. Black skin has been shown to have increased transepidermal water loss and lower levels of ceramides, which are important components of the lipid barrier in the stratum corneum.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, along with the Allergy & Asthma Network, are partnering to create Eczema in Skin of Color, a website to aid physicians and patients in recognizing eczema in people with all skin types.
5. New and emerging therapies are poised to improve outcomes with AD treatment
Ruxolitinib cream, a topical Janus kinase (JAK)-1/JAK2 inhibitor, was approved for AD by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in September 2021. The approval was based on results from the Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in AD (TRuE-AD) clinical trial program, which consisted of phase 3 studies that investigated 1,249 patients aged greater than or equal to 12 years with mild to moderate AD (Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 2-3) with a body surface area of 3%-20% (excluding scalp). The 2023 AAD guidelines for topical treatment recommend ruxolitinib cream for adults with mild to moderate AD.
Tralokinumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the interleukin-13 cytokines, which prevents the release of cytokines, chemokines, and IgE. It was approved by the FDA in 2021 for treatment of moderate to severe AD. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. Approval was based on the phase 3 trials ECZTRA 1, 2, and 3, which assessed the efficacy of tralokinumab in 1,934 adults.
Abrocitinib is an oral, once-daily JAK1 inhibitor for treatment of adults living with refractory, moderate to severe AD. FDA approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale trial program of more than 1,600 patients. Across the trials, abrocitinib demonstrated a consistent safety profile and profound improvements in skin clearance, extent of disease, and severity, as well as rapid improvement in itch after 2 weeks, for some people living with AD vs placebo.
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK1 inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in January 2022 for refractory moderate to severe AD. Approval was based on three double-blind phase 3 trials (Measure Up 1, Measure Up 2, AD Up) in which 2,584 patients with moderate to severe AD were randomized to receive oral upadacitinib 15 mg/d and 30 mg/d. In Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2, upadacitinib was evaluated as monotherapy; in AD Up, upadacitinib was evaluated in combination with topical corticosteroids.
On the horizon
Baricitinib, an oral JAK1/2 inhibitor, is not yet approved by the FDA for AD. It is, however, approved for moderate to severe AD treatment in the European Union and many other countries. A 2022 review of studies evaluating baricitinib for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults (BREEZE-AD1, -AD2, -AD3, -AD4, -AD5, -AD6) reported that current evidence supports baricitinib, used as monotherapy or in combination with topical corticosteroids, as a safe and effective agent that can be used as an alternative to subcutaneous biologics in adults with moderate to severe AD.
Topical JAK inhibitors
A 2023 systematic review (19 studies, 3,600 participants) reported on several topical JAK inhibitors that are effective for treating AD. It suggests a stronger safety profile and better results, compared with systemic JAK inhibitors. The review focused on topical delgocitinib, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, cerdulatinib, and ifidancitinib. All agents were effective in treating AD. All of these topical JAK inhibitors had minimal risk for mild to moderate adverse effects.
Biologics
Lebrikizumab was evaluated in a phase 2b, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. After 16 weeks (280 participants), patients with moderate to severe AD showed a dose-dependent significant improvement in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo. Two phase 3 trials (ADvocate1, ADvocate2) evaluated the safety and efficacy of monotherapy with lebrikizumab in adults and adolescents with moderate to severe AD.
Nemolizumab, assessed in long-term phase 3 trials of AD-associated pruritus, resulted in clinically meaningful improvements from the beginning of treatment to week 68. Nemolizumab is being evaluated in two identical phase 3 studies (Arcadia 1, Arcadia 2) and a long-term extension study.
Dr. Kim is Professor and Vice Chair of Research in the department of dermatology, as well as Director of the Mark Lebwohl Center for Neuroinflammation and Sensation at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He reported conflicts of interest with 23andMe, Abrax Japan, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, and KiiRNA Biotech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, pruritic inflammatory skin condition that typically affects the face (cheeks), neck, arms, and legs but usually spares the groin and axillary regions. AD usually starts in early infancy but also affects some adults. AD is often associated with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE). That it is the first disease to present in a series of allergic diseases – including food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, in order – and has given rise to the “atopic march” theory, which suggests that AD is part of a progression that may lead to subsequent allergic disease at other epithelial barrier surfaces.
.
1. Essential features of AD are pruritus and eczema
The diagnosis of AD is primarily observational. It is made on the basis of patient and family history, pattern of lesions, morphology, and clinical signs. No genetic features or biomarkers are specific enough to reliably aid in diagnosis or severity assessment. Many individual findings are used to diagnose AD, as summarized by the American Academy of Dermatology based on essential, important, associated, and exclusionary features:
- Essential features (must be present for diagnosis) are pruritus and eczema (acute, subacute, or chronic) with typical morphology and age-specific patterns and chronic or relapsing history.
- Important features (usually seen in AD and support the diagnosis) are early age of onset, atopy (personal/family history, IgE reactivity), and xerosis.
- Associated features (nonspecific but suggestive) are atypical vascular response (e.g., delayed blanch response); keratosis pilaris (and some others); ocular/periorbital changes; other regional findings (e.g., perioral changes); and perifollicular accentuation, lichenification, or prurigo lesions.
- Exclusionary conditions (must be excluded to make the AD diagnosis) are scabies, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, ichthyoses, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis, photosensitivity dermatoses, immune deficiency diseases, and erythroderma due to other causes.
AD should be differentiated from other red, scaly skin conditions. It is often difficult to separate AD from seborrheic dermatitis in infancy, and the two conditions may overlap in this age group. Particularly if the condition is not responding to therapy, the diagnosis of AD should be re-reviewed and other disorders considered, including more serious nutritional, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in children and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in adults. Allergic contact dermatitis may be both an alternative diagnosis to AD and an exacerbator of AD in some individuals.
2. Associated comorbidities of AD may exacerbate the condition and lead to other atopic disorders
Reported comorbidities of AD include other atopic or allergic conditions, autoimmune diseases, infections, metabolic conditions, mental health disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Certain aspects of AD, such as chronic pruritus, psychosocial distress, and inflammation, can lead to anxiety, depression, and suicidality. AD is associated with and may predispose to higher risk for other atopic disorders, including asthma, hay fever, food allergy, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Persons with AD also appear to be at higher risk for infectious diseases. The prevalence of cutaneous and systemic infections in patients with AD is significantly higher than those without AD. Infectious complications can include skin and soft-tissue infections, bacteremia, eczema herpeticum, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, and septic arthritis.
3. Climate change has a profound impact on AD
The incidence of AD has increased over the past several decades, and environmental factors such as climate change have been implicated as a potential mechanism. Climate change–related factors affect the skin’s capacity to maintain homeostasis, leading to various cutaneous diseases. AD, psoriasis, pemphigus, acne vulgaris, melasma, and photoaging are all associated with rising levels of air pollution. Elevated temperatures due to global warming induce disruption of the skin microbiome, thereby affecting AD.
Extreme weather events due to climate change, including floods and wildfires, are implicated in cutaneous injuries, skin infections, and acute worsening of inflammatory skin disorders.
4. The impact and appearance of AD varies in different racial groups
It was once believed that AD was just one single disease affecting people of many different races. More recently, it has been proposed that AD is in fact a group of different diseases. Both epidemiologic and genetic factors may play a role in influencing the main features of AD.
Spongiotic processes such as AD that would be pink or erythematous on white skin are often hypopigmented in individuals with darkly pigmented skin. AD has a higher prevalence and severity in Black and mixed-race populations, probably owing to a combination of environmental and intrinsic factors. Black skin has been shown to have increased transepidermal water loss and lower levels of ceramides, which are important components of the lipid barrier in the stratum corneum.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, along with the Allergy & Asthma Network, are partnering to create Eczema in Skin of Color, a website to aid physicians and patients in recognizing eczema in people with all skin types.
5. New and emerging therapies are poised to improve outcomes with AD treatment
Ruxolitinib cream, a topical Janus kinase (JAK)-1/JAK2 inhibitor, was approved for AD by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in September 2021. The approval was based on results from the Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in AD (TRuE-AD) clinical trial program, which consisted of phase 3 studies that investigated 1,249 patients aged greater than or equal to 12 years with mild to moderate AD (Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 2-3) with a body surface area of 3%-20% (excluding scalp). The 2023 AAD guidelines for topical treatment recommend ruxolitinib cream for adults with mild to moderate AD.
Tralokinumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the interleukin-13 cytokines, which prevents the release of cytokines, chemokines, and IgE. It was approved by the FDA in 2021 for treatment of moderate to severe AD. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. Approval was based on the phase 3 trials ECZTRA 1, 2, and 3, which assessed the efficacy of tralokinumab in 1,934 adults.
Abrocitinib is an oral, once-daily JAK1 inhibitor for treatment of adults living with refractory, moderate to severe AD. FDA approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale trial program of more than 1,600 patients. Across the trials, abrocitinib demonstrated a consistent safety profile and profound improvements in skin clearance, extent of disease, and severity, as well as rapid improvement in itch after 2 weeks, for some people living with AD vs placebo.
Upadacitinib, another oral JAK1 inhibitor, was approved by the FDA in January 2022 for refractory moderate to severe AD. Approval was based on three double-blind phase 3 trials (Measure Up 1, Measure Up 2, AD Up) in which 2,584 patients with moderate to severe AD were randomized to receive oral upadacitinib 15 mg/d and 30 mg/d. In Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2, upadacitinib was evaluated as monotherapy; in AD Up, upadacitinib was evaluated in combination with topical corticosteroids.
On the horizon
Baricitinib, an oral JAK1/2 inhibitor, is not yet approved by the FDA for AD. It is, however, approved for moderate to severe AD treatment in the European Union and many other countries. A 2022 review of studies evaluating baricitinib for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults (BREEZE-AD1, -AD2, -AD3, -AD4, -AD5, -AD6) reported that current evidence supports baricitinib, used as monotherapy or in combination with topical corticosteroids, as a safe and effective agent that can be used as an alternative to subcutaneous biologics in adults with moderate to severe AD.
Topical JAK inhibitors
A 2023 systematic review (19 studies, 3,600 participants) reported on several topical JAK inhibitors that are effective for treating AD. It suggests a stronger safety profile and better results, compared with systemic JAK inhibitors. The review focused on topical delgocitinib, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, cerdulatinib, and ifidancitinib. All agents were effective in treating AD. All of these topical JAK inhibitors had minimal risk for mild to moderate adverse effects.
Biologics
Lebrikizumab was evaluated in a phase 2b, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. After 16 weeks (280 participants), patients with moderate to severe AD showed a dose-dependent significant improvement in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo. Two phase 3 trials (ADvocate1, ADvocate2) evaluated the safety and efficacy of monotherapy with lebrikizumab in adults and adolescents with moderate to severe AD.
Nemolizumab, assessed in long-term phase 3 trials of AD-associated pruritus, resulted in clinically meaningful improvements from the beginning of treatment to week 68. Nemolizumab is being evaluated in two identical phase 3 studies (Arcadia 1, Arcadia 2) and a long-term extension study.
Dr. Kim is Professor and Vice Chair of Research in the department of dermatology, as well as Director of the Mark Lebwohl Center for Neuroinflammation and Sensation at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He reported conflicts of interest with 23andMe, Abrax Japan, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, and KiiRNA Biotech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alert! A decade of type 2 diabetes shortens life by 3.5 years
researchers estimate on the basis of data from studies conducted in 19 high-income countries.
They estimated that, among 50-year-olds, life expectancy of those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at age 30 is 14 years shorter than that of their peers without diabetes. Among those diagnosed at age 50, life expectancy is 6 years shorter.
The study was recently published in The Lancet – Diabetes and Endocrinology.
The team analyzed data from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The data were from 97 long-term, prospective cohorts and involved 1.5 million participants who were followed for 23.1 million person-years.
“The strongest associations with earlier age at diagnosis of diabetes were for vascular (for example, myocardial infarction and stroke) and other causes of death – mainly respiratory, neurological, and infectious diseases and external causes,” they reported.
Their findings are consistent with previous studies that suggested that younger individuals who develop type 2 diabetes might have higher body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and lipid levels and that they might experience faster deterioration in glycemic control than individuals who develop diabetes later, potentially leading to premature mortality.
Asked to comment, Anne Peters, MD, director of clinical diabetes programs at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this study, said: “We’ve long known that diabetes reduces life expectancy, and the younger you get it the more years you lose. However, this study was from a broader and larger population base than prior studies.
“In this study, the major reason for death was vascular disease, and undertreatment of cardiovascular risk factors may have occurred in the younger individuals. We also don’t know about glucose control.
“I personally think the findings show that we should treat cardiovascular risk factors more aggressively in people diagnosed with [type 2] diabetes in their 30s and 40s,” urged Dr. Peters.
High priority should be given to prevention globally
“Type 2 diabetes used to be seen as a disease that affected older adults, but we’re increasingly seeing people diagnosed earlier in life,” senior author Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD, from the University of Cambridge (England), explained in a press release. “As we’ve shown, this means they are at risk of a much shorter life expectancy than they would otherwise have.”
The findings suggest that “high priority should be given to developing and implementing interventions that prevent or delay the onset of [type 2 diabetes], especially as its prevalence among younger age groups is increasing globally,” the study authors wrote.
The results “support the idea that the younger an individual is when they develop type 2 diabetes, the more damage their body accumulates from its impaired metabolism,” added co–senior author Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, of the University of Glasgow,
Dr. Peters agreed: “People who develop type 2 diabetes at a younger age might have a different, potentially more aggressive type of type 2 diabetes and perhaps need treatment targets that are lower than people who develop type 2 diabetes when they are older.”
“The findings ... suggest that early detection of diabetes by screening followed by intensive glucose management could help prevent long-term complications from the condition,” Dr. Sattar said.
Dr. Peters added: “An issue for some is pregnancy. ... Many of the medications taken for management of CVD [cardiovascular disease] risk factors are contraindicated in pregnancy (as are many of the medications [for treating type 2 diabetes]).
“We need to be careful to risk reduce but take care of the ‘whole person,’ and if of childbearing age, consider the safest approaches to healthy management,” she emphasized.
Study results: Type 2 diabetes diagnosed at age 30, 40, and 50
Previous studies estimated that adults with type 2 diabetes die 6 years earlier on average in comparison with their counterparts who do not have diabetes, but it was not known how diabetes duration affects life span.
To investigate this, the team analyzed individual records from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Other outcomes were deaths from CVD, cancer, and other causes.
Over a median follow-up of 12.5 years, there were 246,670 deaths: 84,443 from cardiovascular causes, 150, 972 from noncardiovascular causes, and 11,255 from unknown/ill-defined causes.
Compared with participants who did not have a history of type 2 diabetes, the hazard ratios for all-cause mortality, adjusted for age and sex, were 2.69 for participants diagnosed at age 30-39, 2.26 for those diagnosed aged 40-49, 1.84 aged 50-59, 1.57 for those aged 60-69, and 1.39 for those diagnosed 70 and older.
These hazard ratios were similar after adjusting for BMI, systolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol, but they were substantially attenuated after further adjusting for fasting glucose or hemoglobin A1c level.
Similar patterns were observed for cause-specific mortality.
“Every decade of earlier diagnosis of diabetes was associated with about 3-4 years of lower life expectancy, highlighting the need to develop and implement interventions that prevent or delay the onset of diabetes and to intensify the treatment of risk factors among young adults diagnosed with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded the British Heart Foundation, the Medical Research Council, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Health Data Research UK. Dr. Peters is on advisory boards for Vertex, Eli Lilly, and Medscape, receives research funding from Abbott Diabetes Care and Insulet, and has stock options for Omada Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers estimate on the basis of data from studies conducted in 19 high-income countries.
They estimated that, among 50-year-olds, life expectancy of those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at age 30 is 14 years shorter than that of their peers without diabetes. Among those diagnosed at age 50, life expectancy is 6 years shorter.
The study was recently published in The Lancet – Diabetes and Endocrinology.
The team analyzed data from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The data were from 97 long-term, prospective cohorts and involved 1.5 million participants who were followed for 23.1 million person-years.
“The strongest associations with earlier age at diagnosis of diabetes were for vascular (for example, myocardial infarction and stroke) and other causes of death – mainly respiratory, neurological, and infectious diseases and external causes,” they reported.
Their findings are consistent with previous studies that suggested that younger individuals who develop type 2 diabetes might have higher body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and lipid levels and that they might experience faster deterioration in glycemic control than individuals who develop diabetes later, potentially leading to premature mortality.
Asked to comment, Anne Peters, MD, director of clinical diabetes programs at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this study, said: “We’ve long known that diabetes reduces life expectancy, and the younger you get it the more years you lose. However, this study was from a broader and larger population base than prior studies.
“In this study, the major reason for death was vascular disease, and undertreatment of cardiovascular risk factors may have occurred in the younger individuals. We also don’t know about glucose control.
“I personally think the findings show that we should treat cardiovascular risk factors more aggressively in people diagnosed with [type 2] diabetes in their 30s and 40s,” urged Dr. Peters.
High priority should be given to prevention globally
“Type 2 diabetes used to be seen as a disease that affected older adults, but we’re increasingly seeing people diagnosed earlier in life,” senior author Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD, from the University of Cambridge (England), explained in a press release. “As we’ve shown, this means they are at risk of a much shorter life expectancy than they would otherwise have.”
The findings suggest that “high priority should be given to developing and implementing interventions that prevent or delay the onset of [type 2 diabetes], especially as its prevalence among younger age groups is increasing globally,” the study authors wrote.
The results “support the idea that the younger an individual is when they develop type 2 diabetes, the more damage their body accumulates from its impaired metabolism,” added co–senior author Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, of the University of Glasgow,
Dr. Peters agreed: “People who develop type 2 diabetes at a younger age might have a different, potentially more aggressive type of type 2 diabetes and perhaps need treatment targets that are lower than people who develop type 2 diabetes when they are older.”
“The findings ... suggest that early detection of diabetes by screening followed by intensive glucose management could help prevent long-term complications from the condition,” Dr. Sattar said.
Dr. Peters added: “An issue for some is pregnancy. ... Many of the medications taken for management of CVD [cardiovascular disease] risk factors are contraindicated in pregnancy (as are many of the medications [for treating type 2 diabetes]).
“We need to be careful to risk reduce but take care of the ‘whole person,’ and if of childbearing age, consider the safest approaches to healthy management,” she emphasized.
Study results: Type 2 diabetes diagnosed at age 30, 40, and 50
Previous studies estimated that adults with type 2 diabetes die 6 years earlier on average in comparison with their counterparts who do not have diabetes, but it was not known how diabetes duration affects life span.
To investigate this, the team analyzed individual records from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Other outcomes were deaths from CVD, cancer, and other causes.
Over a median follow-up of 12.5 years, there were 246,670 deaths: 84,443 from cardiovascular causes, 150, 972 from noncardiovascular causes, and 11,255 from unknown/ill-defined causes.
Compared with participants who did not have a history of type 2 diabetes, the hazard ratios for all-cause mortality, adjusted for age and sex, were 2.69 for participants diagnosed at age 30-39, 2.26 for those diagnosed aged 40-49, 1.84 aged 50-59, 1.57 for those aged 60-69, and 1.39 for those diagnosed 70 and older.
These hazard ratios were similar after adjusting for BMI, systolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol, but they were substantially attenuated after further adjusting for fasting glucose or hemoglobin A1c level.
Similar patterns were observed for cause-specific mortality.
“Every decade of earlier diagnosis of diabetes was associated with about 3-4 years of lower life expectancy, highlighting the need to develop and implement interventions that prevent or delay the onset of diabetes and to intensify the treatment of risk factors among young adults diagnosed with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded the British Heart Foundation, the Medical Research Council, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Health Data Research UK. Dr. Peters is on advisory boards for Vertex, Eli Lilly, and Medscape, receives research funding from Abbott Diabetes Care and Insulet, and has stock options for Omada Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers estimate on the basis of data from studies conducted in 19 high-income countries.
They estimated that, among 50-year-olds, life expectancy of those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at age 30 is 14 years shorter than that of their peers without diabetes. Among those diagnosed at age 50, life expectancy is 6 years shorter.
The study was recently published in The Lancet – Diabetes and Endocrinology.
The team analyzed data from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The data were from 97 long-term, prospective cohorts and involved 1.5 million participants who were followed for 23.1 million person-years.
“The strongest associations with earlier age at diagnosis of diabetes were for vascular (for example, myocardial infarction and stroke) and other causes of death – mainly respiratory, neurological, and infectious diseases and external causes,” they reported.
Their findings are consistent with previous studies that suggested that younger individuals who develop type 2 diabetes might have higher body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and lipid levels and that they might experience faster deterioration in glycemic control than individuals who develop diabetes later, potentially leading to premature mortality.
Asked to comment, Anne Peters, MD, director of clinical diabetes programs at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this study, said: “We’ve long known that diabetes reduces life expectancy, and the younger you get it the more years you lose. However, this study was from a broader and larger population base than prior studies.
“In this study, the major reason for death was vascular disease, and undertreatment of cardiovascular risk factors may have occurred in the younger individuals. We also don’t know about glucose control.
“I personally think the findings show that we should treat cardiovascular risk factors more aggressively in people diagnosed with [type 2] diabetes in their 30s and 40s,” urged Dr. Peters.
High priority should be given to prevention globally
“Type 2 diabetes used to be seen as a disease that affected older adults, but we’re increasingly seeing people diagnosed earlier in life,” senior author Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD, from the University of Cambridge (England), explained in a press release. “As we’ve shown, this means they are at risk of a much shorter life expectancy than they would otherwise have.”
The findings suggest that “high priority should be given to developing and implementing interventions that prevent or delay the onset of [type 2 diabetes], especially as its prevalence among younger age groups is increasing globally,” the study authors wrote.
The results “support the idea that the younger an individual is when they develop type 2 diabetes, the more damage their body accumulates from its impaired metabolism,” added co–senior author Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, of the University of Glasgow,
Dr. Peters agreed: “People who develop type 2 diabetes at a younger age might have a different, potentially more aggressive type of type 2 diabetes and perhaps need treatment targets that are lower than people who develop type 2 diabetes when they are older.”
“The findings ... suggest that early detection of diabetes by screening followed by intensive glucose management could help prevent long-term complications from the condition,” Dr. Sattar said.
Dr. Peters added: “An issue for some is pregnancy. ... Many of the medications taken for management of CVD [cardiovascular disease] risk factors are contraindicated in pregnancy (as are many of the medications [for treating type 2 diabetes]).
“We need to be careful to risk reduce but take care of the ‘whole person,’ and if of childbearing age, consider the safest approaches to healthy management,” she emphasized.
Study results: Type 2 diabetes diagnosed at age 30, 40, and 50
Previous studies estimated that adults with type 2 diabetes die 6 years earlier on average in comparison with their counterparts who do not have diabetes, but it was not known how diabetes duration affects life span.
To investigate this, the team analyzed individual records from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration and the UK Biobank. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Other outcomes were deaths from CVD, cancer, and other causes.
Over a median follow-up of 12.5 years, there were 246,670 deaths: 84,443 from cardiovascular causes, 150, 972 from noncardiovascular causes, and 11,255 from unknown/ill-defined causes.
Compared with participants who did not have a history of type 2 diabetes, the hazard ratios for all-cause mortality, adjusted for age and sex, were 2.69 for participants diagnosed at age 30-39, 2.26 for those diagnosed aged 40-49, 1.84 aged 50-59, 1.57 for those aged 60-69, and 1.39 for those diagnosed 70 and older.
These hazard ratios were similar after adjusting for BMI, systolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol, but they were substantially attenuated after further adjusting for fasting glucose or hemoglobin A1c level.
Similar patterns were observed for cause-specific mortality.
“Every decade of earlier diagnosis of diabetes was associated with about 3-4 years of lower life expectancy, highlighting the need to develop and implement interventions that prevent or delay the onset of diabetes and to intensify the treatment of risk factors among young adults diagnosed with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded the British Heart Foundation, the Medical Research Council, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Health Data Research UK. Dr. Peters is on advisory boards for Vertex, Eli Lilly, and Medscape, receives research funding from Abbott Diabetes Care and Insulet, and has stock options for Omada Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET – DIABETES AND ENDOCRINOLOGY