User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Ruxolitinib for vitiligo: Experts share experiences from first year
.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the cream formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), a JAK inhibitor, for repigmentation of nonsegmental vitiligo in July 2022 for people aged 12 years and older.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that he likes to use ruxolitinib cream in combination with other treatments.
“In the real world with vitiligo patients, we’re oftentimes doing combinatorial therapy anyway. So phototherapy, specifically, narrow-band UVB, is something that we have a lot of clinical evidence for over the years, and it’s a modality that can combine with topical steroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors.”
He said trials to study combinations will yield better guidance on optimal use of ruxolitinib cream. “In general, vitiligo patients can really benefit from phototherapy,” he said in an interview. (Labeling recommends against combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologics, or potent immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine or cyclosporine.)
This first year has shown that ruxolitinib is an effective option, but counseling patients to expect slow improvement is important so that patients stick with it, he noted.
Documenting what treatments patients with vitiligo have used before is important, he said, as is counseling patients that ruxolitinib is approved only for use on up to 10% of a person’s body surface area. (Product labeling recommends that a thin layer be applied twice a day to affected areas up to 10% of body surface area.)
Ruxolitinib has brought a “louder voice” to vitiligo and has opened up options for patients with the disease, Dr. Chovatiya said. “Having the ability to topically treat people who have very extensive disease really gives us a lot more flexibility than we have had before.”
Good experiences with payers at safety-net hospital
Candrice R. Heath, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said that real-world experience with topical ruxolitinib will be more evident after its been on the market for 18-24 months.
Dr. Heath said she, too, encourages use of narrow-band UVB phototherapy in conjunction with the treatment.
From an insurance reimbursement standpoint, she said that she is glad that there have been fewer hurdles in getting ruxolitinib to patients than she has experienced with other medications.
In her safety-net hospital, she told this news organization, she sees patients with many types of insurance, but most have Medicaid. “So, I’m always expecting the step therapies, denials, pushbacks, etc.,” she said. But the path has been smoother for ruxolitinib coverage, she noted.
Her colleagues are committed to documenting everything the patient has tried, she added, and that helps with prior authorization.
Dr. Heath said that pointing out to insurers that ruxolitinib is the only approved treatment for repigmentation helps facilitate coverage.
“The science is advancing, and I’m happy to be practicing during a time when we actually have something approved for vitiligo,” she said. But she pointed out that phototherapy often is not covered for vitiligo, “which is horrible, when it is readily approved for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.”
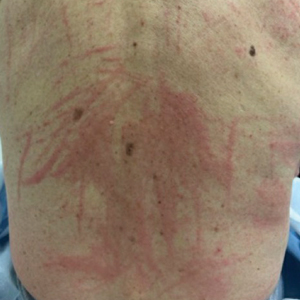
To document progress, Dr. Heath said that she always takes photographs of her patients with vitiligo because “the pictures remind us how far we have come.”
Data spotlight success in adolescents
Data from two trials give a clinical picture of the drug’s safety and efficacy in younger patients.
Adolescents had particularly good results in the first year with ruxolitinib, according to pooled phase 3 data from TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2, this news organization reported.
The findings, presented at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology in Singapore, indicate that more than half of the participants achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in the total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50) at 52 weeks.
The percentages of young patients aged 12-17 years taking twice-daily ruxolitinib who achieved T-VASI 50 at weeks 12, 24, and 52 were 11.5%, 26.9%, and 57.7%, respectively. The corresponding percentages for all in the study population were 10.7%, 22.7%, and 44.4%, respectively.
At the meeting, the presenter, Julien Seneschal, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and head of the vitiligo and pigmentary disorders clinic at the University of Bordeaux, France, said, “This suggests that younger patients can respond better to the treatment.” He noted, however, that there were few adolescents in the studies.
New excitement in the field
Daniel Gutierrez, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at New York University, said the treatment has brought new excitement to the field.
“Patients with vitiligo are very motivated to treat their disease,” he said, because it typically is on the face and other highly visual areas, which can affect their overall perception of self.
Previously, he noted in an interview, the only FDA-approved treatment was monobenzone, but that was for depigmentation rather than repigmentation.
Otherwise, treatments were being used off label, and patients were receiving compounded formulations that often weren’t covered by insurance and often had shorter shelf life.
He said that he still occasionally gets denials from payers who consider vitiligo a cosmetic condition.
“I’ve had more luck with insurance, at least in the New York State area.” He added that sometimes payers require use of a topical calcineurin inhibitor for about 12 weeks before they will cover ruxolitinib.
Dr. Gutierrez also recommends using phototherapy with topical ruxolitinib “because they work on slightly different pathways.”
When he starts patients on a new therapy such as ruxolitinib, he asks them to come back in 3 months, and often by then, progress is evident. Facial areas show the most response, he said, while hands and feet are less likely to show significant improvement.
He said that it’s important for physicians and patients to know that improvements can take weeks or months to be noticeable. “I tell patients not to give up,” he added.
Showing the patients pictures from the current appointment and comparing them with pictures from previous appointments can help them better understand their progress, he said.
Lead investigator adds observations
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Indiana University, Indianapolis, was the lead investigator of the pivotal TruE-V1 and TruE-V2 trials for vitiligo. In that role, he has been treating vitiligo patients with topical ruxolitinib since 2015.
In an interview, he said that many patients “don’t hit their optimal results at 3 months, 6 months, even the year mark. With continued use, many can see continued benefit.”
Other patients, he said, don’t respond within the first 6 months but with continued use may eventually respond, he said.
“Unfortunately, we have no way of knowing, based on clinical characteristics or baseline demographics, whether a patient will be a delayed responder or not or an early responder,” Dr. Rosmarin added.
He provided several observations about people who have stopped taking the medication.
“When people stop,” he said, “some maintain their response, but some start to depigment again. Again, we have no way of predicting who will be in which category.”
He said that once patients have hit their desired response, he usually advises them to taper down to maybe twice a week or to stop treatment, but if they see any recurrence, they should start reusing the medicine.
“We have some patients who have gone 6 or 7 years now before they had a recurrence, but others may start to depigment again in 2 to 3 months,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
As for phototherapy, he said, the combination with topical ruxolitinib is being studied.
“We think the combination is synergistic and better than either alone, but we’re still waiting for data to prove that,” he said.
In his practice, he offers patients the option either to use just ruxolitinib cream or the combination early on. Many patients, because of convenience, say they’ll first try the cream to see if that works.
“The challenge with light [therapy] is that it can be very inconvenient,” he said. Patients have to live close to a phototherapy unit to receive therapy 2-3 times a week or have a phototherapy product in their home.
Next in the pipeline
Experts say the progress doesn’t stop with ruxolitinib cream. Current trials of several medications show there’s more to come for patients with vitiligo.
Dr. Chovatiya said that next up may be oral ritlecitinib (Litfulo), a JAK inhibitor that was approved for severe alopecia areata in June for people aged 12 years and older. Phase 2 results have been published for its use with vitiligo.
“This would be an oral medication that may be able to help people with much more extensive disease as far as vitiligo goes,” he said, adding that he expects approval for a vitiligo indication within a few years.
He pointed out that longer-term safety data will be available because it is already on the market for alopecia.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq), an oral JAK inhibitor, is approved for atopic dermatitis but is being studied for vitiligo as well, he noted. “I’m very excited to see what that holds for patients as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Gutierrez said that he is excited about oral JAK inhibitors but sees potential in finding new ways to transplant melanocytes into areas where there are none.
The pigmentation field has seen new energy since last year’s approval, he said, particularly among people of color.
“We have new options for vitiligo that were lacking compared with other conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis,” he said. “Hopefully, there will be more promising breakthroughs.”
Dr. Rosmarin is the chief investigator for the pivotal trials that led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib. He disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Viela Bio. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Argenx, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Incyte, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, National Eczema Association, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and UCB. Dr. Heath and Dr. Gutierrez report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the cream formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), a JAK inhibitor, for repigmentation of nonsegmental vitiligo in July 2022 for people aged 12 years and older.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that he likes to use ruxolitinib cream in combination with other treatments.
“In the real world with vitiligo patients, we’re oftentimes doing combinatorial therapy anyway. So phototherapy, specifically, narrow-band UVB, is something that we have a lot of clinical evidence for over the years, and it’s a modality that can combine with topical steroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors.”
He said trials to study combinations will yield better guidance on optimal use of ruxolitinib cream. “In general, vitiligo patients can really benefit from phototherapy,” he said in an interview. (Labeling recommends against combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologics, or potent immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine or cyclosporine.)
This first year has shown that ruxolitinib is an effective option, but counseling patients to expect slow improvement is important so that patients stick with it, he noted.
Documenting what treatments patients with vitiligo have used before is important, he said, as is counseling patients that ruxolitinib is approved only for use on up to 10% of a person’s body surface area. (Product labeling recommends that a thin layer be applied twice a day to affected areas up to 10% of body surface area.)
Ruxolitinib has brought a “louder voice” to vitiligo and has opened up options for patients with the disease, Dr. Chovatiya said. “Having the ability to topically treat people who have very extensive disease really gives us a lot more flexibility than we have had before.”
Good experiences with payers at safety-net hospital
Candrice R. Heath, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said that real-world experience with topical ruxolitinib will be more evident after its been on the market for 18-24 months.
Dr. Heath said she, too, encourages use of narrow-band UVB phototherapy in conjunction with the treatment.
From an insurance reimbursement standpoint, she said that she is glad that there have been fewer hurdles in getting ruxolitinib to patients than she has experienced with other medications.
In her safety-net hospital, she told this news organization, she sees patients with many types of insurance, but most have Medicaid. “So, I’m always expecting the step therapies, denials, pushbacks, etc.,” she said. But the path has been smoother for ruxolitinib coverage, she noted.
Her colleagues are committed to documenting everything the patient has tried, she added, and that helps with prior authorization.
Dr. Heath said that pointing out to insurers that ruxolitinib is the only approved treatment for repigmentation helps facilitate coverage.
“The science is advancing, and I’m happy to be practicing during a time when we actually have something approved for vitiligo,” she said. But she pointed out that phototherapy often is not covered for vitiligo, “which is horrible, when it is readily approved for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.”
To document progress, Dr. Heath said that she always takes photographs of her patients with vitiligo because “the pictures remind us how far we have come.”
Data spotlight success in adolescents
Data from two trials give a clinical picture of the drug’s safety and efficacy in younger patients.
Adolescents had particularly good results in the first year with ruxolitinib, according to pooled phase 3 data from TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2, this news organization reported.
The findings, presented at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology in Singapore, indicate that more than half of the participants achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in the total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50) at 52 weeks.
The percentages of young patients aged 12-17 years taking twice-daily ruxolitinib who achieved T-VASI 50 at weeks 12, 24, and 52 were 11.5%, 26.9%, and 57.7%, respectively. The corresponding percentages for all in the study population were 10.7%, 22.7%, and 44.4%, respectively.
At the meeting, the presenter, Julien Seneschal, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and head of the vitiligo and pigmentary disorders clinic at the University of Bordeaux, France, said, “This suggests that younger patients can respond better to the treatment.” He noted, however, that there were few adolescents in the studies.
New excitement in the field
Daniel Gutierrez, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at New York University, said the treatment has brought new excitement to the field.
“Patients with vitiligo are very motivated to treat their disease,” he said, because it typically is on the face and other highly visual areas, which can affect their overall perception of self.
Previously, he noted in an interview, the only FDA-approved treatment was monobenzone, but that was for depigmentation rather than repigmentation.
Otherwise, treatments were being used off label, and patients were receiving compounded formulations that often weren’t covered by insurance and often had shorter shelf life.
He said that he still occasionally gets denials from payers who consider vitiligo a cosmetic condition.
“I’ve had more luck with insurance, at least in the New York State area.” He added that sometimes payers require use of a topical calcineurin inhibitor for about 12 weeks before they will cover ruxolitinib.
Dr. Gutierrez also recommends using phototherapy with topical ruxolitinib “because they work on slightly different pathways.”
When he starts patients on a new therapy such as ruxolitinib, he asks them to come back in 3 months, and often by then, progress is evident. Facial areas show the most response, he said, while hands and feet are less likely to show significant improvement.
He said that it’s important for physicians and patients to know that improvements can take weeks or months to be noticeable. “I tell patients not to give up,” he added.
Showing the patients pictures from the current appointment and comparing them with pictures from previous appointments can help them better understand their progress, he said.
Lead investigator adds observations
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Indiana University, Indianapolis, was the lead investigator of the pivotal TruE-V1 and TruE-V2 trials for vitiligo. In that role, he has been treating vitiligo patients with topical ruxolitinib since 2015.
In an interview, he said that many patients “don’t hit their optimal results at 3 months, 6 months, even the year mark. With continued use, many can see continued benefit.”
Other patients, he said, don’t respond within the first 6 months but with continued use may eventually respond, he said.
“Unfortunately, we have no way of knowing, based on clinical characteristics or baseline demographics, whether a patient will be a delayed responder or not or an early responder,” Dr. Rosmarin added.
He provided several observations about people who have stopped taking the medication.
“When people stop,” he said, “some maintain their response, but some start to depigment again. Again, we have no way of predicting who will be in which category.”
He said that once patients have hit their desired response, he usually advises them to taper down to maybe twice a week or to stop treatment, but if they see any recurrence, they should start reusing the medicine.
“We have some patients who have gone 6 or 7 years now before they had a recurrence, but others may start to depigment again in 2 to 3 months,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
As for phototherapy, he said, the combination with topical ruxolitinib is being studied.
“We think the combination is synergistic and better than either alone, but we’re still waiting for data to prove that,” he said.
In his practice, he offers patients the option either to use just ruxolitinib cream or the combination early on. Many patients, because of convenience, say they’ll first try the cream to see if that works.
“The challenge with light [therapy] is that it can be very inconvenient,” he said. Patients have to live close to a phototherapy unit to receive therapy 2-3 times a week or have a phototherapy product in their home.
Next in the pipeline
Experts say the progress doesn’t stop with ruxolitinib cream. Current trials of several medications show there’s more to come for patients with vitiligo.
Dr. Chovatiya said that next up may be oral ritlecitinib (Litfulo), a JAK inhibitor that was approved for severe alopecia areata in June for people aged 12 years and older. Phase 2 results have been published for its use with vitiligo.
“This would be an oral medication that may be able to help people with much more extensive disease as far as vitiligo goes,” he said, adding that he expects approval for a vitiligo indication within a few years.
He pointed out that longer-term safety data will be available because it is already on the market for alopecia.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq), an oral JAK inhibitor, is approved for atopic dermatitis but is being studied for vitiligo as well, he noted. “I’m very excited to see what that holds for patients as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Gutierrez said that he is excited about oral JAK inhibitors but sees potential in finding new ways to transplant melanocytes into areas where there are none.
The pigmentation field has seen new energy since last year’s approval, he said, particularly among people of color.
“We have new options for vitiligo that were lacking compared with other conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis,” he said. “Hopefully, there will be more promising breakthroughs.”
Dr. Rosmarin is the chief investigator for the pivotal trials that led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib. He disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Viela Bio. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Argenx, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Incyte, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, National Eczema Association, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and UCB. Dr. Heath and Dr. Gutierrez report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the cream formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), a JAK inhibitor, for repigmentation of nonsegmental vitiligo in July 2022 for people aged 12 years and older.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that he likes to use ruxolitinib cream in combination with other treatments.
“In the real world with vitiligo patients, we’re oftentimes doing combinatorial therapy anyway. So phototherapy, specifically, narrow-band UVB, is something that we have a lot of clinical evidence for over the years, and it’s a modality that can combine with topical steroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors.”
He said trials to study combinations will yield better guidance on optimal use of ruxolitinib cream. “In general, vitiligo patients can really benefit from phototherapy,” he said in an interview. (Labeling recommends against combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologics, or potent immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine or cyclosporine.)
This first year has shown that ruxolitinib is an effective option, but counseling patients to expect slow improvement is important so that patients stick with it, he noted.
Documenting what treatments patients with vitiligo have used before is important, he said, as is counseling patients that ruxolitinib is approved only for use on up to 10% of a person’s body surface area. (Product labeling recommends that a thin layer be applied twice a day to affected areas up to 10% of body surface area.)
Ruxolitinib has brought a “louder voice” to vitiligo and has opened up options for patients with the disease, Dr. Chovatiya said. “Having the ability to topically treat people who have very extensive disease really gives us a lot more flexibility than we have had before.”
Good experiences with payers at safety-net hospital
Candrice R. Heath, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said that real-world experience with topical ruxolitinib will be more evident after its been on the market for 18-24 months.
Dr. Heath said she, too, encourages use of narrow-band UVB phototherapy in conjunction with the treatment.
From an insurance reimbursement standpoint, she said that she is glad that there have been fewer hurdles in getting ruxolitinib to patients than she has experienced with other medications.
In her safety-net hospital, she told this news organization, she sees patients with many types of insurance, but most have Medicaid. “So, I’m always expecting the step therapies, denials, pushbacks, etc.,” she said. But the path has been smoother for ruxolitinib coverage, she noted.
Her colleagues are committed to documenting everything the patient has tried, she added, and that helps with prior authorization.
Dr. Heath said that pointing out to insurers that ruxolitinib is the only approved treatment for repigmentation helps facilitate coverage.
“The science is advancing, and I’m happy to be practicing during a time when we actually have something approved for vitiligo,” she said. But she pointed out that phototherapy often is not covered for vitiligo, “which is horrible, when it is readily approved for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.”
To document progress, Dr. Heath said that she always takes photographs of her patients with vitiligo because “the pictures remind us how far we have come.”
Data spotlight success in adolescents
Data from two trials give a clinical picture of the drug’s safety and efficacy in younger patients.
Adolescents had particularly good results in the first year with ruxolitinib, according to pooled phase 3 data from TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2, this news organization reported.
The findings, presented at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology in Singapore, indicate that more than half of the participants achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in the total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50) at 52 weeks.
The percentages of young patients aged 12-17 years taking twice-daily ruxolitinib who achieved T-VASI 50 at weeks 12, 24, and 52 were 11.5%, 26.9%, and 57.7%, respectively. The corresponding percentages for all in the study population were 10.7%, 22.7%, and 44.4%, respectively.
At the meeting, the presenter, Julien Seneschal, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and head of the vitiligo and pigmentary disorders clinic at the University of Bordeaux, France, said, “This suggests that younger patients can respond better to the treatment.” He noted, however, that there were few adolescents in the studies.
New excitement in the field
Daniel Gutierrez, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at New York University, said the treatment has brought new excitement to the field.
“Patients with vitiligo are very motivated to treat their disease,” he said, because it typically is on the face and other highly visual areas, which can affect their overall perception of self.
Previously, he noted in an interview, the only FDA-approved treatment was monobenzone, but that was for depigmentation rather than repigmentation.
Otherwise, treatments were being used off label, and patients were receiving compounded formulations that often weren’t covered by insurance and often had shorter shelf life.
He said that he still occasionally gets denials from payers who consider vitiligo a cosmetic condition.
“I’ve had more luck with insurance, at least in the New York State area.” He added that sometimes payers require use of a topical calcineurin inhibitor for about 12 weeks before they will cover ruxolitinib.
Dr. Gutierrez also recommends using phototherapy with topical ruxolitinib “because they work on slightly different pathways.”
When he starts patients on a new therapy such as ruxolitinib, he asks them to come back in 3 months, and often by then, progress is evident. Facial areas show the most response, he said, while hands and feet are less likely to show significant improvement.
He said that it’s important for physicians and patients to know that improvements can take weeks or months to be noticeable. “I tell patients not to give up,” he added.
Showing the patients pictures from the current appointment and comparing them with pictures from previous appointments can help them better understand their progress, he said.
Lead investigator adds observations
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Indiana University, Indianapolis, was the lead investigator of the pivotal TruE-V1 and TruE-V2 trials for vitiligo. In that role, he has been treating vitiligo patients with topical ruxolitinib since 2015.
In an interview, he said that many patients “don’t hit their optimal results at 3 months, 6 months, even the year mark. With continued use, many can see continued benefit.”
Other patients, he said, don’t respond within the first 6 months but with continued use may eventually respond, he said.
“Unfortunately, we have no way of knowing, based on clinical characteristics or baseline demographics, whether a patient will be a delayed responder or not or an early responder,” Dr. Rosmarin added.
He provided several observations about people who have stopped taking the medication.
“When people stop,” he said, “some maintain their response, but some start to depigment again. Again, we have no way of predicting who will be in which category.”
He said that once patients have hit their desired response, he usually advises them to taper down to maybe twice a week or to stop treatment, but if they see any recurrence, they should start reusing the medicine.
“We have some patients who have gone 6 or 7 years now before they had a recurrence, but others may start to depigment again in 2 to 3 months,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
As for phototherapy, he said, the combination with topical ruxolitinib is being studied.
“We think the combination is synergistic and better than either alone, but we’re still waiting for data to prove that,” he said.
In his practice, he offers patients the option either to use just ruxolitinib cream or the combination early on. Many patients, because of convenience, say they’ll first try the cream to see if that works.
“The challenge with light [therapy] is that it can be very inconvenient,” he said. Patients have to live close to a phototherapy unit to receive therapy 2-3 times a week or have a phototherapy product in their home.
Next in the pipeline
Experts say the progress doesn’t stop with ruxolitinib cream. Current trials of several medications show there’s more to come for patients with vitiligo.
Dr. Chovatiya said that next up may be oral ritlecitinib (Litfulo), a JAK inhibitor that was approved for severe alopecia areata in June for people aged 12 years and older. Phase 2 results have been published for its use with vitiligo.
“This would be an oral medication that may be able to help people with much more extensive disease as far as vitiligo goes,” he said, adding that he expects approval for a vitiligo indication within a few years.
He pointed out that longer-term safety data will be available because it is already on the market for alopecia.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq), an oral JAK inhibitor, is approved for atopic dermatitis but is being studied for vitiligo as well, he noted. “I’m very excited to see what that holds for patients as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Gutierrez said that he is excited about oral JAK inhibitors but sees potential in finding new ways to transplant melanocytes into areas where there are none.
The pigmentation field has seen new energy since last year’s approval, he said, particularly among people of color.
“We have new options for vitiligo that were lacking compared with other conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis,” he said. “Hopefully, there will be more promising breakthroughs.”
Dr. Rosmarin is the chief investigator for the pivotal trials that led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib. He disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Viela Bio. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Argenx, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Incyte, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, National Eczema Association, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and UCB. Dr. Heath and Dr. Gutierrez report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes drug class appears to reduce recurrent gout flares
The glucose-lowering drug class sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors appear to reduce the risk for recurrent gout flares in people with gout and type 2 diabetes, and to lessen excess mortality in those individuals, compared with those who initiated other types of glucose-lowering medications, new data suggest.
Among nearly 6,000 adults with both type 2 diabetes and gout from a U.K. primary care database, initiation of SGLT2 inhibitor treatment was associated with 19% fewer recurrent gout flares and 29% lower mortality.
Moreover, unlike other urate-lowering therapies, there were no apparent transient increases in the risk of gout flares after initiating therapy, Jie Wei, PhD, of Health Management Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
These results are important because current management of gout is suboptimal. Many patients either don’t receive adequate urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol or stop taking them, Dr. Wei and colleagues said.
In addition to lowering glucose, SGLT2 inhibitors also reduce the risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in people regardless of their diabetes status. Previous studies have also found that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the risk for developing gout and of gout flares.
Asked to comment, gout specialist John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview: “I think it’s a well-done paper, with a large dataset. I think it just reinforces the findings from the other papers. Mostly anything that lowers uric acid levels is going to lower recurrent gout attacks, so it all makes sense.”
However, while Dr. FitzGerald thinks the drug class is a good option for people with diabetes or cardiorenal indications for them who also have gout, he doesn’t envision it as first-line for most other patients with gout. “The current treatments are very effective. Allopurinol brings down uric acid levels by 5-7 points. There are patients who fail allopurinol, but those are less than 5%.”
The most common reason patients stop taking allopurinol is the frequent initial gout flare. But that’s preventable, Dr. FitzGerald said, either by titrating up slowly, or by adding colchicine along with it. “By going slowly, you can avoid that flare risk. I think that’s what’s going on with the SGLT2 inhibitor. It’s not a dramatic urate-lowering drug, but it is clinically meaningful. I think that’s what this paper is showing.”
But, he noted, “I think there are so many reasons to start the SGLT2 inhibitors that if somebody also has gout, all the better. And, if somebody is on the margin with diabetes and gout control and can’t go with allopurinol, it would be great to add for both conditions.”
Less gout recurrence, lower mortality
The retrospective study was conducted from Jan. 1, 2013, to March 31, 2022. Among 5,931 patients with both type 2 diabetes and gout, 1,548 (26.1%) initiated an SGLT2 inhibitor (dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, or canagliflozin), while 4,383 (73.9%) initiated treatment with other active comparators, mostly (92.6%) dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors.
Gout flares were identified in the charts for a total of 86% of the participants. The weighted incidence rates for the first recurrent flare were 32.4 versus 41.2 per 1,000 person-years in the SGLT2 inhibitor versus comparator groups, with a weighted absolute rate difference of –8.8/1,000 and weighted hazard ratio of 0.81, a significant difference.
All-cause mortality was 18.8 versus 24.9 per 1,000 person-years, respectively, giving an HR of 0.71 at 5-year follow-up.
Dr. FitzGerald, who chaired the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 gout guidelines, said he anticipates that the SGLT2 inhibitors will be mentioned in the next update to the ACR’s now “living” guidelines, although he was not speaking on the organization’s behalf.
“We talk about losartan in the current [ACR guidelines], about its specific uric acid–lowering effect. Drugs can make uric acid worse or better. For example, thiazides make it higher. I think the SGLT2 [inhibitors] are important, but I don’t think they’re huge. The study is great, and I think the drugs are great, but I don’t think they will change the way gout is managed.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province. Dr. Wei reported receiving grant funding from Xiangya Hospital Central South University Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders and the Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, during the conduct of the study. Dr. FitzGerald reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The glucose-lowering drug class sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors appear to reduce the risk for recurrent gout flares in people with gout and type 2 diabetes, and to lessen excess mortality in those individuals, compared with those who initiated other types of glucose-lowering medications, new data suggest.
Among nearly 6,000 adults with both type 2 diabetes and gout from a U.K. primary care database, initiation of SGLT2 inhibitor treatment was associated with 19% fewer recurrent gout flares and 29% lower mortality.
Moreover, unlike other urate-lowering therapies, there were no apparent transient increases in the risk of gout flares after initiating therapy, Jie Wei, PhD, of Health Management Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
These results are important because current management of gout is suboptimal. Many patients either don’t receive adequate urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol or stop taking them, Dr. Wei and colleagues said.
In addition to lowering glucose, SGLT2 inhibitors also reduce the risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in people regardless of their diabetes status. Previous studies have also found that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the risk for developing gout and of gout flares.
Asked to comment, gout specialist John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview: “I think it’s a well-done paper, with a large dataset. I think it just reinforces the findings from the other papers. Mostly anything that lowers uric acid levels is going to lower recurrent gout attacks, so it all makes sense.”
However, while Dr. FitzGerald thinks the drug class is a good option for people with diabetes or cardiorenal indications for them who also have gout, he doesn’t envision it as first-line for most other patients with gout. “The current treatments are very effective. Allopurinol brings down uric acid levels by 5-7 points. There are patients who fail allopurinol, but those are less than 5%.”
The most common reason patients stop taking allopurinol is the frequent initial gout flare. But that’s preventable, Dr. FitzGerald said, either by titrating up slowly, or by adding colchicine along with it. “By going slowly, you can avoid that flare risk. I think that’s what’s going on with the SGLT2 inhibitor. It’s not a dramatic urate-lowering drug, but it is clinically meaningful. I think that’s what this paper is showing.”
But, he noted, “I think there are so many reasons to start the SGLT2 inhibitors that if somebody also has gout, all the better. And, if somebody is on the margin with diabetes and gout control and can’t go with allopurinol, it would be great to add for both conditions.”
Less gout recurrence, lower mortality
The retrospective study was conducted from Jan. 1, 2013, to March 31, 2022. Among 5,931 patients with both type 2 diabetes and gout, 1,548 (26.1%) initiated an SGLT2 inhibitor (dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, or canagliflozin), while 4,383 (73.9%) initiated treatment with other active comparators, mostly (92.6%) dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors.
Gout flares were identified in the charts for a total of 86% of the participants. The weighted incidence rates for the first recurrent flare were 32.4 versus 41.2 per 1,000 person-years in the SGLT2 inhibitor versus comparator groups, with a weighted absolute rate difference of –8.8/1,000 and weighted hazard ratio of 0.81, a significant difference.
All-cause mortality was 18.8 versus 24.9 per 1,000 person-years, respectively, giving an HR of 0.71 at 5-year follow-up.
Dr. FitzGerald, who chaired the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 gout guidelines, said he anticipates that the SGLT2 inhibitors will be mentioned in the next update to the ACR’s now “living” guidelines, although he was not speaking on the organization’s behalf.
“We talk about losartan in the current [ACR guidelines], about its specific uric acid–lowering effect. Drugs can make uric acid worse or better. For example, thiazides make it higher. I think the SGLT2 [inhibitors] are important, but I don’t think they’re huge. The study is great, and I think the drugs are great, but I don’t think they will change the way gout is managed.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province. Dr. Wei reported receiving grant funding from Xiangya Hospital Central South University Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders and the Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, during the conduct of the study. Dr. FitzGerald reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The glucose-lowering drug class sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors appear to reduce the risk for recurrent gout flares in people with gout and type 2 diabetes, and to lessen excess mortality in those individuals, compared with those who initiated other types of glucose-lowering medications, new data suggest.
Among nearly 6,000 adults with both type 2 diabetes and gout from a U.K. primary care database, initiation of SGLT2 inhibitor treatment was associated with 19% fewer recurrent gout flares and 29% lower mortality.
Moreover, unlike other urate-lowering therapies, there were no apparent transient increases in the risk of gout flares after initiating therapy, Jie Wei, PhD, of Health Management Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
These results are important because current management of gout is suboptimal. Many patients either don’t receive adequate urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol or stop taking them, Dr. Wei and colleagues said.
In addition to lowering glucose, SGLT2 inhibitors also reduce the risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in people regardless of their diabetes status. Previous studies have also found that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the risk for developing gout and of gout flares.
Asked to comment, gout specialist John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview: “I think it’s a well-done paper, with a large dataset. I think it just reinforces the findings from the other papers. Mostly anything that lowers uric acid levels is going to lower recurrent gout attacks, so it all makes sense.”
However, while Dr. FitzGerald thinks the drug class is a good option for people with diabetes or cardiorenal indications for them who also have gout, he doesn’t envision it as first-line for most other patients with gout. “The current treatments are very effective. Allopurinol brings down uric acid levels by 5-7 points. There are patients who fail allopurinol, but those are less than 5%.”
The most common reason patients stop taking allopurinol is the frequent initial gout flare. But that’s preventable, Dr. FitzGerald said, either by titrating up slowly, or by adding colchicine along with it. “By going slowly, you can avoid that flare risk. I think that’s what’s going on with the SGLT2 inhibitor. It’s not a dramatic urate-lowering drug, but it is clinically meaningful. I think that’s what this paper is showing.”
But, he noted, “I think there are so many reasons to start the SGLT2 inhibitors that if somebody also has gout, all the better. And, if somebody is on the margin with diabetes and gout control and can’t go with allopurinol, it would be great to add for both conditions.”
Less gout recurrence, lower mortality
The retrospective study was conducted from Jan. 1, 2013, to March 31, 2022. Among 5,931 patients with both type 2 diabetes and gout, 1,548 (26.1%) initiated an SGLT2 inhibitor (dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, or canagliflozin), while 4,383 (73.9%) initiated treatment with other active comparators, mostly (92.6%) dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors.
Gout flares were identified in the charts for a total of 86% of the participants. The weighted incidence rates for the first recurrent flare were 32.4 versus 41.2 per 1,000 person-years in the SGLT2 inhibitor versus comparator groups, with a weighted absolute rate difference of –8.8/1,000 and weighted hazard ratio of 0.81, a significant difference.
All-cause mortality was 18.8 versus 24.9 per 1,000 person-years, respectively, giving an HR of 0.71 at 5-year follow-up.
Dr. FitzGerald, who chaired the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 gout guidelines, said he anticipates that the SGLT2 inhibitors will be mentioned in the next update to the ACR’s now “living” guidelines, although he was not speaking on the organization’s behalf.
“We talk about losartan in the current [ACR guidelines], about its specific uric acid–lowering effect. Drugs can make uric acid worse or better. For example, thiazides make it higher. I think the SGLT2 [inhibitors] are important, but I don’t think they’re huge. The study is great, and I think the drugs are great, but I don’t think they will change the way gout is managed.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province. Dr. Wei reported receiving grant funding from Xiangya Hospital Central South University Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders and the Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, during the conduct of the study. Dr. FitzGerald reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
These four GI conditions may predict Parkinson’s disease
Early detection of these conditions might help identify patients at risk for PD, potentially prompting preventive strategies, the researchers suggest.
The results of previous experimental studies by the team supported the Braak hypothesis, which states that idiopathic PD originates in the gut in a subset of patients. However, no previous study had investigated a broad range of gastrointestinal symptoms and syndromes that might occur prior to a PD diagnosis.
Given their preclinical work, the authors were not surprised to find that certain GI syndromes were specifically associated with PD, even when compared with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and cerebrovascular disease (CVD), principal author Pankaj Jay Pasricha, MBBS, MD, of Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, said in an interview. However, they were “impressed by the strength of the associations.”
“Experts have known for a very long time that constipation is a potential risk factor for PD, so this study adds to the list of GI conditions that could potentially be risk factors,” he said.
The study was published online in Gut.
Studies converge
To determine the incidence of GI syndromes and interventions preceding PD, the investigators performed a combined case-control and cohort study using a U.S.-based nationwide medical record network.
First, they compared 24,624 individuals with new-onset idiopathic PD with the same number of matched negative controls (NCs), as well as 19,046 people with AD and 23,942 with CVD to investigate the presence of preexisting GI conditions, which the researchers referred to as “exposures.” Overall, the mean age was about 70, and about half of those studied were women.
Eighteen conditions covering the entire GI tract were investigated. These included achalasia, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, paralytic ileus, diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with and without diarrhea, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, fecal incontinence, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and microscopic colitis, as well as appendectomy and vagotomy.
All GI syndromes were significantly increased in the PD group, compared with NCs (odds ratio > 1). However, only preexisting dysphagia (OR, 3.58), gastroparesis (OR, 4.64), functional dyspepsia (OR, 3.39), intestinal pseudo-obstruction (OR, 3.01), diarrhea (OR, 2.85), constipation (OR, 3.32), IBS with constipation (OR, 4.11), IBS with diarrhea (OR, 4.31), IBS without diarrhea (OR, 3.53), and fecal incontinence (OR, 3.76) produced ORs that were numerically greater than the upper limit of the negative exposures.
In addition, only gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS with constipation, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation were specific for PD, compared with the AD and CVD groups (OR > 1). After correction for false discovery rate, though, gastroparesis and constipation did not remain significantly different, compared with the AD and CVD groups.
Other preexisting GI conditions not only were significantly associated with PD but also showed strong associations with the AD and CVD groups.
To validate the case-control analyses, the team set up a complementary cohort study. Eighteen cohorts – each diagnosed with one of the GI conditions in the case-control analysis – were compared with their respective NC cohorts for the prospective risk of developing PD, AD, or CVD within 5 years.
Gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation showed specific associations with PD versus NCs, AD, and CVD in the cohort analysis. Their relative risks versus NCs were 2.43, 2.27, 1.17, and 2.38, respectively.
Functional dyspepsia, IBS with diarrhea, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence were not PD specific, but IBS with constipation and intestinal pseudo-obstruction showed PD specificity in both the case-control (OR, 4.11) and cohort analyses (RR, 1.84).
Appendectomy decreased the risk for PD in the cohort analysis (RR, 0.48), but neither inflammatory bowel disease nor vagotomy was associated with PD.
“This study is the first to establish substantial observational evidence that the clinical diagnosis of not only constipation but also dysphagia, gastroparesis, and IBS without diarrhea might specifically predict the development of PD, whereas other exposures were less specific,” the researchers wrote.
However, Dr. Pasricha said, “there is no need for alarm.” Clinicians should reassure patients that “the overall risk for developing PD is low. The overwhelming majority of patients with these GI conditions will never develop PD.”
His team will be doing experimental work on the biological mechanisms that might explain the current study’s findings. “In addition, the U.S. National Institutes of Health has issued a call for proposals to perform research in patients that could help understand these associations better,” he said.
Body or brain?
The Parkinson’s Foundation’s National Medical Advisor, Michael S. Okun, MD, called the study “fascinating.”
The findings “confirm many other studies showing that GI symptoms can precede a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Although the study was designed to test the Braak hypothesis, “the dataset really cannot confirm or refute Braak pathology, which can only be accomplished with comparison to postmortem samples,” he added.
“The raging debate in the field of body-first versus brain-first Parkinson’s may be somewhat artificial, especially if we consider that Parkinson’s is not one disease,” Dr. Okun noted. “It will take clinical data, pathology, and the collaboration of many researchers to solve the puzzle.”
“The Foundation continues to monitor all the advancements in the ‘gut’ Parkinson field,” he said. “We do not recommend at this time changing the approach to clinical care based on this data.”
No funding or competing interests were declared. Dr. Okun declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early detection of these conditions might help identify patients at risk for PD, potentially prompting preventive strategies, the researchers suggest.
The results of previous experimental studies by the team supported the Braak hypothesis, which states that idiopathic PD originates in the gut in a subset of patients. However, no previous study had investigated a broad range of gastrointestinal symptoms and syndromes that might occur prior to a PD diagnosis.
Given their preclinical work, the authors were not surprised to find that certain GI syndromes were specifically associated with PD, even when compared with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and cerebrovascular disease (CVD), principal author Pankaj Jay Pasricha, MBBS, MD, of Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, said in an interview. However, they were “impressed by the strength of the associations.”
“Experts have known for a very long time that constipation is a potential risk factor for PD, so this study adds to the list of GI conditions that could potentially be risk factors,” he said.
The study was published online in Gut.
Studies converge
To determine the incidence of GI syndromes and interventions preceding PD, the investigators performed a combined case-control and cohort study using a U.S.-based nationwide medical record network.
First, they compared 24,624 individuals with new-onset idiopathic PD with the same number of matched negative controls (NCs), as well as 19,046 people with AD and 23,942 with CVD to investigate the presence of preexisting GI conditions, which the researchers referred to as “exposures.” Overall, the mean age was about 70, and about half of those studied were women.
Eighteen conditions covering the entire GI tract were investigated. These included achalasia, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, paralytic ileus, diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with and without diarrhea, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, fecal incontinence, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and microscopic colitis, as well as appendectomy and vagotomy.
All GI syndromes were significantly increased in the PD group, compared with NCs (odds ratio > 1). However, only preexisting dysphagia (OR, 3.58), gastroparesis (OR, 4.64), functional dyspepsia (OR, 3.39), intestinal pseudo-obstruction (OR, 3.01), diarrhea (OR, 2.85), constipation (OR, 3.32), IBS with constipation (OR, 4.11), IBS with diarrhea (OR, 4.31), IBS without diarrhea (OR, 3.53), and fecal incontinence (OR, 3.76) produced ORs that were numerically greater than the upper limit of the negative exposures.
In addition, only gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS with constipation, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation were specific for PD, compared with the AD and CVD groups (OR > 1). After correction for false discovery rate, though, gastroparesis and constipation did not remain significantly different, compared with the AD and CVD groups.
Other preexisting GI conditions not only were significantly associated with PD but also showed strong associations with the AD and CVD groups.
To validate the case-control analyses, the team set up a complementary cohort study. Eighteen cohorts – each diagnosed with one of the GI conditions in the case-control analysis – were compared with their respective NC cohorts for the prospective risk of developing PD, AD, or CVD within 5 years.
Gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation showed specific associations with PD versus NCs, AD, and CVD in the cohort analysis. Their relative risks versus NCs were 2.43, 2.27, 1.17, and 2.38, respectively.
Functional dyspepsia, IBS with diarrhea, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence were not PD specific, but IBS with constipation and intestinal pseudo-obstruction showed PD specificity in both the case-control (OR, 4.11) and cohort analyses (RR, 1.84).
Appendectomy decreased the risk for PD in the cohort analysis (RR, 0.48), but neither inflammatory bowel disease nor vagotomy was associated with PD.
“This study is the first to establish substantial observational evidence that the clinical diagnosis of not only constipation but also dysphagia, gastroparesis, and IBS without diarrhea might specifically predict the development of PD, whereas other exposures were less specific,” the researchers wrote.
However, Dr. Pasricha said, “there is no need for alarm.” Clinicians should reassure patients that “the overall risk for developing PD is low. The overwhelming majority of patients with these GI conditions will never develop PD.”
His team will be doing experimental work on the biological mechanisms that might explain the current study’s findings. “In addition, the U.S. National Institutes of Health has issued a call for proposals to perform research in patients that could help understand these associations better,” he said.
Body or brain?
The Parkinson’s Foundation’s National Medical Advisor, Michael S. Okun, MD, called the study “fascinating.”
The findings “confirm many other studies showing that GI symptoms can precede a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Although the study was designed to test the Braak hypothesis, “the dataset really cannot confirm or refute Braak pathology, which can only be accomplished with comparison to postmortem samples,” he added.
“The raging debate in the field of body-first versus brain-first Parkinson’s may be somewhat artificial, especially if we consider that Parkinson’s is not one disease,” Dr. Okun noted. “It will take clinical data, pathology, and the collaboration of many researchers to solve the puzzle.”
“The Foundation continues to monitor all the advancements in the ‘gut’ Parkinson field,” he said. “We do not recommend at this time changing the approach to clinical care based on this data.”
No funding or competing interests were declared. Dr. Okun declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early detection of these conditions might help identify patients at risk for PD, potentially prompting preventive strategies, the researchers suggest.
The results of previous experimental studies by the team supported the Braak hypothesis, which states that idiopathic PD originates in the gut in a subset of patients. However, no previous study had investigated a broad range of gastrointestinal symptoms and syndromes that might occur prior to a PD diagnosis.
Given their preclinical work, the authors were not surprised to find that certain GI syndromes were specifically associated with PD, even when compared with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and cerebrovascular disease (CVD), principal author Pankaj Jay Pasricha, MBBS, MD, of Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, said in an interview. However, they were “impressed by the strength of the associations.”
“Experts have known for a very long time that constipation is a potential risk factor for PD, so this study adds to the list of GI conditions that could potentially be risk factors,” he said.
The study was published online in Gut.
Studies converge
To determine the incidence of GI syndromes and interventions preceding PD, the investigators performed a combined case-control and cohort study using a U.S.-based nationwide medical record network.
First, they compared 24,624 individuals with new-onset idiopathic PD with the same number of matched negative controls (NCs), as well as 19,046 people with AD and 23,942 with CVD to investigate the presence of preexisting GI conditions, which the researchers referred to as “exposures.” Overall, the mean age was about 70, and about half of those studied were women.
Eighteen conditions covering the entire GI tract were investigated. These included achalasia, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, paralytic ileus, diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with and without diarrhea, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, fecal incontinence, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and microscopic colitis, as well as appendectomy and vagotomy.
All GI syndromes were significantly increased in the PD group, compared with NCs (odds ratio > 1). However, only preexisting dysphagia (OR, 3.58), gastroparesis (OR, 4.64), functional dyspepsia (OR, 3.39), intestinal pseudo-obstruction (OR, 3.01), diarrhea (OR, 2.85), constipation (OR, 3.32), IBS with constipation (OR, 4.11), IBS with diarrhea (OR, 4.31), IBS without diarrhea (OR, 3.53), and fecal incontinence (OR, 3.76) produced ORs that were numerically greater than the upper limit of the negative exposures.
In addition, only gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS with constipation, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation were specific for PD, compared with the AD and CVD groups (OR > 1). After correction for false discovery rate, though, gastroparesis and constipation did not remain significantly different, compared with the AD and CVD groups.
Other preexisting GI conditions not only were significantly associated with PD but also showed strong associations with the AD and CVD groups.
To validate the case-control analyses, the team set up a complementary cohort study. Eighteen cohorts – each diagnosed with one of the GI conditions in the case-control analysis – were compared with their respective NC cohorts for the prospective risk of developing PD, AD, or CVD within 5 years.
Gastroparesis, dysphagia, IBS without diarrhea, and constipation showed specific associations with PD versus NCs, AD, and CVD in the cohort analysis. Their relative risks versus NCs were 2.43, 2.27, 1.17, and 2.38, respectively.
Functional dyspepsia, IBS with diarrhea, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence were not PD specific, but IBS with constipation and intestinal pseudo-obstruction showed PD specificity in both the case-control (OR, 4.11) and cohort analyses (RR, 1.84).
Appendectomy decreased the risk for PD in the cohort analysis (RR, 0.48), but neither inflammatory bowel disease nor vagotomy was associated with PD.
“This study is the first to establish substantial observational evidence that the clinical diagnosis of not only constipation but also dysphagia, gastroparesis, and IBS without diarrhea might specifically predict the development of PD, whereas other exposures were less specific,” the researchers wrote.
However, Dr. Pasricha said, “there is no need for alarm.” Clinicians should reassure patients that “the overall risk for developing PD is low. The overwhelming majority of patients with these GI conditions will never develop PD.”
His team will be doing experimental work on the biological mechanisms that might explain the current study’s findings. “In addition, the U.S. National Institutes of Health has issued a call for proposals to perform research in patients that could help understand these associations better,” he said.
Body or brain?
The Parkinson’s Foundation’s National Medical Advisor, Michael S. Okun, MD, called the study “fascinating.”
The findings “confirm many other studies showing that GI symptoms can precede a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Although the study was designed to test the Braak hypothesis, “the dataset really cannot confirm or refute Braak pathology, which can only be accomplished with comparison to postmortem samples,” he added.
“The raging debate in the field of body-first versus brain-first Parkinson’s may be somewhat artificial, especially if we consider that Parkinson’s is not one disease,” Dr. Okun noted. “It will take clinical data, pathology, and the collaboration of many researchers to solve the puzzle.”
“The Foundation continues to monitor all the advancements in the ‘gut’ Parkinson field,” he said. “We do not recommend at this time changing the approach to clinical care based on this data.”
No funding or competing interests were declared. Dr. Okun declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GUT
Five questions for COVID experts: How concerned should we be?
COVID-19 hospitalizations have been on the rise for weeks as summer nears its end, but how concerned should you be? SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID, continues to evolve and surprise us. So COVID transmission, hospitalization, and death rates can be difficult to predict.
, especially now that testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge.
Question 1: Are you expecting an end-of-summer COVID wave to be substantial?
Eric Topol, MD: “This wave won’t likely be substantial and could be more of a ‘wavelet.’ I’m not thinking that physicians are too concerned,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
Thomas Gut, DO: “It’s always impossible to predict the severity of COVID waves. Although the virus has generally mutated in ways that favor easier transmission and milder illness, there have been a handful of surprising mutations that were more dangerous and deadly than the preceding strain,” said Dr. Gut, associate chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Robert Atmar, MD: “I’ll start with the caveat that prognosticating for SARS-CoV-2 is a bit hazardous as we remain in unknown territory for some aspects of its epidemiology and evolution,” said Dr. Atmar, a professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “It depends on your definition of substantial. We, at least in Houston, are already in the midst of a substantial surge in the burden of infection, at least as monitored through wastewater surveillance. The amount of virus in the wastewater already exceeds the peak level we saw last winter. That said, the increased infection burden has not translated into large increases in hospitalizations for COVID-19. Most persons hospitalized in our hospital are admitted with infection, not for the consequences of infection.”
Stuart Campbell Ray, MD: “It looks like there is a rise in infections, but the proportional rise in hospitalizations from severe cases is lower than in the past, suggesting that folks are protected by the immunity we’ve gained over the past few years through vaccination and prior infections. Of course, we should be thinking about how that applies to each of us – how recently we had a vaccine or COVID-19, and whether we might see more severe infections as immunity wanes,” said Dr. Ray, who is a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Question 2: Is a return to masks or mask mandates coming this fall or winter?
Dr. Topol: “Mandating masks doesn’t work very well, but we may see wide use again if a descendant of [variant] BA.2.86 takes off.”
Dr. Gut: “It’s difficult to predict if there are any mask mandates returning at any point. Ever since the Omicron strains emerged, COVID has been relatively mild, compared to previous strains, so there probably won’t be any plan to start masking in public unless a more deadly strain appears.”
Dr. Atmar: “I do not think we will see a return to mask mandates this fall or winter for a variety of reasons. The primary one is that I don’t think the public will accept mask mandates. However, I think masking can continue to be an adjunctive measure to enhance protection from infection, along with booster vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “Some people will choose to wear masks during a surge, particularly in situations like commuting where they don’t interfere with what they’re doing. They will wear masks particularly if they want to avoid infection due to concerns about others they care about, disruption of work or travel plans, or concerns about long-term consequences of repeated COVID-19.”
Question 3: Now that COVID testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge, how might that affect their use?
Dr. Topol: “It was already low, and this will undoubtedly further compromise their uptake.”
Dr. Gut: “I do expect that testing will become less common now that tests are no longer free. I’m sure there will be a lower amount of detection in patients with milder or asymptomatic disease compared to what we had previously.”
Dr. Atmar: “If there are out-of-pocket costs for the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, or if the administrative paperwork attached to getting a vaccine is increased, the uptake of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines will likely decrease. It will be important to communicate to the populations targeted for vaccination the potential benefits of such vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “A challenge with COVID-19, all along, has been disparities in access to care, and this will be worse without public support for prevention and testing. This applies to everyone but is especially burdensome for those who are often marginalized in our health care system and society in general. I hope that we’ll find ways to ensure that people who need tests and vaccinations are able to access them, as good health is in everyone’s interest.”
Question 4: Will the new vaccines against COVID work for the currently circulating variants?
Dr. Topol: “The XBB.1.5 boosters will be out Sept. 14. They should help versus EG.5.1 and FL.1.5.1. The FL.1.5.1 variant is gaining now.”
Dr. Gut: “In the next several weeks, we expect the newer monovalent XBB-based vaccines to be offered that offer good protection against current circulating COVID variants along with the new Eris variant.”
Dr. Atmar: “The vaccines are expected to induce immune responses to the currently circulating variants, most of which are strains that evolved from the vaccine strain. The vaccine is expected to be most effective in preventing severe illness and will likely be less effective in preventing infection and mild illness.”
Dr. Ray: “Yes, the updated vaccine design has a spike antigen (XBB.1.5) nearly identical to the current dominant variant (EG.5). Even as variants change, the boosters stimulate B cells and T cells to help protect in a way that is safer than getting COVID-19 infection.”
Question 5: Is there anything we should watch out for regarding the BA.2.86 variant in particular?
Dr. Topol: “The scenario could change if there are new functional mutations added to it.”
Dr. Gut: “BA.2.86 is still fairly uncommon and does not have much data to directly make any informed guesses. However, in general, people that have been exposed to more recent mutations of the COVID virus have been shown to have more protection from newer upcoming mutations. It’s fair to guess that people that have not had recent infection from COVID, or have not had a recent booster, are at higher risk for being infected by any XBB- or BA.2-based strains.”
Dr. Atmar: BA.2.86 has been designated as a variant under monitoring. We will want to see whether it becomes more common and if there are any unexpected characteristics associated with infection by this variant.”
Dr. Ray: “It’s still rare, but it’s been seen in geographically dispersed places, so it’s got legs. The question is how effectively it will bypass some of the immunity we’ve gained. T cells are likely to remain protective, because they target so many parts of the virus that change more slowly, but antibodies from B cells to spike protein may have more trouble recognizing BA.2.86, whether those antibodies were made to a vaccine or a prior variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 hospitalizations have been on the rise for weeks as summer nears its end, but how concerned should you be? SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID, continues to evolve and surprise us. So COVID transmission, hospitalization, and death rates can be difficult to predict.
, especially now that testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge.
Question 1: Are you expecting an end-of-summer COVID wave to be substantial?
Eric Topol, MD: “This wave won’t likely be substantial and could be more of a ‘wavelet.’ I’m not thinking that physicians are too concerned,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
Thomas Gut, DO: “It’s always impossible to predict the severity of COVID waves. Although the virus has generally mutated in ways that favor easier transmission and milder illness, there have been a handful of surprising mutations that were more dangerous and deadly than the preceding strain,” said Dr. Gut, associate chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Robert Atmar, MD: “I’ll start with the caveat that prognosticating for SARS-CoV-2 is a bit hazardous as we remain in unknown territory for some aspects of its epidemiology and evolution,” said Dr. Atmar, a professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “It depends on your definition of substantial. We, at least in Houston, are already in the midst of a substantial surge in the burden of infection, at least as monitored through wastewater surveillance. The amount of virus in the wastewater already exceeds the peak level we saw last winter. That said, the increased infection burden has not translated into large increases in hospitalizations for COVID-19. Most persons hospitalized in our hospital are admitted with infection, not for the consequences of infection.”
Stuart Campbell Ray, MD: “It looks like there is a rise in infections, but the proportional rise in hospitalizations from severe cases is lower than in the past, suggesting that folks are protected by the immunity we’ve gained over the past few years through vaccination and prior infections. Of course, we should be thinking about how that applies to each of us – how recently we had a vaccine or COVID-19, and whether we might see more severe infections as immunity wanes,” said Dr. Ray, who is a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Question 2: Is a return to masks or mask mandates coming this fall or winter?
Dr. Topol: “Mandating masks doesn’t work very well, but we may see wide use again if a descendant of [variant] BA.2.86 takes off.”
Dr. Gut: “It’s difficult to predict if there are any mask mandates returning at any point. Ever since the Omicron strains emerged, COVID has been relatively mild, compared to previous strains, so there probably won’t be any plan to start masking in public unless a more deadly strain appears.”
Dr. Atmar: “I do not think we will see a return to mask mandates this fall or winter for a variety of reasons. The primary one is that I don’t think the public will accept mask mandates. However, I think masking can continue to be an adjunctive measure to enhance protection from infection, along with booster vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “Some people will choose to wear masks during a surge, particularly in situations like commuting where they don’t interfere with what they’re doing. They will wear masks particularly if they want to avoid infection due to concerns about others they care about, disruption of work or travel plans, or concerns about long-term consequences of repeated COVID-19.”
Question 3: Now that COVID testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge, how might that affect their use?
Dr. Topol: “It was already low, and this will undoubtedly further compromise their uptake.”
Dr. Gut: “I do expect that testing will become less common now that tests are no longer free. I’m sure there will be a lower amount of detection in patients with milder or asymptomatic disease compared to what we had previously.”
Dr. Atmar: “If there are out-of-pocket costs for the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, or if the administrative paperwork attached to getting a vaccine is increased, the uptake of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines will likely decrease. It will be important to communicate to the populations targeted for vaccination the potential benefits of such vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “A challenge with COVID-19, all along, has been disparities in access to care, and this will be worse without public support for prevention and testing. This applies to everyone but is especially burdensome for those who are often marginalized in our health care system and society in general. I hope that we’ll find ways to ensure that people who need tests and vaccinations are able to access them, as good health is in everyone’s interest.”
Question 4: Will the new vaccines against COVID work for the currently circulating variants?
Dr. Topol: “The XBB.1.5 boosters will be out Sept. 14. They should help versus EG.5.1 and FL.1.5.1. The FL.1.5.1 variant is gaining now.”
Dr. Gut: “In the next several weeks, we expect the newer monovalent XBB-based vaccines to be offered that offer good protection against current circulating COVID variants along with the new Eris variant.”
Dr. Atmar: “The vaccines are expected to induce immune responses to the currently circulating variants, most of which are strains that evolved from the vaccine strain. The vaccine is expected to be most effective in preventing severe illness and will likely be less effective in preventing infection and mild illness.”
Dr. Ray: “Yes, the updated vaccine design has a spike antigen (XBB.1.5) nearly identical to the current dominant variant (EG.5). Even as variants change, the boosters stimulate B cells and T cells to help protect in a way that is safer than getting COVID-19 infection.”
Question 5: Is there anything we should watch out for regarding the BA.2.86 variant in particular?
Dr. Topol: “The scenario could change if there are new functional mutations added to it.”
Dr. Gut: “BA.2.86 is still fairly uncommon and does not have much data to directly make any informed guesses. However, in general, people that have been exposed to more recent mutations of the COVID virus have been shown to have more protection from newer upcoming mutations. It’s fair to guess that people that have not had recent infection from COVID, or have not had a recent booster, are at higher risk for being infected by any XBB- or BA.2-based strains.”
Dr. Atmar: BA.2.86 has been designated as a variant under monitoring. We will want to see whether it becomes more common and if there are any unexpected characteristics associated with infection by this variant.”
Dr. Ray: “It’s still rare, but it’s been seen in geographically dispersed places, so it’s got legs. The question is how effectively it will bypass some of the immunity we’ve gained. T cells are likely to remain protective, because they target so many parts of the virus that change more slowly, but antibodies from B cells to spike protein may have more trouble recognizing BA.2.86, whether those antibodies were made to a vaccine or a prior variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 hospitalizations have been on the rise for weeks as summer nears its end, but how concerned should you be? SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID, continues to evolve and surprise us. So COVID transmission, hospitalization, and death rates can be difficult to predict.
, especially now that testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge.
Question 1: Are you expecting an end-of-summer COVID wave to be substantial?
Eric Topol, MD: “This wave won’t likely be substantial and could be more of a ‘wavelet.’ I’m not thinking that physicians are too concerned,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
Thomas Gut, DO: “It’s always impossible to predict the severity of COVID waves. Although the virus has generally mutated in ways that favor easier transmission and milder illness, there have been a handful of surprising mutations that were more dangerous and deadly than the preceding strain,” said Dr. Gut, associate chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Robert Atmar, MD: “I’ll start with the caveat that prognosticating for SARS-CoV-2 is a bit hazardous as we remain in unknown territory for some aspects of its epidemiology and evolution,” said Dr. Atmar, a professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “It depends on your definition of substantial. We, at least in Houston, are already in the midst of a substantial surge in the burden of infection, at least as monitored through wastewater surveillance. The amount of virus in the wastewater already exceeds the peak level we saw last winter. That said, the increased infection burden has not translated into large increases in hospitalizations for COVID-19. Most persons hospitalized in our hospital are admitted with infection, not for the consequences of infection.”
Stuart Campbell Ray, MD: “It looks like there is a rise in infections, but the proportional rise in hospitalizations from severe cases is lower than in the past, suggesting that folks are protected by the immunity we’ve gained over the past few years through vaccination and prior infections. Of course, we should be thinking about how that applies to each of us – how recently we had a vaccine or COVID-19, and whether we might see more severe infections as immunity wanes,” said Dr. Ray, who is a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Question 2: Is a return to masks or mask mandates coming this fall or winter?
Dr. Topol: “Mandating masks doesn’t work very well, but we may see wide use again if a descendant of [variant] BA.2.86 takes off.”
Dr. Gut: “It’s difficult to predict if there are any mask mandates returning at any point. Ever since the Omicron strains emerged, COVID has been relatively mild, compared to previous strains, so there probably won’t be any plan to start masking in public unless a more deadly strain appears.”
Dr. Atmar: “I do not think we will see a return to mask mandates this fall or winter for a variety of reasons. The primary one is that I don’t think the public will accept mask mandates. However, I think masking can continue to be an adjunctive measure to enhance protection from infection, along with booster vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “Some people will choose to wear masks during a surge, particularly in situations like commuting where they don’t interfere with what they’re doing. They will wear masks particularly if they want to avoid infection due to concerns about others they care about, disruption of work or travel plans, or concerns about long-term consequences of repeated COVID-19.”
Question 3: Now that COVID testing and vaccinations are no longer free of charge, how might that affect their use?
Dr. Topol: “It was already low, and this will undoubtedly further compromise their uptake.”
Dr. Gut: “I do expect that testing will become less common now that tests are no longer free. I’m sure there will be a lower amount of detection in patients with milder or asymptomatic disease compared to what we had previously.”
Dr. Atmar: “If there are out-of-pocket costs for the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, or if the administrative paperwork attached to getting a vaccine is increased, the uptake of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines will likely decrease. It will be important to communicate to the populations targeted for vaccination the potential benefits of such vaccination.”
Dr. Ray: “A challenge with COVID-19, all along, has been disparities in access to care, and this will be worse without public support for prevention and testing. This applies to everyone but is especially burdensome for those who are often marginalized in our health care system and society in general. I hope that we’ll find ways to ensure that people who need tests and vaccinations are able to access them, as good health is in everyone’s interest.”
Question 4: Will the new vaccines against COVID work for the currently circulating variants?
Dr. Topol: “The XBB.1.5 boosters will be out Sept. 14. They should help versus EG.5.1 and FL.1.5.1. The FL.1.5.1 variant is gaining now.”
Dr. Gut: “In the next several weeks, we expect the newer monovalent XBB-based vaccines to be offered that offer good protection against current circulating COVID variants along with the new Eris variant.”
Dr. Atmar: “The vaccines are expected to induce immune responses to the currently circulating variants, most of which are strains that evolved from the vaccine strain. The vaccine is expected to be most effective in preventing severe illness and will likely be less effective in preventing infection and mild illness.”
Dr. Ray: “Yes, the updated vaccine design has a spike antigen (XBB.1.5) nearly identical to the current dominant variant (EG.5). Even as variants change, the boosters stimulate B cells and T cells to help protect in a way that is safer than getting COVID-19 infection.”
Question 5: Is there anything we should watch out for regarding the BA.2.86 variant in particular?
Dr. Topol: “The scenario could change if there are new functional mutations added to it.”
Dr. Gut: “BA.2.86 is still fairly uncommon and does not have much data to directly make any informed guesses. However, in general, people that have been exposed to more recent mutations of the COVID virus have been shown to have more protection from newer upcoming mutations. It’s fair to guess that people that have not had recent infection from COVID, or have not had a recent booster, are at higher risk for being infected by any XBB- or BA.2-based strains.”
Dr. Atmar: BA.2.86 has been designated as a variant under monitoring. We will want to see whether it becomes more common and if there are any unexpected characteristics associated with infection by this variant.”
Dr. Ray: “It’s still rare, but it’s been seen in geographically dispersed places, so it’s got legs. The question is how effectively it will bypass some of the immunity we’ve gained. T cells are likely to remain protective, because they target so many parts of the virus that change more slowly, but antibodies from B cells to spike protein may have more trouble recognizing BA.2.86, whether those antibodies were made to a vaccine or a prior variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA to step up oversight of cosmetics, assess ‘forever chemicals’
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves canakinumab for gout flares
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved canakinumab (Ilaris) for the treatment of gout flares in adults who cannot be treated with NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids. The drug is also indicated for people who could not tolerate or had an inadequate response to NSAIDs or colchicine.
The drug, a humanized anti–interleukin-1 beta monoclonal antibody, is the first and only biologic approved in the United States for the treatment of gout flares, according to Novartis. It is administered in a single, subcutaneous injection of 150 mg.
“At Novartis, we are committed to bringing medicines that address high unmet needs to patients. We are proud to receive approval on our eighth indication for Ilaris in the U.S. and provide the first biologic medicine option for people with gout flares to help treat this painful and debilitating condition,” the company said in a statement to this news organization.
Canakinumab was first approved in the United States in 2009 for the treatment of children and adults with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Since then, it has been approved for the treatment of several other autoinflammatory diseases, including Still’s disease and recurrent fever syndromes.
In 2011, an FDA advisory panel voted against the approval of canakinumab to treat acute gout flares refractory to NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids, while in 2013, the European Medicine Agency approved the drug for this treatment indication.
Since that FDA advisory committee meeting and the FDA’s subsequent rejection letter, “[Novartis] has conducted additional studies in patients with gout flares and other related populations to further characterize the short- and long-term safety of canakinumab supporting the current application. To further support the benefit-risk [profile of the drug], the indication is for a more restricted population than initially proposed in 2011,” the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research said in a statement to this news organization. “Given these considerations and the available safety information, the Agency determined that canakinumab, at the recommended dosage, has a favorable risk-benefit profile” in the specified patient population.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved canakinumab (Ilaris) for the treatment of gout flares in adults who cannot be treated with NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids. The drug is also indicated for people who could not tolerate or had an inadequate response to NSAIDs or colchicine.
The drug, a humanized anti–interleukin-1 beta monoclonal antibody, is the first and only biologic approved in the United States for the treatment of gout flares, according to Novartis. It is administered in a single, subcutaneous injection of 150 mg.
“At Novartis, we are committed to bringing medicines that address high unmet needs to patients. We are proud to receive approval on our eighth indication for Ilaris in the U.S. and provide the first biologic medicine option for people with gout flares to help treat this painful and debilitating condition,” the company said in a statement to this news organization.
Canakinumab was first approved in the United States in 2009 for the treatment of children and adults with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Since then, it has been approved for the treatment of several other autoinflammatory diseases, including Still’s disease and recurrent fever syndromes.
In 2011, an FDA advisory panel voted against the approval of canakinumab to treat acute gout flares refractory to NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids, while in 2013, the European Medicine Agency approved the drug for this treatment indication.
Since that FDA advisory committee meeting and the FDA’s subsequent rejection letter, “[Novartis] has conducted additional studies in patients with gout flares and other related populations to further characterize the short- and long-term safety of canakinumab supporting the current application. To further support the benefit-risk [profile of the drug], the indication is for a more restricted population than initially proposed in 2011,” the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research said in a statement to this news organization. “Given these considerations and the available safety information, the Agency determined that canakinumab, at the recommended dosage, has a favorable risk-benefit profile” in the specified patient population.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved canakinumab (Ilaris) for the treatment of gout flares in adults who cannot be treated with NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids. The drug is also indicated for people who could not tolerate or had an inadequate response to NSAIDs or colchicine.
The drug, a humanized anti–interleukin-1 beta monoclonal antibody, is the first and only biologic approved in the United States for the treatment of gout flares, according to Novartis. It is administered in a single, subcutaneous injection of 150 mg.
“At Novartis, we are committed to bringing medicines that address high unmet needs to patients. We are proud to receive approval on our eighth indication for Ilaris in the U.S. and provide the first biologic medicine option for people with gout flares to help treat this painful and debilitating condition,” the company said in a statement to this news organization.
Canakinumab was first approved in the United States in 2009 for the treatment of children and adults with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). Since then, it has been approved for the treatment of several other autoinflammatory diseases, including Still’s disease and recurrent fever syndromes.
In 2011, an FDA advisory panel voted against the approval of canakinumab to treat acute gout flares refractory to NSAIDs, colchicine, or repeated courses of corticosteroids, while in 2013, the European Medicine Agency approved the drug for this treatment indication.
Since that FDA advisory committee meeting and the FDA’s subsequent rejection letter, “[Novartis] has conducted additional studies in patients with gout flares and other related populations to further characterize the short- and long-term safety of canakinumab supporting the current application. To further support the benefit-risk [profile of the drug], the indication is for a more restricted population than initially proposed in 2011,” the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research said in a statement to this news organization. “Given these considerations and the available safety information, the Agency determined that canakinumab, at the recommended dosage, has a favorable risk-benefit profile” in the specified patient population.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Raised Linear Plaques on the Back
The Diagnosis: Flagellate Dermatitis
Upon further questioning by dermatology, the patient noted recent ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, which were not a part of his typical diet. Based on the appearance of the rash in the context of ingesting shiitake mushrooms, our patient was diagnosed with flagellate dermatitis. At 6-week followup, the patient’s rash had resolved spontaneously without further intervention.
Flagellate dermatitis usually appears on the torso as linear whiplike streaks.1 The eruption often is pruritic and may be preceded by severe pruritus. Flagellate dermatitis also is a well-documented complication of bleomycin sulfate therapy with an incidence rate of 8% to 66%.2
Other chemotherapeutic causes include peplomycin, bendamustine, docetaxel, cisplatin, and trastuzumab.3 Flagellate dermatitis also is seen in some patients with dermatomyositis.4 A thorough patient history, including medications and dietary habits, is necessary to differentiate flagellate dermatitis from dermatomyositis.
Flagellate dermatitis, also known as shiitake dermatitis, is observed as erythematous flagellate eruptions involving the trunk or extremities that present within 2 hours to 5 days of handling or consuming undercooked or raw shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes),5,6 as was observed in our patient. Lentinan is the polysaccharide component of the shiitake species and is destabilized by heat.6 Ingestion of polysaccharide is associated with dermatitis, particularly in Japan, China, and Korea; however, the consumption of shiitake mushrooms has increased worldwide, and cases increasingly are reported outside of these typical regions. The rash typically resolves spontaneously; therefore, treatment is supportive. However, more severe symptomatic cases may require courses of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.6
In our case, the differential diagnosis consisted of acute urticaria, cutaneous dermatomyositis, dermatographism, and maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis. Acute urticaria displays well-circumscribed edematous papules or plaques, and individual lesions last less than 24 hours. Cutaneous dermatomyositis includes additional systemic manifestations such as fatigue, malaise, and myalgia, as well as involvement of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, or cardiac organs. Dermatographism is evoked by stroking or rubbing of the skin, which results in asymptomatic lesions that persist for 15 to 30 minutes. Cases of maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis more often are seen in children, and the histamine release most often causes gastrointestinal tract symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as flushing, blushing, pruritus, respiratory difficulty, and malaise.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503.
- Yagoda A, Mukherji B, Young C, et al. Bleomycin, an anti-tumor antibiotic: clinical experience in 274 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1972;77:861-870.
- Cohen PR. Trastuzumab-associated flagellate erythema: report in a woman with metastatic breast cancer and review of antineoplastic therapy-induced flagellate dermatoses. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;5:253-264. doi:10.1007/s13555-015-0085-2
- Grynszpan R, Niemeyer-Corbellini JP, Lopes MS, et al. Bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013009764. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-009764
- Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
The Diagnosis: Flagellate Dermatitis
Upon further questioning by dermatology, the patient noted recent ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, which were not a part of his typical diet. Based on the appearance of the rash in the context of ingesting shiitake mushrooms, our patient was diagnosed with flagellate dermatitis. At 6-week followup, the patient’s rash had resolved spontaneously without further intervention.
Flagellate dermatitis usually appears on the torso as linear whiplike streaks.1 The eruption often is pruritic and may be preceded by severe pruritus. Flagellate dermatitis also is a well-documented complication of bleomycin sulfate therapy with an incidence rate of 8% to 66%.2
Other chemotherapeutic causes include peplomycin, bendamustine, docetaxel, cisplatin, and trastuzumab.3 Flagellate dermatitis also is seen in some patients with dermatomyositis.4 A thorough patient history, including medications and dietary habits, is necessary to differentiate flagellate dermatitis from dermatomyositis.
Flagellate dermatitis, also known as shiitake dermatitis, is observed as erythematous flagellate eruptions involving the trunk or extremities that present within 2 hours to 5 days of handling or consuming undercooked or raw shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes),5,6 as was observed in our patient. Lentinan is the polysaccharide component of the shiitake species and is destabilized by heat.6 Ingestion of polysaccharide is associated with dermatitis, particularly in Japan, China, and Korea; however, the consumption of shiitake mushrooms has increased worldwide, and cases increasingly are reported outside of these typical regions. The rash typically resolves spontaneously; therefore, treatment is supportive. However, more severe symptomatic cases may require courses of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.6
In our case, the differential diagnosis consisted of acute urticaria, cutaneous dermatomyositis, dermatographism, and maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis. Acute urticaria displays well-circumscribed edematous papules or plaques, and individual lesions last less than 24 hours. Cutaneous dermatomyositis includes additional systemic manifestations such as fatigue, malaise, and myalgia, as well as involvement of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, or cardiac organs. Dermatographism is evoked by stroking or rubbing of the skin, which results in asymptomatic lesions that persist for 15 to 30 minutes. Cases of maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis more often are seen in children, and the histamine release most often causes gastrointestinal tract symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as flushing, blushing, pruritus, respiratory difficulty, and malaise.
The Diagnosis: Flagellate Dermatitis
Upon further questioning by dermatology, the patient noted recent ingestion of shiitake mushrooms, which were not a part of his typical diet. Based on the appearance of the rash in the context of ingesting shiitake mushrooms, our patient was diagnosed with flagellate dermatitis. At 6-week followup, the patient’s rash had resolved spontaneously without further intervention.
Flagellate dermatitis usually appears on the torso as linear whiplike streaks.1 The eruption often is pruritic and may be preceded by severe pruritus. Flagellate dermatitis also is a well-documented complication of bleomycin sulfate therapy with an incidence rate of 8% to 66%.2
Other chemotherapeutic causes include peplomycin, bendamustine, docetaxel, cisplatin, and trastuzumab.3 Flagellate dermatitis also is seen in some patients with dermatomyositis.4 A thorough patient history, including medications and dietary habits, is necessary to differentiate flagellate dermatitis from dermatomyositis.
Flagellate dermatitis, also known as shiitake dermatitis, is observed as erythematous flagellate eruptions involving the trunk or extremities that present within 2 hours to 5 days of handling or consuming undercooked or raw shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes),5,6 as was observed in our patient. Lentinan is the polysaccharide component of the shiitake species and is destabilized by heat.6 Ingestion of polysaccharide is associated with dermatitis, particularly in Japan, China, and Korea; however, the consumption of shiitake mushrooms has increased worldwide, and cases increasingly are reported outside of these typical regions. The rash typically resolves spontaneously; therefore, treatment is supportive. However, more severe symptomatic cases may require courses of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.6
In our case, the differential diagnosis consisted of acute urticaria, cutaneous dermatomyositis, dermatographism, and maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis. Acute urticaria displays well-circumscribed edematous papules or plaques, and individual lesions last less than 24 hours. Cutaneous dermatomyositis includes additional systemic manifestations such as fatigue, malaise, and myalgia, as well as involvement of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, or cardiac organs. Dermatographism is evoked by stroking or rubbing of the skin, which results in asymptomatic lesions that persist for 15 to 30 minutes. Cases of maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis more often are seen in children, and the histamine release most often causes gastrointestinal tract symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as flushing, blushing, pruritus, respiratory difficulty, and malaise.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503.
- Yagoda A, Mukherji B, Young C, et al. Bleomycin, an anti-tumor antibiotic: clinical experience in 274 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1972;77:861-870.
- Cohen PR. Trastuzumab-associated flagellate erythema: report in a woman with metastatic breast cancer and review of antineoplastic therapy-induced flagellate dermatoses. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;5:253-264. doi:10.1007/s13555-015-0085-2
- Grynszpan R, Niemeyer-Corbellini JP, Lopes MS, et al. Bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013009764. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-009764
- Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503.
- Yagoda A, Mukherji B, Young C, et al. Bleomycin, an anti-tumor antibiotic: clinical experience in 274 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1972;77:861-870.
- Cohen PR. Trastuzumab-associated flagellate erythema: report in a woman with metastatic breast cancer and review of antineoplastic therapy-induced flagellate dermatoses. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;5:253-264. doi:10.1007/s13555-015-0085-2
- Grynszpan R, Niemeyer-Corbellini JP, Lopes MS, et al. Bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013009764. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-009764
- Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.
- Boels D, Landreau A, Bruneau C, et al. Shiitake dermatitis recorded by French Poison Control Centers—new case series with clinical observations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014;52:625-628.
A 77-year-old man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and nonmelanoma skin cancer presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a new rash of 2 days’ duration. He trialed a previously prescribed triamcinolone cream 0.1% without improvement. The patient denied any recent travel, as well as fever, nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits. Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, raised, linear plaques on the mid to lower back.
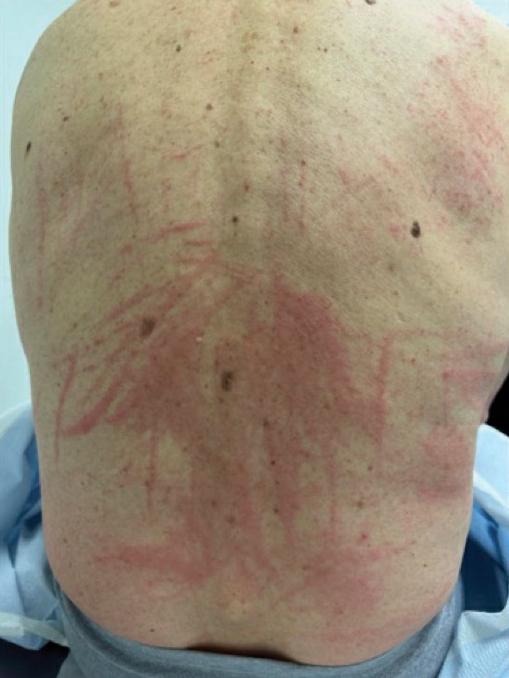
Screening finds high rates of CVD in diabetes, COPD patients
AMSTERDAM – , compared with usual care, in a Dutch study involving more than 1,200 people and 25 primary care practices.
Scaling up this program to larger populations could potentially uncover huge numbers of currently unrecognized people with CVD given the large number of adults with type 2 diabetes plus those with COPD, Amy Groenewegen, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“I think this screening is ready for routine use, but it could be followed by prospective studies that investigate whether it produces more benefits in patient-centered outcomes,” Dr. Groenewegen said in a press briefing. She stressed that it has not yet been clearly proven that patients with these chronic diseases are better off long term when their CVD is detected sooner using the tested approach.
“We need simple ways to identify relevant patients for additional screening and potential treatment” of CVD, commented Lars Kober, MD, designated discussant at the Congress and a cardiologist and professor at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital.
A ‘very simple’ symptom questionnaire
The study is important because it tested a “very simple” symptom questionnaire as the initial screening phase, yet resulted in a CVD diagnostic rate that was two- to threefold higher than in the control patients managed with usual care, Dr. Kober noted.
The Reviving the Early Diagnosis of CVD (RED-CVD) trial randomized 14 primary care practices in the Netherlands to apply a structured screening protocol to adults with type 2 diabetes or COPD, and another 11 practices that served as controls and provided their patients with usual care.
The study included 624 people in the screening arm and 592 in the usual-care arm. Their average age was about 68 years. In the screening arm, 87% had type 2 diabetes and 20% had COPD, including 6.3% with both. In the usual-care arm, 86% had type 2 diabetes, 21% had COPD, with 7.4% having both.
About a quarter of the study cohort had a history of a CVD diagnosis, but they were included for their potential for developing another form of CVD. The study considered three types of CVD: coronary artery disease, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation.
The CVD screening protocol began with an 11-question survey, completed by patients, that asked about their symptoms. The survey was devised by a research team at the University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, who collaborated on the study.
The second phase for people who had suggestive symptoms was a physical examination, measurement of serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (elevated levels signal incident heart failure), and an ECG. People who continued to show findings consistent with CVD in this phase were then referred on a discretionary basis by the attending physician to a specialist.
More than doubling the CVD diagnosis rate
The screening program produced a total of 50 new CVD diagnoses in the screening cohort (8%) and 18 in the control, usual-care arm (3%), for the study’s primary endpoint. The greatest number of events involved heart failure, followed by coronary disease.
The screening questionnaire identified 70% of the people who completed it with suggestive symptoms, such as shortness of breath, claudication, or palpitations. The follow-up assessments of phase two narrowed the group with possible new CVD down to 44% of the people in this arm, and the participating physicians referred 39% to a specialist.
An analysis that adjusted for several demographic and clinical variables and excluded nonobstructive coronary disease as a new CVD diagnosis showed that the systematic screening approach resulted in 2.4-fold more new diagnoses than usual care, reported Dr. Groenewegen, an epidemiologist at University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
RED-CVD received no commercial funding. Dr. Groenewegen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kober has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , compared with usual care, in a Dutch study involving more than 1,200 people and 25 primary care practices.
Scaling up this program to larger populations could potentially uncover huge numbers of currently unrecognized people with CVD given the large number of adults with type 2 diabetes plus those with COPD, Amy Groenewegen, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“I think this screening is ready for routine use, but it could be followed by prospective studies that investigate whether it produces more benefits in patient-centered outcomes,” Dr. Groenewegen said in a press briefing. She stressed that it has not yet been clearly proven that patients with these chronic diseases are better off long term when their CVD is detected sooner using the tested approach.
“We need simple ways to identify relevant patients for additional screening and potential treatment” of CVD, commented Lars Kober, MD, designated discussant at the Congress and a cardiologist and professor at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital.
A ‘very simple’ symptom questionnaire
The study is important because it tested a “very simple” symptom questionnaire as the initial screening phase, yet resulted in a CVD diagnostic rate that was two- to threefold higher than in the control patients managed with usual care, Dr. Kober noted.
The Reviving the Early Diagnosis of CVD (RED-CVD) trial randomized 14 primary care practices in the Netherlands to apply a structured screening protocol to adults with type 2 diabetes or COPD, and another 11 practices that served as controls and provided their patients with usual care.
The study included 624 people in the screening arm and 592 in the usual-care arm. Their average age was about 68 years. In the screening arm, 87% had type 2 diabetes and 20% had COPD, including 6.3% with both. In the usual-care arm, 86% had type 2 diabetes, 21% had COPD, with 7.4% having both.
About a quarter of the study cohort had a history of a CVD diagnosis, but they were included for their potential for developing another form of CVD. The study considered three types of CVD: coronary artery disease, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation.
The CVD screening protocol began with an 11-question survey, completed by patients, that asked about their symptoms. The survey was devised by a research team at the University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, who collaborated on the study.
The second phase for people who had suggestive symptoms was a physical examination, measurement of serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (elevated levels signal incident heart failure), and an ECG. People who continued to show findings consistent with CVD in this phase were then referred on a discretionary basis by the attending physician to a specialist.
More than doubling the CVD diagnosis rate
The screening program produced a total of 50 new CVD diagnoses in the screening cohort (8%) and 18 in the control, usual-care arm (3%), for the study’s primary endpoint. The greatest number of events involved heart failure, followed by coronary disease.
The screening questionnaire identified 70% of the people who completed it with suggestive symptoms, such as shortness of breath, claudication, or palpitations. The follow-up assessments of phase two narrowed the group with possible new CVD down to 44% of the people in this arm, and the participating physicians referred 39% to a specialist.
An analysis that adjusted for several demographic and clinical variables and excluded nonobstructive coronary disease as a new CVD diagnosis showed that the systematic screening approach resulted in 2.4-fold more new diagnoses than usual care, reported Dr. Groenewegen, an epidemiologist at University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
RED-CVD received no commercial funding. Dr. Groenewegen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kober has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , compared with usual care, in a Dutch study involving more than 1,200 people and 25 primary care practices.
Scaling up this program to larger populations could potentially uncover huge numbers of currently unrecognized people with CVD given the large number of adults with type 2 diabetes plus those with COPD, Amy Groenewegen, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“I think this screening is ready for routine use, but it could be followed by prospective studies that investigate whether it produces more benefits in patient-centered outcomes,” Dr. Groenewegen said in a press briefing. She stressed that it has not yet been clearly proven that patients with these chronic diseases are better off long term when their CVD is detected sooner using the tested approach.
“We need simple ways to identify relevant patients for additional screening and potential treatment” of CVD, commented Lars Kober, MD, designated discussant at the Congress and a cardiologist and professor at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital.
A ‘very simple’ symptom questionnaire
The study is important because it tested a “very simple” symptom questionnaire as the initial screening phase, yet resulted in a CVD diagnostic rate that was two- to threefold higher than in the control patients managed with usual care, Dr. Kober noted.
The Reviving the Early Diagnosis of CVD (RED-CVD) trial randomized 14 primary care practices in the Netherlands to apply a structured screening protocol to adults with type 2 diabetes or COPD, and another 11 practices that served as controls and provided their patients with usual care.
The study included 624 people in the screening arm and 592 in the usual-care arm. Their average age was about 68 years. In the screening arm, 87% had type 2 diabetes and 20% had COPD, including 6.3% with both. In the usual-care arm, 86% had type 2 diabetes, 21% had COPD, with 7.4% having both.
About a quarter of the study cohort had a history of a CVD diagnosis, but they were included for their potential for developing another form of CVD. The study considered three types of CVD: coronary artery disease, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation.
The CVD screening protocol began with an 11-question survey, completed by patients, that asked about their symptoms. The survey was devised by a research team at the University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, who collaborated on the study.
The second phase for people who had suggestive symptoms was a physical examination, measurement of serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (elevated levels signal incident heart failure), and an ECG. People who continued to show findings consistent with CVD in this phase were then referred on a discretionary basis by the attending physician to a specialist.
More than doubling the CVD diagnosis rate
The screening program produced a total of 50 new CVD diagnoses in the screening cohort (8%) and 18 in the control, usual-care arm (3%), for the study’s primary endpoint. The greatest number of events involved heart failure, followed by coronary disease.
The screening questionnaire identified 70% of the people who completed it with suggestive symptoms, such as shortness of breath, claudication, or palpitations. The follow-up assessments of phase two narrowed the group with possible new CVD down to 44% of the people in this arm, and the participating physicians referred 39% to a specialist.
An analysis that adjusted for several demographic and clinical variables and excluded nonobstructive coronary disease as a new CVD diagnosis showed that the systematic screening approach resulted in 2.4-fold more new diagnoses than usual care, reported Dr. Groenewegen, an epidemiologist at University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
RED-CVD received no commercial funding. Dr. Groenewegen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kober has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ESC CONGRESS 2023
FDA clears new capabilities for diabetes app BlueStar
The latest clearance, announced on Aug. 23, enables the app-based platform to provide bolus insulin dose recommendations that are based on glucose and trend data from a compatible continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device. On Aug. 15, the FDA cleared the BlueStar to use connected insulin dosing data in personalized bolus insulin dosing recommendations.
“Welldoc is the first company to receive clearance for a CGM-informed bolus calculator specifically designed for adults who manage their diabetes with multiple daily injections of insulin,” according to a company statement.
“With this clearance, Welldoc is filling a significant gap for people who require complex insulin regimens. By connecting directly with CGM data and using both glucose values and trend arrows, the BlueStar solution will provide precise and in-the-moment insulin dosing guidance directly to individuals, helping them reach their glucose targets,” endocrinologist Grazia Aleppo, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in the statement.
The new features extend the platform’s existing digital diet and lifestyle coaching capabilities. Previous FDA clearances included expansions to use most types of available insulins, including bolus and premixed insulin titration for patients with type 2 diabetes, in September 2021 and for basal insulin adjustment in June 2020.
Dr. Aleppo was a principal investigator in Welldoc’s clinical validation study for BlueStar.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest clearance, announced on Aug. 23, enables the app-based platform to provide bolus insulin dose recommendations that are based on glucose and trend data from a compatible continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device. On Aug. 15, the FDA cleared the BlueStar to use connected insulin dosing data in personalized bolus insulin dosing recommendations.
“Welldoc is the first company to receive clearance for a CGM-informed bolus calculator specifically designed for adults who manage their diabetes with multiple daily injections of insulin,” according to a company statement.
“With this clearance, Welldoc is filling a significant gap for people who require complex insulin regimens. By connecting directly with CGM data and using both glucose values and trend arrows, the BlueStar solution will provide precise and in-the-moment insulin dosing guidance directly to individuals, helping them reach their glucose targets,” endocrinologist Grazia Aleppo, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in the statement.
The new features extend the platform’s existing digital diet and lifestyle coaching capabilities. Previous FDA clearances included expansions to use most types of available insulins, including bolus and premixed insulin titration for patients with type 2 diabetes, in September 2021 and for basal insulin adjustment in June 2020.
Dr. Aleppo was a principal investigator in Welldoc’s clinical validation study for BlueStar.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest clearance, announced on Aug. 23, enables the app-based platform to provide bolus insulin dose recommendations that are based on glucose and trend data from a compatible continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device. On Aug. 15, the FDA cleared the BlueStar to use connected insulin dosing data in personalized bolus insulin dosing recommendations.
“Welldoc is the first company to receive clearance for a CGM-informed bolus calculator specifically designed for adults who manage their diabetes with multiple daily injections of insulin,” according to a company statement.
“With this clearance, Welldoc is filling a significant gap for people who require complex insulin regimens. By connecting directly with CGM data and using both glucose values and trend arrows, the BlueStar solution will provide precise and in-the-moment insulin dosing guidance directly to individuals, helping them reach their glucose targets,” endocrinologist Grazia Aleppo, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in the statement.
The new features extend the platform’s existing digital diet and lifestyle coaching capabilities. Previous FDA clearances included expansions to use most types of available insulins, including bolus and premixed insulin titration for patients with type 2 diabetes, in September 2021 and for basal insulin adjustment in June 2020.
Dr. Aleppo was a principal investigator in Welldoc’s clinical validation study for BlueStar.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even an hour’s walk a week lowers risk in type 2 diabetes
although the impact on retinopathy is weaker, reveals a cohort study of U.K. individuals.
The research, based on data from more than 18,000 participants in the U.K. Biobank, suggests that the minimal level of self-reported activity to reduce the risk for both neuropathy and nephropathy may be the equivalent of less than 1.5 hours of walking per week.
The results are “encouraging and reassuring for both physicians and patients,” lead author Frederik P.B. Kristensen, MSc, PhD student, department of clinical epidemiology, Aarhus (Denmark) University, said in an interview.
“Our findings are particularly promising for neuropathy since, currently, no disease-modifying treatment exists, and there are limited preventive strategies available.”
Mr. Kristensen highlighted that “most diabetes research has focused on all-cause mortality and macrovascular complications. In the current study, we also found the same pattern for microvascular complications: Even small amounts of physical activity will benefit your health status.”
The minimal level of activity they identified, he said, is also an “achievable [goal] for most type 2 diabetes patients.”
Mr. Kristensen added, however, that the study was limited by excluding individuals with limited mobility and those living in temporary accommodation or care homes.
And prospective studies are required to determine the dose-response relationship between total, not just leisure-time, activity – ideally measured objectively – and risk for microvascular complications, he observed.
The research was published recently in Diabetes Care.
Impact of exercise on microvascular complications in T2D has been uncertain
The authors point out that microvascular complications – such as nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney problems (nephropathy), and eye complications (retinopathy) – occur in more than 50% of individuals with type 2 diabetes and have a “substantial impact” on quality of life, on top of the impact of macrovascular complications (such as cardiovascular disease), disability, and mortality.
Although physical activity is seen as a “cornerstone in the multifactorial management of type 2 diabetes because of its beneficial effects on metabolic risk factors,” the impact on microvascular complications is “uncertain” and the evidence is limited and “conflicting.”
The researchers therefore sought to examine the dose-response association, including the minimal effective level, between leisure-time physical activity and neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
They conducted a cohort study of individuals aged 37-82 years from the U.K. Biobank who had type 2 diabetes, which was identified using the Eastwood algorithm and/or an A1c greater than or equal to 48 mmol/mol (6.5%).
Individuals with type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes were excluded, as were those with major disabling somatic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and mental disorders, among others.
Leisure-time physical activity was based on the self-reported frequency, duration, and types of physical activities and was combined to calculate the total leisure time activity in MET-hours per week.
Using the American Diabetes Association/World Health Organization recommendations of 150-300 minutes of moderate to vigorous leisure-time physical activity per week, the researchers determined the recommended moderate activity level to be 150 minutes, (equivalent to 2.5 hours, or 7.5 MET-hours per week).
In all, 18,092 individuals with type 2 diabetes were included in the analysis, of whom 37% were women. The mean age was 60 years.
Ten percent of participants performed no leisure-time physical activity, 38% performed activity below the threshold for moderate activity, 20% performed at the recommended level, and 32% were more active.
Those performing no physical activity were more likely to be women, to be younger, to have a higher body mass index, and to have a greater average A1c, as well as have a more unfavorable sociodemographic and behavioral profile.
Over a median follow-up of 12.1 years, 3.7% of the participants were diagnosed with neuropathy, 10.2% with nephropathy, and 11.7% with retinopathy, equating to an incidence per 1,000 person-years of 3.5, 9,8, and 11.4, respectively.
The researchers found that any level of physical activity was associated with an approximate reduction in the risk for neuropathy and nephropathy.
Multivariate analysis indicated that, compared with no physical activity, activity below the recommended level was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for neuropathy of 0.71, whereas the aHR for activity at the recommended level was 0.73 and that for activity above the recommended level was 0.67.
The aHR for nephropathy, compared with no physical activity, was 0.79 for activity below the recommended level, 0.80 for activity at the recommended level, and 0.80 for activity above the recommended level.
The association between physical activity and retinopathy was weaker, however, at aHRs of 0.91, 0.91, and 0.98 for activity below, at, and above the recommended level, respectively.
The researchers suggest that this lower association could be due to differences in the etiology of the different forms of microvascular complications.
Hyperglycemia is the key driver in the development of retinopathy, they note, whereas other metabolic risk factors, such as obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, play a role in neuropathy and nephropathy.
The associations were also less pronounced in women.
Mr. Kristensen said that this is “an important area that needs to be addressed.”
“While different rates between men and women regarding incidence of type 2 diabetes, metabolic risk factors, complications, and the initiation of, and adherence to, therapy have been found,” he continued, “the exact mechanisms remain unclear. We need a further understanding of sex-differences in metabolic regulation, as well as in material living conditions, social and psychological factors, and access to health care, which may influence the risk of complications.”
Mr. Kristensen added, “Sex differences may be present in more areas than we are aware.”
Mr. Kristensen is supported by a PhD grant from Aarhus University. Other authors received funding from the Danish Diabetes Association, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, the New South Wales Government, the Spanish Ministry of Universities, the European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR (Plan de Recuperación) through a Margarita Salas contract of the University of Vigo, and the Government of Andalusia, Research Talent Recruitment Programme. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
although the impact on retinopathy is weaker, reveals a cohort study of U.K. individuals.
The research, based on data from more than 18,000 participants in the U.K. Biobank, suggests that the minimal level of self-reported activity to reduce the risk for both neuropathy and nephropathy may be the equivalent of less than 1.5 hours of walking per week.
The results are “encouraging and reassuring for both physicians and patients,” lead author Frederik P.B. Kristensen, MSc, PhD student, department of clinical epidemiology, Aarhus (Denmark) University, said in an interview.
“Our findings are particularly promising for neuropathy since, currently, no disease-modifying treatment exists, and there are limited preventive strategies available.”
Mr. Kristensen highlighted that “most diabetes research has focused on all-cause mortality and macrovascular complications. In the current study, we also found the same pattern for microvascular complications: Even small amounts of physical activity will benefit your health status.”
The minimal level of activity they identified, he said, is also an “achievable [goal] for most type 2 diabetes patients.”
Mr. Kristensen added, however, that the study was limited by excluding individuals with limited mobility and those living in temporary accommodation or care homes.
And prospective studies are required to determine the dose-response relationship between total, not just leisure-time, activity – ideally measured objectively – and risk for microvascular complications, he observed.
The research was published recently in Diabetes Care.
Impact of exercise on microvascular complications in T2D has been uncertain
The authors point out that microvascular complications – such as nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney problems (nephropathy), and eye complications (retinopathy) – occur in more than 50% of individuals with type 2 diabetes and have a “substantial impact” on quality of life, on top of the impact of macrovascular complications (such as cardiovascular disease), disability, and mortality.
Although physical activity is seen as a “cornerstone in the multifactorial management of type 2 diabetes because of its beneficial effects on metabolic risk factors,” the impact on microvascular complications is “uncertain” and the evidence is limited and “conflicting.”
The researchers therefore sought to examine the dose-response association, including the minimal effective level, between leisure-time physical activity and neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
They conducted a cohort study of individuals aged 37-82 years from the U.K. Biobank who had type 2 diabetes, which was identified using the Eastwood algorithm and/or an A1c greater than or equal to 48 mmol/mol (6.5%).
Individuals with type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes were excluded, as were those with major disabling somatic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and mental disorders, among others.
Leisure-time physical activity was based on the self-reported frequency, duration, and types of physical activities and was combined to calculate the total leisure time activity in MET-hours per week.
Using the American Diabetes Association/World Health Organization recommendations of 150-300 minutes of moderate to vigorous leisure-time physical activity per week, the researchers determined the recommended moderate activity level to be 150 minutes, (equivalent to 2.5 hours, or 7.5 MET-hours per week).
In all, 18,092 individuals with type 2 diabetes were included in the analysis, of whom 37% were women. The mean age was 60 years.
Ten percent of participants performed no leisure-time physical activity, 38% performed activity below the threshold for moderate activity, 20% performed at the recommended level, and 32% were more active.
Those performing no physical activity were more likely to be women, to be younger, to have a higher body mass index, and to have a greater average A1c, as well as have a more unfavorable sociodemographic and behavioral profile.
Over a median follow-up of 12.1 years, 3.7% of the participants were diagnosed with neuropathy, 10.2% with nephropathy, and 11.7% with retinopathy, equating to an incidence per 1,000 person-years of 3.5, 9,8, and 11.4, respectively.
The researchers found that any level of physical activity was associated with an approximate reduction in the risk for neuropathy and nephropathy.
Multivariate analysis indicated that, compared with no physical activity, activity below the recommended level was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for neuropathy of 0.71, whereas the aHR for activity at the recommended level was 0.73 and that for activity above the recommended level was 0.67.
The aHR for nephropathy, compared with no physical activity, was 0.79 for activity below the recommended level, 0.80 for activity at the recommended level, and 0.80 for activity above the recommended level.
The association between physical activity and retinopathy was weaker, however, at aHRs of 0.91, 0.91, and 0.98 for activity below, at, and above the recommended level, respectively.
The researchers suggest that this lower association could be due to differences in the etiology of the different forms of microvascular complications.
Hyperglycemia is the key driver in the development of retinopathy, they note, whereas other metabolic risk factors, such as obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, play a role in neuropathy and nephropathy.
The associations were also less pronounced in women.
Mr. Kristensen said that this is “an important area that needs to be addressed.”
“While different rates between men and women regarding incidence of type 2 diabetes, metabolic risk factors, complications, and the initiation of, and adherence to, therapy have been found,” he continued, “the exact mechanisms remain unclear. We need a further understanding of sex-differences in metabolic regulation, as well as in material living conditions, social and psychological factors, and access to health care, which may influence the risk of complications.”
Mr. Kristensen added, “Sex differences may be present in more areas than we are aware.”
Mr. Kristensen is supported by a PhD grant from Aarhus University. Other authors received funding from the Danish Diabetes Association, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, the New South Wales Government, the Spanish Ministry of Universities, the European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR (Plan de Recuperación) through a Margarita Salas contract of the University of Vigo, and the Government of Andalusia, Research Talent Recruitment Programme. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
although the impact on retinopathy is weaker, reveals a cohort study of U.K. individuals.
The research, based on data from more than 18,000 participants in the U.K. Biobank, suggests that the minimal level of self-reported activity to reduce the risk for both neuropathy and nephropathy may be the equivalent of less than 1.5 hours of walking per week.
The results are “encouraging and reassuring for both physicians and patients,” lead author Frederik P.B. Kristensen, MSc, PhD student, department of clinical epidemiology, Aarhus (Denmark) University, said in an interview.
“Our findings are particularly promising for neuropathy since, currently, no disease-modifying treatment exists, and there are limited preventive strategies available.”
Mr. Kristensen highlighted that “most diabetes research has focused on all-cause mortality and macrovascular complications. In the current study, we also found the same pattern for microvascular complications: Even small amounts of physical activity will benefit your health status.”
The minimal level of activity they identified, he said, is also an “achievable [goal] for most type 2 diabetes patients.”
Mr. Kristensen added, however, that the study was limited by excluding individuals with limited mobility and those living in temporary accommodation or care homes.
And prospective studies are required to determine the dose-response relationship between total, not just leisure-time, activity – ideally measured objectively – and risk for microvascular complications, he observed.
The research was published recently in Diabetes Care.
Impact of exercise on microvascular complications in T2D has been uncertain
The authors point out that microvascular complications – such as nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney problems (nephropathy), and eye complications (retinopathy) – occur in more than 50% of individuals with type 2 diabetes and have a “substantial impact” on quality of life, on top of the impact of macrovascular complications (such as cardiovascular disease), disability, and mortality.
Although physical activity is seen as a “cornerstone in the multifactorial management of type 2 diabetes because of its beneficial effects on metabolic risk factors,” the impact on microvascular complications is “uncertain” and the evidence is limited and “conflicting.”
The researchers therefore sought to examine the dose-response association, including the minimal effective level, between leisure-time physical activity and neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
They conducted a cohort study of individuals aged 37-82 years from the U.K. Biobank who had type 2 diabetes, which was identified using the Eastwood algorithm and/or an A1c greater than or equal to 48 mmol/mol (6.5%).
Individuals with type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes were excluded, as were those with major disabling somatic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and mental disorders, among others.
Leisure-time physical activity was based on the self-reported frequency, duration, and types of physical activities and was combined to calculate the total leisure time activity in MET-hours per week.
Using the American Diabetes Association/World Health Organization recommendations of 150-300 minutes of moderate to vigorous leisure-time physical activity per week, the researchers determined the recommended moderate activity level to be 150 minutes, (equivalent to 2.5 hours, or 7.5 MET-hours per week).
In all, 18,092 individuals with type 2 diabetes were included in the analysis, of whom 37% were women. The mean age was 60 years.
Ten percent of participants performed no leisure-time physical activity, 38% performed activity below the threshold for moderate activity, 20% performed at the recommended level, and 32% were more active.
Those performing no physical activity were more likely to be women, to be younger, to have a higher body mass index, and to have a greater average A1c, as well as have a more unfavorable sociodemographic and behavioral profile.
Over a median follow-up of 12.1 years, 3.7% of the participants were diagnosed with neuropathy, 10.2% with nephropathy, and 11.7% with retinopathy, equating to an incidence per 1,000 person-years of 3.5, 9,8, and 11.4, respectively.
The researchers found that any level of physical activity was associated with an approximate reduction in the risk for neuropathy and nephropathy.
Multivariate analysis indicated that, compared with no physical activity, activity below the recommended level was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for neuropathy of 0.71, whereas the aHR for activity at the recommended level was 0.73 and that for activity above the recommended level was 0.67.
The aHR for nephropathy, compared with no physical activity, was 0.79 for activity below the recommended level, 0.80 for activity at the recommended level, and 0.80 for activity above the recommended level.
The association between physical activity and retinopathy was weaker, however, at aHRs of 0.91, 0.91, and 0.98 for activity below, at, and above the recommended level, respectively.
The researchers suggest that this lower association could be due to differences in the etiology of the different forms of microvascular complications.
Hyperglycemia is the key driver in the development of retinopathy, they note, whereas other metabolic risk factors, such as obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, play a role in neuropathy and nephropathy.
The associations were also less pronounced in women.
Mr. Kristensen said that this is “an important area that needs to be addressed.”
“While different rates between men and women regarding incidence of type 2 diabetes, metabolic risk factors, complications, and the initiation of, and adherence to, therapy have been found,” he continued, “the exact mechanisms remain unclear. We need a further understanding of sex-differences in metabolic regulation, as well as in material living conditions, social and psychological factors, and access to health care, which may influence the risk of complications.”
Mr. Kristensen added, “Sex differences may be present in more areas than we are aware.”
Mr. Kristensen is supported by a PhD grant from Aarhus University. Other authors received funding from the Danish Diabetes Association, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, the New South Wales Government, the Spanish Ministry of Universities, the European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR (Plan de Recuperación) through a Margarita Salas contract of the University of Vigo, and the Government of Andalusia, Research Talent Recruitment Programme. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE