User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
What makes teens choose to use sunscreen?
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
FROM SPD 2023
When treating AD in children, experts consider adherence, other aspects of treatment
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – according to a three-member expert panel mulling over strategies at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In introductory remarks, the three panelists briefly addressed different aspects for controlling AD, including drugs in the pipeline, the potential value of alternative therapies, and whom to blame when compliance is poor.
But panel discussion following these presentations provided an opportunity for audience engagement on practical strategies for improving AD control.
In her formal remarks prior to the panel discussion, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chair of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, and a pediatric dermatologist at the Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, described emerging AD treatments. This included an update on the status of the interleukin-13 (IL-13) inhibitors tralokinumab (Adbry), which was approved by the FDA for treating AD in adults in December 2021, and lebrikizumab, which is thought likely to be soon approved in the United States on the basis of two recently published phase 3 trials.
Along with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe AD in children who do not respond to optimized use of topical therapies, these new biologics appear likely to further expand choices for AD control for adults (and for kids with AD too, if eventually licensed in children), according to the data from the phase 3 studies.
During a panel discussion that followed, Stephen Gellis, MD, pediatric dermatologist and former chief of pediatric dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, raised the point of optimizing tried and true topical therapies before using systemic agents. He noted that parents sometimes pressure clinicians to use a biologic – and that moving too quickly to the latest and most expensive drugs may not be necessary.
Dr. Paller acknowledged that she, like many pediatric dermatologists, employed immunosuppressants as her drugs of choice for many years – commonly starting with a few months of cyclosporine before transitioning to methotrexate, which has a delayed onset of action. In fact, she still uses this regimen in some children.
However, she now prefers dupilumab, which is the first biologic available for children in the United States with an AD indication in children as young as 6 months. She said dupilumab has fewer potential risks than cyclosporine, and it offers clinically meaningful improvement in most children. She noted that current guidelines discourage the use of systemic corticosteroids for AD in children, given their potential toxicity.
She strongly agreed with Dr. Gellis that clinicians should resist pressure to use any systemic agent if children are responding well to topical medications. In her own practice, Dr. Paller moves to systemic medications only after ensuring that there has been adherence to appropriate therapy and that there is not another diagnosis that might explain the recalcitrance to topical agents.
When a systemic medication is considered the next step, Dr. Paller reminded the audience of the importance of presenting the benefits and risks of all the options for AD control, which could include dupilumab and immunosuppressants as initial systemic therapy.
“Many parents choose biologic treatment first, given its lack of requirement for blood monitoring and faster action than methotrexate,” Dr. Paller noted.
Nevertheless, “biologics are much more costly than immunosuppressants, require an injection – which is stressful for the child and the parents – and may not be accessible for our patients,” Dr. Paller said. Cyclosporine and methotrexate are effective and are often the best options for moderate to severe disease in areas of the world where dupilumab is not available, but Dr. Paller most commonly uses these therapies only when reimbursement for dupilumab cannot be secured, injection is not an option, or when dupilumab is not sufficiently effective and tolerated.
Providing different perspectives, the two other panelists discussing the treatment of pediatric AD also saw a role for ensuring that topical agents are not offering adequate AD control before turning to the latest and most sophisticated therapies for AD.
For meeting parent expectations when children are improving slowly on topical therapies, Peter A. Lio, MD, director of the Chicago Integrative Eczema Center and clinical assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, suggested that integrative medicine might be helpful.
For parents not fully comfortable with standard pharmacologic agents, Dr. Lio said there is evidence to support some of the complementary approaches, and these can be reassuring to parents with an interest in alternative medicines.
In Western medicine, it is common to hear terms like “attack,” “kill,” and “suppress,” disease, but alternative therapies are generally coupled with terms like “restore,” “strengthen,” and “tonify,” he said. “Who doesn’t want to be tonified?” he asked, noting that there are many sources of data suggesting that the number of patients seeking alternative medicine is “huge.” The alternative medicines are not generally taught in medical school and remain widely ignored in typical practice, but “our patients are interested even if we are not.”
Yet, there are data to support benefit from some of these alternative therapies, providing a win-win situation for patients who derive satisfaction from nontraditional therapies alone or combined with established pharmaceutical treatments.
Of these, Dr. Lio said there is support for the use of hempseed oil as a moisturizing agent and a strategy for improving barrier function in the skin of patients with AD. In a controlled crossover study, 2 teaspoons per day of dietary hempseed oil, a product that can be purchased in some grocery stores, was associated with significant reductions in skin dryness, itchiness, and use of topical medications relative to the same amount of olive oil, he noted.
Other examples include a compress made with black tea that was associated with an anti-inflammatory effect when followed by a moisturizer, a published study asserts. Although this was a trial in adults with facial dermatitis, Dr. Lio suggested that the same anti-inflammatory effect would be anticipated for other skin conditions, including AD in children.
As a third example, Dr. Lio said topical indigo, a traditional Chinese medicine used for a variety of dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis, has also demonstrated efficacy in a randomized trial, compared with vehicle for mild to severe AD.
Complementary medicines are not for everyone, but they may have a role when managing the expectations of parents who are not fully satisfied or express concern about regimens limited to mainstream therapies alone, according to Dr. Lio. In diseases that are not curable, such as AD, he thinks this is a strategy with potential for benefit and is reassuring to patients.
Another way to avoid moving to riskier or more expensive drugs quickly is to assure patients use the drugs that were prescribed first, according to Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Feldman believes that failure to adhere to therapy is basically the fault of the medical care system, not the patient. He made an analogy to a successful piano teacher, who provides a child with sheet music and then sees the child once a week to track progress. He juxtaposed this piano teacher to one who gives the child sheet music and tells the child to come back in 10 weeks for the recital. It is not hard to guess which approach would be more effective.
“Typically, doctors are worse than that second teacher,” he said. “Doctors are like a piano teacher that does not give you the sheet music but says, ‘Here is a prescription for some sheet music. Take this prescription to the sheet music store. I have no idea how much it will cost or whether your insurance will pay for it. But once you fill this prescription for sheet music, I want you to practice this every day,’ ” he said, adding, “Practicing this sheet music may cause rashes, diarrhea, or serious infection. When the patient next comes in 10-12 weeks later and is not better, the doctor says, ‘I will give you a harder piece of sheet music and maybe two or three other instruments to practice at the same time,’ ” said Dr. Feldman, expressing why the way clinicians practice might explain much of the poor adherence problem.
This largely explains why patients with AD do not immediately respond to the therapies doctors prescribe, Dr. Feldman implied, reiterating the theme that emerged from the AD panel: Better and more options are needed for AD of the most severe types, but better management, not better drugs, is typically what is needed for most patients.
Dr. Feldman, Dr. Lio, and Dr. Paller have financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies, some of which manufacture therapies for atopic dermatitis.
This article was updated July 28, 2023, to clarify the comments and viewpoints of Dr. Amy Paller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – according to a three-member expert panel mulling over strategies at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In introductory remarks, the three panelists briefly addressed different aspects for controlling AD, including drugs in the pipeline, the potential value of alternative therapies, and whom to blame when compliance is poor.
But panel discussion following these presentations provided an opportunity for audience engagement on practical strategies for improving AD control.
In her formal remarks prior to the panel discussion, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chair of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, and a pediatric dermatologist at the Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, described emerging AD treatments. This included an update on the status of the interleukin-13 (IL-13) inhibitors tralokinumab (Adbry), which was approved by the FDA for treating AD in adults in December 2021, and lebrikizumab, which is thought likely to be soon approved in the United States on the basis of two recently published phase 3 trials.
Along with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe AD in children who do not respond to optimized use of topical therapies, these new biologics appear likely to further expand choices for AD control for adults (and for kids with AD too, if eventually licensed in children), according to the data from the phase 3 studies.
During a panel discussion that followed, Stephen Gellis, MD, pediatric dermatologist and former chief of pediatric dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, raised the point of optimizing tried and true topical therapies before using systemic agents. He noted that parents sometimes pressure clinicians to use a biologic – and that moving too quickly to the latest and most expensive drugs may not be necessary.
Dr. Paller acknowledged that she, like many pediatric dermatologists, employed immunosuppressants as her drugs of choice for many years – commonly starting with a few months of cyclosporine before transitioning to methotrexate, which has a delayed onset of action. In fact, she still uses this regimen in some children.
However, she now prefers dupilumab, which is the first biologic available for children in the United States with an AD indication in children as young as 6 months. She said dupilumab has fewer potential risks than cyclosporine, and it offers clinically meaningful improvement in most children. She noted that current guidelines discourage the use of systemic corticosteroids for AD in children, given their potential toxicity.
She strongly agreed with Dr. Gellis that clinicians should resist pressure to use any systemic agent if children are responding well to topical medications. In her own practice, Dr. Paller moves to systemic medications only after ensuring that there has been adherence to appropriate therapy and that there is not another diagnosis that might explain the recalcitrance to topical agents.
When a systemic medication is considered the next step, Dr. Paller reminded the audience of the importance of presenting the benefits and risks of all the options for AD control, which could include dupilumab and immunosuppressants as initial systemic therapy.
“Many parents choose biologic treatment first, given its lack of requirement for blood monitoring and faster action than methotrexate,” Dr. Paller noted.
Nevertheless, “biologics are much more costly than immunosuppressants, require an injection – which is stressful for the child and the parents – and may not be accessible for our patients,” Dr. Paller said. Cyclosporine and methotrexate are effective and are often the best options for moderate to severe disease in areas of the world where dupilumab is not available, but Dr. Paller most commonly uses these therapies only when reimbursement for dupilumab cannot be secured, injection is not an option, or when dupilumab is not sufficiently effective and tolerated.
Providing different perspectives, the two other panelists discussing the treatment of pediatric AD also saw a role for ensuring that topical agents are not offering adequate AD control before turning to the latest and most sophisticated therapies for AD.
For meeting parent expectations when children are improving slowly on topical therapies, Peter A. Lio, MD, director of the Chicago Integrative Eczema Center and clinical assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, suggested that integrative medicine might be helpful.
For parents not fully comfortable with standard pharmacologic agents, Dr. Lio said there is evidence to support some of the complementary approaches, and these can be reassuring to parents with an interest in alternative medicines.
In Western medicine, it is common to hear terms like “attack,” “kill,” and “suppress,” disease, but alternative therapies are generally coupled with terms like “restore,” “strengthen,” and “tonify,” he said. “Who doesn’t want to be tonified?” he asked, noting that there are many sources of data suggesting that the number of patients seeking alternative medicine is “huge.” The alternative medicines are not generally taught in medical school and remain widely ignored in typical practice, but “our patients are interested even if we are not.”
Yet, there are data to support benefit from some of these alternative therapies, providing a win-win situation for patients who derive satisfaction from nontraditional therapies alone or combined with established pharmaceutical treatments.
Of these, Dr. Lio said there is support for the use of hempseed oil as a moisturizing agent and a strategy for improving barrier function in the skin of patients with AD. In a controlled crossover study, 2 teaspoons per day of dietary hempseed oil, a product that can be purchased in some grocery stores, was associated with significant reductions in skin dryness, itchiness, and use of topical medications relative to the same amount of olive oil, he noted.
Other examples include a compress made with black tea that was associated with an anti-inflammatory effect when followed by a moisturizer, a published study asserts. Although this was a trial in adults with facial dermatitis, Dr. Lio suggested that the same anti-inflammatory effect would be anticipated for other skin conditions, including AD in children.
As a third example, Dr. Lio said topical indigo, a traditional Chinese medicine used for a variety of dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis, has also demonstrated efficacy in a randomized trial, compared with vehicle for mild to severe AD.
Complementary medicines are not for everyone, but they may have a role when managing the expectations of parents who are not fully satisfied or express concern about regimens limited to mainstream therapies alone, according to Dr. Lio. In diseases that are not curable, such as AD, he thinks this is a strategy with potential for benefit and is reassuring to patients.
Another way to avoid moving to riskier or more expensive drugs quickly is to assure patients use the drugs that were prescribed first, according to Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Feldman believes that failure to adhere to therapy is basically the fault of the medical care system, not the patient. He made an analogy to a successful piano teacher, who provides a child with sheet music and then sees the child once a week to track progress. He juxtaposed this piano teacher to one who gives the child sheet music and tells the child to come back in 10 weeks for the recital. It is not hard to guess which approach would be more effective.
“Typically, doctors are worse than that second teacher,” he said. “Doctors are like a piano teacher that does not give you the sheet music but says, ‘Here is a prescription for some sheet music. Take this prescription to the sheet music store. I have no idea how much it will cost or whether your insurance will pay for it. But once you fill this prescription for sheet music, I want you to practice this every day,’ ” he said, adding, “Practicing this sheet music may cause rashes, diarrhea, or serious infection. When the patient next comes in 10-12 weeks later and is not better, the doctor says, ‘I will give you a harder piece of sheet music and maybe two or three other instruments to practice at the same time,’ ” said Dr. Feldman, expressing why the way clinicians practice might explain much of the poor adherence problem.
This largely explains why patients with AD do not immediately respond to the therapies doctors prescribe, Dr. Feldman implied, reiterating the theme that emerged from the AD panel: Better and more options are needed for AD of the most severe types, but better management, not better drugs, is typically what is needed for most patients.
Dr. Feldman, Dr. Lio, and Dr. Paller have financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies, some of which manufacture therapies for atopic dermatitis.
This article was updated July 28, 2023, to clarify the comments and viewpoints of Dr. Amy Paller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – according to a three-member expert panel mulling over strategies at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In introductory remarks, the three panelists briefly addressed different aspects for controlling AD, including drugs in the pipeline, the potential value of alternative therapies, and whom to blame when compliance is poor.
But panel discussion following these presentations provided an opportunity for audience engagement on practical strategies for improving AD control.
In her formal remarks prior to the panel discussion, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chair of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, and a pediatric dermatologist at the Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, described emerging AD treatments. This included an update on the status of the interleukin-13 (IL-13) inhibitors tralokinumab (Adbry), which was approved by the FDA for treating AD in adults in December 2021, and lebrikizumab, which is thought likely to be soon approved in the United States on the basis of two recently published phase 3 trials.
Along with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe AD in children who do not respond to optimized use of topical therapies, these new biologics appear likely to further expand choices for AD control for adults (and for kids with AD too, if eventually licensed in children), according to the data from the phase 3 studies.
During a panel discussion that followed, Stephen Gellis, MD, pediatric dermatologist and former chief of pediatric dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, raised the point of optimizing tried and true topical therapies before using systemic agents. He noted that parents sometimes pressure clinicians to use a biologic – and that moving too quickly to the latest and most expensive drugs may not be necessary.
Dr. Paller acknowledged that she, like many pediatric dermatologists, employed immunosuppressants as her drugs of choice for many years – commonly starting with a few months of cyclosporine before transitioning to methotrexate, which has a delayed onset of action. In fact, she still uses this regimen in some children.
However, she now prefers dupilumab, which is the first biologic available for children in the United States with an AD indication in children as young as 6 months. She said dupilumab has fewer potential risks than cyclosporine, and it offers clinically meaningful improvement in most children. She noted that current guidelines discourage the use of systemic corticosteroids for AD in children, given their potential toxicity.
She strongly agreed with Dr. Gellis that clinicians should resist pressure to use any systemic agent if children are responding well to topical medications. In her own practice, Dr. Paller moves to systemic medications only after ensuring that there has been adherence to appropriate therapy and that there is not another diagnosis that might explain the recalcitrance to topical agents.
When a systemic medication is considered the next step, Dr. Paller reminded the audience of the importance of presenting the benefits and risks of all the options for AD control, which could include dupilumab and immunosuppressants as initial systemic therapy.
“Many parents choose biologic treatment first, given its lack of requirement for blood monitoring and faster action than methotrexate,” Dr. Paller noted.
Nevertheless, “biologics are much more costly than immunosuppressants, require an injection – which is stressful for the child and the parents – and may not be accessible for our patients,” Dr. Paller said. Cyclosporine and methotrexate are effective and are often the best options for moderate to severe disease in areas of the world where dupilumab is not available, but Dr. Paller most commonly uses these therapies only when reimbursement for dupilumab cannot be secured, injection is not an option, or when dupilumab is not sufficiently effective and tolerated.
Providing different perspectives, the two other panelists discussing the treatment of pediatric AD also saw a role for ensuring that topical agents are not offering adequate AD control before turning to the latest and most sophisticated therapies for AD.
For meeting parent expectations when children are improving slowly on topical therapies, Peter A. Lio, MD, director of the Chicago Integrative Eczema Center and clinical assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, suggested that integrative medicine might be helpful.
For parents not fully comfortable with standard pharmacologic agents, Dr. Lio said there is evidence to support some of the complementary approaches, and these can be reassuring to parents with an interest in alternative medicines.
In Western medicine, it is common to hear terms like “attack,” “kill,” and “suppress,” disease, but alternative therapies are generally coupled with terms like “restore,” “strengthen,” and “tonify,” he said. “Who doesn’t want to be tonified?” he asked, noting that there are many sources of data suggesting that the number of patients seeking alternative medicine is “huge.” The alternative medicines are not generally taught in medical school and remain widely ignored in typical practice, but “our patients are interested even if we are not.”
Yet, there are data to support benefit from some of these alternative therapies, providing a win-win situation for patients who derive satisfaction from nontraditional therapies alone or combined with established pharmaceutical treatments.
Of these, Dr. Lio said there is support for the use of hempseed oil as a moisturizing agent and a strategy for improving barrier function in the skin of patients with AD. In a controlled crossover study, 2 teaspoons per day of dietary hempseed oil, a product that can be purchased in some grocery stores, was associated with significant reductions in skin dryness, itchiness, and use of topical medications relative to the same amount of olive oil, he noted.
Other examples include a compress made with black tea that was associated with an anti-inflammatory effect when followed by a moisturizer, a published study asserts. Although this was a trial in adults with facial dermatitis, Dr. Lio suggested that the same anti-inflammatory effect would be anticipated for other skin conditions, including AD in children.
As a third example, Dr. Lio said topical indigo, a traditional Chinese medicine used for a variety of dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis, has also demonstrated efficacy in a randomized trial, compared with vehicle for mild to severe AD.
Complementary medicines are not for everyone, but they may have a role when managing the expectations of parents who are not fully satisfied or express concern about regimens limited to mainstream therapies alone, according to Dr. Lio. In diseases that are not curable, such as AD, he thinks this is a strategy with potential for benefit and is reassuring to patients.
Another way to avoid moving to riskier or more expensive drugs quickly is to assure patients use the drugs that were prescribed first, according to Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Feldman believes that failure to adhere to therapy is basically the fault of the medical care system, not the patient. He made an analogy to a successful piano teacher, who provides a child with sheet music and then sees the child once a week to track progress. He juxtaposed this piano teacher to one who gives the child sheet music and tells the child to come back in 10 weeks for the recital. It is not hard to guess which approach would be more effective.
“Typically, doctors are worse than that second teacher,” he said. “Doctors are like a piano teacher that does not give you the sheet music but says, ‘Here is a prescription for some sheet music. Take this prescription to the sheet music store. I have no idea how much it will cost or whether your insurance will pay for it. But once you fill this prescription for sheet music, I want you to practice this every day,’ ” he said, adding, “Practicing this sheet music may cause rashes, diarrhea, or serious infection. When the patient next comes in 10-12 weeks later and is not better, the doctor says, ‘I will give you a harder piece of sheet music and maybe two or three other instruments to practice at the same time,’ ” said Dr. Feldman, expressing why the way clinicians practice might explain much of the poor adherence problem.
This largely explains why patients with AD do not immediately respond to the therapies doctors prescribe, Dr. Feldman implied, reiterating the theme that emerged from the AD panel: Better and more options are needed for AD of the most severe types, but better management, not better drugs, is typically what is needed for most patients.
Dr. Feldman, Dr. Lio, and Dr. Paller have financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies, some of which manufacture therapies for atopic dermatitis.
This article was updated July 28, 2023, to clarify the comments and viewpoints of Dr. Amy Paller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT SPD 2023
Ocular complications of dermatologic treatments: Advice from a pediatric ophthalmologist
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – The, according to one of several clinical messages from a pediatric ophthalmologist who spoke at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“There is a lot of steroid fear out there, which you can argue is actually harmful in itself, because not treating periorbital eczema is related to a lot of eye problems, including chronic discomfort and the eye rubbing that can cause corneal abrasions and keratoconus,” said Sara Grace, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist who is on the clinical staff at Duke University, Durham, N.C. She maintains a practice at North Carolina Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat in Durham.
Although the risks of periorbital steroid absorption are real, a limited course of low potency topical steroids is generally adequate for common periorbital indications, and these appear to be safe.
“There is insufficient evidence to link weak periocular topical corticosteroids such as desonide or hydrocortisone with ocular complications,” said Dr. Grace, suggesting that pediatric dermatologists can be reassured when using these medications at low concentrations.
“Potent periocular steroids have been associated with ocular complications, but this has typically involved exposures over months to years,” Dr. Grace specified.
When topical corticosteroids are applied at high concentrations on the face away from the periorbital area, glaucoma and other feared ophthalmic complications cannot be entirely ruled out, but, again, the risk is low in the absence of “very large quantities” of potent topical agents applied for lengthy periods of time, according to Dr. Grace, basing this observation on case studies.
In children, as in adults, the potential exception is a child with existing ocular disease. In such cases, or in children with risk factors for ocular disease, Dr. Grace recommends referral to an ophthalmologist for a baseline examination prior to a course of topical corticosteroids with the potential of periocular absorption. With a baseline assessment, adverse effects are more easily documented if exposure is prolonged.
The message, although not identical, is similar for use of dupilumab (Dupixent) or other biologics that target the interleukin-13 (IL-13) pathway. The potential for complications cannot be ignored but these are often time-limited and the benefit is likely to exceed the risk in children who have severe atopic dermatitis or other skin conditions for which these treatments are effective.
There are several potential mechanisms by which biologics targeting IL-13 might increase risk of ocular complications, one of which is the role that IL-13 plays in ocular mucus production, regulation of conjunctival goblet cells, and tear production, according to several published reports.
“Up to 30% of children will get some type of eye complication but, fortunately, most of them will not have to stop therapy,” Dr. Grace said. These side effects include conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, dry eye, and itching, but they are typically manageable. Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors can be offered if needed, but many of these conditions will self-resolve. Dr. Grace estimated that less than 1% of patients need to stop treatment because of ophthalmic side effects.
Lesions that obstruct vision
Dr. Grace urged pediatric dermatologists to be aware of the risk for amblyopia in young children with lesions that obstruct vision in one eye. In early development, prolonged obstruction of vision in one eye can alter neural communication with the brain, producing permanent vision impairment.
She explained that clearing the obstructed vision, whether from a capillary hemangioma or any periorbital growth, should be considered urgent to avoid irreversible damage.
Similarly, periorbital port-wine stains associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, which is primarily a vascular disorder that predisposes children to glaucoma, represents a condition that requires prompt attention. Sturge-Weber syndrome is often but not always identified at birth, but it is a condition for which evaluation and treatment should involve the participation of an ophthalmologist.
Meibomian gland disease is another disorder that is often seen first by a pediatric dermatologist but also requires collaborative management. The challenge is sorting out the underlying cause or causes and initiating a therapy that unclogs the gland without having to resort to incision and drainage.
“Drainage is hard to do and is not necessarily effective,” explained Dr. Grace. While scrubs, warmth, and massage frequently are adequate to unclog the gland – which secretes meibum, a complex of lipids that perform several functions in protecting the eye – therapies specific to the cause, such as Demodex-related blepharitis, chalazions, and styes, might be needed.
Dr. Grace indicated that patience is often needed. The process of unclogging these glands often takes time, but she emphasized that a first-line conservative approach is always appropriate to avoid the difficulty and potential problems of incisions.
In general, these messages are not novel, but they provide a refresher for pediatric dermatologists who do not regularly confront complications that involve the eyes. According to session moderator, Elizabeth Neiman, MD, assistant professor of pediatric dermatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the messages regarding topical steroids on the face and the eyes are “important” and worth emphasizing.
“It’s useful to reinforce the point that corticosteroids should be used when needed in the periorbital area [to control skin diseases] if they are used in low concentrations,” Dr. Neiman told this news organization.
Similarly, conjunctivitis and other ocular complications of dupilumab are a source of concern for parents as well as dermatologists. Dr. Neiman indicated that a review of the benefit-to-risk ratio is important when considering these treatments in patients with indications for severe skin disorders.
Dr. Grace and Dr. Nieman have no potential financial conflicts related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – The, according to one of several clinical messages from a pediatric ophthalmologist who spoke at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“There is a lot of steroid fear out there, which you can argue is actually harmful in itself, because not treating periorbital eczema is related to a lot of eye problems, including chronic discomfort and the eye rubbing that can cause corneal abrasions and keratoconus,” said Sara Grace, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist who is on the clinical staff at Duke University, Durham, N.C. She maintains a practice at North Carolina Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat in Durham.
Although the risks of periorbital steroid absorption are real, a limited course of low potency topical steroids is generally adequate for common periorbital indications, and these appear to be safe.
“There is insufficient evidence to link weak periocular topical corticosteroids such as desonide or hydrocortisone with ocular complications,” said Dr. Grace, suggesting that pediatric dermatologists can be reassured when using these medications at low concentrations.
“Potent periocular steroids have been associated with ocular complications, but this has typically involved exposures over months to years,” Dr. Grace specified.
When topical corticosteroids are applied at high concentrations on the face away from the periorbital area, glaucoma and other feared ophthalmic complications cannot be entirely ruled out, but, again, the risk is low in the absence of “very large quantities” of potent topical agents applied for lengthy periods of time, according to Dr. Grace, basing this observation on case studies.
In children, as in adults, the potential exception is a child with existing ocular disease. In such cases, or in children with risk factors for ocular disease, Dr. Grace recommends referral to an ophthalmologist for a baseline examination prior to a course of topical corticosteroids with the potential of periocular absorption. With a baseline assessment, adverse effects are more easily documented if exposure is prolonged.
The message, although not identical, is similar for use of dupilumab (Dupixent) or other biologics that target the interleukin-13 (IL-13) pathway. The potential for complications cannot be ignored but these are often time-limited and the benefit is likely to exceed the risk in children who have severe atopic dermatitis or other skin conditions for which these treatments are effective.
There are several potential mechanisms by which biologics targeting IL-13 might increase risk of ocular complications, one of which is the role that IL-13 plays in ocular mucus production, regulation of conjunctival goblet cells, and tear production, according to several published reports.
“Up to 30% of children will get some type of eye complication but, fortunately, most of them will not have to stop therapy,” Dr. Grace said. These side effects include conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, dry eye, and itching, but they are typically manageable. Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors can be offered if needed, but many of these conditions will self-resolve. Dr. Grace estimated that less than 1% of patients need to stop treatment because of ophthalmic side effects.
Lesions that obstruct vision
Dr. Grace urged pediatric dermatologists to be aware of the risk for amblyopia in young children with lesions that obstruct vision in one eye. In early development, prolonged obstruction of vision in one eye can alter neural communication with the brain, producing permanent vision impairment.
She explained that clearing the obstructed vision, whether from a capillary hemangioma or any periorbital growth, should be considered urgent to avoid irreversible damage.
Similarly, periorbital port-wine stains associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, which is primarily a vascular disorder that predisposes children to glaucoma, represents a condition that requires prompt attention. Sturge-Weber syndrome is often but not always identified at birth, but it is a condition for which evaluation and treatment should involve the participation of an ophthalmologist.
Meibomian gland disease is another disorder that is often seen first by a pediatric dermatologist but also requires collaborative management. The challenge is sorting out the underlying cause or causes and initiating a therapy that unclogs the gland without having to resort to incision and drainage.
“Drainage is hard to do and is not necessarily effective,” explained Dr. Grace. While scrubs, warmth, and massage frequently are adequate to unclog the gland – which secretes meibum, a complex of lipids that perform several functions in protecting the eye – therapies specific to the cause, such as Demodex-related blepharitis, chalazions, and styes, might be needed.
Dr. Grace indicated that patience is often needed. The process of unclogging these glands often takes time, but she emphasized that a first-line conservative approach is always appropriate to avoid the difficulty and potential problems of incisions.
In general, these messages are not novel, but they provide a refresher for pediatric dermatologists who do not regularly confront complications that involve the eyes. According to session moderator, Elizabeth Neiman, MD, assistant professor of pediatric dermatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the messages regarding topical steroids on the face and the eyes are “important” and worth emphasizing.
“It’s useful to reinforce the point that corticosteroids should be used when needed in the periorbital area [to control skin diseases] if they are used in low concentrations,” Dr. Neiman told this news organization.
Similarly, conjunctivitis and other ocular complications of dupilumab are a source of concern for parents as well as dermatologists. Dr. Neiman indicated that a review of the benefit-to-risk ratio is important when considering these treatments in patients with indications for severe skin disorders.
Dr. Grace and Dr. Nieman have no potential financial conflicts related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ASHEVILLE, N.C. – The, according to one of several clinical messages from a pediatric ophthalmologist who spoke at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“There is a lot of steroid fear out there, which you can argue is actually harmful in itself, because not treating periorbital eczema is related to a lot of eye problems, including chronic discomfort and the eye rubbing that can cause corneal abrasions and keratoconus,” said Sara Grace, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist who is on the clinical staff at Duke University, Durham, N.C. She maintains a practice at North Carolina Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat in Durham.
Although the risks of periorbital steroid absorption are real, a limited course of low potency topical steroids is generally adequate for common periorbital indications, and these appear to be safe.
“There is insufficient evidence to link weak periocular topical corticosteroids such as desonide or hydrocortisone with ocular complications,” said Dr. Grace, suggesting that pediatric dermatologists can be reassured when using these medications at low concentrations.
“Potent periocular steroids have been associated with ocular complications, but this has typically involved exposures over months to years,” Dr. Grace specified.
When topical corticosteroids are applied at high concentrations on the face away from the periorbital area, glaucoma and other feared ophthalmic complications cannot be entirely ruled out, but, again, the risk is low in the absence of “very large quantities” of potent topical agents applied for lengthy periods of time, according to Dr. Grace, basing this observation on case studies.
In children, as in adults, the potential exception is a child with existing ocular disease. In such cases, or in children with risk factors for ocular disease, Dr. Grace recommends referral to an ophthalmologist for a baseline examination prior to a course of topical corticosteroids with the potential of periocular absorption. With a baseline assessment, adverse effects are more easily documented if exposure is prolonged.
The message, although not identical, is similar for use of dupilumab (Dupixent) or other biologics that target the interleukin-13 (IL-13) pathway. The potential for complications cannot be ignored but these are often time-limited and the benefit is likely to exceed the risk in children who have severe atopic dermatitis or other skin conditions for which these treatments are effective.
There are several potential mechanisms by which biologics targeting IL-13 might increase risk of ocular complications, one of which is the role that IL-13 plays in ocular mucus production, regulation of conjunctival goblet cells, and tear production, according to several published reports.
“Up to 30% of children will get some type of eye complication but, fortunately, most of them will not have to stop therapy,” Dr. Grace said. These side effects include conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, dry eye, and itching, but they are typically manageable. Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors can be offered if needed, but many of these conditions will self-resolve. Dr. Grace estimated that less than 1% of patients need to stop treatment because of ophthalmic side effects.
Lesions that obstruct vision
Dr. Grace urged pediatric dermatologists to be aware of the risk for amblyopia in young children with lesions that obstruct vision in one eye. In early development, prolonged obstruction of vision in one eye can alter neural communication with the brain, producing permanent vision impairment.
She explained that clearing the obstructed vision, whether from a capillary hemangioma or any periorbital growth, should be considered urgent to avoid irreversible damage.
Similarly, periorbital port-wine stains associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, which is primarily a vascular disorder that predisposes children to glaucoma, represents a condition that requires prompt attention. Sturge-Weber syndrome is often but not always identified at birth, but it is a condition for which evaluation and treatment should involve the participation of an ophthalmologist.
Meibomian gland disease is another disorder that is often seen first by a pediatric dermatologist but also requires collaborative management. The challenge is sorting out the underlying cause or causes and initiating a therapy that unclogs the gland without having to resort to incision and drainage.
“Drainage is hard to do and is not necessarily effective,” explained Dr. Grace. While scrubs, warmth, and massage frequently are adequate to unclog the gland – which secretes meibum, a complex of lipids that perform several functions in protecting the eye – therapies specific to the cause, such as Demodex-related blepharitis, chalazions, and styes, might be needed.
Dr. Grace indicated that patience is often needed. The process of unclogging these glands often takes time, but she emphasized that a first-line conservative approach is always appropriate to avoid the difficulty and potential problems of incisions.
In general, these messages are not novel, but they provide a refresher for pediatric dermatologists who do not regularly confront complications that involve the eyes. According to session moderator, Elizabeth Neiman, MD, assistant professor of pediatric dermatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the messages regarding topical steroids on the face and the eyes are “important” and worth emphasizing.
“It’s useful to reinforce the point that corticosteroids should be used when needed in the periorbital area [to control skin diseases] if they are used in low concentrations,” Dr. Neiman told this news organization.
Similarly, conjunctivitis and other ocular complications of dupilumab are a source of concern for parents as well as dermatologists. Dr. Neiman indicated that a review of the benefit-to-risk ratio is important when considering these treatments in patients with indications for severe skin disorders.
Dr. Grace and Dr. Nieman have no potential financial conflicts related to this topic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT SPD 2023
Rising patient costs tied to private equity ownership
The report was a collaboration of University of California, Berkeley, staff and researchers from two nonprofits, the American Antitrust Institute and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth. It provides “convincing evidence that incentives to put profits before patients have grown stronger with an increase in private equity ownership of physician practices,” lead author Richard Scheffler, PhD, of UC Berkeley said in a statement.
The report also noted that private equity acquisitions of physician groups have risen sixfold in just a decade, increasing from 75 deals in 2012 to 484 deals in 2021.
Separately, the American Medical Association earlier released a separate report on trends in physician practice arrangements, finding that the percentage of physicians working in private equity–owned groups was 4.5% in 2022, the same as in its previous 2020 report. The share of physicians working in private practices fell by 13 percentage points from 60.1% to 46.7% between 2012 and 2022, the AMA reported.
The Berkeley report and the AMA update come amid rising concerns about the effects of the decline of independent physician practices. The U.S. Senate Finance Committee, which oversees most federal health spending, held a June hearing examining the causes and consequences of increased corporate ownership in health care, including a look at physician practices.
“It’s increasingly clear that consolidation in health care is not lowering costs or increasing the quality of Americans’ health care,” Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) said in an email. “For private equity in health care in particular, there needs to be more transparency around ownership so the effect on these business relationships can be better understood.”
Federal and state agencies do not generally track acquisitions of physician practices.
The UC Berkeley report impressively documents the rising influence of private equity in health care, for which it’s tough to find good data, said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, of Washington University in St. Louis. Dr. Maddox, a cardiologist and policy researcher who also has studied the effects of consolidation in health care, examined the new report at the request of this news organization.
“They did a great job with the data,” Dr. Maddox said. “One of the big issues around private equity, and in general, ‘corporatization’ and consolidation of health care, is that there’s not a great way to track ownership changes. It’s really difficult to study.”
Dr. Scheffler and colleagues used data from the commercial firm PitchBook to identify acquisitions of physician practices by private equity firms. They consulted IQVIA’s physician databases – OneKey and SK&A Office-Based Physicians Database – to learn about the location, size, and specialties of acquired practices. They also used data from the nonprofit Health Care Cost Institute, which tracks commercial health plan claims, to assess how private equity acquisitions affected prices.
The researchers then matched the findings for practices acquired by private equity firms from 2015 to 2021 against those for comparable physician practices that remained independent from 2012 to 2021.
The authors then tied private-equity ownership to the following price increases:
- Gastroenterology (14%; 95% confidence interval, 7.9%-20.4%
- Oncology (16.4%; 95% CI, 5.5%-28.4%)
- Dermatology (4.0%; 95% CI, 1%-7.1%)
- Ob.gyn. (8.8%; 95% CI, 3.8%-14%)
- Ophthalmology (8.7%; 95% CI, 5.1%-12.3%)
- Radiology (8.2%; 95% CI, 0.8%-16.1%)
- Orthopedics (7.1%; 95% CI, 2.2%-12.3%)
- Primary care (4.1%; 95% CI, 1.3%-7%)
The analysis also found higher prices for cardiology (8.7%; 95% CI, –6.4% to 26.1%) and urology (4.2%; 95% CI, –2.3% to 11.1%), but neither of these findings was statistically significant, one of the authors, Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of UC Berkeley, said in an email. This was most likely caused by smaller sample sizes for these fields.
Factors driving consolidation
The two reports and the Senate Finance consolidation hearing raised similar issues, including calls to look at the factors driving more physicians out of independent practice, including Medicare reimbursement that may not keep up with rising inflation.
The Berkeley report authors called for Congress to add a broad inflation component to the Medicare physician fee schedule. It also called on Congress to add cases where Medicare, the biggest U.S. purchaser of health care, pays less for services when performed in independent practices than in hospital-affiliated ones.
Shawn Martin, executive vice president and CEO of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group appreciates how the report from UC Berkeley and nonprofit groups echoed recommendations many clinicians have made, including the call for a broad inflation adjustment for the fee schedule.
“To move the needle forward, Congress must advance site-neutral payment policies while also addressing the administrative requirements that take physicians away from the important work of caring for patients,” Mr. Martin said in an email.
Arnold Ventures provided funding for the report, which was a joint project of the American Antitrust Institute, the Nicholas C. Petris Center on Health Care Markets and Consumer Welfare, UC Berkeley, and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The report was a collaboration of University of California, Berkeley, staff and researchers from two nonprofits, the American Antitrust Institute and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth. It provides “convincing evidence that incentives to put profits before patients have grown stronger with an increase in private equity ownership of physician practices,” lead author Richard Scheffler, PhD, of UC Berkeley said in a statement.
The report also noted that private equity acquisitions of physician groups have risen sixfold in just a decade, increasing from 75 deals in 2012 to 484 deals in 2021.
Separately, the American Medical Association earlier released a separate report on trends in physician practice arrangements, finding that the percentage of physicians working in private equity–owned groups was 4.5% in 2022, the same as in its previous 2020 report. The share of physicians working in private practices fell by 13 percentage points from 60.1% to 46.7% between 2012 and 2022, the AMA reported.
The Berkeley report and the AMA update come amid rising concerns about the effects of the decline of independent physician practices. The U.S. Senate Finance Committee, which oversees most federal health spending, held a June hearing examining the causes and consequences of increased corporate ownership in health care, including a look at physician practices.
“It’s increasingly clear that consolidation in health care is not lowering costs or increasing the quality of Americans’ health care,” Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) said in an email. “For private equity in health care in particular, there needs to be more transparency around ownership so the effect on these business relationships can be better understood.”
Federal and state agencies do not generally track acquisitions of physician practices.
The UC Berkeley report impressively documents the rising influence of private equity in health care, for which it’s tough to find good data, said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, of Washington University in St. Louis. Dr. Maddox, a cardiologist and policy researcher who also has studied the effects of consolidation in health care, examined the new report at the request of this news organization.
“They did a great job with the data,” Dr. Maddox said. “One of the big issues around private equity, and in general, ‘corporatization’ and consolidation of health care, is that there’s not a great way to track ownership changes. It’s really difficult to study.”
Dr. Scheffler and colleagues used data from the commercial firm PitchBook to identify acquisitions of physician practices by private equity firms. They consulted IQVIA’s physician databases – OneKey and SK&A Office-Based Physicians Database – to learn about the location, size, and specialties of acquired practices. They also used data from the nonprofit Health Care Cost Institute, which tracks commercial health plan claims, to assess how private equity acquisitions affected prices.
The researchers then matched the findings for practices acquired by private equity firms from 2015 to 2021 against those for comparable physician practices that remained independent from 2012 to 2021.
The authors then tied private-equity ownership to the following price increases:
- Gastroenterology (14%; 95% confidence interval, 7.9%-20.4%
- Oncology (16.4%; 95% CI, 5.5%-28.4%)
- Dermatology (4.0%; 95% CI, 1%-7.1%)
- Ob.gyn. (8.8%; 95% CI, 3.8%-14%)
- Ophthalmology (8.7%; 95% CI, 5.1%-12.3%)
- Radiology (8.2%; 95% CI, 0.8%-16.1%)
- Orthopedics (7.1%; 95% CI, 2.2%-12.3%)
- Primary care (4.1%; 95% CI, 1.3%-7%)
The analysis also found higher prices for cardiology (8.7%; 95% CI, –6.4% to 26.1%) and urology (4.2%; 95% CI, –2.3% to 11.1%), but neither of these findings was statistically significant, one of the authors, Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of UC Berkeley, said in an email. This was most likely caused by smaller sample sizes for these fields.
Factors driving consolidation
The two reports and the Senate Finance consolidation hearing raised similar issues, including calls to look at the factors driving more physicians out of independent practice, including Medicare reimbursement that may not keep up with rising inflation.
The Berkeley report authors called for Congress to add a broad inflation component to the Medicare physician fee schedule. It also called on Congress to add cases where Medicare, the biggest U.S. purchaser of health care, pays less for services when performed in independent practices than in hospital-affiliated ones.
Shawn Martin, executive vice president and CEO of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group appreciates how the report from UC Berkeley and nonprofit groups echoed recommendations many clinicians have made, including the call for a broad inflation adjustment for the fee schedule.
“To move the needle forward, Congress must advance site-neutral payment policies while also addressing the administrative requirements that take physicians away from the important work of caring for patients,” Mr. Martin said in an email.
Arnold Ventures provided funding for the report, which was a joint project of the American Antitrust Institute, the Nicholas C. Petris Center on Health Care Markets and Consumer Welfare, UC Berkeley, and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The report was a collaboration of University of California, Berkeley, staff and researchers from two nonprofits, the American Antitrust Institute and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth. It provides “convincing evidence that incentives to put profits before patients have grown stronger with an increase in private equity ownership of physician practices,” lead author Richard Scheffler, PhD, of UC Berkeley said in a statement.
The report also noted that private equity acquisitions of physician groups have risen sixfold in just a decade, increasing from 75 deals in 2012 to 484 deals in 2021.
Separately, the American Medical Association earlier released a separate report on trends in physician practice arrangements, finding that the percentage of physicians working in private equity–owned groups was 4.5% in 2022, the same as in its previous 2020 report. The share of physicians working in private practices fell by 13 percentage points from 60.1% to 46.7% between 2012 and 2022, the AMA reported.
The Berkeley report and the AMA update come amid rising concerns about the effects of the decline of independent physician practices. The U.S. Senate Finance Committee, which oversees most federal health spending, held a June hearing examining the causes and consequences of increased corporate ownership in health care, including a look at physician practices.
“It’s increasingly clear that consolidation in health care is not lowering costs or increasing the quality of Americans’ health care,” Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) said in an email. “For private equity in health care in particular, there needs to be more transparency around ownership so the effect on these business relationships can be better understood.”
Federal and state agencies do not generally track acquisitions of physician practices.
The UC Berkeley report impressively documents the rising influence of private equity in health care, for which it’s tough to find good data, said Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, MPH, of Washington University in St. Louis. Dr. Maddox, a cardiologist and policy researcher who also has studied the effects of consolidation in health care, examined the new report at the request of this news organization.
“They did a great job with the data,” Dr. Maddox said. “One of the big issues around private equity, and in general, ‘corporatization’ and consolidation of health care, is that there’s not a great way to track ownership changes. It’s really difficult to study.”
Dr. Scheffler and colleagues used data from the commercial firm PitchBook to identify acquisitions of physician practices by private equity firms. They consulted IQVIA’s physician databases – OneKey and SK&A Office-Based Physicians Database – to learn about the location, size, and specialties of acquired practices. They also used data from the nonprofit Health Care Cost Institute, which tracks commercial health plan claims, to assess how private equity acquisitions affected prices.
The researchers then matched the findings for practices acquired by private equity firms from 2015 to 2021 against those for comparable physician practices that remained independent from 2012 to 2021.
The authors then tied private-equity ownership to the following price increases:
- Gastroenterology (14%; 95% confidence interval, 7.9%-20.4%
- Oncology (16.4%; 95% CI, 5.5%-28.4%)
- Dermatology (4.0%; 95% CI, 1%-7.1%)
- Ob.gyn. (8.8%; 95% CI, 3.8%-14%)
- Ophthalmology (8.7%; 95% CI, 5.1%-12.3%)
- Radiology (8.2%; 95% CI, 0.8%-16.1%)
- Orthopedics (7.1%; 95% CI, 2.2%-12.3%)
- Primary care (4.1%; 95% CI, 1.3%-7%)
The analysis also found higher prices for cardiology (8.7%; 95% CI, –6.4% to 26.1%) and urology (4.2%; 95% CI, –2.3% to 11.1%), but neither of these findings was statistically significant, one of the authors, Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of UC Berkeley, said in an email. This was most likely caused by smaller sample sizes for these fields.
Factors driving consolidation
The two reports and the Senate Finance consolidation hearing raised similar issues, including calls to look at the factors driving more physicians out of independent practice, including Medicare reimbursement that may not keep up with rising inflation.
The Berkeley report authors called for Congress to add a broad inflation component to the Medicare physician fee schedule. It also called on Congress to add cases where Medicare, the biggest U.S. purchaser of health care, pays less for services when performed in independent practices than in hospital-affiliated ones.
Shawn Martin, executive vice president and CEO of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group appreciates how the report from UC Berkeley and nonprofit groups echoed recommendations many clinicians have made, including the call for a broad inflation adjustment for the fee schedule.
“To move the needle forward, Congress must advance site-neutral payment policies while also addressing the administrative requirements that take physicians away from the important work of caring for patients,” Mr. Martin said in an email.
Arnold Ventures provided funding for the report, which was a joint project of the American Antitrust Institute, the Nicholas C. Petris Center on Health Care Markets and Consumer Welfare, UC Berkeley, and the Washington Center for Equitable Growth.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Case report describes pediatric RIME triggered by norovirus
, according to a newly published case report.
Lead author Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, said she wanted to get the word out in part because it seems like RIME is occurring more frequently. “I do feel like we’re seeing more cases and from a more diverse number of pathogens,” Dr. Kirkorian told this news organization.
There was a decrease in RIME during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic when people were isolating more, Dr. Kirkorian said. SARS-CoV-2 has been a trigger for some cases, but she did not find that remarkable, given that respiratory viruses are known RIME precursors. The question is why RIME is being triggered more frequently now that people have essentially gone back to their normal lives, she said.
Dr. Kirkorian and colleagues at Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, Washington, wrote about a 5-year-old boy with norovirus-triggered RIME in a case report published in Pediatric Dermatology.
RIME – previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) – tends to arise after a viral infection, with upper respiratory viruses such as mycoplasma and Chlamydophila pneumoniae, influenza, and enterovirus among the common triggers. “We think this is actually your own immune system overreacting to a pathogen,” Dr. Kirkorian said in an interview, adding that the mechanism of RIME is still not understood.
While the norovirus discovery was a surprise, it shows that much is still unknown about this rare condition. “I don’t think we know what is usual and what is unusual,” Dr. Kirkorian said.
In this case, the boy swiftly declined, with progressive conjunctivitis, high fever, and rapidly developing mucositis. By the time the 5-year-old got to Children’s National Hospital, he had a spreading, painful rash, including tense vesicles and bullae involving more than 30% of his total body surface area, and areas of denuded skin on both cheeks and the back of his neck.
He had hemorrhagic mucositis of the lips, a large erosion at the urethral meatus, and hemorrhagic conjunctivitis of both eyes with thick yellow crusting on the eyelids.
The clinicians intubated the boy and admitted him to the intensive care unit. He was given a one-time injection of etanercept (25 mg) followed by 8 days of intravenous cyclosporine at a dose of 5 mg per kilogram, divided twice daily, which helped calm the mucositis and stopped the rash from progressing. There is not an accepted protocol or list of evidence-based therapeutics for RIME, Dr. Kirkorian noted.
The severe eye damage required amniotic membrane grafts. The patient was extubated after 9 days but remained in the hospital for a total of 26 days because he needed to receive nutritional support (the mucositis kept him from eating), and for pain control and weaning of sedation.
As the clinicians searched for a potential triggering virus, they came up empty. Results were negative for adenovirus, Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and varicella zoster. But they noted that the child’s household contacts had all been sick a week before with presumed viral gastroenteritis. They decided to run a stool screen and the polymerase chain reaction for norovirus was positive. The boy never had GI symptoms.
Dr. Kirkorian said in the interview that she has seen other RIME cases where a child did not have symptoms associated with the original virus but did have a sudden onset of mucositis.
Although the definition of RIME is evolving, it is defined in part by mucositis in at least two of three areas: the mouth, eyes, and genitals. “Once you have the inflammation of the mucous membranes you should be on alert to think about more serious conditions,” like RIME, said Dr. Kirkorian. “Why does it manifest with the mucositis? I don’t think we know that,” she added.
RIME recurrence has also been vexing for patients, families and clinicians. In May, at the annual Atlantic Dermatology Conference, held in Baltimore, Dr. Kirkorian also discussed an 11-year-old patient who had RIME after SARS-CoV-2 infection early in the pandemic, resulting in a 22-day hospitalization and placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter and a feeding tube. He improved with cyclosporine and was discharged on systemic tacrolimus.
He was fine for several years, until another COVID infection. He again responded to medication. But not long after, an undetermined viral infection triggered another episode of RIME.
Dr. Kirkorian said there is no way to predict recurrence – making a devastating condition all the more worrisome. “Knowing that it might come back and it’s totally haphazard as to what might make it come back – that is very stressful for families,” she said in the interview.
“Some of the most perplexing patients with RIME are those with recurrent disease,” wrote Warren R. Heymann, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Rowan University, Camden, N.J., wrote in an online column on RIME in the American Academy of Dermatology’s “Dermatology World Insights and Inquiries”.
“Recurrent RIME is of particular interest, given that we could potentially intervene and prevent additional disease,” wrote Camille Introcaso, MD, associate professor of medicine at Rowan University, in response to Dr. Heymann’s remarks. “Although multiple possible mechanisms for the clinical findings of RIME have been proposed, including molecular mimicry between infectious agent proteins and keratinocyte antigens, immune complex deposition, and combinations of medication and infection, the pathophysiology is unknown,” she added.
In the interview, Dr. Kirkorian said that she and colleagues in the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) are trying to assemble more multicenter trials to assess the underlying pathology of RIME, effectiveness of various treatments, and to “find some predictive factors.” Given that RIME is an acute-onset emergency, it is not easy to conduct randomized controlled trials, she added.
Dr. Kirkorian, Dr. Heymann, and Dr. Introcaso report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to a newly published case report.
Lead author Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, said she wanted to get the word out in part because it seems like RIME is occurring more frequently. “I do feel like we’re seeing more cases and from a more diverse number of pathogens,” Dr. Kirkorian told this news organization.
There was a decrease in RIME during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic when people were isolating more, Dr. Kirkorian said. SARS-CoV-2 has been a trigger for some cases, but she did not find that remarkable, given that respiratory viruses are known RIME precursors. The question is why RIME is being triggered more frequently now that people have essentially gone back to their normal lives, she said.
Dr. Kirkorian and colleagues at Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, Washington, wrote about a 5-year-old boy with norovirus-triggered RIME in a case report published in Pediatric Dermatology.
RIME – previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) – tends to arise after a viral infection, with upper respiratory viruses such as mycoplasma and Chlamydophila pneumoniae, influenza, and enterovirus among the common triggers. “We think this is actually your own immune system overreacting to a pathogen,” Dr. Kirkorian said in an interview, adding that the mechanism of RIME is still not understood.
While the norovirus discovery was a surprise, it shows that much is still unknown about this rare condition. “I don’t think we know what is usual and what is unusual,” Dr. Kirkorian said.
In this case, the boy swiftly declined, with progressive conjunctivitis, high fever, and rapidly developing mucositis. By the time the 5-year-old got to Children’s National Hospital, he had a spreading, painful rash, including tense vesicles and bullae involving more than 30% of his total body surface area, and areas of denuded skin on both cheeks and the back of his neck.
He had hemorrhagic mucositis of the lips, a large erosion at the urethral meatus, and hemorrhagic conjunctivitis of both eyes with thick yellow crusting on the eyelids.
The clinicians intubated the boy and admitted him to the intensive care unit. He was given a one-time injection of etanercept (25 mg) followed by 8 days of intravenous cyclosporine at a dose of 5 mg per kilogram, divided twice daily, which helped calm the mucositis and stopped the rash from progressing. There is not an accepted protocol or list of evidence-based therapeutics for RIME, Dr. Kirkorian noted.
The severe eye damage required amniotic membrane grafts. The patient was extubated after 9 days but remained in the hospital for a total of 26 days because he needed to receive nutritional support (the mucositis kept him from eating), and for pain control and weaning of sedation.
As the clinicians searched for a potential triggering virus, they came up empty. Results were negative for adenovirus, Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and varicella zoster. But they noted that the child’s household contacts had all been sick a week before with presumed viral gastroenteritis. They decided to run a stool screen and the polymerase chain reaction for norovirus was positive. The boy never had GI symptoms.
Dr. Kirkorian said in the interview that she has seen other RIME cases where a child did not have symptoms associated with the original virus but did have a sudden onset of mucositis.
Although the definition of RIME is evolving, it is defined in part by mucositis in at least two of three areas: the mouth, eyes, and genitals. “Once you have the inflammation of the mucous membranes you should be on alert to think about more serious conditions,” like RIME, said Dr. Kirkorian. “Why does it manifest with the mucositis? I don’t think we know that,” she added.
RIME recurrence has also been vexing for patients, families and clinicians. In May, at the annual Atlantic Dermatology Conference, held in Baltimore, Dr. Kirkorian also discussed an 11-year-old patient who had RIME after SARS-CoV-2 infection early in the pandemic, resulting in a 22-day hospitalization and placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter and a feeding tube. He improved with cyclosporine and was discharged on systemic tacrolimus.
He was fine for several years, until another COVID infection. He again responded to medication. But not long after, an undetermined viral infection triggered another episode of RIME.
Dr. Kirkorian said there is no way to predict recurrence – making a devastating condition all the more worrisome. “Knowing that it might come back and it’s totally haphazard as to what might make it come back – that is very stressful for families,” she said in the interview.
“Some of the most perplexing patients with RIME are those with recurrent disease,” wrote Warren R. Heymann, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Rowan University, Camden, N.J., wrote in an online column on RIME in the American Academy of Dermatology’s “Dermatology World Insights and Inquiries”.
“Recurrent RIME is of particular interest, given that we could potentially intervene and prevent additional disease,” wrote Camille Introcaso, MD, associate professor of medicine at Rowan University, in response to Dr. Heymann’s remarks. “Although multiple possible mechanisms for the clinical findings of RIME have been proposed, including molecular mimicry between infectious agent proteins and keratinocyte antigens, immune complex deposition, and combinations of medication and infection, the pathophysiology is unknown,” she added.
In the interview, Dr. Kirkorian said that she and colleagues in the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) are trying to assemble more multicenter trials to assess the underlying pathology of RIME, effectiveness of various treatments, and to “find some predictive factors.” Given that RIME is an acute-onset emergency, it is not easy to conduct randomized controlled trials, she added.
Dr. Kirkorian, Dr. Heymann, and Dr. Introcaso report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to a newly published case report.
Lead author Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, said she wanted to get the word out in part because it seems like RIME is occurring more frequently. “I do feel like we’re seeing more cases and from a more diverse number of pathogens,” Dr. Kirkorian told this news organization.
There was a decrease in RIME during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic when people were isolating more, Dr. Kirkorian said. SARS-CoV-2 has been a trigger for some cases, but she did not find that remarkable, given that respiratory viruses are known RIME precursors. The question is why RIME is being triggered more frequently now that people have essentially gone back to their normal lives, she said.
Dr. Kirkorian and colleagues at Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, Washington, wrote about a 5-year-old boy with norovirus-triggered RIME in a case report published in Pediatric Dermatology.
RIME – previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) – tends to arise after a viral infection, with upper respiratory viruses such as mycoplasma and Chlamydophila pneumoniae, influenza, and enterovirus among the common triggers. “We think this is actually your own immune system overreacting to a pathogen,” Dr. Kirkorian said in an interview, adding that the mechanism of RIME is still not understood.
While the norovirus discovery was a surprise, it shows that much is still unknown about this rare condition. “I don’t think we know what is usual and what is unusual,” Dr. Kirkorian said.
In this case, the boy swiftly declined, with progressive conjunctivitis, high fever, and rapidly developing mucositis. By the time the 5-year-old got to Children’s National Hospital, he had a spreading, painful rash, including tense vesicles and bullae involving more than 30% of his total body surface area, and areas of denuded skin on both cheeks and the back of his neck.
He had hemorrhagic mucositis of the lips, a large erosion at the urethral meatus, and hemorrhagic conjunctivitis of both eyes with thick yellow crusting on the eyelids.
The clinicians intubated the boy and admitted him to the intensive care unit. He was given a one-time injection of etanercept (25 mg) followed by 8 days of intravenous cyclosporine at a dose of 5 mg per kilogram, divided twice daily, which helped calm the mucositis and stopped the rash from progressing. There is not an accepted protocol or list of evidence-based therapeutics for RIME, Dr. Kirkorian noted.
The severe eye damage required amniotic membrane grafts. The patient was extubated after 9 days but remained in the hospital for a total of 26 days because he needed to receive nutritional support (the mucositis kept him from eating), and for pain control and weaning of sedation.
As the clinicians searched for a potential triggering virus, they came up empty. Results were negative for adenovirus, Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and varicella zoster. But they noted that the child’s household contacts had all been sick a week before with presumed viral gastroenteritis. They decided to run a stool screen and the polymerase chain reaction for norovirus was positive. The boy never had GI symptoms.
Dr. Kirkorian said in the interview that she has seen other RIME cases where a child did not have symptoms associated with the original virus but did have a sudden onset of mucositis.
Although the definition of RIME is evolving, it is defined in part by mucositis in at least two of three areas: the mouth, eyes, and genitals. “Once you have the inflammation of the mucous membranes you should be on alert to think about more serious conditions,” like RIME, said Dr. Kirkorian. “Why does it manifest with the mucositis? I don’t think we know that,” she added.
RIME recurrence has also been vexing for patients, families and clinicians. In May, at the annual Atlantic Dermatology Conference, held in Baltimore, Dr. Kirkorian also discussed an 11-year-old patient who had RIME after SARS-CoV-2 infection early in the pandemic, resulting in a 22-day hospitalization and placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter and a feeding tube. He improved with cyclosporine and was discharged on systemic tacrolimus.
He was fine for several years, until another COVID infection. He again responded to medication. But not long after, an undetermined viral infection triggered another episode of RIME.
Dr. Kirkorian said there is no way to predict recurrence – making a devastating condition all the more worrisome. “Knowing that it might come back and it’s totally haphazard as to what might make it come back – that is very stressful for families,” she said in the interview.
“Some of the most perplexing patients with RIME are those with recurrent disease,” wrote Warren R. Heymann, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Rowan University, Camden, N.J., wrote in an online column on RIME in the American Academy of Dermatology’s “Dermatology World Insights and Inquiries”.
“Recurrent RIME is of particular interest, given that we could potentially intervene and prevent additional disease,” wrote Camille Introcaso, MD, associate professor of medicine at Rowan University, in response to Dr. Heymann’s remarks. “Although multiple possible mechanisms for the clinical findings of RIME have been proposed, including molecular mimicry between infectious agent proteins and keratinocyte antigens, immune complex deposition, and combinations of medication and infection, the pathophysiology is unknown,” she added.
In the interview, Dr. Kirkorian said that she and colleagues in the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) are trying to assemble more multicenter trials to assess the underlying pathology of RIME, effectiveness of various treatments, and to “find some predictive factors.” Given that RIME is an acute-onset emergency, it is not easy to conduct randomized controlled trials, she added.
Dr. Kirkorian, Dr. Heymann, and Dr. Introcaso report no relevant financial relationships.
Nurse practitioners sue state over right to use ‘doctor’ title
, saying it violates their first amendment right to use the honorific title without fear of regulatory repercussions.
The case highlights ongoing scope-creep battles as the American Medical Association tries to preserve the physician-led team model and nursing organizations and some lawmakers push for greater autonomy for allied professionals.
In the complaint filed in district court in June, plaintiffs Jacqueline Palmer, DNP, Heather Lewis, DNP, and Rodolfo Jaravata-Hanson, DNP, say they fear the state will sanction them. They note that “Doctor Sarah,” another DNP, was fined nearly $20,000 by the state last November for false advertising and fraud after using the moniker in her online advertising and social media accounts.
The fine was part of a settlement that the DNP, Sarah Erny, reached with the state to resolve allegations that she failed to identify her supervising physician and inform the public that she was not a medical doctor.
Under California’s Medical Practice Act, individuals cannot refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Instead, nurse practitioners certified by the California Board of Registered Nursing may use titles like “Certified Nurse Practitioner” and “Advanced Practice Registered Nurse,” corresponding letters such as APRN-CNP, RN, and NP, and phrases like pediatric nurse practitioner to identify specialization.
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
The nonprofit Pacific Legal Foundation represents the plaintiffs. In court records, its attorneys argue that after “years earning their advanced degrees and qualifications ... they should be able to speak truthfully about them in their workplaces, on their business cards, the Internet, and social media, so long as they clarify that they are nurse practitioners.”
State lawmakers’ attempts to clarify the roles of physicians and nurse practitioners have seen mixed results. Florida legislators recently passed a bill to prevent advanced practice nurses from using the honorific title, reserving it only for MDs and DOs. Gov. Ron DeSantis vetoed it last month.
In May, Georgia lawmakers passed the Health Care Practitioners Truth and Transparency Act. It requires advanced practice nurses and physician assistants with doctoral degrees who refer to themselves as doctors in a clinical setting to state they are not medical doctors or physicians.
Still, some health professionals say that the designation should only be used in academic settings or among peers, and that all doctoral degree holders should ditch the moniker at the bedside to ease patient communications.
Named as defendants in the suit are three state officials: California Attorney General Rob Bonta, state Medical Board President Kristina Lawson, and California Board of Registered Nursing Executive Officer Loretta Melby.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, saying it violates their first amendment right to use the honorific title without fear of regulatory repercussions.
The case highlights ongoing scope-creep battles as the American Medical Association tries to preserve the physician-led team model and nursing organizations and some lawmakers push for greater autonomy for allied professionals.
In the complaint filed in district court in June, plaintiffs Jacqueline Palmer, DNP, Heather Lewis, DNP, and Rodolfo Jaravata-Hanson, DNP, say they fear the state will sanction them. They note that “Doctor Sarah,” another DNP, was fined nearly $20,000 by the state last November for false advertising and fraud after using the moniker in her online advertising and social media accounts.
The fine was part of a settlement that the DNP, Sarah Erny, reached with the state to resolve allegations that she failed to identify her supervising physician and inform the public that she was not a medical doctor.
Under California’s Medical Practice Act, individuals cannot refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Instead, nurse practitioners certified by the California Board of Registered Nursing may use titles like “Certified Nurse Practitioner” and “Advanced Practice Registered Nurse,” corresponding letters such as APRN-CNP, RN, and NP, and phrases like pediatric nurse practitioner to identify specialization.
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
The nonprofit Pacific Legal Foundation represents the plaintiffs. In court records, its attorneys argue that after “years earning their advanced degrees and qualifications ... they should be able to speak truthfully about them in their workplaces, on their business cards, the Internet, and social media, so long as they clarify that they are nurse practitioners.”
State lawmakers’ attempts to clarify the roles of physicians and nurse practitioners have seen mixed results. Florida legislators recently passed a bill to prevent advanced practice nurses from using the honorific title, reserving it only for MDs and DOs. Gov. Ron DeSantis vetoed it last month.
In May, Georgia lawmakers passed the Health Care Practitioners Truth and Transparency Act. It requires advanced practice nurses and physician assistants with doctoral degrees who refer to themselves as doctors in a clinical setting to state they are not medical doctors or physicians.
Still, some health professionals say that the designation should only be used in academic settings or among peers, and that all doctoral degree holders should ditch the moniker at the bedside to ease patient communications.
Named as defendants in the suit are three state officials: California Attorney General Rob Bonta, state Medical Board President Kristina Lawson, and California Board of Registered Nursing Executive Officer Loretta Melby.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, saying it violates their first amendment right to use the honorific title without fear of regulatory repercussions.
The case highlights ongoing scope-creep battles as the American Medical Association tries to preserve the physician-led team model and nursing organizations and some lawmakers push for greater autonomy for allied professionals.
In the complaint filed in district court in June, plaintiffs Jacqueline Palmer, DNP, Heather Lewis, DNP, and Rodolfo Jaravata-Hanson, DNP, say they fear the state will sanction them. They note that “Doctor Sarah,” another DNP, was fined nearly $20,000 by the state last November for false advertising and fraud after using the moniker in her online advertising and social media accounts.
The fine was part of a settlement that the DNP, Sarah Erny, reached with the state to resolve allegations that she failed to identify her supervising physician and inform the public that she was not a medical doctor.
Under California’s Medical Practice Act, individuals cannot refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Instead, nurse practitioners certified by the California Board of Registered Nursing may use titles like “Certified Nurse Practitioner” and “Advanced Practice Registered Nurse,” corresponding letters such as APRN-CNP, RN, and NP, and phrases like pediatric nurse practitioner to identify specialization.
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
The nonprofit Pacific Legal Foundation represents the plaintiffs. In court records, its attorneys argue that after “years earning their advanced degrees and qualifications ... they should be able to speak truthfully about them in their workplaces, on their business cards, the Internet, and social media, so long as they clarify that they are nurse practitioners.”
State lawmakers’ attempts to clarify the roles of physicians and nurse practitioners have seen mixed results. Florida legislators recently passed a bill to prevent advanced practice nurses from using the honorific title, reserving it only for MDs and DOs. Gov. Ron DeSantis vetoed it last month.
In May, Georgia lawmakers passed the Health Care Practitioners Truth and Transparency Act. It requires advanced practice nurses and physician assistants with doctoral degrees who refer to themselves as doctors in a clinical setting to state they are not medical doctors or physicians.
Still, some health professionals say that the designation should only be used in academic settings or among peers, and that all doctoral degree holders should ditch the moniker at the bedside to ease patient communications.
Named as defendants in the suit are three state officials: California Attorney General Rob Bonta, state Medical Board President Kristina Lawson, and California Board of Registered Nursing Executive Officer Loretta Melby.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Indian Health Service dermatologist: ‘I saw a real need to be of service’
After completing his dermatology residency at Johns Hopkins Hospital in 2010, Christopher Bengson, MD, MHS, then a Lieutenant Commander in the U.S. Public Health Service, accepted an offer to become a full-time dermatologist at Phoenix Indian Medical Center (PIMC) in Arizona, fulfilling a long desire to provide care for underserved individuals. Thirteen years later, .
As one of the largest hospitals in the IHS system, PIMC provides direct health care services to a population of more than 156,000, including tribal members from The Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation, the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community, and the San Lucy District of the Tohono O’odham Nation, the Tonto Apache Tribe, the Yavapai-Apache Indian Tribe, and the Yavapai-Prescott Indian Tribe. Dr. Bengson also cares for tribal members who travel to PIMC from as far away as Washington State and Hawaii to receive dermatologic care.
“There is a disproportionate number of Native American patients that come in with severe psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp compared to the general U.S. population, and I’ve been surprised by how many have nonmelanoma skin cancers and autoimmune connective tissue diseases like lupus, as the prevailing sentiment among his patients is that Native people do not get skin cancer,” he said in an interview. “Those who travel great distances are those who come see me for the surgical removal of skin cancers.”
Interesting cases he’s seen in his nearly 13 years on the job include Epstein-Barr virus-induced NK/T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma, and necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, “tumors that have generally gone to tertiary care facilities for treatment, but we’ve been able to manage here.”
In 2017, Dr. Bengson was appointed as the IHS’s first chief clinical consultant for dermatology, a post that provides him the opportunity to interface with Native people and IHS-affiliated clinicians nationwide regarding skin-related questions and concerns. As the only full-time dermatologist employed by the IHS, he also views his role as providing an opportunity to change the perception that some Native Americans may still hold about federally delivered health care, “where there may be a cultural distrust of government health care in indigenous communities, driven by generational historical traumas that have come out of boarding schools, population relocation to desolate and isolated areas of the country, and contracts that were simply not honored,” he explained.
“While none of these issues are new, what has been great for me is that I’m going on 13 years of being at the same facility, and I’ve treated family members, their kids, and even their grandkids. In some ways the primary barrier of continuity of care – at least at PIMC – has been eliminated by me just being here for a long period of time.”
In Dr. Bengson’s opinion, efforts to improve access to attract more Native Americans to dermatology are laudable, including the American Academy of Dermatology’s Pathways Program, which aims to increase the number of dermatology residents from Black, Latino, and indigenous communities from approximately 100 residents to 250 residents by 2027, or by over 150%, through community-based engagement strategies that begin in high school.
“To have an objective benchmark is encouraging,” he said. However, he encourages dermatology residency program directors to rethink how they recruit Native Americans, many of whom hail from rural areas. “If you’re recruiting primarily from urban settings, you’re very unlikely to include Native Americans as a larger group of minorities,” he said. “When you look at the number of department chairs who are Native American, it’s on the order of 0.1%, [so] it’s no surprise that dermatologists coming out of a residency program don’t want to go to reservations to provide dermatologic care. We pay a lot of lip service to mentorship programs and things like that, but you need a mentor who follows you through the process – and it’s a long process.”
He believes that residency program directors should reconsider the metrics used to select dermatology residents and should consider the degree of adversity that a Native American applicant may have had to overcome to make it to the residency selection committees.
Despite obstacles to attracting young Native Americans to a career in medicine, Dr. Bengson sees encouraging signs ahead. Some of his Native American patients and family members of patients have enrolled in medical school and have asked to rotate with him at PIMC at the premedical and medical student level. “Some have moved on, not necessarily to dermatology, but to other specialties and careers in health care,” he said. “When you have such high rates of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke in Native American communities, nodulocystic acne and other skin conditions that are not threats to life and limb become less of a priority. We need to get more people in the pipeline to deliver medical services even if it may not be in dermatology, as the need for dedicated health care professionals is so great across all disciplines.”
After completing his dermatology residency at Johns Hopkins Hospital in 2010, Christopher Bengson, MD, MHS, then a Lieutenant Commander in the U.S. Public Health Service, accepted an offer to become a full-time dermatologist at Phoenix Indian Medical Center (PIMC) in Arizona, fulfilling a long desire to provide care for underserved individuals. Thirteen years later, .
As one of the largest hospitals in the IHS system, PIMC provides direct health care services to a population of more than 156,000, including tribal members from The Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation, the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community, and the San Lucy District of the Tohono O’odham Nation, the Tonto Apache Tribe, the Yavapai-Apache Indian Tribe, and the Yavapai-Prescott Indian Tribe. Dr. Bengson also cares for tribal members who travel to PIMC from as far away as Washington State and Hawaii to receive dermatologic care.
“There is a disproportionate number of Native American patients that come in with severe psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp compared to the general U.S. population, and I’ve been surprised by how many have nonmelanoma skin cancers and autoimmune connective tissue diseases like lupus, as the prevailing sentiment among his patients is that Native people do not get skin cancer,” he said in an interview. “Those who travel great distances are those who come see me for the surgical removal of skin cancers.”
Interesting cases he’s seen in his nearly 13 years on the job include Epstein-Barr virus-induced NK/T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma, and necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, “tumors that have generally gone to tertiary care facilities for treatment, but we’ve been able to manage here.”
In 2017, Dr. Bengson was appointed as the IHS’s first chief clinical consultant for dermatology, a post that provides him the opportunity to interface with Native people and IHS-affiliated clinicians nationwide regarding skin-related questions and concerns. As the only full-time dermatologist employed by the IHS, he also views his role as providing an opportunity to change the perception that some Native Americans may still hold about federally delivered health care, “where there may be a cultural distrust of government health care in indigenous communities, driven by generational historical traumas that have come out of boarding schools, population relocation to desolate and isolated areas of the country, and contracts that were simply not honored,” he explained.
“While none of these issues are new, what has been great for me is that I’m going on 13 years of being at the same facility, and I’ve treated family members, their kids, and even their grandkids. In some ways the primary barrier of continuity of care – at least at PIMC – has been eliminated by me just being here for a long period of time.”
In Dr. Bengson’s opinion, efforts to improve access to attract more Native Americans to dermatology are laudable, including the American Academy of Dermatology’s Pathways Program, which aims to increase the number of dermatology residents from Black, Latino, and indigenous communities from approximately 100 residents to 250 residents by 2027, or by over 150%, through community-based engagement strategies that begin in high school.
“To have an objective benchmark is encouraging,” he said. However, he encourages dermatology residency program directors to rethink how they recruit Native Americans, many of whom hail from rural areas. “If you’re recruiting primarily from urban settings, you’re very unlikely to include Native Americans as a larger group of minorities,” he said. “When you look at the number of department chairs who are Native American, it’s on the order of 0.1%, [so] it’s no surprise that dermatologists coming out of a residency program don’t want to go to reservations to provide dermatologic care. We pay a lot of lip service to mentorship programs and things like that, but you need a mentor who follows you through the process – and it’s a long process.”
He believes that residency program directors should reconsider the metrics used to select dermatology residents and should consider the degree of adversity that a Native American applicant may have had to overcome to make it to the residency selection committees.
Despite obstacles to attracting young Native Americans to a career in medicine, Dr. Bengson sees encouraging signs ahead. Some of his Native American patients and family members of patients have enrolled in medical school and have asked to rotate with him at PIMC at the premedical and medical student level. “Some have moved on, not necessarily to dermatology, but to other specialties and careers in health care,” he said. “When you have such high rates of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke in Native American communities, nodulocystic acne and other skin conditions that are not threats to life and limb become less of a priority. We need to get more people in the pipeline to deliver medical services even if it may not be in dermatology, as the need for dedicated health care professionals is so great across all disciplines.”
After completing his dermatology residency at Johns Hopkins Hospital in 2010, Christopher Bengson, MD, MHS, then a Lieutenant Commander in the U.S. Public Health Service, accepted an offer to become a full-time dermatologist at Phoenix Indian Medical Center (PIMC) in Arizona, fulfilling a long desire to provide care for underserved individuals. Thirteen years later, .
As one of the largest hospitals in the IHS system, PIMC provides direct health care services to a population of more than 156,000, including tribal members from The Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation, the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community, and the San Lucy District of the Tohono O’odham Nation, the Tonto Apache Tribe, the Yavapai-Apache Indian Tribe, and the Yavapai-Prescott Indian Tribe. Dr. Bengson also cares for tribal members who travel to PIMC from as far away as Washington State and Hawaii to receive dermatologic care.
“There is a disproportionate number of Native American patients that come in with severe psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp compared to the general U.S. population, and I’ve been surprised by how many have nonmelanoma skin cancers and autoimmune connective tissue diseases like lupus, as the prevailing sentiment among his patients is that Native people do not get skin cancer,” he said in an interview. “Those who travel great distances are those who come see me for the surgical removal of skin cancers.”
Interesting cases he’s seen in his nearly 13 years on the job include Epstein-Barr virus-induced NK/T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma, and necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, “tumors that have generally gone to tertiary care facilities for treatment, but we’ve been able to manage here.”
In 2017, Dr. Bengson was appointed as the IHS’s first chief clinical consultant for dermatology, a post that provides him the opportunity to interface with Native people and IHS-affiliated clinicians nationwide regarding skin-related questions and concerns. As the only full-time dermatologist employed by the IHS, he also views his role as providing an opportunity to change the perception that some Native Americans may still hold about federally delivered health care, “where there may be a cultural distrust of government health care in indigenous communities, driven by generational historical traumas that have come out of boarding schools, population relocation to desolate and isolated areas of the country, and contracts that were simply not honored,” he explained.
“While none of these issues are new, what has been great for me is that I’m going on 13 years of being at the same facility, and I’ve treated family members, their kids, and even their grandkids. In some ways the primary barrier of continuity of care – at least at PIMC – has been eliminated by me just being here for a long period of time.”
In Dr. Bengson’s opinion, efforts to improve access to attract more Native Americans to dermatology are laudable, including the American Academy of Dermatology’s Pathways Program, which aims to increase the number of dermatology residents from Black, Latino, and indigenous communities from approximately 100 residents to 250 residents by 2027, or by over 150%, through community-based engagement strategies that begin in high school.
“To have an objective benchmark is encouraging,” he said. However, he encourages dermatology residency program directors to rethink how they recruit Native Americans, many of whom hail from rural areas. “If you’re recruiting primarily from urban settings, you’re very unlikely to include Native Americans as a larger group of minorities,” he said. “When you look at the number of department chairs who are Native American, it’s on the order of 0.1%, [so] it’s no surprise that dermatologists coming out of a residency program don’t want to go to reservations to provide dermatologic care. We pay a lot of lip service to mentorship programs and things like that, but you need a mentor who follows you through the process – and it’s a long process.”
He believes that residency program directors should reconsider the metrics used to select dermatology residents and should consider the degree of adversity that a Native American applicant may have had to overcome to make it to the residency selection committees.
Despite obstacles to attracting young Native Americans to a career in medicine, Dr. Bengson sees encouraging signs ahead. Some of his Native American patients and family members of patients have enrolled in medical school and have asked to rotate with him at PIMC at the premedical and medical student level. “Some have moved on, not necessarily to dermatology, but to other specialties and careers in health care,” he said. “When you have such high rates of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke in Native American communities, nodulocystic acne and other skin conditions that are not threats to life and limb become less of a priority. We need to get more people in the pipeline to deliver medical services even if it may not be in dermatology, as the need for dedicated health care professionals is so great across all disciplines.”
Dermatologic care in Indian Country marked by unique challenges, opportunities
As a proud member of the Oglala Lakota Nation from the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in southwestern South Dakota, Drew Hicks grew up with limited access to basic health care, let alone the luxury of scheduling an appointment with a dermatologist or another medical specialist.
The area – once home to the Lakota war leader Crazy Horse – encompasses nearly 47,000 residents scattered over about 2.2 million acres, larger than the size of Rhode Island, with land marked by rolling mixed grass prairie, sandhills, and badlands. Some of the Oglala Lakota people live in substandard housing and lack regular access to food, running water, and refrigeration, not to mention cell phone and Internet service. “It’s sparse,” said Mr. Hicks, the son of Tribal ranchers who now is a 3rd-year medical student at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science in Rochester, Minn., and has an early interest in pursuing dermatology. “There is a lot of territory and not a lot of health care serving the population.” From the Hicks home, the nearest place to receive health care is a family medicine practice in Martin, S.D. – about a 15-minute drive on gravel roads in the best of conditions, but in poor weather, it can be difficult, he said. “So, there are environmental challenges besides the limited number of health care providers.”
Clinicians in the practice “did have to be the point of care for everything from dermatologic issues to emergency medicine to delivering a baby, because the next-closest medical facility of any magnitude is 2 hours away,” he said.
Challenges of health literacy and limited access to comprehensive health care at Pine Ridge and other American Indian (AI) and Alaska Native (AN) reservations have long-term consequences. “My own mom struggled to control her blood pressure for years and now has chronic kidney disease,” Mr. Hicks said. “It’s not an uncommon story. Diabetes on the reservation is a big issue.” Then there’s his father, who survived two bouts with melanoma that was diagnosed at an advanced stage. “I think about how that has impacted him, and wonder, had we had a dermatologist who serviced our area, would we have caught things sooner?” he said. “I feel there is so much room for impactful health care deliveries to communities like Pine Ridge.” At the same time, he emphasized, “this isn’t poverty porn. We’re a resilient people. Any effort to engage with AIs or ANs should be from a perspective of a learner, having cultural humility, and seeking out community leaders to help lead you.”
According to the 2020 Census, there are 574 federally recognized sovereign tribal nations in the United States and federal- and state-recognized American Indian reservations in 35 states. AI/AN people make up about 2.9% of the total U.S. population, or 9.7 million, and their life expectancy is an average of 4.4 years less, compared with the general population (a mean of 73.7 vs. 78.1 years, respectively). Because of limited access to dermatologic care in these areas, the risk for developing significant skin conditions and diseases that may go undetected for long stretches of time is increased.
“That can mean advanced skin cancers like basal cell carcinomas that have become larger than what you would see in a typical metropolitan population,” said Lucinda Kohn, MD, assistant professor of dermatology in the Centers for American Indian and Alaska Native Health at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who spent part of her dermatology residency rotating at the Chinle (Ariz.) Service Unit, an Indian Health Service facility, in 2017 and now provides teledermatology and regular in-person dermatology care at that clinic. “The climate there is dry, so you can see bad eczema and dry skin. There’s also a lot of acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. I think the acne and HS is due to the hyperglycemic index diet from the food deserts. Skin disease reflects the climate, the food desert, and the lack of close specialty care.”
Acne scarring common
Some published evidence suggests that acne is more prevalent and severe in AI/AN individuals. In a survey of 158 AI/AN individuals with a mean age of 32 years, 79.1% reported a history of acne, 55.1% reported acne scarring, and 31% reported having active lesions. “Looking back on my experience in high school, I definitely see that in myself and in my peers,” Mr. Hicks said. And, while there are limited published studies about the incidence of melanoma in this population, an analysis from 2006 found that the incidence was 3.1 per 100,000 between 2001 and 2005, which was an increase from 1.6 per 100,000 reported between 1992 and 2000.
There’s a lot to unpack for dermatologists caring for the AI/AN population besides the raw health disparities: a long history of distrust between AI/AN people and the federal government, structural racism, geographic isolation, health literacy challenges, and high rates of poverty and unemployment. And while individuals from federally recognized tribes have a legal right to receive health care provided by the Indian Health Service, a component of the Department of Health & Human Services, the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that in 2017 per capita spending available to the IHS was $4,078, compared with $8,109 for Medicaid, $10,692 for the Veterans Health Administration, and $13,185 for Medicare.
“Everyone deserves healthy skin and good health,” said Dr. Kohn, whose husband is AI and works in AI law. “Knowing that there are pockets of people who lack that access to care really bothers me. I think the American Indians are frequently overlooked. They’re just not even counted for in certain surveys,” she added, noting that categories are usually defined as Black, Hispanic, Asian, or White.
According to Dr. Kohn, who coauthored a chapter titled “Dermatology on American Indian and Alaska Native Reservations,” for the 2021 book “Dermatology in Rural Settings”, 70% of AIs live in urban areas, “so it’s not just people who live on reservations, though the disparity is greatest there.” To help deliver dermatologic care in the rural areas “where you’re on tribal lands, you must partner with the tribes,” she added. “You must get their permission, operate under their laws and regulations and their rules, learn the local customs, learn about the culture, learn the people, and learn their resources before you practice. That’s the only ethical way to practice.” This also means appreciating the fact that some AI/AN individuals may not understand what a dermatologist could do for them. “One of the bigger hurdles to overcome,” she said, is educating the population that dermatologists can cure skin diseases and that there are good medications for treating the diseases.
Shortcomings of teledermatology
Some dermatologists perform teledermatology visits for tribes, often from an office located in a different time zone. “And, they don’t have a sense of what resources are available for the people they’re serving,” Dr. Kohn said. “For example, if they diagnose a potential skin cancer on the face and say, ‘you need a biopsy,’ but the closest dermatologist is 4 hours away, is that really serving the patient? Or, if you tell a patient, ‘I want you to go out and buy Vanicream for your skin,’ but Vanicream costs $17 and the patient can’t even afford to buy food, are you really doing them a service?”
In a survey-based study of 238 AI individuals that is scheduled to be published in late 2023, Dr. Kohn and colleagues asked respondents at two regional powwows in Denver if they would be open to teledermatology – either in their home or in a primary care clinic. Most respondents (70%) lived in urban areas, the rest in rural settings. Nearly half of respondents (42%) “did not want to do teledermatology, even though they couldn’t access in-person dermatology,” Dr. Kohn said. “So, for people who think teledermatology is the answer [to improving access], the respondents to our survey weren’t interested in pursuing that as a solution. I was surprised by that.” When the researchers broke down the responses by age, teenage respondents were even less interested in teledermatology than adults were. “I think there’s something about having someone see you in person, knowing who you are,” she said.
Partnerships with tribes
To foster more sustainable change in the delivery of skin care beyond remote teledermatology and periodic visits from volunteers, some dermatology residencies have established partnerships with tribes, including Massachusetts General Hospital’s teaching partnership with the Rosebud Sioux tribe in Rosebud, S.D., and the University of Utah dermatology department’s resident continuity clinic with Navajo Nation in Montezuma Creek, Utah. In 2016, officials from the Utah Navajo Health System reached out to the University of Utah’s dermatology department to inquire about the potential for creating a teledermatology clinic to serve patients who receive primary care at the Montezuma Creek Community Health Center, located in Southeastern Utah on the northern tip of the Navajo Nation.
Stephanie Klein, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the university, spearheaded the clinic’s launch but soon encountered obstacles that ranged from not being able to visualize the patient’s skin clearly on her computer screen to difficulty making a personal connection with patients despite help from Navajo translators. “It was hard to build a relationship,” she said. A few years later, she drove down to meet with officials of the health system and posed the question: “What is the ideal thing you would want from dermatology?”
Continuity, they told her. “They said that a lot of the services they receive in the form of outreach are rotational, where someone might come in for a day, or a week, or five people may rotate throughout the year,” which did not serve them well, said Dr. Klein, who subsequently collaborated with Utah Navajo Health System clinicians to establish a resident continuity clinic, which launched in January 2021.
The arrangement also serves as a continuity clinic for Dr. Klein as an attending physician. Each month, she and one dermatology resident drive 6.5 hours from Salt Lake City to Montezuma Creek, where they spend 1 or 2 full days seeing about 25 patients referred by the primary care clinicians who work there. About one-quarter of the time they fly, thanks to financial support from a private donor. The flight takes about an hour, then it’s an hour-long drive to the actual clinic. “It’s a commitment,” Dr. Klein said. “A resident can come with me if they commit to the clinic for at least 1 year. This enables us to have continuity of care; it allows us to build relationships with the patients and with the care team there.” As for the prior teledermatology visits she had with residents, “I still do those, but now I do them in between the in-person visits, so I’m not meeting people over telehealth; I’m just following up with them.”

Situated in the high desert among rock formations, the estimated population of Montezuma Creek is just over 320 people. “It’s a beautiful place with otherworldly buttes and mesas, and the Blue Mountains rising up in the distance,” said Lowell Nicholson, MD, a dermatology resident at the University of Utah who is in his second year of a 2-year commitment to the clinic. “But the landscape can be harsh, and it is underserved from an infrastructure perspective,” with large areas with no cell phone service and limited access to running water and refrigeration. “People in general travel quite far to get their medical care and most of the roads are dirt or gravel, so after a big snowstorm or if it’s been raining, they can become impassable.”
Dermatologic conditions they often encounter include vitiligo, photodermatoses, hidradenitis suppurativa, eczema, psoriasis, and severe acne, often with lots of acne-associated scarring. “In general, we tend to see dramatic or advanced presentations of general dermatology diagnoses,” Dr. Nicholson said. “We see a lot of really extensive psoriasis, which can be socially stigmatizing.”
He recalled one middle-aged man who isolated himself from others because his psoriasis became unbearable. The man refused to leave his house, visit family members, or attend tribal meetups. “He tried to see his regular doctor about it and was given topicals, but his disease was just too extensive,” said Dr. Nicholson, who suggested trying a biologic but learned that the man did not have regular access to refrigeration. “That wasn’t going to work, but we started him on an oral medication, apremilast, which has completely cleared his skin,” he said. “He’s doing great. The last time we saw him he was re-engaged with his family, and he told us he was going on dates. We really improved his quality of life.”
Dr. Klein recalled seeing a 6-year-old girl at the clinic with atopic dermatitis so severe that it caused her to miss several days of school. “When she was in school, she was so distracted by the itching – it was so overwhelming,” she said. She was struggling with topical medicines that weren’t effective, but Dr. Klein got her on dupilumab, and during a follow-up visit the girl told her, “This is the first time in my life I can think about things” other than itching.
According to Dr. Nicholson, some patients seen at the Montezuma Creek clinic are on Medicare or carry standard insurance. “Others have a mix, and others are getting all their medications through the Montezuma Creek clinic or through the IHS clinics,” he said. “I have been surprised at the formulary and our ability to get relatively expensive medications for our patients, like biologics and TNF inhibitors. But it takes some creativity to know what is going to work for your patients’ living situation.”
Training more AI/AN dermatologists key
While efforts to increase the culturally respectful and sustainable dermatologic care for AI/AN individuals continue through programs like the continuity clinic at Montezuma Creek, sources interviewed for this story emphasized the importance of training more AI/AN dermatologists. “Of the people who graduate from high school, AIs have the lowest rate of going on to college,” said Dr. Kohn, who serves as a mentor to Mr. Hicks. “Let’s say they get all the way to medical school; it’s about good mentorship and support in what they’re pursuing. We are seeing more AIs in medical school now, something that I personally notice, and I notice it from what Chinle Service Unit tells me. They have received many requests from Native medical students and premed students who want to rotate at Chinle. Native trainees want the experience of being there.”
According to the Association of American Medical Colleges, the number of AI/AN applicants to medical schools increased from 72 in 2020-2021 to 105 in 2021-2022 but dipped slightly to 94 in 2022-2023. Inspired by a passion to serve Pine Ridge or a community like it, Mr. Hicks decided to apply for medical school. While he doesn’t want to “close any doors” on which medical specialty he ultimately chooses to practice, the current front-runner is dermatology, he said, largely because of the influence of Dr. Kohn and two Mayo dermatologists who have become mentors: Molly Lohman, MD, and Hafsa M. Cantwell, MD. “I didn’t see anyone from my background who was a doctor, so having those role models is so important for Native kids to think, ‘I can do this, too,’ and to pursue it,” he said.
As a proud member of the Oglala Lakota Nation from the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in southwestern South Dakota, Drew Hicks grew up with limited access to basic health care, let alone the luxury of scheduling an appointment with a dermatologist or another medical specialist.
The area – once home to the Lakota war leader Crazy Horse – encompasses nearly 47,000 residents scattered over about 2.2 million acres, larger than the size of Rhode Island, with land marked by rolling mixed grass prairie, sandhills, and badlands. Some of the Oglala Lakota people live in substandard housing and lack regular access to food, running water, and refrigeration, not to mention cell phone and Internet service. “It’s sparse,” said Mr. Hicks, the son of Tribal ranchers who now is a 3rd-year medical student at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science in Rochester, Minn., and has an early interest in pursuing dermatology. “There is a lot of territory and not a lot of health care serving the population.” From the Hicks home, the nearest place to receive health care is a family medicine practice in Martin, S.D. – about a 15-minute drive on gravel roads in the best of conditions, but in poor weather, it can be difficult, he said. “So, there are environmental challenges besides the limited number of health care providers.”
Clinicians in the practice “did have to be the point of care for everything from dermatologic issues to emergency medicine to delivering a baby, because the next-closest medical facility of any magnitude is 2 hours away,” he said.
Challenges of health literacy and limited access to comprehensive health care at Pine Ridge and other American Indian (AI) and Alaska Native (AN) reservations have long-term consequences. “My own mom struggled to control her blood pressure for years and now has chronic kidney disease,” Mr. Hicks said. “It’s not an uncommon story. Diabetes on the reservation is a big issue.” Then there’s his father, who survived two bouts with melanoma that was diagnosed at an advanced stage. “I think about how that has impacted him, and wonder, had we had a dermatologist who serviced our area, would we have caught things sooner?” he said. “I feel there is so much room for impactful health care deliveries to communities like Pine Ridge.” At the same time, he emphasized, “this isn’t poverty porn. We’re a resilient people. Any effort to engage with AIs or ANs should be from a perspective of a learner, having cultural humility, and seeking out community leaders to help lead you.”
According to the 2020 Census, there are 574 federally recognized sovereign tribal nations in the United States and federal- and state-recognized American Indian reservations in 35 states. AI/AN people make up about 2.9% of the total U.S. population, or 9.7 million, and their life expectancy is an average of 4.4 years less, compared with the general population (a mean of 73.7 vs. 78.1 years, respectively). Because of limited access to dermatologic care in these areas, the risk for developing significant skin conditions and diseases that may go undetected for long stretches of time is increased.
“That can mean advanced skin cancers like basal cell carcinomas that have become larger than what you would see in a typical metropolitan population,” said Lucinda Kohn, MD, assistant professor of dermatology in the Centers for American Indian and Alaska Native Health at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who spent part of her dermatology residency rotating at the Chinle (Ariz.) Service Unit, an Indian Health Service facility, in 2017 and now provides teledermatology and regular in-person dermatology care at that clinic. “The climate there is dry, so you can see bad eczema and dry skin. There’s also a lot of acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. I think the acne and HS is due to the hyperglycemic index diet from the food deserts. Skin disease reflects the climate, the food desert, and the lack of close specialty care.”
Acne scarring common
Some published evidence suggests that acne is more prevalent and severe in AI/AN individuals. In a survey of 158 AI/AN individuals with a mean age of 32 years, 79.1% reported a history of acne, 55.1% reported acne scarring, and 31% reported having active lesions. “Looking back on my experience in high school, I definitely see that in myself and in my peers,” Mr. Hicks said. And, while there are limited published studies about the incidence of melanoma in this population, an analysis from 2006 found that the incidence was 3.1 per 100,000 between 2001 and 2005, which was an increase from 1.6 per 100,000 reported between 1992 and 2000.
There’s a lot to unpack for dermatologists caring for the AI/AN population besides the raw health disparities: a long history of distrust between AI/AN people and the federal government, structural racism, geographic isolation, health literacy challenges, and high rates of poverty and unemployment. And while individuals from federally recognized tribes have a legal right to receive health care provided by the Indian Health Service, a component of the Department of Health & Human Services, the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that in 2017 per capita spending available to the IHS was $4,078, compared with $8,109 for Medicaid, $10,692 for the Veterans Health Administration, and $13,185 for Medicare.
“Everyone deserves healthy skin and good health,” said Dr. Kohn, whose husband is AI and works in AI law. “Knowing that there are pockets of people who lack that access to care really bothers me. I think the American Indians are frequently overlooked. They’re just not even counted for in certain surveys,” she added, noting that categories are usually defined as Black, Hispanic, Asian, or White.
According to Dr. Kohn, who coauthored a chapter titled “Dermatology on American Indian and Alaska Native Reservations,” for the 2021 book “Dermatology in Rural Settings”, 70% of AIs live in urban areas, “so it’s not just people who live on reservations, though the disparity is greatest there.” To help deliver dermatologic care in the rural areas “where you’re on tribal lands, you must partner with the tribes,” she added. “You must get their permission, operate under their laws and regulations and their rules, learn the local customs, learn about the culture, learn the people, and learn their resources before you practice. That’s the only ethical way to practice.” This also means appreciating the fact that some AI/AN individuals may not understand what a dermatologist could do for them. “One of the bigger hurdles to overcome,” she said, is educating the population that dermatologists can cure skin diseases and that there are good medications for treating the diseases.
Shortcomings of teledermatology
Some dermatologists perform teledermatology visits for tribes, often from an office located in a different time zone. “And, they don’t have a sense of what resources are available for the people they’re serving,” Dr. Kohn said. “For example, if they diagnose a potential skin cancer on the face and say, ‘you need a biopsy,’ but the closest dermatologist is 4 hours away, is that really serving the patient? Or, if you tell a patient, ‘I want you to go out and buy Vanicream for your skin,’ but Vanicream costs $17 and the patient can’t even afford to buy food, are you really doing them a service?”
In a survey-based study of 238 AI individuals that is scheduled to be published in late 2023, Dr. Kohn and colleagues asked respondents at two regional powwows in Denver if they would be open to teledermatology – either in their home or in a primary care clinic. Most respondents (70%) lived in urban areas, the rest in rural settings. Nearly half of respondents (42%) “did not want to do teledermatology, even though they couldn’t access in-person dermatology,” Dr. Kohn said. “So, for people who think teledermatology is the answer [to improving access], the respondents to our survey weren’t interested in pursuing that as a solution. I was surprised by that.” When the researchers broke down the responses by age, teenage respondents were even less interested in teledermatology than adults were. “I think there’s something about having someone see you in person, knowing who you are,” she said.
Partnerships with tribes
To foster more sustainable change in the delivery of skin care beyond remote teledermatology and periodic visits from volunteers, some dermatology residencies have established partnerships with tribes, including Massachusetts General Hospital’s teaching partnership with the Rosebud Sioux tribe in Rosebud, S.D., and the University of Utah dermatology department’s resident continuity clinic with Navajo Nation in Montezuma Creek, Utah. In 2016, officials from the Utah Navajo Health System reached out to the University of Utah’s dermatology department to inquire about the potential for creating a teledermatology clinic to serve patients who receive primary care at the Montezuma Creek Community Health Center, located in Southeastern Utah on the northern tip of the Navajo Nation.
Stephanie Klein, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the university, spearheaded the clinic’s launch but soon encountered obstacles that ranged from not being able to visualize the patient’s skin clearly on her computer screen to difficulty making a personal connection with patients despite help from Navajo translators. “It was hard to build a relationship,” she said. A few years later, she drove down to meet with officials of the health system and posed the question: “What is the ideal thing you would want from dermatology?”
Continuity, they told her. “They said that a lot of the services they receive in the form of outreach are rotational, where someone might come in for a day, or a week, or five people may rotate throughout the year,” which did not serve them well, said Dr. Klein, who subsequently collaborated with Utah Navajo Health System clinicians to establish a resident continuity clinic, which launched in January 2021.
The arrangement also serves as a continuity clinic for Dr. Klein as an attending physician. Each month, she and one dermatology resident drive 6.5 hours from Salt Lake City to Montezuma Creek, where they spend 1 or 2 full days seeing about 25 patients referred by the primary care clinicians who work there. About one-quarter of the time they fly, thanks to financial support from a private donor. The flight takes about an hour, then it’s an hour-long drive to the actual clinic. “It’s a commitment,” Dr. Klein said. “A resident can come with me if they commit to the clinic for at least 1 year. This enables us to have continuity of care; it allows us to build relationships with the patients and with the care team there.” As for the prior teledermatology visits she had with residents, “I still do those, but now I do them in between the in-person visits, so I’m not meeting people over telehealth; I’m just following up with them.”

Situated in the high desert among rock formations, the estimated population of Montezuma Creek is just over 320 people. “It’s a beautiful place with otherworldly buttes and mesas, and the Blue Mountains rising up in the distance,” said Lowell Nicholson, MD, a dermatology resident at the University of Utah who is in his second year of a 2-year commitment to the clinic. “But the landscape can be harsh, and it is underserved from an infrastructure perspective,” with large areas with no cell phone service and limited access to running water and refrigeration. “People in general travel quite far to get their medical care and most of the roads are dirt or gravel, so after a big snowstorm or if it’s been raining, they can become impassable.”
Dermatologic conditions they often encounter include vitiligo, photodermatoses, hidradenitis suppurativa, eczema, psoriasis, and severe acne, often with lots of acne-associated scarring. “In general, we tend to see dramatic or advanced presentations of general dermatology diagnoses,” Dr. Nicholson said. “We see a lot of really extensive psoriasis, which can be socially stigmatizing.”
He recalled one middle-aged man who isolated himself from others because his psoriasis became unbearable. The man refused to leave his house, visit family members, or attend tribal meetups. “He tried to see his regular doctor about it and was given topicals, but his disease was just too extensive,” said Dr. Nicholson, who suggested trying a biologic but learned that the man did not have regular access to refrigeration. “That wasn’t going to work, but we started him on an oral medication, apremilast, which has completely cleared his skin,” he said. “He’s doing great. The last time we saw him he was re-engaged with his family, and he told us he was going on dates. We really improved his quality of life.”
Dr. Klein recalled seeing a 6-year-old girl at the clinic with atopic dermatitis so severe that it caused her to miss several days of school. “When she was in school, she was so distracted by the itching – it was so overwhelming,” she said. She was struggling with topical medicines that weren’t effective, but Dr. Klein got her on dupilumab, and during a follow-up visit the girl told her, “This is the first time in my life I can think about things” other than itching.
According to Dr. Nicholson, some patients seen at the Montezuma Creek clinic are on Medicare or carry standard insurance. “Others have a mix, and others are getting all their medications through the Montezuma Creek clinic or through the IHS clinics,” he said. “I have been surprised at the formulary and our ability to get relatively expensive medications for our patients, like biologics and TNF inhibitors. But it takes some creativity to know what is going to work for your patients’ living situation.”
Training more AI/AN dermatologists key
While efforts to increase the culturally respectful and sustainable dermatologic care for AI/AN individuals continue through programs like the continuity clinic at Montezuma Creek, sources interviewed for this story emphasized the importance of training more AI/AN dermatologists. “Of the people who graduate from high school, AIs have the lowest rate of going on to college,” said Dr. Kohn, who serves as a mentor to Mr. Hicks. “Let’s say they get all the way to medical school; it’s about good mentorship and support in what they’re pursuing. We are seeing more AIs in medical school now, something that I personally notice, and I notice it from what Chinle Service Unit tells me. They have received many requests from Native medical students and premed students who want to rotate at Chinle. Native trainees want the experience of being there.”
According to the Association of American Medical Colleges, the number of AI/AN applicants to medical schools increased from 72 in 2020-2021 to 105 in 2021-2022 but dipped slightly to 94 in 2022-2023. Inspired by a passion to serve Pine Ridge or a community like it, Mr. Hicks decided to apply for medical school. While he doesn’t want to “close any doors” on which medical specialty he ultimately chooses to practice, the current front-runner is dermatology, he said, largely because of the influence of Dr. Kohn and two Mayo dermatologists who have become mentors: Molly Lohman, MD, and Hafsa M. Cantwell, MD. “I didn’t see anyone from my background who was a doctor, so having those role models is so important for Native kids to think, ‘I can do this, too,’ and to pursue it,” he said.
As a proud member of the Oglala Lakota Nation from the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in southwestern South Dakota, Drew Hicks grew up with limited access to basic health care, let alone the luxury of scheduling an appointment with a dermatologist or another medical specialist.
The area – once home to the Lakota war leader Crazy Horse – encompasses nearly 47,000 residents scattered over about 2.2 million acres, larger than the size of Rhode Island, with land marked by rolling mixed grass prairie, sandhills, and badlands. Some of the Oglala Lakota people live in substandard housing and lack regular access to food, running water, and refrigeration, not to mention cell phone and Internet service. “It’s sparse,” said Mr. Hicks, the son of Tribal ranchers who now is a 3rd-year medical student at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science in Rochester, Minn., and has an early interest in pursuing dermatology. “There is a lot of territory and not a lot of health care serving the population.” From the Hicks home, the nearest place to receive health care is a family medicine practice in Martin, S.D. – about a 15-minute drive on gravel roads in the best of conditions, but in poor weather, it can be difficult, he said. “So, there are environmental challenges besides the limited number of health care providers.”
Clinicians in the practice “did have to be the point of care for everything from dermatologic issues to emergency medicine to delivering a baby, because the next-closest medical facility of any magnitude is 2 hours away,” he said.
Challenges of health literacy and limited access to comprehensive health care at Pine Ridge and other American Indian (AI) and Alaska Native (AN) reservations have long-term consequences. “My own mom struggled to control her blood pressure for years and now has chronic kidney disease,” Mr. Hicks said. “It’s not an uncommon story. Diabetes on the reservation is a big issue.” Then there’s his father, who survived two bouts with melanoma that was diagnosed at an advanced stage. “I think about how that has impacted him, and wonder, had we had a dermatologist who serviced our area, would we have caught things sooner?” he said. “I feel there is so much room for impactful health care deliveries to communities like Pine Ridge.” At the same time, he emphasized, “this isn’t poverty porn. We’re a resilient people. Any effort to engage with AIs or ANs should be from a perspective of a learner, having cultural humility, and seeking out community leaders to help lead you.”
According to the 2020 Census, there are 574 federally recognized sovereign tribal nations in the United States and federal- and state-recognized American Indian reservations in 35 states. AI/AN people make up about 2.9% of the total U.S. population, or 9.7 million, and their life expectancy is an average of 4.4 years less, compared with the general population (a mean of 73.7 vs. 78.1 years, respectively). Because of limited access to dermatologic care in these areas, the risk for developing significant skin conditions and diseases that may go undetected for long stretches of time is increased.
“That can mean advanced skin cancers like basal cell carcinomas that have become larger than what you would see in a typical metropolitan population,” said Lucinda Kohn, MD, assistant professor of dermatology in the Centers for American Indian and Alaska Native Health at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who spent part of her dermatology residency rotating at the Chinle (Ariz.) Service Unit, an Indian Health Service facility, in 2017 and now provides teledermatology and regular in-person dermatology care at that clinic. “The climate there is dry, so you can see bad eczema and dry skin. There’s also a lot of acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. I think the acne and HS is due to the hyperglycemic index diet from the food deserts. Skin disease reflects the climate, the food desert, and the lack of close specialty care.”
Acne scarring common
Some published evidence suggests that acne is more prevalent and severe in AI/AN individuals. In a survey of 158 AI/AN individuals with a mean age of 32 years, 79.1% reported a history of acne, 55.1% reported acne scarring, and 31% reported having active lesions. “Looking back on my experience in high school, I definitely see that in myself and in my peers,” Mr. Hicks said. And, while there are limited published studies about the incidence of melanoma in this population, an analysis from 2006 found that the incidence was 3.1 per 100,000 between 2001 and 2005, which was an increase from 1.6 per 100,000 reported between 1992 and 2000.
There’s a lot to unpack for dermatologists caring for the AI/AN population besides the raw health disparities: a long history of distrust between AI/AN people and the federal government, structural racism, geographic isolation, health literacy challenges, and high rates of poverty and unemployment. And while individuals from federally recognized tribes have a legal right to receive health care provided by the Indian Health Service, a component of the Department of Health & Human Services, the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that in 2017 per capita spending available to the IHS was $4,078, compared with $8,109 for Medicaid, $10,692 for the Veterans Health Administration, and $13,185 for Medicare.
“Everyone deserves healthy skin and good health,” said Dr. Kohn, whose husband is AI and works in AI law. “Knowing that there are pockets of people who lack that access to care really bothers me. I think the American Indians are frequently overlooked. They’re just not even counted for in certain surveys,” she added, noting that categories are usually defined as Black, Hispanic, Asian, or White.
According to Dr. Kohn, who coauthored a chapter titled “Dermatology on American Indian and Alaska Native Reservations,” for the 2021 book “Dermatology in Rural Settings”, 70% of AIs live in urban areas, “so it’s not just people who live on reservations, though the disparity is greatest there.” To help deliver dermatologic care in the rural areas “where you’re on tribal lands, you must partner with the tribes,” she added. “You must get their permission, operate under their laws and regulations and their rules, learn the local customs, learn about the culture, learn the people, and learn their resources before you practice. That’s the only ethical way to practice.” This also means appreciating the fact that some AI/AN individuals may not understand what a dermatologist could do for them. “One of the bigger hurdles to overcome,” she said, is educating the population that dermatologists can cure skin diseases and that there are good medications for treating the diseases.
Shortcomings of teledermatology
Some dermatologists perform teledermatology visits for tribes, often from an office located in a different time zone. “And, they don’t have a sense of what resources are available for the people they’re serving,” Dr. Kohn said. “For example, if they diagnose a potential skin cancer on the face and say, ‘you need a biopsy,’ but the closest dermatologist is 4 hours away, is that really serving the patient? Or, if you tell a patient, ‘I want you to go out and buy Vanicream for your skin,’ but Vanicream costs $17 and the patient can’t even afford to buy food, are you really doing them a service?”
In a survey-based study of 238 AI individuals that is scheduled to be published in late 2023, Dr. Kohn and colleagues asked respondents at two regional powwows in Denver if they would be open to teledermatology – either in their home or in a primary care clinic. Most respondents (70%) lived in urban areas, the rest in rural settings. Nearly half of respondents (42%) “did not want to do teledermatology, even though they couldn’t access in-person dermatology,” Dr. Kohn said. “So, for people who think teledermatology is the answer [to improving access], the respondents to our survey weren’t interested in pursuing that as a solution. I was surprised by that.” When the researchers broke down the responses by age, teenage respondents were even less interested in teledermatology than adults were. “I think there’s something about having someone see you in person, knowing who you are,” she said.
Partnerships with tribes
To foster more sustainable change in the delivery of skin care beyond remote teledermatology and periodic visits from volunteers, some dermatology residencies have established partnerships with tribes, including Massachusetts General Hospital’s teaching partnership with the Rosebud Sioux tribe in Rosebud, S.D., and the University of Utah dermatology department’s resident continuity clinic with Navajo Nation in Montezuma Creek, Utah. In 2016, officials from the Utah Navajo Health System reached out to the University of Utah’s dermatology department to inquire about the potential for creating a teledermatology clinic to serve patients who receive primary care at the Montezuma Creek Community Health Center, located in Southeastern Utah on the northern tip of the Navajo Nation.
Stephanie Klein, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the university, spearheaded the clinic’s launch but soon encountered obstacles that ranged from not being able to visualize the patient’s skin clearly on her computer screen to difficulty making a personal connection with patients despite help from Navajo translators. “It was hard to build a relationship,” she said. A few years later, she drove down to meet with officials of the health system and posed the question: “What is the ideal thing you would want from dermatology?”
Continuity, they told her. “They said that a lot of the services they receive in the form of outreach are rotational, where someone might come in for a day, or a week, or five people may rotate throughout the year,” which did not serve them well, said Dr. Klein, who subsequently collaborated with Utah Navajo Health System clinicians to establish a resident continuity clinic, which launched in January 2021.
The arrangement also serves as a continuity clinic for Dr. Klein as an attending physician. Each month, she and one dermatology resident drive 6.5 hours from Salt Lake City to Montezuma Creek, where they spend 1 or 2 full days seeing about 25 patients referred by the primary care clinicians who work there. About one-quarter of the time they fly, thanks to financial support from a private donor. The flight takes about an hour, then it’s an hour-long drive to the actual clinic. “It’s a commitment,” Dr. Klein said. “A resident can come with me if they commit to the clinic for at least 1 year. This enables us to have continuity of care; it allows us to build relationships with the patients and with the care team there.” As for the prior teledermatology visits she had with residents, “I still do those, but now I do them in between the in-person visits, so I’m not meeting people over telehealth; I’m just following up with them.”

Situated in the high desert among rock formations, the estimated population of Montezuma Creek is just over 320 people. “It’s a beautiful place with otherworldly buttes and mesas, and the Blue Mountains rising up in the distance,” said Lowell Nicholson, MD, a dermatology resident at the University of Utah who is in his second year of a 2-year commitment to the clinic. “But the landscape can be harsh, and it is underserved from an infrastructure perspective,” with large areas with no cell phone service and limited access to running water and refrigeration. “People in general travel quite far to get their medical care and most of the roads are dirt or gravel, so after a big snowstorm or if it’s been raining, they can become impassable.”
Dermatologic conditions they often encounter include vitiligo, photodermatoses, hidradenitis suppurativa, eczema, psoriasis, and severe acne, often with lots of acne-associated scarring. “In general, we tend to see dramatic or advanced presentations of general dermatology diagnoses,” Dr. Nicholson said. “We see a lot of really extensive psoriasis, which can be socially stigmatizing.”
He recalled one middle-aged man who isolated himself from others because his psoriasis became unbearable. The man refused to leave his house, visit family members, or attend tribal meetups. “He tried to see his regular doctor about it and was given topicals, but his disease was just too extensive,” said Dr. Nicholson, who suggested trying a biologic but learned that the man did not have regular access to refrigeration. “That wasn’t going to work, but we started him on an oral medication, apremilast, which has completely cleared his skin,” he said. “He’s doing great. The last time we saw him he was re-engaged with his family, and he told us he was going on dates. We really improved his quality of life.”
Dr. Klein recalled seeing a 6-year-old girl at the clinic with atopic dermatitis so severe that it caused her to miss several days of school. “When she was in school, she was so distracted by the itching – it was so overwhelming,” she said. She was struggling with topical medicines that weren’t effective, but Dr. Klein got her on dupilumab, and during a follow-up visit the girl told her, “This is the first time in my life I can think about things” other than itching.
According to Dr. Nicholson, some patients seen at the Montezuma Creek clinic are on Medicare or carry standard insurance. “Others have a mix, and others are getting all their medications through the Montezuma Creek clinic or through the IHS clinics,” he said. “I have been surprised at the formulary and our ability to get relatively expensive medications for our patients, like biologics and TNF inhibitors. But it takes some creativity to know what is going to work for your patients’ living situation.”
Training more AI/AN dermatologists key
While efforts to increase the culturally respectful and sustainable dermatologic care for AI/AN individuals continue through programs like the continuity clinic at Montezuma Creek, sources interviewed for this story emphasized the importance of training more AI/AN dermatologists. “Of the people who graduate from high school, AIs have the lowest rate of going on to college,” said Dr. Kohn, who serves as a mentor to Mr. Hicks. “Let’s say they get all the way to medical school; it’s about good mentorship and support in what they’re pursuing. We are seeing more AIs in medical school now, something that I personally notice, and I notice it from what Chinle Service Unit tells me. They have received many requests from Native medical students and premed students who want to rotate at Chinle. Native trainees want the experience of being there.”
According to the Association of American Medical Colleges, the number of AI/AN applicants to medical schools increased from 72 in 2020-2021 to 105 in 2021-2022 but dipped slightly to 94 in 2022-2023. Inspired by a passion to serve Pine Ridge or a community like it, Mr. Hicks decided to apply for medical school. While he doesn’t want to “close any doors” on which medical specialty he ultimately chooses to practice, the current front-runner is dermatology, he said, largely because of the influence of Dr. Kohn and two Mayo dermatologists who have become mentors: Molly Lohman, MD, and Hafsa M. Cantwell, MD. “I didn’t see anyone from my background who was a doctor, so having those role models is so important for Native kids to think, ‘I can do this, too,’ and to pursue it,” he said.
Humira biosimilars: Five things to know
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.
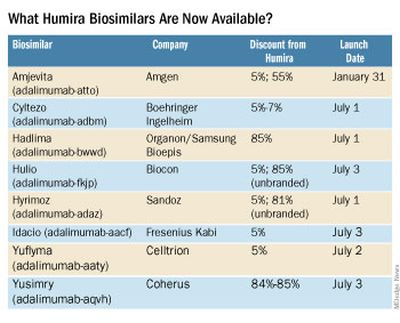
Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.

Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.

Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The sacred office space
Church architecture describes visually the idea of the sacred, which is a fundamental need of man.
– Mario Botta, Swiss architect
My parents are visiting the Holy See today – prima volta in Italia! My mom waited years for this. She isn’t meeting the Pope or attending Mass. Yet, in the Whatsapp pics they sent me, you can see tears well up as she experiences St. Peter’s Basilica. It’s a visceral response to what is just a building and a poignant example of the significance of spaces.
More than just appreciating an edifice’s grandeur or exquisiteness, we are wired to connect with spaces emotionally. Beautiful or significant buildings move us, they make us feel something. Churches, synagogues, or mosques are good examples. They combine spiritual and aesthetic allure. But so too do gorgeous hotels, Apple stores, and posh restaurants. We crave the richness of an environment experienced through our five senses. The glory of sunlight through stained glass, the smell of luxurious scent pumped into a lobby, the weight of a silky new iPhone in your hand. We also have a sixth sense, that feeling we get from knowing that we are standing in a sacred place. A physical space that connects us with something wider and deeper than ourselves.
Virtual may be the peak of convenience, but in-real-life is the pinnacle of experience. Patients will be inconvenienced and pay higher costs to experience their appointment in person. This should not be surprising. Contemplate this: Every year, millions of people will travel across the globe to stand before a wall or walk seven times around a stone building. And millions everyday will perambulate around an Apple Store, willingly paying a higher price for the same product they can buy for less elsewhere. The willingness to pay for certain experiences is remarkably high.
Every day when I cover patient messages, I offer some patients an immediate, free solution to their problem. Just today I exchanged emails with a patient thinking I had addressed her concern by reassuring her that it was a benign seborrheic keratosis. Done. She then replied, “Thanks so much, Dr. Benabio! I still would like to schedule an appointment to come in person.” So much for the efficiency of digital medicine.
Before dismissing these patients as Luddites, understand what they want is the doctor’s office experience. The sights, the smells, the sacredness of what happens here. It is no coincidence that the first clinics were temples. In ancient Greece and Rome, the sick and the gashed made pilgrimages to one of at least 300 Asclepieia, temples of healing. During the medieval period, monasteries doubled as housing for the sick until the church began constructing stand-alone hospitals, often in cross-shaped design with an altar in the middle (eventually that became the nurses station, but without the wine).
Patients entrust us with their lives and their loved ones’ lives and a visit takes on far more significance than a simple service transaction. Forty years on, I can recall visits to Dr. Bellin’s office. He saw pediatric patients out of his Victorian home office with broad, creaky hardwood floors, stained glass, and cast iron radiators. The scent of isopropyl soaked cotton balls and typewriter ink is unforgettable. Far from sterile, it was warm, safe. It was a sacred place, one for which we still sometimes drive by when doing the tour of where I grew up.
We shall forge ahead and continue to offer virtual channels to serve our patients just as any service industry. But don’t force them there. At the same time Starbucks has been building its digital app, it is also building Starbucks Reserve Roasteries. Immense cathedral edifices with warm woods and luxurious brass, the smell of roasting coffee and warm leather perfuming the air. It is where patrons will travel long distances and endure long waits to pay a lot more for a cup of coffee.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Church architecture describes visually the idea of the sacred, which is a fundamental need of man.
– Mario Botta, Swiss architect
My parents are visiting the Holy See today – prima volta in Italia! My mom waited years for this. She isn’t meeting the Pope or attending Mass. Yet, in the Whatsapp pics they sent me, you can see tears well up as she experiences St. Peter’s Basilica. It’s a visceral response to what is just a building and a poignant example of the significance of spaces.
More than just appreciating an edifice’s grandeur or exquisiteness, we are wired to connect with spaces emotionally. Beautiful or significant buildings move us, they make us feel something. Churches, synagogues, or mosques are good examples. They combine spiritual and aesthetic allure. But so too do gorgeous hotels, Apple stores, and posh restaurants. We crave the richness of an environment experienced through our five senses. The glory of sunlight through stained glass, the smell of luxurious scent pumped into a lobby, the weight of a silky new iPhone in your hand. We also have a sixth sense, that feeling we get from knowing that we are standing in a sacred place. A physical space that connects us with something wider and deeper than ourselves.
Virtual may be the peak of convenience, but in-real-life is the pinnacle of experience. Patients will be inconvenienced and pay higher costs to experience their appointment in person. This should not be surprising. Contemplate this: Every year, millions of people will travel across the globe to stand before a wall or walk seven times around a stone building. And millions everyday will perambulate around an Apple Store, willingly paying a higher price for the same product they can buy for less elsewhere. The willingness to pay for certain experiences is remarkably high.
Every day when I cover patient messages, I offer some patients an immediate, free solution to their problem. Just today I exchanged emails with a patient thinking I had addressed her concern by reassuring her that it was a benign seborrheic keratosis. Done. She then replied, “Thanks so much, Dr. Benabio! I still would like to schedule an appointment to come in person.” So much for the efficiency of digital medicine.
Before dismissing these patients as Luddites, understand what they want is the doctor’s office experience. The sights, the smells, the sacredness of what happens here. It is no coincidence that the first clinics were temples. In ancient Greece and Rome, the sick and the gashed made pilgrimages to one of at least 300 Asclepieia, temples of healing. During the medieval period, monasteries doubled as housing for the sick until the church began constructing stand-alone hospitals, often in cross-shaped design with an altar in the middle (eventually that became the nurses station, but without the wine).
Patients entrust us with their lives and their loved ones’ lives and a visit takes on far more significance than a simple service transaction. Forty years on, I can recall visits to Dr. Bellin’s office. He saw pediatric patients out of his Victorian home office with broad, creaky hardwood floors, stained glass, and cast iron radiators. The scent of isopropyl soaked cotton balls and typewriter ink is unforgettable. Far from sterile, it was warm, safe. It was a sacred place, one for which we still sometimes drive by when doing the tour of where I grew up.
We shall forge ahead and continue to offer virtual channels to serve our patients just as any service industry. But don’t force them there. At the same time Starbucks has been building its digital app, it is also building Starbucks Reserve Roasteries. Immense cathedral edifices with warm woods and luxurious brass, the smell of roasting coffee and warm leather perfuming the air. It is where patrons will travel long distances and endure long waits to pay a lot more for a cup of coffee.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Church architecture describes visually the idea of the sacred, which is a fundamental need of man.
– Mario Botta, Swiss architect
My parents are visiting the Holy See today – prima volta in Italia! My mom waited years for this. She isn’t meeting the Pope or attending Mass. Yet, in the Whatsapp pics they sent me, you can see tears well up as she experiences St. Peter’s Basilica. It’s a visceral response to what is just a building and a poignant example of the significance of spaces.
More than just appreciating an edifice’s grandeur or exquisiteness, we are wired to connect with spaces emotionally. Beautiful or significant buildings move us, they make us feel something. Churches, synagogues, or mosques are good examples. They combine spiritual and aesthetic allure. But so too do gorgeous hotels, Apple stores, and posh restaurants. We crave the richness of an environment experienced through our five senses. The glory of sunlight through stained glass, the smell of luxurious scent pumped into a lobby, the weight of a silky new iPhone in your hand. We also have a sixth sense, that feeling we get from knowing that we are standing in a sacred place. A physical space that connects us with something wider and deeper than ourselves.
Virtual may be the peak of convenience, but in-real-life is the pinnacle of experience. Patients will be inconvenienced and pay higher costs to experience their appointment in person. This should not be surprising. Contemplate this: Every year, millions of people will travel across the globe to stand before a wall or walk seven times around a stone building. And millions everyday will perambulate around an Apple Store, willingly paying a higher price for the same product they can buy for less elsewhere. The willingness to pay for certain experiences is remarkably high.
Every day when I cover patient messages, I offer some patients an immediate, free solution to their problem. Just today I exchanged emails with a patient thinking I had addressed her concern by reassuring her that it was a benign seborrheic keratosis. Done. She then replied, “Thanks so much, Dr. Benabio! I still would like to schedule an appointment to come in person.” So much for the efficiency of digital medicine.
Before dismissing these patients as Luddites, understand what they want is the doctor’s office experience. The sights, the smells, the sacredness of what happens here. It is no coincidence that the first clinics were temples. In ancient Greece and Rome, the sick and the gashed made pilgrimages to one of at least 300 Asclepieia, temples of healing. During the medieval period, monasteries doubled as housing for the sick until the church began constructing stand-alone hospitals, often in cross-shaped design with an altar in the middle (eventually that became the nurses station, but without the wine).
Patients entrust us with their lives and their loved ones’ lives and a visit takes on far more significance than a simple service transaction. Forty years on, I can recall visits to Dr. Bellin’s office. He saw pediatric patients out of his Victorian home office with broad, creaky hardwood floors, stained glass, and cast iron radiators. The scent of isopropyl soaked cotton balls and typewriter ink is unforgettable. Far from sterile, it was warm, safe. It was a sacred place, one for which we still sometimes drive by when doing the tour of where I grew up.
We shall forge ahead and continue to offer virtual channels to serve our patients just as any service industry. But don’t force them there. At the same time Starbucks has been building its digital app, it is also building Starbucks Reserve Roasteries. Immense cathedral edifices with warm woods and luxurious brass, the smell of roasting coffee and warm leather perfuming the air. It is where patrons will travel long distances and endure long waits to pay a lot more for a cup of coffee.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.













