User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Methotrexate does not impair sperm quality, small study finds
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
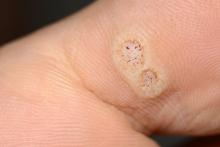
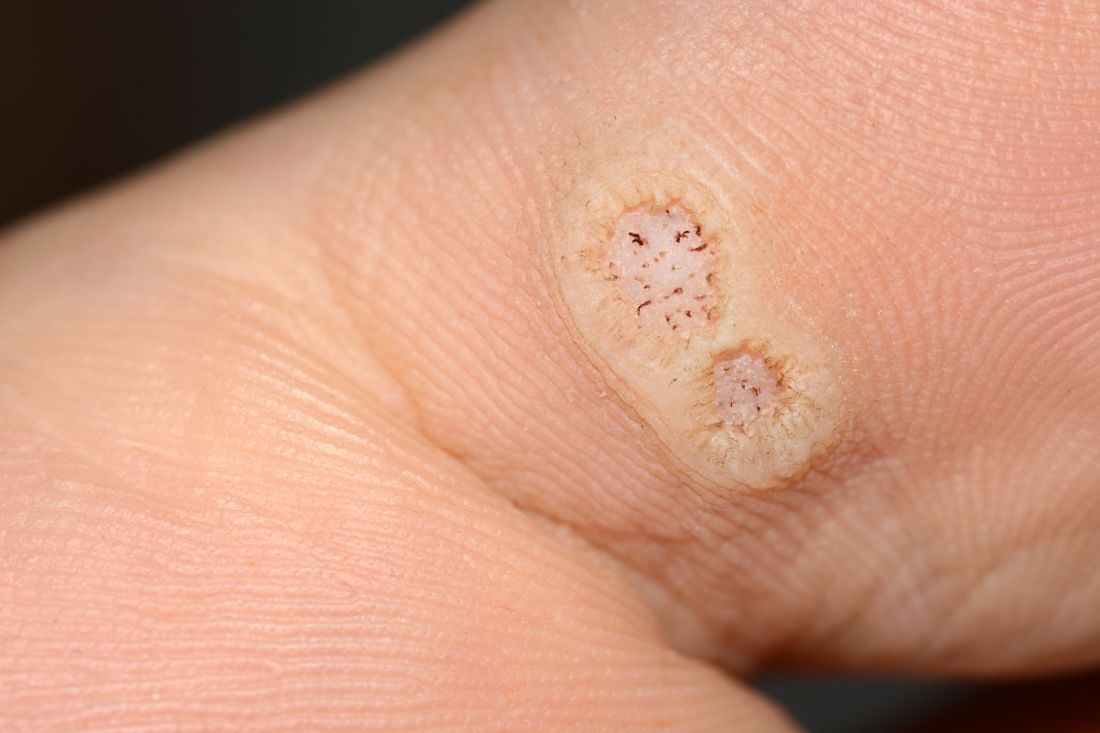
Warts difficult to eradicate in immunocompromised children
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Prognostic factors of SCCs in organ transplant recipients worse compared with general population
, results from a dual cohort study demonstrated.
The findings build on previous research and underscore the need for early diagnosis and aggressive surveillance in this patient population, corresponding author Adele C. Green, MBBS, PhD, professor and senior scientist at the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology. “Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the skin develop up to 77 times more frequently in immunosuppressed organ transplant recipients (OTRs) than the general population,” they wrote. “Because SCCs cause substantially more morbidity and death in the former, they are postulated to be innately more aggressive than in immunocompetent patients, but OTRs’ higher SCC mortality may simply reflect greater SCC tumor burdens per patient.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Green and colleagues drew data from two cohort studies to evaluate five key clinicopathologic indicators of poor SCC outcomes in organ transplant recipients, and in those from the general population in Queensland, Australia: cephalic location, perineural invasion, invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor differentiation, and tumor size greater than 20 mm. The study population included organ transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer, who were enrolled in the Skin Tumours in Allograft Recipients (STAR) study, and those from a population-based cohort, the QSkin Sun and Health Study. STAR consisted of lung transplant recipients and kidney and liver transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer who were recruited from tertiary centers and diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed SCC from 2012 to 2015. QSkin consisted of individuals from Queensland’s general adult population diagnosed with SCCs from 2012 to 2015.
SCC cases in QSkin were ascertained through Australia’s universal health insurance agency and linked with histopathology records. Next, the researchers performed data analysis from both cohort studies to determine the prevalence ratio (PR) of head/neck location, perineural invasion, tumor invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor cellular differentiation, and tumor diameter greater than 20 mm among SCCs among organ transplant recipients compared with the general population.
After combining the two studies, the researchers compared 741 SCCs excised from 191 organ transplant recipients and 2,558 SCCs excised from 1,507 individuals in the general population. Their median ages were similar (62.7 and 63.7 years, respectively) and most were male (78% and 63.4%, respectively).
As for site of involvement, SCCs developed most often on the head and neck in the transplant recipients (38.6%) and on the arms and hands in the general population (35.2%). After adjustment for age and sex, perineural invasion of SCCs was more than twice as common in transplant recipients than among cases in the general population, as was invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat (PR of 2.37 for both associations).
In other findings, compared with SCCs in the general population, poorly vs. well-differentiated SCCs were more than threefold more common in transplant recipients (PR, 3.45), while the prevalence of tumors greater than 20 mm vs. 20 mm or smaller was moderately higher in transplant recipients (PR, 1.52).
“These findings are considered generalizable, confirming that OTRs’ poorer SCC outcomes are associated with not only their sheer numbers of SCC tumors, but also with a strong shift toward more invasive, less differentiated, and larger SCC tumors, in agreement with previous findings,” the researchers wrote. “This shift is likely associated with decreased immunosurveillance resulting from immunosuppressive therapy (since carcinogenesis decelerates with therapy cessation) interacting with effects of high UV radiation exposure.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, chiefly the lack of central review of SCCs to ensure standard assessment of histopathologic features “including caliber of nerves with perineural invasion and cell differentiation; such a review would not have been feasible logistically.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The researchers reported having no disclosures related to the submitted work.
, results from a dual cohort study demonstrated.
The findings build on previous research and underscore the need for early diagnosis and aggressive surveillance in this patient population, corresponding author Adele C. Green, MBBS, PhD, professor and senior scientist at the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology. “Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the skin develop up to 77 times more frequently in immunosuppressed organ transplant recipients (OTRs) than the general population,” they wrote. “Because SCCs cause substantially more morbidity and death in the former, they are postulated to be innately more aggressive than in immunocompetent patients, but OTRs’ higher SCC mortality may simply reflect greater SCC tumor burdens per patient.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Green and colleagues drew data from two cohort studies to evaluate five key clinicopathologic indicators of poor SCC outcomes in organ transplant recipients, and in those from the general population in Queensland, Australia: cephalic location, perineural invasion, invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor differentiation, and tumor size greater than 20 mm. The study population included organ transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer, who were enrolled in the Skin Tumours in Allograft Recipients (STAR) study, and those from a population-based cohort, the QSkin Sun and Health Study. STAR consisted of lung transplant recipients and kidney and liver transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer who were recruited from tertiary centers and diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed SCC from 2012 to 2015. QSkin consisted of individuals from Queensland’s general adult population diagnosed with SCCs from 2012 to 2015.
SCC cases in QSkin were ascertained through Australia’s universal health insurance agency and linked with histopathology records. Next, the researchers performed data analysis from both cohort studies to determine the prevalence ratio (PR) of head/neck location, perineural invasion, tumor invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor cellular differentiation, and tumor diameter greater than 20 mm among SCCs among organ transplant recipients compared with the general population.
After combining the two studies, the researchers compared 741 SCCs excised from 191 organ transplant recipients and 2,558 SCCs excised from 1,507 individuals in the general population. Their median ages were similar (62.7 and 63.7 years, respectively) and most were male (78% and 63.4%, respectively).
As for site of involvement, SCCs developed most often on the head and neck in the transplant recipients (38.6%) and on the arms and hands in the general population (35.2%). After adjustment for age and sex, perineural invasion of SCCs was more than twice as common in transplant recipients than among cases in the general population, as was invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat (PR of 2.37 for both associations).
In other findings, compared with SCCs in the general population, poorly vs. well-differentiated SCCs were more than threefold more common in transplant recipients (PR, 3.45), while the prevalence of tumors greater than 20 mm vs. 20 mm or smaller was moderately higher in transplant recipients (PR, 1.52).
“These findings are considered generalizable, confirming that OTRs’ poorer SCC outcomes are associated with not only their sheer numbers of SCC tumors, but also with a strong shift toward more invasive, less differentiated, and larger SCC tumors, in agreement with previous findings,” the researchers wrote. “This shift is likely associated with decreased immunosurveillance resulting from immunosuppressive therapy (since carcinogenesis decelerates with therapy cessation) interacting with effects of high UV radiation exposure.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, chiefly the lack of central review of SCCs to ensure standard assessment of histopathologic features “including caliber of nerves with perineural invasion and cell differentiation; such a review would not have been feasible logistically.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The researchers reported having no disclosures related to the submitted work.
, results from a dual cohort study demonstrated.
The findings build on previous research and underscore the need for early diagnosis and aggressive surveillance in this patient population, corresponding author Adele C. Green, MBBS, PhD, professor and senior scientist at the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology. “Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the skin develop up to 77 times more frequently in immunosuppressed organ transplant recipients (OTRs) than the general population,” they wrote. “Because SCCs cause substantially more morbidity and death in the former, they are postulated to be innately more aggressive than in immunocompetent patients, but OTRs’ higher SCC mortality may simply reflect greater SCC tumor burdens per patient.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Green and colleagues drew data from two cohort studies to evaluate five key clinicopathologic indicators of poor SCC outcomes in organ transplant recipients, and in those from the general population in Queensland, Australia: cephalic location, perineural invasion, invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor differentiation, and tumor size greater than 20 mm. The study population included organ transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer, who were enrolled in the Skin Tumours in Allograft Recipients (STAR) study, and those from a population-based cohort, the QSkin Sun and Health Study. STAR consisted of lung transplant recipients and kidney and liver transplant recipients at high risk of skin cancer who were recruited from tertiary centers and diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed SCC from 2012 to 2015. QSkin consisted of individuals from Queensland’s general adult population diagnosed with SCCs from 2012 to 2015.
SCC cases in QSkin were ascertained through Australia’s universal health insurance agency and linked with histopathology records. Next, the researchers performed data analysis from both cohort studies to determine the prevalence ratio (PR) of head/neck location, perineural invasion, tumor invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat, poor cellular differentiation, and tumor diameter greater than 20 mm among SCCs among organ transplant recipients compared with the general population.
After combining the two studies, the researchers compared 741 SCCs excised from 191 organ transplant recipients and 2,558 SCCs excised from 1,507 individuals in the general population. Their median ages were similar (62.7 and 63.7 years, respectively) and most were male (78% and 63.4%, respectively).
As for site of involvement, SCCs developed most often on the head and neck in the transplant recipients (38.6%) and on the arms and hands in the general population (35.2%). After adjustment for age and sex, perineural invasion of SCCs was more than twice as common in transplant recipients than among cases in the general population, as was invasion to/beyond subcutaneous fat (PR of 2.37 for both associations).
In other findings, compared with SCCs in the general population, poorly vs. well-differentiated SCCs were more than threefold more common in transplant recipients (PR, 3.45), while the prevalence of tumors greater than 20 mm vs. 20 mm or smaller was moderately higher in transplant recipients (PR, 1.52).
“These findings are considered generalizable, confirming that OTRs’ poorer SCC outcomes are associated with not only their sheer numbers of SCC tumors, but also with a strong shift toward more invasive, less differentiated, and larger SCC tumors, in agreement with previous findings,” the researchers wrote. “This shift is likely associated with decreased immunosurveillance resulting from immunosuppressive therapy (since carcinogenesis decelerates with therapy cessation) interacting with effects of high UV radiation exposure.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, chiefly the lack of central review of SCCs to ensure standard assessment of histopathologic features “including caliber of nerves with perineural invasion and cell differentiation; such a review would not have been feasible logistically.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The researchers reported having no disclosures related to the submitted work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
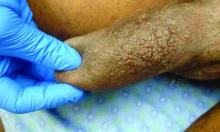
A 63-year-old male presented for evaluation of worsening genital lesions and associated swelling
.1 Clinically, ENV presents as verrucous, hyperkeratotic, cobblestone-like patches, plaques, and nodules with associated nonpitting edema of the affected body area.1 Secondary bacterial infections are common and often worsen the clinical course. The etiology of ENV involves chronic lymphatic obstruction and venous insufficiency, with additional risk factors including obesity, chronic lymphedema, bacterial infection, surgery or trauma, neoplasia, radiation, congestive heart failure, or scleroderma.2,3 While most commonly presenting on the lower extremities, cases have been reported involving the abdomen, sacrum, ears, buttocks, and penoscrotal area.1,2
Regardless of location, the pathogenesis of ENV remains the same. Chronic lymphatic obstruction results in accumulation and lymphostasis of protein-rich dermal fluid, which subsequently precipitates fibroblast proliferation and activation, suppression of the local immune response and development of recurrent lymphangitis, chronic inflammation, and potential secondary bacterial infection.2,4
There is no standard of care for the treatment and management of ENV and recurrence is common. Interventions often involve those used for chronic lymphedema – including leg elevation, compression stockings or devices, skin hygiene, and lymphatic pumping.2,3 Medical management with topical and oral retinoids has been reported, as well as emphasis on weight loss and infection control.1,4 Surgical intervention is often reserved for refractory cases that fail to respond to more conservative management, or severe presentations resulting in extensive functional and aesthetic impairment. Less commonly reported treatment modalities include lymphaticovenular anastomosis and ablative carbon dioxide laser use, although this latter intervention demonstrated minimal improvement in this patient.5,6
Penoscrotal ENV is a rare form of ENV affecting the genital region of males, often resulting in significant disfigurement, functional impairment, and psychosocial distress. Penoscrotal elephantiasis can be idiopathic, due to filarial infections, scleroinflammatory stricture of the urethra, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, and lymphostasis secondary to chronic inflammatory conditions such as streptococcal infections, radiotherapy, surgery, chronic venous stasis, or Kaposi sarcoma.7
In addition, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has been documented multiple times in the literature in association with the development of ENV, detailing lymphatic scarring secondary to chronic inguinal HS as the main pathogenic factor.8,9
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for penoscrotal ENV, which not only improves functionality and cosmesis, but also aids in prevention of rare malignant sequelae, such as lymphangiosarcoma.10 Such interventions can involve lymphangioplasty to aid in lymphatic drainage or excision of the mass and subcutaneous tissue with full-thickness skin grafting for reconstruction.7 Collaboration between urology, plastic surgery, and dermatology is often essential to obtain adequate care with satisfactory outcomes and minimal recurrence for patients with this uncommon condition.
This case and photo were submitted by Marlee Hill, a medical student at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City; and Michael Franzetti, MD, and Jeffrey McBride, MD, department of dermatology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Donna Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hadian Y et al. Dermatol Online J. 2019 Dec 15;25(12):13030/qt6rn1s8ff.
2. Judge N and Kilic A. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2016 Nov 13;10(2):32-4.
3. Dean SM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Jun;64(6):1104-10.
4. Sisto K and Khachemoune A. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(3):141-6.
5. Motegi S et al. Dermatology. 2007;215(2):147-51.
6. Robinson CG et al. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22(6):611-3.
7. Koualla S et al. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2023 Apr 10;S0294-1260(23)00035-3.
8. Lelonek E et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021 Feb 11;101(2):adv00389.
9. Good LM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 May;64(5):993-4.
10. Cerri A et al. Eur J Dermatol. 1998 Oct-Nov;8(7):511-4.
.1 Clinically, ENV presents as verrucous, hyperkeratotic, cobblestone-like patches, plaques, and nodules with associated nonpitting edema of the affected body area.1 Secondary bacterial infections are common and often worsen the clinical course. The etiology of ENV involves chronic lymphatic obstruction and venous insufficiency, with additional risk factors including obesity, chronic lymphedema, bacterial infection, surgery or trauma, neoplasia, radiation, congestive heart failure, or scleroderma.2,3 While most commonly presenting on the lower extremities, cases have been reported involving the abdomen, sacrum, ears, buttocks, and penoscrotal area.1,2
Regardless of location, the pathogenesis of ENV remains the same. Chronic lymphatic obstruction results in accumulation and lymphostasis of protein-rich dermal fluid, which subsequently precipitates fibroblast proliferation and activation, suppression of the local immune response and development of recurrent lymphangitis, chronic inflammation, and potential secondary bacterial infection.2,4
There is no standard of care for the treatment and management of ENV and recurrence is common. Interventions often involve those used for chronic lymphedema – including leg elevation, compression stockings or devices, skin hygiene, and lymphatic pumping.2,3 Medical management with topical and oral retinoids has been reported, as well as emphasis on weight loss and infection control.1,4 Surgical intervention is often reserved for refractory cases that fail to respond to more conservative management, or severe presentations resulting in extensive functional and aesthetic impairment. Less commonly reported treatment modalities include lymphaticovenular anastomosis and ablative carbon dioxide laser use, although this latter intervention demonstrated minimal improvement in this patient.5,6
Penoscrotal ENV is a rare form of ENV affecting the genital region of males, often resulting in significant disfigurement, functional impairment, and psychosocial distress. Penoscrotal elephantiasis can be idiopathic, due to filarial infections, scleroinflammatory stricture of the urethra, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, and lymphostasis secondary to chronic inflammatory conditions such as streptococcal infections, radiotherapy, surgery, chronic venous stasis, or Kaposi sarcoma.7
In addition, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has been documented multiple times in the literature in association with the development of ENV, detailing lymphatic scarring secondary to chronic inguinal HS as the main pathogenic factor.8,9
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for penoscrotal ENV, which not only improves functionality and cosmesis, but also aids in prevention of rare malignant sequelae, such as lymphangiosarcoma.10 Such interventions can involve lymphangioplasty to aid in lymphatic drainage or excision of the mass and subcutaneous tissue with full-thickness skin grafting for reconstruction.7 Collaboration between urology, plastic surgery, and dermatology is often essential to obtain adequate care with satisfactory outcomes and minimal recurrence for patients with this uncommon condition.
This case and photo were submitted by Marlee Hill, a medical student at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City; and Michael Franzetti, MD, and Jeffrey McBride, MD, department of dermatology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Donna Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hadian Y et al. Dermatol Online J. 2019 Dec 15;25(12):13030/qt6rn1s8ff.
2. Judge N and Kilic A. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2016 Nov 13;10(2):32-4.
3. Dean SM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Jun;64(6):1104-10.
4. Sisto K and Khachemoune A. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(3):141-6.
5. Motegi S et al. Dermatology. 2007;215(2):147-51.
6. Robinson CG et al. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22(6):611-3.
7. Koualla S et al. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2023 Apr 10;S0294-1260(23)00035-3.
8. Lelonek E et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021 Feb 11;101(2):adv00389.
9. Good LM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 May;64(5):993-4.
10. Cerri A et al. Eur J Dermatol. 1998 Oct-Nov;8(7):511-4.
.1 Clinically, ENV presents as verrucous, hyperkeratotic, cobblestone-like patches, plaques, and nodules with associated nonpitting edema of the affected body area.1 Secondary bacterial infections are common and often worsen the clinical course. The etiology of ENV involves chronic lymphatic obstruction and venous insufficiency, with additional risk factors including obesity, chronic lymphedema, bacterial infection, surgery or trauma, neoplasia, radiation, congestive heart failure, or scleroderma.2,3 While most commonly presenting on the lower extremities, cases have been reported involving the abdomen, sacrum, ears, buttocks, and penoscrotal area.1,2
Regardless of location, the pathogenesis of ENV remains the same. Chronic lymphatic obstruction results in accumulation and lymphostasis of protein-rich dermal fluid, which subsequently precipitates fibroblast proliferation and activation, suppression of the local immune response and development of recurrent lymphangitis, chronic inflammation, and potential secondary bacterial infection.2,4
There is no standard of care for the treatment and management of ENV and recurrence is common. Interventions often involve those used for chronic lymphedema – including leg elevation, compression stockings or devices, skin hygiene, and lymphatic pumping.2,3 Medical management with topical and oral retinoids has been reported, as well as emphasis on weight loss and infection control.1,4 Surgical intervention is often reserved for refractory cases that fail to respond to more conservative management, or severe presentations resulting in extensive functional and aesthetic impairment. Less commonly reported treatment modalities include lymphaticovenular anastomosis and ablative carbon dioxide laser use, although this latter intervention demonstrated minimal improvement in this patient.5,6
Penoscrotal ENV is a rare form of ENV affecting the genital region of males, often resulting in significant disfigurement, functional impairment, and psychosocial distress. Penoscrotal elephantiasis can be idiopathic, due to filarial infections, scleroinflammatory stricture of the urethra, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, and lymphostasis secondary to chronic inflammatory conditions such as streptococcal infections, radiotherapy, surgery, chronic venous stasis, or Kaposi sarcoma.7
In addition, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has been documented multiple times in the literature in association with the development of ENV, detailing lymphatic scarring secondary to chronic inguinal HS as the main pathogenic factor.8,9
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for penoscrotal ENV, which not only improves functionality and cosmesis, but also aids in prevention of rare malignant sequelae, such as lymphangiosarcoma.10 Such interventions can involve lymphangioplasty to aid in lymphatic drainage or excision of the mass and subcutaneous tissue with full-thickness skin grafting for reconstruction.7 Collaboration between urology, plastic surgery, and dermatology is often essential to obtain adequate care with satisfactory outcomes and minimal recurrence for patients with this uncommon condition.
This case and photo were submitted by Marlee Hill, a medical student at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City; and Michael Franzetti, MD, and Jeffrey McBride, MD, department of dermatology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Donna Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hadian Y et al. Dermatol Online J. 2019 Dec 15;25(12):13030/qt6rn1s8ff.
2. Judge N and Kilic A. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2016 Nov 13;10(2):32-4.
3. Dean SM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Jun;64(6):1104-10.
4. Sisto K and Khachemoune A. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(3):141-6.
5. Motegi S et al. Dermatology. 2007;215(2):147-51.
6. Robinson CG et al. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22(6):611-3.
7. Koualla S et al. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2023 Apr 10;S0294-1260(23)00035-3.
8. Lelonek E et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021 Feb 11;101(2):adv00389.
9. Good LM et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 May;64(5):993-4.
10. Cerri A et al. Eur J Dermatol. 1998 Oct-Nov;8(7):511-4.
FDA warns of tattoo ink tied to dangerous infections
The Food and Drug Administration draft guidance released recently on possible contamination of tattoo ink was not concerning Whitney Donohue, 34, owner of Forget Me Not Tattoo in Billings, Mont.
“I get our ink directly through the manufacturer – not at a store or through Amazon or eBay,” she said. “You never know if it’s going to be repackaged.”
Tattoo artists themselves, she said, regulate the quality of ink they use.
Still, the threat is real, said Bruce Brod, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Health System. “I’ve seen several different infections from tattooing, and they are from organisms that tend to contaminate things in damp, liquid-type environments.”
, dermatologists said.
“Tattooing involves puncturing the epidermis about 100 times per second with needles and depositing ink 1.5 to 2 millimeters below the surface of the skin, deep into the dermis,” the guidance states. “Contaminated tattoo ink can cause infections and serious injuries. Because these inks are injected, pathogens or other harmful substances in these inks can travel from the injection site through the blood and lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.”
The guidance comes as body art continues to get more popular. According to a 2019 poll, 30% of Americans had at least one tattoo – up from 21% in 2012. Forty percent of people 18-34 and 36% of those ages 35-54 had at least one tattoo. And though they are commonplace, tattoos come with medical risks that should be known beforehand, doctors said.
Commonly reported symptoms of tattoo ink–associated infections include rashes, blisters, painful nodules, and severe abscesses. One of the most common bacteria found in contaminated tattoo ink is nontuberculous mycobacteria, which is related to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis and can be found in soil and water.
The guidance lists several unsanitary manufacturing conditions that may lead to ink contamination, including:
- Preparing or packing of tattoo inks in facilities that are hard to sanitize, such as carpeted areas
- Ink or ink components left uncovered, especially near open air ducts
- Unsanitary mixing of tattoo inks, including with unclean utensils or containers
- Lack of appropriate attire by staff, failure to use hairnets, lab coats, aprons, gowns, masks, or gloves
“Infections will often spread along the drainage channels in the skin and create squiggly, uneven lines of big red, lumpy nodules,” Dr. Brod said.
Between 2003 and 2023, there were 18 recalls of tattoo inks that were contaminated with various microorganisms, according to the FDA. In May 2019, the FDA issued a safety alert advising consumers, tattoo artists, and retailers to avoid using or selling certain tattoo inks contaminated with microorganisms.
Reputable ink manufacturers use a process called gamma radiation, which refers to electromagnetic radiation of high frequencies to kill microorganisms in the ink and its packaging.
Most of the trustworthy, high-quality ink manufacturers are well-known among tattoo artists, Ms. Donohue said.
While she has seen customers with sensitive skin have allergic reactions, she has not seen someone come back with an infection in her 9 years working in the tattoo industry.
Because tattoo ink is considered a cosmetic product, there is not much regulatory oversight involved, which means the sterility and quality of ingredients vary, said Teo Soleymani, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology and dermatological surgery at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine.
“Cosmeceuticals aren’t regulated by the FDA like prescription medication,” he said. “What we’ve seen many times is inadvertent contamination during the application process or contamination while the inks are being made.”
In years past, unclean needles spreading hepatitis and HIV were more of a concern, but those rates have dropped significantly, Dr. Soleymani said.
The infections that have increased are from rare bacteria that exist in stagnant water. And they are injected into a part of the body that allows them to evade the immune system, he said: shallow enough that there aren’t many associated blood vessels, but not still below the layer of skin that gets sloughed off every 28 days.
Sometimes, antibiotics alone won’t cut it, and the tattoo will require surgical removal.
“The aesthetic you were going for has to be not only removed, but you’re left with a surgical scar,” Dr. Soleymani said. “Tattoos can be beautiful, but they can come with unwanted visitors that can cause months of misery.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration draft guidance released recently on possible contamination of tattoo ink was not concerning Whitney Donohue, 34, owner of Forget Me Not Tattoo in Billings, Mont.
“I get our ink directly through the manufacturer – not at a store or through Amazon or eBay,” she said. “You never know if it’s going to be repackaged.”
Tattoo artists themselves, she said, regulate the quality of ink they use.
Still, the threat is real, said Bruce Brod, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Health System. “I’ve seen several different infections from tattooing, and they are from organisms that tend to contaminate things in damp, liquid-type environments.”
, dermatologists said.
“Tattooing involves puncturing the epidermis about 100 times per second with needles and depositing ink 1.5 to 2 millimeters below the surface of the skin, deep into the dermis,” the guidance states. “Contaminated tattoo ink can cause infections and serious injuries. Because these inks are injected, pathogens or other harmful substances in these inks can travel from the injection site through the blood and lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.”
The guidance comes as body art continues to get more popular. According to a 2019 poll, 30% of Americans had at least one tattoo – up from 21% in 2012. Forty percent of people 18-34 and 36% of those ages 35-54 had at least one tattoo. And though they are commonplace, tattoos come with medical risks that should be known beforehand, doctors said.
Commonly reported symptoms of tattoo ink–associated infections include rashes, blisters, painful nodules, and severe abscesses. One of the most common bacteria found in contaminated tattoo ink is nontuberculous mycobacteria, which is related to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis and can be found in soil and water.
The guidance lists several unsanitary manufacturing conditions that may lead to ink contamination, including:
- Preparing or packing of tattoo inks in facilities that are hard to sanitize, such as carpeted areas
- Ink or ink components left uncovered, especially near open air ducts
- Unsanitary mixing of tattoo inks, including with unclean utensils or containers
- Lack of appropriate attire by staff, failure to use hairnets, lab coats, aprons, gowns, masks, or gloves
“Infections will often spread along the drainage channels in the skin and create squiggly, uneven lines of big red, lumpy nodules,” Dr. Brod said.
Between 2003 and 2023, there were 18 recalls of tattoo inks that were contaminated with various microorganisms, according to the FDA. In May 2019, the FDA issued a safety alert advising consumers, tattoo artists, and retailers to avoid using or selling certain tattoo inks contaminated with microorganisms.
Reputable ink manufacturers use a process called gamma radiation, which refers to electromagnetic radiation of high frequencies to kill microorganisms in the ink and its packaging.
Most of the trustworthy, high-quality ink manufacturers are well-known among tattoo artists, Ms. Donohue said.
While she has seen customers with sensitive skin have allergic reactions, she has not seen someone come back with an infection in her 9 years working in the tattoo industry.
Because tattoo ink is considered a cosmetic product, there is not much regulatory oversight involved, which means the sterility and quality of ingredients vary, said Teo Soleymani, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology and dermatological surgery at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine.
“Cosmeceuticals aren’t regulated by the FDA like prescription medication,” he said. “What we’ve seen many times is inadvertent contamination during the application process or contamination while the inks are being made.”
In years past, unclean needles spreading hepatitis and HIV were more of a concern, but those rates have dropped significantly, Dr. Soleymani said.
The infections that have increased are from rare bacteria that exist in stagnant water. And they are injected into a part of the body that allows them to evade the immune system, he said: shallow enough that there aren’t many associated blood vessels, but not still below the layer of skin that gets sloughed off every 28 days.
Sometimes, antibiotics alone won’t cut it, and the tattoo will require surgical removal.
“The aesthetic you were going for has to be not only removed, but you’re left with a surgical scar,” Dr. Soleymani said. “Tattoos can be beautiful, but they can come with unwanted visitors that can cause months of misery.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration draft guidance released recently on possible contamination of tattoo ink was not concerning Whitney Donohue, 34, owner of Forget Me Not Tattoo in Billings, Mont.
“I get our ink directly through the manufacturer – not at a store or through Amazon or eBay,” she said. “You never know if it’s going to be repackaged.”
Tattoo artists themselves, she said, regulate the quality of ink they use.
Still, the threat is real, said Bruce Brod, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Health System. “I’ve seen several different infections from tattooing, and they are from organisms that tend to contaminate things in damp, liquid-type environments.”
, dermatologists said.
“Tattooing involves puncturing the epidermis about 100 times per second with needles and depositing ink 1.5 to 2 millimeters below the surface of the skin, deep into the dermis,” the guidance states. “Contaminated tattoo ink can cause infections and serious injuries. Because these inks are injected, pathogens or other harmful substances in these inks can travel from the injection site through the blood and lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.”
The guidance comes as body art continues to get more popular. According to a 2019 poll, 30% of Americans had at least one tattoo – up from 21% in 2012. Forty percent of people 18-34 and 36% of those ages 35-54 had at least one tattoo. And though they are commonplace, tattoos come with medical risks that should be known beforehand, doctors said.
Commonly reported symptoms of tattoo ink–associated infections include rashes, blisters, painful nodules, and severe abscesses. One of the most common bacteria found in contaminated tattoo ink is nontuberculous mycobacteria, which is related to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis and can be found in soil and water.
The guidance lists several unsanitary manufacturing conditions that may lead to ink contamination, including:
- Preparing or packing of tattoo inks in facilities that are hard to sanitize, such as carpeted areas
- Ink or ink components left uncovered, especially near open air ducts
- Unsanitary mixing of tattoo inks, including with unclean utensils or containers
- Lack of appropriate attire by staff, failure to use hairnets, lab coats, aprons, gowns, masks, or gloves
“Infections will often spread along the drainage channels in the skin and create squiggly, uneven lines of big red, lumpy nodules,” Dr. Brod said.
Between 2003 and 2023, there were 18 recalls of tattoo inks that were contaminated with various microorganisms, according to the FDA. In May 2019, the FDA issued a safety alert advising consumers, tattoo artists, and retailers to avoid using or selling certain tattoo inks contaminated with microorganisms.
Reputable ink manufacturers use a process called gamma radiation, which refers to electromagnetic radiation of high frequencies to kill microorganisms in the ink and its packaging.
Most of the trustworthy, high-quality ink manufacturers are well-known among tattoo artists, Ms. Donohue said.
While she has seen customers with sensitive skin have allergic reactions, she has not seen someone come back with an infection in her 9 years working in the tattoo industry.
Because tattoo ink is considered a cosmetic product, there is not much regulatory oversight involved, which means the sterility and quality of ingredients vary, said Teo Soleymani, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology and dermatological surgery at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine.
“Cosmeceuticals aren’t regulated by the FDA like prescription medication,” he said. “What we’ve seen many times is inadvertent contamination during the application process or contamination while the inks are being made.”
In years past, unclean needles spreading hepatitis and HIV were more of a concern, but those rates have dropped significantly, Dr. Soleymani said.
The infections that have increased are from rare bacteria that exist in stagnant water. And they are injected into a part of the body that allows them to evade the immune system, he said: shallow enough that there aren’t many associated blood vessels, but not still below the layer of skin that gets sloughed off every 28 days.
Sometimes, antibiotics alone won’t cut it, and the tattoo will require surgical removal.
“The aesthetic you were going for has to be not only removed, but you’re left with a surgical scar,” Dr. Soleymani said. “Tattoos can be beautiful, but they can come with unwanted visitors that can cause months of misery.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
After Yusimry’s steep discount, little clarity on future adalimumab biosimilar pricing
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts share their sun protection tips for children
“I basically say, ‘sun protection means clothing, shade, [considering the] time of day of exposure, and sunscreen if you are going to be otherwise exposed,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady’s Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said during a panel discussion about sunscreen use at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! He recommends photoprotective gear such as rash guards for surfers and other water sport enthusiasts. When patients ask him if they should use sunscreen, he often replies with a question of his own.
“Do you brush your teeth?” he’ll ask.
“Yes, I do.”
“Well, you should put sunscreen on every day.”
Another panelist, Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she advises new parents to start sun protection efforts early. “Most sunscreens are not approved for use in children under the age of 6 months because testing has not been done in this age group, but I do recommend protective clothing. I also recommend wrap-around sunglasses, which offer 5% more protection from the sun than regular sunglasses.”
In her opinion, stick sunscreens are “a good add-on,” especially for under the eyes and the backs of the hands, but she is not a fan of spray sunscreens, which can leave large areas of skin unprotected if not applied properly.
Fellow panelist Jennifer Huang, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, who has a special interest in taking care of dermatologic conditions of children with cancer, generally recommends mineral-based sunscreens. “There is data to suggest that nonmineral sunscreens are less safe than mineral sunscreens for humans, and mineral sunscreens are considered to be better for the environment,” Dr. Huang said. “Plus, there are more elegant versions of mineral sunscreens that don’t make your skin pasty white.” However, for patients with darker skin tones, “it can be hard to apply a pasty white sunscreen, so I lean on some recommendations for tinted sunscreens, too, so there are options. I specifically recommend sunscreens that have iron oxides in them so that it can block physical rays and help with the cosmetic appearance.”
Moise Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, said that his approach to imparting sunscreen advice to children and their parents involves a mix of spoken information, printed information, and sunscreen samples for children to try in the office, in the presence of a parent. To help patients choose among different samples, be they ointments, gels, or lotions, he will often ask the child: “‘What do you like the feel of better?’ If the child says, ‘I like this one,’ I make sure the parent hears that,” Dr. Levy said.
Next, Dr. Eichenfield, who moderated the discussion, asked his fellow panelists how they would counsel someone who comes to their practice for evaluation of moles and has a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. “I think this is one of the easier counseling sessions, because there are enough kids who are asked about the moles on their skin when they’re at school,” Dr. Hebert said. “I think they’re very ready to wear sun protective clothing and I certainly don’t want any sun exposure that would pose an increased risk for their child.”
In addition to routine sun protection, Dr. Huang recommends annual mole checks for children who have a first-degree relative with a history of malignant melanoma. Other high-risk groups that should undergo annual skin exams include anyone who has received high doses of radiation, bone marrow transplants, prolonged use of voriconazole, or prolonged systemic immunosuppression. Without a known genetic predisposition syndrome, a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer would not raise concern for melanoma in an otherwise healthy child.
Dr. Eichenfield added that freckling used to be the secondary risk factor for melanoma, “but it’s flipped over to a primary risk factor. A history of immunosuppression or prior cancer is a major risk factor in childhood and teenage years.”
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. He has also received research funding from AbbVie, Bausch & Lomb, Galderma Laboratories, and Pfizer. Dr. Hebert disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, Almirall, Amryt Pharma, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Beiersdorf, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma Laboratories, L’Oreal, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Verrica. Dr. Levy disclosed that he is consultant or adviser for Abeona, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Huang disclosed that she is an adviser for EllaOla.
MedscapeLive! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
“I basically say, ‘sun protection means clothing, shade, [considering the] time of day of exposure, and sunscreen if you are going to be otherwise exposed,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady’s Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said during a panel discussion about sunscreen use at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! He recommends photoprotective gear such as rash guards for surfers and other water sport enthusiasts. When patients ask him if they should use sunscreen, he often replies with a question of his own.
“Do you brush your teeth?” he’ll ask.
“Yes, I do.”
“Well, you should put sunscreen on every day.”
Another panelist, Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she advises new parents to start sun protection efforts early. “Most sunscreens are not approved for use in children under the age of 6 months because testing has not been done in this age group, but I do recommend protective clothing. I also recommend wrap-around sunglasses, which offer 5% more protection from the sun than regular sunglasses.”
In her opinion, stick sunscreens are “a good add-on,” especially for under the eyes and the backs of the hands, but she is not a fan of spray sunscreens, which can leave large areas of skin unprotected if not applied properly.
Fellow panelist Jennifer Huang, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, who has a special interest in taking care of dermatologic conditions of children with cancer, generally recommends mineral-based sunscreens. “There is data to suggest that nonmineral sunscreens are less safe than mineral sunscreens for humans, and mineral sunscreens are considered to be better for the environment,” Dr. Huang said. “Plus, there are more elegant versions of mineral sunscreens that don’t make your skin pasty white.” However, for patients with darker skin tones, “it can be hard to apply a pasty white sunscreen, so I lean on some recommendations for tinted sunscreens, too, so there are options. I specifically recommend sunscreens that have iron oxides in them so that it can block physical rays and help with the cosmetic appearance.”
Moise Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, said that his approach to imparting sunscreen advice to children and their parents involves a mix of spoken information, printed information, and sunscreen samples for children to try in the office, in the presence of a parent. To help patients choose among different samples, be they ointments, gels, or lotions, he will often ask the child: “‘What do you like the feel of better?’ If the child says, ‘I like this one,’ I make sure the parent hears that,” Dr. Levy said.
Next, Dr. Eichenfield, who moderated the discussion, asked his fellow panelists how they would counsel someone who comes to their practice for evaluation of moles and has a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. “I think this is one of the easier counseling sessions, because there are enough kids who are asked about the moles on their skin when they’re at school,” Dr. Hebert said. “I think they’re very ready to wear sun protective clothing and I certainly don’t want any sun exposure that would pose an increased risk for their child.”
In addition to routine sun protection, Dr. Huang recommends annual mole checks for children who have a first-degree relative with a history of malignant melanoma. Other high-risk groups that should undergo annual skin exams include anyone who has received high doses of radiation, bone marrow transplants, prolonged use of voriconazole, or prolonged systemic immunosuppression. Without a known genetic predisposition syndrome, a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer would not raise concern for melanoma in an otherwise healthy child.
Dr. Eichenfield added that freckling used to be the secondary risk factor for melanoma, “but it’s flipped over to a primary risk factor. A history of immunosuppression or prior cancer is a major risk factor in childhood and teenage years.”
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. He has also received research funding from AbbVie, Bausch & Lomb, Galderma Laboratories, and Pfizer. Dr. Hebert disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, Almirall, Amryt Pharma, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Beiersdorf, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma Laboratories, L’Oreal, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Verrica. Dr. Levy disclosed that he is consultant or adviser for Abeona, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Huang disclosed that she is an adviser for EllaOla.
MedscapeLive! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
“I basically say, ‘sun protection means clothing, shade, [considering the] time of day of exposure, and sunscreen if you are going to be otherwise exposed,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady’s Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said during a panel discussion about sunscreen use at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! He recommends photoprotective gear such as rash guards for surfers and other water sport enthusiasts. When patients ask him if they should use sunscreen, he often replies with a question of his own.
“Do you brush your teeth?” he’ll ask.
“Yes, I do.”
“Well, you should put sunscreen on every day.”
Another panelist, Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she advises new parents to start sun protection efforts early. “Most sunscreens are not approved for use in children under the age of 6 months because testing has not been done in this age group, but I do recommend protective clothing. I also recommend wrap-around sunglasses, which offer 5% more protection from the sun than regular sunglasses.”
In her opinion, stick sunscreens are “a good add-on,” especially for under the eyes and the backs of the hands, but she is not a fan of spray sunscreens, which can leave large areas of skin unprotected if not applied properly.
Fellow panelist Jennifer Huang, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, who has a special interest in taking care of dermatologic conditions of children with cancer, generally recommends mineral-based sunscreens. “There is data to suggest that nonmineral sunscreens are less safe than mineral sunscreens for humans, and mineral sunscreens are considered to be better for the environment,” Dr. Huang said. “Plus, there are more elegant versions of mineral sunscreens that don’t make your skin pasty white.” However, for patients with darker skin tones, “it can be hard to apply a pasty white sunscreen, so I lean on some recommendations for tinted sunscreens, too, so there are options. I specifically recommend sunscreens that have iron oxides in them so that it can block physical rays and help with the cosmetic appearance.”
Moise Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, said that his approach to imparting sunscreen advice to children and their parents involves a mix of spoken information, printed information, and sunscreen samples for children to try in the office, in the presence of a parent. To help patients choose among different samples, be they ointments, gels, or lotions, he will often ask the child: “‘What do you like the feel of better?’ If the child says, ‘I like this one,’ I make sure the parent hears that,” Dr. Levy said.
Next, Dr. Eichenfield, who moderated the discussion, asked his fellow panelists how they would counsel someone who comes to their practice for evaluation of moles and has a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. “I think this is one of the easier counseling sessions, because there are enough kids who are asked about the moles on their skin when they’re at school,” Dr. Hebert said. “I think they’re very ready to wear sun protective clothing and I certainly don’t want any sun exposure that would pose an increased risk for their child.”
In addition to routine sun protection, Dr. Huang recommends annual mole checks for children who have a first-degree relative with a history of malignant melanoma. Other high-risk groups that should undergo annual skin exams include anyone who has received high doses of radiation, bone marrow transplants, prolonged use of voriconazole, or prolonged systemic immunosuppression. Without a known genetic predisposition syndrome, a family history of nonmelanoma skin cancer would not raise concern for melanoma in an otherwise healthy child.
Dr. Eichenfield added that freckling used to be the secondary risk factor for melanoma, “but it’s flipped over to a primary risk factor. A history of immunosuppression or prior cancer is a major risk factor in childhood and teenage years.”
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. He has also received research funding from AbbVie, Bausch & Lomb, Galderma Laboratories, and Pfizer. Dr. Hebert disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, Almirall, Amryt Pharma, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Beiersdorf, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma Laboratories, L’Oreal, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Verrica. Dr. Levy disclosed that he is consultant or adviser for Abeona, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Huang disclosed that she is an adviser for EllaOla.
MedscapeLive! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
‘New standard of care’ for capecitabine hand-foot syndrome
researchers reported in a study that has been hailed by experts as “practice changing.”
Hand-foot syndrome causes painful, bleeding blisters and ulcers on the palms and soles. It often leads to dose reductions and sometimes even discontinuations, both of which limit the effectiveness of capecitabine, a standard oral chemotherapy drug widely used for colorectal and breast cancers.
In a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Indian researchers reported that a cheap, safe, and widely available over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory gel containing 1% diclofenac reduced the incidence of hand-foot syndrome by 75% among patients with cancer being treated with capecitabine.
Up until now, the oral anti-inflammatory celecoxib (Celebrex) was the only agent proven to prevent the problem, but it’s rarely used because of the risk for strokes, gastric bleeding, and other issues, none of which are a concern with topical diclofenac, which osteoarthritis patients have used safely for years.
The Indian trial, dubbed D-Torch, establishes “1% topical diclofenac gel as the new standard of care to prevent capecitabine-associated hand-foot syndrome,” said investigator and study presenter Atul Batra, MD, a medical oncologist at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi.
Dr. Batra told ASCO Daily News that there is no need for a second trial. “We don’t feel there’s a need to replicate these results” in a larger study “because this was adequately powered, and the results speak for themselves. There’s no confusion about these results. Diclofenac is clearly effective.”
Dr. Batra also commented that his clinic now uses topical diclofenac routinely during capecitabine treatment and that he hopes oncology practices elsewhere will do the same.
Diclofenac gel is sold under the brand name Voltaren and is also available as a generic; in the United States, a 150-gram tube costs about $18 at Walmart.
‘The most practice-changing study’ at ASCO 2023
Audience members at ASCO’s annual meeting immediately saw the importance of the study.
Tarah Ballinger, MD, a breast cancer specialist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said on Twitter that “this might be the most practice changing study I heard at ASCO23.” Topical diclofenac is “widely available, affordable, [and] addresses [a] major” quality of life issue.
The study discussant at the meeting, gastrointestinal cancer specialist Pallavi Kumar, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, concurred: “For me as a GI oncologist, topical diclofenac for prevention of HFS for patients on capecitabine is practice changing,” she said.
The takeaway is “that topical diclofenac significantly reduces the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS in patients receiving capecitabine.” The results are “very impressive,” Dr. Kumar said.
Study details
The idea for the new study came after Batra and colleagues realized that celecoxib, a COX-2 enzyme inhibitor, helps prevent capecitabine hand-foot syndrome (HFS) by blocking a key process that leads to it, the up-regulation of COX-2 and subsequent release of proinflammatory prostaglandins.
They turned to diclofenac gel hoping to get the same effect but more safely; diclofenac is also a COX-2 blocker, and its topical formulation has a strong safety record.
To test the approach, the team randomly assigned 130 patients to topical diclofenac and 133 to placebo – the gel vehicle without the medication – while they were being treated with capecitabine for 12 weeks; 56% were being treated for breast cancer and the rest for gastrointestinal cancers.
Subjects rubbed one fingertip’s worth of gel – about half a gram – on each palm and the back of each hand twice a day. The dose was about 4 grams/day, which is well below maximal dosages for osteoarthritis (up to 32 g/day over all affected joints). Adherence to treatment was about 95% in both arms.
By the end of 12 weeks, the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS was 3.8% in the diclofenac arm (5 patients) versus 15% (n = 20) with placebo (P = .003), a 75% risk reduction.
The incidence of any grade HFS was 6.1% in the treatment group versus 18.1% with placebo (P = .003).
Hand-foot syndrome led to dose reductions of capecitabine in 13.5% of placebo but only 3.8% of those in the diclofenac group (P = .002).
The findings held regardless of whether patients were being treated for breast or GI cancer or if they were men or women.
Other capecitabine-induced adverse events, including diarrhea, mucositis, and myelosuppression, were not significantly different between the groups.
The treatment arms were well balanced, with a median age of 47 years in both groups and women making up about 70% of each. About 40% of subjects in each group were on capecitabine monotherapy with the rest on combination treatments. The mean dose of capecitabine was just over 1,880 mg/m2 in both groups.
At the meeting, Dr. Batra was asked if topical diclofenac would also work for another common problem in oncology: hand-food syndrome occurring as a side-effect with VEGF–tyrosine kinase inhibitors. He didn’t think so because it probably has a different cause than capecitabine HFS, one not strongly related to COX-2 up-regulation.
The study was partly funded by the Indian Supportive Care of Cancer Association. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers reported in a study that has been hailed by experts as “practice changing.”
Hand-foot syndrome causes painful, bleeding blisters and ulcers on the palms and soles. It often leads to dose reductions and sometimes even discontinuations, both of which limit the effectiveness of capecitabine, a standard oral chemotherapy drug widely used for colorectal and breast cancers.
In a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Indian researchers reported that a cheap, safe, and widely available over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory gel containing 1% diclofenac reduced the incidence of hand-foot syndrome by 75% among patients with cancer being treated with capecitabine.
Up until now, the oral anti-inflammatory celecoxib (Celebrex) was the only agent proven to prevent the problem, but it’s rarely used because of the risk for strokes, gastric bleeding, and other issues, none of which are a concern with topical diclofenac, which osteoarthritis patients have used safely for years.
The Indian trial, dubbed D-Torch, establishes “1% topical diclofenac gel as the new standard of care to prevent capecitabine-associated hand-foot syndrome,” said investigator and study presenter Atul Batra, MD, a medical oncologist at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi.
Dr. Batra told ASCO Daily News that there is no need for a second trial. “We don’t feel there’s a need to replicate these results” in a larger study “because this was adequately powered, and the results speak for themselves. There’s no confusion about these results. Diclofenac is clearly effective.”
Dr. Batra also commented that his clinic now uses topical diclofenac routinely during capecitabine treatment and that he hopes oncology practices elsewhere will do the same.
Diclofenac gel is sold under the brand name Voltaren and is also available as a generic; in the United States, a 150-gram tube costs about $18 at Walmart.
‘The most practice-changing study’ at ASCO 2023
Audience members at ASCO’s annual meeting immediately saw the importance of the study.
Tarah Ballinger, MD, a breast cancer specialist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said on Twitter that “this might be the most practice changing study I heard at ASCO23.” Topical diclofenac is “widely available, affordable, [and] addresses [a] major” quality of life issue.
The study discussant at the meeting, gastrointestinal cancer specialist Pallavi Kumar, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, concurred: “For me as a GI oncologist, topical diclofenac for prevention of HFS for patients on capecitabine is practice changing,” she said.
The takeaway is “that topical diclofenac significantly reduces the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS in patients receiving capecitabine.” The results are “very impressive,” Dr. Kumar said.
Study details
The idea for the new study came after Batra and colleagues realized that celecoxib, a COX-2 enzyme inhibitor, helps prevent capecitabine hand-foot syndrome (HFS) by blocking a key process that leads to it, the up-regulation of COX-2 and subsequent release of proinflammatory prostaglandins.
They turned to diclofenac gel hoping to get the same effect but more safely; diclofenac is also a COX-2 blocker, and its topical formulation has a strong safety record.
To test the approach, the team randomly assigned 130 patients to topical diclofenac and 133 to placebo – the gel vehicle without the medication – while they were being treated with capecitabine for 12 weeks; 56% were being treated for breast cancer and the rest for gastrointestinal cancers.
Subjects rubbed one fingertip’s worth of gel – about half a gram – on each palm and the back of each hand twice a day. The dose was about 4 grams/day, which is well below maximal dosages for osteoarthritis (up to 32 g/day over all affected joints). Adherence to treatment was about 95% in both arms.
By the end of 12 weeks, the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS was 3.8% in the diclofenac arm (5 patients) versus 15% (n = 20) with placebo (P = .003), a 75% risk reduction.
The incidence of any grade HFS was 6.1% in the treatment group versus 18.1% with placebo (P = .003).
Hand-foot syndrome led to dose reductions of capecitabine in 13.5% of placebo but only 3.8% of those in the diclofenac group (P = .002).
The findings held regardless of whether patients were being treated for breast or GI cancer or if they were men or women.
Other capecitabine-induced adverse events, including diarrhea, mucositis, and myelosuppression, were not significantly different between the groups.
The treatment arms were well balanced, with a median age of 47 years in both groups and women making up about 70% of each. About 40% of subjects in each group were on capecitabine monotherapy with the rest on combination treatments. The mean dose of capecitabine was just over 1,880 mg/m2 in both groups.
At the meeting, Dr. Batra was asked if topical diclofenac would also work for another common problem in oncology: hand-food syndrome occurring as a side-effect with VEGF–tyrosine kinase inhibitors. He didn’t think so because it probably has a different cause than capecitabine HFS, one not strongly related to COX-2 up-regulation.
The study was partly funded by the Indian Supportive Care of Cancer Association. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers reported in a study that has been hailed by experts as “practice changing.”
Hand-foot syndrome causes painful, bleeding blisters and ulcers on the palms and soles. It often leads to dose reductions and sometimes even discontinuations, both of which limit the effectiveness of capecitabine, a standard oral chemotherapy drug widely used for colorectal and breast cancers.
In a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Indian researchers reported that a cheap, safe, and widely available over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory gel containing 1% diclofenac reduced the incidence of hand-foot syndrome by 75% among patients with cancer being treated with capecitabine.
Up until now, the oral anti-inflammatory celecoxib (Celebrex) was the only agent proven to prevent the problem, but it’s rarely used because of the risk for strokes, gastric bleeding, and other issues, none of which are a concern with topical diclofenac, which osteoarthritis patients have used safely for years.
The Indian trial, dubbed D-Torch, establishes “1% topical diclofenac gel as the new standard of care to prevent capecitabine-associated hand-foot syndrome,” said investigator and study presenter Atul Batra, MD, a medical oncologist at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi.
Dr. Batra told ASCO Daily News that there is no need for a second trial. “We don’t feel there’s a need to replicate these results” in a larger study “because this was adequately powered, and the results speak for themselves. There’s no confusion about these results. Diclofenac is clearly effective.”
Dr. Batra also commented that his clinic now uses topical diclofenac routinely during capecitabine treatment and that he hopes oncology practices elsewhere will do the same.
Diclofenac gel is sold under the brand name Voltaren and is also available as a generic; in the United States, a 150-gram tube costs about $18 at Walmart.
‘The most practice-changing study’ at ASCO 2023
Audience members at ASCO’s annual meeting immediately saw the importance of the study.
Tarah Ballinger, MD, a breast cancer specialist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said on Twitter that “this might be the most practice changing study I heard at ASCO23.” Topical diclofenac is “widely available, affordable, [and] addresses [a] major” quality of life issue.
The study discussant at the meeting, gastrointestinal cancer specialist Pallavi Kumar, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, concurred: “For me as a GI oncologist, topical diclofenac for prevention of HFS for patients on capecitabine is practice changing,” she said.
The takeaway is “that topical diclofenac significantly reduces the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS in patients receiving capecitabine.” The results are “very impressive,” Dr. Kumar said.
Study details
The idea for the new study came after Batra and colleagues realized that celecoxib, a COX-2 enzyme inhibitor, helps prevent capecitabine hand-foot syndrome (HFS) by blocking a key process that leads to it, the up-regulation of COX-2 and subsequent release of proinflammatory prostaglandins.
They turned to diclofenac gel hoping to get the same effect but more safely; diclofenac is also a COX-2 blocker, and its topical formulation has a strong safety record.
To test the approach, the team randomly assigned 130 patients to topical diclofenac and 133 to placebo – the gel vehicle without the medication – while they were being treated with capecitabine for 12 weeks; 56% were being treated for breast cancer and the rest for gastrointestinal cancers.
Subjects rubbed one fingertip’s worth of gel – about half a gram – on each palm and the back of each hand twice a day. The dose was about 4 grams/day, which is well below maximal dosages for osteoarthritis (up to 32 g/day over all affected joints). Adherence to treatment was about 95% in both arms.
By the end of 12 weeks, the incidence of grade 2 or higher HFS was 3.8% in the diclofenac arm (5 patients) versus 15% (n = 20) with placebo (P = .003), a 75% risk reduction.
The incidence of any grade HFS was 6.1% in the treatment group versus 18.1% with placebo (P = .003).
Hand-foot syndrome led to dose reductions of capecitabine in 13.5% of placebo but only 3.8% of those in the diclofenac group (P = .002).
The findings held regardless of whether patients were being treated for breast or GI cancer or if they were men or women.
Other capecitabine-induced adverse events, including diarrhea, mucositis, and myelosuppression, were not significantly different between the groups.
The treatment arms were well balanced, with a median age of 47 years in both groups and women making up about 70% of each. About 40% of subjects in each group were on capecitabine monotherapy with the rest on combination treatments. The mean dose of capecitabine was just over 1,880 mg/m2 in both groups.
At the meeting, Dr. Batra was asked if topical diclofenac would also work for another common problem in oncology: hand-food syndrome occurring as a side-effect with VEGF–tyrosine kinase inhibitors. He didn’t think so because it probably has a different cause than capecitabine HFS, one not strongly related to COX-2 up-regulation.
The study was partly funded by the Indian Supportive Care of Cancer Association. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2023
The road to weight loss is paved with collusion and sabotage
Three big bumps on the weight-loss journey
The search for the Holy Grail. The destruction of the One Ring. The never-ending struggle to Lose Weight.
Like most legendary quests, weight loss is a journey, and we need support to help us achieve our goal. Maybe it’s gaining a new workout partner or finding a similarly-goaled Facebook Group. For a lot of people, it’s as simple as your friends and family. A recent study, however, suggests that the people closest to you may be your worst weight-loss enemies, and they might not even know it.
Researchers at the University of Surrey reviewed the literature on the positives and negatives of social support when it comes to weight loss and identified three types of negative effects: acts of sabotage, feeding behavior, and collusion.
Let’s start with the softest of intentions and work our way up. Collusion is the least negative. Friends and family may just go with the flow, even if it doesn’t agree with the goals of the person who’s trying to lose weight. It can even happen when health care professionals try to help their patients navigate or avoid obesity, ultimately killing with kindness, so to speak.
Next up, feeding behavior. Maybe you know someone whose love language is cooking. There are also people who share food because they don’t want to waste it or because they’re trying to be polite. They act out of the goodness of their hearts, but they’re putting up roadblocks to someone’s goals. These types of acts are usually one-sided, the researchers found. Remember, it’s okay to say, “No thanks.”
The last method, sabotage, is the most sinister. The saboteur may discourage others from eating healthy, undermine their efforts to be physically active, or take jabs at their confidence or self-esteem. Something as simple as criticizing someone for eating a salad or refusing to go on a walk with them can cause a setback.
“We need to explore this area further to develop interventions which could target family and friends and help them be more supportive in helping those they are close to lose weight,” said lead author Jane Odgen, PhD, of the University of Surrey, Guildford, England.
Like we said before, weight loss is a journey. The right support can only improve the odds of success.
Robots vs. mosquitoes
If there’s one thing robots are bad at, it’s giving solid mental health advice to people in crisis. If there’s one thing robots are very, very good at, it’s causing apocalypses. And joyous day for humanity, this time we’re not the ones being apocalypsed.
Yet.
Taiwan has a big mosquito problem. Not only do the mosquitoes in Taiwan carry dengue – among other dangerous diseases – but they’ve urbanized. Not urbanized in the sense that they’ve acquired a taste for organic coffee and avocado toast (that would be the millennial mosquito, a separate but even more terrifying creature), but more that they’ve adapted to reproduce literally anywhere and everywhere. Taiwanese mosquitoes like to breed in roadside sewer ditches, and this is where our genocidal robot comes in.
To combat the new, dangerous form of street-savvy mosquito, researchers built a robot armed with both insecticide and high-temperature, high-pressure water jets and sent it into the sewers of Kaohsiung City. The robot’s goal was simple: Whenever it came across signs of heavy mosquito breeding – eggs, larvae, pupae, and so on – the robot went to work. Utilizing both its primary weapons, the robot scrubbed numerous breeding sites across the city clean.
The researchers could just sit back and wait to see how effective their robot was. In the immediate aftermath, at various monitoring sites placed alongside the ditches, adult mosquito density fell by two-thirds in areas targeted by the robot. That’s nothing to sniff at, and it does make sense. After all, mosquitoes are quite difficult to kill in their adult stage, why not target them when they’re young and basically immobile?
The researchers saw promise with their mosquito-killing robot, but we’ve noticed a rather large issue. Killing two-thirds of mosquitoes is fine, but the third that’s left will be very angry. Very angry indeed. After all, we’re targeting the mosquito equivalent of children. Let’s hope our mosquito Terminator managed to kill mosquito Sarah Connor, or we’re going to have a big problem on our hands a bit later down the line.
This is knot what you were expecting
Physicians who aren’t surgeons probably don’t realize it, but the big thing that’s been getting between the knot-tying specialists and perfect suturing technique all these years is a lack of physics. Don’t believe us? Well, maybe you’ll believe plastic surgeon Samia Guerid, MD, of Lausanne, Switzerland: “The lack of physics-based analysis has been a limitation.” Nuff said.
That’s not enough for you, is it? Fine, we were warned.
Any surgical knot, Dr. Guerid and associates explained in a written statement, involves the “complex interplay” between six key factors: topology, geometry, elasticity, contact, friction, and polymer plasticity of the suturing filament. The strength of a suture “depends on the tension applied during the tying of the knot, [which] permanently deforms, or stretches the filament, creating a holding force.” Not enough tension and the knot comes undone, while too much snaps the filament.
For the experiment, Dr. Guerid tied a few dozen surgical knots, which were then scanned using x-ray micro–computed tomography to facilitate finite element modeling with a “3D continuum-level constitutive model for elastic-viscoplastic mechanical behavior” – no, we have no idea what that means, either – developed by the research team.
That model, and a great deal of math – so much math – allowed the researchers to define a threshold between loose and tight knots and uncover “relationships between knot strength and pretension, friction, and number of throws,” they said.
But what about the big question? The one about the ideal amount of tension? You may want to sit down. The answer to the ultimate question of the relationship between knot pretension and strength is … Did we mention that the team had its own mathematician? Their predictive model for safe knot-tying is … You’re not going to like this. The best way to teach safe knot-tying to both trainees and robots is … not ready yet.
The secret to targeting the knot tension sweet spot, for now, anyway, is still intuition gained from years of experience. Nobody ever said science was perfect … or easy … or quick.
Three big bumps on the weight-loss journey
The search for the Holy Grail. The destruction of the One Ring. The never-ending struggle to Lose Weight.
Like most legendary quests, weight loss is a journey, and we need support to help us achieve our goal. Maybe it’s gaining a new workout partner or finding a similarly-goaled Facebook Group. For a lot of people, it’s as simple as your friends and family. A recent study, however, suggests that the people closest to you may be your worst weight-loss enemies, and they might not even know it.
Researchers at the University of Surrey reviewed the literature on the positives and negatives of social support when it comes to weight loss and identified three types of negative effects: acts of sabotage, feeding behavior, and collusion.
Let’s start with the softest of intentions and work our way up. Collusion is the least negative. Friends and family may just go with the flow, even if it doesn’t agree with the goals of the person who’s trying to lose weight. It can even happen when health care professionals try to help their patients navigate or avoid obesity, ultimately killing with kindness, so to speak.
Next up, feeding behavior. Maybe you know someone whose love language is cooking. There are also people who share food because they don’t want to waste it or because they’re trying to be polite. They act out of the goodness of their hearts, but they’re putting up roadblocks to someone’s goals. These types of acts are usually one-sided, the researchers found. Remember, it’s okay to say, “No thanks.”
The last method, sabotage, is the most sinister. The saboteur may discourage others from eating healthy, undermine their efforts to be physically active, or take jabs at their confidence or self-esteem. Something as simple as criticizing someone for eating a salad or refusing to go on a walk with them can cause a setback.
“We need to explore this area further to develop interventions which could target family and friends and help them be more supportive in helping those they are close to lose weight,” said lead author Jane Odgen, PhD, of the University of Surrey, Guildford, England.
Like we said before, weight loss is a journey. The right support can only improve the odds of success.
Robots vs. mosquitoes
If there’s one thing robots are bad at, it’s giving solid mental health advice to people in crisis. If there’s one thing robots are very, very good at, it’s causing apocalypses. And joyous day for humanity, this time we’re not the ones being apocalypsed.
Yet.
Taiwan has a big mosquito problem. Not only do the mosquitoes in Taiwan carry dengue – among other dangerous diseases – but they’ve urbanized. Not urbanized in the sense that they’ve acquired a taste for organic coffee and avocado toast (that would be the millennial mosquito, a separate but even more terrifying creature), but more that they’ve adapted to reproduce literally anywhere and everywhere. Taiwanese mosquitoes like to breed in roadside sewer ditches, and this is where our genocidal robot comes in.
To combat the new, dangerous form of street-savvy mosquito, researchers built a robot armed with both insecticide and high-temperature, high-pressure water jets and sent it into the sewers of Kaohsiung City. The robot’s goal was simple: Whenever it came across signs of heavy mosquito breeding – eggs, larvae, pupae, and so on – the robot went to work. Utilizing both its primary weapons, the robot scrubbed numerous breeding sites across the city clean.
The researchers could just sit back and wait to see how effective their robot was. In the immediate aftermath, at various monitoring sites placed alongside the ditches, adult mosquito density fell by two-thirds in areas targeted by the robot. That’s nothing to sniff at, and it does make sense. After all, mosquitoes are quite difficult to kill in their adult stage, why not target them when they’re young and basically immobile?
The researchers saw promise with their mosquito-killing robot, but we’ve noticed a rather large issue. Killing two-thirds of mosquitoes is fine, but the third that’s left will be very angry. Very angry indeed. After all, we’re targeting the mosquito equivalent of children. Let’s hope our mosquito Terminator managed to kill mosquito Sarah Connor, or we’re going to have a big problem on our hands a bit later down the line.
This is knot what you were expecting
Physicians who aren’t surgeons probably don’t realize it, but the big thing that’s been getting between the knot-tying specialists and perfect suturing technique all these years is a lack of physics. Don’t believe us? Well, maybe you’ll believe plastic surgeon Samia Guerid, MD, of Lausanne, Switzerland: “The lack of physics-based analysis has been a limitation.” Nuff said.
That’s not enough for you, is it? Fine, we were warned.
Any surgical knot, Dr. Guerid and associates explained in a written statement, involves the “complex interplay” between six key factors: topology, geometry, elasticity, contact, friction, and polymer plasticity of the suturing filament. The strength of a suture “depends on the tension applied during the tying of the knot, [which] permanently deforms, or stretches the filament, creating a holding force.” Not enough tension and the knot comes undone, while too much snaps the filament.
For the experiment, Dr. Guerid tied a few dozen surgical knots, which were then scanned using x-ray micro–computed tomography to facilitate finite element modeling with a “3D continuum-level constitutive model for elastic-viscoplastic mechanical behavior” – no, we have no idea what that means, either – developed by the research team.
That model, and a great deal of math – so much math – allowed the researchers to define a threshold between loose and tight knots and uncover “relationships between knot strength and pretension, friction, and number of throws,” they said.
But what about the big question? The one about the ideal amount of tension? You may want to sit down. The answer to the ultimate question of the relationship between knot pretension and strength is … Did we mention that the team had its own mathematician? Their predictive model for safe knot-tying is … You’re not going to like this. The best way to teach safe knot-tying to both trainees and robots is … not ready yet.
The secret to targeting the knot tension sweet spot, for now, anyway, is still intuition gained from years of experience. Nobody ever said science was perfect … or easy … or quick.
Three big bumps on the weight-loss journey
The search for the Holy Grail. The destruction of the One Ring. The never-ending struggle to Lose Weight.
Like most legendary quests, weight loss is a journey, and we need support to help us achieve our goal. Maybe it’s gaining a new workout partner or finding a similarly-goaled Facebook Group. For a lot of people, it’s as simple as your friends and family. A recent study, however, suggests that the people closest to you may be your worst weight-loss enemies, and they might not even know it.
Researchers at the University of Surrey reviewed the literature on the positives and negatives of social support when it comes to weight loss and identified three types of negative effects: acts of sabotage, feeding behavior, and collusion.
Let’s start with the softest of intentions and work our way up. Collusion is the least negative. Friends and family may just go with the flow, even if it doesn’t agree with the goals of the person who’s trying to lose weight. It can even happen when health care professionals try to help their patients navigate or avoid obesity, ultimately killing with kindness, so to speak.
Next up, feeding behavior. Maybe you know someone whose love language is cooking. There are also people who share food because they don’t want to waste it or because they’re trying to be polite. They act out of the goodness of their hearts, but they’re putting up roadblocks to someone’s goals. These types of acts are usually one-sided, the researchers found. Remember, it’s okay to say, “No thanks.”
The last method, sabotage, is the most sinister. The saboteur may discourage others from eating healthy, undermine their efforts to be physically active, or take jabs at their confidence or self-esteem. Something as simple as criticizing someone for eating a salad or refusing to go on a walk with them can cause a setback.
“We need to explore this area further to develop interventions which could target family and friends and help them be more supportive in helping those they are close to lose weight,” said lead author Jane Odgen, PhD, of the University of Surrey, Guildford, England.
Like we said before, weight loss is a journey. The right support can only improve the odds of success.
Robots vs. mosquitoes
If there’s one thing robots are bad at, it’s giving solid mental health advice to people in crisis. If there’s one thing robots are very, very good at, it’s causing apocalypses. And joyous day for humanity, this time we’re not the ones being apocalypsed.
Yet.
Taiwan has a big mosquito problem. Not only do the mosquitoes in Taiwan carry dengue – among other dangerous diseases – but they’ve urbanized. Not urbanized in the sense that they’ve acquired a taste for organic coffee and avocado toast (that would be the millennial mosquito, a separate but even more terrifying creature), but more that they’ve adapted to reproduce literally anywhere and everywhere. Taiwanese mosquitoes like to breed in roadside sewer ditches, and this is where our genocidal robot comes in.
To combat the new, dangerous form of street-savvy mosquito, researchers built a robot armed with both insecticide and high-temperature, high-pressure water jets and sent it into the sewers of Kaohsiung City. The robot’s goal was simple: Whenever it came across signs of heavy mosquito breeding – eggs, larvae, pupae, and so on – the robot went to work. Utilizing both its primary weapons, the robot scrubbed numerous breeding sites across the city clean.
The researchers could just sit back and wait to see how effective their robot was. In the immediate aftermath, at various monitoring sites placed alongside the ditches, adult mosquito density fell by two-thirds in areas targeted by the robot. That’s nothing to sniff at, and it does make sense. After all, mosquitoes are quite difficult to kill in their adult stage, why not target them when they’re young and basically immobile?
The researchers saw promise with their mosquito-killing robot, but we’ve noticed a rather large issue. Killing two-thirds of mosquitoes is fine, but the third that’s left will be very angry. Very angry indeed. After all, we’re targeting the mosquito equivalent of children. Let’s hope our mosquito Terminator managed to kill mosquito Sarah Connor, or we’re going to have a big problem on our hands a bit later down the line.
This is knot what you were expecting
Physicians who aren’t surgeons probably don’t realize it, but the big thing that’s been getting between the knot-tying specialists and perfect suturing technique all these years is a lack of physics. Don’t believe us? Well, maybe you’ll believe plastic surgeon Samia Guerid, MD, of Lausanne, Switzerland: “The lack of physics-based analysis has been a limitation.” Nuff said.
That’s not enough for you, is it? Fine, we were warned.
Any surgical knot, Dr. Guerid and associates explained in a written statement, involves the “complex interplay” between six key factors: topology, geometry, elasticity, contact, friction, and polymer plasticity of the suturing filament. The strength of a suture “depends on the tension applied during the tying of the knot, [which] permanently deforms, or stretches the filament, creating a holding force.” Not enough tension and the knot comes undone, while too much snaps the filament.
For the experiment, Dr. Guerid tied a few dozen surgical knots, which were then scanned using x-ray micro–computed tomography to facilitate finite element modeling with a “3D continuum-level constitutive model for elastic-viscoplastic mechanical behavior” – no, we have no idea what that means, either – developed by the research team.
That model, and a great deal of math – so much math – allowed the researchers to define a threshold between loose and tight knots and uncover “relationships between knot strength and pretension, friction, and number of throws,” they said.
But what about the big question? The one about the ideal amount of tension? You may want to sit down. The answer to the ultimate question of the relationship between knot pretension and strength is … Did we mention that the team had its own mathematician? Their predictive model for safe knot-tying is … You’re not going to like this. The best way to teach safe knot-tying to both trainees and robots is … not ready yet.
The secret to targeting the knot tension sweet spot, for now, anyway, is still intuition gained from years of experience. Nobody ever said science was perfect … or easy … or quick.
New bill would provide greater length of time to sue doctors
A bill in the Maine legislature would have the medical malpractice statute of limitations clock start running when a patient discovers the negligence, which could be years after treatment took place. And other states could follow suit with similar bills. What danger does this pose for doctors?
As it stands, the time limit for patients to be able to bring a medical malpractice lawsuit varies by state. For physicians, this extends their period of liability and could potentially increase the number of lawsuits against them.
“The theory behind a statute of limitations is that states want to provide a reasonable, but not indefinite, amount of time for someone to bring a case to court,” says Patrick T. O’Rourke, Esq., adjunct professor at University of Colorado School of Law, Boulder.
Without a statute of limitations, people could bring claims many years after the fact, which makes it harder to obtain and preserve evidence, Mr. O’Rourke says.
In most cases, it isn’t necessary for a patient to know the full extent of their injury or that their physician acted wrongfully or negligently for the statute of limitations to begin running.
Time of injury versus time of discovery
Most states’ laws dictate that the statute of limitations begins at a set time “after the cause of action accrues.” That means that the clock starts ticking from the date of the procedure, surgery, or treatment. In most states, that time is 2 or 3 years.
This can bar some patients from taking any action at all because the statute of limitations ran out. Because of these hurdles, the proposed bill in Maine would extend the statute of limitations.
Proponents of the bill say that patients would still have 3 years to file suit; it just changes when the clock starts. But opponents feel it could open the door to a limitless system in which people have an indefinite time to sue.
Many states already have discovery rules that extend the statute of limitations when the harm was not immediately obvious to the patient. The legal expectation is that patients who have significant pain or unexpected health conditions will seek medical treatment to investigate what’s wrong. Patients who don’t address the situation promptly are not protected by the discovery rule.
“It is the injured person’s obligation, once learning of the injury, to take action to protect their rights,” says Mr. O’Rourke.
Some states have also enacted other claims requirements in medical malpractice cases that are prerequisites for bringing lawsuits that have periods attached to them. For instance, in Florida, parties have 10 days to provide relevant medical records during the investigation period for a malpractice suit, and in Maine, before filing any malpractice action, a plaintiff must file a complaint with a prelitigation screening panel.
Medical malpractice statutes of limitations by state
Although each state has a basic statute of limitations, many states also include clauses for discovery rules. For example, in Vermont, in addition to the 3-year statute of limitations, a patient can pursue legal recourse “2 years from the date the injury is or reasonably should have been discovered, whichever occurs later, but not later than 7 years from the date of the incident.”
In some states, such as Virginia, special extensions apply in cases in which fraud, concealment, or intentional misrepresentation prevented discovery of the injury within the statute of limitations. And in most states, the statute of limitations is much longer for cases in which medical malpractice involves a child, usually at least until the child turns 18.
Statutes of limitations by state
1 Year: California, Kentucky, Louisiana, Ohio, Tennessee
2 Years: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, Wyoming
2.5 Years: New York
3 Years: Washington D.C., Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin
4 Years: Minnesota
To protect yourself
Mr. O’Rourke says that if your state enacts a law that extends the statute of limitations for medical malpractice, there aren’t any proactive changes you need to make in terms of your day-to-day practice of medicine.
“Physicians should continue to provide care that is consistent with the standards of care for their specialty and ensure that the documentation accurately reflects the care they rendered,” he says.
Always be candid and up-front about a patient’s condition, Mr. O’Rourke says, especially if malpractice is on the table.
“If a physician misleads a patient about the nature or extent of an injury, that could prevent the statute of limitations from beginning to run,” he says. “Being open and honest about an injury doesn’t mean that a physician must admit any fault. The patient is owed timely, accurate, and candid information about their condition.”
Keep good records
If the statute of limitations increases, you’ll need to have access to the medical records for as long as the statute is in place, but this shouldn’t have an effect on your records keeping if you’re up to date with HIPAA compliance, says Mr. O’Rourke.
“I don’t think an extension of the statute should cause physicians to change their practices, particularly with the retention of medical records, which should be maintained consistently with HIPAA requirements irrespective of the limitations period in a particular state,” he adds.
Keep an eye on malpractice insurance rates
It’s possible that your malpractice insurance could go up as a result of laws that increase the statute of limitations. But Mr. O’Rourke thinks it likely won’t be a significant amount.
He says it’s “theoretically possible” that an increase in a limitations period could result in an increase in your malpractice insurance, since some claims that would otherwise have been barred because of time could then proceed, but the increase would be nominal.
“I would expect any increase to be fairly marginal because the majority of claims will already be accounted for on an actuarial basis,” he says. “I also don’t think that the extension of a limitations period would increase the award of damages in a particular case. The injuries should be the same under either limitations period, so the compensable loss should not increase.”
Anything that makes it easier for patients to recover should increase the cost of professional liability insurance, and vice versa, says Charles Silver, McDonald Endowed Chair in Civil Procedure at University of Texas at Austin School of Law and coauthor of “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works – Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” But the long-term trend across the country is toward declining rates of liability and declining payouts on claims.
“The likelihood of being sued successfully by a former patient is low, as is the risk of having to pay out of pocket to settle a claim,” he says. In 2022, the number of adverse reports nationally was 38,938, and out of those, 10,807 resulted in a payout.
In his research on medical malpractice in Texas, Mr. Silver says physicians who carried $1 million in coverage essentially never faced any personal liability on medical malpractice claims. “[This means] that they never had to write a check to a victim,” he says. “Insurers provided all the money. I suspect that the same is true nationwide.”
Key takeaways
Ultimately, to protect yourself and your practice, you can do the following:
- Know the statute of limitations and discovery rules for your state.
- Review your coverage with your insurer to better understand your liability.
- Keep accurate records for as long as your statute requires.
- Notify your insurer or risk management department as soon as possible in the event of an adverse outcome with a patient, Mr. O’Rourke advises.
“The most important thing a physician can do to avoid being sued, even when negligent, is to treat patients with kindness and respect,” says Mr. Silver. “Patients don’t expect doctors to be perfect, and they rarely sue doctors they like.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A bill in the Maine legislature would have the medical malpractice statute of limitations clock start running when a patient discovers the negligence, which could be years after treatment took place. And other states could follow suit with similar bills. What danger does this pose for doctors?
As it stands, the time limit for patients to be able to bring a medical malpractice lawsuit varies by state. For physicians, this extends their period of liability and could potentially increase the number of lawsuits against them.
“The theory behind a statute of limitations is that states want to provide a reasonable, but not indefinite, amount of time for someone to bring a case to court,” says Patrick T. O’Rourke, Esq., adjunct professor at University of Colorado School of Law, Boulder.
Without a statute of limitations, people could bring claims many years after the fact, which makes it harder to obtain and preserve evidence, Mr. O’Rourke says.
In most cases, it isn’t necessary for a patient to know the full extent of their injury or that their physician acted wrongfully or negligently for the statute of limitations to begin running.
Time of injury versus time of discovery
Most states’ laws dictate that the statute of limitations begins at a set time “after the cause of action accrues.” That means that the clock starts ticking from the date of the procedure, surgery, or treatment. In most states, that time is 2 or 3 years.
This can bar some patients from taking any action at all because the statute of limitations ran out. Because of these hurdles, the proposed bill in Maine would extend the statute of limitations.
Proponents of the bill say that patients would still have 3 years to file suit; it just changes when the clock starts. But opponents feel it could open the door to a limitless system in which people have an indefinite time to sue.
Many states already have discovery rules that extend the statute of limitations when the harm was not immediately obvious to the patient. The legal expectation is that patients who have significant pain or unexpected health conditions will seek medical treatment to investigate what’s wrong. Patients who don’t address the situation promptly are not protected by the discovery rule.
“It is the injured person’s obligation, once learning of the injury, to take action to protect their rights,” says Mr. O’Rourke.
Some states have also enacted other claims requirements in medical malpractice cases that are prerequisites for bringing lawsuits that have periods attached to them. For instance, in Florida, parties have 10 days to provide relevant medical records during the investigation period for a malpractice suit, and in Maine, before filing any malpractice action, a plaintiff must file a complaint with a prelitigation screening panel.
Medical malpractice statutes of limitations by state
Although each state has a basic statute of limitations, many states also include clauses for discovery rules. For example, in Vermont, in addition to the 3-year statute of limitations, a patient can pursue legal recourse “2 years from the date the injury is or reasonably should have been discovered, whichever occurs later, but not later than 7 years from the date of the incident.”
In some states, such as Virginia, special extensions apply in cases in which fraud, concealment, or intentional misrepresentation prevented discovery of the injury within the statute of limitations. And in most states, the statute of limitations is much longer for cases in which medical malpractice involves a child, usually at least until the child turns 18.
Statutes of limitations by state
1 Year: California, Kentucky, Louisiana, Ohio, Tennessee
2 Years: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, Wyoming
2.5 Years: New York
3 Years: Washington D.C., Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin
4 Years: Minnesota
To protect yourself
Mr. O’Rourke says that if your state enacts a law that extends the statute of limitations for medical malpractice, there aren’t any proactive changes you need to make in terms of your day-to-day practice of medicine.
“Physicians should continue to provide care that is consistent with the standards of care for their specialty and ensure that the documentation accurately reflects the care they rendered,” he says.
Always be candid and up-front about a patient’s condition, Mr. O’Rourke says, especially if malpractice is on the table.
“If a physician misleads a patient about the nature or extent of an injury, that could prevent the statute of limitations from beginning to run,” he says. “Being open and honest about an injury doesn’t mean that a physician must admit any fault. The patient is owed timely, accurate, and candid information about their condition.”
Keep good records
If the statute of limitations increases, you’ll need to have access to the medical records for as long as the statute is in place, but this shouldn’t have an effect on your records keeping if you’re up to date with HIPAA compliance, says Mr. O’Rourke.
“I don’t think an extension of the statute should cause physicians to change their practices, particularly with the retention of medical records, which should be maintained consistently with HIPAA requirements irrespective of the limitations period in a particular state,” he adds.
Keep an eye on malpractice insurance rates
It’s possible that your malpractice insurance could go up as a result of laws that increase the statute of limitations. But Mr. O’Rourke thinks it likely won’t be a significant amount.
He says it’s “theoretically possible” that an increase in a limitations period could result in an increase in your malpractice insurance, since some claims that would otherwise have been barred because of time could then proceed, but the increase would be nominal.
“I would expect any increase to be fairly marginal because the majority of claims will already be accounted for on an actuarial basis,” he says. “I also don’t think that the extension of a limitations period would increase the award of damages in a particular case. The injuries should be the same under either limitations period, so the compensable loss should not increase.”
Anything that makes it easier for patients to recover should increase the cost of professional liability insurance, and vice versa, says Charles Silver, McDonald Endowed Chair in Civil Procedure at University of Texas at Austin School of Law and coauthor of “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works – Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” But the long-term trend across the country is toward declining rates of liability and declining payouts on claims.
“The likelihood of being sued successfully by a former patient is low, as is the risk of having to pay out of pocket to settle a claim,” he says. In 2022, the number of adverse reports nationally was 38,938, and out of those, 10,807 resulted in a payout.
In his research on medical malpractice in Texas, Mr. Silver says physicians who carried $1 million in coverage essentially never faced any personal liability on medical malpractice claims. “[This means] that they never had to write a check to a victim,” he says. “Insurers provided all the money. I suspect that the same is true nationwide.”
Key takeaways
Ultimately, to protect yourself and your practice, you can do the following:
- Know the statute of limitations and discovery rules for your state.
- Review your coverage with your insurer to better understand your liability.
- Keep accurate records for as long as your statute requires.
- Notify your insurer or risk management department as soon as possible in the event of an adverse outcome with a patient, Mr. O’Rourke advises.
“The most important thing a physician can do to avoid being sued, even when negligent, is to treat patients with kindness and respect,” says Mr. Silver. “Patients don’t expect doctors to be perfect, and they rarely sue doctors they like.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A bill in the Maine legislature would have the medical malpractice statute of limitations clock start running when a patient discovers the negligence, which could be years after treatment took place. And other states could follow suit with similar bills. What danger does this pose for doctors?
As it stands, the time limit for patients to be able to bring a medical malpractice lawsuit varies by state. For physicians, this extends their period of liability and could potentially increase the number of lawsuits against them.
“The theory behind a statute of limitations is that states want to provide a reasonable, but not indefinite, amount of time for someone to bring a case to court,” says Patrick T. O’Rourke, Esq., adjunct professor at University of Colorado School of Law, Boulder.
Without a statute of limitations, people could bring claims many years after the fact, which makes it harder to obtain and preserve evidence, Mr. O’Rourke says.
In most cases, it isn’t necessary for a patient to know the full extent of their injury or that their physician acted wrongfully or negligently for the statute of limitations to begin running.
Time of injury versus time of discovery
Most states’ laws dictate that the statute of limitations begins at a set time “after the cause of action accrues.” That means that the clock starts ticking from the date of the procedure, surgery, or treatment. In most states, that time is 2 or 3 years.
This can bar some patients from taking any action at all because the statute of limitations ran out. Because of these hurdles, the proposed bill in Maine would extend the statute of limitations.
Proponents of the bill say that patients would still have 3 years to file suit; it just changes when the clock starts. But opponents feel it could open the door to a limitless system in which people have an indefinite time to sue.
Many states already have discovery rules that extend the statute of limitations when the harm was not immediately obvious to the patient. The legal expectation is that patients who have significant pain or unexpected health conditions will seek medical treatment to investigate what’s wrong. Patients who don’t address the situation promptly are not protected by the discovery rule.
“It is the injured person’s obligation, once learning of the injury, to take action to protect their rights,” says Mr. O’Rourke.
Some states have also enacted other claims requirements in medical malpractice cases that are prerequisites for bringing lawsuits that have periods attached to them. For instance, in Florida, parties have 10 days to provide relevant medical records during the investigation period for a malpractice suit, and in Maine, before filing any malpractice action, a plaintiff must file a complaint with a prelitigation screening panel.
Medical malpractice statutes of limitations by state
Although each state has a basic statute of limitations, many states also include clauses for discovery rules. For example, in Vermont, in addition to the 3-year statute of limitations, a patient can pursue legal recourse “2 years from the date the injury is or reasonably should have been discovered, whichever occurs later, but not later than 7 years from the date of the incident.”
In some states, such as Virginia, special extensions apply in cases in which fraud, concealment, or intentional misrepresentation prevented discovery of the injury within the statute of limitations. And in most states, the statute of limitations is much longer for cases in which medical malpractice involves a child, usually at least until the child turns 18.
Statutes of limitations by state
1 Year: California, Kentucky, Louisiana, Ohio, Tennessee
2 Years: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, Wyoming
2.5 Years: New York
3 Years: Washington D.C., Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin
4 Years: Minnesota
To protect yourself
Mr. O’Rourke says that if your state enacts a law that extends the statute of limitations for medical malpractice, there aren’t any proactive changes you need to make in terms of your day-to-day practice of medicine.
“Physicians should continue to provide care that is consistent with the standards of care for their specialty and ensure that the documentation accurately reflects the care they rendered,” he says.
Always be candid and up-front about a patient’s condition, Mr. O’Rourke says, especially if malpractice is on the table.
“If a physician misleads a patient about the nature or extent of an injury, that could prevent the statute of limitations from beginning to run,” he says. “Being open and honest about an injury doesn’t mean that a physician must admit any fault. The patient is owed timely, accurate, and candid information about their condition.”
Keep good records
If the statute of limitations increases, you’ll need to have access to the medical records for as long as the statute is in place, but this shouldn’t have an effect on your records keeping if you’re up to date with HIPAA compliance, says Mr. O’Rourke.
“I don’t think an extension of the statute should cause physicians to change their practices, particularly with the retention of medical records, which should be maintained consistently with HIPAA requirements irrespective of the limitations period in a particular state,” he adds.
Keep an eye on malpractice insurance rates
It’s possible that your malpractice insurance could go up as a result of laws that increase the statute of limitations. But Mr. O’Rourke thinks it likely won’t be a significant amount.
He says it’s “theoretically possible” that an increase in a limitations period could result in an increase in your malpractice insurance, since some claims that would otherwise have been barred because of time could then proceed, but the increase would be nominal.
“I would expect any increase to be fairly marginal because the majority of claims will already be accounted for on an actuarial basis,” he says. “I also don’t think that the extension of a limitations period would increase the award of damages in a particular case. The injuries should be the same under either limitations period, so the compensable loss should not increase.”
Anything that makes it easier for patients to recover should increase the cost of professional liability insurance, and vice versa, says Charles Silver, McDonald Endowed Chair in Civil Procedure at University of Texas at Austin School of Law and coauthor of “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works – Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” But the long-term trend across the country is toward declining rates of liability and declining payouts on claims.
“The likelihood of being sued successfully by a former patient is low, as is the risk of having to pay out of pocket to settle a claim,” he says. In 2022, the number of adverse reports nationally was 38,938, and out of those, 10,807 resulted in a payout.
In his research on medical malpractice in Texas, Mr. Silver says physicians who carried $1 million in coverage essentially never faced any personal liability on medical malpractice claims. “[This means] that they never had to write a check to a victim,” he says. “Insurers provided all the money. I suspect that the same is true nationwide.”
Key takeaways
Ultimately, to protect yourself and your practice, you can do the following:
- Know the statute of limitations and discovery rules for your state.
- Review your coverage with your insurer to better understand your liability.
- Keep accurate records for as long as your statute requires.
- Notify your insurer or risk management department as soon as possible in the event of an adverse outcome with a patient, Mr. O’Rourke advises.
“The most important thing a physician can do to avoid being sued, even when negligent, is to treat patients with kindness and respect,” says Mr. Silver. “Patients don’t expect doctors to be perfect, and they rarely sue doctors they like.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.