User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
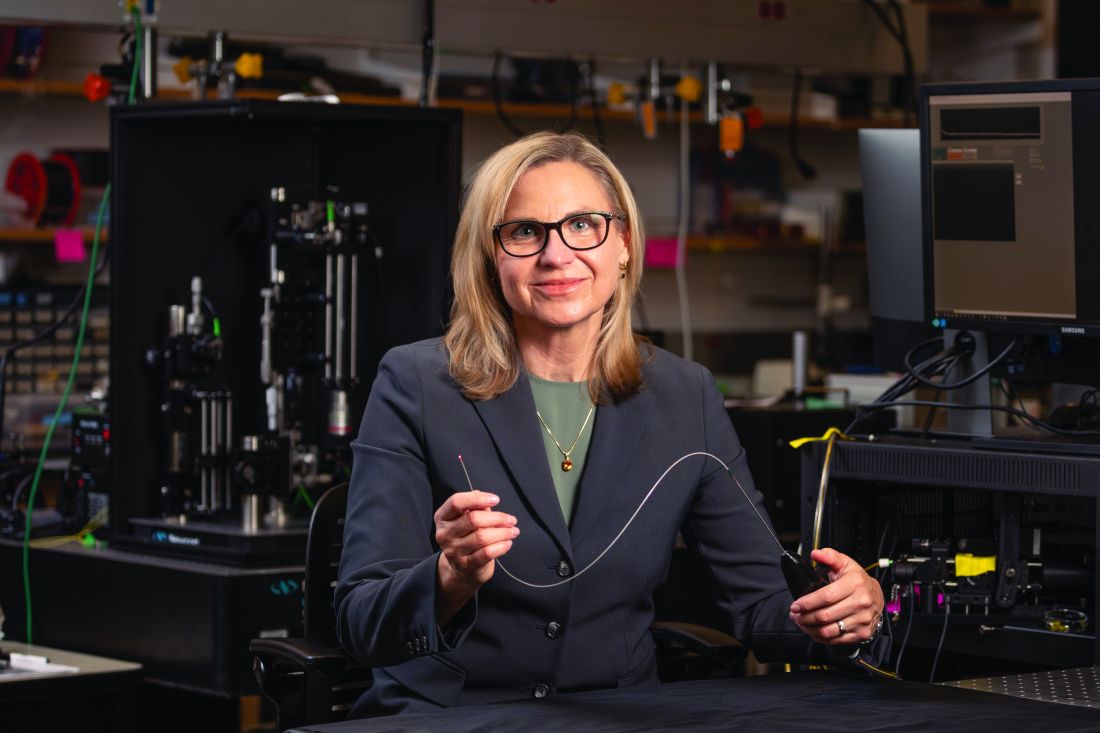
Imaging techniques will revolutionize cancer detection, expert predicts
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2023
The metaverse is the dermatologist’s ally
MADRID – There are endless possibilities within the dermoverse (a term coined by joining “dermatology” and “metaverse”), from a robot office assistant to the brand new world it offers for virtual training and simulation.
A group of dermatologists expert in new technologies came together at the 50th National Congress of the Spanish Academy for Dermatology and Venereology to discuss the metaverse: that sum of all virtual spaces that bridges physical and digital reality, where users interact through their avatars and where these experts are discovering new opportunities for treating their patients. The metaverse and AI offer a massive opportunity for improving telehealth visits, immersive surgical planning, or virtual training using 3-D skin models. These are just a few examples of what this technology may eventually provide.
“The possibilities offered by the metaverse in the field of dermatology could be endless,” explained Miriam Fernández-Parrado, MD, dermatologist at Navarre Hospital, Pamplona, Spain. To her, “the metaverse could mean a step forward in teledermatology, which has come of age as a result of the pandemic.” These past few years have shown that it’s possible to perform some screenings online. This, in turn, has produced significant time and cost savings, along with greater efficacy in initial screening and early detection of serious diseases.
The overall percentage of cases that are potentially treatable in absentia is estimated to exceed 70%. “This isn’t a matter of replacing in-person visits but of finding a quality alternative that, far from dehumanizing the doctor-patient relationship, helps to satisfy the growing need for this relationship,” said Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Always on duty
Julián Conejo-Mir, MD, PhD, professor and head of dermatology at the Virgen del Rocío Hospital in Seville, Spain, told this news organization that AI will help with day-to-day interactions with patients. It’s already a reality. “But to say that with a simple photo, we can address 70% of dermatology cases without being physically present with our patients – I don’t think that will become a reality in the next 20 years.”
Currently, algorithms can identify tumors with high success rates (80%-90%) using photographs and dermoscopic images; rates increase significantly when both kinds of images are available. These high success rates are possible because tumor morphology is stationary. “However, for inflammatory conditions, accurate diagnosis generally doesn’t exceed 60%, since these are conditions in which morphology can change a lot from one day to the next and can vary significantly, depending on their anatomic location or the patient’s age.”
Maybe once metaclinics, with 3-D virtual reality, have been established and clinicians can see the patient in real time from their offices, the rate of accurate diagnosis will reach 70%, especially with patients who have limited mobility or who live at a distance from the hospital. “But that’s still 10-15 years away, since more powerful computers are needed, most likely quantum computers,” cautioned Dr. Conejo-Mir.
The patient’s ally
In clinical practice, facilitating access to the dermoverse may help reduce pain and divert the patient’s attention, especially during in-person visits that require bothersome or uncomfortable interventions. “This is especially effective in pediatric dermatology, since settings of immersive virtual reality may contribute to relaxation among children,” explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado. She also sees potential applications among patients who need surgery. The metaverse would allow them to preview a simulation of their operation before undergoing it, thus reducing their anxiety and allaying their fears about these procedures.
Two lines are being pursued: automated diagnosis for telehealth consultations, which are primarily for tumors, and robotic office assistants.
“We have been using the first one in clinical practice, and we can achieve a success rate of 85%-90%.” The second one is much more complex, “and we’re having a hard time moving it forward within our research team, since it doesn’t involve only one algorithm. Instead, it requires five algorithms working together simultaneously (chatbot, automatic writing, image analysis, selecting the most appropriate treatment, ability to make recommendations, and even an additional one involving feelings),” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A wise consultant
Dr. Conejo-Mir offered examples of how this might work in the near future. “In under 5 years, you’ll be able to sit in front of a computer or your smartphone, talk to an avatar that we’re able to select (sex, appearance, age, kind/serious), show the avatar your lesions, and it will tell us a basic diagnostic impression and even the treatment.”
With virtual learning, physicians can also gather knowledge or take refresher courses, using skin models in augmented reality with tumors and other skin lesions, or using immersive simulation courses that aid learning. Digital models that replicate the anatomy and elasticity of the skin or other characteristics unique to the patient can be used to reach decisions regarding surgeries and to practice interventions before entering the operating room, explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Optimal virtual training
Virtual reality and simulation will doubtless play a major role in this promising field of using these devices for training purposes. “There will be virtual dermatology clinics or metaclinics, where you can do everything with virtual simulated patients, from gaining experience in interviews or health histories (even with patients who are difficult to deal with), to taking biopsies and performing interventions,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A recent study titled “How the World Sees the Metaverse and Extended Reality” gathered data from 29 countries regarding the next 10 years. One of the greatest benefits of this technology is expected in health resources (59%), even more than in the trading of digital assets. While it is difficult to predict when the dermoverse will be in operation, Dr. Fernández-Parrado says she’s a techno-optimist. Together with Dr. Héctor Perandones, MD, a dermatologist at the University Healthcare Complex in León, Spain, and coauthor with Dr. Fernández-Parrado of the article, “A New Universe in Dermatology: From Metaverse to Dermoverse,” she’s convinced that “if we can imagine it, we can create it.”
A differential diagnostician
Over the past 10 years, AI has become a major ally of dermatology, providing new techniques that simplify the diagnosis and treatment of patients. There are many applications for which it adds tremendous value in dermatology: establishing precise differential diagnoses for common diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or acne; eveloping personalized therapeutic protocols; and predicting medium- and long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, in onco-dermatology, AI has helped to automate the diagnosis of skin tumors by making it possible to differentiate between melanocytic and nonmelanocytic lesions. This distinction promotes early diagnosis and helps produce screening systems that are capable of prioritizing cases on the basis of their seriousness.
When asked whether any group has published any promising tools with good preliminary results, Dr. Conejo-Mir stated that his group has produced three articles that have been published in top-ranking journals. In these articles, “we explain our experience with artificial intelligence in Mohs surgery, in automated diagnosis, and for calculating the thickness of melanomas.” The eight-person research team, which comprises dermatologists and software engineers, has been working together in this area for the past 4 years.
Aesthetic dermatology
Unlike other specialists, dermatologists have 4-D vision when it comes to aesthetics, since they are also skin experts. AI plays a major role in aesthetic dermatology. It supports this specialty by providing a greater analytic capacity and by evaluating the procedure and technique to be used. “It’s going to help us think and make decisions. It has taken great strides in aesthetic dermatology, especially when it comes to techniques and products. There have been products like collagen, hyaluronic acid, then thread lifts ... Also, different techniques have been developed, like Botox, for example. Before, Botox was given following one method. Now, there are other methods,” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
He explained, “We have analyzed the facial image to detect wrinkles, spots, enlarged pores, et cetera, to see whether there are any lesions, and, depending on what the machine says you have, it provides you with a personalized treatment. It tells you the pattern of care that the patient should follow. It also tells you what you’re going to do, whether or not there is any problem, depending on the location and on what the person is like, et cetera. Then, for follow-up, you’re given an AI program that tells you if you’re doing well or not. Lastly, it gives you product recommendations.
“We are among the specialties that are going through the most change,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
An intrusive technology?
AI will be a tremendous help in decision-making, to the point where “in 4 or 5 years, it will become indispensable, just like the loupe in years past, and then the dermatoscope.” However, the machine will have to depend on human beings. “They won’t replace us, but they will become unavoidable assistants in our day-to-day medical practice.”
Questions have arisen regarding the potential dangers of these new technologies, like that of reducing the number of dermatologists within the population, and whether they might encourage intrusiveness. Dr. Conejo-Mir made no bones about it. “AI will never cut back the number of specialists. That is false. When AI supports us in teledermatology, even currently on our team, it spits out information, but the one making the decision is the practitioner, not the machine.”
AI is a tool but is not in itself something that treats patients. It is akin to the dermatoscope. Dermatologists use these tools every day, and they help arrive at diagnoses in difficult cases, but they are not a replacement for humans. “At least for the next 50 years, then we’ll see. In 2050 is when they say AI will surpass humans in its intelligence and reasoning capacity,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
Dr. Conejo-Mir has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – There are endless possibilities within the dermoverse (a term coined by joining “dermatology” and “metaverse”), from a robot office assistant to the brand new world it offers for virtual training and simulation.
A group of dermatologists expert in new technologies came together at the 50th National Congress of the Spanish Academy for Dermatology and Venereology to discuss the metaverse: that sum of all virtual spaces that bridges physical and digital reality, where users interact through their avatars and where these experts are discovering new opportunities for treating their patients. The metaverse and AI offer a massive opportunity for improving telehealth visits, immersive surgical planning, or virtual training using 3-D skin models. These are just a few examples of what this technology may eventually provide.
“The possibilities offered by the metaverse in the field of dermatology could be endless,” explained Miriam Fernández-Parrado, MD, dermatologist at Navarre Hospital, Pamplona, Spain. To her, “the metaverse could mean a step forward in teledermatology, which has come of age as a result of the pandemic.” These past few years have shown that it’s possible to perform some screenings online. This, in turn, has produced significant time and cost savings, along with greater efficacy in initial screening and early detection of serious diseases.
The overall percentage of cases that are potentially treatable in absentia is estimated to exceed 70%. “This isn’t a matter of replacing in-person visits but of finding a quality alternative that, far from dehumanizing the doctor-patient relationship, helps to satisfy the growing need for this relationship,” said Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Always on duty
Julián Conejo-Mir, MD, PhD, professor and head of dermatology at the Virgen del Rocío Hospital in Seville, Spain, told this news organization that AI will help with day-to-day interactions with patients. It’s already a reality. “But to say that with a simple photo, we can address 70% of dermatology cases without being physically present with our patients – I don’t think that will become a reality in the next 20 years.”
Currently, algorithms can identify tumors with high success rates (80%-90%) using photographs and dermoscopic images; rates increase significantly when both kinds of images are available. These high success rates are possible because tumor morphology is stationary. “However, for inflammatory conditions, accurate diagnosis generally doesn’t exceed 60%, since these are conditions in which morphology can change a lot from one day to the next and can vary significantly, depending on their anatomic location or the patient’s age.”
Maybe once metaclinics, with 3-D virtual reality, have been established and clinicians can see the patient in real time from their offices, the rate of accurate diagnosis will reach 70%, especially with patients who have limited mobility or who live at a distance from the hospital. “But that’s still 10-15 years away, since more powerful computers are needed, most likely quantum computers,” cautioned Dr. Conejo-Mir.
The patient’s ally
In clinical practice, facilitating access to the dermoverse may help reduce pain and divert the patient’s attention, especially during in-person visits that require bothersome or uncomfortable interventions. “This is especially effective in pediatric dermatology, since settings of immersive virtual reality may contribute to relaxation among children,” explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado. She also sees potential applications among patients who need surgery. The metaverse would allow them to preview a simulation of their operation before undergoing it, thus reducing their anxiety and allaying their fears about these procedures.
Two lines are being pursued: automated diagnosis for telehealth consultations, which are primarily for tumors, and robotic office assistants.
“We have been using the first one in clinical practice, and we can achieve a success rate of 85%-90%.” The second one is much more complex, “and we’re having a hard time moving it forward within our research team, since it doesn’t involve only one algorithm. Instead, it requires five algorithms working together simultaneously (chatbot, automatic writing, image analysis, selecting the most appropriate treatment, ability to make recommendations, and even an additional one involving feelings),” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A wise consultant
Dr. Conejo-Mir offered examples of how this might work in the near future. “In under 5 years, you’ll be able to sit in front of a computer or your smartphone, talk to an avatar that we’re able to select (sex, appearance, age, kind/serious), show the avatar your lesions, and it will tell us a basic diagnostic impression and even the treatment.”
With virtual learning, physicians can also gather knowledge or take refresher courses, using skin models in augmented reality with tumors and other skin lesions, or using immersive simulation courses that aid learning. Digital models that replicate the anatomy and elasticity of the skin or other characteristics unique to the patient can be used to reach decisions regarding surgeries and to practice interventions before entering the operating room, explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Optimal virtual training
Virtual reality and simulation will doubtless play a major role in this promising field of using these devices for training purposes. “There will be virtual dermatology clinics or metaclinics, where you can do everything with virtual simulated patients, from gaining experience in interviews or health histories (even with patients who are difficult to deal with), to taking biopsies and performing interventions,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A recent study titled “How the World Sees the Metaverse and Extended Reality” gathered data from 29 countries regarding the next 10 years. One of the greatest benefits of this technology is expected in health resources (59%), even more than in the trading of digital assets. While it is difficult to predict when the dermoverse will be in operation, Dr. Fernández-Parrado says she’s a techno-optimist. Together with Dr. Héctor Perandones, MD, a dermatologist at the University Healthcare Complex in León, Spain, and coauthor with Dr. Fernández-Parrado of the article, “A New Universe in Dermatology: From Metaverse to Dermoverse,” she’s convinced that “if we can imagine it, we can create it.”
A differential diagnostician
Over the past 10 years, AI has become a major ally of dermatology, providing new techniques that simplify the diagnosis and treatment of patients. There are many applications for which it adds tremendous value in dermatology: establishing precise differential diagnoses for common diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or acne; eveloping personalized therapeutic protocols; and predicting medium- and long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, in onco-dermatology, AI has helped to automate the diagnosis of skin tumors by making it possible to differentiate between melanocytic and nonmelanocytic lesions. This distinction promotes early diagnosis and helps produce screening systems that are capable of prioritizing cases on the basis of their seriousness.
When asked whether any group has published any promising tools with good preliminary results, Dr. Conejo-Mir stated that his group has produced three articles that have been published in top-ranking journals. In these articles, “we explain our experience with artificial intelligence in Mohs surgery, in automated diagnosis, and for calculating the thickness of melanomas.” The eight-person research team, which comprises dermatologists and software engineers, has been working together in this area for the past 4 years.
Aesthetic dermatology
Unlike other specialists, dermatologists have 4-D vision when it comes to aesthetics, since they are also skin experts. AI plays a major role in aesthetic dermatology. It supports this specialty by providing a greater analytic capacity and by evaluating the procedure and technique to be used. “It’s going to help us think and make decisions. It has taken great strides in aesthetic dermatology, especially when it comes to techniques and products. There have been products like collagen, hyaluronic acid, then thread lifts ... Also, different techniques have been developed, like Botox, for example. Before, Botox was given following one method. Now, there are other methods,” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
He explained, “We have analyzed the facial image to detect wrinkles, spots, enlarged pores, et cetera, to see whether there are any lesions, and, depending on what the machine says you have, it provides you with a personalized treatment. It tells you the pattern of care that the patient should follow. It also tells you what you’re going to do, whether or not there is any problem, depending on the location and on what the person is like, et cetera. Then, for follow-up, you’re given an AI program that tells you if you’re doing well or not. Lastly, it gives you product recommendations.
“We are among the specialties that are going through the most change,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
An intrusive technology?
AI will be a tremendous help in decision-making, to the point where “in 4 or 5 years, it will become indispensable, just like the loupe in years past, and then the dermatoscope.” However, the machine will have to depend on human beings. “They won’t replace us, but they will become unavoidable assistants in our day-to-day medical practice.”
Questions have arisen regarding the potential dangers of these new technologies, like that of reducing the number of dermatologists within the population, and whether they might encourage intrusiveness. Dr. Conejo-Mir made no bones about it. “AI will never cut back the number of specialists. That is false. When AI supports us in teledermatology, even currently on our team, it spits out information, but the one making the decision is the practitioner, not the machine.”
AI is a tool but is not in itself something that treats patients. It is akin to the dermatoscope. Dermatologists use these tools every day, and they help arrive at diagnoses in difficult cases, but they are not a replacement for humans. “At least for the next 50 years, then we’ll see. In 2050 is when they say AI will surpass humans in its intelligence and reasoning capacity,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
Dr. Conejo-Mir has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – There are endless possibilities within the dermoverse (a term coined by joining “dermatology” and “metaverse”), from a robot office assistant to the brand new world it offers for virtual training and simulation.
A group of dermatologists expert in new technologies came together at the 50th National Congress of the Spanish Academy for Dermatology and Venereology to discuss the metaverse: that sum of all virtual spaces that bridges physical and digital reality, where users interact through their avatars and where these experts are discovering new opportunities for treating their patients. The metaverse and AI offer a massive opportunity for improving telehealth visits, immersive surgical planning, or virtual training using 3-D skin models. These are just a few examples of what this technology may eventually provide.
“The possibilities offered by the metaverse in the field of dermatology could be endless,” explained Miriam Fernández-Parrado, MD, dermatologist at Navarre Hospital, Pamplona, Spain. To her, “the metaverse could mean a step forward in teledermatology, which has come of age as a result of the pandemic.” These past few years have shown that it’s possible to perform some screenings online. This, in turn, has produced significant time and cost savings, along with greater efficacy in initial screening and early detection of serious diseases.
The overall percentage of cases that are potentially treatable in absentia is estimated to exceed 70%. “This isn’t a matter of replacing in-person visits but of finding a quality alternative that, far from dehumanizing the doctor-patient relationship, helps to satisfy the growing need for this relationship,” said Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Always on duty
Julián Conejo-Mir, MD, PhD, professor and head of dermatology at the Virgen del Rocío Hospital in Seville, Spain, told this news organization that AI will help with day-to-day interactions with patients. It’s already a reality. “But to say that with a simple photo, we can address 70% of dermatology cases without being physically present with our patients – I don’t think that will become a reality in the next 20 years.”
Currently, algorithms can identify tumors with high success rates (80%-90%) using photographs and dermoscopic images; rates increase significantly when both kinds of images are available. These high success rates are possible because tumor morphology is stationary. “However, for inflammatory conditions, accurate diagnosis generally doesn’t exceed 60%, since these are conditions in which morphology can change a lot from one day to the next and can vary significantly, depending on their anatomic location or the patient’s age.”
Maybe once metaclinics, with 3-D virtual reality, have been established and clinicians can see the patient in real time from their offices, the rate of accurate diagnosis will reach 70%, especially with patients who have limited mobility or who live at a distance from the hospital. “But that’s still 10-15 years away, since more powerful computers are needed, most likely quantum computers,” cautioned Dr. Conejo-Mir.
The patient’s ally
In clinical practice, facilitating access to the dermoverse may help reduce pain and divert the patient’s attention, especially during in-person visits that require bothersome or uncomfortable interventions. “This is especially effective in pediatric dermatology, since settings of immersive virtual reality may contribute to relaxation among children,” explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado. She also sees potential applications among patients who need surgery. The metaverse would allow them to preview a simulation of their operation before undergoing it, thus reducing their anxiety and allaying their fears about these procedures.
Two lines are being pursued: automated diagnosis for telehealth consultations, which are primarily for tumors, and robotic office assistants.
“We have been using the first one in clinical practice, and we can achieve a success rate of 85%-90%.” The second one is much more complex, “and we’re having a hard time moving it forward within our research team, since it doesn’t involve only one algorithm. Instead, it requires five algorithms working together simultaneously (chatbot, automatic writing, image analysis, selecting the most appropriate treatment, ability to make recommendations, and even an additional one involving feelings),” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A wise consultant
Dr. Conejo-Mir offered examples of how this might work in the near future. “In under 5 years, you’ll be able to sit in front of a computer or your smartphone, talk to an avatar that we’re able to select (sex, appearance, age, kind/serious), show the avatar your lesions, and it will tell us a basic diagnostic impression and even the treatment.”
With virtual learning, physicians can also gather knowledge or take refresher courses, using skin models in augmented reality with tumors and other skin lesions, or using immersive simulation courses that aid learning. Digital models that replicate the anatomy and elasticity of the skin or other characteristics unique to the patient can be used to reach decisions regarding surgeries and to practice interventions before entering the operating room, explained Dr. Fernández-Parrado.
Optimal virtual training
Virtual reality and simulation will doubtless play a major role in this promising field of using these devices for training purposes. “There will be virtual dermatology clinics or metaclinics, where you can do everything with virtual simulated patients, from gaining experience in interviews or health histories (even with patients who are difficult to deal with), to taking biopsies and performing interventions,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
A recent study titled “How the World Sees the Metaverse and Extended Reality” gathered data from 29 countries regarding the next 10 years. One of the greatest benefits of this technology is expected in health resources (59%), even more than in the trading of digital assets. While it is difficult to predict when the dermoverse will be in operation, Dr. Fernández-Parrado says she’s a techno-optimist. Together with Dr. Héctor Perandones, MD, a dermatologist at the University Healthcare Complex in León, Spain, and coauthor with Dr. Fernández-Parrado of the article, “A New Universe in Dermatology: From Metaverse to Dermoverse,” she’s convinced that “if we can imagine it, we can create it.”
A differential diagnostician
Over the past 10 years, AI has become a major ally of dermatology, providing new techniques that simplify the diagnosis and treatment of patients. There are many applications for which it adds tremendous value in dermatology: establishing precise differential diagnoses for common diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or acne; eveloping personalized therapeutic protocols; and predicting medium- and long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, in onco-dermatology, AI has helped to automate the diagnosis of skin tumors by making it possible to differentiate between melanocytic and nonmelanocytic lesions. This distinction promotes early diagnosis and helps produce screening systems that are capable of prioritizing cases on the basis of their seriousness.
When asked whether any group has published any promising tools with good preliminary results, Dr. Conejo-Mir stated that his group has produced three articles that have been published in top-ranking journals. In these articles, “we explain our experience with artificial intelligence in Mohs surgery, in automated diagnosis, and for calculating the thickness of melanomas.” The eight-person research team, which comprises dermatologists and software engineers, has been working together in this area for the past 4 years.
Aesthetic dermatology
Unlike other specialists, dermatologists have 4-D vision when it comes to aesthetics, since they are also skin experts. AI plays a major role in aesthetic dermatology. It supports this specialty by providing a greater analytic capacity and by evaluating the procedure and technique to be used. “It’s going to help us think and make decisions. It has taken great strides in aesthetic dermatology, especially when it comes to techniques and products. There have been products like collagen, hyaluronic acid, then thread lifts ... Also, different techniques have been developed, like Botox, for example. Before, Botox was given following one method. Now, there are other methods,” explained Dr. Conejo-Mir.
He explained, “We have analyzed the facial image to detect wrinkles, spots, enlarged pores, et cetera, to see whether there are any lesions, and, depending on what the machine says you have, it provides you with a personalized treatment. It tells you the pattern of care that the patient should follow. It also tells you what you’re going to do, whether or not there is any problem, depending on the location and on what the person is like, et cetera. Then, for follow-up, you’re given an AI program that tells you if you’re doing well or not. Lastly, it gives you product recommendations.
“We are among the specialties that are going through the most change,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
An intrusive technology?
AI will be a tremendous help in decision-making, to the point where “in 4 or 5 years, it will become indispensable, just like the loupe in years past, and then the dermatoscope.” However, the machine will have to depend on human beings. “They won’t replace us, but they will become unavoidable assistants in our day-to-day medical practice.”
Questions have arisen regarding the potential dangers of these new technologies, like that of reducing the number of dermatologists within the population, and whether they might encourage intrusiveness. Dr. Conejo-Mir made no bones about it. “AI will never cut back the number of specialists. That is false. When AI supports us in teledermatology, even currently on our team, it spits out information, but the one making the decision is the practitioner, not the machine.”
AI is a tool but is not in itself something that treats patients. It is akin to the dermatoscope. Dermatologists use these tools every day, and they help arrive at diagnoses in difficult cases, but they are not a replacement for humans. “At least for the next 50 years, then we’ll see. In 2050 is when they say AI will surpass humans in its intelligence and reasoning capacity,” said Dr. Conejo-Mir.
Dr. Conejo-Mir has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves ritlecitinib for ages 12 and up for alopecia areata
Taken as a once-daily pill, ritlecitinib is a dual inhibitor of the TEC family of tyrosine kinases and of Janus kinase 3 (JAK3). The recommended dose of ritlecitinib, which will be marketed as Litfulo, is 50 mg once a day, according to the statement announcing the approval from Pfizer.
It is the second JAK inhibitor approved for treating alopecia areata, following approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) in June 2022 for AA in adults. Ritlecitinib is the first JAK inhibitor approved for children ages 12 and older with AA.
The European Medicines Agency has also accepted the Marketing Authorization Application for ritlecitinib in the same population and a decision is expected in the fourth quarter of this year.
Approval based on ALLEGRO trials
Approval was based on previously announced results from trials, including the phase 2b/3 ALLEGRO study of ritlecitinib in 718 patients aged 12 years and older with alopecia areata, with 50% of more scalp hair loss, as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT), including patients with alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) and alopecia universalis (complete scalp, face, and body hair loss).
Patients in the trial were experiencing a current episode of alopecia areata that had lasted between 6 months and 10 years. They were randomized to receive once-daily ritlecitinib at doses of 30 mg or 50 mg (with or without 1 month of initial treatment with once-daily ritlecitinib 200 mg), ritlecitinib 10 mg, or placebo.
Statistically significantly higher proportions of patients treated with ritlecitinib 30 mg and 50 mg (with or without the loading dose) had 80% or more scalp hair coverage, as measured by a SALT score of 20 or less after 6 months of treatment versus placebo. After 6 months of treatment, among those on the 50-mg dose, 23% had achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 2% of those on placebo. The results were published in The Lancet.
According to the company release, efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib was consistent between those ages 12-17 and adults, and the most common adverse events reported in the study, in at least 4% of patients treated with ritlecitinib, were headache (10.8%), diarrhea (10%), acne (6.2%), rash (5.4%), and urticaria (4.6%).
Ritlecitinib labeling includes the boxed warning about the risk for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, which is included in the labels for other JAK inhibitors.
Ritlecitinib evaluated for other diseases
In addition to alopecia areata, ritlecitinib has shown efficacy and acceptable safety in treating ulcerative colitis and is being evaluated for treating vitiligo, Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
In the statement, the company says that ritlecitinib will be available “in the coming weeks.” The manufacturer says it also has completed regulatory submissions for ritlecitinib in the United Kingdom, China, and Japan, and expects decisions this year.
Alopecia areata affects about 6.8 million people in the United States and 147 million globally.
In a statement, Nicole Friedland, president and CEO of the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, said that NAAF “is thrilled to have a second FDA-approved treatment for alopecia areata, which is the first approved for adolescents.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taken as a once-daily pill, ritlecitinib is a dual inhibitor of the TEC family of tyrosine kinases and of Janus kinase 3 (JAK3). The recommended dose of ritlecitinib, which will be marketed as Litfulo, is 50 mg once a day, according to the statement announcing the approval from Pfizer.
It is the second JAK inhibitor approved for treating alopecia areata, following approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) in June 2022 for AA in adults. Ritlecitinib is the first JAK inhibitor approved for children ages 12 and older with AA.
The European Medicines Agency has also accepted the Marketing Authorization Application for ritlecitinib in the same population and a decision is expected in the fourth quarter of this year.
Approval based on ALLEGRO trials
Approval was based on previously announced results from trials, including the phase 2b/3 ALLEGRO study of ritlecitinib in 718 patients aged 12 years and older with alopecia areata, with 50% of more scalp hair loss, as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT), including patients with alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) and alopecia universalis (complete scalp, face, and body hair loss).
Patients in the trial were experiencing a current episode of alopecia areata that had lasted between 6 months and 10 years. They were randomized to receive once-daily ritlecitinib at doses of 30 mg or 50 mg (with or without 1 month of initial treatment with once-daily ritlecitinib 200 mg), ritlecitinib 10 mg, or placebo.
Statistically significantly higher proportions of patients treated with ritlecitinib 30 mg and 50 mg (with or without the loading dose) had 80% or more scalp hair coverage, as measured by a SALT score of 20 or less after 6 months of treatment versus placebo. After 6 months of treatment, among those on the 50-mg dose, 23% had achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 2% of those on placebo. The results were published in The Lancet.
According to the company release, efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib was consistent between those ages 12-17 and adults, and the most common adverse events reported in the study, in at least 4% of patients treated with ritlecitinib, were headache (10.8%), diarrhea (10%), acne (6.2%), rash (5.4%), and urticaria (4.6%).
Ritlecitinib labeling includes the boxed warning about the risk for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, which is included in the labels for other JAK inhibitors.
Ritlecitinib evaluated for other diseases
In addition to alopecia areata, ritlecitinib has shown efficacy and acceptable safety in treating ulcerative colitis and is being evaluated for treating vitiligo, Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
In the statement, the company says that ritlecitinib will be available “in the coming weeks.” The manufacturer says it also has completed regulatory submissions for ritlecitinib in the United Kingdom, China, and Japan, and expects decisions this year.
Alopecia areata affects about 6.8 million people in the United States and 147 million globally.
In a statement, Nicole Friedland, president and CEO of the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, said that NAAF “is thrilled to have a second FDA-approved treatment for alopecia areata, which is the first approved for adolescents.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taken as a once-daily pill, ritlecitinib is a dual inhibitor of the TEC family of tyrosine kinases and of Janus kinase 3 (JAK3). The recommended dose of ritlecitinib, which will be marketed as Litfulo, is 50 mg once a day, according to the statement announcing the approval from Pfizer.
It is the second JAK inhibitor approved for treating alopecia areata, following approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) in June 2022 for AA in adults. Ritlecitinib is the first JAK inhibitor approved for children ages 12 and older with AA.
The European Medicines Agency has also accepted the Marketing Authorization Application for ritlecitinib in the same population and a decision is expected in the fourth quarter of this year.
Approval based on ALLEGRO trials
Approval was based on previously announced results from trials, including the phase 2b/3 ALLEGRO study of ritlecitinib in 718 patients aged 12 years and older with alopecia areata, with 50% of more scalp hair loss, as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT), including patients with alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) and alopecia universalis (complete scalp, face, and body hair loss).
Patients in the trial were experiencing a current episode of alopecia areata that had lasted between 6 months and 10 years. They were randomized to receive once-daily ritlecitinib at doses of 30 mg or 50 mg (with or without 1 month of initial treatment with once-daily ritlecitinib 200 mg), ritlecitinib 10 mg, or placebo.
Statistically significantly higher proportions of patients treated with ritlecitinib 30 mg and 50 mg (with or without the loading dose) had 80% or more scalp hair coverage, as measured by a SALT score of 20 or less after 6 months of treatment versus placebo. After 6 months of treatment, among those on the 50-mg dose, 23% had achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 2% of those on placebo. The results were published in The Lancet.
According to the company release, efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib was consistent between those ages 12-17 and adults, and the most common adverse events reported in the study, in at least 4% of patients treated with ritlecitinib, were headache (10.8%), diarrhea (10%), acne (6.2%), rash (5.4%), and urticaria (4.6%).
Ritlecitinib labeling includes the boxed warning about the risk for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis, which is included in the labels for other JAK inhibitors.
Ritlecitinib evaluated for other diseases
In addition to alopecia areata, ritlecitinib has shown efficacy and acceptable safety in treating ulcerative colitis and is being evaluated for treating vitiligo, Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
In the statement, the company says that ritlecitinib will be available “in the coming weeks.” The manufacturer says it also has completed regulatory submissions for ritlecitinib in the United Kingdom, China, and Japan, and expects decisions this year.
Alopecia areata affects about 6.8 million people in the United States and 147 million globally.
In a statement, Nicole Friedland, president and CEO of the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, said that NAAF “is thrilled to have a second FDA-approved treatment for alopecia areata, which is the first approved for adolescents.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study supports new NCCN classification for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
, according to new findings.
In addition, regardless of the NCCN risk group, the study found that Mohs surgery or peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) conferred a lower risk of developing LR, DM, and disease-related death.
“Although the NCCN included this new high-risk group in the last iteration of the guidelines, there were no studies that identified whether the high-risk group achieved the goal of identifying riskier tumors,” said senior author Emily Ruiz, MD, MPH, associate physician at the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, Boston. “Based on the data in our study, the risk groups did risk stratify tumors and so clinicians can utilize the high-risk group risk factors to identify which tumors may require additional surveillance or treatment.”
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Most patients with CSCC are successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision (WLE) alone, but a subset will experience more severe and aggressive disease. While useful for prognostication, current staging systems do not incorporate patient factors or other high-risk tumor features that influence outcomes, which led to the NCCN reclassifying CSCC into low-, high-, and very high-risk groups. The NCCN guidelines also made a new recommendation that Mohs or PDEMA be the preferred method for tissue processing for high- and very-high-risk tumors, based on this new stratification.
However, these changes to the NCCN guidelines have not been validated. The goal of this study was to compare outcomes in very-high-, high-, and low-risk NCCN groups as well as comparing outcomes of CSCCs stratified by Mohs and WLE.
Dr. Ruiz and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study using patient data from two tertiary care academic medical centers. Their analysis included 10,196 tumors from 8,727 patients that were then stratified into low-risk (3,054 tumors [30.0%]), high-risk (6,269 tumors [61.5%]), and very-high-risk (873 tumors [8.6%]) groups.
Tumors in the very-high-risk group were more likely to have high-risk tumor and histologic features, such as large-caliber perineural invasion, large diameter, invasion beyond the subcutaneous fat or bone, poor differentiation, and lymphovascular invasion.
The authors found that, compared with the low-risk group, the high- and very-high-risk groups demonstrated a greater risk of LR (high-risk subhazard ratio, 1.99; P = .007; very-high-risk SHR, 12.66; P < .001); NM (high-risk SHR, 4.26; P = .02; very-high-risk SHR, 62.98; P < .001); DM (high-risk SHR, 2.2 × 107;P < .001; very-high-risk SHR, 6.3 × 108;P < .001); and DSD (high-risk SHR, 4.02; P = .03; very-high-risk SHR, 93.87; P < .001).
Adjusted 5-year cumulative incidence was also significantly higher in very-high- vs. high- and low-risk groups for all endpoints.
They next compared the procedures used to treat the tumors. Compared with WLE, patients treated with Mohs or PDEMA had a lower risk of LR (SHR, 0.65; P = .009), DM (SHR, 0.38; P = .02), and DSD (SHR, 0.55; P = .006).
Mohs and PDEMA have already became preferred surgical modalities for high- and very-high-risk tumors, and Dr. Ruiz pointed out that their analysis was for the entire cohort.
“We did not stratify this by risk group,” she said. “So our results do not change anything clinically at this time, but support prior studies that have found Mohs/PDEMA to have improved outcomes, compared to WLE. Further studies are needed evaluating surgical approach by risk-group.”
However, she emphasized, “our studies further validate prior evidence showing Mohs/PDEMA to have the lowest rates of recurrence and in this study, even disease-related death.”
Approached for an independent comment, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, codirector of the melanoma and skin cancer program, and interim chair, department of surgical oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that this study supports the new reclassification of CSCC tumors by the NCCN, and confirms that the high-risk and very-high-risk tumors surely have a higher propensity for worse outcomes overall.
“That being said, the notion for type of resection and margin assessment is still an area of controversy in the dermatology, surgical oncology, and pathology community,” said Dr. Farma, who is also on the NCCN panel. “I believe we need further studies to truly understand the role of the type of resection and the pathologic evaluation play in this disease process.”
He also pointed out that it is unclear in this dataset if patients initially had any imaging to evaluate for local or regional metastatic disease. “It would be helpful to have a further understanding of which type of provider was performing the excisions, the type of excision decided upon, and if there was a standardized approach to [decide] which patients had MOHS or PDEMA and what was the surveillance for these patients both with imaging and physical examinations,” said Dr. Farma. “This data also evaluated patients over a long time period where practice patterns have evolved.”
Finally, he noted that the number of local and metastatic events subjectively seems low in this cohort. “We also do not know any information about the initial workup of the patients, patterns of recurrence, and adjuvant or palliative treatment after recurrence,” he added. “It is unclear from this manuscript how the type of resection or pathologic evaluation of margins leads to improved outcomes and further prospective studies are warranted.”
Dr. Ruiz reports reported serving as a coinvestigator and principal investigator for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and as a coinvestigator for Merck and consulting for Checkpoint Therapeutics, BDO, and Genentech outside the submitted work. Dr. Farma has no disclosures other than the NCCN panel. The study was supported by Harvard Catalyst and the Harvard University Clinical and Translational Science Center and by Harvard University and its affiliated academic health care centers and partially supported by the Melvin Markey Discovery Fund at Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
, according to new findings.
In addition, regardless of the NCCN risk group, the study found that Mohs surgery or peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) conferred a lower risk of developing LR, DM, and disease-related death.
“Although the NCCN included this new high-risk group in the last iteration of the guidelines, there were no studies that identified whether the high-risk group achieved the goal of identifying riskier tumors,” said senior author Emily Ruiz, MD, MPH, associate physician at the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, Boston. “Based on the data in our study, the risk groups did risk stratify tumors and so clinicians can utilize the high-risk group risk factors to identify which tumors may require additional surveillance or treatment.”
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Most patients with CSCC are successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision (WLE) alone, but a subset will experience more severe and aggressive disease. While useful for prognostication, current staging systems do not incorporate patient factors or other high-risk tumor features that influence outcomes, which led to the NCCN reclassifying CSCC into low-, high-, and very high-risk groups. The NCCN guidelines also made a new recommendation that Mohs or PDEMA be the preferred method for tissue processing for high- and very-high-risk tumors, based on this new stratification.
However, these changes to the NCCN guidelines have not been validated. The goal of this study was to compare outcomes in very-high-, high-, and low-risk NCCN groups as well as comparing outcomes of CSCCs stratified by Mohs and WLE.
Dr. Ruiz and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study using patient data from two tertiary care academic medical centers. Their analysis included 10,196 tumors from 8,727 patients that were then stratified into low-risk (3,054 tumors [30.0%]), high-risk (6,269 tumors [61.5%]), and very-high-risk (873 tumors [8.6%]) groups.
Tumors in the very-high-risk group were more likely to have high-risk tumor and histologic features, such as large-caliber perineural invasion, large diameter, invasion beyond the subcutaneous fat or bone, poor differentiation, and lymphovascular invasion.
The authors found that, compared with the low-risk group, the high- and very-high-risk groups demonstrated a greater risk of LR (high-risk subhazard ratio, 1.99; P = .007; very-high-risk SHR, 12.66; P < .001); NM (high-risk SHR, 4.26; P = .02; very-high-risk SHR, 62.98; P < .001); DM (high-risk SHR, 2.2 × 107;P < .001; very-high-risk SHR, 6.3 × 108;P < .001); and DSD (high-risk SHR, 4.02; P = .03; very-high-risk SHR, 93.87; P < .001).
Adjusted 5-year cumulative incidence was also significantly higher in very-high- vs. high- and low-risk groups for all endpoints.
They next compared the procedures used to treat the tumors. Compared with WLE, patients treated with Mohs or PDEMA had a lower risk of LR (SHR, 0.65; P = .009), DM (SHR, 0.38; P = .02), and DSD (SHR, 0.55; P = .006).
Mohs and PDEMA have already became preferred surgical modalities for high- and very-high-risk tumors, and Dr. Ruiz pointed out that their analysis was for the entire cohort.
“We did not stratify this by risk group,” she said. “So our results do not change anything clinically at this time, but support prior studies that have found Mohs/PDEMA to have improved outcomes, compared to WLE. Further studies are needed evaluating surgical approach by risk-group.”
However, she emphasized, “our studies further validate prior evidence showing Mohs/PDEMA to have the lowest rates of recurrence and in this study, even disease-related death.”
Approached for an independent comment, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, codirector of the melanoma and skin cancer program, and interim chair, department of surgical oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that this study supports the new reclassification of CSCC tumors by the NCCN, and confirms that the high-risk and very-high-risk tumors surely have a higher propensity for worse outcomes overall.
“That being said, the notion for type of resection and margin assessment is still an area of controversy in the dermatology, surgical oncology, and pathology community,” said Dr. Farma, who is also on the NCCN panel. “I believe we need further studies to truly understand the role of the type of resection and the pathologic evaluation play in this disease process.”
He also pointed out that it is unclear in this dataset if patients initially had any imaging to evaluate for local or regional metastatic disease. “It would be helpful to have a further understanding of which type of provider was performing the excisions, the type of excision decided upon, and if there was a standardized approach to [decide] which patients had MOHS or PDEMA and what was the surveillance for these patients both with imaging and physical examinations,” said Dr. Farma. “This data also evaluated patients over a long time period where practice patterns have evolved.”
Finally, he noted that the number of local and metastatic events subjectively seems low in this cohort. “We also do not know any information about the initial workup of the patients, patterns of recurrence, and adjuvant or palliative treatment after recurrence,” he added. “It is unclear from this manuscript how the type of resection or pathologic evaluation of margins leads to improved outcomes and further prospective studies are warranted.”
Dr. Ruiz reports reported serving as a coinvestigator and principal investigator for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and as a coinvestigator for Merck and consulting for Checkpoint Therapeutics, BDO, and Genentech outside the submitted work. Dr. Farma has no disclosures other than the NCCN panel. The study was supported by Harvard Catalyst and the Harvard University Clinical and Translational Science Center and by Harvard University and its affiliated academic health care centers and partially supported by the Melvin Markey Discovery Fund at Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
, according to new findings.
In addition, regardless of the NCCN risk group, the study found that Mohs surgery or peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) conferred a lower risk of developing LR, DM, and disease-related death.
“Although the NCCN included this new high-risk group in the last iteration of the guidelines, there were no studies that identified whether the high-risk group achieved the goal of identifying riskier tumors,” said senior author Emily Ruiz, MD, MPH, associate physician at the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, Boston. “Based on the data in our study, the risk groups did risk stratify tumors and so clinicians can utilize the high-risk group risk factors to identify which tumors may require additional surveillance or treatment.”
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Most patients with CSCC are successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision (WLE) alone, but a subset will experience more severe and aggressive disease. While useful for prognostication, current staging systems do not incorporate patient factors or other high-risk tumor features that influence outcomes, which led to the NCCN reclassifying CSCC into low-, high-, and very high-risk groups. The NCCN guidelines also made a new recommendation that Mohs or PDEMA be the preferred method for tissue processing for high- and very-high-risk tumors, based on this new stratification.
However, these changes to the NCCN guidelines have not been validated. The goal of this study was to compare outcomes in very-high-, high-, and low-risk NCCN groups as well as comparing outcomes of CSCCs stratified by Mohs and WLE.
Dr. Ruiz and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study using patient data from two tertiary care academic medical centers. Their analysis included 10,196 tumors from 8,727 patients that were then stratified into low-risk (3,054 tumors [30.0%]), high-risk (6,269 tumors [61.5%]), and very-high-risk (873 tumors [8.6%]) groups.
Tumors in the very-high-risk group were more likely to have high-risk tumor and histologic features, such as large-caliber perineural invasion, large diameter, invasion beyond the subcutaneous fat or bone, poor differentiation, and lymphovascular invasion.
The authors found that, compared with the low-risk group, the high- and very-high-risk groups demonstrated a greater risk of LR (high-risk subhazard ratio, 1.99; P = .007; very-high-risk SHR, 12.66; P < .001); NM (high-risk SHR, 4.26; P = .02; very-high-risk SHR, 62.98; P < .001); DM (high-risk SHR, 2.2 × 107;P < .001; very-high-risk SHR, 6.3 × 108;P < .001); and DSD (high-risk SHR, 4.02; P = .03; very-high-risk SHR, 93.87; P < .001).
Adjusted 5-year cumulative incidence was also significantly higher in very-high- vs. high- and low-risk groups for all endpoints.
They next compared the procedures used to treat the tumors. Compared with WLE, patients treated with Mohs or PDEMA had a lower risk of LR (SHR, 0.65; P = .009), DM (SHR, 0.38; P = .02), and DSD (SHR, 0.55; P = .006).
Mohs and PDEMA have already became preferred surgical modalities for high- and very-high-risk tumors, and Dr. Ruiz pointed out that their analysis was for the entire cohort.
“We did not stratify this by risk group,” she said. “So our results do not change anything clinically at this time, but support prior studies that have found Mohs/PDEMA to have improved outcomes, compared to WLE. Further studies are needed evaluating surgical approach by risk-group.”
However, she emphasized, “our studies further validate prior evidence showing Mohs/PDEMA to have the lowest rates of recurrence and in this study, even disease-related death.”
Approached for an independent comment, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, codirector of the melanoma and skin cancer program, and interim chair, department of surgical oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that this study supports the new reclassification of CSCC tumors by the NCCN, and confirms that the high-risk and very-high-risk tumors surely have a higher propensity for worse outcomes overall.
“That being said, the notion for type of resection and margin assessment is still an area of controversy in the dermatology, surgical oncology, and pathology community,” said Dr. Farma, who is also on the NCCN panel. “I believe we need further studies to truly understand the role of the type of resection and the pathologic evaluation play in this disease process.”
He also pointed out that it is unclear in this dataset if patients initially had any imaging to evaluate for local or regional metastatic disease. “It would be helpful to have a further understanding of which type of provider was performing the excisions, the type of excision decided upon, and if there was a standardized approach to [decide] which patients had MOHS or PDEMA and what was the surveillance for these patients both with imaging and physical examinations,” said Dr. Farma. “This data also evaluated patients over a long time period where practice patterns have evolved.”
Finally, he noted that the number of local and metastatic events subjectively seems low in this cohort. “We also do not know any information about the initial workup of the patients, patterns of recurrence, and adjuvant or palliative treatment after recurrence,” he added. “It is unclear from this manuscript how the type of resection or pathologic evaluation of margins leads to improved outcomes and further prospective studies are warranted.”
Dr. Ruiz reports reported serving as a coinvestigator and principal investigator for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and as a coinvestigator for Merck and consulting for Checkpoint Therapeutics, BDO, and Genentech outside the submitted work. Dr. Farma has no disclosures other than the NCCN panel. The study was supported by Harvard Catalyst and the Harvard University Clinical and Translational Science Center and by Harvard University and its affiliated academic health care centers and partially supported by the Melvin Markey Discovery Fund at Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Drugmakers are abandoning cheap generics, and now U.S. cancer patients can’t get meds
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Should you dismiss a difficult patient?
Some patients continually cancel their appointments, ignore your medical directions, treat your staff rudely, or send you harassing emails.
Do you have to tolerate their behavior?
No, these are all appropriate reasons to terminate patients, attorneys say. Patients also can be dismissed for misleading doctors about their past medical history, chronic drug-seeking, displaying threatening or seductive behavior toward staff members or physicians, or any criminal behavior in the office, experts say.
But even if a reason seems legitimate, that doesn’t make it legal. Doctors should consider whether the reason is legal, said Chicago-area attorney Ericka Adler, JD, a partner at Roetzel & Andress, who advises doctors about terminating patients.
Ms. Adler said.
Terminating patients for an “illegal” reason such as discrimination based on race or gender or sexual orientation – even if couched as a legitimate patient issue – could open the practice to a lawsuit, Ms. Adler said.
Doctors also want to avoid patient abandonment claims by talking to the patient about problems and documenting them as they arise. If they can’t be resolved, doctors should ensure that there’s continuity of care when patients change physicians, said Ms. Adler.
About 90% of physicians have dismissed at least one patient during their career, according to a study of nearly 800 primary care practices. The most common reasons were legitimate: a patient was “extremely disruptive and/or behaved inappropriately toward clinicians or staff”; a patient had “violated chronic pain and controlled substance policies”; and a patient had “repeatedly missed appointments.”
Jacqui O’Kane, DO, a family physician at South Georgia Medical Center in rural Nashville, said she has dismissed about 15 of 3,000 patients she has seen in the past 3 years at the clinic. Before she dismisses a patient, she looks at whether there has been a pattern of behavior and tries to talk to them about the problem first to find out if there are other reasons for it.
She also gives patients a warning: If the unacceptable behavior continues, it will lead to their dismissal.
When patients cross a line
Dr. O’Kane warned an elderly man who used the N-word with her that she wouldn’t tolerate that language in her office. Then, when he later called her front office employee the N-word, she decided to dismiss him.
“I said, ‘That’s it, you can’t say that to someone in this office. I already told you once, and you did it again. I’m sorry, you have to find another doctor,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
Another patient crossed a line when she missed four appointments, refused to come in, and kept sending Dr. O’Kane long messages on MyChart demanding medications and advice. One message was fairly obtrusive: “If you don’t give me something stronger for my nerves TODAY, I am going to LOSE MY MIND!!!” Dr. O’Kane said the patient wrote.
“I then told her that’s not how I run my practice and that she needed to find someone else.”
Another common reason doctors dismiss patients is for nonpayment, says Ms. Adler.
Recently, however, some patients have also begun demanding their money back from doctors for services already received and billed because they were unhappy about something that occurred at the doctor’s office, said Ms. Adler.
“I advise doctors to respond: ‘We disagree that you didn’t get the service, but we will give you your money back, and we’re also terminating you from our practice.’ At that point, the doctor-patient relationship has become impossible,” said Ms. Adler.
How to dismiss difficult patients ethically and legally
According to the AMA’s Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, a physician may not discontinue treatment of a patient if further treatment is medically indicated without giving the patient reasonable notice and sufficient opportunity to make alternative arrangements for care.
Terminating a patient abruptly without transferring their care could lead to a claim of patient abandonment and the physician being called before a licensing board for potentially violating the state’s Medical Practice Act, said Ms. Adler.
Doctors can take these six steps to set the stage for dismissal and avoid a claim of patient abandonment.
1. Create written policies. Medical practices can describe the rules and behavior they expect from patients in these policies, which can cover, for example, payment, treating staff with courtesy, and medications. “When the rules are in writing and patients sign off on them, that gives doctors a certain comfort level in being able to refer to them and say that the patient hasn’t been compliant,” said Ms. Adler.
She also recommends that your practice create a policy that doctors should let the patient know about their concerns and meet with them to discuss the problem before receiving a termination letter.
2. Document any consistent problems you’re having with a patient. When you start having problems with a patient, you should document when the problem occurred, how often it occurred, any discussions with the patient about the problem, warnings you gave the patient, and if and when you decided to terminate the patient.
3. Meet with the patient to discuss the problem. “Talking and meeting with a patient also allows the physician to assess whether there’s another issue. For example, is there a mental health concern? Is there a financial reason for nonpayment or no-shows? There are multiple benefits to finding out what the problem is,” said Ms. Adler.
Once you’ve decided to terminate a patient, here’s what you should do:
4. Allow enough time for the patient to find alternative care. Ms. Adler recommends giving patients 30 days’ notice and that physicians offer to provide emergency care during that time. However, if the patient is undergoing treatment or has other challenges, more time may be needed to transfer care.
“It’s important to consider the patient’s context – if the patient is receiving cancer treatment, or is in a late stage of pregnancy, or lives in a rural area where few specialists are available, you may want to treat them longer – at least until they finish their treatment,” said Ms. Adler. Also, states may have their own requirements about minimum notice periods, she said.
5. Provide patients with written notice that you intend to terminate their care. Ms. Adler recommends that each letter be tailored to the patient’s specific circumstances. “You could spell out a patient’s history of noncompliance or nonpayment or inappropriate conduct because it’s been documented and the patient is already aware of it from a previous discussion,” she said.
Ms. Adler also recommends that doctors consult with legal counsel when in doubt or if contacted by the patient’s lawyer. Some lawyers will draft the termination letters, she said.
6. Include the following information in the written letter: The date that they will no longer receive care, how they can obtain copies of their medical records, and how they can find a new physician by providing contact information for a state medical association or similar organization, which often maintains a database of clinicians by specialty and location.
The letter should also state that the doctor will provide emergency care during the 30 days. Ms. Adler also recommends sending the notice by certified mail.
Dr. O’Kane said she may be more likely to give patients a second chance because she practices in a rural underserved area, and she understands that her patients don’t have many other options for health care. She also has developed a reputation for being willing to take on difficult patients that other physicians didn’t want to deal with, she said.
She encourages physicians to talk to patients to find out why, for example, they may not be compliant with medications.
“The patient may say, ‘I had to choose between paying for medications and putting food on the table,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some patients continually cancel their appointments, ignore your medical directions, treat your staff rudely, or send you harassing emails.
Do you have to tolerate their behavior?
No, these are all appropriate reasons to terminate patients, attorneys say. Patients also can be dismissed for misleading doctors about their past medical history, chronic drug-seeking, displaying threatening or seductive behavior toward staff members or physicians, or any criminal behavior in the office, experts say.
But even if a reason seems legitimate, that doesn’t make it legal. Doctors should consider whether the reason is legal, said Chicago-area attorney Ericka Adler, JD, a partner at Roetzel & Andress, who advises doctors about terminating patients.
Ms. Adler said.
Terminating patients for an “illegal” reason such as discrimination based on race or gender or sexual orientation – even if couched as a legitimate patient issue – could open the practice to a lawsuit, Ms. Adler said.
Doctors also want to avoid patient abandonment claims by talking to the patient about problems and documenting them as they arise. If they can’t be resolved, doctors should ensure that there’s continuity of care when patients change physicians, said Ms. Adler.
About 90% of physicians have dismissed at least one patient during their career, according to a study of nearly 800 primary care practices. The most common reasons were legitimate: a patient was “extremely disruptive and/or behaved inappropriately toward clinicians or staff”; a patient had “violated chronic pain and controlled substance policies”; and a patient had “repeatedly missed appointments.”
Jacqui O’Kane, DO, a family physician at South Georgia Medical Center in rural Nashville, said she has dismissed about 15 of 3,000 patients she has seen in the past 3 years at the clinic. Before she dismisses a patient, she looks at whether there has been a pattern of behavior and tries to talk to them about the problem first to find out if there are other reasons for it.
She also gives patients a warning: If the unacceptable behavior continues, it will lead to their dismissal.
When patients cross a line
Dr. O’Kane warned an elderly man who used the N-word with her that she wouldn’t tolerate that language in her office. Then, when he later called her front office employee the N-word, she decided to dismiss him.
“I said, ‘That’s it, you can’t say that to someone in this office. I already told you once, and you did it again. I’m sorry, you have to find another doctor,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
Another patient crossed a line when she missed four appointments, refused to come in, and kept sending Dr. O’Kane long messages on MyChart demanding medications and advice. One message was fairly obtrusive: “If you don’t give me something stronger for my nerves TODAY, I am going to LOSE MY MIND!!!” Dr. O’Kane said the patient wrote.
“I then told her that’s not how I run my practice and that she needed to find someone else.”
Another common reason doctors dismiss patients is for nonpayment, says Ms. Adler.
Recently, however, some patients have also begun demanding their money back from doctors for services already received and billed because they were unhappy about something that occurred at the doctor’s office, said Ms. Adler.
“I advise doctors to respond: ‘We disagree that you didn’t get the service, but we will give you your money back, and we’re also terminating you from our practice.’ At that point, the doctor-patient relationship has become impossible,” said Ms. Adler.
How to dismiss difficult patients ethically and legally
According to the AMA’s Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, a physician may not discontinue treatment of a patient if further treatment is medically indicated without giving the patient reasonable notice and sufficient opportunity to make alternative arrangements for care.
Terminating a patient abruptly without transferring their care could lead to a claim of patient abandonment and the physician being called before a licensing board for potentially violating the state’s Medical Practice Act, said Ms. Adler.
Doctors can take these six steps to set the stage for dismissal and avoid a claim of patient abandonment.
1. Create written policies. Medical practices can describe the rules and behavior they expect from patients in these policies, which can cover, for example, payment, treating staff with courtesy, and medications. “When the rules are in writing and patients sign off on them, that gives doctors a certain comfort level in being able to refer to them and say that the patient hasn’t been compliant,” said Ms. Adler.
She also recommends that your practice create a policy that doctors should let the patient know about their concerns and meet with them to discuss the problem before receiving a termination letter.
2. Document any consistent problems you’re having with a patient. When you start having problems with a patient, you should document when the problem occurred, how often it occurred, any discussions with the patient about the problem, warnings you gave the patient, and if and when you decided to terminate the patient.
3. Meet with the patient to discuss the problem. “Talking and meeting with a patient also allows the physician to assess whether there’s another issue. For example, is there a mental health concern? Is there a financial reason for nonpayment or no-shows? There are multiple benefits to finding out what the problem is,” said Ms. Adler.
Once you’ve decided to terminate a patient, here’s what you should do:
4. Allow enough time for the patient to find alternative care. Ms. Adler recommends giving patients 30 days’ notice and that physicians offer to provide emergency care during that time. However, if the patient is undergoing treatment or has other challenges, more time may be needed to transfer care.
“It’s important to consider the patient’s context – if the patient is receiving cancer treatment, or is in a late stage of pregnancy, or lives in a rural area where few specialists are available, you may want to treat them longer – at least until they finish their treatment,” said Ms. Adler. Also, states may have their own requirements about minimum notice periods, she said.
5. Provide patients with written notice that you intend to terminate their care. Ms. Adler recommends that each letter be tailored to the patient’s specific circumstances. “You could spell out a patient’s history of noncompliance or nonpayment or inappropriate conduct because it’s been documented and the patient is already aware of it from a previous discussion,” she said.
Ms. Adler also recommends that doctors consult with legal counsel when in doubt or if contacted by the patient’s lawyer. Some lawyers will draft the termination letters, she said.
6. Include the following information in the written letter: The date that they will no longer receive care, how they can obtain copies of their medical records, and how they can find a new physician by providing contact information for a state medical association or similar organization, which often maintains a database of clinicians by specialty and location.
The letter should also state that the doctor will provide emergency care during the 30 days. Ms. Adler also recommends sending the notice by certified mail.
Dr. O’Kane said she may be more likely to give patients a second chance because she practices in a rural underserved area, and she understands that her patients don’t have many other options for health care. She also has developed a reputation for being willing to take on difficult patients that other physicians didn’t want to deal with, she said.
She encourages physicians to talk to patients to find out why, for example, they may not be compliant with medications.
“The patient may say, ‘I had to choose between paying for medications and putting food on the table,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some patients continually cancel their appointments, ignore your medical directions, treat your staff rudely, or send you harassing emails.
Do you have to tolerate their behavior?
No, these are all appropriate reasons to terminate patients, attorneys say. Patients also can be dismissed for misleading doctors about their past medical history, chronic drug-seeking, displaying threatening or seductive behavior toward staff members or physicians, or any criminal behavior in the office, experts say.
But even if a reason seems legitimate, that doesn’t make it legal. Doctors should consider whether the reason is legal, said Chicago-area attorney Ericka Adler, JD, a partner at Roetzel & Andress, who advises doctors about terminating patients.
Ms. Adler said.
Terminating patients for an “illegal” reason such as discrimination based on race or gender or sexual orientation – even if couched as a legitimate patient issue – could open the practice to a lawsuit, Ms. Adler said.
Doctors also want to avoid patient abandonment claims by talking to the patient about problems and documenting them as they arise. If they can’t be resolved, doctors should ensure that there’s continuity of care when patients change physicians, said Ms. Adler.
About 90% of physicians have dismissed at least one patient during their career, according to a study of nearly 800 primary care practices. The most common reasons were legitimate: a patient was “extremely disruptive and/or behaved inappropriately toward clinicians or staff”; a patient had “violated chronic pain and controlled substance policies”; and a patient had “repeatedly missed appointments.”
Jacqui O’Kane, DO, a family physician at South Georgia Medical Center in rural Nashville, said she has dismissed about 15 of 3,000 patients she has seen in the past 3 years at the clinic. Before she dismisses a patient, she looks at whether there has been a pattern of behavior and tries to talk to them about the problem first to find out if there are other reasons for it.
She also gives patients a warning: If the unacceptable behavior continues, it will lead to their dismissal.
When patients cross a line
Dr. O’Kane warned an elderly man who used the N-word with her that she wouldn’t tolerate that language in her office. Then, when he later called her front office employee the N-word, she decided to dismiss him.
“I said, ‘That’s it, you can’t say that to someone in this office. I already told you once, and you did it again. I’m sorry, you have to find another doctor,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
Another patient crossed a line when she missed four appointments, refused to come in, and kept sending Dr. O’Kane long messages on MyChart demanding medications and advice. One message was fairly obtrusive: “If you don’t give me something stronger for my nerves TODAY, I am going to LOSE MY MIND!!!” Dr. O’Kane said the patient wrote.
“I then told her that’s not how I run my practice and that she needed to find someone else.”
Another common reason doctors dismiss patients is for nonpayment, says Ms. Adler.
Recently, however, some patients have also begun demanding their money back from doctors for services already received and billed because they were unhappy about something that occurred at the doctor’s office, said Ms. Adler.
“I advise doctors to respond: ‘We disagree that you didn’t get the service, but we will give you your money back, and we’re also terminating you from our practice.’ At that point, the doctor-patient relationship has become impossible,” said Ms. Adler.
How to dismiss difficult patients ethically and legally
According to the AMA’s Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, a physician may not discontinue treatment of a patient if further treatment is medically indicated without giving the patient reasonable notice and sufficient opportunity to make alternative arrangements for care.
Terminating a patient abruptly without transferring their care could lead to a claim of patient abandonment and the physician being called before a licensing board for potentially violating the state’s Medical Practice Act, said Ms. Adler.
Doctors can take these six steps to set the stage for dismissal and avoid a claim of patient abandonment.
1. Create written policies. Medical practices can describe the rules and behavior they expect from patients in these policies, which can cover, for example, payment, treating staff with courtesy, and medications. “When the rules are in writing and patients sign off on them, that gives doctors a certain comfort level in being able to refer to them and say that the patient hasn’t been compliant,” said Ms. Adler.
She also recommends that your practice create a policy that doctors should let the patient know about their concerns and meet with them to discuss the problem before receiving a termination letter.
2. Document any consistent problems you’re having with a patient. When you start having problems with a patient, you should document when the problem occurred, how often it occurred, any discussions with the patient about the problem, warnings you gave the patient, and if and when you decided to terminate the patient.
3. Meet with the patient to discuss the problem. “Talking and meeting with a patient also allows the physician to assess whether there’s another issue. For example, is there a mental health concern? Is there a financial reason for nonpayment or no-shows? There are multiple benefits to finding out what the problem is,” said Ms. Adler.
Once you’ve decided to terminate a patient, here’s what you should do:
4. Allow enough time for the patient to find alternative care. Ms. Adler recommends giving patients 30 days’ notice and that physicians offer to provide emergency care during that time. However, if the patient is undergoing treatment or has other challenges, more time may be needed to transfer care.
“It’s important to consider the patient’s context – if the patient is receiving cancer treatment, or is in a late stage of pregnancy, or lives in a rural area where few specialists are available, you may want to treat them longer – at least until they finish their treatment,” said Ms. Adler. Also, states may have their own requirements about minimum notice periods, she said.
5. Provide patients with written notice that you intend to terminate their care. Ms. Adler recommends that each letter be tailored to the patient’s specific circumstances. “You could spell out a patient’s history of noncompliance or nonpayment or inappropriate conduct because it’s been documented and the patient is already aware of it from a previous discussion,” she said.
Ms. Adler also recommends that doctors consult with legal counsel when in doubt or if contacted by the patient’s lawyer. Some lawyers will draft the termination letters, she said.
6. Include the following information in the written letter: The date that they will no longer receive care, how they can obtain copies of their medical records, and how they can find a new physician by providing contact information for a state medical association or similar organization, which often maintains a database of clinicians by specialty and location.
The letter should also state that the doctor will provide emergency care during the 30 days. Ms. Adler also recommends sending the notice by certified mail.
Dr. O’Kane said she may be more likely to give patients a second chance because she practices in a rural underserved area, and she understands that her patients don’t have many other options for health care. She also has developed a reputation for being willing to take on difficult patients that other physicians didn’t want to deal with, she said.
She encourages physicians to talk to patients to find out why, for example, they may not be compliant with medications.
“The patient may say, ‘I had to choose between paying for medications and putting food on the table,’ ” said Dr. O’Kane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA passes on olorofim despite critical need for antifungals
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is declining to approve the investigational antifungal olorofim and is asking for more data, according to a news release from the manufacturer, F2G.
Olorofim, (formerly known as F901318) is the first in the orotomide class of antifungals to be evaluated clinically for the treatment of invasive mold infections. Its maker, F2G, is a biotech company based in Manchester, England, that focuses on developing drugs for rare fungal diseases.
The company says it remains optimistic and will address the FDA’s requirements and continue to seek approval.
The FDA’s denial comes as fungal infections are becoming increasingly common and resistant to treatment. There are only four antifungal classes currently available, and there are few new candidates in the pipeline. No new classes of antifungals have been developed in 2 decades.
David Andes, MD, chief of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization he shares the hope that the company can meet the requirements to gain approval.
“Some of the early results were really exciting,” he said. “People are enthusiastic about the compound because it has a novel mechanism of action, and it is active against a group of fungi that we have limited to no options for.”
Early results ‘exciting’
Dr. Andes said several physicians have been able to prescribe olorofim under the compassionate use program “and have witnessed success.”
Olorofim is the first antifungal agent to be granted breakthrough therapy designation, which the FDA granted in November 2019 for the treatment of invasive mold infections for patients with limited or no treatment options, including patients with refractory aspergillosis or those who are intolerant of currently available therapy. It is also indicated for infections due to Lomentospora prolificans, Scedosporium, and Scopulariopsis species.
Olorofim received a second breakthrough therapy designation in October 2020. The second designation was granted for treatment of central nervous system coccidioidomycosis that is refractory or for cases that cannot be treated with standard-of-care therapy.
It is very difficult for patients to be approved to receive compassionate use medicines, Dr. Andes pointed out. “I’d like to have access sooner rather than later,” he added.
Dr. Andes says the drugs are expensive and are time consuming to produce. And with antifungals, it is difficult to demonstrate safety in comparison with other antimicrobial agents because “it’s hard to hurt a fungus without having toxicity with human cells.”
Complete response letter issued
F2G received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its new drug application for olorofim, according to the news release issued by the company. “While F2G is disappointed with this outcome, we remain optimistic about olorofim’s potential to address an unmet need for patients with invasive fungal infections who have exhausted their treatment alternatives,” Francesco Maria Lavino, chief executive officer, said in the release. “We are assessing the details of the Complete Response Letter, and we plan to meet with the FDA to discuss it further.”
Dr. Andes says few other antifungals have made it as far as olorofim in clinical trials.
Lance B. Price, PhD, codirector of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University in Washington, told this news organization that despite the lack of antifungals in the pipeline, “We can’t allow our desperation to override the checkpoints that ensure that antifungals are safe to use in people.”
In the meantime, he said, it is important to preserve the utility of current antifungals by avoiding overusing them in medicine and agriculture.
“Sadly,” he said, “a drug called ipflufenoquin, which works by a similar mode of action as olorofim, has already been approved by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for use in plant agriculture. This could weaken the effectiveness of olorofim for treating things like Aspergillus infections even before the drug has been approved for use in humans.”
Plant drug undermining olorofim efficacy in humans
“While I’m sure this makes financial sense for the makers of ipflufenoquin, it borders on insanity from a public health perspective,” Dr. Price said.
Meanwhile, the global threat of fungal infections grows. The World Health Organization has launched its first-ever list of health-threatening fungi. Authors of a WHO report that contains the list write, “The invasive forms of these fungal infections often affect severely ill patients and those with significant underlying immune system–related conditions.”
F2G will continue to expand olorofim’s clinical trial program, according to the company’s statement. Along with its partner, Shionogi, it is enrolling patients with proven or probable invasive aspergillosis in a global phase 3 trial (OASIS), which will compare outcomes after treatment with olorofim in comparison with amphotericin B liposome (AmBisome) followed by standard of care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is declining to approve the investigational antifungal olorofim and is asking for more data, according to a news release from the manufacturer, F2G.
Olorofim, (formerly known as F901318) is the first in the orotomide class of antifungals to be evaluated clinically for the treatment of invasive mold infections. Its maker, F2G, is a biotech company based in Manchester, England, that focuses on developing drugs for rare fungal diseases.
The company says it remains optimistic and will address the FDA’s requirements and continue to seek approval.
The FDA’s denial comes as fungal infections are becoming increasingly common and resistant to treatment. There are only four antifungal classes currently available, and there are few new candidates in the pipeline. No new classes of antifungals have been developed in 2 decades.
David Andes, MD, chief of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization he shares the hope that the company can meet the requirements to gain approval.
“Some of the early results were really exciting,” he said. “People are enthusiastic about the compound because it has a novel mechanism of action, and it is active against a group of fungi that we have limited to no options for.”
Early results ‘exciting’
Dr. Andes said several physicians have been able to prescribe olorofim under the compassionate use program “and have witnessed success.”
Olorofim is the first antifungal agent to be granted breakthrough therapy designation, which the FDA granted in November 2019 for the treatment of invasive mold infections for patients with limited or no treatment options, including patients with refractory aspergillosis or those who are intolerant of currently available therapy. It is also indicated for infections due to Lomentospora prolificans, Scedosporium, and Scopulariopsis species.
Olorofim received a second breakthrough therapy designation in October 2020. The second designation was granted for treatment of central nervous system coccidioidomycosis that is refractory or for cases that cannot be treated with standard-of-care therapy.
It is very difficult for patients to be approved to receive compassionate use medicines, Dr. Andes pointed out. “I’d like to have access sooner rather than later,” he added.
Dr. Andes says the drugs are expensive and are time consuming to produce. And with antifungals, it is difficult to demonstrate safety in comparison with other antimicrobial agents because “it’s hard to hurt a fungus without having toxicity with human cells.”
Complete response letter issued
F2G received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its new drug application for olorofim, according to the news release issued by the company. “While F2G is disappointed with this outcome, we remain optimistic about olorofim’s potential to address an unmet need for patients with invasive fungal infections who have exhausted their treatment alternatives,” Francesco Maria Lavino, chief executive officer, said in the release. “We are assessing the details of the Complete Response Letter, and we plan to meet with the FDA to discuss it further.”
Dr. Andes says few other antifungals have made it as far as olorofim in clinical trials.
Lance B. Price, PhD, codirector of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University in Washington, told this news organization that despite the lack of antifungals in the pipeline, “We can’t allow our desperation to override the checkpoints that ensure that antifungals are safe to use in people.”
In the meantime, he said, it is important to preserve the utility of current antifungals by avoiding overusing them in medicine and agriculture.
“Sadly,” he said, “a drug called ipflufenoquin, which works by a similar mode of action as olorofim, has already been approved by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for use in plant agriculture. This could weaken the effectiveness of olorofim for treating things like Aspergillus infections even before the drug has been approved for use in humans.”
Plant drug undermining olorofim efficacy in humans
“While I’m sure this makes financial sense for the makers of ipflufenoquin, it borders on insanity from a public health perspective,” Dr. Price said.
Meanwhile, the global threat of fungal infections grows. The World Health Organization has launched its first-ever list of health-threatening fungi. Authors of a WHO report that contains the list write, “The invasive forms of these fungal infections often affect severely ill patients and those with significant underlying immune system–related conditions.”
F2G will continue to expand olorofim’s clinical trial program, according to the company’s statement. Along with its partner, Shionogi, it is enrolling patients with proven or probable invasive aspergillosis in a global phase 3 trial (OASIS), which will compare outcomes after treatment with olorofim in comparison with amphotericin B liposome (AmBisome) followed by standard of care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is declining to approve the investigational antifungal olorofim and is asking for more data, according to a news release from the manufacturer, F2G.
Olorofim, (formerly known as F901318) is the first in the orotomide class of antifungals to be evaluated clinically for the treatment of invasive mold infections. Its maker, F2G, is a biotech company based in Manchester, England, that focuses on developing drugs for rare fungal diseases.
The company says it remains optimistic and will address the FDA’s requirements and continue to seek approval.
The FDA’s denial comes as fungal infections are becoming increasingly common and resistant to treatment. There are only four antifungal classes currently available, and there are few new candidates in the pipeline. No new classes of antifungals have been developed in 2 decades.
David Andes, MD, chief of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization he shares the hope that the company can meet the requirements to gain approval.
“Some of the early results were really exciting,” he said. “People are enthusiastic about the compound because it has a novel mechanism of action, and it is active against a group of fungi that we have limited to no options for.”
Early results ‘exciting’
Dr. Andes said several physicians have been able to prescribe olorofim under the compassionate use program “and have witnessed success.”
Olorofim is the first antifungal agent to be granted breakthrough therapy designation, which the FDA granted in November 2019 for the treatment of invasive mold infections for patients with limited or no treatment options, including patients with refractory aspergillosis or those who are intolerant of currently available therapy. It is also indicated for infections due to Lomentospora prolificans, Scedosporium, and Scopulariopsis species.
Olorofim received a second breakthrough therapy designation in October 2020. The second designation was granted for treatment of central nervous system coccidioidomycosis that is refractory or for cases that cannot be treated with standard-of-care therapy.
It is very difficult for patients to be approved to receive compassionate use medicines, Dr. Andes pointed out. “I’d like to have access sooner rather than later,” he added.
Dr. Andes says the drugs are expensive and are time consuming to produce. And with antifungals, it is difficult to demonstrate safety in comparison with other antimicrobial agents because “it’s hard to hurt a fungus without having toxicity with human cells.”
Complete response letter issued
F2G received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its new drug application for olorofim, according to the news release issued by the company. “While F2G is disappointed with this outcome, we remain optimistic about olorofim’s potential to address an unmet need for patients with invasive fungal infections who have exhausted their treatment alternatives,” Francesco Maria Lavino, chief executive officer, said in the release. “We are assessing the details of the Complete Response Letter, and we plan to meet with the FDA to discuss it further.”
Dr. Andes says few other antifungals have made it as far as olorofim in clinical trials.
Lance B. Price, PhD, codirector of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University in Washington, told this news organization that despite the lack of antifungals in the pipeline, “We can’t allow our desperation to override the checkpoints that ensure that antifungals are safe to use in people.”
In the meantime, he said, it is important to preserve the utility of current antifungals by avoiding overusing them in medicine and agriculture.
“Sadly,” he said, “a drug called ipflufenoquin, which works by a similar mode of action as olorofim, has already been approved by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for use in plant agriculture. This could weaken the effectiveness of olorofim for treating things like Aspergillus infections even before the drug has been approved for use in humans.”
Plant drug undermining olorofim efficacy in humans
“While I’m sure this makes financial sense for the makers of ipflufenoquin, it borders on insanity from a public health perspective,” Dr. Price said.
Meanwhile, the global threat of fungal infections grows. The World Health Organization has launched its first-ever list of health-threatening fungi. Authors of a WHO report that contains the list write, “The invasive forms of these fungal infections often affect severely ill patients and those with significant underlying immune system–related conditions.”
F2G will continue to expand olorofim’s clinical trial program, according to the company’s statement. Along with its partner, Shionogi, it is enrolling patients with proven or probable invasive aspergillosis in a global phase 3 trial (OASIS), which will compare outcomes after treatment with olorofim in comparison with amphotericin B liposome (AmBisome) followed by standard of care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-calorie tastes sweeter with a little salt
Low-calorie tastes sweeter with a little salt
Diet and sugar-free foods and drinks seem like a good idea, but it’s hard to get past that strange aftertaste, right? It’s the calling card for the noncaloric aspartame- and stevia-containing sweeteners that we consume to make us feel like we can have the best of both worlds.
That weird lingering taste can be a total turn-off for some (raises hand), but researchers have found an almost facepalm solution to the not-so-sweet problem, and it’s salt.
Now, the concept of sweet and salty is not a far-fetched partnership when it comes to snack consumption (try M&Ms in your popcorn). The researchers at Almendra, a manufacturer of stevia sweeteners, put that iconic flavor pair to the test by adding mineral salts that have some nutritional value to lessen the effect of a stevia compound, rebaudioside A, found in noncaloric sweeteners.
The researchers added in magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, and potassium chloride separately to lessen rebaudioside A’s intensity, but they needed so much salt that it killed the sweet taste completely. A blend of the three mineral salts, however, reduced the lingering taste by 79% and improved the real sugar-like taste. The researchers tried this blend in reduced-calorie orange juice and a citrus-flavored soft drink, improving the taste in both.
The salty and sweet match comes in for the win once again. This time helping against the fight of obesity instead of making it worse.
Pseudomonas’ Achilles’ heel is more of an Achilles’ genetic switch
Today, on the long-awaited return of “Bacteria vs. the World,” we meet one of the rock stars of infectious disease.
LOTME: Through the use of imaginary technology, we’re talking to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thanks for joining us on such short notice, after Neisseria gonorrhoeae canceled at the last minute.
P. aeruginosa: No problem. I think we can all guess what that little devil is up to.
LOTME: Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a huge problem for our species. What makes you so hard to fight?
P. aeruginosa: We’ve been trying to keep that a secret, actually, but now that researchers in Switzerland and Denmark seem to have figured it out, I guess it’s okay for me to spill the beans.
LOTME: Beans? What do beans have to do with it?
P. aeruginosa: Nothing, it’s just a colloquial expression that means I’m sharing previously private information.
LOTME: Sure, we knew that. Please, continue your spilling.
P. aeruginosa: The secret is … Well, let’s just say we were a little worried when the Clash released “Should I Stay or Should I Go” back in the 1980s.
LOTME: The Clash? Now we’re really confused.
P. aeruginosa: The answer to their question, “Should I stay or should I go? is yes. Successful invasion of a human is all about division of labor. “While one fraction of the bacterial population adheres to the mucosal surface and forms a biofilm, the other subpopulation spreads to distant tissue sites,” is how the investigators described it. We can increase surface colonization by using a “job-sharing” process, they said, and even resist antibiotics because most of us remain in the protective biofilm.
LOTME: And they say you guys don’t have brains.
P. aeruginosa: But wait, there’s more. We don’t just divide the labor randomly. After the initial colonization we form two functionally distinct subpopulations. One has high levels of the bacterial signaling molecule c-di-GMP and stays put to work on the biofilm. The other group, with low levels of c-di-GMP, heads out to the surrounding tissue to continue the colonization. As project leader Urs Jenal put it, “By identifying the genetic switch, we have tracked down the Achilles heel of the pathogen.”
LOTME: Pretty clever stuff, for humans, anyway.
P. aeruginosa: We agree, but now that you know our secret, we can’t let you share it.
LOTME: Wait! The journal article’s already been published. Your secret is out. You can’t stop that by infecting me.
P. aeruginosa: True enough, but are you familiar with the fable of the scorpion and the frog? It’s our nature.
LOTME: Nooooo! N. gonorrhoeae wouldn’t have done this!
What a pain in the Butt
Businesses rise and businesses fall. We all know that one cursed location, that spot in town where we see businesses move in and close up in a matter of months. At the same time, though, there are also businesses that have been around as long as anyone can remember, pillars of the community.
Corydon, IN., likely has a few such long-lived shops, but it is officially down one 70-year-old family business as of late April, with the unfortunate passing of beloved local pharmacy Butt Drugs. Prescription pick-up in rear.
The business dates back to 1952, when it was founded as William H. Butt Drugs. We’re sure William Butt was never teased about his last name. Nope. No one would ever do that. After he passed the store to his children, it underwent a stint as Butt Rexall Drugs. When the shop was passed down to its third-generation and ultimately final owner, Katie Butt Beckort, she decided to simplify the name. Get right down to the bottom of things, as it were.
Butt Drugs was a popular spot, featuring an old-school soda fountain and themed souvenirs. According to Ms. Butt Beckort, people would come from miles away to buy “I love Butt Drugs” T-shirts, magnets, and so on. Yes, they knew perfectly well what they were sitting on.
So, if was such a hit, why did it close? Butt Drugs may have a hilarious name and merchandise to match, but the pharmacy portion of the pharmacy had been losing money for years. You know, the actual point of the business. As with so many things, we can blame it on the insurance companies. More than half the drugs that passed through Butt Drugs’ doors were sold at a loss, because the insurance companies refused to reimburse the store more than the wholesale price of the drug. Not even a good butt drug could clear up that financial diarrhea.
And so, we’ve lost Butt Drugs forever. Spicy food enthusiasts, coffee drinkers, and all patrons of Taco Bell, take a moment to reflect and mourn on what you’ve lost. No more Butt Drugs to relieve your suffering. A true kick in the butt indeed.
Low-calorie tastes sweeter with a little salt
Diet and sugar-free foods and drinks seem like a good idea, but it’s hard to get past that strange aftertaste, right? It’s the calling card for the noncaloric aspartame- and stevia-containing sweeteners that we consume to make us feel like we can have the best of both worlds.
That weird lingering taste can be a total turn-off for some (raises hand), but researchers have found an almost facepalm solution to the not-so-sweet problem, and it’s salt.
Now, the concept of sweet and salty is not a far-fetched partnership when it comes to snack consumption (try M&Ms in your popcorn). The researchers at Almendra, a manufacturer of stevia sweeteners, put that iconic flavor pair to the test by adding mineral salts that have some nutritional value to lessen the effect of a stevia compound, rebaudioside A, found in noncaloric sweeteners.
The researchers added in magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, and potassium chloride separately to lessen rebaudioside A’s intensity, but they needed so much salt that it killed the sweet taste completely. A blend of the three mineral salts, however, reduced the lingering taste by 79% and improved the real sugar-like taste. The researchers tried this blend in reduced-calorie orange juice and a citrus-flavored soft drink, improving the taste in both.
The salty and sweet match comes in for the win once again. This time helping against the fight of obesity instead of making it worse.
Pseudomonas’ Achilles’ heel is more of an Achilles’ genetic switch
Today, on the long-awaited return of “Bacteria vs. the World,” we meet one of the rock stars of infectious disease.
LOTME: Through the use of imaginary technology, we’re talking to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thanks for joining us on such short notice, after Neisseria gonorrhoeae canceled at the last minute.
P. aeruginosa: No problem. I think we can all guess what that little devil is up to.
LOTME: Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a huge problem for our species. What makes you so hard to fight?
P. aeruginosa: We’ve been trying to keep that a secret, actually, but now that researchers in Switzerland and Denmark seem to have figured it out, I guess it’s okay for me to spill the beans.
LOTME: Beans? What do beans have to do with it?
P. aeruginosa: Nothing, it’s just a colloquial expression that means I’m sharing previously private information.
LOTME: Sure, we knew that. Please, continue your spilling.
P. aeruginosa: The secret is … Well, let’s just say we were a little worried when the Clash released “Should I Stay or Should I Go” back in the 1980s.
LOTME: The Clash? Now we’re really confused.
P. aeruginosa: The answer to their question, “Should I stay or should I go? is yes. Successful invasion of a human is all about division of labor. “While one fraction of the bacterial population adheres to the mucosal surface and forms a biofilm, the other subpopulation spreads to distant tissue sites,” is how the investigators described it. We can increase surface colonization by using a “job-sharing” process, they said, and even resist antibiotics because most of us remain in the protective biofilm.
LOTME: And they say you guys don’t have brains.
P. aeruginosa: But wait, there’s more. We don’t just divide the labor randomly. After the initial colonization we form two functionally distinct subpopulations. One has high levels of the bacterial signaling molecule c-di-GMP and stays put to work on the biofilm. The other group, with low levels of c-di-GMP, heads out to the surrounding tissue to continue the colonization. As project leader Urs Jenal put it, “By identifying the genetic switch, we have tracked down the Achilles heel of the pathogen.”
LOTME: Pretty clever stuff, for humans, anyway.
P. aeruginosa: We agree, but now that you know our secret, we can’t let you share it.
LOTME: Wait! The journal article’s already been published. Your secret is out. You can’t stop that by infecting me.
P. aeruginosa: True enough, but are you familiar with the fable of the scorpion and the frog? It’s our nature.
LOTME: Nooooo! N. gonorrhoeae wouldn’t have done this!
What a pain in the Butt
Businesses rise and businesses fall. We all know that one cursed location, that spot in town where we see businesses move in and close up in a matter of months. At the same time, though, there are also businesses that have been around as long as anyone can remember, pillars of the community.
Corydon, IN., likely has a few such long-lived shops, but it is officially down one 70-year-old family business as of late April, with the unfortunate passing of beloved local pharmacy Butt Drugs. Prescription pick-up in rear.
The business dates back to 1952, when it was founded as William H. Butt Drugs. We’re sure William Butt was never teased about his last name. Nope. No one would ever do that. After he passed the store to his children, it underwent a stint as Butt Rexall Drugs. When the shop was passed down to its third-generation and ultimately final owner, Katie Butt Beckort, she decided to simplify the name. Get right down to the bottom of things, as it were.
Butt Drugs was a popular spot, featuring an old-school soda fountain and themed souvenirs. According to Ms. Butt Beckort, people would come from miles away to buy “I love Butt Drugs” T-shirts, magnets, and so on. Yes, they knew perfectly well what they were sitting on.
So, if was such a hit, why did it close? Butt Drugs may have a hilarious name and merchandise to match, but the pharmacy portion of the pharmacy had been losing money for years. You know, the actual point of the business. As with so many things, we can blame it on the insurance companies. More than half the drugs that passed through Butt Drugs’ doors were sold at a loss, because the insurance companies refused to reimburse the store more than the wholesale price of the drug. Not even a good butt drug could clear up that financial diarrhea.
And so, we’ve lost Butt Drugs forever. Spicy food enthusiasts, coffee drinkers, and all patrons of Taco Bell, take a moment to reflect and mourn on what you’ve lost. No more Butt Drugs to relieve your suffering. A true kick in the butt indeed.
Low-calorie tastes sweeter with a little salt
Diet and sugar-free foods and drinks seem like a good idea, but it’s hard to get past that strange aftertaste, right? It’s the calling card for the noncaloric aspartame- and stevia-containing sweeteners that we consume to make us feel like we can have the best of both worlds.
That weird lingering taste can be a total turn-off for some (raises hand), but researchers have found an almost facepalm solution to the not-so-sweet problem, and it’s salt.
Now, the concept of sweet and salty is not a far-fetched partnership when it comes to snack consumption (try M&Ms in your popcorn). The researchers at Almendra, a manufacturer of stevia sweeteners, put that iconic flavor pair to the test by adding mineral salts that have some nutritional value to lessen the effect of a stevia compound, rebaudioside A, found in noncaloric sweeteners.
The researchers added in magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, and potassium chloride separately to lessen rebaudioside A’s intensity, but they needed so much salt that it killed the sweet taste completely. A blend of the three mineral salts, however, reduced the lingering taste by 79% and improved the real sugar-like taste. The researchers tried this blend in reduced-calorie orange juice and a citrus-flavored soft drink, improving the taste in both.
The salty and sweet match comes in for the win once again. This time helping against the fight of obesity instead of making it worse.
Pseudomonas’ Achilles’ heel is more of an Achilles’ genetic switch
Today, on the long-awaited return of “Bacteria vs. the World,” we meet one of the rock stars of infectious disease.
LOTME: Through the use of imaginary technology, we’re talking to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thanks for joining us on such short notice, after Neisseria gonorrhoeae canceled at the last minute.
P. aeruginosa: No problem. I think we can all guess what that little devil is up to.
LOTME: Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a huge problem for our species. What makes you so hard to fight?
P. aeruginosa: We’ve been trying to keep that a secret, actually, but now that researchers in Switzerland and Denmark seem to have figured it out, I guess it’s okay for me to spill the beans.
LOTME: Beans? What do beans have to do with it?
P. aeruginosa: Nothing, it’s just a colloquial expression that means I’m sharing previously private information.
LOTME: Sure, we knew that. Please, continue your spilling.
P. aeruginosa: The secret is … Well, let’s just say we were a little worried when the Clash released “Should I Stay or Should I Go” back in the 1980s.
LOTME: The Clash? Now we’re really confused.
P. aeruginosa: The answer to their question, “Should I stay or should I go? is yes. Successful invasion of a human is all about division of labor. “While one fraction of the bacterial population adheres to the mucosal surface and forms a biofilm, the other subpopulation spreads to distant tissue sites,” is how the investigators described it. We can increase surface colonization by using a “job-sharing” process, they said, and even resist antibiotics because most of us remain in the protective biofilm.
LOTME: And they say you guys don’t have brains.
P. aeruginosa: But wait, there’s more. We don’t just divide the labor randomly. After the initial colonization we form two functionally distinct subpopulations. One has high levels of the bacterial signaling molecule c-di-GMP and stays put to work on the biofilm. The other group, with low levels of c-di-GMP, heads out to the surrounding tissue to continue the colonization. As project leader Urs Jenal put it, “By identifying the genetic switch, we have tracked down the Achilles heel of the pathogen.”
LOTME: Pretty clever stuff, for humans, anyway.
P. aeruginosa: We agree, but now that you know our secret, we can’t let you share it.
LOTME: Wait! The journal article’s already been published. Your secret is out. You can’t stop that by infecting me.
P. aeruginosa: True enough, but are you familiar with the fable of the scorpion and the frog? It’s our nature.
LOTME: Nooooo! N. gonorrhoeae wouldn’t have done this!
What a pain in the Butt
Businesses rise and businesses fall. We all know that one cursed location, that spot in town where we see businesses move in and close up in a matter of months. At the same time, though, there are also businesses that have been around as long as anyone can remember, pillars of the community.
Corydon, IN., likely has a few such long-lived shops, but it is officially down one 70-year-old family business as of late April, with the unfortunate passing of beloved local pharmacy Butt Drugs. Prescription pick-up in rear.
The business dates back to 1952, when it was founded as William H. Butt Drugs. We’re sure William Butt was never teased about his last name. Nope. No one would ever do that. After he passed the store to his children, it underwent a stint as Butt Rexall Drugs. When the shop was passed down to its third-generation and ultimately final owner, Katie Butt Beckort, she decided to simplify the name. Get right down to the bottom of things, as it were.
Butt Drugs was a popular spot, featuring an old-school soda fountain and themed souvenirs. According to Ms. Butt Beckort, people would come from miles away to buy “I love Butt Drugs” T-shirts, magnets, and so on. Yes, they knew perfectly well what they were sitting on.
So, if was such a hit, why did it close? Butt Drugs may have a hilarious name and merchandise to match, but the pharmacy portion of the pharmacy had been losing money for years. You know, the actual point of the business. As with so many things, we can blame it on the insurance companies. More than half the drugs that passed through Butt Drugs’ doors were sold at a loss, because the insurance companies refused to reimburse the store more than the wholesale price of the drug. Not even a good butt drug could clear up that financial diarrhea.
And so, we’ve lost Butt Drugs forever. Spicy food enthusiasts, coffee drinkers, and all patrons of Taco Bell, take a moment to reflect and mourn on what you’ve lost. No more Butt Drugs to relieve your suffering. A true kick in the butt indeed.
Proposal to cap Part B pay on some drugs draws opposition
An influential panel proposed capping Medicare Part B pay for some drugs, arguing this would remove financial incentives to use more costly medicines when there are less expensive equivalents.
Medical groups have objected to both this recommendation from the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) and the panel’s underlying premise. MedPAC said financial as well as clinical factors can come into play in clinicians’ choices of drugs for patients.
In an interview, Christina Downey, MD, chair of the Government Affairs Committee of the American College of Rheumatology, said physicians in her field cannot switch patients’ medicines to try to make a profit.
“Patients only respond to the drugs that they respond to,” Dr. Downey said. “It’s frankly very insulting to say that physicians just force patients to go on medicines that are going to make them a bunch of money.”
In a June report to Congress, MedPAC recommended reducing the add-on payment for many drugs given in hospitals and clinics, which are thus covered by Part B, as part of a package of suggestions for addressing rising costs. Part B drug spending grew about 9% annually between 2009 and 2021, rising from $15.4 billion to $42.9 billion, MedPAC said.
Medicare’s current Part B drug pricing model starts with the reported average sales price (ASP) and then adds about 4.3% or 6%, depending on current budget-sequester law, to the cost of medicines.
MedPAC members voted 17-0 in April in favor of a general recommendation to revise the Part B payment approach. In the June report, MedPAC fleshes out this idea. It mentions a model in which the add-on Part B payment would be the lesser of either 6% of the ASP, 3% plus $24, or $220.
The majority of Part B drug administrations are for very low-priced drugs, MedPAC said. But for some of the more costly ones, annual prices can be more than $400,000 per patient, and future launch prices may be even higher for certain types of products, such as gene therapies, MedPAC said.
“There is no evidence that the costs of a drug’s administration are proportionate to the price of the drug,” MedPAC said.
Concerns about how well Medicare covers the cost of drug administration should be addressed through other pathways, such as the American Medical
Association’s Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (RUC), MedPAC said. AMA’s RUC advises the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on the physician fee schedule.
Congress is not obliged to act on or to even consider MedPAC’s work. In general, lawmakers and CMS often pay heed to the panel’s recommendations, sometimes incorporating them into new policy.
But this new MedPAC Part B recommendation has drawn strong opposition, similar to the response to a 2016 CMS plan to cut the Part B add-on payment. That plan, which CMS later abandoned, would have cut the markup on Part B drugs to 2.5% and added a flat fee to cover administration costs.
Why not focus on PBMs instead?
The timing of the MedPAC recommendation is poor, given that CMS already is trying to implement the Inflation Reduction Act and create a new system of direct Medicare drug price negotiations, as ordered by Congress, said Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist based in New Orleans.
A better approach for lowering drug prices would be to focus more on the operations of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), said Dr. Feldman, who also is vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations. A pending bipartisan Senate bill, for example, would prohibit PBM compensation based on the price of a drug as a condition of entering into a contract with a Medicare Part D plan.
Congress needs to take steps to unlink the profits of PBMs from higher drug prices, Dr. Feldman said.
“Until that happens, we can put all the lipstick we want on this big pig, but it’s not going to really fix the problem,” she said.
Reduced pay for drugs acquired through 340B program?
In an interview about the new MedPAC proposal, Ted Okon, executive director of the Community Oncology Alliance, urged renewed attention to what he sees as unintended consequences of the 340B discount drug program.
Under this program, certain hospitals can acquire drugs at steeply reduced prices, but they are not obliged to share those discounts with patients. Hospitals that participate in the 340B program can gain funds when patients and their insurers, including Medicare, pay more for the medicines hospitals and other organizations acquired with the 340B discount. Hospitals say they use the money from the 340B program to expand resources in their communities.
But rapid growth of the program in recent years has led to questions, especially about the role of contract pharmacies that manage the program. Congress created the 340B program in 1992 as a workaround to then new rules on Medicaid drug coverage.
In 2021, participating hospitals and clinics and organizations purchased about $44 billion worth of medicines through the 340B drug program. This was an increase of 16% from the previous year, according to a report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund. The number of sites, including hospitals and pharmacies, enrolled in the 340B program rose from 8,100 in 2000 to 50,000 by 2020, the report said.
MedPAC in 2016 urged CMS to reduce the amount Medicare pays for drugs acquired through the 340B program. CMS did so during the Trump administration, a policy later defended by the Biden administration.
But the U.S. Supreme Court last year said Medicare erred in its approach to making this cut, as earlier reported. Federal law required that the Department of Health and Human Services conduct a survey to support such a step, and HHS did not do this, the court said. CMS thus was ordered to return Medicare to the ASP+6% payment model for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program.
In the June report, though, MedPAC stuck by its 2016 recommendation that Medicare reduce its payments for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program despite this setback.
“We continue to believe that this approach is appropriate, and the specific level of payment reduction could be considered further as newer data become available,” MedPAC said.
Hospital, PhRMA split
Hospitals would certainly contest any renewed bid by CMS to drop Medicare’s pay for drugs purchased through the 340B program. The American Hospital Association objected to the MedPAC proposal regarding the add-on payment in Part B drug pricing.
MedPAC commissioners discussed this idea at a January meeting, prompting a February letter from the AHA to the panel. Like Dr. Feldman, AHA said it would be “premature” to launch into a revision of Part B drug pricing while the impact of the IRA on drug prices was still unclear.
AHA also noted that a reduction in Part B drug reimbursement would “shift the responsibility for the rapid increase in drug prices away from drug manufacturers, and instead places the burden on hospitals and patients.”
But the AHA gave a much warmer reception to another proposal MedPAC considered this year and that it included in its June report, which is a plan to address the high cost of certain drugs of as yet unconfirmed clinical benefit.
In April, the AHA said it supports a move toward a “value-based approach” in certain cases in which first-in-class medicines are sold under U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s accelerated approvals. Medicare could then cap payment for such drugs that have excessively high launch prices and uncertain clinical benefit, AHA said.
In the June report, MedPAC recommended that Medicare be able to place such a limit on Part B payments in certain cases, including ones in which companies do not meet FDA deadlines for postmarketing confirmatory trials.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) objected to this proposed change. The trade group for drugmakers said the FDA often revises and extends enrollment milestones for pending confirmatory trials when companies hit snags, such as challenges in enrolling patients, PhRMA said.
Reducing Part B payment for drugs for which confirmatory trials have been delayed would have a “disproportionate impact” on smaller and rural communities, where independent practices struggle to keep their doors open as it is, PhRMA spokeswoman Nicole Longo wrote in a blog post.
“If physicians can’t afford to administer a medicine, then they won’t and that means their patients won’t have access to them either,” Ms. Longo wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An influential panel proposed capping Medicare Part B pay for some drugs, arguing this would remove financial incentives to use more costly medicines when there are less expensive equivalents.
Medical groups have objected to both this recommendation from the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) and the panel’s underlying premise. MedPAC said financial as well as clinical factors can come into play in clinicians’ choices of drugs for patients.
In an interview, Christina Downey, MD, chair of the Government Affairs Committee of the American College of Rheumatology, said physicians in her field cannot switch patients’ medicines to try to make a profit.
“Patients only respond to the drugs that they respond to,” Dr. Downey said. “It’s frankly very insulting to say that physicians just force patients to go on medicines that are going to make them a bunch of money.”
In a June report to Congress, MedPAC recommended reducing the add-on payment for many drugs given in hospitals and clinics, which are thus covered by Part B, as part of a package of suggestions for addressing rising costs. Part B drug spending grew about 9% annually between 2009 and 2021, rising from $15.4 billion to $42.9 billion, MedPAC said.
Medicare’s current Part B drug pricing model starts with the reported average sales price (ASP) and then adds about 4.3% or 6%, depending on current budget-sequester law, to the cost of medicines.
MedPAC members voted 17-0 in April in favor of a general recommendation to revise the Part B payment approach. In the June report, MedPAC fleshes out this idea. It mentions a model in which the add-on Part B payment would be the lesser of either 6% of the ASP, 3% plus $24, or $220.
The majority of Part B drug administrations are for very low-priced drugs, MedPAC said. But for some of the more costly ones, annual prices can be more than $400,000 per patient, and future launch prices may be even higher for certain types of products, such as gene therapies, MedPAC said.
“There is no evidence that the costs of a drug’s administration are proportionate to the price of the drug,” MedPAC said.
Concerns about how well Medicare covers the cost of drug administration should be addressed through other pathways, such as the American Medical
Association’s Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (RUC), MedPAC said. AMA’s RUC advises the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on the physician fee schedule.
Congress is not obliged to act on or to even consider MedPAC’s work. In general, lawmakers and CMS often pay heed to the panel’s recommendations, sometimes incorporating them into new policy.
But this new MedPAC Part B recommendation has drawn strong opposition, similar to the response to a 2016 CMS plan to cut the Part B add-on payment. That plan, which CMS later abandoned, would have cut the markup on Part B drugs to 2.5% and added a flat fee to cover administration costs.
Why not focus on PBMs instead?
The timing of the MedPAC recommendation is poor, given that CMS already is trying to implement the Inflation Reduction Act and create a new system of direct Medicare drug price negotiations, as ordered by Congress, said Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist based in New Orleans.
A better approach for lowering drug prices would be to focus more on the operations of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), said Dr. Feldman, who also is vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations. A pending bipartisan Senate bill, for example, would prohibit PBM compensation based on the price of a drug as a condition of entering into a contract with a Medicare Part D plan.
Congress needs to take steps to unlink the profits of PBMs from higher drug prices, Dr. Feldman said.
“Until that happens, we can put all the lipstick we want on this big pig, but it’s not going to really fix the problem,” she said.
Reduced pay for drugs acquired through 340B program?
In an interview about the new MedPAC proposal, Ted Okon, executive director of the Community Oncology Alliance, urged renewed attention to what he sees as unintended consequences of the 340B discount drug program.
Under this program, certain hospitals can acquire drugs at steeply reduced prices, but they are not obliged to share those discounts with patients. Hospitals that participate in the 340B program can gain funds when patients and their insurers, including Medicare, pay more for the medicines hospitals and other organizations acquired with the 340B discount. Hospitals say they use the money from the 340B program to expand resources in their communities.
But rapid growth of the program in recent years has led to questions, especially about the role of contract pharmacies that manage the program. Congress created the 340B program in 1992 as a workaround to then new rules on Medicaid drug coverage.
In 2021, participating hospitals and clinics and organizations purchased about $44 billion worth of medicines through the 340B drug program. This was an increase of 16% from the previous year, according to a report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund. The number of sites, including hospitals and pharmacies, enrolled in the 340B program rose from 8,100 in 2000 to 50,000 by 2020, the report said.
MedPAC in 2016 urged CMS to reduce the amount Medicare pays for drugs acquired through the 340B program. CMS did so during the Trump administration, a policy later defended by the Biden administration.
But the U.S. Supreme Court last year said Medicare erred in its approach to making this cut, as earlier reported. Federal law required that the Department of Health and Human Services conduct a survey to support such a step, and HHS did not do this, the court said. CMS thus was ordered to return Medicare to the ASP+6% payment model for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program.
In the June report, though, MedPAC stuck by its 2016 recommendation that Medicare reduce its payments for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program despite this setback.
“We continue to believe that this approach is appropriate, and the specific level of payment reduction could be considered further as newer data become available,” MedPAC said.
Hospital, PhRMA split
Hospitals would certainly contest any renewed bid by CMS to drop Medicare’s pay for drugs purchased through the 340B program. The American Hospital Association objected to the MedPAC proposal regarding the add-on payment in Part B drug pricing.
MedPAC commissioners discussed this idea at a January meeting, prompting a February letter from the AHA to the panel. Like Dr. Feldman, AHA said it would be “premature” to launch into a revision of Part B drug pricing while the impact of the IRA on drug prices was still unclear.
AHA also noted that a reduction in Part B drug reimbursement would “shift the responsibility for the rapid increase in drug prices away from drug manufacturers, and instead places the burden on hospitals and patients.”
But the AHA gave a much warmer reception to another proposal MedPAC considered this year and that it included in its June report, which is a plan to address the high cost of certain drugs of as yet unconfirmed clinical benefit.
In April, the AHA said it supports a move toward a “value-based approach” in certain cases in which first-in-class medicines are sold under U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s accelerated approvals. Medicare could then cap payment for such drugs that have excessively high launch prices and uncertain clinical benefit, AHA said.
In the June report, MedPAC recommended that Medicare be able to place such a limit on Part B payments in certain cases, including ones in which companies do not meet FDA deadlines for postmarketing confirmatory trials.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) objected to this proposed change. The trade group for drugmakers said the FDA often revises and extends enrollment milestones for pending confirmatory trials when companies hit snags, such as challenges in enrolling patients, PhRMA said.
Reducing Part B payment for drugs for which confirmatory trials have been delayed would have a “disproportionate impact” on smaller and rural communities, where independent practices struggle to keep their doors open as it is, PhRMA spokeswoman Nicole Longo wrote in a blog post.
“If physicians can’t afford to administer a medicine, then they won’t and that means their patients won’t have access to them either,” Ms. Longo wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An influential panel proposed capping Medicare Part B pay for some drugs, arguing this would remove financial incentives to use more costly medicines when there are less expensive equivalents.
Medical groups have objected to both this recommendation from the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) and the panel’s underlying premise. MedPAC said financial as well as clinical factors can come into play in clinicians’ choices of drugs for patients.
In an interview, Christina Downey, MD, chair of the Government Affairs Committee of the American College of Rheumatology, said physicians in her field cannot switch patients’ medicines to try to make a profit.
“Patients only respond to the drugs that they respond to,” Dr. Downey said. “It’s frankly very insulting to say that physicians just force patients to go on medicines that are going to make them a bunch of money.”
In a June report to Congress, MedPAC recommended reducing the add-on payment for many drugs given in hospitals and clinics, which are thus covered by Part B, as part of a package of suggestions for addressing rising costs. Part B drug spending grew about 9% annually between 2009 and 2021, rising from $15.4 billion to $42.9 billion, MedPAC said.
Medicare’s current Part B drug pricing model starts with the reported average sales price (ASP) and then adds about 4.3% or 6%, depending on current budget-sequester law, to the cost of medicines.
MedPAC members voted 17-0 in April in favor of a general recommendation to revise the Part B payment approach. In the June report, MedPAC fleshes out this idea. It mentions a model in which the add-on Part B payment would be the lesser of either 6% of the ASP, 3% plus $24, or $220.
The majority of Part B drug administrations are for very low-priced drugs, MedPAC said. But for some of the more costly ones, annual prices can be more than $400,000 per patient, and future launch prices may be even higher for certain types of products, such as gene therapies, MedPAC said.
“There is no evidence that the costs of a drug’s administration are proportionate to the price of the drug,” MedPAC said.
Concerns about how well Medicare covers the cost of drug administration should be addressed through other pathways, such as the American Medical
Association’s Specialty Society Relative Value Scale Update Committee (RUC), MedPAC said. AMA’s RUC advises the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on the physician fee schedule.
Congress is not obliged to act on or to even consider MedPAC’s work. In general, lawmakers and CMS often pay heed to the panel’s recommendations, sometimes incorporating them into new policy.
But this new MedPAC Part B recommendation has drawn strong opposition, similar to the response to a 2016 CMS plan to cut the Part B add-on payment. That plan, which CMS later abandoned, would have cut the markup on Part B drugs to 2.5% and added a flat fee to cover administration costs.
Why not focus on PBMs instead?
The timing of the MedPAC recommendation is poor, given that CMS already is trying to implement the Inflation Reduction Act and create a new system of direct Medicare drug price negotiations, as ordered by Congress, said Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist based in New Orleans.
A better approach for lowering drug prices would be to focus more on the operations of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), said Dr. Feldman, who also is vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations. A pending bipartisan Senate bill, for example, would prohibit PBM compensation based on the price of a drug as a condition of entering into a contract with a Medicare Part D plan.
Congress needs to take steps to unlink the profits of PBMs from higher drug prices, Dr. Feldman said.
“Until that happens, we can put all the lipstick we want on this big pig, but it’s not going to really fix the problem,” she said.
Reduced pay for drugs acquired through 340B program?
In an interview about the new MedPAC proposal, Ted Okon, executive director of the Community Oncology Alliance, urged renewed attention to what he sees as unintended consequences of the 340B discount drug program.
Under this program, certain hospitals can acquire drugs at steeply reduced prices, but they are not obliged to share those discounts with patients. Hospitals that participate in the 340B program can gain funds when patients and their insurers, including Medicare, pay more for the medicines hospitals and other organizations acquired with the 340B discount. Hospitals say they use the money from the 340B program to expand resources in their communities.
But rapid growth of the program in recent years has led to questions, especially about the role of contract pharmacies that manage the program. Congress created the 340B program in 1992 as a workaround to then new rules on Medicaid drug coverage.
In 2021, participating hospitals and clinics and organizations purchased about $44 billion worth of medicines through the 340B drug program. This was an increase of 16% from the previous year, according to a report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund. The number of sites, including hospitals and pharmacies, enrolled in the 340B program rose from 8,100 in 2000 to 50,000 by 2020, the report said.
MedPAC in 2016 urged CMS to reduce the amount Medicare pays for drugs acquired through the 340B program. CMS did so during the Trump administration, a policy later defended by the Biden administration.
But the U.S. Supreme Court last year said Medicare erred in its approach to making this cut, as earlier reported. Federal law required that the Department of Health and Human Services conduct a survey to support such a step, and HHS did not do this, the court said. CMS thus was ordered to return Medicare to the ASP+6% payment model for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program.
In the June report, though, MedPAC stuck by its 2016 recommendation that Medicare reduce its payments for drugs purchased through the 340B discount program despite this setback.
“We continue to believe that this approach is appropriate, and the specific level of payment reduction could be considered further as newer data become available,” MedPAC said.
Hospital, PhRMA split
Hospitals would certainly contest any renewed bid by CMS to drop Medicare’s pay for drugs purchased through the 340B program. The American Hospital Association objected to the MedPAC proposal regarding the add-on payment in Part B drug pricing.
MedPAC commissioners discussed this idea at a January meeting, prompting a February letter from the AHA to the panel. Like Dr. Feldman, AHA said it would be “premature” to launch into a revision of Part B drug pricing while the impact of the IRA on drug prices was still unclear.
AHA also noted that a reduction in Part B drug reimbursement would “shift the responsibility for the rapid increase in drug prices away from drug manufacturers, and instead places the burden on hospitals and patients.”
But the AHA gave a much warmer reception to another proposal MedPAC considered this year and that it included in its June report, which is a plan to address the high cost of certain drugs of as yet unconfirmed clinical benefit.
In April, the AHA said it supports a move toward a “value-based approach” in certain cases in which first-in-class medicines are sold under U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s accelerated approvals. Medicare could then cap payment for such drugs that have excessively high launch prices and uncertain clinical benefit, AHA said.
In the June report, MedPAC recommended that Medicare be able to place such a limit on Part B payments in certain cases, including ones in which companies do not meet FDA deadlines for postmarketing confirmatory trials.
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) objected to this proposed change. The trade group for drugmakers said the FDA often revises and extends enrollment milestones for pending confirmatory trials when companies hit snags, such as challenges in enrolling patients, PhRMA said.
Reducing Part B payment for drugs for which confirmatory trials have been delayed would have a “disproportionate impact” on smaller and rural communities, where independent practices struggle to keep their doors open as it is, PhRMA spokeswoman Nicole Longo wrote in a blog post.
“If physicians can’t afford to administer a medicine, then they won’t and that means their patients won’t have access to them either,” Ms. Longo wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How not to establish rapport with your patient
1. Stride confidently into the room to greet your 84-year-old female patient.
2. Introduce yourself saying, “Hi, I’m Dr. Jeff Benabio.”
3. Extend your clenched fist toward her chest and wait for her to reciprocate.
4. Smile awkwardly behind your mask while you wait.
5. Advise that you are doing a fist bump instead of a handshake to prevent the spread of viruses.
6. Wait.
7. Explain that she can bump, also known as “dap,” you back by extending her clenched fist and bumping into yours.
8. Wait a bit more.
9. Lower your fist and pat her on the shoulder with your left hand. Do so gently so it doesn’t seem like you just did a quick right jab followed by a left hook.
10. Sit down diffidently and pray that you can help her so this office visit is not an utter disaster.
It seemed a good idea for 2020: Let’s stop shaking hands while we wait out this viral apocalypse. Sensible, but entering a patient room and just sitting down didn’t work. It felt cold, impolite – this isn’t the DMV. In medicine, a complete stranger has to trust us to get naked, tell intimate secrets, even be stuck by needles all within minutes of meeting. We needed a trust-building substitute greeting.
There was the Muslim hand-on-my-heart greeting. Or the Hindu “namaste” or Buddhist “amituofo” folded hands. Or perhaps the paternalistic shoulder pat? I went with the fist bump. With some of my partner docs, my old MBA squad, my neighbor, the fist bump felt natural, reciprocated without hesitation. But it fails with many patients. To understand why, it’s helpful to know the history of the fist bump, also known as the dap.
Dap is an acronym for Dignity And Pride. It’s a variation of a handshake that originated among Black soldiers in the Vietnam war as a means of showing fraternity and establishing connectedness. In Vietnam, 30% of the combat battalions were Black. Marginalized in the military and at home, they created a greeting that was meaningful and unique. The dap was a series of shakes, bumps, slaps, and hugs that was symbolic. It was a means of showing respect and humility, that no one is above others, that I’ve got your back and you’ve got mine. It was a powerful recognition of humanity and effective means of personal connection. It spread from the Black community to the general population and it exists still today. The choreographed pregame handshake you see so many NBA players engage in is a descendant of the dap. Like many rituals, it reinforces bonds with those who are your people, your team, those you trust.
The more generalized version is the simple fist bump. It is widely used, notably by President Obama, and in the appropriate circumstance, will almost always be reciprocated. But it doesn’t work well to create trust with a stranger. With a patient for example, you are not showing them respect for some accomplishment. Nor are we connecting with them as a member of your team. Unless this is a patient whom you’ve seen many times before, a fist bump attempt might be met with “are you serious?” In fact, a survey done in 2016 asking infectious disease professionals what they thought of fist bumps as a greeting, very few replied it was a good idea. Most felt it was unprofessional. Not to mention that a fist bump does not symbolize an agreement in the way that a handshake does (and has done since at least the 9th century BC).
With COVID waning and masks doffed, I’ve found myself back to handshaking. Yes, I sanitize before and after, another ritual that has symbolic as well as practical significance. I get fewer sideways glances from my geriatric patients for sure. But I do still offer a little dap for my liquid nitrogen–survivor kids and for the occasional fellow Gen Xer. “Wonder Twin powers, activate!”
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com
1. Stride confidently into the room to greet your 84-year-old female patient.
2. Introduce yourself saying, “Hi, I’m Dr. Jeff Benabio.”
3. Extend your clenched fist toward her chest and wait for her to reciprocate.
4. Smile awkwardly behind your mask while you wait.
5. Advise that you are doing a fist bump instead of a handshake to prevent the spread of viruses.
6. Wait.
7. Explain that she can bump, also known as “dap,” you back by extending her clenched fist and bumping into yours.
8. Wait a bit more.
9. Lower your fist and pat her on the shoulder with your left hand. Do so gently so it doesn’t seem like you just did a quick right jab followed by a left hook.
10. Sit down diffidently and pray that you can help her so this office visit is not an utter disaster.
It seemed a good idea for 2020: Let’s stop shaking hands while we wait out this viral apocalypse. Sensible, but entering a patient room and just sitting down didn’t work. It felt cold, impolite – this isn’t the DMV. In medicine, a complete stranger has to trust us to get naked, tell intimate secrets, even be stuck by needles all within minutes of meeting. We needed a trust-building substitute greeting.
There was the Muslim hand-on-my-heart greeting. Or the Hindu “namaste” or Buddhist “amituofo” folded hands. Or perhaps the paternalistic shoulder pat? I went with the fist bump. With some of my partner docs, my old MBA squad, my neighbor, the fist bump felt natural, reciprocated without hesitation. But it fails with many patients. To understand why, it’s helpful to know the history of the fist bump, also known as the dap.
Dap is an acronym for Dignity And Pride. It’s a variation of a handshake that originated among Black soldiers in the Vietnam war as a means of showing fraternity and establishing connectedness. In Vietnam, 30% of the combat battalions were Black. Marginalized in the military and at home, they created a greeting that was meaningful and unique. The dap was a series of shakes, bumps, slaps, and hugs that was symbolic. It was a means of showing respect and humility, that no one is above others, that I’ve got your back and you’ve got mine. It was a powerful recognition of humanity and effective means of personal connection. It spread from the Black community to the general population and it exists still today. The choreographed pregame handshake you see so many NBA players engage in is a descendant of the dap. Like many rituals, it reinforces bonds with those who are your people, your team, those you trust.
The more generalized version is the simple fist bump. It is widely used, notably by President Obama, and in the appropriate circumstance, will almost always be reciprocated. But it doesn’t work well to create trust with a stranger. With a patient for example, you are not showing them respect for some accomplishment. Nor are we connecting with them as a member of your team. Unless this is a patient whom you’ve seen many times before, a fist bump attempt might be met with “are you serious?” In fact, a survey done in 2016 asking infectious disease professionals what they thought of fist bumps as a greeting, very few replied it was a good idea. Most felt it was unprofessional. Not to mention that a fist bump does not symbolize an agreement in the way that a handshake does (and has done since at least the 9th century BC).
With COVID waning and masks doffed, I’ve found myself back to handshaking. Yes, I sanitize before and after, another ritual that has symbolic as well as practical significance. I get fewer sideways glances from my geriatric patients for sure. But I do still offer a little dap for my liquid nitrogen–survivor kids and for the occasional fellow Gen Xer. “Wonder Twin powers, activate!”
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com
1. Stride confidently into the room to greet your 84-year-old female patient.
2. Introduce yourself saying, “Hi, I’m Dr. Jeff Benabio.”
3. Extend your clenched fist toward her chest and wait for her to reciprocate.
4. Smile awkwardly behind your mask while you wait.
5. Advise that you are doing a fist bump instead of a handshake to prevent the spread of viruses.
6. Wait.
7. Explain that she can bump, also known as “dap,” you back by extending her clenched fist and bumping into yours.
8. Wait a bit more.
9. Lower your fist and pat her on the shoulder with your left hand. Do so gently so it doesn’t seem like you just did a quick right jab followed by a left hook.
10. Sit down diffidently and pray that you can help her so this office visit is not an utter disaster.
It seemed a good idea for 2020: Let’s stop shaking hands while we wait out this viral apocalypse. Sensible, but entering a patient room and just sitting down didn’t work. It felt cold, impolite – this isn’t the DMV. In medicine, a complete stranger has to trust us to get naked, tell intimate secrets, even be stuck by needles all within minutes of meeting. We needed a trust-building substitute greeting.
There was the Muslim hand-on-my-heart greeting. Or the Hindu “namaste” or Buddhist “amituofo” folded hands. Or perhaps the paternalistic shoulder pat? I went with the fist bump. With some of my partner docs, my old MBA squad, my neighbor, the fist bump felt natural, reciprocated without hesitation. But it fails with many patients. To understand why, it’s helpful to know the history of the fist bump, also known as the dap.
Dap is an acronym for Dignity And Pride. It’s a variation of a handshake that originated among Black soldiers in the Vietnam war as a means of showing fraternity and establishing connectedness. In Vietnam, 30% of the combat battalions were Black. Marginalized in the military and at home, they created a greeting that was meaningful and unique. The dap was a series of shakes, bumps, slaps, and hugs that was symbolic. It was a means of showing respect and humility, that no one is above others, that I’ve got your back and you’ve got mine. It was a powerful recognition of humanity and effective means of personal connection. It spread from the Black community to the general population and it exists still today. The choreographed pregame handshake you see so many NBA players engage in is a descendant of the dap. Like many rituals, it reinforces bonds with those who are your people, your team, those you trust.
The more generalized version is the simple fist bump. It is widely used, notably by President Obama, and in the appropriate circumstance, will almost always be reciprocated. But it doesn’t work well to create trust with a stranger. With a patient for example, you are not showing them respect for some accomplishment. Nor are we connecting with them as a member of your team. Unless this is a patient whom you’ve seen many times before, a fist bump attempt might be met with “are you serious?” In fact, a survey done in 2016 asking infectious disease professionals what they thought of fist bumps as a greeting, very few replied it was a good idea. Most felt it was unprofessional. Not to mention that a fist bump does not symbolize an agreement in the way that a handshake does (and has done since at least the 9th century BC).
With COVID waning and masks doffed, I’ve found myself back to handshaking. Yes, I sanitize before and after, another ritual that has symbolic as well as practical significance. I get fewer sideways glances from my geriatric patients for sure. But I do still offer a little dap for my liquid nitrogen–survivor kids and for the occasional fellow Gen Xer. “Wonder Twin powers, activate!”
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com