User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Should the Body Roundness Index Replace BMI?
In daily practice, physicians need a quick and simple way to assess whether a patient’s weight presents a health risk. For decades, the body mass index (BMI) has been used for this purpose, with calculations based on height and weight. Despite its convenience, BMI has faced increasing criticism.
According to experts, BRI may more accurately identify people with high levels of visceral fat than BMI. It’s well documented that abdominal fat is strongly linked to higher risks for obesity-related diseases.
Studies Support BRI
Several studies have suggested that BRI could be a valuable tool for assessing health risks. In June of this year, researchers from China reported a significant U-shaped association between BRI and overall mortality in a paper published in JAMA Network Open. People with very low or very high BRI had an increased risk for death, noted Xiaoqian Zhang, MD, from Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, and his colleagues.
A study published in September in the Journal of the American Heart Association showed that elevated BRI over several years was associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. “The BRI can be included as a predictive factor for cardiovascular disease incidence,” stated the authors, led by Man Yang, MD, from Nanjing Medical University in Nanjing, China.
Why Replace BMI?
Why is a replacement for BMI necessary? When asked by this news organization, Manfred Müller, MD, senior professor at the Institute of Human Nutrition and Food Science at the University of Kiel, in Germany, explained: “BMI was designed to provide a simple value that was as independent of body size as possible, that could detect obesity and estimate related disease risks. But scientifically, BMI has always been a very crude measure to characterize disease risks.”
Müller was part of a research group led by US mathematician Diana Thomas, PhD, who, at the time, worked at Montclair State University, Montclair, New Jersey, and now holds a position at the US Military Academy at West Point, in New York. The group developed and published the BRI in 2013.
BMI Classifies Bodybuilders as Obese
The researchers justified their search for a “better” anthropometric measure with two aspects of BMI that still constitute the main points of criticism of the widely used index today:
BMI incorrectly classifies individuals with significant muscle mass, like bodybuilders, as obese, as it doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle mass.
BMI provides no information about fat distribution in the body — whether it’s concentrated in the hips or the abdomen, for example.
In practice, this means that a person with a normal BMI could already have prediabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, which might go undetected if no further investigations are conducted based solely on their BMI.
The BRI aims to solve this problem. As the name suggests, this index seeks to capture a person’s “roundness.” The formula for calculating BRI includes waist circumference and height but excludes body weight:
BRI = 364.2 − 365.5 × √(1 − [Waist circumference in cm/2π]²/[0.5 × Height in cm]²)
In their 2013 article, Thomas, Müller, and colleagues wrote that it still needed to be proven whether their newly developed index correlated with mortality and the risk for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases — and whether it was sufficiently better than BMI to justify the more complex calculation.
Could BRI Replace BMI?
Opinions differ on whether the BRI should replace the BMI. Zhang’s team concluded that the BRI needs to be validated in additional independent cohorts. If it does, it could become a practical screening tool in patient care.
Yang’s research group is optimistic about the BRI’s future: “The longitudinal trajectory of the BRI could be used as a novel indicator of cardiovascular disease risk, which provides a new possibility for cardiovascular disease prevention,” they wrote.
However, even BRI Co-creator Thomas has concerns. “Our entire medical system has been built around the BMI,” she told JAMA, referring to factors such as children’s growth charts and dosage recommendations for medications. That cannot be changed overnight.
Any anthropometric measure intended to replace BMI would need to be rigorously validated across all age groups, genders, and ethnicities. The impact of interventions such as bariatric surgery, diet, and exercise on the new measure would also need to be demonstrated.
Anthropometric Measures Only for Clinical Use
Even if BRI proves to be a “better” metric than BMI for patient care, Müller believes it would be no more suitable for research than BMI. “Regardless of the anthropometric measure, these are practical tools for everyday use,” he stressed.
“A high BRI, like a high BMI, is a risk factor — similar to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, or smoking — but it is not a disease,” he added. “In practice, as a physician, I know that a patient with a high BMI or BRI has an increased risk. I need to pay attention to that patient.”
Problems arise when indices like BMI or BRI are used in research. “These ‘invented’ anthropometric measures have no biological basis, which can harm obesity research,” Müller emphasized.
He cited the example of genetic research into obesity, which seeks to identify associations between specific genetic patterns and BMI values. “Why should weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared be genetically determined?” he asked. “These measures are human-made constructs that have nothing to do with biology.”
Müller believes that the use of BMI has created a “gray area in obesity research” that may account for many of the “unexplained” phenomena in this field.
The BMI Might Be Responsible for the ‘Healthy Obese’
One such phenomenon is the much-discussed “healthy obese,” referring to individuals with a BMI over 30 who do not have high blood sugar, high blood pressure, metabolic disorders, or elevated uric acid levels. “It’s speculated that it must be due to genetic factors, but in reality, the classification is simply wrong,” Müller said.
According to Müller, research should rely on other methods to determine obesity or relevant fat. For example, to assess diabetes risk, liver fat needs to be measured through enzyme tests, ultrasonography, CT, or MRI.
Visceral fat is also important in assessing cardiometabolic risk. “In the doctor’s office, it’s acceptable to estimate this by looking at waist circumference or even BRI. But for research, that’s inadequate,” noted Müller. Direct measurement of trunk fat with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or visceral fat with CT or MRI is needed.
“You always have to distinguish between research and patient care. In daily practice, measures like BRI or BMI are sufficient for assessing cardiometabolic risk. But in research, they are not,” Müller explained. To accurately study the disease risks associated with obesity, one must be aware that “with BMI, you cannot create scientifically valid patient or population groups because this value is far too imprecise.”
This story was translated from Medscape’s German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In daily practice, physicians need a quick and simple way to assess whether a patient’s weight presents a health risk. For decades, the body mass index (BMI) has been used for this purpose, with calculations based on height and weight. Despite its convenience, BMI has faced increasing criticism.
According to experts, BRI may more accurately identify people with high levels of visceral fat than BMI. It’s well documented that abdominal fat is strongly linked to higher risks for obesity-related diseases.
Studies Support BRI
Several studies have suggested that BRI could be a valuable tool for assessing health risks. In June of this year, researchers from China reported a significant U-shaped association between BRI and overall mortality in a paper published in JAMA Network Open. People with very low or very high BRI had an increased risk for death, noted Xiaoqian Zhang, MD, from Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, and his colleagues.
A study published in September in the Journal of the American Heart Association showed that elevated BRI over several years was associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. “The BRI can be included as a predictive factor for cardiovascular disease incidence,” stated the authors, led by Man Yang, MD, from Nanjing Medical University in Nanjing, China.
Why Replace BMI?
Why is a replacement for BMI necessary? When asked by this news organization, Manfred Müller, MD, senior professor at the Institute of Human Nutrition and Food Science at the University of Kiel, in Germany, explained: “BMI was designed to provide a simple value that was as independent of body size as possible, that could detect obesity and estimate related disease risks. But scientifically, BMI has always been a very crude measure to characterize disease risks.”
Müller was part of a research group led by US mathematician Diana Thomas, PhD, who, at the time, worked at Montclair State University, Montclair, New Jersey, and now holds a position at the US Military Academy at West Point, in New York. The group developed and published the BRI in 2013.
BMI Classifies Bodybuilders as Obese
The researchers justified their search for a “better” anthropometric measure with two aspects of BMI that still constitute the main points of criticism of the widely used index today:
BMI incorrectly classifies individuals with significant muscle mass, like bodybuilders, as obese, as it doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle mass.
BMI provides no information about fat distribution in the body — whether it’s concentrated in the hips or the abdomen, for example.
In practice, this means that a person with a normal BMI could already have prediabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, which might go undetected if no further investigations are conducted based solely on their BMI.
The BRI aims to solve this problem. As the name suggests, this index seeks to capture a person’s “roundness.” The formula for calculating BRI includes waist circumference and height but excludes body weight:
BRI = 364.2 − 365.5 × √(1 − [Waist circumference in cm/2π]²/[0.5 × Height in cm]²)
In their 2013 article, Thomas, Müller, and colleagues wrote that it still needed to be proven whether their newly developed index correlated with mortality and the risk for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases — and whether it was sufficiently better than BMI to justify the more complex calculation.
Could BRI Replace BMI?
Opinions differ on whether the BRI should replace the BMI. Zhang’s team concluded that the BRI needs to be validated in additional independent cohorts. If it does, it could become a practical screening tool in patient care.
Yang’s research group is optimistic about the BRI’s future: “The longitudinal trajectory of the BRI could be used as a novel indicator of cardiovascular disease risk, which provides a new possibility for cardiovascular disease prevention,” they wrote.
However, even BRI Co-creator Thomas has concerns. “Our entire medical system has been built around the BMI,” she told JAMA, referring to factors such as children’s growth charts and dosage recommendations for medications. That cannot be changed overnight.
Any anthropometric measure intended to replace BMI would need to be rigorously validated across all age groups, genders, and ethnicities. The impact of interventions such as bariatric surgery, diet, and exercise on the new measure would also need to be demonstrated.
Anthropometric Measures Only for Clinical Use
Even if BRI proves to be a “better” metric than BMI for patient care, Müller believes it would be no more suitable for research than BMI. “Regardless of the anthropometric measure, these are practical tools for everyday use,” he stressed.
“A high BRI, like a high BMI, is a risk factor — similar to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, or smoking — but it is not a disease,” he added. “In practice, as a physician, I know that a patient with a high BMI or BRI has an increased risk. I need to pay attention to that patient.”
Problems arise when indices like BMI or BRI are used in research. “These ‘invented’ anthropometric measures have no biological basis, which can harm obesity research,” Müller emphasized.
He cited the example of genetic research into obesity, which seeks to identify associations between specific genetic patterns and BMI values. “Why should weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared be genetically determined?” he asked. “These measures are human-made constructs that have nothing to do with biology.”
Müller believes that the use of BMI has created a “gray area in obesity research” that may account for many of the “unexplained” phenomena in this field.
The BMI Might Be Responsible for the ‘Healthy Obese’
One such phenomenon is the much-discussed “healthy obese,” referring to individuals with a BMI over 30 who do not have high blood sugar, high blood pressure, metabolic disorders, or elevated uric acid levels. “It’s speculated that it must be due to genetic factors, but in reality, the classification is simply wrong,” Müller said.
According to Müller, research should rely on other methods to determine obesity or relevant fat. For example, to assess diabetes risk, liver fat needs to be measured through enzyme tests, ultrasonography, CT, or MRI.
Visceral fat is also important in assessing cardiometabolic risk. “In the doctor’s office, it’s acceptable to estimate this by looking at waist circumference or even BRI. But for research, that’s inadequate,” noted Müller. Direct measurement of trunk fat with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or visceral fat with CT or MRI is needed.
“You always have to distinguish between research and patient care. In daily practice, measures like BRI or BMI are sufficient for assessing cardiometabolic risk. But in research, they are not,” Müller explained. To accurately study the disease risks associated with obesity, one must be aware that “with BMI, you cannot create scientifically valid patient or population groups because this value is far too imprecise.”
This story was translated from Medscape’s German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In daily practice, physicians need a quick and simple way to assess whether a patient’s weight presents a health risk. For decades, the body mass index (BMI) has been used for this purpose, with calculations based on height and weight. Despite its convenience, BMI has faced increasing criticism.
According to experts, BRI may more accurately identify people with high levels of visceral fat than BMI. It’s well documented that abdominal fat is strongly linked to higher risks for obesity-related diseases.
Studies Support BRI
Several studies have suggested that BRI could be a valuable tool for assessing health risks. In June of this year, researchers from China reported a significant U-shaped association between BRI and overall mortality in a paper published in JAMA Network Open. People with very low or very high BRI had an increased risk for death, noted Xiaoqian Zhang, MD, from Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, and his colleagues.
A study published in September in the Journal of the American Heart Association showed that elevated BRI over several years was associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. “The BRI can be included as a predictive factor for cardiovascular disease incidence,” stated the authors, led by Man Yang, MD, from Nanjing Medical University in Nanjing, China.
Why Replace BMI?
Why is a replacement for BMI necessary? When asked by this news organization, Manfred Müller, MD, senior professor at the Institute of Human Nutrition and Food Science at the University of Kiel, in Germany, explained: “BMI was designed to provide a simple value that was as independent of body size as possible, that could detect obesity and estimate related disease risks. But scientifically, BMI has always been a very crude measure to characterize disease risks.”
Müller was part of a research group led by US mathematician Diana Thomas, PhD, who, at the time, worked at Montclair State University, Montclair, New Jersey, and now holds a position at the US Military Academy at West Point, in New York. The group developed and published the BRI in 2013.
BMI Classifies Bodybuilders as Obese
The researchers justified their search for a “better” anthropometric measure with two aspects of BMI that still constitute the main points of criticism of the widely used index today:
BMI incorrectly classifies individuals with significant muscle mass, like bodybuilders, as obese, as it doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle mass.
BMI provides no information about fat distribution in the body — whether it’s concentrated in the hips or the abdomen, for example.
In practice, this means that a person with a normal BMI could already have prediabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, which might go undetected if no further investigations are conducted based solely on their BMI.
The BRI aims to solve this problem. As the name suggests, this index seeks to capture a person’s “roundness.” The formula for calculating BRI includes waist circumference and height but excludes body weight:
BRI = 364.2 − 365.5 × √(1 − [Waist circumference in cm/2π]²/[0.5 × Height in cm]²)
In their 2013 article, Thomas, Müller, and colleagues wrote that it still needed to be proven whether their newly developed index correlated with mortality and the risk for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases — and whether it was sufficiently better than BMI to justify the more complex calculation.
Could BRI Replace BMI?
Opinions differ on whether the BRI should replace the BMI. Zhang’s team concluded that the BRI needs to be validated in additional independent cohorts. If it does, it could become a practical screening tool in patient care.
Yang’s research group is optimistic about the BRI’s future: “The longitudinal trajectory of the BRI could be used as a novel indicator of cardiovascular disease risk, which provides a new possibility for cardiovascular disease prevention,” they wrote.
However, even BRI Co-creator Thomas has concerns. “Our entire medical system has been built around the BMI,” she told JAMA, referring to factors such as children’s growth charts and dosage recommendations for medications. That cannot be changed overnight.
Any anthropometric measure intended to replace BMI would need to be rigorously validated across all age groups, genders, and ethnicities. The impact of interventions such as bariatric surgery, diet, and exercise on the new measure would also need to be demonstrated.
Anthropometric Measures Only for Clinical Use
Even if BRI proves to be a “better” metric than BMI for patient care, Müller believes it would be no more suitable for research than BMI. “Regardless of the anthropometric measure, these are practical tools for everyday use,” he stressed.
“A high BRI, like a high BMI, is a risk factor — similar to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, or smoking — but it is not a disease,” he added. “In practice, as a physician, I know that a patient with a high BMI or BRI has an increased risk. I need to pay attention to that patient.”
Problems arise when indices like BMI or BRI are used in research. “These ‘invented’ anthropometric measures have no biological basis, which can harm obesity research,” Müller emphasized.
He cited the example of genetic research into obesity, which seeks to identify associations between specific genetic patterns and BMI values. “Why should weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared be genetically determined?” he asked. “These measures are human-made constructs that have nothing to do with biology.”
Müller believes that the use of BMI has created a “gray area in obesity research” that may account for many of the “unexplained” phenomena in this field.
The BMI Might Be Responsible for the ‘Healthy Obese’
One such phenomenon is the much-discussed “healthy obese,” referring to individuals with a BMI over 30 who do not have high blood sugar, high blood pressure, metabolic disorders, or elevated uric acid levels. “It’s speculated that it must be due to genetic factors, but in reality, the classification is simply wrong,” Müller said.
According to Müller, research should rely on other methods to determine obesity or relevant fat. For example, to assess diabetes risk, liver fat needs to be measured through enzyme tests, ultrasonography, CT, or MRI.
Visceral fat is also important in assessing cardiometabolic risk. “In the doctor’s office, it’s acceptable to estimate this by looking at waist circumference or even BRI. But for research, that’s inadequate,” noted Müller. Direct measurement of trunk fat with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or visceral fat with CT or MRI is needed.
“You always have to distinguish between research and patient care. In daily practice, measures like BRI or BMI are sufficient for assessing cardiometabolic risk. But in research, they are not,” Müller explained. To accurately study the disease risks associated with obesity, one must be aware that “with BMI, you cannot create scientifically valid patient or population groups because this value is far too imprecise.”
This story was translated from Medscape’s German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Being ‘Manly’ a Threat to a Man’s Health?
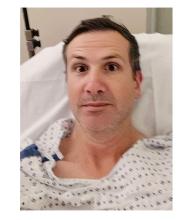
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here.
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
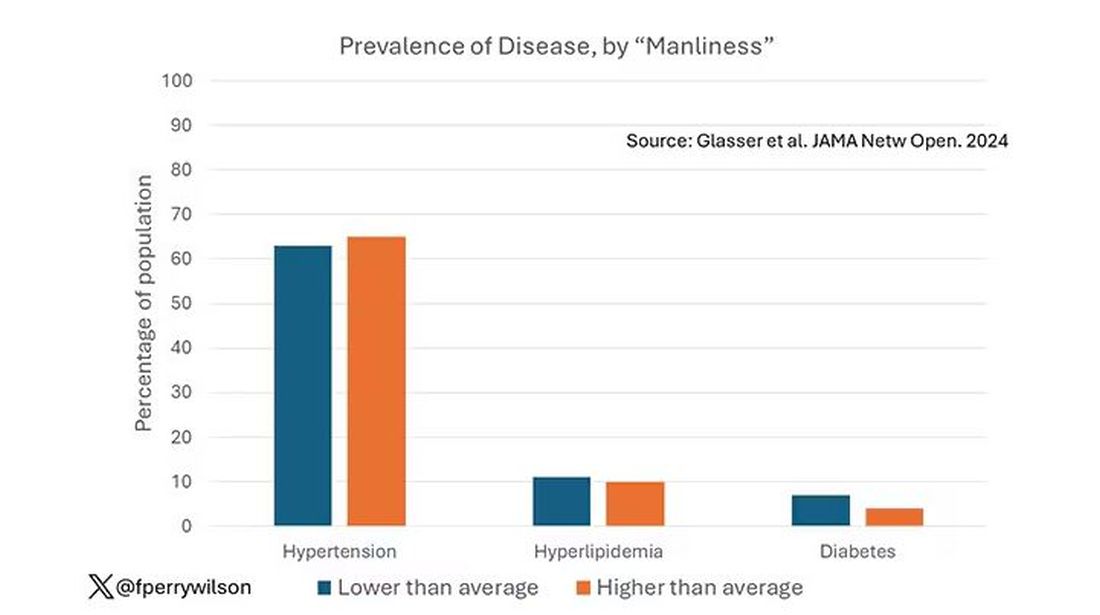
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
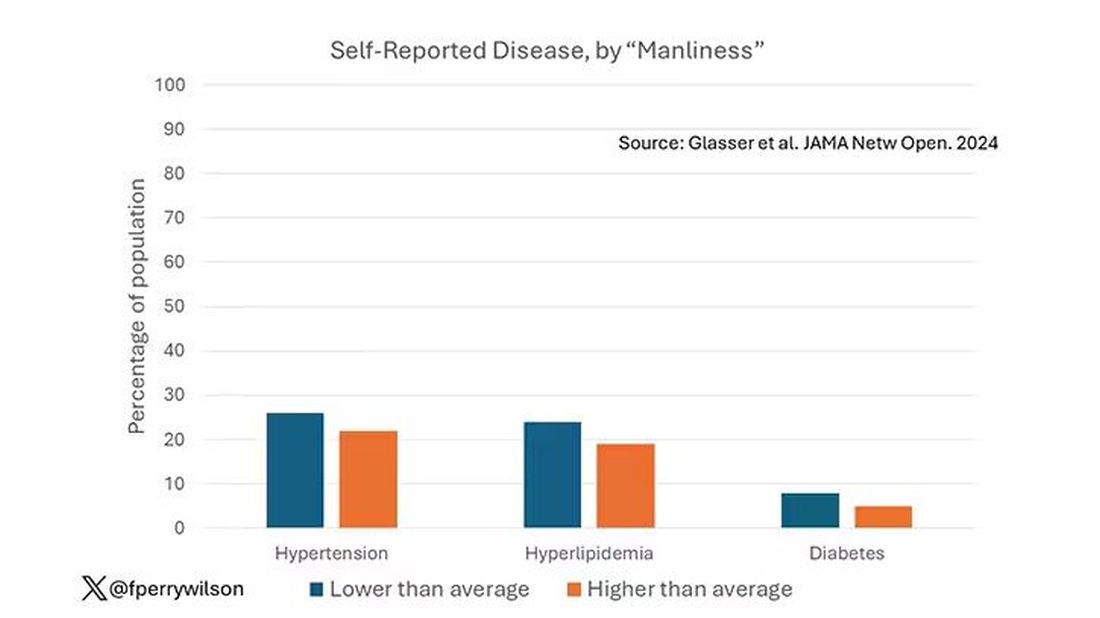
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
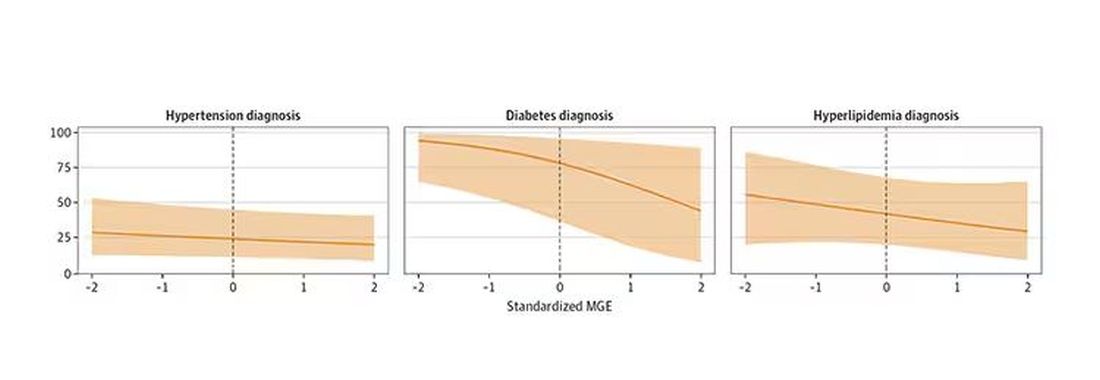
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here.
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here.
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Know the Ins and Outs of Prescribing Obesity Medications in Pediatric Patients
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — The rationale for using obesity medications in pediatric patients is that it’s using “a biological intervention to treat a biologically based disease,” according to Claudia Fox, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), Fox provided
“This field is changing so rapidly that even over the course of the last 3 or 4 months, the verbiage around what we should be calling these interventions has changed,” Fox noted. Instead of “anti-obesity” medications, “most of us are now using the term obesity medications to highlight or to reduce chances of stigma and bias that can come along with this topic.”
Jessica Ivers, MD, a pediatrician at Swedish Pediatrics in Seattle, Washington, said she found the session very informative, particularly because she doesn’t think many pediatricians currently feel very comfortable prescribing obesity medications.
“It answered questions that any general pediatrician would have, and it’s kind of a new field that people are learning about,” Ivers said. “I think we just need more education. It’s just too new, and people haven’t had the education and the support from colleagues to [use the medications].”
Fox first reminded attendees of precisely what obesity is: A chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that involves the accumulation and/or distribution of excess body fat that results in impaired health. AAP clinical practice guidelines currently advise that youth aged 12 years or older who have obesity be offered weight loss pharmacotherapy as an adjunct to lifestyle treatment, taking into consideration the indications, risks, and benefits of each medication.
That doesn’t necessarily mean every child aged 12 years or older with a body mass index (BMI) of at least the 95th percentile should be prescribed one of these medications, Fox said. But pediatricians should start becoming familiar with the options and recognize that part of reducing the stigma of this disease is emphasizing that these medications are prescribed not for “weight loss” but to treat the disease of obesity, Fox said. The guidelines advise “early, intensive care” and focusing on the whole child, “using a family-centered and nonstigmatizing approach that acknowledges obesity’s biologic, social, and structural drivers.”
Offer the Full Spectrum of Care Early On
Early intervention means starting obesity treatment at diagnosis, without watchful waiting or the previously recommended staged approach. Instead of trying lifestyle therapy for 3-6 months, then considering the addition of medication, and then considering bariatric surgery, “we should be offering the full spectrum of obesity care as appropriate for that individual patient,” Fox said.
Some children with severe obesity may need the combination of lifestyle therapy and pharmacotherapy right up front, whereas another might be able to try lifestyle therapy alone for a while first. “What we know is that, for most interventions, whether it is lifestyle therapy, a medication, or bariatric surgery, early response typically predicts longer-term response,” Fox said. A study conducted by her group, for example, found that a 3% BMI reduction after 1 month with lifestyle therapy was very predictive of clinically meaningful BMI reduction at 1 year.
As with any medical treatment, physicians need to weigh the risks of the medication — short-term side effects and unknown long-term risks (or benefits) — against the risks of not treating. Because obesity is a progressive disease, “if we don’t treat it, most will develop comorbid conditions, or worsening of their already present comorbid conditions, and this does indeed lead to shortened life expectancy,” Fox said. Those who should be treated with medication are obviously those in whom the benefits outweigh the risks, Fox said, which depends on their age, their comorbidities, the severity of obesity, and the safety and efficacy of medication options.
“If I have a patient who has maybe class 2 obesity but no other comorbid conditions, I may be less inclined to start an obesity medication than a kid who has class 1 obesity and obstructive sleep apnea, for instance,” Fox said. “Some of the medications are very, very potent and effective. If you have a kid who maybe has less severe forms of obesity, perhaps they don’t need something that’s so potent.”
BMI trajectory is also a factor to consider. She said she may not be too concerned about a 16-year-old who has always been at the 95th percentile and is otherwise healthy, but the situation is different for a 16-year-old who used to be in the 25th percentile and has rapidly progressed to the 50th and then 75th percentiles in a trajectory heading straight up.
Another factor that may come into play is the patient and family preferences, though Fox noted that weight bias and stigma often interfere here. If obesity medications are brought up, the family may bring up the need for more exercise and better meal prep at home.
“They have this sense that they just need to try harder, that if they did that, the obesity would somehow get better on its own,” Fox said. “That’s an internalized bias that it’s somehow their fault, rather than realizing that this is indeed a biological disorder.”
Finally, clinicians may want to consider the child’s response to lifestyle therapy and whether they have already had bariatric surgery because these medications can be prescribed in people who did not have an adequate response to surgery.
Overview of the Medications
There are currently six obesity medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in youth: Phentermine, orlistat, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, semaglutide, and setmelanotide.
Of these, orlistat is rarely used now because it results in the least amount of change in BMI (about a 3% loss change in BMI), has a lot of gastrointestinal side effects, often is not covered by insurance, and is expensive out of pocket. Setmelanotide is indicated only in those aged 6 years or older who have obesity because of Bardet-Biedl syndrome or one of three other rare genetic conditions: a POMC, LEPR, or PCSK1 deficiency. Fox therefore focused on the other medications besides these two.
While nearly all the currently available obesity medications are only approved in those aged 12 years or older, Fox noted that studies are ongoing at younger ages, so some of these medications may receive approval in younger populations in the future. The only one currently available for a younger age is liraglutide, which is approved down to 6 years old in children with type 2 diabetes.
“Very young kids who have very severe forms of obesity need intervention, and unfortunately, at this point, we really don’t have much to offer them,” Fox said.
Fox highlighted six key factors to consider in selecting a medication for those aged 12 years or older, though one of these, in the US healthcare system, can tend to trump all the others. Those factors are mechanism of action, side effect profile, effects on other diagnoses, patient/family preferences, provider comfort, and finally — the potentially overruling one — insurance coverage and access.
“These days, insurance coverage and access are really the No. 1 driver when I’m seeing a patient,” Fox said. “The first thing I do is look at their insurance and then also look at what kind of updates our pharmacist has given us about which medication is currently in stock.”
Each medication has different properties that should be considered with the child’s health profile. For example, topiramate is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor so likely shouldn’t be prescribed in a child who is taking any other carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Fox said she probably wouldn’t prescribe phentermine in a child with severe anxiety because it might enhance the anxiety effect. But if a child has migraines, she may be more inclined to try phentermine/topiramate first because the topiramate may help with the migraines. Similarly, if a child has type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, she may lean toward one of the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist drugs.
Liraglutide and Semaglutide
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both GLP-1 receptor agonists administered subcutaneously to reduce appetite, increase satiety, slow gastric emptying, and reduce the food reward response in the brain. Liraglutide can result in up to 4.5%-5% change in BMI, and semaglutide, the most potent of all the medications, can result in up to a 17% change in BMI.
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved for patients aged 12 years or older who weigh at least 60 kg and have a BMI of at least the 95th percentile. Liraglutide is also approved for those aged 10 years or older with type 2 diabetes. Both are contraindicated in those with a family history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia II. The risks to watch for include pancreatitis and gallbladder disease. Also keep in mind if you have a patient with type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance; prescribing a GLP-1 agonist is appropriate, but their insulin needs will decrease, necessitating close monitoring of their blood glucose, Fox noted.
These GLP-1 medications can be considered for those who have insurance coverage for them, who have diabetes or prediabetes, who are comfortable with daily (liraglutide) or weekly (semaglutide) injections, who have food cravings, and who have poor satiety or satiation. Without insurance, these medications are very expensive.
The most common side effects include injection site reactions and nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, though all these usually fade and can be minimized with small portions and slower eating if needed. Less common possible side effects can include abdominal pain, constipation, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and hypoglycemia. If patients develop severe belly pain that radiates to their back, they should be assessed for pancreatitis.
It’s also important to demonstrate for patients how to do the injections, Fox said. Liraglutide dosing begins at 0.6 mg daily for a week, followed by a week at 1.2 mg, a week at 1.8 mg, a week at 2.4 mg, and then 3 mg daily. Semaglutide dosing starts at 0.25 mg weekly for 4 weeks, then going up each subsequent month as needed to 0.5 mg, then 1 mg, then 1.7 mg, and finally 2.4 mg. Though there’s no standard follow-up schedule for these medications, Fox suggested considering monthly visits for the first 3 months and then every 2-3 months to assess heart rate and blood pressure, the injection site, adherence, side effects, and the effect on BMI and eating.
“Are they getting appetite suppression, but not too much appetite suppression?” Fox said. “Just like in eating disorder treatment, we want our patients to eat regularly spaced meals. If their appetite is so suppressed that they are hardly eating anything, that’s a problem.”
Fox also offered the following additional pearls about these medications:
- Though manufacturers have struggled to keep up with demand, the shortages of these medications are improving. However, beware the compounding pharmacies filling the gap because compounded medications are not FDA approved, and quality control issues are a concern.
- Prior authorizations are usually needed, and common reasons for denial to anticipate include lack of documentation on not having contraindications, the patient not following a low-calorie diet or engaging in physical activity, and the patient not having seen a registered dietitian.
- Patients should expect gastrointestinal side effects, but ondansetron can be prescribed to lessen the intensity.
Phentermine/Topiramate
Phentermine/topiramate extended-release is a once-daily oral tablet, with the phentermine acting to reduce appetite (by simulating the release of norepinephrine) and the topiramate reducing caloric intake and food reward response (by increasing gamma-aminobutyric acid activity). It’s approved for those aged 12 years or older with a BMI of at least the 95th percentile and should be considered in those with strong hunger, low energy, binge eating disorder, or migraines, as well as those who have insurance coverage for it. It can result in up to a 10% change in BMI.
Contraindications include pregnancy, substance use, cardiovascular disease (though it’s okay in patients with controlled hypertension), hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) use. Fox emphasized the teratogenic effects, so patients capable of pregnancy need to be on reliable birth control. The most common side effects include paresthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, and constipation.
A risk of topiramate is kidney stones, so patients should drink a lot of water, especially in hot weather, Fox said. Other risks can include metabolic acidosis, suicidality, poor cognitive function, high blood pressure, and renal impairment.
“If your patient is struggling academically, I might use this medication a bit more cautiously, particularly when the dose gets above 100 mg a day,” Fox said. “That’s when the cognitive effects tend to emerge more strongly.”
Patients with congenital heart disease should meet with their cardiologist before starting this medication, and although patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can take this, there is a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome because phentermine has a little bit of serotonergic activity, she said.
Before prescribing, do an exam to ensure the patient doesn’t have a heart murmur, isn’t hypertensive, isn’t pregnant, has normal kidney function, and has bicarbonate in a reasonable range. Dosing begins with a daily 3.75/23-mg capsule for 2 weeks, followed by 2 weeks at 7.5 mg/46 mg. As with the GLP-1 drugs, Fox advises considering monthly follow-ups for the first 3 months and then visits every 2-3 months. Each visit should include the assessment of cardiovascular health, heart rate, blood pressure, side effects, pregnancy risk, and the medication’s effect on BMI and eating. If the patient is tolerating a dose of 7.5 mg/46 mg, it can be increased to 11.25 mg/69 mg for 2 weeks and then to 15 mg/92 mg. Bicarbonate and creatinine should be checked every 6-12 months; if bicarbonate < 18 mEq/L, the dose should be reduced and then bicarbonate should be checked again a month later.
Fox noted that this drug is expected to go off patent in late 2024 or in 2025, which will substantially reduce the cost. It’s also possible to prescribe phentermine and topiramate separately, which may reduce costs or help with insurance coverage and can allow for evening dosing of topiramate.
Phentermine
Phentermine alone is only approved for those older than 16 years who have a BMI of at least 30, or at least 27 with weight-related comorbidities, and it’s not approved for use longer than 12 weeks. It results in a BMI change of up to 5%. It should be considered in those with strong hunger and low energy and in those who don’t have adequate insurance coverage because out-of-pocket costs can be as little as $5/mo.
Contraindications are the same as those for the combined pill above: Substance use, cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, MAOI use, and agitation. Again, take caution with patients who have hypertension, have congenital heart disease, or take SSRIs or insulin.
Side effects can include palpitations, tachycardia, dry mouth, headache, insomnia, and anxiety. The dose starts at 15 mg daily, and Fox advises following a similar follow-up as with the other medications, at which clinicians should assess BMI, the medication’s effect on eating, cardiovascular health, and side effects and have a discussion about off-label use. Off-label use refers to prescriptions lasting longer than 12 weeks, but it’s arguably safer than attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder stimulants because of the lower addiction potential, Fox said.
What Else to Know
Because obesity is a chronic disease, treatment will be ongoing, Fox noted. A lot of people will ask when or where the “off-ramp” for these medications is, but many people will need these medications long term just as someone with other chronic diseases requires lifetime pharmacotherapy. The treatment intensity will vary based on disease severity and individual characteristics, Fox said.
For those feeling overwhelmed by the options, Fox advises clinicians to start by picking one medication to learn and then spending the time to read the FDA package insert in full. Get samples and then closely follow patients to learn that medication well before moving on to learn another. She also noted the opportunity for pediatricians to see a pediatric obesity medicine fellowship.
No external funding was used for the presentation. Fox is a site principal investigator for clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. Ivers had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — The rationale for using obesity medications in pediatric patients is that it’s using “a biological intervention to treat a biologically based disease,” according to Claudia Fox, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), Fox provided
“This field is changing so rapidly that even over the course of the last 3 or 4 months, the verbiage around what we should be calling these interventions has changed,” Fox noted. Instead of “anti-obesity” medications, “most of us are now using the term obesity medications to highlight or to reduce chances of stigma and bias that can come along with this topic.”
Jessica Ivers, MD, a pediatrician at Swedish Pediatrics in Seattle, Washington, said she found the session very informative, particularly because she doesn’t think many pediatricians currently feel very comfortable prescribing obesity medications.
“It answered questions that any general pediatrician would have, and it’s kind of a new field that people are learning about,” Ivers said. “I think we just need more education. It’s just too new, and people haven’t had the education and the support from colleagues to [use the medications].”
Fox first reminded attendees of precisely what obesity is: A chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that involves the accumulation and/or distribution of excess body fat that results in impaired health. AAP clinical practice guidelines currently advise that youth aged 12 years or older who have obesity be offered weight loss pharmacotherapy as an adjunct to lifestyle treatment, taking into consideration the indications, risks, and benefits of each medication.
That doesn’t necessarily mean every child aged 12 years or older with a body mass index (BMI) of at least the 95th percentile should be prescribed one of these medications, Fox said. But pediatricians should start becoming familiar with the options and recognize that part of reducing the stigma of this disease is emphasizing that these medications are prescribed not for “weight loss” but to treat the disease of obesity, Fox said. The guidelines advise “early, intensive care” and focusing on the whole child, “using a family-centered and nonstigmatizing approach that acknowledges obesity’s biologic, social, and structural drivers.”
Offer the Full Spectrum of Care Early On
Early intervention means starting obesity treatment at diagnosis, without watchful waiting or the previously recommended staged approach. Instead of trying lifestyle therapy for 3-6 months, then considering the addition of medication, and then considering bariatric surgery, “we should be offering the full spectrum of obesity care as appropriate for that individual patient,” Fox said.
Some children with severe obesity may need the combination of lifestyle therapy and pharmacotherapy right up front, whereas another might be able to try lifestyle therapy alone for a while first. “What we know is that, for most interventions, whether it is lifestyle therapy, a medication, or bariatric surgery, early response typically predicts longer-term response,” Fox said. A study conducted by her group, for example, found that a 3% BMI reduction after 1 month with lifestyle therapy was very predictive of clinically meaningful BMI reduction at 1 year.
As with any medical treatment, physicians need to weigh the risks of the medication — short-term side effects and unknown long-term risks (or benefits) — against the risks of not treating. Because obesity is a progressive disease, “if we don’t treat it, most will develop comorbid conditions, or worsening of their already present comorbid conditions, and this does indeed lead to shortened life expectancy,” Fox said. Those who should be treated with medication are obviously those in whom the benefits outweigh the risks, Fox said, which depends on their age, their comorbidities, the severity of obesity, and the safety and efficacy of medication options.
“If I have a patient who has maybe class 2 obesity but no other comorbid conditions, I may be less inclined to start an obesity medication than a kid who has class 1 obesity and obstructive sleep apnea, for instance,” Fox said. “Some of the medications are very, very potent and effective. If you have a kid who maybe has less severe forms of obesity, perhaps they don’t need something that’s so potent.”
BMI trajectory is also a factor to consider. She said she may not be too concerned about a 16-year-old who has always been at the 95th percentile and is otherwise healthy, but the situation is different for a 16-year-old who used to be in the 25th percentile and has rapidly progressed to the 50th and then 75th percentiles in a trajectory heading straight up.
Another factor that may come into play is the patient and family preferences, though Fox noted that weight bias and stigma often interfere here. If obesity medications are brought up, the family may bring up the need for more exercise and better meal prep at home.
“They have this sense that they just need to try harder, that if they did that, the obesity would somehow get better on its own,” Fox said. “That’s an internalized bias that it’s somehow their fault, rather than realizing that this is indeed a biological disorder.”
Finally, clinicians may want to consider the child’s response to lifestyle therapy and whether they have already had bariatric surgery because these medications can be prescribed in people who did not have an adequate response to surgery.
Overview of the Medications
There are currently six obesity medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in youth: Phentermine, orlistat, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, semaglutide, and setmelanotide.
Of these, orlistat is rarely used now because it results in the least amount of change in BMI (about a 3% loss change in BMI), has a lot of gastrointestinal side effects, often is not covered by insurance, and is expensive out of pocket. Setmelanotide is indicated only in those aged 6 years or older who have obesity because of Bardet-Biedl syndrome or one of three other rare genetic conditions: a POMC, LEPR, or PCSK1 deficiency. Fox therefore focused on the other medications besides these two.
While nearly all the currently available obesity medications are only approved in those aged 12 years or older, Fox noted that studies are ongoing at younger ages, so some of these medications may receive approval in younger populations in the future. The only one currently available for a younger age is liraglutide, which is approved down to 6 years old in children with type 2 diabetes.
“Very young kids who have very severe forms of obesity need intervention, and unfortunately, at this point, we really don’t have much to offer them,” Fox said.
Fox highlighted six key factors to consider in selecting a medication for those aged 12 years or older, though one of these, in the US healthcare system, can tend to trump all the others. Those factors are mechanism of action, side effect profile, effects on other diagnoses, patient/family preferences, provider comfort, and finally — the potentially overruling one — insurance coverage and access.
“These days, insurance coverage and access are really the No. 1 driver when I’m seeing a patient,” Fox said. “The first thing I do is look at their insurance and then also look at what kind of updates our pharmacist has given us about which medication is currently in stock.”
Each medication has different properties that should be considered with the child’s health profile. For example, topiramate is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor so likely shouldn’t be prescribed in a child who is taking any other carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Fox said she probably wouldn’t prescribe phentermine in a child with severe anxiety because it might enhance the anxiety effect. But if a child has migraines, she may be more inclined to try phentermine/topiramate first because the topiramate may help with the migraines. Similarly, if a child has type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, she may lean toward one of the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist drugs.
Liraglutide and Semaglutide
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both GLP-1 receptor agonists administered subcutaneously to reduce appetite, increase satiety, slow gastric emptying, and reduce the food reward response in the brain. Liraglutide can result in up to 4.5%-5% change in BMI, and semaglutide, the most potent of all the medications, can result in up to a 17% change in BMI.
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved for patients aged 12 years or older who weigh at least 60 kg and have a BMI of at least the 95th percentile. Liraglutide is also approved for those aged 10 years or older with type 2 diabetes. Both are contraindicated in those with a family history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia II. The risks to watch for include pancreatitis and gallbladder disease. Also keep in mind if you have a patient with type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance; prescribing a GLP-1 agonist is appropriate, but their insulin needs will decrease, necessitating close monitoring of their blood glucose, Fox noted.
These GLP-1 medications can be considered for those who have insurance coverage for them, who have diabetes or prediabetes, who are comfortable with daily (liraglutide) or weekly (semaglutide) injections, who have food cravings, and who have poor satiety or satiation. Without insurance, these medications are very expensive.
The most common side effects include injection site reactions and nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, though all these usually fade and can be minimized with small portions and slower eating if needed. Less common possible side effects can include abdominal pain, constipation, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and hypoglycemia. If patients develop severe belly pain that radiates to their back, they should be assessed for pancreatitis.
It’s also important to demonstrate for patients how to do the injections, Fox said. Liraglutide dosing begins at 0.6 mg daily for a week, followed by a week at 1.2 mg, a week at 1.8 mg, a week at 2.4 mg, and then 3 mg daily. Semaglutide dosing starts at 0.25 mg weekly for 4 weeks, then going up each subsequent month as needed to 0.5 mg, then 1 mg, then 1.7 mg, and finally 2.4 mg. Though there’s no standard follow-up schedule for these medications, Fox suggested considering monthly visits for the first 3 months and then every 2-3 months to assess heart rate and blood pressure, the injection site, adherence, side effects, and the effect on BMI and eating.
“Are they getting appetite suppression, but not too much appetite suppression?” Fox said. “Just like in eating disorder treatment, we want our patients to eat regularly spaced meals. If their appetite is so suppressed that they are hardly eating anything, that’s a problem.”
Fox also offered the following additional pearls about these medications:
- Though manufacturers have struggled to keep up with demand, the shortages of these medications are improving. However, beware the compounding pharmacies filling the gap because compounded medications are not FDA approved, and quality control issues are a concern.
- Prior authorizations are usually needed, and common reasons for denial to anticipate include lack of documentation on not having contraindications, the patient not following a low-calorie diet or engaging in physical activity, and the patient not having seen a registered dietitian.
- Patients should expect gastrointestinal side effects, but ondansetron can be prescribed to lessen the intensity.
Phentermine/Topiramate
Phentermine/topiramate extended-release is a once-daily oral tablet, with the phentermine acting to reduce appetite (by simulating the release of norepinephrine) and the topiramate reducing caloric intake and food reward response (by increasing gamma-aminobutyric acid activity). It’s approved for those aged 12 years or older with a BMI of at least the 95th percentile and should be considered in those with strong hunger, low energy, binge eating disorder, or migraines, as well as those who have insurance coverage for it. It can result in up to a 10% change in BMI.
Contraindications include pregnancy, substance use, cardiovascular disease (though it’s okay in patients with controlled hypertension), hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) use. Fox emphasized the teratogenic effects, so patients capable of pregnancy need to be on reliable birth control. The most common side effects include paresthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, and constipation.
A risk of topiramate is kidney stones, so patients should drink a lot of water, especially in hot weather, Fox said. Other risks can include metabolic acidosis, suicidality, poor cognitive function, high blood pressure, and renal impairment.
“If your patient is struggling academically, I might use this medication a bit more cautiously, particularly when the dose gets above 100 mg a day,” Fox said. “That’s when the cognitive effects tend to emerge more strongly.”
Patients with congenital heart disease should meet with their cardiologist before starting this medication, and although patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can take this, there is a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome because phentermine has a little bit of serotonergic activity, she said.
Before prescribing, do an exam to ensure the patient doesn’t have a heart murmur, isn’t hypertensive, isn’t pregnant, has normal kidney function, and has bicarbonate in a reasonable range. Dosing begins with a daily 3.75/23-mg capsule for 2 weeks, followed by 2 weeks at 7.5 mg/46 mg. As with the GLP-1 drugs, Fox advises considering monthly follow-ups for the first 3 months and then visits every 2-3 months. Each visit should include the assessment of cardiovascular health, heart rate, blood pressure, side effects, pregnancy risk, and the medication’s effect on BMI and eating. If the patient is tolerating a dose of 7.5 mg/46 mg, it can be increased to 11.25 mg/69 mg for 2 weeks and then to 15 mg/92 mg. Bicarbonate and creatinine should be checked every 6-12 months; if bicarbonate < 18 mEq/L, the dose should be reduced and then bicarbonate should be checked again a month later.
Fox noted that this drug is expected to go off patent in late 2024 or in 2025, which will substantially reduce the cost. It’s also possible to prescribe phentermine and topiramate separately, which may reduce costs or help with insurance coverage and can allow for evening dosing of topiramate.
Phentermine
Phentermine alone is only approved for those older than 16 years who have a BMI of at least 30, or at least 27 with weight-related comorbidities, and it’s not approved for use longer than 12 weeks. It results in a BMI change of up to 5%. It should be considered in those with strong hunger and low energy and in those who don’t have adequate insurance coverage because out-of-pocket costs can be as little as $5/mo.
Contraindications are the same as those for the combined pill above: Substance use, cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, MAOI use, and agitation. Again, take caution with patients who have hypertension, have congenital heart disease, or take SSRIs or insulin.
Side effects can include palpitations, tachycardia, dry mouth, headache, insomnia, and anxiety. The dose starts at 15 mg daily, and Fox advises following a similar follow-up as with the other medications, at which clinicians should assess BMI, the medication’s effect on eating, cardiovascular health, and side effects and have a discussion about off-label use. Off-label use refers to prescriptions lasting longer than 12 weeks, but it’s arguably safer than attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder stimulants because of the lower addiction potential, Fox said.
What Else to Know
Because obesity is a chronic disease, treatment will be ongoing, Fox noted. A lot of people will ask when or where the “off-ramp” for these medications is, but many people will need these medications long term just as someone with other chronic diseases requires lifetime pharmacotherapy. The treatment intensity will vary based on disease severity and individual characteristics, Fox said.
For those feeling overwhelmed by the options, Fox advises clinicians to start by picking one medication to learn and then spending the time to read the FDA package insert in full. Get samples and then closely follow patients to learn that medication well before moving on to learn another. She also noted the opportunity for pediatricians to see a pediatric obesity medicine fellowship.
No external funding was used for the presentation. Fox is a site principal investigator for clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. Ivers had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — The rationale for using obesity medications in pediatric patients is that it’s using “a biological intervention to treat a biologically based disease,” according to Claudia Fox, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), Fox provided
“This field is changing so rapidly that even over the course of the last 3 or 4 months, the verbiage around what we should be calling these interventions has changed,” Fox noted. Instead of “anti-obesity” medications, “most of us are now using the term obesity medications to highlight or to reduce chances of stigma and bias that can come along with this topic.”
Jessica Ivers, MD, a pediatrician at Swedish Pediatrics in Seattle, Washington, said she found the session very informative, particularly because she doesn’t think many pediatricians currently feel very comfortable prescribing obesity medications.
“It answered questions that any general pediatrician would have, and it’s kind of a new field that people are learning about,” Ivers said. “I think we just need more education. It’s just too new, and people haven’t had the education and the support from colleagues to [use the medications].”
Fox first reminded attendees of precisely what obesity is: A chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that involves the accumulation and/or distribution of excess body fat that results in impaired health. AAP clinical practice guidelines currently advise that youth aged 12 years or older who have obesity be offered weight loss pharmacotherapy as an adjunct to lifestyle treatment, taking into consideration the indications, risks, and benefits of each medication.
That doesn’t necessarily mean every child aged 12 years or older with a body mass index (BMI) of at least the 95th percentile should be prescribed one of these medications, Fox said. But pediatricians should start becoming familiar with the options and recognize that part of reducing the stigma of this disease is emphasizing that these medications are prescribed not for “weight loss” but to treat the disease of obesity, Fox said. The guidelines advise “early, intensive care” and focusing on the whole child, “using a family-centered and nonstigmatizing approach that acknowledges obesity’s biologic, social, and structural drivers.”
Offer the Full Spectrum of Care Early On
Early intervention means starting obesity treatment at diagnosis, without watchful waiting or the previously recommended staged approach. Instead of trying lifestyle therapy for 3-6 months, then considering the addition of medication, and then considering bariatric surgery, “we should be offering the full spectrum of obesity care as appropriate for that individual patient,” Fox said.
Some children with severe obesity may need the combination of lifestyle therapy and pharmacotherapy right up front, whereas another might be able to try lifestyle therapy alone for a while first. “What we know is that, for most interventions, whether it is lifestyle therapy, a medication, or bariatric surgery, early response typically predicts longer-term response,” Fox said. A study conducted by her group, for example, found that a 3% BMI reduction after 1 month with lifestyle therapy was very predictive of clinically meaningful BMI reduction at 1 year.
As with any medical treatment, physicians need to weigh the risks of the medication — short-term side effects and unknown long-term risks (or benefits) — against the risks of not treating. Because obesity is a progressive disease, “if we don’t treat it, most will develop comorbid conditions, or worsening of their already present comorbid conditions, and this does indeed lead to shortened life expectancy,” Fox said. Those who should be treated with medication are obviously those in whom the benefits outweigh the risks, Fox said, which depends on their age, their comorbidities, the severity of obesity, and the safety and efficacy of medication options.
“If I have a patient who has maybe class 2 obesity but no other comorbid conditions, I may be less inclined to start an obesity medication than a kid who has class 1 obesity and obstructive sleep apnea, for instance,” Fox said. “Some of the medications are very, very potent and effective. If you have a kid who maybe has less severe forms of obesity, perhaps they don’t need something that’s so potent.”
BMI trajectory is also a factor to consider. She said she may not be too concerned about a 16-year-old who has always been at the 95th percentile and is otherwise healthy, but the situation is different for a 16-year-old who used to be in the 25th percentile and has rapidly progressed to the 50th and then 75th percentiles in a trajectory heading straight up.
Another factor that may come into play is the patient and family preferences, though Fox noted that weight bias and stigma often interfere here. If obesity medications are brought up, the family may bring up the need for more exercise and better meal prep at home.
“They have this sense that they just need to try harder, that if they did that, the obesity would somehow get better on its own,” Fox said. “That’s an internalized bias that it’s somehow their fault, rather than realizing that this is indeed a biological disorder.”
Finally, clinicians may want to consider the child’s response to lifestyle therapy and whether they have already had bariatric surgery because these medications can be prescribed in people who did not have an adequate response to surgery.
Overview of the Medications
There are currently six obesity medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in youth: Phentermine, orlistat, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, semaglutide, and setmelanotide.
Of these, orlistat is rarely used now because it results in the least amount of change in BMI (about a 3% loss change in BMI), has a lot of gastrointestinal side effects, often is not covered by insurance, and is expensive out of pocket. Setmelanotide is indicated only in those aged 6 years or older who have obesity because of Bardet-Biedl syndrome or one of three other rare genetic conditions: a POMC, LEPR, or PCSK1 deficiency. Fox therefore focused on the other medications besides these two.
While nearly all the currently available obesity medications are only approved in those aged 12 years or older, Fox noted that studies are ongoing at younger ages, so some of these medications may receive approval in younger populations in the future. The only one currently available for a younger age is liraglutide, which is approved down to 6 years old in children with type 2 diabetes.
“Very young kids who have very severe forms of obesity need intervention, and unfortunately, at this point, we really don’t have much to offer them,” Fox said.
Fox highlighted six key factors to consider in selecting a medication for those aged 12 years or older, though one of these, in the US healthcare system, can tend to trump all the others. Those factors are mechanism of action, side effect profile, effects on other diagnoses, patient/family preferences, provider comfort, and finally — the potentially overruling one — insurance coverage and access.
“These days, insurance coverage and access are really the No. 1 driver when I’m seeing a patient,” Fox said. “The first thing I do is look at their insurance and then also look at what kind of updates our pharmacist has given us about which medication is currently in stock.”
Each medication has different properties that should be considered with the child’s health profile. For example, topiramate is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor so likely shouldn’t be prescribed in a child who is taking any other carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Fox said she probably wouldn’t prescribe phentermine in a child with severe anxiety because it might enhance the anxiety effect. But if a child has migraines, she may be more inclined to try phentermine/topiramate first because the topiramate may help with the migraines. Similarly, if a child has type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, she may lean toward one of the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist drugs.
Liraglutide and Semaglutide
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both GLP-1 receptor agonists administered subcutaneously to reduce appetite, increase satiety, slow gastric emptying, and reduce the food reward response in the brain. Liraglutide can result in up to 4.5%-5% change in BMI, and semaglutide, the most potent of all the medications, can result in up to a 17% change in BMI.
Liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved for patients aged 12 years or older who weigh at least 60 kg and have a BMI of at least the 95th percentile. Liraglutide is also approved for those aged 10 years or older with type 2 diabetes. Both are contraindicated in those with a family history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia II. The risks to watch for include pancreatitis and gallbladder disease. Also keep in mind if you have a patient with type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance; prescribing a GLP-1 agonist is appropriate, but their insulin needs will decrease, necessitating close monitoring of their blood glucose, Fox noted.
These GLP-1 medications can be considered for those who have insurance coverage for them, who have diabetes or prediabetes, who are comfortable with daily (liraglutide) or weekly (semaglutide) injections, who have food cravings, and who have poor satiety or satiation. Without insurance, these medications are very expensive.
The most common side effects include injection site reactions and nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, though all these usually fade and can be minimized with small portions and slower eating if needed. Less common possible side effects can include abdominal pain, constipation, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and hypoglycemia. If patients develop severe belly pain that radiates to their back, they should be assessed for pancreatitis.
It’s also important to demonstrate for patients how to do the injections, Fox said. Liraglutide dosing begins at 0.6 mg daily for a week, followed by a week at 1.2 mg, a week at 1.8 mg, a week at 2.4 mg, and then 3 mg daily. Semaglutide dosing starts at 0.25 mg weekly for 4 weeks, then going up each subsequent month as needed to 0.5 mg, then 1 mg, then 1.7 mg, and finally 2.4 mg. Though there’s no standard follow-up schedule for these medications, Fox suggested considering monthly visits for the first 3 months and then every 2-3 months to assess heart rate and blood pressure, the injection site, adherence, side effects, and the effect on BMI and eating.
“Are they getting appetite suppression, but not too much appetite suppression?” Fox said. “Just like in eating disorder treatment, we want our patients to eat regularly spaced meals. If their appetite is so suppressed that they are hardly eating anything, that’s a problem.”
Fox also offered the following additional pearls about these medications:
- Though manufacturers have struggled to keep up with demand, the shortages of these medications are improving. However, beware the compounding pharmacies filling the gap because compounded medications are not FDA approved, and quality control issues are a concern.
- Prior authorizations are usually needed, and common reasons for denial to anticipate include lack of documentation on not having contraindications, the patient not following a low-calorie diet or engaging in physical activity, and the patient not having seen a registered dietitian.
- Patients should expect gastrointestinal side effects, but ondansetron can be prescribed to lessen the intensity.
Phentermine/Topiramate
Phentermine/topiramate extended-release is a once-daily oral tablet, with the phentermine acting to reduce appetite (by simulating the release of norepinephrine) and the topiramate reducing caloric intake and food reward response (by increasing gamma-aminobutyric acid activity). It’s approved for those aged 12 years or older with a BMI of at least the 95th percentile and should be considered in those with strong hunger, low energy, binge eating disorder, or migraines, as well as those who have insurance coverage for it. It can result in up to a 10% change in BMI.
Contraindications include pregnancy, substance use, cardiovascular disease (though it’s okay in patients with controlled hypertension), hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) use. Fox emphasized the teratogenic effects, so patients capable of pregnancy need to be on reliable birth control. The most common side effects include paresthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, and constipation.
A risk of topiramate is kidney stones, so patients should drink a lot of water, especially in hot weather, Fox said. Other risks can include metabolic acidosis, suicidality, poor cognitive function, high blood pressure, and renal impairment.
“If your patient is struggling academically, I might use this medication a bit more cautiously, particularly when the dose gets above 100 mg a day,” Fox said. “That’s when the cognitive effects tend to emerge more strongly.”
Patients with congenital heart disease should meet with their cardiologist before starting this medication, and although patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can take this, there is a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome because phentermine has a little bit of serotonergic activity, she said.
Before prescribing, do an exam to ensure the patient doesn’t have a heart murmur, isn’t hypertensive, isn’t pregnant, has normal kidney function, and has bicarbonate in a reasonable range. Dosing begins with a daily 3.75/23-mg capsule for 2 weeks, followed by 2 weeks at 7.5 mg/46 mg. As with the GLP-1 drugs, Fox advises considering monthly follow-ups for the first 3 months and then visits every 2-3 months. Each visit should include the assessment of cardiovascular health, heart rate, blood pressure, side effects, pregnancy risk, and the medication’s effect on BMI and eating. If the patient is tolerating a dose of 7.5 mg/46 mg, it can be increased to 11.25 mg/69 mg for 2 weeks and then to 15 mg/92 mg. Bicarbonate and creatinine should be checked every 6-12 months; if bicarbonate < 18 mEq/L, the dose should be reduced and then bicarbonate should be checked again a month later.
Fox noted that this drug is expected to go off patent in late 2024 or in 2025, which will substantially reduce the cost. It’s also possible to prescribe phentermine and topiramate separately, which may reduce costs or help with insurance coverage and can allow for evening dosing of topiramate.
Phentermine
Phentermine alone is only approved for those older than 16 years who have a BMI of at least 30, or at least 27 with weight-related comorbidities, and it’s not approved for use longer than 12 weeks. It results in a BMI change of up to 5%. It should be considered in those with strong hunger and low energy and in those who don’t have adequate insurance coverage because out-of-pocket costs can be as little as $5/mo.
Contraindications are the same as those for the combined pill above: Substance use, cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, MAOI use, and agitation. Again, take caution with patients who have hypertension, have congenital heart disease, or take SSRIs or insulin.
Side effects can include palpitations, tachycardia, dry mouth, headache, insomnia, and anxiety. The dose starts at 15 mg daily, and Fox advises following a similar follow-up as with the other medications, at which clinicians should assess BMI, the medication’s effect on eating, cardiovascular health, and side effects and have a discussion about off-label use. Off-label use refers to prescriptions lasting longer than 12 weeks, but it’s arguably safer than attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder stimulants because of the lower addiction potential, Fox said.
What Else to Know
Because obesity is a chronic disease, treatment will be ongoing, Fox noted. A lot of people will ask when or where the “off-ramp” for these medications is, but many people will need these medications long term just as someone with other chronic diseases requires lifetime pharmacotherapy. The treatment intensity will vary based on disease severity and individual characteristics, Fox said.
For those feeling overwhelmed by the options, Fox advises clinicians to start by picking one medication to learn and then spending the time to read the FDA package insert in full. Get samples and then closely follow patients to learn that medication well before moving on to learn another. She also noted the opportunity for pediatricians to see a pediatric obesity medicine fellowship.
No external funding was used for the presentation. Fox is a site principal investigator for clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. Ivers had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAP 2024
Thyroid Cancer Overdiagnosis Continues Despite Cautions
according to a recently published global study.
The proportion of thyroid cancer cases attributable to overdiagnosis globally was higher in women (78%) than in men (68%), with this rate varying substantially across countries, wrote Mengmeng Li, PhD, of the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China, and coauthors in an October paper in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Overdiagnosis refers to the diagnosis of lesions that would not cause symptoms and that would not progress, if left alone.
Increased testing for thyroid cancer, fueled in large part by the expansion of imaging technologies and progressively more intense and disorganized scrutiny of the thyroid, led many people to be treated for often indolent lesions, exposing them to potential side effects as well as financial and emotional distress.
Li and coauthors estimate that more than 1.7 million people might have been overdiagnosed between 2013 and 2017 in 63 countries.
“Overdiagnosis clearly emerged in some high-resource countries with private-based health systems in which access to healthcare overrules regulatory controls (eg, in the USA) and in some high-quality public health systems with easy and broad access to thyroid gland diagnostic examinations (eg, in Canada),” Li and coauthors wrote. “Conversely, thyroid cancer is less commonly diagnosed in those countries in which access to diagnosis is guided by strong regulatory rules (eg, in Nordic countries).”
Their study drew from almost 40 years of research, including the latest available data from the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer’s (IARC’s) Global Cancer Observatory. Li and coauthors examined patterns in the time trends of thyroid cancer, mortality data, and trends in diagnosis of thyroid cancer before testing became common in many nations.
This approach is needed in estimating overdiagnosis, where it’s not possible to see what’s happening on a case-by-case level, Salvatore Vaccarella, PhD, a scientist at IARC’s Cancer Surveillance Branch, said in an interview.
Researchers can’t tell whether an individual’s detected early-stage cancers would have remained indolent for years or eventually would have put their life at risk, he said. Instead, the patterns emerge through larger studies of the reported cases of cancer like thyroid tumors and then looking at separate datasets on mortality.
“We can only see that as a big phenomenon when we look at population-based data,” Vaccarella said.
Persisting Problem
Recognition of the harms of overdiagnosis has resulted in some reduction of the incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, Li and coauthors wrote. After adjusting for age, incidence has fallen from 19 per 100,000 women in 2013 to 16 per 100,000 women in 2017. The proportion of thyroid cancer attributed to overdiagnosis has dropped from 76% to 68% in the country.
The paper adds to the evidence suggesting that the rise in screening has not changed mortality rates for thyroid cancer. For example, Li and coauthors reported seeing “a small decrease in thyroid cancer mortality rates over time in some European countries, but this decline (less than 1 per 100,000 women) is marginal compared with the increases in incidence (reaching around 100 per 100,000 women).”
“Moreover, previous data show that the downward mortality trends had begun before the wide use of ultrasonography for early detection and that period and birth cohort effects have been declining, probably due to treatment advances and reduced prevalence of risk factors, such as the reduction in iodine deficiency,” they wrote.
In an interview, Amanda Davis, MD, of AnMed, a nonprofit health system based in Anderson, South Carolina, said the new paper from Li and Vaccarella provides further evidence for a cautious approach to thyroid nodules given concerns about overdiagnosis.
If early detection of cancer via discovery of thyroid nodules actually helped patients, mortality rates would have dropped with expansion of screening and the resulting diagnoses, said Davis, who is an associate program director at AnMed’s family medicine residency program and affiliate professor at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In many cases, people learn they have thyroid lesions after being tested for other conditions such as ultrasound done on carotid arteries to check for stroke risk. The most common form of thyroid cancer is the papillary form. Papillary thyroid cancer tends to be slow growing, carries a low risk for distant metastasis, and in many cases poses little risk. Some small (< 1 cm) papillary thyroid cancers can be monitored with active surveillance as opposed to thyroid lobectomy.
“So just finding more nodules incidentally or through screening ultrasound and even finding more papillary cancers via these methods does not make people healthier or decrease mortality,” Davis said.
“So just finding more things and even finding more papillary cancers does not increase our ability to treat people and keep them alive longer,” Davis said.
The 5-year survival rate for thyroid cancer overall is 98.1% and varies from 99.9% for localized disease to 55.3% for distant disease, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) said in a 2017 publication in JAMA. The task force that year gave a “D” rating on screening of asymptomatic people for thyroid cancer. That means there’s moderate certainty that screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic persons results in harms that outweigh the benefits. The decision to give this “D” rating meant this screening is not recommended. That’s still the panel’s view.
“You can think of it as a “D” for ‘don’t screen for thyroid cancer,’ ” in people who present no symptoms of this illness, John Wong, MD, the vice chair of the USPSTF, said in an interview.
In primary care, the challenge is assessing thyroid nodules detected when people undergo testing for another reason, such as an ultrasound of the carotid artery to check for stroke risk.
Thyroid nodules can be detected by ultrasonography in up to 68% of the general population, reported a study in American Family Physician. Nodules with suspicious features or ≥ 1 cm require fine needle aspiration. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology can be used to classify samples, with molecular testing applied to guide treatment when fine needle aspiration yields an indeterminate result.
New Thinking on Thyroid Cancer
There’s been a shift in recent years in the approach to how physicians should proceed if certain kinds of thyroid cancer are detected, Cari M. Kitahara, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute noted in a comment accompanying the Li paper.
“Clinicians need to be judicious in the use of thyroid ultrasonography, the diagnostic follow-up of incidentally detected thyroid nodules, and determining the optimal course of treatment,” Kitahara wrote. “For low-risk and incidentally detected tumors, strong consideration should be given to less intensive treatment options (eg, lobectomy, delayed treatment, and active surveillance).”
The American Thyroid Association guidelines encourage de-escalation of treatment for low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma up to 4 cm.
Physicians often need to make clear to patients how a diagnosis of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer differs from other oncology diagnoses, R. Michael Tuttle, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, said in an interview.
“I’ll frequently say that everything you’ve ever learned about cancer, you need to forget,” Tuttle said.
Some patients will mistakenly think any cancer diagnosis is a likely death sentence, meaning they should rush to get aggressive treatment. Tuttle has been a leader for many years in efforts in advancing active surveillance as an option for certain people with low-risk thyroid cancer.
“I often start my consultation by saying: ‘We’re going to choose between two right answers here. One right answer is watching right. One right answer is going to surgery,’ ” Tuttle said.
Patients with low-risk thyroid cancer tend to fall into two camps, with maximalists likely to seek quick treatment and minimalists more inclined for surveillance if that’s an option for them, Tuttle said. As opinions have shifted within the medical community about approaches to low-risk thyroid cancer, there’s also been some growing awareness among the public about thyroid overdiagnosis.
“Ten or 15 years ago, people thought we were crazy” to consider active surveillance as an option for low-risk thyroid cancers,” Tuttle said. “Now we have swung, at least in some of the public opinion, to this recognition that every little speck of cancer doesn’t need to be immediately taken out of your body.”
Some patients express regret about having learned that they have low-risk thyroid cancer, Tuttle said.
“Over the last 5 years, it’s not uncommon for patients to ask me, ‘Is this one of those that needs to be treated now, or is this one of those that we wish we would have never found?’ Or people will say, ‘My doctor talked me into an ultrasound, I didn’t want it’ or ‘I had a car wreck, and I found this nodule and I wished I had never found it.’ ”
This study from Li and coauthors was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, the Young Talents Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, the Italian Association for Cancer Research, and the Italian Ministry of Health. Davis and Tuttle had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a recently published global study.
The proportion of thyroid cancer cases attributable to overdiagnosis globally was higher in women (78%) than in men (68%), with this rate varying substantially across countries, wrote Mengmeng Li, PhD, of the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China, and coauthors in an October paper in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Overdiagnosis refers to the diagnosis of lesions that would not cause symptoms and that would not progress, if left alone.
Increased testing for thyroid cancer, fueled in large part by the expansion of imaging technologies and progressively more intense and disorganized scrutiny of the thyroid, led many people to be treated for often indolent lesions, exposing them to potential side effects as well as financial and emotional distress.
Li and coauthors estimate that more than 1.7 million people might have been overdiagnosed between 2013 and 2017 in 63 countries.
“Overdiagnosis clearly emerged in some high-resource countries with private-based health systems in which access to healthcare overrules regulatory controls (eg, in the USA) and in some high-quality public health systems with easy and broad access to thyroid gland diagnostic examinations (eg, in Canada),” Li and coauthors wrote. “Conversely, thyroid cancer is less commonly diagnosed in those countries in which access to diagnosis is guided by strong regulatory rules (eg, in Nordic countries).”
Their study drew from almost 40 years of research, including the latest available data from the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer’s (IARC’s) Global Cancer Observatory. Li and coauthors examined patterns in the time trends of thyroid cancer, mortality data, and trends in diagnosis of thyroid cancer before testing became common in many nations.
This approach is needed in estimating overdiagnosis, where it’s not possible to see what’s happening on a case-by-case level, Salvatore Vaccarella, PhD, a scientist at IARC’s Cancer Surveillance Branch, said in an interview.
Researchers can’t tell whether an individual’s detected early-stage cancers would have remained indolent for years or eventually would have put their life at risk, he said. Instead, the patterns emerge through larger studies of the reported cases of cancer like thyroid tumors and then looking at separate datasets on mortality.
“We can only see that as a big phenomenon when we look at population-based data,” Vaccarella said.
Persisting Problem
Recognition of the harms of overdiagnosis has resulted in some reduction of the incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, Li and coauthors wrote. After adjusting for age, incidence has fallen from 19 per 100,000 women in 2013 to 16 per 100,000 women in 2017. The proportion of thyroid cancer attributed to overdiagnosis has dropped from 76% to 68% in the country.
The paper adds to the evidence suggesting that the rise in screening has not changed mortality rates for thyroid cancer. For example, Li and coauthors reported seeing “a small decrease in thyroid cancer mortality rates over time in some European countries, but this decline (less than 1 per 100,000 women) is marginal compared with the increases in incidence (reaching around 100 per 100,000 women).”
“Moreover, previous data show that the downward mortality trends had begun before the wide use of ultrasonography for early detection and that period and birth cohort effects have been declining, probably due to treatment advances and reduced prevalence of risk factors, such as the reduction in iodine deficiency,” they wrote.
In an interview, Amanda Davis, MD, of AnMed, a nonprofit health system based in Anderson, South Carolina, said the new paper from Li and Vaccarella provides further evidence for a cautious approach to thyroid nodules given concerns about overdiagnosis.
If early detection of cancer via discovery of thyroid nodules actually helped patients, mortality rates would have dropped with expansion of screening and the resulting diagnoses, said Davis, who is an associate program director at AnMed’s family medicine residency program and affiliate professor at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In many cases, people learn they have thyroid lesions after being tested for other conditions such as ultrasound done on carotid arteries to check for stroke risk. The most common form of thyroid cancer is the papillary form. Papillary thyroid cancer tends to be slow growing, carries a low risk for distant metastasis, and in many cases poses little risk. Some small (< 1 cm) papillary thyroid cancers can be monitored with active surveillance as opposed to thyroid lobectomy.
“So just finding more nodules incidentally or through screening ultrasound and even finding more papillary cancers via these methods does not make people healthier or decrease mortality,” Davis said.
“So just finding more things and even finding more papillary cancers does not increase our ability to treat people and keep them alive longer,” Davis said.
The 5-year survival rate for thyroid cancer overall is 98.1% and varies from 99.9% for localized disease to 55.3% for distant disease, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) said in a 2017 publication in JAMA. The task force that year gave a “D” rating on screening of asymptomatic people for thyroid cancer. That means there’s moderate certainty that screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic persons results in harms that outweigh the benefits. The decision to give this “D” rating meant this screening is not recommended. That’s still the panel’s view.
“You can think of it as a “D” for ‘don’t screen for thyroid cancer,’ ” in people who present no symptoms of this illness, John Wong, MD, the vice chair of the USPSTF, said in an interview.
In primary care, the challenge is assessing thyroid nodules detected when people undergo testing for another reason, such as an ultrasound of the carotid artery to check for stroke risk.
Thyroid nodules can be detected by ultrasonography in up to 68% of the general population, reported a study in American Family Physician. Nodules with suspicious features or ≥ 1 cm require fine needle aspiration. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology can be used to classify samples, with molecular testing applied to guide treatment when fine needle aspiration yields an indeterminate result.
New Thinking on Thyroid Cancer
There’s been a shift in recent years in the approach to how physicians should proceed if certain kinds of thyroid cancer are detected, Cari M. Kitahara, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute noted in a comment accompanying the Li paper.
“Clinicians need to be judicious in the use of thyroid ultrasonography, the diagnostic follow-up of incidentally detected thyroid nodules, and determining the optimal course of treatment,” Kitahara wrote. “For low-risk and incidentally detected tumors, strong consideration should be given to less intensive treatment options (eg, lobectomy, delayed treatment, and active surveillance).”
The American Thyroid Association guidelines encourage de-escalation of treatment for low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma up to 4 cm.
Physicians often need to make clear to patients how a diagnosis of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer differs from other oncology diagnoses, R. Michael Tuttle, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, said in an interview.
“I’ll frequently say that everything you’ve ever learned about cancer, you need to forget,” Tuttle said.
Some patients will mistakenly think any cancer diagnosis is a likely death sentence, meaning they should rush to get aggressive treatment. Tuttle has been a leader for many years in efforts in advancing active surveillance as an option for certain people with low-risk thyroid cancer.
“I often start my consultation by saying: ‘We’re going to choose between two right answers here. One right answer is watching right. One right answer is going to surgery,’ ” Tuttle said.
Patients with low-risk thyroid cancer tend to fall into two camps, with maximalists likely to seek quick treatment and minimalists more inclined for surveillance if that’s an option for them, Tuttle said. As opinions have shifted within the medical community about approaches to low-risk thyroid cancer, there’s also been some growing awareness among the public about thyroid overdiagnosis.
“Ten or 15 years ago, people thought we were crazy” to consider active surveillance as an option for low-risk thyroid cancers,” Tuttle said. “Now we have swung, at least in some of the public opinion, to this recognition that every little speck of cancer doesn’t need to be immediately taken out of your body.”
Some patients express regret about having learned that they have low-risk thyroid cancer, Tuttle said.
“Over the last 5 years, it’s not uncommon for patients to ask me, ‘Is this one of those that needs to be treated now, or is this one of those that we wish we would have never found?’ Or people will say, ‘My doctor talked me into an ultrasound, I didn’t want it’ or ‘I had a car wreck, and I found this nodule and I wished I had never found it.’ ”
This study from Li and coauthors was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, the Young Talents Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, the Italian Association for Cancer Research, and the Italian Ministry of Health. Davis and Tuttle had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a recently published global study.
The proportion of thyroid cancer cases attributable to overdiagnosis globally was higher in women (78%) than in men (68%), with this rate varying substantially across countries, wrote Mengmeng Li, PhD, of the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China, and coauthors in an October paper in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Overdiagnosis refers to the diagnosis of lesions that would not cause symptoms and that would not progress, if left alone.
Increased testing for thyroid cancer, fueled in large part by the expansion of imaging technologies and progressively more intense and disorganized scrutiny of the thyroid, led many people to be treated for often indolent lesions, exposing them to potential side effects as well as financial and emotional distress.
Li and coauthors estimate that more than 1.7 million people might have been overdiagnosed between 2013 and 2017 in 63 countries.
“Overdiagnosis clearly emerged in some high-resource countries with private-based health systems in which access to healthcare overrules regulatory controls (eg, in the USA) and in some high-quality public health systems with easy and broad access to thyroid gland diagnostic examinations (eg, in Canada),” Li and coauthors wrote. “Conversely, thyroid cancer is less commonly diagnosed in those countries in which access to diagnosis is guided by strong regulatory rules (eg, in Nordic countries).”
Their study drew from almost 40 years of research, including the latest available data from the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer’s (IARC’s) Global Cancer Observatory. Li and coauthors examined patterns in the time trends of thyroid cancer, mortality data, and trends in diagnosis of thyroid cancer before testing became common in many nations.
This approach is needed in estimating overdiagnosis, where it’s not possible to see what’s happening on a case-by-case level, Salvatore Vaccarella, PhD, a scientist at IARC’s Cancer Surveillance Branch, said in an interview.
Researchers can’t tell whether an individual’s detected early-stage cancers would have remained indolent for years or eventually would have put their life at risk, he said. Instead, the patterns emerge through larger studies of the reported cases of cancer like thyroid tumors and then looking at separate datasets on mortality.
“We can only see that as a big phenomenon when we look at population-based data,” Vaccarella said.
Persisting Problem
Recognition of the harms of overdiagnosis has resulted in some reduction of the incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, Li and coauthors wrote. After adjusting for age, incidence has fallen from 19 per 100,000 women in 2013 to 16 per 100,000 women in 2017. The proportion of thyroid cancer attributed to overdiagnosis has dropped from 76% to 68% in the country.
The paper adds to the evidence suggesting that the rise in screening has not changed mortality rates for thyroid cancer. For example, Li and coauthors reported seeing “a small decrease in thyroid cancer mortality rates over time in some European countries, but this decline (less than 1 per 100,000 women) is marginal compared with the increases in incidence (reaching around 100 per 100,000 women).”
“Moreover, previous data show that the downward mortality trends had begun before the wide use of ultrasonography for early detection and that period and birth cohort effects have been declining, probably due to treatment advances and reduced prevalence of risk factors, such as the reduction in iodine deficiency,” they wrote.
In an interview, Amanda Davis, MD, of AnMed, a nonprofit health system based in Anderson, South Carolina, said the new paper from Li and Vaccarella provides further evidence for a cautious approach to thyroid nodules given concerns about overdiagnosis.
If early detection of cancer via discovery of thyroid nodules actually helped patients, mortality rates would have dropped with expansion of screening and the resulting diagnoses, said Davis, who is an associate program director at AnMed’s family medicine residency program and affiliate professor at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In many cases, people learn they have thyroid lesions after being tested for other conditions such as ultrasound done on carotid arteries to check for stroke risk. The most common form of thyroid cancer is the papillary form. Papillary thyroid cancer tends to be slow growing, carries a low risk for distant metastasis, and in many cases poses little risk. Some small (< 1 cm) papillary thyroid cancers can be monitored with active surveillance as opposed to thyroid lobectomy.
“So just finding more nodules incidentally or through screening ultrasound and even finding more papillary cancers via these methods does not make people healthier or decrease mortality,” Davis said.
“So just finding more things and even finding more papillary cancers does not increase our ability to treat people and keep them alive longer,” Davis said.
The 5-year survival rate for thyroid cancer overall is 98.1% and varies from 99.9% for localized disease to 55.3% for distant disease, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) said in a 2017 publication in JAMA. The task force that year gave a “D” rating on screening of asymptomatic people for thyroid cancer. That means there’s moderate certainty that screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic persons results in harms that outweigh the benefits. The decision to give this “D” rating meant this screening is not recommended. That’s still the panel’s view.
“You can think of it as a “D” for ‘don’t screen for thyroid cancer,’ ” in people who present no symptoms of this illness, John Wong, MD, the vice chair of the USPSTF, said in an interview.
In primary care, the challenge is assessing thyroid nodules detected when people undergo testing for another reason, such as an ultrasound of the carotid artery to check for stroke risk.
Thyroid nodules can be detected by ultrasonography in up to 68% of the general population, reported a study in American Family Physician. Nodules with suspicious features or ≥ 1 cm require fine needle aspiration. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology can be used to classify samples, with molecular testing applied to guide treatment when fine needle aspiration yields an indeterminate result.
New Thinking on Thyroid Cancer
There’s been a shift in recent years in the approach to how physicians should proceed if certain kinds of thyroid cancer are detected, Cari M. Kitahara, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute noted in a comment accompanying the Li paper.
“Clinicians need to be judicious in the use of thyroid ultrasonography, the diagnostic follow-up of incidentally detected thyroid nodules, and determining the optimal course of treatment,” Kitahara wrote. “For low-risk and incidentally detected tumors, strong consideration should be given to less intensive treatment options (eg, lobectomy, delayed treatment, and active surveillance).”
The American Thyroid Association guidelines encourage de-escalation of treatment for low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma up to 4 cm.
Physicians often need to make clear to patients how a diagnosis of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer differs from other oncology diagnoses, R. Michael Tuttle, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, said in an interview.
“I’ll frequently say that everything you’ve ever learned about cancer, you need to forget,” Tuttle said.
Some patients will mistakenly think any cancer diagnosis is a likely death sentence, meaning they should rush to get aggressive treatment. Tuttle has been a leader for many years in efforts in advancing active surveillance as an option for certain people with low-risk thyroid cancer.
“I often start my consultation by saying: ‘We’re going to choose between two right answers here. One right answer is watching right. One right answer is going to surgery,’ ” Tuttle said.
Patients with low-risk thyroid cancer tend to fall into two camps, with maximalists likely to seek quick treatment and minimalists more inclined for surveillance if that’s an option for them, Tuttle said. As opinions have shifted within the medical community about approaches to low-risk thyroid cancer, there’s also been some growing awareness among the public about thyroid overdiagnosis.
“Ten or 15 years ago, people thought we were crazy” to consider active surveillance as an option for low-risk thyroid cancers,” Tuttle said. “Now we have swung, at least in some of the public opinion, to this recognition that every little speck of cancer doesn’t need to be immediately taken out of your body.”
Some patients express regret about having learned that they have low-risk thyroid cancer, Tuttle said.
“Over the last 5 years, it’s not uncommon for patients to ask me, ‘Is this one of those that needs to be treated now, or is this one of those that we wish we would have never found?’ Or people will say, ‘My doctor talked me into an ultrasound, I didn’t want it’ or ‘I had a car wreck, and I found this nodule and I wished I had never found it.’ ”
This study from Li and coauthors was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, the Young Talents Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, the Italian Association for Cancer Research, and the Italian Ministry of Health. Davis and Tuttle had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
FIT Completion and Yield Similar in Younger and Older Adults
, a new study has found.
The study also found a similar low 3% rate of CRC detected at colonoscopy in both the younger and older adults.
“Our study suggests that adults ages 45-49 have a colorectal cancer risk that is similar to what we see in adults age 50,” senior author Jeffrey K. Lee, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research (DOR) in Oakland, California, said in a news release.
“The low number of cancers we found also provides support for initially offering younger adults a non-invasive test, like FIT, to determine which patients would benefit from a colonoscopy,” Lee noted.
Timely and Important Question
“This study addresses a timely and important clinical question, namely, is FIT an acceptable screening modality in patients aged 45-49,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“The finding that FIT completion and yield in younger patients is similar to those aged 50 and above is good news because it supports the use of this screening modality in the younger cohort,” said Gellad, section chief, gastroenterology, Durham VA Health Care System.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the age to start CRC screening from 50 to 45 years, in response to studies showing an increased rate of CRC in adults aged 45-49 years.
The decision to start CRC screening at age 45 was made based on modeling studies, which are dependent on assumptions, co-first author Theodore R. Levin, MD, who is also a gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente DOR, said in an interview.
“We thought it was important to collect real-world data on the experience of screening in this age group. We had no basis to know whether younger people would take up screening or if the yield of screening would be sufficiently high to warrant starting screening in this age group,” said Levin.
The researchers compared FIT screening completion and outcomes in 213,928 patients aged 45-49 years and 53,804 patients aged 50 years who received a FIT kit for the first time. The patients were from Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Washington, and Colorado.
Overall, FIT completion rates were slightly higher in the younger adults than in the 50-year-olds (38.9% vs 37.5%; adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.05), although the younger patients from Colorado were substantially less apt to complete a FIT (30.7% vs 40.2%; aRR, 0.77).
In the overall 45- to 49-year age group, 3.6% of adults had a positive FIT result, only slightly lower than the 4% positivity rate in the 50-year age group (aRR, 0.91).
About two thirds of adults in both groups who had a positive FIT result went on to have a colonoscopy within 3 months of receiving the test result.
Adenoma detection during colonoscopy was slightly lower in the younger than in the older group (58.8% vs 67.7%; aRR, 0.88). However, yields were similar for adenoma with advanced histology (13.2% vs 15.9%; aRR, 0.86), polyp with high-grade dysplasia (3.4% vs 5.1%; aRR, 0.68), sessile serrated lesion (10.3% vs 11.7%; aRR, 0.92), and CRC (2.8% vs 2.7%; aRR, 1.10).
FIT First Fits With Younger Adults’ Busy Lives
“Overall, people under 50 have lower incidence of cancer than people in their 50s, 60s, and 70s. However, if you do a test like FIT first, you can improve the yield of colonoscopy, which is a much more efficient strategy,” Levin said.
He noted that younger people are the least likely to be screened.
“They are busy with work and family responsibilities and may not realize that they are at risk for CRC. It is important to offer them a test that is easy to perform and does not require them to miss a day of work or arrange for a driver. They should be offered an option to screen with a stool-based test as an easy way to fit CRC screening into their busy lives,” Levin said.
Gellad said the study also highlights the limitations of FIT, “namely, that the low uptake and suboptimal colonoscopy follow-up of positive tests, also extend into the lower age group.”
Additionally, Gellad said he hopes other large systems will replicate this study to address the generalizability of these findings outside the Kaiser system.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Sydney R. Garfield Memorial Fund. Disclosures for study authors are available with the original article. Gellad consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a co-founder of Higgs Boson, Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study has found.
The study also found a similar low 3% rate of CRC detected at colonoscopy in both the younger and older adults.
“Our study suggests that adults ages 45-49 have a colorectal cancer risk that is similar to what we see in adults age 50,” senior author Jeffrey K. Lee, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research (DOR) in Oakland, California, said in a news release.
“The low number of cancers we found also provides support for initially offering younger adults a non-invasive test, like FIT, to determine which patients would benefit from a colonoscopy,” Lee noted.
Timely and Important Question
“This study addresses a timely and important clinical question, namely, is FIT an acceptable screening modality in patients aged 45-49,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“The finding that FIT completion and yield in younger patients is similar to those aged 50 and above is good news because it supports the use of this screening modality in the younger cohort,” said Gellad, section chief, gastroenterology, Durham VA Health Care System.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the age to start CRC screening from 50 to 45 years, in response to studies showing an increased rate of CRC in adults aged 45-49 years.
The decision to start CRC screening at age 45 was made based on modeling studies, which are dependent on assumptions, co-first author Theodore R. Levin, MD, who is also a gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente DOR, said in an interview.
“We thought it was important to collect real-world data on the experience of screening in this age group. We had no basis to know whether younger people would take up screening or if the yield of screening would be sufficiently high to warrant starting screening in this age group,” said Levin.
The researchers compared FIT screening completion and outcomes in 213,928 patients aged 45-49 years and 53,804 patients aged 50 years who received a FIT kit for the first time. The patients were from Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Washington, and Colorado.
Overall, FIT completion rates were slightly higher in the younger adults than in the 50-year-olds (38.9% vs 37.5%; adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.05), although the younger patients from Colorado were substantially less apt to complete a FIT (30.7% vs 40.2%; aRR, 0.77).
In the overall 45- to 49-year age group, 3.6% of adults had a positive FIT result, only slightly lower than the 4% positivity rate in the 50-year age group (aRR, 0.91).
About two thirds of adults in both groups who had a positive FIT result went on to have a colonoscopy within 3 months of receiving the test result.
Adenoma detection during colonoscopy was slightly lower in the younger than in the older group (58.8% vs 67.7%; aRR, 0.88). However, yields were similar for adenoma with advanced histology (13.2% vs 15.9%; aRR, 0.86), polyp with high-grade dysplasia (3.4% vs 5.1%; aRR, 0.68), sessile serrated lesion (10.3% vs 11.7%; aRR, 0.92), and CRC (2.8% vs 2.7%; aRR, 1.10).
FIT First Fits With Younger Adults’ Busy Lives
“Overall, people under 50 have lower incidence of cancer than people in their 50s, 60s, and 70s. However, if you do a test like FIT first, you can improve the yield of colonoscopy, which is a much more efficient strategy,” Levin said.
He noted that younger people are the least likely to be screened.
“They are busy with work and family responsibilities and may not realize that they are at risk for CRC. It is important to offer them a test that is easy to perform and does not require them to miss a day of work or arrange for a driver. They should be offered an option to screen with a stool-based test as an easy way to fit CRC screening into their busy lives,” Levin said.
Gellad said the study also highlights the limitations of FIT, “namely, that the low uptake and suboptimal colonoscopy follow-up of positive tests, also extend into the lower age group.”
Additionally, Gellad said he hopes other large systems will replicate this study to address the generalizability of these findings outside the Kaiser system.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Sydney R. Garfield Memorial Fund. Disclosures for study authors are available with the original article. Gellad consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a co-founder of Higgs Boson, Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study has found.
The study also found a similar low 3% rate of CRC detected at colonoscopy in both the younger and older adults.
“Our study suggests that adults ages 45-49 have a colorectal cancer risk that is similar to what we see in adults age 50,” senior author Jeffrey K. Lee, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research (DOR) in Oakland, California, said in a news release.
“The low number of cancers we found also provides support for initially offering younger adults a non-invasive test, like FIT, to determine which patients would benefit from a colonoscopy,” Lee noted.
Timely and Important Question
“This study addresses a timely and important clinical question, namely, is FIT an acceptable screening modality in patients aged 45-49,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“The finding that FIT completion and yield in younger patients is similar to those aged 50 and above is good news because it supports the use of this screening modality in the younger cohort,” said Gellad, section chief, gastroenterology, Durham VA Health Care System.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the age to start CRC screening from 50 to 45 years, in response to studies showing an increased rate of CRC in adults aged 45-49 years.
The decision to start CRC screening at age 45 was made based on modeling studies, which are dependent on assumptions, co-first author Theodore R. Levin, MD, who is also a gastroenterologist and research scientist at Kaiser Permanente DOR, said in an interview.
“We thought it was important to collect real-world data on the experience of screening in this age group. We had no basis to know whether younger people would take up screening or if the yield of screening would be sufficiently high to warrant starting screening in this age group,” said Levin.
The researchers compared FIT screening completion and outcomes in 213,928 patients aged 45-49 years and 53,804 patients aged 50 years who received a FIT kit for the first time. The patients were from Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Washington, and Colorado.
Overall, FIT completion rates were slightly higher in the younger adults than in the 50-year-olds (38.9% vs 37.5%; adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.05), although the younger patients from Colorado were substantially less apt to complete a FIT (30.7% vs 40.2%; aRR, 0.77).
In the overall 45- to 49-year age group, 3.6% of adults had a positive FIT result, only slightly lower than the 4% positivity rate in the 50-year age group (aRR, 0.91).
About two thirds of adults in both groups who had a positive FIT result went on to have a colonoscopy within 3 months of receiving the test result.
Adenoma detection during colonoscopy was slightly lower in the younger than in the older group (58.8% vs 67.7%; aRR, 0.88). However, yields were similar for adenoma with advanced histology (13.2% vs 15.9%; aRR, 0.86), polyp with high-grade dysplasia (3.4% vs 5.1%; aRR, 0.68), sessile serrated lesion (10.3% vs 11.7%; aRR, 0.92), and CRC (2.8% vs 2.7%; aRR, 1.10).
FIT First Fits With Younger Adults’ Busy Lives
“Overall, people under 50 have lower incidence of cancer than people in their 50s, 60s, and 70s. However, if you do a test like FIT first, you can improve the yield of colonoscopy, which is a much more efficient strategy,” Levin said.
He noted that younger people are the least likely to be screened.
“They are busy with work and family responsibilities and may not realize that they are at risk for CRC. It is important to offer them a test that is easy to perform and does not require them to miss a day of work or arrange for a driver. They should be offered an option to screen with a stool-based test as an easy way to fit CRC screening into their busy lives,” Levin said.
Gellad said the study also highlights the limitations of FIT, “namely, that the low uptake and suboptimal colonoscopy follow-up of positive tests, also extend into the lower age group.”
Additionally, Gellad said he hopes other large systems will replicate this study to address the generalizability of these findings outside the Kaiser system.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Sydney R. Garfield Memorial Fund. Disclosures for study authors are available with the original article. Gellad consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a co-founder of Higgs Boson, Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ultraprocessed Foods Associated With Relapse Risk in Crohn’s Disease
VIENNA —
Certain subgroups of UPFs, specifically bread, pastries, and starch as well as oil and spreads, exhibited the strongest association with relapse risks of approximately threefold.
“In addition to treating active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we want to maintain remission for the long term,” Chen Sarbagili Shabat, PhD, clinical dietitian from Tel Aviv Medical Center in Israel, said in an interview. “It’s highly important. We know environmental factors are associated with the disease, which is why we can treat active disease with diet. Likewise, we can manage CD in a remission state with diet.”
This is the first prospective study of this particular level of UPFs in people with Crohn’s disease who are in remission, noted Shabat, who presented the findings at United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Previously, a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies showed that a diet high in UPFs is associated with a 70% increased risk for development of CD, and a longitudinal study showed that “Western” dietary patterns were associated with relapse risk in patients with IBD, Shabat reported.
Effect of High vs Low Intake of UPFs
The current single-center, prospective cohort study, followed 111 patients with CD every 3 months until relapse for up to 1 year.
Participants were aged 18-75 years (mean age, 38 years), with a median disease duration of 8.7 years. They were required to have maintained steroid-free clinical remission (Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI), < 5) for 3 months or more. The median duration of clinical remission at recruitment was 3 years.
Data collection included HBI level, medication type and dosage to ensure constant therapy and full compliance, and a stool sample for fecal calprotectin measurement.
The primary outcome comprised a clinical relapse HBI ≥ 5 over the 12-month follow-up or a change in disease activity requiring a change in medication, hospitalization, or any IBD-related surgery.
Participants were asked to complete a processed food questionnaire to assess the intake of UPFs and a food frequency questionnaire to assess the total intake of energy, macronutrients, and micronutrients. UPFs were divided into high and low intakes using a median cutoff of 3.6 servings/day.
The low intake group included 57 participants, and the high intake group included 54.
A total of 24 patients (21.6%) experienced a clinical relapse event, 7 in the low intake group vs 17 in the high intake group (hazard ratio [HR], 3.86; 95% CI, 1.30-11.47; P = .015 after adjustments).
In a subset of 97 patients with baseline fecal calprotectin measurements, 6 (n = 50) in the low intake group experienced a clinical relapse vs 15 (n = 47) in the high intake group (HR, 4.32; 95% CI, 1.36-13.73; P = .013 after adjustments).
Fecal calprotectin results were also suggestive of an association between high intake of UPFs and gut inflammation, Shabat reported.
Food Groups and Emulsifiers
UPFs were divided into subgroups: Bread, pastries, and starch; oils and spreads; ultraprocessed meat; sweet products and desserts; and ultraprocessed beverages.
The highest associations with relapse were in the subgroup of bread, pastries, and starch (HR, 3.37; 95% CI, 1.26-8.25) and the subgroup of oils and spreads (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.02-7.45).
“The selection of healthy food is highly important, especially since we know that certain food ingredients can contribute to the pathogenesis of CD,” Shabat said. Patients can use partial enteral nutrition to provide 40%-50% of daily caloric intake in order to maintain remission, but she acknowledged it can be really difficult to adhere to.
She concluded by asserting that the study results, along with future research, should contribute to establishing nutritional guidelines to reduce UPF consumption in patients with CD in order to maintain remission.
Commenting on the study, Kevin Whelan, PhD, professor of dietetics and head of the Department of Nutritional Sciences at King’s College London in England, said that he was intrigued by the subgroup analysis that showed breads, pastries, oils, and spreads as having the strongest association with relapse risk.
He also remarked that these foods almost ubiquitously contain emulsifiers, and so the association might have less to do with UPFs in general and more to do with emulsifiers.
Concurring, Shabat noted that, while emulsifiers can negatively influence the microbiota and the gut barrier function, as well as contribute to intestinal inflammation, further mechanistic studies are required to understand these effects.
We need to determine if all additives have the same effect on the inflammatory process and also need studies looking at UPFs alone, she added.
Shabat reported receiving personal fees from Nestle Health Science (Wolfson Medical Center IP) for consulting and speaking and from Takeda and Ferring for speaking. Whelan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA —
Certain subgroups of UPFs, specifically bread, pastries, and starch as well as oil and spreads, exhibited the strongest association with relapse risks of approximately threefold.
“In addition to treating active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we want to maintain remission for the long term,” Chen Sarbagili Shabat, PhD, clinical dietitian from Tel Aviv Medical Center in Israel, said in an interview. “It’s highly important. We know environmental factors are associated with the disease, which is why we can treat active disease with diet. Likewise, we can manage CD in a remission state with diet.”
This is the first prospective study of this particular level of UPFs in people with Crohn’s disease who are in remission, noted Shabat, who presented the findings at United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Previously, a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies showed that a diet high in UPFs is associated with a 70% increased risk for development of CD, and a longitudinal study showed that “Western” dietary patterns were associated with relapse risk in patients with IBD, Shabat reported.
Effect of High vs Low Intake of UPFs
The current single-center, prospective cohort study, followed 111 patients with CD every 3 months until relapse for up to 1 year.
Participants were aged 18-75 years (mean age, 38 years), with a median disease duration of 8.7 years. They were required to have maintained steroid-free clinical remission (Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI), < 5) for 3 months or more. The median duration of clinical remission at recruitment was 3 years.
Data collection included HBI level, medication type and dosage to ensure constant therapy and full compliance, and a stool sample for fecal calprotectin measurement.
The primary outcome comprised a clinical relapse HBI ≥ 5 over the 12-month follow-up or a change in disease activity requiring a change in medication, hospitalization, or any IBD-related surgery.
Participants were asked to complete a processed food questionnaire to assess the intake of UPFs and a food frequency questionnaire to assess the total intake of energy, macronutrients, and micronutrients. UPFs were divided into high and low intakes using a median cutoff of 3.6 servings/day.
The low intake group included 57 participants, and the high intake group included 54.
A total of 24 patients (21.6%) experienced a clinical relapse event, 7 in the low intake group vs 17 in the high intake group (hazard ratio [HR], 3.86; 95% CI, 1.30-11.47; P = .015 after adjustments).
In a subset of 97 patients with baseline fecal calprotectin measurements, 6 (n = 50) in the low intake group experienced a clinical relapse vs 15 (n = 47) in the high intake group (HR, 4.32; 95% CI, 1.36-13.73; P = .013 after adjustments).
Fecal calprotectin results were also suggestive of an association between high intake of UPFs and gut inflammation, Shabat reported.
Food Groups and Emulsifiers
UPFs were divided into subgroups: Bread, pastries, and starch; oils and spreads; ultraprocessed meat; sweet products and desserts; and ultraprocessed beverages.
The highest associations with relapse were in the subgroup of bread, pastries, and starch (HR, 3.37; 95% CI, 1.26-8.25) and the subgroup of oils and spreads (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.02-7.45).
“The selection of healthy food is highly important, especially since we know that certain food ingredients can contribute to the pathogenesis of CD,” Shabat said. Patients can use partial enteral nutrition to provide 40%-50% of daily caloric intake in order to maintain remission, but she acknowledged it can be really difficult to adhere to.
She concluded by asserting that the study results, along with future research, should contribute to establishing nutritional guidelines to reduce UPF consumption in patients with CD in order to maintain remission.
Commenting on the study, Kevin Whelan, PhD, professor of dietetics and head of the Department of Nutritional Sciences at King’s College London in England, said that he was intrigued by the subgroup analysis that showed breads, pastries, oils, and spreads as having the strongest association with relapse risk.
He also remarked that these foods almost ubiquitously contain emulsifiers, and so the association might have less to do with UPFs in general and more to do with emulsifiers.
Concurring, Shabat noted that, while emulsifiers can negatively influence the microbiota and the gut barrier function, as well as contribute to intestinal inflammation, further mechanistic studies are required to understand these effects.
We need to determine if all additives have the same effect on the inflammatory process and also need studies looking at UPFs alone, she added.
Shabat reported receiving personal fees from Nestle Health Science (Wolfson Medical Center IP) for consulting and speaking and from Takeda and Ferring for speaking. Whelan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA —
Certain subgroups of UPFs, specifically bread, pastries, and starch as well as oil and spreads, exhibited the strongest association with relapse risks of approximately threefold.
“In addition to treating active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we want to maintain remission for the long term,” Chen Sarbagili Shabat, PhD, clinical dietitian from Tel Aviv Medical Center in Israel, said in an interview. “It’s highly important. We know environmental factors are associated with the disease, which is why we can treat active disease with diet. Likewise, we can manage CD in a remission state with diet.”
This is the first prospective study of this particular level of UPFs in people with Crohn’s disease who are in remission, noted Shabat, who presented the findings at United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Previously, a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies showed that a diet high in UPFs is associated with a 70% increased risk for development of CD, and a longitudinal study showed that “Western” dietary patterns were associated with relapse risk in patients with IBD, Shabat reported.
Effect of High vs Low Intake of UPFs
The current single-center, prospective cohort study, followed 111 patients with CD every 3 months until relapse for up to 1 year.
Participants were aged 18-75 years (mean age, 38 years), with a median disease duration of 8.7 years. They were required to have maintained steroid-free clinical remission (Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI), < 5) for 3 months or more. The median duration of clinical remission at recruitment was 3 years.
Data collection included HBI level, medication type and dosage to ensure constant therapy and full compliance, and a stool sample for fecal calprotectin measurement.
The primary outcome comprised a clinical relapse HBI ≥ 5 over the 12-month follow-up or a change in disease activity requiring a change in medication, hospitalization, or any IBD-related surgery.
Participants were asked to complete a processed food questionnaire to assess the intake of UPFs and a food frequency questionnaire to assess the total intake of energy, macronutrients, and micronutrients. UPFs were divided into high and low intakes using a median cutoff of 3.6 servings/day.
The low intake group included 57 participants, and the high intake group included 54.
A total of 24 patients (21.6%) experienced a clinical relapse event, 7 in the low intake group vs 17 in the high intake group (hazard ratio [HR], 3.86; 95% CI, 1.30-11.47; P = .015 after adjustments).
In a subset of 97 patients with baseline fecal calprotectin measurements, 6 (n = 50) in the low intake group experienced a clinical relapse vs 15 (n = 47) in the high intake group (HR, 4.32; 95% CI, 1.36-13.73; P = .013 after adjustments).
Fecal calprotectin results were also suggestive of an association between high intake of UPFs and gut inflammation, Shabat reported.
Food Groups and Emulsifiers
UPFs were divided into subgroups: Bread, pastries, and starch; oils and spreads; ultraprocessed meat; sweet products and desserts; and ultraprocessed beverages.
The highest associations with relapse were in the subgroup of bread, pastries, and starch (HR, 3.37; 95% CI, 1.26-8.25) and the subgroup of oils and spreads (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.02-7.45).
“The selection of healthy food is highly important, especially since we know that certain food ingredients can contribute to the pathogenesis of CD,” Shabat said. Patients can use partial enteral nutrition to provide 40%-50% of daily caloric intake in order to maintain remission, but she acknowledged it can be really difficult to adhere to.
She concluded by asserting that the study results, along with future research, should contribute to establishing nutritional guidelines to reduce UPF consumption in patients with CD in order to maintain remission.
Commenting on the study, Kevin Whelan, PhD, professor of dietetics and head of the Department of Nutritional Sciences at King’s College London in England, said that he was intrigued by the subgroup analysis that showed breads, pastries, oils, and spreads as having the strongest association with relapse risk.
He also remarked that these foods almost ubiquitously contain emulsifiers, and so the association might have less to do with UPFs in general and more to do with emulsifiers.
Concurring, Shabat noted that, while emulsifiers can negatively influence the microbiota and the gut barrier function, as well as contribute to intestinal inflammation, further mechanistic studies are required to understand these effects.
We need to determine if all additives have the same effect on the inflammatory process and also need studies looking at UPFs alone, she added.
Shabat reported receiving personal fees from Nestle Health Science (Wolfson Medical Center IP) for consulting and speaking and from Takeda and Ferring for speaking. Whelan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM UEG 2024
Starting Mammograms at Age 40: Will Women Benefit?
Last April, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) revised its breast cancer screening guidelines to recommend average-risk women start their screening mammograms at age 40, instead of age 50, and continue every other year until age 74.
The USPSTF’s recent recommendations align with those from major organizations, including the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American College of Radiology. The latest update comes from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which recommended a start age of 40 and continued screening either annually or every 2 years.
For USPSTF, the decision to recommend the earlier screening age, instead of keeping the choice an individualized one, was largely driven by the steady rise in breast cancer diagnoses among women in their 40s, alongside evidence that Black women are more likely to get breast cancer younger and die from the disease compared with White women.
But is this recommendation to screen earlier a change for the better?
Opinions vary.
USPSTF member John Wong, MD, chief of clinical decision making and a primary care physician at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, believes the new recommendation is the right move.
“It is now clear that screening every other year starting at age 40 has the potential to save about 20% more lives among all women and there is even greater potential benefit for Black women, who are much more likely to die from breast cancer,” Wong told Medscape last year.
However, in a recent Viewpoint in JAMA Internal Medicine, experts from the University of California San Francisco expressed their reservations about shifting the recommended screening age a decade earlier.
The trio — Karla Kerlikowske, MD, Laura Esserman, MD, and Jeffrey Tice, MD — called the new recommendations “surprising” given the lack of new randomized control trial data to support the change as well as data that show breast cancer deaths have been decreasing among women, including younger women.
More specifically, breast cancer deaths for women under 50 have decreased from 5.9 to 3.9 per 100,000 individuals between 2000 and 2020 — a decline that can likely be attributed to better treatments rather than increased screening effectiveness, the Viewpoint authors said.
However, moving the screening age earlier would not markedly improve survival for most women, the authors argued. According to USPSTF modeling, starting mammograms at age 40 instead of 50 could avert only 1.3 additional breast cancer deaths per 1000 women screened biennially and 1.8 additional breast cancer deaths among Black women.
Starting screening at 40, however, does come with an array of potential harms. These include 65 more benign biopsies per 1000 women screened, 1 in 2 women with a false-positive mammography result (503 per 1000), and 1 in 500 women with an over-diagnosed breast cancer, meaning the cancer would not have become clinically evident in their lifetime.
The use of digital breast tomosynthesis can slightly reduce the number of false-positives and benign biopsies compared to older mammography techniques, but these small improvements did not sway the overall pro-con assessment for the Viewpoint authors.
“False-positive results require additional imaging and are associated with anxiety for patients,” the authors noted. “Women who have benign biopsies may experience the potential adverse effects of biopsies, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring unnecessarily; and over-diagnosis may lead to unnecessary treatment.”
Kenneth Lin, MD, MPH, family physician and associate director of the Lancaster General Hospital Family Medicine Residency in Pennsylvania, agreed that starting mammograms at age 40 is not a change for the better.
Lin and colleagues conducted an analysis based on data from the USPSTF’s 2016 breast cancer screening report that similarly found 1 additional breast cancer death prevented per 1000 women screened starting at 40 vs 50, at a cost of 576 more false-positive results, 67 more benign breast biopsies, and 2 women diagnosed and treated unnecessarily.
Overall, “there is no compelling evidence to change our clinical approach to breast cancer screening for women in their 40s: individual decision-making based on patient preferences and values,” Lin wrote in a recent Medscape commentary.
But several experts not involved in the USPSTF recommendations agree with the change.
The updated recommendation to begin mammograms at age 40 for women at average risk “aligns with accumulating data suggesting that earlier and more frequent screening can save more lives, and is widely seen as a positive step,” said Lisa Abramson, MD, a radiologist specializing in breast imaging with Mount Sinai Health System and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Melissa Fana, MD, a breast surgical oncologist at NYU Langone Health, agreed that the revised recommendation is justified and “will undoubtedly save lives.”
“The recent change in the screening recommendation was meant to be inclusive, and provide women, particularly women aged 40 to 49 the opportunity to screen with mammography,” Fana said.
One major argument in favor of earlier screening is that it will help address racial inequities in breast cancer diagnoses, treatment, and deaths. Despite a 5% lower incidence of breast cancer, Black women are more likely to be diagnosed with distant-stage cancer or more aggressive breast cancer subtypes, such as triple-negative, compared with White women, and are more likely to die from breast cancer.
“We hope that the earlier initiation of mammography screening across the board will have a great net benefit in outcomes for Black women especially, who have been shown to have the poorest outcomes when it comes to breast cancer, in part because of long-standing inequities in social determinants of health,” said Cherie C. Hill, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, who coauthored the recent ACOG recommendations.
The Viewpoint authors Kerlikowske, Esserman and Tice agreed that Black women may benefit more from earlier screening. However, earlier screening does not address the underlying disparities in treatment and follow-up care for Black women, and it is unclear whether screening alone will help improve breast cancer mortality rates for Black women, the authors noted.
There is one place where experts seem to align: the importance of educating patients about their personal risk.
The Viewpoint authors favor a risk-based approach to help women decide whether to start screening before age 50.
“Engaging women in informed decision-making based on their invasive and advanced breast cancer risk would be a patient-centered approach toward tailored screening, informing when to consider starting screening and how often to screen,” the experts wrote.
For a woman to truly make an educated decision on whether she would like to screen or wait after age 40, she would at least need to know what her specific lifetime risk of developing breast cancer is, not the average risk is for American women in general, Fana told this news organization.
“Risk assessment calculators are widely available and include factors such as family history and reproductive history, and this information can evolve over time and affect lifetime risk,” Fana noted. But “some women just do not get this information.”
Abramson explained that ob.gyns. and primary care physicians will likely play a larger role in the early assessment of breast cancer risk, including discussions about genetic testing and personal risk factors starting as early as age 25.
“For clinicians, the emphasis may be on educating patients about their individual risk, ensuring timely mammograms, and referring higher-risk individuals for further testing or consultations with specialists,” Abramson added.
Esserman reported being a Blue Cross Medical Advisory Panel member, an uncompensated board member of Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative, which funds the I-SPY trial through the University of California, San Francisco, and having an investigator-initiated trial for high-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) funded through UCSF by Moderna for a DCIS phase 1 study. Tice and Kerlikowske reported receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute outside the submitted work. Abramson and Fana have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Last April, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) revised its breast cancer screening guidelines to recommend average-risk women start their screening mammograms at age 40, instead of age 50, and continue every other year until age 74.
The USPSTF’s recent recommendations align with those from major organizations, including the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American College of Radiology. The latest update comes from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which recommended a start age of 40 and continued screening either annually or every 2 years.
For USPSTF, the decision to recommend the earlier screening age, instead of keeping the choice an individualized one, was largely driven by the steady rise in breast cancer diagnoses among women in their 40s, alongside evidence that Black women are more likely to get breast cancer younger and die from the disease compared with White women.
But is this recommendation to screen earlier a change for the better?
Opinions vary.
USPSTF member John Wong, MD, chief of clinical decision making and a primary care physician at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, believes the new recommendation is the right move.
“It is now clear that screening every other year starting at age 40 has the potential to save about 20% more lives among all women and there is even greater potential benefit for Black women, who are much more likely to die from breast cancer,” Wong told Medscape last year.
However, in a recent Viewpoint in JAMA Internal Medicine, experts from the University of California San Francisco expressed their reservations about shifting the recommended screening age a decade earlier.
The trio — Karla Kerlikowske, MD, Laura Esserman, MD, and Jeffrey Tice, MD — called the new recommendations “surprising” given the lack of new randomized control trial data to support the change as well as data that show breast cancer deaths have been decreasing among women, including younger women.
More specifically, breast cancer deaths for women under 50 have decreased from 5.9 to 3.9 per 100,000 individuals between 2000 and 2020 — a decline that can likely be attributed to better treatments rather than increased screening effectiveness, the Viewpoint authors said.
However, moving the screening age earlier would not markedly improve survival for most women, the authors argued. According to USPSTF modeling, starting mammograms at age 40 instead of 50 could avert only 1.3 additional breast cancer deaths per 1000 women screened biennially and 1.8 additional breast cancer deaths among Black women.
Starting screening at 40, however, does come with an array of potential harms. These include 65 more benign biopsies per 1000 women screened, 1 in 2 women with a false-positive mammography result (503 per 1000), and 1 in 500 women with an over-diagnosed breast cancer, meaning the cancer would not have become clinically evident in their lifetime.
The use of digital breast tomosynthesis can slightly reduce the number of false-positives and benign biopsies compared to older mammography techniques, but these small improvements did not sway the overall pro-con assessment for the Viewpoint authors.
“False-positive results require additional imaging and are associated with anxiety for patients,” the authors noted. “Women who have benign biopsies may experience the potential adverse effects of biopsies, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring unnecessarily; and over-diagnosis may lead to unnecessary treatment.”
Kenneth Lin, MD, MPH, family physician and associate director of the Lancaster General Hospital Family Medicine Residency in Pennsylvania, agreed that starting mammograms at age 40 is not a change for the better.
Lin and colleagues conducted an analysis based on data from the USPSTF’s 2016 breast cancer screening report that similarly found 1 additional breast cancer death prevented per 1000 women screened starting at 40 vs 50, at a cost of 576 more false-positive results, 67 more benign breast biopsies, and 2 women diagnosed and treated unnecessarily.
Overall, “there is no compelling evidence to change our clinical approach to breast cancer screening for women in their 40s: individual decision-making based on patient preferences and values,” Lin wrote in a recent Medscape commentary.
But several experts not involved in the USPSTF recommendations agree with the change.
The updated recommendation to begin mammograms at age 40 for women at average risk “aligns with accumulating data suggesting that earlier and more frequent screening can save more lives, and is widely seen as a positive step,” said Lisa Abramson, MD, a radiologist specializing in breast imaging with Mount Sinai Health System and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Melissa Fana, MD, a breast surgical oncologist at NYU Langone Health, agreed that the revised recommendation is justified and “will undoubtedly save lives.”
“The recent change in the screening recommendation was meant to be inclusive, and provide women, particularly women aged 40 to 49 the opportunity to screen with mammography,” Fana said.
One major argument in favor of earlier screening is that it will help address racial inequities in breast cancer diagnoses, treatment, and deaths. Despite a 5% lower incidence of breast cancer, Black women are more likely to be diagnosed with distant-stage cancer or more aggressive breast cancer subtypes, such as triple-negative, compared with White women, and are more likely to die from breast cancer.
“We hope that the earlier initiation of mammography screening across the board will have a great net benefit in outcomes for Black women especially, who have been shown to have the poorest outcomes when it comes to breast cancer, in part because of long-standing inequities in social determinants of health,” said Cherie C. Hill, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, who coauthored the recent ACOG recommendations.
The Viewpoint authors Kerlikowske, Esserman and Tice agreed that Black women may benefit more from earlier screening. However, earlier screening does not address the underlying disparities in treatment and follow-up care for Black women, and it is unclear whether screening alone will help improve breast cancer mortality rates for Black women, the authors noted.
There is one place where experts seem to align: the importance of educating patients about their personal risk.
The Viewpoint authors favor a risk-based approach to help women decide whether to start screening before age 50.
“Engaging women in informed decision-making based on their invasive and advanced breast cancer risk would be a patient-centered approach toward tailored screening, informing when to consider starting screening and how often to screen,” the experts wrote.
For a woman to truly make an educated decision on whether she would like to screen or wait after age 40, she would at least need to know what her specific lifetime risk of developing breast cancer is, not the average risk is for American women in general, Fana told this news organization.
“Risk assessment calculators are widely available and include factors such as family history and reproductive history, and this information can evolve over time and affect lifetime risk,” Fana noted. But “some women just do not get this information.”
Abramson explained that ob.gyns. and primary care physicians will likely play a larger role in the early assessment of breast cancer risk, including discussions about genetic testing and personal risk factors starting as early as age 25.
“For clinicians, the emphasis may be on educating patients about their individual risk, ensuring timely mammograms, and referring higher-risk individuals for further testing or consultations with specialists,” Abramson added.
Esserman reported being a Blue Cross Medical Advisory Panel member, an uncompensated board member of Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative, which funds the I-SPY trial through the University of California, San Francisco, and having an investigator-initiated trial for high-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) funded through UCSF by Moderna for a DCIS phase 1 study. Tice and Kerlikowske reported receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute outside the submitted work. Abramson and Fana have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Last April, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) revised its breast cancer screening guidelines to recommend average-risk women start their screening mammograms at age 40, instead of age 50, and continue every other year until age 74.
The USPSTF’s recent recommendations align with those from major organizations, including the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American College of Radiology. The latest update comes from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which recommended a start age of 40 and continued screening either annually or every 2 years.
For USPSTF, the decision to recommend the earlier screening age, instead of keeping the choice an individualized one, was largely driven by the steady rise in breast cancer diagnoses among women in their 40s, alongside evidence that Black women are more likely to get breast cancer younger and die from the disease compared with White women.
But is this recommendation to screen earlier a change for the better?
Opinions vary.
USPSTF member John Wong, MD, chief of clinical decision making and a primary care physician at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, believes the new recommendation is the right move.
“It is now clear that screening every other year starting at age 40 has the potential to save about 20% more lives among all women and there is even greater potential benefit for Black women, who are much more likely to die from breast cancer,” Wong told Medscape last year.
However, in a recent Viewpoint in JAMA Internal Medicine, experts from the University of California San Francisco expressed their reservations about shifting the recommended screening age a decade earlier.
The trio — Karla Kerlikowske, MD, Laura Esserman, MD, and Jeffrey Tice, MD — called the new recommendations “surprising” given the lack of new randomized control trial data to support the change as well as data that show breast cancer deaths have been decreasing among women, including younger women.
More specifically, breast cancer deaths for women under 50 have decreased from 5.9 to 3.9 per 100,000 individuals between 2000 and 2020 — a decline that can likely be attributed to better treatments rather than increased screening effectiveness, the Viewpoint authors said.
However, moving the screening age earlier would not markedly improve survival for most women, the authors argued. According to USPSTF modeling, starting mammograms at age 40 instead of 50 could avert only 1.3 additional breast cancer deaths per 1000 women screened biennially and 1.8 additional breast cancer deaths among Black women.
Starting screening at 40, however, does come with an array of potential harms. These include 65 more benign biopsies per 1000 women screened, 1 in 2 women with a false-positive mammography result (503 per 1000), and 1 in 500 women with an over-diagnosed breast cancer, meaning the cancer would not have become clinically evident in their lifetime.
The use of digital breast tomosynthesis can slightly reduce the number of false-positives and benign biopsies compared to older mammography techniques, but these small improvements did not sway the overall pro-con assessment for the Viewpoint authors.
“False-positive results require additional imaging and are associated with anxiety for patients,” the authors noted. “Women who have benign biopsies may experience the potential adverse effects of biopsies, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring unnecessarily; and over-diagnosis may lead to unnecessary treatment.”
Kenneth Lin, MD, MPH, family physician and associate director of the Lancaster General Hospital Family Medicine Residency in Pennsylvania, agreed that starting mammograms at age 40 is not a change for the better.
Lin and colleagues conducted an analysis based on data from the USPSTF’s 2016 breast cancer screening report that similarly found 1 additional breast cancer death prevented per 1000 women screened starting at 40 vs 50, at a cost of 576 more false-positive results, 67 more benign breast biopsies, and 2 women diagnosed and treated unnecessarily.
Overall, “there is no compelling evidence to change our clinical approach to breast cancer screening for women in their 40s: individual decision-making based on patient preferences and values,” Lin wrote in a recent Medscape commentary.
But several experts not involved in the USPSTF recommendations agree with the change.
The updated recommendation to begin mammograms at age 40 for women at average risk “aligns with accumulating data suggesting that earlier and more frequent screening can save more lives, and is widely seen as a positive step,” said Lisa Abramson, MD, a radiologist specializing in breast imaging with Mount Sinai Health System and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Melissa Fana, MD, a breast surgical oncologist at NYU Langone Health, agreed that the revised recommendation is justified and “will undoubtedly save lives.”
“The recent change in the screening recommendation was meant to be inclusive, and provide women, particularly women aged 40 to 49 the opportunity to screen with mammography,” Fana said.
One major argument in favor of earlier screening is that it will help address racial inequities in breast cancer diagnoses, treatment, and deaths. Despite a 5% lower incidence of breast cancer, Black women are more likely to be diagnosed with distant-stage cancer or more aggressive breast cancer subtypes, such as triple-negative, compared with White women, and are more likely to die from breast cancer.
“We hope that the earlier initiation of mammography screening across the board will have a great net benefit in outcomes for Black women especially, who have been shown to have the poorest outcomes when it comes to breast cancer, in part because of long-standing inequities in social determinants of health,” said Cherie C. Hill, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, who coauthored the recent ACOG recommendations.
The Viewpoint authors Kerlikowske, Esserman and Tice agreed that Black women may benefit more from earlier screening. However, earlier screening does not address the underlying disparities in treatment and follow-up care for Black women, and it is unclear whether screening alone will help improve breast cancer mortality rates for Black women, the authors noted.
There is one place where experts seem to align: the importance of educating patients about their personal risk.
The Viewpoint authors favor a risk-based approach to help women decide whether to start screening before age 50.
“Engaging women in informed decision-making based on their invasive and advanced breast cancer risk would be a patient-centered approach toward tailored screening, informing when to consider starting screening and how often to screen,” the experts wrote.
For a woman to truly make an educated decision on whether she would like to screen or wait after age 40, she would at least need to know what her specific lifetime risk of developing breast cancer is, not the average risk is for American women in general, Fana told this news organization.
“Risk assessment calculators are widely available and include factors such as family history and reproductive history, and this information can evolve over time and affect lifetime risk,” Fana noted. But “some women just do not get this information.”
Abramson explained that ob.gyns. and primary care physicians will likely play a larger role in the early assessment of breast cancer risk, including discussions about genetic testing and personal risk factors starting as early as age 25.
“For clinicians, the emphasis may be on educating patients about their individual risk, ensuring timely mammograms, and referring higher-risk individuals for further testing or consultations with specialists,” Abramson added.
Esserman reported being a Blue Cross Medical Advisory Panel member, an uncompensated board member of Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative, which funds the I-SPY trial through the University of California, San Francisco, and having an investigator-initiated trial for high-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) funded through UCSF by Moderna for a DCIS phase 1 study. Tice and Kerlikowske reported receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute outside the submitted work. Abramson and Fana have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cendakimab That Targets IL-13 Shows Promise in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM UEG 2024
New mRNA Vaccine May Shield Against C difficile Infections
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Will Psychedelics Break the Major Depression Logjam?
With tens of millions of Euros in the offing, researchers across the European Union have eagerly taken up the gauntlet to find novel interventions for difficult-to-treat mental health and pain conditions. Their target is psychedelics, including classic compounds like psilocybin and atypical ones like ketamine and MDMA. Some of these still carry a stigma as party drugs and spiritual gateways to holotropic experiences.
Twelve groups make up the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology’s psychedelic research network. Along with several affiliates, the groups span nine countries (Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Switzerland, Germany, the Netherlands, the Czech Republic, Greece, and the United Kingdom) and are focused on the use of psychedelic compounds as potential treatments for psychiatric conditions like treatment-resistant depression, addiction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anorexia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
One of the largest endeavors is PsyPal, a 4-year, randomized controlled trial investigating the potential of psilocybin for treating psychological distress in palliative care patients with life-limiting conditions. PsyPal is the first multisite clinical trial funded by the European Union to explore psychedelic-assisted therapy.
At PsyPal’s helm is Robert Schoevers, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and Department Head at University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG), Groningen, the Netherlands, a major hub for psychedelic research.
Schoevers is a bit of a pioneer who said he entered psychedelic research somewhat reluctantly. A decade ago, a colleague showed him a few papers on ketamine and depression. Because UMCG has a large population of patients with treatment-resistant depression, he agreed to do a pilot study. Since then, he has put together an interdisciplinary team of 25 researchers, published numerous papers, and currently has seven studies, including PsyPal, in various stages of progress.
Schoevers is also building a large national consortium that aims to investigate and, if shown effective, implement novel psychiatry treatments much more rapidly and efficiently than current drug development and approval processes, which can take 12 years or longer. He has just secured millions in government funding to start this process.
Next year, Schoevers and his team will decide to test either MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or psilocybin for depression in a large clinical trial, with the aim of getting a treatment as near to formal registration as possible. This will involve working with the European Medicines Agency and its Dutch counterpart, talking to experts who are familiar with the US Food and Drug Administration’s rejection of Lykos Therapeutics’ MDMA treatment for PTSD, and working directly with patients through the National Patient Alliance. The team is also talking to insurers and pharma companies.
The ultimate goal is to “see if we can build a platform in the Netherlands that would have a European perspective, serve as a point of entry for researchers with good ideas, and [attract] public funding as well as companies who have interesting compounds we think would be worthwhile to study,” Schoevers said.
His multiple endeavors emphasize a transdisciplinary and transdiagnostic approach he has been honing for decades. He and his colleagues are investigating the clinical, psychological, and neurobiological parallels between different treatment- resistant conditions and seeking to understand how contextual factors might influence patients, experiences, and outcomes.
Connecting the Dots
Jens H. van Dalfsen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in biological psychiatry, is the principal investigator of another UMCG group looking into the neurobiological mechanisms of major depressive disorder and treatment-resistant depression. His team’s strategy entails an elaborate coordination between the preclinical and clinical research settings.
For example, Sarah Massetti, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is using blood samples collected in clinical trials to investigate the molecular mechanisms underpinning the neuroplasticity and immune-modulating effects produced by psychedelic compounds.
Another line of research spearheaded by Rutger Boesjes, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is exploring the interactions between drugs like ketamine and the circadian system and how they might relate to antidepressant responses in animal models. It could be that the timing of administration of these drugs is relevant, he explained.
The Patient Factor
How psychedelics work and in whom is a big question for the UMCG team and across the research landscape.
“When researchers and the general public talk about psychedelics, they frequently refer to how they promote synaptic plasticity and new connections in the brain,” said van Dalfsen. “But traditional compounds also do that. So the ultimate question that we’ve been exploring is whether findings reflect an actual pharmacological effect or if expectancy also plays a role. In other words: How can we explain why psychedelics might or might not be effective in treatment-resistant patients?” he explained.
This is where the connection to the clinical experience becomes paramount and Joost Breeksema, PhD, comes in.
Breeksema divides his time between UMCG research and his role as executive director and co-founder of the Open Foundation, a nonprofit dedicated to advancing scientific psychedelic research. The work he’s doing outside the university is helping to frame the investigations of the wider group.
So far he has conducted two qualitative studies.
One was an off-label study in which patients with treatment-resistant depression were administered esketamine.
The other was a randomized clinical trial in which participants were blinded to a single 10- or 25-mg dose of psilocybin versus a 1-mg psilocybin microdose placebo that is too small to invoke any effects.
A key insight was the degree to which participants were unprepared for the intensity of their experiences, especially with regards to ketamine. Breeksema said the sessions might not have been so intense or negative for some participants had they been informed beforehand to expect the drugs could provoke “quite overwhelming experiences” and had they been accompanied by an experienced guide providing reassurance and support.
The format for the psilocybin trial met part of this criteria. Participants received a micro (placebo), medium, or high dose in a single session accompanied by two trained therapists. They then engaged in two sessions afterward to process their experiences. A single psilocybin experience appeared to be not enough or too much depending on the dose they were assigned and if they had prior experience with the compound.
Trial participants also felt they needed more help making sense of the experience. “This is a common and important theme,” said Breeksema. “Think about it. If you’ve been depressed for 10, 15 years and … you uncover something and break through something that’s been stuck, you need to process it.”
Jeanine Kamphuis, PhD, a psychiatrist and senior researcher at UMCG and one of the trial study co-authors, explained that they want to find a way to identify who will be too overwhelmed by these experiences if the dose should be adjusted or if some time needs to pass between dosing sessions. They also want to spend more time preparing patients for these sessions.
She emphasized that the studies have provided a reality check. “These are not wonder pills or wonder experiences. And in these types of patients, they’re not intended for a personal growth experience,” she said. “You have a patient who is sitting in front of you who seeks therapy and relief from very severe mood complaints, and the suffering is high,” she said, adding that expectancy bias further complicates patient participation and, likely, outcomes.
The Challenges
For all the potential and opportunity that psychedelics may hold for treatment, UMCG’s work has underscored some challenges.
The field of psychedelic research is characterized by methodological issues, explained van Dalfsen, such as blinding, expectancy, and overestimation of treatment effects. When looking at efficacy, “Is it the compound or the expectancy and promise? This is why it’s important to study how the drugs differ from each other in their biological effects and why they are or are not effective,” he said.
The team has also experienced issues with trial recruitment.
Martijn Godschalk, MD, a PhD candidate in psychiatry, has been addressing this problem while working on RESET-TRD, a phase 3, randomized controlled trial comparing an oral esketamine drink with electroconvulsive therapy in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
He’s been coordinating with local university hospitals, general hospitals, and municipal healthcare clinics to meet inclusion criteria and ensure the trial has enough power to demonstrate effectiveness. In turn, these sites are able to participate in a trial they wouldn’t normally be involved in due to lack of resources.
But Godschalk said he was concerned that many patients have gotten wind of the hype surrounding psychedelic treatments within psychiatry — a factor that has contributed to recruitment challenges. “There are a lot of patients who are interested in the non-registered drug and don’t necessarily have an interest in the other [control] arm,” he said.
Despite the challenges, the classic psychedelics such as MDMA and psilocybin “seem to catalyze a psychological process that may be harder to get with regular psychotherapies,” said Schoevers.
He remains cautious, noting there are still unanswered questions, such as who are the best candidates for these drugs and whether they might cause harm in certain patients while benefiting others. “I do think that this is the first time in 20 or 30 years that there is a group of potential treatments that would really make a difference.”
Schoevers received grants and other funding from The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research & Development, Horizon 2020, Horizon 2023, the National Institute of Mental Health (USA), UMCG, Stichting tot Steun VCVGZ, Nationaal programma Groningen, Healthcare Innovation Funds, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Compass Pathways, Clexio Biosciences, and GH research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With tens of millions of Euros in the offing, researchers across the European Union have eagerly taken up the gauntlet to find novel interventions for difficult-to-treat mental health and pain conditions. Their target is psychedelics, including classic compounds like psilocybin and atypical ones like ketamine and MDMA. Some of these still carry a stigma as party drugs and spiritual gateways to holotropic experiences.
Twelve groups make up the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology’s psychedelic research network. Along with several affiliates, the groups span nine countries (Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Switzerland, Germany, the Netherlands, the Czech Republic, Greece, and the United Kingdom) and are focused on the use of psychedelic compounds as potential treatments for psychiatric conditions like treatment-resistant depression, addiction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anorexia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
One of the largest endeavors is PsyPal, a 4-year, randomized controlled trial investigating the potential of psilocybin for treating psychological distress in palliative care patients with life-limiting conditions. PsyPal is the first multisite clinical trial funded by the European Union to explore psychedelic-assisted therapy.
At PsyPal’s helm is Robert Schoevers, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and Department Head at University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG), Groningen, the Netherlands, a major hub for psychedelic research.
Schoevers is a bit of a pioneer who said he entered psychedelic research somewhat reluctantly. A decade ago, a colleague showed him a few papers on ketamine and depression. Because UMCG has a large population of patients with treatment-resistant depression, he agreed to do a pilot study. Since then, he has put together an interdisciplinary team of 25 researchers, published numerous papers, and currently has seven studies, including PsyPal, in various stages of progress.
Schoevers is also building a large national consortium that aims to investigate and, if shown effective, implement novel psychiatry treatments much more rapidly and efficiently than current drug development and approval processes, which can take 12 years or longer. He has just secured millions in government funding to start this process.
Next year, Schoevers and his team will decide to test either MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or psilocybin for depression in a large clinical trial, with the aim of getting a treatment as near to formal registration as possible. This will involve working with the European Medicines Agency and its Dutch counterpart, talking to experts who are familiar with the US Food and Drug Administration’s rejection of Lykos Therapeutics’ MDMA treatment for PTSD, and working directly with patients through the National Patient Alliance. The team is also talking to insurers and pharma companies.
The ultimate goal is to “see if we can build a platform in the Netherlands that would have a European perspective, serve as a point of entry for researchers with good ideas, and [attract] public funding as well as companies who have interesting compounds we think would be worthwhile to study,” Schoevers said.
His multiple endeavors emphasize a transdisciplinary and transdiagnostic approach he has been honing for decades. He and his colleagues are investigating the clinical, psychological, and neurobiological parallels between different treatment- resistant conditions and seeking to understand how contextual factors might influence patients, experiences, and outcomes.
Connecting the Dots
Jens H. van Dalfsen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in biological psychiatry, is the principal investigator of another UMCG group looking into the neurobiological mechanisms of major depressive disorder and treatment-resistant depression. His team’s strategy entails an elaborate coordination between the preclinical and clinical research settings.
For example, Sarah Massetti, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is using blood samples collected in clinical trials to investigate the molecular mechanisms underpinning the neuroplasticity and immune-modulating effects produced by psychedelic compounds.
Another line of research spearheaded by Rutger Boesjes, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is exploring the interactions between drugs like ketamine and the circadian system and how they might relate to antidepressant responses in animal models. It could be that the timing of administration of these drugs is relevant, he explained.
The Patient Factor
How psychedelics work and in whom is a big question for the UMCG team and across the research landscape.
“When researchers and the general public talk about psychedelics, they frequently refer to how they promote synaptic plasticity and new connections in the brain,” said van Dalfsen. “But traditional compounds also do that. So the ultimate question that we’ve been exploring is whether findings reflect an actual pharmacological effect or if expectancy also plays a role. In other words: How can we explain why psychedelics might or might not be effective in treatment-resistant patients?” he explained.
This is where the connection to the clinical experience becomes paramount and Joost Breeksema, PhD, comes in.
Breeksema divides his time between UMCG research and his role as executive director and co-founder of the Open Foundation, a nonprofit dedicated to advancing scientific psychedelic research. The work he’s doing outside the university is helping to frame the investigations of the wider group.
So far he has conducted two qualitative studies.
One was an off-label study in which patients with treatment-resistant depression were administered esketamine.
The other was a randomized clinical trial in which participants were blinded to a single 10- or 25-mg dose of psilocybin versus a 1-mg psilocybin microdose placebo that is too small to invoke any effects.
A key insight was the degree to which participants were unprepared for the intensity of their experiences, especially with regards to ketamine. Breeksema said the sessions might not have been so intense or negative for some participants had they been informed beforehand to expect the drugs could provoke “quite overwhelming experiences” and had they been accompanied by an experienced guide providing reassurance and support.
The format for the psilocybin trial met part of this criteria. Participants received a micro (placebo), medium, or high dose in a single session accompanied by two trained therapists. They then engaged in two sessions afterward to process their experiences. A single psilocybin experience appeared to be not enough or too much depending on the dose they were assigned and if they had prior experience with the compound.
Trial participants also felt they needed more help making sense of the experience. “This is a common and important theme,” said Breeksema. “Think about it. If you’ve been depressed for 10, 15 years and … you uncover something and break through something that’s been stuck, you need to process it.”
Jeanine Kamphuis, PhD, a psychiatrist and senior researcher at UMCG and one of the trial study co-authors, explained that they want to find a way to identify who will be too overwhelmed by these experiences if the dose should be adjusted or if some time needs to pass between dosing sessions. They also want to spend more time preparing patients for these sessions.
She emphasized that the studies have provided a reality check. “These are not wonder pills or wonder experiences. And in these types of patients, they’re not intended for a personal growth experience,” she said. “You have a patient who is sitting in front of you who seeks therapy and relief from very severe mood complaints, and the suffering is high,” she said, adding that expectancy bias further complicates patient participation and, likely, outcomes.
The Challenges
For all the potential and opportunity that psychedelics may hold for treatment, UMCG’s work has underscored some challenges.
The field of psychedelic research is characterized by methodological issues, explained van Dalfsen, such as blinding, expectancy, and overestimation of treatment effects. When looking at efficacy, “Is it the compound or the expectancy and promise? This is why it’s important to study how the drugs differ from each other in their biological effects and why they are or are not effective,” he said.
The team has also experienced issues with trial recruitment.
Martijn Godschalk, MD, a PhD candidate in psychiatry, has been addressing this problem while working on RESET-TRD, a phase 3, randomized controlled trial comparing an oral esketamine drink with electroconvulsive therapy in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
He’s been coordinating with local university hospitals, general hospitals, and municipal healthcare clinics to meet inclusion criteria and ensure the trial has enough power to demonstrate effectiveness. In turn, these sites are able to participate in a trial they wouldn’t normally be involved in due to lack of resources.
But Godschalk said he was concerned that many patients have gotten wind of the hype surrounding psychedelic treatments within psychiatry — a factor that has contributed to recruitment challenges. “There are a lot of patients who are interested in the non-registered drug and don’t necessarily have an interest in the other [control] arm,” he said.
Despite the challenges, the classic psychedelics such as MDMA and psilocybin “seem to catalyze a psychological process that may be harder to get with regular psychotherapies,” said Schoevers.
He remains cautious, noting there are still unanswered questions, such as who are the best candidates for these drugs and whether they might cause harm in certain patients while benefiting others. “I do think that this is the first time in 20 or 30 years that there is a group of potential treatments that would really make a difference.”
Schoevers received grants and other funding from The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research & Development, Horizon 2020, Horizon 2023, the National Institute of Mental Health (USA), UMCG, Stichting tot Steun VCVGZ, Nationaal programma Groningen, Healthcare Innovation Funds, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Compass Pathways, Clexio Biosciences, and GH research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With tens of millions of Euros in the offing, researchers across the European Union have eagerly taken up the gauntlet to find novel interventions for difficult-to-treat mental health and pain conditions. Their target is psychedelics, including classic compounds like psilocybin and atypical ones like ketamine and MDMA. Some of these still carry a stigma as party drugs and spiritual gateways to holotropic experiences.
Twelve groups make up the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology’s psychedelic research network. Along with several affiliates, the groups span nine countries (Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Switzerland, Germany, the Netherlands, the Czech Republic, Greece, and the United Kingdom) and are focused on the use of psychedelic compounds as potential treatments for psychiatric conditions like treatment-resistant depression, addiction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anorexia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
One of the largest endeavors is PsyPal, a 4-year, randomized controlled trial investigating the potential of psilocybin for treating psychological distress in palliative care patients with life-limiting conditions. PsyPal is the first multisite clinical trial funded by the European Union to explore psychedelic-assisted therapy.
At PsyPal’s helm is Robert Schoevers, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and Department Head at University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG), Groningen, the Netherlands, a major hub for psychedelic research.
Schoevers is a bit of a pioneer who said he entered psychedelic research somewhat reluctantly. A decade ago, a colleague showed him a few papers on ketamine and depression. Because UMCG has a large population of patients with treatment-resistant depression, he agreed to do a pilot study. Since then, he has put together an interdisciplinary team of 25 researchers, published numerous papers, and currently has seven studies, including PsyPal, in various stages of progress.
Schoevers is also building a large national consortium that aims to investigate and, if shown effective, implement novel psychiatry treatments much more rapidly and efficiently than current drug development and approval processes, which can take 12 years or longer. He has just secured millions in government funding to start this process.
Next year, Schoevers and his team will decide to test either MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or psilocybin for depression in a large clinical trial, with the aim of getting a treatment as near to formal registration as possible. This will involve working with the European Medicines Agency and its Dutch counterpart, talking to experts who are familiar with the US Food and Drug Administration’s rejection of Lykos Therapeutics’ MDMA treatment for PTSD, and working directly with patients through the National Patient Alliance. The team is also talking to insurers and pharma companies.
The ultimate goal is to “see if we can build a platform in the Netherlands that would have a European perspective, serve as a point of entry for researchers with good ideas, and [attract] public funding as well as companies who have interesting compounds we think would be worthwhile to study,” Schoevers said.
His multiple endeavors emphasize a transdisciplinary and transdiagnostic approach he has been honing for decades. He and his colleagues are investigating the clinical, psychological, and neurobiological parallels between different treatment- resistant conditions and seeking to understand how contextual factors might influence patients, experiences, and outcomes.
Connecting the Dots
Jens H. van Dalfsen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in biological psychiatry, is the principal investigator of another UMCG group looking into the neurobiological mechanisms of major depressive disorder and treatment-resistant depression. His team’s strategy entails an elaborate coordination between the preclinical and clinical research settings.
For example, Sarah Massetti, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is using blood samples collected in clinical trials to investigate the molecular mechanisms underpinning the neuroplasticity and immune-modulating effects produced by psychedelic compounds.
Another line of research spearheaded by Rutger Boesjes, a PhD candidate in biological psychiatry, is exploring the interactions between drugs like ketamine and the circadian system and how they might relate to antidepressant responses in animal models. It could be that the timing of administration of these drugs is relevant, he explained.
The Patient Factor
How psychedelics work and in whom is a big question for the UMCG team and across the research landscape.
“When researchers and the general public talk about psychedelics, they frequently refer to how they promote synaptic plasticity and new connections in the brain,” said van Dalfsen. “But traditional compounds also do that. So the ultimate question that we’ve been exploring is whether findings reflect an actual pharmacological effect or if expectancy also plays a role. In other words: How can we explain why psychedelics might or might not be effective in treatment-resistant patients?” he explained.
This is where the connection to the clinical experience becomes paramount and Joost Breeksema, PhD, comes in.
Breeksema divides his time between UMCG research and his role as executive director and co-founder of the Open Foundation, a nonprofit dedicated to advancing scientific psychedelic research. The work he’s doing outside the university is helping to frame the investigations of the wider group.
So far he has conducted two qualitative studies.
One was an off-label study in which patients with treatment-resistant depression were administered esketamine.
The other was a randomized clinical trial in which participants were blinded to a single 10- or 25-mg dose of psilocybin versus a 1-mg psilocybin microdose placebo that is too small to invoke any effects.
A key insight was the degree to which participants were unprepared for the intensity of their experiences, especially with regards to ketamine. Breeksema said the sessions might not have been so intense or negative for some participants had they been informed beforehand to expect the drugs could provoke “quite overwhelming experiences” and had they been accompanied by an experienced guide providing reassurance and support.
The format for the psilocybin trial met part of this criteria. Participants received a micro (placebo), medium, or high dose in a single session accompanied by two trained therapists. They then engaged in two sessions afterward to process their experiences. A single psilocybin experience appeared to be not enough or too much depending on the dose they were assigned and if they had prior experience with the compound.
Trial participants also felt they needed more help making sense of the experience. “This is a common and important theme,” said Breeksema. “Think about it. If you’ve been depressed for 10, 15 years and … you uncover something and break through something that’s been stuck, you need to process it.”
Jeanine Kamphuis, PhD, a psychiatrist and senior researcher at UMCG and one of the trial study co-authors, explained that they want to find a way to identify who will be too overwhelmed by these experiences if the dose should be adjusted or if some time needs to pass between dosing sessions. They also want to spend more time preparing patients for these sessions.
She emphasized that the studies have provided a reality check. “These are not wonder pills or wonder experiences. And in these types of patients, they’re not intended for a personal growth experience,” she said. “You have a patient who is sitting in front of you who seeks therapy and relief from very severe mood complaints, and the suffering is high,” she said, adding that expectancy bias further complicates patient participation and, likely, outcomes.
The Challenges
For all the potential and opportunity that psychedelics may hold for treatment, UMCG’s work has underscored some challenges.
The field of psychedelic research is characterized by methodological issues, explained van Dalfsen, such as blinding, expectancy, and overestimation of treatment effects. When looking at efficacy, “Is it the compound or the expectancy and promise? This is why it’s important to study how the drugs differ from each other in their biological effects and why they are or are not effective,” he said.
The team has also experienced issues with trial recruitment.
Martijn Godschalk, MD, a PhD candidate in psychiatry, has been addressing this problem while working on RESET-TRD, a phase 3, randomized controlled trial comparing an oral esketamine drink with electroconvulsive therapy in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
He’s been coordinating with local university hospitals, general hospitals, and municipal healthcare clinics to meet inclusion criteria and ensure the trial has enough power to demonstrate effectiveness. In turn, these sites are able to participate in a trial they wouldn’t normally be involved in due to lack of resources.
But Godschalk said he was concerned that many patients have gotten wind of the hype surrounding psychedelic treatments within psychiatry — a factor that has contributed to recruitment challenges. “There are a lot of patients who are interested in the non-registered drug and don’t necessarily have an interest in the other [control] arm,” he said.
Despite the challenges, the classic psychedelics such as MDMA and psilocybin “seem to catalyze a psychological process that may be harder to get with regular psychotherapies,” said Schoevers.
He remains cautious, noting there are still unanswered questions, such as who are the best candidates for these drugs and whether they might cause harm in certain patients while benefiting others. “I do think that this is the first time in 20 or 30 years that there is a group of potential treatments that would really make a difference.”
Schoevers received grants and other funding from The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research & Development, Horizon 2020, Horizon 2023, the National Institute of Mental Health (USA), UMCG, Stichting tot Steun VCVGZ, Nationaal programma Groningen, Healthcare Innovation Funds, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Compass Pathways, Clexio Biosciences, and GH research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.